Holter Monitoring (24-h Electrocardiography) of Holstein Calves
|
|
|
- Neil Roberts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Scientiae Veterinariae, : RESEARCH ARTICLE Pub ISSN Holter Monitoring (24-h Electrocardiography) of Holstein Calves Rebecca Bastos Pessoa, Camila Freitas Batista, Kamila Reis Santos, Jéssyca Beraldi Bellinazzi, Alice Maria Melville Paiva Della Libera & Maria Helena Matiko Akao Larsson ABSTRACT Background: Twenty-four h electrocardiographic monitoring is a noninvasive method of assessing cardiac rhythm. Holter monitoring in farm animals can help assessing heart rate variability and its relationship with stress and production. Several authors have reviewed the normal cardiac rhythm of bovines, but there is little information on heart rhythm in calves. The goal of this research is to elucidate which cardiac rhythms may be considered physiological in Holstein calves, from 3 to 6 months old. Materials, Methods & Results: Twenty-four h ambulatory electrocardiography (Holter monitoring) was performed in 10 male Holstein calves, with ages ranging from 3 to 6 months old. The animals came from private farms in São Paulo state and were housed in a semi-open stall during the study. The animals had their hair clipped from the third to the fifth intercostal spaces on both sides of the chest, from the sternal region to the glenohumeral joint, and seven electrodes were positioned in a diagonal configuration. Decoding of the recordings was performed using specialized software and in order to minimize digital mistakes, all of the beats marked as ectopic by the software were manually revised by the authors. Mean heart rate was 83.2 ± beats per min (bpm), maximum heart rate was ± bpm, and minimum heart rate was 53.7 ± 7.45 bpm. In 90% of the calves, normal sinus rhythm was predominant, whereas in 10%, sinus arrhythmia (SA) was prevalent. Second degree atrioventricular blocks (AV blocks) were observed in 30% of the animals and supraventricular premature beats (SPB) were detected in 50%. Holter monitoring was repeated after three months in three of the animals; two showed no arrhythmias at the second exam, and in the other, the frequency of AV blocks was decreased by 88.64%. Discussion: In the present study, the authors observed a relatively high incidence of arrhythmias in Holstein calves, although there is little information available in the literature for comparison. The use of Holter monitoring is much more sensitive in the assessment of arrhythmias than a standard electrocardiogram, since it records the cardiac rhythm for 24 to 48 h, as opposed to only 2 to 3 min. Therefore, it is possible that the arrhythmias found in the calves in the current study were physiological events otherwise unidentified by conventional electrocardiogram. The AV blocks observed in the animals of the present study were intermittent and apparently non-related to any particular event or situation, so it was not possible to demonstrate whether they disappeared after exercise. As for the supraventricular ectopic beats, they are frequent in older bovines, mainly in dairy cows, and are usually related to increased vagal tone, stress, hormonal changes, ectopic atrial focus, and peak lactation volume overload. The animals used in the present study were otherwise healthy, and did not demonstrate any clinical signs of gastrointestinal dysfunction or other disease that might have justified an increase in their vagal tone. In addition, the decrease in the number of rhythm abnormalities in the older calves that were submitted to a second Holter exam supports the hypothesis that supraventricular ectopic beats and second degree AV blocks of Mobitz type II may be normal in calves up to six months old. Keywords: electrocardiography, veterinary cardiology, Holstein, calves, buiatrics. Received: 14 January 2016 Accepted: 4 June 2016 Published: 30 June 2016 Department of Internal Medicine of the School of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science, University of São Paulo (USP), São Paulo, SP, Brazil. COR- RESPONDENCE: R.B. Pessoa [rebeccapessoa@uol.com.br - Fax: +55 (11) ]. Department of Internal Medicine of the School of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science, USP. Avenida Prof. Dr. Orlando Marques de Paiva n. 87. CEP São Paulo, SP, Brazil. 1
2 INTRODUCTION Twenty-four h electrocardiographic monitoring is a noninvasive method of assessing cardiac rhythm. It is much more sensitive in the assessment of arrhythmias than a standard electrocardiogram (ECG), since it records the cardiac rhythm for 24 to 48 h, as opposed to only 2 to 3 min [7]. Besides aiding the diagnosis of cardiac arrhythmias, it is also indicated to correlate clinical manifestations with periods of arrhythmia, assess the need for treatment of arrhythmias, evaluate the efficacy of antiarrhythmic therapy, and detect occult cardiomyopathies [7]. Most of the research on Holter monitoring in farm animals has aimed to assess heart rate variability and its relationship with stress and production [2]. Several authors have reviewed the normal cardiac rhythm of bovines, but there is little information on heart rhythm in calves. There is disagreement in the literature as to whether sinus arrhythmia is rare in bovines, or if it is actually frequent [4,10]. There are reports of arrhythmia in Holstein dairy cows, which involve mainly atrial fibrillation [3,9]. There are also reports of atrioventricular blocks (AV blocks) and atrial and ventricular ectopic beats, but these are low in number [10]. Nevertheless, the small amount of research involving Holter monitoring in ruminants indicates that some types of arrhythmias may have been underestimated in this species, since most of the research has used conventional ECG. Therefore, the goal of this research is to elucidate which cardiac rhythms may be considered physiological in Holstein calves. MATERIALS AND METHODS 2 Ten male Holstein calves were used in the present study. They came from private farms in São Paulo state, and during the experiment, they were aged from three to six months. The animals were housed in a semi-open stall at the Veterinary Hospital of Cattle and Small Ruminants of the School of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science of the University of São Paulo. The animals were fed with concentrated food two times a day and ad libitum hay and water. A full clinical examination was performed in each of the animals before the beginning of every recording. The animals had their hair clipped from the third to the fifth intercostal spaces on both sides of the chest, from the sternal region to the glenohumeral joint. Seven electrodes were positioned in a diagonal configuration, with three of them on the right side of the chest, and four on the left side. The wires and recorders were protected by one layer of elastic bandage and two layers of adhesive tape. The recorders used included analogical (Dynamis) 1 and digital (DMS 300-6) 2 devices. Decoding of the recordings was performed using specialized software (CardioScan 10) 2. In order to minimize digital mistakes, all of the beats marked as ectopic by the software were manually revised by the authors. Analysis of the results included a 24-h summary of medium, maximum, and minimum heart rates, predominant heart rhythm, number of ectopic beats per hour, and atrioventricular or sinus abnormalities. In order to estimate the mean time of bradycardia and tachycardia in each animal, the 24-h summary of heart rate was used, and rates above 100 beats per min were considered tachycardia, while those below 70 beats per min were considered bradycardia. Sinus arrhythmia was diagnosed when consecutive RR intervals differed by more than 10% in their length. Statistical analysis was made using Graph Pad Instat software 3. RESULTS The results are summarized in Tables 1 and 2. Calves 1, 2, and 9 are identified as 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b, 9a, and 9b because each of them underwent the Holter exam twice, with an interval of approximately 3 months between the recordings. No ectopic beats were identified in calves 1 and 9 during the second recording, and the frequency of AV blocks was decreased by 88.64% in calf 2. The estimated percentage of bradycardia and tachycardia in the recordings for each animal is summarized in Table 3. DISCUSSION Heart rhythm abnormalities in bovines are not rare, but their significance is not always clear [10]. In the present study, the authors observed a relatively high incidence of arrhythmias in Holstein calves, although there is little information available in the literature for comparison. Most of the reports regarding assessment of heart rhythm in bovines have been performed using conventional ECG [6,10] and have focused mainly on heart rate variability [5]. The use of 24-h ambulatory ECG in the present study enabled the standardization of normal cardiac rhythms in Holstein calves as well as the identification of possibly underestimated arrhythmias in this population.
