Purpose Provide instructions for collection of optimal urine specimens to ensure accurate test results.
|
|
|
- Laura Paul
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Policy S:PC-2110 Page 1 Fairview Health Services Department Laboratory / Nursing Section Acute Care: Collection Category Provision of Care Subject URINE COLLECTION, RANDOM/CATHETER/OTHER Purpose Provide instructions for collection of optimal urine specimens to ensure accurate test results. Policy The type of urine specimen needed for tests varies with the type of test to be performed. The specimen may be collected as a random (any time), first morning, double voided, clean catch midstream, or timed urine. The specimen may be obtained from a urinary catheter or by suprapubic aspiration. Refer to the alphabetical listing of tests for urine specimen requirements and handling. Procedure Collection: Always collect urine before a genital or rectal examination to prevent contamination from the vagina or from prostatic secretions. Tightly secure lid; Label the specimen container following Patient Identification and Laboratory Specimen Labeling procedure. Place specimen in specimen transport bag and attach request form to outside pocket or bag. Deliver to the laboratory within 1 hour of collection to ensure validity of cultures and preservation of cells, casts, glucose, ketones, and the pigments bilirubin and urobilinogen. Refrigerate urine if it cannot be delivered immediately. RANDOM Collect with a single voiding made directly into a sterile leakproof container. Avoid contamination with feces, vaginal exudate, or menses. If obtained from a clean, dry bedpan or urinal, mix specimen by agitation before pouring into specimen container. A first morning clean catch (uncontaminated) midstream collection is preferred. Clean-Catch, Midstream Use for collection of urine culture specimen. The first voided, overnight urine will have the highest bacterial count, but may not be readily available. Urine specimens collected in a bedpan, urinal, or at home are not suitable for culture. Provide the patient with written instructions and a kit for urine collection containing a non-irritating cleansing agent like benzalkonium chloride, chlorhexidine, or povidone-iodine swabs. Use aseptic technique to prevent contamination with urethral, perineal, vaginal or fecal bacteria that may cause misleading positive cultures. Random, First Voided (overnight) This is the most concentrated urine specimen and is collected on awakening. Use for routine urinalysis, especially protein and nitrate (for the presence of bacteria); also specific gravity (indicator of renal concentrating ability) when fluids are restricted overnight. Second Voided (Double Voided) This is a urine specimen that is freshly voided (not overnight or in the bladder for many hours). Use for glucose, better cell morphology for tumor cells, or CMV inclusion bodies. To collect: 1. Hydrate patient by instructing the patient to drink one glass of water every 15 minutes for 2 hours. 2. At the end of two hours, instruct patient to void and discard the urine. 3. One hour later, instruct the patient to void into sterile leakproof container.
2 Procedure for Females: 1. Wash hands with soap and water; dry with disposable paper towel. 2. Kneel or squat over a bedpan or straddle the toilet bowl to facilitate separating the folds of skin (labia) that cover the vagina and urinary opening. 3. Expose the urinary opening (urethral meatus) by separating the labia with thumb and forefinger of one hand. Keep the labial fold separated during the collection. 4. Clean the area around the urinary opening with three antiseptic-moistened swabs. Wipe with a front to back motion down each side of the urethral meatus with two of the swabs. Use the third swab to wipe down the center from front to back. Remove excess antiseptic with another swab or sterile gauze. 5. Void a small amount of urine into toilet or bedpan. Without interrupting the flow, catch about one oz. (30 ml) of urine in a sterile container. (To prevent contamination of the specimen, do not touch inner surface of container or lid). Void any excess urine into toilet or bedpan. 6. Tightly secure lid. Label container with patient name and identification number. 7. Deliver specimen to the laboratory immediately or refrigerate specimen. Procedure for Males: 1. Wash hands with soap and water; dry with disposable paper towel. 2. Before attempting to collect this specimen, make sure bladder is moderately full. This minimizes the risk of contamination by prostatic fluid. 3. Retract the foreskin and clean the tip of the penis (urethral meatus and glans) with an antiseptic-moistened swab, wiping in a circular motion away from the urinary opening. Discard swab and use another swab or sterile gauze to remove excess antiseptic. 4. Void a small amount of urine into toilet or bedpan. Without interrupting the flow, catch about one oz. (30 ml) of urine in a sterile container. (To prevent contamination of the specimen, do not touch inner surface of container or lid). Void any excess urine into toilet or bedpan. 5. Tightly secure lid. Label container with patient name and identification number. 6. Deliver specimen to the laboratory immediately or refrigerate specimen. RANDOM, PEDIATRICS OR INFANTS Use pediatric and newborn urine specimen collection bags with hypoallergenic skin adhesive for children who are too young to collect a urine specimen. Cleanse, rinse, and dry the urethral meatus. Place a collection bag over the penis and scrotum for male infants. For female infants tape the bag to the perineum starting at the part between the anus and vagina. As soon as a urine specimen is available or within 30 minutes, remove the bag to prevent skin damage; if no specimen is collected, attach a new collection bag. Page 2 SUPRAPUBIC ASPIRATION FOR INFANTS Use in cases of unresolved urinary tract infection or when a suitable specimen is not available by voiding. May be used for culturing anaerobic organisms. Avoid when genitourinary tract anomalies are present. Diaper should be dry and the infant not have
