NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
|
|
|
- Dana Henry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation for faecal incontinence Faecal incontinence occurs when a person loses the ability to control their bowel movements, resulting in unplanned leakage of faeces. It can happen as a result of congenital problems with the anal sphincter (the ring of muscle that keeps the anus closed), or following childbirth, injury to or disease of the nervous system or spinal cord, prolapse of the rectum or pelvic organs, surgery involving the colon or anus, or pelvic radiotherapy. In this procedure, an inflatable circular cuff is placed under the skin around the anus, so it fits around the neck of the anal sphincter. A pump is implanted under the skin in the lower half of the abdomen which aims to allow movement of fluid to and from the cuff, to open or close the anus and allow bowel movements to be controlled. Introduction This overview has been prepared to assist members of the Interventional Procedures Advisory Committee (IPAC) in making recommendations about the safety and efficacy of an interventional procedure. It is based on a rapid review of the medical literature and specialist opinion. It should not be regarded as a definitive assessment of the procedure. Date prepared This overview was prepared in April Procedure name Transabdominal implantation of an artificial anal sphincter for faecal incontinence Specialty societies Association of Coloproctology of Great Britain and Ireland. IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 1 of 15
2 Description Indications and current treatment Faecal incontinence occurs when a person loses control of their bowel and is unable to retain faeces in the rectum. Faecal incontinence can be caused by a wide variety of conditions that affect either the anatomy or function of the anal sphincter. Perineal injury during vaginal delivery is a common cause of faecal incontinence in women. Faecal incontinence can also be caused by neurological or spinal disease/injury (for example, stroke, multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injury). It may also occur following pelvic organ and/or rectal prolapse, colonic resection or anal surgery, or pelvic radiotherapy. For some patients faecal incontinence may be the result of surgical correction of congenital anorectal conditions, such as anorectal atresia or Hirschprung s disease, or the result of other anorectal surgery. Frail older people, people with diarrhoea, people with severe cognitive impairment or learning disabilities, and people with urinary incontinence are also at risk. Faecal incontinence is associated with a high level of physical disability and social stigma. Its true incidence may be under-reported due to the sensitive and embarrassing nature of the condition. Typically, first-line treatment for faecal incontinence is conservative, such as antidiarrhoeal medication and dietary management. This may be followed by pelvic floor muscle training, biofeedback therapy and electrical stimulation. If conservative treatments have been unsuccessful, surgery, such as sphincter repair, may be recommended in patients with severe faecal incontinence. In patients for whom local surgery fails or is inappropriate, other surgical options include sacral nerve stimulation, stimulated graciloplasty (creation of a new sphincter from other suitable muscles) or implantation of an artificial anal sphincter (anorectal or transabdominal). More severe cases may require a permanent colostomy. What the procedure involves The procedure involves the implantation of three device components. The first is a sphincter cuff (consisting of an expander and a gel filled pillow) that is implanted around the anus. The control pump and balloon reservoir are then inserted into the abdominal space. All the components are joined together by tubing that allows the flow of saline solution between each component. The inflatable cuff keeps the anal canal closed. To evacuate the bowel, the patient needs to press the control pump's button against the abdominal wall. This deflates the cuff and opens the anus by pumping fluid from the sphincter cuff to the balloon reservoir. The sphincter remains open until the patient wishes to close it by pressing the button on the pump. This opens the pump allowing fluid to automatically return to the cuff. As the balloon reservoir refills IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 2 of 15
3 the sphincter cuff gently squeezes the upper anal canal/lower rectum producing angulation between the rectum and anal canal. Under general or other appropriate anaesthesia,a lower mid-line incision is made, extending from the pubic symphysis to the umbilicus. A small window is then cut in the pelvic peritoneum and the inflatable sphincter cuff is a sphincter cuff (consisting of an expander and a gel filled pillow) is placed around the neck of the anal sphincter. The expander component of the cuff is placed behind the anorectal junction and the gel filled pillow placed in front. The two components are then secured using a strap. A subcutaneous pouch is then created for the control pump, usually in the right iliac fossa. A balloon reservoir is placed within the peritoneal cavity in the pelvis. The connecting tubes from the sphincter cuff and the pressure regulating balloon reservoir are brought through the abdominal wall from the pelvis. These tubes are connected to the control pump and the abdomen is closed. The aim of this procedure is to reduce the rate of infection and complications associated with the anorectal approach. Efficacy The evidence is based on one case series of 12 patients. At a median follow-up of 59 months (range: months), 75% (9/12) of patients had a functioning implant, with 5 of the 9 patients requiring surgical revision. Four patients required surgical revision to replace the operating pump and one due to disruption of the strap. Continence (assessed using the Cleveland Clinical continence score) was evaluable in 10 patients. The median Cleveland Clinic continence scores improved from 16 (range: 7 20) before to 3 (range: 0 7) after surgery. Safety Three patients (25%) had the device removed because of complications. One patient developed pseudomembranous colitis in the perioperative period. Two other patients had the device removed because of infection after revision surgery. Literature review Rapid review of literature The medical literature was searched to identify studies and reviews relevant to transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation for faecal incontinence. Searches were conducted of the following databases, covering the period from their commencement to 16 April 2008: MEDLINE, PREMEDLINE, IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 3 of 15
