Evaluation of KIM-1 and NGAL as Early Indicators for Assessment of Gentamycin- Induced Nephrotoxicity In Vivo and In Vitro
|
|
|
- Harold Boyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2016 The Author(s) Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published by S. Karger AG, Basel Luo Accepted: et al.: Evaluation October 10, of 2016 Tissue KIM-1 and NGAL As Nephrotoxicity Biomarkers This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND) ( Usage and distribution for commercial purposes as well as any distribution of modified material requires written permission. Original Paper Evaluation of KIM-1 and NGAL as Early Indicators for Assessment of Gentamycin- Induced Nephrotoxicity In Vivo and In Vitro Qi-Hui Luo Meng-Lu Chen Zheng-Li Chen Chao Huang An-Chun Cheng Jing Fang Li Tang Yi Geng Key Laboratory of Animal Disease and Human Health of Sichuan Province, College of Veterinary Medicine, Sichuan Agricultural University, Chengdu, Sichuan , China Key Words Gentamycin Nephrotoxicity KIM-1 NGAL HK-2 cells Abstract Background/Aims: The aminolycoside Gentamicin is a widely used antibiotic, applied in equine medicine. Despite its clinical use, concerns remain regarding the potential toxic side-effects, such as nephrotoxicity. Early detection of renal damage is critical in preclinical drug development. This study was aimed to determine whether kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) may be early indicators in the assessment of Gentamycin-induced nephrotoxicity. Methods: In our study, a model of Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in male Sprague Dawley rats treated for up to 7 days at 50 or 100mg/kg/day was used to monitor the expressions of novel biomarkers of renal toxicity during the progression of acute kidney injury (AKI). Additionally, biomarkers were assessed in human kidney proximal epithelial cells (HK-2) treated with Gentamicin for 2, 6, 12, 24, 36 or 48h in vitro. Results: Repeated administration of Gentamicin to rats for 1, 3, or 7 days resulted in a dose- and time-dependent increase in the expression of KIM-1 and NGAL. The expressions of the two biomarkers changed prior to renal tubule damage and increases in serum creatinine (SCr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels, suggesting their usefulness for predicting Gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) in vivo. Conclusions: In contrast, no significant increase in the expression of the biomarker genes and proteins were evident in HK-2 cells after treated by Gentamycin for up to 48h, suggesting that they may not be suitable endpoints for sensitive detection of nephrotoxic effects in vitro The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel Qi-Hui Luoand Meng-Lu Chen contributed equally to this work and therefore share first authorship. Zheng-li Chen Key Laboratory of Animal Disease and Human Health of Sichuan Province, College of Veterinary Medicine, Sichuan Agricultural University, NO.211 Huiming road, Wenjiang, Chengdu, Sichuan (China), Tel , Fax , chzhli75@163.com
2 912 Introduction More than 50 years since their introduction, aminoglycosides have represented highly effective antimicrobial agents especially in Gram-negative infections despite nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. An understanding of the antibiotic s nephrotoxicity therefore has substantial clinical significance [1]. But early detection of renal damage is difficult. The monitoring of patients in clinical trials was primarily based on serum creatinine (SCr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and the detection of urinary components like electrolytes, enzymes, and other waste products [2]. Owing to the poor sensitivity and specificity of these traditional markers of renal injury, new indicators for earlier and more accurate detection are needed, and to aid in predictive safety assessment during drug development [2, 3]. Many protein products might serve as novel biomarkers for the initiation phase of AKI have been studied, including kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), Neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) and others [4-6]. KIM-1 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein which is undetectable in healthy kidneys. The increased expression of this protein was found at very high levels on the apical membrane of proximal tubule cells after ischemic and nephrotoxic injury [7]. Urinary KIM-1 outperforms SCr, BUN and urinary NAG in multiple rat models of kidney injury and may facilitate sensitive, specific and accurate prediction of human nephrotoxicity in preclinical drug SCreens [8]. NGAL, also known as lipocalin-2, was found in activated neutrophils, in accordance with its role as an innate antibacterial factor [9]. NGAL may eventually have prognostic value in predicting not only acute, but also chronic, worsening in renal function in patients already affected by chronic nephropathies [10]. However, the ability of the two putative biomarkers of nephrotoxicity to indicate or even predict mild histopathological changes following exposure to aminoglycosides still needs to be evaluated. In this study, we investigated the expressions of KIM-1 and NGAL in rats treated with Gentamicin for up to 7 days. Although the majority of toxicological investigations have been performed in vivo experiments using animals, the use of non-animal in vitro test methods which have become invaluable tools can provide important information on the mechanism of toxicity [11]. We therefore investigated the effects of Gentamicin on novel kidney biomarkers in stable HK-2 cells for up to 48h. The principal goal was to determine if changes in the expression of the newly identified biomarkers correlate with the progressive damage to the kidney as evidenced by histopathology and might even precede traditional endpoints of nephrotoxicity. Materials And Methods Animals and Cells Male Sprague-Dawley rats ( g) were housed under conditions of 23 ± 2 C and 40 70% relative humidity at all times in an alternating 12 h light-dark cycle. All experiments were conducted according to the Guidelines for Animal Experiments. Gentamicin sulfate (Sichuan Changzheng pharmaceutical co., Ltd, Chengdu, China) was intravenously administered at 0, 50 or 100 mg/kg/d (n = 5 rats/dose group/time point) and the animals were necropsied on days 1, 3 or 7 for toxicity evaluation. HK-2 cells were cultured in DMEM medium with 10% fetal bovine serum, stored in a humidified incubator (95% air with 5% CO 2 ) at 37 C. Gentamicin was diluted with cell culture medium to reach the desired concentrations (100μg/ml). Gene expressions were detected at various time points (2hr, 6hr, 12hr, 24hr, 36hr and 48hr). Blood chemistry Rats were fasted overnight before necropsy and bled from the abdominal aorta with 3 ml collected into serum separator tubes and centrifuged 1,500g for 10 min at 4 C. Isolated plasma and serum samples were stored at 80 C until use. SCr and BUN were measured using a standard clinical chemistry analyzer.
