Case Report HYBRID SURGICAL APPROACH USING AMPLATZER OCCLUDER FOR TREATMENT OF VSD IN A CAT. Akiko Uemura and Ryou Tanaka
|
|
|
- Brent Burke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Macedonian Veterinary Review Mac Vet Rev 2017; 40 (2): Available online at Case Report HYBRID SURGICAL APPROACH USING AMPLATZER OCCLUDER FOR TREATMENT OF VSD IN A CAT Akiko Uemura and Ryou Tanaka Department of Veterinary Surgery, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Animal Medical Center, 3-5-8, Saiwaicho, Fuchu-shi, Tokyo, , Japan Received 3 April 2017; Received in revised form 27 May 2017; Accepted 8 June 2017 ABSTRACT Ventricular septal defect (VSD) is among the most common feline congenital heart malformations. Although usually treated by pulmonary artery banding or pharmacotherapy, neither method is curative. Curative procedures have been performed in humans. Treatment of VSD is usually not required in dogs and cats, but is necessary in cases of non-restrictive VSD. Dogs with non-restrictive VSD are treated either using surgical correction under open-heart surgery, or percutaneous insertion of an occluder under interventional radiation. In our experience, neither method alone is appropriate for treating ventricular septal defect in cats with non-restrictive VSDs. We have applied a hybrid surgical method in a 13-month-old, female Maine Coon cat weighing 3.5 kg. A catheter was inserted and an occluder placed directly at the defect through thoracotomy. This method is less invasive than open-heart surgery and requires no special equipment, using direct puncture of the heart to minimize the distance to the defect and improving maneuverability. By combining the advantages of both surgical defect closure and occlusion guided by interventional ultrasound, treatment that could not be performed with either method alone became possible. In this case, the VSD could not be embolized, but some important points were suggested regarding surgical treatment of VSD in cats. One is that a sizing balloon catheter may be the most accurate method to measure VSD in cats. Amplatzer occlusion of a large non-restrictive VSD in a cat is currently not an option, but the described hybrid technique may still be an option for smaller non-restrictive VSDs. However, criteria and adjustments must be considered carefully. Key words: VSD, cat, hybrid technique, defect closure, Amplatzer occluder, sizing balloon INTRODUCTION Ventricular septal defect (VSD) is among the most common feline congenital heart malformations (1, 2). In cats, restrictive VSDs do not require treatment (3), but non-restrictive VSDs receive either palliative surgery or medical treatment to reduce pulmonary hypertension and excessive pulmonary blood flow. VSD closure has not yet been aggressively attempted in cats (4, 5). Surgical closure of the defect is ideal for nonrestrictive VSD in humans and dogs. The procedure Corresponding author: Dr. Ryou Tanaka, PhD address: ryo@vet.ne.jp Present address: Department of Veterinary Surgery, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Animal Medical Center, 3-5-8, Saiwaicho, Fuchu-shi, Tokyo , Japan Phone: ; Fax: Copyright: 2017 Uemura A. This is an open-access article published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. Available Online First: 4 July 2017 Published on: 15 October includes open-heart surgery using cardiopulmonary bypass (6, 7) and percutaneous interventional radiology (IVR) (8, 9, 10, 11). Although open-heart surgeries have been reported in some feline cases (12, 13), extracorporeal circulation poses a significant risk in this species. In cats, small vessel size limits its use to cases of patent ductus arteriosus, through a femoral vein approach (14). The hybrid technique used in the present study involves a combination of surgical defect occlusion and IVR, and is performed via a thoracotomy incision, with the catheter directly inserted into the heart. The procedure is not dependent on peripheral blood vessel size, and is less invasive than open-heart surgery. Moreover, because the sheath directly punctures the right ventricle (RV) (Fig. 1), operability is improved compared to IVR. The hybrid technique combines the advantages of surgical defect occlusion and IVR. In the present study, the hybrid technique was attempted for the first time in a cat with VSD. The goal of the present paper is to report the advantages and disadvantages of this technique in a cat.
2 Uemura A. and Tanaka R. Figure 1. The hybrid technique used in the present study. The sheath directly punctures the RV (*). Operability is markedly improved compared to IVR, because little curve is encountered and the distance from the apex of the RV to the VSD is short CASE REPORT A 13-month-old, 3.5-kg, female Maine Coon cat was referred to our institution for exercise intolerance and respiratory distress (day 1). Abdominal and mouth breathing with tachypnea were evident at presentation. Blood pressure (BP) was 126/82 (98) mmhg (systolic/diastolic (mean)). Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) showed a VSD (diameter, 6.3 mm; defect border to aortic valve, 3.1 mm; defect border to tricuspid valve, 4.1 mm) and leftto-right shunt (flow rate, 4.9 m/s). Pulmonic ejection velocity was 3.3 m/s. Pulmonary blood flow to systemic blood flow ratio (Qp/Qs; calculated as stroke volume (SV) of pulmonary artery/sv of aorta) from pulsed Doppler ultrasonography was Left ventricular dimension in diastole was 34.4 mm and E wave was 1.2 m/s. Based on these findings, the cat was diagnosed with nonrestrictive VSD. Physical closure of the defect was recommended based on VSD size, the calculated flow ratio and the presence of clinical signs. Initial treatment comprised pimobendan at 0.25 mg/kg twice daily and furosemide at 2.0 mg/kg/day to treat the volume overload and congestive left heart failure. Considering the risks of open-heart surgery and IVR in cats, a hybrid defect occlusion technique using an Amplatzer (Amplatzer VSD occlusion device; Shanghai Shape Memory Alloy Co., Ltd. (SHSMA); Shanghai, PRC) occluder was selected. A left fifth intercostal thoracotomy was performed under general inhalation anesthesia maintained with isoflurane ( %, Isoflurane for Animals; Intervet K.K., Tokyo, Japan) (day 5). Transesophageal echocardiography imaging (TEE) identified a 7.6-mm VSD, with an interventricular septum (IVS) of 6.9 mm around the apex, and 4.1 mm around the membranous septum. A purse string suture was placed on the vertex cordis part of the RV, transfixing an 18-G indwelling needle at the center of the purse string suture. A inch guide wire was inserted via the indwelling needle. After removing the indwelling-needle, an 11-Fr sheath was inserted and guided by guidewire for the sheath to the RV. Under TEE