2 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Carmella McCarthy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 2.01 THIAZIDE, OSMOTIC & LOOP DIURETICS - THIAZIDES [TD], POTASSIUM SPARING [PSD], LOOP DIURETICS [LD] Frusemide Inj 10mg/ml, 2ml (Lasix) [Furosemide] [LD] Frusemide Tab 40mg (Lasix) [Furosemide] [LD] Hydrochlorothiazide Tab 25mg (Esidrex) [TD] Mannitol Inj 10% (10g/100ml) & 25% (25g/100ml) 500ml Acute pulmonary oedema: slow IV initially 20-50mg, if needed increase by 20mg steps every 2 hours; child mg/kg/DAY, max 20mg daily. IV inj: if single effective dose is < 50mg inject undiluted slowly over 1-2 min at max rate 0.5mg/kg/min; if > 50mg dilute 20mg in ml of WFI/NS, infuse min at max rate of 4mg/min. Oedema initially 40mg in the morning; maintenance 20mg daily, resistant oedema up to 80mg daily; child 1-3mg/kg/DAY (max 40mg/day). Oedema 25-50mg daily in the morning; max 100mg daily, elderly initially 12.5mg daily. Hypertension mg daily in the morning; elderly initially 12.5mg daily. IV infusion g/kg of a 5-25% (5-25g/100ml) solution adjusted to response. Test dose: IV 200mg/kg of a 15-25% solution over 3-5 min to give a urine flow of 1ml/kg/HOUR at least, over the next 2-3 hours. 8
2 *Spironolactone Tab 25mg (Aldactone) [PSD] Oedema, mg daily, increased if needed to 400mg daily in resistant oedema; usual maintenance dose mg daily; child initially 3mg/kg/DAY in divided doses. Thiazides [TD] have a fast onset (1-2 hrs) and prolonged action duration (12-24 hrs). Administer in the morning. May cause postural hypotension especially in the elderly. High doses of thiazides [TD] and loop diuretics [LD] can cause hypokalaemia. IV frusemide in large bolus doses may cause ototoxicity, so doses > 50mg should be diluted in 100ml of NS and given at a rate not exceeding 4mg/min. Potassium-sparing diuretics [PSD] such as spironolactone should be used cautiously in patients on ACE inhibitors as they may cause severe hyperkalaemia. Do not give concurrently with potassium supplements ANTIANGINAL DRUGS, NITRATES Atenolol Tab 50mg (Tenormin) Isosorbide Dinitrate Tab 20mg SR (Isordil) Nitroglycerin Sublingual Spray 0.4mg/dose, 200 doses (Glytrin) [Nitroglycerin=Glyceryl trinitrate (GTN)] Nitroglycerin Inj 1mg/ml [Nitroglycerin=Glyceryl trinitrate (GTN)] Angina: mg in 1 or 2 divided dose. Prophylaxis of angina: 20-40mg every 12 hours; left ventricular failure mg daily in divided doses. When needed: spray 1-2 doses under tongue and then close mouth. MI or severe ischaemia, by IV infusion, give 5-200ug/min titrated to patient response, diluted in D5/NS, max conc 400ug/ml. 9
3 2.03 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS 2.03a CENTRALLY-ACTING & VASODILATOR ANTIHYPERTENSIVES *Nitroprusside, Sodium Inj 50mg/5ml [Vasodilator] (Protect from light.) Hypertensive crisis; IV infusion dilute 50mg in mls of D5 to give conc of ug/ml, and infuse at an initial rate of 0.3ug/kg/min, titrate slowly according to response; max 10ug/kg/min. Note: use IV pump and monitor BP closely. Nitroprusside: Avoid using for > 72 hrs as accumulation of cyanide metabolites occurs (cause tachycardia, sweating, hyperventilation, arrhythmias). Tail infusion off slowly over min to avoid rebound effect. Stop if no marked response with max dose in 10 min. Protect the solution completely from light in storage and when in use. Most serious peripheral vascular disorders may be due to occlusion of vessels, either by spasm/sclerotic plaque. Advise patients on lifestyle changes including smoking cessation and exercise training, and consider low-dose aspirin to prevent cardiovascular events. 2.03b BETA-BLOCKERS ANGINA, HYPERTENSION, CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Atenolol Tab 50mg (Tenormin) *Labetalol HCl Inj 100mg/20ml (Trandate) Hypertension & angina, mg daily. IV Inj 50mg, repeat after 5 min prn; IV infusion at a max rate of 2mg/min, titrate to response; max 200mg both routes. Inject slow IV undiluted over 1-2 min, for IV infusion further dilute 100mg with mls of D5/NS and infuse over 50-60min. 10
4 Metoprolol Tab 100mg (Betaloc/Lopressor) Propranolol HCl Inj 1mg/ml (Inderal/Avlocardyl) Propranolol Tab 40mg (Inderal/Avlocardyl) mg twice daily, max 300mg daily. Arrhythmias & thyrotoxic crisis: IV Inj 1mg (undiluted over 1 min); repeat every 2-4 minutes according to response; max 5mg. Hypertension, 80mg twice daily, max 320mg daily (half dose for portal hypertension). Angina, 40mg 2-3 times daily to 240mg/day. Arrhythmia & thyrotoxic crisis, 10-40mg 3-4 times daily. Child: 1-5mg/kg/DAY in divided doses every 6-12 hours. Max: 8mg/kg/DAY. Beta-blockers: NOT if asthma or history of obstructive airways disease. Labetolol: Severe hepatocellular damage reported, monitor liver function. Beta-blockers may mask signs/symptoms of hypoglycaemia and affect glucose tolerance. Avoid in patients with frequent hypoglycaemic episodes or in those with poor blood glucose control. Risk of precipitating heart failure when beta-blockers used in conjunction with verapamil. 2.03c CALCIUM CHANNEL ANTAGONISTS Diltiazem HCl Cap 90mg SR, 120mg SR & 180mg SR (Tildiem Retard) NF Angina and mild to moderate hypertension: initially mg twice daily, max 360mg daily in divided doses. Non-modified release/non-sr formulations: initially 30mg 3 times daily (elderly patient 30mg twice daily); max 360mg daily in divided doses. 11
5 Nifedipine Tab 20mg SR (Adalat) Verapamil HCl Inj 5mg/2ml (Isoptin) Verapamil HCl Tab 40mg or 80mg (Isoptin) Verapamil HCl Tab 240mg SR (Securon SR) Initially 20mg-100mg daily with food in 1-2 divided doses, according to manufacturer s directions (different for each SR formulation) Arrhythmias: slow IV 5-10mg (over 2-4 min) of max conc 2.5mg/ml in NS/D5 with ECG monitoring; paroxysmal tachyarrhythmias: further 5mg after 5-10 min if needed. DO NOT administer to patients recently given beta-blockers (hypotension/asystole risk). Arrhythmias: mg 3 times a day. Hypertension: mg daily in 2-3 divided doses. Angina or hypertension: 240mg daily, max 240mg twice daily. Prophylaxis after MI where betablockers are inappropriate: 240mg the morning & 120mg in the evening. Calcium Channel Antagonists can cause dizziness, headache, peripheral oedema (worse than with verapamil and diltiazem). Most common: flushing, rash, and gingival hyperplasia. Constipation is more common with verapamil. Disturbances of cardiac conduction and disruption of left ventricular failure are more likely with either verapamil or diltiazem. Avoid abrupt withdrawal, may induce hypertensive crisis/rebound. Contraindication (C/I): concurrent intravenous beta-blocker therapy, CHF, hypersensitivity, hypotension. 12