3 913 Table 1. Sequence of Forward and Reverse Primers for Real-Time PCR Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry After fixation in 4% paraformaldehyde for 48h, the kidneys were rinsed in tap water, dehydrated in a graded alcohol series, embedded in paraffin, and cut into 5μm thick sections. The paraffin sections were processed for hematoxylin eosin staining and immunohistochemistry. Detections of biomarkers were used rabbit anti-kim-1/tim-1 (Abcam, USA) and rabbit anti-ngal/lcn2 (Millipore, USA). Sections were incubated with biotinylated secondary antibody (mouse anti-rabbit, Invitrogen, USA) and following incubation with Streptavidin Peroxidase conjugate (Invitrogen, USA), peroxidase activity was visualized using AEC/DAB substrate-chromogen mixture (Invitrogen, USA). Quantitative Realtime PCR RNA was isolated from kidney tissue or cell samples using the Total RNA Extractor Kit (Sangon Biotech Co.,Ltd. Shanghai, China) and further purified using the RNeasy Kit (Takara, Dalian, China) including DNase treatment. RNA integrity was confirmed by 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis and the concertation was measured by spectrophotometry measuring the absorbance at 260 nm and 280nm. Complimentary DNA (cdna) was synthesized from 1μg RNA using the Prime SCript RT reagent Kit (Takara, Dalian, China). Quantitative real-time PCR was performed using the Bio-rad CFX96 Sequence Detection System in 25-μl reactions containing 2 mastermix with SYBR Green I, 2μl of cdna and 0.5μl of each primer. Amplification was carried out using the following temperature profile: 3 min enzyme activation at 95 C, followed by 40 cycles of 95 C for 10s, 60 C for 30s, and 72 C for 10s. Primer sequences are shown in Table 1. PCR product formation was determined by measuring the fluorescence signal emitted by the incorporation of SYBR Green I. Gene expression changes relative to untreated controls were determined by the 2 - Ct method. Statistical analysis Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA and Dunnett s test using the SPSS 19.0 software (USA). Values significantly different from control are indicated as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < Results In Vivo Study After the single intravenous administration of Gentamicin at 50mg/kg and 100mg/kg, traditional biomarkers for nephrotoxicity, SCr and BUN levels, and kidney histopathology were examined on Days 1, 3 and 7. No noteworthy findings were recorded in the control group at any time point. SCr and BUN levels were significantly increased on Day 7 (Fig.1), which was consistent with the progression of histological damage (Fig.2a). Mild tubular cell vacuolar degenerations were seen treated by 50mg/kg bw Gentamcin (no shown). Tubular cell degenerations, necrosis, tubular dilatation, hyaline cast tubules and inflammation were observed in the distal and proximal tubules in the Gentamicin-treated rats on Day7 (Fig.2a). As previously reported [12, 13], Gentamicin treatment resulted in histopathological changes, depending on dose and treatment time. Consistent with progression of renal damage, KIM-1 and NGAL were undetectable in renal tubules of control kidneys, but they were detected as early as Day1 in kidneys of both low-dose (no shown) and high-dose animals (Fig.2). In the treated animals, an increase
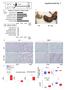
4 914 Fig. 1. Levelsl of SCr and BUN in rats treated with Gentamicin: Data are expressed as 0, 50 or 100 mg/kg bw Gentamicin for 1, 3, and 7 days. Data are presented as mean fold change ± SD compared with control animals (n=5). Statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA and Dunnett s test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Fig. 2. (a)hematoxylin and eosin-stained kidney sections of rats treated with 100mg/kg bw gentamicin for up to 7 days, showing normal renal architecture in control group, slight tubular cell vacuolar degenerations in the proximal tubules 3 days after Gentamicn treatment and tubular cell degeneration, necrosis, tubular dilatation and inflammation observed in the distal and proximal tubules in Gentamicin-treated rats at 7 days. (b) Marked KIM-1 induction in tubules with cellular degeneration in kidneys of rats treated with 100mg/ kg bw Gentamicin for up to 7 days. (c) Treatment with 100mg/kg bw Gentamicin for up to 7 days resulted in NGAL observed at the apical side of distal tubules in the cortex and in the deep OSOM. Original magnification 400. of KIM-1 staining was seen first in the OSOM and cortex at day 1, occurred in epithelial cells of S3 tubules that were affected by Gentamicin toxicity as seen by cell degeneration and regeneration. Its intensity and extent increased with the treatment duration, in close
5 915 Table 2. Changes in Gene Exprission of noval Biomarkers of Nephrotoxicity in HK-2 cells after Treatment with Gentamicn for 2, 6, 12, 24, 36 or 48h Fig. 3. Changes in mrna expression of KIM-1 and NGAL biomarkers of nephrotoxicity in kidneys of SD rats repeatedly dosed with 0, 50 or 100 mg/kg bw Gentamicin for 1, 3, and 7 days. Data are presented as mean fold change ± SD compared with control animals (n=5). Statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA and Dunnett s test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). correlation with the histopathological changes (Fig.2b). NGAL was exclusively detected at the apical side of some distal tubules in the cortex and in the deep OSOM (Fig.2c). Time and dose-related effects on the two biomarkers expressions were observed at the target site of Gentamicin toxicity. Repeated administration of 50 or 100 mg/kg bw Gentamicin to male SD rats resulted in a dose- and time-dependent increase in the expression of genes suggested as candidate biomarkers of renal injury (Fig. 3). Changes in the expression of KIM-1 and NGAL were found to correlate with the progressive histopathological alterations observed in kidneys of Gentamicin-treated animals and preceded changes of clinical parameters indicative of impaired kidney function. Induction of KIM-1 and NGAL gene expressions were the earliest responses of the kidney following Gentamicn treatment, evident as early as Day1 in both low-dose and high-dose animals, where only subtle histopathological changes were observed. Furthermore, the degree of KIM-1 mrna increase in the individual animals was more upregulated in high-dose animals after Gentamicin treated for 7 days (Fig.3C). In Vitro Study In contrast to the significance of biomarkers expression in vivo, treatment of HK-2 cells with 100μg/ml Gentamicin for up to 48h, comapred with controls, did not result in marked changes in the mrna expression of KIM-1 and NGAL (Table 2). Both of the two biomarkers were expressed at low levels in vitro, and no increase in mrna was observed after treatment with Gentamicin.
6 916 Discussion The kidney is one of the routinely assessed organs during preclinical safety evaluations. The present study was designed to assess the value of novel tissue biomarkers for improved detection of kidney injury in rats using the aminoglycoside antibiotic Gentamicin as a model compound [14-16]. Gentamicin may accumulate in epithelial tubular cells causing a range of effects starting with loss of the brush border in epithelial cells and ending in overt tubular necrosis, activation of apoptosis and massive proteolysis which was confirmed in our study. Our data clearly reveal that Gentamicin induced renal injury in all study animals, as reflected by increased tissue KIM-1 and NGAL. We observed upregulation of mrna expression of KIM-1 and NGAL in kidney of rats following treatment with Gentamicin in the absence of effects on traditional clinical chemistry markers of nephrotoxicity. These increases were evident 1 day after treated by Gentamicin and lasted for 3 and 7 days, respectively. Both the time-course and the degree of the response correlated well with the severity of tissue injury. Changes in marker gene expression were subsequently confirmed by immunohistochemistry. Our observations that expression of KIM-1 and NGAL occurs within 1 day after treated by Gentaimcin accept that these two biomarkers reflected renal injury faster and more accurately than SCr and BUN [6, 8]. Changes in the expression of NGAL were one of the earliest effects observed in kidneys of animals treated with 50 or 100 mg/kg bw Gentamicin, occurring at time-points at which had few histopathological changes in epithelial tubular cells were injured evident. As compared with NGAL, the mrna level of KIM-1 was more prominent after treated by Gentamicin for 7 days. Upregulation of the two genes were thought to be associated with proliferation/regeneration and repair in response to toxicity or disease [8, 10], consistent with the histopathological alterations observed following treatment with Gentamicin. An ancillary aim of this study was to determine if the two novel kidney biomarkers might also serve as sensitive endpoints for in vitro toxicity testing. Development of reliable in vitro test systems may contribute to reduction of animal experiments required for drug and chemical safety assessment [11]. It is known that Gentamicin inhibits the activiity of lysosomal phospholipases in proximal tubular epithelial cells. Both in vivo and in vitro studies showed that Gentamicin has enhanced the generation of reactive oxygen metabolities (ROS) [17].Therefore, mrna expressions of KIM-1 and NGAL were studied in HK-2 cells, which may allow rapid screening of large numbers of compounds. However, treatment resulted in only minor alterations in gene expression following exposure to Gentamicin. KIM-1 and NGAL, which were sensitive markers for toxicity in vivo, were not significantly affected by treatment. Similar effects were also observed in Ochratoxin A-treated NRK-52E cells, which was explanted that, in contrast to the kidney, some of the marker genes were already expressed at relatively high levels in vitro [18]. This is supported by the fact that expression of NGAL reported to increase during isolation and cultivation of proximal tubular cells [19]. Both KIM-1 and NGAL were thought to be associated with proliferation/regeneration which may not occur in monolayers of cultured kidney cells in response to a continuous nephrotoxic insult. Thus, it is not feasible to complete replacement of animal studies with Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. However, in vitro assays may still be valuable tools for evaluation some drug s potential nephrotoxicity [20]. This may serve to reduce the need for animal testing, particularly within pharmaceutical industries, because potent nephrotoxins may be excluded from further development and only those candidates showing no effects in vitro may need to be tested in vivo. Measuring these novel biomarkers may enable clinicians to make an early diagnosis of aminoglycosides-induced AKI, which does not evolve into acute renal failure. Support for this notion comes from numerous clinical studies in which plasma KIM-1 and NGAL or urinary excretion of these biomarkers increased a few hours after the induction of AKI of various etiologies, including kidney transplant rejection [21, 22], nephron sparing surgery [23] and nephrotoxic drugs induced nephropathy [24].
