Open Access Diagnosis and Treatment of Vascular Surgery Related Infection
|
|
|
- Dominic Thomas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Send Orders for Reprints to 250 The Open Biomedical Engineering Journal, 2015, 9, Open Access Diagnosis and Treatment of Vascular Surgery Related Infection Yong-Gan Zhang *, Xue-Li Guo, Yan Song, Chao-Feng Miao, Chuang Zhang and Ning-Heng Chen Department of Vascular Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital, Zhengzhou University, China Abstract: Surgical site infection (SSI) is an important component of infections acquired from hospital. The most significant feature of vascular surgery different from other surgeries is frequent application of artificial grafts. Once SSI occurs after vascular operations with grafts, it might results in a serious disaster. Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative Staphylococcus are the most common pathogenic bacteria for SSI after vascular surgery. Although SSI in vascular surgery often lacks of typical clinical characters, some clinical symptoms, laboratory data and certain imaging procedures may help to diagnose. In most cases of SSI after vascular procedures, the artificial grafts must be removed and sensitive antibiotics should be administered. However, for different cases, personalized management plan should be made depending on the severity and location of SSI. Keywords: Antibiotics, diagnosis, infection, treatment, vascular surgery. 1. INTRODUCTION Vascular surgery is a new interdisciplinary subject of medicine. Besides has the general characteristics of other surgical disciplines, vascular surgery is characterized in that a variety of artificial graft (artificial blood vessels, stents, stent grafts) are widely used in clinical. Most vascular surgical operation is clean operation, but the chance of infection is usually increased, due to the application of artificial graft, and that vascular surgery patients are often elderly, and may be combined with a variety of internal medicine diseases such as diabetes, hypertension and heart disease, immune disease, weak body resistance. Once surgical site infection (SSI) is induced, the consequences would be disastrous. It s not enough, sometimes, with antibiotic therapy alone for graft infection, and if necessary, removal of the infected vascular graft and revascularization pathway have to be operated [1-3], otherwise SSI can cause serious limb loss, organ failure, and even death. 2. RISK FACTORS Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci are the most common pathogens of vascular surgery SSI. According to statistics, both early (within 4 months after operation) and late (more than 4 months after graft infection), one forth to a half risk is caused by Staphylococcus aureus, gram-negative bacteria, and fungal infections are rare, generally only occurs in immunosuppressed patients (Table 1) [2] Preoperative Pollution The epidermis is the main source of bacteria. The graft surface can be contaminated by microbe through the following 3 ways: (1) Through transplantation of direct planting. *Address correspondence to this author at the Department of Vascular Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital, Zhengzhou University, China; zhangyongganli@sina.com An important way for the occurrence of the operation process of bacteria; and sweat glands, lymph node contact; graft and artery wall lesions connected; intestinal grafts or exudate pollution, exposure to injury or open gastrointestinal or genitourinary tract. (2) Through the operation incision. (3) By blood or lymphatic spread. Table 1. Binary logistic regression analysisa of factors associated with surgical wound infection after lower limb vascular surgery. Risk factor OR 95% CI p CFU/mL >155,000 on the second postoperative day Diabetes Elective redo surgery Infra-inguinal surgery Male gender Note. OR = odds ratio; CI = confidence interval; CFU = colony-forming unit. a Regression model with CFU/mL >155,000 on the second postoperative day, diabetes, elective redo surgery, infra-inguinal surgery, and sex as covariates Bacteria Planting by Vascular Graft The spread of bacteria by hematogenous pathway and planted in the graft or endovascular stent graft infection occurred is a common cause, but it is a very important mechanism. The animal experiments, perfused 10 7 colony forming units (CFUs) of Staphylococcus aureus, experimental animal almost 100% in postoperative graft infection [3] occurred. In elderly patients with vascular disease, vascular catheter insertion, urinary tract infection or infection of the tissues (pneumonia or infected foot ulcer) often become the source of graft bacteria, and the occurrence of postoperative graft / Bentham Open
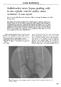
2 Diagnosis and Treatment of Vascular Surgery Related Infection The Open Biomedical Engineering Journal, 2015, Volume Fig. (1). Scatterplot of total bacterial counts (colony-forming units /ml) in patients with and without surgical site infection (y-axis in log 10 scale). Note. SSI = surgical site infection. infection [3]. After several years of operation, when the change in the immune system, causing vascular graft infection exists in the blood can be contaminated bacteria. Some people think, possible mechanism of late graft infection: for transplantation when vascular surface pathogenic bacteria [4] dormancy Infection around Vascular Graft Because of the skin, gastrointestinal or genitourinary tract pollution, vascular graft infection can be caused around. 3. DIAGNOSIS 3.1. Clinical Symptoms Vascular graft infection is lack of typical clinical manifestations, such as aortic graft infection, may be manifested as unexplained bacteremia, or simply manifested as abdominal distension and muscle tension; lower extremity, groin or neck vascular transplantation, if graft infection can appear to invade surrounding tissue, vascular grafts exposed around the tumor, wound drainage sinus formation or pulsatile anastomotic aneurysm. In short, as long as there are no signs suggesting vascular graft infection, should be further examined Laboratory Tests Once the vascular graft infection, the patient may have inflammation phenomenon of fever, white blood cell counts increased, erythrocyte sedimentation rate higher nonspecific (Fig 1, Table 2) [2, 3]. Routine laboratory tests should include analysis of urine and blood culture, and of any possible sources of infection bacteria. But the patient laboratory only two thirds positive results, and the vessel of Staphylococcus epidermidis delayed periallograft infection, all laboratory results can be negative. Table 2. Type and number of bacterial and fungal isolates recovered from 42 vascular surgical sites. Type Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus No. Methicillin-resistant 10 Methicillin-sensitive 5 S. epidermidis 6 Enterococcus 7 Streptococcus spp 2 Methicillin-resistant S. epidermidis 1 Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus 1 Bacteroides spp 7 Total 39 Gram-negative Escherichia coli 7 Pseudomonas 3 Haemophilus 1 Proteus 1 Citrobacter 1 Klebsiella 1 Enterobacter 2 Propionibacterium acnes 2 Total 18 Candida 2 No growth 2
