l / I lll US B2 AGE GENDER
|
|
|
- Marshall Perkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
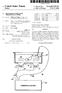
1 (12) United States Patent Stein I lll US B2 (10) Patent o.: US 6,730,035 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) ULTRASOIC APPARATUS AD METHOD FOR PROVIDIG QUATITATIVE IDICATIO OF RISK OF COROARY HEART DISEASE (75) Inventor: James H. Stein, Madison, WI (US) (73) Assignee: Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation, Madison, WI (US) ( *) otice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by O days. (21) Appl. o.: 10/290,421 (22) Filed: (65) ov. 7, 2002 Prior Publication Data US 2003/ Al Dec. 11, 2003 Related U.S. Application Data ( 60) Provisional application o. 60/386,905, filed on Jun. 5, (51) Int. CI.7... A61B 8/00 (52) U.S. Cl /449 (58) Field of Search /437, 443, 600/449, ; 128/ (56) References Cited U.S. PATET DOCUMETS 6,132,373 A 10/2000 Ito et al. OTHER PUBLICATIOS Rodis, Howard. et a 1, "The Role of Carotid Arterial Intima-Media Thickness in Predicting Clinical Coronary Events" American College of Physicians Annals of Internal Medicine, Feb. 15, : * Schisterman, Enrique F., et al., Coronary Plaque as a Replacement for Age in the Framingham Risk Equation, 51st Annual Scientific Session, American College of Cardiology, Aug. 27, Grundy, Scott M., Coronary Calcium as a Risk Factor: Role in Global Risk Assessment, Journal of American College of Cardiology, vol. 37, o. 6, Grundy, Scott M., Coronary Plaque as a Replacement for Age as a risk Factor in Global Risk Assessment, Am J Cardiol 2001; 88(suppl):8E-11E. * cited by examiner Primary Examiner-Francis J. Jaworski (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Quarles & Brady LLP (57) ABSTRACT An ultrasound machine measures coronary intima-medial thickness and relates it to a statistically derived vascular age. Quantitative risk of coronary heart disease may be calculated using vascular age to substitute for chronological age in publicly available risk assessment data. 20 Claims, 2 Drawing Sheets 52 l / AGE GEDER RACE./ BODY SIZE i T. CHOL - HDLC B. PRESSURE DIABETES SMOKIG 38 FRAMIGHAM VASCULAR AGE 1-AG_E %'---R--'-I S--iK 46 10
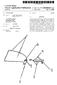
2 U.S. Patent May 4, 2004 Sheet 1 of 2 US 6,730,035 B i tr'<. 26 _l FIG. 1 CIMT I ARIC :-. :. : AGE FIG. 3 70' 67 FIG FIG. 7 FIG. 8
3 AGE / GEDER / RACE / B. PRESSURE DIABETES SMOKIG VASCULAR AGE IAGEI 1111% RISKI -/46 FIG. 5 IPUT O- ULTRASOUD PATIET DATA l MEASURE CIMT APPLY CIMT TO FIT CURVE t APPLY VASCULAR AGE TO AGE I FRAMIGHAM l OUTPUT VASCULAR AGE, % RISK d r:jj.... =... '-<,J;.. 0 = 'JJ , 0 e rj'j. _,.a-... Q b (It ""-ii I ,..., ,_,_,_,_,,_,_,_ FRAMIGHAM /es: 1!%>i 52
4 1 ULTRASOIC APPARATUS AD METHOD FOR PROVIDIG QUATITATIVE IDICATIO OF RISK OF COROARY HEART DISEASE CROSS-REFERECE TO RELATED APPLICATIOS This application is based on provisional application o. 60/386,905 filed Jun. 5, 2002 and entitled "Mathematical Algorithms Allowing Determination of Vascular Age" and claims the benefit thereof. STATEMET REGARDIG FEDERALLY SPOSORED RESEARCH OR DEVELOPMET This invention was made with United States government support awarded by the following agencies: IH RR The United States has certain rights in this invention. BACKGROUD OF THE IVETIO The present invention relates to ultrasonic medical equipment, and in particular, to a method employable with such equipment to assess risk of coronary heart disease (CHD). A key challenge in healthcare is identifying individuals who are at high risk for CHD and who thus would be candidates for intensive medical intervention either in the form of additional diagnostic testing or the initiation of proven therapeutic strategies. One method of assessing risk of coronary heart disease is the Framingham Global CHD Risk Assessment (henceforth the "Framingham Assessment"). See, "Prediction of Coronary Heart Disease Using Risk Factor Categories", Circulation 1998; 97: Wilson et al. US 6,730,035 B CHD and CIMT, long-term monitoring without treatment of patients with high CIMT may not be possible. BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE IVETIO The present inventors have recognized that a quantitatively rigorous relationship between CIMT and risk of CHD may be derived from the existing Framingham Assessment data by converting CIMT into an equivalent "vascular age" and substituting this "vascular age" for the chronological age used in the Framingham Assessment. The conversion of CIMT to vascular age can be done using studies that relate increase in CIMT to age in a standard population. One such study is the ARIC study described in "High Resolution B Mode Ultrasound Scanning Methods in the Arteriosclerosis 15 Risk in Community Study (ARIC) J. euroimaging, 1991; 1:68-73, Bond et al These latter studies generally show a range of CIMT values for individuals of a given age within the population and thus cannot be used to relate CIMT to actual chronological age. evertheless, vascular age may be equated to the age of the study population at which the given individual's CIMT equals the population's mean or other statistical center value. The concept of vascular age allows connection between these two disparate studies, for example, that of the Framingham Assessment and ARIC, to provide a quantitative relationship between CIMT and risk of coronary heart disease. Specifically then, the present invention provides an ultra- 30 sonic diagnostic machine having an ultrasonic transducer that is positionable near the carotid artery to obtain echo signals from the carotid artery. A processing circuit communicating with the ultrasound transducer operates to process the echo signal to review the carotid intima-medial The Framingham Assessment, based on a long-term study 35 thickness (CIMT) and to apply the revealed CIMT to stored data relating CIMT of a population to a quantified risk of of a population of individuals, relates age, cigarette coronary heart disease (CHD). This quantified risk of heart smoking, blood pressure, total cholesterol and high-density disease is then output. lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, and diabetes to a quantitative Thus, it is one object of the invention to provide the risk of CHD typically expressed in a percent chance of quantitative relationship between CIMT and risk of CHD having a CHD event (heart attack or cardiac death) in ten such as may guide selection of treatment regimens. years. A drawback to the Framingham Assessment is that age The stored data used by the ultrasound machine may dominates all other risk factors even though the risks of combine first data relating the CIMT to a vascular age and coronary heart disease between individuals of the same age second data relating vascular age to quantified risk of CHD. can differ substantially. The explanation for the relationship 45 The first data may be the ARIC data and the second data may between age and CHD events most likely is increasing be the data of the Framingham Assessment. coronary plaque burden that occurs with advancing age. For Thus, it is another object of the invention to establish a this reason, it is generally recognized that a measure of relationship between CIMT and risk of CHD using preexisting studies. coronary plaque burden might provide a better indicator of the probability of developing coronary heart disease for an 50 individual than age alone. The first data may relate multiple CIMT values to a given age but may be used to provide a single vascular age from a single CIMT value by a mathematical or statistical curve There are a number of methods of measuring coronary plaque burden, including measurement of carotid intimamedial thickness (CIMT) with B mode ultrasound sonography. Such measurements provide a non-invasive and highly reproducible technique for quantifying sub-clinical atherosclerosis. Measurement of CIMT is currently not used widely as a clinical tool, however. In part, this is because there is no established relationship between various patient factors, 60 CIMT, and quantitative risk of cardiac heart disease. Ideally, the Framingham study would be repeated, but the age replaced by a CIMT measurement. Unfortunately, such studies take many years to complete and the future study is hampered by ethical concerns resulting from our understanding of the significance of some of the risk factors. For example, given the knowledge of the relationship between 55 fitting process. Thus, it is another object of the invention to employ existing studies describing CIMT as a function of age to create a virtual study relating CIMT values to vascular age. The processing circuit may provide for input of patient data selected from the group consisting of: chronological age, gender, race, and body size. At least one of these patient data may also be applied to at least one of the first and second data sets. Thus, it is another object of the invention to take advantage of the other patient input factors that may be used along 65 with CIMT to establish quantified risk of CHD. In one embodiment of the invention, the output from the ultrasound diagnostic machine may be vascular age.
