Lipocalin-like Prostaglandin D Synthase (L-PGDS)concentration in aqueous humour in patients with open-angle Glaucoma
|
|
|
- Francine Barnett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich Year: 2014 Lipocalin-like Prostaglandin D Synthase (L-PGDS)concentration in aqueous humour in patients with open-angle Glaucoma Bauer, G; Killer, H E; Forrer, A; Huber, A R; Jaggi, G P Abstract: PURPOSE:: To report on the concentration of lipocalin-like prostaglandin D synthase (L- PGDS) in the aqueous humour (AH) in patients with open-angle glaucoma (OAG). PATIENTS AND METHODS:: Prospective assessment in 20 patients (13 female, 7 male, mean age 74±10.6 y) who underwent surgery for OAG. AH was sampled and analyzed for L-PGDS concentration. AH from 26 patients (11 female, 15 male, 72.4±14.4 y) without glaucoma who underwent cataract surgery, served as control subjects. RESULTS:: The L-PGDS concentration in the AH sampled from the anterior chamber in the OAG group (5.9±2.4 mg/l) was significantly (P<0.001) higher than in the control group (3.3±1.3 mg/l). There were no significant differences between the concentrations of L-PGDS between the left and the right eye or between genders. CONCLUSIONS:: L-PGDS concentration in the AH of patients with OAG was significantly elevated compared with its concentration in the AH of nonglaucomatous eyes. As L-PGDS is a biologically pluripotent protein, its possible role in glaucoma warrants further examination. DOI: Posted at the Zurich Open Repository and Archive, University of Zurich ZORA URL: Published Version Originally published at: Bauer, G; Killer, H E; Forrer, A; Huber, A R; Jaggi, G P (2014). Lipocalin-like Prostaglandin D Synthase (L-PGDS)concentration in aqueous humour in patients with open-angle Glaucoma. Journal of Glaucoma, 23(3): DOI:
2 ORIGINAL STUDY Lipocalin-like Prostaglandin D Synthase (L-PGDS) Concentration in Aqueous Humour in Patients With Open-angle Glaucoma Gregor Bauer, MD,*w Hanspeter E. Killer, MD,*z Andreas Forrer, MD,* Andreas R. Huber, MD,y and Gregor P. Jaggi, MD*w Purpose: To report on the concentration of lipocalin-like prostaglandin D synthase (L-PGDS) in the aqueous humour (AH) in patients with open-angle glaucoma (OAG). Patients and Methods: Prospective assessment in 20 patients (13 female, 7 male, mean age 74 ± 10.6 y) who underwent surgery for OAG. AH was sampled and analyzed for L-PGDS concentration. AH from 26 patients (11 female, 15 male, 72.4 ± 14.4 y) without glaucoma who underwent cataract surgery, served as control subjects. Results: The L-PGDS concentration in the AH sampled from the anterior chamber in the OAG group (5.9 ± 2.4 mg/l) was significantly (P < 0.001) higher than in the control group (3.3 ± 1.3 mg/l). There were no significant differences between the concentrations of L-PGDS between the left and the right eye or between genders. Conclusions: L-PGDS concentration in the AH of patients with OAG was significantly elevated compared with its concentration in the AH of nonglaucomatous eyes. As L-PGDS is a biologically pluripotent protein, its possible role in glaucoma warrants further examination. Key Words: lipocalin-like prostaglandin D synthase, b-trace, openangle glaucoma, aqueous humour (J Glaucoma 2012;00: ) The pathology of open-angle glaucoma (OAG) is still poorly understood. Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) is the best established risk factor for the development and progression of OAG, 1,2 but there remain patients who develop typical glaucomatous field and disc changes despite IOPs consistently in the range generally considered normal. In some of these patients, who are said to have normaltension glaucoma (NTG) or low-tension glaucoma, 3 vascular dysregulation is thought to be a risk factor for the development of disc cupping and visual field loss. 4 In others, recent research regarding the pathophysiology of the disorder has focused on the anatomy of the subarachnoid space (SAS) surrounding the orbital portion of the optic Received for publication January 5, 2012; accepted July 3, From the Departments of *Ophthalmology; ylaboratory Medicine, Kantonsspital Aarau, Aarau; weye Clinic, University Hospital of Zurich, Zurich; and zeye Institute, University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland. Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest. Reprints: Hanspeter E. Killer, MD, Department of Ophthalmology, Kantonsspital Aarau, Aarau CH-5001, Switzerland ( killer@ ksa.ch). Copyright r 2012 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins DOI: /IJG.0b013e31826a7dea nerve and of the content of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in this space. 5 In addition the effect of the translaminar pressure gradient on the lamina cribrosa may be important. 6,7 Additional research in this area has focused on humoral abnormalities in patients with OAG. A number of molecules are currently under investigation, such as endothelin-1, 8 vascular endothelial growth factor, 9 tumor necrosis factor-alpha, 10 matrix metalloproteinases, and their inhibitors. 11 Lipocalin-like prostaglandin D synthase (L-PGDS, also called b-trace protein) is a mainly brain-derived protein with a molecular mass of 28 kd. It is the most abundant protein in CSF. 12,13 It has been reported to induce neuronal cell protection and neuronal cell loss, depending on the receptor pathway it signals to target cells In the rat eye, L-PGDS was found in the retinal pigment epithelium and in the interphotoreceptor matrix. 17,18 In addition, messenger ribonucleic acid for prostaglandin D 2 has been described in the retina. 19 The retinal pigment epithelium is suggested to be the predominant site of production for prostaglandin D 2, which is synthesized by L-PGDS, in the eye. 18 Astrocytes (in vitro) are another source of L-PGDS production. 20 Recently it has been shown that L-PGDS inhibits astrocyte proliferation and adenosine triphosphate production in vitro. 21 L-PGDS has also been shown to be upregulated in the local CSF in patients with papilledema from a variety of causes. 22 In addition, a study of patients with NTG demonstrated a L-PGDS concentration gradient between the CSF obtained from the SAS surrounding the optic nerve during optic nerve sheath fenestration and the lumbar CSF obtained by lumbar puncture. 23 L-PGDS is a pluripotent protein in the central nervous system and in some structures of the eyeball. In order to evaluate its potential role in OAG we measured its concentration in the anterior chamber of glaucomatous eyes and in eyes without glaucoma. To the best of our knowledge this is the first quantitative analysis of L-PGDS concentration in the aqueous humour (AH) of human OAG patients. PATIENTS AND METHODS Twenty patients (overall mean age, 73.8 ± 10.6 y) 13 women (mean age, 78.0 ± 7.7 y) and 7 men (mean age, 65.9 ± 11.2 y) with a diagnosis of OAG based on optic disc appearance and visual field defects were recruited for a prospective study. Twenty-six patients (mean age, 72.4 ± 14.4 y) 11 women (mean age, 77.3 ± 9.2 y) and 15 men (mean age, 68.7 ± 16.6 y) with normal appearance of their optic discs and without pseudoexfoliation (PEX) or obvious anterior chamber angle abnormalities and without J Glaucoma Volume 00, Number 00,
3 Bauer et al J Glaucoma Volume 00, Number 00, 2012 known visual field defects undergoing cataract surgery, were enrolled prospectively and served as controls. All patients and controls underwent complete ophthalmological examination. None of the OAG patients had undergone previous trabeculectomy and none had undergone cataract surgery within the last 6 months. All of the OAG patients had been treated with IOPlowering topical medication for at least several weeks at the time of surgery and sampling of AH, and 3 also had been taking acetazolamide for several weeks. Sixteen of the 20 patients (80%) underwent trabeculectomy because of insufficient IOP lowering or adverse effects of the topical and/or systemic treatment. Of these 16 patients, 12 (mean age, 72.8 ± 10.5 y) underwent trabeculectomy only, whereas 4 (69.8 ± 10.8 y) underwent combined trabeculectomy and cataract surgery. The remaining 4 OAG patients (80.8 ± 9.9 y) had IOPs that were deemed to be in the appropriate range, were tolerating their topical medication well, and underwent only cataract surgery. Mean IOP in the OAG patients was 22.0 ± 6.0 mm Hg, ranging from 13 to 34 mm Hg (median, 21.5 mm Hg). Mean IOP in the control group was 14.4 ± 3.1 mm Hg, ranging from 10 to 19 mm Hg (median, 14.5 mm Hg) (Table 1). AH (0.1 to 0.2 ml) was sampled from the anterior chamber at the beginning of the operation using a 26-G needle (Terumo, Belgium) and a sterile syringe (Omnifix U- 100 Insulin, Braun, Germany). Special care was taken not to apply fluids before sampling AH so as not to induce diluting effects. L-PGDS concentration was measured using a fully automated, standard BNII nephelometer (Dade Behring, Marburg, Germany) and commercial reagents. Before determination of L-PGDS, 7-point calibration curves were generated. If necessary, samples were diluted so that the results would fall in the linear range. Daily controls with appropriate standards are obtained to guarantee stability of the system. The minimal quantity of fluid required for reliable nephelometry is 0.02 ml. At least 3 measurements were performed from each sample and mean value was