3 voided in minutes before the procedure. When the infant is well hydrated and the bladder is full, prepare the skin and using aseptic technique, perform suprapubic aspiration of urine from bladder through the abdominal wall above the pubis using a sterile syringe and needle. Aspirate 1 ml urine into a sterile syringe. Transfer into sterile container. For anaerobic cultures, expel air from syringe and inject urine sample into an anaerobic vial. URINARY BLADDER CATHETERIZATION Use for routine urinalysis, culture or timed collection. Catheterization is used for patients unable to void. In women, catheterization may be needed to determine whether residual urine is present or in some instances, to avoid contamination of urine for culture when clean-catch midstream specimens are not satisfactory. In adult males, catheterized specimens are collected when there is urinary retention or when measurement of residual urine is required. Catheterization increases risk of bacterial infections by introducing organisms into the bladder from the urethra. In-out catheterization is performed using a sterile catheterization set and sterile gloves. After skin preparation, insert a lubricated catheter until urine flows into a collection basin. After a few mls have been discarded, collect urine into a sterile container. URINE FROM INDWELLING CATHETER Urine from drainage bags is not suitable for culture because rapid bacterial growth occurs in the stagnant urine leading to false results. Clean the catheter above the bag with an alcohol wipe. Collect a few ml of urine with a sterile syringe and needle. Transfer into sterile container. (Some indwelling urinary catheters will leak after puncture, and are not suitable for the technique). FOUR GLASS COLLECTION SEQUENCE Use to determine origin of bacteruria, pyuria, or hematuria in the male when this is not obvious. The test involves prostatic massage. Microscopic examination (for leukocytes, red cells and bacteria) and bacterial culture are performed on each specimen. (In some instances when cultures are not ordered if microscopic examination is negative.) Label four sterile containers. Collect urine under supervision after cleansing the urethral meatus with benzalkonium chloride or chlorhexidine, rinsing and drying: Label Specimen Patient Instructions U1 #1 Void ml urine into the container; secure cover. U2 #2 Void the next ml into the second container; secure cover. EPS #3 Expressed prostatic secretion (EPS). Massage the prostate and collect secretions into third container; secure cover. The volume may be very small. U3 #4 Void urine again into last specimen container; secure cover. U1 represents a urine washing of the anterior urethra. Positive results in only U1 indicates anterior urethritis. Trichomonas yeasts or bacteria may be found. Positive findings in all three voided urine specimens indicate upper and/or lower urinary tract infection. Positive findings in EPS and U2 only may indicate a prostatic source of infection. SUSPECTED FISTULA Use in patients with suspected fistula of the urinary tract and the gut; the fistulous connection is not always demonstrable by imaging methods. Fistulas may occur with carcinoma of the colon, with regional ileitis (Crohn s disease), and with diverticulitis and cause persistent urinary tract infections. A marker substance is ingested by mouth, either a poorly absorbed dye (phenol red) or finely granulated activated charcoal in gelatin capsules. (When a fistulous connection Page 3
4 is present the dye or charcoal appears in the urine.) Depending on intestinal transit time urine is collected from one to three days later. Collect a 24 hour timed urine specimen. Avoid fecal contamination since the marker will be present in the feces. Refer to urine, timed collection instructions. Urine is centrifuged and the sediment examined microscopically for charcoal particles. TIMED COLLECTION Some tests require a preservative be added to the container for a timed urine specimen prior to starting the collection. Refer to the collection information in the alphabetical listing by: 1. Instruct the patient to avoid contact with the preservatives in the collection bottles. 2. Instruct the patient to empty their bladder at a specified time (e.g., 0800). Discard urine (or submit this urine for other tests as appropriate) since it was formed prior to the collection period. Record the time and date; this is the beginning of the collection period. 3. Collect all subsequent urine passed during the collection period. 4. Instruct the patient to void at exactly the ending time of the collection period (e.g., for 24 hour collection, 0800 the next day). Record the time and date of completion. a. Keep the urine container on ice or refrigerated during the collection. (A specimen for uric acid is the only test that should be collected at room temperature.) b. Collection of all urine during the time period is critical to the accuracy of the test. Portions of the timed collection should not be used for other testing. 5. Determine the total elapsed time of the collection period and record this information on the request form. References 1. CLSI: Urinalysis; Approved Guideline-Third Edition. CLSI document GP16-A3. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; Simindinger J, Mansour FK, Slockbower JM, Specimens for urinalysis. In: JM Slockbower, TA Blumenfeld. Eds. Collection and handling of laboratory specimens: A practical guide. St. Louis: J.B. Lippincott Company, 1983: Young DS, Bermes EW, Specimen collection and processing: sources of biological variation. In: CA Burtis, CA and Ashwood, ER eds. Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry, 3rd Edition. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company, 1999: File Location Acutecare\Web_Intranet\Collection\SPC_2110Urine Original Date 4/92 Revised 3/99; 4/02 5/07, 5/09 Original Author(s): C Senn and P Bormann Last Revised/Approved by: K Garin, N Young-Dixon, J Forys Last Reviewed/Approved by: K Garin, J Forys, N Young-Dixon, P Ferrieri 5/08 P Ferrieri Reviewed 5/04; 5/05; 6/06; 5/08, 5/09 Medical Director Approval Page 4
5 PATIENT INFORMATION - CLEAN CATCH MISTREAM URINE COLLECTION Dear Patient: Your doctor has requested a urine specimen. To minimize the contamination by organisms outside the urinary tract, you must obtain what s called a clean-catch midstream specimen. To collect this specimen, follow the instructions below: PROCEDURE FOR MALES (photocopy as needed) 1. Before attempting to collect this specimen, make sure your bladder is moderately full. This minimizes the risk of contamination by prostatic fluid. 2. Retract your foreskin, and clean the tip of your penis (urethral meatus and glans) with an antiseptic-moistened swab, wiping in a circular motion away from the urinary opening. Discard this swab, and use another swab to remove excess antiseptic. 3. Begin urination, passing the first portion into a toilet or urinal. Without interrupting the flow, catch the mid-portion of urine in a sterile specimen container. (To prevent contamination of the specimen, do not touch the inner surface of the container or lid.) 4. Replace the lid of the specimen container. If you are not going to deliver the specimen to the laboratory immediately, refrigerate the specimen. Page 5