3 Table 1. Holter parameters of Holstein calves from three to six months old. São Paulo, Calf identification QRS/min Length of recording (min) Holter parameters Interf (%) HR mean HR max HR min HR> 100 (min) HR<70 (min) Mean ± SD ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± QRS/min= number of QRS complexes per min of recording; Interf= interference; HR= heart rate; HR>100= period of time HR was higher than 100 bpm; HR<70= period of time HR was lower than 70 bpm. Table 2. Number of arrhythmias detected by the Holter exam in Holstein calves. São Paulo, Arrhythmia Calf identification SV SV paired SVT VE VE paired VT Pause> 2s 2nd degree AV block MI 2nd degree AV block MII 1a b a b a b Mean ± SD ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± SV= supraventricular ectopic beats; SV paired= paired supraventricular ectopic beats; SVT= supraventricular tachycardia; VE= ventricular ectopic beats; VE paired= paired ventricular ectopic beats; VT= ventricular tachycardia; 2 nd degree AV block MI= second degree atrioventricular block of Mobitz type I; 2 nd degree AV block MII= second degree atrioventricular block of Mobitz type II. 3
4 Table 3. Percentage of time in bradycardia and tachycardia observed in Holstein calves. São Paulo, Calf identification Time (%) HR>100 bpm HR<70 bpm AV blocks are not as common in bovines as they are in horses [10], but they have been reported in this species by authors using conventional ECG [6,10]. In the present study, this conduction abnormality was observed in 30% of the animals, and second degree AV block was the most common type. In this type of block, electric conduction from the atria to the ventricle is temporarily interrupted, and isolated P waves are present on the tracing, although most of the electric impulses are conducted and generate normal QRS complexes. In horses, second degree AV block is considered physiological when it disappears after exercise, and is related to increased vagal tone [8]. The AV blocks observed in the animals of the present study were intermittent and apparently nonrelated to any particular event or situation, so it was not possible to demonstrate whether they disappeared after exercise. There are reports of second degree AV blocks in both healthy and sick cattle, but the majority of these were related to calves presenting diarrhea or plant poisoning [6,10].While second degree AV blocks have been described in cattle, there is a predominance of first degree AV blocks [6]. In horses, second degree Mobitz type I episodes are more frequent, and they are characterized by a gradual increase in the length of the PR segment before an isolated P wave is identified [8]. In the present investigation, a predominance of second degree AV blocks of Mobitz type II was observed in calves, which represents new information regarding the cardiac rhythm of this species. Supraventricular ectopic beats are frequent in older bovines, mainly in dairy cows, and are related to the occurrence of atrial fibrillation [1]. This type of arrhythmia is usually caused by increased vagal tone, stress related to hormones, ectopic atrial focus, and volume overload associated with peak lactation [3]. CONCLUSION It is possible that the arrhythmias found in the calves in the current study were physiological events. The animals were otherwise healthy, and did not demonstrate any clinical signs of gastrointestinal dysfunction or other disease that might have justified an increase in their vagal tone. In addition, the decrease in the number of rhythm abnormalities in the older calves that were submitted to a second Holter exam supports the hypothesis that supraventricular ectopic beats and second degree AV blocks of Mobitz type II may be normal in calves up to six months old. Nevertheless, more studies are necessary to establish whether there are any particularities in the development of the atrioventricular node of Holstein calves, or if there are some factors associated with an increase in the vagal tone of these animals that may justify the rhythm disturbances observed. It is also necessary to investigate whether these arrhythmias occur only in Holstein calves or if adult cows or other breeds may also be involved. MANUFACTURERS 1 Cardio Sistemas Comercial e Industrial Ltda. São Paulo, SP, Brazil. 2 DMS Brasil. São Paulo, SP, Brazil. 3 Graph Pad Software. San Diego, CA, USA. 4
5 Ethical approval. All procedures, treatments and animal care were in compliance with the guidelines of the Comissão de Ética no Uso de Animais - CEUA of the School of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science, University of São Paulo. Declaration of interest. The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of paper. REFERENCES 1 Constable P.D., Muir W.W. III, Bonagura J.D., Rings D.M. & St. Jean G Clinical and electrocardiographic characterization of cattle with atrial premature complexes. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association. 9: Hagen K., Langbein J., Schmied C., Lexer D. & Waiblinger S Heart rate variability in dairy cows-influences of breed and milking system. Physiology & Behavior. 85(2): Machida N., Nakamura T., Kiryu K. & Kagota K Electrocardiographic features and incidence of atrial fibrillation in apparently healthy dairy cows. Journal of Veterinary Medicine Series A. 40: Machida N., Okamoto Y., Minami S., Yamaga Y. & Kagota K Cardiac arrhythmias in normal Holstein heifers. Journal of the Japan Veterinary Medical Association. 44: Mohr E., Langbein J. & Nürnberg G Heart rate variability: a noninvasive approach to measure stress in calves and cows. Physiology & Behavior. 75(1-2): Naghadeh B.D., Dezfouli M.R. & Rezakhani A A survey on frequency of A-V blocks in cattle. Journal of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine University of Tehran. 54: Petrie J Practical application of holter monitoring in dogs and cats. Clinical Techniques in Small Animal Practice. 20: Reef V.B Arrhythmias. In: Marr C.M. (Ed). Cardiology of the Horse. London: W.B. Saunders Co., pp Rezakhani A., Oloumi M.M. & Ahmadi R Atrial fibrillation in a cow with fetal maceration. Canadian Veterinary Journal. 37: Rezakhani A., Paphan A.A. & Gheisari H.R Cardiac dysrhythmias in clinically healthy heifers and cows. Revue de Médecine Vétérinaire. 155: Scheer P., Svoboda P., Doubek J., Radvanová J., Radvan M. & Kantorová I The electrocardiographic Holter monitoring in experimental veterinary practice. Physiological Research. 59:
Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation
 Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation Objectives 2 To understand the Basic ECG To understand the meaning of Dysrhythmia To describe the normal heart conduction system. To describe the normal impulse pathways.
Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation Objectives 2 To understand the Basic ECG To understand the meaning of Dysrhythmia To describe the normal heart conduction system. To describe the normal impulse pathways.
ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology)
 ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology) Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. GOAL: Reduce Anxiety about ECGs Back to
ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology) Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. GOAL: Reduce Anxiety about ECGs Back to
Rate: The atrial and ventricular rates are equal; heart rate is greater than 100 bpm (usually between bpm).
 Sinus Bradycardia Regularity: The R-R intervals are constant; the rhythm is regular. Rate: The atrial and ventricular rates are equal; heart rate is less than 60 bpm. P wave: There is a uniform P wave
Sinus Bradycardia Regularity: The R-R intervals are constant; the rhythm is regular. Rate: The atrial and ventricular rates are equal; heart rate is less than 60 bpm. P wave: There is a uniform P wave
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2
8/20/2012. Learning Outcomes (Cont d)
 1 2 3 4 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2 Identify premature junctional complexes
1 2 3 4 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2 Identify premature junctional complexes
Lecture outline. Electrical properties of the heart. Automaticity. Excitability. Refractoriness. The ABCs of ECGs Back to Basics Part I
 Lecture outline The ABCs of ECGs Back to Basics Part I Meg Sleeper VMD, DACVIM (cardiology) University of Florida Veterinary School Electrical properties of the heart Action potentials Normal intracardiac
Lecture outline The ABCs of ECGs Back to Basics Part I Meg Sleeper VMD, DACVIM (cardiology) University of Florida Veterinary School Electrical properties of the heart Action potentials Normal intracardiac
Twenty-four Hour Ambulatory Electrocardiography (Holter Monitoring) in Normal Unsedated Cats
 Acta Scientiae Veterinariae, 2014. 42: 1196. RESEARCH ARTICLE Pub. 1196 ISSN 1679-9216 Twenty-four Hour Ambulatory Electrocardiography (Holter Monitoring) in Normal Unsedated Cats Fernanda Lie Yamaki 1,
Acta Scientiae Veterinariae, 2014. 42: 1196. RESEARCH ARTICLE Pub. 1196 ISSN 1679-9216 Twenty-four Hour Ambulatory Electrocardiography (Holter Monitoring) in Normal Unsedated Cats Fernanda Lie Yamaki 1,
Ambulatory ECG Monitoring. Gill Bouncir Blackpool Victoria Hospital
 Ambulatory ECG Monitoring Gill Bouncir Blackpool Victoria Hospital History Developed in late 1950 s as a result of research of Dr Norman Holter TYPES Holter - continuous recording. Event recorder- patient
Ambulatory ECG Monitoring Gill Bouncir Blackpool Victoria Hospital History Developed in late 1950 s as a result of research of Dr Norman Holter TYPES Holter - continuous recording. Event recorder- patient
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia PSVT.
 Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Step by step approach to EKG rhythm interpretation:
 Sinus Rhythms Normal sinus arrhythmia Small, slow variation of the R-R interval i.e. variation of the normal sinus heart rate with respiration, etc. Sinus Tachycardia Defined as sinus rhythm with a rate
Sinus Rhythms Normal sinus arrhythmia Small, slow variation of the R-R interval i.e. variation of the normal sinus heart rate with respiration, etc. Sinus Tachycardia Defined as sinus rhythm with a rate
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 5: Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 5.1 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 5: Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 5.1 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings
ECG interpretation basics
 ECG interpretation basics Michał Walczewski, MD Krzysztof Ozierański, MD 21.03.18 Electrical conduction system of the heart Limb leads Precordial leads 21.03.18 Precordial leads Precordial leads 21.03.18
ECG interpretation basics Michał Walczewski, MD Krzysztof Ozierański, MD 21.03.18 Electrical conduction system of the heart Limb leads Precordial leads 21.03.18 Precordial leads Precordial leads 21.03.18
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
Module 1: Introduction to ECG & Normal ECG
 Module 1: Introduction to ECG & Normal ECG Importance of Correct anatomical positions Measurements & Morphologies ONLY accurate if Precise anatomical positions adhered to Standardised techniques are used
Module 1: Introduction to ECG & Normal ECG Importance of Correct anatomical positions Measurements & Morphologies ONLY accurate if Precise anatomical positions adhered to Standardised techniques are used
WHAT S THAT RHYTHM I AM HEARING? GUIDE TO AUSCULTATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS IN HORSES
 WHAT S THAT RHYTHM I AM HEARING? GUIDE TO AUSCULTATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS IN HORSES Michelle Henry Barton DVM, PhD, DACVIM University of Georgia, Athens, GA INTRODUCTION The purpose of this talk is to review
WHAT S THAT RHYTHM I AM HEARING? GUIDE TO AUSCULTATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS IN HORSES Michelle Henry Barton DVM, PhD, DACVIM University of Georgia, Athens, GA INTRODUCTION The purpose of this talk is to review
EKG Abnormalities. Adapted from:
 EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE. Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology
 PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology Medical University of Łódź The heart is made up of four chambers Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle
PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology Medical University of Łódź The heart is made up of four chambers Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle
CRC 431 ECG Basics. Bill Pruitt, MBA, RRT, CPFT, AE-C
 CRC 431 ECG Basics Bill Pruitt, MBA, RRT, CPFT, AE-C Resources White s 5 th ed. Ch 6 Electrocardiography Einthoven s Triangle Chest leads and limb leads Egan s 10 th ed. Ch 17 Interpreting the Electrocardiogram
CRC 431 ECG Basics Bill Pruitt, MBA, RRT, CPFT, AE-C Resources White s 5 th ed. Ch 6 Electrocardiography Einthoven s Triangle Chest leads and limb leads Egan s 10 th ed. Ch 17 Interpreting the Electrocardiogram
AGE-RELATED CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS IN CLINICALLY HEALTHY IRANIAN NAJDI GOATS
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2012), 15, No 1, 37 43 AGE-RELATED CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS IN CLINICALLY HEALTHY IRANIAN NAJDI GOATS M. POURJAFAR, K. BADIEI, A. A. CHALMEH, A. R. SANATI, A. SHAHBAZI,
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2012), 15, No 1, 37 43 AGE-RELATED CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS IN CLINICALLY HEALTHY IRANIAN NAJDI GOATS M. POURJAFAR, K. BADIEI, A. A. CHALMEH, A. R. SANATI, A. SHAHBAZI,
I have no conflicts of interest relative to this lecture.
