Migrainous headache, the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. Dr Manuela Fontebasso Headache Specialist, Author and Headache Education Facilitator
|
|
|
- Lawrence Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Migrainous headache, the menstrual cycle and pregnancy Dr Manuela Fontebasso Headache Specialist, Author and Headache Education Facilitator
2 What sort of headaches? Migraine with and without aura Tension Type Headache Cluster Headache Episodic or Chronic Daily headaches Chronic migraine Medication overuse Headache 1. Clinical Guidance 150, available at: Accessed January Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. ICHD-3 beta. Cephalalgia 2013; 33 (9)
3 Migraine Lasts from 4 hours to 3 days May, or may not be associated with aura Usually a moderate to severe pain Is associated with symptoms and features nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea light, sound smell sensitivity feel clumsy, dizzy speech affected Tends to prevent day-to-day activities Acute treatment may not always be effective Increasingly frequent headache days increases the possibility of medication overuse headache developing with time Consider preventative medication if the number of headache days edges towards 6 to 8 days each month 1. Clinical Guidance 150, available at: Accessed January Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. ICHD-3 beta. Cephalalgia 2013; 33 (9)
4 Tension Type Headache Usually short lived Usually a mild to moderate pain Is NOT associated with symptoms or features Tends NOT to prevent day-to-day activities Increasingly frequent headache days increases the possibility of medication overuse headache developing with time Consider preventative medication if the number of headache days edges towards 6 to 8 days each month 1. Clinical Guidance 150, available at: Accessed January Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. ICHD-3 beta. Cephalalgia 2013; 33 (9)
5 Cluster Headache Lasts from 15 minutes to 3 hours Usually a severe to very severe pain Is associated with symptoms and on the same side of the headache e.g. red eye, watery eye, runny or blocked nose Tends to cause restlessness, agitation and sleep disturbance Acute treatment may not always be effective, especially if the attacks are short lived Preventative medication may be successful in shortening an episode of cluster, and can prevent a flare of symptoms of chronic cluster headache 1. Clinical Guidance 150, available at: Accessed January Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. ICHD-3 beta. Cephalalgia 2013; 33 (9)
6 Medication Overuse Headache A chronic headache tending to occur on a daily or near daily basis Varies from a mild to a severe headache, through the day and from day-to-day Can, on occasion, prevent day-to-day activities When acute medication is stopped, the headache will get worse before it gets better but the only way to break the cycle Use preventative medication to manage the headache pain whilst stopping acute medication 1. Clinical Guidance 150, available at: Accessed January Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. ICHD-3 beta. Cephalalgia 2013; 33 (9)
7 Optimising treatment Treat the right headache with the right treatment Tailor the treatment to best meet the need of the patient involve the patient in the decision making Agree a clear plan optimise acute treatment minimise headache days agree a review session Engage the GP or Practice Nurse in the support process Review the patient until they feel in control of their headache 1. Clinical Guidance 150, available at: Accessed January Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. ICHD-3 beta. Cephalalgia 2013; 33 (9)
8 The Acute treatment of Migraine
9 Goals of Acute Migraine Treatment Treat high impact headache only minimises risk of medication overuse headache developing Treat the aura or premonitory symptoms early may maximise the effect of the headache treatment may prevent the onset of the headache or reduce its severity Treat the headache early To make the treatment more effective Increase the chance of being headache free at 2 hours To minimise the chance of headache recurrence reduce the total number of headache days minimise the risk of medication overuse headache developing
10 CLINICAL PATTERNS - MIGRAINE - Signs & Symptoms Headache Normal Appetite Awake/Sleep Tired yawning Light tolerance Noise Smell Fluid balance Craving Heightened perception Fluid retention Anorexia Nausea Vomiting Vomiting Sleepy yawning Deep sleep Photophobia Photophobia Phonophobia Phonophobia Osmophobia Osmophobia Limited food tolerance Tired Feeling High Low Diuresis Normal Normal I Premonitory II Aura III Headache IV V Resolution Recovery Normal
11 Diet and Lifestyle Advice Diet regular meals adequate fluids combination triggers Stress Counselling, relaxation, yoga Sleep patterns shifts, travel, social functions The higher the threshold the less likely you are to get a headache The lower the threshold the more likely you are to get a headache Encourage you to put yourself top of the heap some of the time Ideally EVERY day
12 Goal setting Acute treatment Complete resolution of symptoms within 2 to 4 hours with no recurrence of symptoms during that attack treat early, ideally within one hour of the start of the headache use a combination to maximise the benefit NSAID, anti-emetic and/or triptan If the first combination does not work try another AT REVIEW Check the dose or delivery system of the medication the patient is taking Check timing premonitory, aura or headache How long before the patient is headache free? Does the headache return that day or the next day? What does the patient do if the headache returns during this attack?