6 PATIENT INFORMATION - CLEAN CATCH MISTREAM URINE COLLECTION Dear Patient: Your doctor has requested a urine specimen. To minimize the contamination by organisms outside the urinary tract, you must obtain what s called a clean-catch midstream specimen. To collect this specimen, follow the instructions below: PROCEDURE FOR FEMALES 1. If you re menstruating, inform the doctor. He/she may want to postpone this test until after your menstrual period ends. However, if he/she wants to perform the test immediately, you can prevent contamination of the urine specimen with vaginal discharge or menstrual flow by inserting a tampon. (photocopy as needed) 4. Clean the area around the urinary opening with three antiseptic-moistened swabs: one for each side of the urethral meatus and the third for the meatus itself. Wipe with a front-toback motion. Remove excess antiseptic with another swab. 2. Kneel or squat over a bedpan or straddle the toilet bowl, to facilitate separating the folds of skin (labia) that cover the vagina and urinary opening. 5. Begin urination, passing the first portion into a bedpan or toilet bowl. Without interrupting the flow, catch the mid-portion of urine in a sterile container. (To prevent contamination of the specimen, do not touch the inner surface of the container or lid.) 3. Expose the urinary opening (urethral meatus) by separating the labia with your thumb and forefinger. Keep the labial folds separated during the collection. 6. Replace the lid of the specimen container. If you are not going to deliver the specimen to the laboratory immediately, refrigerate the specimen. Page 6
Collection of Specimen
 Collection of Specimen Purpose This procedure helps the student nurse to identify different types of specimen and their purposes. Objectives At the end of this procedure, the student nurse should be able
Collection of Specimen Purpose This procedure helps the student nurse to identify different types of specimen and their purposes. Objectives At the end of this procedure, the student nurse should be able
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Urinary System Diseases/Disorders. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Urinary System Diseases/Disorders LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Identify the purposes
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Urinary System Diseases/Disorders LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Identify the purposes
NHS GREATER GLASGOW & CLYDE CONTROL OF INFECTION COMMITTEE STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE (SOP) INSERTION & MAINTENANCE OF INDWELLING
 Page Page 1 of 6 AIM STATEMENT REQUIREMENTS LOCATION TIMING PROCEDURE To minimise the risk of secondary infection as a result of urinary catheterisation. A urinary catheter bypasses the body s normal defence
Page Page 1 of 6 AIM STATEMENT REQUIREMENTS LOCATION TIMING PROCEDURE To minimise the risk of secondary infection as a result of urinary catheterisation. A urinary catheter bypasses the body s normal defence
Published Date: 12-Jun-2018
 POLICY A written primary care provider s order is required for the placement of a urinary catheter. Insertion and removal is a two person procedure. If unsuccessful after two attempts, notify MRP for further
POLICY A written primary care provider s order is required for the placement of a urinary catheter. Insertion and removal is a two person procedure. If unsuccessful after two attempts, notify MRP for further
SPECIMEN COLLECTION-WAIVED TESTING
 SPECIMEN COLLECTION-WAIVED TESTING POLICY 1. Application for waived testing will be submitted to CLIA (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments) on a yearly basis. 2. All laboratory specimens: PURPOSE
SPECIMEN COLLECTION-WAIVED TESTING POLICY 1. Application for waived testing will be submitted to CLIA (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments) on a yearly basis. 2. All laboratory specimens: PURPOSE
Chapter 18. Assisting With Urinary Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 18 Assisting With Urinary Elimination The urinary system: The Urinary System Removes waste products from the blood Maintains the body s water balance 2 Normal Urination The healthy adult produces
Chapter 18 Assisting With Urinary Elimination The urinary system: The Urinary System Removes waste products from the blood Maintains the body s water balance 2 Normal Urination The healthy adult produces
Instruction Guide to Sterile Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Men Using the Cure Catheter Closed System
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Specimen Collection Policies
 Specimen Collection Policies Purpose Great River Medical Center Laboratory is a hospital-based and outreach laboratory with specific standards of excellence. To best serve our patients, all specimens will
Specimen Collection Policies Purpose Great River Medical Center Laboratory is a hospital-based and outreach laboratory with specific standards of excellence. To best serve our patients, all specimens will
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls
 Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow
Microbiology Collection
 Microbiology Collection Notify the Microbiology Laboratory at 920-738-6317 if any of the following etiological agents are suspected to be present in the specimens sent to the laboratory. Bacillius anthracis
Microbiology Collection Notify the Microbiology Laboratory at 920-738-6317 if any of the following etiological agents are suspected to be present in the specimens sent to the laboratory. Bacillius anthracis
Achieving Independence. A Guide to Self-Catheterization with the Bard Touchless Plus Intermittent Catheter System
 Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization with the Bard Touchless Plus Intermittent Catheter System Achieving Independence Introducing the Bard Touchless Plus Catheter One
Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization with the Bard Touchless Plus Intermittent Catheter System Achieving Independence Introducing the Bard Touchless Plus Catheter One
Instruction Guide to Sterile Intermittent Catheterization For Parents of Girls Using the Cure Catheter Closed System
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care
 Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care Table of Contents 1 What is a catheter?... 2 2 Why does the child need a catheter?... 2 3 Normal Urine... 2 4 How to do a clean urethral catheterization
Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care Table of Contents 1 What is a catheter?... 2 2 Why does the child need a catheter?... 2 3 Normal Urine... 2 4 How to do a clean urethral catheterization
Instruction For Use for All Silicon Foley Catheter
 General Description: All Silicone Foley Catheter for single use is a thin, is a flexible tube passed through the urethra and into the bladder to drain urine. It is the most common type of indwelling urinary
General Description: All Silicone Foley Catheter for single use is a thin, is a flexible tube passed through the urethra and into the bladder to drain urine. It is the most common type of indwelling urinary
TOWN OF FAIRFIELD PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING
 TOWN OF FAIRFIELD PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING PROGRAM: School Health APPROVED BY: Board of Health School Medical Advisor POLICY & PROCEDURE: Clean Intermittent Catheterization DATE: 5/9/94 DEFINITION: POLICY
TOWN OF FAIRFIELD PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING PROGRAM: School Health APPROVED BY: Board of Health School Medical Advisor POLICY & PROCEDURE: Clean Intermittent Catheterization DATE: 5/9/94 DEFINITION: POLICY
URINE SPECIMEN FOR CULTURE Urine Specimen Collection - Male - Clean-Catch Urine Specimens Wet paper towel and open soap towelette.