 PATHWAYS AROUND THE PITFALLS OF EKG RHYTHM INTERPRETATION Donald D. Brown, MD April 4, 2019 I have no conflicts of interest relative to this lecture. OBJECTIVES FOR PATHWAYS AROUND PITFALLS OF EKG RHYTHM
PATHWAYS AROUND THE PITFALLS OF EKG RHYTHM INTERPRETATION Donald D. Brown, MD April 4, 2019 I have no conflicts of interest relative to this lecture. OBJECTIVES FOR PATHWAYS AROUND PITFALLS OF EKG RHYTHM
physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer Turquoise team
 15 physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer 22-3-2016 Turquoise team Cardiac Arrhythmias and Their Electrocardiographic Interpretation Today, we are going to talk about the abnormal excitation. As we said before,
15 physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer 22-3-2016 Turquoise team Cardiac Arrhythmias and Their Electrocardiographic Interpretation Today, we are going to talk about the abnormal excitation. As we said before,
HTEC 91. Performing ECGs: Procedure. Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Topic for Today: Sinus Rhythms. Characteristics of NSR. Conduction Pathway
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 3 Performing ECGs: Procedure o ECG protocol: you may NOT do ECG if you have not signed up! If you are signed up and the room is occupied with people who did
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 3 Performing ECGs: Procedure o ECG protocol: you may NOT do ECG if you have not signed up! If you are signed up and the room is occupied with people who did
CORONARY ARTERIES. LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral wall of left vent Anterior 2/3 of interventricluar septum R & L bundle branches
 CORONARY ARTERIES RCA Right atrium Right ventricle SA node 55% AV node 90% Posterior wall of left ventricle in 90% Posterior third of interventricular septum 90% LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral
CORONARY ARTERIES RCA Right atrium Right ventricle SA node 55% AV node 90% Posterior wall of left ventricle in 90% Posterior third of interventricular septum 90% LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral
Arrhythmia Management Joshua M. Cooper, MD, FHRS, FACC
 Arrhythmia Management Joshua M. Cooper, MD, FHRS, FACC Professor of Medicine Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology Temple University Health System Plumbing Electrical System Bradyarrhythmias Sinus Node
Arrhythmia Management Joshua M. Cooper, MD, FHRS, FACC Professor of Medicine Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology Temple University Health System Plumbing Electrical System Bradyarrhythmias Sinus Node
Dr.Binoy Skaria 13/07/15
 Dr.Binoy Skaria binoyskaria@hotmail.com binoy.skaria@heartofengland.nhs.uk 13/07/15 Acknowledgement Medtronic, Google images & Elsevier for slides Natalie Ryan, Events Manager, HEFT- for organising the
Dr.Binoy Skaria binoyskaria@hotmail.com binoy.skaria@heartofengland.nhs.uk 13/07/15 Acknowledgement Medtronic, Google images & Elsevier for slides Natalie Ryan, Events Manager, HEFT- for organising the
EKG Competency for Agency
 EKG Competency for Agency Name: Date: Agency: 1. The upper chambers of the heart are known as the: a. Atria b. Ventricles c. Mitral Valve d. Aortic Valve 2. The lower chambers of the heart are known as
EKG Competency for Agency Name: Date: Agency: 1. The upper chambers of the heart are known as the: a. Atria b. Ventricles c. Mitral Valve d. Aortic Valve 2. The lower chambers of the heart are known as
ECG Interpretation Made Easy
 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
-RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University. OBHG Education Subcommittee
 -RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University The Normal Conduction System Sinus Node Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia
-RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University The Normal Conduction System Sinus Node Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia
Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II
 Bundle-branch blocks Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II Most common electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormality Appears as a wider than normal S complex Occurs when one of the two bundle branches can t conduct
Bundle-branch blocks Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II Most common electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormality Appears as a wider than normal S complex Occurs when one of the two bundle branches can t conduct
PACIFIC MEDICAL TRAINING Arrhythmia Interpretation
 PACIFIC MEDICAL TRAINING Arrhythmia Interpretation Introduction Activity Summary Target Audience Educational Objectives Nursing Educational Objective Faculty Physician Continuing Medical Education Nursing
PACIFIC MEDICAL TRAINING Arrhythmia Interpretation Introduction Activity Summary Target Audience Educational Objectives Nursing Educational Objective Faculty Physician Continuing Medical Education Nursing
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material
 1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
The Electrocardiogram
 The Electrocardiogram Chapters 11 and 13 AUTUMN WEDAN AND NATASHA MCDOUGAL The Normal Electrocardiogram P-wave Generated when the atria depolarizes QRS-Complex Ventricles depolarizing before a contraction
The Electrocardiogram Chapters 11 and 13 AUTUMN WEDAN AND NATASHA MCDOUGAL The Normal Electrocardiogram P-wave Generated when the atria depolarizes QRS-Complex Ventricles depolarizing before a contraction
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease
 Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT
 Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-ecgs-made-easy-5thedition-by-aehlert/ TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT Chapter 5 TRUE/FALSE 1. The AV junction consists
Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-ecgs-made-easy-5thedition-by-aehlert/ TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT Chapter 5 TRUE/FALSE 1. The AV junction consists
Degrees AV blocks in athletes
 Degrees AV blocks in athletes Name: BCA Age: 22yo Sex: Male Race: Black Weight: 82 kg Height: 1.96m Biotype: Athletic rofession: professional basketball player Date: 2/09/2001 Clinical diagnosis: athlete
Degrees AV blocks in athletes Name: BCA Age: 22yo Sex: Male Race: Black Weight: 82 kg Height: 1.96m Biotype: Athletic rofession: professional basketball player Date: 2/09/2001 Clinical diagnosis: athlete
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a syndrome of pre-excitation of the
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a syndrome of pre-excitation of the
BEDSIDE ECG INTERPRETATION
 BEDSIDE ECG INTERPRETATION Presented by: Ryan Dean, RN, MSN, CCRN, CCNS, CFRN Flight Nurse 2017 Based on presentations originally by Gennifer DePaoli, RN Objectives Hospital policies Electrical conduction
BEDSIDE ECG INTERPRETATION Presented by: Ryan Dean, RN, MSN, CCRN, CCNS, CFRN Flight Nurse 2017 Based on presentations originally by Gennifer DePaoli, RN Objectives Hospital policies Electrical conduction
SIMPLY ECGs. Dr William Dooley
 SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley Content Basic ECG interpretation pattern Some common (examined) abnormalities Presenting ECGs in context Setting up an ECG Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space
SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley Content Basic ECG interpretation pattern Some common (examined) abnormalities Presenting ECGs in context Setting up an ECG Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space
Please check your answers with correct statements in answer pages after the ECG cases.
 ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
CRITICAL CARE OF THE CARDIAC PATIENT WEBINAR VET 2017
 CRITICAL CARE OF THE CARDIAC PATIENT WEBINAR VET 2017 The Heart The heart is undoubtedly the most important organ in the body. Unfortunately, when it is not functioning properly, it can have dire consequences.
CRITICAL CARE OF THE CARDIAC PATIENT WEBINAR VET 2017 The Heart The heart is undoubtedly the most important organ in the body. Unfortunately, when it is not functioning properly, it can have dire consequences.
How To Think About Rhythms and Conduction
 How To Think About Rhythms and Conduction Frank Yanowitz, MD Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) University of Utah School of Medicine Medical Director, IHC ECG Services Intermountain Healthcare http://ecg.utah.edu
How To Think About Rhythms and Conduction Frank Yanowitz, MD Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) University of Utah School of Medicine Medical Director, IHC ECG Services Intermountain Healthcare http://ecg.utah.edu
ID: BFH_ Start time: :00:00. Examination summary
 ECG analysis report Personal data Examination details Start time: 2000-01-01 00:00:00 Interpreting physician: Auto End time: 2000-01-02 01:39:16 Duration: 1d 01h 39min 16s Nondiagnostic part: 5.85% Examination
ECG analysis report Personal data Examination details Start time: 2000-01-01 00:00:00 Interpreting physician: Auto End time: 2000-01-02 01:39:16 Duration: 1d 01h 39min 16s Nondiagnostic part: 5.85% Examination
Bradydysrhythmias and Atrioventricular Conduction Blocks
 Emerg Med Clin N Am 24 (2006) 1 9 Bradydysrhythmias and Atrioventricular Conduction Blocks Jacob W. Ufberg, MD*, Jennifer S. Clark, MD Department of Emergency Medicine, Temple University School of Medicine,
Emerg Med Clin N Am 24 (2006) 1 9 Bradydysrhythmias and Atrioventricular Conduction Blocks Jacob W. Ufberg, MD*, Jennifer S. Clark, MD Department of Emergency Medicine, Temple University School of Medicine,
The prevalence of cardiac arrhythmia in Khuzestan buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis)
 CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIA IN BUFFALOES 99 The prevalence of cardiac arrhythmia in Khuzestan buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) A. GHADRDAN MASHHADI 1, R. HAJI HAJIKOLAI 1, A. REZAKHANI 2, R. FATEMI 1, S. KAMALI 1 1
CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIA IN BUFFALOES 99 The prevalence of cardiac arrhythmia in Khuzestan buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) A. GHADRDAN MASHHADI 1, R. HAJI HAJIKOLAI 1, A. REZAKHANI 2, R. FATEMI 1, S. KAMALI 1 1
Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep
 Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep Only 53 Slides! Gauresh H Kashyap, MD, FACP, FCCP, FAASM 1 2 Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep Out of 400 Patients with OSA, 48% had some Arrhythmias 20% - 2 PVCs/min 7% - Bradycardia
Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep Only 53 Slides! Gauresh H Kashyap, MD, FACP, FCCP, FAASM 1 2 Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep Out of 400 Patients with OSA, 48% had some Arrhythmias 20% - 2 PVCs/min 7% - Bradycardia
CASE 10. What would the ST segment of this ECG look like? On which leads would you see this ST segment change? What does the T wave represent?
 CASE 10 A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency center with complaints of chest pain with radiation to the left arm and jaw. He reports feeling anxious, diaphoretic, and short of breath. His past history
CASE 10 A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency center with complaints of chest pain with radiation to the left arm and jaw. He reports feeling anxious, diaphoretic, and short of breath. His past history
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH
 ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
Diploma in Electrocardiography
 The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE INTENSIVE CARE UNIT
 ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Nicole Van Israël, DVM, CESOpht, CertSAM, CertVC, DECVIM-CA (Cardiology), MSc, MRCVS European Specialist in Veterinary Cardiology Animal CardioPulmonary Consultancy
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Nicole Van Israël, DVM, CESOpht, CertSAM, CertVC, DECVIM-CA (Cardiology), MSc, MRCVS European Specialist in Veterinary Cardiology Animal CardioPulmonary Consultancy
2017 BDKA Review. Regularity Rate P waves PRI QRS Interpretation. Regularity Rate P waves PRI QRS Interpretation 1/1/2017
 1. 2017 BDKA Review 2. 3. 4. Interpretation 5. QT 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. QT 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. QT 19. 20. QT 21. 22. QT 23. 24. Where are pacer spikes? Before the P wave or before the QRS complex?
1. 2017 BDKA Review 2. 3. 4. Interpretation 5. QT 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. QT 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. QT 19. 20. QT 21. 22. QT 23. 24. Where are pacer spikes? Before the P wave or before the QRS complex?
Interpreting Electrocardiograms (ECG) Physiology Name: Per:
 Interpreting Electrocardiograms (ECG) Physiology Name: Per: Introduction The heart has its own system in place to create nerve impulses and does not actually require the brain to make it beat. This electrical
Interpreting Electrocardiograms (ECG) Physiology Name: Per: Introduction The heart has its own system in place to create nerve impulses and does not actually require the brain to make it beat. This electrical
24 Hour Holter Report
 Mass Veterinary Cardiology Services Inc 35 Suffield St Agawam, MA 11 413-372-5127/413-734-1292 413-372-5127 Exam Date: SEP 4 13-8:25am Record No: 7332 Provider: NANCY MORRIS DVM, DACVIM-C Medical Record
Mass Veterinary Cardiology Services Inc 35 Suffield St Agawam, MA 11 413-372-5127/413-734-1292 413-372-5127 Exam Date: SEP 4 13-8:25am Record No: 7332 Provider: NANCY MORRIS DVM, DACVIM-C Medical Record
FLB s What Are Those Funny-Looking Beats?