7 917 The goal of reducing or protecting against aminoglycosides nephrotoxicity has attracted much effort and attention during the last decade [25-27]. As this research was designed to evaluate novel biomarkers used in Gentamicin-induced early renal injury, we did not study how these markers express after exposure to Gentamicin for a long time. Future investigations are required to not only confirm a potential application of KIM-1 and NGAL as useful biomarkers for such a diagnosis but also as parameters to prevent the development and progression of chronic kidney disease. Conclusion Alterations in the excretion of KIM-1 and NGAL were detected before marked changes in clinical chemistry parameters were evident, providing further support for the use of the two biomarkers as sensitive, mechanistically anchored indicators of Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in vivo. In contract, results from this study do not support their use as reliable endpoints of toxicity in vitro. Disclosure Statement The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Acknowledgement The work is supported by the National Key Scientific Instrument and Equipment Development Project of China (2013YQ ), the National Key Technology R&D Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology (2014BAI03B01). References 1 Ali BH, Abdel Gayoum AA, Bashir AA: Gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rat: Some biochemical correlates. Pharmacol Toxicol 1992;70: Fuchs TC, Hewitt P: Biomarkers for drug-induced renal damage and nephrotoxicity-an overview for applied toxicology. AAPS J 2011;13: Sistare FD, Dieterle F, Troth S, Holder DJ, Gerhold D, Andrews-Cleavenger D, Baer W, Betton G, Bounous D, Carl K, Collins N, Goering P, Goodsaid F, Gu YZ, Guilpin V, Harpur E, Hassan A, Jacobson-Kram D, Kasper P, Laurie D, Lima BS, Maciulaitis R, Mattes W, Maurer G, Obert LA, Ozer J, Papaluca-Amati M, Phillips JA, Pinches M, Schipper MJ, Thompson KL, Vamvakas S, Vidal JM, Vonderscher J, Walker E, Webb C, Yu Y: Towards consensus practices to qualify safety biomarkers for use in early drug development. Nat Biotechnol 2010;28: Ozer JS, Dieterle F, Troth S, Perentes E, Cordier A, Verdes P, Staedtler F, Mahl A, Grenet O, Roth DR, Wahl D, Legay F, Holder D, Erdos Z, Vlasakova K, Jin H, Yu Y, Muniappa N, Forest T, Clouse HK, Reynolds S, Bailey WJ, Thudium DT, Topper MJ, Skopek TR, Sina JF, Glaab WE, Vonderscher J, Maurer G, Chibout SD, Sistare FD, Gerhold DL: A panel of urinary biomarkers to monitor reversibility of renal injury and a serum marker with improved potential to assess renal function. Nat Biotechnol 2010;28: Gardiner L, Akintola A, Chen G, Catania JM, Vaidya V, Burghardt RC, Bonventre JV, Trzeciakowski J, Parrish AR: Structural equation modeling highlights the potential of kim-1 as a biomarker for chronic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol 2012;35: Sinha V, Vence LM, Salahudeen AK: Urinary tubular protein-based biomarkers in the rodent model of cisplatin nephrotoxicity: A comparative analysis of serum creatinine, renal histology, and urinary kim-1,
8 918 ngal, and nag in the initiation, maintenance, and recovery phases of acute kidney injury. J Investig Med 2013;61: Guo L, Takino T, Endo Y, Domoto T, Sato H: Shedding of kidney injury molecule-1 by membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase. J Biochem 2012;152: Vaidya VS, Ozer JS, Dieterle F, Collings FB, Ramirez V, Troth S, Muniappa N, Thudium D, Gerhold D, Holder DJ, Bobadilla NA, Marrer E, Perentes E, Cordier A, Vonderscher J, Maurer G, Goering PL, Sistare FD, Bonventre JV: Kidney injury molecule-1 outperforms traditional biomarkers of kidney injury in preclinical biomarker qualification studies. Nat Biotechnol 2010;28: Zhao C, Ozaeta P, Fishpaugh J, Rupprecht K, Workman R, Grenier F, Ramsay C: Structural characterization of glycoprotein ngal, an early predictive biomarker for acute kidney injury. Carbohydr Res 2010;345: Bolignano D, Donato V, Coppolino G, Campo S, Buemi A, Lacquaniti A, Buemi M: Neutrophil gelatinaseassociated lipocalin (ngal) as a marker of kidney damage. Am J Kidney Dis 2008;52: Broadhead CL, Combes RD: The current status of food additives toxicity testing and the potential for application of the three Rs. Altern Lab Anim 2001;29: Hariprasad G, Kumar M, Rani K, Kaur P, Srinivasan A: Aminoglycoside induced nephrotoxicity: Molecular modeling studies of calreticulin-gentamicin complex. J Mol Model 2012;18: Paragas N, Qiu A, Hollmen M, Nickolas TL, Devarajan P, Barasch J: Ngal-siderocalin in kidney disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012;1823: Sun X, Zhang B, Hong X, Zhang X, Kong X: Histone deacetylase inhibitor, sodium butyrate, attenuates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity by increasing prohibitin protein expression in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2013;707: Zhou Y, Vaidya VS, Brown RP, Zhang J, Rosenzweig BA, Thompson KL, Miller TJ, Bonventre JV, Goering PL: Comparison of kidney injury molecule-1 and other nephrotoxicity biomarkers in urine and kidney following acute exposure to gentamicin, mercury, and chromium. Toxicol Sci 2008;101: Com E, Boitier E, Marchandeau JP, Brandenburg A, Schroeder S, Hoffmann D, Mally A, Gautier JC: Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic evaluation of gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2012;258: Zhipeng W, Li L, Qibing M, Linna L, Yuhua R, Rong Z: Increased expression of heat shock protein (hsp)72 in a human proximal tubular cell line (hk-2) with gentamicin-induced injury. J Toxicol Sci 2006;31: Rached E, Hoffmann D, Blumbach K, Weber K, Dekant W, Mally A: Evaluation of putative biomarkers of nephrotoxicity after exposure to ochratoxin a in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol Sci 2008;103: Weiland C, Ahr HJ, Vohr HW, Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H: Characterization of primary rat proximal tubular cells by gene expression analysis. Toxicol In Vitro 2007;21: Sohn SJ, Kim SY, Kim HS, Chun YJ, Han SY, Kim SH, Moon A: In vitro evaluation of biomarkers for cisplatininduced nephrotoxicity using hk-2 human kidney epithelial cells. Toxicol Lett 2013;217: Zhang PL, Rothblum LI, Han WK, Blasick TM, Potdar S, Bonventre JV: Kidney injury molecule-1 expression in transplant biopsies is a sensitive measure of cell injury. Kidney Int 2008;73: Jin ZK, Tian PX, Wang XZ, Xue WJ, Ding XM, Zheng J, Ding CG, Mao TC, Duan WL, Xi M: Kidney injury molecule-1 and osteopontin: New markers for prediction of early kidney transplant rejection. Mol Immunol 2013;54: Abassi Z, Shalabi A, Sohotnik R, Nativ O, Awad H, Bishara B, Frajewicki V, Sukhotnik I, Abbasi A, Nativ O: Urinary ngal and kim-1: Biomarkers for assessment of acute ischemic kidney injury following nephron sparing surgery. J Urol 2013;189: Vinken P, Starckx S, Barale-Thomas E, Looszova A, Sonee M, Goeminne N, Versmissen L, Buyens K, Lampo A: Tissue kim-1 and urinary clusterin as early indicators of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Toxicol Pathol 2012;40: Ali BH: Agents ameliorating or augmenting experimental gentamicin nephrotoxicity: Some recent research. Food Chem Toxicol 2003;41: Ali BH, Al Za'abi M, Blunden G, Nemmar A: Experimental gentamicin nephrotoxicity and agents that modify it: A mini-review of recent research. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2011;109: Taye A, Ibrahim BM: Activation of renal haeme oxygenase-1 alleviates gentamicin-induced acute nephrotoxicity in rats. J Phar Pharmacol 2013;65:
A panel of urinary biomarkers to monitor reversibility of renal injury and a serum marker with improved potential to assess renal function
 A panel of urinary biomarkers to monitor reversibility of renal injury and a serum marker with improved potential to assess renal function 21 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. Josef S Ozer 1,,7,
A panel of urinary biomarkers to monitor reversibility of renal injury and a serum marker with improved potential to assess renal function 21 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. Josef S Ozer 1,,7,
The NGAL Turbidimetric Immunoassay Reagent Kit
 Antibody and Immunoassay Services Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, University of Hong Kong The NGAL Turbidimetric Immunoassay Reagent Kit Catalogue number: 51300 For the quantitative determination of NGAL
Antibody and Immunoassay Services Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, University of Hong Kong The NGAL Turbidimetric Immunoassay Reagent Kit Catalogue number: 51300 For the quantitative determination of NGAL
changing the diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury
 changing the diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury NGAL NGAL is a novel biomarker for diagnosing acute kidney injury (AKI). The key advantage of NGAL is that it responds earlier than other renal
changing the diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury NGAL NGAL is a novel biomarker for diagnosing acute kidney injury (AKI). The key advantage of NGAL is that it responds earlier than other renal
Research Article. KIM-1 as a biomarker to predict and diagnose Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
 Available online wwwjocprcom Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 216, 8(4):56-61 Research Article ISSN : 975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 KIM-1 as a biomarker to predict and diagnose Acute Kidney
Available online wwwjocprcom Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 216, 8(4):56-61 Research Article ISSN : 975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 KIM-1 as a biomarker to predict and diagnose Acute Kidney
Kidney injury molecule-1 expression is closely associated with renal allograft damage
 Kidney injury molecule-1 expression is closely associated with renal allograft damage Lianlian Song 1,2, Lijuan Xue 1, Jinyu Yu 1, Jun Zhao 1, Wenlan Zhang 1, Yaowen Fu 1 * 1 Urology and Nephrology Center,
Kidney injury molecule-1 expression is closely associated with renal allograft damage Lianlian Song 1,2, Lijuan Xue 1, Jinyu Yu 1, Jun Zhao 1, Wenlan Zhang 1, Yaowen Fu 1 * 1 Urology and Nephrology Center,
Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as a Biomarker of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Morbid Obesity Who Underwent Bariatric Surgery
 Published online: October 31, 213 1664 5529/13/31 11$38./ This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial 3. Unported license (CC BY-NC) (www.karger.com/oa-license),
Published online: October 31, 213 1664 5529/13/31 11$38./ This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial 3. Unported license (CC BY-NC) (www.karger.com/oa-license),
Citation for the original published paper (version of record):
 http://www.diva-portal.org Postprint This is the accepted version of a paper published in Clinical Biochemistry. This paper has been peerreviewed but does not include the final publisher proof-corrections
http://www.diva-portal.org Postprint This is the accepted version of a paper published in Clinical Biochemistry. This paper has been peerreviewed but does not include the final publisher proof-corrections
A08 Using Kidney Biomarkers for AKI 2: Differential Diagnosis, Interventions and Prognosis
 A08 Using Kidney Biomarkers for AKI 2: Differential Diagnosis, Interventions and Prognosis Kent Doi, MD, PhD Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, The Univ of Tokyo, Japan Using kidney biomarkers: Key
A08 Using Kidney Biomarkers for AKI 2: Differential Diagnosis, Interventions and Prognosis Kent Doi, MD, PhD Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, The Univ of Tokyo, Japan Using kidney biomarkers: Key
Biomarkers of renal diseases. By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik
 By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Introduction Renal system performs several functions Excretory Waste products like urea, creatinine, drug, toxins clearance Regulatory Water, electrolyte and acid base balance
By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Introduction Renal system performs several functions Excretory Waste products like urea, creatinine, drug, toxins clearance Regulatory Water, electrolyte and acid base balance
Collaborative Approaches for Developing Kidney Safety Biomarkers
 Collaborative Approaches for Developing Kidney Safety Biomarkers John Michael Sauer, PhD Executive Director of the Predictive Safety Testing Consortium (PSTC) C-Path: A Public-Private Partnership Act as
Collaborative Approaches for Developing Kidney Safety Biomarkers John Michael Sauer, PhD Executive Director of the Predictive Safety Testing Consortium (PSTC) C-Path: A Public-Private Partnership Act as
NGAL, a new markers for acute kidney injury
 NGAL, a new markers for acute kidney injury Prof. J. Delanghe, MD, PhD Dept. Clinical Chemistry Ghent University Lecture Feb 8, 2011 Serum creatinine is an inadequate marker for AKI. > 50% of renal
NGAL, a new markers for acute kidney injury Prof. J. Delanghe, MD, PhD Dept. Clinical Chemistry Ghent University Lecture Feb 8, 2011 Serum creatinine is an inadequate marker for AKI. > 50% of renal
Pharmacogenomics/biomarker consultation
 PMDA's Summary of their Assessment Review of Seven Renal Safety Biomarkers Submitted in August 2010 by the Critical Path Institute's Predictive Safety Testing Consortium (PSTC). Unofficial English translation
PMDA's Summary of their Assessment Review of Seven Renal Safety Biomarkers Submitted in August 2010 by the Critical Path Institute's Predictive Safety Testing Consortium (PSTC). Unofficial English translation
Record of the Consultation on Pharmacogenomics/Biomarkers
 This English version of the record of the consultation has been published by PMDA. In the event of inconsistency between the Japanese original and this English translation, the former shall prevail. (Attachment
This English version of the record of the consultation has been published by PMDA. In the event of inconsistency between the Japanese original and this English translation, the former shall prevail. (Attachment
Biomarkers for the Prevention of Drug Induced AKI (D-AKI)
 Biomarkers for the Prevention of Drug Induced AKI (D-AKI) Sandra Kane-Gill, PharmD, MSc, FCCM, FCCP Associate Professor, University of Pittsburgh Critical Care Medication Safety Pharmacist, UPMC OBJECTIVE
Biomarkers for the Prevention of Drug Induced AKI (D-AKI) Sandra Kane-Gill, PharmD, MSc, FCCM, FCCP Associate Professor, University of Pittsburgh Critical Care Medication Safety Pharmacist, UPMC OBJECTIVE
