Essentials of headache
|
|
|
- Julianna Rodgers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Earn 3 CPD Points online Essentials of headache and migraine Dr Johan Smuts Neurologist Pretoria Introduction Headaches are among the most common disorders of health worldwide. They are frequently difficult to treat and are often associated with significant disability and impairment of quality of life. 1 During a lifetime, just over three-quarters of the population will experience tension-type headache (TTH) and one in six will suffer from migraine. Headache may be exacerbated by normal physiological changes (e.g. hormonal cycles), medical and psychological comorbidities, as well as inappropriate use or overuse of over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications. All of these factors complicate both diagnosis and management and, if management is inadequate, acute episodic pain may progress to a chronic pain state that might be very difficult to treat. Consequently, the ideal approach to headache is a multidisciplinary one, where appropriate use of pharmacotherapy and combinations of medications with complementary mechanisms of action can significantly improve the long-term outcome. Dr Dion Opperman Neurologist Cape Town KEY MESSAGES Headache is best managed by the general practitioner, who is informed about the patient s personal and social circumstances Primary care practitioners need to be alert to red flag signs indicating the need for immediate referral Common pathological mechanisms link headache and psychiatric morbidity The most effective acute treatment for migraine is a triptan, such as zolmitriptan, rizatriptan or naratriptan. Response to these agents varies between individuals Prophylactic therapy must follow tested clinical principles useful guidance is provided by the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) Memantine use has recently been shown in a double-blind placebo-controlled study to reduce monthly migraine attack frequency by 62% Careful clinical assessment, consideration of comorbidities and a multidisciplinary approach can reduce morbidity caused by headache and migraine. Chronic migraine This article was made possible by an unrestricted educational grant from Cipla, which had no control over content. The International Headache Society defines chronic migraine as headaches on 15 days/month for 3 months, of which 8 days fulfil the criteria for migraine without aura, which were successfully treated with acute care medications, such as ergots or triptans. 2 Chronic migraine evolves from episodic migraine, with an incidence of 2.5% in episodic migraine sufferers, such that the prevalence is approximately 2-4% of the population. It often leads to overuse of acute medication, leading to exacerbation in the form of medication overuse headache (MOH). March
2 Medication overuse headache MOH is the third most common headache type with a prevalence of 1-2%. It is characterised by headache on 15 or more days every month and is caused by chronic excessive use of medication to treat headache. It is therefore avoidable. All medications used for the acute symptomatic treatment of headache (OTC and prescription) can cause MOH. Although the pathogenesis of MOH probably varies depending on the different causative Quality of life People suffering from headache have significantly impaired quality of life. Around one in three people with migraine will experience four or more serious attacks per month and two-thirds will have up to four. Considering that migraine episodes may last up to 72 hours, just one episode per month can impair normal activities for up to three days. Repeated headache attacks are often accompanied by constant fear of the next episode and disruption of family life, social life, relationships and employment. 1 Fewer than 10% of migraineurs are free from impairment during the headache. The majority require bedrest. agents, frequency of use is important, with low daily doses being more likely to cause MOH than larger weekly doses. The headache is persistent and often worse on awakening in the morning, leading to a vicious cycle of headache and analgesic use, the latter sometimes used pre-emptively with the intention of preventing the progressively worsening, oppressive and persistent pain. 1 Headaches predominantly affect the economically active population - people aged between late teens and their 50s. Therefore, in addition to costs of treatment, they represent a significant financial burden to both family and the economy in terms of lost working hours and reduced productivity. Inability to cope and unreliable performance at work can undermine both career and financial prospects and can place considerable strain on relationships. Up to three-quarters of patients report that migraine has adverse effects on relationships with partners, children and co-workers as well as on work performance. Multidisciplinary approach to treatment The majority of patients with headache are best managed by the general practitioner, who is likely to be the one most informed about the patient s personal and social circumstances. However, early referral is recommended where a specific diagnosis indicates it or where there are warning signs that suggest more specialised investigation and management are required (Table 1). Migraine or other headaches during pregnancy or in the postnatal period, as well as menstrual migraines, which may respond to hormonal manipulation (e.g. the oral contraceptive pill), may require referral to a gynaecologist. Headache and the psychiatrist Chronic pain is strongly associated with psychiatric comorbidities, particularly anxiety, depression and insomnia. 4 However, there is a bidirectional relationship between chronic pain and these symptoms. Patients with somatisation, health-seeking behaviours and poor sleep are at high risk of developing chronic widespread pain, including musculoskeletal pain and headaches. The risk increases in tandem with severity of anxiety, depression or sleep problems, and those with multiple predisposing factors are at the highest risk. 5 There is strong epidemiological and clinical evidence to suggest common pathological mechanisms linking headache and psychiatric morbidity. Depression and/or anxiety are comorbid in as many as 80% of migraine suffers. The monoamines (serotonin, noradrenaline and dopamine), which have a central role in these psychiatric morbidities, also play important roles in migraine and in 2 March 2018