5 3 Thus, it is another object of the invention to provide a simple unit for assessing CIMT data that can be readily understood by physicians and patients. These particular objects and advantages may apply to only some embodiments falling within the claims and thus do not define the scope of the invention. BRIEF DESCRIPTIO OF THE DRAWIGS FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a patient's head showing the carotid artery and the proper positioning of an ultrasonic transducer for the measurements used in the present invention; FIG. 2 is a fragmentary enlarged view of a bifurcation of the carotid artery used to locate positions for measurement of CIMT; FIG. 3 is a graph showing in simplified representation the ARIC data such as provides a range of CIMT values for different age groups within the ARIC population and showing a curve fitted to this data to deduce a vascular age from CIMT; FIG. 4 is a data flow diagram showing collection of CIMT data obtained from an ultrasound machine together with other patient data and conversion of this data to vascular age by use of a surface derived from the ARIC data of FIG. 3; and the further use of the vascular age, both as direct output to the physician and as an input to the Framingham Assessment to provide a quantitative measurement of risk of CHD; FIG. 5 is a flow chart showing the steps of FIG. 4; FIG. 6 is a graph showing treatment options that may depend on a quantifiable risk of heart disease and showing uncertainty in the Framingham study for an individual as may be reduced by the present invention; FIG. 7 is a cross-sectional view of the artery of FIG. 2 showing an alternative measurement of CIMT possible with 3-D ultrasound machines; and FIG. 8 is a figure showing a display of a B mode ultrasound image of the artery of FIG. 2 together with display of a region of interest and cursor ruler lines for automatic CIMT measurement. DETAILED DESCRIPTIO OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMET Referring now to FIG. 1, an ultrasound probe 10 may be directed toward the common carotid artery 12 of a patient 14 near the branching or bifurcation 16 of the carotid artery 12 into internal carotid artery 18 and exterior carotid artery 20. The ultrasound transducer may, for example, be an 8-megahertz linear array vascular ultrasound transducer (8L5) sold by Acuson of Mountain View, Calif. for use with the Acuson Sequoia ultrasound machine, or a similar transducer made by another vendor. As shown in FIG. 2, the ultrasound probe 10 may be directed to transmit a generally planar beam 22, defining a coplanar image plane, that is perpendicular to the lumen of the carotid artery 12 to provide a generally ring-shaped cross-sectional image 24 of a single lumen before the bifurcation 16. The planar beam 22 is established to be essentially perpendicular to the axis of the lumen by adjusting the angle to increase the sharpness of the walls of the cross sectional image 24. The ultrasound probe 10 may then be moved in a superior direction 26 past the general enlargement of the carotid artery into a bulb 28, shown in cross sectional image 24', to continue to the carotid bifurcation 16 characterized by the US 6,730,035 B2 4 presence of a flow divider 30 and two lumens as indicated by cross sectional image 24". At this time, the ultrasound probe 10 may be rotated about its axis ninety degrees producing planar beam 22' to provide a cross section parallel 5 to the lumen encompassing three locations along a distal wall of the carotid artery 12. The three locations include a common segment 31 defined as the distal one centimeter of the carotid artery 12 immediately proximal to the onset of increased spatial separation of the walls of the common carotid artery (i.e., immediately 10 before the origin of the bulb 28), the bifurcation segment 33 defined as the distal one centimeter of the bulb 28 characterized by the presence of the flow divider 30 between the interior carotid arteries 18 and exterior carotid arteries 20 and the internal segment 35 defined as the proximal one centimeter of the internal carotid artery 18 starting immediately beyond the flow divider 30. At each of these segments 31, 33, and 35, the thickness of the intimal and medial layers of the distal walls is measured. Alternatively, images of the far wall ( or near wall if normative values are available) can be obtained at multiple, predefined, protocolspecified interrogation angles. The combined thickness of the intimal and medial layers can be measured using, for example, software commercially available from Freeland Systems of Indianapolis, Ind., under the trade name Access Point 2000, or similar software such as that available from Camtronics, Inc., Hartland, Wis. A composite CIMT value may then be calculated as a mean of the averages or means of each of these segments according to the standardized protocol from the ARIC study. Referring now to FIG. 3, the ARIC study established a relationship between CIMT and age ( and gender and race) indicated by scatter plots points 34 reflecting the fact that in the populations studied in the ARI C study individuals of the 35 same given age had different CIMT values varying over a substantial range. Generally, therefore, a given CIMT value cannot be mapped to a particular age using the ARIC data. In order to overcome this problem, a curve 36 is fit to these scatter plot points 34 to provide a best fit. A number of different best-fit criteria are possible, with a linear regression being used in the preferred embodiment. Vascular age can be determined by linear regression modeling using published nomograms of CIMT percentiles (5'\ 10'\ 25'\ 50'\ 75'\ 90'\ and 95 th ) according to 45 chronological age, sex, and race. Linear regression models are first constructed for each of the CIMT percentile functions for each carotid arterial segment 31, 33, and 35: by sex (male and female), race (white and black), and age (5-year increments from years old). Composite CIMT values 50 can then be used to determine the vascular age defined as the age at which the composite CIMT value for an individual of a given race and sex would represent the median value (50 th percentile). Specifically, the linear 50 th percentile function by chro- 55 nological age, sex, and race can be used to assign a vascular age to the subject having a given composite CIMT value such that if each of the subject's segmental scores were at the 50 th percentile for their chronological age, sex, and race, then their composite CIMT would be at the 50 th percentile 60 and their vascular age would be equal to their chronological age. For example, a 45-year black female with a composite CIMT of mm would have a CIMT percentile of 50% and a vascular age of 50 years; however, a 45-year black female with a composite CIMT of mm would have a 65 CIMT percentile of 71 % and a vascular age of 55 years, representing the age at which a composite CIMT value of mm represents the 50 th percentile.