6 2.03d ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS Enalapril Maleate Tab 5mg (Renitec) Initially 2.5-5mg in the morning (1 st dose at night), usual maintenance 10-20mg in the morning, max 40mg daily. ACE Inhibitors (ACE/I) can cause very rapid falls of BP in volumedepleted patients, so discontinue diuretics or reduce dose 2-3 days before ACE/I initiation. Give first ACE/I dose at bedtime. Resume diuretics if needed after a few weeks. If diuretics cannot be stopped, supervise medically for 2 hrs after first ACE/I dose, or until stable BP. Monitor renal function (baseline creatinine) and assess within 1 week of initiating therapy. If >10% increase in creatinine levels review therapy. Reassess regularly (3-4 times/yr). Drug interaction caution if used with calcium channel antagonists, see product leaflets OTHER DRUGS FOR ARRHYTHMIAS *Amiodarone Inj 50mg/ml (Cordarone) Advanced cardiac life support (ACLS): 300mg IV by rapid infusion; if necessary, supplementary doses of 150mg IV by rapid infusion may be considered; max 1.2g/DAY. Max IV rate 30 mg/min, usually at 1-6mg/ml; conc > 2 mg/ml via central line. Dilute 300mg in 300ml of D5 to give 1mg/ml conc. 13
7 Lidocaine HCl Inj 1% 10mg/ml 20ml or 50ml vials, 10ml Minijet; 2% 20mg/ml 20ml or 50ml vials, 10ml Minijet; & 20% 200mg/ml (Xylocard/Xylocaine) [Lidocaine = Lignocaine] Magnesium Sulphate Inj 50% 5g/10ml [Mg = 500mg/10ml = 20mmoles/10ml] Arrhythmia: Adult IV bolus load mg over 2-3min, repeated after 5 min if needed up to 300mg in first hour; followed by IV infusion at 1-4mg/min, dose 20-50ug/kg with ECG monitoring, max 4.5mg/kg or 300mg in any one-hour period. Child, 1mg/kg/DOSE IV bolus every 5-10 minutes to max 5mg/kg, maintenance 10-50ug/kg/min. Ventricular arrhythmias: may be given IM 300mg into the deltoid or quadriceps muscle. Give IM as a 10% solution (dilute 1.5ml of 20% solution in 1.5ml WFI). Inject IV undiluted over 2-3 min. For IV infusion, dilute 1g (5ml of 20% solution or 50ml of 2% solution) with D5/NS to make up to ml to give 1-2mg/ml ( %). Ventricular tachycardia + low magnesium: IV bolus 1-2g (4-8mmol Mg or 2-4ml) slowly over 1-2min, repeat prn, or IV infusion 2.5g (10mmol or 5ml) in 100ml D5/NS, over 1 hr. Hypomagnesaemia, emergency: 1-2g (4-8mmol Mg or 2-4ml) in 100ml D5 infused over 1-2 min. Severe deficiency: IV infusion 5g (20mmol Mg or 10ml) diluted in 1000ml D5/NS given over 3 hrs. Mild deficiency: adult IM undiluted 1g (5mmol Mg or 2ml) q6h for four doses per 24hrs. An IV calcium solution (e.g.10% calcium gluconate) should be readily available when magnesium sulphate injection is administered. 14
8 Procainamide Inj 100mg/ml (Pronestyl) Antiarrhythmia: adult, IV initial 100mg diluted, given at max rate 50mg/min, repeat every 5 min until arrhythmia is controlled or up to max total dose of 1g; maintenance infusion diluted and given at rate 2-6mg/min. Alternatively, adult IM 50mg/kg/DAY in divided doses given every 3-6 hours. Child, IV slow 10-15mg/kg over 15min then 20-80ug/kg/min OR mg/kg/DAY in divided doses given q4h, max 2g/24h. Inject IM undiluted deep into a muscle mass. For IV injection further dilute 100mg with 25-50ml of D5, inject slowly over 2-5 min. For IV infusion, dilute 200mg with mls of D5, give over min. All anti-arrhythmics are potentially pro-arrhythmic. If using more than one antiarrhythmic care is needed as fatal interactions can occur. Avoid rapid changes and combinations. Amiodarone is intended for use only in patients with life-threatening arrhythmias because of substantial toxicity CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES, INOTROPIC & VASOCONSTRICTOR SYMPATHOMIMETICS *Digoxin Tab 250ug (Lanoxin) Rapid digitalisation, mg in divided doses over 24 hrs; less urgent digitalisation/ maintenance ug daily; elderly half dose. 15
9 *Digoxin Inj 500ug/2ml (Lanoxin) Dopamine HCl Inj 200mg/5ml Ephedrine HCl Inj 30mg/ml Epinephrine Inj 1mg/ml [Adrenaline 1:1000] Epinephrine Inj 100ug/ml (0.1mg/ml), pre-filled syringe 10mls (1mg/10mls) [Adrenaline 1:10 000] Loading dose for IV urgent cases (check patient has not received cardiac glycosides within 2 weeks before): 0.5-1mg in divided doses q4-8h, then ug daily orally. May be injected slow IV undiluted, or infused by further diluting 500ug with 500ml of D5/NS/WFI over 10-20min. Cardiogenic shock: slow IV infusion via large vein 2-5ug/kg/min, increase in 5-10ug/kg/min increments adjusted according to response, max 50ug/kg/min. Dilute 200mg with mls of D5/NS/LR, max conc 6mg/ml, range mg/ml. Hypotension prevention in epidural/ spinal anaesthesia: slow IV Inj 3-6mg (max 9mg) repeated every 3-4 minutes, max cumulative dose 30mg Slow IV inj: further dilute 30mg with 10-20ml WFI, max conc 3mg/ml. Anaphylaxis: undiluted SC/IM, adult 500ug (0.5ml), 6-12 yo 250ug (0.25ml), 6 mth-6 yo 120ug (0.12ml), < 6 mth 50ug (0.05ml). Cardiac Arrest: slow IV bolus inj 1mg (undiluted) q3-5min, max 100ug/kg every 3-5 minutes; IM/SC ug (undiluted 1-5mls) every minutes; or IV cont infusion in NS (max concentration 64ug/ml), at a rate of 1-10ug/kg/min. IV infusion: dilute 1mg with mls of NS. 16
10 Phenylephrine Inj 1% (10mg/ml) (Neosynephrine) Acute mild-moderate hypotension: SC/IM undiluted 2-5mg, repeat dose at min intervals, max total dose 10mg; slow IV mg ( ug), repeat dose at min intervals, injected slow IV diluted in D5/NS as 1mg/ml solution, over 3 minutes. Digoxin: hypokalaemia predisposes to digoxin toxicity. Use with caution in pregnancy, elderly and renal impairment, avoid rapid IV administration. Excessive dosage may cause nausea & vomiting, GI & visual disturbances, CNS & heart symptoms ANTICOAGULANTS & HAEMOSTATICS *Acetylsalicylic Acid (Aspirin) Tab Soluble 100mg Heparin Sodium Inj 5,000 units/ml, 5ml [NOT FOR IM INJECTION] [NB: These doses do not apply to LMWH.] mg daily dissolved in a glass of water DVT/PE treatment: adult, IV loading dose 5000 units, then cont infuse unit/hr (15-25unit/kg/hr) or units IV Inj q4h or units SC q12h [Determine dose for maintenance by APTT time of times of normal.] DVT/PE prophylaxis, SC 5000 units q8-12h post-surgery until patient is ambulant; in pregnancy, units given every 12 hours. The IV dose may be administered undiluted or diluted with ml NS over 24 hours. 17