3 Red flag signs indicating the need for immediate referral (adapted from SIGN guidance) 3 New onset or change in headache in patients >50 years of age Thunderclap: rapid time to peak headache intensity (seconds to five minutes) Focal neurological symptoms (e.g. limb weakness, numbness, aura <5 minutes or >1 hour) Non-focal neurological symptoms (e.g. cognitive disturbance, ataxia, loss of coordination) Abnormal neurological examination Asymmetry of pupillary response Papilloedema Change in headache frequency, characteristics or associated symptoms Headache that changes with posture Headache on waking (migraine is the most frequent cause of morning headache) Headache precipitated by physical exertion, sexual activity or a valsalva manoeuvre (e.g. coughing, laughing, straining) Patients with risk factors for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis Jaw claudication or visual disturbance Neck stiffness (signs of meningeal irritation) Fever (systemic illness) New-onset headache in a patient with a history of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) New-onset headache in a patient with a history of cancer Infection Progressive visual or neurological changes migraine chronification. Comorbid psychiatric conditions affect both prognosis and treatment of headache and increase the risk of suicide in those suffering from severe or persistent headache. Traumatic experiences during childhood may affect brain development, causing disturbances in the monoamine systems, whereas post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is associated with changes in both the monoamine systems and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and therefore with pain syndromes that may be difficult to treat. Pharmacotherapy for migraine Pharmacotherapy for migraine may take the form of acute treatment of individual headaches or prophylactic therapy. Acute therapy for migraine 1. The most effective acute treatment for migraine is a triptan (sumatriptan, zolmitriptan, rizatriptan, naratriptan) administered early in the headache. The effect of individual triptans is idiosyncratic and patients who do not respond to one may have a good response to another A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), such as ibuprofen, is inexpensive and may be effective alone or in combination with a triptan For migraines that persist despite initial treatment, administration of oxygen or olanzapine may be beneficial. 4. Opioids should be avoided and are generally only suitable for chronic pain in carefully selected patients under specialist care. March
4 Prophylactic therapy for migraine The goal of prophylactic therapy is to reduce attack frequency, severity and duration, improve responsiveness of acute attacks to treatment and reduce migraineassociated disability. Prophylactic therapy may be considered for patients in whom migraine attacks have a significant impact on health and daily activities, despite appropriate use of acute medications, trigger management and lifestyle modification, or where there is a high frequency of migraine attacks with risk for medication overuse (>3 moderate or severe headache days a month when acute medications are not reliably effective, or >8 headache days a month even when acute medications are optimally effective). Therapy may be considered effective when headache frequency is reduced by 50% or more. General principles for prophylactic therapy are as follows: 3 Most preventive drugs should be titrated slowly to an effective or maximum dose in order to minimise side effects Preventive medication should be given a trial of at least 6-8 weeks following dose titration Choice of medication should be guided by side effect profile and the presence of comorbidities. Adherence to treatment is likely to be better with medications that are taken once daily After 6-12 months of effective prophylaxis, gradual tapering and withdrawal should be considered If headache frequency increases with drug withdrawal, the dose can be increased again or, in the case of discontinuation, the drug may be restarted. Potential options for prophylactic therapy are listed in Table 1. Medications with high-quality evidence that supports a strong recommendation for efficacy include topiramate, propranolol and amitriptyline. Table 1. Pharmacotherapy for migraine prophylaxis 6-10 Drug Potential adverse effects Comments Amitriptyline Beta-blockers (e.g. propranolol, metoprolol) Candesartan Duloxetine Sedation, dry mouth, constipation, dizziness, confusion, weight gain, urinary retention, orthostatic hypotension, reflex tachycardia, palpitations Drowsiness, fatigue, lethargy, nightmares, depression, hallucinations, memory disturbance, decreased exercise tolerance, orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia, erectile dysfunction, stroke (patients with aura) Nausea/ vomiting, constipation, anorexia, dry mouth, dizziness Good initial choice for migraine prophylaxis; Useful for patients with depression/anxiety, insomnia or associated TTH; Start with low dose (10mg) and increase slowly (10mg weekly or every two weeks) Few side effects; Usual dose is 16mg Useful in patients with depression Flunarizine Weight gain, hypotension, dizziness, somnolence Avoid in depressed patients Lisinopril Cough, dizziness Usual dose is 20mg Topiramate Valproic acid Paraesthesias, fatigue, drowsiness, nausea, weight loss, taste perversion, cognitive impairment, language disorder, visual field loss, acute myopia with glaucoma (rare) Nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal disorders, abnormal liver function tests, weight gain, tremor, hair loss, hyperandrogenism and ovarian cysts Useful in overweight patients; Use with caution in depressed patients; Start with low dose and increase slowly; Usual target dose is 100mg Venlafaxine Nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, tachycardia Useful in patients with depression 4 March 2018
5 Refractory headache Patients with headache that is refractory to monotherapy may benefit from combination therapy, which may also permit lower doses of the combined individual medications. The following combinations may be useful in patients with refractory migraine: Memantine Increased glutamate transmission may be important in the pathogenesis of chronic pain. In patients with chronic migraine, glutamate levels in the cerebrospinal fluid are increased, suggesting that glutamate is important in progression from episodic to chronic migraine. Memantine is an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist approved for the treatment of dementia associated with Alzheimer s disease. It has also been shown in a number of clinical studies to be effective in migraine prophylaxis and improves cognitive performance in these patients Botulinum toxin Observations that migraine might be improved in patients receiving injections of onabotulinum toxin A (OBTA) for wrinkles prompted studies of the potential for this treatment approach in patients with migraine. In comparison with placebo, Conclusions Headaches and migraine are extremely common and among the primary reasons for visits to general practitioners, specialists and emergency departments. Although serious pathology is rare, headache is responsible for substantial disability, impaired quality of life, and considerable Beta-blocker and topiramate Beta-blocker and valproate Beta-blocker and amitriptyline Amitriptyline and topiramate Patients requiring prophylactic polypharmacy should be considered for specialist