Repair of massive stent-induced tracheoesophageal fistula
|
|
|
- Bennett Knight
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Repair of massive stent-induced tracheoesophageal fistula Yong Han, MD, Kun Liu, MD, Xiaofei Li, MD, Xiaoping Wang, MD, Yongan Zhou, MD, Zhongping Gu, MD, Qunfeng Ma, MD, Tao Jiang, MD, Lijun Huang, MD, Tao Zhang, MD, and Qingshu Cheng, MD Objective: The purpose of this report was to discuss a new surgical procedure in treating esophageal stent related large tracheoesophageal fistula without tracheal resection. Methods: Clinical records of 5 patients with esophageal stent-related large tracheoesophageal fistulas treated in this hospital between 1997 and 2006 were reviewed. Result: All patients had insertion of a covered self-expanding esophageal stent, 1 for benign esophageal stricture and 4 for esophageal perforation resulting from various causes. A double patch technique, in which the esophageal wall was used as a protective patch repairing the defect on the trachea, was performed with an esophagectomy and gastric replacement. No significant complications occurred in the perioperative period. All patients recovered uneventfully. Conclusions: Use of the adjacent esophageal wall as a patch to close a defect on the trachea is a safe procedure with a favorable outcome. It should therefore be recommended as a reliable surgical procedure in treating massive stent-induced tracheoesophageal fistulas and other complicated tracheoesophageal fistulas that tracheal resection could not safely address. However, the esophagus was damaged to a certain degree. Acquired tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) usually results from erosion of the adjacent walls of the trachea and esophagus due to a variety of causes. Besides trauma and malignancy, cuff-related tracheal injury has become the most common etiology of these fistulas. 1 However, several patients with TEF caused by esophageal stent related injury were treated in our hospital. The esophageal stents were usually placed in the thoracic segments of the inflamed esophagus, and the fistulas were always too large for primary repair. Because of the large defect, persistent infection, and friability of the tissues, outcome and quality of life would be poor after tracheal resection. In our practice, 5 esophageal stent related TEF patients were treated without tracheal resection by a new surgical procedure in which the esophageal wall was applied as a protective patch on the fistula when the esophagus was damaged to a certain degree at the same time, and the results were satisfactory. CLINICAL DATA Our group comprised 4 male patients and 1 female patient. The youngest was 11 years old and the eldest 55 years with an average of 34.4 years. The main causative factor for TEF in every one of them was the placement of self-expanding esophageal stents. These were used in 4 cases for esophageal perforation resulting from various causes and in 1 case for From the Department of Thoracic Surgery, Tangdu Hospital of The Fourth Military Medical University, Xi an, Shaanxi, China. Received for publication Feb 2, 2008; revisions received June 2, 2008; accepted for publication July 5, Address for reprints: Qingshu Cheng, MD, Department of Thoracic Surgery Tangdu Hospital, The Fourth Military Medical University, Xi an China ( chechest@fmmu.edu.cn). J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2009;137: /$36.00 Copyright Ó 2009 by The American Association for Thoracic Surgery doi: /j.jtcvs esophageal stricture resulting from chemical burn in other hospitals. All of them had cough on swallowing, dysphagia, and dyspnea 2 months to 2 years after placement of the stents. The TEFs were located on the middle segment of the esophagus in 4 of the 5 patients and on the lower segment in the other patient. The length of defects on the membranous portion of the trachea ranged from 1 to 3 cm. RESULT A double patch technique, in which the esophageal wall was used as a protective patch repairing the defect on the trachea, was applied to each of them despite the complexity and extent of the TEF. No significant complications occurred in the perioperative period. All the patients recovered uneventfully. They were followed up for 14 months to 9 years. All of them tolerated oral feeding normally with a good quality of life, and none of them showed any symptom or sign of recurrence of the TEF (Table 1). DOUBLE PATCH TEF REPAIR The double patch repair primarily creates a protective base over the massive defect on the membranous wall of the trachea to provide a solution for TEF when tracheal repair and resection cannot be undertaken safely and easily for various reasons: a long defect on the trachea, inflammation around the defect, technical difficulty in separating the esophagus from the trachea safely, difficulty in airway management, anesthesia, and other reasons. Furthermore, esophageal function was damaged to a certain degree or the defect was massive in the esophagus as well. We used the patient s own viable esophageal tissue to repair the TEF rather than applying tracheal resection, so as to reduce the incidence of airway dehiscence after the repair in large TEFs. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery c Volume 137, Number 4 813
2 Han et al Abbreviation and Acronym TEF ¼ tracheoesophageal fistula OPERATIVE PROCEDURE The fistula was approached with a right posterolateral thoracotomy through the fifth intercostal space. A single-lumen endotracheal tube for ventilation was inserted and the endotracheal tube balloon was passed distal to the tracheal defect. When the defect was near the carina, the cuff would be sent into left or right main bronchus to ensure ventilation. The thoracic segment of the esophagus was mobilized above and below the fistula, approximately 1 to 2 cm away from the fusion of the trachea with the esophagus. The esophagus was not separated from the trachea around the fistula. A longitudinal incision was made along the esophagus to split open the esophageal lumen 2 to 3 cm beside the fistula opening. The stents were removed carefully and completely through this incision. The esophagus was transected 2 cm proximal and distal to the fistula site to form two esophageal patches, a long one and a short one, with the fistula in between (Figure 1, A). The esophageal mucosa of the patches was cauterized. The short patch was sutured full-thickness to the left edges of the fistula with single-layer interrupted absorbable sutures through the fistula (Figure 1, B) and closed the fistula completely (Figure 1, C). The short patch suture was covered with the long esophageal wall patch (Figure 1, D). The stomach was mobilized through the opened diaphragmatic hiatus or with a laparotomy. Esophageal continuity was restored in the same stage with an esophagogastrostomy and the anastomosis was placed on an appropriate level above the repair site of the tracheal defect. TECHNICAL TIPS Do not free the esophagus from the trachea around the fused fistula within 2 cm, to ensure the blood supply of the patches. Suck the bloody secretions away from the esophageal lumen to eliminate the possibility of aspiration through the fistula. The stomach conduit can be pulled up through the enlarged hiatus or with a laparotomy, depending on the patient s condition. DISCUSSION Acquired, benign TEF occurs as a rare complication of various disorders. Use of a covered self-expanding esophageal stent, a well-accepted palliative management in treating esophageal stricture and perforation, is becoming a more frequent cause of TEF in our practice. Large-sized pressure necrosis on the esophageal wall as well as the membranous portion of the trachea caused by the stent itself has become a cause for the development of large TEF. Diagnosis of TEF can be made by computed tomographic scan, barium and/or water-soluble contrast esophagography, esophageal endoscopy, or bronchoscopy, and it may be useful in selected cases to inject methylene blue into the esophageal lumen during the course of bronchoscopy. There have been case reports of TEFs repaired with plastic self-expanding esophageal stents 2 and most recently endoscopic repair using fibrin glue and endoscopic suturing. 3,4 However, for benign TEF, surgical correction is almost the only way to cure the TEF. Several techniques of repair have been described. 5 Closing the defect of both the trachea and esophagus directly was used safely and with a high success rate in most cases. However, when the defect of the membranous tracheal wall is too large for single closure, a tracheal resection and/or reconstruction might be needed. The larger the TEF, the more likely a repair will be complicated by leakage at the repaired site owing to the tension at the anastomosis. This cannot always be avoided despite careful patient selection and meticulous surgical technique, especially if a resection has to be performed in the presence of the infection. The outcome and quality of life are often poor after these procedures, with high morbidity and mortality. TABLE 1. Clinical data of the patients Patient Sex Age Diagnosis Treatment Follow-up 1 Male 11 TEF occurred 8 mo after stent placement for Tracheal fistula repair, partial esophagectomy 9y esophageal caustic injury colon interposition 2 Male 38 TEF occurred 2 months after stent placement Tracheal fistula repair, esophagogastrostomy 3 y for esophageal rupture caused by traffic accident 3 Male 22 TEF occurred 5 months after stent placement Tracheal fistula repair, esophagogastrostomy 14 mo for esophageal perforation caused by traffic accident 4 Male 55 TEF occurred 2 years after stent placement for Tracheal fistula repair, esophagogastrostomy 15 mo esophageal rupture caused by chest trauma 5 Female 46 TEF occurred 8 months after stent placement for esophageal rupture caused by chest trauma Tracheal fistula repair, esophagogastrostomy 2 y 814 The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery c April 2009