11 Heparin Sodium Inj 1,000 units/ml in 5ml [NOT FOR IM INJECTION] Heparin Sodium 100units/ml units in NaCl Injection (Heparin Saline) Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Nadroparin 7500AxaICU/0.3ml, AxaICU/0.4ml, & 15,000 AxaICU/0.6ml (Fraxiparine) SMALL ADULT/CHILD, IV infusion loading dose 50 units/kg, then units/kg/hour, or SC 250units/kg q12h. Give IV undiluted or diluted with ml NS over 24 hours. NF units administer as a flush through catheters or IV cannula, q4h or prn. NF SC Inj. Surgical prophylaxis, for 10 days: General 0.3ml daily, 1 st Inj 2-4 hrs pre-surgery; orthopaedic 100 AxaICU/kg/DAY for 3 days, given 12 hrs pre- & post-surgery, then 150AxaICU/kg/DAY from 4 th post-op day onwards. Treatment 0.1ml/10kg q12h. Phytomenadione (Vitamin K 1 ) Inj 10mg/ml [ADULT USE ONLY] Protamine Sulphate Inj 10mg/ml, 5ml Streptokinase Inj units vial Hypoprothrombinaemia or haemorrhage due to anticoagulant therapy: IM 10-20mg. Slow IV inj ONLY for potentially fatal haemorrhage from warfarin overdose, mg, max 50mg (not > 1mg/min). CHECK: Some commercial preps unsuitable for IV use. Slow IV Inj (undiluted or dilute in D5/NS) over 10 min, 1mg neutralises units heparin when given within 15 min; if longer, less protamine needed (heparin excretion rapid), max 50mg total dose. MI: infuse IV units over 60 min. Reconstitute vial with 5mls of D5/NS and further dilute in 45mls of D5/NS. Use reconstituted solution within 8 hours. 18
12 Tranexamic Acid Inj 100mg/ml, 5ml (Transamin/Exacyl) Warfarin Sodium Tab 2mg, 3mg & 5mg Haemorrhage from excessive fibrinolysis: Slow IV undiluted 1g q8h or 10-15mg/kg q8h, max rate 100mg (1ml) per minute. Loading dose: 10mg on day 1, 5mg on days 2 and 3. Subsequent dosages determined by INR values. For rapid effect consider heparin IV/SC for first 2-3 days. NOTE: See current guidelines for warfarin dosing details. Aspirin C/I: active peptic ulceration, haemophilia/bleeding disorders. Treatment using full dose unfractionated heparin should be controlled by monitoring of coagulation parameters. Monitor platelet counts if patient on for more than 5 days. Heparin may cause haemorrhage; effects are reversible by protamine sulphate ANTIHYPERLIPIDAEMIC AGENTS Simvastatin Tab 20mg (Zocor) NF 10mg at night, adjusted at intervals of not less than 4 weeks; max 80mg/day. Rhabdomyolysis associated with lipid-regulating drugs may be increased in patients with renal impairment, hypothyroidism, and patients on concomitant ciclosporin treatment. Concomitant treatment with a fibrate and a statin may also increase risk of serious muscle toxicity. Advice patients to report promptly unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, and weakness. 19
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system
 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
5 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
 5 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 5.01 NON-STEROIDAL ANTIILAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDS) *Acetylsalicylic Acid (Aspirin) Tab Soluble 300mg Diclofenac Sodium Tab 25mg, Supp 25mg, 50mg & 100mg (Voltaren) 300-900mg every
5 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 5.01 NON-STEROIDAL ANTIILAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDS) *Acetylsalicylic Acid (Aspirin) Tab Soluble 300mg Diclofenac Sodium Tab 25mg, Supp 25mg, 50mg & 100mg (Voltaren) 300-900mg every
Adenosine. poison/drug induced. flushing, chest pain, transient asystole. Precautions: tachycardia. fibrillation, atrial flutter. Indications: or VT
 Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
5mg/5mL Liquid 25mg Tablets 50mg Tablets 100mg Tablets 50mg/5mL Suspension Special standardise strength 25mg Tablets
 Chapter 2- Cardiovascular Category Drug name Strength / dose / form BCU 2.1 Positive Inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac Digoxin 62.5 microgram Tablets Glycosides 125 microgram Tablets 250 microgram Tablets
Chapter 2- Cardiovascular Category Drug name Strength / dose / form BCU 2.1 Positive Inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac Digoxin 62.5 microgram Tablets Glycosides 125 microgram Tablets 250 microgram Tablets
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
13.01 INHALATIONAL & IV ANAESTHETICS
 13 ANAESTHETICS 13.01 INHALATIONAL & IV ANAESTHETICS Halothane (Fluothane) 250ml Isoflurane (Forane) 250ml *Ketamine (as HCl) Inj 50mg/ml, 10ml (Ketalar) *Nitrous Oxide Inhalation Gas [Cylinder neck: colour
13 ANAESTHETICS 13.01 INHALATIONAL & IV ANAESTHETICS Halothane (Fluothane) 250ml Isoflurane (Forane) 250ml *Ketamine (as HCl) Inj 50mg/ml, 10ml (Ketalar) *Nitrous Oxide Inhalation Gas [Cylinder neck: colour
6 th Floor and 7 East Nurses Guide Intravenous Drip List Approved for RN Administration University of Kentucky Chandler Medical Center
 RATE Abciximab (Reopro) Alteplase (tpa, Activase) All units 6S and 6W ONLY Platelet aggregation inhibitor Thrombolytic agent Bolus: 0.25 mg/kg IV over 5 min Infusion: 0.125 0.9 mg/kg (max 90 mg); 10% of
RATE Abciximab (Reopro) Alteplase (tpa, Activase) All units 6S and 6W ONLY Platelet aggregation inhibitor Thrombolytic agent Bolus: 0.25 mg/kg IV over 5 min Infusion: 0.125 0.9 mg/kg (max 90 mg); 10% of
Chapter / Section / Drug
 2 Cardiovascular System 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs Digoxin Digoxin specific antibody ( DigiFab ) 2.2 Diuretics 2.2.1 Thiazides and related diuretics Indapamide (1 st Line) Bendroflumethiazide Metolazone
2 Cardiovascular System 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs Digoxin Digoxin specific antibody ( DigiFab ) 2.2 Diuretics 2.2.1 Thiazides and related diuretics Indapamide (1 st Line) Bendroflumethiazide Metolazone
Dose. Route. Units. Given. Special situations. Dose. Route. Units. Given. Special situations
 Chapter 3 Cardiology Georgia Woodfield ASPIRIN FONDAPARINUX 300 once only in acute MI 75 in primary/ secondary prevention of thrombus formation and thromboembolic disease or PR; can also be given via nasogastric
