Nasal Alar Necrosis. John D. Rachel, MD; Robert H. Mathog, MD
|
|
|
- Victoria Sparks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
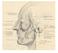
1 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2000 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Nasal Alar Necrosis John D. Rachel, MD; Robert H. Mathog, MD Objective: To describe an unrecognized clinical entity, nasal alar necrosis, and propose recommendations regarding the diagnosis, pathophysiology, and management of these cases. Study Design: Retrospective review of four patients with this condition. Methods: Histories, treatments, and outcomes were evaluated using office and hospital chart data. Results: We noted that three patients had prior trauma or surgery, other than to the nose, in the head and neck region. All four patients had comorbidities such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, depression, or tobacco abuse. Three patients had sensory deficits over the distribution of the maxillary nerve, and three volunteered that they had a habit of picking the crusted wound. Two patients improved over several months with aggressive wound care. One patient refused treatment and another underwent successful reconstruction. Conclusions: After malignant and granulomatous diseases were ruled out, our evaluations suggested that the pathogenesis was multifactorial including several factors alone or in combination, such as, hypoesthesia, self-mutilation, and an inadequate blood supply. Deficits in vascularity and sensory innervation must be considered as potential obstacles in reconstruction. Psychological problems causing factitious wounding may complicate therapeutic interventions. Key Words: Nasal alar necrosis, pathophysiology, diagnosis, management. Laryngoscope, 110: , 2000 INTRODUCTION Nasal alar necrosis is a rare condition resulting in a cosmetic defect. Although necrosis can occur after prolonged nasotracheal intubation and rhinoplasty, a progressive destructive process can also occur with no other obvious causes. The literature contains several case reports suggesting a multifocal etiology including the loss of nerve function to the affected area. 1,2 This paucity of information prompts us to report on four patients presenting with this condition with reference to the pathophysiology, outcomes, and treatments available. Presented at the Meeting of the Middle Section of the American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc., Cincinnati, Ohio, January 22, From the Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan. Editor s Note: This Manuscript was accepted for publication May 22, Send Correspondence to Robert H. Mathog, MD, Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, 5E-UHC, 540 East Canfield Avenue, Detroit, MI 48201, U.S.A. MATERIALS AND METHODS Histories, treatments, and outcomes were evaluated retrospectively using office and hospital chart data. A literature search of 30 years was completed to analyze previously reported causes and management of the condition. Inclusion criteria were alar necrosis of unknown cause. Any patients with direct injury to the nose or known destructive processes were excluded (i.e.,: gunshot wounds, knife wounds, animal bites, tumors, or granulomatous disorders). RESULTS The patients in this series had necrosis of one of the ala nasi. Table I describes the historical background of the four patients in this series. Three patients had either prior trauma or surgery, other than to the nose, in the head and neck region. All four patients had comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, hypothyroidism, depression, or a history of tobacco abuse. Three patients had a sensory loss over the distribution of the maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve and three patients volunteered that they had a habit of picking the crusted area. Case 1 This 39-year-old woman was involved in a motor vehicle accident in August 1992 and sustained multiple injuries (Fig. 1). She had a history of depression, hypothyroidism, and tobacco use, but denied a history of intravenous drug abuse. After injury she complained of left-sided facial pain. She had multiple nerve blocks, but when these failed she underwent a trigeminal rhizotomy. This procedure was successful in providing complete anesthesia over the distribution of the nerve and she experienced total remission of pain. Three months later a small lesion developed in the left nasal ala. Biopsy revealed focal ulceration, epidermal hyperplasia, and hyperkeratosis with no evidence of malignancy or granulomatous disease. She admitted to frequent manual manipulation of the site secondary to the constant irritation. The patient was treated with aggressive wound care and was asked to avoid picking at the ulcer, but the lesion progressed to necrosis of the entire ala. Recommendations for reconstruction of the defect were refused and the patient continued to suffer from a persistent ulcer at that site. Case 2 This 48-year-old man with a history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, depression, and tobacco use developed mucormycosis of the sinuses in April 1993 (Fig. 2). He 1437
2 TABLE I. Patient Background. Patient No. Condition Sensory loss Y Y Y N Picking habit Y Y Y N Diabetes N Y N Y Hypertension N Y N Y Hypothyroidism Y N N N Depression Y Y Y Y Tobacco use Y Y N Y underwent debridement of the right maxillary and ethmoid sinuses with decompression of the optic nerve, followed by amphotericin-b. Sensation over the distribution of the maxillary nerve and vision from the right eye were lost. In October 1996 he returned to the operating room for treatment of a frontal sinus mucocele with a frontal sinus obliteration. In May 1997 the patient presented to the office after a 4-mm ulceration developed in the right ala. His wife stated that the patient was frequently picking at Fig. 2. Case 2. Anterior view of remaining right nasal alar defect. the site, but he denied the habit. He agreed to a wound care regimen and avoided further digital manipulation of the site. The ulceration healed, leaving a defect of the alar