3 252 The Open Biomedical Engineering Journal, 2015, Volume 9 Zhang et al Special Inspection Vessels Using vascular ultrasound, CT and MRI, can be detected in vascular plants infected graft shift caused by the abscess or anastomotic aneurysm, selective joint use of such special vascular examination, diagnosis of vascular graft infection sensitivity can reach more than 80%, the specificity was 50% ~ 90%, and to help determine the surgical approach and the scope of 3; angiography in the planning of treatment has a guiding role; on suspicion of aortic graft infection patients must be two-way angiography, in order to understand the host and graft patency by the extent of infection and the proximal and distal vessels, in order to make further treatment. 4. TREATMENT Without the use of artificial vascular surgical operation shift plant, the postoperative SSI treatment is same with other disciplines, including the principle of surgical debridement, washing, dressing and antibiotics when necessary. The use of artificial graft vascular surgical operation of plants, if SSI, has the special treatment, the standard surgical treatment plant blood vessel graft infection is: removal of the infected vascular graft, for extra anatomic bypass graft. But because of graft infection at different degree and scope, clinicians should according to the specific circumstances of vascular graft infection, to develop individualized treatment (Table 3) [1] Local Processing Local treatment of plant blood vessel graft infection includes transplantation of vascular bed to infection fully debridement and drainage, need debridement, remove of purulent necrotic tissue, and the persistent aortic stump debridement treatment. Positive vascular graft is an effective local treatment of retained vascular grafts, reduce the basis of amputation. Through effective treatment, 70% cases can be successfully preserved vascular graft [5-8]. Vascular graft infection is widespread or involving the anastomosis, artificial blood vessels should be removed, both ends of the artery by single strand suture. Persistent aortic wall and surrounding tissues, especially in the presence of suppurative change or pseudoaneurysm arterial wall, should debridement to normal form artery, artery stump covered with sterile tissue with activity. Artery debridement must be used to confirm the histological examination, such as arterial wall bacterial cultures were positive, need long-term antibiotic therapy. The removal of residual bed infection of vascular graft, thoroughly debridement, removal of necrotic tissue purulent, until the normal tissue exposure, the wound, the closed negative pressure drainage tube, do sufficient drainage Revascularization The occurrence of vascular graft infection, limb collateral circulation only when fully established, only consider the Table 3. Predictors of cure at one year in 51 patients with aortic prosthetic vascular graft infections. Variable Univariate Analysis Multivariate Analysis HR 95% CI p-value HR 95% CI p-value Age Female gender Location of the Graft Thoracic 1 Abdominal, with noiliac-femoral graft involvement Abdominal withiliac-femoral graft involvement Intubation >24 hours Early surgical graft revision <24 hours after implantation Polymicrobial infection Type of Surgical Treatment Graft retention and debridement Graft replacement Local Surgical Therapy Associated with Graft Revisions/Replacements Vacuum-assisted closure Plastic surgery Antimicrobial Therapy Antimicrobial regimen that included rifampicin
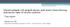
4 Diagnosis and Treatment of Vascular Surgery Related Infection The Open Biomedical Engineering Journal, 2015, Volume simple removal of infected vascular grafts, without vascular reconstruction. But such cases are rare, usually removed vascular grafts were performed after revascularization. The general remove of the infected vascular graft, the need for extra anatomic bypass grafting, in order to save the organs and limbs. After removal of the infected graft, in situ with autogenous vein, artery allograft or antibiotic containing artificial blood vessel revascularization, extra anatomic bypass graft compared with more standard, simplify the operation process, shorten the operation time, improve the superiority and graft patency rate. But for in situ vascular transplantation, prone to infection and infection of retransplantation vascular anastomosis, so only without systemic infection, and perivascular per gram of tissue culture of less than 10 5 units (CFUs), cloning is possible in situ transplantation of blood vessel [9-11]. Revascularization of transplanted autologous vascular material selection is the best, followed by artificial blood vessel, but in most cases not suitable for autologous vascular graft, can only use artificial blood vessels, through normal tissue without bacterial infection is consistent with the normal host artery (Fig. 2) [1]. The general remove of the infected vascular graft, the need for extra anatomic bypass, in order to save the organs and limbs. The following is the classification of treatment according to different parts of the vascular graft infection Aortic, Iliac Artery Vascular Graft Infection The aorta and iliac artery vascular graft infection, the most reasonable treatment principle is: first the right axillary artery to bilateral femoral artery bypass surgery; complete dissection, with sterile dressings covering all the wounds, and then open the complete removal of vascular graft infection. In extra anatomic revascularization, should be heparin therapy; artificial blood vessel and remove the infection, with heparin antagonists. The extra anatomic bypass surgery and postoperative complications, statistical data shows that: the operation mortality was 11% ~ 27%, the amputation rate occurred as 9%~27% [12,13], so as to have allogeneic vascular grafts, may be considered for in situ revascularization, can significantly reduce postoperative complications. But most of the medical institutions are unconditional access to these vessels Aorta Bilateral Femoral Artery Vascular Graft Infection Aorta bilateral femoral artery graft infection treatment is difficult, because the inguinal region of vascular graft infection, affect the lower limb blood supply, for extra anatomic bypass reconstruction, the distal anastomosis should be built in the deep femoral artery or superficial femoral artery to artery, even, in order to avoid the occurrence of lower extremity ischemic necrosis. The graft should choose diameter greater than 5mm or PTFE artificial blood vessels of saphenous vein. Occurred in the late postoperative and localized in the inguinal region of vascular graft infection, can be considered part of the partial resection of the infected vessels, after thorough debridement, in situ revascularization; postoperative intravenous antibiotics for 2~4 weeks, and continued to take 3 months Femoral and Tibial Artery Vascular Graft Infection Inguinales artificial vascular bypass vascular graft infection, are generally required to remove the artificial blood vessel. The treatment should follow the principle of treatment of vascular aortic graft infection, although the mortality rate is low, but the possibility of amputation is higher than 50% [14-17]. Such as the removal of the infected vessels, ankle arterial pressure or forearm pressure greater than 40mmHg (1mmHg = 0.133kPa), suggesting that body can delay the establishment of collateral circulation, graft revascularization, and anti-inflammatory treatment, control of infection after revascularization, again to increase vascular grafting patency rate, reduce complications. Fig. (2). Comparison of time to treatment failure in different types of prosthetic vascular graft infections. infections are compared with respect to the location of the prosthetic vascular graft using kaplan-meier estimates.