Chapter 3 Cardiology Georgia Woodfield ASPIRIN FONDAPARINUX 300 once only in acute MI 75 in primary/ secondary prevention of thrombus formation and thromboembolic disease or PR; can also be given via nasogastric
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Beta-blockers. Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol.
 Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters. Dilution not necessary (Available in prefilled syringe)
 Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters Acetazolamide 500 mg Reconstitute with at least 5ml sterile water (max concentration should not exceed 100mg/ml) 100-500 mg/min Hypotension
Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters Acetazolamide 500 mg Reconstitute with at least 5ml sterile water (max concentration should not exceed 100mg/ml) 100-500 mg/min Hypotension
Core Safety Profile. Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Film-coated tablets 1.25 mg, 2.5 mg, 3.75 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg and 10 mg. Date of FAR:
 Core Safety Profile Active substance: Bisoprolol Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Film-coated tablets 1.25 mg, 2.5 mg, 3.75 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg and 10 mg P - RMS: FI/H/PSUR/0002/002 Date of FAR: 13.12.2011
Core Safety Profile Active substance: Bisoprolol Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Film-coated tablets 1.25 mg, 2.5 mg, 3.75 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg and 10 mg P - RMS: FI/H/PSUR/0002/002 Date of FAR: 13.12.2011
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAMME:- MEDICATION
 CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAMME:- MEDICATION AIM OF THIS SESSION Understand the reasons for taking your medications, Discuss the common side effects associated with these medications - knowing when to
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAMME:- MEDICATION AIM OF THIS SESSION Understand the reasons for taking your medications, Discuss the common side effects associated with these medications - knowing when to
Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists
 Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists (CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS) Classification Mechanism of Anti-ischemic Actions Indications Drug Interaction with Verapamil Contraindications Adverse Effects Treatment of Drug
Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists (CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS) Classification Mechanism of Anti-ischemic Actions Indications Drug Interaction with Verapamil Contraindications Adverse Effects Treatment of Drug
Cardiac Catheter Labs Intravenous Drug Therapy Guide
 Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Contact Name and Job Title (author) Cardiac Catheter Lab IV Medicines Guideline Helen Buxton ( Senior Cath Lab
Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Contact Name and Job Title (author) Cardiac Catheter Lab IV Medicines Guideline Helen Buxton ( Senior Cath Lab
Younger adults with a family history of premature artherosclerotic disease should have their cardiovascular risk factors measured.
 Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2018 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2018 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2016 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2016 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Angina Pectoris. Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room
 Angina Pectoris Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Campus of Virginia Commonwealth University
Angina Pectoris Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Campus of Virginia Commonwealth University
3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 3.01 ANTIASTHMATICS 3.01a BETA 2 AGONIST ASTHMA, CHRONIC BRONCHITIS & EMPHYSEMA Salbutamol Inhaler 100ug/dose [Albuterol] (Ventolin) Salbutamol Sulphate Respirator Solution 0.5% (5mg/ml),
3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 3.01 ANTIASTHMATICS 3.01a BETA 2 AGONIST ASTHMA, CHRONIC BRONCHITIS & EMPHYSEMA Salbutamol Inhaler 100ug/dose [Albuterol] (Ventolin) Salbutamol Sulphate Respirator Solution 0.5% (5mg/ml),
Chapter 2 - Cardiovascular System. Primary Care Prescribing Formulary - Preferred Drug Choices
 Chapter 2 - Cardiovascular System Primary Care Prescribing Formulary - Preferred Drug Choices Drug group Drug choice Comments/notes Cardiac glycosides Thiazide diuretics Loop diuretics Aldosterone antagonist
Chapter 2 - Cardiovascular System Primary Care Prescribing Formulary - Preferred Drug Choices Drug group Drug choice Comments/notes Cardiac glycosides Thiazide diuretics Loop diuretics Aldosterone antagonist
Evaluation and Management of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (HF) with Reduced Ejection Fraction Systolic Heart Failure (HFrEF)(EF<40%
 Evaluation and Management of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (HF) with Reduced Ejection Fraction Systolic Heart Failure (HFrEF)(EF
Evaluation and Management of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (HF) with Reduced Ejection Fraction Systolic Heart Failure (HFrEF)(EF
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY, THE ALGORHITHM
 MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY, THE ALGORHITHM Are Particular Anti-hypertensives More Effective or Harmful Than Others in Hypertension in Pregnancy? Existing data is inadequate Methyldopa and
MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY, THE ALGORHITHM Are Particular Anti-hypertensives More Effective or Harmful Than Others in Hypertension in Pregnancy? Existing data is inadequate Methyldopa and
Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Cardiac chest pain or suspected Myocardial Infarction.
 s Aspirin Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory agent and an inhibitor of platelet function. Useful agent in the treatment of various thromboembolic diseases such as acute myocardial infarction.
s Aspirin Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory agent and an inhibitor of platelet function. Useful agent in the treatment of various thromboembolic diseases such as acute myocardial infarction.
