Childhood hypertension and family history of hypertension in primary school children in Port Harcourt
|
|
|
- Stanley Price
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Niger J Paed 2013; 40 (2): Okoh BAN Alikor EAD ORIGINAL Childhood hypertension and family history in primary school children in Port Harcourt DOI: Accepted: 11th November 2012 Okoh BAN ( ) Alikor EAD Department of Paediatrics, University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital, P.M.B. 6173, Port Harcourt, Rivers State. Tel: bomadatown@yahoo.com. Introduction, independent of other factors such as age and weight, is a major risk factor for hypertension. 1 Blood pressure (BP) tracking studies 2-4 suggest that hypertension in adulthood often has its origin in childhood. The Bogalusa Heart Study 2 found that children in the top quintile of systolic BP were 3.6 times more likely to develop clinical hypertension by age 31 than their peers. Similarly, 48% of hypertensive adults had shown elevated childhood systolic BP. Besides BP tracking, various observations 3,4 suggest a genetic susceptibility to high BP and cardiovascular disease. Two population studies 3,4 have confirmed a predictive power of family history (particularly maternal hypertension) on higher BP levels in childhood and overt hypertension in later life. The tracking phenomenon as well as the familial aggregation of (high) blood pressure Abstract Objective: To determine the relationship between childhood hypertension and family history of hypertension in primary school children in Port Harcourt. Methods: A stratified multi-staged sampling technique was used to recruit pupils between 6-12 years of age, from thirteen primary schools located in three school districts. Data was collected using a pretested questionnaire completed by parents / guardians. The average of three blood pressure measurements, weight and height were taken for each pupil, using standardized techniques. was defined as average systolic and / or diastolic blood pressure greater than or equal to the 95 th percentile for age, gender and height using the standard blood pressure charts. of hypertension was defined as either parent indicating on the submitted questionnaire that they were hypertensive (diagnosed by a physician and/or on antihypertensive drugs) or had a family history. Results: A total of 1302 pupils with 717 (55.1%) females and 585 (44.9%) males were studied, giving a female to male ratio of 1.2:1. The mean age of pupils studied was 8.82±1.91 years. Sixty one (4.7%) of the pupils examined had hypertension. Of the 1302 pupils, 316 (24.3%) had a family history of hypertension. The mean systolic (p<0.001) and diastolic (p=0.220) blood pressures were higher in children with a family history than in those without. Of the pupils that had a family history, 7.9% had hypertension, while 3.7% of those that did not have a family history, were found to be hypertensive (p=0.001). Conclusion: A family history of hypertension was associated with a higher prevalence of childhood hypertension than was seen in children without a family history. Key words: Childhood,. forms a possible basis for early detection -prone children. Routine BP measurement in childhood will therefore give an opportunity for the early prevention of adult hypertension starting from the childhood years. High BP aggregating in families is associated with shared family environment and genetics. 1 Not only does the occurrence of two hypertensive parents increase the genetic component of elevated BP in offspring, but a shared environment (health habits inducive to hypertension) could further increase a child s tendency to become hypertensive. Heritability measures how much of family aggregation is due to genetic factors. Children from families with hypertension tend to have higher blood pressures than do children from normotensive families. 3 Siblings of children with high BP have significantly higher BP than do siblings of children with low BP. 5
2 In a study in Lagos, Nigeria, 6 adolescents with a family history had significantly higher systolic and diastolic BPs than controls (those with no family history ). In a similar study in Kano, Nigeria, Mijinyawa et al 7 noted that adolescent hypertensives were twice more likely to have a family history than their normotensive counterparts. Early prevention is of public health importance as cardiovascular disease, of which hypertension is a major risk factor, has been found to be the leading cause of death in the United States and other developed countries. 8 is also a risk factor for renal damage and stroke which are major causes of morbidity and mortality. 9,10 Although leading causes of morbidity and mortality in Nigeria and other developing countries are presently preventable factors like infectious diseases, with improved health care that comes with development, a shift in the trend is expected to less -obviously preventable causes like cardiovascular disease in adults. Despite the few studies 6,7 that have been conducted in Nigeria, there is still paucity of information on the relationship between childhood hypertension and a family history in Nigeria. This study was undertaken to determine the relationship, if any, between childhood hypertension and family history in primary school children in Port Harcourt. Materials and methods The study was carried out in Port Harcourt city (PHC), capital of Rivers State of Nigeria. Rivers State is located in the south-south geo-political zone of Nigeria. Port Harcourt is a cosmopolitan city with diverse Nigerian ethnic groups and foreigners living in the city. Port Harcourt is the nerve center of the oil industry. The urban nature of the area and oil exploration and production activities has caused a great influx of people from all over Rivers State, neighbouring states and indeed, the entire country. The study was a cross-sectional population-based study carried out from 1 st February to 31 st May A stratified multi-staged sampling technique was used to recruit pupils between 6-12 years of age, from thirteen primary schools located in the three school districts in Port Harcourt. A minimum sample size of 1300 was calculated at a confidence interval of 98.5%. Data was collected using a pre-tested questionnaire completed by parents / guardians. A total of 1302 questionnaires were retrieved. The schools were first stratified into 3 school districts. They were also stratified according to school proprietorship into private and public. The thirteen schools were then selected by simple random method from the three school districts according to the ratio of schools in these districts. Six (3 public and 3 private) schools were selected from Diobu, 5 (3 public and 2 private) from Township and 2 (1 public and 1 private) from Trans- Amadi school districts. In schools with more than one arm of a class, one arm was selected randomly to represent the others, while in schools with only one arm of a class, that arm was chosen. Arms were selected from all six classes in all the selected schools. In each selected school an average of 100 pupils aged 6-12 years were recruited. Sixteen to seventeen pupils were selected randomly from each class using the class register. Blood pressure was measured using the mercury gravity sphygmomanometer. The measurements were taken in the sitting position with exposed outstretched right arm on a table, using appropriate cuff size for age, the cuff bladder completely encircling the arm covering 75% of the arm between the acromion and olecranon. The bell of the stethoscope was placed over the brachial pulse at the proximal medial part of the anti-cubital fossa. For each measurement, the cuff was rapidly inflated to occlude the brachial artery, and then deflated slowly allowing the mercury column of the sphygmomanometer to fall at a rate of approximately 2-5 mm Hg per second. The first Korotkoff sound was taken as systolic BP and the fifth Korotkoff sound as the diastolic BP. Blood pressure was measured three times for each child in the same visit with at least two minutes interval between measurements. The average was then estimated as the blood pressure level of the subject. The charts on BP levels for boys and girls by age and height percentiles 11 were used to classify hypertension in the subjects after determining their height percentiles from the CDC growth charts. For children with a raised BP, two additional BP measurements were made at least a week apart. Data was collated and analyzed using the Epi-info version statistical software. In this study, hypertension was defined as average of 3 measured systolic and/or diastolic BP that is greater than or equal to the 95 th percentile for gender, age, and height using the standard BP charts developed by the National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents, United States of America. 11 Pre-hypertension was defined as an average of three measured systolic and/or diastolic BP greater than the 90 th percentile but less than the 95 th percentile; stage one hypertension as that greater than or equal to the 95 th percentile but less than the 99 th percentile; and stage two hypertension as that greater than or equal to the 99 th percentile. Ethical consideration 185 Ethical clearance was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital. Permission was obtained from the Rivers State Ministry of Education, the Head teachers of the index schools and the parents / guardians of the pupils. Parents of children that were found to be pre-hypertensive or hypertensive were counseled and the children referred to the paediatric clinic of the University of Port Harcourt Teaching hospital for expert management.
