Keep catheter. Anticoagulate. Yes. Symptoms resolved? Yes. No Catheter needed? Other access sites available? Yes. Anticoagulate. Place new catheter
|
|
|
- Laureen Shields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chief Anticoagulation and Thrombosis Service UCSF, SF VA MED CTR Thromboembolism Q&A Management of the Hospitalized Patient, SF, CA October 2012 CASES & ANSWERS 1. A 55 year old woman being treated for osteomyelitis of the spine develops right upper extremity swelling. U/S reveals a DVT in the subclavian and axillary vein. She has a PICC line in that arm. How do you manage this? a. Does she need anticoagulation? b. She will need another 3 weeks of IV antibiotics. Do you remove the PICC Line? Venous thrombosis Septic thrombophlebitis? No Yes Keep catheter Anticoagulate Yes Yes Severely symptomatic? No Catheter needed? Symptoms resolved? Yes Removal after fibrinolysis Antibiotics Anticoagulation if no contraindication Elevate involved extremity Remove catheter Anticoagulate If SVC syndrome or severe symptoms & low bleeding risk No No Other access sites available? Keep catheter Anticoagulate No Consider thrombolysis Consider thrombolysis Remove catheter Anticoagulate Yes Remove catheter Place new catheter Anticoagulate Management of catheter related venous thrombosis Anticoagulation generally recommended for 3 months one catheter is removed ACCP 2012 UE DVT (Stephan Moll MD, CLOTCONNECT.ORG) If DVT that involves the axillary or more proximal veins, anticoagulation therapy alone is suggested, rather than thrombolytic therapy. Length of anticoagulation: at least 3 months. In upper extremity DVT not associated with a central venous catheter: 3 months of anticoagulation is recommended. In upper extremity DVT associated with a central venous catheter: o Suggestion is to not remove the catheter if it is functional and there is an ongoing need for the catheter. Anticoagulation should be given as long as the catheter is in place. o If the catheter is removed, anticoagulation should continue for 3 months thereafter.
2 2. A 45 year old man presents with complaints of moderate but persistent calf pain and swelling. He was kicked playing soccer a five days ago and symptoms have developed since then. Ultrasound shows DVT in the posterior tibeal vein. What do you recommend? ACCP 2012 Distal leg DVT (Stephan Moll MD, CLOTCONNECT.ORG) a) Severe symptoms: Treat with anticoagulants. Length of treatment: 3 months (no matter whether DVT was associated with a transient risk factor (surgery, hospitalization, estrogen therapy, etc.) or was unprovoked (= idiopathic). b) No, mild or moderate symptoms (and no risk factors for clot extension see below): o o o No anticoagulation needed. Physician to obtain several ( serial ) Doppler ultrasound leg examinations over the next 2 weeks to make sure the DVT has not extended (which it does in about 15 % of patients). If DVT has extended: treat with anticoagulants for 3 months. If extension of clot has not occurred within the first 2 weeks, it is unlikely to occur subsequently. Risk factors for extension: positive D-dimer, DVT that is extensive or close to the proximal veins, no reversible provoking factor for DVT present, active cancer, previous history of blood clots, and inpatient status 3. A 55 year-old man presents with pleuritic chest pain. His BP is 120/70, HR 105, RR is 18, and his O2 sat is 97%. His physical exam is unremarkable. A chest CT shows multiple pulmonary emboli. ECG is normal. a. What is this patient's risk of early mortality related to PE? b. What anticoagulant regiman will you start and when? c. Will he be admitted and if so for how long? 2
3 PE-related early Hypotension ECHO/CTa/Biomarkers PESI score Management mortality High >15% YES Admit to ICU Thrombolysis and anticoagulation Intermediate 3-15% NO ECHO-RV dysfunction CTa- RV/LV ratio > 1.0 Low <3% NO ECHO-no RV dysfunction CTa-RV/LV ratio<1.0 No BNP or troponin elevation >II or HIGH I-II or LOW Inpatient treatment Consider thrombolysis on case by case basis Expedited discharge; OR consider outpatient treatment** Aujesky et al July Outpatient vs Inpatient tx PE Lancet 2011 **all PESI 1 or II. NOTE-they excluded O2 sat < 90% or p02 60, BP< 100, high bleed risk (stroke in 10 day s gi bleed in 14, <75K platelets, CrCl<30,on warfarin already, homeless, substance use, BMI> 150 Risk scoring system (Class I-II are low, class II-V are high) Risk Factor Points Age Points=age Male 10 Cancer 30 Heart failure 10 Chronic lung disease 10 HR > SBP < 100 mmhg 20 RR >30 20 Temp < Δ mental status 60 O2 sat <90% 20 Severity class Points 30 day mortality I 0-65 <1.7% II <3.5% III <7.1% IV % V > % Aujesky et al Eur Heart Journal 2006 Risk Factor points Age 1 if > 80 Cancer 1 Heart failure lung 1 disease SBP < 100 mmhg 1 O2 sat <90% 1 Severity class Points 30 day mortality LOW 0 1% HIGH 1 or more 10% Jimenez, D. et al. Arch Intern Med
4 3a.His PESI score is 65, placing him in Class I, very low risk of PE related mortality. You decide to discharge him to home. He weighs 100 kg. He has CKD with CrCl of 39 ml/min. What dose of enoxaparin do you recommend? Suggested anticoagulation regimens for the initial treatment of VTE. Event DVT or nonmassive PE Deep venous thrombosis, upper extremity Submassive PE Massive PE VTE in severe renal insufficiency VTE in Cancer Treatment (choose one) LMWH Enoxaparin 1 mg/kg subcutaneously twice daily Tinzaparin 175units/kg subcutaneously daily Dalteparin 200units/kg subcutaneously daily Subcutaneous UFH: apttmonitoring 17,5000 every 12 hours (initial dose) with aptt monitoring Subcutaneous UFH: no aptt monitoring 330units/kg x 1 then 250units/kg every 12 hours Fondiparinux 7.5mg-10mg subcutaneously daily, depending on weight IV unfractionated heparin bolus of 5,000 units followed by a continuous infusion of at least 30,000 units for the 1st 24 hours weight-based regimen of 80 units/kg bolus followed by a continuous infusion of 18u/kg/hr. Note: begin warfarin with initial dose of parenteral anticoagulant as selected above See DVT, lower extremity Consider thrombolysis in appropriate candidates See DVT, lower extremity Risk stratification suggested to guide triage and possibly therapy. IV Unfractionated heparin Thrombolytic therapy (choose one) tpa-100mg infusion over 2 hours, followed by IV unfractionated heparin Bolus tpa if actual cardiac arrest Urokinase, 4,400 IU/kg loading dose followed by 2,2000IU/kg for 12 hours. Note: for urokinase, heparin infusion should be administered concurrently Unfractionated heparin (See Deep venous thrombosis, lower extremity) Dalteparin (See Deep venous thrombosis, lower extremity) Continue LMWH therapy for 3-6 months, no transition to warfarin Use UFH preferentially in the following scenarios: Immediate risk of bleeding o T1/2 of UFH 1-2 hours, LMWH ranges from 2-8 hours o UFH 100% reversible with protamine, LMWH only 60% 4