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/45389 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Meer, L. van Title: Anti sense and sensibility : renal and skin effects of (antisense)
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/45389 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Meer, L. van Title: Anti sense and sensibility : renal and skin effects of (antisense)
Cystatin C (serum, plasma, urine)
 Cystatin C (serum, plasma, urine) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Cystatin C (serum, plasma and urine) 1.2 Alternative names Cystatin 3, post-gamma-globulin, neuroendocrine basic
Cystatin C (serum, plasma, urine) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Cystatin C (serum, plasma and urine) 1.2 Alternative names Cystatin 3, post-gamma-globulin, neuroendocrine basic
Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive
 Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
RENAL FUNCTION BIOMARKERS
 HERNÁN TRIMARCHI HOSPITAL BRITÁNICO DE BUENOS AIRES ARGENTINA 2015 1 DISCLOSURES Served as a consultant and/or has received lecture honoraria from: ALEXION BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB GENZYME NOVARTIS PFIZER
HERNÁN TRIMARCHI HOSPITAL BRITÁNICO DE BUENOS AIRES ARGENTINA 2015 1 DISCLOSURES Served as a consultant and/or has received lecture honoraria from: ALEXION BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB GENZYME NOVARTIS PFIZER
Ellagic acid protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: a dose-dependent study
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2013; 17: 299-310 Ellagic acid protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: a dose-dependent study N. AL-KHARUSI, H.A. BABIKER, S.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2013; 17: 299-310 Ellagic acid protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: a dose-dependent study N. AL-KHARUSI, H.A. BABIKER, S.
Renal Klotho expression in patients with acute kidney injury is associated with the severity of the injury
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2015;30:489-495 Renal Klotho expression in patients with acute kidney injury is associated with the severity of the injury Min Young Seo 1, Jihyun Yang 1, Jun Yong
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2015;30:489-495 Renal Klotho expression in patients with acute kidney injury is associated with the severity of the injury Min Young Seo 1, Jihyun Yang 1, Jun Yong
Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon
 Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011 Epidemiology & Definition Pathophysiology Clinical Studies Management Summary Hobart W. Harris,
Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011 Epidemiology & Definition Pathophysiology Clinical Studies Management Summary Hobart W. Harris,
Outline. Overview of Current Biomarkers in Kidney Disease
 Overview of Current Biomarkers in Kidney Disease Joseph V. Bonventre MD PhD Chief, Renal Division Chief, Biomedical Engineering Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Disclosure:
Overview of Current Biomarkers in Kidney Disease Joseph V. Bonventre MD PhD Chief, Renal Division Chief, Biomedical Engineering Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Disclosure:
COMMITTEE FOR HUMAN MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FINAL REPORT ON THE PILOT JOINT EMEA/FDA VXDS EXPERIENCE ON QUALIFICATION OF NEPHROTOXICITY BIOMARKERS.
 European Medicines Agency Pre-authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 3 July 28 Doc. Ref. EMEA/25885/28 Rev. 1 COMMITTEE FOR HUMAN MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FINAL REPORT ON THE PILOT JOINT
European Medicines Agency Pre-authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 3 July 28 Doc. Ref. EMEA/25885/28 Rev. 1 COMMITTEE FOR HUMAN MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FINAL REPORT ON THE PILOT JOINT
In vivo mechanism study of NGAL in rat renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
 In vivo mechanism study of NGAL in rat renal ischemia-reperfusion injury X.J. Zang 1, S.X. An 2, Z. Feng 1, Y.P. Xia 1, Y. Song 1 and Q. Yu 2 1 Department of Nephrology, Songjiang Branch of the First Affiliated
In vivo mechanism study of NGAL in rat renal ischemia-reperfusion injury X.J. Zang 1, S.X. An 2, Z. Feng 1, Y.P. Xia 1, Y. Song 1 and Q. Yu 2 1 Department of Nephrology, Songjiang Branch of the First Affiliated
HYDRATION & EXERCISE : IMPLICATIONS FOR KIDNEY HEALTH
 64 TH AMERICAN COLLEGE OF SPORTS MEDICINE ANNUAL MEETING HYDRATION & EXERCISE : IMPLICATIONS FOR KIDNEY HEALTH May 31 st 5.30pm-7.00pm Room 103 Colorado Convention Center Denver AGENDA Session chaired
64 TH AMERICAN COLLEGE OF SPORTS MEDICINE ANNUAL MEETING HYDRATION & EXERCISE : IMPLICATIONS FOR KIDNEY HEALTH May 31 st 5.30pm-7.00pm Room 103 Colorado Convention Center Denver AGENDA Session chaired
Urinary kidney injury molecule 1 as an early diagnostic biomarker of obstructive acute kidney injury and development of a rapid detection method
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 15: 1229-1235, 2017 Urinary kidney injury molecule 1 as an early diagnostic biomarker of obstructive acute kidney injury and development of a rapid detection method YINGLI JIN
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 15: 1229-1235, 2017 Urinary kidney injury molecule 1 as an early diagnostic biomarker of obstructive acute kidney injury and development of a rapid detection method YINGLI JIN
Enzymuria determination in children treated with aminoglycosides drugs
 Human & Experimental Toxicology (2008) 27: 879 882 www.het.sagepub.com treated with aminoglycosides drugs A Mohammadi-Karakani 1,2, S Asgharzadeh-Haghighi 1, M Ghazi-Khansari 2, A Seyed-Ebrahimi 1, A Ghasemi
Human & Experimental Toxicology (2008) 27: 879 882 www.het.sagepub.com treated with aminoglycosides drugs A Mohammadi-Karakani 1,2, S Asgharzadeh-Haghighi 1, M Ghazi-Khansari 2, A Seyed-Ebrahimi 1, A Ghasemi
SAFE-T consortium. DIKI BM Summary Data Package. Novel clinical biomarkers of Drug-Induced Kidney Injury
 1 SAFE-T consortium Summary Data Package Novel clinical biomarkers of Drug-Induced Kidney Injury The Drug induced kidney injury work package of Innovative Medicines Initiative SAFE-T Consortium Document
1 SAFE-T consortium Summary Data Package Novel clinical biomarkers of Drug-Induced Kidney Injury The Drug induced kidney injury work package of Innovative Medicines Initiative SAFE-T Consortium Document
Supporting Information For
 Supporting Information For MicroRNA-Catalyzed Cancer Therapeutics Based on DNA-Programmed Nanoparticle Complex Xucheng Luo, 1 Zhi Li, 1 Ganglin Wang, 1 Xuewen He, 2,3 Xiaoqin Shen, 1 Quanhong Sun, 1 Li
Supporting Information For MicroRNA-Catalyzed Cancer Therapeutics Based on DNA-Programmed Nanoparticle Complex Xucheng Luo, 1 Zhi Li, 1 Ganglin Wang, 1 Xuewen He, 2,3 Xiaoqin Shen, 1 Quanhong Sun, 1 Li
Introduction. Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats
 Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supplemental Figure 1. (A) Western blot for the expression of RIPK1 in HK-2 cells treated with or without LPS (1 µg/ml) for indicated times.