3 FIGURE 1. Double patch technique. A, The long and short patches with the fistula in between. B, The short patch was sutured full-thickness to the left edges. C, The fistula was closed with the short patch. D, The short patch was covered with the long esophageal wall patch. In the presence of these difficulties, a patch to repair the defect on the trachea instead of resection may be fashioned. Autologous cartilage, muscle flaps, pericardium, or xenograft pericardium has been used to repair the defect. Some cases have even involved the use of a polytetrafluoroethylene patch (W.L. Gore & Associates, Inc, Flagstaff, Ariz) 6 or split-thickness skin graft. 7 However, more convenient and viable materials for TEF repair are still sought, especially for large and complicated TEFs. As esophageal mucosa has been demonstrated to be a suitable viable material, 8,9 it may be advisable to patch the wide tracheal defect with the wall of the esophagus, which has been described by Jougon and Couraud 10 in treating a patient with a large TEF with good results after 4 years. In view of persistent infection, the large defect in the trachea, and friability of the tissues in our patients, we used a double patch TEF repair for patients. In this procedure, the esophageal wall was used to build a double-layered protective patch onto the tracheal defect through overlapping of both the long and short flaps. The continuity and blood supply of the esophageal flaps with the trachea were well preserved, which accordingly reduced the incidence of complications such as leakage and recurrence of TEF. Inasmuch as no tracheal resection and reconstruction were needed, the incidence of complications and the complexity of the operation were greatly reduced. The appropriate lesions for this procedure are large TEFs for which tracheal resection could not be undertaken safely and easily for various reason. It is not advisable to apply this approach to patients with a small and simple TEF in whom the defect of both the trachea and esophagus can be closed directly. In our cases, the defect on the esophagus was also massive and damaged to a certain degree by the scarred mucosa and inflammation; therefore, esophageal resection seemed unavoidable (Figure 2). The esophagus might be preserved by recruiting only part of its circumference for tracheal reconstruction in some selected small TEFs, but it might not be routinely used in large ones. On the basis of our present results, we believe that esophageal reconstruction with stomach for managing massive stent-induced TEFs and large complicated or recurrent TEFs is worthwhile. Inasmuch as tracheal resection and reconstruction were not needed, the incidence of complications and the complexity of the operation would be greatly reduced. In the meanwhile, this operative step proved to be safe and reliable. It adds no morbidity but does add significant early and long-term clinical benefit. Direct closure of the esophageal defect can result in narrowing of the esophagus with consequent swallowing problems. By contrast, esophageal reconstruction with stomach results in much better quality of life for the patients in the long term. How to harvest the stomach conduit depends on the condition of the patient. The conduit was mobilized completely by an experienced surgeon through the diaphragmatic hiatus in our patients. The procedure required only one abdominal incision and benefited the recovery of pulmonary function after the operation. However, for patients with a history of abdominal surgery, a large spleen, and for non-asian The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery c Volume 137, Number 4 815
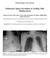
4 Han et al FIGURE 2. Bronchoscopic and intraoperative photographs of a 38-year-old male patient. TEF occurred 2 months after stent placement for esophageal rupture caused by a traffic accident. A, Bronchogram showed a large fistula in the membranous tracheal wall. B, Computed tomographic scan showed TEF with esophageal stent. C, The esophagus was opened, the fistula defect was found, and the stent was moved. D, Two esophageal patches were made and the fistula defect was exposed. E, Bronchogram 10 days after the operation showed that the defect was nicely repaired. patients, because of body habitus constraints, it would be challenging and risky to mobilize the stomach in this way. Therefore, a laparotomy approach might be a better choice for these patients. In summary, the salient feature of the procedure is that the portion of the esophageal wall with the fistula was made to form the double patch protective flap over the defect on the trachea. The fact that the incidence of complications is 816 The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery c April 2009
5 reasonably low indicates that it would be a reliable procedure in managing complicated and large TEFs. We are grateful to Miss Fang Zhao for preparing the illustrations and Claude Deschamps, MD (Mayo Clinic), for his critical reading of the manuscript. References 1. Flege JB Jr. Tracheoesophageal fistula caused by cuffed tracheostomy tube. Ann Surg. 1967;166: Adler DG, Pleskow DK. Closure of a benign tracheoesophageal fistula by using a coated, self-expanding plastic stent in a patient with a history of esophageal atresia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61: Raju GS, Thompson C, Zwischenberger JB. Emerging endoscopic options in the management of esophageal leaks [videos]. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;62: Broto J, Asensio M, Verne JMT. Endoscopic treatment of tracheo-esophageal fistulas: fact or fiction? Circ Pediatr. 2003;16: Macchiarini P, Verhoye JP, Chapelier A, Fadel E, Dartevelle P. Evaluation and outcome of different surgical techniques for postintubation tracheoesophageal fistulas. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000;119: Bardini R, Radicchi V, Parimbelli P, Tosato SM, Narne S. Repair of a recurrent benign tracheoesophageal fistula with a Gore-Tex membrane. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;76: Huang PM, Lee YC, Huang SC. Full thickness skin graft as a adjunct in the repair of a recurrent benign tracheoesophageal fistula. Thorac Cardivasc Surg. 2005;53: Utley JR, Dillon ML, Todd EP, Griffen WO, Zeok JV. Giant tracheosophageal fistula: management by esophageal diversion. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1978; 75: Bartlett R. A procedure for management of acquired tracheoesophageal fistula in ventilator patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1976;71: Jougon J, Couraud L. Esophageal patching for an unsuturable tracheoesophageal fistula. Eur J Cardiothoracic Surg. 1998;14: The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery c Volume 137, Number 4 817
Case Report Reoperation for complicated tracheoesophageal fistula after surgery of a tracheal lymphoma
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(6):9659-9663 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0051182 Case Report Reoperation for complicated tracheoesophageal fistula after surgery of a tracheal lymphoma Wei Dai 1, Qiang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(6):9659-9663 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0051182 Case Report Reoperation for complicated tracheoesophageal fistula after surgery of a tracheal lymphoma Wei Dai 1, Qiang
Surgical Management of Acquired Nonmalignant Tracheoesophageal and Bronchoesophageal Fistulae
 Surgical Management of Acquired Nonmalignant Tracheoesophageal and Bronchoesophageal Fistulae K. Robert Shen, MD, Mark S. Allen, MD, Stephen D. Cassivi, MD, MS, Francis C. Nichols III, MD, Dennis A. Wigle,
Surgical Management of Acquired Nonmalignant Tracheoesophageal and Bronchoesophageal Fistulae K. Robert Shen, MD, Mark S. Allen, MD, Stephen D. Cassivi, MD, MS, Francis C. Nichols III, MD, Dennis A. Wigle,
Esophageal Perforation
 Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Tracheal Trauma: Management and Treatment. Kosmas Iliadis, MD, PhD, FECTS
 Tracheal Trauma: Management and Treatment Kosmas Iliadis, MD, PhD, FECTS Thoracic Surgeon Director of Thoracic Surgery Department Hygeia Hospital, Athens INTRODUCTION Heterogeneous group of injuries mechanism
Tracheal Trauma: Management and Treatment Kosmas Iliadis, MD, PhD, FECTS Thoracic Surgeon Director of Thoracic Surgery Department Hygeia Hospital, Athens INTRODUCTION Heterogeneous group of injuries mechanism
Alyssa Brzenski MD May 2, 2012
 Alyssa Brzenski MD May 2, 2012 Overview Background Pre repair bronchoscopy Thorascopic repair To extubate or not? Esophageal atresia treatment of long gap esophageal atresia Complications following TEF/EA
Alyssa Brzenski MD May 2, 2012 Overview Background Pre repair bronchoscopy Thorascopic repair To extubate or not? Esophageal atresia treatment of long gap esophageal atresia Complications following TEF/EA
Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy
 American Association of Thoracic Surgery (AATS) 95 th Annual Meeting Seattle, WA April 29, 2015 General Thoracic Masters of Surgery Video Session Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy James D. Luketich MD,
American Association of Thoracic Surgery (AATS) 95 th Annual Meeting Seattle, WA April 29, 2015 General Thoracic Masters of Surgery Video Session Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy James D. Luketich MD,
AATS Focus on Thoracic Surgery: Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy: Are We Still Getting Better in 2017?