4 EMBASE, Cochrane Library and other databases. Trial registries and the Internet were also searched. No language restriction was applied to the searches (see appendix C for details of search strategy). The following selection criteria (table 1) were applied to the abstracts identified by the literature search. Where selection criteria could not be determined from the abstracts the full paper was retrieved. Table 1 Inclusion criteria for identification of relevant studies Characteristic Publication type Patient Intervention/test Outcome Language Criteria Clinical studies were included. Emphasis was placed on identifying good quality studies. Abstracts were excluded where no clinical outcomes were reported, or where the paper was a review, editorial, or a laboratory or animal study. Conference abstracts were also excluded because of the difficulty of appraising study methodology, unless they reported specific adverse events that were not available in the published literature. Patients with faecal incontinence. Transabdominal implantation of an artificial anal sphincter. Articles were retrieved if the abstract contained information relevant to the safety and/or efficacy. Non-English-language articles were excluded unless they were thought to add substantively to the English-language evidence base. List of studies included in the overview This overview is based on 12 patients from one case series study. Other studies that were considered to be relevant to the procedure but were not included in the main extraction table (table 2) have been listed in appendix A. Existing assessments of this procedure There were no published assessments from other organisations identified at the time of the literature search. Related NICE guidance Below is a list of NICE guidance related to this procedure. Appendix B gives details of the recommendations made in each piece of guidance listed below. Interventional procedures Artificial anal sphincter implantation. NICE interventional procedures guidance 66 (2004). Available from IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 4 of 15
5 Stimulated graciloplasty for faecal incontinence. NICE interventional procedures guidance 159 (2006). Available from Injectable bulking agents for faecal incontinence. NICE interventional procedures guidance 210 (2007). Available from Sacral nerve stimulation for faecal incontinence. NICE interventional procedures guidance 99 (2004). Available from Clinical guidelines Faecal incontinence: the management of faecal incontinence in adults. NICE clinical guideline 49 (2007). Available from IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 5 of 15
6 Table 2 Summary of key efficacy and safety findings on transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation for faecal incontinence Study details Key efficacy findings Key safety findings Comments Finlay G et al (2004) 1 Operative success Three patients required device First clinical paper published Study type: Case series Implantation was achieved in all 12 patients. removal due to complications. on this procedure. Country: UK Study period: Not stated Study population: The principal cause of faecal incontinence was idiopathic faecal incontinence (6 patients), obstetric sphincter injury (3 patients) and imperforate anus (3 patients) n = 12 Age: 47 years (range years) Sex: 83% (10) females, 17% (2) males Inclusion criteria: All patients were or had been incontinent to solid stool on at least 5 days each week. All patients had undergone at least one surgical procedure that had failed to alleviate their symptoms. Technique: The prosthetic anal sphincter cuff was implanted at the anal canal junction and the pump implanted in a subcutaneous pouch in the iliac fossa. However the authors stated that the device was removed in 3 of the first 6 patients. The device was then modified and, with the benefit of clinical experience, no devices were removed in the next 6 patients. 75% (9/12) patients had a functioning implant after a median follow-up of 59 months. 5 of the 9 patients required further surgical revision: due to disruption of the strap (1 patient) to replace the operating pump (4 patients). Continence (assessed using the Cleveland Clinical continence score (maximal incontinence score of 20). Results are based on 10 evaluable patients. Continence score pre-procedure; 16 (range 7 20) Continence score 1 year post-procedure; 3 (range 0 7). A patient was readmitted to hospital soon after discharge with severe pseudomembranous colitis that failed to respond to conservative measures. The patient was found to have a perforation of the right colon which required emergency total colectomy and removal of the device. Another patient developed a streptococcal infection at the pump site 5 months after implantation, and required device removal. The third patient developed a disruption of the strap that joined the two components of the sphincter. This led to loss of bowel control. The strap was subsequently re-sutured during a further laparotomy, but the device became infected and was removed 4 months later. Limited evidence reported on efficacy outcomes. Early complications led to changes in protocol in terms of antibiotics as well as device modification. Patients with severe faecal incontinence. Follow-up: Median follow-up 59 months (range months) Conflict of interest: All authors have declared having a shareholding in the company which holds the patent for the device used in this procedure. Two patients required a admission to hospital for bowel washout (as a result of faecal impacation). IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 6 of 15
7 Validity and generalisability of the studies The case series included in Table 2 is the first clinical report using the transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation for faecal incontinence. It is based on a small number of patients and with a median follow-up of 59 months (minimum 30 months). The authors noted that early complications led to device modifications during the course of the study. High complication rates have been reported with other methods of anorectal implantation of artificial anal sphincters. The full clinical guideline on faecal incontinence notes that in 14 case series with a total of 402 patients, 20% (95% confidence interval [CI], 13% to 27%) of patients had complications associated with wound infection, while 50% (95% CI, 44% to 55%) had other complications. Specialist Advisers opinions Specialist advice was sought from consultants who have been nominated or ratified by their Specialist Society or Royal College. The advice received is their individual opinion and does not represent the view of the society. Mr D Bartolo, Dr Hunt,Mr E Kiff, Professor R Phillips, Professor J Monson, Professor N Mortenson, Mr P Sagar, Professor N Williams (Association of Coloproctology of Great Britain and Ireland). It is in effect a stenosing procedure that relies on delaying the passage of a formed stool. The technology is very similar to anorectal implantation of an artificial anal sphincter, which has been in use for several years. There are only preliminary data available on this technique. It should be associated with less infection and less risk of migration through the skin than the perineal procedure. IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 7 of 15