monitoring, the Amplatzer VSD occlusion device (12-mm disc on LV side, 12-mm disc on RV side, 8-mm waist, 6-mm height; SHSMA) was inserted via an 11-Fr sheath through the RV. A guidewire was not necessary for the Amplatzer, because the distance from sheath to defect was very short. Distance from the edge of the LV-side disk to the aortic valve was about 2 mm. The defect was almost completely occluded, without any apparent aortic outflow tract stenosis or adverse movements of the aortic valve (Fig. 2). However, the defect was too large to achieve firm fixation, and the device was easily displaced upon moving the delivery wire. The device was therefore retrieved before detachment to avoid dislodgement. The cat recovered uneventfully and was discharged 9 days after surgery (day 14). TTE showed that left-to-right shunt flow rate was decreased (3.0 m/s) and the E wave was increased (1.3 m/s) (day 59). RV pressure was increased and heart congestion was worsened even under pharmacotherapy (pimobendan at 0.25 mg/kg twice daily, benazepril at 0.4 mg/kg once daily, and furosemide at 2.0 mg/kg/day). Based on these clinical data, we considered that the condition of the cat was continuing to deteriorate. Hybrid defect occlusion was performed with a median sternotomy approach instead of intercostal thoracotomy (day 59), because the RV was so dilated that the position of the heart seemed to be affected during the previous surgery. Under general anesthesia, a 6-Fr sheath was 184
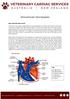
3 Hybrid surgical approach using amplatzer occluder for cat VSD treatment Figure 2. On day 5, the Amplatzer (circle) (12-mm disc on the left ventricle (LV) side just under the aortic valve, 12-mm disc on the RV side; waist, 8 mm; height, 6 mm) was inserted from the RV. The defect was almost completely occluded without aortic blood flow blockage, and hemodynamic exacerbation was not observed during insertion, despite protrusion of the device a few millimeters into the LV outflow tract. LA, left atrium; RV, right ventricle; AO, aorta placed in the RV, and using a inch guide wire, a 7-Fr sizing balloon catheter (SBC) was inserted to measure the defect size (maximum diameter, 11 mm). An ACDO (Amplatz Canine Duct Occluder; 14-mm disc on LV side, 16-mm disc on RV side, 9-mm waist, 6-mm height; Infiniti Medical LLC, California, CA, USA) was inserted from the RV, and the distal disc was deployed in the LV while the proximal disc was deployed in the RV (Fig. 3). The distance from the edge of the LV side disk to the aortic valve was about 1 mm. Although the defect was occluded and firm fixation was achieved, exacerbation of the hemodynamics was observed after device implantation. Interference with aortic flow along with decreased LV outflow tract blood flow velocity, low peripheral oxygen saturation (<70%), bradycardia, and hypotension were observed 1-2 min after device placement. Based on these observations, the cat was deemed unsuitable for defect closure. Pulmonary artery banding was conducted instead of device placement. The cat recovered uneventfully and was discharged on day 63. Her clinical signs were limited to overall improvement, decreased tachypnea, and Qp/Qs decreased to 2.28 from TTE on day 248. However, volume overload and congestive left heart failure haven t clearly recovered. Figure 3. On day 59, the ACDO (circle) (14-mm disc on the LV side just under the aortic valve, 16-mm disc on the RV side; waist, 9 mm; height, 6 mm) was inserted from the RV. Although the defect was occluded and firm fixation was achieved, exacerbation of hemodynamics was observed after device implantation. LV, left ventricle; LA, left atrium; RV, right ventricle; AO, aorta 185
4 Uemura A. and Tanaka R. DISCUSSION The attempted hybrid method offered two advantages. First, the approach is simplified by puncturing the RV with a sheath and inserting the catheter through the defect under TEE guidance. TEE allows simultaneous monitoring of the RV, LV, defect, and aorta, enabling clear visualization of the occlusion device for easy evaluation of device position. Although the devices used were either unstable or interfered with LV outflow, these issues were easily detected on TEE. Second, advantages over open-heart surgery were observed. Even though the hybrid method was repeated within a short period of time, this cat showed no postoperative complications such as cardiac arrest, bleeding tendency, arrhythmia, or reductions in renal or liver function. The hybrid method is considered less invasive and postoperative management is less demanding compared to openheart surgery. The hybrid method offers advantages over IVR as well (15). Although the cat weighed only 3.5 kg, an 11-Fr catheter could be inserted into the RV. With the hybrid method, a comparatively larger device was available, regardless of peripheral blood vessel size. The disadvantages of this method include difficult evaluation of defect size and availability of appropriate occlusion devices. A significant difference in defect size was observed between TTE, TEE, and SBC - the SBC being the most reliable method in this case. Two potential reasons for this significant difference may be considered. First, the defect involved the membranous part of the interventricular septum, which is highly elastic. Second, the defect was oval in shape, not circular. TTE and TEE can only measure one dimension. However, the SBC can measure the greatest extent of the VSD, and so may offer the best method to measure the VSD defect in cats, especially for the membranous part of the defect. Another disadvantage was that this particular method using a human or canine Amplatzer device is inappropriate for cats with very large defects. Large devices may interfere with cardiac function, such as aortic blood flow in this case. The height of the device was 6 mm, and the IVS was 4.1 mm around the membranous defect. The device thus protruded about 1 mm into the LV outflow tract, which may obstruct flow in the small feline heart. Indications depending on defect location require further investigation, since no criteria have yet been established in feline VSD suitable for device embolisation. In humans, criteria have been devised not only for suitability depending on the anatomical classification of the VSD (i.e., involving membranous or muscular parts), but also stating that a distance of at least 3 mm from the defect border to the aortic valve is necessary (16), while a distance of <4 mm to the tricuspid valve leads to complications such as postoperative arrhythmia (17). Our case met the above criteria, but LV outflow was still obstructed. Stricter criteria are thus necessary for feline VSD. In addition to the above criteria, distance from the defect border to the device edge may need to be