 AATS Focus on Thoracic Surgery: Mastering Surgical Innovation Las Vegas, NV October 28, 2017 Session VIII: Video Session Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy: Are We Still Getting Better in 2017? James D.
AATS Focus on Thoracic Surgery: Mastering Surgical Innovation Las Vegas, NV October 28, 2017 Session VIII: Video Session Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy: Are We Still Getting Better in 2017? James D.
Esophageal injuries. 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119
 Esophageal injuries 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119 Pre-test 1 What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries? A. Traffic accidents B. Gunshot wounds C. Iatrogenic Pre-test 2 Which contrast agent
Esophageal injuries 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119 Pre-test 1 What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries? A. Traffic accidents B. Gunshot wounds C. Iatrogenic Pre-test 2 Which contrast agent
Physical Exam. Vitals stable on room air Abdomen soft, non-distented Normal external genitalia Patent anus No limb anomalies
 Case Presentation 1 day-old full-term baby girl noted to have drooling of saliva and increased secretions at birth Fetal US @32wks had shown polyhydramnios Birth weight 3515g Apgar 7@1min and 8@5min Unable
Case Presentation 1 day-old full-term baby girl noted to have drooling of saliva and increased secretions at birth Fetal US @32wks had shown polyhydramnios Birth weight 3515g Apgar 7@1min and 8@5min Unable
Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized
 Slide Tracheoplasty for Congenital Tracheal Stenosis Peter B. Manning, MD Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized by the presence of complete cartilaginous tracheal rings and
Slide Tracheoplasty for Congenital Tracheal Stenosis Peter B. Manning, MD Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized by the presence of complete cartilaginous tracheal rings and
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Varied Presentation and Management of Tracheal Polyps in Children Vinod M Raj 1, Varun Hathiramani 2, Swathi
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Varied Presentation and Management of Tracheal Polyps in Children Vinod M Raj 1, Varun Hathiramani 2, Swathi
T ageal fistulas result from complications of mechanical
 Management of Acquired Nonmalignant Tracheoesophageal Fistula Douglas J. Mathisen, MD, Hermes C. Grillo, MD, John C. Wain, MD, and Alan D. Hilgenberg, MD Department of Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital,
Management of Acquired Nonmalignant Tracheoesophageal Fistula Douglas J. Mathisen, MD, Hermes C. Grillo, MD, John C. Wain, MD, and Alan D. Hilgenberg, MD Department of Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital,
Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon
 Technique for Managing Tracheo-Innominate Artery Fistula Gorav Ailawadi, MD Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon complication (0.1-1%) following both open and percutaneous tracheostomy.
Technique for Managing Tracheo-Innominate Artery Fistula Gorav Ailawadi, MD Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon complication (0.1-1%) following both open and percutaneous tracheostomy.
Reconstructive surgery for combined tracheo-esophageal injuries and their sequelae q
 European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 20 (2001) 1025 1029 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejcts Reconstructive surgery for combined tracheo-esophageal injuries and their sequelae q V.V. Sokolov, M.M. Bagirov*
European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 20 (2001) 1025 1029 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejcts Reconstructive surgery for combined tracheo-esophageal injuries and their sequelae q V.V. Sokolov, M.M. Bagirov*
Stenting for Esophageal Cancer Technical Issues and Outcomes
 Stenting for Esophageal Cancer Technical Issues and Outcomes Moishe Liberman Director C.E.T.O.C. Division of Thoracic Surgery Centre Hospitalier de l Université de Montréal Disclosures Research and Educational
Stenting for Esophageal Cancer Technical Issues and Outcomes Moishe Liberman Director C.E.T.O.C. Division of Thoracic Surgery Centre Hospitalier de l Université de Montréal Disclosures Research and Educational
A video demonstration of the Li s anastomosis the key part of the non-tube no fasting fast track program for resectable esophageal carcinoma
 Surgical Technique A video demonstration of the the key part of the non-tube no fasting fast track program for resectable esophageal carcinoma Yan Zheng*, Yin Li*, Zongfei Wang, Haibo Sun, Ruixiang Zhang
Surgical Technique A video demonstration of the the key part of the non-tube no fasting fast track program for resectable esophageal carcinoma Yan Zheng*, Yin Li*, Zongfei Wang, Haibo Sun, Ruixiang Zhang
Esophageal injuries. Pre-test /11/10. 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119. O What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries?
 Esophageal injuries 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119 Pre-test 1 O What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries? A. Traffic accidents B. Gunshot wounds C. Iatrogenic 1 Pre-test 2 O Which contrast
Esophageal injuries 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119 Pre-test 1 O What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries? A. Traffic accidents B. Gunshot wounds C. Iatrogenic 1 Pre-test 2 O Which contrast
Combined Collis-Nissen Reconstruction. of the esophagogastric junction at. Mark B. Orringer, M.D., and Herbert Sloan, M.D.