rim. Case 3 This 43-year-old female was assaulted with a gun shot wound to the face in March 1986 (Fig. 3). She suffered blindness bilaterally with numbness of the right face. The patient presented in October 1996 with ulceration of the nose that had persisted for several years. Examination revealed a lesion of the right ala with crusting along the caudal septum and scarring of the upper right lip. She also admitted to digital manipulation. The ulcerated area improved with application of bacitracin ointment and daily saline douches over several months. She was well healed with a depressed ala at the time of this writing. Fig. 1. Case 1. Lateral view of left nasal alar necrosis with focal ulceration and erythema Case 4 This 55-year-old man with a history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and depression presented in June 1993 with an 18-month history of a nonhealing left-sided nasal ulcer (Fig. 4). He denied any history of surgery or trauma in the head and neck region and denied a picking habit. A sensory examination of the face was within normal limits. Examination of the nose demonstrated neartotal erosion of the nasal ala with exophytic granulation
3 Fig. 3. Case 3. Ulcerated right nasal sill lesion. Fig. 5. Case 4. Intraoperative reconstructive photograph of stage 1. tissue along the borders of the lesion. Biopsy results were negative for malignancy or granulomatous disease. He underwent a two-stage reconstruction with a nasolabial flap and septal cartilage graft with subsequent debulking of the flap in August 1993 (Fig. 5). Fig. 4. Case 4. Oblique view. Preoperative photograph demonstrating a deep full-thickness defect. DISCUSSION Necrosis of the nasal ala is a rare phenomenon that occurs after invasive treatment for trigeminal neuralgia. 1,2 In a case reported by Nusem-Horowitz et al., 1 such a lesion occurred 3 weeks after retrogasserian alcohol injection for treatment of facial pain. The mechanism was thought to be a delayed avascular necrosis of the ala nasi as a result of either damage to the sympathetic plexus accompanying the feeding vessels or a distal microembolic effect during the injection. In a similar case, Srinivas et al. 2 noted erosion after this procedure and attributed it to a picking habit. Others reported a similar lesion of neuroparalytic keratitis after corneal anesthesia from interruption of trigeminal pathways and minor trauma. 3,4 Our series also included causal elements of external trauma, factitious self-induced destruction of tissue, and loss of sensation. In one of our patients (described in case 1) an alar lesion developed within 3 months of the onset of facial anesthesia. This then progressed to necrosis of the entire alar subunit. She admitted to frequent manipulation and refused treatment of the lesion, despite its nonhealing nature and cosmetic deformity. The patient described in case 2 denied any manipulation of the site, but his wife stated that he was constantly picking at the ulcer. The patient in case 3 admitted to occasionally touching the wound, which she stopped with the onset of treatment. The lesions described in cases 1, 2, and 3 were also related to numbness. In case 4, the patient had normal sensation of the face and no history of trauma or prior surgery. None of our patients had overt evidence of a reduced blood supply (avascular necrosis) to the side of the face. Factitious or self-induced injury was prevalent in our patients. It has been suggested that the skin is highly vulnerable to self-inflicted lesions because it is accessible and serves as an important medium of communication between the individual and the social environment. 5,6 Disorders of wound healing may be manifestations of psychoneuroses. Various personality disorders are associated with factitious skin lesions and can range from the sane but dishonest to the severely disturbed. Munchausen s syndrome is a psychiatric disturbance associated with factitious wounding in which the intrapsychic gains are a 1439
4 result of a poorly adapted response to stress in an unbalanced personality. Zohar et al. 7 describe cases in which damage to the external auditory canal, nose, and cheeks was self-inflicted or inflicted by parents (Munchausen s syndrome by proxy) with the goal of obtaining medical attention. Once the diagnosis of a self-inflicted wound is entertained, it is difficult to confirm unless the patient is observed traumatizing the wound or acknowledges involvement. None of our patients appeared to have this type of personality or evidence of self-mutilation, although the underlying disorder is difficult to diagnose and treat. Another not-so-obvious cause that must be considered is avascular necrosis as a result of disrupted blood flow. The vascular anatomy has been well described in the literature In cadaver dissections Toriumi et al. 8 demonstrated that most specimens have an independent blood supply to each side of the nose that varies from one side to the other. The superficial arterial supply to the external structures of the nose is derived from both the internal and the external carotid arteries. An external branch of the ophthalmic artery, the dorsal nasal artery, runs downward along the lateral surface of the nose and is supplemented by branches of the infraorbital artery. The external nasal branch of the anterior ethmoid artery courses over the dorsal surface of the nasal bones and proceeds to the nasal tip, where it contributes to the arterial arcade of the nasal tip. The lateral nasal artery branches off the angular artery and passes medially along the cephalic margin of the of the lateral crura, giving off branches that course in a caudal direction over the lateral crura toward the nostril rim. The artery then passes medially over the domes and continues down the columella to the base of the nose. The columellar arteries branch off the facial artery or the superior labial artery and meet the lateral nasal artery over the dome of the nose to form an alar arcade that runs along the cephalic margin of the lateral crura. In most cases the lateral nasal artery feeds the alar arcade from above and the columellar artery from below. A subdermal plexus is found superficial to the alar arcade and receives contributions from the lateral nasal, anterior ethmoid, and columellar arteries. The sympathetic control to these blood vessels of the external nose originates as preganglionic fibers in the thoracolumbar region of the spinal cord, which pass into the vagosympathetic trunk to relay in the superior cervical ganglion. The postganglionic sympathetic fibers follow the internal carotid artery and reach the nose via the ethmoidal and infraorbital branches of the trigeminal nerve as well as the inferior lateral nasal branch of the greater palatine nerve. 