5 Renal Failure o Dosing less reliable with CrCl < 30 ml/min Extremes of weight o Dose effect of LMWH may be less predictable in patients <50kg and BMI>30 kg/m2 Massive PE and submassive PE when considering thrombolysis Enoxaparin has been shown to accumulate in low weight individuals with antixa levels 50 % higher in this population. (Female patients weighing 45 kg or less and male patients weighing 57 kg or less). Heparin levels should be monitored in patients nearing lower weight limit. Enoxaparin in renal insufficiency Consider use of unfractionated heparin in low weight patients. Enoxaparin has also been shown to accumulate in patients with moderate renal insufficieny (CrCl ml/min). While prescribing information does not offer guidance on dosage adjustment in this population there is literature supporting use of lower dosing. Consider anti-xa level monitoring in patients with renal insufficiency, particulary those who may be on therapy > 10days. Overall Recommendations for renal insufficiency (based on studies): Treatment Doses Enoxaparin 1 st 48hrs: 1mg/kg q12hrs* Maintenance: dose adjust based on renal function*: Est CrCl (ml/min) Fraction of usual daily dose ^Accumulation for use > 10 days is unknown, consider monitoring of anti Xa levels, and adjust * from Barras 2008 &2010 (adapted from Green et al 2005) Barras (2008) 14 : Individualized Compared with Conventional Dosing of Enoxaparin 122 patients were randomized into standardized dosing vs. individualized dosing Usual dose of 1mg/kg q12hrs is used for the first 2 days because PK analysis show subtherapeutic concentration of factor Xa is more likely in the first 48hrs Endpoints Individualized arm Conventional arm P value N=46 N= 54 Any bleeding 1 (2%) 9 (15%) 0.03 Composite bleeding and bruising 6 (12%) 21 (40%)
6 Barras (2010) 16 : Individualized dosing of enoxaparin for subjects with renal impairment is superior to conventional dosing at achieving therapeutic concentrations Endpoints Therapeutic Xa levels (0.5 1) Supratherapeutic Xa (> 1) Subthreapeutic Xa levels (<0.5) Individualized arm N=46 Conventional arm N= 54 Pvalue 69.9% 42.6% % 37.1% % 15.7% 0.97 Barras MA, Duffull SB, Atherton JJ, Green B. Individualized compared with conventional dosing of enoxaparin. Clin Pharmacol Ther Jun;83(6): Green B, Greenwood M, Saltissi D et al. Dosing strategy for enoxaparin in patients with renal impairment presenting with acute coronary syndromes. Br J Clin Phmarcol. 2005; 59: Barras MA, Duffull SB, Atherton JJ, Green B. Individualized dosing of enoxaparin for subjects with renal impairment is superior to conventional dosing at achieving therapeutic concentrations. Ther Drug Monit Aug;32(4): A 68 year old woman falls and fractures her hip. She is in CHF on admission so OR time is delayed. On HD #3 she becomes acutely short of breath and is found to have PE and DVT. How do you manage her anticoagulation perioperatively? ACCP 2012 Vena cava filter (Stephan Moll MD, CLOTCONNECT.ORG) Should only be placed in the patient with an acute DVT who cannot tolerate blood thinners because of active bleeding or a high risk for bleeding. We do not consider that a permanent IVC filter, of itself, is an indication for extended anticoagulation. 6
7 Indication for IVC Filter Placement Acute VTE and contraindication to anticoagulation VTE despite anticoagulation Preoperatively in patients who have had recent VTE (within one month) and must have anticoagulation interrupted for surgery Proximal DVT in patient with poor cardiopulmonary reserve ACCP( 1) AHA (2) British Committee for Standards in Hematology (3) Thrombosis Interest Group of Canada (4) YES YES YES YES If proximal DVT present NO YES MAYBE High intensity oral anticoagulation or LMWH should be considered prior to placement of filter YES (VTE within 4 weeks prior to surgery) NO Anticoagulation should be intensified or alternative agent started. IVC filter will not prevent progression YES (VTE within 2 weeks prior to major surgery) YES There is no agreement on definition of poor reserve Free-floating thrombus NO NO Thrombolysis with NO NO proximal DVT Primary prophylaxis in selected high risk patients (surgical, trauma etc) NO NO 7
8 5. How long will you recommend the 55 yo man with unprovoked PE this patient stay on anticoagulation? a. 3 months b. 6 months c. 12 months d. Indefinitely 5a How long will you recommend the 68 yo woman with provoked PE stay on anticoagulation? e. 3 months f. 6 months g. 12 months h. Indefinitely THROMBOTICS T Trauma, travel H heme- P. Vera, ET, PNH, DIC, MM, MGUS, sickle cell R nephrotic syndrome O oral contraceptives/hrt/pregnancy/tamoxifen M malignancy B bedbound/immobilization O obesity T thrombophilia, thrombosis history I inflammatory states: IBD/Behcets syndrome/lupus C catheters S surgery 8
9 When evaluating a patient with thrombosis always consider the systemic diseases that can accompany VTE Systemic disease Clinical Features Diagnostic Data Inflammatory bowel disease Nephrotic syndrome Bloody diarrhea, aphthous ulcers, arthritis, rash Periorbital edema, peripheral edema, HTN, hypercholesterolemia Histologic analysis of intestinal biopsy specimens Urine protein analysis Behcets Myeloproliferative disorders (P. Vera, Essential thrombocytosis) Oral ulcers, genital ulcers, ophthalmologic issues Pruritis, plethora -- CBC, JAK-2 mutation Sickle cell disease Anemia, sickle crises Evaluation of the blood smear, hemoglobin electrophoresis Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome Livedo, arthritis, rash Lupus anticoagulant, ELISA for anticardiolipin antibody IgG and IgM (assess 3 months after acute event) Cancer Weight loss, night sweats CBC, LFTS, PSA, pap smear, routine cancer screening Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria Hemolytic anemia CBC, Flow cytometry for CD55, CD59 Pregnancy Amenorrhea Urine pregnancy test (all women of childbearing age) 9
10 Indication 8th ACCP guidelines 2008 BTS guidelines 2003 ASH recommendations 2008 First episode of VTE secondary to a transient risk factor First episode of idiopathic (unprovoked) VTE Other (recurrent, active cancer,...) 3 months (Grade 1A). At least 3 Months, prefer long-term treatment if risk/benefit ratio ok (Grade 1A). Long term (Grade 1A). 4 6 weeks (grade A). 3 months (Grade A). At least 6 months (Grade C). 3 months 6 months Long term if APLS, AT deficiency or recurrence Parletti, D-dimer testing to determine the duration of anticoagulation therapy. N Engl J Med Oct 26;355(17): Clinical Risk score Clinical predictors Leg red or swollen or hyperpigment 5-7 mos after event D-dimer >250 ug/l on AC BMI >30kg/m2 Age> 65 Female patients with 0-1 risk factor had recurrence risk of 1.6%: 2 = 14% Rodgers et al CMAJ August
11 VIENNE PREDICTION RULE DASH D-dimer (+2) Age > 50 (+1) Sex-male (+1) Hormones (-2) Score Annualized Risk 1 3.1% 2 6.4% % Tosetto A et al J Thromb Haemost EICHINGER CIRCULATION 2010 Recurrent VTE ASA 6.6% Placebo 11.2 % VTE 40% No difference in major bleeding 11 Becattini C et al. N Engl J Med 2012
12 5c. Do either of these patients need a work up for laboratory thrombophilia? In general, testing for thrombophilia should be avoided in patients in the acute setting of thrombosis. Acute thrombosis will affect antithrombin, protein C, protein S, factor VIII, lupus anticoagulant assays and antiphospholipid antibody assays. In addition, warfarin and heparin can interfere with protein C, S, antithrombin and lupus anticoagulant assays. Presence of common thrombophilia (ie., factor V Leiden, prothrombin gene mutation, hyperhomocysteinemia) does not strongly influence the risk of recurrent VTE and therefore will not likely influence recommendations for duration of therapy. Acutely, even presence of significant thrombophilia will not influence recommendations for anticoagulation in first idiopathic DVT/PE (with the rare exception of significant antithrombin deficiency, where patients may be less sensitive to heparin). test Acute VTE Heparin Warfarin Anticardiolipin antibodies elevated No effect No effect Lupus anticoagulant prolonged prolonged prolonged Protein C, S decreased No effect decreased Antithrombin level decreased No effect decreased Factor VIII level increased No effect No effect Consider Work up for Laboratory Thrombophilia (age < 50 years old) Women of childbearing years Patients with suspicion for APLS Strong family history of VTE Patients with recurrent VTE Results will influence therapy (duration) 12