referral. In a recent placebo-controlled study in patients with chronic migraine, memantine was associated with an average 62% reduction in monthly attack frequency (vs 17% in the placebo group) and significantly greater reduction in the number of migraine days and headache severity. Memantine was associated with a greater reduction in number of days absent from work and significant improvements in disability score. It was well tolerated; side effects were uncommon and generally mild. 12 although OBTA injection was not shown to significantly reduce frequency of migraine episodes, it was associated with a significant reduction in headache days and clinically relevant improvements in functioning and health-related quality of life. 10 costs in terms of expenditure on healthcare and to the economy. Careful clinical assessment, consideration of comorbidities and a multidisciplinary approach to investigation and management can help reduce morbidity and prevent unnecessary suffering and waste of resources. It is Table 2. The American Headache Society Choosing Wisely recommendations Don t perform neuroimaging studies in patients with stable headaches that meet criteria for migraine 2. Don t perform CT imaging for headache when MRI is available, except in emergency settings 3. Don t recommend surgical deactivation of migraine trigger points outside of a clinical trial 4. Don t prescribe opioid- or butalbital-containing medications as first-line treatment for recurrent headache disorders 5. Don t recommend prolonged or frequent use of OTC pain medications for headache. March
6 important to remember that inappropriate management not only increases costs, but may lead to MOH and chronic pain syndromes that are extremely difficult to treat. In this regard, it is worthwhile taking note of the five Choosing Wisely proposals recommended by the American Headache Society (Table 2). References 1. World Health Organization (WHO). Atlas of Headache Disorders and Resources in the World Available at headache_disorders/en/. Accessed 22 March International Headache Society. International Classification of Headache Disorders. 3 rd edition (Beta version), Available at: Accessed 22 March Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. Diagnosis and Management of Headache in Adults. A National Clinical Guideline. Edinburgh: SIGN 107, Available at Accessed 22 March Gore M, Brandenburg NA, Dukes E, et al. Pain severity in diabetic peripheral neuropathy is associated with patient functioning, symptom levels of anxiety and depression, and sleep. J Pain Symptom Manage 2005; 30(4): Gupta A, Silman AJ, Ray D, et al. The role of psychosocial factors in predicting the onset of chronic widespread pain: results from a prospective populationbased study. Rheumatology 2007; 46(4): Dodick DW. Chronic daily headache. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: Chetty S, Baalbergen E, Bhigjee AI, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of neuropathic pain: expert panel recommendations for South Africa. S Afr Med J 2012; 102(5): Loj J, Solomon GD. Migraine prophylaxis: Who, why, and how. Cleve Clin J Med 2006; 73(9): Silberstein SD, Holland S, Freitag F, et al. Evidence-based guideline update: Pharmacologic treatment for episodic migraine prevention in adults. Neurology 2012; 78: Gooriah R, Nimeri R, Ahmed F. Evidence-based treatments for adults with migraine. Pain Res Treat DOI: /2015/ Bigal M, Rapoport A, Sheftell F, et al. Memantine in the preventative treatment of refractory migraine. Headache 2008; 48(9): Huang L, Bocek M, Jordan JK, Sheehan AH. Memantine for the prevention of primary headache disorders. Ann Pharmacother 2014; 48(11): Noruzzadeh R, Modabbernia A, Aghamollaii V, et al. Memantine for prophylactic treatment of migraine without aura: a randomised double-blind placebocontrolled study. Headache 2016; 56: Loder E, Weizenbaum E, Frishberg B, et al. Choosing wisely in headache medicine: The American Headache Society s list of five things physicians and patients should question. Headache 2013; 53: This article is based on presentations by Dr Johan Smuts and Dr Dion Opperman at the Cipla Psychiatry Forum on 18 March 2017 at the Arabella Hotel, Kleinmond, Western Cape. The article was written for denovo Medica by Dr David Webb. Earn CPD points online Visit Log in or register and start earning CPD points today. Certificates will be ed to you. Disclaimer The views and opinions expressed in the article are those of the presenters and do not necessarily reflect those of the publisher or its sponsor. In all clinical instances, medical practitioners are referred to the product insert documentation as approved by relevant control authorities. Published by 70 Arlington Street, Everglen, Cape Town, 7550 Tel: (021) I info@denovomedica.com 6 March 2018
A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline. Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN
 A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November 2008. PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS)
A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November 2008. PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS)
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines
 How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
Management of headache
 Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS
 HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline. Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford
 Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford Overview The process of guideline development illustrated with the headache guideline Reflections on the process Key recommendations
Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford Overview The process of guideline development illustrated with the headache guideline Reflections on the process Key recommendations
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in
 HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
Treatments for migraine
 Treatments for migraine Information for patients and carers Department of Neurology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Contents Page About this leaflet Abortive medication for migraine Painkillers Antisickness medication
Treatments for migraine Information for patients and carers Department of Neurology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Contents Page About this leaflet Abortive medication for migraine Painkillers Antisickness medication
Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE
 Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Dubai Standards of Care (Migraine)
 Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Migraine) Preface Migraine is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of migraine is done through various different strategies.
Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Migraine) Preface Migraine is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of migraine is done through various different strategies.
