A new method for CSF shunt patency assessment
|
|
|
- Virgil Bradford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A new method for CSF shunt patency assessment Marek Swoboda, Matias G. Hochman, Jenna S Fritz, Mark E. Mattiucci, Frederick J Fritz NeuroDx Development LLC CSF shunts employed to treat hydrocephalus patients malfunction frequently, usually by obstruction, but the symptoms of shunt failure are non-specific [5]. Diagnosis of shunt malfunction by conventional means is difficult, expensive, and associated with risks to the patient (exposure to radiation from CT Scans, risk of infection from shunt taps and radionuclide testing) [5]. A new diagnostic method to assess shunt patency which combines a non-invasive CSF flow generator and a thermal CSF flow meter has emerged. The presented method estimates the hydraulic resistance of the shunt system in addition to measuring shunt flow. The authors believe that this new technique will increase sensitivity and specificity in the diagnosis of shunt patency compare to existing methods. The method was tested in vitro in 16 popular shunt systems, the results show that it can differentiate between patent, partially obstructed and fully obstructed shunts in 15 out of 16 shunt systems. This work opens a new possibility of shunt patency assessment using a non-invasive, inexpensive and easy to use procedure. keywords: CSF shunt, CSF shunt patency, hydrocephalus, CSF shunt obstruction, Thermal dilution device 1. Background. Approximately 69,000 people are diagnosed with hydrocephalus each year in the United States [1]. The most common treatment for hydrocephalus is diversion of CSF from the brain ventricles to the peritoneal cavity by means of a permanent prosthetic shunt. However, the one-year failure rate of implanted shunts has been estimated to be approximately 40% [2,3], and the mean period to failure is typically only five to ten years [4]. Obstruction, usually from tissue in-growth or clots at the inflow catheter, is overwhelmingly the greatest cause of shunt failure [2, 5-8]. Shunt failure can rapidly progress to life-threatening elevation in intracranial pressure, so revision surgery and replacement of the blocked catheter is indicated. However, symptoms of shunt obstruction (headache, nausea, lethargy) are non-specific, and it has been calculated that three false alarms are seen at the emergency department for every true shunt malfunction [5]. Computed Tomography (CT) remains the standard approach for differentiating an obstructed shunt from a false alarm [5, 9], however this technique produces a static image, resulting in the need for serial imaging to confirm CSF build-up. Repeat radiation exposures of these patients (often children) from repeat CT scans is a recognized and growing concern among neurosurgeons [10]. Radionuclide shunt flow testing and shunt taps are invasive and pose a risk of infection, so they are not used to investigate every headache. New technologies under development are complex (ultrasound tracking of bubbles),
2 lacking in precision (FLIR) or require implantation (implanted thermal flow technologies) and have not reached the clinic. Thermodilution methods were developed [12] to facilitate rapid and non-invasive detection of cerebrospinal fluid flow through subcutaneous shunts where obstruction is suspected. Those methods employ thermal dilution technology - detecting a transcutaneous change in temperature as cooled cerebrospinal fluid flows through the subcutaneous portion of a shunt. An example of such method is shown in Figure 1. A thermal stimulus (ice) is applied to the skin surface. It cools down neighboring tissue. The temperature differential generated within tissue volume changes the amount of heat ΔQ within shunt tubing. With CSF mass flow the ΔQ is transferred downstream where it causes tissue temperature change, this temperature change is registered on the skin surface by an array of thermistors. The presence or absence of CSF flow is interpreted by a change in temperature on the skin surface (Figure 1). 1.1 Clinical utility of Thermal CSF Flow Detection The clinical utility of thermal CSF flow detection is limited by intermittent CSF flow and partial occlusion. The FDA 510(k) application for one thermal CSF flow detector [23] demonstrated that the detection device exhibits 100% accuracy in detecting lack of flow through a subcutaneous shunt in an animal model [11]. However, the clinical utility of the device (or any single-point flow test) in identifying shunt obstruction is based on the assumption that CSF flows constantly through patent (unobstructed) shunts. This premise has been insufficiently supported through prior characterization of CSF flow in asymptomatic patients whether CSF flows constantly or intermittently through normal shunts was not known. A study of 100 asymptomatic and symptomatic pediatric hydrocephalus patients at Boston Children s Hospital [12] found that patients with patent shunts exhibited CSF flow during only 54% of tests. This result is almost identical to that previously reported using radionuclide tracing, in which only 53% of subjects with patent shunts exhibited CSF flow at the time of testing [13]. These results strongly suggest that CSF flows only intermittently (approximately 50% of the time) through patent shunts [14]. Intermittent CSF flow can therefore Figure 1 A generic representation of a thermodilution method for CSF flow detection in shunt tubing implanted under the skin surface. Heat transfer linked to CSF mass flow generates thermal response downstream the thermal stimulus.
3 cause false positive ( obstructed ) test results, and limits the diagnostic specificity of flow detectors such as dilution thermal CSF flow detection device. Perhaps more importantly, this study identified ten symptomatic patients with thermodilution results of Flow but CT scans which indicated enlarged ventricles (evidence of elevated ICP and an obstructed shunt). These patients went on to shunt revision surgery during which it was determined that their shunts were only partially occluded and were flowing. Bench tests described below show that when shunts are over 95% blocked (see table 1.), a build-up of CSF and consequent rise in ICP can cause CSF to flow within a normal range of flow rates even though the ICP is dangerously elevated. Thermodilution or radionuclide methods will detect this flow even though this flow, due to shunt's high hydraulic resistance to outflow, is insufficient to resolve the pathology. Partial occlusion causes false negative test results and limits the diagnostic sensitivity of thermal CSF flow detection. The occurrence of intermittent flow in patent shunts, and low but measurable flow in partially-occluded shunts necessitates more than a method for detecting the presence or absence of CSF flow through a shunt at the time of testing. What is needed is a tool for measuring the resistance to flow through a shunt (i.e. its level of occlusion), in order to differentiate clinically-relevant obstruction from physiological (temporary) CSF stasis. By measuring resistance one can easily assess blockage level and flow capacity of the shunt Flow generator This need led to the development of a hand-held, non-invasive CSF flow generator which interrogates the shunt by delivering specific vibration pulses to the shunt valve dome. This generates controlled, reproducible CSF flow through patent, but not occluded or partially occluded shunts. This temporary increase in flow can then be detected via thermal dilution. The flow generator has been designed as a simple vibrator vibrating at 60Hz for 60 seconds. The acceleration delivered to the dome was approximately from 0.6 to 1 g (5.9 to 9.8 m/s 2 ). The vibrator consists of a plastic foot with a miniature DC motor mounted on it. The DC motor is outfitted with a counterweight. The device s vibration frequency, duration and duty cycle are controlled by an electronic circuit. In some cases, in order to scale the flow rate, vibration with less than 100% duty cycle was used (pulsing rather than continuous vibration). Our experiments show that duty cycle doesn't change the principle features of the system but decreases the flow rate proportionally to the % of the duty cycle. A prototype of the flow generator is shown in figure 2. Figure 2 Flow generator is a simple mechanical vibrator which gently vibrates the shunt valve dome through the scalp tissue. It uses a specific frequency and vibration pattern to maximize pumping efficiency and protect ventricles from excessive suction Problem statement The flow generator can be integrated into the thermodilution diagnostic procedure only if it meets certain functional and clinical requirements. To answer the technical validity