13 6. A 33 year old woman diagnosed with left lower extremity DVT 3 months ago maintained on warfarin present with complaints of pleuritic chest and shortness of breath. A CT angio of the chest reveals new bilateral subsegmental pulmonary emboli. She reports compliance with her warfarin therapy and has an INR of 2.5 at the time of admission. She is admitted to your service for recurrent VTE. a. How do you manage this? VTE DESPITE ANTICOAGULATION Medication adherence Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome Cancer DIC/Trousseaus Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia Myeloproliferative disorder Antithrombin deficiency Structural defect Anticoagulant Therapy for Warfarin failure Transition to LMWH then transition to warfarin with higher target OR continue LMWH Anticoagulant therapy for LMWH failure Change to BID dosing Increase dosing by 25% Follow anti-xa levels year old man with history of AFIB, diabetes, hypertension is having total hip arthroplasty. He is on warfarin as an outpatient for stroke prophylaxis. How do you mange his anticoagulation in perioperative period? 13
14 For high bleed risk procedures wait a full hours before starting full dose anticoagulation. Recommend stepwise increase from prophylaxis to intermediate ro treatment dose of heparin/low molecular weight heparin Spyropoulus et al How I treat anticoagulated patients undergong an elective procedure or surgery. Blood 2012;120:
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center
 Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE
 Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE-SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN FRANCISCO Financial Disclosures-NONE
Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE-SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN FRANCISCO Financial Disclosures-NONE
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
Understanding Best Practices in Anticoagulation Therapy in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism. Rajat Deo, MD, MTR
 Understanding Best Practices in Anticoagulation Therapy in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism Rajat Deo, MD, MTR Director of Translational Research in Cardiac Arrhythmias Division of Cardiovascular Medicine
Understanding Best Practices in Anticoagulation Therapy in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism Rajat Deo, MD, MTR Director of Translational Research in Cardiac Arrhythmias Division of Cardiovascular Medicine
Acute Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis. Barbara LeVarge MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Pulmonary Hypertension Center COPYRIGHT
 Acute Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis Barbara LeVarge MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Pulmonary Hypertension Center Acute PE and DVT No disclosures. Acute PE and DVT Learning objectives
Acute Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis Barbara LeVarge MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Pulmonary Hypertension Center Acute PE and DVT No disclosures. Acute PE and DVT Learning objectives
Venous thrombosis is common and often occurs spontaneously, but it also frequently accompanies medical and surgical conditions, both in the community
 Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Disclosures. DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Questions To Ask. Dr. Susanna Shin - DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) None
 Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Risk factors for DVT. Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Anticoagulation (cont d) Diagnosis 1/5/2018. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
DVT - initial management NSCCG
 Background information Information resources for patients and carers Updates to this care map Synonyms Below knee DVT and bleeding risks Patient with confirmed DVT Scan confirms superficial thrombophlebitis
Background information Information resources for patients and carers Updates to this care map Synonyms Below knee DVT and bleeding risks Patient with confirmed DVT Scan confirms superficial thrombophlebitis
Acute and long-term treatment of PE. Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia
 Acute and long-term treatment of PE Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia Acute and long-term treatment of VTE What is the optimal acute phase treatment for the patient? Intravenous thrombolysis One
Acute and long-term treatment of PE Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia Acute and long-term treatment of VTE What is the optimal acute phase treatment for the patient? Intravenous thrombolysis One
Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting Calgary, Alberta, October 2014 Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update Benjamin Bell, MD FRCPC James Douketis, MD FRCPC On Behalf of Thrombosis Canada
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting Calgary, Alberta, October 2014 Venous Thromboembolic Disease Update Benjamin Bell, MD FRCPC James Douketis, MD FRCPC On Behalf of Thrombosis Canada
UC SF. Division of General Internal Medicine UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA SAN FRANCISCO, DIVISION OF HOSPITAL MEDICINE
 Updates in the Management of Venous Thromboembolism Margaret C. Fang, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF Division of Hospital Medicine Medical Director, Anticoagulation Clinic Venous Thromboembolism
Updates in the Management of Venous Thromboembolism Margaret C. Fang, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF Division of Hospital Medicine Medical Director, Anticoagulation Clinic Venous Thromboembolism
DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE)
 DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE) Introduction VTE (DVT/PE) is an important complication in hospitalized patients Hospitalization for acute medical illness
DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE) Introduction VTE (DVT/PE) is an important complication in hospitalized patients Hospitalization for acute medical illness
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Approved by: Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Vice President and Chief Medical Officer; and Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: Date Approved January
Approved by: Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Vice President and Chief Medical Officer; and Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: Date Approved January
Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy. Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016
 Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016 Conflicts of Interest No conflicts of interest to report Objectives At the end of the program participants will be
Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016 Conflicts of Interest No conflicts of interest to report Objectives At the end of the program participants will be
PE and DVT. Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP
 PE and DVT Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call +256777363201 Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP OBJECTIVES DEFINE DVT AND P.E PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DVT CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF DVT/PE INVESTIGATE DVT MANAGEMENT
PE and DVT Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call +256777363201 Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP OBJECTIVES DEFINE DVT AND P.E PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DVT CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF DVT/PE INVESTIGATE DVT MANAGEMENT
Top 5 (or so) Hematology Consults. Tom DeLoughery, MD FACP FAWM. Oregon Health and Sciences University DISCLOSURE
 Top 5 (or so) Hematology Consults Tom FACP FAWM Oregon Health and Sciences University DISCLOSURE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) Speaker Bureau - None Consultant/Research none 1 What I am Talking About
Top 5 (or so) Hematology Consults Tom FACP FAWM Oregon Health and Sciences University DISCLOSURE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) Speaker Bureau - None Consultant/Research none 1 What I am Talking About
Updates in venous thromboembolism. Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia
 Updates in venous thromboembolism Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia News for VTE Diagnosis Treatment the acute phase the agents Pulmonary embolism: diagnosis Vein ultrasonography Meta-analysis 15
Updates in venous thromboembolism Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia News for VTE Diagnosis Treatment the acute phase the agents Pulmonary embolism: diagnosis Vein ultrasonography Meta-analysis 15
Rapid Fire-Top Articles You Need to Know
 Rapid Fire-Top Articles You Need to Know TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE- SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN FRANCISCO Financial Disclosures-NONE
Rapid Fire-Top Articles You Need to Know TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE- SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN FRANCISCO Financial Disclosures-NONE
Approach to Thrombosis
 Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
PE Pathway. The charts are listed as follows:
 PE Pathway This document comprises 6 simple flow charts to assist clinicians in the investigation and treatment of suspected or confirmed Acute Pulmonary Emboli. The pathway has been put together using
PE Pathway This document comprises 6 simple flow charts to assist clinicians in the investigation and treatment of suspected or confirmed Acute Pulmonary Emboli. The pathway has been put together using
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance on the recommended duration of anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism (VTE). BACKGROUND: Recurrent episodes of VTE
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance on the recommended duration of anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism (VTE). BACKGROUND: Recurrent episodes of VTE
Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE
 Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE Financial Disclosures-NONE TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE- SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA,
Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE Financial Disclosures-NONE TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE- SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA,
Updates in Coagulation Thrombophilia testing and direct oral anticoagulants. Kevin Y. Chen, MD Hematology and Medical Oncology October 13, 2017
 Updates in Coagulation Thrombophilia testing and direct oral anticoagulants Kevin Y. Chen, MD Hematology and Medical Oncology October 13, 2017 No conflicts of interest Introduction to thrombosis Hemostasis
Updates in Coagulation Thrombophilia testing and direct oral anticoagulants Kevin Y. Chen, MD Hematology and Medical Oncology October 13, 2017 No conflicts of interest Introduction to thrombosis Hemostasis
Updates in Management of Pulmonary Embolism (PE) David Ming, MD Duke Hospital Medicine July 24, 2017 Hilton Head, SC
 Updates in Management of Pulmonary Embolism (PE) David Ming, MD Duke Hospital Medicine July 24, 2017 Hilton Head, SC Objectives Highlight clinical features and presentation of acute PE Analyze strategies
Updates in Management of Pulmonary Embolism (PE) David Ming, MD Duke Hospital Medicine July 24, 2017 Hilton Head, SC Objectives Highlight clinical features and presentation of acute PE Analyze strategies
Objectives. Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis. Case VTE WHY DO IT? Question: Who Is At Risk?
 Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis Rishi Garg, MD Department of Medicine Identify patients at risk for VTE Options for VTE prophylaxis Current Recommendations (based on The Seventh ACCP
Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis Rishi Garg, MD Department of Medicine Identify patients at risk for VTE Options for VTE prophylaxis Current Recommendations (based on The Seventh ACCP
ANTICOAG & THROMBOSIS CASES
 ANTICOAG & THROMBOSIS CASES Tracy Minichiello, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Chief, SF VA Anticoagulation & Thrombosis Service Disclosures I have nothing to disclose
ANTICOAG & THROMBOSIS CASES Tracy Minichiello, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Chief, SF VA Anticoagulation & Thrombosis Service Disclosures I have nothing to disclose
Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. PE - Clinical
 Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
Medical Patients: A Population at Risk
 Case Vignette A 68-year-old woman with obesity was admitted to the Medical Service with COPD and pneumonia and was treated with oral corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and antibiotics. She responded well
Case Vignette A 68-year-old woman with obesity was admitted to the Medical Service with COPD and pneumonia and was treated with oral corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and antibiotics. She responded well
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT?
 How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients. David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center
 DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
VTE: New Evidence, Best Practices, and Controversies
 VTE: New Evidence, Best Practices, and Controversies Steven Deitelzweig, MD, MMM, SFHM Associate Professor of Medicine University of Queensland School of Medicine System Chairman Hospital Medicine Medical
VTE: New Evidence, Best Practices, and Controversies Steven Deitelzweig, MD, MMM, SFHM Associate Professor of Medicine University of Queensland School of Medicine System Chairman Hospital Medicine Medical
PE service. 65 years old lady. What would you do next? Risk stratification. What would you do next? Regional College Lecture PE Management
 PE service Regional College Lecture PE Management Update in medicine (Eastern) Cambridge 29 th June 2017 Dr Rachel M Limbrey DM FRCP University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust Ambulatory acute
PE service Regional College Lecture PE Management Update in medicine (Eastern) Cambridge 29 th June 2017 Dr Rachel M Limbrey DM FRCP University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust Ambulatory acute
NOTE: The first appearance of terms in bold in the body of this document (except titles) are defined terms please refer to the Definitions section.