 Supplemental Figure 1. (A) Western blot for the expression of RIPK1 in HK-2 cells treated with or without LPS (1 µg/ml) for indicated times. Western blots shown are representative results from 3 independent
Supplemental Figure 1. (A) Western blot for the expression of RIPK1 in HK-2 cells treated with or without LPS (1 µg/ml) for indicated times. Western blots shown are representative results from 3 independent
Focus Application. Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity
 xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving Function of the xcelligence System to Optimize Endpoint Viability and
xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving Function of the xcelligence System to Optimize Endpoint Viability and
Focus Application. Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity
 xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving
xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal. regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation
 Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Urinary biomarkers in acute kidney injury. Max Bell MD, PhD Karolinska University Hospital Solna/Karolinska Institutet
 Urinary biomarkers in acute kidney injury Max Bell MD, PhD Karolinska University Hospital Solna/Karolinska Institutet Development of AKI-biomarkers Early markers of AKI, do we need them? GFR drop Normal
Urinary biomarkers in acute kidney injury Max Bell MD, PhD Karolinska University Hospital Solna/Karolinska Institutet Development of AKI-biomarkers Early markers of AKI, do we need them? GFR drop Normal
Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy
 Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy J. Guan 1,2, L. Long 1, Y.-Q. Chen 1, Y. Yin 1, L. Li 1, C.-X. Zhang 1, L. Deng 1 and L.-H. Tian
Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy J. Guan 1,2, L. Long 1, Y.-Q. Chen 1, Y. Yin 1, L. Li 1, C.-X. Zhang 1, L. Deng 1 and L.-H. Tian
Summary 255 Research Summary
 Chapter 10 Summary Nephrolithiasis remains a public health problem around the world, affecting 12% of the adult population. The prevalence and incidence of kidney stones are increasing with global warming,
Chapter 10 Summary Nephrolithiasis remains a public health problem around the world, affecting 12% of the adult population. The prevalence and incidence of kidney stones are increasing with global warming,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Sprague-Dawley Rats Treated with
 The Use of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis to Detect Renal Damage in Sprague-Dawley Rats Treated with Gentamicin Sulfate* GERALD J. KOLAJA, DONALD A. VANDERMEER, WILLIAM H. PACKWOOD,
The Use of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis to Detect Renal Damage in Sprague-Dawley Rats Treated with Gentamicin Sulfate* GERALD J. KOLAJA, DONALD A. VANDERMEER, WILLIAM H. PACKWOOD,
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
Renal Disease and PK/PD. Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology
 Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
IN VITRO HORMESIS EFFECTS OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON KIDNEY CELLS OF THREE-DAY-OLD MALE RATS
 292 Tang, An, Du, Zhang, Zhou 292 IN VITRO HORMESIS EFFECTS OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON KIDNEY CELLS OF THREE-DAY-OLD MALE RATS Qin-qing Tang, a Xiao-jing An, a Jun Du, a Zheng-xiang Zhang, a Xiao-jun Zhou a
292 Tang, An, Du, Zhang, Zhou 292 IN VITRO HORMESIS EFFECTS OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON KIDNEY CELLS OF THREE-DAY-OLD MALE RATS Qin-qing Tang, a Xiao-jing An, a Jun Du, a Zheng-xiang Zhang, a Xiao-jun Zhou a
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy
 Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Biomarkers of kidney injury
 Biomarkers ISSN: 1354-750X (Print) 1366-5804 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/ibmk20 Anja Urbschat, Nicholas Obermüller & Axel Haferkamp To cite this article: Anja Urbschat, Nicholas
Biomarkers ISSN: 1354-750X (Print) 1366-5804 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/ibmk20 Anja Urbschat, Nicholas Obermüller & Axel Haferkamp To cite this article: Anja Urbschat, Nicholas
The levels of mrna expression in the mouse brain were measured at 52 dpi after the brains were divided into five regions: cortex, hippocampus,
 Supplemental material Supplemental method RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and real-time PCR The levels of mrna expression in the mouse brain were measured at 52 dpi after the brains were divided
Supplemental material Supplemental method RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and real-time PCR The levels of mrna expression in the mouse brain were measured at 52 dpi after the brains were divided
Dr.Nahid Osman Ahmed 1
 1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
Research Article. NGAL as a biomarker to predict and diagnose Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
 Available online wwwjocprcom Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 215, 7(5):224-232 Research Article ISSN : 975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 NGAL as a biomarker to predict and diagnose Acute Kidney
Available online wwwjocprcom Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 215, 7(5):224-232 Research Article ISSN : 975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 NGAL as a biomarker to predict and diagnose Acute Kidney
Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 82-86 Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma P.-Q. WANG, Y.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 82-86 Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma P.-Q. WANG, Y.-X.
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
24 (TUDCA) TUDCA TUDCA. [DOI] /j.issn
![24 (TUDCA) TUDCA TUDCA. [DOI] /j.issn 24 (TUDCA) TUDCA TUDCA. [DOI] /j.issn](/thumbs/88/114567389.jpg) 968 2017 11 1 42 11 [ ] Wistar 56 6 50 10% 8 24 (TUDCA) (VFW) (FBG) (FINS) (HOMA-IR) (TC) (TG) (SBP) (DBP) N- - -D- (NAG) (m-alb) (BUN) (Scr) VFW FINS HOMA-IR TC TG SBP DBP NAG (P0.05)
968 2017 11 1 42 11 [ ] Wistar 56 6 50 10% 8 24 (TUDCA) (VFW) (FBG) (FINS) (HOMA-IR) (TC) (TG) (SBP) (DBP) N- - -D- (NAG) (m-alb) (BUN) (Scr) VFW FINS HOMA-IR TC TG SBP DBP NAG (P0.05)
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
 Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Discovery & Validation of Kidney Injury Biomarkers
 Dublin Academic Medical Centre Discovery & Validation of Kidney Injury Biomarkers Patrick Murray, MD, FASN, FRCPI, FJFICMI Professor, University College Dublin, Mater Misericordiae University Hospital,
Dublin Academic Medical Centre Discovery & Validation of Kidney Injury Biomarkers Patrick Murray, MD, FASN, FRCPI, FJFICMI Professor, University College Dublin, Mater Misericordiae University Hospital,
THE EFFECT OF ASCORBIC ACID ON RENAL FUNCTION IN DOGS WITH ISCHEMIA REPERFUSION INJURY
 Nigerian Veterinary Journal 2010 Vol 31(1):66-70 THE EFFECT OF ASCORBIC ACID ON RENAL FUNCTION IN DOGS WITH ISCHEMIA REPERFUSION INJURY KISANI 1 A.I* and AKINRIMADE 2 J.F 1 Department of Veterinary Surgery
Nigerian Veterinary Journal 2010 Vol 31(1):66-70 THE EFFECT OF ASCORBIC ACID ON RENAL FUNCTION IN DOGS WITH ISCHEMIA REPERFUSION INJURY KISANI 1 A.I* and AKINRIMADE 2 J.F 1 Department of Veterinary Surgery
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Transplant Proc. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 July 14.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Transplant Proc. 1990 February ; 22(1): 17 20. The Effects of FK 506 on Renal Function After Liver Transplantation J. McCauley, J.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Transplant Proc. 1990 February ; 22(1): 17 20. The Effects of FK 506 on Renal Function After Liver Transplantation J. McCauley, J.