13 1. Clinical Guidance 150, available at: Accessed Sept BASH Guidelines, available at: accessed Sept 2017 Acute treatment simple painkillers Soluble aspirin 900mg, domperidone 10 to 30mg or metoclopramide 10mg might have tried this but at a lower dose Naproxen 500mg to 1g, no more than once a day often of benefit for those who have menstrual migraine Ibuprofen 400mg to 600mg up to three times a day useful as dose can be repeated in the day Diclofenac 100mg, as a suppository if early nausea and vomiting Migramax, 1 sachet in water and repeat in 2 hours if needed for those patients who can t take or tolerate triptans Paracetamol, in a soluble format, 1500mg as a single dose if unable to take NSAID
14 Acute treatment -Triptans Migraine specific Only to be taken as the headache starts May cause side effects which include tingling, chest tightness, throat tightness Should stop all the symptoms of the attack Don t work for everybody 50 to 80% of people get a reduction in headache 20 to 50% become headache free 25 to 50% of people find the headache can return There are 7 different triptans available as a tablet, a wafer, a nasal spray, an injection Minimise perceived cost by optimising acute treatment and minimising headache days
15 1. Clinical Guidance 150, available at: Accessed Sept BASH Guidelines, available at: accessed Sept 2017 Triptans available in the UK Sumatriptan 50 & 100mg tablet 20mg nasal spray 6mg injection 10mg Adolescent nasal spray for 12 to 18 year olds RADIS 50 &100mg Zolmitriptan 2.5 mg tablet 2.5 & 5mg rapimelt 5mg nasal spray Naratriptan 2.5mg tablet Rizatriptan 5 & 10mg tablet 10mg wafer Almotriptan 12.5mg tablet Eletriptan 20 & 40mg tablet best taken as 80mg dose Frovatriptan 2.5mg tablet
16 Triptans Contraindications Not licensed under 18 or over 60 sumatriptan adolescent nasal spray is licensed for 12 to 18 year olds Significant liver disease History of cardiovascular disease angina, previous heart attack TIA or previous stroke Badly controlled blood pressure if well controlled then can be taken Using St John s Wort Using ergotamine At the same time as taking another triptan
17 Acute treatment top tips Only take the triptan at the start of the headache Raise awareness of the headache threshold Think about diet and lifestyle factors to raise the headache threshold Optimise the acute treatment to prevent headache recurrence offer flexibility in dose and delivery system Raise awareness that if the treatment becomes less effective there is a probability that medication overuse headache is developing If there are more than 6 to 8 treatment days a month there is a probability that medication overuse headache is developing
18 Medication overuse Headache
19 Medication overuse Headache Associated with the uncritical use of painkillers Use them more often Increase the strength of the tablets taken Take them just in case Can occur when taking Simple painkillers more often than four days in the week Combination painkillers more often than three days in the week Triptans, opiates or ergotamine more often than two days in the week Only when treating headache not other causes of pain Unless you have a history of migraine
20 Headache intensity Medication Overuse Headache* Increased frequency of headache, associated with increased frequency of the use of painkillers. Withdrawal of all painkillers Daily headache with spikes of more severe pain Stop all acute analgesic medication Return of episodic headache Migraine attacks * Adapted from MIPCA guidelines, 1997 Frequent daily headaches
21 Codeine the hidden extra Boots Tension Headache relief - 10mg Codis 500-8mg Nurofen Plus mg Panadol Ultra mg Paracodol - 8mg Propain - 10mg Solpadeine Max mg Solpadeine Migraine 12.8mg Syndol - 10mg Veganin - 8mg
22 Caffeine friend or foe? Coffee, 150ml, 60 to 150mg Coffee, decaff, 150ml, 2 to 5mg Tea, 150ml, 40 to 80mg Hot cocoa, 150ml, 1 to 8mg Diet coca cola, 12oz, 45mg Coca cola, 12oz, 64mg Dr Pepper, 12oz, 61mg Pepsi Cola, 12oz, 43mg WHY? Because 200mg of caffeine taken on a daily basis for 2 weeks can cause a headache when the caffeine is stopped or the level drops
23 Hidden caffeine Anadin extra 45mg 5 tablets is 220mg Anadin maximum strength 32mg 6 tablets is 192mg Boots Tension Headache Relief 30mg 6 tablets is 180mg Hedex Extra 65mg Panadol Extra 65mg Propain 50mg 4 tablets is 260mg 4 tablets is 260mg 4 tablets is 200mg Solpadeine Headache 65mg 4 tablets is 260mg Syndol 30mg 6 tablets is 180mg
24 Medication overuse Headache Treat migraine aggressively and effectively BUT not too often Keep treatment days to 6 or less each month Ten triptan days per month over a 3 month period means there is a probability that triptan rebound headache is developing
25 Get back to episodic migraine Optimise diet and lifestyle Plan a stop date THEN STOP ALL your painkillers but tell the patient to continue to take all their medication for other health problems Start the preventative medication on the same day The patient MUST NOT take any acute treatment for at least 6 to 8 weeks Headaches will get worse before they get better Review the number of headache days every month Plan how to treat the migraine
26 Preventative headache treatment
27 1. Clinical Guidance 150, available at: Accessed Sept BASH Guidelines, available at: accessed Sept 2017 Preventative treatment the challenge There are no ideal drugs They can reduce the number of headache days BUT will not stop all the headaches Any drug has the potential to cause side effects BUT only in some of the people some of the time Drug choice may be guided by other health problems Sometimes the side effects form part of the plan The drug chosen must be taken long enough to work The drug chosen must be taken at a high enough dose to work Start low and build slow To minimise side effects and find the lowest effective dose
28 1. Clinical Guidance 150, available at: Accessed Sept BASH Guidelines, available at: accessed Sept 2017 Drugs used in headache reduction Beta-blockers Propranolol Atenolol Metoprolol Tricyclic antidepressants Amitriptyline Imipramine Nortriptyline Dosulepin ARB Candesartan ACE Lisinopril Anti-epilepsy drugs Topiramate Sodium valproate Gabapentin If also have chronic pain Calcium Channel Blockers Verapamil Cluster headache only Pizotifen Methysergide Tertiary centre only
29 Preventative medication goal setting Aim to reduce the total number of headache days Increase the effectiveness of any acute treatment Agree an initial target dose Agree a dose titration schedule Agree a review date Use a diary card to review the response to acute medication and the change in headache days
30 1. Clinical Guidance 150, available at: Accessed Sept BASH Guidelines, available at: accessed Sept 2017 Most common preventatives used Propranolol Slow release, single daily dose Up to maximum 240mg Amitriptyline 10 to 100mg At night or in split doses 2 hours before bedtime Or 12 hours before you want to get up Candesartan 4mg to 16mg Lisinopril Start at 2.5mg Increase by 2.5mg increments every 2 weeks Max dose of 20mg Topiramate 50mg twice a day Start at 15mg or 25mg If side effects develop step back to last best tolerated dose
31 Preventative medication at review How good is the acute treatment response? How quickly does the pain become more manageable? How soon do you get back to normal? How soon does the headache go completely? Does the headache go away and stay away? How effective is the preventative medication? Is there a reduction in the number headache days? Are there any side effects from the medication?