 TITLE VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM PROPHYLAXIS SCOPE Provincial Acute and Sub-Acute Care Facilities APPROVAL AUTHORITY Alberta Health Services Executive Committee SPONSOR Vice President, Quality and Chief Medical
TITLE VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM PROPHYLAXIS SCOPE Provincial Acute and Sub-Acute Care Facilities APPROVAL AUTHORITY Alberta Health Services Executive Committee SPONSOR Vice President, Quality and Chief Medical
Pulmonary Thromboembolism
 Pulmonary Thromboembolism James Allen, MD Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism 1,500,000 new cases per year in the United States Often asymptomatic 300,000 deaths per year DVT or PE present in 10% of ICU
Pulmonary Thromboembolism James Allen, MD Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism 1,500,000 new cases per year in the United States Often asymptomatic 300,000 deaths per year DVT or PE present in 10% of ICU
Thrombophilia. Diagnosis and Management. Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI
 Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
THROMBOSIS RISK FACTOR ASSESSMENT
 Name: Procedure: Doctor: Date: THROMBOSIS RISK FACTOR ASSESSMENT CHOOSE ALL THAT APPLY EACH RISK FACTOR REPRESENTS 1 POINT Age 41 60 years Minor Surgery Planned History of Prior Major Surgery (< 1 month)
Name: Procedure: Doctor: Date: THROMBOSIS RISK FACTOR ASSESSMENT CHOOSE ALL THAT APPLY EACH RISK FACTOR REPRESENTS 1 POINT Age 41 60 years Minor Surgery Planned History of Prior Major Surgery (< 1 month)
CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevalence Patho-physiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Management of DVT/PE Prevention VTE Patho-physiology
CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevalence Patho-physiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Management of DVT/PE Prevention VTE Patho-physiology
This chapter will describe the effectiveness of antithrombotic
 Antithrombotic Therapy for Venous Thromboembolic Disease The Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy Harry R. Büller, MD, Chair; Giancarlo Agnelli, MD; Russel D. Hull, MBBS,
Antithrombotic Therapy for Venous Thromboembolic Disease The Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy Harry R. Büller, MD, Chair; Giancarlo Agnelli, MD; Russel D. Hull, MBBS,
Frequently Asked Questions about Cancer Associated Thrombosis
 + Frequently Asked Questions about Cancer Associated Thrombosis Atlantic Canada Oncology Group Annual Meeting June 13 th, 2015 Sudeep Shivakumar, Dalhousie University + Conflict of Interest Disclosures
+ Frequently Asked Questions about Cancer Associated Thrombosis Atlantic Canada Oncology Group Annual Meeting June 13 th, 2015 Sudeep Shivakumar, Dalhousie University + Conflict of Interest Disclosures
Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders
 SURGICAL GRAND ROUNDS March 17 th, 2007 Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders Guillermo Escobar, M.D. LMWH vs UFH Jayer s sales pitch: FALSE LMW is
SURGICAL GRAND ROUNDS March 17 th, 2007 Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders Guillermo Escobar, M.D. LMWH vs UFH Jayer s sales pitch: FALSE LMW is
Acute and long-term treatment of VTE. Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia
 Acute and long-term treatment of VTE Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia Acute and long-term treatment of VTE The goals The acute PE phase After the acute phase Treatment for VTE Goals of acute treatment
Acute and long-term treatment of VTE Cecilia Becattini University of Perugia Acute and long-term treatment of VTE The goals The acute PE phase After the acute phase Treatment for VTE Goals of acute treatment
Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2015
 Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2015 General Principles: There is compelling data in the medical literature to support
Outpatient Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) Clinical Practice Guideline August 2015 General Principles: There is compelling data in the medical literature to support
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS. Pankaj Handa Department of General Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS Pankaj Handa Department of General Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital My Talk Today 1.Introduction 2. Are All Cancer Patients at Risk of VTE? 3. Should All VTE Patients Be Screened
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS Pankaj Handa Department of General Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital My Talk Today 1.Introduction 2. Are All Cancer Patients at Risk of VTE? 3. Should All VTE Patients Be Screened
Update on the Management of Cancer Associated VTE
 Update on the Management of Cancer Associated VTE Jean M. Connors, MD 2018 Master Class Course Anticoagulation Management Services BWH/DFCI Hemostatic Antithrombotic Stewardship BWH Associate Professor
Update on the Management of Cancer Associated VTE Jean M. Connors, MD 2018 Master Class Course Anticoagulation Management Services BWH/DFCI Hemostatic Antithrombotic Stewardship BWH Associate Professor
Thrombophilia. Stephan Moll, MD Medicine, Heme-Coag UNC Chapel Hill, NC. GASCO Atlanta Sept 8 th, Disclosures. Conflicts of interest: NONE
 LA APLA 1 3 ACA Anti-ß2-GP I 2 45 Thrombophilia Stephan Moll, MD Medicine, Heme-Coag UNC Chapel Hill, NC GASCO Atlanta Sept 8 th, 2017 Disclosures Conflicts of interest: NONE Off-label product use discussion:
LA APLA 1 3 ACA Anti-ß2-GP I 2 45 Thrombophilia Stephan Moll, MD Medicine, Heme-Coag UNC Chapel Hill, NC GASCO Atlanta Sept 8 th, 2017 Disclosures Conflicts of interest: NONE Off-label product use discussion:
INDICATIONS FOR THROMBO-PROPHYLAXIS AND WHEN TO STOP ANTICOAGULATION BEFORE ELECTIVE SURGERY
 INDICATIONS FOR THROMBO-PROPHYLAXIS AND WHEN TO STOP ANTICOAGULATION BEFORE ELECTIVE SURGERY N.E. Pearce INTRODUCTION Preventable death Cause of morbidity and mortality Risk factors Pulmonary embolism
INDICATIONS FOR THROMBO-PROPHYLAXIS AND WHEN TO STOP ANTICOAGULATION BEFORE ELECTIVE SURGERY N.E. Pearce INTRODUCTION Preventable death Cause of morbidity and mortality Risk factors Pulmonary embolism
Dr. Riaz JanMohamed Consultant Haematologist The Hillingdon Hospital Foundation Trust
 MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) IN THE COMMUNITY SETTING & ANTICOAGULATION CLINICS THE PAST, PRESENT AND THE FUTURE Dr. Riaz JanMohamed Consultant Haematologist The Hillingdon Hospital
MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) IN THE COMMUNITY SETTING & ANTICOAGULATION CLINICS THE PAST, PRESENT AND THE FUTURE Dr. Riaz JanMohamed Consultant Haematologist The Hillingdon Hospital
Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC 1 st workshop: update to VTE guidelines in 2016 2 nd workshop: VTE controversies + new horizons André Roussin MD, FRCP, CSPQ CHUM
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC 1 st workshop: update to VTE guidelines in 2016 2 nd workshop: VTE controversies + new horizons André Roussin MD, FRCP, CSPQ CHUM
Venous thromboembolic diseases: diagnosis, management and thrombophilia testing (2012) NICE guideline CG144
 Venous thromboembolic diseases: diagnosis, management and thrombophilia testing (2012) NICE guideline CG144 Appendix A: Summary of new evidence from Summary of evidence from previous year Diagnosis Diagnostic
Venous thromboembolic diseases: diagnosis, management and thrombophilia testing (2012) NICE guideline CG144 Appendix A: Summary of new evidence from Summary of evidence from previous year Diagnosis Diagnostic
Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT?