11 With the loss of blood flow, tissue is susceptible to ischemia and necrosis. In our series we believe the patients had an intact vascular anatomy or would have adequate collateral contributions from the feeding vessels in this region to supply the nasal ala and surrounding tissues. Three patients did not receive injections in or near the vessels, which rules out the possibility of a distal microembolic effect. Avascular necrosis as a result of impaired blood flow autoregulation by the sympathetic system must be considered because there was trauma to these nerves in three of our patients The loss of sensation also appears contributory. Sensory innervation to the external nose is derived from the ophthalmic and maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve. The ophthalmic nerve gives rise to the nasociliary nerve, which in turn branches into the anterior and posterior ethmoidal nerves. These fibers follow their respective arteries and also the infratrochlear nerve, providing distribution to the eyelids and the skin of the upper part of the side of the nose. The infraorbital nerve, a branch of the maxillary division of the fifth cranial nerve, supplies the lateral nasal wall. The loss of innervation to the ala would render the region anesthetic and even minor trauma could go unrealized and cause ulceration with tissue loss. The potential for a diminished blood supply, coupled with persistent irritation, may contribute to the development and chronicity of these lesions. Reconstructive strategies for the ala vary with the depth and location of the defect. 12,13 The complexity and challenge of the repair generally escalates with the loss of additional tissue layers that provide support and lining. Nasal alar defects that extend into deep soft tissue or approach the alar rim can lead to collapse of the alar rim, producing a functional as well as a cosmetic deficit. Various techniques have been developed for reconstruction of a defect involving the nasal ala In two of the four patients in this series, a superficial or partialthickness defect was evident. In these defects, healing by secondary intention provided an acceptable result. This treatment requires meticulous wound care that maintains a moist wound environment free of infection. The other two patients presented with deep fullthickness defects requiring replacement of mucosa, supporting cartilage, and overlying skin. In case 4, the inner lining was created using a turnover cutaneous flap; support was provided with septal cartilage and coverage by a nasolabial flap. The patient underwent revision of the flap at a later date. In case 1 the patient had a large fullthickness defect. She was presented with a reconstruction plan using a nasolabial flap for internal lining and a forehead flap for external lining. The patient, however, refused surgery and the defect remains under some control with local wound care. CONCLUSION Nasal alar necrosis developed in the patients in this series as a complicating condition of an underlying disease or an inciting event. Patients with nasal alar necrosis can provide a diagnostic and reconstructive challenge. Defects in vascularity and sensory innervation must be considered as causes of the condition and obstacles in reconstruction. Moreover, psychological problems causing factitious wounding may complicate preventative and therapeutic interventions. BIBLIOGRAPHY 1. Nusem-Horowitz S, Wolf M, Kronenberg J. Nasal alar necrosis: a complication of retrogasserian alcohol injection. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1994;52: Srinivas K, Balasubramaniam V, Ramamurthi B. Erosion of ala nasi following trigeminal root injection. J Assoc Physicians India 1972;20: Burchiel K. Percutaneous retrogasserian glycerol rhizolysis
5 in the management of trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 1988;69: Fraioli B, Ferrante L, Santoro A, et al. Recent progress in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: glycerol into the trigeminal cistern and percutaneous gasserian compression by means of Fogarty s catheter. Acta Neurochir Suppl 1984; 33: Cohen IK, Diegelman R, Lindbled W. Wound Healing Biochemical and Clinical Aspects. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1992: Greene D, Murr A. Factitious orbital emphysema: an unusual presentation of Munchausen s syndrome. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1998;119: Zohar Y, Avidan G, Shvili Y, Laurian N. Otolaryngologic cases of Munchausen s syndrome. Laryngoscope 1987;97: Toriumi D, Mueller R, Grosch T, Bhattadharyya T, Larrabee W. Vascular anatomy of the nose and the external rhinoplasty approach. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1996; 122: Oneal R, Beil R, Schlesinger J. Surgical anatomy of the nose. Clin Plast Surg 1996;23: Rohrich R, Gunter J Friedman R. Nasal tip blood supply: an anatomic study validating the safety of the transcolumellar incision in rhinoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 1995;95: Proctor DF, Andersen IB. The Nose-Upper Airway Physiology and the Atmospheric Environment. Amsterdam: Elsevier Biomedical Press, Burget GC, Menick FJ. Aesthetic Reconstruction of the Nose. St. Louis: Mosby-Year Book, Humpherys T, Goldberg L, Wiemer R. Repair of defects of the nasal ala. Dermatol Surg 1997;23: Kroll S. Nasal alar reconstruction using the nasolabial turnover flap. Laryngoscope 1991;101: Hauben D, Sagi A. A simple method for alar rim reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 1987;80: Fader D, Baker S, Johnson T. The staged cheek-to-nose interpolation flap for reconstruction of the nasal alar rim/ lobule. J Am Acad Dermatol 1997;37: Ratner D, Skouge J. Surgical pearl: the use of free cartilage grafts in nasal alar reconstruction. J Am Acad Dermatol 1997;36:
Anatomy of. External NOSE. By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC
 Anatomy of External NOSE By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 24 th Nov. 2017 The External Nose Descriptions of the nose always begin with that part of it which is covered by the skin, i.e., the EXPOSED PART
Anatomy of External NOSE By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 24 th Nov. 2017 The External Nose Descriptions of the nose always begin with that part of it which is covered by the skin, i.e., the EXPOSED PART
Trigeminal Trophic Syndrome: Report of 2 Cases
 Trigeminal Trophic Syndrome: Report of 2 Cases Yoko Osaki, MD, Tateki Kubo, MD, PhD, Kyosuke Minami, MD, and Daisuke Maeda, MD Department of Plastic Surgery, Osaka Rosai Hospital, Sakai, Japan Correspondence:
Trigeminal Trophic Syndrome: Report of 2 Cases Yoko Osaki, MD, Tateki Kubo, MD, PhD, Kyosuke Minami, MD, and Daisuke Maeda, MD Department of Plastic Surgery, Osaka Rosai Hospital, Sakai, Japan Correspondence:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Reconstruction of the Nasal Columella. David A. Sherris, MD; Jon Fuerstenberg, MD; Daniel Danahey, MD, PhD; Peter A.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reconstruction of the Nasal Columella David A. Sherris, MD; Jon Fuerstenberg, MD; Daniel Danahey, MD, PhD; Peter A. Hilger, MD Objective: To report techniques successful for nasal columella
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reconstruction of the Nasal Columella David A. Sherris, MD; Jon Fuerstenberg, MD; Daniel Danahey, MD, PhD; Peter A. Hilger, MD Objective: To report techniques successful for nasal columella
Columella Lengthening with a Full-Thickness Skin Graft for Secondary Bilateral Cleft Lip and Nose Repair
 Original Article Columella Lengthening with a Full-Thickness Skin Graft for Secondary Bilateral Cleft Lip and Nose Repair Yoon Seok Lee 1, Dong Hyeok Shin 1, Hyun Gon Choi 1, Jee Nam Kim 1, Myung Chul
Original Article Columella Lengthening with a Full-Thickness Skin Graft for Secondary Bilateral Cleft Lip and Nose Repair Yoon Seok Lee 1, Dong Hyeok Shin 1, Hyun Gon Choi 1, Jee Nam Kim 1, Myung Chul
Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
Surgical treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer of the head and neck: expanding reconstructive options van der Eerden, P.A.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Surgical treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer of the head and neck: expanding reconstructive options van der Eerden, P.A. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Surgical treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer of the head and neck: expanding reconstructive options van der Eerden, P.A. Link to publication Citation for published
Scientific Forum. Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the Alar Rim
 Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the lar Rim Richard Ellenbogen, MD; and Greg azell, MD ackground: lthough the alar rim has frequently been neglected in correction
Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the lar Rim Richard Ellenbogen, MD; and Greg azell, MD ackground: lthough the alar rim has frequently been neglected in correction
FOLLOWING INTRODUCTION OF
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Alternative 1-Step Nasal Reconstruction Technique Kazuo Kishi, MD, PhD; Nobuaki Imanishi, MD, PhD; Yusuke Shimizu, MD; Ruka Shimizu, MD, PhD; Keisuke Okabe, MD; Hideo Nakajima, MD, PhD
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Alternative 1-Step Nasal Reconstruction Technique Kazuo Kishi, MD, PhD; Nobuaki Imanishi, MD, PhD; Yusuke Shimizu, MD; Ruka Shimizu, MD, PhD; Keisuke Okabe, MD; Hideo Nakajima, MD, PhD
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Nasal Soft-Tissue Triangle Deformities
 339 Hossam M.T. Foda, MD 1 1 Division of Facial Plastic Surgery, Otolaryngology Department, Alexandria Medical School, Alexandria, Egypt Facial Plast Surg 2016;32:339 344. Address for correspondence Hossam
339 Hossam M.T. Foda, MD 1 1 Division of Facial Plastic Surgery, Otolaryngology Department, Alexandria Medical School, Alexandria, Egypt Facial Plast Surg 2016;32:339 344. Address for correspondence Hossam
The sebaceous glands (glands of Zeis) open directly into the eyelash follicles, ciliary glands (glands of Moll) are modified sweat glands that open
 The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
There are numerous suture techniques described for nasal. Septocolumellar Suture in Closed Rhinoplasty ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Erdem Tezel, MD, and Ayhan Numanoğlu, MD Abstract: Several surgeons advise a variety of tip sutures and describe their own techniques in open approach. Septocolumellar suture is one of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Erdem Tezel, MD, and Ayhan Numanoğlu, MD Abstract: Several surgeons advise a variety of tip sutures and describe their own techniques in open approach. Septocolumellar suture is one of
Anatomic Relations Summary. Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh
 Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Use of tent-pole graft for setting columella-lip angle in rhinoplasty
 Agrawal et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:13 DOI: 10.20517/2347-9264.2018.17 Plastic and Aesthetic Research Letter to Editor Open Access Use of tent-pole graft for setting columella-lip angle in rhinoplasty
Agrawal et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:13 DOI: 10.20517/2347-9264.2018.17 Plastic and Aesthetic Research Letter to Editor Open Access Use of tent-pole graft for setting columella-lip angle in rhinoplasty
Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery
 Objectives Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery Identify important functional anatomy and aesthetic units of the face. Describe techniques used in facial reconstruction. Discuss postoperative
Objectives Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery Identify important functional anatomy and aesthetic units of the face. Describe techniques used in facial reconstruction. Discuss postoperative
Trigeminal Nerve (V)
 Trigeminal Nerve (V) Lecture Objectives Discuss briefly how the face is developed. Follow up the course of trigeminal nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Describe
Trigeminal Nerve (V) Lecture Objectives Discuss briefly how the face is developed. Follow up the course of trigeminal nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Describe
THE NASAL SUPERFICIAL ARterial
 Nasal Arterial Vasculature Medical and Surgical Applications ORIGINAL ARTICLE Yves Saban, MD; Chiara Andretto Amodeo, MD; David Bouaziz, MD; Roberto Polselli, MD Objectives: To analyze the nasal superficial
Nasal Arterial Vasculature Medical and Surgical Applications ORIGINAL ARTICLE Yves Saban, MD; Chiara Andretto Amodeo, MD; David Bouaziz, MD; Roberto Polselli, MD Objectives: To analyze the nasal superficial
Large full-thickness nasal tip defects after Mohs
 RECONSTRUCTIVE CONUNDRUM Repair of a Large, Exposed-Cartilage Nasal Tip Defect Using Nasalis-Based Subcutaneous Pedicle Flaps and Full-Thickness Skin Grafting DIEGO E. MARRA, MD, EDGAR F. FINCHER, MD,
RECONSTRUCTIVE CONUNDRUM Repair of a Large, Exposed-Cartilage Nasal Tip Defect Using Nasalis-Based Subcutaneous Pedicle Flaps and Full-Thickness Skin Grafting DIEGO E. MARRA, MD, EDGAR F. FINCHER, MD,
Willis et al.: Treatment Options in Trigeminal Trophic Syndrome. A Multi-Institutional Case Series. Case Report
 The Laryngoscope VC 2011 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Case Report Treatment Options in Trigeminal Trophic Syndrome: A Multi-Institutional Case Series Mark Willis,
The Laryngoscope VC 2011 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Case Report Treatment Options in Trigeminal Trophic Syndrome: A Multi-Institutional Case Series Mark Willis,
Alireza Bakhshaeekia and Sina Ghiasi-hafezi. 1. Introduction. 2. Patients and Methods
 Plastic Surgery International Volume 0, Article ID 4578, 4 pages doi:0.55/0/4578 Clinical Study Comparing the Alteration of Nasal Tip Sensibility and Sensory Recovery Time following Open Rhinoplasty with
Plastic Surgery International Volume 0, Article ID 4578, 4 pages doi:0.55/0/4578 Clinical Study Comparing the Alteration of Nasal Tip Sensibility and Sensory Recovery Time following Open Rhinoplasty with
Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Overview
 Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Overview Name Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Latin Nervus Ethmoidalis anterior Etymology Pain Differential Diagnosis - Enrico Dellacà M.D Ph.D. Nerve from Latin nervus meaning sinew,
Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Overview Name Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Latin Nervus Ethmoidalis anterior Etymology Pain Differential Diagnosis - Enrico Dellacà M.D Ph.D. Nerve from Latin nervus meaning sinew,
RECONSTRUCTION of large surgical
 Triple-Flap Technique for Reconstruction of Large Nasal Defects Timothy W. Wild, MD, DDS; C. Patrick Hybarger, MD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objective: To determine the usefulness of a triple-flap technique for
Triple-Flap Technique for Reconstruction of Large Nasal Defects Timothy W. Wild, MD, DDS; C. Patrick Hybarger, MD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objective: To determine the usefulness of a triple-flap technique for
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
 Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy. Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali
 Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Lina Mansour. Reyad Jabiri. 0 P a g e
 2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD
 Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD Axial Based upon a named artery. Survival length depends upon the artery not the width of the flap. Random Has random unnamed vessels supplying it. Survival length is directly proportional
Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD Axial Based upon a named artery. Survival length depends upon the artery not the width of the flap. Random Has random unnamed vessels supplying it. Survival length is directly proportional
NASAL ANATOMY. Elena Rizzo Riera R1 ORL HUSE
 NASAL ANATOMY Elena Rizzo Riera R1 ORL HUSE NASAL ANATOMY The nose is a highly contoured pyramidal structure situated centrally in the face and it is composed by: ü Skin ü Mucosa ü Bone ü Cartilage ü Supporting
NASAL ANATOMY Elena Rizzo Riera R1 ORL HUSE NASAL ANATOMY The nose is a highly contoured pyramidal structure situated centrally in the face and it is composed by: ü Skin ü Mucosa ü Bone ü Cartilage ü Supporting
Epidemiology 3002). Epidemiology and Pathophysiology
 Epidemiology Maxillofacial trauma or injuries are commonly encountered in the practice of emergency medicine and are presenting one of the most challenging problems to the attending surgeons or physicians
Epidemiology Maxillofacial trauma or injuries are commonly encountered in the practice of emergency medicine and are presenting one of the most challenging problems to the attending surgeons or physicians
Charlin S Syndrome Following a Routine Septorhinoplasty
 Kavyani et al. 103 Case Report Charlin S Syndrome Following a Routine Septorhinoplasty Ali Kavyani1*, Ali Manafi2 1. 2. Department of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences,
Kavyani et al. 103 Case Report Charlin S Syndrome Following a Routine Septorhinoplasty Ali Kavyani1*, Ali Manafi2 1. 2. Department of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences,
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi
 By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
Triple Plane Dissection in Open Primary Rhinoplasty in Middle Eastern Noses
 Triple Plane Dissection in Open Primary Rhinoplasty in Middle Eastern Noses Ahmed Elshahat, MD Plastic Surgery Department, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University; and Eldemerdash Hospital, Cairo, Egypt