calculated. Three different surgeons from the same department were involved; all measurements were made in the same laboratory. Statistical analyses were conducted with SPSS statistical analysis software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL). An independent 2-tailed t test and the Spearmans nonparametric correlation coefficient r were used, unequal variances were assumed. This study was designed and performed according to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the local ethics committee. Written informed consent was provided by all patients and control subjects. RESULTS The subjects in the OAG and control groups did not differ significantly in age for women (P = 0.84) or men (P = 0.64). In the 20 OAG patients, the mean concentration of L-PGDS in the AH was 5.9 ± 2.4 mg/l, with no difference between right and left eyes [P = 0.79; right eyes (n = 12): 5.8 ± 2.8 mg/l; left eyes (n = 8): 6.1 ± 1.7 mg/l], or between women and men [P = 0.48; women (n = 13): 5.7 ± 2.7 mg/l; men (n = 7): 6.4 ± 1.8 mg/l). In the 12 OAG patients who underwent trabeculectomy, mean L-PGDS concentration in the AH was 6.2 ± 2.6 mg/l, whereas in the 4 patients who underwent combined trabeculectomy and cataract surgery, mean L-PGDS was 5.8 ± 2.9 mg/l. In the 4 OAG patients who underwent only cataract surgery, mean L-PGDS concentration in the AH was 5.4 ± 1.8 mg/l. In the 26 control subjects, the mean concentration of L-PGDS in AH was 3.3 ± 1.3 mg/l. As in the case of the OAG patients, there was no difference in L-PGDS concentration between right and left eyes [P = 0.87; right eyes (n = 16): 3.3 ± 1.5 mg/l; left eyes (n = 10): 3.2 ± 1.0 mg/l] or between women and men [P = 0.93; women (n = 11): 3.3 ± 1.5 mg/l; men (n = 15): 3.3 ± 1.2 mg/l]; however, the mean L-PGDS concentration in the AH obtained from the OAG patients was significantly higher than the concentration from the controls (P < 0.001; Fig. 1). In the OAG group, there were no significant differences in concentration of L-PGDS in AH among patients who underwent trabeculectomy, combined trabeculectomy, and cataract surgery, or just cataract surgery (P > 0.53), nor were there significant differences between the OAG patients with PEX and without PEX (P = 0.13; mean for OAG with PEX = 7.1 ± 3.1 mg/l; mean for OAG without PEX = 5.1 ± 1.5 mg/l). Mean L-PGDS concentration in the AH from 16 OAG patients treated with topical prostaglandin analogs was 5.8 ± 2.0 mg/l, which was not significantly (P = 0.75) different from the 4 OAG patients who were not being treated with topical prostaglandin analog therapy (6.5 ± 4.1 mg/l). Mean IOP in the OAG group (22.0 ± 6.0 mm Hg) was significantly (P = 0.003) higher than in the control group (14.4 ± 3.1 mm Hg). The IOP differences between women and men were not significant in the OAG group (P = 0.40) or in the control group (P = 0.64), nor were there significant differences in IOP between right and left eyes in either the OAG group (P = 0.75) or the control group (P = 0.81). The preoperative IOP in the 4 OAG patients who underwent cataract surgery was significantly lower than the preoperative IOP in the 12 OAG patients who underwent trabeculectomy (P = 0.002) but did not differ significantly from that of the 4 OAG patients who underwent combined trabeculectomy and cataract surgery (P = 0.16). There was no significant difference (P = 0.99) in IOP between the 16 OAG patients who were being treated with prostaglandin analogs and the 4 OAG patients who were not being treated with any of these drugs. There was also no significant difference in preoperative IOP between OAG patients with and without PEX (P = 0.29; mean for OAG with PEX = 23.8 ± 6.3 mm Hg; mean for OAG without PEX = 20.8 ± 5.8 mm Hg). There was no significant correlation (Spearman correlation coefficient) between L-PGDS concentration and age (P = 0.63, r = 0.074) or systemic dosage of acetazolamide (P = 0.098, r = 0.247); however, if analyzing all patients and controls together in 1 group, L-PGDS concentration was significantly correlated with preoperative IOP (P = 0.006, r = 0.40), whereas when OAG patients and controls were analyzed separately, there was no significant correlation between L-PGDS concentration and IOP (OAG patients: P =0.204,r =0.297;controls: P =0.88, r = 0.031; Fig. 2). Subgroup analysis of the 4 OAG patients who underwent cataract surgery only together with the control group did not reveal a significant correlation between L-PGDS concentration and IOP (P = 0.678, r = 0.79). These 4 OAG patients showed a significantly lower IOP than the rest of the OAG group (P = 0.002), as did the control group (P = 0.003). Comparing only these 4 OAG patients with the control group and assuming unequal 2 r 2012 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
4 J Glaucoma Volume 00, Number 00, 2012 L-PGDS in Glaucomatous Aqueous Humour TABLE 1. Values for Preoperative (Pre-OP) Intraocular Pressure (IOP) and for Lipocaline-like Prostaglandin D Synthase (L-PGDS) Concentration in Aqueous Humour (mg/l) of Open-angle Glaucoma Patients and Nonglaucomatous Controls (Co) Undergoing Trabeculectomy (TE), Cataract Surgery (Cat), or Combined Surgery (TECat) Patients and Controls Aqueous Humour Pre-OP IOP and Medication Case Number OP Gender Age PEX Side L-PGDS (mg/l) IOP (mm Hg) AAA PA BB a-2a AAA syst (mg) Glaucoma-Patients 1 TE M 79 X L X X X 2 TE F 78 R X X X 3 TE M 58 X R X X X X TE F 83 L X X X 5 TE M 58 L X X X TE F 77 R X X 7 TE M 81 X L X X X TE M 72 L X X X 9 TE F 62 L X X X X 10 TE F 82 X R X X X 11 TE F 84 X R X X X 12 TE M 59 L X X X 13 Cat F 90 R X X X 14 Cat F 78 R X X X 15 Cat F 68 R X 16 Cat F 87 L X 17 TECat F 78 X R X X 18 TECat F 75 X R X X X 19 TECat F 72 X R X X X 20 TECat M 54 R X X X X Controls Co1 Cat F 59 L Co2 Cat F 85 R Co3 Cat F 84 R Co4 Cat F 85 L Co5 Cat F 83 L Co6 Cat M 85 R Co7 Cat M 78 L Co8 Cat F 65 R Co9 Cat F 69 R Co10 Cat M 70 L Co11 Cat M 76 R Co12 Cat M 71 R Co13 Cat M 79 L Co14 Cat M 82 R Co15 Cat F 73 R Co16 Cat M 65 L Co17 Cat M 25 R Co18 Cat M 43 R Co19 Cat F 83 R Co20 Cat F 84 R Co21 Cat M 61 R Co22 Cat M 80 R Co23 Cat F 80 L Co24 Cat M 57 L Co25 Cat M 80 R Co26 Cat M 79 L Reported for pseudoexfoliation (PEX) and IOP lowering medication, for example, acetazolamide (AAA) topical or systemic (syst), prostaglandin analogs (PA), b-blocker (BB), and a-2-agonists (a-2a). F indicates female; L, left; M, male; R, right. r 2012 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 3
5 Bauer et al J Glaucoma Volume 00, Number 00, 2012 LPGDS in AH [mg/l] Controls Co2 Co18 Co20 Glaucoma Subgroup Co OAG OAG PA FIGURE 1. Concentration (mg/l) of lipocaline-like prostaglandin D synthase (L-PGDS) in aqueous humour (AH) of open-angle glaucoma patients, separated for patients treated with topical prostaglandin analogous (OAG PA) medication and glaucoma patients without prostaglandin analogous (OAG), and simple cataract patients serving as controls (Co). Box plot indicating median, upper, and lower quartile and SD of values, numbers representing outliers (confidence interval 95%) corresponding with case number in Table 1. preoperative IOP [mm Hg] Subgroup Co OAG OAG PA LPGDS in AH [mg/l] FIGURE 2. Scatter plot of concentration of lipocaline-like prostaglandin D synthase (L-PGDS; mg/l) in the aqueous humour (AH) and preoperatively intraocular pressure (IOP; mm Hg) measured by goldmann applanation tonometry, of open-angle glaucoma patients with prostaglandin analogous topical medication (OAG PA) and without prostaglandin analogous topical medication (OAG), and nonglaucomatous cataract patients serving as controls (Co) variances, there was no statistically significant difference for L-PGDS concentration (P = 0.096), whereas there was a significant difference in IOP (controls mean: 14.4 ± 3.1 mm Hg, 4 purely cataract surgery OAG patients 17.0 ± 1.4 mm Hg; P = 0.022). Assuming equal variances and comparing the same 2 subgroups the unpaired 2-tailed t test showed an insignificant difference for IOP (P = 0.116) but a significant difference for L-PGDS concentration (P = 0.007). DISCUSSION In this study of the substance L-PGDS in the AH of patients with OAG compared with control subjects without OAG, we found the concentration of L-PGDS in the AH of the OAG patients (mean 5.9 ± 2.4 mg/l) to be significantly higher than in the controls (3.3 ± 1.3 mg/l). The concentration of L-PGDS in the serum of normal human adults is very low (< 0.55 mg/l), 24 whereas reference values for L-PGDS in normal human CSF are at least 30 times higher (15.3 ± 2.7 mg/l). 