8 Key efficacy outcomes are lower pressure occlusion - potentially less to go wrong; but more invasive placement and not sufficiently distal to obviate some mucous leakage. Artificial anal sphincter implantations have not been carried out in large numbers because of the high explant (removal) rate related to infection. A theoretical difficulty may be replacing the device (as with other artificial anal sphincters), but while replacement is relatively easy through the perineum, this procedure requires a low rectal dissection through an abdominal incision. Safety concerns will be similar to those associated with other artificial sphincters, such as erosion and septic complications, however it is argued that the design of the device should reduce the complication rate. Long term follow-up is important. Most cases of faecal incontinence are now treated with sacral nerve stimulation and there are few indications for this technique. Issues for consideration by IPAC The clinical guidance on faecal incontinence refers to artificial anal sphincters and IPG 66. The manufacturer states that 24 patients have had the procedure with up to 11 year follow-up. IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 8 of 15
9 References 1. Finlay, IG.Richardson W and Hajivassiliou, C.A. (2004) Outcome after implantation of a novel prosthetic anal sphincter in humans.british Journal of Surgery IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 9 of 15
10 Appendix A: Additional papers on transabdominal n artificial bowel sphincter implantation for faecal incontinence The following table outlines the studies that are considered potentially relevant to the overview but were not included in the main data extraction table (table 2). It is by no means an exhaustive list of potentially relevant studies. Article Hajivassiliou CA and Finlay IG. (1998) Effect of a novel prosthetic anal neosphincter on human colonic blood flow. British Journal of Surgery 85: Number of patients/follow-up Direction of conclusions 11 patients. The study does not report on safety and efficacy outcomes in patients with faecal incontinence Reasons for noninclusion in table 2 The study does not report on safety and efficacy outcomes in patients with faecal incontinence IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 10 of 15
11 Appendix B: Related NICE guidance for transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implanation for faecal incontinence Guidance Interventional procedures Recommendations Artificial anal sphincter implantation. NICE interventional procedures guidance 66 (2004). 1.1 Current evidence on the safety and efficacy of artificial anal sphincter implantation does not appear adequate for this procedure to be used without special arrangements for consent and for audit or research. 1.2 Clinicians wishing to undertake artificial anal sphincter implantation should take the following actions. Inform the clinical governance leads in their Trusts. Ensure that patients understand the uncertainty about the procedure s safety and efficacy and provide them with clear written information. Use of the Institute s Information for the Public is recommended. Audit and review clinical outcomes of all patients having artificial anal sphincter implantation. 1.3 Publication of safety and efficacy outcomes will be useful in reducing the current uncertainty. The Institute may review the procedure upon publication of further evidence. 1.4 It is recommended that this procedure is carried out only in units with a specialist interest in faecal incontinence. Stimulated graciloplasty for faecal incontinence. NICE interventional procedures guidance 159 (2006). 1.1 Current evidence on the safety and efficacy of stimulated graciloplasty for faecal incontinence is limited, but appears sufficient to support the use of this procedure for carefully selected patients in whom other treatments have failed or are contraindicated, provided that the normal arrangements are in place for consent, audit and clinical governance. 1.2 This procedure should be performed only in specialist units by clinicians with specific training and experience in the assessment and treatment of faecal incontinence. IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 11 of 15
12 Guidance Recommendations Injectable bulking agents for faecal incontinence. NICE interventional procedures guidance 210 (2007). 1.1 Current evidence on the safety and efficacy of injectable bulking agents for faecal incontinence does not appear adequate for this procedure to be used without special arrangements for consent and for audit or research, which should take place in the context of a clinical trial or formal audit protocol that includes information on well-defined patient groups. 1.2 Clinicians wishing to inject bulking agents for the treatment of faecal incontinence should take the following actions. Inform the clinical governance leads in their Trusts. Ensure that patients understand the uncertainty about the procedure s safety and efficacy, and provide them with clear written information. In addition, use of the Institute s information for patients ( Understanding NICE guidance ) is recommended (available from Audit and review clinical outcomes of all patients receiving injectable bulking agents for faecal incontinence (see section 3.1). 1.3 The procedure should only be performed in units specialising in the assessment and treatment of faecal incontinence. The Institute may review the procedure upon publication of further evidence. Sacral nerve stimulation for faecal incontinence. NICE interventional procedures guidance 99 (2004) 1.1 Current evidence on the safety and efficacy of sacral nerve stimulation for faecal incontinence appears adequate to support the use of this procedure, provided that the normal arrangements are in place for consent, audit and clinical governance. 1.2 The procedure should only be performed in specialist units by clinicians with a particular interest in the assessment and treatment of faecal incontinence. IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 12 of 15
13 Guidance Recommendations Clinical guidelines Faecal incontinence. NICE clinical guideline 49 (2007) If a trial of sacral nerve stimulation is unsuccessful, an individual can be considered for a neosphincter, for which the two options are a stimulated graciloplasty or an artificial anal sphincter. People should be informed of the potential benefits and limitations of both procedures. Those offered these procedures should be informed that they may experience evacuatory disorders and/or serious infection, either of which may necessitate removal of the device. People being considered for either procedure should be assessed and managed at a specialist centre with experience of performing these procedures. If an artificial anal sphincter is to be used, there are special arrangements that should be followed, as indicated in NICE interventional procedures guidance People who have an implanted sacral nerve stimulation device, stimulated graciloplasty or an artificial anal sphincter should be offered training and ongoing support at a specialist centre. These people should be monitored, have regular reviews and be given a point of contact. IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 13 of 15