6 US 6,730,035 B2 5 Using this modeling, a given CIMT value may be mapped to a unique vascular age. It should be noted that vascular age will generally not match the chronological age of the patient 14 but will be a statistical construction in which the vascular age of the patient 14 is an age of ARIC data at which the 5 patient's CIMT is near the middle of the range of the scatter plot points 34. Referring now to FIG. 4, the linear regression curve 36 as extended across other patient variables of the ARIC study such as age, gender, and race and potentially across new variables such as body size creates a multidimensional surface 38 mapping values of the patient variables to a unique vascular age. As a practical matter, the surface 38 may be stored as one or more data table and vascular age may be determined by interpolation between data table values as is well understood in the art. Referring now to FIG. 5, a first step of the present invention indicated by process block 42 collects the patient data described above including, for example, age, gender, race and body size. This information may be entered into an 20 ultrasound machine 46 by means of a keyboard 50 or the data may be directly imported from the ultrasound machine into a software program and displayed on a display 52 according to techniques well known in the art. 25 At process block 54, the above-described CIMT measurement is performed using the ultrasound probe 10. The CIMT data 56 and the patient data 58 form arguments that are applied to the -dimensional surface 38 to produce a vascular age as indicated by process block 60. This 30 determination of vascular age of process block 60 may be performed by processing circuitry contained in the ultrasound machine 46, however, it is also contemplated that the vascular age may be computed by a separate computing device. The vascular age may then be output to the display of the ultrasound machine 46 to provide an intuitive measure of CIMT. Generally, the patient will compare his or her vascular age to his or her actual chronological age to get a sense of his or her risk of coronary heart disease. The ultrasound machine 46 or the separate computing device may store the Framingham Assessment data 62 providing inputs for chronological age as well as inputs for cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, smoking, total cholesterol and diabetes. As represented by process block 66, these latter 45 five inputs 64 are then applied to the Framingham Assessment data 62 with the vascular age being substituted for the chronological age expected from the Framingham analysis. This application of data generally involves finding a row in the Framingham Assessment data 62 matching each of the 50 characteristics or most closely matching each of inputs 64 and vascular age. The Framingham Assessment data 62 then yields a percent risk of CHD according to this well-known study. This risk is output as indicated by process block 68. The present invention thus allows the inputting of the CIMT as well as other information such as age, gender, and race data into the Framingham study through the use of the concept of vascular age. Referring now to FIG. 6, although the Framingham 60 Assessment accurately reflects risk of CHD for a population, or an individual, it will provide an uncertainty 70 measurable in a range of percent risk of CHD. This uncertainty may span ranges of risk 72A, 72B and 72C associated with different treatment options. It is expected that use of the 65 present invention will reduce the uncertainty as indicated by 70' thereby clarifying treatment options. This expected 6 improvement may be established by obtaining additional information from the ARIC study indicating whether individuals in that study had a clinical manifestation of coronary heart disease in the period following their measurement. The results obtained by the present invention would then be compared to actual outcomes of the ARIC population to confirm clinical significance. Referring now to FIG. 7, the present invention is not limited to two dimensional ultrasound machines but may 10 find application in three dimensional ultrasound machines which collect a volume of ultrasonic data and can display a cross-sectional image of the carotid artery 12. In this case, the intima-medial separation 67 may be measured, for example, in a ring extending circumferentially around the 15 carotid artery in a plane perpendicular to the lumen of the artery rather than in a line segment along the distal portion of the lumen as described above. The measurements taken in the ring can be averaged together and substituted for the 55 measurements described with respect to FIG. 2. Three rings may be measured intersecting the common section 31, the bifurcation segment 33, and the internal segment 35. While one embodiment of the present invention contemplates that the measurement of CIMT will be performed manually, in an alternative embodiment the measurements of CIMT may be performed automatically by the ultrasound machine 36 which may also perform the averaging necessary for the software described. Such automatic measuring is known in the art and is described, for example, in U.S. Pat. o. 6,132,373 issued Oct. 17, 2000 hereby incorporated by reference. Referring to FIG. 8, alternatively a combination of manual and automatic measurement techniques may be used in which an operator of the ultrasound machine 46 locates a region of interest cursor 90 being generally a rectangle over the image of the carotid artery 12 displayed on the display 52. The region of interest cursor 90 allows the operator to identify the appropriate regions (common section 31, the bifurcation segment 33, and the internal segment 35.). Once the region of interest cursor is located, defining the length along the wall of the carotid artery 12, thickness cursors 92 may be placed on either side of the intimal and medial layers of the distal wall at a particular location. The CIMT value may then be automatically computed based on starting points of the thickness cursors 92 extrapolated by computer analyses of the image data using region extraction algorithms well known in the art. It is specifically intended that the present invention not be limited to the embodiments and illustrations contained herein, but include modified forms of those embodiments including portions of the embodiments and combinations of elements of different embodiments as come within the scope of the following claims. I claim: 1. A diagnostic ultrasound machine comprising: an ultrasonic transducer positionable near the carotid artery to obtain echo signals from the carotid artery; a processing circuit communicating with the ultrasonic transducer and operating to: (i) process the echo signal to reveal carotid intimamedial thickness (CIMT); (ii) apply the revealed CIMT to stored first data relating the CIMT to vascular age to determine vascular age (iii) apply the determined vascular age to stored second data relating vascular age to the quantified risk of heart disease, and (iv) output the quantified of risk of heart disease.
7 7 2. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 1 wherein the first data is derived from data relating age to CIMT in a study population. 3. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 2 wherein the data relating age to CIMT is ARIC data. 4. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 2 wherein multiple CIMT values related to a single age are combined by curve fitting to yield a single vascular age for a single CIMT value. US 6,730,035 B2 5. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 1 wherein 10 the second data is data relating chronological age to quantified risk of heart disease and wherein the first and second data are combined by taking vascular age deduced from the first data set and inputting it as chronological age into the second data set The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 5 wherein the second data is Framingham data. 7. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 1 wherein the processing circuit further provides for input of patient data selected from the group consisting of: chronological 20 age, gender, race and body size and wherein at least one of these patient data are also applied to at least one of the first and second data sets. 8. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 1 wherein the measure of risk of heart disease is expressed in percent chance of heart disease within ten years. 9. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 1 wherein the measure of CIMT is an average of carotid intima-medial thickness over a predetermined region of the carotid artery. 10. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 9 wherein the predetermined region is near the carotid bifurcation. 11. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 9 wherein the predetermined region is an axial line along the carotid artery. 12. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 1 wherein 35 the processing circuitry collects a three-dimensional image set of the carotid artery and wherein the predetermined region is a circumferential ring of the carotid artery. 13. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 1 wherein the processing circuitry provides automatic measurement of the CIMT. 14. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 1 wherein the processing circuitry further output an image of the 5 8 carotid artery and accepts user input locating points on the image for the automatic measurement. 15. A diagnostic ultrasound machine comprising: an ultrasonic transducer positionable near the carotid artery to obtain echo signals from the carotid artery; a processing circuit communicating with the ultrasonic transducer and operating to: (i) process the echo signal to reveal carotid intimamedial thickness (CIMT); (ii) apply the revealed CIMT to stored data relating CIMT of a population to a vascular age indicating statistical derived age of an individual having the revealed CIMT in a standard population; and (iii) output the vascular age. 16. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 15 wherein the stored data is derived from data relating age to CIMT in a study population. 17. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 16 wherein the data relating age to CIMT is ARIC data. 18. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim 16 wherein multiple CIMT values related to a single age are combined by curve fitting to yield a single vascular age for a single CIMT value. 19. The diagnostic ultrasonic machine of claim wherein the processing circuit further provides for input of patient data selected from the group consisting of: chronological age, gender, race and body size and wherein at least one of these patient data are also applied to the stored data. 20. A method of deducing a quantified risk of heart 30 disease for an individual having a given chronological age and a given carotid intima-medial thickness (CIMT) comprising the steps of: ( a) deducing a vascular age of the individual differing from the given chronological age such as would place the individual's given CIMT in a median of CIMT for that vascular age for a standard population; (b) using the vascular age as an input for chronological age in a Framingham model of heart disease to provide an estimate of cardiac heart disease; and (c) providing the individual with the vascular age and estimate of cardiac heart disease. * * * * *
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,691,578 B1
 USOO6691578B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,691,578 B1 Puskas (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS FOR 4,710,233 A 12/1987 Hohmann et al.... 205/701 ULTRASOUND
USOO6691578B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,691,578 B1 Puskas (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS FOR 4,710,233 A 12/1987 Hohmann et al.... 205/701 ULTRASOUND
( 12 ) United States Patent
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Ingwer et al. US009907655B2 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 907, 655 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Mar. 6, 2018 ( 54 ) COMPONENTS FOR ARTIFICIAL JOINTS ( 56 ) References Cited U. S.
( 12 ) United States Patent Ingwer et al. US009907655B2 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 907, 655 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Mar. 6, 2018 ( 54 ) COMPONENTS FOR ARTIFICIAL JOINTS ( 56 ) References Cited U. S.
1 ADJUSTMENT THRESHOLD-N. United States Patent (19) Donehoo et al. 5,660,184. Aug. 26, 1997 PATIENT'S HEARTBEAT PACEMAKEREVENT QRS DETECTION THRESHOLD
 United States Patent (19) Donehoo et al. US00566O184A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,660,184 Aug. 26, 1997 54 PACEMAKER PULSE DETECTION AND ARTIFACT REJECTION 75 Inventors: Robert F. Donehoo, Lutz;
United States Patent (19) Donehoo et al. US00566O184A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,660,184 Aug. 26, 1997 54 PACEMAKER PULSE DETECTION AND ARTIFACT REJECTION 75 Inventors: Robert F. Donehoo, Lutz;
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll
 (12) United States Patent Masini I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US006558426Bl (10) Patent No.: US 6,558,426 Bl (45) Date of Patent: May 6, 2003 (54)
(12) United States Patent Masini I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US006558426Bl (10) Patent No.: US 6,558,426 Bl (45) Date of Patent: May 6, 2003 (54)
Lesson 07: Ultrasound Transducers. This lesson contains 73 slides plus 16 multiple-choice questions.
