Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect Role of Real-Time 3D Color Doppler Echocardiography for Interventional Catheterization
|
|
|
- Oswin Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Chung-Hsien Su et al. Acta Cardiol Sin 2005;21: Pediatric Cardiology Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect Role of Real-Time 3D Color Doppler Echocardiography for Interventional Catheterization Chung-Hsien Su, 1 Ken-Pen Weng, Jia-Kan Chang, 1 Chu-Chuan Lin, Yu-Tung Hwang, Cheng-Liang Lee, Kwan-Yen Chien, Fong-Lin Chen, 4 Chin-Kong Yu, 5 Wang-Shong Liu, 6 Ta-Cheng Huang and Kai-Sheng Hsieh Background: Atrial septal defect (ASD) is easily thought to be a round hole in the atrial septum from the image of two-dimensional (2D) echocardiography. Even surgeons can not get the true morphology of an atrial septal defect because they only see the defect when the heart is already in a collapsed, non-beating condition. Pediatric interventional cardiologists, on the contrary, need to know the exact morphology in the beating heart so that a therapeutic device can be safely deployed. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the accuracy of real-time three-dimensional echocardiography (RT-3D Echo) in visualizing the morphological characteristics of ASD and its potential as a new method for selecting the size of the Amplatzer septal occluder. Materials and Methods: Between February 2003 and December 2003, a total of 12 patients with secundum-type ASD underwent simultaneously 2D transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) and RT-3D Echo during interventional catheterization. The stretched balloon diameter, 2D TEE images, and RT-3D Echo images were recorded and analyzed in detail. Results: Twelve patients, aged from 3.0 to 36.0 years (mean years), safely underwent the interventional catheterization. The mean Qp/Qs was (range ). The mean size (waist) of the 12 devices was mm (range 7-36 mm). The mean SBD was mm (range mm). The mean 2D-TEE ASD measurement was mm (range mm). The mean RT-3D ASD measurement was mm (range mm). Analyses of the RT-3D Echo imaging showed that the ASD is not a flat hole in the septum. The ASD curves in three dimensions. The curvature varied differently in different directions, thus generating a complex spatial structure. The calculated curvature angles along long axis of defects were degrees. Good correlations were found between device diameter (waist) and SBD (r = 0.995), 2D diameter (r = 0.987), and 3D diameter (r = 0.997). The best correlation was found between device diameter (waist) and 3D diameter measured by planimetry of RT-3D Echo (r = 0.997). Conclusions: The complex 3D nature of the ASD in the beating heart could only be well appreciated by the RT Color 3D Echo. The conventional 2D image provided only partial and thus distorted image of ASD. Thus, the application of RT-3D Echo provides a useful tool for evaluation of ASD for those patients undergoing interventional transcatheter closure. Key Words: Atrial septal defect Congenital heart disease Real-time three-dimensional echocardiography Interventional catheterization Received: July 13, 2005 Accepted: September 14, Department of Pediatrics, Cheng-Hsin Rehabilitation Medical Center; 2 Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital; 3 National Yang-Ming University; 4 Department of Pediatrics, Chung-Shan Medical College; 5 Department of Pediatrics, God s Heart Hospital; 6 Department of Pediatrics, Chi-Mei Foundation Medical Center. Address correspondence and reprint requests to: Kai-Sheng Hsieh, Department of Pediatrics, Veterans General Hospital-Kaohsiung, 386, Ta-Chung 1 st Road, Kaohsiung 813, Taiwan. Tel: INTRODUCTION Morphologic characteristics of atrial septal defect (ASD) including size measurement and spatial relationship between the ASD and neighboring structures are of paramount importance for the successful deployment of a transcatheter septal occluder. Pediatric interventional 146 Acta Cardiol Sin 2005;21:146 52
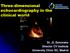
2 RT-3D Echo in Sizing ASD cardiologists need to know the exact morphology of an ASD in the beating heart so that the therapeutic device can be safely deployed. The traditional non-invasive method for evaluating the size and position of ASD is 2D transthoracic echocardiography (TTE). It usually underestimates maximal ASD size and provides limited ASD imaging because only one cross-sectional image is available at any one time. 1-5 Two-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) can provide much clearer ASD imaging than TTE. 5-7 However, this approach has an obvious limitation for clinical routine since it requires general anesthesia in children. New three-dimensional echocardiographic development allows the use of the transthoracic approach for surface imaging The newly introduced real-time three-dimensional echocardiography (RT-3D Echo) can visualize the overall structure of the atrial septum, which provides information including position, size during the cardiac cycle, and the exact morphology of surrounding rims. The aim of this study was to evaluate the accuracy of real-time three-dimensional echocardiography (RT-3D Echo) in visualizing the morphological characteristics of ASD and its potential as a new method for selecting the size of the Amplatzer septal occluder (ASO). MATERIALS AND METHODS Twelve consecutive patients diagnosed to have secundum-type ASD with 2D transthoracic echocardiography between Feb and Dec were enrolled in the protocol of transcatheter device closure using the Amplatzer septal occluder. During interventional catheterization, they simultaneously underwent 2D-TEE and RT-3D Echo. Patients ranged in aged from 3.0 to 36.0 years (mean years), and their weights ranged from 14.1 to 65.2 kg (mean kg). Informed consent was obtained from all patients or their guardians. RT-3D Echo studies were performed using the Philips Sonos 7500 ultrasound system equipped with xmatrix probe and software package including 3D data acquisition and analysis. All of the images were obtained using a dedicated RT-3D probe (in apical 4-chamber and short-axis view) with 3000 elements for ultra-fast spatial image acquisition and a dedicated computer for on-line image processing and real-time cine-loop display. RT- 3D Echo data acquisition was done while the patients were quiet and cooperative during several heartbeats. The reference position was selected based on the whole structure of ASD being in the region of interest. The digital data were stored and then reconstructed for whole anatomical structure of the sector. Maximal ASD size measurements were made on RT-3D Echo imaging using planimetry obtained from the right atrial-sided 3D-curved plane. Analysis of the RT-3D Color Echo image showed that the ASD was not a flat hole in the septum. The view from right atrium and left atrium showed ASD in cineloop with changing shapes and size during cardiac cycle (Figure 1). Planimetry was performed, including measurement of diameters (Figure 2). The maximal diameter of the defect was measured in each patient by picking up the two farthest points from the 3D-curved plane during the cardiac cycle. 11 Figure 1. Changing shapes and size of ASD during cardiac cycle: (A) diastole; (B) systole. 147 Acta Cardiol Sin 2005;21:146 52
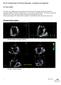