 URINE SPECIMEN FOR CULTURE Urine Specimen Collection - Male - Clean-Catch Urine Specimens Wet paper towel and open soap towelette. Retract the foreskin if uncircumcised, and cleanse end of penis with soap
URINE SPECIMEN FOR CULTURE Urine Specimen Collection - Male - Clean-Catch Urine Specimens Wet paper towel and open soap towelette. Retract the foreskin if uncircumcised, and cleanse end of penis with soap
Clostridium difficile Specimen Collection
 Clostridium difficile Specimen Collection Collect stool specimens into a clean, airtight container with no preservative. All stool specimens should be tested as soon as possible. Ideally, stool specimens
Clostridium difficile Specimen Collection Collect stool specimens into a clean, airtight container with no preservative. All stool specimens should be tested as soon as possible. Ideally, stool specimens
CPT Code: Serum Urea Nitrogen, Urine Urea Nitrogen in mg/dl, 24 hour Urine Urea Nitrogen, Urea Clearance
 UREA CLEARANCE UREACL Specimen Required: 2.5 ml blood, gel tube and total collection 24 hour urine Special Instructions: Refrigerate urine during collection. Provide starting date and time, and ending
UREA CLEARANCE UREACL Specimen Required: 2.5 ml blood, gel tube and total collection 24 hour urine Special Instructions: Refrigerate urine during collection. Provide starting date and time, and ending
How to Change a. Foley catheter. Patient Education Rehabilitation Nursing. Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver
 Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives step-bystep instructions for changing a Foley catheter, which is a tube in your bladder to
Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives step-bystep instructions for changing a Foley catheter, which is a tube in your bladder to
Assisting in the Analysis of Urine. Copyright 2011, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Assisting in the Analysis of Urine Urinalysis Why is Urine is analyzed? To detect extrinsic conditions those in which the kidney is functioning normally, but abnormal end-products of metabolism are excreted
Assisting in the Analysis of Urine Urinalysis Why is Urine is analyzed? To detect extrinsic conditions those in which the kidney is functioning normally, but abnormal end-products of metabolism are excreted
UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material
 UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) for Bladder Emptying FAQ What
UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) for Bladder Emptying FAQ What
Patient Urinary Catheter Passport
 Useful contact details Name Contact Number Produced by Adapted from Worth by Michelle Pickering, Continence Specialist Practitioner Hambleton and Richmondshire Locality Continence Advisory Service and
Useful contact details Name Contact Number Produced by Adapted from Worth by Michelle Pickering, Continence Specialist Practitioner Hambleton and Richmondshire Locality Continence Advisory Service and
Instruction Guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization for Parents of Boys Using the Hydrophilic Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Unit Title: Urinary Catheterisation
 Unit Credit Value: 3 Unit Level: Three Unit Guided Learning Hours: 21 Ofqual Unit Reference Number: M/505/7684 Unit Review Date: 31/10/2018 Unit Sector: 1.2 Nursing and Subjects and Vocations Allied to
Unit Credit Value: 3 Unit Level: Three Unit Guided Learning Hours: 21 Ofqual Unit Reference Number: M/505/7684 Unit Review Date: 31/10/2018 Unit Sector: 1.2 Nursing and Subjects and Vocations Allied to
University College Hospital. Discharge information for patients after HIFU (High Intensity Focused Ultrasound) Urology Directorate
 University College Hospital Discharge information for patients after HIFU (High Intensity Focused Ultrasound) Urology Directorate 2 If you would like this document in another language or format, or require
University College Hospital Discharge information for patients after HIFU (High Intensity Focused Ultrasound) Urology Directorate 2 If you would like this document in another language or format, or require
EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE
 EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Skills: 30 points Objectives: 1. State the specimen of choice for chemical analysis of urine. 2. List two macroscopic observations of urine and
EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Skills: 30 points Objectives: 1. State the specimen of choice for chemical analysis of urine. 2. List two macroscopic observations of urine and
My Urinary Catheter Passport Looking after my urinary catheter
 Feedback We welcome your comments. If you have any ideas about how we could do something better or feedback about positive aspects of the service please let us know. If you have a complaint please let
Feedback We welcome your comments. If you have any ideas about how we could do something better or feedback about positive aspects of the service please let us know. If you have a complaint please let
More than 100 different tests can be done on urine. A regular urinalysis often includes the following tests:
 Urine Test Table of Contents Test Overview Why It Is Done How To Prepare How It Is Done How It Feels Risks Results What Affects the Test What To Think About References Credits Test Overview A urine test
Urine Test Table of Contents Test Overview Why It Is Done How To Prepare How It Is Done How It Feels Risks Results What Affects the Test What To Think About References Credits Test Overview A urine test
Instruction Guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization for Parents of Boys Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Patient Preparation Unique patient preparation requirements are listed under each test in the Test Directory.