 Lesson 07: Ultrasound Transducers This lesson contains 73 slides plus 16 multiple-choice questions. This lesson was derived from pages 33 through 42 in the textbook: Ultrasound Transducers Ultrasound Transducers
Lesson 07: Ultrasound Transducers This lesson contains 73 slides plus 16 multiple-choice questions. This lesson was derived from pages 33 through 42 in the textbook: Ultrasound Transducers Ultrasound Transducers
IIII. United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,776,150 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998
 United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 54) SUTURE ASSIST DEVICE 75) Inventors: Leo J. Nolan; John P. Measamer, both of Cincinnati; James D. Staley, Jr., Loveland; Robert F. Welch, Maineville, all of Ohio
United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 54) SUTURE ASSIST DEVICE 75) Inventors: Leo J. Nolan; John P. Measamer, both of Cincinnati; James D. Staley, Jr., Loveland; Robert F. Welch, Maineville, all of Ohio
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,334,451 B1
 USOO6334451B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 6,334,451 B1 Yang (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) TOOTHBRUSH WITH FILLIG OF 1,340,043 A 5/1920 Grace... 132/311 TOOTHPASTE 1,451,941. A
USOO6334451B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 6,334,451 B1 Yang (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) TOOTHBRUSH WITH FILLIG OF 1,340,043 A 5/1920 Grace... 132/311 TOOTHPASTE 1,451,941. A
CLINICAL STUDY. Yasser Khalil, MD; Bertrand Mukete, MD; Michael J. Durkin, MD; June Coccia, MS, RVT; Martin E. Matsumura, MD
 117 CLINICAL STUDY A Comparison of Assessment of Coronary Calcium vs Carotid Intima Media Thickness for Determination of Vascular Age and Adjustment of the Framingham Risk Score Yasser Khalil, MD; Bertrand
117 CLINICAL STUDY A Comparison of Assessment of Coronary Calcium vs Carotid Intima Media Thickness for Determination of Vascular Age and Adjustment of the Framingham Risk Score Yasser Khalil, MD; Bertrand
Intima-Media Thickness
 European Society of Cardiology Stockholm, 30th August 2010 Intima-Media Thickness Integration of arterial assessment into clinical practice Prof Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss, MD Institute of Exercise and Health
European Society of Cardiology Stockholm, 30th August 2010 Intima-Media Thickness Integration of arterial assessment into clinical practice Prof Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss, MD Institute of Exercise and Health
CardioHealth Station. powered by. Healthcare CardioHealth
 CardioHealth Station FDA cleared, in-office ultrasound imaging that helps you directly identify atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) allowing you to make a more informed decision about your patients
CardioHealth Station FDA cleared, in-office ultrasound imaging that helps you directly identify atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) allowing you to make a more informed decision about your patients
(12) United States Patent Clapp et al. US 7,206,386 B2 Apr. 17, 2007 US B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 US007206386B2 (12) United States Patent Clapp et al. (io) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,206,386 B2 Apr. 17, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION WITH THE HEARING IMPAIRED (75)
US007206386B2 (12) United States Patent Clapp et al. (io) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,206,386 B2 Apr. 17, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION WITH THE HEARING IMPAIRED (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,128,575 B1. Sohn (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2006
 US007128575B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,128,575 B1 Sohn (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2006 (54) TOOTHELEVATOR 1,762,888 A 6/1930 Roberts... 433/159 2,030,798 A 2/1936 Krajeski......
US007128575B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,128,575 B1 Sohn (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2006 (54) TOOTHELEVATOR 1,762,888 A 6/1930 Roberts... 433/159 2,030,798 A 2/1936 Krajeski......
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080040891A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0040891 A1 Tyler (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 21, 2008 (54) EXERCISE EQUIPMENT HANDLE GRIPS Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080040891A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0040891 A1 Tyler (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 21, 2008 (54) EXERCISE EQUIPMENT HANDLE GRIPS Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 US007094007B2 (12) United States Patent Satran et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 22, 2006 (54) TANGENTIAL CUTTING INSERT AND MILLING CUTTER (75) Inventors: Amir Satran, Kfar Vradim (IL);
US007094007B2 (12) United States Patent Satran et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 22, 2006 (54) TANGENTIAL CUTTING INSERT AND MILLING CUTTER (75) Inventors: Amir Satran, Kfar Vradim (IL);
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US006319006B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,319,006 B1 Scherer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2001 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCINGA DRILL 5,967,777 * 10/1999 Klein 5 a1...... 433/75 ASSISTANCE
(12) United States Patent US006319006B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,319,006 B1 Scherer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2001 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCINGA DRILL 5,967,777 * 10/1999 Klein 5 a1...... 433/75 ASSISTANCE
Diploma of Medical Ultrasonography (DMU) Physical Principles of Ultrasound and Instrumentation Syllabus
 Diploma of Medical Ultrasonography (DMU) Physical Principles of Ultrasound and Instrumentation Syllabus Page 1 of 7 11/18 Candidates are expected to cover all of the content of this syllabus when preparing
Diploma of Medical Ultrasonography (DMU) Physical Principles of Ultrasound and Instrumentation Syllabus Page 1 of 7 11/18 Candidates are expected to cover all of the content of this syllabus when preparing
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/28524 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Djaberi, Roxana Title: Cardiovascular risk assessment in diabetes Issue Date: 2014-09-04
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/28524 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Djaberi, Roxana Title: Cardiovascular risk assessment in diabetes Issue Date: 2014-09-04
(12) United States Patent
 US007043040B2 (12) United States Patent Westerkull (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) HEARING AID APPARATUS (75) Inventor: Patrick Westerkull, Hovås (SE) (73) Assignee: P&B Research
US007043040B2 (12) United States Patent Westerkull (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) HEARING AID APPARATUS (75) Inventor: Patrick Westerkull, Hovås (SE) (73) Assignee: P&B Research
United States Patent (19) Hensel
 United States Patent (19) Hensel - 54 75 73 1 51 5 58 56) FLUID BEARNG CONSTRUCTION EMPLOYING THRUST PLATE WITH PRESSURE COMPENSATION PORTS Inventor: Robert J. Hensel, Gaston, Oreg. Assignee: Synektron
United States Patent (19) Hensel - 54 75 73 1 51 5 58 56) FLUID BEARNG CONSTRUCTION EMPLOYING THRUST PLATE WITH PRESSURE COMPENSATION PORTS Inventor: Robert J. Hensel, Gaston, Oreg. Assignee: Synektron
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: carotid_intimal_medial_thickness 12/2006 10/2016 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Ultrasonographic
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: carotid_intimal_medial_thickness 12/2006 10/2016 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Ultrasonographic
(12) United States Patent
 US008556757B2 (12) United States Patent Kilshaw (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2013 (54) BICYCLE GEAR MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Richard J. Kilshaw, Lake Oswego, OR (US) *) Notice: Subject
US008556757B2 (12) United States Patent Kilshaw (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2013 (54) BICYCLE GEAR MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Richard J. Kilshaw, Lake Oswego, OR (US) *) Notice: Subject
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090305855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0305855A1 Terre (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) ABDOMINAL EXERCISE MACHINE (57) ABSTRACT An abdominal exercise
(19) United States US 20090305855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0305855A1 Terre (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) ABDOMINAL EXERCISE MACHINE (57) ABSTRACT An abdominal exercise
Improving Headphone Fit Using Design Of Cable
 Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series October 27, 2017 Improving Headphone Fit Using Design Of Cable N/A Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series October 27, 2017 Improving Headphone Fit Using Design Of Cable N/A Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
Role of imaging in risk assessment models: the example of CIMT
 Role of imaging in risk assessment models: the example of CIMT Diederick E. Grobbee, MD, PhD, FESC Professor of Clinical Epidemiology Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical
Role of imaging in risk assessment models: the example of CIMT Diederick E. Grobbee, MD, PhD, FESC Professor of Clinical Epidemiology Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical
Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis
 Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology 2008 Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis The purpose of this exercise is to allow students to recapitulate issues discussed throughout the course which
Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology 2008 Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis The purpose of this exercise is to allow students to recapitulate issues discussed throughout the course which
United States Patent (19) Groesch et al.