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 12 Page December 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.02 Original Research Article Fractional
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.02 Original Research Article Fractional
REVIEW ARTICLE NEWER BIOMARKERS IN EARLY DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY
 JCD REVIEW ARTICLE NEWER BIOMARKERS IN EARLY DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY SAPTARSHI MUKHOPADHYAY* *FACULTY (DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE), B R SINGH HOSPITAL (EASTERN RAILWAY), KOLKATA. INTRODUCTION renal disease. It
JCD REVIEW ARTICLE NEWER BIOMARKERS IN EARLY DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY SAPTARSHI MUKHOPADHYAY* *FACULTY (DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE), B R SINGH HOSPITAL (EASTERN RAILWAY), KOLKATA. INTRODUCTION renal disease. It
allergy Asia Pacific Contribution of serum IL-4 and IgE to the early prediction of horse serum allergies in guinea pigs Original Article INTRODUCTION
 pissn 2233-8276 eissn 2233-8268 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.5415/ap.2012.2.4.264 Asia Pac Allergy 2012;2:264-268 Contribution of serum IL-4 and IgE to the early prediction of horse serum allergies
pissn 2233-8276 eissn 2233-8268 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.5415/ap.2012.2.4.264 Asia Pac Allergy 2012;2:264-268 Contribution of serum IL-4 and IgE to the early prediction of horse serum allergies
Heart Failure and Cardio-Renal Syndrome 1: Pathophysiology. Biomarkers of Renal Injury and Dysfunction
 CRRT 2011 San Diego, CA 22-25 February 2011 Heart Failure and Cardio-Renal Syndrome 1: Pathophysiology Biomarkers of Renal Injury and Dysfunction Dinna Cruz, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Nephrology San Bortolo
CRRT 2011 San Diego, CA 22-25 February 2011 Heart Failure and Cardio-Renal Syndrome 1: Pathophysiology Biomarkers of Renal Injury and Dysfunction Dinna Cruz, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Nephrology San Bortolo
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(7): /ISSN: /IJCEP Chuchard Punsawad 1,2, Parnpen Viriyavejakul 3
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(7):7856-7864 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0056431 Original Article Increased expression of kidney injury molecule-1 and matrix metalloproteinase-3 in severe Plasmodium
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(7):7856-7864 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0056431 Original Article Increased expression of kidney injury molecule-1 and matrix metalloproteinase-3 in severe Plasmodium
Interest of NGAL as early marker of Acute Kidney Injury CLINIQUES UNIVERSITAIRES SAINT-LUC
 Interest of NGAL as early marker of Acute Kidney Injury P Wallemacq, Clinical Chemistry Department, M Mourad, Surgery and Abdominal Transplantation Cliniques universitaires St Luc, Université Catholique
Interest of NGAL as early marker of Acute Kidney Injury P Wallemacq, Clinical Chemistry Department, M Mourad, Surgery and Abdominal Transplantation Cliniques universitaires St Luc, Université Catholique
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Product Datasheet. CD133 Antibody NB Unit Size: 0.1 mg
 Product Datasheet CD133 Antibody NB120-16518 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 8 Protocols, Publications, Related Products,
Product Datasheet CD133 Antibody NB120-16518 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 8 Protocols, Publications, Related Products,
Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population
 Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population M.A. Khan 1 *, L. Zhu 1 *, M. Tania 1, X.L. Xiao 2 and J.J. Fu 1 1 Key Laboratory of Epigenetics and Oncology, The Research Center
Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population M.A. Khan 1 *, L. Zhu 1 *, M. Tania 1, X.L. Xiao 2 and J.J. Fu 1 1 Key Laboratory of Epigenetics and Oncology, The Research Center
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
Blood Urea Nitrogen Detection Kit
 Discovery through partnership Excellence through quality StressXpress Blood Urea Nitrogen Detection Kit Catalog# SKT-213 (2 Plate kit) Quantitative colorimetric measurement of urea nitrogen TABLE OF CONTENTS
Discovery through partnership Excellence through quality StressXpress Blood Urea Nitrogen Detection Kit Catalog# SKT-213 (2 Plate kit) Quantitative colorimetric measurement of urea nitrogen TABLE OF CONTENTS
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells *
 Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 16, Suppl. 2, 2007, 325 329 Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells * H.H. Wu 1, J.Y. Yang 1,2, K.
Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 16, Suppl. 2, 2007, 325 329 Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells * H.H. Wu 1, J.Y. Yang 1,2, K.
Kim-1/Tim-1 and Immune Cells: Shifting Sands
 Kim-1/Tim-1 and Immune Cells: Shifting Sands The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed
Kim-1/Tim-1 and Immune Cells: Shifting Sands The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed
24 h. P > h. R doi /j. issn
 38 4 2015 4 Vol. 38 No. 4 Apr. 2015 Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 271 2 ~ 3 * 1 2 2 2 2 2 1# 1 201203 2 2 ~ 3 55 2 18 37 24 2 0 8 16 24 24 h 2 P > 0. 05 P < 0. 05 P < 0.
38 4 2015 4 Vol. 38 No. 4 Apr. 2015 Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 271 2 ~ 3 * 1 2 2 2 2 2 1# 1 201203 2 2 ~ 3 55 2 18 37 24 2 0 8 16 24 24 h 2 P > 0. 05 P < 0. 05 P < 0.
Evaluation of the wound healing response post deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRAcel
 12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRAcel Un-Cheol.Yeo, M.D. S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRAcel Un-Cheol.Yeo, M.D. S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
Pair-fed % inkt cells 0.5. EtOH 0.0
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
Partial Nephrectomy: Does Ischemia Matter?
