CSF. Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System
|
|
|
- Rosemary Charles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System
2 By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions Diseases
3 CEREBROSPINAL FLUID SYSTEM Capacity of entire cerebral cavity enclosing the brain and spinal cord to 1700 milliliters Cerebrospinal fluid milliliters
4 C.S.F Location Ventricles of brain Cisterns around & outside the brain Subarachnoid space around: Brain Spinal cord All these chambers are connected with one another Constant pressure
5 Ventricles of Brain (Right Lateral aspect) CSF
6 Ventricles of Brain (Anterior aspect) CSF
7 Choroid Plexus in a lateral Ventricle
8 Formation of CSF CSF Sites: >2/3 by Choroid plexus in 4 ventricles mainly in two lateral ventricles <1/3 by Ependymal surfaces of all the ventricles and by the arachnoidal membranes Choroid plexus: Cauliflower like growth of blood vessels covered by thin epithelium, projecting into all ventricles Mechanism of secretion: Active transport of Na Passive transport of Chloride Osmosis of water ml/day (0.2 ml/min) Total ml
9 Composition CSF And Characteristics 1. Osmotic pressure is equal to that of plasma 2. [Na+] is nearly equal to that of plasma 3. [Cl - ] 15% greater than plasma 4. [K + ] is 40% less 5. Ca ++ is also less 6. Glucose is 30% less (64mg%) 7. Protein. Only 20-25mg% as compared to 6000mg% in plasma 8. Cells. Very few lymphocytes (1-5 cell/mm 3 ) 9. Specific gravity = 1.005
10 Circulation of C.S.F Lateral Ventricles Monro 3 rd Ventricle Aqueduct of Sylvius (Mesencephalic Aqueduct) Subarachnoid Space 2 Luschka (lat.) 1 Magendie 4 th Ventricle
11
12 Pathway of CSF CSF
13 Flow of CSF CSF
14 Flow of CSF cisterna magna- a fluid space that lies behind the medulla and beneath the cerebellum CSF The cisterna magna is continuous with the subarachnoid space
15 CSF flows upward-- cisterna magna through the subarachnoid spaces surrounding the cerebrum---arachnoidal villi -- sagittal venous sinus and others fluid empties into the venous blood through pores of these villi
16 Absorption CSF To the venous system by bulk fluid through arachnoid granulations, located in the superior sagital sinus by pressure gradient. Arachnoid granulations : Projections of arachnoidal membrane in venous sinuses:- Arachnoid villi (Microscopic) Collection of Arachnoid villi:- Arachnoidal Granulations (Macroscopic) Endothelial cells cover the villi and absorb through vesicular passages directly through the bodies of the cells CSF Dissolved protein molecules RBC, WBC
17 Drainage of a PERIVASCULAR SPACE into the subarachnoid space Lymphatic system
18 Perivascular Spaces and Cerebrospinal Fluid. ends of large arteries and veins penetrate inward-- carry pia mater (the membrane that covers the brain) pia loosely adherent to vessels -- perivascular space, exists between it and each vessel CSF
19 Lymphatic Function of the Perivascular Spaces protein leak from brain capillaries----interstitial spaces of brain----perivascular spaces----- subarachnoid spaces absorbed through the arachnoidal villi ---- large cerebral veins In case of infection in the brain, dead white blood cells and infectious debris are carried away through the perivascular spaces
20 CSF Pressure 130 mm H 2 O (10 mmhg) lying in horizontal position Range: mm H 2 O C.S.F absorption stops below 68 mm H 2 O
21 Regulation of CSF Pressure CSF Balance between formation and reabsorption Formation Almost constant rate Abnormally high amount of cells or proteins may block the reabsorption
22 Reabsorption Arachnoidal villi function like valves that allow cerebrospinal fluid and its contents to flow readily into the blood of the venous sinuses while not allowing blood to flow backward in the opposite direction Due to pressure gradient CSF flows into venous sinuses when its pressure is 1.5 mm Hg greater than the pressure of the blood in the venous sinuses. CSF
23 Normally pressure does not rise due to reabsorption in case of increased pressure CSF Increase in CSF pressure occurs (diseases) : The villi get blocked by large particulate matter fibrosis excesses of blood cells that have leaked into the cerebrospinal fluid Diseases of villi result in reabsorption Number of villi Quality of villi
24 Effects of CSF Pressure Hydrocephalus Excess water in cranial vault Types Communicating Non-Communicating