32 Preventative medication changes to consider Optimise the acute treatment response Try each treatment or treatment combination Evaluate the response in three consecutive attacks Optimise the preventative treatment response Review side effects Consider a dose change if few or no side effects Consider a drug change If side effects are a problem If the maximum dose is reached Agree a review appointment
33 Preventative medication - conclusion Preventative medication can help some of the people some of the time The goal is to reduce the number of headache days with the fewest side effects at the lowest dose Different headaches need different preventative drugs Different patients respond to different drugs and dosages Finding the right drug and the right drug dose takes time and persistence
34 Contraception, Menstrual migraine, Migraine in pregnancy and breast feeding I am not going to talk about the peri and post menopause and HRT
35 Oestrogen Fact or myth In adults migraine is 3 times more common in women than men Studies show that the size and speed of the fall in oestrogen levels prior to the start of the period is associated with the onset of migraine Prostaglandins have been shown to be able to trigger a migraine like headache Prostaglandins levels in the blood rise during a migraine attack released by the lining of the womb during a period Bille B Migraine in school children Acta Paediatr Scand 1962; 51 suppl 136: Somerville BW, Neurology 1972; 22: and 1972; 22: Fettes I. PostGrad Med 1997; 101: 67-77
36 Migraine and the Menstrual Cycle Menstrual Migraine without aura day 1 +/ - 2 days of each cycle At no other times in the cycle Affects 10% of women Menstrually Related Migraine without aura day 1 +/ - 2 days of each cycle AND at other times in the cycle Need diary cards to make the diagnosis Headache classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society The International Classification of Headache Disorders 2 nd edition Cephalalgia Suppl
37 Migraine and Premenstrual Syndrome Attacks occur in second half of cycle after ovulation Associated with other PMS symptoms Need diary cards to make diagnosis PMS symptoms must clear on Day 1 of period Women with PMS may experience severe headache symptoms but not actually fulfil IHS criteria for migraine. Headache classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society The International Classification of Headache Disorders 2 nd edition Cephalalgia Suppl
38 Migraine and Stroke Risk Migraine with aura is associated with an increased risk of ischaemic stroke There is NO evidence to show that there is an increased risk of stroke in migraine sufferers over the age of 45 years The annual incidence of stroke in Europe is 1 to 3 per 100,000 women under the age of 35 years 10 per 100,000 women over the age of 35 years The risk is VERY SMALL but important to consider other risk factors 1.Gudmundsson LA, Scher AI, Aspelund T et al Migraine with aura and risk of cardiovsacular and all cause mortality in men and women/bmj c The IHS Task Force. Cephalalgia, 2000; 20: MacGregor EA. Hormonal Contraception and migraine. Faculty of Family Planning Fact Sheet. Review no. 2001/01
39 Combined hormonal Contraceptives (CHC), migraine and stroke risk CHC s are a risk factor for ischaemic stroke Relative risk (RR) is 16 if you have migraine Smoking increases the risk of ischaemic stroke RR is 10 if you have migraine Risks are additive RR is 34.4 if you take CHC s and smoke and have migraine Vital to minimise all vascular risk factors if you have migraine with aura (Tzourio et al BMJ 310: and Chang et al BMJ 318: 13-18)
40 CHC s and current UK advice CHC s can be used if NO aura and NO additional risk factors CHC s can be used with caution if NO aura and one additional risk factor CHC s CANNOT be used if there is aura NO aura BUT more than one additional risk factor There are severe and prolonged attacks Ergotamine is being used (which it should not be) (WHO Improving Access to Quality Care in Family Planning. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Use. Second edition. WHO/RHR/00.02.) (MacGregor EA, Guillebaud J. Recommendations for clinical practice. Br J Fam Planning 1998; 24: 53-60) (Bousser M-G, Kittner SJ. Oral contraceptives and stroke. Cephalalgia 2000; 20: ) (EA MacGregor Migraine and use of combined hormonal contraceptives: a clinical review J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care 2007; 33 (3): )
41 Menstrual migraine acute treatment Attacks often harder to treat Attacks associated with a greater degree of disability Attacks associated with more aggressive symptoms and features Have to find most effective acute treatment means maximum dose of any acute drug means use drugs in combination Triptan, NSAID and anti-emetic EA MacGregor Managing Menstrual migraine: A clinical review J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care 2007; 33 (1): 36-47
42 Menstrual migraine diary Days of the month At least three consecutive months M M M M M H M M M M M H H H M M M M M M M M M M H H M M M M H H H H M = Menstruation H = Headache
43 Menstrual migraine using NSAID or triptan Using a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) Naproxen 500mg up to twice daily (bd) or mefenamic acid 500mg up to three times daily (tds) Using a triptan Frovatriptan 2.5mg bd, Zolmitriptan 2.5mg tds or Naratriptan 1mg bd Use an NSAID (naproxen) and Frovatriptan Start 2 to 3 days before the expected onset of the attack and use for 7 days Can extend NSAID into period if needed EA MacGregor Managing Menstrual migraine: A clinical review J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care 2007; 33 (1): 36-47
44 Menstrual migraine without aura Migraine in the pill free week Use an oestrogen dominant pill Marvelon or Dianette Tricycle the COCP take three packets consecutively BUT if get break through bleeding or not tolerated Revert to monthly cycle Use NSAID daily in pill free week Seasonale is a CHC available in the USA designed to give women one period in the spring, summer, autumn and winter. It contains 30mcg ethinyloestradiol and 150mcg levonorgestrel in each pill Lybrel is a CHC (now only available as a generic called Amethyst) in the USA which is taken continuously. It contains 20mcg ethinyloestradiol and 90mcg levonorgestrel in each pill Use top up topical oestrogen (as patch or gel) in pill free week Current evidence suggests you can take the COCP continuously and come to no harm EA MacGregor Managing Menstrual migraine: A clinical review J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care 2007; 33 (1): 36-47
45 Acute treatment safety profiles in pregnancy Amundsen, S. et. al. Nat. Reviews Neurol.11, (2015) Thanks to Dr Shazia Afridi for this slide
46 Triptan meta-analysis 2015 The challenges No randomised controlled trials Study identified publications that looked at pregnancy outcomes following pre natal exposure to triptans from 1991 to 2013 Identified six studies, 4,208 infants of women who had used sumatriptan or any other triptan Found NO increased rate of major congenital malformations prematurity BUT there was an increased risk of spontaneous abortion Marchencko A et al Headache; 55:
47 Triptan use in pregnancy Women who have used triptans in early pregnancy can be reassured that exposure has not been associated with adverse outcomes Triptan use during pregnancy is only recommended if no other treatment is effective it is always a balance of risk versus benefit informed decision making Sumatriptan safety data base shows 4.3% risk of first trimester birth defects 3 to 5% have been shown in the general population Rizatriptan safety data base similar results but fewer numbers MacGregor EA, Migraine in pregnancy and lactation: a clinical review. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care 2007:33 (2) 83 to 93
48 Decision making while breastfeeding Need to consider bioavailability amount found in breast milk limited data available summary of product characteristics recommend caution avoid breast feeding for 12 to 24 hours after dose Sumatriptan has the most extensive data base low level of excretion in breast milk 0.5% of oral dose Eletriptan one study, 80mg dose 0.02% of dose in breast milk MacGregor EA, Migraine in pregnancy and lactation: a clinical review. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care 2007:33 (2) 83 to 93
49 Acute migraine treatment while breastfeeding Paracetamol Drug of choice Aspirin Avoid, risk of Reyes Syndrome NSAID Very low concentration in breast milk Anti-emetics wide variety of agents recommend domperidone ( preferred to metoclopramide) Ergotamine Avoid as may inhibit lactation MacGregor EA, Migraine in pregnancy and lactation: a clinical review. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care 2007:33 (2) 83 to 93
50 Safety profile for preventative medication
51 Conclusion 1 Understand the patient journey Understand the patients psychosocial journey Understand the impact of the headache to the patient their friends and family work Adopt a holistic approach to care Involve the patient in the decision making Optimise acute treatment Offer flexibility Balance of benefits against side effects Minimise the number of headache days
52 Conclusion - 2 Optimise preventative medication The goal is to reduce the number of headache days with the fewest side effects at the lowest dose Different headaches need different preventative drugs Different patients respond to different drugs and dosages Finding the right drug and the right drug dose takes time and persistence start low build slow use for at least 3 months to assess response
53 Conclusion - 3 If hormones are relevant core principles apply Adopt a holistic approach to care Involve the patient in the decision making Risk needs to be discussed Optimise acute treatment Consider standard prophylaxis options Hormonal manipulation may not suit everybody risks need to be discussed and considered
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines
 How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
Treatments for migraine
 Treatments for migraine Information for patients and carers Department of Neurology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Contents Page About this leaflet Abortive medication for migraine Painkillers Antisickness medication
Treatments for migraine Information for patients and carers Department of Neurology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Contents Page About this leaflet Abortive medication for migraine Painkillers Antisickness medication
Management of headache
 Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Migraine. What are the symptoms of a migraine attack?