 Combined Collis-Nissen Reconstruction of the Esophagogastric Junction Mark B. Orringer, M.D., and Herbert Sloan, M.D. ABSTRACT Recent reports have indicated that combined Collis-Belsey reconstruction of
Combined Collis-Nissen Reconstruction of the Esophagogastric Junction Mark B. Orringer, M.D., and Herbert Sloan, M.D. ABSTRACT Recent reports have indicated that combined Collis-Belsey reconstruction of
DUMON-NOVATECH Y-STENTS: A FOUR-YEAR EXPERIENCE WITH 50 TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TUMORS INVOLVING THE CARINA
 Solunum 3, Özel Sayı 2: 260-264, 2001 DUMON-NOVATECH Y-STENTS: A FOUR-YEAR EXPERIENCE WITH 50 TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TUMORS INVOLVING THE CARINA Jean F DUMON* M C DUMON* SUMMARY This article reports a 4-year
Solunum 3, Özel Sayı 2: 260-264, 2001 DUMON-NOVATECH Y-STENTS: A FOUR-YEAR EXPERIENCE WITH 50 TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TUMORS INVOLVING THE CARINA Jean F DUMON* M C DUMON* SUMMARY This article reports a 4-year
Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes. Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center
 Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Neonatal and Pediatric Tracheostomy Tracheostomy
Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Neonatal and Pediatric Tracheostomy Tracheostomy
External trauma (MVA, surf board, assault, etc.) Internal trauma (Endotracheal intubation, tracheostomy) Other
 Etiology External trauma (MVA, surf board, assault, etc.) Internal trauma (Endotracheal intubation, tracheostomy) Other Systemic diseases (vasculitis, etc.) Chemo/XRT Idiopathic Trans nasal Esophagoscope
Etiology External trauma (MVA, surf board, assault, etc.) Internal trauma (Endotracheal intubation, tracheostomy) Other Systemic diseases (vasculitis, etc.) Chemo/XRT Idiopathic Trans nasal Esophagoscope
The Learning Curve for Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy
 The Learning Curve for Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy AATS Focus on Thoracic Surgery Mastering Surgical Innovation Las Vegas Nevada Oct. 27-28 2017 Scott J Swanson, M.D. Professor of Surgery Harvard
The Learning Curve for Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy AATS Focus on Thoracic Surgery Mastering Surgical Innovation Las Vegas Nevada Oct. 27-28 2017 Scott J Swanson, M.D. Professor of Surgery Harvard
Sreeni Jonnalagadda, MD., FASGE Professor of Medicine, UMKC Director of Interventional Endoscopy Saint Luke s Hospital, Kansas City
 Sreeni Jonnalagadda, MD., FASGE Professor of Medicine, UMKC Director of Interventional Endoscopy Saint Luke s Hospital, Kansas City Peptic stricture Shtki Schatzki s ring Esophageal cancer Radiation therapy
Sreeni Jonnalagadda, MD., FASGE Professor of Medicine, UMKC Director of Interventional Endoscopy Saint Luke s Hospital, Kansas City Peptic stricture Shtki Schatzki s ring Esophageal cancer Radiation therapy
Tracheobronchial ruptures (TBR) are life-threatening
 Conservative Treatment for Postintubation Tracheobronchial Rupture Jacques Jougon, MD, Michel Ballester, MD, Emmanuel Choukroun, MD, Jean Dubrez, MD, Gilles Reboul, MD, and Jean-François Velly, MD Thoracic
Conservative Treatment for Postintubation Tracheobronchial Rupture Jacques Jougon, MD, Michel Ballester, MD, Emmanuel Choukroun, MD, Jean Dubrez, MD, Gilles Reboul, MD, and Jean-François Velly, MD Thoracic
Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia
 Patient and Family Education Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia What is tracheoesophageal fistula? The word fistula means abnormal connection. Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is a condition
Patient and Family Education Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia What is tracheoesophageal fistula? The word fistula means abnormal connection. Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is a condition
Endoscopic Management of Perforations
 Endoscopic Management of Perforations Gregory G. Ginsberg, MD Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine Gastroenterology Division Executive Director of Endoscopic Services
Endoscopic Management of Perforations Gregory G. Ginsberg, MD Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine Gastroenterology Division Executive Director of Endoscopic Services
Thoracoscopic repair of esophageal atresia with a distal fistula lessons from the first 10 operations
 Original paper Thoracoscopic repair of esophageal atresia with a distal fistula lessons from the first 10 operations Paweł Nachulewicz 1, Kamila Zaborowska 1, Błażej Rogowski 1, Anita Kalińska 1, Marzena
Original paper Thoracoscopic repair of esophageal atresia with a distal fistula lessons from the first 10 operations Paweł Nachulewicz 1, Kamila Zaborowska 1, Błażej Rogowski 1, Anita Kalińska 1, Marzena
Anastomotic Complications after Esophagectomy. Bryan Meyers, MD MPH Thoracic Surgery Washington University School of Medicine
 Anastomotic Complications after Esophagectomy Bryan Meyers, MD MPH Thoracic Surgery Washington University School of Medicine Use of Stomach as Conduit Simplest choice after esophagectomy Single anastomosis
Anastomotic Complications after Esophagectomy Bryan Meyers, MD MPH Thoracic Surgery Washington University School of Medicine Use of Stomach as Conduit Simplest choice after esophagectomy Single anastomosis
Abstract Introduction We present the experiences from two European centers performing the
 Original Article 3 The Foker Technique (FT) and Kimura Advancement (KA) for the Treatment of Children with Long-Gap Esophageal Atresia (LGEA): Lessons Learned at Two European Centers Mariusz Sroka 1 Robin
Original Article 3 The Foker Technique (FT) and Kimura Advancement (KA) for the Treatment of Children with Long-Gap Esophageal Atresia (LGEA): Lessons Learned at Two European Centers Mariusz Sroka 1 Robin
Use of the Silicone T-tube to Treat Tracheal Stenosis or Tracheal Injury
 Use of the Silicone T-tube to Treat Stenosis or Injury Chang-Jer Huang MD Backgound: stenosis or tracheal is a troublesome disease. Traditional temporary tracheostomy and reconstruction can resolve some
Use of the Silicone T-tube to Treat Stenosis or Injury Chang-Jer Huang MD Backgound: stenosis or tracheal is a troublesome disease. Traditional temporary tracheostomy and reconstruction can resolve some
Pediatric partial cricotracheal resection: A new technique for the posterior cricoid anastomosis
 Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2006) 135, 318-322 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Pediatric partial cricotracheal resection: A new technique for the posterior cricoid anastomosis Mark E. Boseley, MD, and Christopher
Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2006) 135, 318-322 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Pediatric partial cricotracheal resection: A new technique for the posterior cricoid anastomosis Mark E. Boseley, MD, and Christopher
Esophageal anastomotic techniques
 Esophageal anastomotic techniques Raphael Bueno, MD, Brigham and Women s Hospital Slide 1 Good afternoon, I would like thank the association and Dr and Dr for inviting me to speak today. Slide 2 I am trying
Esophageal anastomotic techniques Raphael Bueno, MD, Brigham and Women s Hospital Slide 1 Good afternoon, I would like thank the association and Dr and Dr for inviting me to speak today. Slide 2 I am trying
TRACHEOSTOMY. Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion
 TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
A new approach to left sleeve pneumonectomy: complete VATS left pneumonectomy followed by right thoracotomy for carinal resection and reconstruction
 Fujino et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:91 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0496-2 CASE REPORT A new approach to left sleeve pneumonectomy: complete VATS left pneumonectomy followed by right thoracotomy
Fujino et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:91 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0496-2 CASE REPORT A new approach to left sleeve pneumonectomy: complete VATS left pneumonectomy followed by right thoracotomy
CARCINOMA IN A RECONSTRUCTED (ESOPHAGUS. By PERCY H. JAYES, M.B., F.R.C.S. From The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead
 CARCINOMA IN A RECONSTRUCTED (ESOPHAGUS By PERCY H. JAYES, M.B., F.R.C.S. From The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead THE purpose of this short paper is twofold: first, to report a condition which
CARCINOMA IN A RECONSTRUCTED (ESOPHAGUS By PERCY H. JAYES, M.B., F.R.C.S. From The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead THE purpose of this short paper is twofold: first, to report a condition which
Airway Remodeling: Preliminary Experience with Bio-Absorbable Airway Stents in Adults Jaus MO, Gonfiotti A, Barale D, Macchiarini P
 Airway Remodeling: Preliminary Experience with Bio-Absorbable Airway Stents in Adults Jaus MO, Gonfiotti A, Barale D, Macchiarini P University Hospital Careggi Florence, Italy Disclosure Statement THE
Airway Remodeling: Preliminary Experience with Bio-Absorbable Airway Stents in Adults Jaus MO, Gonfiotti A, Barale D, Macchiarini P University Hospital Careggi Florence, Italy Disclosure Statement THE
SETTING Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center. RESPONSIBLE PARTY Haiquan Chen MD.
 OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery Guido Barbagli Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery Arezzo - Italy
 Guido Barbagli Arezzo - Italy E-mail: info@urethralcenter.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it SHANGHAI February 6 8, 2009 Prof. Qiang FU Professor FU day Professor FU and night Anterior urethroplasty using
Guido Barbagli Arezzo - Italy E-mail: info@urethralcenter.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it SHANGHAI February 6 8, 2009 Prof. Qiang FU Professor FU day Professor FU and night Anterior urethroplasty using
Lung cancer or primary malignant tumors of the mediastinum
 Technique of Superior Vena Cava Resection for Lung Carcinomas David R. Jones, MD Division of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Department of Surgery, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville,
Technique of Superior Vena Cava Resection for Lung Carcinomas David R. Jones, MD Division of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Department of Surgery, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville,
Esophageal Diverticulum. Ahmed Hozain, PGY III Kings County Hospital University Hospital of Brooklyn, Surgery Grand Rounds May 18 th, 2017
 Esophageal Diverticulum Ahmed Hozain, PGY III Kings County Hospital University Hospital of Brooklyn, Surgery Grand Rounds May 18 th, 2017 Case Presentation 53 YOF presented to KCHC with sx of dysphagia
Esophageal Diverticulum Ahmed Hozain, PGY III Kings County Hospital University Hospital of Brooklyn, Surgery Grand Rounds May 18 th, 2017 Case Presentation 53 YOF presented to KCHC with sx of dysphagia
Clinical Case Presentation. Jared B. Smith, M.D. Surgical Grand Rounds, August 21, 2006
 Clinical Case Presentation Jared B. Smith, M.D. Surgical Grand Rounds, August 21, 2006 Clinical History CC: Can t swallow anything HPI: 50 y.o. male from western Colorado, greater than 2 years of emesis
Clinical Case Presentation Jared B. Smith, M.D. Surgical Grand Rounds, August 21, 2006 Clinical History CC: Can t swallow anything HPI: 50 y.o. male from western Colorado, greater than 2 years of emesis
CHAPTER 7 Procedures on Respiratory System
 CHAPTER 7 Propunere noua clasificare proceduri folosind codificarea ICD-10-AM versiunea 3, 30 martie 2004 Procedures on Respiratory System BLOCK 520 Examination procedures on larynx 41764-03 Fibreoptic
CHAPTER 7 Propunere noua clasificare proceduri folosind codificarea ICD-10-AM versiunea 3, 30 martie 2004 Procedures on Respiratory System BLOCK 520 Examination procedures on larynx 41764-03 Fibreoptic
Esophageal Stent Placement for the Treatment of Acute Intrathoracic Anastomotic Leak After Esophagectomy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES: SURGERY: The Annals of Thoracic Surgery CME Program is located online at http://cme.ctsnetjournals.org. To take the CME activity related to this article, you must have either an STS
ORIGINAL ARTICLES: SURGERY: The Annals of Thoracic Surgery CME Program is located online at http://cme.ctsnetjournals.org. To take the CME activity related to this article, you must have either an STS
Title: Use of self-expanding nitinol stents in the pediatric management of refractory esophageal caustic stenosis
 Title: Use of self-expanding nitinol stents in the pediatric management of refractory esophageal caustic stenosis Authors: Verónica Alonso, Devicka Ojha, Harsha Nalluri, Juan Carlos de Agustín DOI: 10.17235/reed.2017.4959/2017
Title: Use of self-expanding nitinol stents in the pediatric management of refractory esophageal caustic stenosis Authors: Verónica Alonso, Devicka Ojha, Harsha Nalluri, Juan Carlos de Agustín DOI: 10.17235/reed.2017.4959/2017
Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy
 Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy M A R K B E R R Y, M D A S S O C I AT E P R O F E S S O R D E PA R T M E N T OF C A R D I O T H O R A C I C S U R G E R Y S TA N F O R D U N I V E R S I T Y S E P T E M
Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy M A R K B E R R Y, M D A S S O C I AT E P R O F E S S O R D E PA R T M E N T OF C A R D I O T H O R A C I C S U R G E R Y S TA N F O R D U N I V E R S I T Y S E P T E M
Subglottic stenosis, with involvement of the lower larynx
 Laryngotracheal Resection and Reconstruction John D. Mitchell, MD n, Subglottic stenosis is being recognized with increasing frequency in adults, and may be the most frequent indication for airway intervention
Laryngotracheal Resection and Reconstruction John D. Mitchell, MD n, Subglottic stenosis is being recognized with increasing frequency in adults, and may be the most frequent indication for airway intervention
Benign Bronchoesophageal Fistula in Adults: Endoscopic Closure as Primary Treatment
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 4, No. 4, December 2010, pp. 508-513 original article Benign Bronchoesophageal Fistula in Adults: Endoscopic Closure as Primary Treatment Ji Yong Ahn, Hwoon-Yong Jung, Ji Young Choi,
Gut and Liver, Vol. 4, No. 4, December 2010, pp. 508-513 original article Benign Bronchoesophageal Fistula in Adults: Endoscopic Closure as Primary Treatment Ji Yong Ahn, Hwoon-Yong Jung, Ji Young Choi,
Long-gap Oesophageal Atresia
 Long-gap Atresia A guide for parents Nate (6 weeks old) Atresia Research Association Are there different types of OA? There are four main types of oesophageal atresia with or without TOF. These include
Long-gap Atresia A guide for parents Nate (6 weeks old) Atresia Research Association Are there different types of OA? There are four main types of oesophageal atresia with or without TOF. These include
Surgical treatment for patients with tracheal and subgllotic stenosis
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 3, November, 2009. pp. 132-138 Surgical treatment for patients with tracheal and subgllotic stenosis Mohammad Naeimi, MD.
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 3, November, 2009. pp. 132-138 Surgical treatment for patients with tracheal and subgllotic stenosis Mohammad Naeimi, MD.
CASE REPORTS. Giant Esophagus. An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy
 CASE REPORTS An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy and Dilatation of the Esophagus and Proximal Stomach Mark H. Wall, M.D., Epifanio E. Espinas, M.D., Arthur W. Silver, M.D., and Francis X.
CASE REPORTS An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy and Dilatation of the Esophagus and Proximal Stomach Mark H. Wall, M.D., Epifanio E. Espinas, M.D., Arthur W. Silver, M.D., and Francis X.
Case Report. Management of recurrent distal tracheal stenosis using an endoprosthesis: a case report* Abstract. Introduction.