25 1. Communicating hydrocephalus fluid flows readily from the ventricular system into the subarachnoid space 2. Non-communicating hydrocephalus fluid flow out of one or more of the ventricles is blocked block in the aqueduct of Sylvius-- closure before birth
26 Hydrocephalus CSF Communicating Hydrocephalus Blockage of fluid flow in subarachnoid space Blockage of Arachnoid villi Fluid collects outside and inside brain Non-Communicating Hydrocephalus Block in Aqueduct of Sylvius Atresia (Closure) Brain tumors
27 Effects of hydrocephalus Swelling of head in children Brain damage
28 Diseases related to CSF (Brain edema) When systems for protecting against transudation of fluid into the brain break down e.g. Brain concussion Blow to head High blood pressure Mechanism Capillary Pressure Damage to capillary walls Coma and death
29 Effects of Brain Edema Brain compression Brain damage Compression of blood vessels Initiation of two vicious cycles
30 Two vicious cycles due to Brain Edema CSF Capillary Pressure EDEMA Arteriolar Dilatation Compression of blood vessels Brain ischemia Blood flow Contd
31 Cerebral Blood flow Two vicious cycles due to Brain Edema Contd CSF Capillary Permeability EDEMA O 2 Delivery Compression of blood vessels
32 Treatment of Brain Edema Emergency Osmotic diuretics Mannitol Ventricular needle puncture
33 Cushioning Function of C.S.F Specific gravity of brain and CSF is about same so a blow to head (if not too severe) moves the entire brain simultaneously with skull
34 Diseases related to CSF (Brain injury) Coupe Damage/injury to the brain on the same side of trauma Countercoup Damage/injury to the brain on the opposite side of trauma
35 Effects of CSF Pressure 1. Papilledema 2. Hydrocephalus
36 Effects of CSF Pressure Papilledema : Edema of the Optic Disc Retinal edema Mechanism: 1. Fluid pushed into Optic nerve sheath Spaces between optic nerve fibers 2. outward flow of fluid in optic nerves 3. outward flow of blood in retinal veins Significance of Papilledema Clinical diagnosis of CSF Pressure by ophthalmoscope Effects of Papilledema Blindness/ blurred vision CSF
37 Blood-CSF and Blood- Brain Barriers CSF Blood-CSF barrier tight junctions between adjacent choroid epithelial cells Blood-brain barrier tight junctions between adjacent endothelial cells of brain capillaries
38 Blood-CSF and Blood- Brain Barriers All areas of brain parenchyma except Some areas of hypothalamus, pineal gland, area postrema Sensory receptors Osmolarity, glucose Controlled permeability Highly permeable to Water, CO 2, O 2, most lipid-soluble substances Slightly permeable to Electrolytes e.g. Na +, Cl -, Impermeable to K+ Plasma proteins, most lipid-non-soluble organic molecules Therapeutic drugs CSF
39 Functions of C.S.F 1. Acts as fluid buffer (cushioning the CNS against injury) 2. Acts as reservoir to regulate the contents of the cranium 3. May act as a medium of nutrient exchange in the CNS However brain carries out its metabolic exchanges directly 4. Clinical - Diagnostic Therapeutic
40 THANK YOU CSF
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Blood Brain Barrier (BBB)
 Cerebral Blood Flow, Cerebral Spinal Fluid, and Brain Metabolism Part Two Guyton Chapter 61 Morgan & Mikhail, 4 th ed, Chapter 25 (or Morgan & Mikhail 5 th ed, Chapter 26) Blood Brain Barrier (BBB) Cerebral
Cerebral Blood Flow, Cerebral Spinal Fluid, and Brain Metabolism Part Two Guyton Chapter 61 Morgan & Mikhail, 4 th ed, Chapter 25 (or Morgan & Mikhail 5 th ed, Chapter 26) Blood Brain Barrier (BBB) Cerebral
CEREBRO SPINAL FLUID ANALYSIS IN BRAIN TUMOUR
 CEREBRO SPINAL FLUID ANALYSIS IN BRAIN TUMOUR Sankar K 1, Shankar N 2, Anushya 3, ShymalaDevi 4, Purvaja 5 3,4,5 III Biomedical Student, Alpha college of Engineering, Chennai. kssankar10@yahoo.co.in 1,
CEREBRO SPINAL FLUID ANALYSIS IN BRAIN TUMOUR Sankar K 1, Shankar N 2, Anushya 3, ShymalaDevi 4, Purvaja 5 3,4,5 III Biomedical Student, Alpha college of Engineering, Chennai. kssankar10@yahoo.co.in 1,
Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves. Chapter 14 Part A
 Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Part A Central Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) is responsible for: Receiving impulses from receptors Integrating information Sending
Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Part A Central Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) is responsible for: Receiving impulses from receptors Integrating information Sending