greater and device height may need to be smaller. In the first surgery, distance from the edge of the LV side disk to the aortic valve was about 2 mm, and no hemodynamic deterioration was evident. In the second surgery, the distance was 1 mm, and hemodynamic deterioration occurred. At least 2 mm from the edge of the LV side disk to the aortic valve may thus be needed for treating VSDs in cat. In order to avoid interference with blood flow and cardiac movement, development of flatter devices with a low profile would be desirable. CONCLUSION Amplatzer occlusion of a large non-restrictive VSD in a cat using the herein described hybrid technique is currently not an option, because the available devices designed for humans or dogs are too large for cats. Amplatzer occlusion via the hybrid technique may still be an option for smaller non-restrictive VSDs that meet strict criteria. The present study showed that large devices could be inserted through the puncture hole in the RV in a cat without major complications. However, careful consideration of strict, detailed criteria and adaptive methods is necessary. CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT The authors declared that they have no potential conflict of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article. REFERENCES 1. Tidholm, A., Ljungvall, I., Michal, J., Haggstrom, J., Hoglund, K. (2015). Congenital heart defects in cats: A retrospective study of 162 cats ( ). J Vet Cardiol. 17, Suppl 1. S PMid:
5 Hybrid surgical approach using amplatzer occluder for cat VSD treatment 2. Cote Kam, E., Meurs, K.M., Sleeper, M.M. (2011). Feline cardiology. (pp ). Wiley-Blackwell Bomassi, E., Misbach, C., Tissier, R., Gouni, V., Trehiou-Sechi, E., et al. (2015). Signalment, clinical features, echocardiographic findings, and outcome of dogs and cats with ventricular septal defects: 109 cases ( ). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 247 (2): PMid: Eyster, G.E., Whipple, R.D., Anderson, L.K., Evans, A.T., O Handley, P. (1977). Pulmonary artery banding for ventricular septal defect in dogs and cats. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 170 (4): PMid: Sheridan, J.P., Mann, P.G., Stock, J.E. (1971). Pulmonary artery banding in the cat: a case report. J Small Anim Pract. 12 (1): PMid: Warden, H.E., Cohen, M., Read, R.C., Lillehei, C.W. (1954). Controlled cross circulation for open intracardiac surgery: physiologic studies and results of creation and closure of ventricular septal defects. J Thorac Surg. 28(3): ; PMid: Breznock, E.M., Hilwig, R.W., Vasko, J.S., Hamlin, R.L. (1970). Surgical correction of an interventricular septal defect in the dog. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 157 (10): PMid: Fujii, Y., Fukuda, T., Machida, N., Yamane, T., Wakao, Y. (2004). Transcatheter closure of congenital ventricular septal defects in 3 dogs with a detachable coil. J Vet Intern Med. 18(6): PMid: Shimizu, M., Tanaka, T., Hirao, H., Kobayashi, M., Shimamura, S., et al. (2005). Percutaneous transcatheter coil embolization of a ventricular septal defect in a dog. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 226 (1): 52-63, Margiocco, M.L., Bulmer, B.J., Sisson, D.D. (2008). Percutaneous occlusion of a muscular ventricular septal defect with an Amplatzer muscular VSD occluder Amplatzer J Vet Cardiol 10(1): PMid: Lock, J.E., Block, P.C., McKay, R.G., Baim, D.S., Keane, J.F. (1988). Transcatheter closure of ventricular septal defects. Circulation 78 (2): PMid: Uechi, M., Hirada, K., Mizukoshi, T., Mizuno, T., Mizuno, M., et al. (2011). Surgical closure of an atrial septal defect using cardiopulmonary bypass in a cat. Vet Surg. 40 (4): PMid: Borenstein. N, Gouni, V., Behr, L., Trehiou-Sechi, E., Petit, A., et al. (2015). Surgical treatment of cor triatriatum sinister in a cat under cardiopulmonary bypass. Vet Surg. 44 (8): PMid: Schneider, M., Hildebrandt, N. (2003). Transvenous embolization of the patent ductus arteriosus with detachable coils in 2 cats. J Vet Intern Med. 17 (3): PMid: Saunders, A.B., Carlson, J.A., Nelson, D.A., Gordon, S.G., Miller, M.W. (2013). Hybrid technique for ventricular septal defect closure in a dog using an Amplatzer (R) Duct Occluder II. J Vet Cardiol. 15 (3): PMid: Koneti, N.R., Sreeram, N., Penumatsa, R.R., Arramraj, S.K., Karunakar, V., et al. (2012). Transcatheter retrograde closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defects in children with the Amplatzer duct occluder II device. J Am Coll Cardiol. 60 (23): PMid: Zhou, D., Pan, W., Guan, L., Ge, J. (2012). Transcatheter closure of perimembranous and intracristal ventricular septal defects with the SHSMA occluder. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 79 (4): PMid: Please cite this article as: Uemura A., Tanaka R. Hybrid surgical approach using amplatzer occluder for treatment of VSD in a cat. Mac Vet Rev 2017; 40 (2):
Hybrid Muscular VSD Closure in Small Weight Children
 Hybrid Muscular VSD Closure in Small Weight Children Shakeel A Qureshi, on behalf of: John P. Cheatham, MD George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Director Cardiac Catheterization &
Hybrid Muscular VSD Closure in Small Weight Children Shakeel A Qureshi, on behalf of: John P. Cheatham, MD George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Director Cardiac Catheterization &
Type Size AP/PS RP/RS Qp/Qs. Ia Resistive <0.3 < Ib Resistive <0.3 < IIa Resistive <0.5 >2
 Transcatheter closure of VSD using Duct Occluder device Nguyen Lan Hieu, MD, PhD Hanoi Medical University Vietnam Heart Institute Anatomy of VSD 1. Perimembranous VSD: Aneurysm septal membranous(tv or
Transcatheter closure of VSD using Duct Occluder device Nguyen Lan Hieu, MD, PhD Hanoi Medical University Vietnam Heart Institute Anatomy of VSD 1. Perimembranous VSD: Aneurysm septal membranous(tv or
Jian Fang 1, Shaobo Xie 2, Lunchao Ma 2, Chao Yang 2. Original Article
 Original Article Anatomic and surgical factors affecting the switch from minimally invasive transthoracic occlusion to open surgery during ventricular septal defect repair Jian Fang 1, Shaobo Xie 2, Lunchao
Original Article Anatomic and surgical factors affecting the switch from minimally invasive transthoracic occlusion to open surgery during ventricular septal defect repair Jian Fang 1, Shaobo Xie 2, Lunchao
Percutaneous VSD closure
 Percutaneous VSD closure Gianfranco Butera San Donato Milanese - Italy Patients selection Pts having hemodynamically significant VSD Left ventricular enlargement (left ventricular overload),defined as
Percutaneous VSD closure Gianfranco Butera San Donato Milanese - Italy Patients selection Pts having hemodynamically significant VSD Left ventricular enlargement (left ventricular overload),defined as
Septal Defects. How does the heart work?