3 186 Results A total of 1302 pupils participated in the study. Seven hundred and seventeen (55.1%) were females and 585 (44.9%) males giving a female to male ratio of 1.2:1. The age range of the pupils was from 6 to 12 years, with a mean age of 8.82±1.91 years and mode of 9years (17.7%). The systolic blood pressure of the subjects ranged from 70 to 153mm Hg with a mean of 98.09±10.21 mm Hg while the diastolic blood pressure ranged from 39 to 97mm Hg with a mean of 61.84±10.73 mm Hg. Sixty one (4.7%) of the pupils examined had hypertension. Thirty eight (5.3%) of the 717 females in the study were found to be hypertensive while 23 (3.9%) of the 585 males were hypertensive. The study subjects were grouped into two almost equal age groups; 6 8 years and 9 12 years. Thirty five (6%) of the 588 children in 6 to 8 year age group had hypertension while 26 (3.6%) of the 714 in the 9 to 12 year age group had hypertension. The observation however, did not reach statistical significance (χ 2 = 3.85, df = 1, p = 0.05). All respondents that had either parent indicate in the submitted questionnaire, that he / she was hypertensive (diagnosed by a physician and/or on antihypertensive drugs) or had a family history, were considered to have a family history. Of the 1302 pupils, 318 (24.4%) had a family history of hypertension. The mean systolic blood pressure of ±10.97mm Hg for children with a family history was significantly higher than 97.44±9.87mm Hg for those with no family history (t = 4.07, df = 1, p < 0.001). The mean diastolic blood pressure of 62.30±8.33mm Hg for children with a family history of hypertension was also higher than that of 61.69±7.49mm Hg, for those with no family history. The difference observed was however, not statistically significant (t = 1.23, df = 1, p = 0.220). Of the 318 pupils that had a family history, 25 (7.9%) had hypertension, while 36 (3.7%) of the 984 that did not have a family history, had hypertension (Table 1). The difference in the two groups was statistically significant (χ 2 = 8.59, df = 1, p = 0.001). The relative risk of having hypertension in children with a positive family history was Table 1: Relationship between hypertension and family history of ypertension χ 2 = 8.59, df = 1, p = Present 25 (7.9) 293 (92.1) 318 Absent 36 (3.7) 948 (96.3) (4.7) 1241 (95.3) 1302 (100) Table 2 shows that among the female pupils, 17 (10%) of the 170 that had a positive family history were found to be hypertensive compared to 21 (3.8%) of the 547 that did not have a positive family history. The difference was statistically significant (χ 2 = 8.62, df = 1, p = 0.001) and the relative risk for having hypertension in female pupils with a positive family history was Among the male pupils, 8 (5.4%) of the 148 that had a positive family history were found to be hypertensive compared to 15 (3.4%) of the 437 that did not have a positive family history. The observed difference however did not reach statistical significance (χ 2 = 0.68, df = 1, p = 0.15) but the relative risk for having hypertension in male pupils with a positive family history was Among pupils aged 6 8 years, 16 (9%) of 178 that had a positive family history were found to be hypertensive compared to 19 (4.6%) of 410 that did not have a positive family history. The difference was statistically significant (χ 2 = 3.46, df = 1, p = 0.02) and the relative risk for having hypertension in pupils aged 6 8 years with a positive family history of hypertension was Among pupils aged 9 12 years, 9 (6.4%) of the 140 that had a positive family history of hypertension were found to be hypertensive compared to 17 (3%) of the 574 that did not have a positive family history. The difference was also statistically significant (χ 2 = 2.93, df = 1, p = 0.03) and the relative risk for having hypertension in pupils aged 9 12 years with a positive family history was 1.04 (Table 2). Table 2: Relationship between hypertension and family history among gender and age groups p value Females Present 17 (10) 153 (90) 170 p = Absent 21 (3.8) 526 (96.2) 547 Males Present 8 (5.4) 140 (94.6) 148 p = Absent 15 (3.4) 422 (96.6) years Present 16 (9) 162 (91) 178 p = 0.02 Absent 19 (4.6) 391 (95.4) years Present 9 (6.4) 131 (93.6) 140 p = 0.03 Absent 17 (3) 557 (97) 574 Two hundred and three (15.6%) pupils had a paternal history while 236 (18.1%) had a maternal history. Nineteen (9.4%) of the 203 pupils with a paternal history (father or father s parents hypertensive) were hypertensive, compared to 42 (3.8%) of the 1099 pupils with no paternal history. This difference was statistically significant (χ 2 = , df = 1, p < 0.001). Eighteen (7.6%) of the 236 pupils with a maternal history (mother or mother s parents hypertensive) were hypertensive, compared to 43 (4%) of 1066 pupils
4 with no maternal history. The difference was also statistically significant (χ 2 = 4.811, df = 1, p = 0.013) (Table 3). Table 3: Relationship between hypertension and paternal/ maternal history Paternal Two (8.3%) of the 24 pupils that reported hypertension in both parents where hypertensive, while 15 (8.9%) of the 168 pupils that reported hypertension in only one of their two parents were hypertensive. The difference between the two groups was not statistically significant (Fisher exact = 0.641) Discussion p value Present 19 (9.4) 184 (90.6) 203 p < Absent 42 (3.8) 1057 (96.2) 1099 Maternal Present 18 (7.6) 218 (92.4) 236 p = Absent 43 (4) 1023 (96) 1066 The higher mean systolic and diastolic BP in children with a positive family history found in this study is similar to findings of other studies. 6,12-14 In a study in Lagos, Nigeria, 6 adolescents with a family history had significantly higher systolic and diastolic BPs than controls (those with no family history ). A study in Finland 12 showed that children whose parents were hypertensive had 4- to 6-mm Hg higher systolic and 3- to 4-mm Hg higher diastolic blood pressures than children of normotensive parents (P<0.001). van Hooft 13 showed that no clear differences existed in BPs between 8-year-old children of parents with relatively high BP compared with those of children with no family history of high BP. However, at 20 years of age, a 7-mm Hg difference in both systolic and diastolic BPs was found. Also, an Indian study 14 showed that young normotensives with a positive family history had significantly higher blood pressure (P<0.05) and also increased resting heart rate (P<0.05) than young normotensives with a negative family history. Similarly, the higher prevalence (7.9%) in children with a family history found in this study is in keeping with previous studies. 7,15,16 Mijinyawa et al 7 noted that adolescent hypertensives in Kano, Nigeria were twice more likely to have a family history than their normotensive 187 counterparts. In a study conducted among urban Asian Indian adolescents, 15 systolic (statistically not significant) and diastolic hypertension were associated with a history of clinical hypertension in either of the parents. In a similar study in Indian children, 16 the incidence of hypertension in children with hypertensive families was as high as 30% as against none of the children from the control group (from normotensive families). An additional 27% in the study group had prehypertension as compared to none in controls. Contrary to findings in this study, a study conducted on children in Italy 17 did not show a significant association between family history and childhood hypertension. The fact that the Italian study was on sample of 377 children identified by primary care referral and sent for further investigation for cardiovascular risk in children for either elevated BP values and/or family history of cardiovascular disease, defined as the presence of at least one among hypertension, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, early ischemic heart and cerebrovascular disease, and not a random study of the general population may account for the different findings in the two studies. This study showed a higher prevalence in both female (10%) and male (5.4%) pupils with a positive family history. However, only that observed among the