 Migraine Migraine causes attacks of headaches, often with feeling sick or vomiting. Treatment options include: avoiding possible 'triggers', painkillers, antiinflammatory painkillers, anti-sickness medicines,
Migraine Migraine causes attacks of headaches, often with feeling sick or vomiting. Treatment options include: avoiding possible 'triggers', painkillers, antiinflammatory painkillers, anti-sickness medicines,
SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine
 GUIDELINES SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine STEVE CHAPLIN In February 2018, the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) published a new guideline on the pharmacological management
GUIDELINES SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine STEVE CHAPLIN In February 2018, the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) published a new guideline on the pharmacological management
Migraine Management. Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital
 Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital
 Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital Honorarium from Current Pain and Headache Reports; Section Editor Unusual
Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital Honorarium from Current Pain and Headache Reports; Section Editor Unusual
Headache is the most common symptom in patients with Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH). Not everybody with IIH gets headache.
 Headaches in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Headache is the most common symptom in patients with Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (). Not everybody with gets headache. Headaches can be there
Headaches in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Headache is the most common symptom in patients with Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (). Not everybody with gets headache. Headaches can be there
Medication For Migraine Chart: Table 1: Acute Treatment when the attack begins
 Medication For Migraine Chart: Table 1: Acute Treatment when the attack begins Page a Analgesics (painkillers) Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Prescription required Brand Name Formulation
Medication For Migraine Chart: Table 1: Acute Treatment when the attack begins Page a Analgesics (painkillers) Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Prescription required Brand Name Formulation
Recognition and treatment of medication overuse headache
 Recognition and treatment of medication overuse headache Marcus Lewis MA, MRCGP, DRCOG, DFSRH 20 Mean weekly headache index 15 10 5 Medication overuse headache is a common condition responsible for a high
Recognition and treatment of medication overuse headache Marcus Lewis MA, MRCGP, DRCOG, DFSRH 20 Mean weekly headache index 15 10 5 Medication overuse headache is a common condition responsible for a high
Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE
 Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Vestibular Migraine. Information for patients and carers. Department of Neurology and Otolaryngology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary
 Vestibular Migraine Information for patients and carers Department of Neurology and Otolaryngology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary What is vestibular migraine? Migraine is a disabling headache disorder that affects
Vestibular Migraine Information for patients and carers Department of Neurology and Otolaryngology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary What is vestibular migraine? Migraine is a disabling headache disorder that affects
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT
 ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
Acute Migraine Treatment: What you and your family should know to help you make the best choices with your doctor
 Acute Migraine Treatment: What you and your family should know to help you make the best choices with your doctor TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR MIGRAINES! ABOUT THIS PATIENT GUIDE: Migraine attacks are often debilitating
Acute Migraine Treatment: What you and your family should know to help you make the best choices with your doctor TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR MIGRAINES! ABOUT THIS PATIENT GUIDE: Migraine attacks are often debilitating
COMBINATION THERAPIES PREVENTATIVE THERAPIES BETA BLOCKERS
 ACUTE THEAPIES TIPTANS TICYCLIC ANTIDEPESSANTS When starting acute treatment, healthcare professionals should warn patients about the risk of developing medication-overuse headache. ASPIIN Aspirin (900
ACUTE THEAPIES TIPTANS TICYCLIC ANTIDEPESSANTS When starting acute treatment, healthcare professionals should warn patients about the risk of developing medication-overuse headache. ASPIIN Aspirin (900
Management options for Migraine. Prof. Dr. Khwaja Nazimuddin Head Dept. of Internal Medicine BIRDEM
 Management options for Migraine Prof. Dr. Khwaja Nazimuddin Head Dept. of Internal Medicine BIRDEM Assessment The Migraine Disability Assessment Score MIDAS Complete loss of work Partial loss of work Off
Management options for Migraine Prof. Dr. Khwaja Nazimuddin Head Dept. of Internal Medicine BIRDEM Assessment The Migraine Disability Assessment Score MIDAS Complete loss of work Partial loss of work Off
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in
 HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
Migraine Management. Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital
 Migraine Management Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital Referral Criteria for Migraine Migraine Management Migraine Diagnosis Spot on Health Migraine pathway
Migraine Management Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital Referral Criteria for Migraine Migraine Management Migraine Diagnosis Spot on Health Migraine pathway
Goals. Primary Headache Syndromes. One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders
 Goals One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders Impact of primary headache syndromes Non pharmacologic Rx of migraine individualized to patient triggers Complementary and alternative Rx of migraine
Goals One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders Impact of primary headache syndromes Non pharmacologic Rx of migraine individualized to patient triggers Complementary and alternative Rx of migraine
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation.