14 Appendix C: Literature search for transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation for faecal incontinence : Transabdominal implantation of an artificial anal sphincter for faecal incontinence Database Date searched Version searched Cochrane Library 15/4/08 Issue 1, 2008 CRD databases (DARE & 15/4/08 - HTA) Embase 15/4/ to 2008 Week 15 Medline 15/4/ to April Week Medline in Process (MiP) 15/4/ to Present CINAHL 15/4/ to date (via Dialog) British Library Inside 11/4/08 - Conferences The National Research 11/4/08 - Register (NRR) Archive Controlled Trials Registry 11/4/08 - The following search strategy was used to identify papers in MEDLINE. A similar strategy was used to identify papers in other databases. 1 Prosthesis Implantation/ 2 "Prostheses and Implants"/ 3 (Prosthe$ adj3 Implant$).tw. 4 (Artificial$ adj3 Implant$).tw. 5 Prosthe$.tw. 6 Artificial$.tw. 7 Implant$.tw. 8 Endoprosthe$.tw. 9 or/ Anal Canal/ 11 ((Anal$ or Anus$) adj3 Canal$).tw. 12 ((Anal$ or Anus$) adj3 Sphincter$).tw. 13 (Anorectal$ adj3 Disease$).tw. 14 (Anorectal$ adj3 Junction$).tw. 15 (Puborectali$ adj3 Muscle$).tw. 16 or/ Fecal Incontinence/ 18 Anus Diseases/ IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 14 of 15
15 19 Encopresis/ 20 ((Fec$ or Faec$) adj3 Incontinen$).tw. 21 ((Anal$ or Anus$) adj3 Diseas$).tw. 22 Encopre$.tw. 23 ((Anal$ or Anus$) adj3 Incontinen$).tw. 24 or/ PAS.tw and and 16 and or Animals/ 30 Humans/ not (29 and 30) not 31 IP overview: transabdominal artificial bowel sphincter implantation Page 15 of 15
A70.4 Insertion of neurostimulator electrodes into peripheral nerve Z12.2 Posterior tibial nerve R15.X Faecal incontinence
 The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has issued full guidance to the NHS in England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland on Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS) for
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has issued full guidance to the NHS in England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland on Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS) for
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of arthroscopic femoro acetabular surgery for hip impingement syndrome Hip impingement
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of arthroscopic femoro acetabular surgery for hip impingement syndrome Hip impingement
PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS. A08/S/d Colorectal: Faecal Incontinence (Adult)
 A08/S/d 2013/14 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR COLORECTAL: FAECAL INCONTINENCE (ADULT) PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No. Service Commissioner Lead Provider
A08/S/d 2013/14 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR COLORECTAL: FAECAL INCONTINENCE (ADULT) PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No. Service Commissioner Lead Provider
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of individually magnetic resonance imaging-designed unicompartmental interpositional
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of individually magnetic resonance imaging-designed unicompartmental interpositional
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed defaecation syndrome
 Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed Issued: June 2010 www.nice.org.uk/ipg351 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed Issued: June 2010 www.nice.org.uk/ipg351 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of incisionless otoplasty Incisionless surgery to correct protruding ears Protruding
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of incisionless otoplasty Incisionless surgery to correct protruding ears Protruding
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of therapeutic percutaneous image-guided aspiration of spinal cysts This procedure
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of therapeutic percutaneous image-guided aspiration of spinal cysts This procedure
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of minimally invasive two-incision surgery for total hip replacement Introduction This
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of minimally invasive two-incision surgery for total hip replacement Introduction This
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE The management of faecal incontinence in adults 1.1 Short title Faecal incontinence 2 Background (a) (b) (c) The National Institute
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE The management of faecal incontinence in adults 1.1 Short title Faecal incontinence 2 Background (a) (b) (c) The National Institute
Infracoccygeal sacropexy using mesh for uterine prolapse repair
 Infracoccygeal sacropexy using mesh for uterine Issued: January 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg280 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Infracoccygeal sacropexy using mesh for uterine Issued: January 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg280 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Faecal Incontinence Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
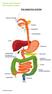 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of endoscopic augmentation of the lower oesophageal sphincter using hydrogel
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of endoscopic augmentation of the lower oesophageal sphincter using hydrogel
Surgical repair of vaginal wall prolapse using mesh
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Surgical repair of vaginal wall prolapse using mesh Vaginal wall prolapse happens when the normal support
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Surgical repair of vaginal wall prolapse using mesh Vaginal wall prolapse happens when the normal support
Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Faecal Incontinence
 Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Faecal Incontinence Questions & Answers GLASGOW COLORECTAL CENTRE Ross Hall Hospital 221 Crookston Road Glasgow G52 3NQ e-mail: info@colorectalcentre.co.uk Ph: Main hospital
Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Faecal Incontinence Questions & Answers GLASGOW COLORECTAL CENTRE Ross Hall Hospital 221 Crookston Road Glasgow G52 3NQ e-mail: info@colorectalcentre.co.uk Ph: Main hospital
Biodegradable spacer insertion to reduce rectal toxicity during radiotherapy for prostate cancer
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Biodegradable spacer insertion to reduce rectal toxicity during radiotherapy for prostate cancer Radiotherapy
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Biodegradable spacer insertion to reduce rectal toxicity during radiotherapy for prostate cancer Radiotherapy
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Interventional procedure overview of stimulated graciloplasty
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME 019 Interventional procedure overview of stimulated graciloplasty Introduction This overview has been prepared
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME 019 Interventional procedure overview of stimulated graciloplasty Introduction This overview has been prepared