 United States Patent (19) Groesch et al. 54 DUMMY FOR CAR CRASH TESTING 75) Inventors: Lothar Groesch; Gabriel Netzer, both of Stuttgart; Lothar Kassing, Nufringen, all of Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Groesch et al. 54 DUMMY FOR CAR CRASH TESTING 75) Inventors: Lothar Groesch; Gabriel Netzer, both of Stuttgart; Lothar Kassing, Nufringen, all of Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee:
On the feasibility of speckle reduction in echocardiography using strain compounding
 Title On the feasibility of speckle reduction in echocardiography using strain compounding Author(s) Guo, Y; Lee, W Citation The 2014 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS 2014), Chicago, IL.,
Title On the feasibility of speckle reduction in echocardiography using strain compounding Author(s) Guo, Y; Lee, W Citation The 2014 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS 2014), Chicago, IL.,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO948.0458B2 (12) United States Patent Chiang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 1, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (62) (30) ULTRASONIC POSITONING DEVICE FOR EPIDURAL SPACE
USOO948.0458B2 (12) United States Patent Chiang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 1, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (62) (30) ULTRASONIC POSITONING DEVICE FOR EPIDURAL SPACE
Is the Ankle-Brachial Index a Useful Screening Test for Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic, Middle-Aged Adults?
 Is the Ankle-Brachial Index a Useful Screening Test for Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic, Middle-Aged Adults? Rachael A. Wyman, MD; Jon G. Keevil, MD; Kjersten L. Busse, RN, MSN; Susan E. Aeschlimann,
Is the Ankle-Brachial Index a Useful Screening Test for Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic, Middle-Aged Adults? Rachael A. Wyman, MD; Jon G. Keevil, MD; Kjersten L. Busse, RN, MSN; Susan E. Aeschlimann,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120258416A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0258416A1 Tong (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 11, 2012 (54) METHOD TO DEFINE, MEASURE, AND Publication Classification
US 20120258416A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0258416A1 Tong (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 11, 2012 (54) METHOD TO DEFINE, MEASURE, AND Publication Classification
Paper No Filed: October 23, 2017 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD
 Trials@uspto.gov Paper No. 8 571-272-7822 Filed: October 23, 2017 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD ABIOMED, INC. and ABIOMED R&D, INC., Petitioner, v.
Trials@uspto.gov Paper No. 8 571-272-7822 Filed: October 23, 2017 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD ABIOMED, INC. and ABIOMED R&D, INC., Petitioner, v.
Objective Calcium score carotid IMT hs-crp
 P3952 Role of coronary calcium score, carotid intima-media thickness and C-reactive protein in predicting extent of coronary artery disease in young patients. Bedside Poster P3952 Role of coronary calcium
P3952 Role of coronary calcium score, carotid intima-media thickness and C-reactive protein in predicting extent of coronary artery disease in young patients. Bedside Poster P3952 Role of coronary calcium
Preclinical Detection of CAD: Is it worth the effort? Michael H. Crawford, MD
 Preclinical Detection of CAD: Is it worth the effort? Michael H. Crawford, MD 1 Preclinical? No symptoms No physical findings No diagnostic ECG findings No chest X-ray X findings No diagnostic events 2
Preclinical Detection of CAD: Is it worth the effort? Michael H. Crawford, MD 1 Preclinical? No symptoms No physical findings No diagnostic ECG findings No chest X-ray X findings No diagnostic events 2
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O130096A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0130096 A1 LaCroce (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 10, 2003 (54) BARBELL WITH PLURAL HAND GRIPPING Publication Classification
US 2003O130096A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0130096 A1 LaCroce (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 10, 2003 (54) BARBELL WITH PLURAL HAND GRIPPING Publication Classification
Carotid Ultrasound Scans for Assessing Cardiovascular Risk
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/lipid-luminations/carotid-ultrasound-scans-for-assessing-cardiovascularrisk/4004/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/lipid-luminations/carotid-ultrasound-scans-for-assessing-cardiovascularrisk/4004/
United States Patent (19) Annoni
 United States Patent (19) Annoni (54. TOOTH TRANSILLUMINATING LIGHT HOLDER 76) Inventor: Jerry D. Annoni, 450 Maple Ave., Vallejo, Calif. 94591 (21) Appl. No.: 427,850 22 Filed: Sep. 29, 1982 51) Int.
United States Patent (19) Annoni (54. TOOTH TRANSILLUMINATING LIGHT HOLDER 76) Inventor: Jerry D. Annoni, 450 Maple Ave., Vallejo, Calif. 94591 (21) Appl. No.: 427,850 22 Filed: Sep. 29, 1982 51) Int.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. Giannelli (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2003
 US 20030166439A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0166439 A1 Giannelli (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2003 (54) ROWING MACHINE Publication Classification (76) Inventor:
US 20030166439A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0166439 A1 Giannelli (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2003 (54) ROWING MACHINE Publication Classification (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0039210 A1 Yates et al. US 20090039210A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 12, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) CPAP HOSE SUPPORT SYSTEM Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0039210 A1 Yates et al. US 20090039210A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 12, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) CPAP HOSE SUPPORT SYSTEM Inventors:
DC-40 Ultrasound System. powerful efficient sleek
 DC-40 Ultrasound System powerful efficient sleek To deliver on the promise of quality healthcare within reach, Mindray s DC-40, the next generation of shared service ultrasound systems, incorporates innovative
DC-40 Ultrasound System powerful efficient sleek To deliver on the promise of quality healthcare within reach, Mindray s DC-40, the next generation of shared service ultrasound systems, incorporates innovative
IHIH IIII. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,417, Date of Patent: May 23, Kawai et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kawai et al. 54 METHOD FOR EXTRACTING AMARGIN LINE FOR DESIGNING AN ARTIFICIAL CROWN 75) Inventors: Masaharu Kawai, Kanagawa; Katsuya Miyoshi, Tokyo; Masami Baba, Saitama, all
United States Patent (19) Kawai et al. 54 METHOD FOR EXTRACTING AMARGIN LINE FOR DESIGNING AN ARTIFICIAL CROWN 75) Inventors: Masaharu Kawai, Kanagawa; Katsuya Miyoshi, Tokyo; Masami Baba, Saitama, all
y 2. (12) United States Patent VbOt W N 35 (10) Patent No.: US 8,855,348 B2 HAD CIRCUIT ACTIVE TELECOIL (45) Date of Patent: Oct.
 USOO8855348B2 (12) United States Patent Johnson (54) TELECOIL INA DETACHABLE DIRECT AUDIO INPUT ACCESSORY (75) Inventor: Andrew Joseph Johnson, Edina, MN (US) (73) Assignee: Starkey Laboratories, Inc.,
USOO8855348B2 (12) United States Patent Johnson (54) TELECOIL INA DETACHABLE DIRECT AUDIO INPUT ACCESSORY (75) Inventor: Andrew Joseph Johnson, Edina, MN (US) (73) Assignee: Starkey Laboratories, Inc.,
GE Healthcare 9900 Innovation Drive Wauwatosa, WI U.S.A.
 2011 General Electric Company All rights reserved. General Electric Company reserves the right to make changes in specifications and features shown herein, or discontinue the product described at any time
2011 General Electric Company All rights reserved. General Electric Company reserves the right to make changes in specifications and features shown herein, or discontinue the product described at any time
E. }2. E. 156/578 X mountant on the Slide to Spread evenly over the Slide with a
 USOO.5989386A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,989,386 Elliott (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54 COVERSLIPPICK-UP AND LAYDOWN 4,428,793 1/1984 Sato et al.. APPARATUS 4,455,188 6/1984 Stormby.