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy
 HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache
 MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 CGRP Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
CGRP Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care. December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary
 Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Adult with headache. Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention
 Adult with headache Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention London Strategic Clinical Networks London Neuroscience Strategic Clinical Network
Adult with headache Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention London Strategic Clinical Networks London Neuroscience Strategic Clinical Network
25/09/2018 HEADACHE. Dr Nick Pendleton
 HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2018 1 Small Group Work Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache
HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2018 1 Small Group Work Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 CGRP Page 1 of 13 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
CGRP Page 1 of 13 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
HEADACHE. Dr Nick Pendleton. September Headache
 HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2017 Headache Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache Raised ICP
HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2017 Headache Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache Raised ICP
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates
 Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
Strategies in Migraine Care
 Strategies in Migraine Care Julie L. Roth, MD Rhode Island Hospital Assistant Professor, Neurology The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University March 28, 2015 Financial Disclosures None. Objectives
Strategies in Migraine Care Julie L. Roth, MD Rhode Island Hospital Assistant Professor, Neurology The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University March 28, 2015 Financial Disclosures None. Objectives
Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital
 Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital Honorarium from Current Pain and Headache Reports; Section Editor Unusual
Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital Honorarium from Current Pain and Headache Reports; Section Editor Unusual
Long-Term Care Updates
 Long-Term Care Updates September 2017 By Lindsay Slowiczek, PharmD Migraines are often considered to be a condition affecting younger or middle-aged patients, during which patients experience episodic,
Long-Term Care Updates September 2017 By Lindsay Slowiczek, PharmD Migraines are often considered to be a condition affecting younger or middle-aged patients, during which patients experience episodic,
Primary Care Adult Headache Management Pathway (formerly North West Headache Management Guideline for Adults) Version 1.0
 Primary Care Adult Headache Management Pathway (formerly rth West Headache Management Guideline for Adults) Version 1.0 1 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1.0 October 2018 Reformatted
Primary Care Adult Headache Management Pathway (formerly rth West Headache Management Guideline for Adults) Version 1.0 1 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1.0 October 2018 Reformatted
Risk Factors, Clinical Course, and Barriers to Care in Adults and Pediatrics. Rebecca R. Buttaccio, PA-C Dent Neurologic Institute
 Risk Factors, Clinical Course, and Barriers to Care in Adults and Pediatrics Rebecca R. Buttaccio, PA-C Dent Neurologic Institute Speaker for Avanir Disclosures Learning Objectives 1. Review the risk factors
Risk Factors, Clinical Course, and Barriers to Care in Adults and Pediatrics Rebecca R. Buttaccio, PA-C Dent Neurologic Institute Speaker for Avanir Disclosures Learning Objectives 1. Review the risk factors
MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache
 MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older with a diagnosis of primary headache
MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older with a diagnosis of primary headache
KEY MESSAGES. It is often under-recognised and 30-50% of MDD cases in primary care and medical settings are not detected.
 KEY MESSAGES Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a significant mental health problem that disrupts a person s mood and affects his psychosocial and occupational functioning. It is often under-recognised
KEY MESSAGES Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a significant mental health problem that disrupts a person s mood and affects his psychosocial and occupational functioning. It is often under-recognised
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา
 ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
Guidelines MANAGEMENT OF MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER (MDD)
 MANAGEMENT OF MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER (MDD) Guidelines CH Lim, B Baizury, on behalf of Development Group Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Major Depressive Disorder A. Introduction Major depressive
MANAGEMENT OF MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER (MDD) Guidelines CH Lim, B Baizury, on behalf of Development Group Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Major Depressive Disorder A. Introduction Major depressive
Recognition and treatment of medication overuse headache
 Recognition and treatment of medication overuse headache Marcus Lewis MA, MRCGP, DRCOG, DFSRH 20 Mean weekly headache index 15 10 5 Medication overuse headache is a common condition responsible for a high
Recognition and treatment of medication overuse headache Marcus Lewis MA, MRCGP, DRCOG, DFSRH 20 Mean weekly headache index 15 10 5 Medication overuse headache is a common condition responsible for a high
Paediatric headaches. Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services. Brevity, levity, repetition
 Paediatric headaches Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services Brevity, levity, repetition Paediatric)headache?)! Headache!in!children!is!not!that!common.!The!question!is!which!headaches!do!I!
Paediatric headaches Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services Brevity, levity, repetition Paediatric)headache?)! Headache!in!children!is!not!that!common.!The!question!is!which!headaches!do!I!
MIGRAINE UPDATE. Objectives & Disclosures. Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment.
 MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
Migraine Management. Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital
 Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
COMBINATION THERAPIES PREVENTATIVE THERAPIES BETA BLOCKERS
 ACUTE THEAPIES TIPTANS TICYCLIC ANTIDEPESSANTS When starting acute treatment, healthcare professionals should warn patients about the risk of developing medication-overuse headache. ASPIIN Aspirin (900
ACUTE THEAPIES TIPTANS TICYCLIC ANTIDEPESSANTS When starting acute treatment, healthcare professionals should warn patients about the risk of developing medication-overuse headache. ASPIIN Aspirin (900
MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND
 MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND HEADACHE IN MEN: THE FACTS This leaflet was composed by Paolo Rossi M.D., Ph.D. of the European Headache Alliance to mark European Migraine Day of Action 2014. Why a leaflet
MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND HEADACHE IN MEN: THE FACTS This leaflet was composed by Paolo Rossi M.D., Ph.D. of the European Headache Alliance to mark European Migraine Day of Action 2014. Why a leaflet
Chronic Daily Headaches
 Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
A case of a patient with chronic headache. Focus on Migraine. None related to the presentation Grants to conduct clinical trials from: Speaker bureau:
 Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
colds and flu Introduction KEY MESSAGES
 colds and flu New insights: Cold and flu Introduction Colds and flu are responsible for more visits to the pharmacy than any other infectious illness. While severity of influenza differs from year to year,
colds and flu New insights: Cold and flu Introduction Colds and flu are responsible for more visits to the pharmacy than any other infectious illness. While severity of influenza differs from year to year,
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE
 MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
Neurological Dilemmas in Primary Care
 Neurological Dilemmas in Primary Care David Clark, DO dclark@oregonneurology.com When to test? How to test? Pitfalls in testing? When to treat? How to treat? How long to treat? Neurological Dilemmas Seizure
Neurological Dilemmas in Primary Care David Clark, DO dclark@oregonneurology.com When to test? How to test? Pitfalls in testing? When to treat? How to treat? How long to treat? Neurological Dilemmas Seizure
Outpatient Headache Care Guideline
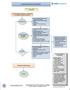 1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
Elavil (amitriptyline)
 Generic name: Amitriptyline Available strengths: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg tablets; 10 mg/ml injection Available in generic: Yes Drug class: Tricyclic antidepressant General Information
Generic name: Amitriptyline Available strengths: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg tablets; 10 mg/ml injection Available in generic: Yes Drug class: Tricyclic antidepressant General Information
Norpramin (desipramine)
 Generic name: Desipramine Available strengths: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg tablets Available in generic: Yes Drug class: Tricyclic antidepressant General Information Norpramin (desipramine)
Generic name: Desipramine Available strengths: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg tablets Available in generic: Yes Drug class: Tricyclic antidepressant General Information Norpramin (desipramine)
Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept
 Headaches in Children February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neuromuscular Center Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH 1 Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept Burton Gutierrez Kan
Headaches in Children February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neuromuscular Center Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH 1 Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept Burton Gutierrez Kan
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation.