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of tenotomy of horizontal eye muscles for nystagmus (with reattachment at their
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of tenotomy of horizontal eye muscles for nystagmus (with reattachment at their
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control SURGERY TO TREAT URINARY INCONTINENCE AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is Urinary Incontinence? Urinary incontinence
BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control SURGERY TO TREAT URINARY INCONTINENCE AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is Urinary Incontinence? Urinary incontinence
OHTAC Recommendation
 OHTAC Recommendation Sacral Nerve Stimulation for the Management of Urge Incontinence, Urgency-Frequency, Urinary Retention and Fecal Incontinence March 2, 2005 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory
OHTAC Recommendation Sacral Nerve Stimulation for the Management of Urge Incontinence, Urgency-Frequency, Urinary Retention and Fecal Incontinence March 2, 2005 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of collagen paste for closing an anal fistula An anal fistula is a narrow tunnel
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of collagen paste for closing an anal fistula An anal fistula is a narrow tunnel
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of endoscopic radiofrequency therapy of the anal sphincter for faecal incontinence
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of endoscopic radiofrequency therapy of the anal sphincter for faecal incontinence
Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists
 Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists Disclosures none Outline Definition Etiologies Exam findings Additional testing Medical management Surgical options What is fecal incontinence? Recurrent
Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists Disclosures none Outline Definition Etiologies Exam findings Additional testing Medical management Surgical options What is fecal incontinence? Recurrent
Biodegradable spacer insertion to reduce rectal toxicity during radiotherapy for prostate cancer
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Biodegradable spacer insertion to reduce rectal toxicity during radiotherapy for prostate cancer Radiotherapy
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Biodegradable spacer insertion to reduce rectal toxicity during radiotherapy for prostate cancer Radiotherapy
Novel Options for the Management of Fecal Incontinence
 Novel Options for the Management of Fecal Incontinence Arnold Wald, MD, MACG University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison WI ANORECTAL CONTINENCE MECHANISMS Reservoir Elements
Novel Options for the Management of Fecal Incontinence Arnold Wald, MD, MACG University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison WI ANORECTAL CONTINENCE MECHANISMS Reservoir Elements
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566
 Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
Faecal incontinence. Faecal incontinence: the management of faecal incontinence in adults
 Issue date: June 2007 Faecal incontinence Faecal incontinence: the management of faecal incontinence in adults NICE clinical guideline 49 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Acute Care NICE
Issue date: June 2007 Faecal incontinence Faecal incontinence: the management of faecal incontinence in adults NICE clinical guideline 49 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Acute Care NICE
Dear Colleagues, EXTENSION OF PAUSE TO THE USE OF VAGINAL MESH
 29/03/2019 NHS Improvement and NHS England Wellington House 133-155 Waterloo Road London SE1 8UG 020 3747 0000 www.england.nhs.uk www.improvement.nhs.uk To: Regional Directors, Trust Medical Directors,
29/03/2019 NHS Improvement and NHS England Wellington House 133-155 Waterloo Road London SE1 8UG 020 3747 0000 www.england.nhs.uk www.improvement.nhs.uk To: Regional Directors, Trust Medical Directors,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of percutaneous mitral valve leaflet repair for mitral regurgitation Mitral regurgitation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of percutaneous mitral valve leaflet repair for mitral regurgitation Mitral regurgitation
Third & Fourth Degree Tears guideline (GL926)
 Third & Fourth Degree Tears guideline (GL926) Approval Approval Group Job Title, Chair of Committee Date Maternity & Children s Services Clinical Governance Committee Chair, Maternity Clinical Governance
Third & Fourth Degree Tears guideline (GL926) Approval Approval Group Job Title, Chair of Committee Date Maternity & Children s Services Clinical Governance Committee Chair, Maternity Clinical Governance
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
 Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Consent Advice No. 9 June 2010 REPAIR OF THIRD- AND FOURTH-DEGREE PERINEAL TEARS FOLLOWING CHILDBIRTH This is the first edition of this guidance. This
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Consent Advice No. 9 June 2010 REPAIR OF THIRD- AND FOURTH-DEGREE PERINEAL TEARS FOLLOWING CHILDBIRTH This is the first edition of this guidance. This
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men
 Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men (formerly ACPWH) Useful resources Websites Pelvic Obstetric & Gynaecological Physiotherapy - pogp.csp.org.uk Bladder and Bowel Foundation - www.bladderandbowelfoundation.org
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men (formerly ACPWH) Useful resources Websites Pelvic Obstetric & Gynaecological Physiotherapy - pogp.csp.org.uk Bladder and Bowel Foundation - www.bladderandbowelfoundation.org
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583
 Sacrocolpopexy using mesh to repair vaginal vault prolapse Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583 Your responsibility This guidance represents the view of
Sacrocolpopexy using mesh to repair vaginal vault prolapse Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583 Your responsibility This guidance represents the view of
Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence)
 Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence) What is Accidental Bowel Leakage (ABL)? Accidental bowel leakage is the inability to control solid or liquid stool. This is the inability to control gas and
Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence) What is Accidental Bowel Leakage (ABL)? Accidental bowel leakage is the inability to control solid or liquid stool. This is the inability to control gas and
Bowel Cancer in England and Wales A summary report about the management and outcomes of people with bowel cancer
 Bowel Cancer in England and Wales A summary report about the management and outcomes of people with bowel cancer Based on findings from the National Bowel Cancer Audit Background How are patients diagnosed?
Bowel Cancer in England and Wales A summary report about the management and outcomes of people with bowel cancer Based on findings from the National Bowel Cancer Audit Background How are patients diagnosed?