4 and clinical utility question, one has to experimentally evaluate the following hypotheses: Hypothesis 1. The flow generator is capable of generating robust flow in patent (but not occluded) shunts in a broad and representative range of commercially available shunt valves. Hypothesis 2. The combined flow generator plus the thermal CSF flow detection method can reliably differentiate between patent flow and partially occluded flow. Hypothesis 3. Vibrational CSF flow generation is safe it generates limited CSF drainage, it does not generate strong ventricular suction and it does not damage shunt valves nor change the setting of programmable valves. 2. Materials and methods Experimental setup and conditions In our bench top experiment, we used a ventricle simulator, ventricular shunt catheter, shunt valve, distal catheter, Medtronic CSF drainage system and an optical flow meter (drop counter). The system for flow rate studies is shown in figure 3. In the thermal portion of this study, we also used a thermal skin simulator and a thermal CSF flow detector thermal dilution device. We tested responses to flow generation with a drop counter flow meter and subsequently with the thermal CSF flow detector. When experimenting with thermodilution system, the drop counter flow meter and the Medtronic drainage system were replaced by a thermally active mock skin with shunt tubing embedded in it (thermal skin simulator). The thermodilution sensor was placed on the thermally active mock skin over the distal portion of the shunt tubing emulating regular clinical application. This setup simulated thermal behavior of human skin with implanted shunt tubing, and allowed us to replicate the physics of the thermal dilution method of assessing CSF flow. The resistance introduced by the thermal skin simulator was similar to the Medtronic drainage system and negligible in the order of 0.1 [mmhg/ml/h]. Proximal and distal resistances were simulated by needle resistors placed in series with shunt tubing. Needle resistors simulate occlusion of shunt tubing by narrowing the lumen. A short explanation of this approach is offered below. Figure 3 Benchtop setup
5 Note: Illustration of proximal occlusion and hydraulic resistances. Shunt occlusion is a complex process and the authors are not trying to describe it in this paper. For illustrative purposes, we decided to show a specific example of occlusion which can help the reader visualize resistance values used in our experiments. In this example, we utilized a 20cm of 1 mm ID shunt tubing (it can represent a section of the proximal catheters). The original cross-sectional area of the shunt corresponds to 100% patency. Decreased (occluded) cross-sectional areas are described as % of the original area of the lumen. We assume that the shunt gets occluded by deposits on the inner walls of the tubing and that the deposits are uniformly distributed over the inner surface of the tubing, resulting in uniform narrowing of the lumen. Corresponding hydraulic resistances are shown in figure 4 and table 1. The table 1 shows several examples of patency and corresponding hydraulic resistances. The numbers in the table follow the model described above - 20cm of 1mm ID tubing with 7 different levels of occlusion expressed as % of the original 1 mm ID lumen. One can see that when the lumen gets down to 10% of its original cross-sectional area (90% Patency % Resistance [ml/h] Table 1. The % occlusion and corresponding hydraulic occlusions for a uniformly occluded 20 cm 1mm ID shunt catheter. occluded), the hydraulic resistance of the 20 cm 1 mm OD tubing reaches 1.6 [mmhg/ml/h]. Hydraulic resistance rises rapidly as occlusion levels exceed 90%. For lower occlusion levels (e.g. 30% patent or 70% occluded) the resulting hydraulic resistance is negligible. 2.1 Flow generation in patent and occluded shunts To test how flow rate is modulated by proximal resistance, we used the setup shown in Resistance [mmhg/ml/h] vs patency [%] Resistance [mmhg/ml/h] Patency [%] Figure. 4 Shows the relationship between hydraulic resistance of the 20 cm shunt tubing (1 mm ID) and its patency calculated as a percentage of cross-sectional area of the original (patent) lumen of the tubing. We assume, in this model, that the lumen is uniformly occluded, decreasing cross-sectional area of the shunt lumen. This is only for illustrative purposes; the occlusion mechanisms are many and can occur in different places of the proximal catheter.
6 figure 3. The resistances of the proximal catheter were simulated by calibrated needle resistors placed in series with proximal and distal catheters. The distal resistance was kept constant at a low level of approximately 0.1 [mmhg/ml/h]. The ICP was kept at ~ 5cm of H2O and the abdominal pressure at 0. Partial proximal occlusion was simulated by a needle resistor of 4 [mmhg/ml/h], comparable to approximately 95% occlusion Flow rate vs. Distal and Proximal patency To test two dimensional proximal and distal resistance flow dependency, both distal and proximal obstructions were simulated by needle resistors. We decided to choose one common shunt system (Medtronic Strata with Siphon Control) to study its behavior in two dimensional parameter space namely how the CSF flow generated by the flow generator changes for various combinations of proximal and distal resistances. The distal and proximal resistances were varied from 0 to 4 [mmhg/ml/h] on the proximal side and from 0 to 3 [mmhg/ml/h] on the distal side Abdominal pressure - flow relationship In order to answer how the difference between ICP and ABP values influences CSF flow generated by the flow generator, we used the same setup as in but for each combination of proximal and distal resistances, we varied the pressure difference between the proximal and distal ends. The pressures were 10, 5, 0, -5, -10 [cmh 2 O]. This experiment emulated changes to ICP from positive to negative (e.g. changes from supine to sitting position) or buildup of the abdominal pressure Differentiating between patent, partially obstructed and totally obstructed shunts using the thermal CSF flow detection device (proximal patency-the most common case in pediatric hydrocephalus) In this part of the study, we designed a simple test to assess how the method differentiates between patent, partially patent and obstructed shunts, using the same setup as in 2.1. Six shunt valves were tested, the Medtronic Strata and Delta, the Sophysa Polaris, the Integra Ultra VS neonate and Integra DP and the Codman Hakim. The proximal hydraulic resistance was varied between 0.1 (patent), 4 (partial occlusion) and infinity (completely occluded shunt) [mmhg/ml/h]. Resistances were simulated by needle resistors connected in series with catheter tubing. Patent and partially occluded shunts were tested under two different initial conditions flowing (at 3 to 5 ml/h) or non-flowing. ICP was adjusted to achieve these flow rates. Patent shunts were tested at 0 cmh2o (no flow) and approximately 5cmH2O (flowing). Partially occluded shunts were tested at 10 cmh2o (no flow) and approximately 18 cmh2o (to simulate flow with elevated ICP). Totally occluded shunts were tested at 18 cmh2o. The abdominal pressure was set at 0. The flow rate generated by the flow generator was tested with a calibrated optical flow meter (drop counter). The flow meter counts drops inside the Medtronic drainage system via optical means, thus it doesn't introduce any additional resistance Assessing the impact of skin thickness and hair. This experiment replicated the procedure from but instead of testing occluded and partially occluded systems, we focused on patent shunts. Several shunt systems were tested with two levels of skin thickness and hair (4 cases, namely thin, medium and thick skin and medium skin with hair). Synthetic hair was used Safety Assessing pressures inside the dome. In this experiment we used Strata with Siphon Control valves. To test pressure
7 amplitude inside the dome, we inserted a rigid catheter through the flat bottom of the dome and measured pressure using a standard medical pressure transducer EDWARDS PX272. A special care was given to minimize the dead volume in the junction between the valve and the pressure transducer. Frequency of the flow generator was 60 Hz. Pre-stress force applied by the flow generator foot to the valve dome was approximately 1.27 Newtons. The valve dome was covered by artificial skin (SynDaver) 5mm thick to mimic mechanical properties of the human scalp tissue. Assessing pressure at the tip of the ventricular catheter. The same type of transducer was used to measure P T pressure at the end of the ventricular catheter (see figure 3). Pressures generated by manual shunt pumping (1 sec push and quick release) were compared with pressures generated by the flow generator vibrating at 60Hz for 60 seconds. 3. Results Hypothesis 1. The flow generator is capable of generating robust flow in patent (but not occluded) shunts in a broad and representative range of commercially available shunt valves. Figure 5. shows flow rate increase due to vibrational flow generation for three popular valves including one with a siphon control device (MDT Strata). The flow generator does generate a robust, temporary increase in CSF flow rate in patent shunts but only very limited flow in partially occluded shunts and no flow in occluded shunts. Figure 5 Change in flow in three shunt systems treated with Flow generator. Two initial conditions: natural flow and no flow (<1ml/h). Partial occlusion was represented by a needle resistor of 4 [mmhg/ml/h]
8 Flow rate vs Distal and Proximal resistance Highest flow rates were registered at lowest proximal and distal resistance values (see figure 6). low single digits values which can be below the thermal LOD (Limit Of Detection) of the thermal CSF flow detector Abdominal pressure influence Abdominal pressure shows a strong mmhgh/ml 1 mmhgh/ml mmhgh/ml mmhgh/ml 4 3 Figure 6 Flow rate [ml/h] vs Distal and Proximal Resistance [mmhg/ml/h]. Peak flow occurs when both resistances (distal and proximal) are close to zero. The system seems to be more sensitive to proximal resistance in the low resistance region (0-2 mmhg/ml/h). For the patent system, the flow rate is several times higher than for any non-zero combination of proximal and distal resistances. In the region of high resistances of 2-4 mmhg/ml/h, flow generator flow drops to monotonic relationship with flow generator flow (see figure 7). Flow rate drops sharply with increasing abdominal pressure. From the data we gathered, it is evident that typically the flow generator flow rate is stopped if the abdominal pressure exceeds intracranial pressure by more than 5 cmh 2 O.