 Septal Defects How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right side
Septal Defects How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right side
For Personal Use. Copyright HMP 2013
 Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(2):E42-E44 Percutaneous Closure of Iatrogenic Ventricular Septal Defect Following Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement Using Two Different Approaches Takashi Matsumoto,
Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(2):E42-E44 Percutaneous Closure of Iatrogenic Ventricular Septal Defect Following Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement Using Two Different Approaches Takashi Matsumoto,
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
 Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
1. Definition/Overview
 VCAwestlaspecialty.com VCA West Los Angeles recently performed closure of a patent ductus arteriosus via percutaneous transarterial embolization with an Amplatz canine ductal occluder on a female, four-month-old
VCAwestlaspecialty.com VCA West Los Angeles recently performed closure of a patent ductus arteriosus via percutaneous transarterial embolization with an Amplatz canine ductal occluder on a female, four-month-old
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Patient guide: pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system. Catheter occlusion of. Patent Ductus Arteriosus. with the
 Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Transcatheter closure of the patent ductus arteriosus using the new Amplatzer duct occluder: Initial clinical applications in children
 Transcatheter closure of the patent ductus arteriosus using the new Amplatzer duct occluder: Initial clinical applications in children Basil Thanopoulos, MD, PhD, a Nikolaos Eleftherakis, MD, a Konstantinos
Transcatheter closure of the patent ductus arteriosus using the new Amplatzer duct occluder: Initial clinical applications in children Basil Thanopoulos, MD, PhD, a Nikolaos Eleftherakis, MD, a Konstantinos
Case submission for CSI Asia-Pacific Case 2
 Case submission for CSI Asia-Pacific 2018- Case 2 Title Page Case category: Coarctation and ducts, valves Title: Simultaneous balloon aortic valvuloplasty with transcatheter closure of large hypertensive
Case submission for CSI Asia-Pacific 2018- Case 2 Title Page Case category: Coarctation and ducts, valves Title: Simultaneous balloon aortic valvuloplasty with transcatheter closure of large hypertensive
Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia
 Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
 Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Daphne T. Hsu, MD dh17@columbia.edu Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition from fetal to mature
Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD
 Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD John P. Cheatham, MD, MSCAI George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Co-Director, The Heart Center, Nationwide Children s Hospital Professor, Pediatrics
Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD John P. Cheatham, MD, MSCAI George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Co-Director, The Heart Center, Nationwide Children s Hospital Professor, Pediatrics
IMAGES. in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY. Abstract
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2008 Apr-Jun; 10(2): 11 17. PMCID: PMC3232589 Transcatheter closure of symptomatic aortopulmonary window in an infant F Pillekamp, 1 T Hannes, 1
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2008 Apr-Jun; 10(2): 11 17. PMCID: PMC3232589 Transcatheter closure of symptomatic aortopulmonary window in an infant F Pillekamp, 1 T Hannes, 1
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital
 Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
Percutaneous atrial septal defect closure with the Occlutech Figulla Flex ASD Occluder.
 Percutaneous atrial septal defect closure with the Occlutech Figulla Flex ASD Occluder. First case with a novel delivery system. Werner Budts, Md, PhD, FESC Congenital and Structural Cardiology University
Percutaneous atrial septal defect closure with the Occlutech Figulla Flex ASD Occluder. First case with a novel delivery system. Werner Budts, Md, PhD, FESC Congenital and Structural Cardiology University
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease
 5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
IMAGES. in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2005 Jan-Mar; 7(1): 12 17. PMCID: PMC3232568 Stent implantation for coarctation facilitated by the anterograde trans-septal approach N Sreeram and
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2005 Jan-Mar; 7(1): 12 17. PMCID: PMC3232568 Stent implantation for coarctation facilitated by the anterograde trans-septal approach N Sreeram and
Transcatheter closure of interatrial
 372 Br HeartJf 1994;72:372-377 PRACTICE REVIEWED Department of Paediatric Cardiology, Royal Brompton Hospital, London A N Redington M L Rigby Correspondence to: Dr A N Redington, Department of Paediatric
372 Br HeartJf 1994;72:372-377 PRACTICE REVIEWED Department of Paediatric Cardiology, Royal Brompton Hospital, London A N Redington M L Rigby Correspondence to: Dr A N Redington, Department of Paediatric
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION -LEFT HEART CATHETERIZATION. Original Date: October 2015 Page 1 of 5
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION -LEFT HEART CATHETERIZATION CPT Codes: 93451, 93452, 93453, 93454, 93455, 93456, 93457, 93458, 93459, 93460, 93461 LCD ID Number:
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION -LEFT HEART CATHETERIZATION CPT Codes: 93451, 93452, 93453, 93454, 93455, 93456, 93457, 93458, 93459, 93460, 93461 LCD ID Number:
Case Report Hemostasis of Left Atrial Appendage Bleed With Lariat Device
 273 Case Report Hemostasis of Left Atrial Appendage Bleed With Lariat Device Amena Hussain MD, Muhamed Saric MD, Scott Bernstein MD, Douglas Holmes MD, Larry Chinitz MD NYU Langone Medical Center, United
273 Case Report Hemostasis of Left Atrial Appendage Bleed With Lariat Device Amena Hussain MD, Muhamed Saric MD, Scott Bernstein MD, Douglas Holmes MD, Larry Chinitz MD NYU Langone Medical Center, United