Chapter 14. The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid
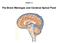 Chapter 14 The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Meninges of the Brain Skull Brain: Blood vessel Pia mater Gray matter White matter Dura mater: Periosteal layer Meningeal layer Arachnoid villus
Chapter 14 The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Meninges of the Brain Skull Brain: Blood vessel Pia mater Gray matter White matter Dura mater: Periosteal layer Meningeal layer Arachnoid villus
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord. Major Divisions of the nervous system:
 Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
The Nervous System. PowerPoint Lecture Slides C H A P T E R 7. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
Central Nervous System: Part 2
 Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Skeletal muscle. Flow increases and decreases with each muscular contraction - as a result of compression of the blood vessels by contracted muscle
 Regional blood flow Skeletal muscle Extreme increases during exercises Flow increases and decreases with each muscular contraction - as a result of compression of the blood vessels by contracted muscle
Regional blood flow Skeletal muscle Extreme increases during exercises Flow increases and decreases with each muscular contraction - as a result of compression of the blood vessels by contracted muscle
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Blood Vessels. Chapter 20
 Blood Vessels Chapter 20 Summary of the Characteristics of Arteries and Veins Characteristic Artery Vein Wall thickness thick thin Shape in cross section round flattened Thickest tunic media externa Collagen
Blood Vessels Chapter 20 Summary of the Characteristics of Arteries and Veins Characteristic Artery Vein Wall thickness thick thin Shape in cross section round flattened Thickest tunic media externa Collagen
The Nervous System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
Physiology of Circulation
 Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
Histology of the CNS
 Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
ICP CSF Spinal Cord Anatomy Cord Transection. Alicia A C Waite March 2nd, 2017
 ICP CSF Spinal Cord Anatomy Cord Transection Alicia A C Waite March 2nd, 2017 Monro-Kellie doctrine Intracranial volume = brain volume (85%) + blood volume (10%) + CSF volume (5%) Brain parenchyma Skull
ICP CSF Spinal Cord Anatomy Cord Transection Alicia A C Waite March 2nd, 2017 Monro-Kellie doctrine Intracranial volume = brain volume (85%) + blood volume (10%) + CSF volume (5%) Brain parenchyma Skull
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
action potential afferent neuron Weblike; specifically, the weblike middle layer of the three meninges. arachnoid astrocytes autonomic nervous system
 action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
Body Fluids and Fluid Compartments
 Body Fluids and Fluid Compartments Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The chemical reactions of life take place in aqueous solutions. The dissolved substances in a solution are called solutes. In the human body, solutes
Body Fluids and Fluid Compartments Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The chemical reactions of life take place in aqueous solutions. The dissolved substances in a solution are called solutes. In the human body, solutes
NANOS Patient Brochure
 NANOS Patient Brochure Pseudotumor Cerebri Copyright 2016. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for
NANOS Patient Brochure Pseudotumor Cerebri Copyright 2016. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF]
![CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF] CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF]](/thumbs/89/100552494.jpg) CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF] All question is compulsory Minimum passing mark is 15. 1. Full form of a) CSF = b) LDH = c) ADA = 2. If patient serum glucose level is 300 mg%,than expected csf glucose level
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF] All question is compulsory Minimum passing mark is 15. 1. Full form of a) CSF = b) LDH = c) ADA = 2. If patient serum glucose level is 300 mg%,than expected csf glucose level
Microcirculation and Edema. Faisal I. Mohammed MD, PhD.