Triple Plane Dissection in Open Primary Rhinoplasty in Middle Eastern Noses Ahmed Elshahat, MD Plastic Surgery Department, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University; and Eldemerdash Hospital, Cairo, Egypt
Correction of the Retracted Alar Base
 218 William D. Losquadro, M.D. 1 Anthony Bared, M.D. 2 Dean M. Toriumi, M.D. 2 1 Mount Kisco Medical Group, Katonah, New York 2 Division of Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Otolaryngology
218 William D. Losquadro, M.D. 1 Anthony Bared, M.D. 2 Dean M. Toriumi, M.D. 2 1 Mount Kisco Medical Group, Katonah, New York 2 Division of Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Otolaryngology
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Pterygopalatine fossa: The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped depression, It is located between the maxilla,
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Pterygopalatine fossa: The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped depression, It is located between the maxilla,
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
Effect of Depressor Septi Resection in Rhinoplasty on Upper Lip Length
 Research Original Investigation Effect of Depressor Septi Resection in Rhinoplasty on Upper Lip Length Yan Ho, MD; Robert Deeb, MD; Richard Westreich, MD; William Lawson, MD, DDS IMPORTANCE Resection of
Research Original Investigation Effect of Depressor Septi Resection in Rhinoplasty on Upper Lip Length Yan Ho, MD; Robert Deeb, MD; Richard Westreich, MD; William Lawson, MD, DDS IMPORTANCE Resection of
RECONSTRUCTION OF SUBTOTAL DEFECTS OF THE NOSE BY ABDOMINAL TUBE FLAP. By MICHAL KRAUSS. Plastic Surgery Hospital, Polanica-Zdroj, Poland
 RECONSTRUCTION OF SUBTOTAL DEFECTS OF THE NOSE BY ABDOMINAL TUBE FLAP By MICHAL KRAUSS Plastic Surgery Hospital, Polanica-Zdroj, Poland RECONSTRUCTION of the nose is one of the composite procedures in
RECONSTRUCTION OF SUBTOTAL DEFECTS OF THE NOSE BY ABDOMINAL TUBE FLAP By MICHAL KRAUSS Plastic Surgery Hospital, Polanica-Zdroj, Poland RECONSTRUCTION of the nose is one of the composite procedures in
cally, a distinct superior crease of the forehead marks this spot. The hairline and
 4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
The overprojected ( Pinocchio ) tip and the ptotic
 Featured Operative Technique Management of the Overprojected Nose and Ptotic Nasal Tip William E. Silver, MD, FCS; and Giancarlo F. Zuliani, MD The overprojected ( Pinocchio ) tip and the ptotic tip are
Featured Operative Technique Management of the Overprojected Nose and Ptotic Nasal Tip William E. Silver, MD, FCS; and Giancarlo F. Zuliani, MD The overprojected ( Pinocchio ) tip and the ptotic tip are
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
Fundamental to the evolution of rhinoplasty COSMETIC. Classifying Deformities of the Columella Base in Rhinoplasty.
 COSMETIC Classifying Deformities of the Columella Base in Rhinoplasty Michael R. Lee, M.D. Georges Tabbal, M.D. T. Jonathan Kurkjian, M.D. Jason Roostaeian, M.D. Rod J. Rohrich, M.D. Dallas, Texas Background:
COSMETIC Classifying Deformities of the Columella Base in Rhinoplasty Michael R. Lee, M.D. Georges Tabbal, M.D. T. Jonathan Kurkjian, M.D. Jason Roostaeian, M.D. Rod J. Rohrich, M.D. Dallas, Texas Background:
Analyzing and controlling nasal tip projection COSMETIC. A Multivariate Analysis of Nasal Tip Deprojection
 COSMETIC A Multivariate Analysis of Nasal Tip Deprojection Jacob G. Unger, M.D. Michael R. Lee, M.D. Robert K. Kwon, M.D. Rod J. Rohrich, M.D. Dallas, Texas Background: Projection of the nasal tip is a
COSMETIC A Multivariate Analysis of Nasal Tip Deprojection Jacob G. Unger, M.D. Michael R. Lee, M.D. Robert K. Kwon, M.D. Rod J. Rohrich, M.D. Dallas, Texas Background: Projection of the nasal tip is a
MedStar Health considers Septoplasty-Rhinoplasty medically necessary for the following indications:
 MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL MP.038.MH Septoplasty-Rhinoplasty This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar MA DSNP CSNP MedStar CareFirst
MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL MP.038.MH Septoplasty-Rhinoplasty This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar MA DSNP CSNP MedStar CareFirst
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY NASOLABIAL FLAP FOR ORAL CAVITY RECONSTRUCTION Harry Wright, Scott Stephan, James Netterville Designed as a true myocutaneous flap pedicled
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY NASOLABIAL FLAP FOR ORAL CAVITY RECONSTRUCTION Harry Wright, Scott Stephan, James Netterville Designed as a true myocutaneous flap pedicled
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
1 The nasal bones are deeper and are therefore MATERIAL AND METHODS. At the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
 Technical Experiences Reconstruction of the Nasal Tip Valerio Cervelli, MD, DJ Bottini, PhD, Pietro Gentile, MD Rome, Italy Defects of the nasal tip present complex problems in terms of reconstruction,
Technical Experiences Reconstruction of the Nasal Tip Valerio Cervelli, MD, DJ Bottini, PhD, Pietro Gentile, MD Rome, Italy Defects of the nasal tip present complex problems in terms of reconstruction,
The orbit-1. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
Pearls for Keeping it Simple in Cutaneous Reconstruction
 Pearls for Keeping it Simple in Cutaneous Reconstruction Jerry D. Brewer, MD, MS, FAAD brewer.jerry@mayo.edu Professor of Dermatology Division of Dermatologic Surgery Department of Dermatology Mayo Clinic
Pearls for Keeping it Simple in Cutaneous Reconstruction Jerry D. Brewer, MD, MS, FAAD brewer.jerry@mayo.edu Professor of Dermatology Division of Dermatologic Surgery Department of Dermatology Mayo Clinic
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheets, Distributions Page 1
 Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Lesson Plans and Objectives: Review material for article Prep work for article Picture recovery Review for placement on-line.