 Specimen Collection Lab results are only as good as the specimen provided. Patient preparation, venipuncture technique, specimen handling, and transportation can all affect the quantity of results. Health
Specimen Collection Lab results are only as good as the specimen provided. Patient preparation, venipuncture technique, specimen handling, and transportation can all affect the quantity of results. Health
CATHETER PASSPORT. Looking after your Urinary Catheter. The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter.
 CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
The Urinary System. 1. Define important words in this chapter. 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system
 109 16 The Urinary System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system 3. Discuss changes in the urinary system due to aging 4. List normal qualities
109 16 The Urinary System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system 3. Discuss changes in the urinary system due to aging 4. List normal qualities
CLINICAL LABORATORY SERVICES
 13. SPECIMEN COLLECTION AND HANDLING GUIDELINES 13.1. General guidelines For microbiology investigations the prompt and accurate isolation of infecting agents is directly influenced by the quality of the
13. SPECIMEN COLLECTION AND HANDLING GUIDELINES 13.1. General guidelines For microbiology investigations the prompt and accurate isolation of infecting agents is directly influenced by the quality of the
SAMPLE. Collecting a faeces specimen
 7. Perform steps 10 16 of the common steps (see pp. 39 43). Evidence base: PHE (2014a) To ensure that: the patient is safe and comfortable. the specimen has been correctly collected and documented in the
7. Perform steps 10 16 of the common steps (see pp. 39 43). Evidence base: PHE (2014a) To ensure that: the patient is safe and comfortable. the specimen has been correctly collected and documented in the
Guide for Use. Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System
 Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Touch free, sterile, and self-contained, Hollister Apogee Plus intermittent catheter empowers you to maintain your independence and live
Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Touch free, sterile, and self-contained, Hollister Apogee Plus intermittent catheter empowers you to maintain your independence and live
Urinalysis in the Older Adult / Care Home Environment
 A Guide to: Urinalysis in the Older Adult / Care Home Environment Urinalysis Guidelines April 2018 Approval: March18 Review: March21 On behalf of: NHS Redditch and Bromsgrove CCG, NHS South Worcestershire
A Guide to: Urinalysis in the Older Adult / Care Home Environment Urinalysis Guidelines April 2018 Approval: March18 Review: March21 On behalf of: NHS Redditch and Bromsgrove CCG, NHS South Worcestershire
Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter
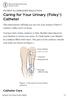 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
Effective Date: SPECIMEN COLLECTION FOR CULTURE OF BACTERIAL PATHOGENS QUICK REFERENCE
 1 of 9 Policy #: Subject: 611 (PLH-611-06) Effective Date: 9/30/2004 Reviewed Date: 8/1/2016 SPECIMEN COLLECTION FOR CULTURE OF BACTERIAL PATHOGENS QUICK REFERENCE Approved by: Laboratory Director, Jerry
1 of 9 Policy #: Subject: 611 (PLH-611-06) Effective Date: 9/30/2004 Reviewed Date: 8/1/2016 SPECIMEN COLLECTION FOR CULTURE OF BACTERIAL PATHOGENS QUICK REFERENCE Approved by: Laboratory Director, Jerry
Self-Catheterization for Females
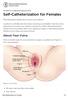 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Self-Catheterization for Females This information explains how to insert your catheter. A catheter is a flexible tube that drains urine from your bladder. Your doctor has
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Self-Catheterization for Females This information explains how to insert your catheter. A catheter is a flexible tube that drains urine from your bladder. Your doctor has
Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters
 Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters This leaflet provides you with information and instructions on caring for clients who have an indwelling
Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters This leaflet provides you with information and instructions on caring for clients who have an indwelling
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female)
 Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female) Refer to National Infection Prevention and Control Manual for information on aseptic technique/cleaning equipment. Equipment
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female) Refer to National Infection Prevention and Control Manual for information on aseptic technique/cleaning equipment. Equipment
Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis
 Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis Reviewed & ratified by: Dr V Taylor-Jones & Ms C Tierney. Urinalysis Aims and Objectives Aim: For the student to be able to safely conduct a urinalysis on
Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis Reviewed & ratified by: Dr V Taylor-Jones & Ms C Tierney. Urinalysis Aims and Objectives Aim: For the student to be able to safely conduct a urinalysis on
Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS
 Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS Information for Patients and Carers F:\CONTINENCE\Acute Urianary Retention\04-12\005- Indwelling Urinary Cathter Leaflet - A4-13-02-09.doc
Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS Information for Patients and Carers F:\CONTINENCE\Acute Urianary Retention\04-12\005- Indwelling Urinary Cathter Leaflet - A4-13-02-09.doc
TISSUE COLLECTION. SCPA 603- Histopathological Techniques for Routine and Research
 TISSUE COLLECTION SCPA 603- Histopathological Techniques for Routine and Research Somphong Narkpinit, MD. Department of Pathobiology Faculty of Science, Mahidol University somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th Learning
TISSUE COLLECTION SCPA 603- Histopathological Techniques for Routine and Research Somphong Narkpinit, MD. Department of Pathobiology Faculty of Science, Mahidol University somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th Learning
Teaching Intermittent Catheterisation. Liz Croxon Clinical Facilitator National Rehabilitation Hospital Dunlaoghaire
 Teaching Intermittent Catheterisation Liz Croxon Clinical Facilitator National Rehabilitation Hospital Dunlaoghaire Aim of Workshop To provide knowledge of the principles and practises of teaching a client
Teaching Intermittent Catheterisation Liz Croxon Clinical Facilitator National Rehabilitation Hospital Dunlaoghaire Aim of Workshop To provide knowledge of the principles and practises of teaching a client
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Collection and Transportation of Clinical Specimens
 Collection and Transportation of Clinical Specimens IDK II Faculty of Nursing Universitas Indonesia PDF Created with deskpdf PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com The laboratory diagnosis of an