Chapter 23. Media Directory. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Hypertension: Classified into Three Categories
 Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Intravenous Infusions
 Intravenous Infusions 1) An IV insulin infusion can be used for patients: a) with out of control diabetes b) with DKA (Diabetic Ketoacidosis) c) after a heart attack 2) Hyperglycemia is an adaptive response
Intravenous Infusions 1) An IV insulin infusion can be used for patients: a) with out of control diabetes b) with DKA (Diabetic Ketoacidosis) c) after a heart attack 2) Hyperglycemia is an adaptive response
Antihypertensives. Diagnostic category
 Measurement of blood pressure At first assessment, take both arms then choose the one with the higher reading. Beware of orthostatic hypotension. Measure BP in sitting position, and repeat after patient
Measurement of blood pressure At first assessment, take both arms then choose the one with the higher reading. Beware of orthostatic hypotension. Measure BP in sitting position, and repeat after patient
ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments
 ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 8
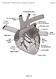 Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker
 PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
Managing IHD and acute Myocardial Infarction
 Managing IHD and acute Myocardial Infarction In Ireland- 1 out of every 10 deaths ( 22% of all premature deaths) in 2006 were due to CVD 30,000 15,000 0 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Source
Managing IHD and acute Myocardial Infarction In Ireland- 1 out of every 10 deaths ( 22% of all premature deaths) in 2006 were due to CVD 30,000 15,000 0 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Source
Heart Failure. Dr. Alia Shatanawi
 Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS PRODUCT SUMMARY 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Sterile Potassium Chloride Concentrate 15%. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 15% of Potassium Chloride in
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS PRODUCT SUMMARY 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Sterile Potassium Chloride Concentrate 15%. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 15% of Potassium Chloride in
Antihypertensive drugs: I. Thiazide and other diuretics:
 Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
IV Medication Drip Chart
 IV Medication Drip Chart Index Summary chart 2 IV Medication drip chart Amiodarone 2 Atracurium 2, 5 Cisatracurium 2, 5 Dexmedetomidine 2 Dobutamine 2, 6 Dopamine 2, 6 Epinephrine 2, 7 Esmolol 2, 7 Etomidate
IV Medication Drip Chart Index Summary chart 2 IV Medication drip chart Amiodarone 2 Atracurium 2, 5 Cisatracurium 2, 5 Dexmedetomidine 2 Dobutamine 2, 6 Dopamine 2, 6 Epinephrine 2, 7 Esmolol 2, 7 Etomidate
ANGINA PECTORIS. angina pectoris is a symptom of myocardial ischemia in the absence of infarction
 Pharmacology Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. ANGINA PECTORIS A. Definition angina pectoris is a symptom of myocardial ischemia in the absence of infarction angina usually implies severe chest pain or discomfort during
Pharmacology Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. ANGINA PECTORIS A. Definition angina pectoris is a symptom of myocardial ischemia in the absence of infarction angina usually implies severe chest pain or discomfort during
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood:
 Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
NEWBORN EMERGENCY TRANSPORT SERVICE MEDICAL GUIDELINES
 WOMEN AND NEWBORN HEALTH SERVICE King Edward Memorial Hospital NEWBORN EMERGENCY TRANSPORT SERVICE MEDICAL GUIDELINES Transport Medication List Title of policy: Transport Medication List Date Revised:
WOMEN AND NEWBORN HEALTH SERVICE King Edward Memorial Hospital NEWBORN EMERGENCY TRANSPORT SERVICE MEDICAL GUIDELINES Transport Medication List Title of policy: Transport Medication List Date Revised:
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs
 Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Angina pectoris due to coronary atherosclerosis : Atenolol is indicated for the long term management of patients with angina pectoris.
 Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology
 ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology Relates to HLT404C Apply Advanced Resuscitation Techniques Introduction There are no studies that addressed the order of drug administration. There is inadequate evidence to define
ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology Relates to HLT404C Apply Advanced Resuscitation Techniques Introduction There are no studies that addressed the order of drug administration. There is inadequate evidence to define
Antihypertensives. Antihypertensive Classes. RAAS Inhibitors. Renin-Angiotensin Cascade. Angiotensin Receptors. Approaches to Hypertension Treatment
 Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
Adrenergic Receptor as part of ANS
 Adrenergic Receptor as part of ANS Actions of Adrenoceptors Beta-1 adrenergic receptor Located on the myocytes of the heart Specific actions of the β1 receptor include: 0 Increase cardiac output, by 0
Adrenergic Receptor as part of ANS Actions of Adrenoceptors Beta-1 adrenergic receptor Located on the myocytes of the heart Specific actions of the β1 receptor include: 0 Increase cardiac output, by 0
Medications. Your prescriptions can be filled by your home pharmacy or by the Michigan Medicine Taubman Center outpatient pharmacy.
 Medications Your prescriptions can be filled by your home pharmacy or by the Michigan Medicine Taubman Center outpatient pharmacy. What do I need to know about medications after my heart attack? When you
Medications Your prescriptions can be filled by your home pharmacy or by the Michigan Medicine Taubman Center outpatient pharmacy. What do I need to know about medications after my heart attack? When you
Objectives: This presentation will help you to:
 emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
GENERIC (TRADE) NAME CAT. INDICATION/DOSE
 7 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 7.01 CORTICOSTEROIDS Dexamethasone Inj 8mg/2ml (as sodium phosphate) (Decadron) Hydrocortisone Inj 100mg/2ml or 100mg vial (as sodium succinate) (Solu-Cortef) Prednisolone Tab 5mg, 25mg
7 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 7.01 CORTICOSTEROIDS Dexamethasone Inj 8mg/2ml (as sodium phosphate) (Decadron) Hydrocortisone Inj 100mg/2ml or 100mg vial (as sodium succinate) (Solu-Cortef) Prednisolone Tab 5mg, 25mg
DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION
 DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION NAME OF MEDICINE Magnesium Sulfate BP DESCRIPTION DBL Magnesium Sulfate Concentrated Injection is a clear, colourless, sterile solution. Each ampoule contains
DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION NAME OF MEDICINE Magnesium Sulfate BP DESCRIPTION DBL Magnesium Sulfate Concentrated Injection is a clear, colourless, sterile solution. Each ampoule contains
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. Active substance: enoximone
 PACKAGE LEAFLET 1 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Perfan Injection 100 mg/20 ml Concentrate for Solution for Injection Active substance: enoximone Read all of this leaflet carefully before you
PACKAGE LEAFLET 1 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Perfan Injection 100 mg/20 ml Concentrate for Solution for Injection Active substance: enoximone Read all of this leaflet carefully before you
PACKAGE INSERT TEMPLATE FOR SALBUTAMOL TABLET & SALBUTAMOL SYRUP
 PACKAGE INSERT TEMPLATE FOR SALBUTAMOL TABLET & SALBUTAMOL SYRUP Brand or Product Name [Product name] Tablet 2mg [Product name] Tablet 4mg [Product name] Syrup 2mg/5ml Name and Strength of Active Substance(s)
PACKAGE INSERT TEMPLATE FOR SALBUTAMOL TABLET & SALBUTAMOL SYRUP Brand or Product Name [Product name] Tablet 2mg [Product name] Tablet 4mg [Product name] Syrup 2mg/5ml Name and Strength of Active Substance(s)
Adult Drug Reference. Dopamine Drip Chart. Pediatric Drug Reference. Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES
 Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS)
 DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROBLEMS
 PHARMACOLOGICAL PROBLEMS 1. A 69 year old woman suffering from CHF has been treated with.25 mg Digoxin tablet daily for last 3 months. But the heart failure is not controlled adequately. What will be the
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROBLEMS 1. A 69 year old woman suffering from CHF has been treated with.25 mg Digoxin tablet daily for last 3 months. But the heart failure is not controlled adequately. What will be the
Top 200 Section 4. Cardiovascular Drugs
 Top 200 Section 4 Cardiovascular Drugs Objectives After finishing this presentation the audience should be able to: Describe conditions/disease states that would make a person a candidate for drug therapy.