5 254 The Open Biomedical Engineering Journal, 2015, Volume 9 Zhang et al Innominate Artery, Subclavian Artery and Carotid Artery Vascular Graft Infection Intrathoracic vascular graft infection, the treatment principle is: to remove the entire graft, vascular reconstruction with autologous vascular graft materials as much as possible, and intravenous injection of antibiotics. The remove of grafts, in order to control the proximal vessels, often require incision and median clavicle, cardiopulmonary bypass. Because the upper limb ischemia underwent transthoracic or extrathoracic bypass surgery, and the occurrence of vascular graft infection, resection of the infected vascular graft, generally do not need immediate revascularization; because the upper limb necrosis due to ischemia and rarely occur. Re revascularization in complete control after infection, and can increase the success rate of transplantation operation. Carotid artery bypass vascular graft infection, artery ligation in general can t tolerate simple, only when the carotid stump pressure is greater than 70mmHg, it can only simple ligation of common carotid artery and internal carotid artery [18]. But in order to ensure the blood perfusion of cerebral circulation, prevent the occurrence of shock, it should be possible for revascularization. Carotid endarterectomy artificial patch infection, should be artificial patch resection of the carotid artery, using autologous vascular patch, in the process of operation, the carotid artery bypass is safe and effective measures of cerebral blood flow Stents and Endovascular Infection The endovascular exclusion in the surgical trauma, the intestinal tract and other organs significantly reduce interference, shorten the operation time, intraoperative and postoperative blood transfusion without the above factors, significantly reduce the chance of graft infection. Therefore, intraluminal vascular graft infections are more rare. But the endoscopic operation of complex technology and instruments are more numerous, the need for surgery in the DSA, so as to increase the chance of graft infection. Once the endovascular graft infection, often associated with sepsis and infection of the aneurysm and thrombus shedding bacteria, the most common pathogenic bacteria were Staphylococcus aureus, artery plants and infection involving the shift treatment including removal of the cavity, parallel extra anatomic bypass, according to different parts of the vascular graft infection. Select the vascular reconstruction schemes of different [19]. CONCLUSION Antibiotic-loaded PMMA beads may serve as an adjunct in the management of VSSIs and may also expand treatment options for graft preservation or in situ reconstruction, with expected recurrent infection rate approaching 20%. Further experience with this adjunct may help elucidate its role in the management of this complicated problem, including the need for bead exchanges, until perigraft cultures are free of microbes. CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Declared none. REFERENCES [1] S. Erb, J.A. Sidler, L. Elzi, L. Gurke, M. Battegay, A.F. Widmer, and M. Weisser, Surgical and antimicrobial treatment of prosthetic vascular graft infections at different surgical sites: a retrospective study of treatment outcomes, PLoS One, vol. 9, no. 11, [2] J. Turtiainen, T. Hakala, T. Hakkarainen, and J. Karhukorpi, The impact of surgical wound bacterial colonization on the incidence of surgical site infection after lower limb vascular surgery: a prospective observational study, European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, vol. 47, no. 4, pp , [3] P.A. Stone, A.Y. Mousa, S.M. Hass, D.D. Dearing, J.R. Campbell, A. Parker, S. Thompson, and A.F. AbuRahma, Antibiotic-loaded polymethylmethacrylate beads for the treatment of extracavitary vascular surgical site infections, Journal of Vascular Surgery, vol. 55, no. 6, pp , [4] W.W. Wu, and C.W. Liu, Diagnosis and treatment of surgical site infection in vascular surgery, Chinese Journal of Practical Surgery, vol. 31, no. 12, pp , (in Chinese) [5] M.S. Calderwood, A. Ma, Y.M. Khan, M.A. Olsen, D.W. Bratzler, D.S. Yokoe, D.C. Hooper, K. Stevenson, V.J. Fraser, R. Platt, and S.S. Huang, CDC Prevention Epicenters Program. Use of Medicare diagnosis and procedure codes to improve detection of surgical site infections following hip arthroplasty, knee arthroplasty, and vascular surgery, Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, vol. 33, no. 1, pp , [6] J. Amour, A. Birenbaum, O. Langeron, M. Y. Le, M. Bertrand, P. Coriat, B. Riou, M. Bernard, and P. Hausfater, Influence of renal dysfunction on the accuracy of procalcitonin for the diagnosis of postoperative infection after vascular surgery, Critical Care Medicine, vol. 36, no. 4, pp , [7] C.E.P.C. Almeida, L. Reis, L. Carvalho, and C.M.C. Almeida, Collagen implant with gentamicin sulphate reduces surgical site infection in vascular surgery: a prospective cohort study, International Journal of Surgery, vol. 12, no. 10, pp , [8] A. Ramcharan, J. Penders, E. Smeets, M. Rouflart, F. van Tiel, C. Bruggeman, C. Baeten, S. Breukink, J. Tordoir, and E. Stobberingh, Cross-sectional study on surveillance of surgical site infections after vascular surgery, Future Microbiology vol. 8, no. 11, pp , [9] Z.Q. Xie, and W.Q. Peng, Species and antimicrobial resistance of pathogenic bacteria causing surgical infections, Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology, vol. 23, no. 16, pp , [10] S.T. Hussain, Local application of gentamicin-containing collagen implant in the prophylaxis and treatment of surgical site infection following vascular surgery, International Journal of Surgery, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. S5-S9, [11] J. Turtiainen, and T. Hakala, Surgical wound infections after peripheral vascular surgery, Scandinavian Journal of Surgery, vol. 103, no. 4, pp , [12] S.J. Liu, C.X. Yin, M.C. Ding, and Y.Z. Wang, Distribution and drug resistance of pathogens causing surgical incision infections in vascular surgery department, Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology, vol. 24, no. 17, pp , [13] L. Neumayer, P. Hosokawa, K. Itani, M. El-Tamer, W.G. Henderson, and S.F. Khuri, Multivariable predictors of postoperative surgical site infection after general and vascular surgery: results from the patient safety in surgery study, Journal of the American College of Surgeons, vol. 204, no. 6, pp , [14] M. Mirzaie, J.D. Schmitto, T. Tirilomis, S. Fatehpur, O.J. Liakopoulos, N. Teucher, H. Durge, and F.A. Schendube, Surgical management of vascular graft infection in severely ill patients by partial resection of the infected prosthesis, European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, vol. 33, no. 5, pp , [15] S. Homer-Vanniasinkam, Surgical site and vascular infections: treatment and prophylaxis, International Journal of Infectious Diseases, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. S17-S22, [16] E. Frei, K. Hodgkiss-Harlow, P.J. Rossi, C. E. Jr. Edmiston, and D.F. Bandyk, Microbial pathogenesis of bacterial biofilms: a
6 Diagnosis and Treatment of Vascular Surgery Related Infection The Open Biomedical Engineering Journal, 2015, Volume causative factor of vascular surgical site infection, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, vol. 45, no. 8, pp , [17] J. van der Slegt, J. A. J. W. Kluytmans, P. G. H. Mulder, E. J. Veen, G. H. Ho, and L. van der Laan, Surgical site infection after multiple groin incisions in peripheral vascular surgery, Surgical Infections, vol. 15, no. 6, pp , [18] A. Dua, S.S. Desai, G.R. Seabrook, K.R. Brown, B.D. Lewis, P.J. Rossi, C.E. Edmiston, and C.J. Lee, The effect of surgical care improvement project measures on national trends on surgical site infections in open vascular procedures, Journal of Vascular Surgery, vol. 60, no. 6, pp , [19] E. Ott, F.C. Bange, D. Sohr, O. Teebken, and F. Mattner, Risk factors associated with surgical site infections following vascular surgery at a German university hospital, Epidemiology and Infection, vol. 141, no. 6, pp , Received: May 26, 2015 Revised: July 14, 2015 Accepted: August 10, 2015 Zhang et al.; Licensee Bentham Open. This is an open access article licensed under the terms of the ( which permits unrestricted, noncommercial use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the work is properly cited.