25 The range of L-PGDS concentration in AH found in the OAG and in the control group is between the normal values for serum and CSF. A local L-PGDS production in structures of the eye, has already been demonstrated in mice and rats. 19 Additional proof for local production of L-PGDS in the eye was indicated in a study that investigated the concentration of L-PGDS in the subretinal fluid in retinal detachment. The authors of this study found that the L-PGDS concentration correlated with the duration of the detachment, 26 being high in patients with a short history of symptoms and low in longstanding detachments. The present study describes an interesting and significant correlation between the L-PGDS concentrations in the AH and the preoperatively IOP if analyzing all patients and controls at once; specifically, the higher the preoperatively measured IOP, the higher the L-PGDS concentration in the AH. Even if a selection bias could lead to this correlation (because mainly patients with so far insufficient IOP lowering treatment were indicated for interventional therapy of OAG), it seems possible that there is IOP sensitive increase in L-PGDS expression of the intraocular tissue in patients with OAG. However, if subgrouping and analyzing OAG and control patients separately we were not able to find a significant correlation between L-PGDS concentration and IOP. Because of the small number of samples, which is probably the main limitation of this study, further subgroup analysis seem not to yield reliable results, which can be seen in the Results section (ie, analysis of the small subgroup of the 4 OAG patients who underwent only cataract surgery and who had lower IOP values than the rest of the OAG group). Therefore, the question of mechanosensitivity needs to be addressed in a larger cohort of OAG patients and in patients with NTG. The possible role of L-PGDS in the pathophysiology of glaucoma needs to be addressed and concerning its possible pathophysiological mechanisms. Several mechanisms may be involved. L-PGDS is a prostaglandin synthase with a pluripotent activity. In particular, it has apoptosis-inducing properties in neuronal tissue. 13,15,16,25 In addition, immunofluorescence studies in nonhuman primate brains has demonstrated a close spatial relationship of L-PGDS to astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. 27 These cell types are mainly located in white matter tissue, such as the optic nerve. The hallmark of glaucomatous optic neuropathy is excavation of 4 r 2012 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
6 J Glaucoma Volume 00, Number 00, 2012 L-PGDS in Glaucomatous Aqueous Humour the optic disc due to the progressive loss of nerve fibers. In contrast to the normal disc, the lamina cribrosa, which builds the barrier between the SAS and the vitreous cavity, in a patient with glaucoma can possibly loose its tightness as the space that might be left empty by the degenerated nerve fibers could function as a canal. Therefore a connection between the SAS and the vitreous cavity could be postulated. Through this route, L-PGDS from the CSF might enter the eyeball and the anterior chamber. In order to elucidate the relation between elevated L-PGDS levels in AH and IOP, further studies measuring L-PGDS concentrations in AH of patients with NTG and patients with ocular hypertension are needed. This study does not address the question whether the elevated L-PGDS concentration in the AH of OAG patients is part of the pathomechanism of glaucomatous optic disc changes or is an epiphenomena, the consequence of the pathological changes in the metabolism of glaucomatous eyes in general; however, in light of the recently reported effect of L-PGDS on astrocytes and their adenosine triphosphate production in vitro 21 and the previously reported effects on other neuronal cells, 28,29 it seems feasible that L-PGDS concentration could play an important role in modulating apoptosis or survival of neuronal cells in glaucomatous optic neuropathy. REFERENCES 1. Heijl A, Bengtsson B, Hyman L, et al. Natural history of openangle glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2009;116: Weinreb RN, Khaw PT. Primary open-angle glaucoma. Lancet. 2004;363: Lee BL, Bathija R, Weinreb RN. The definition of normaltension glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 1998;7: Grieshaber MC, Mozaffarieh M, Flammer J. What is the link between vascular dysregulation and glaucoma? Surv Ophthalmol. 2007;52(suppl 2): Killer HE, Jaggi GP, Flammer J, et al. Is open-angle glaucoma caused by impaired cerebrospinal fluid circulation: around the optic nerve? Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008;36: Berdahl JP, Allingham RR, Johnson DH. Cerebrospinal fluid pressure is decreased in primary open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2008;115: Morgan WH, Yu DY, Balaratnasingam C. The role of cerebrospinal fluid pressure in glaucoma pathophysiology: the dark side of the optic disc. J Glaucoma. 2008;17: Ghanem AA, Elewa AM, Arafa LF. Endothelin-1 and nitric oxide levels in patients with glaucoma. Ophthalmic Res. 2011;46: Hu DN, Ritch R, Liebmann J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor is increased in aqueous humor of glaucomatous eyes. J Glaucoma. 2002;11: Balaiya S, Edwards J, Tillis T, et al. Tumor necrosis factoralpha (TNF-a) levels in aqueous humor of primary open angle glaucoma. Clin Ophthalmol. 2011;5: Määttä M, Tervahartiala T, Harju M, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in aqueous humor of patients with primary open-angle glaucoma, exfoliation syndrome, and exfoliation glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 2005;14: Hoffmann A, Conradt HS, Gross G, et al. Purification and chemical characterization of beta-trace protein from human cerebrospinal fluid: its identification as prostaglandin D synthase. J Neurochem. 1993;61: Urade Y, Hayaishi O. Biochemical, structural, genetic, physiological, and pathophysiological features of lipocalintype prostaglandin D synthase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000; 1482: Liang X, Wu L, Hand T, et al. Prostaglandin D 2 mediates neuronal protection via the DP1 receptor. J Neurochem. 2005; 92: Ragolia L, Palaia T, Paric E, et al. Elevated L-PGDS activity contributes to PMA-induced apoptosis concomitant with downregulation of PI3-K. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003;284: Taniike M, Mohri I, Eguchi N, et al. Perineuronal oligodendrocytes protect against neuronal apoptosis through the production of lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase in a genetic demyelinating model. J Neurosci. 2002;22: Beuckmann CT, Gordon WC, Kanaoka Y, et al. Lipocalintype prostaglandin D synthase (beta-trace) is located in pigment epithelial cells of rat retina and accumulates within interphotoreceptor matrix. J Neurosci. 1996;16: Goh Y, Urade Y, Fujimoto N, et al. Content and formation of prostaglandins and distribution of prostaglandin-related enzyme activities in the rat ocular system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987;921: Gerashchenko DY, Beuckmann CT, Marcheselli VL, et al. Localization of lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase (betatrace) in iris, ciliary body, and eye fluids. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998;39: Giacomelli S, Leone MG, Grima J, et al. Astrocytes synthesize and secrete prostaglandin D synthetase in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1310: Xin X, Huber A, Meyer P, et al. L-PGDS (betatrace protein) inhibits astrocyte proliferation and mitochondrial ATP production in vitro. J Mol Neurosci. 2009;39: Killer HE, Jaggi GP, Flammer J, et al. The optic nerve: a new window into cerebrospinal fluid composition? Brain. 2006;129(pt 4): Killer HE, Jaggi GP, Flammer J, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid dynamics between the intracranial and the subarachnoid space of the optic nerve. Is it always bidirectional? Brain. 2007;130(pt 2): Risch L, Lisec I, Jutzi M, et al. Rapid, accurate and noninvasive detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage using combined determination of beta-trace protein in secretion and serum. Clin Chim Acta. 2005;351: Link H, Olsson JE. Beta-trace protein concentration in CSF in neurological disorders. Acta Neurol Scand. 1972;48: Jaggi GP, Flammer J, Huber AR, et al. Lipocalin-like prostaglandin D synthase in subretinal fluid of detached retinas in humans. Retina. 2008;28: Olsson JE, Blomstrand C, Haglid KG. Cellular distribution of beta-trace protein in CNS and brain tumours. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974;37: Taniguchi H, Mohri I, Okabe-Arahori H, et al. Prostaglandin D 2 protects neonatal mouse brain from hypoxic ischemic injury. J Neurosci. 2007;27: Taniguchi H, Mohri I, Okabe-Arahori H, et al. Early induction of neuronal lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase after hypoxic-ischemic injury in developing brains. Neurosci Lett. 2007;420: r 2012 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 5
Glaucoma. Glaucoma. Optic Disc Cupping
 Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Bruce James A group of diseases in which damage to the optic nerve occurs as a result of intraocualar pressure being above the physiological norm for that eye Stoke Mandeville
Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Bruce James A group of diseases in which damage to the optic nerve occurs as a result of intraocualar pressure being above the physiological norm for that eye Stoke Mandeville
Spontaneous Intraocular Pressure Reduction in Normal-Tension Glaucoma and Associated Clinical Factors
 CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Spontaneous Intraocular Pressure Reduction in Normal-Tension Glaucoma and Associated Clinical Factors Akihiro Oguri, Tetsuya Yamamoto and Yoshiaki Kitazawa Department of Ophthalmology,
CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Spontaneous Intraocular Pressure Reduction in Normal-Tension Glaucoma and Associated Clinical Factors Akihiro Oguri, Tetsuya Yamamoto and Yoshiaki Kitazawa Department of Ophthalmology,
Present relevant clinical findings of four landmark glaucoma trials OHTS, EMGT, CNTGS and CIGTS.