females was statistically significant. The opposite was observed among adult males and females by Goldstein et al. 18 The fact that their study was among adults, while the present study was in children aged 6 12 years may account for this difference. This study showed a higher (not statistically significant) prevalence in children with two hypertensive parents than those with one hypertensive parent. This is similar to findings by Goldstein et al 18 who found that healthy men with two hypertensive parents had higher daytime and night-time ambulatory BP than men with normotensive parents, and with one hypertensive parent had intermediate BP levels. The increased blood pressure and prevalence observed in this study in the offspring of hypertensive parents emphasize the importance of genetic influence on hypertension in children. Children belonging to hypertensive families should therefore, be targeted for primary prevention in a vigorous manner (blood pressure monitoring) along with dietary and lifestyle modification. It is also imperative to screen these children to identify markers to assist in prediction of development of essential hypertension in adulthood. References 1. Lauer RM, Burns TL, Clarke WR, Mahoney LT: Childhood predictors of future blood pressure. 1991;18(3 Suppl): I74 I Bao W, Threefoot SA, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS. Essential hypertension predicted by tracking of elevated blood pressure from childhood to adulthood: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Am J Hypertens. 1995; 8: Munger RG, Rrineas RJ, Gomez- Marin O. Persistent elevation of blood pressure among children with a family history : the Minneapolis Children's Blood Pressure Study. J Hypertens. 1988; 6:
5 4. Friedman GD, Selby JV, Quesenberry CP Jr, Armstrong MA, Klatsky AL. Precursors of essential hypertension: body weight, alcohol and salt use and parental history of hypertension. Prev Med. 1988; 17: Brandoa A, Brandoa A, Araujo E. Familial aggregation of arterial blood pressure and possible genetic influence ; 19: Amadi C, Mbakwem A, Oke A, Ajuluchukwu J. Left Ventricular Mass of Normotensive Adolescent Progeny of Nigeria Hypertensives. The Internet Journal of Cardiology. 2011; 10 (1): DOI: /1ad9 7. Mijinyawa MS, Iliyasu Z, Borodo MM. Prevalence among teenage students in Kano, Nigeria. Niger J Med. 2008; 17 (2): Tanne JH. Children should have blood pressure and cholesterol checked by age of 5. BMJ. 2002; 325:8. 9. Parekh RS, Caroll CE, Wolfe RA, Port FK. Cardiovascular mortality in children and young adults with end-stage kidney disease. J Pediatr. 2002; 141: Mitsnefes M, Stablein D. in paediatric patients on long-term dialysis: a report of the North American Paediatric Renal Transplant Cooperataive Study (NAPRTCS). Am J Kidney Dis. 2005; 45: Aram VC, George LB, Henry RB, William CC, Lee AG, Joseph LI Jr et al. Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertens. 2003; 42: Niinikoski H, Jula A, Viikari J, Rönnemaa T, Heino P, Lagström H et al. Blood Pressure Is Lower in Children and Adolescents With a Low-Saturated-Fat Diet Since Infancy ; 53: van Hooft IM, Hofman A, Grobbee DE, Valkenburg HA. Change in blood pressure in offspring of parents with high or low blood pressure: the Dutch and Offspring Study. J Hypertens. 1988; 6 (suppl): S594 S Dayananda G, Murthy N. Blood Pressure changes in normotensive subjects with & without family History of. JPBS. 2009; 22: Goel R, Misra A, Agarwal SK, Vikram N. Correlates among urban Asian Indian adolescents. Arch Dis Child. 2010; 95: Joshi S, Gupta S, Tank S, Malik S, Salgaonkar DS. Essential : Antecedents in Children. Indian Pediatr. 2003; 40: Genovesia S, Brambillab P, Giussanib M, Galbiatia S, Mastriania S, Pieruzzia F et al. Insulin resistance, prehypertension, hypertension and blood pressure values in paediatric age. J Hypertens. 2012; 30: Goldstein IB, Shapiro D, Guthrie D. Ambulatory blood pressure and family history in healthy men and women. AJH 2006; 19:
BIOPHYSICAL PROFILE OF BLOOD PRESSURE IN SCHOOLCHILDREN
 BIOPHYSICAL PROFILE OF BLOOD PRESSURE IN SCHOOLCHILDREN M. Verma J. Chhatwal S.M. George ABSTRACT The study was conducted in an industrial and prosperous city of Punjab to evaluate the biophysical profile
BIOPHYSICAL PROFILE OF BLOOD PRESSURE IN SCHOOLCHILDREN M. Verma J. Chhatwal S.M. George ABSTRACT The study was conducted in an industrial and prosperous city of Punjab to evaluate the biophysical profile
Variation of blood pressure among the adolescent students Mushroor S 1, Islam MZ 2, Amir RA 3, Ahmed N 4, Amin MR 5
 Original Article Variation of blood pressure among the adolescent students Mushroor S 1, Islam MZ 2, Amir RA 3, Ahmed N 4, Amin MR 5 Abstract The increase in the burden of chronic disease associated with
Original Article Variation of blood pressure among the adolescent students Mushroor S 1, Islam MZ 2, Amir RA 3, Ahmed N 4, Amin MR 5 Abstract The increase in the burden of chronic disease associated with
A hypertensive father, but not hypertensive mother, determines blood pressure in normotensive male offspring through body mass index
 Journal of Human Hypertension (1998) 12, 441 445 1998 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE A hypertensive father, but not hypertensive
Journal of Human Hypertension (1998) 12, 441 445 1998 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE A hypertensive father, but not hypertensive
Hypertension with Comorbidities Treatment of Metabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents
 Hypertension with Comorbidities Treatment of Metabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents Stella Stabouli Ass. Professor Pediatrics 1 st Department of Pediatrics Hippocratio Hospital Evaluation of
Hypertension with Comorbidities Treatment of Metabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents Stella Stabouli Ass. Professor Pediatrics 1 st Department of Pediatrics Hippocratio Hospital Evaluation of
Left ventricular mass in offspring of hypertensive parents: does it predict the future?
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiovascular Research Volume 7 Number 1 Left ventricular mass in offspring of hypertensive parents: does it predict the future? P Jaiswal, S Mahajan, S Diwan, S Acharya,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiovascular Research Volume 7 Number 1 Left ventricular mass in offspring of hypertensive parents: does it predict the future? P Jaiswal, S Mahajan, S Diwan, S Acharya,
Original article: A study on the prevalence of hypertension among young adults in a coastal district of Karnataka, South India
 Original article: A study on the prevalence of among young adults in a coastal district of Karnataka, South India Reddy VS 1, Jacob GP 2, Ballala K 3, Ravi C 4, Ravi B 5, Gandhi P 6, Tadkal P 7, Singh
Original article: A study on the prevalence of among young adults in a coastal district of Karnataka, South India Reddy VS 1, Jacob GP 2, Ballala K 3, Ravi C 4, Ravi B 5, Gandhi P 6, Tadkal P 7, Singh
Noise at school independently raises the odds for hypertension in children and adolescents
 12th ICBEN Congress on Noise as a Public Health Problem Noise at school independently raises the odds for hypertension in children and adolescents Goran Belojevic 1, Jelena Ilic Zivojinovic 1, Katarina
12th ICBEN Congress on Noise as a Public Health Problem Noise at school independently raises the odds for hypertension in children and adolescents Goran Belojevic 1, Jelena Ilic Zivojinovic 1, Katarina
Chapter 08. Health Screening and Risk Classification
 Chapter 08 Health Screening and Risk Classification Preliminary Health Screening and Risk Classification Protocol: 1) Conduct a Preliminary Health Evaluation 2) Determine Health /Disease Risks 3) Determine
Chapter 08 Health Screening and Risk Classification Preliminary Health Screening and Risk Classification Protocol: 1) Conduct a Preliminary Health Evaluation 2) Determine Health /Disease Risks 3) Determine
Blood Pressure Competency Training
 Blood Pressure Competency Training WORKBOOK Table of Contents 3..... Introduction 4..... Background 6..... Equipment Accurate blood pressure What impacts a patient s blood pressure Strategies for proper