3 Chung-Hsien Su et al. Figure 2. Planimetry of diameters: (A) diameters of maximal area; (B) maximal diameter of systole; (C) maximal diameter of diastole. The catheterization protocol for deployment of the ASO was described previously. 12 The stretched balloon diameter (SBD) was measured by the balloon sizing maneuver. 13 In left anterior oblique view, the balloon was inflated with diluted contrast until a waist appeared. The SBD was determined outside the body by passing the same amount of contrast medium into the balloon and measuring the size by passing it through a calibrated sizing plate. The size of ASO was determined according to measurement of SBD on the basis of known surrounding anatomical structures by RT-3D Echo. Statistical analysis All data were expressed as mean SD. Measurements of maximal ASD size obtained by 2D TEE, balloon sizing method, and RT-3D Echo were compared with the deployed device size using linear regression analysis and paired t-test for continuous variables. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS All of the 12 patients underwent successful transcatheter closure with no residual shunt. All patients underwent 2D-TEE and RT-3D Echo. Balloon sizing measurements were done for 12 devices. The mean Qp/Qs was (range ). The mean size (waist) of the 12 devices was mm (range 7-36 mm). The mean SBD was mm (range mm). The mean 2D-TEE ASD measurement was mm (range mm). The RT-3D ASD measurement was mm (range mm). RT-3D Echo reconstruction was successfully done in all twelve patients. RT-3D Echo imaging provided an en face view demonstrating the size, position, number of defects, and surrounding rims of the ASD anatomy. This made the measurements more accurate and reliable. RT-3D Echo showed that ASDs curved in three dimensions. The curvature varied differently in different directions, thus generating a complex spatial structure. The surface area of the ASD changed significantly during the cardiac cycle, with a maximum size in late ventricular systole and a minimum size in late left ventricular diastole. 13 To express the curved 3D-plane of ASD as digitized value, curvature angles were calculated (Figure 3). The calculated curvature angles along long axis of defects were degrees (Figure 4). As seen in Table 1, good correlations were found between device diameter (waist) and SBD (r = 0.995), 2D diameter (r = 0.987), and 3D diameter (r = 0.997). The best correlation was found between device diameter (waist) and 3D diameter measured by planimetry of RT-3D Echo (r = 0.997). DISCUSSION Transcatheter closure of ASDs has recently become an increasingly attractive alternative to surgical repair in selected cases. The ASO device has a very high complete closure and is effective in closing ASDs up to a stretched diameter of 38 mm. 12,14,15 However, an extremely precise assessment of ASDs is crucial for optimal ASO selection and procedural success. The most frequently used methods for ASO device Acta Cardiol Sin 2005;21:
4 RT-3D Echo in Sizing ASD Figure 3. Curved plane of ASD. Marked points around the margin of defect in the 3D model formed an irregular circle and the curved plane of ASD. (A) front view. (B) oblique view. Figure 4. Angle of curved plane along the long axis. The calculated curvature angles along the long axis of defects were degrees. Table 1. Correlation between device diameter (waist) and ASD size measurements Measurement Mean diff. (mm) Device diameter vs SBD < Device diameter vs 2D diameter < Device diameter vs 3D diameter < ASD, atrial septal defect; Mean diff., mean difference; SBD, stretched balloon diameter; 2D diameter, measured by 2D transesophageal echocardiography; 3D diameter, by real-time three-dimensional echocardiography. selection and deployment include balloon-sizing maneuver 16,17 and transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) monitoring. 12,14,15 However, both of these methods have their disadvantages. Balloon-sizing is not very accurate r p and may be associated with three pitfalls. First, balloon-sizing can itself cause damage, enlarging the defect by tearing the flap valve of the septum primum. Second, the accuracy of ASD size measurement depends on the force applied in retrieving the balloon through the defect and on the angle of balloon popping through the septum. Third, balloon-sizing may cause arrhythmias or obstruction of venous return. On the other hand, TEE is a technique that needs general anaesthesia with or without endotracheal intubation, owing to the poor acceptance of an esophageal probe for the entire duration of the procedure and has the potential risks of aspiration, airway obstruction, esophageal perforation, and vocal cord dysfuntcion. 18,19 Two-dimensional TEE imaging is superior to fluoroscopy because it provides clearer imaging. 5 However, only limited structure is shown and the maximal ASD size tends to be underestimated if the probe is not on the line between the longest diameter. In patients with an elongated oval-shaped defect, two-dimensional TEE significantly underestimates the maximal diameter of the ASD. In this series, real-time three-dimensional echocardiography well demonstrated the morphologic characteristics of atrial septal defects. It could present the overall structure of the ASD, which provided information about the position and size in different stage of cardiac cycle, and the actual anatomy of the surrounding rim. It allowed a proper measurement of the ASD and selection of an appropriately sized device, also facilitating all stages of the deployment process monitoring. Our results were compatible with previous findings. 8, Acta Cardiol Sin 2005;21:146 52
5 Chung-Hsien Su et al. The SBD has long been regarded as the gold standard for the measurement of maximal ASD size. 1,13,15,24,25 In this series, the size of ASO was determined according to the measured SBD on the basis of the surrounding anatomical structures presented by RT-3D Echo to assure the success of the deployment. We found good correlation (r = 0.997) between 3D diameter and ASO size, which was even better than the correlation (r = 0.995) between SBD and ASO size. These facts represent that RT-3D Echo showed not only the immediate anatomical characteristics, but also the accurate ASD size which successful deployment most needs. Previous reports have confirmed that 3-D echo is a useful method to evaluate ASD size. 8,20-23 Our study adds a new and quantitative use for RT-3D Echo. First, it proposes a standardized plane for accurate measurements of the ASD. Second, it defines a method for the selection of an ASO device, thus eliminating the cumbersome balloon-sizing maneuver. Third, it identifies the RT-3D Echo four-chamber (or short-axis) section as a view that can replace TEE monitoring during the procedure and avoid the need for general anesthesia. Fourth, RT-3D echo imaging establishes the safety and feasibility of using RT-3D echo alone as an adjunct to fluoroscopy and as the primary means of transcatheter closure of ASDs. Fifth, our study supports the accuracy of RT-3D-Echo-derived ASD evaluation, so as to avoid improper deformation of the circular waist of the ASO when it is stretched into ASD. Therefore, the application of RT-3D Echo provides a useful tool for evaluation of patients preparing for transcatheter septal occlusion. REFERENCES 1. Das GS, Voss G, Jarvis G, et al. Experimental atrial septal defect closure with a new, transcatheter, self-centering device. Circulation 1993;88: Mehta RH, Helmcke F, Nanda NC, et al. Uses and limitations of transthoracic echocardiography in the assessment of atrial septal defect in the adult. Am J Cardiol 1991;67: Godart F, Rey C, Francart C, et al. Two-dimensional echocardiographic and color Doppler measurements of atrial septal defect, and comparison with the balloon-stretched diameter. Am J Cardiol 1993;72: Faletra F, Scarpini S, Moreo A, et al. Color Doppler echocardiographic assessment of atrial septal defect size: correlation with surgical measurements. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1991;4: Hellenbrand WE, Fahey JT, McGowan FX, et al. Transesophageal echocardiographic guidance of transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect. Am J Cardiol 1990;66: Hanrath P, Schluter M, Langenstein BA, et al. Detection of ostium secundum atrial septal defects by transoesophageal cross-sectional echocardiography. Br Heart J 1983;49: Morimoto K, Matsuzaki M, Tohma Y, et al. Diagnosis and quantitative evaluation of secundum-type atrial septal defect by transesophageal Doppler echocardiography. Am J Cardiol 1990; 66: Lange A, Walayat M, Turnbull CM, et al. Assessment of atrial septal defect morphology by transthoracic three-dimensional echocardiography using standard grey scale and Doppler myocardial imaging techniques: comparison with magnetic resonance imaging and intraoperative findings. Heart 1997; 78: Acar P, Maunoury C, Antonietti T, et al. Left ventricular ejection fraction in children measured by three-dimensional echocardiography using a new transthoracic integrated 3D-probe: a comparison with equilibrium radionuclide angiography. Eur Heart J 1998;19: Chu-Chuan Lin, Kai-Sheng Hsieh, Ta-Cheng Huang, et al. Evaluation of complex congenital heart disease with real-time three-dimensional echocardiography. Acta Cardiol Sin 2004; 20: Acar P, Saliba Z, Bonhoeffer P, et al. Influence of atrial septal defect anatomy in patient selection and assessment of closure with the Cardioseal device; a three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiographic reconstruction. Eur Heart J 2000;21: Masura J, Gavora P, Formanek A, Hijazi ZM. Transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects using the new self-centering Amplatzer septal occluder: initial human experience. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn 1997;42: Gu X, Han YM, Berry J, et al. A new technique for sizing of atrial septal defects. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 1999;46: Thanopoulos BD, Laskari CV, Tsaousis GS, et al. Closure of atrial septal defects with the Amplatzer occlusion device: preliminary results. J Am Coll Cardiol 1998;31: Hijazi ZM, Cao Q, Patel HT, et al. Transesophageal echocardiographic results of catheter closure of atrial septal defect in children and adults using the Amplatzer device. Am J Cardiol 2000;85: King TD, Thompson SL, Mills NL. Measurement of atrial septal defect during cardiac catheterization: experimental and clinical results. Am J Cardiol 1978;41: Hijazi ZM, Cao Q, Patel HT, et al. Transesophageal echocardiographic results of catheter closure of atrial septal defect in children and adults using the Amplatzer device. Am J Cardiol 2000;85: Daniel WG, Erbel R, Kasper W, et al. Safety of transesophageal Acta Cardiol Sin 2005;21:
6 RT-3D Echo in Sizing ASD echocardiography: a multicenter survey of 10,419 examinations. Circulation 1991;83: Urbanowicz JH, Kernoff RS, Oppenheim G, et al. Transesophageal echocardiography and its potential for esophageal damage. Anesthesiology 1990;72: Franke A, Kuhl HP, Rulands D, et al. Quantitative analysis of the morphology of secundum-type atrial septal defects and their dynamic change using transesophageal three-dimensional echocardiography. Circulation 1997;96:323II-327II. 21. Acar P, Saliba Z, Bonhoeffer P, et al. Assessment of the geometric profile of the Amplatzer and Cardioseal septal occluders by three-dimensional echocardiography. Heart 2001: 85: Marx GR, Fulton DR, Pandian NG, et al. Delineation of site, relative size and dynamic geometry of atrial septal defects by real-time three-dimensional echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 1995;25: Sugeng L, Weinert L, Thiele K, Lang RM. Real-time three-dimensional echocardiography using a novel matrix array transducer. Echocardiography 2003;20: Berger F, Ewert P, Bjornstad PG, et al. Transcatheter closure as standard treatment for most interatrial defects: experience in 200 patients treated with the Amplatzer Septal Occluder. Cardiol Young 1999;9: Chan KC, Godcxman MJ, Walsh K, et al. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect and interatrial communications with a new self expanding nitinol double disc device (Amplatzer septal occluder): multicentre UK experience. Heart 1999;82: Acta Cardiol Sin 2005;21:146 52
7 Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2005;21: ( 11.6 ± 8.2 ) 2.4 ± 1.9 ( : ) 23.1 ± 9.2 ( : 7-36 ) 19.9 ± 7.6 ( : ) 19.2 ± 7.1 ( : ) 21.2 ± 9.0 ( : ) 166 ± 5.4 (r = 0.995) (r = 0.987) (r = 0.997) (r = 0.997) 152
Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure
 Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure L. LUANN MINICH, M.D., and A. REBECCA SNIDER, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, C.S. Mott Children
Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure L. LUANN MINICH, M.D., and A. REBECCA SNIDER, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, C.S. Mott Children
Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defects with Superior-anterior Rim Deficiency Using Amplatzer Septal Occluder
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defects with Superior-anterior Rim Deficiency Using Amplatzer Septal Occluder Chien-Fu Huang, 1 Chih-Yuan Fang, 2 Sheung-Fat Ko, 3 Shao-Ju Chien,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defects with Superior-anterior Rim Deficiency Using Amplatzer Septal Occluder Chien-Fu Huang, 1 Chih-Yuan Fang, 2 Sheung-Fat Ko, 3 Shao-Ju Chien,
Feasibility of real-time three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography for guidance of percutaneous atrial septal defect closure
 European Journal of Echocardiography (2009) 10, 543 548 doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jen337 Feasibility of real-time three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography for guidance of percutaneous atrial septal
European Journal of Echocardiography (2009) 10, 543 548 doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jen337 Feasibility of real-time three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography for guidance of percutaneous atrial septal
ATRIAL SEPTAL CLOSURE AND LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE OCCLUSION: INDICATIONS AND GUIDANCE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGY
 ATRIAL SEPTAL CLOSURE AND LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE OCCLUSION: INDICATIONS AND GUIDANCE Aristides G. Panlilio, MD, FPCP, FPCC,FPSE, FASE Philippine Heart Center Chinese General Hospital and Medical Center
ATRIAL SEPTAL CLOSURE AND LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE OCCLUSION: INDICATIONS AND GUIDANCE Aristides G. Panlilio, MD, FPCP, FPCC,FPSE, FASE Philippine Heart Center Chinese General Hospital and Medical Center
Outcome of Transcatheter Closure of Oval Shaped Atrial Septal Defect with Amplatzer Septal Occluder
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.5.1104 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 54(5):1104-1109, 2013 Outcome of Transcatheter Closure of Oval Shaped Atrial Septal Defect
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.5.1104 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 54(5):1104-1109, 2013 Outcome of Transcatheter Closure of Oval Shaped Atrial Septal Defect
Jian Fang 1, Shaobo Xie 2, Lunchao Ma 2, Chao Yang 2. Original Article
 Original Article Anatomic and surgical factors affecting the switch from minimally invasive transthoracic occlusion to open surgery during ventricular septal defect repair Jian Fang 1, Shaobo Xie 2, Lunchao
Original Article Anatomic and surgical factors affecting the switch from minimally invasive transthoracic occlusion to open surgery during ventricular septal defect repair Jian Fang 1, Shaobo Xie 2, Lunchao
2D/3D in Evaluation of Atrial Septum
 2D/3D in Evaluation of Atrial Septum Roberto M Lang, MD OSTIUM SECUNDUM ASD: 2D AND 3D TNSESOPHAGEAL ECHO 1 Biplane views 90 0 3D Acquisi on Acquire 3D volume Lang RM et al. JASE 2012;25:3 46. Right atrial
2D/3D in Evaluation of Atrial Septum Roberto M Lang, MD OSTIUM SECUNDUM ASD: 2D AND 3D TNSESOPHAGEAL ECHO 1 Biplane views 90 0 3D Acquisi on Acquire 3D volume Lang RM et al. JASE 2012;25:3 46. Right atrial
Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects with transthoracic echocardiography
 Cardiology in the Young (2011), 21, 204 208 doi:10.1017/s1047951110001782 r Cambridge University Press, 2010 Original Article Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects with transthoracic echocardiography
Cardiology in the Young (2011), 21, 204 208 doi:10.1017/s1047951110001782 r Cambridge University Press, 2010 Original Article Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects with transthoracic echocardiography
Contemporary echocardiographic guiding tools for device closure of interatrial communications
 Review Article Contemporary echocardiographic guiding tools for device closure of interatrial communications Thomas Bartel, Silvana Müller Department of Medicine, Cardiology Division (Cardiology), Innsbruck
Review Article Contemporary echocardiographic guiding tools for device closure of interatrial communications Thomas Bartel, Silvana Müller Department of Medicine, Cardiology Division (Cardiology), Innsbruck
Original Article Safe and effective guidance by intracardiac echocardiography for transcatheter closure in atrial septal defects
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(6):9815-9819 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0006687 Original Article Safe and effective guidance by intracardiac echocardiography for transcatheter closure in atrial septal
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(6):9815-9819 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0006687 Original Article Safe and effective guidance by intracardiac echocardiography for transcatheter closure in atrial septal
Atrial Septal Defect Closure. Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs
 Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs ADVANCED ANGIOPLASTY Incorporating The Left Main 5 Plus Course Conflicts of Interest The following companies have supported educational courses held
Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs ADVANCED ANGIOPLASTY Incorporating The Left Main 5 Plus Course Conflicts of Interest The following companies have supported educational courses held
Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia
 Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
When Does 3D Echo Make A Difference?