 FLB s What Are Those Funny-Looking Beats? Reading Assignment (pages 27-45 in Outline ) The 5-Step Method ECG #: Mearurements: Rhythm (s): Conduction: Waveform: Interpretation: A= V= PR= QRS= QT= Axis=
FLB s What Are Those Funny-Looking Beats? Reading Assignment (pages 27-45 in Outline ) The 5-Step Method ECG #: Mearurements: Rhythm (s): Conduction: Waveform: Interpretation: A= V= PR= QRS= QT= Axis=
Arrhythmic Complications of MI. Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine
 Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
Cardiology Flash Cards
 Cardiology Flash Cards EKG in a nut shell www.brain101.info Conduction System www.brain101.info 2 Analyzing EKG Step by step Steps in Analyzing ECG'S 1. Rhythm: - Regular _ Sinus, Junctional or Ventricular.
Cardiology Flash Cards EKG in a nut shell www.brain101.info Conduction System www.brain101.info 2 Analyzing EKG Step by step Steps in Analyzing ECG'S 1. Rhythm: - Regular _ Sinus, Junctional or Ventricular.
Skin supplied by T1-4 (medial upper arm and neck) T5-9- epigastrium Visceral afferents from skin and heart are the same dorsal root ganglio
 Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis
 Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
SIMPLY ECGs. Dr William Dooley
 SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley 1 No anatomy just interpretation 2 Setting up an ECG 3 Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space at sternal border 2 V2-4 th Left intercostal space at sternal border
SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley 1 No anatomy just interpretation 2 Setting up an ECG 3 Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space at sternal border 2 V2-4 th Left intercostal space at sternal border
Practical Approach to Arrhythmias
 Outline Practical Approach to Arrhythmias Julia Shih, VMD, DACVIM (Cardiology) October 27, 2018 Conduction System ECG Acquisition ECG Interpretation Heart rate Rhythm Arrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Supraventricular
Outline Practical Approach to Arrhythmias Julia Shih, VMD, DACVIM (Cardiology) October 27, 2018 Conduction System ECG Acquisition ECG Interpretation Heart rate Rhythm Arrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Supraventricular
Basic EKG Interpretation. Nirja Parikh, PT, DPT
 Basic EKG Interpretation Nirja Parikh, PT, DPT Electrocardiogram (EKG) Using surface electrodes record the electrical activity of the heart electrical activity (usually) correlates to mechanical function
Basic EKG Interpretation Nirja Parikh, PT, DPT Electrocardiogram (EKG) Using surface electrodes record the electrical activity of the heart electrical activity (usually) correlates to mechanical function
Arrhythmia Study Guide 3 Junctional and Ventricular Rhythms
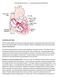 Arrhythmia Study Guide 3 Junctional and Ventricular Rhythms JUNCTIONAL RHYTHMS The AV Junction (Bundle of His and surrounding cells) only acts as pacemaker of the heart when the SA Node is not firing normally
Arrhythmia Study Guide 3 Junctional and Ventricular Rhythms JUNCTIONAL RHYTHMS The AV Junction (Bundle of His and surrounding cells) only acts as pacemaker of the heart when the SA Node is not firing normally
EKG Intermediate Tips, tricks, tools
 Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System 2018 ALCTE Summer Conference EKG Intermediate Tips, tricks, tools Brian Gober, MAT, ATC, NRP, CSCS Education Services Manager ECC Training Center Coordinator
Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System 2018 ALCTE Summer Conference EKG Intermediate Tips, tricks, tools Brian Gober, MAT, ATC, NRP, CSCS Education Services Manager ECC Training Center Coordinator
Repetitive narrow QRS tachycardia in a 61-year-old female patient with recent palpitations
 Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2018) 15: 193 198 2018 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Case Report Open Access Repetitive narrow QRS tachycardia in a 61-year-old female patient with recent palpitations
Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2018) 15: 193 198 2018 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Case Report Open Access Repetitive narrow QRS tachycardia in a 61-year-old female patient with recent palpitations
This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of
 Snímka 1 Electrocardiography basics This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of Snímka 2 Lecture overview 1. Cardiac conduction system functional
Snímka 1 Electrocardiography basics This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of Snímka 2 Lecture overview 1. Cardiac conduction system functional
National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8)
 Page 1 of 12 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8) Tracking Information Publication Number 100-3 Manual Section Number 20.8 Manual
Page 1 of 12 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8) Tracking Information Publication Number 100-3 Manual Section Number 20.8 Manual
Chad Morsch B.S., ACSM CEP
 What Is Cardiac Stress Testing? Chad Morsch B.S., ACSM CEP A Cardiac Stress Test is a test used to measure the heart's ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical environment. Cardiac
What Is Cardiac Stress Testing? Chad Morsch B.S., ACSM CEP A Cardiac Stress Test is a test used to measure the heart's ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical environment. Cardiac
Second Degree Atrioventricular Block
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Physician Assistant Studies, Department 2-18-2011 Second Degree Atrioventricular Block James
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Physician Assistant Studies, Department 2-18-2011 Second Degree Atrioventricular Block James
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress ECG INTERPRETATION Adrian Boswood MA VetMB DVC DECVIM-CA(Cardiology) MRCVS The Royal Veterinary College, Hawkshead
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress ECG INTERPRETATION Adrian Boswood MA VetMB DVC DECVIM-CA(Cardiology) MRCVS The Royal Veterinary College, Hawkshead
Sustained tachycardia with wide QRS
 Sustained tachycardia with wide QRS Courtesy from Prof. Antonio Américo Friedmann. Electrocardiology Service of University of Faculty of São Paulo. Opinions from colleagues Greetings to everyone, In a
Sustained tachycardia with wide QRS Courtesy from Prof. Antonio Américo Friedmann. Electrocardiology Service of University of Faculty of São Paulo. Opinions from colleagues Greetings to everyone, In a