 121 Case Report Management of recurrent distal tracheal stenosis using an endoprosthesis: a case report* André Germano Leite 1, Douglas Kussler 2 Abstract The authors report the case of a patient with
121 Case Report Management of recurrent distal tracheal stenosis using an endoprosthesis: a case report* André Germano Leite 1, Douglas Kussler 2 Abstract The authors report the case of a patient with
Despite the great number of intubations and diagnostic
 Management of Iatrogenic Tracheobronchial Injuries: A Retrospective Analysis of 29 Cases Thomas Schneider, MD, Konstantina Storz, MD, Hendrik Dienemann, MD, PhD, and Hans Hoffmann, MD, PhD Department of
Management of Iatrogenic Tracheobronchial Injuries: A Retrospective Analysis of 29 Cases Thomas Schneider, MD, Konstantina Storz, MD, Hendrik Dienemann, MD, PhD, and Hans Hoffmann, MD, PhD Department of
Departement of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University Sumatera Utara
 SSS EESOPHAGEAL HPOSAGEAL DISORDERS IN SURGICAL PERSPECTIVE Departement of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University Sumatera Utara CONTENT 1. Esophageal Atresia 2. Achalasia 3. Esophageal Rupture 4. Tumor
SSS EESOPHAGEAL HPOSAGEAL DISORDERS IN SURGICAL PERSPECTIVE Departement of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University Sumatera Utara CONTENT 1. Esophageal Atresia 2. Achalasia 3. Esophageal Rupture 4. Tumor
Non malignant Tracheo-Esophageal fistula : Our experience
 272 Darbari et al IJTCVS Non malignant Tracheo-Esophageal fistula : Our experience Anshuman Darbari, MS, Abhishek Suryavanshi, MS, Shekhar Tandon, M. Ch., Girish Chandra, MD, Prashant Kumar Singh, MS Department
272 Darbari et al IJTCVS Non malignant Tracheo-Esophageal fistula : Our experience Anshuman Darbari, MS, Abhishek Suryavanshi, MS, Shekhar Tandon, M. Ch., Girish Chandra, MD, Prashant Kumar Singh, MS Department
Routine reinforcement of bronchial stump after lobectomy or pneumonectomy with pedicled pericardial flap (PPF)
 Routine reinforcement of bronchial stump after lobectomy or pneumonectomy with pedicled pericardial flap (PPF) Abstract The results of 25 cases underwent a pedicled pericardial flap coverage for the bronchial
Routine reinforcement of bronchial stump after lobectomy or pneumonectomy with pedicled pericardial flap (PPF) Abstract The results of 25 cases underwent a pedicled pericardial flap coverage for the bronchial
Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks
 Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks Ali A. Siddiqui, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Interventional Endoscopy Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia, PA When Do You Suspect a Luminal
Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks Ali A. Siddiqui, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Interventional Endoscopy Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia, PA When Do You Suspect a Luminal
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005
 Close this window to return to IVIS Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005 Hosted by: Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the WSAVA Surgery
Close this window to return to IVIS Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005 Hosted by: Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the WSAVA Surgery
Hong Kong Society of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons CLINICAL MEETING 29 NOV 2012
 Hong Kong Society of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons CLINICAL MEETING 29 NOV 2012 Esophageal Leiomyoma Introduction Case presentation Operative video Discussion Esophageal Leiomyoma Benign tumors of the
Hong Kong Society of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons CLINICAL MEETING 29 NOV 2012 Esophageal Leiomyoma Introduction Case presentation Operative video Discussion Esophageal Leiomyoma Benign tumors of the
Although the widespread use of high-volume lowpressure
 EVALUATION AND OUTCOME OF DIFFERENT SURGICAL TECHNIQUES FOR POSTINTUBATION TRACHEOESOPHAGEAL FISTULAS Paolo Macchiarini, MD, PhD a Jean-Philippe Verhoye, MD b Alain Chapelier, MD, PhD b Elie Fadel, MD
EVALUATION AND OUTCOME OF DIFFERENT SURGICAL TECHNIQUES FOR POSTINTUBATION TRACHEOESOPHAGEAL FISTULAS Paolo Macchiarini, MD, PhD a Jean-Philippe Verhoye, MD b Alain Chapelier, MD, PhD b Elie Fadel, MD
Surgical Repair of Iatrogenic Cervical Tracheal Stenosis
 Surgical Repair of Iatrogenic Cervical Tracheal Stenosis Nirmal K. Veeramachaneni, MD, and Bryan F. Meyers, MD, MPH he advent of intensive care unit management has increased the potential opportunities
Surgical Repair of Iatrogenic Cervical Tracheal Stenosis Nirmal K. Veeramachaneni, MD, and Bryan F. Meyers, MD, MPH he advent of intensive care unit management has increased the potential opportunities
An 8-year experience of esophageal atresia repair in Sarvar children hospital (Mashhad- IRAN)
 An 8-year experience of esophageal atresia repair in Sarvar children hospital (Mashhad- IRAN) Mehran Hiradfar* Ahmad Bazrafshan* Marjan Judi** Mohammad Gharavi*** - Reza Shojaeian**** * Associate professor
An 8-year experience of esophageal atresia repair in Sarvar children hospital (Mashhad- IRAN) Mehran Hiradfar* Ahmad Bazrafshan* Marjan Judi** Mohammad Gharavi*** - Reza Shojaeian**** * Associate professor
Covered stenting in patients with lifting of gastric and high esophago-tracheal fistula
 European Radiology Springer-Verlag 2003 DOI 10.1007/s00330-002-1818-z Tips and Tricks in Radiology Covered stenting in patients with lifting of gastric and high esophago-tracheal fistula T. Lehnert J.
European Radiology Springer-Verlag 2003 DOI 10.1007/s00330-002-1818-z Tips and Tricks in Radiology Covered stenting in patients with lifting of gastric and high esophago-tracheal fistula T. Lehnert J.
Review of Posttracheostomy And Postintubation Tracheal Stenosis With Special Regard to Etiology and Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Review of Posttracheostomy And Postintubation Tracheal Stenosis With Special Regard to Etiology and A Sarper, A Ayten,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Review of Posttracheostomy And Postintubation Tracheal Stenosis With Special Regard to Etiology and A Sarper, A Ayten,
R the resumption of the normal swallowing mechanism
 Reconstruction the Left Colon of the Esophagus With Min-Hsiung Huang, MD, Chih-Yi Sung, MD, Hon-Ki Hsu, MD, Biing-ShiunHuang, MD, Wen-Hu Hsu, MD, and Kwang-Yu Chien, MD Division of Thoracic Surgery, Department
Reconstruction the Left Colon of the Esophagus With Min-Hsiung Huang, MD, Chih-Yi Sung, MD, Hon-Ki Hsu, MD, Biing-ShiunHuang, MD, Wen-Hu Hsu, MD, and Kwang-Yu Chien, MD Division of Thoracic Surgery, Department
CROSS CODER. Sample page. Anesthesia. codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS. Essential links from CPT. Power up your coding optum360coding.
 CROSS CODER 2019 Anesthesia Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS Power up your coding optum360coding.com Contents Introduction...i CPT Anesthesia to Procedure Code Crosswalk... i Format...
CROSS CODER 2019 Anesthesia Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS Power up your coding optum360coding.com Contents Introduction...i CPT Anesthesia to Procedure Code Crosswalk... i Format...