 Lesson Plans and Objectives: Review material for article Prep work for article Picture recovery Review for placement on-line. After reading the article, the staff will be able to: Define facial trauma
Lesson Plans and Objectives: Review material for article Prep work for article Picture recovery Review for placement on-line. After reading the article, the staff will be able to: Define facial trauma
Nasal region. cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?
 Nasal region skull bones: nasal and frontal processes of maxilla cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?) 1 Nasal cavity Roof
Nasal region skull bones: nasal and frontal processes of maxilla cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?) 1 Nasal cavity Roof
NASAL FRACTURES. Andrew H. Murr, MD FACS Professor Chief of Service Department of Otolaryngology/ Head and Neck Surgery San Francisco General Hospital
 NASAL FRACTURES Andrew H. Murr, MD FACS Professor Chief of Service Department of Otolaryngology/ Head and Neck Surgery San Francisco General Hospital Roger Boles, M.D. Endowed Chair in Otolaryngology Education
NASAL FRACTURES Andrew H. Murr, MD FACS Professor Chief of Service Department of Otolaryngology/ Head and Neck Surgery San Francisco General Hospital Roger Boles, M.D. Endowed Chair in Otolaryngology Education
Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve
 19 Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve.1 Introduction 0. The Central Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 1..1 Origin 1.. Trigeminal Nuclei.3 The Peripheral Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 4.3.1 Ophthalmic Nerve 4.3.
19 Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve.1 Introduction 0. The Central Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 1..1 Origin 1.. Trigeminal Nuclei.3 The Peripheral Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 4.3.1 Ophthalmic Nerve 4.3.
Subciliary versus Subtarsal Approaches to Orbitozygomatic Fractures
 CME Subciliary versus Subtarsal Approaches to Orbitozygomatic Fractures Rod J. Rohrich, M.D., Jeffrey E. Janis, M.D., and William P. Adams, Jr., M.D. Dallas, Texas Learning Objectives: After studying this
CME Subciliary versus Subtarsal Approaches to Orbitozygomatic Fractures Rod J. Rohrich, M.D., Jeffrey E. Janis, M.D., and William P. Adams, Jr., M.D. Dallas, Texas Learning Objectives: After studying this
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery FACIAL FRACTURES
 Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
The Effectiveness of Modified Vertical Dome Division Technique in Reducing Nasal Tip Projection in Rhinoplasty
 IJMS Vol 36, No 3, September 2011 Original Article The Effectiveness of Modified Vertical Dome Division Technique in Reducing Nasal Tip Projection in Rhinoplasty Behrooz Gandomi 1, Mohammad Hossein Arzaghi
IJMS Vol 36, No 3, September 2011 Original Article The Effectiveness of Modified Vertical Dome Division Technique in Reducing Nasal Tip Projection in Rhinoplasty Behrooz Gandomi 1, Mohammad Hossein Arzaghi
Naso-Orbital Complex Reconstruction with Titanium Mesh and Canthopexy
 Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com DOI: 10.4172/2472-1905.100011 Naso-Orbital Complex Reconstruction with Titanium Mesh and Canthopexy Abstract Context: We are introducing the reconstruction
Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com DOI: 10.4172/2472-1905.100011 Naso-Orbital Complex Reconstruction with Titanium Mesh and Canthopexy Abstract Context: We are introducing the reconstruction
CHAPTER 17 FACIAL AESTHETIC SURGERY. Christopher C. Surek, DO and Mohammed S. Alghoul, MD. I. BROW LIFT (Figures 1 and 2)
 CHAPTER 17 FACIAL AESTHETIC SURGERY Christopher C. Surek, DO and Mohammed S. Alghoul, MD I. BROW LIFT (Figures 1 and 2) A. Open Coronal Brow Lift Technique 1. Coronal incision is made in the hair-bearing
CHAPTER 17 FACIAL AESTHETIC SURGERY Christopher C. Surek, DO and Mohammed S. Alghoul, MD I. BROW LIFT (Figures 1 and 2) A. Open Coronal Brow Lift Technique 1. Coronal incision is made in the hair-bearing
*in general the blood supply of the nose comes from branches of the internal and external carotid arteries.
 In the previous lecture we talked about the anatomy of the nasal cavity, today we will talk about its blood supply, venous drainage, innervations, and finally about the paranasal sinuses. When we describe
In the previous lecture we talked about the anatomy of the nasal cavity, today we will talk about its blood supply, venous drainage, innervations, and finally about the paranasal sinuses. When we describe
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
The Orbit. The Orbit OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION 9/25/2014. The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? Openings in the orbit
 The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION JEFFREY M. GAMBLE, OD COLUMBIA EYE CONSULTANTS OPTOMETRY & UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY CLINICAL
The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION JEFFREY M. GAMBLE, OD COLUMBIA EYE CONSULTANTS OPTOMETRY & UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY CLINICAL
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔. 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機
 Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY PARAMEDIAN FOREHEAD FLAP NASAL RECONSTRUCTION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Brian Cervenka, Travis Tollefson, Patrik Pipkorn The paramedian forehead
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY PARAMEDIAN FOREHEAD FLAP NASAL RECONSTRUCTION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Brian Cervenka, Travis Tollefson, Patrik Pipkorn The paramedian forehead
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Our algorithm for nasal reconstruction *
 Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery (2006) 59, 239 247 Our algorithm for nasal reconstruction * T. Yoon*, J. Benito-Ruiz, E. García-Díez, J.M. Serra-Renom Department of Plastic, Reconstructive
Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery (2006) 59, 239 247 Our algorithm for nasal reconstruction * T. Yoon*, J. Benito-Ruiz, E. García-Díez, J.M. Serra-Renom Department of Plastic, Reconstructive
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
LOCAL ANESTHESIA IN PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of local anesthesia in pediatric dentistry must be made in conjunction
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of local anesthesia in pediatric dentistry must be made in conjunction
Surgical Treatment of Nasal Obstruction
 Surgical Treatment of Nasal Obstruction P. Daniel Knott, MD FACS Director, Division of Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Department of Otolaryngology/Head and Neck Surgery UCSF Medical Center Nothing
Surgical Treatment of Nasal Obstruction P. Daniel Knott, MD FACS Director, Division of Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Department of Otolaryngology/Head and Neck Surgery UCSF Medical Center Nothing
be very thin and variable. Facial nerve branches that exit the parotid gland are deep to the SMAS.