 Microcirculation and Edema Faisal I. Mohammed MD, PhD. Objectives: Point out the structure and function of the microcirculation. Describe how solutes and fluids are exchang in capillaries. Outline what
Microcirculation and Edema Faisal I. Mohammed MD, PhD. Objectives: Point out the structure and function of the microcirculation. Describe how solutes and fluids are exchang in capillaries. Outline what
Central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord Collections of cell body and dendrites (grey matter) are called nuclei/nucleus Nucleus can also
 Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Microcirculation and Edema- L1 L2
 Microcirculation and Edema- L1 L2 Faisal I. Mohammed MD, PhD. University of Jordan 1 Objectives: Point out the structure and function of the microcirculation. Describe how solutes and fluids are exchanged
Microcirculation and Edema- L1 L2 Faisal I. Mohammed MD, PhD. University of Jordan 1 Objectives: Point out the structure and function of the microcirculation. Describe how solutes and fluids are exchanged
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES
 BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
Spinal Cord and Properties of Cerebrospinal Fluid: Options for Drug Delivery. SMA Foundation New York
 Spinal Cord and Properties of Cerebrospinal Fluid: Options for Drug Delivery New York Why Do We Need to Know about the Spinal Cord Anatomy and Properties of Cerebrospinal Fluid? SMA therapeutics need to
Spinal Cord and Properties of Cerebrospinal Fluid: Options for Drug Delivery New York Why Do We Need to Know about the Spinal Cord Anatomy and Properties of Cerebrospinal Fluid? SMA therapeutics need to
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Bellringer: The central nervous system is comprised of: What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Brain. b.
 Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
SPINAL CORD AND PROPERTIES OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID: OPTIONS FOR DRUG DELIVERY
 SPINAL CORD AND PROPERTIES OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID: OPTIONS FOR DRUG DELIVERY WHY DO WE NEED TO KNOW ABOUT THE SPINAL CORD ANATOMY AND PROPERTIES OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID? SMA therapeutics need to reach cells
SPINAL CORD AND PROPERTIES OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID: OPTIONS FOR DRUG DELIVERY WHY DO WE NEED TO KNOW ABOUT THE SPINAL CORD ANATOMY AND PROPERTIES OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID? SMA therapeutics need to reach cells
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
The Nervous System. Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes =
 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic System
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well
 Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well describe the factors which regulate cardiac output describe the sympathetic and parasympathetic control of heart
Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well describe the factors which regulate cardiac output describe the sympathetic and parasympathetic control of heart
Physiology of Circulation. Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 16/12/2018
 Physiology of Circulation Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 16/12/2018 Overview of the circulation The function of the circulation is to: 1. transport nutrients to the body tissues 2. transport waste products away 3. conduct
Physiology of Circulation Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 16/12/2018 Overview of the circulation The function of the circulation is to: 1. transport nutrients to the body tissues 2. transport waste products away 3. conduct
HST-583 Cerebrovascular anatomy and neural regulation of CNS blood flow
 HST.583: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology Dr. Randy Gollub HST-583 Cerebrovascular anatomy and neural regulation
HST.583: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology Dr. Randy Gollub HST-583 Cerebrovascular anatomy and neural regulation
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System. Anatomy of the CNS
 CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
Introduction to the Organization of the Brain 98% of the body s neural tissue is in the brain
 Introduction to the Organization of the Brain 98% of the body s neural tissue is in the brain An avg. human brain weighs 1.4 kg (3lbs.) and has a volume of 1200 cc brains average about 10% bigger than
Introduction to the Organization of the Brain 98% of the body s neural tissue is in the brain An avg. human brain weighs 1.4 kg (3lbs.) and has a volume of 1200 cc brains average about 10% bigger than
Nervous System: An Introduction. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Nervous system. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
DRUG DISTRIBUTION. Distribution Blood Brain Barrier Protein Binding
 DRUG DISTRIBUTION Distribution Blood Brain Barrier Protein Binding DRUG DISTRIBUTION Drug distribution is a reversible transport of drug through the body by the systemic circulation The drug molecules
DRUG DISTRIBUTION Distribution Blood Brain Barrier Protein Binding DRUG DISTRIBUTION Drug distribution is a reversible transport of drug through the body by the systemic circulation The drug molecules