9 Flow [ml/h] Pressure gradient accross the valve [cmh2o] Fig. 7 Shunt flow with flow generator applied versus pressure gradient across the shunt valve. An example of abdominal pressure influence on flow generator generated flow. In this case both proximal and distal resistances were set to zero Hypothesis 2. The combined flow generator plus the thermal CSF flow detection method can reliably differentiate between patent flow and partially occluded flow. Results are shown in figure 8. Clear differentiation is visible between patent and Figure 8. Thermodilution response to flows in shunts treated with flow generator. Clearly visible differences between patent, partially obstructed and totally obstructed valves. The shunt systems had 5ml/h of natural flow prior to flow generator application.
10 partially occluded shunts. Completely occluded shunts show even lower thermal response to flow generation. Partial proximal obstruction was tested using resistance of 4 mmhg/ml/h. ventricular tip of the catheter reflect the high hydraulic resistance caused by high velocity flow in the catheter. Strong pressure changes inside the dome are damped down to very Figure 9. shows thermal response variability caused by different skin thickness (SynDaver) and hair. Data was collected for 9 types of patent valves. Thermal responses vary by less than 0.18 C with all temperature drops above 0.5 C Safety. Fig.9 skin thickness and hair influence. Skin thickness simulated by Syndaver skin Hypothesis 3. Vibrational flow generation is safe it generates limited CSF drainage, does not generate strong ventricular and does not damage valves nor change the setting of programmable valves. Pressure generated by the flow generator inside the dome and at the ventricular tip are shown in figure 10. Pressures recorded during flow generation inside the dome and at the modest levels at the ventricular tip by the hydraulic resistance of the ventricular catheter. In the example in Figure 10, the dome peak-topeak pressure is tenfold higher than the catheter tip peak-to-peak. The comparison between manual pumping and vibrational flow generation is shown in Figure 11. Manual pumping generates pressures greater by an order of magnitude than those generated by the flow generator. Additionally, manual pumping creates a suction which lasts for nearly a second (the time it takes for the dome to refill) while vibrational flow generation generates a suction which lasts for 1/60 th of a second. Figure 10 An example of a typical pressure waveform recorded inside the dome (dashed) and at the tip of catheter.
11 We tested several programmable valves and checked opening pressures and check valve action (we checked for possible back flows, due to valve damage) prior to and after flow generation testing. The opening pressure and check-valve action were not affected by the flow generator. During our extensive testing (for some valves the cumulative flow generation time was in order of several hours and more than hundred procedures per valve), we never observed a valve malfunction. 4. Conclusions CSF flow intermittency limits the accuracy and clinical utility of all flow based methods for assessing shunt function. Promising results shown in this paper suggest that the flow generator can be combined with flow based methods, including the thermal CSF flow detector, to provide better shunt patency assessment than flow based methods alone. The combination of a flow generator and a thermal flow meter seems to be an inexpensive, safe and reliable alternative to all existing techniques including radionuclide and MRI modalities. Our initial data suggest that this method could serve not only as a proximal resistance measurement but also, as a distal resistance assessment, especially when the abdominal pressure is kept at the low level (no more than 5cmH 2 O above the intracranial pressure). The simplest way of applying this method would be a "total obstruction level assessment" since the flow generated by the flow generator drops as a function of total resistance (proximal and distal) (see figure 6). The vibrational flow generation effect is based on a solid mechanism, which is not compromised by a wide range of proximal and distal resistances. The method works even with relatively thick scalps and hair. We tested most types of popular valves and obtained relatively consistent results. We think that the method is ready for its clinical debut and should be tested on a population of symptomatic and asymptomatic patients in order to show its clinical usefulness. Fig.11. An example of a typical pressures measured at the ventricular tip of the catheter. Manual pumping shows greater suction generated inside the ventricle.
12 The proximal catheter adds a significant amount of resistance and pressure damping between the dome and the ventricular end of the catheter. This is caused by high flow rates (higher the flow rates, the higher the resistance) This is key to flow generator s safety and efficacy. The strong pressures generated in the dome reliably open and close the shunt valve and generate robust flow through the valve but at the same time the small suction pressure generated at the ventricular tip is 10 fold lower than suction generated by manual shunt pumping (see Figure 11). 5. References 1. Bondurant, C. and D. Jiminez, Epidemiology of cerebrospinal fluid shunting. Pediatr Neurosurg, : p Drake, J., et al., Randomized trial of cerebrospinal fluid shunt valve design in pediatric hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery, : p Kestle, J., et al., Lack of benefit of endoscopic ventriculoperitoneal shunt insertion: a multicenter randomized trial. J Neurosurg, : p McGirt, M., et al., Shunt survival and etiology of failures. Pediatr Neurosurg, : p Zorc, J., et al., Radiographic evaluation for suspected cerebrospinal fluid shunt obstruction. Pediatr Emerg Care, : p Collins, P., A. Hockley, and D. Woollam, Surface ultrastructure of tissues occluding ventricular catheters. J Neurosurg, : p Sainte-Rose, C., Shunt obstruction: A preventable complication? Pediatr Neurosurg, : p Ventureyra, E. and M. Higgins, A new ventricular catheter for the prevention and treatment of proximal obstruction in cerebrospinal fluid shunts. Neurosurgery, : p Iskandar, B., et al., Pitfalls in the diagnosis of ventricular shunt dysfunction: radiology reports and ventricular size. Pediatrics, : p Frank E, Buonocore M, Hein L. Magnetic resonance imaging analysis of extremely slow flow in a model shunt system. Child Nerv Syst 8:73 75, Thermal dilution device 510(k) premarket notification K s/pdf8/k pdf 12. Madsen, J. et al., Evaluation of the Thermal dilution device Noninvasive Thermal Technique for Shunt Flow Detection in Hydrocephalus Patients. Neurosugery 68: , Hidaka M, Matsumae M, Kaoru I. Tsugane R. Saito I, Dynamic measurement of the flow rate in cerebrospinal fluid shunts in hydrocephalic patients. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 28: Martin AJ, Drake JM, Lemaire C, Henkelman RM. Cerebrospinal fluid shunts: flow measurements with MKR imaging. Radiology 173: , Hori H, Moretti G, Rebora A, Crovato F: The thickness of human of human scalp: normal and bald. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology 1972; Vol 58 No 6, Lupin AJ, Gardiner RJ: Scalp thickness in the temporal region : its relevance to the development of cochlear implants. Cochlear Implants International 2001; 2(1), Jay O, Havenith G: Skin cooling on contact with cold materials: The effect of Blood flow during short term exposure. The Annals of Occupational Hygiene 2004, Vol 48. No 2, Hodges PW, Gandevia SC: Changes in intra-abdominal pressure during postural and respiratory activation of the human
13 diaphragm. Journal of Apllied Physiology 2000, 89: Gisolf J, van Lieshout JJ, van Heusden K, et al. : Human cerebral venous outflow pathway depends on posture and central venous pressure. Journal of Physiology, 2004, P. Hodges, S Gandevia Changes in intraabdominal pressure during postural and respiratory activation of the human diaphragm. Journal of Applied Physiology 89: , R. Daugherty, Joseph B Franzini Fluid Mechanics with Engineering applications McGraw -Hill Company New York p G. Cinalli W.J. Maixner, C. Sainte-Rose, Pediatric Hydrocephalus, Springer Milano 2004.pp Thermal dilution device 510(k) application Corresponding author: Marek Swoboda Address: 324B Wall St Princeton NJ USA phone: dr.marekswoboda@gmail.com
Infusion studies in clinical practice. Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London
 Infusion studies in clinical practice Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London 10 th September 2018 infusion study + hydrocephalus 216 publications Clinical
Infusion studies in clinical practice Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London 10 th September 2018 infusion study + hydrocephalus 216 publications Clinical
Shunt malfunction and Slight edema surrounding the ventricles: Ten case series
 ISSN: 47-5 Volume Number 8 (August-04) pp. 4-45 www.ijcrar.com Shunt malfunction and Slight edema surrounding the ventricles: Ten case series Firooz Salehpoor, Arastoo Pezeshki, Amirhossein Haghir *, Aidin
ISSN: 47-5 Volume Number 8 (August-04) pp. 4-45 www.ijcrar.com Shunt malfunction and Slight edema surrounding the ventricles: Ten case series Firooz Salehpoor, Arastoo Pezeshki, Amirhossein Haghir *, Aidin
Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts
 Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is the build up of an excess
Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is the build up of an excess
Imaging appearances of programmable ventricular shunt systems : What the radiologist needs to know
 Imaging appearances of programmable ventricular shunt systems : What the radiologist needs to know Poster No.: C-2030 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Gontsarova, S. C. Thust, J.