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME 074 Introduction Interventional procedure overview of percutaneous endoscopic colostomy This overview has been
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME 074 Introduction Interventional procedure overview of percutaneous endoscopic colostomy This overview has been
Pelvic Floor Disorders. Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon
 Pelvic Floor Disorders Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon What is Pelvic Floor Disorder Surgical perspective symptoms of RED, FI or prolapse on the background
Pelvic Floor Disorders Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon What is Pelvic Floor Disorder Surgical perspective symptoms of RED, FI or prolapse on the background
Treatments for Fecal Incontinence A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treatments for Fecal Incontinence A Review of the Research for Adults e Is This Information Right for Me? This information is right for you if: Your health care professional* said you or your loved one
Treatments for Fecal Incontinence A Review of the Research for Adults e Is This Information Right for Me? This information is right for you if: Your health care professional* said you or your loved one
PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY. ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System
 PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System WHAT IS ANORECTAL MANOMETRY? Anorectal manometry is a test used to evaluate the function and coordination of the sphincter and pelvic
PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System WHAT IS ANORECTAL MANOMETRY? Anorectal manometry is a test used to evaluate the function and coordination of the sphincter and pelvic
Medicines and Technologies Programme Adoption Scoping Report MTG315 Peristeen
 Medicines and Technologies Programme Adoption Scoping Report MTG315 Peristeen SUMMARY for MTAC1 meeting Contributors questioned why NICE are writing guidance on this system alone when it is viewed and
Medicines and Technologies Programme Adoption Scoping Report MTG315 Peristeen SUMMARY for MTAC1 meeting Contributors questioned why NICE are writing guidance on this system alone when it is viewed and
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of direct C1 lateral mass screw procedure for cervical spine stabilisation Introduction
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of direct C1 lateral mass screw procedure for cervical spine stabilisation Introduction
Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy
 A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of superior rectal artery embolisation for haemorrhoids Haemorrhoids (piles) are
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of superior rectal artery embolisation for haemorrhoids Haemorrhoids (piles) are
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of electrically-stimulated intravesical chemotherapy for superficial bladder
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of electrically-stimulated intravesical chemotherapy for superficial bladder
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction. Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield
 GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of interstitial photodynamic therapy for malignant parotid tumours The parotid
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of interstitial photodynamic therapy for malignant parotid tumours The parotid
Peristeen and the Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Score (NBD) for pediatric patients with spina bifida
 Peristeen and the Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Score (NBD) for pediatric patients with spina bifida Coloplast develops products and services that make life easier for people with very personal and private
Peristeen and the Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Score (NBD) for pediatric patients with spina bifida Coloplast develops products and services that make life easier for people with very personal and private
2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL)
 2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL) SECTION B PART 1 - SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No. Service
2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL) SECTION B PART 1 - SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No. Service
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of inserting a biodegradable subacromial spacer for rotator cuff tears The rotator
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of inserting a biodegradable subacromial spacer for rotator cuff tears The rotator
A Case of Fecal Incontinence: Medical and Interventional Treatment Options
 A Case of Fecal Incontinence: Medical and Interventional Treatment Options HPI JP is a 69 year-old F with a 12-month history of FI. Her symptoms began after a colonoscopy She has been experiencing passive
A Case of Fecal Incontinence: Medical and Interventional Treatment Options HPI JP is a 69 year-old F with a 12-month history of FI. Her symptoms began after a colonoscopy She has been experiencing passive
Tertiary, regional and local pelvic floor service providers: the future. model? Andrew Williams
 Tertiary, regional and local pelvic floor service providers: the future Andrew Williams model? Pelvic Floor Unit Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust Background 23% women suffer at least one pelvic
Tertiary, regional and local pelvic floor service providers: the future Andrew Williams model? Pelvic Floor Unit Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust Background 23% women suffer at least one pelvic
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of percutaneous endoscopic laser lumbar discectomy Symptomatic lumbar disc prolapse
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of percutaneous endoscopic laser lumbar discectomy Symptomatic lumbar disc prolapse
Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces
 Rationale Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces These guidelines are to provide the required information for designated registered nurses, health care assistants and bank support workers to perform
Rationale Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces These guidelines are to provide the required information for designated registered nurses, health care assistants and bank support workers to perform
Instructions for Use
 CONTINENCE RESTORATION SYSTEM Instructions for Use Humanitarian Device Authorized by Federal (USA) Law for use in the treatment of fecal incontinence in patients who are not candidates for or have previously
CONTINENCE RESTORATION SYSTEM Instructions for Use Humanitarian Device Authorized by Federal (USA) Law for use in the treatment of fecal incontinence in patients who are not candidates for or have previously
CONTINENCE MODULE 1 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMALE LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS
 CONTINENCE MODULE 1 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMALE LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS The minimum standards required to initiate specialised conservative
CONTINENCE MODULE 1 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMALE LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS The minimum standards required to initiate specialised conservative
Prosthetic intervertebral disc replacement in the cervical spine: Cost-effectiveness compared with cervical discectomy with or without vertebral
 Prosthetic intervertebral disc replacement in the cervical spine: Cost-effectiveness compared with cervical discectomy with or without vertebral fusion Author: William Horsley NHS North East Treatment
Prosthetic intervertebral disc replacement in the cervical spine: Cost-effectiveness compared with cervical discectomy with or without vertebral fusion Author: William Horsley NHS North East Treatment
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of laparoscopic mesh pectopexy for apical prolapse of the uterus or vagina Apical
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of laparoscopic mesh pectopexy for apical prolapse of the uterus or vagina Apical
Faecal incontinence. The management of faecal incontinence in adults. Issued: June NICE clinical guideline 49. guidance.nice.org.
 Faecal incontinence The management of faecal incontinence in adults Issued: June 2007 NICE clinical guideline 49 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg49 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre for Clinical
Faecal incontinence The management of faecal incontinence in adults Issued: June 2007 NICE clinical guideline 49 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg49 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre for Clinical
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction. Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Surgical treatment of urinary stress incontinence with tension free vaginal tape
 Surgical treatment of urinary stress incontinence with tension free vaginal tape Gynaecology department 01935 384 385 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk Many surgical operations are available for the treatment of
Surgical treatment of urinary stress incontinence with tension free vaginal tape Gynaecology department 01935 384 385 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk Many surgical operations are available for the treatment of
MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW
 MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW ANAL MANOMETRY MEASURES PRESSURE ALLOWS INTERPRITATION SENSATION RAIR RECTAL COMPLIANCE MOTIVATION OF THE PATIENT FUNCTION OF THE PUDENDAL NERVE WHEN TO USE ANAL MANOMETRY
MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW ANAL MANOMETRY MEASURES PRESSURE ALLOWS INTERPRITATION SENSATION RAIR RECTAL COMPLIANCE MOTIVATION OF THE PATIENT FUNCTION OF THE PUDENDAL NERVE WHEN TO USE ANAL MANOMETRY
ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Benign Anorectal Disorders
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Benign Anorectal Disorders Arnold Wald, MD, MACG 1, Adil E. Bharucha, MBBS, MD 2, Bard C. Cosman, MD, MPH, FASCRS 3 and William E. Whitehead, PhD, MACG 4 1 Division
ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Benign Anorectal Disorders Arnold Wald, MD, MACG 1, Adil E. Bharucha, MBBS, MD 2, Bard C. Cosman, MD, MPH, FASCRS 3 and William E. Whitehead, PhD, MACG 4 1 Division
MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW
 MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW ANAL MANOMETRY MEASURES PRESSURE ALLOWS INTERPRITATION SENSATION RAIR RECTAL COMPLIANCE MOTIVATION OF THE PATIENT FUNCTION OF THE PUDENDAL NERVE WHEN TO USE ANAL MANOMETRY
MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW ANAL MANOMETRY MEASURES PRESSURE ALLOWS INTERPRITATION SENSATION RAIR RECTAL COMPLIANCE MOTIVATION OF THE PATIENT FUNCTION OF THE PUDENDAL NERVE WHEN TO USE ANAL MANOMETRY
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy
 Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Antigrade Colonic Enema (ACE) Information for patients Spinal Injuries
 Antigrade Colonic Enema (ACE) Information for patients Spinal Injuries page 2 of 8 This leaflet has been produced in support of the explanation and counselling provided by your urologist and nurse specialist.