Chapter 4 Cell Membrane Transport
 Chapter 4 Cell Membrane Transport Plasma Membrane Review o Functions Separate ICF / ECF Allow exchange of materials between ICF / ECF such as obtaining O2 and nutrients and getting rid of waste products
Chapter 4 Cell Membrane Transport Plasma Membrane Review o Functions Separate ICF / ECF Allow exchange of materials between ICF / ECF such as obtaining O2 and nutrients and getting rid of waste products
Physiology of Circulation
 Physiology of Circulation Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. 12/8/2005 1 PHYSIOLOGY OF CIRCULATION BLOOD FLOW THROUGH THE CAPILLARIES LYMPHATIC SYSTEM BLOOD PRESSURE 12/8/2005 2 1 Fig.21.08 12/8/2005 3 The Blood Pressure
Physiology of Circulation Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. 12/8/2005 1 PHYSIOLOGY OF CIRCULATION BLOOD FLOW THROUGH THE CAPILLARIES LYMPHATIC SYSTEM BLOOD PRESSURE 12/8/2005 2 1 Fig.21.08 12/8/2005 3 The Blood Pressure
Head Trauma Inservice (October)
 John Tramell - Head Trauma Inservice, October 2005.doc Page 1 Head Trauma Inservice (October) Head trauma is the leading cause of death in trauma patients. Having a basic understanding of the anatomy and
John Tramell - Head Trauma Inservice, October 2005.doc Page 1 Head Trauma Inservice (October) Head trauma is the leading cause of death in trauma patients. Having a basic understanding of the anatomy and
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy Examination 1
 Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy Examination 1 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your scantron answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet ID
Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy Examination 1 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your scantron answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet ID
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 71
 71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
Cardiovascular System. Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Blood Supply of the CNS
 Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Sinusoids and venous sinuses
 LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System
 Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Nervous System: An Introduction. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b
 Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Neurotransmitter: dopamine. Physiology of additive drugs. Dopamine and reward. Neurotransmitter: dopamine
 Physiology of additive drugs Cocaine, methamphetamine, marijuana, and opiates influence the neurotransmitter dopamine. Neurotransmitter: dopamine Dopamine - a neurotransmitter associated with several functions,
Physiology of additive drugs Cocaine, methamphetamine, marijuana, and opiates influence the neurotransmitter dopamine. Neurotransmitter: dopamine Dopamine - a neurotransmitter associated with several functions,
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES
 NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: OBJECTIVES OSTEOLOGY. Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD
 Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more
 Nervous system Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Devoid from connective
Nervous system Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Devoid from connective
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Student Objectives
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Student Objectives Chapter 14 Textbook and Laboratory Manual Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions Name the ventricles of the brain and describe
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Student Objectives Chapter 14 Textbook and Laboratory Manual Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions Name the ventricles of the brain and describe
Chapter 2. Central Nervous System; the brain and spinal cord
 Chapter 2 Central Nervous System; the brain and spinal cord CNS 1. Topography; - what are the main components of the brain - how do you recognize them? 2. The location of the major functional areas of
Chapter 2 Central Nervous System; the brain and spinal cord CNS 1. Topography; - what are the main components of the brain - how do you recognize them? 2. The location of the major functional areas of
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord
 SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
Chapter 23. Circulation
 Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Ch 3 Membrane Transports
 Ch 3 Membrane Transports what's so dynamic about cell membranes? living things get nutrients and energy from the envrionment this is true of the entire organism and each cell this requires transport in/out
Ch 3 Membrane Transports what's so dynamic about cell membranes? living things get nutrients and energy from the envrionment this is true of the entire organism and each cell this requires transport in/out
Microcirculation. Lecture Block 11 (contributions from Brett Burton)
 Lecture Block 11 (contributions from Brett Burton) Elements of Arterioles, capillaries, venules Structure and function: transport Fluid balance Lymph system Vessels of the Circulatory System Diameter Aorta
Lecture Block 11 (contributions from Brett Burton) Elements of Arterioles, capillaries, venules Structure and function: transport Fluid balance Lymph system Vessels of the Circulatory System Diameter Aorta