USOO.5989386A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,989,386 Elliott (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54 COVERSLIPPICK-UP AND LAYDOWN 4,428,793 1/1984 Sato et al.. APPARATUS 4,455,188 6/1984 Stormby.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0265315 A1 Kusogullariet al. US 20120265315A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2012 (54) SHOULDER PROSTHESIS (75) Inventors: Levent
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0265315 A1 Kusogullariet al. US 20120265315A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2012 (54) SHOULDER PROSTHESIS (75) Inventors: Levent
Report For Center Created Gender D.O.B Page 1 Sean Breen HeartSmart IMT plus 3/29/2012 Male 11/26/1973 B C D E
 Report For Center Created Gender D.O.B Page 1 Carotid Assessment A B C D E Good Satisfactory Concern Serious Highest Risk Intima-Media Thickness Additional Findings Plaque Character Percent Stenosis Comments:
Report For Center Created Gender D.O.B Page 1 Carotid Assessment A B C D E Good Satisfactory Concern Serious Highest Risk Intima-Media Thickness Additional Findings Plaque Character Percent Stenosis Comments:
ULTRASOUND IMAGING EE 472 F2018. Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah
 ULTRASOUND IMAGING EE 472 F2018 Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah www.k-space.org Recommended Textbook Diagnostic Ultrasound: Physics and Equipment, 2nd ed., by Peter R. Hoskins (Editor), Kevin Martin (Editor),
ULTRASOUND IMAGING EE 472 F2018 Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah www.k-space.org Recommended Textbook Diagnostic Ultrasound: Physics and Equipment, 2nd ed., by Peter R. Hoskins (Editor), Kevin Martin (Editor),
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning
 Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.690,305 B2
 US0076903 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.690,305 B2 Harjula et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2010 (54) INCREMENT CHARGE FOR 4,408,534 A * 10, 1983 Araki et al.... 102.288 FIN-STABILIZED
US0076903 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.690,305 B2 Harjula et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2010 (54) INCREMENT CHARGE FOR 4,408,534 A * 10, 1983 Araki et al.... 102.288 FIN-STABILIZED
Application of Phased Array Radar Theory to Ultrasonic Linear Array Medical Imaging System
 Application of Phased Array Radar Theory to Ultrasonic Linear Array Medical Imaging System R. K. Saha, S. Karmakar, S. Saha, M. Roy, S. Sarkar and S.K. Sen Microelectronics Division, Saha Institute of
Application of Phased Array Radar Theory to Ultrasonic Linear Array Medical Imaging System R. K. Saha, S. Karmakar, S. Saha, M. Roy, S. Sarkar and S.K. Sen Microelectronics Division, Saha Institute of
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 US007052479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,052.479 B2 Drennan (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 2006 (54) TRACTION DEVICE 3,762.405 A * 10/1973 De George... 602/23 3,771,519 A * 11/1973 Haake......
US007052479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,052.479 B2 Drennan (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 2006 (54) TRACTION DEVICE 3,762.405 A * 10/1973 De George... 602/23 3,771,519 A * 11/1973 Haake......
Society for Behavioral Medicine 33 rd Annual Meeting New Orleans, LA
 Society for Behavioral Medicine 33 rd Annual Meeting New Orleans, LA John M. Violanti, PhD* a ; LuendaE. Charles, PhD, MPH b ; JaK. Gu, MSPH b ; Cecil M. Burchfiel, PhD, MPH b ; Michael E. Andrew, PhD
Society for Behavioral Medicine 33 rd Annual Meeting New Orleans, LA John M. Violanti, PhD* a ; LuendaE. Charles, PhD, MPH b ; JaK. Gu, MSPH b ; Cecil M. Burchfiel, PhD, MPH b ; Michael E. Andrew, PhD
United States Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit
 United States Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit IN RE RAYMOND GIANNELLI 2013-1167 Appeal from the United States Patent and Trademark Office, Patent Trial and Appeal Board, in Serial No. 10/378,261.
United States Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit IN RE RAYMOND GIANNELLI 2013-1167 Appeal from the United States Patent and Trademark Office, Patent Trial and Appeal Board, in Serial No. 10/378,261.
ARIC Manuscript Proposal #1233. PC Reviewed: 4_/_10/07 Status: _A Priority: 2_ SC Reviewed: Status: Priority:
 ARIC Manuscript Proposal #1233 PC Reviewed: 4_/_10/07 Status: _A Priority: 2_ SC Reviewed: Status: Priority: 1.a. Full Title: Subclinical atherosclerosis precedes type 2 diabetes in the ARIC study cohort
ARIC Manuscript Proposal #1233 PC Reviewed: 4_/_10/07 Status: _A Priority: 2_ SC Reviewed: Status: Priority: 1.a. Full Title: Subclinical atherosclerosis precedes type 2 diabetes in the ARIC study cohort
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080082047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0082047 A1 Harmon (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2008 (54) VEIN HOLDER (52) U.S. Cl.... 604/115 (76) Inventor: Stoney
US 20080082047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0082047 A1 Harmon (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2008 (54) VEIN HOLDER (52) U.S. Cl.... 604/115 (76) Inventor: Stoney
United States Patent (19) James
 United States Patent (19) James 54 DEVICE FOR DISPENSING MEDICAMENTS (75) Inventor: Michael James, Welwyn Garden City, England Allen & Hanburys Limited, London, 73 Assignee: England (21) Appl. No.: 767,518
United States Patent (19) James 54 DEVICE FOR DISPENSING MEDICAMENTS (75) Inventor: Michael James, Welwyn Garden City, England Allen & Hanburys Limited, London, 73 Assignee: England (21) Appl. No.: 767,518
Sepetka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 3, ) VARIABLE STIFFNESS CATHETER 4,739,768 4/1988 Engelson.
 United States Patent (19) 11 USOO5308342A Patent Number: Sepetka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 3, 1994 54) VARIABLE STIFFNESS CATHETER 4,739,768 4/1988 Engelson. o 4,775,371 10/1988 Mueller, Jr.... 604/280
United States Patent (19) 11 USOO5308342A Patent Number: Sepetka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 3, 1994 54) VARIABLE STIFFNESS CATHETER 4,739,768 4/1988 Engelson. o 4,775,371 10/1988 Mueller, Jr.... 604/280
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,932,771 B2. Whitmore et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 23, 2005
 USOO6932771B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,932,771 B2 Whitmore et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 23, 2005 (54) TISSUE WARMING DEVICE AND METHOD (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Willet
USOO6932771B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,932,771 B2 Whitmore et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 23, 2005 (54) TISSUE WARMING DEVICE AND METHOD (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Willet
SONIMAGE HS1. Premium Portable Ultrasound
 SONIMAGE HS1 Premium Portable Ultrasound EXIT SET F2 F1 User User Gain FREEZE PREMIUM PORTABLE ULTRASOUND DESIGNED FOR YOU Sonimage HS1 2 Sonimage HS1 is Konica Minolta s Premium Portable Ultrasound designed
SONIMAGE HS1 Premium Portable Ultrasound EXIT SET F2 F1 User User Gain FREEZE PREMIUM PORTABLE ULTRASOUND DESIGNED FOR YOU Sonimage HS1 2 Sonimage HS1 is Konica Minolta s Premium Portable Ultrasound designed
Using Coronary Artery Calcium Score in the Quest for Cardiac Health. Robert J. Hage, D.O.