Collection and Transportation of Clinical Specimens IDK II Faculty of Nursing Universitas Indonesia PDF Created with deskpdf PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com The laboratory diagnosis of an
CLEAN INTERMITTENT SELF CATHETERISATION
 CLEAN INTERMITTENT SELF CATHETERISATION INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Catheter size :-... Regime:-......... Follow up appointment... UROLOGY SYDNEY Level 1, St George Medical Centre, 1 South Street, Kogarah
CLEAN INTERMITTENT SELF CATHETERISATION INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Catheter size :-... Regime:-......... Follow up appointment... UROLOGY SYDNEY Level 1, St George Medical Centre, 1 South Street, Kogarah
Intermittent Self-Catheterization. A Guide for Men and Women
 Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Men and Women 1986 2013 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon,
Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Men and Women 1986 2013 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon,
Patient Urinary Catheter Passport
 Useful contact details: Continence Service (Community) 01724 298325 Continence Service (Goole) 01482 336951 Continence Service (SGH) 01724 282282 Ext 2823 Continence Service (DPOW) 01472 874111 Infection
Useful contact details: Continence Service (Community) 01724 298325 Continence Service (Goole) 01482 336951 Continence Service (SGH) 01724 282282 Ext 2823 Continence Service (DPOW) 01472 874111 Infection
SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats
 SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats These SOPs were developed by the Office of the University Veterinarian and reviewed by Virginia Tech IACUC to provide a reference and guidance to investigators during
SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats These SOPs were developed by the Office of the University Veterinarian and reviewed by Virginia Tech IACUC to provide a reference and guidance to investigators during
Guide for Use. Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System
 Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Touch free, sterile, and self-contained, Hollister Apogee Plus intermittent catheter empowers you to maintain your independence and live
Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Touch free, sterile, and self-contained, Hollister Apogee Plus intermittent catheter empowers you to maintain your independence and live
Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela
 Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela Microbiology Department Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela Microbiology Department Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia Urinary Tract Infection
Continence Promotion. CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS
 Continence Promotion. 1 CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS CHARACTERISTICS OF URINE 2 A liquid excrement consisting of water, salts, and urea, which is made in the kidneys then released through
Continence Promotion. 1 CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS CHARACTERISTICS OF URINE 2 A liquid excrement consisting of water, salts, and urea, which is made in the kidneys then released through
Best Practice Guidance 12_Version 1.2. Title: Collection of Biological Samples
 This document is for guidance on the collection of biological samples that have been granted ethical approval under CUREC procedures. Certain research involving the taking of samples that consist of, or
This document is for guidance on the collection of biological samples that have been granted ethical approval under CUREC procedures. Certain research involving the taking of samples that consist of, or
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA LEARNING OBJECTIVES DEFINITION. KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer
 MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
Instruction Guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization for Parents of Girls Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Suprapubic and Mitrofanoff Catheter Care
 Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
Clinical Microbiology and Virology Transport
 Refer to the MLabs Test Catalog for specific specimen type and volume requirements for a particular test or tests. Aerobic Transport (BD ESwab Kit) A sterile package containing a polypropylene screw-cap
Refer to the MLabs Test Catalog for specific specimen type and volume requirements for a particular test or tests. Aerobic Transport (BD ESwab Kit) A sterile package containing a polypropylene screw-cap
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Men Using the Hydrophilic Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today
 III. THE ROUTINE URINALYSIS A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today 1. Cave man noted change in urine properties associated with disease 2. Babylonians and Egyptians noted
III. THE ROUTINE URINALYSIS A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today 1. Cave man noted change in urine properties associated with disease 2. Babylonians and Egyptians noted
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Women Using the Extra Long Cure Medical Pocket Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
 CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Hamid Emadi M.D Associate professor of Infectious diseases Department Tehran university of medical science The most common nosocomial infection The urinary
CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Hamid Emadi M.D Associate professor of Infectious diseases Department Tehran university of medical science The most common nosocomial infection The urinary
What is a catheter? What do I need to learn about catheter care?
 Catheter care What is a catheter? A catheter is a tube that drains urine from your child s body. The catheter is connected to tubing and a bag to collect the urine. Catheters come in different sizes and
Catheter care What is a catheter? A catheter is a tube that drains urine from your child s body. The catheter is connected to tubing and a bag to collect the urine. Catheters come in different sizes and
Guide for Use. Advance Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System
 Advance Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Hollister Advance Plus intermittent catheter features Touch Free technique enabling users to catheterize with confidence virtually anytime,
Advance Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Hollister Advance Plus intermittent catheter features Touch Free technique enabling users to catheterize with confidence virtually anytime,
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Session Outline. Routine Urinalysis a historical perspective. Unit 2; Session 8
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 8 Session Outline Historical perspective Importance of testing Basic urine composition Types of collection Timing of collection Urine preservatives Urinalysis
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 8 Session Outline Historical perspective Importance of testing Basic urine composition Types of collection Timing of collection Urine preservatives Urinalysis
Urinary Catheter Care