 Course title: The Glaucoma Compass Course length: 1 hour +/- 31 slides Corse Description: Even with the technology and available information, glaucoma decision making can still be confusing. How should
Course title: The Glaucoma Compass Course length: 1 hour +/- 31 slides Corse Description: Even with the technology and available information, glaucoma decision making can still be confusing. How should
4/06/2013. Medication Observation POAG. Proportion. Native American 0.1% 0.4%
 Clinical Research in Glaucoma: Putting Science into Practice J. James Thimons, O.D., FAAO Chairman, National Glaucoma Society www.nationalglaucomasociety.org Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS)
Clinical Research in Glaucoma: Putting Science into Practice J. James Thimons, O.D., FAAO Chairman, National Glaucoma Society www.nationalglaucomasociety.org Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS)
Effect of brimonidine on intraocular pressure in normal tension glaucoma: A short term clinical trial
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 7, 2003 / pp. 611-615 Effect of brimonidine on intraocular pressure in normal tension glaucoma: A short term clinical trial S.A. GANDOLFI, L. CIMINO, P.
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 7, 2003 / pp. 611-615 Effect of brimonidine on intraocular pressure in normal tension glaucoma: A short term clinical trial S.A. GANDOLFI, L. CIMINO, P.
Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma. Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4. Abstract
 Original article Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 4 Professor, Department of
Original article Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 4 Professor, Department of
Glaucoma Clinical Update. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012
 Glaucoma Clinical Update Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Objectives Understand the different categories of glaucoma Recognize the symptoms and signs of open angle and angle-closure
Glaucoma Clinical Update Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Objectives Understand the different categories of glaucoma Recognize the symptoms and signs of open angle and angle-closure
THE EYE: RETINA AND GLOBE
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15. Your histology and gross anatomy books should be useful. Reading: Histology of the Eye from any histology book
Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15. Your histology and gross anatomy books should be useful. Reading: Histology of the Eye from any histology book
Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature of
 1.2.4 OPHTHALMOLOGICAL ABNORMALITIES Ocular abnormalities are well documented in patients with NPS 6 62 81 95. 1.2.4.1 Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature
1.2.4 OPHTHALMOLOGICAL ABNORMALITIES Ocular abnormalities are well documented in patients with NPS 6 62 81 95. 1.2.4.1 Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature
Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012
 Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012 Goals of Collaboration Patient-centred and evidence based approach Timely access
Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012 Goals of Collaboration Patient-centred and evidence based approach Timely access
OCULAR PHARMACOLOGY GLAUCOMA. increased intraocular pressure. normally mm Hg. when to Tx no fixed level.
 OCULAR PHARMACOLOGY GLAUCOMA increased intraocular pressure normally 12 20 mm Hg. when to Tx no fixed level. literature sets ~21 mm Hg as upper limit of normal. some safe at 30 mm Hg some may have damage
OCULAR PHARMACOLOGY GLAUCOMA increased intraocular pressure normally 12 20 mm Hg. when to Tx no fixed level. literature sets ~21 mm Hg as upper limit of normal. some safe at 30 mm Hg some may have damage
Intro to Glaucoma/2006
 Intro to Glaucoma/2006 Managing Patients with Glaucoma is Exciting Interesting Challenging But can often be frustrating! Clinical Challenges To identify patients with risk factors for possible glaucoma.
Intro to Glaucoma/2006 Managing Patients with Glaucoma is Exciting Interesting Challenging But can often be frustrating! Clinical Challenges To identify patients with risk factors for possible glaucoma.
Aqueous Levels of Anti-Helicobacter Pylori IgG Antibody in Patients with Primary Open Angle and Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma
 Aqueous Levels of Anti-Helicobacter Pylori IgG Antibody in Patients with Primary Open Angle and Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma Mohammad Reza Razeghinejad 1, Eskandar Kamali-Sarvestani 2,3, Mohsen Farvardin
Aqueous Levels of Anti-Helicobacter Pylori IgG Antibody in Patients with Primary Open Angle and Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma Mohammad Reza Razeghinejad 1, Eskandar Kamali-Sarvestani 2,3, Mohsen Farvardin
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure and Glaucoma
 Review Article Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure and Glaucoma Jost B. Jonas 1, MD; Ningli Wang 2, MD 1Department of Ophthalmology, Medical Faculty Mannheim, University of Heidelberg, Germany 2Beijing Tongren
Review Article Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure and Glaucoma Jost B. Jonas 1, MD; Ningli Wang 2, MD 1Department of Ophthalmology, Medical Faculty Mannheim, University of Heidelberg, Germany 2Beijing Tongren
Micro-Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (Aqueous Stents)
 Micro-Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (Aqueous Stents) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.029 02/01/2019 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2019 Section:
Micro-Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (Aqueous Stents) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.029 02/01/2019 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2019 Section:
Associate Prof. Banu Bozkurt, MD, FEBO. Selcuk University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Ophthalmology, Konya, Turkey
 Associate Prof. Banu Bozkurt, MD, FEBO Selcuk University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Ophthalmology, Konya, Turkey Reduction of IOP to the target therapeutic Lowering IOP range protects is not always
Associate Prof. Banu Bozkurt, MD, FEBO Selcuk University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Ophthalmology, Konya, Turkey Reduction of IOP to the target therapeutic Lowering IOP range protects is not always
VI.2.2 Summary of treatment benefits
 EU-Risk Management Plan for Bimatoprost V01 aetiology), both OAG and ACG can be secondary conditions. Secondary glaucoma refers to any case in which another disorder (e.g. injury, inflammation, vascular
EU-Risk Management Plan for Bimatoprost V01 aetiology), both OAG and ACG can be secondary conditions. Secondary glaucoma refers to any case in which another disorder (e.g. injury, inflammation, vascular
Is NTG different from POAG?
 Is NTG different from POAG? Sunita Radhakrishnan, M.D Glaucoma Center of San Francisco Glaucoma Research and Education Group Subset of POAG 1 Connective tissue structure within ONH Ganglion cell susceptibility
Is NTG different from POAG? Sunita Radhakrishnan, M.D Glaucoma Center of San Francisco Glaucoma Research and Education Group Subset of POAG 1 Connective tissue structure within ONH Ganglion cell susceptibility
Eye Fluids. Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 Eye Fluids 1 Reference Books: Text Book of Medical physiology (Guyton and Hall) Eleventh edition 2 Fluid System of the Eye (Intraocular Fluid) The eye is filled with intraocular fluid, which maintains
Eye Fluids 1 Reference Books: Text Book of Medical physiology (Guyton and Hall) Eleventh edition 2 Fluid System of the Eye (Intraocular Fluid) The eye is filled with intraocular fluid, which maintains
The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3%
 The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3% of our population age > 40 have glaucoma In the past:
The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3% of our population age > 40 have glaucoma In the past:
Clinical Discussions in Glaucoma
 Clinical Discussions in Glaucoma Joseph W. Sowka, OD, FAAO, Diplomate Professor of Optometry Nova Southeastern University, College of Optometry 3200 South University Drive Fort Lauderdale, Florida 33328
Clinical Discussions in Glaucoma Joseph W. Sowka, OD, FAAO, Diplomate Professor of Optometry Nova Southeastern University, College of Optometry 3200 South University Drive Fort Lauderdale, Florida 33328
Delayed Correction of Hypotony Maculopathy in a Patient with Glaucoma and Thyroid-Related Orbitopathy
 Published online: October 14, 2015 2015 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1663 2699/15/0063 0356$39.50/0 This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International
Published online: October 14, 2015 2015 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1663 2699/15/0063 0356$39.50/0 This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International
Dr Taha Abdel Monein Labib Professor of Eye Surgery Cairo University.