 When Does 3D Echo Make A Difference? Wendy Tsang, MD, SM Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Toronto General Hospital, University Health Network 1 Practical Applications of 3D Echocardiography Recommended
When Does 3D Echo Make A Difference? Wendy Tsang, MD, SM Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Toronto General Hospital, University Health Network 1 Practical Applications of 3D Echocardiography Recommended
IMAGES. in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. PMCID: PMC3232598 Three-dimensional trans-esophageal Echocardiographic Evaluation of Atrial Septal Defects: A Pictorial Essay Vinay K Sharma, S
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. PMCID: PMC3232598 Three-dimensional trans-esophageal Echocardiographic Evaluation of Atrial Septal Defects: A Pictorial Essay Vinay K Sharma, S
Intracardiac Echocardiography-Guided Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect A New Efficient Device Selection Method
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 42, No. 9, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(03)01231-2
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 42, No. 9, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(03)01231-2
Hybrid Muscular VSD Closure in Small Weight Children
 Hybrid Muscular VSD Closure in Small Weight Children Shakeel A Qureshi, on behalf of: John P. Cheatham, MD George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Director Cardiac Catheterization &
Hybrid Muscular VSD Closure in Small Weight Children Shakeel A Qureshi, on behalf of: John P. Cheatham, MD George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Director Cardiac Catheterization &
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Revealing new insights. irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging. Ultrasound cardiology. irotate and xplane
 Ultrasound cardiology irotate and xplane Revealing new insights irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging Annemien van den Bosch and Jackie McGhie Department of Cardiology, Erasmus
Ultrasound cardiology irotate and xplane Revealing new insights irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging Annemien van den Bosch and Jackie McGhie Department of Cardiology, Erasmus
A case report: Percutaneous transcatheter treatment of Lutembacher syndrome
 A case report: Percutaneous transcatheter treatment of Lutembacher syndrome Dr. Sainath Hegde* Dr. Tukaram Aute** *Registrar, Dept of Cardiology, M.G.M Hospital, Aurangabad. **Asst. Prof, Dept of Cardiology,
A case report: Percutaneous transcatheter treatment of Lutembacher syndrome Dr. Sainath Hegde* Dr. Tukaram Aute** *Registrar, Dept of Cardiology, M.G.M Hospital, Aurangabad. **Asst. Prof, Dept of Cardiology,
Assessing ASDs prior to device closure using 3D echocardiography. Just pretty pictures or a useful clinical tool?
 European Journal of Echocardiography (2008) 9, 478 482 doi:10.1016/j.euje.2007.07.001 Assessing ASDs prior to device closure using 3D echocardiography. Just pretty pictures or a useful clinical tool? G.J.
European Journal of Echocardiography (2008) 9, 478 482 doi:10.1016/j.euje.2007.07.001 Assessing ASDs prior to device closure using 3D echocardiography. Just pretty pictures or a useful clinical tool? G.J.
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We. ACHD Patients
 Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Predictors of unfavorable outcome after atrial septal defect closure in adults
 after atrial septal defect closure in adults H. M. Gabriel 1, M. Humenberger 1, R. Rosenhek 1, GP. Diller 2, G. Kaleschke 2, TH. Binder 1, P. Probst 1, G. Maurer 1, H. Baumgartner 2 (1) Medical University
after atrial septal defect closure in adults H. M. Gabriel 1, M. Humenberger 1, R. Rosenhek 1, GP. Diller 2, G. Kaleschke 2, TH. Binder 1, P. Probst 1, G. Maurer 1, H. Baumgartner 2 (1) Medical University
A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Method for
 Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 1(1), 59-64 (1999) INVITED PAPER Use of MRI in ASD Asessment A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Method for Evaluating Atrial Septa1 Defects Godtfred Holmvang Cardiac
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 1(1), 59-64 (1999) INVITED PAPER Use of MRI in ASD Asessment A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Method for Evaluating Atrial Septa1 Defects Godtfred Holmvang Cardiac
Midter m Outcomes of Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defect Using the Amplatzer Septal Occluder in Children
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2005;10:251-256 Midter m Outcomes of Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defect Using the Amplatzer Septal Occluder in Children AKT CHAU, BHY CHUNG, KS LUN, YF CHEUNG, TC
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2005;10:251-256 Midter m Outcomes of Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defect Using the Amplatzer Septal Occluder in Children AKT CHAU, BHY CHUNG, KS LUN, YF CHEUNG, TC
AMPLATZER Septal Occluder Structural Heart Therapy. Over 15 years of. Demonstrated. Clinical Experience. We ll show you our data. Ask to see theirs.
 AMPLATZER Septal Occluder Structural Heart Therapy Over 15 years of Demonstrated Clinical Experience We ll show you our data. Ask to see theirs. Leading the Standard of Care 1,2 The AMPLATZER Septal Occluder
AMPLATZER Septal Occluder Structural Heart Therapy Over 15 years of Demonstrated Clinical Experience We ll show you our data. Ask to see theirs. Leading the Standard of Care 1,2 The AMPLATZER Septal Occluder
Percutaneous atrial septal defect closure with the Occlutech Figulla Flex ASD Occluder.
 Percutaneous atrial septal defect closure with the Occlutech Figulla Flex ASD Occluder. First case with a novel delivery system. Werner Budts, Md, PhD, FESC Congenital and Structural Cardiology University
Percutaneous atrial septal defect closure with the Occlutech Figulla Flex ASD Occluder. First case with a novel delivery system. Werner Budts, Md, PhD, FESC Congenital and Structural Cardiology University
Device Closure of ASD in Children Using the Amplatzer Devices: Indications and catheter preparations, technique, and outcome [15]
![Device Closure of ASD in Children Using the Amplatzer Devices: Indications and catheter preparations, technique, and outcome [15] Device Closure of ASD in Children Using the Amplatzer Devices: Indications and catheter preparations, technique, and outcome [15]](/thumbs/73/69533656.jpg) Device Closure of ASD in Children Using the Amplatzer Devices: Indications and catheter preparations, technique, and outcome [15] SCAI Fellow Course Fall 2014 Ralf J Holzer MD MSc FSCAI Medical Director
Device Closure of ASD in Children Using the Amplatzer Devices: Indications and catheter preparations, technique, and outcome [15] SCAI Fellow Course Fall 2014 Ralf J Holzer MD MSc FSCAI Medical Director
Original Article Safe and efectivef guidance by intracardiac echocardiography for transcatheter closure in atrial septal defects
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(5):8015-8019 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0007568 Original Article Safe and efectivef guidance by intracardiac echocardiography for transcatheter closure in atrial septal
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(5):8015-8019 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0007568 Original Article Safe and efectivef guidance by intracardiac echocardiography for transcatheter closure in atrial septal
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 33, No. 5, by the American College of Cardiology ISSN /99/$20.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 33, No. 5, 1999 1999 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(99)00011-X Transcatheter
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 33, No. 5, 1999 1999 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(99)00011-X Transcatheter
Intracardiac echocardiography: an ideal guiding tool for device closure of interatrial communications
 Eur J Echocardiography (2005) 6, 92e96 Intracardiac echocardiography: an ideal guiding tool for device closure of interatrial communications Thomas Bartel a, *, Thomas Konorza a, Ulrich Neudorf b, Tiko
Eur J Echocardiography (2005) 6, 92e96 Intracardiac echocardiography: an ideal guiding tool for device closure of interatrial communications Thomas Bartel a, *, Thomas Konorza a, Ulrich Neudorf b, Tiko
INTEGRATING ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY WITH CATHETER INTERVENTIONS FOR CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE. Krishna Kumar SevenHills Hospital, Mumbai, India
 INTEGRATING ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY WITH CATHETER INTERVENTIONS FOR CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Krishna Kumar SevenHills Hospital, Mumbai, India Why talk about it? What is the big deal? Are we not stating the obvious?