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida
 Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida
 Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M
 Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M The goal Treat pain Heal ulcer Preserve limb Preserve life The options Conservative Endovascular Surgical bypass Primary amputation
Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M The goal Treat pain Heal ulcer Preserve limb Preserve life The options Conservative Endovascular Surgical bypass Primary amputation
Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections
 Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections Christophe Van de Wiele, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Orthopedic prostheses: world market 1996 Prosthetic
Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections Christophe Van de Wiele, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Orthopedic prostheses: world market 1996 Prosthetic
Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures SVS Practice Guidelines
 Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures 2018 SVS Practice Guidelines vsweb.org/svsguidelines About the guidelines Published in the July 2018 issue of Journal of Vascular
Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures 2018 SVS Practice Guidelines vsweb.org/svsguidelines About the guidelines Published in the July 2018 issue of Journal of Vascular
Surgical Privileges Form: Vascular Surgery
 Surgical Form: Vascular Surgery Clinical Request Applicant s Name:. License No. (If Any):... Date:... Scope of Practice:. Facility:.. Place of Work:. CATEGORY I: GENERAL PRIVILEGES 1. Admitting privileges
Surgical Form: Vascular Surgery Clinical Request Applicant s Name:. License No. (If Any):... Date:... Scope of Practice:. Facility:.. Place of Work:. CATEGORY I: GENERAL PRIVILEGES 1. Admitting privileges
Morbidity Audit and Logbook Tool SNOMED Board Reporting Terms for SET and IMG Vascular Surgery AMPUTATION AORTA
 SNOMED s for SET and IMG Vascular Surgery AMPUTATION Amputation above-knee Amputation of leg through tibia and fibula Amputation of the foot Amputation of toe Through knee amputation Ray amputation of
SNOMED s for SET and IMG Vascular Surgery AMPUTATION Amputation above-knee Amputation of leg through tibia and fibula Amputation of the foot Amputation of toe Through knee amputation Ray amputation of
A 10-year experience of infection following carotid endarterectomy with patch angioplasty
 From the Eastern Vascular Society A 10-year experience of infection following carotid endarterectomy with patch angioplasty Patrick A. Stone, MD, Mohit Srivastava, MD, John E. Campbell, MD, Albeir Y. Mousa,
From the Eastern Vascular Society A 10-year experience of infection following carotid endarterectomy with patch angioplasty Patrick A. Stone, MD, Mohit Srivastava, MD, John E. Campbell, MD, Albeir Y. Mousa,
ISF criteria (International sepsis forum consensus conference of infection in the ICU) Secondary peritonitis
 Appendix with supplementary material. This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. Supplementary Tables Table S1. Definitions
Appendix with supplementary material. This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. Supplementary Tables Table S1. Definitions
Interesting Case Series. Omental Flap for Thoracic Aortic Graft Infection
 Interesting Case Series Omental Flap for Thoracic Aortic Graft Infection Andrew A. Marano, BA, Adam M. Feintisch, MD, and Mark S. Granick, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Rutgers
Interesting Case Series Omental Flap for Thoracic Aortic Graft Infection Andrew A. Marano, BA, Adam M. Feintisch, MD, and Mark S. Granick, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Rutgers
AORTIC GRAFT INFECTION
 NURSING CARE Theresa O Keefe NUM Vascular Unit PAH Vascular infections are serious They are associated with high morbidity and mortality The primary cause of surgical wound infections is contamination
NURSING CARE Theresa O Keefe NUM Vascular Unit PAH Vascular infections are serious They are associated with high morbidity and mortality The primary cause of surgical wound infections is contamination
Case Report Surgical Treatment for Profunda Femoris Artery Aneurysms: Five Case Reports
 Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 375278, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/375278 Case Report Surgical Treatment for Profunda Femoris Artery Aneurysms: Five Case Reports Kimihiro
Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 375278, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/375278 Case Report Surgical Treatment for Profunda Femoris Artery Aneurysms: Five Case Reports Kimihiro
Pressure Injury Complications: Diagnostic Dilemmas
 Pressure Injury Complications: Diagnostic Dilemmas Aimée D. Garcia, MD, CWS, FACCWS Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Geriatrics Section Baylor College of Medicine Medical Director, Wound Clinic
Pressure Injury Complications: Diagnostic Dilemmas Aimée D. Garcia, MD, CWS, FACCWS Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Geriatrics Section Baylor College of Medicine Medical Director, Wound Clinic
Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2)
 Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2) Definition Vascular surgery is the specialty concerned with the diagnosis and management of congenital and acquired diseases of the
Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2) Definition Vascular surgery is the specialty concerned with the diagnosis and management of congenital and acquired diseases of the
Stent-graft infection: Conservative treatment, endovascular relining, or conversion?
 Stent-graft infection: Conservative treatment, endovascular relining, or conversion? L. Chiche, J Gaudric, C. Jouhannet, T. Khalife, C. Goulfier, F. Koskas Department of Vascular Surgery, CHU Pitié-Salpêtrière,
Stent-graft infection: Conservative treatment, endovascular relining, or conversion? L. Chiche, J Gaudric, C. Jouhannet, T. Khalife, C. Goulfier, F. Koskas Department of Vascular Surgery, CHU Pitié-Salpêtrière,
Schedule of Benefits. for Professional Fees Vascular Procedures
 Schedule of Benefits for Professional Fees 2018 Vascular Procedures ANASTOMOSIS RULES 820 Arteriovenous anastomosis in arm 1453 Arteriovenous anastomosis, open by basilic vein transposition 1465 Splenorenal
Schedule of Benefits for Professional Fees 2018 Vascular Procedures ANASTOMOSIS RULES 820 Arteriovenous anastomosis in arm 1453 Arteriovenous anastomosis, open by basilic vein transposition 1465 Splenorenal
Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization:
 Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization: Long Term Result For Critical Limb Ischemia With Unreconstructable Distal Arteries Pramook Mutirangura Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj
Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization: Long Term Result For Critical Limb Ischemia With Unreconstructable Distal Arteries Pramook Mutirangura Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj
PERPHERAL ARTERY ANEURYSM. By Pooja Sharma and Susanna Sebastianpillai
 PERPHERAL ARTERY ANEURYSM By Pooja Sharma and Susanna Sebastianpillai Defintions True Aneurysm Involves all three layers of the vessel. Have two basic shapes; Fusiform = symmetric widening of the vessels
PERPHERAL ARTERY ANEURYSM By Pooja Sharma and Susanna Sebastianpillai Defintions True Aneurysm Involves all three layers of the vessel. Have two basic shapes; Fusiform = symmetric widening of the vessels
Healthcare-associated infections acquired in intensive care units
 SURVEILLANCE REPORT Annual Epidemiological Report for 2015 Healthcare-associated infections acquired in intensive care units Key facts In 2015, 11 788 (8.3%) of patients staying in an intensive care unit
SURVEILLANCE REPORT Annual Epidemiological Report for 2015 Healthcare-associated infections acquired in intensive care units Key facts In 2015, 11 788 (8.3%) of patients staying in an intensive care unit
Clinical Study Negative Pressure Incision Management System in the Prevention of Groin Wound Infection in Vascular Surgery Patients
 Surgery Research and Practice Volume 2015, Article ID 303560, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/303560 Clinical Study Negative Pressure Incision Management System in the Prevention of Groin Wound
Surgery Research and Practice Volume 2015, Article ID 303560, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/303560 Clinical Study Negative Pressure Incision Management System in the Prevention of Groin Wound
Arteriovenostomy for renal dialysis 39.27, 39.42
 Surgery categories NHSN Surgery codes (Reference: NHSN Operative Procedure Category Mappings to ICD-9-CM Codes, October 2010 www.cdc.gov/nhsn/pdfs/pscmanual/9pscssicurrent.pdf) Operative aortic aneurysm
Surgery categories NHSN Surgery codes (Reference: NHSN Operative Procedure Category Mappings to ICD-9-CM Codes, October 2010 www.cdc.gov/nhsn/pdfs/pscmanual/9pscssicurrent.pdf) Operative aortic aneurysm
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in liver transplant A multicenter survey endorsed by the European Liver and Intestine Transplant Association
 Antimicrobial prophylaxis in liver transplant A multicenter survey endorsed by the European Liver and Intestine Transplant Association Els Vandecasteele, Jan De Waele, Dominique Vandijck, Stijn Blot, Dirk
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in liver transplant A multicenter survey endorsed by the European Liver and Intestine Transplant Association Els Vandecasteele, Jan De Waele, Dominique Vandijck, Stijn Blot, Dirk
Do the newest grafts achieve comparable results to saphenous vein bypass? THE HEPARIN-BONDED eptfe GRAFT. C. Pratesi
 Do the newest grafts achieve comparable results to saphenous vein bypass? THE HEPARIN-BONDED eptfe GRAFT C. Pratesi Department of Vascular Surgery University of Florence-Italy www.chirvasc-unifi.it FEMORO-POPLITEAL
Do the newest grafts achieve comparable results to saphenous vein bypass? THE HEPARIN-BONDED eptfe GRAFT C. Pratesi Department of Vascular Surgery University of Florence-Italy www.chirvasc-unifi.it FEMORO-POPLITEAL
Abscess. A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body.
 Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
 CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Hamid Emadi M.D Associate professor of Infectious diseases Department Tehran university of medical science The most common nosocomial infection The urinary
CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Hamid Emadi M.D Associate professor of Infectious diseases Department Tehran university of medical science The most common nosocomial infection The urinary
National Vascular Registry
 National Vascular Registry Bypass Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or postcode.
National Vascular Registry Bypass Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or postcode.
Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections
 Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections Objectives How do you to diagnose, classify and manage DFI? How do you diagnose
Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections Objectives How do you to diagnose, classify and manage DFI? How do you diagnose
Case 37 Clinical Presentation
 Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Surgical Management of Osteomyelitis & Infected Hardware. Michael L. Sganga, DPM Orthopedics New England Natick, MA
 Surgical Management of Osteomyelitis & Infected Hardware Michael L. Sganga, DPM Orthopedics New England Natick, MA Disclosures None relevant to the content of this material Overview Implants Timing Tenants
Surgical Management of Osteomyelitis & Infected Hardware Michael L. Sganga, DPM Orthopedics New England Natick, MA Disclosures None relevant to the content of this material Overview Implants Timing Tenants
Combat Extremity Vascular Trauma
 Combat Extremity Vascular Trauma Training teams to be a TEAM Chatt A. Johnson LTC, MC, USA 08 March 2010 US Army Trauma Training Center Core Discussion Series Outline: Combat Vascular Injury Physiologic
Combat Extremity Vascular Trauma Training teams to be a TEAM Chatt A. Johnson LTC, MC, USA 08 March 2010 US Army Trauma Training Center Core Discussion Series Outline: Combat Vascular Injury Physiologic
UTI IN ELDERLY. Zeinab Naderpour
 UTI IN ELDERLY Zeinab Naderpour Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most frequent bacterial infection in elderly populations. While urinary infection in the elderly person is usually asymptomatic, symptomatic
UTI IN ELDERLY Zeinab Naderpour Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most frequent bacterial infection in elderly populations. While urinary infection in the elderly person is usually asymptomatic, symptomatic
PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD
 PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD Bala Ramanan, MBBS 1 st year vascular surgery fellow Introduction The epidemic of diabetes and ageing of our population ensures critical limb ischemia will continue to grow.
PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD Bala Ramanan, MBBS 1 st year vascular surgery fellow Introduction The epidemic of diabetes and ageing of our population ensures critical limb ischemia will continue to grow.
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students. Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile.. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile.. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products,
Does Using a Laparoscopic Approach to Cholecystectomy Decrease the Risk of Surgical Site Infection?
 ANNALS OF SURGERY Vol. 237, No. 3, 358 362 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Does Using a Laparoscopic Approach to Cholecystectomy Decrease the Risk of Surgical Site Infection? Chesley Richards,
ANNALS OF SURGERY Vol. 237, No. 3, 358 362 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Does Using a Laparoscopic Approach to Cholecystectomy Decrease the Risk of Surgical Site Infection? Chesley Richards,
Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy
 Revascularization of Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy Michael Conte David Dawson David L. Dawson, MD Revised Presentation Title A Selective Approach
Revascularization of Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy Michael Conte David Dawson David L. Dawson, MD Revised Presentation Title A Selective Approach
National Vascular Registry
 National Vascular Registry Angioplasty Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or
National Vascular Registry Angioplasty Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or
Infected Lower Extremity Aneurysms C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD
 Infected Lower Extremity Aneurysms C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD University Hospital of Brooklyn Department of Surgery History 52F c PMHx of HTN, asthma p/w fever, malaise s/p one week of ABx for presumed
Infected Lower Extremity Aneurysms C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD University Hospital of Brooklyn Department of Surgery History 52F c PMHx of HTN, asthma p/w fever, malaise s/p one week of ABx for presumed
Discussion of Complex Clinical Scenarios and Variable Review ACS NSQIP Clinical Support Team
 Discussion of Complex Clinical Scenarios and Variable Review CS NSQIP Clinical Support Team SCR Open Q& Calls The CS NSQIP Clinical Team is trialing Open format Q& calls for NSQIP SCRs Participation in
Discussion of Complex Clinical Scenarios and Variable Review CS NSQIP Clinical Support Team SCR Open Q& Calls The CS NSQIP Clinical Team is trialing Open format Q& calls for NSQIP SCRs Participation in
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sprung CL, Annane D, Keh D, et al. Hydrocortisone therapy for
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sprung CL, Annane D, Keh D, et al. Hydrocortisone therapy for
Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis
 Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis Michal Holub Department of Infectious Diseases First Faculty of Medicine Charles University in Prague and University Military Hospital Bacteremia and Sepsis bacteremia
Sepsis and Infective Endocarditis Michal Holub Department of Infectious Diseases First Faculty of Medicine Charles University in Prague and University Military Hospital Bacteremia and Sepsis bacteremia
Visceral aneurysm. Diagnosis and Interventions M.NEDEVSKA
 Visceral aneurysm Diagnosis and Interventions M.NEDEVSKA History 1953 De Bakeyand Cooley Visceral aneurysm VAAs rare, reported incidence of 0.01 to 0.2% on routine autopsies. Clinically important Potentially
Visceral aneurysm Diagnosis and Interventions M.NEDEVSKA History 1953 De Bakeyand Cooley Visceral aneurysm VAAs rare, reported incidence of 0.01 to 0.2% on routine autopsies. Clinically important Potentially
CT computed tomography
 14 733 737 2005 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 65 22 4 CT computed tomography 7 14 733 737 2005 1 3 65 1993 1 Tel: 045-787-2645 236-0004 3-9 2 2005 6 10 2005 8 29 2001 9 30mg / 22 Klebsiella pneumoniae 4 CT computed tomography
14 733 737 2005 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 65 22 4 CT computed tomography 7 14 733 737 2005 1 3 65 1993 1 Tel: 045-787-2645 236-0004 3-9 2 2005 6 10 2005 8 29 2001 9 30mg / 22 Klebsiella pneumoniae 4 CT computed tomography
Disclosures! Infection & Nonunions. Infection workup. Skip early infection. Culture (+) fractures. Gross Infection
 The Infected Nonunion Paul Tornetta III, MD Professor Boston Medical Center Disclosures! Publications: Rockwood and Green, Tornetta and Ricci TIFS, Tornetta and Einhorn; Subspecialty series, Court-Brown,
The Infected Nonunion Paul Tornetta III, MD Professor Boston Medical Center Disclosures! Publications: Rockwood and Green, Tornetta and Ricci TIFS, Tornetta and Einhorn; Subspecialty series, Court-Brown,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students. Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile in urinary bladder.. It contains fluids,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile in urinary bladder.. It contains fluids,
2018 CPT CODING CHANGES
 17 2018 CPT coding changes by Samuel Smith, MD, FACS; Megan McNally, MD, FACS; and Jan Nagle, MS, RPh JAN 2018 BULLETIN American College of Surgeons 18 Significant changes in Current Procedural Terminology
17 2018 CPT coding changes by Samuel Smith, MD, FACS; Megan McNally, MD, FACS; and Jan Nagle, MS, RPh JAN 2018 BULLETIN American College of Surgeons 18 Significant changes in Current Procedural Terminology
Role of irrigation and Debridement in PJI. S.M Kazemi associate professor, orthopedic surgeon SBM University Tehran Iran
 Role of irrigation and Debridement in PJI S.M Kazemi associate professor, orthopedic surgeon SBM University Tehran Iran M Kazemi associate professor, orthopedic surgeon SBM University Tehran Iran Role
Role of irrigation and Debridement in PJI S.M Kazemi associate professor, orthopedic surgeon SBM University Tehran Iran M Kazemi associate professor, orthopedic surgeon SBM University Tehran Iran Role
PSOAS ABSCESS. Dr Noman Ullah Wazir
 PSOAS ABSCESS Dr Noman Ullah Wazir Psoas Major muscle The psoas major is a long fusiform muscle located on the side of the lumbar region of the vertebral column and brim of the lesser pelvis. Psoas Major
PSOAS ABSCESS Dr Noman Ullah Wazir Psoas Major muscle The psoas major is a long fusiform muscle located on the side of the lumbar region of the vertebral column and brim of the lesser pelvis. Psoas Major
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries. Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through them.
 Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI?
 Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI? Peter F. Lawrence, M.D. Gonda Vascular Center Division of Vascular Surgery
Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI? Peter F. Lawrence, M.D. Gonda Vascular Center Division of Vascular Surgery
a Total Hip Prosthesis by Clostridum perfringens. A Case Report
 Haematogenous Infection of a Total Hip Prosthesis by Clostridum perfringens. A Case Report CHAPTER 5 CHAPTER 5 5.1. Introduction In orthopaedic surgery, an infection of a prosthesis is a very serious,
Haematogenous Infection of a Total Hip Prosthesis by Clostridum perfringens. A Case Report CHAPTER 5 CHAPTER 5 5.1. Introduction In orthopaedic surgery, an infection of a prosthesis is a very serious,
SETTING Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center. RESPONSIBLE PARTY Haiquan Chen MD.
 OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW
 CONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2015 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: 2015 PQRS MEASURES IN CONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP: #43 Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG):
CONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2015 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: 2015 PQRS MEASURES IN CONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP: #43 Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG):
Central Venous Access Devices and Infection
 Central Venous Access Devices and Infection Dr Andrew Daley Microbiology & Infectious Diseases Women s & Children s Health Melbourne Background Types of infection! Local site infection! Blood stream infection!
Central Venous Access Devices and Infection Dr Andrew Daley Microbiology & Infectious Diseases Women s & Children s Health Melbourne Background Types of infection! Local site infection! Blood stream infection!
SANWICH TECHNIQUE TO REDUCE COMPLICATIONS WHEN TREATING BILATERAL INTERNAL ILIAC ARTERY
 SANWICH TECHNIQUE TO REDUCE COMPLICATIONS WHEN TREATING BILATERAL INTERNAL ILIAC ARTERY TRAN TRA GIANG.MD Interventional cardiovascular department Hanoi Heart Hospital, Hanoi, Viet Nam Nothing to Disclose
SANWICH TECHNIQUE TO REDUCE COMPLICATIONS WHEN TREATING BILATERAL INTERNAL ILIAC ARTERY TRAN TRA GIANG.MD Interventional cardiovascular department Hanoi Heart Hospital, Hanoi, Viet Nam Nothing to Disclose
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis. Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017
 320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
Aerobic bacteria isolated from diabetic septic wounds
 Aerobic bacteria isolated from diabetic septic wounds Eithar Mohammed Mahgoub*, Mohammed Elfatih A. Omer Faculty of Pharmacy, Omdurman Islamic University Department of Pharmaceutical Microbiology, Omdurman
Aerobic bacteria isolated from diabetic septic wounds Eithar Mohammed Mahgoub*, Mohammed Elfatih A. Omer Faculty of Pharmacy, Omdurman Islamic University Department of Pharmaceutical Microbiology, Omdurman
Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline
 Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cerebrovascular Abdominal Peripheral Arterial - Duplex Imaging Peripheral Arterial
Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cerebrovascular Abdominal Peripheral Arterial - Duplex Imaging Peripheral Arterial
Selected Operative Procedure Categories for KNHSS SSI Surveillance
 Selected Operative Procedure Categories for KNHSS SSI Surveillance Breast Surgery Excision of lesion or tissue of breast including radical, modified, or quadrant resection, lumpectomy, incisional biopsy,
Selected Operative Procedure Categories for KNHSS SSI Surveillance Breast Surgery Excision of lesion or tissue of breast including radical, modified, or quadrant resection, lumpectomy, incisional biopsy,
Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment
 Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment The incidence of infection following implantation of cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) is increasing at a faster rate
Infected cardiac-implantable electronic devices: diagnosis, and treatment The incidence of infection following implantation of cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) is increasing at a faster rate
Bacteriemia and sepsis
 Bacteriemia and sepsis Case 1 An 80-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his son, who noted that his father had become lethargic and has decreased urination over the past 4 days. The patient
Bacteriemia and sepsis Case 1 An 80-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his son, who noted that his father had become lethargic and has decreased urination over the past 4 days. The patient
John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division
 John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division John Campbell, MD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity,
John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division John Campbell, MD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity,
A new technique for reconstruction of the aortic bifurcation with saphenous vein panel graft
 CASE REPORTS A new technique for reconstruction of the aortic bifurcation with saphenous vein panel graft Alexandros Mallios, MD, Benoit Boura, MD, Faris Alomran, MD, and Myriam Combes, MD, Paris, France
CASE REPORTS A new technique for reconstruction of the aortic bifurcation with saphenous vein panel graft Alexandros Mallios, MD, Benoit Boura, MD, Faris Alomran, MD, and Myriam Combes, MD, Paris, France
Urinary tract infection. Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Lecturer of pediatrics Jazan faculty of medicine
 Urinary tract infection Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Lecturer of pediatrics Jazan faculty of medicine Objectives To differentiate between types of urinary tract infections To recognize the epidemiology of UTI in
Urinary tract infection Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Lecturer of pediatrics Jazan faculty of medicine Objectives To differentiate between types of urinary tract infections To recognize the epidemiology of UTI in
2017 ICD 10 PCS Code Updates
 2017 ICD 10 PCS Code Updates Kimberly Cunningham CPC, CIC, CCS Copyright/Disclaimer text No part of this presentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means (graphically, electronically,
2017 ICD 10 PCS Code Updates Kimberly Cunningham CPC, CIC, CCS Copyright/Disclaimer text No part of this presentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means (graphically, electronically,
Nellix Endovascular System: Clinical Outcomes and Device Overview
 Nellix Endovascular System: Clinical Outcomes and Device Overview Jeffrey P. Carpenter, MD Professor and Chief, Department of Surgery CAUTION: Investigational device. This product is under clinical investigation
Nellix Endovascular System: Clinical Outcomes and Device Overview Jeffrey P. Carpenter, MD Professor and Chief, Department of Surgery CAUTION: Investigational device. This product is under clinical investigation
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Axillobrachial artery bypass grafting with in situ cephalic vein for axillary artery occlusion: A case report