 Nikki Hardness, DO Aashish Kabra, MD John Logan, MD Jeremy Weiss, DO Elizabeth Kelly McKnight, PA Phone: (303) 388-9321 What is a urinary catheter? Urinary Catheter Care A urinary catheter is a long, hollow,
Nikki Hardness, DO Aashish Kabra, MD John Logan, MD Jeremy Weiss, DO Elizabeth Kelly McKnight, PA Phone: (303) 388-9321 What is a urinary catheter? Urinary Catheter Care A urinary catheter is a long, hollow,
Running title: Specimen Collection: Guidelines for Best Practices
 BASIC GUIDELINES FOR COLLECTION There are several guiding principles that should be considered and understood prior to obtaining/collecting any specimen. 1. Collect the material from the site in which
BASIC GUIDELINES FOR COLLECTION There are several guiding principles that should be considered and understood prior to obtaining/collecting any specimen. 1. Collect the material from the site in which
Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC)
 Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Male and Female Catheterisation
 Male and Female Catheterisation Practical Skills Teaching Year 3 Medical Students MB BCh 2012-2013 Contents Introduction to workshop... 3 Overall Session Aim... 4 Intended Learning Outcomes... 4 Workshop
Male and Female Catheterisation Practical Skills Teaching Year 3 Medical Students MB BCh 2012-2013 Contents Introduction to workshop... 3 Overall Session Aim... 4 Intended Learning Outcomes... 4 Workshop
ALPROLIX Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), Fc Fusion Protein INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Do not Do not YOUR KIT CONTAINS:
 ALPROLIX Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), Fc Fusion Protein INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Read the Instructions for Use before you start using ALPROLIX and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
ALPROLIX Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), Fc Fusion Protein INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Read the Instructions for Use before you start using ALPROLIX and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
Urinary Catheter Passport
 Urinary Catheter Passport Catheter Change Record and Looking After Your Urinary Catheter Please take this booklet with you if you are admitted to hospital or have an appointment Patient details Name Address
Urinary Catheter Passport Catheter Change Record and Looking After Your Urinary Catheter Please take this booklet with you if you are admitted to hospital or have an appointment Patient details Name Address
Managing your suprapubic catheter
 Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Sterile Intermittent Catheterization for Women
 INSTRUCTION GUIDE A note about our preferred catheter: Comfort Medical s preferred A note about our catheter is called the Cure preferred catheter: Catheter, manufactured by Cure Medical. Cure ofers irepolished
INSTRUCTION GUIDE A note about our preferred catheter: Comfort Medical s preferred A note about our catheter is called the Cure preferred catheter: Catheter, manufactured by Cure Medical. Cure ofers irepolished
Intermittent Self-Catheterization
 Intermittent Self-ization Create Medic Co.,Ltd. Marketing Department Suzuki Masaru If the bodily function emptying bladder, a physiological phenomenon in daily life, is impaired due to some kind of disease,
Intermittent Self-ization Create Medic Co.,Ltd. Marketing Department Suzuki Masaru If the bodily function emptying bladder, a physiological phenomenon in daily life, is impaired due to some kind of disease,
No Catheter No CAUTI. The Urinary System. Urinary Catheters. External catheters. Intermittent catheters. Indwelling Urethral Catheters
 No Catheter No CAUTI Urinary Catheters preventing complications and promoting comfort for patients Gwen Regan, RGN, MSc, PgDip (IPC) ADON Practice Development Community Healthcare Organisation 9 The Urinary
No Catheter No CAUTI Urinary Catheters preventing complications and promoting comfort for patients Gwen Regan, RGN, MSc, PgDip (IPC) ADON Practice Development Community Healthcare Organisation 9 The Urinary
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter
 Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter
 Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter Equipment required collect prior to procedure Perform this procedure as an aseptic technique to minimise the risk of introducing Clean the
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter Equipment required collect prior to procedure Perform this procedure as an aseptic technique to minimise the risk of introducing Clean the
Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care. Specimen Collection
 Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care Specimen Collection Version 1.01 May 2015 Harrogate and District NHS Foundation Trust Specimen Collection May 2015 Version
Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care Specimen Collection Version 1.01 May 2015 Harrogate and District NHS Foundation Trust Specimen Collection May 2015 Version
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL TITLE: ISSUED FOR: NURSING PROCEDURE PUREWICK FEMALE EXTERNAL CATHETER USE AND MANAGEMENT PROCEDURE (cat17) Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 1/17 4/18 1 of 6 RESPONSIBILITY: RN,
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL TITLE: ISSUED FOR: NURSING PROCEDURE PUREWICK FEMALE EXTERNAL CATHETER USE AND MANAGEMENT PROCEDURE (cat17) Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 1/17 4/18 1 of 6 RESPONSIBILITY: RN,
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Boys
 Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Boys What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow plastic
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Boys What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow plastic
FreshRN Podcast Season 4, Episode 6. All Things Urinary Catheters
 FreshRN Podcast Season 4, Episode 6 All Things Urinary Catheters Key Focus: Catheters can lead to infections, which can be fatal. CAUTI - Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection CAUTI is a type of
FreshRN Podcast Season 4, Episode 6 All Things Urinary Catheters Key Focus: Catheters can lead to infections, which can be fatal. CAUTI - Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection CAUTI is a type of
Intermittent Self-Catheterization. A Guide for Women
 Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Women 1986 2016 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon, Noah Fallis,
Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Women 1986 2016 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon, Noah Fallis,
Yield of Suprapubic Aspirate versus Bag Collection in Diagnosis of UTI in Children 0 to 6 Months of Age
 Proceeding S.Z.P.G.M.I. Vol: 25(2): pp. 61-65, 2011. Yield of Suprapubic Aspirate versus Bag Collection in Diagnosis of UTI in Children 0 to 6 Months of Age Lubna Riaz, Muhammad Aslam, Waqar Hussain, Anita
Proceeding S.Z.P.G.M.I. Vol: 25(2): pp. 61-65, 2011. Yield of Suprapubic Aspirate versus Bag Collection in Diagnosis of UTI in Children 0 to 6 Months of Age Lubna Riaz, Muhammad Aslam, Waqar Hussain, Anita
Collection (Specimen Source Required on all tests) Sputum: >5 ml required. First morning specimen preferred.