 I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
Faculty Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Acute Treatment Strategies
 WWW.AMERICANHEADACHESOCIETY.ORG Acute Treatment Strategies Content developed by: Lawrence C. Newman, MD, FAHS Donna Gutterman, PharmD Faculty Disclosures LAWRENCE C. NEWMAN, MD, FAHS Dr. Newman has received
WWW.AMERICANHEADACHESOCIETY.ORG Acute Treatment Strategies Content developed by: Lawrence C. Newman, MD, FAHS Donna Gutterman, PharmD Faculty Disclosures LAWRENCE C. NEWMAN, MD, FAHS Dr. Newman has received
Dubai Standards of Care (Migraine)
 Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Migraine) Preface Migraine is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of migraine is done through various different strategies.
Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Migraine) Preface Migraine is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of migraine is done through various different strategies.
Strategies in Migraine Care
 Strategies in Migraine Care Julie L. Roth, MD Rhode Island Hospital Assistant Professor, Neurology The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University March 28, 2015 Financial Disclosures None. Objectives
Strategies in Migraine Care Julie L. Roth, MD Rhode Island Hospital Assistant Professor, Neurology The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University March 28, 2015 Financial Disclosures None. Objectives
MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND. Migraine & Women. Her life can be hers AGAIN
 MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND Migraine & Women Her life can be hers AGAIN What is Migraine? Migraine and Women Migraine is 3 times more common in women than in men, this is largely due to hormonal changes
MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND Migraine & Women Her life can be hers AGAIN What is Migraine? Migraine and Women Migraine is 3 times more common in women than in men, this is largely due to hormonal changes
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines
 Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Maternity. Migraine in pregnancy Information for women
 Maternity Migraine in pregnancy Information for women You have been given this leaflet as you have a diagnosis of migraines. It contains advice to help you manage your migraines safely during your pregnancy.
Maternity Migraine in pregnancy Information for women You have been given this leaflet as you have a diagnosis of migraines. It contains advice to help you manage your migraines safely during your pregnancy.
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา
 ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE
 MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care. December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary
 Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Current Migraine Treatment Therapy. Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN
 Current Migraine Treatment Therapy Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN Migraine a Disease Process Migraines are a chronic disease process similar to many other chronic medical conditions Migraine has a low mortality
Current Migraine Treatment Therapy Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN Migraine a Disease Process Migraines are a chronic disease process similar to many other chronic medical conditions Migraine has a low mortality
What You Should Know About Your HEADACHE. Learn more about headache types, triggers, and treatments, when to get help, and how to help yourself
 What You Should Know About Your HEADACHE Learn more about headache types, triggers, and treatments, when to get help, and how to help yourself Introduction The purpose of this brochure is to give you a
What You Should Know About Your HEADACHE Learn more about headache types, triggers, and treatments, when to get help, and how to help yourself Introduction The purpose of this brochure is to give you a
Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D.
 Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D. Objectives Present patient case Review epidemiology/pathophysiology
Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D. Objectives Present patient case Review epidemiology/pathophysiology
Disclosures. Triptans for Kids 5/16/13
 5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline. Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford
 Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford Overview The process of guideline development illustrated with the headache guideline Reflections on the process Key recommendations
Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford Overview The process of guideline development illustrated with the headache guideline Reflections on the process Key recommendations
Adult with headache. Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention
 Adult with headache Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention London Strategic Clinical Networks London Neuroscience Strategic Clinical Network
Adult with headache Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention London Strategic Clinical Networks London Neuroscience Strategic Clinical Network
MIGRAINE UPDATE. Objectives & Disclosures. Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment.
 MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
Migraine. A booklet for people with migraine and their carers. Consultation. Consultation. draft. draft. Scottish guidelines
 Migraine Scottish guidelines A booklet for people with migraine and their carers Cover image courtesy of Migraine Action (migraineart.org.uk) Patient quotes kindly supplied by The Migraine Trust Scottish
Migraine Scottish guidelines A booklet for people with migraine and their carers Cover image courtesy of Migraine Action (migraineart.org.uk) Patient quotes kindly supplied by The Migraine Trust Scottish
25/09/2018 HEADACHE. Dr Nick Pendleton
 HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2018 1 Small Group Work Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache
HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2018 1 Small Group Work Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache
Ana Podgorac Belgrade, May 2012
 Headache and reproductive life Ana Podgorac Belgrade, May 2012 52 years old woman, English teacher in primary school, married, mother of two, with a history of migraine without aura. Over the last 6 months
Headache and reproductive life Ana Podgorac Belgrade, May 2012 52 years old woman, English teacher in primary school, married, mother of two, with a history of migraine without aura. Over the last 6 months
Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert
 Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert Childhood headache: Is it really difficult to manage? It shouldn t be... But it can be...
Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert Childhood headache: Is it really difficult to manage? It shouldn t be... But it can be...
HEADACHE. Dr Nick Pendleton. September Headache
 HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2017 Headache Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache Raised ICP
HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2017 Headache Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache Raised ICP
MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND HELPLINE
 MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND HELPLINE 1850 200 378 1 WHAT IS MIGRAINE? Migraine is the most common neurological condition in the world, affecting about 12-15% of people. It is three times more common
MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND HELPLINE 1850 200 378 1 WHAT IS MIGRAINE? Migraine is the most common neurological condition in the world, affecting about 12-15% of people. It is three times more common
What is in this leaflet
 Package leaflet: Information for the user 2.5 mg film-coated tablets Naratriptan Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
Package leaflet: Information for the user 2.5 mg film-coated tablets Naratriptan Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
M0BCore Safety Profile. Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: ordispersible tablet SE/H/PSUR/0022/002 Date of FAR:
 M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Zolmitriptan Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: ordispersible tablet P-RMS: SE/H/PSUR/0022/002 Date of FAR: 15.03.2014 4.3 Contraindications Zolmitriptan is contraindicated
M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Zolmitriptan Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: ordispersible tablet P-RMS: SE/H/PSUR/0022/002 Date of FAR: 15.03.2014 4.3 Contraindications Zolmitriptan is contraindicated
Reducing the impact of migraine in the workplace
 Reducing the impact of migraine in the workplace Exeter NHS Headache Clinic, St Thomas Health Centre, Exeter. The objective of this leaflet is to: Confirm a likely diagnosis of migraine. Outline the causes
Reducing the impact of migraine in the workplace Exeter NHS Headache Clinic, St Thomas Health Centre, Exeter. The objective of this leaflet is to: Confirm a likely diagnosis of migraine. Outline the causes
HEADACHE. Summary of British Association on the Study of Headaches {click to visit}
 F:M=3:1 Affects 15% adults HEADACHE Summary of British Association on the Study of Headaches {click to visit} Primary: Migraine (with aura 1/3, without aura 2/3) Tension Cluster Other Secondary Neuralgia
F:M=3:1 Affects 15% adults HEADACHE Summary of British Association on the Study of Headaches {click to visit} Primary: Migraine (with aura 1/3, without aura 2/3) Tension Cluster Other Secondary Neuralgia
BOTULINUM TOXIN POLICY TO INCLUDE:
 BOTULINUM TOXIN POLICY TO INCLUDE: Blepharospasm in adults, Hemi facial spasm in adults, spasmodic torticollis (cervical dystonia), focal spasticity treatment of dynamic equinus foot deformity, focal spasticity
BOTULINUM TOXIN POLICY TO INCLUDE: Blepharospasm in adults, Hemi facial spasm in adults, spasmodic torticollis (cervical dystonia), focal spasticity treatment of dynamic equinus foot deformity, focal spasticity
Index. Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Truths about Headaches (2017) Most headaches were muscle-tension headaches
 Agenda Case presentation Migraine Morphology Primary and Premonitory Phase Secondary Headache Aura Headache Primer on Pain Medication Overuse Headache Case Presentation RT is a 25 year old woman with daily
Agenda Case presentation Migraine Morphology Primary and Premonitory Phase Secondary Headache Aura Headache Primer on Pain Medication Overuse Headache Case Presentation RT is a 25 year old woman with daily
How could I be having migraine when I don't have a headache?