 Carotid artery stenosis and risk of stroke Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT? Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS Faculty of Medicine of University of Porto Munich, 2016
Carotid artery stenosis and risk of stroke Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT? Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS Faculty of Medicine of University of Porto Munich, 2016
Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism
 Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism Ethan Cumbler M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Hospitalist Medicine Section University of Colorado Denver May 2010 No Conflicts of Interest Objectives
Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism Ethan Cumbler M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Hospitalist Medicine Section University of Colorado Denver May 2010 No Conflicts of Interest Objectives
With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis
 BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital April
BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital April
Inferior Vena Cava Filters
 Inferior Vena Cava Filters and the American Society of Hematology Choosing Wisely Campaign Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, HMDC MACOI Chief - Division of Specialty Medicine Professor and Chair - Section of Internal
Inferior Vena Cava Filters and the American Society of Hematology Choosing Wisely Campaign Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, HMDC MACOI Chief - Division of Specialty Medicine Professor and Chair - Section of Internal
Pulmonary Embolism Pathway
 Pulmonary Embolism Pathway Ambulatory Care Pathway Dr. A. Zafar, Dr. A. Rehman, Dr. T. Malik September, 2011. Patient Identification Label Pulmonary Embolism Pathway Clinical History Comments Hospital
Pulmonary Embolism Pathway Ambulatory Care Pathway Dr. A. Zafar, Dr. A. Rehman, Dr. T. Malik September, 2011. Patient Identification Label Pulmonary Embolism Pathway Clinical History Comments Hospital
Changing the Ambulatory Training Paradigm: The Design and Implementation of an Outpatient Pulmonology Fellowship Curriculum
 Online Data Supplement Changing the Ambulatory Training Paradigm: The Design and Implementation of an Outpatient Pulmonology Fellowship Curriculum Stacey M. Kassutto, C. Jessica Dine, Maryl Kreider, Rupal
Online Data Supplement Changing the Ambulatory Training Paradigm: The Design and Implementation of an Outpatient Pulmonology Fellowship Curriculum Stacey M. Kassutto, C. Jessica Dine, Maryl Kreider, Rupal
Anticoagulation in Special populations. Ng Heng Joo Department of Haematology Singapore General Hospital
 Anticoagulation in Special populations Ng Heng Joo Department of Haematology Singapore General Hospital roymatheson.com Objectives Safer anticoagulation for The elderly Chronic kidney disease Obese patients
Anticoagulation in Special populations Ng Heng Joo Department of Haematology Singapore General Hospital roymatheson.com Objectives Safer anticoagulation for The elderly Chronic kidney disease Obese patients
10/8/2012. Disclosures. Making Sense of AT9: Review of the 2012 ACCP Antithrombotic Guidelines. Goals and Objectives. Outline
 Disclosures Making Sense of AT9: Review of the 2012 ACCP Antithrombotic Guidelines No relevant conflicts of interest related to the topic presented. Cyndy Brocklebank, PharmD, CDE Chronic Disease Management
Disclosures Making Sense of AT9: Review of the 2012 ACCP Antithrombotic Guidelines No relevant conflicts of interest related to the topic presented. Cyndy Brocklebank, PharmD, CDE Chronic Disease Management
PULMONARY EMBOLISM/VTE CARE PROCESS MODEL
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM/VTE CARE PROCESS MODEL IMCP FALL CONFERENCE 2017 Scott Stevens, MD Co-Director, Thrombosis Clinic & Thrombosis Research Group Intermountain Medical Center Professor of Clinical Medicine
PULMONARY EMBOLISM/VTE CARE PROCESS MODEL IMCP FALL CONFERENCE 2017 Scott Stevens, MD Co-Director, Thrombosis Clinic & Thrombosis Research Group Intermountain Medical Center Professor of Clinical Medicine
Implications from the ACCP 2012 Consensus Guidelines for the Management of Thrombosis: a case based approach
 Implications from the ACCP 2012 Consensus Guidelines for the Management of Thrombosis: a case based approach Prof. I. Baumgartner Head Clinical and Interventional Angiology About the ACCP guidelines Widely
Implications from the ACCP 2012 Consensus Guidelines for the Management of Thrombosis: a case based approach Prof. I. Baumgartner Head Clinical and Interventional Angiology About the ACCP guidelines Widely
PULMONARY EMBOLISM MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES This document is adapted from the NICE guidelines titled Venous thromboembolic diseases: the management of venous thromboembolic diseases and the role of thrombophilia
PULMONARY EMBOLISM MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES This document is adapted from the NICE guidelines titled Venous thromboembolic diseases: the management of venous thromboembolic diseases and the role of thrombophilia
Thrombolysis in PE. Outline. Disclosure. Overview on Pulmonary Embolism. Hot Topics in Emergency Medicine 2012 Midyear Clinical Meeting
 Disclosure Thrombolysis in PE Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP reports no relevant financial relationships. Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP Outline 55 YOF presents to ED with SOB PMH of DVT + noncompliance
Disclosure Thrombolysis in PE Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP reports no relevant financial relationships. Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP Outline 55 YOF presents to ED with SOB PMH of DVT + noncompliance
Updates in Anticoagulation for Atrial Fibrillation and Venous Thromboembolism
 Disclosures Updates in Anticoagulation for Atrial Fibrillation and Venous Thromboembolism No financial conflicts of interest Member of the ABIM Focused- Practice in Hospital Medicine Self Examination Process
Disclosures Updates in Anticoagulation for Atrial Fibrillation and Venous Thromboembolism No financial conflicts of interest Member of the ABIM Focused- Practice in Hospital Medicine Self Examination Process
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Outline of This Presentation
 Slide 1 Current Approaches to Venous Thromboembolism Prevention in Orthopedic Patients Hujefa Vora, MD Maria Fox, RN June 9, 2017 Slide 2 Slide 3 Outline of This Presentation Pathophysiology of venous
Slide 1 Current Approaches to Venous Thromboembolism Prevention in Orthopedic Patients Hujefa Vora, MD Maria Fox, RN June 9, 2017 Slide 2 Slide 3 Outline of This Presentation Pathophysiology of venous
Duration of anticoagulation
 Duration of anticoagulation P. Fontana Service d angiologie et d hémostase Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Pomeriggio formativo in coagulazione, Bellinzona, 19.10.2017 Conflict of interest AstraZeneca,
Duration of anticoagulation P. Fontana Service d angiologie et d hémostase Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Pomeriggio formativo in coagulazione, Bellinzona, 19.10.2017 Conflict of interest AstraZeneca,
Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism: 2017 Update and Future Directions
 Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism: 2017 Update and Future Directions Kush R Desai, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, IL Disclosures
Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism: 2017 Update and Future Directions Kush R Desai, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, IL Disclosures
Scott M. Stevens, MD. Co-Director, Thrombosis Clinic. Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine
 Scott M. Stevens, MD Co-Director, Thrombosis Clinic Intermountain Medical Center Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine The University of Utah School of Medicine No Relevant Financial Relationships Research
Scott M. Stevens, MD Co-Director, Thrombosis Clinic Intermountain Medical Center Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine The University of Utah School of Medicine No Relevant Financial Relationships Research
Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis. Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS
 Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS Catheter-based thrombolysis Local administration of lytic agent Higher local
Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS Catheter-based thrombolysis Local administration of lytic agent Higher local
RISK STRATIFICATION OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE SYMPTOMATIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM. David Jiménez, MD, PhD, FCCP Ramón y Cajal Hospital, IRYCIS Madrid, Spain
 RISK STRATIFICATION OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE SYMPTOMATIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM David Jiménez, MD, PhD, FCCP Ramón y Cajal Hospital, IRYCIS Madrid, Spain Potential Conflicts of Interest Financial conflicts of
RISK STRATIFICATION OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE SYMPTOMATIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM David Jiménez, MD, PhD, FCCP Ramón y Cajal Hospital, IRYCIS Madrid, Spain Potential Conflicts of Interest Financial conflicts of
Venous Thrombosis. Magnitude of the Problem. DVT 2 Million PE 600,000. Death 60,000. Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year.