Perimembranous VSD: When Do We Ask For A Surgical Closure? LI Xin. Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Queen Mary Hospital Hong Kong
 Perimembranous VSD: When Do We Ask For A Surgical Closure? LI Xin Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Queen Mary Hospital Hong Kong Classification (by Kirklin) I. Subarterial (10%) Outlet, conal, supracristal,
Perimembranous VSD: When Do We Ask For A Surgical Closure? LI Xin Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery Queen Mary Hospital Hong Kong Classification (by Kirklin) I. Subarterial (10%) Outlet, conal, supracristal,
Notes by Sandra Dankwa 2009 HF- Heart Failure DS- Down Syndrome IE- Infective Endocarditis ET- Exercise Tolerance. Small VSD Symptoms -asymptomatic
 Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey
 Endovascular Treatment of Acute Descending Thoracic Aortic Dissections Nimesh D. Desai, MD, PhD, and Joseph E. Bavaria, MD Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey type III or Stanford
Endovascular Treatment of Acute Descending Thoracic Aortic Dissections Nimesh D. Desai, MD, PhD, and Joseph E. Bavaria, MD Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey type III or Stanford
CONGENITAL HEART DEFECTS IN ADULTS
 CONGENITAL HEART DEFECTS IN ADULTS THE ROLE OF CATHETER INTERVENTIONS Mario Carminati CONGENITAL HEART DEFECTS IN ADULTS CHD in natural history CHD with post-surgical sequelae PULMONARY VALVE STENOSIS
CONGENITAL HEART DEFECTS IN ADULTS THE ROLE OF CATHETER INTERVENTIONS Mario Carminati CONGENITAL HEART DEFECTS IN ADULTS CHD in natural history CHD with post-surgical sequelae PULMONARY VALVE STENOSIS
Foetal Cardiology: How to predict perinatal problems. Prof. I.Witters Prof.M.Gewillig UZ Leuven
 Foetal Cardiology: How to predict perinatal problems Prof. I.Witters Prof.M.Gewillig UZ Leuven Cardiopathies Incidence : 8-12 / 1000 births ( 1% ) Most frequent - Ventricle Septum Defect 20% - Atrium Septum
Foetal Cardiology: How to predict perinatal problems Prof. I.Witters Prof.M.Gewillig UZ Leuven Cardiopathies Incidence : 8-12 / 1000 births ( 1% ) Most frequent - Ventricle Septum Defect 20% - Atrium Septum
Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale using the internal jugular venous approach
 New methods in diagnosis and therapy Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale using the internal jugular venous approach Przemysław Węglarz 1,2, Ewa Konarska-Kuszewska 2, Tadeusz Zębik 2, Piotr Kuszewski
New methods in diagnosis and therapy Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale using the internal jugular venous approach Przemysław Węglarz 1,2, Ewa Konarska-Kuszewska 2, Tadeusz Zębik 2, Piotr Kuszewski
Percutaneous occluder device closure through femoral vein guidance by transthoracic echocardiography in adult atrial septal defect patients
 Original Article Percutaneous occluder device closure through femoral vein guidance by transthoracic echocardiography in adult atrial septal defect patients Yixin Jia, Xu Meng, Yan Li, Chunlei Xu, Wen
Original Article Percutaneous occluder device closure through femoral vein guidance by transthoracic echocardiography in adult atrial septal defect patients Yixin Jia, Xu Meng, Yan Li, Chunlei Xu, Wen
Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure
 Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure L. LUANN MINICH, M.D., and A. REBECCA SNIDER, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, C.S. Mott Children
Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure L. LUANN MINICH, M.D., and A. REBECCA SNIDER, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, C.S. Mott Children
Index. interventional.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablation, of mitral leaflets, 80 Accucinch Annuloplasty system, for mitral regurgitation, 79, 94 95 Accutrak delivery system, for CoreValve
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablation, of mitral leaflets, 80 Accucinch Annuloplasty system, for mitral regurgitation, 79, 94 95 Accutrak delivery system, for CoreValve
Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia
 Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 33, No. 5, by the American College of Cardiology ISSN /99/$20.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 33, No. 5, 1999 1999 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(99)00011-X Transcatheter
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 33, No. 5, 1999 1999 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(99)00011-X Transcatheter
Imaging Evaluation of the Ventricular Septum
 Imaging Evaluation of the Ventricular Septum Craig E Fleishman, MD FACC FASE The Heart Center at Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando SCAI Fall Fellows Course 2013 Las Vegas Disclosure Information
Imaging Evaluation of the Ventricular Septum Craig E Fleishman, MD FACC FASE The Heart Center at Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando SCAI Fall Fellows Course 2013 Las Vegas Disclosure Information
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Perimembranous ventricular septal defects (pmvsds) are
 Transcatheter Closure of Congenital Perimembranous Ventricular Septal Defect in Children Using Symmetric Occluders: An 8-Year Multiinstitutional Experience Lei Wang, MD, PhD,* Sancheng Cao, MD, Jun Li,
Transcatheter Closure of Congenital Perimembranous Ventricular Septal Defect in Children Using Symmetric Occluders: An 8-Year Multiinstitutional Experience Lei Wang, MD, PhD,* Sancheng Cao, MD, Jun Li,
INTEGRATING ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY WITH CATHETER INTERVENTIONS FOR CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE. Krishna Kumar SevenHills Hospital, Mumbai, India
 INTEGRATING ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY WITH CATHETER INTERVENTIONS FOR CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Krishna Kumar SevenHills Hospital, Mumbai, India Why talk about it? What is the big deal? Are we not stating the obvious?
INTEGRATING ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY WITH CATHETER INTERVENTIONS FOR CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Krishna Kumar SevenHills Hospital, Mumbai, India Why talk about it? What is the big deal? Are we not stating the obvious?