INTEGRATING ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY WITH CATHETER INTERVENTIONS FOR CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Krishna Kumar SevenHills Hospital, Mumbai, India Why talk about it? What is the big deal? Are we not stating the obvious?
Determinants of Cardiopulmonary Functional Improvement After Transcatheter Atrial Septal Defect Closure in Asymptomatic Adults
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 43, No. 10, 2004 2004 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/04/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2003.10.067
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 43, No. 10, 2004 2004 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/04/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2003.10.067
Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defects in a Center With Limited Resources: Outcomes and Short Term Follow-Up
 Iran J Pediatr. 2015 December; 25(6): e3906. Published online 2015 December 23. doi: 10.5812/ijp.3906 Research Article Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defects in a Center With Limited Resources:
Iran J Pediatr. 2015 December; 25(6): e3906. Published online 2015 December 23. doi: 10.5812/ijp.3906 Research Article Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defects in a Center With Limited Resources:
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Three-dimensional echocardiography in the clinical world
 Three-dimensional echocardiography in the clinical world Dr. JL Zamorano Director CV Institute University Clinic SC, Madrid Advantages of 3D. Spatial manipulation. Optimal alineation of structures. Views
Three-dimensional echocardiography in the clinical world Dr. JL Zamorano Director CV Institute University Clinic SC, Madrid Advantages of 3D. Spatial manipulation. Optimal alineation of structures. Views
Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defects in the Elderly
 REVIEW DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.2.47 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defects in the Elderly
REVIEW DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.2.47 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defects in the Elderly
Percutaneous VSD closure
 Percutaneous VSD closure Gianfranco Butera San Donato Milanese - Italy Patients selection Pts having hemodynamically significant VSD Left ventricular enlargement (left ventricular overload),defined as
Percutaneous VSD closure Gianfranco Butera San Donato Milanese - Italy Patients selection Pts having hemodynamically significant VSD Left ventricular enlargement (left ventricular overload),defined as
6). However, for cases in which an ASO cannot
 Hiroshima J. Med. Sci. Vol. 64, No. 1 2, 1~7, June, 1 HIJM 64 1 1 A Logical Method of Selecting an Approach for Amplatzer Septal Occluder Implantation: Using Transesophageal Echocardiography to Reduce
Hiroshima J. Med. Sci. Vol. 64, No. 1 2, 1~7, June, 1 HIJM 64 1 1 A Logical Method of Selecting an Approach for Amplatzer Septal Occluder Implantation: Using Transesophageal Echocardiography to Reduce
Eight-French Intracardiac Echocardiography
 Circulation Journal Official Journal of the Japanese Circulation Society http://www.j-circ.or.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiovascular Intervention Eight-French Intracardiac Echocardiography Safe and Effective
Circulation Journal Official Journal of the Japanese Circulation Society http://www.j-circ.or.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiovascular Intervention Eight-French Intracardiac Echocardiography Safe and Effective
Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defects: Results in Patients with Large and Extreme Defects
 Heart, Lung and Circulation (2014) 23, 127 131 1443-9506/04/$36.00 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hlc.2013.07.020 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defects: Results in Patients
Heart, Lung and Circulation (2014) 23, 127 131 1443-9506/04/$36.00 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hlc.2013.07.020 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defects: Results in Patients
Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect Area Changes During Cardiac Cycle by Live Three-Dimensional Echocardiography
 J Cardiol 2006 Apr; 47 4 : 181 187 Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect Area Changes During Cardiac Cycle by Live Three-Dimensional Echocardiography Ming-Xing Ling-Yun Xin-Fang Qing Xiao-Fang Ya-Li Jing
J Cardiol 2006 Apr; 47 4 : 181 187 Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect Area Changes During Cardiac Cycle by Live Three-Dimensional Echocardiography Ming-Xing Ling-Yun Xin-Fang Qing Xiao-Fang Ya-Li Jing
Surgical Approach To An Unsuccessful Device Closure of Atrial Septal Defect. U Yetkin, B Özpak,? Yürekli, K Ergüne?, N Eren, O Ergene, A Gürbüz
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Surgical Approach To An Unsuccessful Device Closure of Atrial Septal Defect U Yetkin, B Özpak,? Yürekli, K Ergüne?,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Surgical Approach To An Unsuccessful Device Closure of Atrial Septal Defect U Yetkin, B Özpak,? Yürekli, K Ergüne?,
Experience with Intracardiac Echocardiography for Guiding Transcatheter Device Closure of Atrial Septal Defects
 Original ORIGINAL Article ARTICLE Korean Circulation J 2006;36:612-616 ISSN 1738-5520 c 2006, The Korean Society of Circulation Experience with Intracardiac Echocardiography for Guiding Transcatheter Device
Original ORIGINAL Article ARTICLE Korean Circulation J 2006;36:612-616 ISSN 1738-5520 c 2006, The Korean Society of Circulation Experience with Intracardiac Echocardiography for Guiding Transcatheter Device
Transcatheter closure of the patent ductus arteriosus using the new Amplatzer duct occluder: Initial clinical applications in children
 Transcatheter closure of the patent ductus arteriosus using the new Amplatzer duct occluder: Initial clinical applications in children Basil Thanopoulos, MD, PhD, a Nikolaos Eleftherakis, MD, a Konstantinos
Transcatheter closure of the patent ductus arteriosus using the new Amplatzer duct occluder: Initial clinical applications in children Basil Thanopoulos, MD, PhD, a Nikolaos Eleftherakis, MD, a Konstantinos
Multimodality Imaging of Septal Defects
 Multimodality Imaging of Septal Defects Ohio-ACC 2018 Annual Meeting October 27, 2018 Kan N. Hor, MD Director, Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging Associate Professor of Pediatrics The Heart Center, Nationwide
Multimodality Imaging of Septal Defects Ohio-ACC 2018 Annual Meeting October 27, 2018 Kan N. Hor, MD Director, Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging Associate Professor of Pediatrics The Heart Center, Nationwide
ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗ ΑΣΘΕΝΩΝ ΜΕ ΜΕΣΟΚΟΛΠΙΚΗ ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΑ ΖΑΧΑΡΑΚΗ ΑΓΓΕΛΙΚΗ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΗΡΑΚΛΕΙΟ - ΚΡΗΤΗ
 ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗ ΑΣΘΕΝΩΝ ΜΕ ΜΕΣΟΚΟΛΠΙΚΗ ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΑ ΖΑΧΑΡΑΚΗ ΑΓΓΕΛΙΚΗ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΗΡΑΚΛΕΙΟ - ΚΡΗΤΗ European Accreditation in TTE, TEE and CHD Echocardiography NOTHING TO DECLARE ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT TYPES SECUNDUM
ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗ ΑΣΘΕΝΩΝ ΜΕ ΜΕΣΟΚΟΛΠΙΚΗ ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΑ ΖΑΧΑΡΑΚΗ ΑΓΓΕΛΙΚΗ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΗΡΑΚΛΕΙΟ - ΚΡΗΤΗ European Accreditation in TTE, TEE and CHD Echocardiography NOTHING TO DECLARE ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT TYPES SECUNDUM
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List Cardiology
 Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List Cardiology Category CPT Code CPT Code Description 33206 Insertion of new or replacement of permanent pacemaker with transvenous electrode(s); atrial 33207 Insertion
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List Cardiology Category CPT Code CPT Code Description 33206 Insertion of new or replacement of permanent pacemaker with transvenous electrode(s); atrial 33207 Insertion
For Personal Use. Copyright HMP 2013
 Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(2):E42-E44 Percutaneous Closure of Iatrogenic Ventricular Septal Defect Following Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement Using Two Different Approaches Takashi Matsumoto,
Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(2):E42-E44 Percutaneous Closure of Iatrogenic Ventricular Septal Defect Following Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement Using Two Different Approaches Takashi Matsumoto,
Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect in Patients Over 60 Years Old
 Original Article Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect in Patients Over 60 Years Old Saet Byul Woo, MD 1, So-Ick
Original Article Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect in Patients Over 60 Years Old Saet Byul Woo, MD 1, So-Ick
Transcatheter Atrial Septal Defect Closure with Right Aortic Arch Is it really difficult? M Tokue, H Hara, K Sugi, M Nakamura
 5th Asia Pacific Congenital & Structural Heart Intervention Symposium 2014 10 12 October 2014, Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre Organizer: Hong Kong Society of Congenital & Structural Heart Disease
5th Asia Pacific Congenital & Structural Heart Intervention Symposium 2014 10 12 October 2014, Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre Organizer: Hong Kong Society of Congenital & Structural Heart Disease
Early and Late Complications Associated With Transcatheter Occlusion of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 39, No. 6, 2002 2002 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/02/$22.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(02)01711-4
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 39, No. 6, 2002 2002 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/02/$22.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(02)01711-4
Fabien Praz, Andreas Wahl, Sophie Beney, Stephan Windecker, Heinrich P. Mattle*, Bernhard Meier
 Procedural Outcome after Percutaneous Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale using the Amplatzer PFO Occluder Without Intra-Procedural Echocardiography in 1,000 Patients Fabien Praz, Andreas Wahl, Sophie Beney,
Procedural Outcome after Percutaneous Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale using the Amplatzer PFO Occluder Without Intra-Procedural Echocardiography in 1,000 Patients Fabien Praz, Andreas Wahl, Sophie Beney,
Secundum atrial septal defect (ASD) is a common congenital heart disease and
 Device closure of atrial septal defects with the Amplatzer septal occluder: Safety and outcome in infants Karim A. Diab, MD, a Qi-Ling Cao, MD, a Emile A. Bacha, MD, b and Ziyad M. Hijazi, MD, MPH a Objective:
Device closure of atrial septal defects with the Amplatzer septal occluder: Safety and outcome in infants Karim A. Diab, MD, a Qi-Ling Cao, MD, a Emile A. Bacha, MD, b and Ziyad M. Hijazi, MD, MPH a Objective:
Real-Time Three-Dimensional Transesophageal Echocardiography in Transcutaneous, Catheter-Based Procedures for Repair of Structural Heart Diseases
 Real-Time Three-Dimensional Transesophageal Echocardiography in Transcutaneous, Catheter-Based Procedures for Repair of Structural Heart Diseases Gila Perk, MD, Carlos Ruiz, MD, PhD, Muhamed Saric, MD,
Real-Time Three-Dimensional Transesophageal Echocardiography in Transcutaneous, Catheter-Based Procedures for Repair of Structural Heart Diseases Gila Perk, MD, Carlos Ruiz, MD, PhD, Muhamed Saric, MD,
Left atrial function. Aliakbar Arvandi MD
 In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis
 JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis Similarities and differences in Tricuspid vs. Mitral Valve Anatomy and Imaging. Echo evaluation
JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis Similarities and differences in Tricuspid vs. Mitral Valve Anatomy and Imaging. Echo evaluation
The earliest application of intracardiac imaging
 Intracardiac Echocardiography for Structural Heart Defects A review of ICE innovations, devices, and techniques. BY ZAHID AMIN, MD; QI-LING CAO, MD; AND ZIYAD M. HIJAZI, MD The earliest application of
Intracardiac Echocardiography for Structural Heart Defects A review of ICE innovations, devices, and techniques. BY ZAHID AMIN, MD; QI-LING CAO, MD; AND ZIYAD M. HIJAZI, MD The earliest application of
Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD
 Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD John P. Cheatham, MD, MSCAI George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Co-Director, The Heart Center, Nationwide Children s Hospital Professor, Pediatrics
Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD John P. Cheatham, MD, MSCAI George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Co-Director, The Heart Center, Nationwide Children s Hospital Professor, Pediatrics
Transesophageal Echocardiography in Children: An Interactive Session on Common Congenital Cardiac Defects
 Transesophageal Echocardiography in Children: An Interactive Session on Common Congenital Cardiac Defects Wanda C. Miller-Hance, M.D. Objective: At the conclusion of this workshop the participant should
Transesophageal Echocardiography in Children: An Interactive Session on Common Congenital Cardiac Defects Wanda C. Miller-Hance, M.D. Objective: At the conclusion of this workshop the participant should
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
EDITOR S PICK CURRENT STATUS OF FULLY AUTOMATED SOFTWARE WITH THREE-DIMENSIONAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY FOR THE QUANTIFICATION OF LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION
 ITOR S PICK This paper, courtesy of Yang and Takeuchi, provides a timely and well-considered update on the current status of fully-automated software with three-dimensional echocardiography for quantifying
ITOR S PICK This paper, courtesy of Yang and Takeuchi, provides a timely and well-considered update on the current status of fully-automated software with three-dimensional echocardiography for quantifying
Conflict of Interests
 The Left Ventricle: How Should We Quantify Its Size and Function; Is It Time for 3D in Everyone? Roberto M Lang, MD Conflict of Interests Philips Medical Imaging Research Grants Speakers bureau Advisory
The Left Ventricle: How Should We Quantify Its Size and Function; Is It Time for 3D in Everyone? Roberto M Lang, MD Conflict of Interests Philips Medical Imaging Research Grants Speakers bureau Advisory
ENVIRONMENT Operating Room, Simulation Suite, Echo Lab. Operating Room, Simulation Suite. Simulation Suite, Echo Lab.