 Using Coronary Artery Calcium Score in the Quest for Cardiac Health Robert J. Hage, D.O. Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States in both men and women. About 610,000 people die
Using Coronary Artery Calcium Score in the Quest for Cardiac Health Robert J. Hage, D.O. Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States in both men and women. About 610,000 people die
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,461,697 B1
 USOO646.1697B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,461,697 B1 Slat et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) POLYETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE 4,149,645 A 4/1979 Valyi MULTI-LAYER PREFORM USED
USOO646.1697B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,461,697 B1 Slat et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) POLYETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE 4,149,645 A 4/1979 Valyi MULTI-LAYER PREFORM USED
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2
 US00710851 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2 Niznick (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 19, 2006 (54) ENDOSSEOUS DENTAL IMPLANT 6,733,291 B1* 5/2004 Hurson... 433,173 20O2/O110784 A1*
US00710851 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2 Niznick (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 19, 2006 (54) ENDOSSEOUS DENTAL IMPLANT 6,733,291 B1* 5/2004 Hurson... 433,173 20O2/O110784 A1*
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0020415A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0020415 A1 Reno (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOMETRIC EXERCISE EQUIPMENT WITH Publication Classification PORTABLE
US 2005.0020415A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0020415 A1 Reno (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOMETRIC EXERCISE EQUIPMENT WITH Publication Classification PORTABLE
Physical Principles of Ultrasound
 Physical Principles of Ultrasound Grateful appreciation to Richard A. Lopchinsky, MD, FACS and Nancy H. Van Name, RDMS, RTR, and MarleneKattaron, RDMS 2000 UIC All Rights Reserved. Course Objectives Identify
Physical Principles of Ultrasound Grateful appreciation to Richard A. Lopchinsky, MD, FACS and Nancy H. Van Name, RDMS, RTR, and MarleneKattaron, RDMS 2000 UIC All Rights Reserved. Course Objectives Identify
Programmable Multi-Dose Intransal Drug Delivery Device
 University of Kentucky UKnowledge Mechanical Engineering Faculty Patents Mechanical Engineering 9-27-2005 Programmable Multi-Dose Intransal Drug Delivery Device Daniel Wermeling University of Kentucky,
University of Kentucky UKnowledge Mechanical Engineering Faculty Patents Mechanical Engineering 9-27-2005 Programmable Multi-Dose Intransal Drug Delivery Device Daniel Wermeling University of Kentucky,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0143905 A1 Goyal et al. US 20170143905A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) NEEDLE-FREE INUECTION GUIDE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0143905 A1 Goyal et al. US 20170143905A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) NEEDLE-FREE INUECTION GUIDE
Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Coronary Ca Score
 Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Coronary Ca Score Dr. Ghormallah Alzahrani Cardiac imaging division, Adult Cardiology department Prince Sultan Cardiac Center ( PSCC) Madina, June 2 Coronary Calcium
Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Coronary Ca Score Dr. Ghormallah Alzahrani Cardiac imaging division, Adult Cardiology department Prince Sultan Cardiac Center ( PSCC) Madina, June 2 Coronary Calcium
Ezetimibe and SimvastatiN in Hypercholesterolemia EnhANces AtherosClerosis REgression (ENHANCE)
 Ezetimibe and SimvastatiN in Hypercholesterolemia EnhANces AtherosClerosis REgression (ENHANCE) Thomas Dayspring, MD, FACP Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Medicine and Dentistry
Ezetimibe and SimvastatiN in Hypercholesterolemia EnhANces AtherosClerosis REgression (ENHANCE) Thomas Dayspring, MD, FACP Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Medicine and Dentistry
Method and system for altering consciousness
 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 5,123,899 Gall June 23, 1992 Method and system for altering consciousness Abstract A system for altering the states of human consciousness involves the simultaneous application
( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 5,123,899 Gall June 23, 1992 Method and system for altering consciousness Abstract A system for altering the states of human consciousness involves the simultaneous application
Vivid T8 Ultrasound. Cardiac and shared services. Together like never before from GE.
 Vivid T8 Ultrasound Cardiac and shared services. Together like never before from GE. Vivid cardiac. Shared services. Paired for excellent performance. In the Vivid T8, we ve taken the established cardiac
Vivid T8 Ultrasound Cardiac and shared services. Together like never before from GE. Vivid cardiac. Shared services. Paired for excellent performance. In the Vivid T8, we ve taken the established cardiac
76 Inventors: late Stella YErin, 5,479,944 1/1996 Petruson /858
 USOO593.1799A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,931,799 Guastella et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 1999 54 PARASEPTAL SPLINT FOR USE IN 4,340,040 7/1982 Straith... 606/204.45 SURGICAL NASAL
USOO593.1799A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,931,799 Guastella et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 1999 54 PARASEPTAL SPLINT FOR USE IN 4,340,040 7/1982 Straith... 606/204.45 SURGICAL NASAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160135857A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0135857 A1 Marrero, SR. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CURVEDTIBIOTALARFUSION NAIL AND Publication Classification
US 20160135857A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0135857 A1 Marrero, SR. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CURVEDTIBIOTALARFUSION NAIL AND Publication Classification
Tissue Strain Analytics Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging and Quantification
 Whitepaper Tissue Strain Analytics Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging and Quantification ACUSON S2000 Ultrasound System Answers for life. Page 1 Tissue Strain Analytics: Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging and Quantification
Whitepaper Tissue Strain Analytics Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging and Quantification ACUSON S2000 Ultrasound System Answers for life. Page 1 Tissue Strain Analytics: Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging and Quantification
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CORONARY CALCIUM SCORING
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
Change in Elasticity Caused by Flow-Mediated Dilation Measured Only for Intima Media Region of Brachial Artery
 Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Vol. 44, No. 8, 25, pp. 6297 631 #25 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Change in Elasticity Caused by Flow-Mediated Dilation Measured Only for Intima Media Region
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Vol. 44, No. 8, 25, pp. 6297 631 #25 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Change in Elasticity Caused by Flow-Mediated Dilation Measured Only for Intima Media Region
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701 65099A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0165099 A1 Buddharaju (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2017 (54) CONDOM CATHETER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A61F 5/453
(19) United States US 201701 65099A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0165099 A1 Buddharaju (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2017 (54) CONDOM CATHETER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A61F 5/453
Epidemiologic studies have established a. Risk Factors for Subclinical Carotid Atherosclerosis Among Current Smokers CLINICAL STUDY
 166 PREVENTIVE CARDIOLOGY FALL 2010 CLINICAL STUDY Risk Factors for Subclinical Carotid Atherosclerosis Among Current Smokers Heather M. Johnson, MD; Megan E. Piper, PhD; Douglas E. Jorenby, PhD; Michael
166 PREVENTIVE CARDIOLOGY FALL 2010 CLINICAL STUDY Risk Factors for Subclinical Carotid Atherosclerosis Among Current Smokers Heather M. Johnson, MD; Megan E. Piper, PhD; Douglas E. Jorenby, PhD; Michael
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070050.058A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0050058 A1 Zuziak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) PLACEMAT FOR CALCULATING AND Related U.S. Application
US 20070050.058A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0050058 A1 Zuziak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) PLACEMAT FOR CALCULATING AND Related U.S. Application
Diagnostic approach to heart disease
 Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0174911 A1 Naruse US 2006O174911A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 10, 2006 (54) ELECTRIC DENTAL FLOSS (76) Inventor: Haruhiko Naruse,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0174911 A1 Naruse US 2006O174911A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 10, 2006 (54) ELECTRIC DENTAL FLOSS (76) Inventor: Haruhiko Naruse,
Proven Performance. Enhanced Care.
 www.siemens.com/ultrasound Proven Performance. Enhanced Care. ACUSON Antares Ultrasound System Powering Advanced Care We designed the ACUSON Antares ultrasound system for use in multiple specialties, allowing
www.siemens.com/ultrasound Proven Performance. Enhanced Care. ACUSON Antares Ultrasound System Powering Advanced Care We designed the ACUSON Antares ultrasound system for use in multiple specialties, allowing
ARBITER 6-HALTS HDL And LDL Treatment Strategies
 ARBITER 6-HALTS HDL And LDL Treatment Strategies Extended-Release Niacin or Ezetimibe and Carotid Intima Media Thickness Allen J. Taylor, M.D. Todd C. Villines, M.D. Eric J. Stanek, Pharm.D. Patrick J.