ABCs of ECGs. Shelby L. Durler
 ABCs of ECGs Shelby L. Durler Objectives Review the A&P of the cardiac conduction system Placement and obtaining 4-lead and 12-lead ECGs Overview of the basics of ECG rhythm interpretation Intrinsic
ABCs of ECGs Shelby L. Durler Objectives Review the A&P of the cardiac conduction system Placement and obtaining 4-lead and 12-lead ECGs Overview of the basics of ECG rhythm interpretation Intrinsic
CORONARY ARTERIES HEART
 CARDIAC/ECG MODULE THE HEART CORONARY ARTERIES FIBRILLATING HEART CORONARY ARTERIES HEART PRACTICE RHYTHMS PRACTICE RHYTHMS ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION SA Node (60 100) Primary pacemaker AV Node (40 60) ***Creates
CARDIAC/ECG MODULE THE HEART CORONARY ARTERIES FIBRILLATING HEART CORONARY ARTERIES HEART PRACTICE RHYTHMS PRACTICE RHYTHMS ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION SA Node (60 100) Primary pacemaker AV Node (40 60) ***Creates
Cardiac Dysrhythmias and Sports
 Sudden unexpected death during athletic participation is the overriding consideration in advising individuals with dysrhythmias about participation in sports. The incidence of sudden death is 1 to 2 per
Sudden unexpected death during athletic participation is the overriding consideration in advising individuals with dysrhythmias about participation in sports. The incidence of sudden death is 1 to 2 per
ECG. Prepared by: Dr.Fatima Daoud Reference: Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology,12 th edition Chapters: 11,12,13
 ECG Prepared by: Dr.Fatima Daoud Reference: Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology,12 th edition Chapters: 11,12,13 The Concept When the cardiac impulse passes through the heart, electrical current
ECG Prepared by: Dr.Fatima Daoud Reference: Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology,12 th edition Chapters: 11,12,13 The Concept When the cardiac impulse passes through the heart, electrical current
CARDIOLOGY FOR DUMMIES
 CARDIOLOGY FOR DUMMIES Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Dipl ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine, Fac. of Veterinary Medicine, Ghent University, Salisburylaan 133, B-9820 Merelbeke, Belgium
CARDIOLOGY FOR DUMMIES Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Dipl ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine, Fac. of Veterinary Medicine, Ghent University, Salisburylaan 133, B-9820 Merelbeke, Belgium
Answer: The electrical current has difficulty traveling down the normal conduction pathway.
 1 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 8: Heart Block Dysrhythmias 2 3 4 5 6 Learning Outcomes 8.1 Describe the various heartblock dysrhythmias 8.2 Identify first degree heartblock
1 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 8: Heart Block Dysrhythmias 2 3 4 5 6 Learning Outcomes 8.1 Describe the various heartblock dysrhythmias 8.2 Identify first degree heartblock
ADVANCED PATIENT MONITORING DURING ANAESTHESIA: PART TWO
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk ADVANCED PATIENT MONITORING DURING ANAESTHESIA: PART TWO Author : CARL BRADBROOK Categories : Vets Date : October 14, 2013
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk ADVANCED PATIENT MONITORING DURING ANAESTHESIA: PART TWO Author : CARL BRADBROOK Categories : Vets Date : October 14, 2013
HSCRIBE 5 HOLTER ANALYSIS SYSTEM
 HSCRIBE 5 HOLTER ANALYSIS SYSTEM freedom Your patients will be free to go about their miniature devices will let them forget they The H3+ digital recorder gives new meaning to the word compact, while providing
HSCRIBE 5 HOLTER ANALYSIS SYSTEM freedom Your patients will be free to go about their miniature devices will let them forget they The H3+ digital recorder gives new meaning to the word compact, while providing
Clinical Guidance. Extrasystoles in the neonatal period. Author: Peter Lillitos
 1 Clinical Guidance Extrasystoles in the neonatal period Author: Peter Lillitos Contents Page 2: Definition of extrasystoles/ectopic beats Page 3: Algorithm of management Page 4-5: Ordering investigations
1 Clinical Guidance Extrasystoles in the neonatal period Author: Peter Lillitos Contents Page 2: Definition of extrasystoles/ectopic beats Page 3: Algorithm of management Page 4-5: Ordering investigations
ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know. Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series
 ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series Aims and objectives To be able to interpret basic ECG abnormalities To be able to recognise commonly tested
ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series Aims and objectives To be able to interpret basic ECG abnormalities To be able to recognise commonly tested
2:1 Block with Wenckebach Mechanism in Children Due to Different Etiologies F Laloğlu 1, N Ceviz 1, H Keskin 2, H Olgun 1 ABSTRACT
 2:1 Block with Wenckebach Mechanism in Children Due to Different Etiologies F Laloğlu 1, N Ceviz 1, H Keskin 2, H Olgun 1 ABSTRACT Objective: In children 2:1 Atrioventricular Block (AVB) with Wenckebach
2:1 Block with Wenckebach Mechanism in Children Due to Different Etiologies F Laloğlu 1, N Ceviz 1, H Keskin 2, H Olgun 1 ABSTRACT Objective: In children 2:1 Atrioventricular Block (AVB) with Wenckebach
Northwest Community Healthcare Paramedic Education Program AV Conduction Defects/AV Blocks Connie J. Mattera, M.S., R.N., EMT-P
 Northwest Community Healthcare Paramedic Education Program AV Conduction Defects/ Connie J. Mattera, M.S., R.N., EMT-P Reading assignments: Bledsoe Vol. 3: pp. 88-93; 120-121 (atropine, norepinephrine,
Northwest Community Healthcare Paramedic Education Program AV Conduction Defects/ Connie J. Mattera, M.S., R.N., EMT-P Reading assignments: Bledsoe Vol. 3: pp. 88-93; 120-121 (atropine, norepinephrine,
Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc.
 Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc. The Miracle of Living February 21, 2018 Matthew Ostrom MD,FACC,FHRS Division of
Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc. The Miracle of Living February 21, 2018 Matthew Ostrom MD,FACC,FHRS Division of
a lecture series by SWESEMJR
 Electrolyte disturbances Hypokalaemia Decreased extracellular potassium increases excitability in the myocardial cells and consequently the effect of very severe hypokalaemia is ventricular arrhythmia.
Electrolyte disturbances Hypokalaemia Decreased extracellular potassium increases excitability in the myocardial cells and consequently the effect of very severe hypokalaemia is ventricular arrhythmia.
Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances
 Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
Minding your P s and Q s Understanding ECG s. Samantha Knell, RVT
 Minding your P s and Q s Understanding ECG s Samantha Knell, RVT In Veterinary field for 20 years RVT since 7/2015 Team Leader at Rockville CVCA since 8/2016 Vice President of Maryland Veterinary Technician
Minding your P s and Q s Understanding ECG s Samantha Knell, RVT In Veterinary field for 20 years RVT since 7/2015 Team Leader at Rockville CVCA since 8/2016 Vice President of Maryland Veterinary Technician
3/26/15 HTEC 91. EKG Sign-in Book. The Cardiac Cycle. Parts of the ECG. Waves. Waves. Review of protocol Review of placement of chest leads (V1, V2)
 EKG Sign-in Book HTEC 91 Review of protocol Review of placement of chest leads (V1, V2) Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 2 http://www.cvphysiology.com/arrhythmias/a013c.htm The Cardiac Cycle Represents
EKG Sign-in Book HTEC 91 Review of protocol Review of placement of chest leads (V1, V2) Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 2 http://www.cvphysiology.com/arrhythmias/a013c.htm The Cardiac Cycle Represents
Collin County Community College
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 5 The Heart 1 The Heart Beat and the EKG 2 1 The Heart Beat and the EKG P-wave = Atrial depolarization QRS-wave = Ventricular depolarization
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 5 The Heart 1 The Heart Beat and the EKG 2 1 The Heart Beat and the EKG P-wave = Atrial depolarization QRS-wave = Ventricular depolarization
SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF LIFE-THREATENING CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS
 SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF LIFE-THREATENING CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Vessela Tzvetanova Krasteva, Irena Ilieva Jekova Centre of Biomedical Engineering Prof. Ivan Daskalov - Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Acad.G.Bonchev
SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF LIFE-THREATENING CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Vessela Tzvetanova Krasteva, Irena Ilieva Jekova Centre of Biomedical Engineering Prof. Ivan Daskalov - Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Acad.G.Bonchev
EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam
 as EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam Name: Date: ID# Unit Assume each strip is a 6 second strip. Passing is 80%. 1. Identify the following rhythm: a. Asystole b. Ventricular fibrillation c. Atrial fibrillation
as EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam Name: Date: ID# Unit Assume each strip is a 6 second strip. Passing is 80%. 1. Identify the following rhythm: a. Asystole b. Ventricular fibrillation c. Atrial fibrillation
ECG Interpretation and Clinical Significance
 Confirming Pages ECG Interpretation and Clinical Significance Chapter Outline 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 5.10 Learning Outcomes Key Terms Introduction (p. 114) Identifying the Components of the
Confirming Pages ECG Interpretation and Clinical Significance Chapter Outline 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 5.10 Learning Outcomes Key Terms Introduction (p. 114) Identifying the Components of the
The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph
 AF A The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary
AF A The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary
Cardiac Telemetry Self Study: Part One Cardiovascular Review 2017 THINGS TO REMEMBER
 Please review the above anatomy of the heart. THINGS TO REMEMBER There are 3 electrolytes that affect cardiac function o Sodium, Potassium, and Calcium When any of these electrolytes are out of the normal
Please review the above anatomy of the heart. THINGS TO REMEMBER There are 3 electrolytes that affect cardiac function o Sodium, Potassium, and Calcium When any of these electrolytes are out of the normal
Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of
Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of
Dr. Schroeder has no financial relationships to disclose
 Valerie A Schroeder MD MS Assistant Professor University of Kansas Medical Center READING THE WAVES- THE HEART S ELECTRICAL MESSAGE FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE Dr. Schroeder has no financial relationships to
Valerie A Schroeder MD MS Assistant Professor University of Kansas Medical Center READING THE WAVES- THE HEART S ELECTRICAL MESSAGE FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE Dr. Schroeder has no financial relationships to
ACLS Study Guide for Precourse Self-Assessment
 20 rhythm strips on Precourse Self-Assessment with the following matching choices: Agonal Rhythm/Asystole Atrial Fibrillation Flutter Ventricular Fibrillation Monomorphic Ventricular Normal Sinus Rhythm
20 rhythm strips on Precourse Self-Assessment with the following matching choices: Agonal Rhythm/Asystole Atrial Fibrillation Flutter Ventricular Fibrillation Monomorphic Ventricular Normal Sinus Rhythm
Testing the Accuracy of ECG Captured by Cronovo through Comparison of ECG Recording to a Standard 12-Lead ECG Recording Device
 Testing the Accuracy of ECG Captured by through Comparison of ECG Recording to a Standard 12-Lead ECG Recording Device Data Analysis a) R-wave Comparison: The mean and standard deviation of R-wave amplitudes
Testing the Accuracy of ECG Captured by through Comparison of ECG Recording to a Standard 12-Lead ECG Recording Device Data Analysis a) R-wave Comparison: The mean and standard deviation of R-wave amplitudes
EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Cardiac Pacing and ICDs
 EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Cardiac Pacing and ICDs Dear EHRA Member, Dear Colleague, As you know, the EHRA Accreditation Process is becoming increasingly recognised as an important step for
EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Cardiac Pacing and ICDs Dear EHRA Member, Dear Colleague, As you know, the EHRA Accreditation Process is becoming increasingly recognised as an important step for
Current ECG interpretation guidelines in the screening of athletes
 REVIEW ARTICLE 7 How to differentiate physiological adaptation to intensive physical exercise from pathologies Current ECG interpretation guidelines in the screening of athletes Gemma Parry-Williams, Sanjay
REVIEW ARTICLE 7 How to differentiate physiological adaptation to intensive physical exercise from pathologies Current ECG interpretation guidelines in the screening of athletes Gemma Parry-Williams, Sanjay
KERN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CERRO COSO COLLEGE HCRS C255 COURSE OUTLINE OF RECORD
 KERN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CERRO COSO COLLEGE HCRS C255 COURSE OUTLINE OF RECORD 1. DISCIPLINE AND COURSE NUMBER: HCRS C255 2. COURSE TITLE: Basic Cardiac Rhythm Interpretation 3. SHORT BANWEB TITLE:
KERN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CERRO COSO COLLEGE HCRS C255 COURSE OUTLINE OF RECORD 1. DISCIPLINE AND COURSE NUMBER: HCRS C255 2. COURSE TITLE: Basic Cardiac Rhythm Interpretation 3. SHORT BANWEB TITLE:
If the P wave > 0.12 sec( 3 mm) usually in any lead. Notched P wave usually in lead I,aVl may be lead II Negative terminal portion of P wave in V1, 1
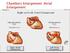 If the P wave > 0.12 sec( 3 mm) usually in any lead. Notched P wave usually in lead I,aVl may be lead II Negative terminal portion of P wave in V1, 1 mm depth and 3 mm width( most specific) Since Mitral
If the P wave > 0.12 sec( 3 mm) usually in any lead. Notched P wave usually in lead I,aVl may be lead II Negative terminal portion of P wave in V1, 1 mm depth and 3 mm width( most specific) Since Mitral