Antigrade Colonic Enema (ACE) Information for patients Spinal Injuries page 2 of 8 This leaflet has been produced in support of the explanation and counselling provided by your urologist and nurse specialist.
Surgery for stress incontinence:
 Surgery for stress incontinence: information for you aashara Published February 2005 by the RCOG Contents Key points About this information What is stress incontinence? Do I need an operation? What operation
Surgery for stress incontinence: information for you aashara Published February 2005 by the RCOG Contents Key points About this information What is stress incontinence? Do I need an operation? What operation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE. Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence 2 Background a) The National
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence 2 Background a) The National
Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma
 Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma Dr. Shamaila Butt Gastroenterology Research Registrar GI Physiology unit University College Hospital London GI manifestations in Scleroderma Oesophagus
Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma Dr. Shamaila Butt Gastroenterology Research Registrar GI Physiology unit University College Hospital London GI manifestations in Scleroderma Oesophagus
1) What conditions is vaginal mesh used to commonly treat? Vaginal mesh is used to treat two different health issues in women:
 Vaginal Mesh Frequently Asked Questions 1) What conditions is vaginal mesh used to commonly treat? Vaginal mesh is used to treat two different health issues in women: a) stress urinary incontinence (SUI)
Vaginal Mesh Frequently Asked Questions 1) What conditions is vaginal mesh used to commonly treat? Vaginal mesh is used to treat two different health issues in women: a) stress urinary incontinence (SUI)
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet Background Faecal incontinence is a common health problem, affecting over 1% of community-dwelling adults (1;2). Chronic constipation may affect 3-5% of the population depending
Patient Information Leaflet Background Faecal incontinence is a common health problem, affecting over 1% of community-dwelling adults (1;2). Chronic constipation may affect 3-5% of the population depending
Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives
 Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives 1 Aims of this self assessment competency To equip Midwives with the knowledge and skills to teach pelvic floor
Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives 1 Aims of this self assessment competency To equip Midwives with the knowledge and skills to teach pelvic floor
Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia Difficulty
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia Difficulty
Postpartum Complications
 ACOG Postpartum Toolkit Postpartum Complications Introduction The effects of pregnancy on many organ systems begin to resolve spontaneously after birth of the infant and delivery of the placenta. The timeline
ACOG Postpartum Toolkit Postpartum Complications Introduction The effects of pregnancy on many organ systems begin to resolve spontaneously after birth of the infant and delivery of the placenta. The timeline
2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL)
 E10d 2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL) SECTION B PART 1 - SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No.
E10d 2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL) SECTION B PART 1 - SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No.
INSERTION OF AN ARTIFICIAL URINARY SPHINCTER IN MEN
 INSERTION OF AN ARTIFICIAL URINARY SPHINCTER IN MEN Procedure Specific Information What is the evidence base for this information? This publication includes advice from consensus panels, the British Association
INSERTION OF AN ARTIFICIAL URINARY SPHINCTER IN MEN Procedure Specific Information What is the evidence base for this information? This publication includes advice from consensus panels, the British Association
A. Service Specifications
 A. Service Specifications SCHEDULE 2 THE SERVICES Service Specification No: Service Commissioner Lead Specialised Complex Surgery for Urinary Incontinence and Vaginal and Uterine Prolapse For local completion
A. Service Specifications SCHEDULE 2 THE SERVICES Service Specification No: Service Commissioner Lead Specialised Complex Surgery for Urinary Incontinence and Vaginal and Uterine Prolapse For local completion
What you should know about your diagnosis of incontinence
 What you should know about your diagnosis of incontinence What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? WHAT IS NORMAL URINARY FUNCTION? Urine is a normal waste product of the body that is manufactured by the kidneys
What you should know about your diagnosis of incontinence What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? WHAT IS NORMAL URINARY FUNCTION? Urine is a normal waste product of the body that is manufactured by the kidneys
Sacral nerve stimulation for faecal incontinence
 NHS National Institute for Clinical Excellence Sacral nerve stimulation for faecal incontinence Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the public November
NHS National Institute for Clinical Excellence Sacral nerve stimulation for faecal incontinence Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the public November
Anorectal physiology test
 Anorectal physiology test We hope this factsheet will help to answer some of your questions about having an anorectal physiology test. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don t hesitate
Anorectal physiology test We hope this factsheet will help to answer some of your questions about having an anorectal physiology test. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don t hesitate
An effective and minimally invasive bridge between conservative therapy and invasive surgery for BCD (bowel control disorder).