Imaging appearances of programmable ventricular shunt systems : What the radiologist needs to know Poster No.: C-2030 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Gontsarova, S. C. Thust, J.
Original Article. Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction. Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH
 Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip
 197 Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip Ching-Yi Lee 1, Chieh-Tsai Wu 1, Kuang-Lin Lin 2, Hsun-Hui Hsu 3 Abstract-
197 Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip Ching-Yi Lee 1, Chieh-Tsai Wu 1, Kuang-Lin Lin 2, Hsun-Hui Hsu 3 Abstract-
Researcher 2018;10(3)
 Comparative study between frontal and posterior parietal ventriculo-peritoneal shunts in management of hydrocephalus Prof. Dr. Abdelhalim Moasa, Dr. Mohamed Hasan and Mohamed Abdelrazek Department of Neurosurgery,
Comparative study between frontal and posterior parietal ventriculo-peritoneal shunts in management of hydrocephalus Prof. Dr. Abdelhalim Moasa, Dr. Mohamed Hasan and Mohamed Abdelrazek Department of Neurosurgery,
Principlesof shunt testing in-vivo Zofia Czosnyka, Matthew Garnett, Eva Nabbanja, Marek Czosnyka
 Principlesof shunt testing in-vivo Zofia Czosnyka, Matthew Garnett, Eva Nabbanja, Marek Czosnyka Neurosurgery Unit, Addenbrooke s Hospital, Cambridge, UK Shunt helps to control hydrocephalus not to cure
Principlesof shunt testing in-vivo Zofia Czosnyka, Matthew Garnett, Eva Nabbanja, Marek Czosnyka Neurosurgery Unit, Addenbrooke s Hospital, Cambridge, UK Shunt helps to control hydrocephalus not to cure
Adult hydrocephalus and shunts. Information for patients
 Adult hydrocephalus and shunts Information for patients Contents What is hydrocephalus? 3 Causes 4 Symptoms 4 What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds
Adult hydrocephalus and shunts Information for patients Contents What is hydrocephalus? 3 Causes 4 Symptoms 4 What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds
Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children
 Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 584567, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/584567 Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children Eva Brichtova, 1
Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 584567, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/584567 Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children Eva Brichtova, 1
Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections in Patients with Hydrocephalus
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Venous sinus stents (for the treatment of venous sinus stenosis and idiopathic intracranial hypertension) Lysholm Department of Neuroradiology If you would
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Venous sinus stents (for the treatment of venous sinus stenosis and idiopathic intracranial hypertension) Lysholm Department of Neuroradiology If you would
UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS
 UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS Offering solutions for patients. 1 UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS Dear Reader: Your doctor has either recommended the CODMAN HAKIM Precision Fixed Pressure Valve, the CODMAN HAKIM
UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS Offering solutions for patients. 1 UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS Dear Reader: Your doctor has either recommended the CODMAN HAKIM Precision Fixed Pressure Valve, the CODMAN HAKIM
CATCH A WAVE.. INTRODUCTION NONINVASIVE HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING 4/12/2018
 WAVES CATCH A WAVE.. W I S C O N S I N P A R A M E D I C S E M I N A R A P R I L 2 0 1 8 K E R I W Y D N E R K R A U S E R N, C C R N, E M T - P Have you considered that if you don't make waves, nobody
WAVES CATCH A WAVE.. W I S C O N S I N P A R A M E D I C S E M I N A R A P R I L 2 0 1 8 K E R I W Y D N E R K R A U S E R N, C C R N, E M T - P Have you considered that if you don't make waves, nobody
Pro 01: Development and In Vitro Evaluation of a Hydraulic System for a Mini axial Flow Blood Pump
 Pro 01: Development and In Vitro Evaluation of a Hydraulic System for a Mini axial Flow Blood Pump Background: Fully implantable rotary blood pumps are used for mechanical circulatory support of heart
Pro 01: Development and In Vitro Evaluation of a Hydraulic System for a Mini axial Flow Blood Pump Background: Fully implantable rotary blood pumps are used for mechanical circulatory support of heart
Evaluation of Shunt Malfunction Using Shunt Site Reservoir
 Original Paper Pediatr Neurosurg 2000;32:180 186 Received: January 27, 1999 Accepted: April 27, 2000 Evaluation of Shunt Malfunction Using Shunt Site Reservoir S. Sood A.I. Canady Steven D. Ham Section
Original Paper Pediatr Neurosurg 2000;32:180 186 Received: January 27, 1999 Accepted: April 27, 2000 Evaluation of Shunt Malfunction Using Shunt Site Reservoir S. Sood A.I. Canady Steven D. Ham Section
BMI Medical. Ventricular Catheter T
 Shunting System Ventricular Catheter 01101 01101T Barium-impregnated silicone catheter provides resistance to kinking and compression. Stainless steel stylet allows catheter to be directed during catheter
Shunting System Ventricular Catheter 01101 01101T Barium-impregnated silicone catheter provides resistance to kinking and compression. Stainless steel stylet allows catheter to be directed during catheter
CODING SHEET HYDROCEPHALUS REIMBURSEMENT. All Medicare information is current as of the time of printing.
 CODING SHEET HYDROCEPHALUS REIMBURSEMENT All Medicare information is current as of the January 2014 Hydrocephalus ing Coding Options Commonly Billed Codes for Physicians, Hospitals, and Ambulatory Surgery
CODING SHEET HYDROCEPHALUS REIMBURSEMENT All Medicare information is current as of the January 2014 Hydrocephalus ing Coding Options Commonly Billed Codes for Physicians, Hospitals, and Ambulatory Surgery
NEUROSURGERY LiquoGuard
 NEUROSURGERY LiquoGuard Member of CENTROTEC Group a new InTRODUCTION TO LiquoGuard CSF Management LiquoGuard (Liquor = German for CSF) represents a revolutionary step in CSF drainage, maximizing patient
NEUROSURGERY LiquoGuard Member of CENTROTEC Group a new InTRODUCTION TO LiquoGuard CSF Management LiquoGuard (Liquor = German for CSF) represents a revolutionary step in CSF drainage, maximizing patient
NEUROSURGEON VS. HOSPITALIST Pediatric Hospital Medicine meeting Nashville, TN July 21, 2017*±
 NEUROSURGEON VS. HOSPITALIST Pediatric Hospital Medicine meeting Nashville, TN July 21, 2017*± *no pediatricians were harmed in the making of this presentation ±nonetheless, please do not try this at home
NEUROSURGEON VS. HOSPITALIST Pediatric Hospital Medicine meeting Nashville, TN July 21, 2017*± *no pediatricians were harmed in the making of this presentation ±nonetheless, please do not try this at home
Department of Neurosurgery, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, Wisconsin
 clinical article J Neurosurg Pediatr 17:270 277, 2016 Noninvasive measurement of cerebrospinal fluid flow using an ultrasonic transit time flow sensor: a preliminary study Thomas Pennell, MS, 1 Juneyoung
clinical article J Neurosurg Pediatr 17:270 277, 2016 Noninvasive measurement of cerebrospinal fluid flow using an ultrasonic transit time flow sensor: a preliminary study Thomas Pennell, MS, 1 Juneyoung
Radiological evaluation of ventriculoperitoneal shunt systems
 Radiological evaluation of ventriculoperitoneal shunt systems Poster No.: C-702 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: T. Rodt, C. von Falck, C. Tschan, M. Diensthuber, J. Zajaczek,
Radiological evaluation of ventriculoperitoneal shunt systems Poster No.: C-702 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: T. Rodt, C. von Falck, C. Tschan, M. Diensthuber, J. Zajaczek,
Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure
 Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure Dr Gari Clifford Adapted from slides by Prof. Lionel Tarassenko Blood pressure Blood is pumped around the body by the heart. It makes its way around the body
Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure Dr Gari Clifford Adapted from slides by Prof. Lionel Tarassenko Blood pressure Blood is pumped around the body by the heart. It makes its way around the body
Hydrocephalus. Patient and Family Education. What is hydrocephalus? What are the signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus?