Uptofate Study Summary
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Uptofate Study Summary Acyanotic Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent foramen ovale Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coartation Pulmonary stenosis Cyanotic Tetralogy
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Uptofate Study Summary Acyanotic Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent foramen ovale Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coartation Pulmonary stenosis Cyanotic Tetralogy
TGA atrial vs arterial switch what do we need to look for and how to react
 TGA atrial vs arterial switch what do we need to look for and how to react Folkert Meijboom, MD, PhD, FES Dept ardiology University Medical entre Utrecht The Netherlands TGA + atrial switch: Follow-up
TGA atrial vs arterial switch what do we need to look for and how to react Folkert Meijboom, MD, PhD, FES Dept ardiology University Medical entre Utrecht The Netherlands TGA + atrial switch: Follow-up
Congenital heart disease. By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics
 Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
ATRIAL SEPTAL CLOSURE AND LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE OCCLUSION: INDICATIONS AND GUIDANCE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGY
 ATRIAL SEPTAL CLOSURE AND LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE OCCLUSION: INDICATIONS AND GUIDANCE Aristides G. Panlilio, MD, FPCP, FPCC,FPSE, FASE Philippine Heart Center Chinese General Hospital and Medical Center
ATRIAL SEPTAL CLOSURE AND LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE OCCLUSION: INDICATIONS AND GUIDANCE Aristides G. Panlilio, MD, FPCP, FPCC,FPSE, FASE Philippine Heart Center Chinese General Hospital and Medical Center
Cardiolog procedure availabl a Davie Veterinar Specialist
 Cardiolog Procedure An overview of the procedures and techniques available to our Cardiology patients. Cardiolog procedure availabl a Davie Veterinar Specialist - Patent Ductus Arteriosus Occlusion - Pulmonic
Cardiolog Procedure An overview of the procedures and techniques available to our Cardiology patients. Cardiolog procedure availabl a Davie Veterinar Specialist - Patent Ductus Arteriosus Occlusion - Pulmonic
Transcatheter closure of right coronary artery fistula to the right ventricle
 Case Report Transcatheter closure of right coronary artery fistula to the right ventricle Abstract Coronary artery fistula (CAF) is an uncommon anomaly usually congenital but can be acquired. Although,
Case Report Transcatheter closure of right coronary artery fistula to the right ventricle Abstract Coronary artery fistula (CAF) is an uncommon anomaly usually congenital but can be acquired. Although,
Transcatheter Atrial Septal Defect Closure with Right Aortic Arch Is it really difficult? M Tokue, H Hara, K Sugi, M Nakamura
 5th Asia Pacific Congenital & Structural Heart Intervention Symposium 2014 10 12 October 2014, Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre Organizer: Hong Kong Society of Congenital & Structural Heart Disease
5th Asia Pacific Congenital & Structural Heart Intervention Symposium 2014 10 12 October 2014, Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre Organizer: Hong Kong Society of Congenital & Structural Heart Disease
For Personal Use. Copyright HMP 2013
 12-00415 Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(4):E69-E71 A Concert in the Heart. Bilateral Melody Valve Implantation in the Branch Pulmonary Arteries Nicola Maschietto, MD, PhD and Ornella Milanesi,
12-00415 Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(4):E69-E71 A Concert in the Heart. Bilateral Melody Valve Implantation in the Branch Pulmonary Arteries Nicola Maschietto, MD, PhD and Ornella Milanesi,
Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease
 Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease Michael Vogel Kinderherz-Praxis München CHD missed in childhood Subsequent lesions after repaired CHD Follow-up of cyanotic heart disease CHD missed in
Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease Michael Vogel Kinderherz-Praxis München CHD missed in childhood Subsequent lesions after repaired CHD Follow-up of cyanotic heart disease CHD missed in
IMAGES. in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2006 Jul-Sep; 8(3): 1 6. PMCID: PMC3232564 A large, single pulmonary arteriovenous fistula presenting hours after birth AH McBrien, 1 AJ Sands,
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2006 Jul-Sep; 8(3): 1 6. PMCID: PMC3232564 A large, single pulmonary arteriovenous fistula presenting hours after birth AH McBrien, 1 AJ Sands,
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT
 ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
Atrial Septal Defect Closure. Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs
 Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs ADVANCED ANGIOPLASTY Incorporating The Left Main 5 Plus Course Conflicts of Interest The following companies have supported educational courses held
Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs ADVANCED ANGIOPLASTY Incorporating The Left Main 5 Plus Course Conflicts of Interest The following companies have supported educational courses held
A case report: Percutaneous transcatheter treatment of Lutembacher syndrome
 A case report: Percutaneous transcatheter treatment of Lutembacher syndrome Dr. Sainath Hegde* Dr. Tukaram Aute** *Registrar, Dept of Cardiology, M.G.M Hospital, Aurangabad. **Asst. Prof, Dept of Cardiology,
A case report: Percutaneous transcatheter treatment of Lutembacher syndrome Dr. Sainath Hegde* Dr. Tukaram Aute** *Registrar, Dept of Cardiology, M.G.M Hospital, Aurangabad. **Asst. Prof, Dept of Cardiology,
Percutaneous Device Closure of Congenital VSDs Current techniques and results for treating ventricular septal defects.
 Percutaneous Device Closure of Congenital VSDs Current techniques and results for treating ventricular septal defects. BY KARIM A. DIAB, MD; QI-LING CAO, MD; AND ZIYAD M. HIJAZI, MD, MPH During the past
Percutaneous Device Closure of Congenital VSDs Current techniques and results for treating ventricular septal defects. BY KARIM A. DIAB, MD; QI-LING CAO, MD; AND ZIYAD M. HIJAZI, MD, MPH During the past
Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do?
 Leading Article Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do? Duminda Samarasinghe 1 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2010; 39: 39-43 (Key words: Congenital heart disease) Congenital heart disease
Leading Article Congenital heart disease: When to act and what to do? Duminda Samarasinghe 1 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2010; 39: 39-43 (Key words: Congenital heart disease) Congenital heart disease
Ozge Korkmaz, 1 Osman Beton, 2 Sabahattin Goksel, 1 HakkJ Kaya, 2 and Ocal Berkan Introduction. 2. Case Report
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 7941051, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7941051 Case Report Thoracic Stent Graft Implantation for Aortic Coarctation with Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 7941051, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7941051 Case Report Thoracic Stent Graft Implantation for Aortic Coarctation with Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016
 1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Transthoracic closure of atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect without cardiopulmonary bypass
 Transthoracic closure of atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect without cardiopulmonary bypass L. Wan, B.-T. Yu, Q.-C. Wu, L. Zeng, Q. Wang, J. Tang, Q.-R. Xu, H. Xu, W.-J. Wang, Y.-P. Cao
Transthoracic closure of atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect without cardiopulmonary bypass L. Wan, B.-T. Yu, Q.-C. Wu, L. Zeng, Q. Wang, J. Tang, Q.-R. Xu, H. Xu, W.-J. Wang, Y.-P. Cao
A challenging case of successful ASD closure without echocardiographic guidance in an 86-year old with severe kyphoscoliosis and platypnoeaorthodeoxia
 A challenging case of successful ASD closure without echocardiographic guidance in an 86-year old with severe kyphoscoliosis and platypnoeaorthodeoxia syndrome. Dr Anvesha Singh, Dr James Ogle, Dr Derek
A challenging case of successful ASD closure without echocardiographic guidance in an 86-year old with severe kyphoscoliosis and platypnoeaorthodeoxia syndrome. Dr Anvesha Singh, Dr James Ogle, Dr Derek
Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology. Emma Walker 7 th May 2016
 Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology Emma Walker 7 th May 2016 Cardiovascular Examination! General:! Make it fun!! Change how you act depending on their age! Introduction! Introduce yourself & check
Paediatrics Revision Session Cardiology Emma Walker 7 th May 2016 Cardiovascular Examination! General:! Make it fun!! Change how you act depending on their age! Introduction! Introduce yourself & check
Cardiac Intervention in Fetus. Gyeong-hee Yoo, M.D. Department of Pediatrics Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital
 10 1111 Cardiac Intervention in Fetus Gyeong-hee Yoo, M.D. Department of Pediatrics Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital Fetal echocardiography Serial f/u intrauterine course of disease Cardiac anomaly
10 1111 Cardiac Intervention in Fetus Gyeong-hee Yoo, M.D. Department of Pediatrics Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital Fetal echocardiography Serial f/u intrauterine course of disease Cardiac anomaly
Therapeutic Cardiac Catheterizations for Children with Congenital Heart Disease
 Therapeutic Cardiac Catheterizations for Children with Congenital Heart Disease Introduction A therapeutic cardiac catheterization is a procedure performed to treat your child s heart defect. A doctor
Therapeutic Cardiac Catheterizations for Children with Congenital Heart Disease Introduction A therapeutic cardiac catheterization is a procedure performed to treat your child s heart defect. A doctor
Repair or Replacement
 Surgical intervention post MitraClip Device: Repair or Replacement Saudi Heart Association, February 21-24 Rüdiger Lange, MD, PhD Nicolo Piazza, MD, FRCPC, FESC German Heart Center, Munich, Germany Division
Surgical intervention post MitraClip Device: Repair or Replacement Saudi Heart Association, February 21-24 Rüdiger Lange, MD, PhD Nicolo Piazza, MD, FRCPC, FESC German Heart Center, Munich, Germany Division
Pulmonic Stenosis. How does the heart work?