 Migraine Your doctor thinks you may have migraine. Classic migraine attacks start with visual symptoms (often zig-zag colored lights or flashes of light expanding to one side over 10-30 minutes) followed
Migraine Your doctor thinks you may have migraine. Classic migraine attacks start with visual symptoms (often zig-zag colored lights or flashes of light expanding to one side over 10-30 minutes) followed
The 45-year-old woman with monthly headaches. Anne MacGregor Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry
 The 45-year-old woman with monthly headaches Anne MacGregor Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Learning Objectives Use of diary cards for establishing patterns of attacks Importance
The 45-year-old woman with monthly headaches Anne MacGregor Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Learning Objectives Use of diary cards for establishing patterns of attacks Importance
Reducing the Impact of Migraine in the Workplace
 HEADACHE UK An alliance working for people with headache A Programme on behalf of Reducing the Impact of Migraine in the Workplace Content Outline of programme Background 3 Aim of programme Information
HEADACHE UK An alliance working for people with headache A Programme on behalf of Reducing the Impact of Migraine in the Workplace Content Outline of programme Background 3 Aim of programme Information
2 What you need to know before you take Naramig
 Package Leaflet: Information for the User Naramig 2.5 mg film-coated tablets naratriptan hydrochloride tablets for migraine Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because
Package Leaflet: Information for the User Naramig 2.5 mg film-coated tablets naratriptan hydrochloride tablets for migraine Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because
Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Treatment Of Menstrual Migraine 11/10/2017. Research grants Aralez, Allergan
 Treatment Of Menstrual Migraine Christine Lay, MD Director, Centre for Headache Associate Professor University of Toronto Disclosures Research grants Aralez, Allergan Unrestricted educational grants Aralez,
Treatment Of Menstrual Migraine Christine Lay, MD Director, Centre for Headache Associate Professor University of Toronto Disclosures Research grants Aralez, Allergan Unrestricted educational grants Aralez,
Maxilief Effervescent Tablets
 Package Leaflet: Information for the user Maxilief Effervescent Tablets Paracetamol Codeine Phosphate Hemihydrate Caffeine 500mg 8mg 30mg Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this
Package Leaflet: Information for the user Maxilief Effervescent Tablets Paracetamol Codeine Phosphate Hemihydrate Caffeine 500mg 8mg 30mg Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this
Triptans Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Triptans Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS AND DOSAGE 1-13,14,23,24 Agents Amerge (naratriptan) 1, 2.5 tablets Axert (almotriptan) 6.25, 12.5 tablets migraine attacks with/without
Triptans Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS AND DOSAGE 1-13,14,23,24 Agents Amerge (naratriptan) 1, 2.5 tablets Axert (almotriptan) 6.25, 12.5 tablets migraine attacks with/without
Diagnosis Isabelle Farrugia B.Pharm.(Hons.),M.S.(UIC) Completion of Assessment Questions following this article
 Management of Migraine Isabelle Farrugia B.Pharm.(Hons.),M.S.(UIC) Completion of Assessment Questions following this article entitles members to one credit towards C.E. requirement. Migraine is a complex
Management of Migraine Isabelle Farrugia B.Pharm.(Hons.),M.S.(UIC) Completion of Assessment Questions following this article entitles members to one credit towards C.E. requirement. Migraine is a complex
A case of a patient with chronic headache. Focus on Migraine. None related to the presentation Grants to conduct clinical trials from: Speaker bureau:
 Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Triptan Quantity Limit
 *- Florida Healthy Kids Triptan Quantity Limit Override(s) Quantity Limit Approval Duration 1 year Oral Tablets Axert (almotriptan) tablets Relpax (eletriptan) tablets 6 tablets (6.25 mg) 12 tablets (12.5
*- Florida Healthy Kids Triptan Quantity Limit Override(s) Quantity Limit Approval Duration 1 year Oral Tablets Axert (almotriptan) tablets Relpax (eletriptan) tablets 6 tablets (6.25 mg) 12 tablets (12.5
Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes
 Presenter Disclosure Information 2:45 3:45pm Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes SPEAKER Gerald W. Smetana, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Gerald W.Smetana, MD,
Presenter Disclosure Information 2:45 3:45pm Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes SPEAKER Gerald W. Smetana, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Gerald W.Smetana, MD,
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
SIGN 155 Pharmacological management of migraine. A national clinical guideline February Evidence
 SIGN 155 Pharmacological management of migraine A national clinical guideline February 2018 Evidence KEY TO EVIDENCE STATEMENTS AND ECOMMENDATIONS LEVELS OF EVIDENCE High-quality meta-analyses, systematic
SIGN 155 Pharmacological management of migraine A national clinical guideline February 2018 Evidence KEY TO EVIDENCE STATEMENTS AND ECOMMENDATIONS LEVELS OF EVIDENCE High-quality meta-analyses, systematic
Faculty Disclosure. Karen L. Bremer, MD. Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest.
 Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
Manging Migraine in Children & Adults
 Manging Migraine in Children & Adults Heather Sim, Chief Executive heather.sim85@gmail.com RCN School Nurses Conference August 2017 1 What are migraines and what triggers them? How do migraines affect
Manging Migraine in Children & Adults Heather Sim, Chief Executive heather.sim85@gmail.com RCN School Nurses Conference August 2017 1 What are migraines and what triggers them? How do migraines affect
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache
 MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
Understanding. Migraine. Amy, diagnosed in 1989, with her family.
 Understanding Migraine Amy, diagnosed in 1989, with her family. What Is a Migraine? A migraine is a recurring moderate to severe headache. The pain usually occurs on one side of the head. It is typically
Understanding Migraine Amy, diagnosed in 1989, with her family. What Is a Migraine? A migraine is a recurring moderate to severe headache. The pain usually occurs on one side of the head. It is typically
HEADACHE: Types, Tips & Treatment Suggestions
 Headaches are one of the most common complaints patients present with in primary care settings. They are often correlated with stress, tension and a litany of existing medical conditions. Often, patients
Headaches are one of the most common complaints patients present with in primary care settings. They are often correlated with stress, tension and a litany of existing medical conditions. Often, patients
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy
 HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
Migraine much more than just a headache
 Migraine much more than just a headache Session hosted by Teva UK Limited PUU4 11:15 12:15 UK/NHSS/18/0021b Date of Preparation: August 2018 The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker
Migraine much more than just a headache Session hosted by Teva UK Limited PUU4 11:15 12:15 UK/NHSS/18/0021b Date of Preparation: August 2018 The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker
Headache. Section 1. Migraine headache. Clinical presentation
 Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS. Let s Manage Pain
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Let s Manage Pain 1 About this booklet Persistent pain, also called chronic pain, is pain which continues for longer than expected. Pain can affect all areas of your life. People
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Let s Manage Pain 1 About this booklet Persistent pain, also called chronic pain, is pain which continues for longer than expected. Pain can affect all areas of your life. People
100% Effective Natural Hormone Treatment Menopause, Andropause And Other Hormone Imbalances Impair Healthy Healing In People Over The Age Of 30!
 This Free E Book is brought to you by Natural Aging.com. 100% Effective Natural Hormone Treatment Menopause, Andropause And Other Hormone Imbalances Impair Healthy Healing In People Over The Age Of 30!
This Free E Book is brought to you by Natural Aging.com. 100% Effective Natural Hormone Treatment Menopause, Andropause And Other Hormone Imbalances Impair Healthy Healing In People Over The Age Of 30!
Web: Medication overuse headache and undergoing a detox programme
 Web: www.migraine.org.uk Medication overuse headache and undergoing a detox programme Web: www.migraine.org.uk/moh What is medication overuse headache? Medication taken to help relieve migraine attacks
Web: www.migraine.org.uk Medication overuse headache and undergoing a detox programme Web: www.migraine.org.uk/moh What is medication overuse headache? Medication taken to help relieve migraine attacks
Preventive treatment of migraine. Rebecca Burch, MD Brigham and Women s Faulkner Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
 Preventive treatment of migraine Rebecca Burch, MD Brigham and Women s Faulkner Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA No disclosures Disclosures Many preventive treatments for migraine are not FDA-approved
Preventive treatment of migraine Rebecca Burch, MD Brigham and Women s Faulkner Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA No disclosures Disclosures Many preventive treatments for migraine are not FDA-approved
Premenstrual Syndrome
 page 1 Premenstrual Syndrome Q: What is premenstrual syndrome (PMS)? A: Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is a group of symptoms linked to the menstrual cycle. PMS symptoms occur in the week or two weeks before
page 1 Premenstrual Syndrome Q: What is premenstrual syndrome (PMS)? A: Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is a group of symptoms linked to the menstrual cycle. PMS symptoms occur in the week or two weeks before
Preparing for your Appointment: HEADACHE. How bad is your typical headache pain on the 0-10 pain scale with 10 being the worst pain?
 Preparing for your Appointment: HEADACHE Write down your symptoms: When did the headaches begin? Where are your headaches located? How bad is your typical headache pain on the 0-10 pain scale with 10 being
Preparing for your Appointment: HEADACHE Write down your symptoms: When did the headaches begin? Where are your headaches located? How bad is your typical headache pain on the 0-10 pain scale with 10 being
Short Clinical Guidelines: Headache, Key Points for Diagnosis and Treatment
 Clinical Highlights 1. Headache is diagnosed by history and physical examination with limited need for imaging or laboratory tests. 2. Warning signs of possible disorder other than primary headache are:
Clinical Highlights 1. Headache is diagnosed by history and physical examination with limited need for imaging or laboratory tests. 2. Warning signs of possible disorder other than primary headache are:
Progesterone. What is progesterone? Important information. Before taking this medicine
 Progesterone Generic Name: progesterone (proe JESS te rone) Brand Names: First Progesterone MC10, Menopause Formula Progesterone, Prometrium What is progesterone? Progesterone is a female hormone important
Progesterone Generic Name: progesterone (proe JESS te rone) Brand Names: First Progesterone MC10, Menopause Formula Progesterone, Prometrium What is progesterone? Progesterone is a female hormone important
Outpatient Headache Care Guideline
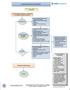 1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
Information for you. Managing premenstrual syndrome (PMS) What is PMS?
 Managing premenstrual syndrome (PMS) Information for you Published in August 2009 What is PMS? Premenstrual syndrome or PMS is the name given to a collection of physical and emotional symptoms that can
Managing premenstrual syndrome (PMS) Information for you Published in August 2009 What is PMS? Premenstrual syndrome or PMS is the name given to a collection of physical and emotional symptoms that can
OH, MY ACHING HEAD! I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING SECONDARY HEADACHES
 1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder
 ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
Welcome to the program!