Blood Pressure Competency Training WORKBOOK Table of Contents 3..... Introduction 4..... Background 6..... Equipment Accurate blood pressure What impacts a patient s blood pressure Strategies for proper
Data Collection Worksheet
 Data Collection Worksheet 1. Has a doctor or nurse ever said that you have: High blood pressure or hypertension? [ ] No [ ] Yes [ ] Not Sure 1.a. If Yes, then at what age were you first told this? Age
Data Collection Worksheet 1. Has a doctor or nurse ever said that you have: High blood pressure or hypertension? [ ] No [ ] Yes [ ] Not Sure 1.a. If Yes, then at what age were you first told this? Age
Evaluation of blood pressure in school children aged years
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Nadesan B et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017 Jul;4(4):1218-1224 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Nadesan B et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017 Jul;4(4):1218-1224 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR
 Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
BLOOD PRESSURE RESPONSE TO COLD PRESSOR TEST IN SIBLINGS OF HYPERTENSIVES
 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2003; 47 (4) : 453 458 BLOOD PRESSURE RESPONSE TO COLD PRESSOR TEST IN SIBLINGS OF HYPERTENSIVES R. K. RAJASHEKAR*, YERUVA NIVEDITHA AND SUMITABHA GHOSH Department of Physiology,
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2003; 47 (4) : 453 458 BLOOD PRESSURE RESPONSE TO COLD PRESSOR TEST IN SIBLINGS OF HYPERTENSIVES R. K. RAJASHEKAR*, YERUVA NIVEDITHA AND SUMITABHA GHOSH Department of Physiology,
THE NEW ARMENIAN MEDICAL JOURNAL DISTRIBUTION, AWARENESS, TREATMENT, AND CONTROL OF ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION IN YEREVAN (ARMENIA)
 THE NEW ARMENIAN MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol.5 (2011), Nо 2, p.29-34 DISTRIBUTION, AWARENESS, TREATMENT, AND CONTROL OF ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION IN YEREVAN (ARMENIA) Zelveian P.H. 1, 2, Podosyan G.A. 2 1 Institute
THE NEW ARMENIAN MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol.5 (2011), Nо 2, p.29-34 DISTRIBUTION, AWARENESS, TREATMENT, AND CONTROL OF ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION IN YEREVAN (ARMENIA) Zelveian P.H. 1, 2, Podosyan G.A. 2 1 Institute
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2016) 5(10):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 10 (2016) pp. 294-300 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.510.033
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 10 (2016) pp. 294-300 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.510.033
Profile of Blood Pressure in Adolescent School Going Children of Guwahati City of India.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. IV (May. 2016), PP 04-09 www.iosrjournals.org Profile of Blood Pressure in Adolescent
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. IV (May. 2016), PP 04-09 www.iosrjournals.org Profile of Blood Pressure in Adolescent
Assessing Overweight in School Going Children: A Simplified Formula
 Journal of Applied Medical Sciences, vol. 4, no. 1, 2015, 27-35 ISSN: 2241-2328 (print version), 2241-2336 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2015 Assessing Overweight in School Going Children: A Simplified Formula
Journal of Applied Medical Sciences, vol. 4, no. 1, 2015, 27-35 ISSN: 2241-2328 (print version), 2241-2336 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2015 Assessing Overweight in School Going Children: A Simplified Formula
Physical activity, body mass index and blood pressure in primary school pupils attending private schools.
 Physical activity, body mass index and blood pressure in primary school pupils attending private schools. Wilson E Sadoh 1, Ayebo E Sadoh 2, Alphonsus N Onyiriuka 1 1. Department of Child Health, School
Physical activity, body mass index and blood pressure in primary school pupils attending private schools. Wilson E Sadoh 1, Ayebo E Sadoh 2, Alphonsus N Onyiriuka 1 1. Department of Child Health, School
Using the New Hypertension Guidelines
 Using the New Hypertension Guidelines Kamal Henderson, MD Department of Cardiology, Preventive Medicine, University of North Carolina School of Medicine Kotchen TA. Historical trends and milestones in
Using the New Hypertension Guidelines Kamal Henderson, MD Department of Cardiology, Preventive Medicine, University of North Carolina School of Medicine Kotchen TA. Historical trends and milestones in
Prevalence of Hypertension in Semi-Urban area of Nepal
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of Hypertension in Semi-Urban area of Nepal Koju R*, Manandhar K*, Gurung R*, Pant P*, Bedi TRS* *Department of Internal Medicine, Dhulikhel Hospital KUH ABSTRACT Hypertension
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of Hypertension in Semi-Urban area of Nepal Koju R*, Manandhar K*, Gurung R*, Pant P*, Bedi TRS* *Department of Internal Medicine, Dhulikhel Hospital KUH ABSTRACT Hypertension
ARTICLE. Dietary Nutrients and Blood Pressure in Urban Minority Adolescents at Risk for Hypertension
 ARTICLE Dietary Nutrients and Blood Pressure in Urban Minority Adolescents at Risk for Hypertension Bonita Falkner, MD; Katherine Sherif, MD; Suzanne Michel, MPH, RD; Harvey Kushner, PhD Objective: To
ARTICLE Dietary Nutrients and Blood Pressure in Urban Minority Adolescents at Risk for Hypertension Bonita Falkner, MD; Katherine Sherif, MD; Suzanne Michel, MPH, RD; Harvey Kushner, PhD Objective: To
The measurement of blood pressure and hypertension. Handout Fenyvesi Tamás III.Department of Medicine
 The measurement of blood pressure and hypertension Handout Fenyvesi Tamás III.Department of Medicine 1 2 History of the blood pressure measurement direct Stephen HALES 1726 horse carotid indirect Riva-Rocci
The measurement of blood pressure and hypertension Handout Fenyvesi Tamás III.Department of Medicine 1 2 History of the blood pressure measurement direct Stephen HALES 1726 horse carotid indirect Riva-Rocci
PART I: HEART ANATOMY
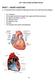 Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
PREVALENCE OF HYPERTENSION AND ITS ASSOCIATED RISK FACTORS AMONG SCHOOL AGE CHILDREN
 PREVALENCE OF HYPERTENSION AND ITS ASSOCIATED RISK FACTORS AMONG SCHOOL AGE CHILDREN DR.AZAD ABDUL JABAR HALEEM AL-MEZORI- Dohuk Medical school/ University of Duhok-Kurdistan- Iraq Prof. Dr. AbbasAl-Rabaty-HawlerMedical
PREVALENCE OF HYPERTENSION AND ITS ASSOCIATED RISK FACTORS AMONG SCHOOL AGE CHILDREN DR.AZAD ABDUL JABAR HALEEM AL-MEZORI- Dohuk Medical school/ University of Duhok-Kurdistan- Iraq Prof. Dr. AbbasAl-Rabaty-HawlerMedical
Lecture #3 - Blood Pressure Recording Procedure. Equipment
 Lecture #3 - Blood Pressure Recording Procedure CKiD Blood Pressure Training Equipment Mabis Medic-Kit aneroid sphygmomanometer Mabis Medic-Kit assortment of cuff sizes Stethoscope with bell (pediatric
Lecture #3 - Blood Pressure Recording Procedure CKiD Blood Pressure Training Equipment Mabis Medic-Kit aneroid sphygmomanometer Mabis Medic-Kit assortment of cuff sizes Stethoscope with bell (pediatric
Section 03: Pre Exercise Evaluations and Risk Factor Assessment
 Section 03: Pre Exercise Evaluations and Risk Factor Assessment ACSM Guidelines: Chapter 3 Pre Exercise Evaluations ACSM Manual: Chapter 3 Risk Factor Assessments HPHE 4450 Dr. Cheatham Purpose The extent
Section 03: Pre Exercise Evaluations and Risk Factor Assessment ACSM Guidelines: Chapter 3 Pre Exercise Evaluations ACSM Manual: Chapter 3 Risk Factor Assessments HPHE 4450 Dr. Cheatham Purpose The extent
Prevalence, awareness of hypertension in rural areas of Kurnool
 Original article: Prevalence, awareness of hypertension in rural areas of Kurnool Dr. Sudhakar Babu*, Dr.Aruna MS** *Associate Professor, Dept of Community Medicine, Vishwa Bharathi Medical College Kurnool,
Original article: Prevalence, awareness of hypertension in rural areas of Kurnool Dr. Sudhakar Babu*, Dr.Aruna MS** *Associate Professor, Dept of Community Medicine, Vishwa Bharathi Medical College Kurnool,