 Venous Thrombosis Magnitude of the Problem DVT 2 Million Postthrombotic Syndrome 800,000 PE 600,000 Death 60,000 Silent PE 1 Million Pulmonary Hypertension 30,000 Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year
Venous Thrombosis Magnitude of the Problem DVT 2 Million Postthrombotic Syndrome 800,000 PE 600,000 Death 60,000 Silent PE 1 Million Pulmonary Hypertension 30,000 Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) in Myeloma. Christine Chen May 2017
 Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) in Myeloma Christine Chen May 2017 Objectives 1. Review the magnitude of the problem and why myeloma patients are at risk of VTE 2. Discuss thromboprophylaxis approaches in
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) in Myeloma Christine Chen May 2017 Objectives 1. Review the magnitude of the problem and why myeloma patients are at risk of VTE 2. Discuss thromboprophylaxis approaches in
Catheter-directed Thrombolysis for Pulmonary Embolism
 Catheter-directed Thrombolysis for Pulmonary Embolism Is It Good Advice to Lyse? Texas Society of Health-System Pharmacists April 7, 2018 Rebecca L. Attridge, PharmD, MSc, BCPS Associate Professor, University
Catheter-directed Thrombolysis for Pulmonary Embolism Is It Good Advice to Lyse? Texas Society of Health-System Pharmacists April 7, 2018 Rebecca L. Attridge, PharmD, MSc, BCPS Associate Professor, University
Thrombosis. Tom DeLoughery, MD FACP. Oregon Health and Sciences University
 Thrombosis Tom DeLoughery, MD FACP Oregon Health and Sciences University DISCLOSURE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) Speaker Bureau - None Consultant Amgen, Alexion What I am Talking About New Anticoagulants
Thrombosis Tom DeLoughery, MD FACP Oregon Health and Sciences University DISCLOSURE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) Speaker Bureau - None Consultant Amgen, Alexion What I am Talking About New Anticoagulants
Spontane und Tumor-assoziierte VTE: womit wie lange antikoagulieren
 Spontane und Tumor-assoziierte VTE: womit wie lange antikoagulieren Paul Kyrle Allgemeines Krankenhaus Wien Disclosures relevant for this presentation Consultancies, member of advisory boards, speaker
Spontane und Tumor-assoziierte VTE: womit wie lange antikoagulieren Paul Kyrle Allgemeines Krankenhaus Wien Disclosures relevant for this presentation Consultancies, member of advisory boards, speaker
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a pervasive LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM *
 LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM * Geno J. Merli, MD ABSTRACT There are more than 170 000 hospital admissions each year for deep vein thrombosis
LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM * Geno J. Merli, MD ABSTRACT There are more than 170 000 hospital admissions each year for deep vein thrombosis
PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT-
 University Goce Delcev, Faculty of Medical sciences, Stip University Clinic of Cardiology, Skopje R. Of Macedonia PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT- Gordana Kamceva MD mr.sci Acknowledgment Marija Vavlukis
University Goce Delcev, Faculty of Medical sciences, Stip University Clinic of Cardiology, Skopje R. Of Macedonia PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT- Gordana Kamceva MD mr.sci Acknowledgment Marija Vavlukis
Hemostasis. PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures
 Hemostasis PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures Disorders of Hemostasis - Hemophilia - von Willebrand Disease HEMOPHILIA A defect in the thrombin propagation phase
Hemostasis PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures Disorders of Hemostasis - Hemophilia - von Willebrand Disease HEMOPHILIA A defect in the thrombin propagation phase
These are guidelines only and can be deviated from if it is thought to be in the patient s best interest.