 Dr Taha Abdel Monein Labib Professor of Eye Surgery Cairo University. Although the clinical picture of glaucoma is well described, the exact mechanism leading to this specific type of damage to the optic
Dr Taha Abdel Monein Labib Professor of Eye Surgery Cairo University. Although the clinical picture of glaucoma is well described, the exact mechanism leading to this specific type of damage to the optic
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
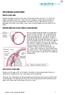 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
Role of Central Corneal Thickness in Circadian Intraocular Pressure Fluctuations among Patients with Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
 Role of Central Corneal Thickness in Circadian Intraocular Pressure Fluctuations among Patients with Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Mohannad Albdour MD*, Karanjit Kooner MD, PHD** ABSTRACT Objectives: To
Role of Central Corneal Thickness in Circadian Intraocular Pressure Fluctuations among Patients with Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Mohannad Albdour MD*, Karanjit Kooner MD, PHD** ABSTRACT Objectives: To
Lifetime Risk of Blindness in Open-Angle Glaucoma.
 Lifetime Risk of Blindness in Open-Angle Glaucoma. Peters, Dorothea; Bengtsson, Boel; Heijl, Anders Published in: American Journal of Ophthalmology DOI: 10.1016/j.ajo.2013.05.027 2013 Link to publication
Lifetime Risk of Blindness in Open-Angle Glaucoma. Peters, Dorothea; Bengtsson, Boel; Heijl, Anders Published in: American Journal of Ophthalmology DOI: 10.1016/j.ajo.2013.05.027 2013 Link to publication
Divakar Gupta Glaucoma Fellow, Duke Eye Center 5/14/16
 Divakar Gupta Glaucoma Fellow, Duke Eye Center 5/14/16 Pathophysiology of glaucoma Consider risk factors of glaucoma Understand the side effects of glaucoma medications Diagnostic testing Leading cause
Divakar Gupta Glaucoma Fellow, Duke Eye Center 5/14/16 Pathophysiology of glaucoma Consider risk factors of glaucoma Understand the side effects of glaucoma medications Diagnostic testing Leading cause
A. Incorrect! Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor given orally or by intravenous injection.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 20: Drugs that Treat Glaucoma Question No. 1 of 10 1. is a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Question #01 (A) Acetazolamide (B) Clonidine (C) Dorzolamide (D) Apraclonidine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 20: Drugs that Treat Glaucoma Question No. 1 of 10 1. is a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Question #01 (A) Acetazolamide (B) Clonidine (C) Dorzolamide (D) Apraclonidine
The glaucomas represent a variety of pathophysiologic processes
 Intracranial Pressure in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma, Normal Tension Glaucoma, and Ocular Hypertension: A Case Study John P. Berdahl, 1 Michael P. Fautsch, 2 Sandra S. Stinnett, 1 and R. Rand Allingham
Intracranial Pressure in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma, Normal Tension Glaucoma, and Ocular Hypertension: A Case Study John P. Berdahl, 1 Michael P. Fautsch, 2 Sandra S. Stinnett, 1 and R. Rand Allingham
Fluctuation of Intraocular Pressure and Glaucoma Progression in the Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial
 Fluctuation of Intraocular Pressure and Glaucoma Progression in the Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial Boel Bengtsson, PhD, 1 M. Cristina Leske, MD, MPH, 2 Leslie Hyman, PhD, 2 Anders Heijl, MD, PhD, 1 Early
Fluctuation of Intraocular Pressure and Glaucoma Progression in the Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial Boel Bengtsson, PhD, 1 M. Cristina Leske, MD, MPH, 2 Leslie Hyman, PhD, 2 Anders Heijl, MD, PhD, 1 Early
The Missing Piece in Glaucoma?
 Open Journal of Ophthalmology, 2016, 6, 56-62 Published Online February 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojoph http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojoph.2016.61008 The Missing Piece in Glaucoma? Syed
Open Journal of Ophthalmology, 2016, 6, 56-62 Published Online February 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojoph http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojoph.2016.61008 The Missing Piece in Glaucoma? Syed
Ocular hypertension is present in approximately 8%
 ORIGINAL STUDY The Probability of Glaucoma From Ocular Hypertension Determined by Ophthalmologists in Comparison to a Risk Calculator Steven L. Mansberger, MD, MPH and George A. Cioffi, MD Objective: To
ORIGINAL STUDY The Probability of Glaucoma From Ocular Hypertension Determined by Ophthalmologists in Comparison to a Risk Calculator Steven L. Mansberger, MD, MPH and George A. Cioffi, MD Objective: To
relative s privacy, do not identify your relative by full name in any assignment.
 Overview Do you or a family member have glaucoma? Do you wonder what this diagnosis means? Glaucoma affects tens of millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, many people lack accurate information
Overview Do you or a family member have glaucoma? Do you wonder what this diagnosis means? Glaucoma affects tens of millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, many people lack accurate information
Curriculum for the Glaucoma EBO EGS Subspecialty exam and the FEBOD Glaucoma diploma
 Curriculum for the Glaucoma EBO EGS Subspecialty exam and the FEBOD Glaucoma diploma Introduction This document defines the requirements for the subspecialty exam in Glaucoma, organized by the EBO (European
Curriculum for the Glaucoma EBO EGS Subspecialty exam and the FEBOD Glaucoma diploma Introduction This document defines the requirements for the subspecialty exam in Glaucoma, organized by the EBO (European
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CORNEAL ULTRASOUND PACHYMETRY. POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Technology Assessment
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CORNEAL ULTRASOUND,, PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CORNEAL ULTRASOUND,, PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
Micro-Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (Aqueous Stents)
 Micro-Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (Aqueous Stents) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.029 02/01/2019 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2019 Section:
Micro-Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (Aqueous Stents) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.029 02/01/2019 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2019 Section:
Aqueous Humor Levels of Soluble Fas and Fas-ligand in Patients with Primary Open Angle and Pseudoexfoliation
 ISSN 1735-1383 Iran. J. Immunol. December 2007, 4 (4), 215 219 Mohammad Reza Razeghinejad, Eskandar Kamali-Sarvestani Aqueous Humor Levels of Soluble Fas and Fas-ligand in Patients with Primary Open Angle
ISSN 1735-1383 Iran. J. Immunol. December 2007, 4 (4), 215 219 Mohammad Reza Razeghinejad, Eskandar Kamali-Sarvestani Aqueous Humor Levels of Soluble Fas and Fas-ligand in Patients with Primary Open Angle
Corneal hysteresis in patients with glaucoma-like optic discs, ocular hypertension and glaucoma
 Murphy et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:1 DOI 10.1186/s12886-016-0396-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Corneal hysteresis in patients with glaucoma-like optic discs, ocular hypertension and glaucoma Melissa
Murphy et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:1 DOI 10.1186/s12886-016-0396-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Corneal hysteresis in patients with glaucoma-like optic discs, ocular hypertension and glaucoma Melissa
Correlating central corneal thickness and intraocular pressure in ocular hypertension and glaucoma
 VOL. 3 NO. 1 PHILIPPINE JOURNAL OF Ophthalmology JANUARY ORIGINAL ARTICLE JUNE 07 Jonathan G. Soriano, MD 1 Ma. Margarita L. Lat-Luna, MD 1, 3 Patricia M. Khu, MD 1, 1 Department of Ophthalmology and Visual
VOL. 3 NO. 1 PHILIPPINE JOURNAL OF Ophthalmology JANUARY ORIGINAL ARTICLE JUNE 07 Jonathan G. Soriano, MD 1 Ma. Margarita L. Lat-Luna, MD 1, 3 Patricia M. Khu, MD 1, 1 Department of Ophthalmology and Visual
The Pathology and Pathogenesis of Acute Glaucoma in Dogs. Richard R Dubielzig
 The Pathology and Pathogenesis of Acute Glaucoma in Dogs Richard R Dubielzig Overview of Glaucoma Intraocular Pressure too High to Support a Healthy Optic Nerve Terminology used in the classification of
The Pathology and Pathogenesis of Acute Glaucoma in Dogs Richard R Dubielzig Overview of Glaucoma Intraocular Pressure too High to Support a Healthy Optic Nerve Terminology used in the classification of
Science & Technologies
 STANDARD COMPUTERIZED PERIMETRY IN FUNCTION OF DIAGNOSTIC GLAUCOMA Iljaz Ismaili, 1 Gazepov Strahil, 2, Goshevska Dashtevska Emilija 1 1 University Eye Clinic,Skopje 2 Clinical Hospital, Shtip Abstract
STANDARD COMPUTERIZED PERIMETRY IN FUNCTION OF DIAGNOSTIC GLAUCOMA Iljaz Ismaili, 1 Gazepov Strahil, 2, Goshevska Dashtevska Emilija 1 1 University Eye Clinic,Skopje 2 Clinical Hospital, Shtip Abstract
Glaucoma is the leading cause of blindness worldwide
 ORIGINAL STUDY Relationship Between Serum Glucose Levels and Intraocular Pressure, a Population-based Cross-sectional Study Eytan Cohen, MD,*wz Michal Kramer, MD,zy Tzippy Shochat, MSC,8 Elad Goldberg,