 Pulmonic Stenosis How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Pulmonic Stenosis How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome: Echocardiographic Assessment
 Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome: Echocardiographic Assessment Craig E Fleishman, MD, FACC, FASE Director, Non-invasive Cardiac Imaging The Hear Center at Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando SCAI
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome: Echocardiographic Assessment Craig E Fleishman, MD, FACC, FASE Director, Non-invasive Cardiac Imaging The Hear Center at Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando SCAI
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List Cardiology
 Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List Cardiology Category CPT Code CPT Code Description 33206 Insertion of new or replacement of permanent pacemaker with transvenous electrode(s); atrial 33207 Insertion
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List Cardiology Category CPT Code CPT Code Description 33206 Insertion of new or replacement of permanent pacemaker with transvenous electrode(s); atrial 33207 Insertion
Technical option of surgical approach for trouble-shooting
 JHRS Corner Device and lead trouble-shooting - standard strategy and technical option - Technical option of surgical approach for trouble-shooting Katsuhiko IMAI Department of Cardiovascular surgery, Hiroshima
JHRS Corner Device and lead trouble-shooting - standard strategy and technical option - Technical option of surgical approach for trouble-shooting Katsuhiko IMAI Department of Cardiovascular surgery, Hiroshima
Cath Lab Essentials: Basic Hemodynamics for the Cath Lab and ICU
 Cath Lab Essentials: Basic Hemodynamics for the Cath Lab and ICU Ailin Barseghian El-Farra, MD, FACC Assistant Professor, Interventional Cardiology University of California, Irvine Department of Cardiology
Cath Lab Essentials: Basic Hemodynamics for the Cath Lab and ICU Ailin Barseghian El-Farra, MD, FACC Assistant Professor, Interventional Cardiology University of California, Irvine Department of Cardiology
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with absent pulmonary valve
 Repair of Tetralogy of Fallot with Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Karl F. Welke, MD, and Ross M. Ungerleider, MD, MBA Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with absent pulmonary valve syndrome (APVS) occurs in 5%
Repair of Tetralogy of Fallot with Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Karl F. Welke, MD, and Ross M. Ungerleider, MD, MBA Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with absent pulmonary valve syndrome (APVS) occurs in 5%
The 1st transvascular patent ductus arteriosus
 J Vet Intern Med 2012;26:85 92 Occlusion Devices and Approaches in Canine Patent Ductus Arteriosus: Comparison of Outcomes M. K. Singh, M. D. Kittleson, P. H. Kass, and L. G. Griffiths Background: A comparison
J Vet Intern Med 2012;26:85 92 Occlusion Devices and Approaches in Canine Patent Ductus Arteriosus: Comparison of Outcomes M. K. Singh, M. D. Kittleson, P. H. Kass, and L. G. Griffiths Background: A comparison
The catheter-based treatment of valvular disease and aortic
 Access Issues in Abdominal/ Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair and Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement René Bombien, MD, PhD, and Ali Khoynezhad, MD, PhD The catheter-based treatment of valvular disease
Access Issues in Abdominal/ Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair and Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement René Bombien, MD, PhD, and Ali Khoynezhad, MD, PhD The catheter-based treatment of valvular disease
Research Presentation June 23, Nimish Muni Resident Internal Medicine
 Research Presentation June 23, 2009 Nimish Muni Resident Internal Medicine Research Question In adult patients with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot, how does Echocardiography compare to MRI in evaluating
Research Presentation June 23, 2009 Nimish Muni Resident Internal Medicine Research Question In adult patients with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot, how does Echocardiography compare to MRI in evaluating
Διαδερμική θεραπεία των παραβαλβιδικών διαφυγών Σ.Ράμμος
 ΔΜΙΝΑΡΙΟ ΔΠΙΣΗΜΟΝΙΚΩΝ ΔΝΩΔΩΝ ΔΛΛΗΝΙΚΟΤ ΚΟΛΛΔΓΙΟΤ ΚΑΡ ΙΟΛΟΓΙΑ 2-4.10.2015 Δπιζηημονική Ένωζη Δπεμβαηικής Καρδιολογίας Βαλβιδοπάθειες, Γιαδερμικές παρεμβάζεις Διαδερμική θεραπεία των παραβαλβιδικών διαφυγών
ΔΜΙΝΑΡΙΟ ΔΠΙΣΗΜΟΝΙΚΩΝ ΔΝΩΔΩΝ ΔΛΛΗΝΙΚΟΤ ΚΟΛΛΔΓΙΟΤ ΚΑΡ ΙΟΛΟΓΙΑ 2-4.10.2015 Δπιζηημονική Ένωζη Δπεμβαηικής Καρδιολογίας Βαλβιδοπάθειες, Γιαδερμικές παρεμβάζεις Διαδερμική θεραπεία των παραβαλβιδικών διαφυγών
SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
 SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Mr. W. Brawn Birmingham Children s Hospital. Aims of surgery The aim of surgery in congenital heart disease is to correct or palliate the heart
SURGICAL TREATMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Mr. W. Brawn Birmingham Children s Hospital. Aims of surgery The aim of surgery in congenital heart disease is to correct or palliate the heart
Index. interventional.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alagille syndrome, pulmonary artery stenosis in, 143 145, 148 149 Amplatz devices for atrial septal defect closure, 42 46 for coronary
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alagille syndrome, pulmonary artery stenosis in, 143 145, 148 149 Amplatz devices for atrial septal defect closure, 42 46 for coronary
The earliest application of intracardiac imaging
 Intracardiac Echocardiography for Structural Heart Defects A review of ICE innovations, devices, and techniques. BY ZAHID AMIN, MD; QI-LING CAO, MD; AND ZIYAD M. HIJAZI, MD The earliest application of