 Calgary Headache Assessment & Management Program (CHAMP) EDUCATION SESSION Welcome to the program! What is the Purpose of this To provide you with: Session? accurate and current headache information the
Calgary Headache Assessment & Management Program (CHAMP) EDUCATION SESSION Welcome to the program! What is the Purpose of this To provide you with: Session? accurate and current headache information the
Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache
 doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01488.x Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache L Pageler 1,2, Z Katsarava 2, HC Diener 2 & V Limmroth 1,2 1 Department of Neurology,
doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01488.x Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache L Pageler 1,2, Z Katsarava 2, HC Diener 2 & V Limmroth 1,2 1 Department of Neurology,
Package leaflet: Information for the user. Sumatriptan Amneal 100 mg tablets. sumatriptan
 Package leaflet: Information for the user Sumatriptan Amneal 50 mg tablets Sumatriptan Amneal 100 mg tablets sumatriptan Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because
Package leaflet: Information for the user Sumatriptan Amneal 50 mg tablets Sumatriptan Amneal 100 mg tablets sumatriptan Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET IMIGRAN MIGRANE RELIEF 50mg film coated tablets Sumatriptan Patient information leaflet In this leaflet: 1. what these tablets do 2. check before you take 3. how to take the
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET IMIGRAN MIGRANE RELIEF 50mg film coated tablets Sumatriptan Patient information leaflet In this leaflet: 1. what these tablets do 2. check before you take 3. how to take the
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 CGRP Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
CGRP Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
What is new in the migraine world! Modar Khalil Consultant neurologist Hull Royal Infirmary
 What is new in the migraine world! Modar Khalil Consultant neurologist Hull Royal Infirmary Overview Understanding the burden Commonly used terms Acute therapy What we currently have What we are going
What is new in the migraine world! Modar Khalil Consultant neurologist Hull Royal Infirmary Overview Understanding the burden Commonly used terms Acute therapy What we currently have What we are going
Headaches in Children and Adolescents. Paul Shillito
 Headaches in Children and Adolescents Paul Shillito Topics For Discussion What s different about childhood migraine Chronic daily headache (CDH) Tumours and other things to worry about Management of childhood
Headaches in Children and Adolescents Paul Shillito Topics For Discussion What s different about childhood migraine Chronic daily headache (CDH) Tumours and other things to worry about Management of childhood
READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION ORILISSA. elagolix (as elagolix sodium) tablets
 READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION ORILISSA elagolix (as elagolix sodium) tablets Read this carefully before you start taking ORILISSA and each time you
READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION ORILISSA elagolix (as elagolix sodium) tablets Read this carefully before you start taking ORILISSA and each time you
10/17/2017 CHRONIC MIGRAINES BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES PATIENT CASE EPIDEMIOLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY
 BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES JENNIFER SHIN, PHARMD PGY2 AMBULATORY CARE PHARMACY RESIDENT COMMUNITYCARE HEALTH CENTERS PHARMACOTHERAPY ROUNDS OCTOBER 20, 2017
BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES JENNIFER SHIN, PHARMD PGY2 AMBULATORY CARE PHARMACY RESIDENT COMMUNITYCARE HEALTH CENTERS PHARMACOTHERAPY ROUNDS OCTOBER 20, 2017
Coldrex MaxGrip Lemon Powder for oral solution
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Coldrex MaxGrip Lemon Powder for oral solution PARACETAMOL, PHENYLEPHRINE, ASCORBIC ACID This leaflet is a copy of the Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Coldrex MaxGrip Lemon Powder for oral solution PARACETAMOL, PHENYLEPHRINE, ASCORBIC ACID This leaflet is a copy of the Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient
THE WOMAN WHO COULD NOT DECIDE WHICH MEDICATION TO TAKE
 Rapoport Ch 05.qxd 10/15/08 1:06 PM Page 25 CHAPTER 5 THE WOMAN WHO COULD NOT DECIDE WHICH MEDICATION TO TAKE ALLAN PURDY, MD, FRCPC FRED SHEFTELL, MD ALAN RAPOPORT, MD STEWART J. TEPPER, MD Case History
Rapoport Ch 05.qxd 10/15/08 1:06 PM Page 25 CHAPTER 5 THE WOMAN WHO COULD NOT DECIDE WHICH MEDICATION TO TAKE ALLAN PURDY, MD, FRCPC FRED SHEFTELL, MD ALAN RAPOPORT, MD STEWART J. TEPPER, MD Case History
Adult & Pediatric Patients. Stanford Health Care, Division Pain Medicine
 Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients Theresa Mallick Searle, MS, RN BC, ANP BC Disclosures Speakers Bureau: Allergan, Depomed Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients
Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients Theresa Mallick Searle, MS, RN BC, ANP BC Disclosures Speakers Bureau: Allergan, Depomed Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients
Painless, progressive weakness Could this be Motor Neurone Disease?
 APPENDIX 1 Painless, progressive weakness Could this be Motor Neurone Disease? 1. Does the patient have one or more of these? Bulbar features Limb features Respiratory features Cognitive features (rare)
APPENDIX 1 Painless, progressive weakness Could this be Motor Neurone Disease? 1. Does the patient have one or more of these? Bulbar features Limb features Respiratory features Cognitive features (rare)
SUMAVEL DOSEPRO (sumatriptan succinate) solution for injection
 SUMAVEL DOSEPRO (sumatriptan succinate) solution for injection Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit
SUMAVEL DOSEPRO (sumatriptan succinate) solution for injection Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit
July 2012 Target Population. Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings.
 Guideline for Primary Care Management of Headache in Adults July 2012 Target Population Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings. Exclusions: This guideline does not provide recommendations
Guideline for Primary Care Management of Headache in Adults July 2012 Target Population Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings. Exclusions: This guideline does not provide recommendations
Do you suffer from Headaches? - November/Dec 2011
 Do you suffer from Headaches? - November/Dec 2011 Inside this month's issue Headaches Acute single headaches Recurring Headaches: Migraine What causes Migraine? Treatments for migraine & prevention Headaches
Do you suffer from Headaches? - November/Dec 2011 Inside this month's issue Headaches Acute single headaches Recurring Headaches: Migraine What causes Migraine? Treatments for migraine & prevention Headaches
Improving Headache Care
 Greater Manchester Neuroscience Centre Improving Headache Care (without breaking the bank) Implementation of useful referral guidelines Scale of the problem Over 10% population suffer from headache 2%
Greater Manchester Neuroscience Centre Improving Headache Care (without breaking the bank) Implementation of useful referral guidelines Scale of the problem Over 10% population suffer from headache 2%
10/31/2017 PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE DISCLOSURES WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Primary Care 67%
 PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Regional Headache Specialist Kaiser LAMC 1 WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Column1 Primary Care 67% Primary Care Headache Specialty Other
PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Regional Headache Specialist Kaiser LAMC 1 WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Column1 Primary Care 67% Primary Care Headache Specialty Other