ORIGINAL STUDY Relationship Between Serum Glucose Levels and Intraocular Pressure, a Population-based Cross-sectional Study Eytan Cohen, MD,*wz Michal Kramer, MD,zy Tzippy Shochat, MSC,8 Elad Goldberg,
Pre-operative intraocular pressure does not influence outcome of trabeculectomy surgery: a retrospective cohort study
 Nesaratnam et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2015) 15:17 DOI 10.1186/s12886-015-0007-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Pre-operative intraocular pressure does not influence outcome of trabeculectomy surgery: a retrospective
Nesaratnam et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2015) 15:17 DOI 10.1186/s12886-015-0007-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Pre-operative intraocular pressure does not influence outcome of trabeculectomy surgery: a retrospective
GLAUCOMA SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES
 SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES Introduction These are summary benchmarks for the Academy s Preferred Practice Pattern (PPP) guidelines. The Preferred Practice Pattern series
SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES Introduction These are summary benchmarks for the Academy s Preferred Practice Pattern (PPP) guidelines. The Preferred Practice Pattern series
SAFE, PERMANENT EYE-COLOR CHANGE
 SAFE, PERMANENT EYE-COLOR CHANGE Prepared by Gregg Homer JSD (PhD) February 1, 2012 THE PIGMENTARY GLAUCOMA ISSUE Glaucoma Defined Glaucoma is currently defined as a disturbance of the structural or functional
SAFE, PERMANENT EYE-COLOR CHANGE Prepared by Gregg Homer JSD (PhD) February 1, 2012 THE PIGMENTARY GLAUCOMA ISSUE Glaucoma Defined Glaucoma is currently defined as a disturbance of the structural or functional
9/25/2017 CASE. 67 years old On 2 topical meds since 3 years. Rx: +3.0 RE LE
 CASE 67 years old On 2 topical meds since 3 years Rx: +3.0 /-0.5@65 RE +2.5/-0.5@115 LE IOP : 17 RE 19 LE CD: 0.5 RE 0.6 LE 1 67 years old On 2 topical meds since 3 years Rx: +3.0 /-0.5@65 RE +2.5/-0.5@115
CASE 67 years old On 2 topical meds since 3 years Rx: +3.0 /-0.5@65 RE +2.5/-0.5@115 LE IOP : 17 RE 19 LE CD: 0.5 RE 0.6 LE 1 67 years old On 2 topical meds since 3 years Rx: +3.0 /-0.5@65 RE +2.5/-0.5@115
effect of previous argon laser trabeculoplasty
 Graefe s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (2006) 244: 1073 1076 CLINICAL INVESTIGATION DOI 10.1007/s00417-005-0198-x Esther Arranz-Marquez Miguel A. Teus Effect of previous argon laser trabeculoplasty on the ocular
Graefe s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (2006) 244: 1073 1076 CLINICAL INVESTIGATION DOI 10.1007/s00417-005-0198-x Esther Arranz-Marquez Miguel A. Teus Effect of previous argon laser trabeculoplasty on the ocular
Prevalence Of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma in Diabetic Patients
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. III (June. 2017), PP 147-151 www.iosrjournals.org Prevalence Of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. III (June. 2017), PP 147-151 www.iosrjournals.org Prevalence Of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF GLAUCOMA
 PRACTICAL APPROACH TO MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF GLAUCOMA DR. RAVI THOMAS, DR. RAJUL PARIKH, DR. SHEFALI PARIKH IJO MAY 2008 PRESENTER AT JDOS : DR. RAHUL SHUKLA T.N. SHUKLA EYE HOSPITAL TERMINOLOGY POAG: PRIMARY
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF GLAUCOMA DR. RAVI THOMAS, DR. RAJUL PARIKH, DR. SHEFALI PARIKH IJO MAY 2008 PRESENTER AT JDOS : DR. RAHUL SHUKLA T.N. SHUKLA EYE HOSPITAL TERMINOLOGY POAG: PRIMARY
Efficacy and Tolerability of Latanoprost 0.005% in Treatment of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma (POAG)
 Original Article Efficacy and Tolerability of Latanoprost.5% in Treatment of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma (POAG) Muhammad Imran Janjua, Saira Bano, Ali Raza Pak J Ophthalmol 217, Vol. 33, No. 3.....................................................................................................
Original Article Efficacy and Tolerability of Latanoprost.5% in Treatment of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma (POAG) Muhammad Imran Janjua, Saira Bano, Ali Raza Pak J Ophthalmol 217, Vol. 33, No. 3.....................................................................................................
11/30/2009. Glaukosis: ancient greek term meaning sparkling or shining appearance of pupil
 Normal Ocular Anatomy Glaucoma Dr Sunil Deokule, MD Asst. Prof and Glaucoma Specialist University of Kentucky Definition Glaukosis: ancient greek term meaning sparkling or shining appearance of pupil Optic
Normal Ocular Anatomy Glaucoma Dr Sunil Deokule, MD Asst. Prof and Glaucoma Specialist University of Kentucky Definition Glaukosis: ancient greek term meaning sparkling or shining appearance of pupil Optic
Body Height, Estimated Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure and Open-Angle Glaucoma. The Beijing Eye Study 2011
 Body Height, Estimated Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure and Open-Angle Glaucoma. The Beijing Eye Study 2011 Jost B. Jonas 1,2., Ningli Wang 3., Ya Xing Wang 1, Qi Sheng You 1, Xiaobin Xie 3, Diya Yang 3, Liang
Body Height, Estimated Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure and Open-Angle Glaucoma. The Beijing Eye Study 2011 Jost B. Jonas 1,2., Ningli Wang 3., Ya Xing Wang 1, Qi Sheng You 1, Xiaobin Xie 3, Diya Yang 3, Liang
Clinical Guidance and Monitoring for Change. Cecilia Fenerty MD FRCOphth Manchester Royal Eye Hospital
 Clinical Guidance and Monitoring for Change Cecilia Fenerty MD FRCOphth Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Glaucoma Referral Criteria 2000 Original referral scheme Simple criteria based on IOP/Disc/Field Solitary
Clinical Guidance and Monitoring for Change Cecilia Fenerty MD FRCOphth Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Glaucoma Referral Criteria 2000 Original referral scheme Simple criteria based on IOP/Disc/Field Solitary
Study of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Within Normal Hemivisual Field in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma and Normal-Tension Glaucoma
 Study of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Within Normal Hemivisual Field in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma and Normal-Tension Glaucoma Chiharu Matsumoto, Shiroaki Shirato, Mai Haneda, Hiroko Yamashiro
Study of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Within Normal Hemivisual Field in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma and Normal-Tension Glaucoma Chiharu Matsumoto, Shiroaki Shirato, Mai Haneda, Hiroko Yamashiro
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Effect of Central Corneal Thickness, Corneal Curvature, and Axial Length on Applanation Tonometry
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Effect of Central Corneal Thickness, Corneal Curvature, and Axial Length on Applanation Tonometry Markus Kohlhaas, MD; Andreas G. Boehm, MD; Eberhard Spoerl, PhD; Antje Pürsten, Dipl-Ing
CLINICAL SCIENCES Effect of Central Corneal Thickness, Corneal Curvature, and Axial Length on Applanation Tonometry Markus Kohlhaas, MD; Andreas G. Boehm, MD; Eberhard Spoerl, PhD; Antje Pürsten, Dipl-Ing
53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note.
 Case 1 Normal Tension Glaucoma 53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note. Table 1. Right Eye Left Eye Visual acuity 6/6 6/6 Ishihara
Case 1 Normal Tension Glaucoma 53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note. Table 1. Right Eye Left Eye Visual acuity 6/6 6/6 Ishihara
Neovascular Glaucoma Associated with Cilioretinal Artery Occlusion Combined with Perfused Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
 Neovascular Glaucoma Associated with Cilioretinal Artery Occlusion Combined with Perfused Central Retinal Vein Occlusion Man-Seong Seo,* Jae-Moon Woo* and Jeong-Jin Seo *Department of Ophthalmology, Chonnam
Neovascular Glaucoma Associated with Cilioretinal Artery Occlusion Combined with Perfused Central Retinal Vein Occlusion Man-Seong Seo,* Jae-Moon Woo* and Jeong-Jin Seo *Department of Ophthalmology, Chonnam
Goals. Glaucoma PARA PEARL TO DO. Vision Loss with Glaucoma
 Glaucoma Janet R. Fett, OD Drs. Kincaid, Fett and Tharp So Sioux City, NE eyewear21@hotmail.com Goals Understand Glaucoma Disease process Understand how your data (objective and subjective) assists in
Glaucoma Janet R. Fett, OD Drs. Kincaid, Fett and Tharp So Sioux City, NE eyewear21@hotmail.com Goals Understand Glaucoma Disease process Understand how your data (objective and subjective) assists in
Practical approach to medical management of glaucoma DR. RATHINI LILIAN DAVID
 Practical approach to medical management of glaucoma DR. RATHINI LILIAN DAVID Glaucoma is one of the major causes of visual loss worldwide. The philosophy of glaucoma management is to preserve the visual
Practical approach to medical management of glaucoma DR. RATHINI LILIAN DAVID Glaucoma is one of the major causes of visual loss worldwide. The philosophy of glaucoma management is to preserve the visual
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA
 OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
Gonioscopy and 3-Mirror Retinal Evaluation Workshop Edeline Lu, O.D., FAAO Benedicte Gonzalez, O.D., MPH, FAAO Tina Zheng, O.D.