 Patient and Family Education Hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus happens when too much fluid builds up in the cavities (ventricles) of your child s brain causing pressure. This handout includes information on
Patient and Family Education Hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus happens when too much fluid builds up in the cavities (ventricles) of your child s brain causing pressure. This handout includes information on
Intra-Arterial Blood Pressure Monitoring
 Intra-Arterial Blood Pressure Monitoring Verghese Cherian Associate Professor of Anesthesiology Hershey Medical Center Intra-Arterial Blood Pressure (IABP) measurement has several advantages over a non-invasive
Intra-Arterial Blood Pressure Monitoring Verghese Cherian Associate Professor of Anesthesiology Hershey Medical Center Intra-Arterial Blood Pressure (IABP) measurement has several advantages over a non-invasive
Anesthetic Management of Laparoscopic Surgery for a Patient with
 Anesthetic Management of Laparoscopic Surgery for a Patient with a Ventriculoperitoneal shunt Abstract With the advances in the management of hydrocephalus, patients with ventriculoperitoneal shunt are
Anesthetic Management of Laparoscopic Surgery for a Patient with a Ventriculoperitoneal shunt Abstract With the advances in the management of hydrocephalus, patients with ventriculoperitoneal shunt are
A multicenter prospective cohort study of the Strata valve for the management of hydrocephalus in pediatric patients
 J Neurosurg (Pediatries 2) 102:141-145, 2005 A multicenter prospective cohort study of the Strata valve for the management of hydrocephalus in pediatric patients J ohn R. W. K kstlk, M.D., M ario n L.
J Neurosurg (Pediatries 2) 102:141-145, 2005 A multicenter prospective cohort study of the Strata valve for the management of hydrocephalus in pediatric patients J ohn R. W. K kstlk, M.D., M ario n L.
Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunts
 Refer to: Sells CJ, Shurtleff DB: Cerebrospinal fluid shunts. West J Med 127:93-98, Aug 1977 Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunts CLIFFORD J. SELLS, MD, and DAVID B. SHURTLEFF, MD, Seattle Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Refer to: Sells CJ, Shurtleff DB: Cerebrospinal fluid shunts. West J Med 127:93-98, Aug 1977 Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunts CLIFFORD J. SELLS, MD, and DAVID B. SHURTLEFF, MD, Seattle Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Unfortunately, shunt malfunction is one of the
 J Neurosurg Pediatrics 14:160 166, 2014 AANS, 2014 Utility of computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of ventricular morphology in suspected cerebrospinal fluid shunt malfunction Clinical
J Neurosurg Pediatrics 14:160 166, 2014 AANS, 2014 Utility of computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of ventricular morphology in suspected cerebrospinal fluid shunt malfunction Clinical
Hydrocephalus in children. Eva Brichtova, M.D., Ph.D., Department of Pediatric Sugery, Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University Hospital Brno
 Hydrocephalus in children Eva Brichtova, M.D., Ph.D., Department of Pediatric Sugery, Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University Hospital Brno Ventricle system Ventricle system, cerebral cisterns Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus in children Eva Brichtova, M.D., Ph.D., Department of Pediatric Sugery, Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University Hospital Brno Ventricle system Ventricle system, cerebral cisterns Hydrocephalus
Understanding Peripheral
 Patient Information Guide Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease Innova Vascular Self-Expanding Stent System Table of Contents Glossary... 2 What is Peripheral Artery Disease?... 4 Treating Peripheral
Patient Information Guide Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease Innova Vascular Self-Expanding Stent System Table of Contents Glossary... 2 What is Peripheral Artery Disease?... 4 Treating Peripheral
3908 ½ River Ave. Newport Beach, California contact[at]dollecommunications[dot]com. Hydrocephalus Consult Report Published On-Line
![3908 ½ River Ave. Newport Beach, California contact[at]dollecommunications[dot]com. Hydrocephalus Consult Report Published On-Line 3908 ½ River Ave. Newport Beach, California contact[at]dollecommunications[dot]com. Hydrocephalus Consult Report Published On-Line](/thumbs/96/127081733.jpg) STEPHEN M. DOLLE Hydrocephalus Monitoring & Consults 3908 ½ River Ave. Newport Beach, California 92663 contact[at]dollecommunications[dot]com Hydrocephalus Consult Report Published On-Line March 4, 2014
STEPHEN M. DOLLE Hydrocephalus Monitoring & Consults 3908 ½ River Ave. Newport Beach, California 92663 contact[at]dollecommunications[dot]com Hydrocephalus Consult Report Published On-Line March 4, 2014
Carry this card with you at all times. Show this card to any medical professional treating you. Patient Implant Card. Option ELITE Vena Cava Filter.
 Patient Guide A Safe Option for a Healthier You! P/N: P-2017-0175-00 Rev B 1. Static magnetic field of 3 Tesla or less. 2. Spatial gradient magnetic field of 720 Gauss/cm or less. 3. Maximum whole body
Patient Guide A Safe Option for a Healthier You! P/N: P-2017-0175-00 Rev B 1. Static magnetic field of 3 Tesla or less. 2. Spatial gradient magnetic field of 720 Gauss/cm or less. 3. Maximum whole body
Hydrocephalus 1/16/2015. Hydrocephalus. Functions of Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Flow of CSF
 Hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus Ruth Arms, MSN, CNS-BC, SCRN Hydrocephalus is the buildup of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain. The excess fluid increases the size of the ventricles
Hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus Ruth Arms, MSN, CNS-BC, SCRN Hydrocephalus is the buildup of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain. The excess fluid increases the size of the ventricles
Evaluation of CSF Shunt Function: Value of Functional Examination with Contrast Material
 143 Evaluation of CSF Shunt Function: Value of Functional Examination with Contrast Material Edward C. Benzel 1 Mansour Mirfakhraee 2 Theresa A. Hadden 1 Functional positive-contrast shuntography includes
143 Evaluation of CSF Shunt Function: Value of Functional Examination with Contrast Material Edward C. Benzel 1 Mansour Mirfakhraee 2 Theresa A. Hadden 1 Functional positive-contrast shuntography includes
MRI MEASUREMENTS OF CRANIOSPINAL AND INTRACRANIAL VOLUME CHANGE IN HEALTHY AND HEAD TRAUMA CASES
 1of 4 MRI MEASUREMENTS OF CRANIOSPINAL AND INTRACRANIAL VOLUME CHANGE IN HEALTHY AND HEAD TRAUMA CASES N. Alperin, Y. Kadkhodayan, B. Varadarajalu, C. Fisher, B. Roitberg Department of Radiology and Neurosurgery,
1of 4 MRI MEASUREMENTS OF CRANIOSPINAL AND INTRACRANIAL VOLUME CHANGE IN HEALTHY AND HEAD TRAUMA CASES N. Alperin, Y. Kadkhodayan, B. Varadarajalu, C. Fisher, B. Roitberg Department of Radiology and Neurosurgery,
Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy
 Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion
 Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion Jason Silver August 26, 2009 Presentation Outline Introduction Thesis Objectives Mathematical Model and Principles Methods
Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion Jason Silver August 26, 2009 Presentation Outline Introduction Thesis Objectives Mathematical Model and Principles Methods
Technique. Technique. Technique. Monitoring 1. Local anesthetic? Aseptic technique Hyper-extend (if radial)
 Critical Care Monitoring Hemodynamic Monitoring Arterial Blood Pressure Cannulate artery Uses 2 Technique Sites Locate artery, prep 3 1 Technique Local anesthetic? Aseptic technique Hyper-extend (if radial)
Critical Care Monitoring Hemodynamic Monitoring Arterial Blood Pressure Cannulate artery Uses 2 Technique Sites Locate artery, prep 3 1 Technique Local anesthetic? Aseptic technique Hyper-extend (if radial)
Invasive Measurement of Blood Pressure
 Invasive Measurement of Blood Pressure Arterial Lines & Pulmonary Artery Lines Key Points Invasive Measurement of Blood Pressure: - understand blood flow through the body - understand Pulmonary Artery
Invasive Measurement of Blood Pressure Arterial Lines & Pulmonary Artery Lines Key Points Invasive Measurement of Blood Pressure: - understand blood flow through the body - understand Pulmonary Artery
(Hi-dro-SEF-ah-lus) Hydrocephalus is a build-up of Cerebrospinal Fluid, or CSF within the spaces inside the brain, called ventricles.