 I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
CHRONIC HEADACHES IN CHILDHOOD
 CHRONIC HEADACHES IN CHILDHOOD EDWIN LIU, MD PEDIATRIC NEUROLOGISTS OF PALM BEACH PEDIATRIC SLEEP CENTERS OF FLORIDA ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR FSU ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR NOVA SOUTHEASTERN PEDIATRIC
CHRONIC HEADACHES IN CHILDHOOD EDWIN LIU, MD PEDIATRIC NEUROLOGISTS OF PALM BEACH PEDIATRIC SLEEP CENTERS OF FLORIDA ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR FSU ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR NOVA SOUTHEASTERN PEDIATRIC
BOTULINUM TOXIN POLICY TO INCLUDE:
 BOTULINUM TOXIN POLICY TO INCLUDE: Blepharospasm in adults, Hemi facial spasm in adults, spasmodic torticollis (cervical dystonia), focal spasticity treatment of dynamic equinus foot deformity, focal spasticity
BOTULINUM TOXIN POLICY TO INCLUDE: Blepharospasm in adults, Hemi facial spasm in adults, spasmodic torticollis (cervical dystonia), focal spasticity treatment of dynamic equinus foot deformity, focal spasticity
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines
 Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine
 GUIDELINES SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine STEVE CHAPLIN In February 2018, the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) published a new guideline on the pharmacological management
GUIDELINES SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine STEVE CHAPLIN In February 2018, the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) published a new guideline on the pharmacological management
Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache
 doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01488.x Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache L Pageler 1,2, Z Katsarava 2, HC Diener 2 & V Limmroth 1,2 1 Department of Neurology,
doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01488.x Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache L Pageler 1,2, Z Katsarava 2, HC Diener 2 & V Limmroth 1,2 1 Department of Neurology,
Faculty Disclosures. Learning Objectives
 WWW.AMERICANHEADACHESOCIETY.ORG Case Study 1 and Q & A Content developed by: Lawrence C. Newman, MD, FAHS Donna Gutterman, PharmD Faculty Disclosures LAWRENCE C. NEWMAN, MD, FAHS Dr. Newman has received
WWW.AMERICANHEADACHESOCIETY.ORG Case Study 1 and Q & A Content developed by: Lawrence C. Newman, MD, FAHS Donna Gutterman, PharmD Faculty Disclosures LAWRENCE C. NEWMAN, MD, FAHS Dr. Newman has received
MEASURE #1: MEDICATION PRESCRIBED FOR ACUTE MIGRAINE ATTACK Headache
 MEASURE #1: MEDICATION PRESCRIBED FOR ACUTE MIGRAINE ATTACK Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of migraine who were prescribed a guideline recommended
MEASURE #1: MEDICATION PRESCRIBED FOR ACUTE MIGRAINE ATTACK Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of migraine who were prescribed a guideline recommended
What You Should Know About Your HEADACHE. Learn more about headache types, triggers, and treatments, when to get help, and how to help yourself
 What You Should Know About Your HEADACHE Learn more about headache types, triggers, and treatments, when to get help, and how to help yourself Introduction The purpose of this brochure is to give you a
What You Should Know About Your HEADACHE Learn more about headache types, triggers, and treatments, when to get help, and how to help yourself Introduction The purpose of this brochure is to give you a
Migraine Management. Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital
 Migraine Management Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital Referral Criteria for Migraine Migraine Management Migraine Diagnosis Spot on Health Migraine pathway
Migraine Management Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital Referral Criteria for Migraine Migraine Management Migraine Diagnosis Spot on Health Migraine pathway
Pain CONCERN. Medicines for long-term pain. Antidepressants
 Pain CONCERN Medicines for long-term pain Antidepressants Many people living with long-term pain (also known as chronic or persistent pain) are worried about using medicines like antidepressants. They
Pain CONCERN Medicines for long-term pain Antidepressants Many people living with long-term pain (also known as chronic or persistent pain) are worried about using medicines like antidepressants. They
Appendix 4B - Guidance for the use of Pharmacological Agents for the Treatment of Depression in Adults (18 years and over)
 Appendix 4B - Guidance for the use of Pharmacological Agents for the Treatment of Depression in Adults (18 years and over) Introduction / Background Treatment comes after diagnosis Diagnosis is based on
Appendix 4B - Guidance for the use of Pharmacological Agents for the Treatment of Depression in Adults (18 years and over) Introduction / Background Treatment comes after diagnosis Diagnosis is based on
Faculty Disclosure. Karen L. Bremer, MD. Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest.
 Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
July 2012 Target Population. Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings.