 Gonioscopy and 3-Mirror Retinal Evaluation Workshop Edeline Lu, O.D., FAAO Benedicte Gonzalez, O.D., MPH, FAAO Tina Zheng, O.D., FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others
Gonioscopy and 3-Mirror Retinal Evaluation Workshop Edeline Lu, O.D., FAAO Benedicte Gonzalez, O.D., MPH, FAAO Tina Zheng, O.D., FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others
Glaucoma. Glaucoma. Glaucoma. Trevor Arnold, MS, DVM, DACVO
 Glaucoma Trevor Arnold, MS, DVM, DACVO Glaucoma Physiology of Aqueous Humor Produced in the ciliary body Flows out the iridocorneal angle and ciliary cleft High intraocular pressures are caused by a decreased
Glaucoma Trevor Arnold, MS, DVM, DACVO Glaucoma Physiology of Aqueous Humor Produced in the ciliary body Flows out the iridocorneal angle and ciliary cleft High intraocular pressures are caused by a decreased
Systemic inflammation after myocardial infarction
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2013 Systemic inflammation after myocardial infarction Rudiger, Alain DOI:
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2013 Systemic inflammation after myocardial infarction Rudiger, Alain DOI:
Switch from BAK-preserved to preservative-free latanoprost decreases anterior chamber flare in POAG patients
 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0792-z ORIGINAL PAPER Switch from BAK-preserved to preservative-free latanoprost decreases anterior chamber flare in POAG patients Ph. A. Kestelyn. Ph. G. Kestelyn. D.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0792-z ORIGINAL PAPER Switch from BAK-preserved to preservative-free latanoprost decreases anterior chamber flare in POAG patients Ph. A. Kestelyn. Ph. G. Kestelyn. D.
Around The Globe in 60 Minutes
 Around The Globe in 60 Minutes Around the GLOBE in Sixty Minutes Basic Ocular Anatomy, Examination, and Diagnostic Techniques Introduction Focusing on canine and feline ocular anatomy and basic examination
Around The Globe in 60 Minutes Around the GLOBE in Sixty Minutes Basic Ocular Anatomy, Examination, and Diagnostic Techniques Introduction Focusing on canine and feline ocular anatomy and basic examination
Disc Hemorrhages in Patients with both Normal Tension Glaucoma and Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion in Different Eyes
 Korean Journal of Ophthalmology 21(4):222-227, 2007 DOI : 10.3341/kjo.2007.21.4.222 Disc Hemorrhages in Patients with both Normal Tension Glaucoma and Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion in Different Eyes Young
Korean Journal of Ophthalmology 21(4):222-227, 2007 DOI : 10.3341/kjo.2007.21.4.222 Disc Hemorrhages in Patients with both Normal Tension Glaucoma and Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion in Different Eyes Young
diagnose and treat glaucoma and any resulting visual impairment.
 Overview Do you have a client who has been diagnosed with glaucoma? Do you wonder what this diagnosis means? If so, you are not alone. Glaucoma affects tens of millions of people worldwide. Despite its
Overview Do you have a client who has been diagnosed with glaucoma? Do you wonder what this diagnosis means? If so, you are not alone. Glaucoma affects tens of millions of people worldwide. Despite its
One-year Results of a Schlemm s Canal Microstent for IOP Reduction in Open Angle Glaucoma
 One-year Results of a Schlemm s Canal Microstent for IOP Reduction in Open Angle Glaucoma Thomas W. Samuelson, MD Minnesota Eye Consultants On Behalf of the HYDRUS I Investigators 1 Disclosures This study
One-year Results of a Schlemm s Canal Microstent for IOP Reduction in Open Angle Glaucoma Thomas W. Samuelson, MD Minnesota Eye Consultants On Behalf of the HYDRUS I Investigators 1 Disclosures This study
Glaucoma: what should the general practitioner know?
 Glaucoma: what should the general practitioner know? Abstract Labuschagne MJ, MBChB, MMed(Ophth)(UFS) Department of Ophthalmology (M1), School of Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of the
Glaucoma: what should the general practitioner know? Abstract Labuschagne MJ, MBChB, MMed(Ophth)(UFS) Department of Ophthalmology (M1), School of Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of the
The Effect of Phacoemulsification with Posterior Chamber Intraocular Lens Implantation on Intraocular Pressure and Anterior Chamber Depth
 The Effect of Phacoemulsification with Posterior Chamber Intraocular Lens Implantation on Intraocular Pressure and Anterior Chamber Depth Mohammad Javad Mohamadi, MD 1 Reza Soltani Moghadam, MD 1 Hasan
The Effect of Phacoemulsification with Posterior Chamber Intraocular Lens Implantation on Intraocular Pressure and Anterior Chamber Depth Mohammad Javad Mohamadi, MD 1 Reza Soltani Moghadam, MD 1 Hasan
Aqueous Humor Adrenomedullin Levels Differ in Patients With Different Types of Glaucoma
 Aqueous Humor Adrenomedullin Levels Differ in Patients With Different Types of Glaucoma Cem Evereklioglu*, Selim Doganay*, Hamdi Er* and Muhittin Yurekli Departments of *Ophthalmology and Molecular Biology,
Aqueous Humor Adrenomedullin Levels Differ in Patients With Different Types of Glaucoma Cem Evereklioglu*, Selim Doganay*, Hamdi Er* and Muhittin Yurekli Departments of *Ophthalmology and Molecular Biology,
Special Senses: The Eye
 Unit 4 Special Senses: The Eye ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Senses General senses of touch Temperature Pressure Pain Special senses Smell Taste Sight Hearing Equilibrium The Eye and Vision
Unit 4 Special Senses: The Eye ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Senses General senses of touch Temperature Pressure Pain Special senses Smell Taste Sight Hearing Equilibrium The Eye and Vision
Clinical Research in Glaucoma
 Clinical Research in Glaucoma J. James Thimons, O.D., FAAO Chairman, National Glaucoma Society www.nationalglaucomasociety.org Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS) Primary Goals Evaluate the safety
Clinical Research in Glaucoma J. James Thimons, O.D., FAAO Chairman, National Glaucoma Society www.nationalglaucomasociety.org Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS) Primary Goals Evaluate the safety
Medicine. Observational Study. 1. Introduction OPEN
 Observational Study Medicine The association between prelaminar tissue thickness and peripapillary choroidal thickness in untreated normal-tension glaucoma patients Ji-Hye Park, MD, PhD a, Chungkwon Yoo,
Observational Study Medicine The association between prelaminar tissue thickness and peripapillary choroidal thickness in untreated normal-tension glaucoma patients Ji-Hye Park, MD, PhD a, Chungkwon Yoo,
Dr. D. Y. Patil Medical College, Pimpri, Pune
 Dr. D. Y. Patil Medical College, Pimpri, Pune - 411 018 Period : 04/July/16 to 22/September/16 Semester : 7 th Semester Department : Ophthalmology Lecture Lesson Plan Sr No Date Topic Learning objectives
Dr. D. Y. Patil Medical College, Pimpri, Pune - 411 018 Period : 04/July/16 to 22/September/16 Semester : 7 th Semester Department : Ophthalmology Lecture Lesson Plan Sr No Date Topic Learning objectives
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Steven L. Mansberger, MD; Pamela A. Sample, PhD; Linda Zangwill, PhD; Robert N. Weinreb, MD
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Achromatic and Short-Wavelength Automated Perimetry in Patients With Glaucomatous Large Cups Steven L. Mansberger, MD; Pamela A. Sample, PhD; Linda Zangwill, PhD; Robert N. Weinreb, MD
CLINICAL SCIENCES Achromatic and Short-Wavelength Automated Perimetry in Patients With Glaucomatous Large Cups Steven L. Mansberger, MD; Pamela A. Sample, PhD; Linda Zangwill, PhD; Robert N. Weinreb, MD
A,kCetazolamide lowers intraocular pressure
 Ocular and systemic effects of acetazolamide in nephrectomized rabbits Zvi Friedman,* Theodore Krupin, and Bernard Becker The effects of acetazolamide on intraocular pressure (IOP) were studied on rabbits
Ocular and systemic effects of acetazolamide in nephrectomized rabbits Zvi Friedman,* Theodore Krupin, and Bernard Becker The effects of acetazolamide on intraocular pressure (IOP) were studied on rabbits
A LITTLE ANATOMY. three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera. 2. middle - uvea. anterior - iris,ciliary body. posterior - choroid
 GLAUCOMA A LITTLE ANATOMY three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera 2. middle - uvea anterior - iris,ciliary body posterior - choroid connection at the pars plana between post and ant uvea 3. retina
GLAUCOMA A LITTLE ANATOMY three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera 2. middle - uvea anterior - iris,ciliary body posterior - choroid connection at the pars plana between post and ant uvea 3. retina
Two Pits in a Pod: Using EDI-OCT to evaluate the lamina cribrosa in a patient with openangle glaucoma and multiple optic pits