 Hydrocephalus in adults What is hydrocephalus? (Hi-dro-SEF-ah-lus) Hydrocephalus is a build-up of Cerebrospinal Fluid, or CSF within the spaces inside the brain, called ventricles. There are 4 ventricles
Hydrocephalus in adults What is hydrocephalus? (Hi-dro-SEF-ah-lus) Hydrocephalus is a build-up of Cerebrospinal Fluid, or CSF within the spaces inside the brain, called ventricles. There are 4 ventricles
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE MONITORING AND DRAINAGE OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID VIA Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 7/88 1/18 1 of 9 RESPONSIBILITY:
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE MONITORING AND DRAINAGE OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID VIA Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 7/88 1/18 1 of 9 RESPONSIBILITY:
Top Vent Study: Optimizing Urine Collection System Flow to Improve Patient Outcomes
 Top Vent Study: Optimizing Urine Collection System Flow to Improve Patient Outcomes Stephen Tully, R&D Project Engineer, Tyco Healthcare Group LP, Kendall Division, Mansfield, MA Top Vent Study: Optimizing
Top Vent Study: Optimizing Urine Collection System Flow to Improve Patient Outcomes Stephen Tully, R&D Project Engineer, Tyco Healthcare Group LP, Kendall Division, Mansfield, MA Top Vent Study: Optimizing
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
NCVH. Ultrasongraphy: State of the Art Vein Forum 2015 A Multidisciplinary Approach to Otptimizing Venous Circulation From Wounds to WOW
 Ultrasongraphy: State of the Art 2015 NCVH New Cardiovascular Horizons Vein Forum 2015 A Multidisciplinary Approach to Otptimizing Venous Circulation From Wounds to WOW Anil K. Chagarlamudi, M.D. Cardiovascular
Ultrasongraphy: State of the Art 2015 NCVH New Cardiovascular Horizons Vein Forum 2015 A Multidisciplinary Approach to Otptimizing Venous Circulation From Wounds to WOW Anil K. Chagarlamudi, M.D. Cardiovascular
Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD)
 Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD) Dr. Vijay Tarnal MBBS, FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Neuroanesthesiology Division of Head & Neck Anesthesiology Michigan Medicine
Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD) Dr. Vijay Tarnal MBBS, FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Neuroanesthesiology Division of Head & Neck Anesthesiology Michigan Medicine
Intracranial pressure: measurement and monitoring. CSF pressure as a golden standard. Intraparenchymal pressure. Sensors, drifts, errors and
 Intracranial pressure: measurement and monitoring. CSF pressure as a golden standard. Intraparenchymal pressure. Sensors, drifts, errors and monitoring techniques GUILLAUME J, JANNY P. [Continuous intracranial
Intracranial pressure: measurement and monitoring. CSF pressure as a golden standard. Intraparenchymal pressure. Sensors, drifts, errors and monitoring techniques GUILLAUME J, JANNY P. [Continuous intracranial
Catheter-directed Thrombolysis
 Scan for mobile link. Catheter-directed Thrombolysis Catheter-directed thrombolysis treats vascular blockages and improves blood flow by dissolving abnormal blood clots. A blood clot, or thrombus, can
Scan for mobile link. Catheter-directed Thrombolysis Catheter-directed thrombolysis treats vascular blockages and improves blood flow by dissolving abnormal blood clots. A blood clot, or thrombus, can
A telescopic ventriculoatrial shunt that elongates with growth
 A telescopic ventriculoatrial shunt that elongates with growth Technical note BURTON L. WISE, M.D. Department of Surgery (Neurosurgery) and Neurological Institute, Mount Zion Hospital and Medical Center,
A telescopic ventriculoatrial shunt that elongates with growth Technical note BURTON L. WISE, M.D. Department of Surgery (Neurosurgery) and Neurological Institute, Mount Zion Hospital and Medical Center,
BACTISEAL Endoscopic Ventricular Catheter (REF & )
 BACTISEAL Endoscopic Ventricular Catheter (REF 82-3087 & 82-3088) LCN 206966-001/E 2011 2017 DePuy Synthes. All rights reserved. Revised 07/17 206966-001-E.indd 1 ENGLISH IMPORTANT INFORMATION Please Read
BACTISEAL Endoscopic Ventricular Catheter (REF 82-3087 & 82-3088) LCN 206966-001/E 2011 2017 DePuy Synthes. All rights reserved. Revised 07/17 206966-001-E.indd 1 ENGLISH IMPORTANT INFORMATION Please Read
Biomedical Instrumentation
 Biomedical Instrumentation Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr naydin@ieee.org http://www.yildiz.edu.tr/~naydin Therapeutic and Prosthetic Devices 1 Figure 13.1 Block diagram of an asynchronous
Biomedical Instrumentation Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr naydin@ieee.org http://www.yildiz.edu.tr/~naydin Therapeutic and Prosthetic Devices 1 Figure 13.1 Block diagram of an asynchronous
Patient guide: pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system. Catheter occlusion of. Patent Ductus Arteriosus. with the
 Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
Introduction. Cardiac Imaging Modalities MRI. Overview. MRI (Continued) MRI (Continued) Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03
 Introduction Cardiac Imaging Modalities Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03 Coronary heart disease: the vessels that supply oxygen-carrying blood to the heart, become narrowed and unable to carry a normal amount
Introduction Cardiac Imaging Modalities Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03 Coronary heart disease: the vessels that supply oxygen-carrying blood to the heart, become narrowed and unable to carry a normal amount
Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Monitoring. Intracranial Pressure Monitoring
 Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Monitoring What is intracranial pressure (ICP) and why is it measured? Intracranial pressure is the pressure of fluid inside the head, sometimes
Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Monitoring What is intracranial pressure (ICP) and why is it measured? Intracranial pressure is the pressure of fluid inside the head, sometimes
Flow-diverting stents (in the Treatment of intracranial aneurysms)
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Flow-diverting stents (in the Treatment of intracranial aneurysms) Lysholm Department of Neuroradiology If you would like this document in another language
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Flow-diverting stents (in the Treatment of intracranial aneurysms) Lysholm Department of Neuroradiology If you would like this document in another language
Editorial. Reid Hoshide, Hal Meltzer 1, Cecilia Dalle-Ore 1, David Gonda, Daniel Guillaume 2, Clark C. Chen. Abstract
 SNI: Randomized Controlled Trials OPEN ACCESS For entire Editorial Board visit : http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com Editor: James I. Ausman, MD, PhD University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA Editorial
SNI: Randomized Controlled Trials OPEN ACCESS For entire Editorial Board visit : http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com Editor: James I. Ausman, MD, PhD University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA Editorial
Even with increasing nonshunt options for
 RESEARCH HUMAN CLINICAL STUDIES Noninvasive Thermal Evaluation of Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Patency and Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow Using a Flow Enhancing Device Mustafa Q. Hameed, MD David Zurakowski, PhD
RESEARCH HUMAN CLINICAL STUDIES Noninvasive Thermal Evaluation of Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Patency and Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow Using a Flow Enhancing Device Mustafa Q. Hameed, MD David Zurakowski, PhD
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt with Communicating Peritoneal & Subcutaneous Pseudocysts Formation
 International Journal of Health Sciences, Qassim University, Vol. 8, No. 1 (January-March 2014) Case Report Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt with Communicating Peritoneal & Subcutaneous Pseudocysts Formation
International Journal of Health Sciences, Qassim University, Vol. 8, No. 1 (January-March 2014) Case Report Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt with Communicating Peritoneal & Subcutaneous Pseudocysts Formation
About Your Programmable VP Shunt for Pediatric Patients
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Your Programmable VP Shunt for Pediatric Patients This information will help you learn about your prog rammable ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt. For the rest of this
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Your Programmable VP Shunt for Pediatric Patients This information will help you learn about your prog rammable ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt. For the rest of this
The arrest of treated hydrocephalus in children
 J Neurosurg 61:752-756, 1984 The arrest of treated hydrocephalus in children A radionuclide study IAN H. JOHNSTON, F.R.C.S., ROBERT HOWMAN-GILES, F.R.A.C.P., AND IAN R. WHITTLE, M.B., B.S. T. Y. Nelson
J Neurosurg 61:752-756, 1984 The arrest of treated hydrocephalus in children A radionuclide study IAN H. JOHNSTON, F.R.C.S., ROBERT HOWMAN-GILES, F.R.A.C.P., AND IAN R. WHITTLE, M.B., B.S. T. Y. Nelson
STANDARDIZED PROCEDURE REPROGRAMMING AND REFILLING INTRATHECAL BACLOFEN PUMPS and ACCESSING THE CATHETER ACCESS PORT (Adult,Peds)
 I. Definition The purpose of this procedure is to allow the Advanced Health Practitioner (AHP) to reprogram and refill intrathecal Baclofen pumps, as well as access the catheter access port for those AHPs
I. Definition The purpose of this procedure is to allow the Advanced Health Practitioner (AHP) to reprogram and refill intrathecal Baclofen pumps, as well as access the catheter access port for those AHPs
Breast Cancer Screening
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Screening What is breast cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to find disease before symptoms begin. The goal of screening is to detect disease
Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Screening What is breast cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to find disease before symptoms begin. The goal of screening is to detect disease
GUIDANCE NOTE. Application of MEMS Ultrasonic Transducers to Flow Measurement.