 CASE REPORTS Axillobrachial artery bypass grafting with in situ cephalic vein for axillary artery occlusion: A case report Evan S. Cohen,/VII), Robert B. Holtzman, MD, and George W. Johnson, Jr., MD, Houston,
CASE REPORTS Axillobrachial artery bypass grafting with in situ cephalic vein for axillary artery occlusion: A case report Evan S. Cohen,/VII), Robert B. Holtzman, MD, and George W. Johnson, Jr., MD, Houston,
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Surveillance of Surgical Site Infection in Surgical Hospital Wards in Bulgaria,
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.361
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.361
Indications: following: embolization. artery that has diseases 5. The evaluation. of suspected. such entities. a cold hand. biopsy
 Peripheral Arterial Ultrasound Protocol Using Color and Spectral Doppler Reviewed by: Mark Yuhasz, MD Last Review Date: January 2015 Contact: (866) 761 4200, Option 1 Indications: The indications for peripheral
Peripheral Arterial Ultrasound Protocol Using Color and Spectral Doppler Reviewed by: Mark Yuhasz, MD Last Review Date: January 2015 Contact: (866) 761 4200, Option 1 Indications: The indications for peripheral
Improved results with conventional. management of infrarenal aortic infection. 6-9
 Improved results with conventional management of infrarenal aortic infection Richard A. Yeager, MD, Lloyd M. Taylor, Jr, MD, Gregory L. Moneta, MD, James M. Edwards, MD, Alexander D. Nicoloff, MD, Donald
Improved results with conventional management of infrarenal aortic infection Richard A. Yeager, MD, Lloyd M. Taylor, Jr, MD, Gregory L. Moneta, MD, James M. Edwards, MD, Alexander D. Nicoloff, MD, Donald
Online Supplement for:
 Online Supplement for: INFLUENCE OF COMBINED INTRAVENOUS AND TOPICAL ANTIBIOTIC PROPHYLAXIS ON THE INCIDENCE OF INFECTIONS, ORGAN DYSFUNCTIONS, AND MORTALITY IN CRITICALLY ILL SURGICAL PATIENTS A PROSPECTIVE,
Online Supplement for: INFLUENCE OF COMBINED INTRAVENOUS AND TOPICAL ANTIBIOTIC PROPHYLAXIS ON THE INCIDENCE OF INFECTIONS, ORGAN DYSFUNCTIONS, AND MORTALITY IN CRITICALLY ILL SURGICAL PATIENTS A PROSPECTIVE,
Transfusion and Blood Stream Infections after Coronary Surgery
 1 Transfusion and Blood Stream Infections after Coronary Surgery Tuomas Tauriainen, a Eeva-Maija Kinnunen, a Idamaria Laitinen, a Vesa Anttila, b Tuomas Kiviniemi, b Juhani K.E. Airaksinen, b and Fausto
1 Transfusion and Blood Stream Infections after Coronary Surgery Tuomas Tauriainen, a Eeva-Maija Kinnunen, a Idamaria Laitinen, a Vesa Anttila, b Tuomas Kiviniemi, b Juhani K.E. Airaksinen, b and Fausto
2006 NKF-DOQI Guidelines Preferred Vascular Access Order 1. Radiocephalic (wrist) fistula 2. Brachiocephalic (elbow) fistula 3. Basilic vein transposi
 Stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease Assessing the Results of AV Access: Realistic Outcomes in 2009 Sean P. Roddy, MD Albany, NY Defined as a GFR
Stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease Assessing the Results of AV Access: Realistic Outcomes in 2009 Sean P. Roddy, MD Albany, NY Defined as a GFR
Postoperative Surgical Site Infection after Incisional Hernia Repair: Link to Previous Surgical Site Infection? Zulfiqar Ali, AG Rehan
 Original Article Postoperative Surgical Site Infection after Incisional Hernia Repair: Link to Previous Surgical Site Infection? Zulfiqar Ali, AG Rehan ABSTRACT Objective: Aim of the study was to determine
Original Article Postoperative Surgical Site Infection after Incisional Hernia Repair: Link to Previous Surgical Site Infection? Zulfiqar Ali, AG Rehan ABSTRACT Objective: Aim of the study was to determine
Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study
 The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study Authors: Merribeth Bruntz, DPM, MS* 1,2, Heather Young, MD 3,4, Robert W.
The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study Authors: Merribeth Bruntz, DPM, MS* 1,2, Heather Young, MD 3,4, Robert W.
Treatment of Prosthetic Graft Infection after Thoracic Aorta Replacement
 Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2014; 20: 304 309 Online June 4, 2013 doi: 10.5761/atcs.oa.13-00059 Original Article Treatment of Prosthetic Graft Infection after Thoracic Aorta Replacement Tamaki Takano, MD,
Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2014; 20: 304 309 Online June 4, 2013 doi: 10.5761/atcs.oa.13-00059 Original Article Treatment of Prosthetic Graft Infection after Thoracic Aorta Replacement Tamaki Takano, MD,
Interesting Case Series. A Case of Fournier s Gangrene
 Interesting Case Series A Case of Fournier s Gangrene Anthony Maurice Kordahi, MD, and Ahmed S. Suliman, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, University of California San Diego Correspondence: kordahi.amk@gmail.com
Interesting Case Series A Case of Fournier s Gangrene Anthony Maurice Kordahi, MD, and Ahmed S. Suliman, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, University of California San Diego Correspondence: kordahi.amk@gmail.com
Basics of Interventional Radiology Coding 2017
 Basics of Interventional Radiology Coding 2017 Prepared and Published By: MedLearn Publishing A Division of Panacea Healthcare Solutions, Inc. 287 East Sixth Street, Suite 400 St. Paul, MN 55101 1-800-252-1578
Basics of Interventional Radiology Coding 2017 Prepared and Published By: MedLearn Publishing A Division of Panacea Healthcare Solutions, Inc. 287 East Sixth Street, Suite 400 St. Paul, MN 55101 1-800-252-1578
Disclosure. Speaker name: Prof. Hesham Aly Sharaf El-Din. I do not have any potential conflict of interest
 Disclosure Speaker name: Prof. Hesham Aly Sharaf El-Din I do not have any potential conflict of interest Introduction 5% of patients with upper limb AVF develop ipsilateral hand ischemia, recently termed
Disclosure Speaker name: Prof. Hesham Aly Sharaf El-Din I do not have any potential conflict of interest Introduction 5% of patients with upper limb AVF develop ipsilateral hand ischemia, recently termed
Primary foci of hematogenous periprosthetic joint infections
 Primary foci of hematogenous periprosthetic joint infections Dr. Anastasia Rakow Dr. Nora Renz Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin C.S., w. 73 y.o. 07/2015: presentation with painful knee prosthesis, back
Primary foci of hematogenous periprosthetic joint infections Dr. Anastasia Rakow Dr. Nora Renz Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin C.S., w. 73 y.o. 07/2015: presentation with painful knee prosthesis, back
Promising first experience of endovascular treatment of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms
 Promising first experience of endovascular treatment of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms Stevo Duvnjak, EBIR,FCIRSE Tomas Balezantis Jes Lindholdt Faculty disclosure Stevo Duvnjak, Tomas Balezantis,
Promising first experience of endovascular treatment of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms Stevo Duvnjak, EBIR,FCIRSE Tomas Balezantis Jes Lindholdt Faculty disclosure Stevo Duvnjak, Tomas Balezantis,
Amputations. Chapter 23
 Amputations Chapter 23 Amputations Introduction Battle casualties who sustain amputations have the most severe extremity injuries. Historically, 1 in 3 patients with a major amputation (proximal to the