 Partial Nephrectomy: Does Ischemia Matter? Karim Touijer, MD, MPH Attending Surgeon Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Associate Professor of Urology Weill Cornell Medical College, New York No disclosures
Partial Nephrectomy: Does Ischemia Matter? Karim Touijer, MD, MPH Attending Surgeon Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Associate Professor of Urology Weill Cornell Medical College, New York No disclosures
BCH 447. Estimation of Serum Urea
 BCH 447 Estimation of Serum Urea 1 Objective: Estimation of Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in serum sample. 2 -Urea: Urea is the highest non-protein nitrogen compound in the blood. Urea is the major excretory
BCH 447 Estimation of Serum Urea 1 Objective: Estimation of Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in serum sample. 2 -Urea: Urea is the highest non-protein nitrogen compound in the blood. Urea is the major excretory
Novel Biomarkers in Critically Ill Patients and the Emergency Room
 Novel Biomarkers in Critically Ill Patients and the Emergency Room Jay L. Koyner MD Section of Nephrology University of Chicago Research Funding: NIDDK, Abbvie, Astute, Argutus Outline Background / Pitfalls
Novel Biomarkers in Critically Ill Patients and the Emergency Room Jay L. Koyner MD Section of Nephrology University of Chicago Research Funding: NIDDK, Abbvie, Astute, Argutus Outline Background / Pitfalls
Case - Acute Renal Failure
 Case - Acute Renal Failure 73 yo diabetic F w hx of mild HBP but normal renal function develops infection of R foot. Over 1 week fever, chills, inflammation swelling of her R foot and leg. She takes Motrin
Case - Acute Renal Failure 73 yo diabetic F w hx of mild HBP but normal renal function develops infection of R foot. Over 1 week fever, chills, inflammation swelling of her R foot and leg. She takes Motrin
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
Evaluation of the wound healing response post - deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRACEL
 12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post - deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRACEL Un-Cheol.Yeo, MD S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post - deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRACEL Un-Cheol.Yeo, MD S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Supplemental Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Effect of hyperphosphatemia on gene expression of the Na-Pi cotransporter in rats
 Effect of hyperphosphatemia on gene expression of the Na-Pi cotransporter in rats C. Zhang 1,2 *, L.-M. Shi 3 *, Y. Li 4 *, Q.-G Zhu 2 *, C.-L. Jin 2, H.-P. Wang 2, L. Zhou 2, X.-P. Hu 1, L. Zhang 1, H.
Effect of hyperphosphatemia on gene expression of the Na-Pi cotransporter in rats C. Zhang 1,2 *, L.-M. Shi 3 *, Y. Li 4 *, Q.-G Zhu 2 *, C.-L. Jin 2, H.-P. Wang 2, L. Zhou 2, X.-P. Hu 1, L. Zhang 1, H.
International Conference on Biomedical and Biological Engineering (BBE 2016)
 International Conference on Biomedical and Biological Engineering (BBE 2016) Injury Mechanism of Sub-Micron Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate and Dihydrate Crystals on Renal Epithelial Cells Poonam BHADJA, Kai
International Conference on Biomedical and Biological Engineering (BBE 2016) Injury Mechanism of Sub-Micron Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate and Dihydrate Crystals on Renal Epithelial Cells Poonam BHADJA, Kai
Peli1 negatively regulates T-cell activation and prevents autoimmunity
 Peli1 negatively regulates T-cell activation and prevents autoimmunity Mikyoung Chang 1,*, Wei Jin 1,5,*, Jae-Hoon Chang 1, Yi-chuan Xiao 1, George Brittain 1, Jiayi Yu 1, Xiaofei Zhou 1, Yi-Hong Wang
Peli1 negatively regulates T-cell activation and prevents autoimmunity Mikyoung Chang 1,*, Wei Jin 1,5,*, Jae-Hoon Chang 1, Yi-chuan Xiao 1, George Brittain 1, Jiayi Yu 1, Xiaofei Zhou 1, Yi-Hong Wang
Supplemental Fig. 1 A. C57BL/6 (B6) C. Number of colonies in culture media B6. B6 + Abx
 A. Day C57BL/6 (B6) n=9 B6 + Abx (12 weeks) n=9 B. Supplemental Fig. 1 day 1 I/R 4min Sacrifice C. Number of colonies in culture media B6 Escherichia coli Lactbacillus spp. Lactobacillus murinus Enterococcus
A. Day C57BL/6 (B6) n=9 B6 + Abx (12 weeks) n=9 B. Supplemental Fig. 1 day 1 I/R 4min Sacrifice C. Number of colonies in culture media B6 Escherichia coli Lactbacillus spp. Lactobacillus murinus Enterococcus
Knockout TM SR : ; ; ; : R ; R : A : X(2013) , ,, B. , (Knockout TM
 33 1 Vol.33 No.1 013 1 Dec. 013 Reproduction & Contraception doi: 10.7669/j.issn.03-37X.013.1.0804 E-mail: randc_journal@163.com Knockout TM SR ; ; ; 400014 : FBS Knockout TM SRKSR : FBS KSR HE TUNEL RT-PCR
33 1 Vol.33 No.1 013 1 Dec. 013 Reproduction & Contraception doi: 10.7669/j.issn.03-37X.013.1.0804 E-mail: randc_journal@163.com Knockout TM SR ; ; ; 400014 : FBS Knockout TM SRKSR : FBS KSR HE TUNEL RT-PCR
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
Effects of COX-2 Inhibitor on the Proliferation of MCF-7 and LTED MCF-7 Cells
 Mahidol University Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2008; 35(1-4): 47-51. Original Article Effects of COX-2 Inhibitor on the Proliferation of MCF-7 and LTED MCF-7 Cells K. Poemsantitham, N. Sookvanichsilp
Mahidol University Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2008; 35(1-4): 47-51. Original Article Effects of COX-2 Inhibitor on the Proliferation of MCF-7 and LTED MCF-7 Cells K. Poemsantitham, N. Sookvanichsilp
Original Article Others INTRODUCTION. Diabetes Metab J 2012;36: pissn eissn
 Original Article Others Diabetes Metab J 12;36:7-313 http://dx.doi.org/.93/dmj.12.36.4.7 pissn 2233-79 eissn 2233-87 D I A B E T E S & M E T A B O L I S M J O U R N A L Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated
Original Article Others Diabetes Metab J 12;36:7-313 http://dx.doi.org/.93/dmj.12.36.4.7 pissn 2233-79 eissn 2233-87 D I A B E T E S & M E T A B O L I S M J O U R N A L Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated
INTERNATIONAL CONCIL FOR HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED GUIDELINE Q3D(R1)
 INTERNATIONAL CONCIL FOR HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED GUIDELINE GUIDELINE FOR ELEMENTAL IMPURITIES (R1) Draft version Endorsed on 18 May 2018
INTERNATIONAL CONCIL FOR HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED GUIDELINE GUIDELINE FOR ELEMENTAL IMPURITIES (R1) Draft version Endorsed on 18 May 2018
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Bin Liu, Lei Yang, Binfang Huang, Mei Cheng, Hui Wang, Yinyan Li, Dongsheng Huang, Jian Zheng,
 The American Journal of Human Genetics, Volume 91 Supplemental Data A Functional Copy-Number Variation in MAPKAPK2 Predicts Risk and Survival of Lung Cancer Bin Liu, Lei Yang, Binfang Huang, Mei Cheng,
The American Journal of Human Genetics, Volume 91 Supplemental Data A Functional Copy-Number Variation in MAPKAPK2 Predicts Risk and Survival of Lung Cancer Bin Liu, Lei Yang, Binfang Huang, Mei Cheng,
Tubular markers do not predict the decline in glomerular filtration rate in type 1 diabetic patients with overt nephropathy
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2011 International Society of Nephrology original article see commentary on page 1042 Tubular markers do not predict the decline in glomerular filtration rate in type
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2011 International Society of Nephrology original article see commentary on page 1042 Tubular markers do not predict the decline in glomerular filtration rate in type