Navigational bronchoscopy-guided dye marking to assist resection of a small lung nodule
 Case Report on Aerodigestive Endoscopy Navigational bronchoscopy-guided dye marking to assist resection of a small lung nodule Jennifer L. Sullivan 1, Michael G. Martin 2, Benny Weksler 1 1 Division of
Case Report on Aerodigestive Endoscopy Navigational bronchoscopy-guided dye marking to assist resection of a small lung nodule Jennifer L. Sullivan 1, Michael G. Martin 2, Benny Weksler 1 1 Division of
Translaryngeal tracheostomy
 Translaryngeal tracheostomy Issued: August 2013 NICE interventional procedure guidance 462 guidance.nice.org.uk/ipg462 NICE has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme
Translaryngeal tracheostomy Issued: August 2013 NICE interventional procedure guidance 462 guidance.nice.org.uk/ipg462 NICE has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme
1. Epidemiology of Esophageal Cancer 2. Operative Strategies 3. Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy 4. Video
 Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy Guilherme M Campos, MD, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery Director G.I. Motility Center Director Bariatric Surgery Program University of California San Francisco ESOPHAGEAL
Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy Guilherme M Campos, MD, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery Director G.I. Motility Center Director Bariatric Surgery Program University of California San Francisco ESOPHAGEAL
Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) and Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
 Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) and Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Clare McLaren Great Ormond Street Hospital London Introduction IVUS and OCT supplementary techniques to angiography provide information
Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) and Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Clare McLaren Great Ormond Street Hospital London Introduction IVUS and OCT supplementary techniques to angiography provide information
Aliu Sanni MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center August 16, 2012
 Aliu Sanni MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center August 16, 2012 Case Presentation 60yr old AAF with PMH of CAD s/p PCI 1983, CVA, GERD, HTN presented with retrosternal chest pain on 06/12 Associated dysphagia
Aliu Sanni MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center August 16, 2012 Case Presentation 60yr old AAF with PMH of CAD s/p PCI 1983, CVA, GERD, HTN presented with retrosternal chest pain on 06/12 Associated dysphagia
90 th Annual Meeting The American Association for Thoracic Surgery May 1, 2010 Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Slide Tracheoplasty
 90 th Annual Meeting The American Association for Thoracic Surgery May 1, 2010 Toronto, Ontario, Canada Congenital Skills Course Slide Tracheoplasty Carl Lewis Backer, MD A.C. Buehler Professor of Surgery
90 th Annual Meeting The American Association for Thoracic Surgery May 1, 2010 Toronto, Ontario, Canada Congenital Skills Course Slide Tracheoplasty Carl Lewis Backer, MD A.C. Buehler Professor of Surgery
Tracheal Stenosis Following Cuffed Tube Tracheostomy
 Tracheal Stenosis Following Cuffed Tube Tracheostomy Anatomical Variation and Selected Treatment Armand A. Lefemine, M.D., Kenneth MacDonnell, M.D., and Hyung S. Moon, M.D. ABSTRACT Tracheal stenosis resulting
Tracheal Stenosis Following Cuffed Tube Tracheostomy Anatomical Variation and Selected Treatment Armand A. Lefemine, M.D., Kenneth MacDonnell, M.D., and Hyung S. Moon, M.D. ABSTRACT Tracheal stenosis resulting
Surgical Management of Graft Redundancy after Colon Interposition for Esophageal Reconstruction. Case 1
 Case Report imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Medical & Clinical Reviews DOI: 10.21767/2471-299X.1000059 Surgical Management of Graft Redundancy after Colon Interposition for Esophageal Reconstruction Abdelkader
Case Report imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Medical & Clinical Reviews DOI: 10.21767/2471-299X.1000059 Surgical Management of Graft Redundancy after Colon Interposition for Esophageal Reconstruction Abdelkader
Guido Barbagli. Center for Reconstructive ti Urethral lsurgery
 Guido Barbagli Center for Reconstructive ti Urethral lsurgery Arezzo - Italy E-mail: guido@rdn.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it Portuguese Andrological Association National Meeting June 21-23, 2008 Oporto
Guido Barbagli Center for Reconstructive ti Urethral lsurgery Arezzo - Italy E-mail: guido@rdn.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it Portuguese Andrological Association National Meeting June 21-23, 2008 Oporto
Therapeutic Bronchoscopy Etiology - Benign Stenosis Post - intubation Trauma Post - operative Inflammatory Idiopathic
 Endobronchial Palliation of Airway Disease Douglas E. Wood, MD Professor and Chief Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery Vice-Chair, Department of Surgery Endowed Chair in Lung Cancer Research University
Endobronchial Palliation of Airway Disease Douglas E. Wood, MD Professor and Chief Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery Vice-Chair, Department of Surgery Endowed Chair in Lung Cancer Research University
Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form.
 : Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Surgery Type of Article: Case Report Title: What is the treatment
: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Surgery Type of Article: Case Report Title: What is the treatment
The pure distal left main bronchial sleeve resection with total lung parenchymal preservation: report of two cases and literature review
 Case Report The pure distal left main bronchial sleeve resection with total lung parenchymal preservation: report of two cases and literature review Jian Tang 1, Min Cao 1, Liqiang Qian 2, Yujie Fu 1,
Case Report The pure distal left main bronchial sleeve resection with total lung parenchymal preservation: report of two cases and literature review Jian Tang 1, Min Cao 1, Liqiang Qian 2, Yujie Fu 1,
Colon Patch Esophagoplasty: A Clinical Study For Chemical Burn Esophageal Stricture
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Colon Patch Esophagoplasty: A Clinical Study For Chemical Burn Esophageal Stricture M Hourang, V Mehrabi Citation M Hourang, V Mehrabi. Colon
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Colon Patch Esophagoplasty: A Clinical Study For Chemical Burn Esophageal Stricture M Hourang, V Mehrabi Citation M Hourang, V Mehrabi. Colon
Idiopathic laryngotracheal stenosis
 Surgical Technique Idiopathic laryngotracheal stenosis Christina L. Costantino, Douglas J. Mathisen Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA 02114, USA Correspondence to: Douglas J. Mathisen, MD. Massachusetts
Surgical Technique Idiopathic laryngotracheal stenosis Christina L. Costantino, Douglas J. Mathisen Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA 02114, USA Correspondence to: Douglas J. Mathisen, MD. Massachusetts
pulmonary and critical care pearls
 pulmonary and critical care pearls A 63-Year-Old Woman With Subcutaneous Emphysema Following Endotracheal Intubation* Bassam Hashem, MD; James K. Smith, MD, FCCP; and W. Bruce Davis, MD, FCCP (CHEST 2005;
pulmonary and critical care pearls A 63-Year-Old Woman With Subcutaneous Emphysema Following Endotracheal Intubation* Bassam Hashem, MD; James K. Smith, MD, FCCP; and W. Bruce Davis, MD, FCCP (CHEST 2005;
The treatment strategy for tracheoesophageal fistula
 Review Article on Airway Obstruction The treatment strategy for tracheoesophageal fistula Mingyao Ke, Xuemei Wu, Junli Zeng Department of Respiratory Centre, No. 2 Hospital Xiamen, Xiamen 361000, China
Review Article on Airway Obstruction The treatment strategy for tracheoesophageal fistula Mingyao Ke, Xuemei Wu, Junli Zeng Department of Respiratory Centre, No. 2 Hospital Xiamen, Xiamen 361000, China
Case Presentation Surgery Grand Round. Amid Keshavarzi, MD UCHSC 4/9/2006
 Case Presentation Surgery Grand Round Amid Keshavarzi, MD UCHSC 4/9/2006 Case Presentation 12 y/o female Presented to OSH after accidental swallowing of plastic fork in the bus, CXR/AXR form OSH did not
Case Presentation Surgery Grand Round Amid Keshavarzi, MD UCHSC 4/9/2006 Case Presentation 12 y/o female Presented to OSH after accidental swallowing of plastic fork in the bus, CXR/AXR form OSH did not
Uniportal video-assisted thoracic surgery for esophageal cancer
 Surgical Technique on Esophageal Surgery Uniportal video-assisted thoracic surgery for esophageal cancer Hasan F. Batirel Thoracic Surgery Department, Marmara University Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey Correspondence
Surgical Technique on Esophageal Surgery Uniportal video-assisted thoracic surgery for esophageal cancer Hasan F. Batirel Thoracic Surgery Department, Marmara University Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey Correspondence
Video-assisted thoracic surgery right upper lobe bronchial sleeve resection
 Original Article on Thoracic Surgery Video-assisted thoracic surgery right upper lobe bronchial sleeve resection Qianli Ma, Deruo Liu Department of Thoracic Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing
Original Article on Thoracic Surgery Video-assisted thoracic surgery right upper lobe bronchial sleeve resection Qianli Ma, Deruo Liu Department of Thoracic Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing
LIST OF CLINICAL PRIVILEGES CARDIOTHORACIC SURGERY
 LIST OF CLINICAL PRIVILEGES CARDIOTHORACIC SURGERY AUTHORITY: Title 10, U.S.C. Chapter 55, Sections 1094 and 1102. PRINCIPAL PURPOSE: To define the scope and limits of practice for individual providers.
LIST OF CLINICAL PRIVILEGES CARDIOTHORACIC SURGERY AUTHORITY: Title 10, U.S.C. Chapter 55, Sections 1094 and 1102. PRINCIPAL PURPOSE: To define the scope and limits of practice for individual providers.