UNIT 4: BLOOD VESSELS
 UNIT 4: BLOOD VESSELS Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NRS237, Physiology Generalized Structure of Blood Vessels 1 Tunica interna (tunica intima) Endothelial layer that lines the lumen of all vessels In vessels
UNIT 4: BLOOD VESSELS Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NRS237, Physiology Generalized Structure of Blood Vessels 1 Tunica interna (tunica intima) Endothelial layer that lines the lumen of all vessels In vessels
Mechanisms of fluid movement into, through and out of the brain: evaluation of the evidence
 Hladky and Barrand Fluids and Barriers of the CNS 2014, 11:26 FLUIDS AND BARRIERS OF THE CNS REVIEW Open Access Mechanisms of fluid movement into, through and out of the brain: evaluation of the evidence
Hladky and Barrand Fluids and Barriers of the CNS 2014, 11:26 FLUIDS AND BARRIERS OF THE CNS REVIEW Open Access Mechanisms of fluid movement into, through and out of the brain: evaluation of the evidence
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow. Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD
 Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD Outline 1- Physical laws governing blood flow and blood pressure 2- Overview of vasculature 3- Arteries 4. Capillaries and venules
Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD Outline 1- Physical laws governing blood flow and blood pressure 2- Overview of vasculature 3- Arteries 4. Capillaries and venules
Nervous System. Part Two
 Nervous System Part Two CNS: Spinal Cord Protected by bone, fluid, & membranes Composed of gray and white matter Serves as conduction pathway btwn brain and peripheral nerves Extends from base of brain
Nervous System Part Two CNS: Spinal Cord Protected by bone, fluid, & membranes Composed of gray and white matter Serves as conduction pathway btwn brain and peripheral nerves Extends from base of brain
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Tomography vs Topography. Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain. Learning Objective
 Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
PHYSIOLOGY OF CSF AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF HYDROCEPHALUS
 PHYSIOLOGY OF CSF AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF HYDROCEPHALUS Introduction Dynamic component of CNS Invaluable tool to diagnosis Physiological reservoir of human proteome Reflects the physiologic state of CNS
PHYSIOLOGY OF CSF AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF HYDROCEPHALUS Introduction Dynamic component of CNS Invaluable tool to diagnosis Physiological reservoir of human proteome Reflects the physiologic state of CNS
The CNS Part II pg
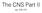 The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
The Nervous System An overview
 Nervous System The Nervous System An overview Includes Nerve tissue Sense organs Functions to Sense environment Process information it receives Respond to information 1 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Nervous System The Nervous System An overview Includes Nerve tissue Sense organs Functions to Sense environment Process information it receives Respond to information 1 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
PHYSIOLOGY WEEK 9. vascular physiology - ED Primary Exam Teaching
 PHYSIOLOGY WEEK 9 vascular physiology - ED Primary Exam Teaching CONCEPTS OF BLOOD FLOW Vascular distensibility - when pressure in the arterioles is increased, this dilates the arterioles and therefore
PHYSIOLOGY WEEK 9 vascular physiology - ED Primary Exam Teaching CONCEPTS OF BLOOD FLOW Vascular distensibility - when pressure in the arterioles is increased, this dilates the arterioles and therefore
Eye Fluids. Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 Eye Fluids 1 Reference Books: Text Book of Medical physiology (Guyton and Hall) Eleventh edition 2 Fluid System of the Eye (Intraocular Fluid) The eye is filled with intraocular fluid, which maintains
Eye Fluids 1 Reference Books: Text Book of Medical physiology (Guyton and Hall) Eleventh edition 2 Fluid System of the Eye (Intraocular Fluid) The eye is filled with intraocular fluid, which maintains
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
Cardiovascular System L-5 Special Circulations, hemorrhage and shock. Dr Than Kyaw March 2012
 Cardiovascular System L-5 Special Circulations, hemorrhage and shock Dr Than Kyaw March 2012 Special circulation (Coronary, Pulmonary, and Cerebral circulations) Introduction Special attention to circulation
Cardiovascular System L-5 Special Circulations, hemorrhage and shock Dr Than Kyaw March 2012 Special circulation (Coronary, Pulmonary, and Cerebral circulations) Introduction Special attention to circulation
Papilledema. Golnaz Javey, M.D. and Jeffrey J. Zuravleff, M.D.
 Papilledema Golnaz Javey, M.D. and Jeffrey J. Zuravleff, M.D. Papilledema specifically refers to optic nerve head swelling secondary to increased intracranial pressure (IICP). Optic nerve swelling from
Papilledema Golnaz Javey, M.D. and Jeffrey J. Zuravleff, M.D. Papilledema specifically refers to optic nerve head swelling secondary to increased intracranial pressure (IICP). Optic nerve swelling from
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