Top 200 Section 4 Cardiovascular Drugs Objectives After finishing this presentation the audience should be able to: Describe conditions/disease states that would make a person a candidate for drug therapy.
Resuscitation Fluids
 Resuscitation Fluids Acceptable Fluids (also known as): Sodium Chloride Hartmann s Solution (Ringer-Lactate Solution, Compound Sodium Lactate) 4.5% Albumin Solution (PPS) Gelofusine 20ml/kg Bolus Can be
Resuscitation Fluids Acceptable Fluids (also known as): Sodium Chloride Hartmann s Solution (Ringer-Lactate Solution, Compound Sodium Lactate) 4.5% Albumin Solution (PPS) Gelofusine 20ml/kg Bolus Can be
Medical Treatment for acute Decompensated Heart Failure. Vlasis Ninios Cardiologist St. Luke s s Hospital Thessaloniki 2011
 Medical Treatment for acute Decompensated Heart Failure Vlasis Ninios Cardiologist St. Luke s s Hospital Thessaloniki 2011 2010 HFSA guidelines for ADHF 2009 focused update of the 2005 American College
Medical Treatment for acute Decompensated Heart Failure Vlasis Ninios Cardiologist St. Luke s s Hospital Thessaloniki 2011 2010 HFSA guidelines for ADHF 2009 focused update of the 2005 American College
Drugs affecting the blood
 Drugs affecting the blood Antianaemia drugs IRON-DEFICIENCY ANAEMIA Anaemia has many different aetiologies. It occurs when the haemoglobin concentration falls below the normal range for the age and sex
Drugs affecting the blood Antianaemia drugs IRON-DEFICIENCY ANAEMIA Anaemia has many different aetiologies. It occurs when the haemoglobin concentration falls below the normal range for the age and sex
Cardiology. Self Learning Package. Module 5: Pharmacology: Treatment of Acute Coronary. Prevention
 Cardiology Self Learning Package Module 5: Pharmacology: Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndromes, Module 5: Pharmacology: Hyperlipidaemia, Treatment of Acute Coronary Hypertension, Symdrome, Hyperlipidaemia,
Cardiology Self Learning Package Module 5: Pharmacology: Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndromes, Module 5: Pharmacology: Hyperlipidaemia, Treatment of Acute Coronary Hypertension, Symdrome, Hyperlipidaemia,
7/7/ CHD/MI LVH and LV dysfunction Dysrrhythmias Stroke PVD Renal insufficiency and failure Retinopathy. Normal <120 Prehypertension
 Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Adult Critical Care Intravenous Infusions Titration Protocol
 Adult Critical Care Intravenous Infusions Protocol Nursing staff to titrate drip to achieve goal ordered by provider in assigned time intervals. Amiodarone (Pacerone ) Argatroban Non-heparin anticoagulant
Adult Critical Care Intravenous Infusions Protocol Nursing staff to titrate drip to achieve goal ordered by provider in assigned time intervals. Amiodarone (Pacerone ) Argatroban Non-heparin anticoagulant
Medicine Dr. Omed Lecture 2 Stable and Unstable Angina
 Medicine Dr. Omed Lecture 2 Stable and Unstable Angina Risk stratification in stable angina. High Risk; *post infarct angina, *poor effort tolerance, *ischemia at low workload, *left main or three vessel
Medicine Dr. Omed Lecture 2 Stable and Unstable Angina Risk stratification in stable angina. High Risk; *post infarct angina, *poor effort tolerance, *ischemia at low workload, *left main or three vessel
Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Diabetic. Target less than 130/80mmHg
 Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Non-diabetic Diabetic Very elderly (older than 80 years) Target less than 140/90mmHg Target less than 130/80mmHg Consider SBP target less than 150mmHg Non-diabetic
Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Non-diabetic Diabetic Very elderly (older than 80 years) Target less than 140/90mmHg Target less than 130/80mmHg Consider SBP target less than 150mmHg Non-diabetic
Treatment of T Angina reatment of By Ali Alalawi
 Treatment of Angina By Ali Alalawi Determinants of Oxygen Demand Need to improve ratio of: Coronary blood flow / cardiac work Or Cardiac O2 Supply / Cardiac Requirement Coronary Circulation vs Other Circulation
Treatment of Angina By Ali Alalawi Determinants of Oxygen Demand Need to improve ratio of: Coronary blood flow / cardiac work Or Cardiac O2 Supply / Cardiac Requirement Coronary Circulation vs Other Circulation
Pharmacology. Drugs affecting the Cardiovascular system (Antianginal Drugs)
 Lecture 7 (year3) Dr Noor Al-Hasani Pharmacology University of Baghdad College of dentistry Drugs affecting the Cardiovascular system (Antianginal Drugs) Atherosclerotic disease of the coronary arteries,
Lecture 7 (year3) Dr Noor Al-Hasani Pharmacology University of Baghdad College of dentistry Drugs affecting the Cardiovascular system (Antianginal Drugs) Atherosclerotic disease of the coronary arteries,
Hypertension (JNC-8)
 Hypertension (JNC-8) Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 17, 2018, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D.! The 8 th Joint
Hypertension (JNC-8) Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 17, 2018, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D.! The 8 th Joint
CHAPTER 12 HYPERTENSION IN SPECIAL GROUPS HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY
 CHAPTER 12 HYPERTENSION IN SPECIAL GROUPS HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY v Mild preeclampsia is managed by close observation of the mother and fetus preferably in hospital. If the diastolic blood pressure remains
CHAPTER 12 HYPERTENSION IN SPECIAL GROUPS HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY v Mild preeclampsia is managed by close observation of the mother and fetus preferably in hospital. If the diastolic blood pressure remains
perioperative management of cardiovascular drugs
 perioperative management of cardiovascular drugs Dave Pappin and Vanessa Helliwell, Exeter, UK. Email: vanessahelliwell@doctors.org.uk It is estimated that by 2010 cardiovascular disease will be the leading
perioperative management of cardiovascular drugs Dave Pappin and Vanessa Helliwell, Exeter, UK. Email: vanessahelliwell@doctors.org.uk It is estimated that by 2010 cardiovascular disease will be the leading
METOTRUST XL-25/50 Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets
 METOTRUST XL-25/50 Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets COMPOSITION Each film-coated tablet of Metotrust XL-25 contains: Metoprolol Succinate USP 23.75 mg equivalent to Metoprolol Tartrate 25
METOTRUST XL-25/50 Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets COMPOSITION Each film-coated tablet of Metotrust XL-25 contains: Metoprolol Succinate USP 23.75 mg equivalent to Metoprolol Tartrate 25
Heart failure. Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs. CHF = congestive heart failure. increased blood volume, interstitial fluid
 Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA
 CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
Section 3, Lecture 2
 59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate).
 VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
Cardiac Medications At A Glance
 Cardiac Medications At A Glance 1) Anticoagulants (Also known as Blood Thinners.) Dalteparin (Fragmin), Danaparoid (Orgaran) Enoxaparin (Lovenox) Heparin (various) Tinzaparin (Innohep) Warfarin (Coumadin)
Cardiac Medications At A Glance 1) Anticoagulants (Also known as Blood Thinners.) Dalteparin (Fragmin), Danaparoid (Orgaran) Enoxaparin (Lovenox) Heparin (various) Tinzaparin (Innohep) Warfarin (Coumadin)
P-RMS: LT/H/PSUR/0004/001
 Core Safety Profile Active substance: Dalteparine Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Solution for injection, 2500 I.U./0.2ml, 2500 I.U./ml, 5000 I.U./0.2ml, 7500 I.U./0.3ml, 7500 I.U./0.75ml, 10000 I.U./0.4ml,
Core Safety Profile Active substance: Dalteparine Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Solution for injection, 2500 I.U./0.2ml, 2500 I.U./ml, 5000 I.U./0.2ml, 7500 I.U./0.3ml, 7500 I.U./0.75ml, 10000 I.U./0.4ml,
 www.yassermetwally.com MANAGEMENT OF CEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE (ICH): A QUICK GUIDE Overview 10% of strokes is caused by ICH. Main Causes: Less than 40 years old: vascular malformations and illicit drug use.
www.yassermetwally.com MANAGEMENT OF CEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE (ICH): A QUICK GUIDE Overview 10% of strokes is caused by ICH. Main Causes: Less than 40 years old: vascular malformations and illicit drug use.
Atrial Fibrillation Version 2 11/4/15 This order set must be used with an admission order set if patient not already admitted.
 Patient Name: Diagnosis: Allergies with reaction type: Atrial Fibrillation Version 2 11/4/15 This order set must be used with an admission order set if patient not already admitted. Telemetry Medical Telemetry:
Patient Name: Diagnosis: Allergies with reaction type: Atrial Fibrillation Version 2 11/4/15 This order set must be used with an admission order set if patient not already admitted. Telemetry Medical Telemetry:
Bisoprolol Fumarate 2.5 mg, 5 mg and 10 mg Tablet
 Bisoprolol Fumarate 2.5 mg, 5 mg and 10 mg Tablet Description Betapro is a preparation of Bisoprolol Fumarate. Bisoprolol is used alone or in combination with other medications to treat high blood pressure.
Bisoprolol Fumarate 2.5 mg, 5 mg and 10 mg Tablet Description Betapro is a preparation of Bisoprolol Fumarate. Bisoprolol is used alone or in combination with other medications to treat high blood pressure.
Results of Ischemic Heart Disease
 Ischemic Heart Disease: Angina and Myocardial Infarction Ischemic heart disease; syndromes causing an imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply (inadequate myocardial blood flow) related to
Ischemic Heart Disease: Angina and Myocardial Infarction Ischemic heart disease; syndromes causing an imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply (inadequate myocardial blood flow) related to
Drugs used in obstetrics
 Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs may be used to modify uterine contractions. These include oxytocic drugs used to stimulate uterine contractions both in induction of labour and to
Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs may be used to modify uterine contractions. These include oxytocic drugs used to stimulate uterine contractions both in induction of labour and to
Cardiovascular drugs
 chapter 13 Cardiovascular drugs Cardiovascular drugs act on the heart or blood vessels to control the cardiovascular system. They are used to treat a variety of conditions from hypertension to chronic
chapter 13 Cardiovascular drugs Cardiovascular drugs act on the heart or blood vessels to control the cardiovascular system. They are used to treat a variety of conditions from hypertension to chronic
ANTI-ARRHYTHMICS AND WARFARIN. Dr Nithish Jayakumar
 ANTI-ARRHYTHMICS AND WARFARIN Dr Nithish Jayakumar Contents 1. Anti-arrhythmics Pacemaker and myocardial potentials Drug classes mechanisms; s/e; contra-indications Management of common arrhythmias 2.
ANTI-ARRHYTHMICS AND WARFARIN Dr Nithish Jayakumar Contents 1. Anti-arrhythmics Pacemaker and myocardial potentials Drug classes mechanisms; s/e; contra-indications Management of common arrhythmias 2.