 Type Acid Fast (Mycobacteria) Sputum: >5 ml required. First morning specimen preferred. For blood, sodium heparin tube preferred. Lithium heparin acceptable. Do not centrifuge.. delay. Swabs are not appropriate
Type Acid Fast (Mycobacteria) Sputum: >5 ml required. First morning specimen preferred. For blood, sodium heparin tube preferred. Lithium heparin acceptable. Do not centrifuge.. delay. Swabs are not appropriate
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Women Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SPECIMEN COLLECTION. Dr. Hala Al -Daghistani
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SPECIMEN COLLECTION Dr. Hala Al -Daghistani The goal of the specimen collector must be to maintain the viability of the organisms with minimal contamination Basic principles of specimen
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SPECIMEN COLLECTION Dr. Hala Al -Daghistani The goal of the specimen collector must be to maintain the viability of the organisms with minimal contamination Basic principles of specimen
Intermittent Self-Catheterization. A Guide for Women
 Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Women 1986 2012 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon, Noah Fallis,
Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Women 1986 2012 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon, Noah Fallis,
Apogee. Intermittent Catheter Guide for Use
 Apogee Intermittent Catheter Guide for Use Personal Care Plan This is your Personal Care Plan, which should be completed by your healthcare professional. Name: Telephone Number: Clinician (Doctor/Nurse):
Apogee Intermittent Catheter Guide for Use Personal Care Plan This is your Personal Care Plan, which should be completed by your healthcare professional. Name: Telephone Number: Clinician (Doctor/Nurse):
limbsandthings.com Advanced Catheterisation Trainer User Guide For more skills training products visit Limbs & Things Ltd.
 Advanced Catheterisation Trainer Product No: 60150 User Guide For more skills training products visit limbsandthings.com Limbs & Things Ltd. Sussex Street, St Philips Bristol, BS2 0RA, UK sales@limbsandthings.com
Advanced Catheterisation Trainer Product No: 60150 User Guide For more skills training products visit limbsandthings.com Limbs & Things Ltd. Sussex Street, St Philips Bristol, BS2 0RA, UK sales@limbsandthings.com
Electron Microscopy Sciences
 Electron Microscopy Sciences INSTRUCTIONAL MANUAL CAT. #26750 Series EMS Rapid Pro Processing System Protocol: Cytology P.O. Box 550 s1560 Industry Road s Hatfield PA 19440 1 Cytology Protocol Cytologic
Electron Microscopy Sciences INSTRUCTIONAL MANUAL CAT. #26750 Series EMS Rapid Pro Processing System Protocol: Cytology P.O. Box 550 s1560 Industry Road s Hatfield PA 19440 1 Cytology Protocol Cytologic
Light yellow to dark golden yellow Clear ph range Specific gravity Sediments
 #11 Objectives: Understand specific gravity and identify normal specific gravity values for urine Learn to use a urine hydrometer to measure specific gravity Define specific gravity and identify normal
#11 Objectives: Understand specific gravity and identify normal specific gravity values for urine Learn to use a urine hydrometer to measure specific gravity Define specific gravity and identify normal
Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization. Nova Scotia Rehabilitation Centre
 2014 Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Nova Scotia Rehabilitation Centre Why do I need to do this? Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Your bladder may not empty completely when you go to the
2014 Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Nova Scotia Rehabilitation Centre Why do I need to do this? Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Your bladder may not empty completely when you go to the
Self Catheterisation for Men
 Intermittent Self Catheterisation for Men www.fittleworth.com Opening Hours: 8 am to 8 pm Monday to Friday 9 am to 1 pm Saturday National: 0800 378 846 Scotland: 0800 783 7148 Intermittent Self Catheterisation
Intermittent Self Catheterisation for Men www.fittleworth.com Opening Hours: 8 am to 8 pm Monday to Friday 9 am to 1 pm Saturday National: 0800 378 846 Scotland: 0800 783 7148 Intermittent Self Catheterisation
Urinary Catheter Passport SAMPLE COPY. A guide to looking after a urinary catheter. (for service users and healthcare workers) 2nd Edition
 Urinary Catheter Passport A guide to looking after a urinary catheter (for service users and healthcare workers) 2nd Edition Contact details Urinary Catheter Passport Service user Name Address Postcode
Urinary Catheter Passport A guide to looking after a urinary catheter (for service users and healthcare workers) 2nd Edition Contact details Urinary Catheter Passport Service user Name Address Postcode
University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street. Urinary sheaths. Urology Directorate
 University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street Urinary sheaths Urology Directorate If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter, contact
University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street Urinary sheaths Urology Directorate If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter, contact
CONTINUING CARE RESIDENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE
 CONTINUING CARE RESIDENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE NUMBER II-C-30 PAGE 1 OF 12 APPROVED BY: SITE: CATEGORY: Vice President & Senior Operating Officer, Rehab & Continuing Care Edmonton General, Youville Home,
CONTINUING CARE RESIDENT CARE MANUAL PROCEDURE NUMBER II-C-30 PAGE 1 OF 12 APPROVED BY: SITE: CATEGORY: Vice President & Senior Operating Officer, Rehab & Continuing Care Edmonton General, Youville Home,
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS
 PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
CATHETERIZATION TRAINER ON A STAND
 CATHETERIZATION TRAINER ON A STAND Parts identification: Clamp Prostate velcro strap (male genitalia only) Genitalia stand male female Urethra channel Bladder tubing and luer locks Female genitalia Male
CATHETERIZATION TRAINER ON A STAND Parts identification: Clamp Prostate velcro strap (male genitalia only) Genitalia stand male female Urethra channel Bladder tubing and luer locks Female genitalia Male
SASKPIC April 16, 2014
 SASKPIC April 16, 2014 1 Why do we need a Continuing Care guideline? Most current guidelines and tools for UTI prevention focus on acute care Age related changes to the urinary tract predispose older adults
SASKPIC April 16, 2014 1 Why do we need a Continuing Care guideline? Most current guidelines and tools for UTI prevention focus on acute care Age related changes to the urinary tract predispose older adults