 Goals and Objectives, Perioperative Transesophageal Echocardiography, CA-3 year UCSD DEPARTMENT OF ANESTHESIOLOGY PERIOPERATIVE TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY GOALS AND OBJECTIVES, CA-3 YEAR PATIENT
Goals and Objectives, Perioperative Transesophageal Echocardiography, CA-3 year UCSD DEPARTMENT OF ANESTHESIOLOGY PERIOPERATIVE TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY GOALS AND OBJECTIVES, CA-3 YEAR PATIENT
Welcome Number 6. The background of the Cardiac Sonographer Network News masthead is a diagnostic image:
 Number 6 Welcome Number 6 Welcome to the newsletter created just for you: sonographers who perform pediatric echocardiograms in primarily adult echo labs. Each issue features tips on echocardiography of
Number 6 Welcome Number 6 Welcome to the newsletter created just for you: sonographers who perform pediatric echocardiograms in primarily adult echo labs. Each issue features tips on echocardiography of
Diagnostic approach to heart disease
 Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
Introduction. Sébastien Hascoet 1,2 *, Khaled Hadeed 1, Pauline Marchal 1, Yves Dulac 1, Xavier Alacoque 3, Francois Heitz 4, and Philippe Acar 1
 European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging (2015) 16, 747 755 doi:10.1093/ehjci/jeu316 The relation between atrial septal defect shape, diameter, and area using three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography
European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging (2015) 16, 747 755 doi:10.1093/ehjci/jeu316 The relation between atrial septal defect shape, diameter, and area using three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography
Percutaneous occluder device closure through femoral vein guidance by transthoracic echocardiography in adult atrial septal defect patients
 Original Article Percutaneous occluder device closure through femoral vein guidance by transthoracic echocardiography in adult atrial septal defect patients Yixin Jia, Xu Meng, Yan Li, Chunlei Xu, Wen
Original Article Percutaneous occluder device closure through femoral vein guidance by transthoracic echocardiography in adult atrial septal defect patients Yixin Jia, Xu Meng, Yan Li, Chunlei Xu, Wen
Treatment of Inter-MitraClip Regurgitation Due to Posterior Leaflet Cleft by Use of The Amplatzer Vascular Plug II device
 Volume 1, Issue 3 Case Report ISSN: 2572-9292 Treatment of Inter-MitraClip Regurgitation Due to Posterior Leaflet Cleft by Use of The Amplatzer Vascular Plug II device Neha M. Mantri, Gagan D. Singh, Thomas
Volume 1, Issue 3 Case Report ISSN: 2572-9292 Treatment of Inter-MitraClip Regurgitation Due to Posterior Leaflet Cleft by Use of The Amplatzer Vascular Plug II device Neha M. Mantri, Gagan D. Singh, Thomas
Little is known about the degree and time course of
 Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Reliability of Echocardiography Measurement of Patent Ductus Arteriosus Minimum Diameter: A Meta-analysis
 International Journal of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease 4(): 15-19, 016 DOI: 10.13189/ijccd.016.04001 http://www.hrpub.org Reliability of Echocardiography Measurement of Patent Ductus Arteriosus
International Journal of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease 4(): 15-19, 016 DOI: 10.13189/ijccd.016.04001 http://www.hrpub.org Reliability of Echocardiography Measurement of Patent Ductus Arteriosus
evicore cardiology procedures and services requiring prior authorization
 evicore cardiology procedures and services requiring prior authorization Moda Health Commercial Group and Individual Members* *Check EBT to verify member enrollment in evicore program Radiology Advanced
evicore cardiology procedures and services requiring prior authorization Moda Health Commercial Group and Individual Members* *Check EBT to verify member enrollment in evicore program Radiology Advanced
Imaging Evaluation of the Ventricular Septum
 Imaging Evaluation of the Ventricular Septum Craig E Fleishman, MD FACC FASE The Heart Center at Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando SCAI Fall Fellows Course 2013 Las Vegas Disclosure Information
Imaging Evaluation of the Ventricular Septum Craig E Fleishman, MD FACC FASE The Heart Center at Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando SCAI Fall Fellows Course 2013 Las Vegas Disclosure Information
Clinical material and methods. Fukui Cardiovascular Center, Fukui, Japan
 Mitral Valve Regurgitation after Atrial Septal Defect Repair in Adults Shohei Yoshida, Satoshi Numata, Yasushi Tsutsumi, Osamu Monta, Sachiko Yamazaki, Hiroyuki Seo, Takaaki Samura, Hirokazu Ohashi Fukui
Mitral Valve Regurgitation after Atrial Septal Defect Repair in Adults Shohei Yoshida, Satoshi Numata, Yasushi Tsutsumi, Osamu Monta, Sachiko Yamazaki, Hiroyuki Seo, Takaaki Samura, Hirokazu Ohashi Fukui
Learning Objectives. Denver Health Medical Center. Nothing to Disclose... Advanced Topics in Anesthesia
 Nothing to Disclose... Learning Objectives 1. Describe which clinical situations are appropriate for TEE monitoring in noncardiac surgery including indications / contraindications for TEE placement. 2.
Nothing to Disclose... Learning Objectives 1. Describe which clinical situations are appropriate for TEE monitoring in noncardiac surgery including indications / contraindications for TEE placement. 2.
For Personal Use. Copyright HMP 2013
 12-00415 Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(4):E69-E71 A Concert in the Heart. Bilateral Melody Valve Implantation in the Branch Pulmonary Arteries Nicola Maschietto, MD, PhD and Ornella Milanesi,
12-00415 Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(4):E69-E71 A Concert in the Heart. Bilateral Melody Valve Implantation in the Branch Pulmonary Arteries Nicola Maschietto, MD, PhD and Ornella Milanesi,
Closure of Atrial Septal Defects With the Amplatzer Occlusion Device: Preliminary Results
 1110 JACC Vol. 31, No. 5 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Closure of Atrial Septal Defects With the Amplatzer Occlusion Device: Preliminary Results BASIL (VASILIOS) D. THANOPOULOS, MD, CLEO V. LASKARI, MD, GEORGE
1110 JACC Vol. 31, No. 5 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Closure of Atrial Septal Defects With the Amplatzer Occlusion Device: Preliminary Results BASIL (VASILIOS) D. THANOPOULOS, MD, CLEO V. LASKARI, MD, GEORGE
Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defect Preserves Right Ventricular Function
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defect Preserves Right Ventricular Function CARDIOLOGY Research Article Osama Sanad Arafa 1, Tarek HelmyAboelazm 1, Shaimaa Ahmed Mostafa 1 *,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defect Preserves Right Ventricular Function CARDIOLOGY Research Article Osama Sanad Arafa 1, Tarek HelmyAboelazm 1, Shaimaa Ahmed Mostafa 1 *,
Cardiology Fellowship Manual. Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 P a g e
 Cardiology Fellowship Manual Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 P a g e UNIV. OF NEBRASKA CHILDREN S HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENTER DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM CARDIAC IMAGING ROTATION GOALS
Cardiology Fellowship Manual Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 P a g e UNIV. OF NEBRASKA CHILDREN S HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENTER DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM CARDIAC IMAGING ROTATION GOALS
Transesophageal Doppler Color Flow Mapping Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect
 11 lacc Vol. 16. No.4 October 199: 11-6 Transesophageal Doppler Color Flow Mapping Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect RAJENDRA H. MEHTA, MD, FREDERCK HELMCKE, MD, NAVN C. NANDA, MD, FACC, MNG HSUNG, MD,*
11 lacc Vol. 16. No.4 October 199: 11-6 Transesophageal Doppler Color Flow Mapping Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect RAJENDRA H. MEHTA, MD, FREDERCK HELMCKE, MD, NAVN C. NANDA, MD, FACC, MNG HSUNG, MD,*
The role of intraoperative TOE in congenital cardiac surgery
 The role of intraoperative TOE in congenital cardiac surgery Justiaan Swanevelder Dept of Anaesthesia Groote Schuur and Red Cross War Memorial Children s Hospitals University of Cape Town, South Africa
The role of intraoperative TOE in congenital cardiac surgery Justiaan Swanevelder Dept of Anaesthesia Groote Schuur and Red Cross War Memorial Children s Hospitals University of Cape Town, South Africa
For Personal Use. Copyright HMP 2013
 Case Report With Brief Review J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(4):E78-E80 Percutaneous Transjugular Device Closure of Postoperative Residual Atrial Septal Defect Saktheeswaran Mahesh Kumar, MD, DM, Sasidharan
Case Report With Brief Review J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(4):E78-E80 Percutaneous Transjugular Device Closure of Postoperative Residual Atrial Septal Defect Saktheeswaran Mahesh Kumar, MD, DM, Sasidharan
Case Report Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect as a Cause of Palpitations and Dyspnea in an Adult: A Diagnostic Imaging Challenge
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 128462, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/128462 Case Report Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect as a Cause of Palpitations and Dyspnea in an Adult:
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 128462, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/128462 Case Report Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect as a Cause of Palpitations and Dyspnea in an Adult:
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research
 Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Ko et al. CT and Echocardiography of trial Septal Defect Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Sheung-Fat Ko 1 Chi-Di Liang 2 Hon-Kan Yip 3 Chung-Cheng Huang
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Ko et al. CT and Echocardiography of trial Septal Defect Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Sheung-Fat Ko 1 Chi-Di Liang 2 Hon-Kan Yip 3 Chung-Cheng Huang
Part II: Fundamentals of 3D Echocardiography: Acquisition and Application
 Part II: Fundamentals of 3D Echocardiography: Acquisition and Application Dr. Bruce Bollen 3D matrix array TEE probes provide options for both 2D and 3D imaging. Indeed, their utility in obtaining multiple
Part II: Fundamentals of 3D Echocardiography: Acquisition and Application Dr. Bruce Bollen 3D matrix array TEE probes provide options for both 2D and 3D imaging. Indeed, their utility in obtaining multiple
Original Article. Non Surgical Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect by Percutaneous Transcatheter Amplatzer Septal Occluder.