Intracardiac Echocardiography for Structural Heart Defects A review of ICE innovations, devices, and techniques. BY ZAHID AMIN, MD; QI-LING CAO, MD; AND ZIYAD M. HIJAZI, MD The earliest application of
CY2017 Hospital Outpatient: Vascular Procedure APCs and Complexity Adjustments
 CY2017 Hospital Outpatient: Vascular Procedure APCs and Complexity Adjustments Comprehensive Ambulatory Payment Classifications (c-apcs) In CY2015 and in an effort to help pay providers for quality, not
CY2017 Hospital Outpatient: Vascular Procedure APCs and Complexity Adjustments Comprehensive Ambulatory Payment Classifications (c-apcs) In CY2015 and in an effort to help pay providers for quality, not
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Procedure (TAVI)
 Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Perioperative Management of DORV Case
 Perioperative Management of DORV Case James P. Spaeth, MD Department of Anesthesia Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center University of Cincinnati Objectives: 1. Discuss considerations regarding
Perioperative Management of DORV Case James P. Spaeth, MD Department of Anesthesia Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center University of Cincinnati Objectives: 1. Discuss considerations regarding
Index. cardiology.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACHD. See Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD), 503 512 across life span prevalence of, 504 506
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACHD. See Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD), 503 512 across life span prevalence of, 504 506
Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD s
 Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD s Dr Damien Kenny, MB, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Director of the Cardiac Catheterization Hybrid Suite Co-Director of the Rush Adult Congenital Heart Disease
Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD s Dr Damien Kenny, MB, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Director of the Cardiac Catheterization Hybrid Suite Co-Director of the Rush Adult Congenital Heart Disease
Originally Posted: November 15, 2014 BRUIT IN THE GROIN
 Originally Posted: November 15, 2014 BRUIT IN THE GROIN Resident(s): Donald ML Tse, MD Attending(s): KT Tan, MD Program/Dept(s): University Health Network/Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, ON, Canada CHIEF
Originally Posted: November 15, 2014 BRUIT IN THE GROIN Resident(s): Donald ML Tse, MD Attending(s): KT Tan, MD Program/Dept(s): University Health Network/Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, ON, Canada CHIEF
AMPLATZER Septal Occluder
 AMPLATZER Septal Occluder A Patient s Guide to the Non-Surgical Closure of the Atrial Septal Defect Using the AMPLATZER Septal Occluder System leadership through innovation TM AGA Medical Corporation 5050
AMPLATZER Septal Occluder A Patient s Guide to the Non-Surgical Closure of the Atrial Septal Defect Using the AMPLATZER Septal Occluder System leadership through innovation TM AGA Medical Corporation 5050
Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery
 Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery Dr. Amira Esmat, El Tantawy, MD Professor of Pediatrics Consultant Pediatric Cardiac Interventionist Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 23/2/2017
Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery Dr. Amira Esmat, El Tantawy, MD Professor of Pediatrics Consultant Pediatric Cardiac Interventionist Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 23/2/2017
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We. ACHD Patients
 Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
The need for right ventricular outflow tract reconstruction
 Polytetrafluoroethylene Bicuspid Pulmonary Valve Implantation James A. Quintessenza, MD The need for right ventricular outflow tract reconstruction and pulmonary valve replacement is increasing for many
Polytetrafluoroethylene Bicuspid Pulmonary Valve Implantation James A. Quintessenza, MD The need for right ventricular outflow tract reconstruction and pulmonary valve replacement is increasing for many
Bioprosthetic Mitral Valve Dysfunction: Innovation and Evolution of a New Therapeutic Technique
 Bioprosthetic Mitral Valve Dysfunction: Innovation and Evolution of a New Therapeutic Technique Charanjit S. Rihal MD MBA Professor and Chair Division of Cardiovascular Diseases Mayo Clinic DISCLOSURES
Bioprosthetic Mitral Valve Dysfunction: Innovation and Evolution of a New Therapeutic Technique Charanjit S. Rihal MD MBA Professor and Chair Division of Cardiovascular Diseases Mayo Clinic DISCLOSURES
Repair of very severe tricuspid regurgitation following detachment of the tricuspid valve
 OPEN ACCESS Images in cardiology Repair of very severe tricuspid regurgitation following detachment of the tricuspid valve Ahmed Mahgoub 1, Hassan Kamel 2, Walid Simry 1, Hatem Hosny 1, * 1 Aswan Heart
OPEN ACCESS Images in cardiology Repair of very severe tricuspid regurgitation following detachment of the tricuspid valve Ahmed Mahgoub 1, Hassan Kamel 2, Walid Simry 1, Hatem Hosny 1, * 1 Aswan Heart
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE
 By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
Implantation of Cardioverter Defibrillator After Percutaneous Closure of Atrial Septal Defect
 The Ochsner Journal 10:27 31, 2010 f Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Implantation of Cardioverter Defibrillator After Percutaneous Closure of Atrial Septal Defect Anas Bitar, MD, Maria Malaya
The Ochsner Journal 10:27 31, 2010 f Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Implantation of Cardioverter Defibrillator After Percutaneous Closure of Atrial Septal Defect Anas Bitar, MD, Maria Malaya
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