Comparison of Abnormal Cholesterol in Children, Adolescent & Adults in the United States, : Review
 European Journal of Environment and Public Health, 2017, 1(1), 04 ISSN: 2468-1997 Comparison of Abnormal Cholesterol in Children, Adolescent & Adults in the United States, 2011-2014: Review Rasaki Aranmolate
European Journal of Environment and Public Health, 2017, 1(1), 04 ISSN: 2468-1997 Comparison of Abnormal Cholesterol in Children, Adolescent & Adults in the United States, 2011-2014: Review Rasaki Aranmolate
Comparison of Lipoprotein (a) and Apolipoproteins in Children with and without Familial History of Premature Coronary Artery Disease
 Short Comunication Iran J Pediatr Jun 2008; Vol 18 ( No 2), Pp:159-162 Comparison of Lipoprotein (a) and Apolipoproteins in Children with and without Familial History of Premature Coronary Artery Disease
Short Comunication Iran J Pediatr Jun 2008; Vol 18 ( No 2), Pp:159-162 Comparison of Lipoprotein (a) and Apolipoproteins in Children with and without Familial History of Premature Coronary Artery Disease
ORIGINAL ARTICLE AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE IN OBESITY. Introduction. Patients and Methods
 Vol. 2, Issue 1, pages 31-36 ORIGINAL ARTICLE AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE IN OBESITY By Alejandro de la Sierra, MD Luis M. Ruilope, MD Hypertension Units, Hospital Clinico, Barcelona & Hospital 12 de Octubre,
Vol. 2, Issue 1, pages 31-36 ORIGINAL ARTICLE AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE IN OBESITY By Alejandro de la Sierra, MD Luis M. Ruilope, MD Hypertension Units, Hospital Clinico, Barcelona & Hospital 12 de Octubre,
major public health burden
 HYPERTENSION INTRODUCTION Hypertension is one of the major public health burden in the recent times. Hypertension remains a challenging medical condition among the noncommunicable diseases of ever growing
HYPERTENSION INTRODUCTION Hypertension is one of the major public health burden in the recent times. Hypertension remains a challenging medical condition among the noncommunicable diseases of ever growing
Reference Values and Simplified Methods for Interpretation of Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents
 Reference Values and Simplified Methods for Interpretation of Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents Simonetti G.D. Istituto Pediatrico della Svizzera Italiana Ente Ospedaliero Cantonale e Università
Reference Values and Simplified Methods for Interpretation of Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents Simonetti G.D. Istituto Pediatrico della Svizzera Italiana Ente Ospedaliero Cantonale e Università
Risk Factors for Heart Disease
 Risk Factors for Heart Disease Risk Factors we cannot change (Age, Gender, Family History) Risk Factors we can change (modifiable) Smoking Blood pressure Cholesterol Diabetes Inactivity Overweight Stress
Risk Factors for Heart Disease Risk Factors we cannot change (Age, Gender, Family History) Risk Factors we can change (modifiable) Smoking Blood pressure Cholesterol Diabetes Inactivity Overweight Stress
Genetic factors. A number of genetic factors or interactions between genes play a major role in essential hypertension.
 Hypertension Blood pressure is a measurement of the force against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood through your body. Hypertension is another term used to describe high blood pressure.
Hypertension Blood pressure is a measurement of the force against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood through your body. Hypertension is another term used to describe high blood pressure.
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE. MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL (equ04)
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 2/80 7/17 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN, Patient Care Technician Multi-skilled
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 2/80 7/17 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN, Patient Care Technician Multi-skilled
Awareness of Hypertension, Risk Factors and Complications among Attendants of a Primary Health Care Center In Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 6, Issue 1 Ver. VIII (Jan. - Feb. 2017), PP 16-21 www.iosrjournals.org Awareness of Hypertension, Risk
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 6, Issue 1 Ver. VIII (Jan. - Feb. 2017), PP 16-21 www.iosrjournals.org Awareness of Hypertension, Risk
FOUNDATIONS OF NUTRITION Hypertension. Research Paper. By Jessica Richardson S A L T L A K E C O M M U N I T Y C O L L E G E
 FOUNDATIONS OF NUTRITION 1020-055 Hypertension Research Paper By Jessica Richardson 2011 S A L T L A K E C O M M U N I T Y C O L L E G E In researching my family health history I have found there is a
FOUNDATIONS OF NUTRITION 1020-055 Hypertension Research Paper By Jessica Richardson 2011 S A L T L A K E C O M M U N I T Y C O L L E G E In researching my family health history I have found there is a
PLANK 1 Direct Care Staff Trained in Accurate BP Measurement
 Direct Care Staff Trained in Accurate BP Measurement 1. 2. 3. 5. 22 to 26 cm Small adult (12X22 cm) 27 to 34 cm Adult (16X30 cm) 35 to 44 cm Large adult (16X36 cm) 45 to 52 cm Adult thigh (16X42 cm) widths
Direct Care Staff Trained in Accurate BP Measurement 1. 2. 3. 5. 22 to 26 cm Small adult (12X22 cm) 27 to 34 cm Adult (16X30 cm) 35 to 44 cm Large adult (16X36 cm) 45 to 52 cm Adult thigh (16X42 cm) widths
Webinar Logistics. Now What Do I Need To Do? Blood Pressure in Kids January NC Department of Health and Human Services Division of Public Health
 NC Department of Health and Human Services Division of Public Health Now What Do I Need To Do? Blood Pressure in Kids January 2018 Gerri Mattson, MD, MSPH, FAAP Pediatric Medical Consultant Children and
NC Department of Health and Human Services Division of Public Health Now What Do I Need To Do? Blood Pressure in Kids January 2018 Gerri Mattson, MD, MSPH, FAAP Pediatric Medical Consultant Children and
science-u.org What affects blood Blood Pressure Directions You Will Need BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME Minutes
 What affects blood pressure? BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME 25-60 Minutes You Will Need Sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff) Stethoscope Blood pressure cuffs and stethoscopes can be found online
What affects blood pressure? BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME 25-60 Minutes You Will Need Sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff) Stethoscope Blood pressure cuffs and stethoscopes can be found online
Childhood obesity and blood pressure: back to the future?
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Pediatrics Faculty Papers Department of Pediatrics 11-1-2011 Childhood obesity and blood pressure: back to the future? Bonita Falkner
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Pediatrics Faculty Papers Department of Pediatrics 11-1-2011 Childhood obesity and blood pressure: back to the future? Bonita Falkner
Blood Pressure LIMBO How Low To Go?
 Blood Pressure LIMBO How Low To Go? Joseph L. Kummer, MD, FACC Bryan Heart Spring Conference April 21 st, 2018 Hypertension Epidemiology Over a billion people have hypertension Major cause of morbidity
Blood Pressure LIMBO How Low To Go? Joseph L. Kummer, MD, FACC Bryan Heart Spring Conference April 21 st, 2018 Hypertension Epidemiology Over a billion people have hypertension Major cause of morbidity
LEARNING OUTCOME The students will be able to elicit vital signs correctly on human volunteers/patients
 Vital signs (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, respiratory rate, pain) are physiological parameters that a healthcare professional requires when dealing with patients. Accurate measurement of vital signs
Vital signs (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, respiratory rate, pain) are physiological parameters that a healthcare professional requires when dealing with patients. Accurate measurement of vital signs
LAB: Blood Pressure Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System!