 Guideline for Primary Care Management of Headache in Adults July 2012 Target Population Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings. Exclusions: This guideline does not provide recommendations
Guideline for Primary Care Management of Headache in Adults July 2012 Target Population Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings. Exclusions: This guideline does not provide recommendations
What is new in the migraine world! Modar Khalil Consultant neurologist Hull Royal Infirmary
 What is new in the migraine world! Modar Khalil Consultant neurologist Hull Royal Infirmary Overview Understanding the burden Commonly used terms Acute therapy What we currently have What we are going
What is new in the migraine world! Modar Khalil Consultant neurologist Hull Royal Infirmary Overview Understanding the burden Commonly used terms Acute therapy What we currently have What we are going
Aleksandra Radojičić. Headache Center, Neurology Clinic, Clinical Center of Serbia
 European Headache School Belgrade 2012 MEDICATION OVERUSE HEADACHE Aleksandra Radojičić Headache Center, Neurology Clinic, Clinical Center of Serbia Historical data First cases were described in XVII century
European Headache School Belgrade 2012 MEDICATION OVERUSE HEADACHE Aleksandra Radojičić Headache Center, Neurology Clinic, Clinical Center of Serbia Historical data First cases were described in XVII century
Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description
 Measure Title Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description Percentage of s age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of primary headache who were prescribed
Measure Title Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description Percentage of s age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of primary headache who were prescribed
Management options for Migraine. Prof. Dr. Khwaja Nazimuddin Head Dept. of Internal Medicine BIRDEM
 Management options for Migraine Prof. Dr. Khwaja Nazimuddin Head Dept. of Internal Medicine BIRDEM Assessment The Migraine Disability Assessment Score MIDAS Complete loss of work Partial loss of work Off
Management options for Migraine Prof. Dr. Khwaja Nazimuddin Head Dept. of Internal Medicine BIRDEM Assessment The Migraine Disability Assessment Score MIDAS Complete loss of work Partial loss of work Off
How could I be having migraine when I don't have a headache?
 Migraine Your doctor thinks you may have migraine. Classic migraine attacks start with visual symptoms (often zig-zag colored lights or flashes of light expanding to one side over 10-30 minutes) followed
Migraine Your doctor thinks you may have migraine. Classic migraine attacks start with visual symptoms (often zig-zag colored lights or flashes of light expanding to one side over 10-30 minutes) followed
Dementia Medications Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors (AChEIs) and Glutamate (NMDA) Receptor Antagonist
 Dementia Medications Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors (AChEIs) and Glutamate (NMDA) Receptor Antagonist Medication Dosage Indication for Use Aricept (donepezil) Exelon (rivastigmine) 5mg 23mg* ODT 5mg Solution
Dementia Medications Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors (AChEIs) and Glutamate (NMDA) Receptor Antagonist Medication Dosage Indication for Use Aricept (donepezil) Exelon (rivastigmine) 5mg 23mg* ODT 5mg Solution
Specific Objectives A. Topics to be lectured and discussed at the plenary sessions
 Specific Objectives A. Topics to be lectured and discussed at the plenary sessions 0. Introduction: Good morning ICHD-III! Let s start at the very beginning. When you read you begin with A-B-C, so when
Specific Objectives A. Topics to be lectured and discussed at the plenary sessions 0. Introduction: Good morning ICHD-III! Let s start at the very beginning. When you read you begin with A-B-C, so when
Headaches. Mini Medical School. November 10, A. Laine Green MSc, MD FRCP(C) Assistant Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology)
 Headaches. Mini Medical School. November 10, 2016 A. Laine Green MSc, MD FRCP(C) Assistant Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology) Artist Agnes Cecile Disclosures I have received an honorarium from
Headaches. Mini Medical School. November 10, 2016 A. Laine Green MSc, MD FRCP(C) Assistant Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology) Artist Agnes Cecile Disclosures I have received an honorarium from
M0BCore Safety Profile. Active substance: Bromazepam Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Tablets 6 mg FR/H/PSUR/0066/001 Date of FAR:
 M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Bromazepam Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Tablets 6 mg P-RMS: FR/H/PSUR/0066/001 Date of FAR: 26.11.2013 4.3 Contraindications Bromazepam must not be administered
M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Bromazepam Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Tablets 6 mg P-RMS: FR/H/PSUR/0066/001 Date of FAR: 26.11.2013 4.3 Contraindications Bromazepam must not be administered
Goals. Primary Headache Syndromes. One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders
 Goals One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders Impact of primary headache syndromes Non pharmacologic Rx of migraine individualized to patient triggers Complementary and alternative Rx of migraine
Goals One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders Impact of primary headache syndromes Non pharmacologic Rx of migraine individualized to patient triggers Complementary and alternative Rx of migraine
Index. Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Migraine Associated Dizziness. Department of Neuro-otology
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Migraine Associated Dizziness Department of Neuro-otology If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Migraine Associated Dizziness Department of Neuro-otology If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of
Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Gocovri (amantadine) Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary This prior authorization applies to Commercial, NetResults A series, SourceRx and Health Insurance Marketplace formularies.
Gocovri (amantadine) Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary This prior authorization applies to Commercial, NetResults A series, SourceRx and Health Insurance Marketplace formularies.
DRUG THERAPY CHOICES FOR THE DEMENTED PATIENT Past, Present and Future
 DRUG THERAPY CHOICES FOR THE DEMENTED PATIENT Past, Present and Future Daniel S. Sitar Professor Emeritus University of Manitoba Email: Daniel.Sitar@umanitoba.ca March 6, 2018 INTRODUCTION EPIDEMIOLOGY
DRUG THERAPY CHOICES FOR THE DEMENTED PATIENT Past, Present and Future Daniel S. Sitar Professor Emeritus University of Manitoba Email: Daniel.Sitar@umanitoba.ca March 6, 2018 INTRODUCTION EPIDEMIOLOGY
Measure Components Numerator Statement
 MEASURE #5: OVERUSE OF OPIOID CONTAINING MEDICATIONS FOR PRIMARY HEADACHE DISORDERS Headache For Quality Improvement Only. Not to be used for Public Reporting or Accountability Measure Description Percentage
MEASURE #5: OVERUSE OF OPIOID CONTAINING MEDICATIONS FOR PRIMARY HEADACHE DISORDERS Headache For Quality Improvement Only. Not to be used for Public Reporting or Accountability Measure Description Percentage
4. A consensus definition of CFS/ME has been agreed by international experts for the purposes of research and includes the following:-
 DWP MEDICAL GUIDANCE VERSION 10 (May 2007) CHRONIC FATIGUE SYNDROME AND MYALGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS/ENCEPHALOPATHY What is it? (Definition) 1. The term chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is used to describe
DWP MEDICAL GUIDANCE VERSION 10 (May 2007) CHRONIC FATIGUE SYNDROME AND MYALGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS/ENCEPHALOPATHY What is it? (Definition) 1. The term chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is used to describe
Pamelor (nortriptyline)
 Generic name: Nortriptyline Available strengths: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg capsules; 10 mg/5 ml oral solution Available in generic: Yes Drug class: Tricyclic antidepressant General Information Pamelor
Generic name: Nortriptyline Available strengths: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg capsules; 10 mg/5 ml oral solution Available in generic: Yes Drug class: Tricyclic antidepressant General Information Pamelor
Clinical case. Clinical case 3/15/2018 OVERVIEW. Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment. Refractory headache.
 OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
Migraine Headache Prophylaxis in Adolescents
 I Migraine Headache Prophylaxis in Adolescents It s estimated that up to 28 percent of adolescents between the ages of 15 and 19 (mostly females) are affected by migraine (Lewis, Yonker, Winner, & Sowell,
I Migraine Headache Prophylaxis in Adolescents It s estimated that up to 28 percent of adolescents between the ages of 15 and 19 (mostly females) are affected by migraine (Lewis, Yonker, Winner, & Sowell,
Migraine in Children. Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014
 Migraine in Children Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014 Headaches in Children One of the most common concerns reported by children 3% for children age 3-7 years 4-11% for children age 7-11
Migraine in Children Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014 Headaches in Children One of the most common concerns reported by children 3% for children age 3-7 years 4-11% for children age 7-11
Psychotropic Medication. Including Role of Gradual Dose Reductions
 Psychotropic Medication Including Role of Gradual Dose Reductions What are they? The phrase psychotropic drugs is a technical term for psychiatric medicines that alter chemical levels in the brain which
Psychotropic Medication Including Role of Gradual Dose Reductions What are they? The phrase psychotropic drugs is a technical term for psychiatric medicines that alter chemical levels in the brain which
Lost in Translation: Making Sense of Clinical Treatment Guidelines
 Lost in Translation: Making Sense of Clinical Treatment Guidelines Charles E. Argoff, MD, CPE Disclosures: Charles Argoff Financial Disclosure: Consultant: Teva, Daiichi Sakyo, Pfizer, Nektar, Purdue,
Lost in Translation: Making Sense of Clinical Treatment Guidelines Charles E. Argoff, MD, CPE Disclosures: Charles Argoff Financial Disclosure: Consultant: Teva, Daiichi Sakyo, Pfizer, Nektar, Purdue,
Faculty Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Acute Treatment Strategies
 WWW.AMERICANHEADACHESOCIETY.ORG Acute Treatment Strategies Content developed by: Lawrence C. Newman, MD, FAHS Donna Gutterman, PharmD Faculty Disclosures LAWRENCE C. NEWMAN, MD, FAHS Dr. Newman has received
WWW.AMERICANHEADACHESOCIETY.ORG Acute Treatment Strategies Content developed by: Lawrence C. Newman, MD, FAHS Donna Gutterman, PharmD Faculty Disclosures LAWRENCE C. NEWMAN, MD, FAHS Dr. Newman has received
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Migraine much more than just a headache
 Migraine much more than just a headache Session hosted by Teva UK Limited PUU4 11:15 12:15 UK/NHSS/18/0021b Date of Preparation: August 2018 The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker
Migraine much more than just a headache Session hosted by Teva UK Limited PUU4 11:15 12:15 UK/NHSS/18/0021b Date of Preparation: August 2018 The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker
SANDOMIGRAN (pizotifen malate)
 SANDOMIGRAN (pizotifen malate) S N CH 3 Pizotifen. COOH CH OH CH 2 COOH MALATE DESCRIPTION Pizotifen is a cycloheptathiophene derivative structurally related to cyproheptadine and the tricyclic antidepressants.
SANDOMIGRAN (pizotifen malate) S N CH 3 Pizotifen. COOH CH OH CH 2 COOH MALATE DESCRIPTION Pizotifen is a cycloheptathiophene derivative structurally related to cyproheptadine and the tricyclic antidepressants.