Blanchard Valley Hospital Pharmacy Code Blue Overview
 Blanchard Valley Hospital Pharmacy Code Blue Overview Adapted from Gary Spanik, RPh Edited by Kate Reeves, Pharm D, RPh Jon Manocchio, Pharm D, RPh Pharmacist Responsibilities Be aware of basic ACLS tenets
Blanchard Valley Hospital Pharmacy Code Blue Overview Adapted from Gary Spanik, RPh Edited by Kate Reeves, Pharm D, RPh Jon Manocchio, Pharm D, RPh Pharmacist Responsibilities Be aware of basic ACLS tenets
Elements for a public summary
 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, occurs in a large percentage of the adult population. Primary (essential) hypertension
VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, occurs in a large percentage of the adult population. Primary (essential) hypertension
Document 3 Summary of Data and Guidance for Medical Professionals
 Document 3 Summary of Data and Guidance for Medical Professionals Anvirzel Anvirzel is a novel antitumor compound extracted from the plant Nerium oleander, which belongs to the family Apocynaceae. Anvirzel
Document 3 Summary of Data and Guidance for Medical Professionals Anvirzel Anvirzel is a novel antitumor compound extracted from the plant Nerium oleander, which belongs to the family Apocynaceae. Anvirzel
Magnesium Sulphate - Management of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy
 1. Purpose Magnesium sulphate is the anticonvulsant of choice for pre-eclampsia prophylaxis and treatment. This clinical guideline outlines the indications, contraindications, administration and monitoring
1. Purpose Magnesium sulphate is the anticonvulsant of choice for pre-eclampsia prophylaxis and treatment. This clinical guideline outlines the indications, contraindications, administration and monitoring
Admit date (YYYY/MM/DD): Cardiologist On-Call: Diagnosis: Lab Tests. CBC, Electrolytes, Urea, Creatinine, Glucose, INR, PTT, Urinalysis
 of nurse 1. Admit under ward Attending Physician: Dr. Admit date (YYYY/MM/DD): Cardiologist On-Call: Diagnosis: Lab Tests 2. On admission (if not already performed in Emergency Department or in Coronary
of nurse 1. Admit under ward Attending Physician: Dr. Admit date (YYYY/MM/DD): Cardiologist On-Call: Diagnosis: Lab Tests 2. On admission (if not already performed in Emergency Department or in Coronary
Shared Care Guideline Metolazone for fluid management in CKD (Adults)
 Shared Care Guideline Metolazone for fluid management in CKD (Adults) It is vital for safe and appropriate patient care that there is a clear understanding of where clinical and prescribing responsibility
Shared Care Guideline Metolazone for fluid management in CKD (Adults) It is vital for safe and appropriate patient care that there is a clear understanding of where clinical and prescribing responsibility
Clinical Practice Guidelines Edition (Updated February 2018)
 The Formulary is published by the Pre-Hospital Emergency Care Council (PHECC) to support Emergency First Responders to be competent in the use of medications permitted under Clinical Practice Guidelines
The Formulary is published by the Pre-Hospital Emergency Care Council (PHECC) to support Emergency First Responders to be competent in the use of medications permitted under Clinical Practice Guidelines
Cardiovascular Health Practice Guideline Outpatient Management of Coronary Artery Disease 2003
 Authorized By: Medical Management Guideline Committee Approval Date: 12/13/01 Revision Date: 12/11/03 Beta-Blockers Nitrates Calcium Channel Blockers MEDICATIONS Indicated in post-mi, unstable angina,
Authorized By: Medical Management Guideline Committee Approval Date: 12/13/01 Revision Date: 12/11/03 Beta-Blockers Nitrates Calcium Channel Blockers MEDICATIONS Indicated in post-mi, unstable angina,
Chapter 26. Media Directory. Dysrhythmias. Diagnosis/Treatment of Dysrhythmias. Frequency in Population Difficult to Predict
 Chapter 26 Drugs for Dysrythmias Slide 33 Slide 35 Media Directory Propranolol Animation Amiodarone Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Dysrhythmias Abnormalities of electrical
Chapter 26 Drugs for Dysrythmias Slide 33 Slide 35 Media Directory Propranolol Animation Amiodarone Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Dysrhythmias Abnormalities of electrical
MANAGEMENT OF BLEEDING AND EXCESSIVE ANTICOAGULATION IN ADULTS RECEIVING ANTI-COAGULANTS
 Hairmyres Hospital MANAGEMENT OF BLEEDING AND EXCESSIVE ANTICOAGULATION IN ADULTS RECEIVING ANTI-COAGULANTS Bleeding in patients on anticoagulants, even in the absence of over-anticoagulation, can be life-threatening
Hairmyres Hospital MANAGEMENT OF BLEEDING AND EXCESSIVE ANTICOAGULATION IN ADULTS RECEIVING ANTI-COAGULANTS Bleeding in patients on anticoagulants, even in the absence of over-anticoagulation, can be life-threatening
DRUG GUIDELINE. HYDRALAZINE (Intravenous severe hypertension in pregnancy)
 DRUG GUIDELINE HYDRALAZINE (Intravenous severe hypertension SCOPE (Area): FOR USE IN: Labour Ward, HDU, Theatre and ED EXCLUSIONS: Paediatrics (seek Paediatrician advice) and other general wards. SCOPE
DRUG GUIDELINE HYDRALAZINE (Intravenous severe hypertension SCOPE (Area): FOR USE IN: Labour Ward, HDU, Theatre and ED EXCLUSIONS: Paediatrics (seek Paediatrician advice) and other general wards. SCOPE
Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis
 Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis The H 1 -receptor antagonists are generally referred to as antihistamines. They inhibit the wheal, pruritus, sneezing
Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis The H 1 -receptor antagonists are generally referred to as antihistamines. They inhibit the wheal, pruritus, sneezing
ANESTHESIA DRUG REVIEW
 ANESTHESIA REVIEW CAPA S 39 TH ANNUAL CONFERENCE PALM SPRINGS OCTOBER 10, 2015 ROBERT F. KOPEL, MD, FACP, FCCP HOAG HOSPITAL CARDIAC ANESTHESIOLOGIST ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR UCLA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
ANESTHESIA REVIEW CAPA S 39 TH ANNUAL CONFERENCE PALM SPRINGS OCTOBER 10, 2015 ROBERT F. KOPEL, MD, FACP, FCCP HOAG HOSPITAL CARDIAC ANESTHESIOLOGIST ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR UCLA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Mr. Eknath Kole M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali)
 M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali) Drug Class Actions Therapeutic Uses Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Other Quinidine IA -Binds to open and inactivated Na+ -Decreases the slope of Phase 4 spontaneous depolarization
M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali) Drug Class Actions Therapeutic Uses Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Other Quinidine IA -Binds to open and inactivated Na+ -Decreases the slope of Phase 4 spontaneous depolarization
Titrating Critical Care Medications
 Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
ASTHALIN Respules (Salbutamol sulphate)
 Published on: 28 Jan 2016 ASTHALIN Respules (Salbutamol sulphate) Composition Each 2.5 ml respule contains: Salbutamol Sulphate IP equivalent to Salbutamol IP. 2.5 mg Normal saline solution.q.s. Dosage
Published on: 28 Jan 2016 ASTHALIN Respules (Salbutamol sulphate) Composition Each 2.5 ml respule contains: Salbutamol Sulphate IP equivalent to Salbutamol IP. 2.5 mg Normal saline solution.q.s. Dosage