 LAB: Blood Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System! Lab Objectives. At the completion of the lab, you should be able to: measure pulse or heart rate (HR) and respiratory rate (RR);
LAB: Blood Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System! Lab Objectives. At the completion of the lab, you should be able to: measure pulse or heart rate (HR) and respiratory rate (RR);
Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse. City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved
 Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved Course Content: Definition of Blood Pressure Normal Blood Pressure Readings Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved Course Content: Definition of Blood Pressure Normal Blood Pressure Readings Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
Protocol 4: Measuring Blood Pressure
 Zool 430L Protocols Page 8 of 12 Protocol 4: Measuring Blood Pressure 4.1 Via Auscultation (listening through stethoscope) The estimate of blood pressure is obtained by cutting off blood flow with a known
Zool 430L Protocols Page 8 of 12 Protocol 4: Measuring Blood Pressure 4.1 Via Auscultation (listening through stethoscope) The estimate of blood pressure is obtained by cutting off blood flow with a known
Association of BMI on Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure In Normal and Obese Children
 Association of BMI on Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure In Normal and Obese Children Gundogdu Z 1 1Specialist in child and health diseases, Kocaeli Metropolitan Municipality Maternity and Children
Association of BMI on Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure In Normal and Obese Children Gundogdu Z 1 1Specialist in child and health diseases, Kocaeli Metropolitan Municipality Maternity and Children
Adolescent Hypertension Roles of obesity and hyperuricemia. Daniel Landau, MD Pediatrics, Soroka University Medical Center
 Adolescent Hypertension Roles of obesity and hyperuricemia Daniel Landau, MD Pediatrics, Soroka University Medical Center Blood Pressure Tables BP standards based on sex, age, and height provide a precise
Adolescent Hypertension Roles of obesity and hyperuricemia Daniel Landau, MD Pediatrics, Soroka University Medical Center Blood Pressure Tables BP standards based on sex, age, and height provide a precise
We have recently published blood pressure (BP) percentiles
 Blood Pressure Differences by Ethnic Group Among United States Children and Adolescents Bernard Rosner, Nancy Cook, Ron Portman, Steve Daniels, Bonita Falkner Abstract Large differences in blood pressure
Blood Pressure Differences by Ethnic Group Among United States Children and Adolescents Bernard Rosner, Nancy Cook, Ron Portman, Steve Daniels, Bonita Falkner Abstract Large differences in blood pressure
HOW CONSISTENT ARE THE BLOOD PRESSURE AND PULSE RATE MEASUREMENTS OF THE ELECTRONIC BP APPARATUS AND THE MANUAL SPHYGMOMANOMETER
 HOW CONSISTENT ARE THE BLOOD PRESSURE AND PULSE RATE MEASUREMENTS OF THE ELECTRONIC BP APPARATUS AND THE MANUAL SPHYGMOMANOMETER Naser KA. Teaching Hospital Peradeniya, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka Zawahir S
HOW CONSISTENT ARE THE BLOOD PRESSURE AND PULSE RATE MEASUREMENTS OF THE ELECTRONIC BP APPARATUS AND THE MANUAL SPHYGMOMANOMETER Naser KA. Teaching Hospital Peradeniya, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka Zawahir S
High-Normal Blood Pressure Progression to Hypertension in the Framingham Heart Study
 22 High- Blood Pressure Progression to Hypertension in the Framingham Heart Study Mark Leitschuh, L. Adrienne Cupples, William Kannel, David Gagnon, and Aram Chobanian This study sought to determine if
22 High- Blood Pressure Progression to Hypertension in the Framingham Heart Study Mark Leitschuh, L. Adrienne Cupples, William Kannel, David Gagnon, and Aram Chobanian This study sought to determine if
Hands on Sports Therapy KNOWLEDGE REVIEW QUESTIONS 2004 Thomson Learning It can help to shape a basic fitness training programme
 Hands on Sports Therapy KNOWLEDGE REVIEW QUESTIONS 2004 Thomson Learning 1 CHAPTER 13 Knowledge Review Q1: Why is fitness testing useful? A1: Fitness testing is useful for various reasons: 1. It can help
Hands on Sports Therapy KNOWLEDGE REVIEW QUESTIONS 2004 Thomson Learning 1 CHAPTER 13 Knowledge Review Q1: Why is fitness testing useful? A1: Fitness testing is useful for various reasons: 1. It can help
For instance, it can harden the arteries, decreasing the flow of blood and oxygen to the heart. This reduced flow can cause
 High Blood Pressure Blood pressure is the force of blood against your artery walls as it circulates through your body. Blood pressure normally rises and falls throughout the day, but it can cause health
High Blood Pressure Blood pressure is the force of blood against your artery walls as it circulates through your body. Blood pressure normally rises and falls throughout the day, but it can cause health
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease in suburban population of 3 municipalities in Nepal
 Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease in suburban population of 3 municipalities in Nepal Koju R, Gurung R, Pant P, Humagain S, Yogol CM, Koju A, Manandhar K, Karmacharya B, Bedi TRS Address for Correspondence:
Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease in suburban population of 3 municipalities in Nepal Koju R, Gurung R, Pant P, Humagain S, Yogol CM, Koju A, Manandhar K, Karmacharya B, Bedi TRS Address for Correspondence:
Vital Signs. Vital Signs. Pulse. Temperature. Respiration. Blood Pressure
 Vital Signs Jarvis, Chapter 9 Vital Signs Classic Vital Signs TPR/BP Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood Pressure Additional Vital Signs Height Weight BMI (Kg/m2) or (702Xlbs/in2) Supine, orthostatic
Vital Signs Jarvis, Chapter 9 Vital Signs Classic Vital Signs TPR/BP Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood Pressure Additional Vital Signs Height Weight BMI (Kg/m2) or (702Xlbs/in2) Supine, orthostatic
CAMOSUN COLLEGE BIOLOGY 144 (2010) LABS
 LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
AFFORDABLE TECHNOLOGY
 World Health Organization AFFORDABLE TECHNOLOGY BLOOD PRESSURE MEASURING DEVICES FOR LOW RESOURCE SETTINGS CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Blood Pressure Measurement in Low Resource Settings Annex 1: Blood Pressure
World Health Organization AFFORDABLE TECHNOLOGY BLOOD PRESSURE MEASURING DEVICES FOR LOW RESOURCE SETTINGS CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Blood Pressure Measurement in Low Resource Settings Annex 1: Blood Pressure
Children with Hypertension in ED
 Children with Hypertension in ED By Prof. Sanaa AK Helmy Professor of Anesthesia, Intensive Care and Pain Management, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University Vice-chairman of the Egyptian Society of Emergency
Children with Hypertension in ED By Prof. Sanaa AK Helmy Professor of Anesthesia, Intensive Care and Pain Management, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University Vice-chairman of the Egyptian Society of Emergency
The relationship between BMI and blood pressure in school-age children in Izmir, Turkey
 Progress in Nutrition 2018; Vol. 20, N. 3: 372-377 DOI: 10.23751/pn.v20i3.6079 Mattioli 1885 Original article The relationship between BMI and blood pressure in school-age children in Izmir, Turkey Meryem
Progress in Nutrition 2018; Vol. 20, N. 3: 372-377 DOI: 10.23751/pn.v20i3.6079 Mattioli 1885 Original article The relationship between BMI and blood pressure in school-age children in Izmir, Turkey Meryem
Thesis for doctoral degree (Ph.D.) 2008 ROLE OF AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING AFTER PEDIATRIC RENAL TRANSPLANTATION Rafael Tomás Krmar
 Thesis for doctoral degree (Ph.D.) 2008 Thesis for doctoral degree (Ph.D.) 2008 ROLE OF AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING AFTER PEDIATRIC RENAL TRANSPLANTATION Rafael Tomás Krmar ROLE OF AMBULATORY
Thesis for doctoral degree (Ph.D.) 2008 Thesis for doctoral degree (Ph.D.) 2008 ROLE OF AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING AFTER PEDIATRIC RENAL TRANSPLANTATION Rafael Tomás Krmar ROLE OF AMBULATORY
Body mass index, allergic rhinitis and asthma in children
 Original Articles Body mass index, allergic rhinitis and asthma in children M A M Fernando 1, P H R S Senathilake 2, B J C Perera 3 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2004; 33: 102-5 (Key words: Body mass
Original Articles Body mass index, allergic rhinitis and asthma in children M A M Fernando 1, P H R S Senathilake 2, B J C Perera 3 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2004; 33: 102-5 (Key words: Body mass
Validation of the SEJOY BP-1307 upper arm blood pressure monitor for home. blood pressure monitoring according to the European Society of Hypertension
 Validation of the SEJOY BP-1307 upper arm blood pressure monitor for home blood pressure monitoring according to the European Society of Hypertension International Protocol revision 2010 Short title: Validation
Validation of the SEJOY BP-1307 upper arm blood pressure monitor for home blood pressure monitoring according to the European Society of Hypertension International Protocol revision 2010 Short title: Validation
Blood Pressure Measurement During Pregnancy: Auscultatory Versus Oscillatory Methods