Amputations Chapter 23 Amputations Introduction Battle casualties who sustain amputations have the most severe extremity injuries. Historically, 1 in 3 patients with a major amputation (proximal to the
Neurological Complications of TEVAR. Frank J Criado, MD. Union Memorial-MedStar Health Baltimore, MD USA
 ISES Online Neurological Complications of Frank J Criado, MD TEVAR Union Memorial-MedStar Health Baltimore, MD USA frank.criado@medstar.net Paraplegia Incidence is 0-4% after surgical Rx of TAAs confined
ISES Online Neurological Complications of Frank J Criado, MD TEVAR Union Memorial-MedStar Health Baltimore, MD USA frank.criado@medstar.net Paraplegia Incidence is 0-4% after surgical Rx of TAAs confined
Fluorescence Angiography in Limb Salvage
 Fluorescence Angiography in Limb Salvage Ryan H. Fitzgerald, DPM, FACFAS Associate Professor of Surgery-University Of South Carolina School of Medicine, Greenville Etiology of Lower extremity wounds Neuropathy
Fluorescence Angiography in Limb Salvage Ryan H. Fitzgerald, DPM, FACFAS Associate Professor of Surgery-University Of South Carolina School of Medicine, Greenville Etiology of Lower extremity wounds Neuropathy
Case report. Infected endograft with perigraft abscess, graft-enteric fistula following endovascular repair of Leriche s syndrome
 Infected endograft with perigraft abscess, graft-enteric fistula following endovascular repair of Leriche s syndrome Case report Mladenova NB Department of Radiology, Acibadem City Clinic Tokuda Hospital
Infected endograft with perigraft abscess, graft-enteric fistula following endovascular repair of Leriche s syndrome Case report Mladenova NB Department of Radiology, Acibadem City Clinic Tokuda Hospital
SELECTIVE ANTEGRADE TECHNIQUE OF CHOICE
 SELECTIVE ANTEGRADE CEREBRAL PERFUSION IS THE TECHNIQUE OF CHOICE MARKO TURINA University of Zurich Zurich, Switzerland What is so special about the operation on the aortic arch? Disease process is usually
SELECTIVE ANTEGRADE CEREBRAL PERFUSION IS THE TECHNIQUE OF CHOICE MARKO TURINA University of Zurich Zurich, Switzerland What is so special about the operation on the aortic arch? Disease process is usually
Importance of the third arterial graft in multiple arterial grafting strategies
 Research Highlight Importance of the third arterial graft in multiple arterial grafting strategies David Glineur Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Cliniques St Luc, Bouge and the Department of Cardiovascular
Research Highlight Importance of the third arterial graft in multiple arterial grafting strategies David Glineur Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Cliniques St Luc, Bouge and the Department of Cardiovascular
Talent Abdominal Stent Graft
 Talent Abdominal with THE Xcelerant Hydro Delivery System Expanding the Indications for EVAR Treat More Patients Short Necks The Talent Abdominal is the only FDA-approved device for proximal aortic neck
Talent Abdominal with THE Xcelerant Hydro Delivery System Expanding the Indications for EVAR Treat More Patients Short Necks The Talent Abdominal is the only FDA-approved device for proximal aortic neck
Subclavian artery Stenting
 Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
Hybrid Repair of a Complex Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm
 Hybrid Repair of a Complex Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm Virendra I. Patel MD MPH Assistant Professor of Surgery Massachusetts General Hospital Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Disclosure
Hybrid Repair of a Complex Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm Virendra I. Patel MD MPH Assistant Professor of Surgery Massachusetts General Hospital Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Disclosure
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection
 Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
ICD-10-PCS GUIDELINE/ CODE CHANGES
 ICD-10-PCS GUIDELINE/ CODE CHANGES 2016 TO 2017 75,789 TOTAL PCS CODES Medical, Surgical, Administration, Measurement and Monitoring, Extracorporeal Therapies, and New Technology all have changes As expected
ICD-10-PCS GUIDELINE/ CODE CHANGES 2016 TO 2017 75,789 TOTAL PCS CODES Medical, Surgical, Administration, Measurement and Monitoring, Extracorporeal Therapies, and New Technology all have changes As expected
Infection Control. Student Orientation
 Infection Control Student Orientation Basic, but important, Principles of Cross Transmission Presence of microorganisms on hands or in environment does not necessarily = cross transmission or infection
Infection Control Student Orientation Basic, but important, Principles of Cross Transmission Presence of microorganisms on hands or in environment does not necessarily = cross transmission or infection
Balgrist Shoulder Course 2017
 Diagnosis and Management of Infection in Revision Shoulder Arthroplasty Joseph P. Iannotti MD, PhD Maynard Madden Professor and Chairman Orthopaedic and Rheumatologic Institute Cleveland Clinic Conflict
Diagnosis and Management of Infection in Revision Shoulder Arthroplasty Joseph P. Iannotti MD, PhD Maynard Madden Professor and Chairman Orthopaedic and Rheumatologic Institute Cleveland Clinic Conflict
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement
 Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Appendix A: Summary of evidence from surveillance
 Appendix A: Summary of evidence from surveillance 8-year surveillance (2017) Surgical site infections: prevention and treatment (2008) NICE guideline CG74 Summary of evidence from surveillance... 1 Research
Appendix A: Summary of evidence from surveillance 8-year surveillance (2017) Surgical site infections: prevention and treatment (2008) NICE guideline CG74 Summary of evidence from surveillance... 1 Research
Coffey et al ND 6 HA, 5 TSA, and 5 other MRSA (3) and Staphylococcus epidermidis (3)
 Page 1 of 6 TABLE E-1 Outcomes of the Treatment of Periprosthetic Shoulder Infections* ä Study No. Presentation Prosthesis Most Common Pathogens Braman et al. 68 7 1 acute, 2 subacute, 2 HA and 5 TSA Staphylococcus
Page 1 of 6 TABLE E-1 Outcomes of the Treatment of Periprosthetic Shoulder Infections* ä Study No. Presentation Prosthesis Most Common Pathogens Braman et al. 68 7 1 acute, 2 subacute, 2 HA and 5 TSA Staphylococcus
Epidemiology. 16% incidence in knee. dislocation
 Epidemiology Highest risk group: Young male between 15 and 45 years (USA) Mortality Ratio after trauma : male/female: 7/1 Peripheral vascular injuries : 70%-80% of all cases of vascular trauma : Vascular
Epidemiology Highest risk group: Young male between 15 and 45 years (USA) Mortality Ratio after trauma : male/female: 7/1 Peripheral vascular injuries : 70%-80% of all cases of vascular trauma : Vascular
Modification in aortic arch replacement surgery
 Gao et al. Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery (2018) 13:21 DOI 10.1186/s13019-017-0689-y LETTER TO THE EDITOR Modification in aortic arch replacement surgery Feng Gao 1,2*, Yongjie Ye 2, Yongheng Zhang
Gao et al. Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery (2018) 13:21 DOI 10.1186/s13019-017-0689-y LETTER TO THE EDITOR Modification in aortic arch replacement surgery Feng Gao 1,2*, Yongjie Ye 2, Yongheng Zhang