 An effective and minimally invasive bridge between conservative therapy and invasive surgery for BCD (bowel control disorder). Mederi Therapeutics has developed this kit to help you raise awareness of
An effective and minimally invasive bridge between conservative therapy and invasive surgery for BCD (bowel control disorder). Mederi Therapeutics has developed this kit to help you raise awareness of
Colostomy & Ileostomy
 Colostomy & Ileostomy Indications, problems and preference By Waleed Omar Professor of Colorectal surgery, Mansoura University. Disclosure I have no disclosures. Presentation outline Stoma: Definition
Colostomy & Ileostomy Indications, problems and preference By Waleed Omar Professor of Colorectal surgery, Mansoura University. Disclosure I have no disclosures. Presentation outline Stoma: Definition
WORKING TOGETHER FOR THE NHS 20/07/2018
 20/07/2018 NHS Improvement and NHS England Wellington House 133-155 Waterloo Road London SE1 8UG 020 3747 0000 www.england.nhs.uk www.improvement.nhs.uk To: Regional Directors, Trust Medical Directors,
20/07/2018 NHS Improvement and NHS England Wellington House 133-155 Waterloo Road London SE1 8UG 020 3747 0000 www.england.nhs.uk www.improvement.nhs.uk To: Regional Directors, Trust Medical Directors,
Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels.
 Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels. Abscess A localised collection of pus in a cavity that is formed by the decay of diseased
Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels. Abscess A localised collection of pus in a cavity that is formed by the decay of diseased
CONTINENCE MODULE 3 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF CONSTIPATION AND FAECAL INCONTINENCE
 CONTINENCE MODULE 3 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF CONSTIPATION AND FAECAL INCONTINENCE The minimum standards required to initiate specialised conservative treatment
CONTINENCE MODULE 3 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF CONSTIPATION AND FAECAL INCONTINENCE The minimum standards required to initiate specialised conservative treatment
Sacral Neuromodulation Beyond Pelvic Pain!!!
 Sacral Neuromodulation Beyond Pelvic Pain!!! Dr. Hirachand S Mutagi. Senior Consultant Pain Physician. Head -Sakra World Hospital. Director ReLeaf Pain Services. Rapid advances in neurostimulation therapy
Sacral Neuromodulation Beyond Pelvic Pain!!! Dr. Hirachand S Mutagi. Senior Consultant Pain Physician. Head -Sakra World Hospital. Director ReLeaf Pain Services. Rapid advances in neurostimulation therapy
HARTMANNS PROCEDURE. Patient information Leaflet
 HARTMANNS PROCEDURE Patient information Leaflet April 2017 WHAT IS A HARTMANNS PROCEDURE? This operation is necessary to remove the area of bowel that is diseased. The operation removes a piece of your
HARTMANNS PROCEDURE Patient information Leaflet April 2017 WHAT IS A HARTMANNS PROCEDURE? This operation is necessary to remove the area of bowel that is diseased. The operation removes a piece of your
Rectal irrigation (DROP-List)
 B171 February 2017 2.0 Community Interest Company Rectal irrigation (DROP-List) This is one of a number of bulletins providing further information on medicines and medical devices contained in the PrescQIPP
B171 February 2017 2.0 Community Interest Company Rectal irrigation (DROP-List) This is one of a number of bulletins providing further information on medicines and medical devices contained in the PrescQIPP
Consultation Guide: Specialised gynaecology surgery and complex urogynaecology conditions service specifications
 Consultation Guide: Specialised gynaecology surgery and complex urogynaecology conditions service specifications Consultation guide: Specialised gynaecology surgery and complex urogynaecology conditions
Consultation Guide: Specialised gynaecology surgery and complex urogynaecology conditions service specifications Consultation guide: Specialised gynaecology surgery and complex urogynaecology conditions
Open repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA)
 Open repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions Preparation for your Appointments We want you to be active in your healthcare. By telling us
Open repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions Preparation for your Appointments We want you to be active in your healthcare. By telling us
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 266 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of microwave ablation for atrial fibrillation as an associated procedure with other
266 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of microwave ablation for atrial fibrillation as an associated procedure with other
Summary and conclusion. Summary And Conclusion
 Summary And Conclusion Summary and conclusion Rectal prolapse remain a disorder for which no single ideal treatment was approved for all cases. Complete rectal prolapse (procidentia) is the circumferential
Summary And Conclusion Summary and conclusion Rectal prolapse remain a disorder for which no single ideal treatment was approved for all cases. Complete rectal prolapse (procidentia) is the circumferential
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men
 Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men Why are my pelvic floor muscles important? Your pelvic floor muscles are important for bladder and bowel control. These muscles help to keep the bladder
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men Why are my pelvic floor muscles important? Your pelvic floor muscles are important for bladder and bowel control. These muscles help to keep the bladder
The cost of the Axonics sacral neuromodulation system is 475 for the trial phase, 9,210 for a
 pat hways Axonics sacral al neuromodulation system for overactive bladder and faecal incontinence Medtech innovation briefing Published: 10 December 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib164 Summary The technology
pat hways Axonics sacral al neuromodulation system for overactive bladder and faecal incontinence Medtech innovation briefing Published: 10 December 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib164 Summary The technology
Injection of Urethral Bulking Agents
 Injection of Urethral Bulking Agents Department of Gynaecology Patient Information What are urethral bulking agents? Urethral bulking agents are substances that are injected to support the bladder neck.
Injection of Urethral Bulking Agents Department of Gynaecology Patient Information What are urethral bulking agents? Urethral bulking agents are substances that are injected to support the bladder neck.
IPAC date: May of 13
 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence IP685/3 Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (transcatheter aortic valve replacement) for aortic stenosis Consultation Comments table IPAC date: May
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence IP685/3 Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (transcatheter aortic valve replacement) for aortic stenosis Consultation Comments table IPAC date: May
A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence
 A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence Q: What is SUI? A: Stress urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary leakage of urine. The problem afflicts approximately 18 million
A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence Q: What is SUI? A: Stress urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary leakage of urine. The problem afflicts approximately 18 million
Commissioning guide:
 2017 Commissioning guide: Sponsoring Organisation: Association of Coloproctology of Great Britain and Ireland Date of evidence search: 2016 Date of publication: January 2017, revised from November 2014
2017 Commissioning guide: Sponsoring Organisation: Association of Coloproctology of Great Britain and Ireland Date of evidence search: 2016 Date of publication: January 2017, revised from November 2014