 Two Pits in a Pod: Using EDI-OCT to evaluate the lamina cribrosa in a patient with openangle glaucoma and multiple optic pits Abstract: EDI-OCT imaging is used to evaluate glaucoma by examining the thinning
Two Pits in a Pod: Using EDI-OCT to evaluate the lamina cribrosa in a patient with openangle glaucoma and multiple optic pits Abstract: EDI-OCT imaging is used to evaluate glaucoma by examining the thinning
Ocular Hypertension: General Characteristics and Estimated Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure. The Beijing Eye Study 2011
 Ocular Hypertension: General Characteristics and Estimated Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure. The Beijing Eye Study 2011 Jost B. Jonas 1,2., Ningli Wang 3., Ya Xing Wang 1., Qi Sheng You 1, Diya Yang 3, Liang
Ocular Hypertension: General Characteristics and Estimated Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure. The Beijing Eye Study 2011 Jost B. Jonas 1,2., Ningli Wang 3., Ya Xing Wang 1., Qi Sheng You 1, Diya Yang 3, Liang
Glaucoma surgery with or without adjunctive antiproliferatives in normal tension glaucoma: 2 Visual field progression
 696 Glaucoma Unit, Moorfields Eye Hospital, City Road, London EC1V 2PD, UK W L Membrey C Bunce D P Poinoosawmy F W Fitzke R A Hitchings Correspondence to: R A Hitchings roger.hitchings@virgin.net Accepted
696 Glaucoma Unit, Moorfields Eye Hospital, City Road, London EC1V 2PD, UK W L Membrey C Bunce D P Poinoosawmy F W Fitzke R A Hitchings Correspondence to: R A Hitchings roger.hitchings@virgin.net Accepted
Optic Nerve Disorders: Structure and Function and Causes
 Optic Nerve Disorders: Structure and Function and Causes Using Visual Fields, OCT and B-scan Ultrasound to Diagnose and Follow Optic Nerve Visual Losses Ohio Ophthalmological Society and Ophthalmic Tech
Optic Nerve Disorders: Structure and Function and Causes Using Visual Fields, OCT and B-scan Ultrasound to Diagnose and Follow Optic Nerve Visual Losses Ohio Ophthalmological Society and Ophthalmic Tech
GLAUCOMA. An Overview
 GLAUCOMA An Overview Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com --()-- IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your
GLAUCOMA An Overview Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com --()-- IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your
PRECISION PROGRAM. Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide. Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique
 Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide PRECISION PROGRAM Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique Available at www.ozurdexprecisionprogram.com Provides step-by-step directions with
Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide PRECISION PROGRAM Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique Available at www.ozurdexprecisionprogram.com Provides step-by-step directions with
CSF. Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System
 Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
Department of Ophthalmology
 Period : 03/July/17 to 07/September/17 Semester : 7 th Semester Department of Ophthalmology Lecture Lesson Plan Sr 1 03.07.17 Uvea-Anatomy, Uvea-Anatomy, Classification of Uveitis Dr R Paranjpe Classification
Period : 03/July/17 to 07/September/17 Semester : 7 th Semester Department of Ophthalmology Lecture Lesson Plan Sr 1 03.07.17 Uvea-Anatomy, Uvea-Anatomy, Classification of Uveitis Dr R Paranjpe Classification
Department of Ophthalmology
 Department of Ophthalmology Period : 02/July/18 to 30/August/18 Semester : 7 th Semester Lecture Lesson Plan Sr. Date Topic Lesson plan Name of Faculty No. 1 02.07.18 Lens- Lens-Anatomy, Classification
Department of Ophthalmology Period : 02/July/18 to 30/August/18 Semester : 7 th Semester Lecture Lesson Plan Sr. Date Topic Lesson plan Name of Faculty No. 1 02.07.18 Lens- Lens-Anatomy, Classification
Research Article Long-Term Clinical Course of Normal-Tension Glaucoma: 20 Years of Experience
 Hindawi Ophthalmology Volume 2017, Article ID 2651645, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2651645 Research Article Long-Term Clinical Course of Normal-Tension Glaucoma: 20 Years of Experience Sang Wook
Hindawi Ophthalmology Volume 2017, Article ID 2651645, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2651645 Research Article Long-Term Clinical Course of Normal-Tension Glaucoma: 20 Years of Experience Sang Wook
The evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer in pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma using scanning laser polarimetry
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 4, 2003 / pp. 377-382 The evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer in pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma using scanning laser polarimetry
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 4, 2003 / pp. 377-382 The evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer in pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma using scanning laser polarimetry
Relationship between Diabetes and Intraocular Pressure
 Relationship between Diabetes and Intraocular Pressure Mohammad Khalaj, Sajjad Fereydooni, and Ameneh Barikani Children Growth Research Center, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Qazvin, Iran ORIGINAL
Relationship between Diabetes and Intraocular Pressure Mohammad Khalaj, Sajjad Fereydooni, and Ameneh Barikani Children Growth Research Center, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Qazvin, Iran ORIGINAL
Diurnal IOP fluctuation: not an independent risk factor for glaucomatous visual field loss in high-risk ocular hypertension.
 Diurnal IOP fluctuation: not an independent risk factor for glaucomatous visual field loss in high-risk ocular hypertension. Bengtsson, Boel; Heijl, Anders Published in: Graefe's Archive for Clinical and
Diurnal IOP fluctuation: not an independent risk factor for glaucomatous visual field loss in high-risk ocular hypertension. Bengtsson, Boel; Heijl, Anders Published in: Graefe's Archive for Clinical and
PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY Sanjay Upadhyay 1, Jayantilal Shah 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY Sanjay Upadhyay 1, Jayantilal Shah 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor,
Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension in Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome
 Original Article Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension in Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome Azfar Ahmed Mirza, Noor Bakht Nizamani, Mariya Nazish Memon, Sajjad Ali Surhio, Khalid I. Talpur Pak J Ophthalmol 2015, Vol.
Original Article Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension in Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome Azfar Ahmed Mirza, Noor Bakht Nizamani, Mariya Nazish Memon, Sajjad Ali Surhio, Khalid I. Talpur Pak J Ophthalmol 2015, Vol.
Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 2015;113:T6[1-13] by the American Ophthalmological Society.
![Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 2015;113:T6[1-13] by the American Ophthalmological Society. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 2015;113:T6[1-13] by the American Ophthalmological Society.](/thumbs/85/92235589.jpg) OCULAR PERFUSION PRESSURE VS ESTIMATED TRANS LAMINA CRIBROSA PRESSURE DIFFERENCE IN GLAUCOMA: THE CENTRAL INDIA EYE AND MEDICAL STUDY (AN AMERICAN OPHTHALMOLOGICAL SOCIETY THESIS) By Jost B. Jonas MD,
OCULAR PERFUSION PRESSURE VS ESTIMATED TRANS LAMINA CRIBROSA PRESSURE DIFFERENCE IN GLAUCOMA: THE CENTRAL INDIA EYE AND MEDICAL STUDY (AN AMERICAN OPHTHALMOLOGICAL SOCIETY THESIS) By Jost B. Jonas MD,
Optic nerve head morphometry in healthy adults using confocal laser scanning tomography
 761 SCIENTIFIC REPORT Optic nerve head morphometry in healthy adults using confocal laser scanning tomography M M Hermann, I Theofylaktopoulos, N Bangard, C Jonescu-Cuypers, S Coburger, M Diestelhorst...
761 SCIENTIFIC REPORT Optic nerve head morphometry in healthy adults using confocal laser scanning tomography M M Hermann, I Theofylaktopoulos, N Bangard, C Jonescu-Cuypers, S Coburger, M Diestelhorst...
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Conversion of Ocular Hypertensives into Glaucoma: A Retrospective Study Aditi Singh 1, Shibi
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Conversion of Ocular Hypertensives into Glaucoma: A Retrospective Study Aditi Singh 1, Shibi
The Use of SLT in Secondary Open Angle Glaucomas ( PEXG, PDG)
 The Use of SLT in Secondary Open Angle Glaucomas ( PEXG, PDG) Prof. S. Melamed The Sam Rothberg Glaucoma Center Tel Aviv University Medical School Israel Wear and Tear Glaucoma * Particulate Matter Glaucoma
The Use of SLT in Secondary Open Angle Glaucomas ( PEXG, PDG) Prof. S. Melamed The Sam Rothberg Glaucoma Center Tel Aviv University Medical School Israel Wear and Tear Glaucoma * Particulate Matter Glaucoma