ARBITER 6-HALTS HDL And LDL Treatment Strategies Extended-Release Niacin or Ezetimibe and Carotid Intima Media Thickness Allen J. Taylor, M.D. Todd C. Villines, M.D. Eric J. Stanek, Pharm.D. Patrick J.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,405,401 B1. Hellerud et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002
 USOO6405401B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Hellerud et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002 (54) TOOTHBRUSH HAVING A BRISTLE D364,740 S : 12/1995 Loew PATTERN WHICH PROVIDES ENHANCED D372.584
USOO6405401B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Hellerud et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002 (54) TOOTHBRUSH HAVING A BRISTLE D364,740 S : 12/1995 Loew PATTERN WHICH PROVIDES ENHANCED D372.584
Vivid T8 Ultrasound. Cardiac and shared services. Together like never before from GE. Take rugged reliability to challenging conditions.
 Vivid T8 Ultrasound Cardiac and shared services. Together like never before from GE. Vivid cardiac. Shared services. Paired for excellent performance. In the Vivid T8, we ve taken the established cardiac
Vivid T8 Ultrasound Cardiac and shared services. Together like never before from GE. Vivid cardiac. Shared services. Paired for excellent performance. In the Vivid T8, we ve taken the established cardiac
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors
 Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT
 DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT JTO OFFICE OF COUNSEL (PATENTS) 1176 HOWELL STREET BUILDING 112T, CODE OOOC * NEWPORT, RHODE ISLAND 02841-1708 PHONE: 401 832-4736
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFARE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT JTO OFFICE OF COUNSEL (PATENTS) 1176 HOWELL STREET BUILDING 112T, CODE OOOC * NEWPORT, RHODE ISLAND 02841-1708 PHONE: 401 832-4736
Guide to Small Animal Vascular Imaging using the Vevo 770 Micro-Ultrasound System
 Guide to Small Animal Vascular Imaging using the Vevo 770 Micro-Ultrasound System January 2007 Objectives: After completion of this module, the participant will be able to accomplish the following: Understand
Guide to Small Animal Vascular Imaging using the Vevo 770 Micro-Ultrasound System January 2007 Objectives: After completion of this module, the participant will be able to accomplish the following: Understand
Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations
 Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations August 19, 2017 Smonporn Boonyaratavej MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital
Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations August 19, 2017 Smonporn Boonyaratavej MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital
(51) Int Cl.: A61B 6/14 ( ) A61B 6/00 ( ) A61B 6/08 ( ) A61B 6/04 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 123 223 A1 (43) Date of publication: 2.11.09 Bulletin 09/48 (21) Application number: 081649.7 (1) Int Cl.: A61B 6/14 (06.01) A61B 6/00 (06.01) A61B 6/08
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 123 223 A1 (43) Date of publication: 2.11.09 Bulletin 09/48 (21) Application number: 081649.7 (1) Int Cl.: A61B 6/14 (06.01) A61B 6/00 (06.01) A61B 6/08
50 3 % % 2. ta. SN & (12) United States Patent US 7, B1. Jun. 10, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.:
 USOO7384414B1 (1) United States Patent Marshall et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,384.414 B1 Jun., 008 (54) SAFETY PEN NEEDLE WITH (75) (73) (*) (1) () (51) (5) (58) (56) NON-INUECTION END
USOO7384414B1 (1) United States Patent Marshall et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,384.414 B1 Jun., 008 (54) SAFETY PEN NEEDLE WITH (75) (73) (*) (1) () (51) (5) (58) (56) NON-INUECTION END
CVD Risk Assessment. Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic
 CVD Risk Assessment Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic What is Risk? A cumulative probability of an event, usually expressed as percentage e.g.: 5 CV events in 00 pts = 5% risk This
CVD Risk Assessment Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic What is Risk? A cumulative probability of an event, usually expressed as percentage e.g.: 5 CV events in 00 pts = 5% risk This
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Kesling 54) ORTHODONTIC HOOKASSEMBLY AND APPLIANCE 75 Inventor: Christopher K. Kesling, LaPorte, Ind. 73 Assignee: TP Orthodontics, Inc., LaPorte, Ind. 21 Appl. No.: 852,046 22
United States Patent (19) Kesling 54) ORTHODONTIC HOOKASSEMBLY AND APPLIANCE 75 Inventor: Christopher K. Kesling, LaPorte, Ind. 73 Assignee: TP Orthodontics, Inc., LaPorte, Ind. 21 Appl. No.: 852,046 22
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Brown et al. USOO6494.914B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,494.914 B2 Dec. 17, 2002 (54) UNICONDYLAR FEMORAL PROSTHESIS AND INSTRUMENTS (75) Inventors: David Ray Brown,
(12) United States Patent Brown et al. USOO6494.914B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,494.914 B2 Dec. 17, 2002 (54) UNICONDYLAR FEMORAL PROSTHESIS AND INSTRUMENTS (75) Inventors: David Ray Brown,
United States Patent (19) 3,787,641 Santori - 45) Jan. 22, 1974
 United States Patent (19) 3,787,641 Santori - 45) Jan. 22, 1974 (54) BoNE CONDUCTION MICROPHONE ASSEMBLY Primary Examiner-Ralph D. Blakeslee 75 Inventor: Charles - M. Santori, San Jose, Calif., Attorney,
United States Patent (19) 3,787,641 Santori - 45) Jan. 22, 1974 (54) BoNE CONDUCTION MICROPHONE ASSEMBLY Primary Examiner-Ralph D. Blakeslee 75 Inventor: Charles - M. Santori, San Jose, Calif., Attorney,
Trilateral Project WM4
 ANNEX 2: Comments of the JPO Trilateral Project WM4 Comparative studies in new technologies Theme: Comparative study on protein 3-dimensional (3-D) structure related claims 1. Introduction As more 3-D
ANNEX 2: Comments of the JPO Trilateral Project WM4 Comparative studies in new technologies Theme: Comparative study on protein 3-dimensional (3-D) structure related claims 1. Introduction As more 3-D
Principles of Ultrasound. Cara C. Prideaux, M.D. University of Utah PM&R Sports Medicine Fellow March 14, 2012
 Principles of Ultrasound Cara C. Prideaux, M.D. University of Utah PM&R Sports Medicine Fellow March 14, 2012 None Disclosures Outline Introduction Benefits and Limitations of US Ultrasound (US) Physics
Principles of Ultrasound Cara C. Prideaux, M.D. University of Utah PM&R Sports Medicine Fellow March 14, 2012 None Disclosures Outline Introduction Benefits and Limitations of US Ultrasound (US) Physics
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1
 USOO6413232B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1 Townsend et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) ORTHOPEDIC KNEE BRACE HAVING AN 5,807,294. A 9/1998 Cawley et al. ADJUSTABLE
USOO6413232B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1 Townsend et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) ORTHOPEDIC KNEE BRACE HAVING AN 5,807,294. A 9/1998 Cawley et al. ADJUSTABLE
(12) United States Patent
 US00895.3827B2 (12) United States Patent Sacha et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,953,827 B2 Feb. 10, 2015 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) HEARNGAD WITH INTEGRATED
US00895.3827B2 (12) United States Patent Sacha et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,953,827 B2 Feb. 10, 2015 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) HEARNGAD WITH INTEGRATED
Terminology Tissue Appearance
 By Marc Nielsen, MD Advantages/Disadvantages Generation of Image Ultrasound Machine/Transducer selection Modes of Ultrasound Terminology Tissue Appearance Scanning Technique Real-time Portable No ionizing
By Marc Nielsen, MD Advantages/Disadvantages Generation of Image Ultrasound Machine/Transducer selection Modes of Ultrasound Terminology Tissue Appearance Scanning Technique Real-time Portable No ionizing
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Figone et al. 11 Patent Number: 4,834,212 (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 1989 54) (76) 21) 22 (51) (52) (58) SOUND MUFFLER FOR COVERING THE MOUTH Inventors: Moira J. Figone; Frank
United States Patent (19) Figone et al. 11 Patent Number: 4,834,212 (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 1989 54) (76) 21) 22 (51) (52) (58) SOUND MUFFLER FOR COVERING THE MOUTH Inventors: Moira J. Figone; Frank
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O130094A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0130094A1 Graham (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) ORTHODONTIC ACCESSORY ARCH BAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 433/20
(19) United States US 2005O130094A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0130094A1 Graham (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) ORTHODONTIC ACCESSORY ARCH BAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 433/20