 CLINICAL STUDIES Blood Pressure Measurement During Pregnancy: Auscultatory Versus Oscillatory Methods Linda A. Green, RN, MS, Robin D. Froman, RN, PhD, FAAN Objective: To determine the equivalence of auscultatory
CLINICAL STUDIES Blood Pressure Measurement During Pregnancy: Auscultatory Versus Oscillatory Methods Linda A. Green, RN, MS, Robin D. Froman, RN, PhD, FAAN Objective: To determine the equivalence of auscultatory
Inclusion Criteria: 3 years of age and have had at least 2 visits in the last year Exclusion Criteria: BMI 85 th percentile
 Inclusion Criteria: 3 years of age and have had at least 2 visits in the last year Exclusion Criteria: BMI 85 th percentile Document the Measurement of Blood Pressure (BP) 90% of patients diagnosed with
Inclusion Criteria: 3 years of age and have had at least 2 visits in the last year Exclusion Criteria: BMI 85 th percentile Document the Measurement of Blood Pressure (BP) 90% of patients diagnosed with
Lessons from conducting research in an American Indian community: The Pima Indians of Arizona
 Lessons from conducting research in an American Indian community: The Pima Indians of Arizona Peter H. Bennett, M.B., F.R.C.P. Scientist Emeritus National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney
Lessons from conducting research in an American Indian community: The Pima Indians of Arizona Peter H. Bennett, M.B., F.R.C.P. Scientist Emeritus National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney
UCLA Nutrition Bytes. Title. Permalink. Journal ISSN. Author. Publication Date. Calcium and Hypertension. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/68b658ss
 UCLA Nutrition Bytes Title Calcium and Hypertension Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/68b658ss Journal Nutrition Bytes, 4(2) ISSN 1548-601X Author Martinez, Christina Publication Date 1998-01-01
UCLA Nutrition Bytes Title Calcium and Hypertension Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/68b658ss Journal Nutrition Bytes, 4(2) ISSN 1548-601X Author Martinez, Christina Publication Date 1998-01-01
and bias, which are known to be present in self-home and in professional office BP measurements taken using the auscultatory technique [7].
![and bias, which are known to be present in self-home and in professional office BP measurements taken using the auscultatory technique [7]. and bias, which are known to be present in self-home and in professional office BP measurements taken using the auscultatory technique [7].](/thumbs/86/94636218.jpg) Devices and technology 37 Validation of the A&D UM-11 professional hybrid device for office blood pressure measurement according to the International Protocol George S. Stergiou, Periklis P. Giovas, Charilaos
Devices and technology 37 Validation of the A&D UM-11 professional hybrid device for office blood pressure measurement according to the International Protocol George S. Stergiou, Periklis P. Giovas, Charilaos
Essential Hypertension
 Essential Hypertension Introduction Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common condition that affects 1 out of every 3 adults. Hypertension is also called the Silent Killer because it often has
Essential Hypertension Introduction Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common condition that affects 1 out of every 3 adults. Hypertension is also called the Silent Killer because it often has
Dr Doris M. W Kinuthia
 Dr Doris M. W Kinuthia Objectives Normal blood pressures in children Measurement of blood pressure in children Aetiology of Hypertension in children Evaluation of children with hypertension Treatment of
Dr Doris M. W Kinuthia Objectives Normal blood pressures in children Measurement of blood pressure in children Aetiology of Hypertension in children Evaluation of children with hypertension Treatment of
Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Registered in Primary Health Care in Bahrain
 Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Page 1 of 10 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.25, No.1, March 2003 Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Registered in Primary
Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Page 1 of 10 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.25, No.1, March 2003 Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Registered in Primary
Blood pressure charts for pediatrics
 Blood pressure charts for pediatrics Blood pressure screening is essential throughout life. Adult blood pressure assessments have static thresholds of 140/90 for hypertension and 90/60 for hypotension
Blood pressure charts for pediatrics Blood pressure screening is essential throughout life. Adult blood pressure assessments have static thresholds of 140/90 for hypertension and 90/60 for hypotension
Techniques of Vital Signs. John Gazewood, MD, MSPH Department of Family Medicine
 Techniques of Vital Signs John Gazewood, MD, MSPH Department of Family Medicine Objectives Define normal in several ways. Describe correct technique of measuring vital signs. Describe correct technique
Techniques of Vital Signs John Gazewood, MD, MSPH Department of Family Medicine Objectives Define normal in several ways. Describe correct technique of measuring vital signs. Describe correct technique
Importance of Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Adolescents
 Importance of Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Adolescents Josep Redon, MD, PhD, FAHA Internal Medicine Hospital Clinico Universitario de Valencia University of Valencia CIBERObn Instituto de Salud
Importance of Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Adolescents Josep Redon, MD, PhD, FAHA Internal Medicine Hospital Clinico Universitario de Valencia University of Valencia CIBERObn Instituto de Salud
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE IS AN EStablished
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Trends in Blood Pressure Among Children and Adolescents Paul Muntner, PhD Jiang He, MD, PhD Jeffrey A. Cutler, MD Rachel P. Wildman, PhD Paul K. Whelton, MD, MSc HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Trends in Blood Pressure Among Children and Adolescents Paul Muntner, PhD Jiang He, MD, PhD Jeffrey A. Cutler, MD Rachel P. Wildman, PhD Paul K. Whelton, MD, MSc HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE
Prevalence of Pre Hypertension Among the Women Aged Years in Coastal and Non Coastal Areas
 2016 IJSRST Volume 2 Issue 5 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X Themed Section: Science and Technology Prevalence of Pre Hypertension Among the Women Aged 20-60 Years in Coastal and Non Coastal
2016 IJSRST Volume 2 Issue 5 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X Themed Section: Science and Technology Prevalence of Pre Hypertension Among the Women Aged 20-60 Years in Coastal and Non Coastal
The Fourth Report on the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents
 National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents The Fourth Report on the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure in Children
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents The Fourth Report on the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure in Children
In this activity, you will learn and practice many of the techniques used in the health/ medical profession for assessing a patient's cardiac health.
 Cardiac Vital Measurement Lab In this activity, you will learn and practice many of the techniques used in the health/ medical profession for assessing a patient's cardiac health. 1 By now you should know
Cardiac Vital Measurement Lab In this activity, you will learn and practice many of the techniques used in the health/ medical profession for assessing a patient's cardiac health. 1 By now you should know
Comparison of arbitrary definitions of circadian time periods with those determined by wrist actigraphy in analysis of ABPM data
 Journal of Human Hypertension (1999) 13, 449 453 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of arbitrary definitions of
Journal of Human Hypertension (1999) 13, 449 453 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of arbitrary definitions of
Primary hypertension in adults
 Primary hypertension in adults NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised Hypertension Welcome NICE published an updated guideline on the diagnosis
Primary hypertension in adults NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised Hypertension Welcome NICE published an updated guideline on the diagnosis
Physiology lecture 15 Hemodynamic
 Physiology lecture 15 Hemodynamic Dispensability (D) : proportional change in volume per unit change in pressure D = V/ P*V It is proportional (divided by the original volume). Compliance (C) : total change
Physiology lecture 15 Hemodynamic Dispensability (D) : proportional change in volume per unit change in pressure D = V/ P*V It is proportional (divided by the original volume). Compliance (C) : total change
Importance Of Taking Manual Blood Pressure In Both Arms
 Importance Of Taking Manual Blood Pressure In Both Arms Its importance to health is now well-recognised, in that high blood pressure can lead to Have a look at our slide show on how to take a blood pressure
Importance Of Taking Manual Blood Pressure In Both Arms Its importance to health is now well-recognised, in that high blood pressure can lead to Have a look at our slide show on how to take a blood pressure
HYPERTENSION: ARE WE GOING TOO LOW?