 Non Surgical Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect by Percutaneous Transcatheter Amplatzer Septal Occluder Original Article M. Abdullah* Sadiq M. Alhammash* Ali K. Kuraidi* Isam Victor* Muthanna H.
Non Surgical Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect by Percutaneous Transcatheter Amplatzer Septal Occluder Original Article M. Abdullah* Sadiq M. Alhammash* Ali K. Kuraidi* Isam Victor* Muthanna H.
Bogdan A. Popescu. University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania. EAE Course, Bucharest, April 2010
 Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania EAE Course, Bucharest, April 2010 This is how it started Mitral stenosis at a glance 2D echo narrow diastolic opening of MV leaflets
Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania EAE Course, Bucharest, April 2010 This is how it started Mitral stenosis at a glance 2D echo narrow diastolic opening of MV leaflets
Case Report Hemostasis of Left Atrial Appendage Bleed With Lariat Device
 273 Case Report Hemostasis of Left Atrial Appendage Bleed With Lariat Device Amena Hussain MD, Muhamed Saric MD, Scott Bernstein MD, Douglas Holmes MD, Larry Chinitz MD NYU Langone Medical Center, United
273 Case Report Hemostasis of Left Atrial Appendage Bleed With Lariat Device Amena Hussain MD, Muhamed Saric MD, Scott Bernstein MD, Douglas Holmes MD, Larry Chinitz MD NYU Langone Medical Center, United
MITRAL STENOSIS. Joanne Cusack
 MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defect with Amplatzer Device in Children and Adolescents: Short and Midterm results; an Iranian Experience
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Jun 2011; Vol 21 (No 2), Pp: 166-172 Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defect with Amplatzer Device in Children and Adolescents: Short and Midterm results; an Iranian
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Jun 2011; Vol 21 (No 2), Pp: 166-172 Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defect with Amplatzer Device in Children and Adolescents: Short and Midterm results; an Iranian
A challenging case of successful ASD closure without echocardiographic guidance in an 86-year old with severe kyphoscoliosis and platypnoeaorthodeoxia
 A challenging case of successful ASD closure without echocardiographic guidance in an 86-year old with severe kyphoscoliosis and platypnoeaorthodeoxia syndrome. Dr Anvesha Singh, Dr James Ogle, Dr Derek
A challenging case of successful ASD closure without echocardiographic guidance in an 86-year old with severe kyphoscoliosis and platypnoeaorthodeoxia syndrome. Dr Anvesha Singh, Dr James Ogle, Dr Derek
Glenmark Cardiac Centre Mumbai, India
 ASD device closure: Long term follow up Bharat Dalvi, MD Glenmark Cardiac Centre Mumbai, India Our experience 1998 to 2011 1566 patients 912 patients > 4 years FU Exclusive with ASO Clinical, electrocardiographic
ASD device closure: Long term follow up Bharat Dalvi, MD Glenmark Cardiac Centre Mumbai, India Our experience 1998 to 2011 1566 patients 912 patients > 4 years FU Exclusive with ASO Clinical, electrocardiographic
Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defect with Amplatzer Septal Occluder in Adults: Immediate, Short, and Intermediate-Term Results
 TEHRAN HEART CENTER Original Article Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defect with Amplatzer Septal Occluder in Adults: Immediate, Short, and Intermediate-Term Results Mostafa Behjati, MD *, Mansour
TEHRAN HEART CENTER Original Article Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defect with Amplatzer Septal Occluder in Adults: Immediate, Short, and Intermediate-Term Results Mostafa Behjati, MD *, Mansour
BASIL D. THANOPOULOS MD, PhD Associate Professor Honorary Consultant, RBH, London, UK
 TRANSCATHETER CLOSURE OF ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT AND PFO BASIL D. THANOPOULOS MD, PhD Associate Professor Honorary Consultant, RBH, London, UK TRANSCATHETER CLOSURE OF ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT AND PFO BASIL D.
TRANSCATHETER CLOSURE OF ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT AND PFO BASIL D. THANOPOULOS MD, PhD Associate Professor Honorary Consultant, RBH, London, UK TRANSCATHETER CLOSURE OF ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT AND PFO BASIL D.
Patent Foramen Ovale Closure Without Echocardiographic Control: Use of Standby Intracardiac Ultrasound
 JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS VOL. 1, NO. 4, 2008 2008 BY THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY FOUNDATION ISSN 1936-8798/08/$34.00 PUBLISHED BY ELSEVIER INC. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcin.2008.05.006 Patent Foramen
JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS VOL. 1, NO. 4, 2008 2008 BY THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY FOUNDATION ISSN 1936-8798/08/$34.00 PUBLISHED BY ELSEVIER INC. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcin.2008.05.006 Patent Foramen
Delayed Infective Endocarditis with Mycotic Aneurysm Rupture below the Mechanical Valved Conduit after the Bentall Procedure
 Case Report Acta Cardiol Sin 2014;30:341 345 Delayed Infective Endocarditis with Mycotic Aneurysm Rupture below the Mechanical Valved Conduit after the Bentall Procedure Mei-Ling Chen, 1,3 Michael Y. Chen,
Case Report Acta Cardiol Sin 2014;30:341 345 Delayed Infective Endocarditis with Mycotic Aneurysm Rupture below the Mechanical Valved Conduit after the Bentall Procedure Mei-Ling Chen, 1,3 Michael Y. Chen,
Multidetector computed tomography in the evaluation of atrial septal defects
 Multidetector computed tomography in the evaluation of atrial septal defects Poster No.: C-0502 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: S. Espejo, R. Ysamat, B. Cajal, M. Pan,
Multidetector computed tomography in the evaluation of atrial septal defects Poster No.: C-0502 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: S. Espejo, R. Ysamat, B. Cajal, M. Pan,
Fermeture percutanée des CIA : matériels disponibles et résultats. Transcatheter closure of ASD : devices and results
 Fermeture percutanée des CIA : matériels disponibles et résultats Transcatheter closure of ASD : devices and results François Godart, University of Lille 2, France 12 e Congrès Médico-Chirurgical de la
Fermeture percutanée des CIA : matériels disponibles et résultats Transcatheter closure of ASD : devices and results François Godart, University of Lille 2, France 12 e Congrès Médico-Chirurgical de la
CARDIAC INTERVENTIONS IN PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY: THE FUTURE
 CARDIAC INTERVENTIONS IN PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY: THE FUTURE Vikas Kohli From the: Senior Consultant Pediatric Cardiology, Apollo Centre of Advance Pediatrics, Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi-110044.
CARDIAC INTERVENTIONS IN PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY: THE FUTURE Vikas Kohli From the: Senior Consultant Pediatric Cardiology, Apollo Centre of Advance Pediatrics, Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi-110044.
Atrial septal defects (ASDs) are one of the most
 Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defects An update on ASD occlusion devices. BY VICTOR-XAVIER TADROS, MD, MSc, AND ANITA W. ASGAR, MD, FRCPC, FACC Atrial septal defects (ASDs) are one of the most
Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defects An update on ASD occlusion devices. BY VICTOR-XAVIER TADROS, MD, MSc, AND ANITA W. ASGAR, MD, FRCPC, FACC Atrial septal defects (ASDs) are one of the most