Radiology. Gastrointestinal. Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact. Farooq P. Agha
 Gastrointest Radiol 9:9%103 (1984) Gastrointestinal Radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1984 Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact Farooq P. Agha Department of Radiology,
Gastrointest Radiol 9:9%103 (1984) Gastrointestinal Radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1984 Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact Farooq P. Agha Department of Radiology,
The first stents designed for use in the biliary tree and
 Imaging and Advanced Technology Michael B. Wallace, Section Editor Expandable Gastrointestinal Stents TODD H. BARON Department of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
Imaging and Advanced Technology Michael B. Wallace, Section Editor Expandable Gastrointestinal Stents TODD H. BARON Department of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
Discussing feline tracheal disease
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Discussing feline tracheal disease Author : ANDREW SPARKES Categories : Vets Date : March 24, 2008 ANDREW SPARKES aims to
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Discussing feline tracheal disease Author : ANDREW SPARKES Categories : Vets Date : March 24, 2008 ANDREW SPARKES aims to
Posterior leaflet prolapse is the most common lesion seen
 Techniques for Repairing Posterior Leaflet Prolapse of the Mitral Valve Robin Varghese, MD, MS, and David H. Adams, MD Posterior leaflet prolapse is the most common lesion seen in degenerative mitral valve
Techniques for Repairing Posterior Leaflet Prolapse of the Mitral Valve Robin Varghese, MD, MS, and David H. Adams, MD Posterior leaflet prolapse is the most common lesion seen in degenerative mitral valve
MINIMALLY INVASIVE ESOPHAGECTOMY FOR CANCER: where do we stand?
 MINIMALLY INVASIVE ESOPHAGECTOMY FOR CANCER: where do we stand? Ph Nafteux, MD Copenhagen, Nov 3rd 2011 Department of Thoracic Surgery, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium W. Coosemans, H. Decaluwé, Ph.
MINIMALLY INVASIVE ESOPHAGECTOMY FOR CANCER: where do we stand? Ph Nafteux, MD Copenhagen, Nov 3rd 2011 Department of Thoracic Surgery, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium W. Coosemans, H. Decaluwé, Ph.
Open Access. Noriaki Sadanaga 1*, Keigo Morinaga 2 and Hiroshi Matsuura 1
 Sadanaga et al. Surgical Case Reports (2015) 1:22 DOI 10.1186/s40792-015-0020-x Open Access Secondary reconstruction with a transverse colon covered with a pectoralis major muscle flap and split thickness
Sadanaga et al. Surgical Case Reports (2015) 1:22 DOI 10.1186/s40792-015-0020-x Open Access Secondary reconstruction with a transverse colon covered with a pectoralis major muscle flap and split thickness
Parenchyma-sparing lung resections are a potential therapeutic
 Lung Segmentectomy for Patients with Peripheral T1 Lesions Bryan A. Whitson, MD, Rafael S. Andrade, MD, and Michael A. Maddaus, MD Parenchyma-sparing lung resections are a potential therapeutic option
Lung Segmentectomy for Patients with Peripheral T1 Lesions Bryan A. Whitson, MD, Rafael S. Andrade, MD, and Michael A. Maddaus, MD Parenchyma-sparing lung resections are a potential therapeutic option
Tracheoesophageal fistula after total resection of gastric conduit for gastro-aortic fistula due to gastric ulcer
 Sakatoku et al. Surgical Case Reports (2017) 3:90 DOI 10.1186/s40792-017-0371-6 CASE REPORT Open Access Tracheoesophageal fistula after total resection of gastric conduit for gastro-aortic fistula due
Sakatoku et al. Surgical Case Reports (2017) 3:90 DOI 10.1186/s40792-017-0371-6 CASE REPORT Open Access Tracheoesophageal fistula after total resection of gastric conduit for gastro-aortic fistula due
All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies
 Page 1 of 5 Scope: All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies Population: All ICU personnel Outcomes: To standardize and outline the steps necessary to safely perform a percutaneous tracheostomy
Page 1 of 5 Scope: All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies Population: All ICU personnel Outcomes: To standardize and outline the steps necessary to safely perform a percutaneous tracheostomy
Interesting Case Series. Pulmonary Injury Secondary to Feeding Tube Misplacement
 Interesting Case Series Pulmonary Injury Secondary to Feeding Tube Misplacement Thomas R. Resch, MD, Leigh A. Price, MD, and Stephen M. Milner, MBBS, BDS, FRCS (Ed), FACS Johns Hopkins Burn Center, The
Interesting Case Series Pulmonary Injury Secondary to Feeding Tube Misplacement Thomas R. Resch, MD, Leigh A. Price, MD, and Stephen M. Milner, MBBS, BDS, FRCS (Ed), FACS Johns Hopkins Burn Center, The
Surgery has been proven to be beneficial for selected patients
 Thoracoscopic Lung Volume Reduction Surgery Robert J. McKenna, Jr, MD Surgery has been proven to be beneficial for selected patients with severe emphysema. Compared with medical management, lung volume
Thoracoscopic Lung Volume Reduction Surgery Robert J. McKenna, Jr, MD Surgery has been proven to be beneficial for selected patients with severe emphysema. Compared with medical management, lung volume
Management of Esophageal Cancer: Evidence Based Review of Current Guidelines. Madhuri Rao, MD PGY-5 SUNY Downstate Medical Center
 Management of Esophageal Cancer: Evidence Based Review of Current Guidelines Madhuri Rao, MD PGY-5 SUNY Downstate Medical Center Case Presentation 68 y/o male PMH: NIDDM, HTN, hyperlipidemia, CAD s/p stents,
Management of Esophageal Cancer: Evidence Based Review of Current Guidelines Madhuri Rao, MD PGY-5 SUNY Downstate Medical Center Case Presentation 68 y/o male PMH: NIDDM, HTN, hyperlipidemia, CAD s/p stents,
IATROGENIC OESOPHAGEAL PERFORATION
 IATROGENIC OESOPHAGEAL PERFORATION TAOLE MOKOENA DPhil FRCS PROFESSOR OF SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA 17 TH Controversies and Problems in Surgery Symposium 4-5 October 2013 Introduction Perforation of
IATROGENIC OESOPHAGEAL PERFORATION TAOLE MOKOENA DPhil FRCS PROFESSOR OF SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA 17 TH Controversies and Problems in Surgery Symposium 4-5 October 2013 Introduction Perforation of
Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy- Valuable. Jayer Chung, MD University of Colorado Health Sciences Center December 11, 2006
 Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy- Valuable Jayer Chung, MD University of Colorado Health Sciences Center December 11, 2006 Overview Esophageal carcinoma What is minimally invasive esophagectomy (MIE)?
Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy- Valuable Jayer Chung, MD University of Colorado Health Sciences Center December 11, 2006 Overview Esophageal carcinoma What is minimally invasive esophagectomy (MIE)?
PARTIAL CRICOIDECTOMY WITH PRIMARY THYROTRACHEAL ANASTOMOSIS FOR POSTINTUBATION SUBGLOTTIC STENOSIS
 PARTIAL CRICOIDECTOMY WITH PRIMARY THYROTRACHEAL ANASTOMOSIS FOR POSTINTUBATION SUBGLOTTIC STENOSIS Paolo Macchiarini, MD, PhD a Jean-Philippe Verhoye, MD b Alain Chapelier, MD, PhD b Elie Fadel, MD b
PARTIAL CRICOIDECTOMY WITH PRIMARY THYROTRACHEAL ANASTOMOSIS FOR POSTINTUBATION SUBGLOTTIC STENOSIS Paolo Macchiarini, MD, PhD a Jean-Philippe Verhoye, MD b Alain Chapelier, MD, PhD b Elie Fadel, MD b