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary DULOXETINE Pharmalex 30 mg hard gastro-resistant capsules DULOXETINE Pharmalex 60 mg hard gastro-resistant capsules
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary DULOXETINE Pharmalex 30 mg hard gastro-resistant capsules DULOXETINE Pharmalex 60 mg hard gastro-resistant capsules VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Depression
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary DULOXETINE Pharmalex 30 mg hard gastro-resistant capsules DULOXETINE Pharmalex 60 mg hard gastro-resistant capsules VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Depression
10th Medicine Review Course st July Prakash Kumar
 10th Medicine Review Course 2018 21 st July 2018 Drug Therapy for Parkinson's disease Prakash Kumar National Neuroscience Institute Singapore General Hospital Sengkang General Hospital Singhealth Duke-NUS
10th Medicine Review Course 2018 21 st July 2018 Drug Therapy for Parkinson's disease Prakash Kumar National Neuroscience Institute Singapore General Hospital Sengkang General Hospital Singhealth Duke-NUS
Is Yoga an Effective Treatment for Reducing the Frequency of Episodic Migraine?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Yoga an Effective Treatment for Reducing
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Yoga an Effective Treatment for Reducing
10/17/2017 CHRONIC MIGRAINES BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES PATIENT CASE EPIDEMIOLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY
 BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES JENNIFER SHIN, PHARMD PGY2 AMBULATORY CARE PHARMACY RESIDENT COMMUNITYCARE HEALTH CENTERS PHARMACOTHERAPY ROUNDS OCTOBER 20, 2017
BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES JENNIFER SHIN, PHARMD PGY2 AMBULATORY CARE PHARMACY RESIDENT COMMUNITYCARE HEALTH CENTERS PHARMACOTHERAPY ROUNDS OCTOBER 20, 2017
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, II. Management of Refractory Headaches
 Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, 2016 II. Management of Refractory Headaches Case presentation 1: A case of intractable daily-persistent headache Keio University School
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, 2016 II. Management of Refractory Headaches Case presentation 1: A case of intractable daily-persistent headache Keio University School
Adolescent Migraine Treatment O F A
 Adolescent Migraine Treatment M A R C Y Y O N K E R, M D F A H S D I R E C T O R, P E D I A T R I C H E A D A C H E P R O G R A M A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R, C H I L D H E A L T H, U O F A Goals
Adolescent Migraine Treatment M A R C Y Y O N K E R, M D F A H S D I R E C T O R, P E D I A T R I C H E A D A C H E P R O G R A M A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R, C H I L D H E A L T H, U O F A Goals
Mood Disorders for Care Coordinators
 Mood Disorders for Care Coordinators David A Harrison, MD, PhD Assistant Professor, Dept of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences University of Washington School of Medicine Introduction 1 of 3 Mood disorders
Mood Disorders for Care Coordinators David A Harrison, MD, PhD Assistant Professor, Dept of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences University of Washington School of Medicine Introduction 1 of 3 Mood disorders
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR BENZODIAZEPINES AS ANXIOLYTICS OR HYPNOTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR BENZODIAZEPINES AS ANXIOLYTICS OR HYPNOTICS Guideline Title Summary of Product Characteristics for Benzodiazepines as Anxiolytics or Hypnotics Legislative basis Directive
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR BENZODIAZEPINES AS ANXIOLYTICS OR HYPNOTICS Guideline Title Summary of Product Characteristics for Benzodiazepines as Anxiolytics or Hypnotics Legislative basis Directive
PFIZER INC. THERAPEUTIC AREA AND FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS: See United States Package Insert (USPI)
 PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
Current Migraine Treatment Therapy. Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN
 Current Migraine Treatment Therapy Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN Migraine a Disease Process Migraines are a chronic disease process similar to many other chronic medical conditions Migraine has a low mortality
Current Migraine Treatment Therapy Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN Migraine a Disease Process Migraines are a chronic disease process similar to many other chronic medical conditions Migraine has a low mortality
Can I send this headache patient home? Dr Nicola Giffin Consultant Neurologist Bath, Nov 2017
 Can I send this headache patient home? Dr Nicola Giffin Consultant Neurologist Bath, Nov 2017 SAH v benign thunderclap headaches Other pathologies not apparent on CT Severe primary headaches: management
Can I send this headache patient home? Dr Nicola Giffin Consultant Neurologist Bath, Nov 2017 SAH v benign thunderclap headaches Other pathologies not apparent on CT Severe primary headaches: management
Drugs for Emotional and Mood Disorders Chapter 16
 Drugs for Emotional and Mood Disorders Chapter 16 NCLEX-RN Review Question 1 Choices Please note Question #1 at the end of Ch 16 pg 202 & Key pg 805 answer is #4 1. Psychomotor symptoms 2. Tachycardia,
Drugs for Emotional and Mood Disorders Chapter 16 NCLEX-RN Review Question 1 Choices Please note Question #1 at the end of Ch 16 pg 202 & Key pg 805 answer is #4 1. Psychomotor symptoms 2. Tachycardia,
Emilio Sternieri Anna Ferrari Arrigo F.G. Cicero
 J Headache Pain (2003) 4:13 17 Springer-Verlag 2003 REVIEW Emilio Sternieri Anna Ferrari Arrigo F.G. Cicero Clinical considerations preliminary to application of the Italian Society for the Study of Headache
J Headache Pain (2003) 4:13 17 Springer-Verlag 2003 REVIEW Emilio Sternieri Anna Ferrari Arrigo F.G. Cicero Clinical considerations preliminary to application of the Italian Society for the Study of Headache
INTERCONTINENTAL JOURNAL OF HUMAN RESOURCE RESEARCH REVIEW A STUDY ON PSYCHOSOMATIC DISORDER AND WORKING WOMEN
 Peer Reviewed Journal of Inter-Continental Management Research Consortium http:// ISSN: 2320-9704- Online ISSN:2347-1662-Print A STUDY ON PSYCHOSOMATIC DISORDER AND WORKING WOMEN *JANANI.T.S **Dr.J.P.KUMAR
Peer Reviewed Journal of Inter-Continental Management Research Consortium http:// ISSN: 2320-9704- Online ISSN:2347-1662-Print A STUDY ON PSYCHOSOMATIC DISORDER AND WORKING WOMEN *JANANI.T.S **Dr.J.P.KUMAR
A Chiropractic Approach to Managing Migraine
 www.migraine.org.uk A Chiropractic Approach to Managing Migraine What is chiropractic? Chiropractic is a primary healthcare profession that specialises in the diagnosis, treatment and overall management
www.migraine.org.uk A Chiropractic Approach to Managing Migraine What is chiropractic? Chiropractic is a primary healthcare profession that specialises in the diagnosis, treatment and overall management
Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention
 Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention Amanda Janisch, PharmD PGY2 Ambulatory Care Pharmacy Resident MCHS SWMN, Mankato, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures No financial interest
Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention Amanda Janisch, PharmD PGY2 Ambulatory Care Pharmacy Resident MCHS SWMN, Mankato, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures No financial interest
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT
 ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