 The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #1 Facial Trauma
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #1 Facial Trauma The face is vital to human appearance and function. Facial injuries can impair a patient
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #1 Facial Trauma The face is vital to human appearance and function. Facial injuries can impair a patient
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
A new classification system of nasal contractures
 Original Article J Cosmet Med 2017;1(2):106-111 https://doi.org/10.25056/jcm.2017.1.2.106 pissn 2508-8831, eissn 2586-0585 A new classification system of nasal contractures Geunuck Chang 1, Donghak Jung
Original Article J Cosmet Med 2017;1(2):106-111 https://doi.org/10.25056/jcm.2017.1.2.106 pissn 2508-8831, eissn 2586-0585 A new classification system of nasal contractures Geunuck Chang 1, Donghak Jung
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
Fracture frontal bone and its management
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 1, 2013 Fracture frontal bone and its management Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/14/ ISSN: 2250-0359
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 1, 2013 Fracture frontal bone and its management Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/14/ ISSN: 2250-0359
Extended Bilaminar Forehead Flap With Cantilevered Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Full-Thickness Nasal Defects
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:566 570, 2005 Extended Bilaminar Forehead Flap With Cantilevered Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Full-Thickness Nasal Defects Jason K. Potter, DDS, MD,* Yadranko Ducic, MD,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:566 570, 2005 Extended Bilaminar Forehead Flap With Cantilevered Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Full-Thickness Nasal Defects Jason K. Potter, DDS, MD,* Yadranko Ducic, MD,
Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 704 708 CASE REPORT Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases Lütfi Eroğlu a, *, Osman Ata Uysal b a Faculty of Medicine, Department of Plastic and
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 704 708 CASE REPORT Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases Lütfi Eroğlu a, *, Osman Ata Uysal b a Faculty of Medicine, Department of Plastic and
MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine Maxilla MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal
MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine Maxilla MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal
CME. Nasal Reconstruction
 CME Nasal Reconstruction Frederick J. Menick, M.D. Tucson, Ariz. Learning Objectives: After studying this article, the participant should be able to: 1. Understand nasal wound healing and develop an organized
CME Nasal Reconstruction Frederick J. Menick, M.D. Tucson, Ariz. Learning Objectives: After studying this article, the participant should be able to: 1. Understand nasal wound healing and develop an organized
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Nose & Mouth OUTLINE. Nose. - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls. - Paranasal Sinuses. - Neurovascular Structures. Mouth. - Oral Cavity & Its Contents
 Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
The Versatile Naso-Labial Flaps in Facial Reconstruction
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 17, No. 4, December: 245-250, 2005 The Versatile Naso-Labial Flaps in Facial Reconstruction HAMDY H. EL-MARAKBY, M.D., F.R.C.S. The Departments of National
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 17, No. 4, December: 245-250, 2005 The Versatile Naso-Labial Flaps in Facial Reconstruction HAMDY H. EL-MARAKBY, M.D., F.R.C.S. The Departments of National
The orbit-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-2 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Eyelids The eyelids (act like the curtains) protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure The upper eyelid
The orbit-2 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Eyelids The eyelids (act like the curtains) protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure The upper eyelid
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy
 Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of Anatomy
 5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
Closed rhinoplasty. Yadranko Ducic, MD, MSc, FRCS(C), FACS, Robert DeFatta, MD, PhD. From the Center for Aesthetic Surgery, Colleyville, Texas.
 Operative Techniques in Otolaryngology (2007) 18, 233-242 Closed rhinoplasty Yadranko Ducic, MD, MSc, FRCS(C), FACS, Robert DeFatta, MD, PhD From the Center for Aesthetic Surgery, Colleyville, Texas. KEYWORDS
Operative Techniques in Otolaryngology (2007) 18, 233-242 Closed rhinoplasty Yadranko Ducic, MD, MSc, FRCS(C), FACS, Robert DeFatta, MD, PhD From the Center for Aesthetic Surgery, Colleyville, Texas. KEYWORDS
SCOPE OF PRACTICE PGY-6 PGY-7 PGY-8
 PGY-6 Round on all plastic surgery inpatients every day. Assess progress of patients and identify real or potential problems. Review patients progress with attending physicians daily and participate in
PGY-6 Round on all plastic surgery inpatients every day. Assess progress of patients and identify real or potential problems. Review patients progress with attending physicians daily and participate in
MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY: AN OVERVIEW
 MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY: AN OVERVIEW SKIN CANCER: Skin cancer is far and away the most common malignant tumor found in humans. The most frequent types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous
MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY: AN OVERVIEW SKIN CANCER: Skin cancer is far and away the most common malignant tumor found in humans. The most frequent types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous
The upper buccal sulcus approach, an alternative for post-trauma rhinoplasty
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 218 223 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00117-6 The
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 218 223 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00117-6 The