 HYPERTENSION: ARE WE GOING TOO LOW? George L. Bakris, M.D.,F.A.S.N.,F.A.S.H., F.A.H.A. Professor of Medicine Director, ASH Comprehensive Hypertension Center University of Chicago Medicine Chicago, IL USA
HYPERTENSION: ARE WE GOING TOO LOW? George L. Bakris, M.D.,F.A.S.N.,F.A.S.H., F.A.H.A. Professor of Medicine Director, ASH Comprehensive Hypertension Center University of Chicago Medicine Chicago, IL USA
From the desk of the: THE VIRTUAL NEPHROLOGIST
 Hypertension, also referred to as high blood pressure or HTN, is a medical condition in which the blood pressure is chronically elevated. It is a very common illness. One out of three American adults has
Hypertension, also referred to as high blood pressure or HTN, is a medical condition in which the blood pressure is chronically elevated. It is a very common illness. One out of three American adults has
Blood Pressure Screening of School Children in a Multiracial School District: The Healthy Kids Project
 nature publishing group BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS Blood Pressure Screening of School Children in a Multiracial School District: The Healthy Kids Project William E. Moore 1,2, June E. Eichner 1,2, Eve M. Cohn
nature publishing group BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS Blood Pressure Screening of School Children in a Multiracial School District: The Healthy Kids Project William E. Moore 1,2, June E. Eichner 1,2, Eve M. Cohn
Dr Diana R Holdright. MD, FRCP, FESC, FACC, MBBS, DA, BSc. Consultant Cardiologist HYPERTENSION.
 Dr Diana R Holdright MD, FRCP, FESC, FACC, MBBS, DA, BSc. Consultant Cardiologist HYPERTENSION www.drholdright.co.uk Blood pressure is the pressure exerted on the walls of the arteries when the heart pumps;
Dr Diana R Holdright MD, FRCP, FESC, FACC, MBBS, DA, BSc. Consultant Cardiologist HYPERTENSION www.drholdright.co.uk Blood pressure is the pressure exerted on the walls of the arteries when the heart pumps;
Clinical Recommendations: Patients with Periodontitis
 The American Journal of Cardiology and Journal of Periodontology Editors' Consensus: Periodontitis and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Friedewald VE, Kornman KS, Beck JD, et al. J Periodontol 2009;
The American Journal of Cardiology and Journal of Periodontology Editors' Consensus: Periodontitis and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Friedewald VE, Kornman KS, Beck JD, et al. J Periodontol 2009;
How To Measure Vital Signs
 How To Measure Vital Signs How to Use This Tutorial This tutorial is intended for healthcare providers or students to teach basic vital signs skills Use the navigation buttons below to move through the
How To Measure Vital Signs How to Use This Tutorial This tutorial is intended for healthcare providers or students to teach basic vital signs skills Use the navigation buttons below to move through the
Slide notes: References:
 1 2 3 Cut-off values for the definition of hypertension are systolic blood pressure (SBP) 135 and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) 85 mmhg for home blood pressure monitoring (HBPM) and daytime ambulatory
1 2 3 Cut-off values for the definition of hypertension are systolic blood pressure (SBP) 135 and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) 85 mmhg for home blood pressure monitoring (HBPM) and daytime ambulatory
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUG THERAPY IN CONSIDERATION OF CIRCADIAN BLOOD PRESSURE VARIATION*
 Progress in Clinical Medicine 1 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUG THERAPY IN CONSIDERATION OF CIRCADIAN BLOOD PRESSURE VARIATION* Keishi ABE** Asian Med. J. 44(2): 83 90, 2001 Abstract: J-MUBA was a large-scale clinical
Progress in Clinical Medicine 1 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUG THERAPY IN CONSIDERATION OF CIRCADIAN BLOOD PRESSURE VARIATION* Keishi ABE** Asian Med. J. 44(2): 83 90, 2001 Abstract: J-MUBA was a large-scale clinical
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease remains the leading
 AHA Scientific Statement American Heart Association Guidelines for Primary Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Beginning in Childhood Rae-Ellen W. Kavey, MD; Stephen R. Daniels, MD, PhD;
AHA Scientific Statement American Heart Association Guidelines for Primary Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Beginning in Childhood Rae-Ellen W. Kavey, MD; Stephen R. Daniels, MD, PhD;
Prognostic significance of blood pressure measured in the office, at home and during ambulatory monitoring in older patients in general practice
 (2005) 19, 801 807 & 2005 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic significance of blood pressure measured in the office, at home and
(2005) 19, 801 807 & 2005 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic significance of blood pressure measured in the office, at home and
Hypertension awareness, treatment, and control
 O r i g i n a l P a p e r Prevalence of Self-Reported High Blood Pressure Awareness, Advice Received From Health Professionals, and Actions Taken to Reduce High Blood Pressure Among US Adults Healthstyles
O r i g i n a l P a p e r Prevalence of Self-Reported High Blood Pressure Awareness, Advice Received From Health Professionals, and Actions Taken to Reduce High Blood Pressure Among US Adults Healthstyles
HYPERTENSION, WITH AN ESTImated
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Underdiagnosis of Hypertension in Children and Adolescents Matthew L. Hansen, MD Paul W. Gunn, BS David C. Kaelber, MD, PhD HYPERTENSION, WITH AN ESTImated prevalence of between 2%
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Underdiagnosis of Hypertension in Children and Adolescents Matthew L. Hansen, MD Paul W. Gunn, BS David C. Kaelber, MD, PhD HYPERTENSION, WITH AN ESTImated prevalence of between 2%
UPPER BODY FAT MARKER: AN USEFUL SCREENING TOOL OF HYPERTENSIVE RISK IN SCHOOL GOING ADOLESCENT BOYS
 wjpmr, 2017,3(11), 94-98 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.103 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.wjpmr.com Research Article ISSN 2455-3301 WJPMR UPPER BODY FAT MARKER: AN USEFUL SCREENING TOOL
wjpmr, 2017,3(11), 94-98 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.103 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.wjpmr.com Research Article ISSN 2455-3301 WJPMR UPPER BODY FAT MARKER: AN USEFUL SCREENING TOOL
How Low Do We Go? Update on Hypertension
 How Low Do We Go? Update on Beth L. Abramson, MD, FRCPC, FACC As presented at the University of Toronto s Saturday at the University Session (September 2003) Arecent World Health Organization report states
How Low Do We Go? Update on Beth L. Abramson, MD, FRCPC, FACC As presented at the University of Toronto s Saturday at the University Session (September 2003) Arecent World Health Organization report states
2. Measure a subject's blood pressure and heart rate both at rest and during exercise.
 Lab Activity 11 The Cardiovascular System Student Learning Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Define, explain and correctly use the key terms. 2. Measure a subject's blood
Lab Activity 11 The Cardiovascular System Student Learning Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Define, explain and correctly use the key terms. 2. Measure a subject's blood
CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION
 CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION 3.1 BACKGROUND Diabetes mellitus (DM) and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) have reached epidemic proportions
CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION 3.1 BACKGROUND Diabetes mellitus (DM) and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) have reached epidemic proportions