 GUIDANCE NOTE Application of MEMS Ultrasonic Transducers www.tuvnel.com Application of MEMS Ultrasonic Transducers Introduction This Guidance Note provides a review of the key issues associated with the
GUIDANCE NOTE Application of MEMS Ultrasonic Transducers www.tuvnel.com Application of MEMS Ultrasonic Transducers Introduction This Guidance Note provides a review of the key issues associated with the
SOLUTION MATCH Ospedale Pediatrico Bambin Gesù is looking for a remote monitoring and symptom reporting solution to detect problems with shunts in
 SOLUTION MATCH Ospedale Pediatrico Bambin Gesù is looking for a remote monitoring and symptom reporting solution to detect problems with shunts in paediatrics ABOUT Ospedale Pediatrico Bambin Gesù Bambino
SOLUTION MATCH Ospedale Pediatrico Bambin Gesù is looking for a remote monitoring and symptom reporting solution to detect problems with shunts in paediatrics ABOUT Ospedale Pediatrico Bambin Gesù Bambino
NANOS Patient Brochure
 NANOS Patient Brochure Pseudotumor Cerebri Copyright 2016. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for
NANOS Patient Brochure Pseudotumor Cerebri Copyright 2016. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for
Effect of Electromagnetic Navigated Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Placement on Failure Rates
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.53.3.150 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 53 : 150-154, 2013 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2013 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.53.3.150 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 53 : 150-154, 2013 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2013 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
RELEASED. first steps. Icon Icon name What it means
 Icon Icon name What it means Connection The connection icon appears green when the Sensor feature is on and your transmitter is successfully communicating with your pump. The connection icon appears gray
Icon Icon name What it means Connection The connection icon appears green when the Sensor feature is on and your transmitter is successfully communicating with your pump. The connection icon appears gray
Design and Simulation of Blocked Blood Vessel for Early Detection of Heart Diseases
 Proceedings of the 215 2nd International Symposium on Physics and Technology of Sensors, 8-1th March, 215, Pune, India Design and Simulation of Blocked Blood Vessel for Early Detection of Heart Diseases
Proceedings of the 215 2nd International Symposium on Physics and Technology of Sensors, 8-1th March, 215, Pune, India Design and Simulation of Blocked Blood Vessel for Early Detection of Heart Diseases
Chapter 4 Varicocele Classification
 Chapter 4 Varicocele Classification In this chapter, we examine the several classification modes have been used to diagnose and grade varicocele, including physical exam, venographic examination, color
Chapter 4 Varicocele Classification In this chapter, we examine the several classification modes have been used to diagnose and grade varicocele, including physical exam, venographic examination, color
PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists
 PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists Craig A. McPherson, MD, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Constantine Manthous, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Clinical
PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists Craig A. McPherson, MD, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Constantine Manthous, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Clinical
Children's (Pediatric) Contrast-enhanced Voiding Urosonography
 Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) Contrast-enhanced Voiding Urosonography Pediatric contrast-enhanced voiding urosonography uses ultrasound to examine a child's bladder and urinary tract. It
Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) Contrast-enhanced Voiding Urosonography Pediatric contrast-enhanced voiding urosonography uses ultrasound to examine a child's bladder and urinary tract. It
Introduction What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? How Do Doctors Treat Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 9
 Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Breast Cancer. What is breast cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
INTRODUCING. An advanced, less invasive way to treat glaucoma
 INTODUCING An advanced, less invasive way to treat glaucoma What is the XEN Gel Stent? The XEN Gel Stent is a new way to treat glaucoma. It is a very small tube made of a soft gelatin material. The implant
INTODUCING An advanced, less invasive way to treat glaucoma What is the XEN Gel Stent? The XEN Gel Stent is a new way to treat glaucoma. It is a very small tube made of a soft gelatin material. The implant
DRG STIMULATION FOR CHRONIC PAIN FOCUS ON YOUR LIFE NOT YOUR PAIN
 FOCUS ON YOUR LIFE NOT YOUR PAIN DRG STIMULATION FOR CHRONIC PAIN Focus on your friendships, not on your pain. FOCUS ON YOUR LIFE, NOT ON YOUR PAIN. Chronic pain is personal, and it can be difficult to
FOCUS ON YOUR LIFE NOT YOUR PAIN DRG STIMULATION FOR CHRONIC PAIN Focus on your friendships, not on your pain. FOCUS ON YOUR LIFE, NOT ON YOUR PAIN. Chronic pain is personal, and it can be difficult to
Carotid Stenosis (carotid artery disease)
 1 Carotid Stenosis (carotid artery disease) Overview Carotid stenosis is a narrowing of the carotid arteries, the two major arteries that carry oxygenrich blood from the heart to the brain. Also called
1 Carotid Stenosis (carotid artery disease) Overview Carotid stenosis is a narrowing of the carotid arteries, the two major arteries that carry oxygenrich blood from the heart to the brain. Also called
ENGR 83 Final Project
 ENGR 83 Final Project Affordable Flowmeter for Measurement of Low- Flowrate Suspended- Particulate Flow Julian Leland ENGR 83, 2011 Swarthmore College Introduction Measurement of fluid flow is an important
ENGR 83 Final Project Affordable Flowmeter for Measurement of Low- Flowrate Suspended- Particulate Flow Julian Leland ENGR 83, 2011 Swarthmore College Introduction Measurement of fluid flow is an important
Mechanical Vibration Causes, Effect, Analysis & Prevention Techniques
 Training Title Mechanical Vibration Causes, Effect, Analysis & Prevention Techniques Training Duration 5 days Training Date Ref ME125 Mechanical Vibration Causes, Effect, Analysis & Prevention Techniques
Training Title Mechanical Vibration Causes, Effect, Analysis & Prevention Techniques Training Duration 5 days Training Date Ref ME125 Mechanical Vibration Causes, Effect, Analysis & Prevention Techniques
Safety Issue of Static Magnetic Field (1)
 MRI Safety Safety Issue of Static Magnetic Field (1) Currently, typical MRI utilizes static field with strengths of 0.5 to 3 Tesla (FDA guideline is max 4 T for infants < 1 month and 8 T for others) 1
MRI Safety Safety Issue of Static Magnetic Field (1) Currently, typical MRI utilizes static field with strengths of 0.5 to 3 Tesla (FDA guideline is max 4 T for infants < 1 month and 8 T for others) 1
ACUSON Sequoia C512 Echocardiography System The ultimate in imaging
 ACUSON Sequoia C512 Echocardiography System The ultimate in imaging Optimum imaging for every patient ACUSON Sequoia C512 Patient Specific Imaging Programmable Waveform Generator Coherent Pulse Formation
ACUSON Sequoia C512 Echocardiography System The ultimate in imaging Optimum imaging for every patient ACUSON Sequoia C512 Patient Specific Imaging Programmable Waveform Generator Coherent Pulse Formation
Gambro Renal Products Technical Assistance Services
 Gambro Renal Products Technical Assistance Services http://tech.usa-gambro.com 800/525-2623 303/232-6800 Technical Update PH,TR,11060 12/2008 TROUBLESHOOTING Equipment Type: Phoenix Dialysis System Subject:
Gambro Renal Products Technical Assistance Services http://tech.usa-gambro.com 800/525-2623 303/232-6800 Technical Update PH,TR,11060 12/2008 TROUBLESHOOTING Equipment Type: Phoenix Dialysis System Subject:
Surgical treatments in severe IIH
 Surgical treatments in severe IIH You will have been told by your Doctor that you need to have a surgical procedure for Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension. This may be because all the other treatments
Surgical treatments in severe IIH You will have been told by your Doctor that you need to have a surgical procedure for Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension. This may be because all the other treatments
CAREFULLY READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS PRIOR TO USE
 CAREFULLY READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS PRIOR TO USE INDICATIONS FOR USE The LATERA Absorbable Nasal Implant is indicated for supporting upper and lower lateral nasal cartilage. CAUTION: Federal law restricts
CAREFULLY READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS PRIOR TO USE INDICATIONS FOR USE The LATERA Absorbable Nasal Implant is indicated for supporting upper and lower lateral nasal cartilage. CAUTION: Federal law restricts
Breast Cancer. What is breast cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Pressure. 3. Direct Pressure. Pressure in Human Body. Pressures and Ranges. Effects of Kinetic Energy. Effect of Gravitational Force
 3. Direct Fundamental concepts Diaphragm-type pressure transducers Dynamics of catheter-transducer system Catheter-tip pressure transducers Implantable pressure transducers measurements in small vessels
3. Direct Fundamental concepts Diaphragm-type pressure transducers Dynamics of catheter-transducer system Catheter-tip pressure transducers Implantable pressure transducers measurements in small vessels
University of Groningen. Quantitative CT myocardial perfusion Pelgrim, Gert
 University of Groningen Quantitative CT myocardial perfusion Pelgrim, Gert IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Quantitative CT myocardial perfusion Pelgrim, Gert IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
WHILE it is generally agreed that elevation
 The Derivation of Coronary Sinus Flow During Elevation of Right Ventricular Pressure By HERMAN M. GELLER, B.S., M.D., MARTIN BRANDFONBRENEU, M.D., AND CARL J. WIGGERS, M.D., The derivation of coronary
The Derivation of Coronary Sinus Flow During Elevation of Right Ventricular Pressure By HERMAN M. GELLER, B.S., M.D., MARTIN BRANDFONBRENEU, M.D., AND CARL J. WIGGERS, M.D., The derivation of coronary
Pelvic Ultrasound.
 Pelvic Ultrasound Before Your Exam: Drink 32 oz. of water one hour before your examination time. Try to drink all the liquid within 30 minutes. Do not urinate before the exam. Arrive for your exam with
Pelvic Ultrasound Before Your Exam: Drink 32 oz. of water one hour before your examination time. Try to drink all the liquid within 30 minutes. Do not urinate before the exam. Arrive for your exam with
Understanding Peripheral
 Patient Information Guide Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease ELUVIA Drug-Eluting Vascular Stent System Table of Contents Glossary...2 What is Peripheral Artery Disease?...4 Treating Peripheral Artery
Patient Information Guide Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease ELUVIA Drug-Eluting Vascular Stent System Table of Contents Glossary...2 What is Peripheral Artery Disease?...4 Treating Peripheral Artery
Alessandro Della Puppa
 Intraoperative measurement of arterial blood flow in complex cerebral aneurysms surgery Studio flussimetrico intra-operatorio nel clipping degli aneurismi complessi Alessandro Della Puppa NEUROSURGERY
Intraoperative measurement of arterial blood flow in complex cerebral aneurysms surgery Studio flussimetrico intra-operatorio nel clipping degli aneurismi complessi Alessandro Della Puppa NEUROSURGERY
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING
 ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
BRINEURA (cerliponase alfa)
 BRINEURA (cerliponase alfa) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices
BRINEURA (cerliponase alfa) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices
Clinical Trial Glossary
 Clinical Trial Glossary Adverse event An unfavorable change in health that can occur during a clinical trial or study or within a certain time period after. These can range from mild (e.g., nausea) to
Clinical Trial Glossary Adverse event An unfavorable change in health that can occur during a clinical trial or study or within a certain time period after. These can range from mild (e.g., nausea) to
Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care. The High-Flow Port Designed for Apheresis
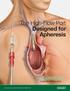 Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care The High-Flow Port Designed for Apheresis Optimized for Long Device Life Bench Tested up to 1,000 Accesses 1 Bard is proud to introduce the first and only
Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care The High-Flow Port Designed for Apheresis Optimized for Long Device Life Bench Tested up to 1,000 Accesses 1 Bard is proud to introduce the first and only
Quality Metrics. Stroke Related Procedure Outcomes
 Quality Metrics Stroke Related Procedure Outcomes Below is a description of some of the stroke-related procedures performed at St. Dominic Hospital in Jackson, with quality information on the complication
Quality Metrics Stroke Related Procedure Outcomes Below is a description of some of the stroke-related procedures performed at St. Dominic Hospital in Jackson, with quality information on the complication
Scottish Surveillance of Healthcare Associated Infection Programme (SSHAIP) Health Protection Scotland (HPS) SSI Surveillance Protocol 7th Edition
 1 Contents Female reproductive system operations (Abdominal hysterectomy and Caesarean section)... 3 Intra-abdominal infections... 3 Endometritis... 4 Other infections of the female reproductive tract...
1 Contents Female reproductive system operations (Abdominal hysterectomy and Caesarean section)... 3 Intra-abdominal infections... 3 Endometritis... 4 Other infections of the female reproductive tract...
THE MEDTRONIC TRANSCATHETER AORTIC VALVE REPLACEMENT (TAVR) SYSTEM
 THE MEDTRONIC TRANSCATHETER AORTIC VALVE REPLACEMENT (TAVR) SYSTEM 1 A Guide for Patients With Severe Aortic Stenosis medtronic.com/tavr Table of Contents 2 3 We have created this booklet to help you learn
THE MEDTRONIC TRANSCATHETER AORTIC VALVE REPLACEMENT (TAVR) SYSTEM 1 A Guide for Patients With Severe Aortic Stenosis medtronic.com/tavr Table of Contents 2 3 We have created this booklet to help you learn
Certification Review. Module 28. Medical Coding. Radiology
 Module 28 is the study of x-rays, using radiant energy and other imaging techniques, such as resonance imaging or ultrasound, to diagnose illnesses and diseases. Vocabulary Barium enema (BE): lower gastrointestinal
Module 28 is the study of x-rays, using radiant energy and other imaging techniques, such as resonance imaging or ultrasound, to diagnose illnesses and diseases. Vocabulary Barium enema (BE): lower gastrointestinal
Noninvasive cardiac imaging refers
 CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE Introduction to Noninvasive Cardiac Imaging Ron Blankstein, MD Noninvasive cardiac imaging refers to a combination of methods that can be used to obtain images related to the structure
CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE Introduction to Noninvasive Cardiac Imaging Ron Blankstein, MD Noninvasive cardiac imaging refers to a combination of methods that can be used to obtain images related to the structure