 Clinical Guideline Venothromboembolism prophylaxis: Trauma and Orthopaedics Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a recognised complication associated with inactivity and surgical procedures. Therefore, all
Clinical Guideline Venothromboembolism prophylaxis: Trauma and Orthopaedics Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a recognised complication associated with inactivity and surgical procedures. Therefore, all
Objectives DVT PE 5/11/2011. Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Virchow s Triad. VTE Incidence
 Objectives Current Concepts in the Diagnosis and Management of Venous Thromboembolism 1. Discuss antithrombotic treatment options for venous thromboembolism. 2. Describe the role of thrombolytic therapy
Objectives Current Concepts in the Diagnosis and Management of Venous Thromboembolism 1. Discuss antithrombotic treatment options for venous thromboembolism. 2. Describe the role of thrombolytic therapy
Focus: l embolia polmonare Per quanto la terapia anticoagulante orale? Giulia Magnani 27 Gennaio, 2018
 Focus: l embolia polmonare Per quanto la terapia anticoagulante orale? Giulia Magnani 27 Gennaio, 2018 NO DISCLOSURE Pulmonary Embolism Venous thromboembolism (VT) is the third most common cause of cardiovascular
Focus: l embolia polmonare Per quanto la terapia anticoagulante orale? Giulia Magnani 27 Gennaio, 2018 NO DISCLOSURE Pulmonary Embolism Venous thromboembolism (VT) is the third most common cause of cardiovascular
Misunderstandings of Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis
 Misunderstandings of Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis Veerendra Chadachan Senior Consultant Dept of General Medicine (Vascular Medicine and Hypertension) Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Case scenario
Misunderstandings of Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis Veerendra Chadachan Senior Consultant Dept of General Medicine (Vascular Medicine and Hypertension) Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Case scenario
Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales
 Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales Merimbula, 6 th November 2010 University of Sydney Department of Surgery Westmead Hospital
Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales Merimbula, 6 th November 2010 University of Sydney Department of Surgery Westmead Hospital
Treatment Options and How They Work
 Treatment Options and How They Work Robin Offord Director of Clinical Pharmacy UCL Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust robin.offord@uclh.nhs.uk Introducing the term anticoagulant... What they do Inhibit the
Treatment Options and How They Work Robin Offord Director of Clinical Pharmacy UCL Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust robin.offord@uclh.nhs.uk Introducing the term anticoagulant... What they do Inhibit the
Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease
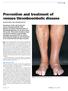 REVIEW Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease SUSAN McNEILL AND CATHERINE BAGOT Awareness of the risk factors for venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease and timely administration of thromboprophylaxis
REVIEW Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease SUSAN McNEILL AND CATHERINE BAGOT Awareness of the risk factors for venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease and timely administration of thromboprophylaxis
UPDATE ON TREATMENT OF ACUTE VENOUS THROMBOSIS
 UPDATE ON TREATMENT OF ACUTE VENOUS THROMBOSIS Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS 16 th National Congress of the Italian Society of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Bologna, 2017 Disclosure I have the following
UPDATE ON TREATMENT OF ACUTE VENOUS THROMBOSIS Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS 16 th National Congress of the Italian Society of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Bologna, 2017 Disclosure I have the following
Pulmonary Embolectomy:
 Pulmonary Embolectomy: Recommendation for early surgical intervention Tomas A. Salerno, M.D. Professor of Surgery, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and Jackson Memorial Hospital Epidemiology
Pulmonary Embolectomy: Recommendation for early surgical intervention Tomas A. Salerno, M.D. Professor of Surgery, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and Jackson Memorial Hospital Epidemiology
Managing Perioperative Anticoagulation. Edie Shen MD
 Managing Perioperative Anticoagulation Edie Shen MD Anticoagulation VKA Warfarin (Coumadin) DOACs Direct Thrombin Inhibitor Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Factor Xa Inhibitor Rivaroxaban(Xarelto) Apixaban(Eliquis)
Managing Perioperative Anticoagulation Edie Shen MD Anticoagulation VKA Warfarin (Coumadin) DOACs Direct Thrombin Inhibitor Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Factor Xa Inhibitor Rivaroxaban(Xarelto) Apixaban(Eliquis)
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF MASSIVE AND SUBMASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULT PATIENTS.
 RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF MASSIVE AND SUBMASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULT PATIENTS. Target Audience: Physicians managing adult patients with massive and submassive pulmonary emboli in the
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF MASSIVE AND SUBMASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN ADULT PATIENTS. Target Audience: Physicians managing adult patients with massive and submassive pulmonary emboli in the
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM. Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow
 CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
Disclosures. Overview. Have you ever. The Perioperative Management of Anticoagulants. No financial conflicts of interest to disclose
 Disclosures No financial conflicts of interest to disclose The Perioperative Management of Anticoagulants Margaret C. Fang, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF Division of Hospital Medicine Medical
Disclosures No financial conflicts of interest to disclose The Perioperative Management of Anticoagulants Margaret C. Fang, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF Division of Hospital Medicine Medical
Is Oral Rivaroxaban Safe and Effective in the Treatment of Patients with Symptomatic DVT?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 1-1-2013 Is Oral Rivaroxaban Safe and Effective
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 1-1-2013 Is Oral Rivaroxaban Safe and Effective
ESIM 2014 Clinical Case Presentation Israel. Ben-Sasson Maayan Bnei-Zion medical center Haifa
 ESIM 2014 Clinical Case Presentation Israel Ben-Sasson Maayan Bnei-Zion medical center Haifa Presentation A 24 YO male,a ping-pong player, presented to the ER with acute onset of right upper extremity
ESIM 2014 Clinical Case Presentation Israel Ben-Sasson Maayan Bnei-Zion medical center Haifa Presentation A 24 YO male,a ping-pong player, presented to the ER with acute onset of right upper extremity
Anticoagulation in Special populations. Ng Heng Joo Department of Haematology Singapore General Hospital
 Anticoagulation in Special populations Ng Heng Joo Department of Haematology Singapore General Hospital roymatheson.com Objectives Safer anticoagulation for The elderly Chronic kidney disease Obese patients
Anticoagulation in Special populations Ng Heng Joo Department of Haematology Singapore General Hospital roymatheson.com Objectives Safer anticoagulation for The elderly Chronic kidney disease Obese patients
Epidemiology. Update on Pulmonary Embolism. Keys to PE Management 5/5/2014. Diagnosis. Risk stratification. Treatment
 Update on Pulmonary Embolism Steven M. Dean, DO, FACP, RPVI Program Director- Vascular Medicine Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Cardiovascular Medicine The Ohio State University Keys
Update on Pulmonary Embolism Steven M. Dean, DO, FACP, RPVI Program Director- Vascular Medicine Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Cardiovascular Medicine The Ohio State University Keys
Perioperative VTE Prophylaxis
 Perioperative VTE Prophylaxis Gregory J. Misky, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine University Of Colorado Denver You recommend the following 72 y.o. man admitted for an elective R hip repair. Patient
Perioperative VTE Prophylaxis Gregory J. Misky, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine University Of Colorado Denver You recommend the following 72 y.o. man admitted for an elective R hip repair. Patient
Clinical Controversies in Perioperative Medicine
 Update on Perioperative Medicine Clinical Controversies in Perioperative Medicine Hugo Quinny Cheng, MD Division of Hospital Medicine University of California, San Francisco Cardiac Medications & Perioperative
Update on Perioperative Medicine Clinical Controversies in Perioperative Medicine Hugo Quinny Cheng, MD Division of Hospital Medicine University of California, San Francisco Cardiac Medications & Perioperative
1. SCOPE of GUIDELINE:
 Page 1 of 35 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention Guideline: Thromboprophylaxis AUTHORIZATION: VP, Medicine Date Approved: May 17, 2012 Date Revised: Vancouver Coastal Health
Page 1 of 35 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention Guideline: Thromboprophylaxis AUTHORIZATION: VP, Medicine Date Approved: May 17, 2012 Date Revised: Vancouver Coastal Health
