PROMOTING URINARY CONTINENCE IN LTC
|
|
|
- Eugene Hall
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROMOTING URINARY CONTINENCE IN LTC Kelly Kruse RN APRN - BC MS, Continence Consultant Polling Question 1 What is your professional role? CNA LPN RN MDS Coordinator Director of Nursing Healthcare Provider (NP, MD, etc) Quality Assurance Administrator
2 Defining UI International Continence Society (2002) defines as an involuntary loss of urine which is objectively demonstrable and a social or hygienic problem Not a disease but rather a symptom that corresponds to various social and pathophysiological factors Contrary to popular belief, it is not an inevitable part of aging It is often curable and always manageable UI is high throughout the world and affects 17 million Americans Twice as common for women as men Prevalence is highest in the elderly with 50% of the homebound and 70% LTC residents incontinent (DuBeau et al., 2006) Increasing problem for adults over age 65 UI and falls are the leading reasons for nursing home admission (Abrams et al., 2009)
3 Prevalence in LTC and Community Dwelling Settings Watson and colleagues (2000) found in LTC: 50% of residents are incontinent of urine Non-random sample of nursing homes, only 15% of residents were assessed for UI and of these only 3% received treatment. 99% of residents wore absorbent products. (Palmer and Newman, 2004) In community-dwelling settings: it is estimated that 15-30% of these older adults have UI (Fantl, Newman, Colling, et al., 1996; AHRQ Measure Summary NQMC-7119, 2012) Impact on Health Status Significant UI related Co-Morbidities: Depression, isolation and low self-esteem Skin Breakdown Urinary Tract Infections Falls and fall related injuries UI has a more severe impact on frail older adults when compared to healthy elders (Abrams et al., 2009)
4 Economic Impact Expensive! $32 billion spent annually on UI = $3,546 per individual with UI Pads and laundry make up 55% of money spent 1% spent on evaluation and management 44% of expenses are incurred following adverse consequences of UI Critical Question: Why are expenses for evaluation and management so low? AHRQ Measure Summary NQMC-7119, 2012 Current Responses of Health Care Systems to UI Nurses have always recognized UI as a health concern but have not always addressed Traditionally seen continence as the role of a nurse specialist or urologist Beginning to change practice to address Primary Care providers are just now beginning to recognize their role in identifying UI. PCPs in key positions to identify UI Most common response of PCPs is to refer to Urology Medicare issued new CMS Surveyor Guidelines The Long Term Care Survey Quality Measures have been identified
5 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Response Revised CMS Surveyor Guidelines Surveyor Guidance for Incontinence and Catheter Use (effective June 27, 2005) Goal: To improve care and reduce costs Focus: Identification of UI in nursing home residents Assessment and Evaluation Development of Individualized Treatment Plans Implementation of nursing interventions Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence (UI) Over the past 2 decades many advances made in the treatment of incontinence Problem: More is known about the treatment of UI than is currently applied in practice
6 Many reasons: Care giver and clinician insufficient knowledge of UI Reluctance of patients to discuss Inadequately individualized care Understanding Common Misperceptions of Bladder Problems in Frail Older Adults
7 Myth #1: UI is inevitable with age Fact: While older adults are at an increased risk for UI to develop due to changes in kidney and bladder function with aging, UI is not an inevitable part of aging Many interventions can prevent, slow the progress or reverse UI Myth #2: There is only one type of UI. Fact: This false belief often leads to ineffective management and treatment of UI. There are many types of UI - transient, stress, urge, overflow, functional, mixed, reflux and total. Without an accurate diagnosis it is difficult to provide effective treatment.
8 Transient UI Appears suddenly and is present 6 months or less Usually treatable factors Can also be treatment induced ( i.e. restricted mobility, changes in fluid intake, medications) Should be identified immediately and referred for evaluation - if UI persists >6 months it becomes established and prognosis is poorer One study of 53 nursing homes, investigators identified potentially reversible causes of UI in 81% of residents Quick Assessment for Patients Experiencing a Sudden Change in Continence Status D delirium, diapers, dementia R restricted mobility, retention I infection, impaction, inflammation, dietary irritants P pharmaceuticals, polyuria
9 What Does This Look Like in Practice? Transient UI Nursing Assessment Tool Overactive Bladder with or without Urge UI The most common type of UI in older adults post-menopausal women persons with neurologic conditions Involuntary urination that occurs soon after feeling an urgent need to void Loss of urine before getting to the toilet Inability to suppress the need to urinate
10 ICS definition: Urgency with or without urge UI, usually with frequency and nocturia Urgency sudden, compelling desire to pass urine which is difficult to deter Urge UI involuntary leakage of urine accompanied or immediately preceded by urgency Frequency complaint of voiding too often by day Nocturia waking up one or more times to void Stress UI Most common type of UI found in women prior to menopause (female athletes, post-partum women) Very likely to occur in men with prostatectomy and radiation (37-65% after prostate surgery) Urine loss with increased intrabdominal pressure Short urethra, poor pelvic floor muscle tone
11 Overflow UI (Urinary Retention) Involuntary loss of urine associated with over distention of the bladder Occurs when bladder becomes so distended that voiding attempts result in frequent release of small amounts of urine, often dribbling Possible causes: obstruction of the urethra by fecal impaction enlarged prostate smooth muscle relaxants (relax the bladder and increase capacity) impaired ability to contract due to peripheral neuropathy
12 Functional UI Inability to reach the toilet because of environmental barriers, physical limitations, loss of memory, disorientation Dependent on others and have no genitourinary problems other than UI Higher rates of functional incontinence are present in adults who are institutionalized Mixed UI Urine loss has features of two or more types of UI Most common with increasing age Stress and Urge UI
13 Less Common Reflux Incontinence the bladder empties autonomically but the person has no sensation of the need to void i.e. spinal cord injuries Total Incontinence continuous and unpredictable loss of urine resulting from surgery, trauma or anatomical malformation Myth #3: There are no effective treatments for UI. It is unavoidable in nursing home residents. Fact: There is much evidence showing that UI is treatable in community and long term care settings Nurses can support continence including: Behavioral Interventions Toileting regimes Bladder urge inhibition/retraining Fluid management Bowel plan to address constipation
14 Preservation of Mobility and Function Walking/toileting/core strength Pelvic muscle exercises Interventions to treat and manage contributing factors Environment/clothing Assistive toileting devices Appropriate absorbent product use Consultation/Referral for: Vaginal Estrogen Replacement Incontinence Devices i.e. pessaries Pharmacologic Treatments for Urge UI and BPH Myth #4: UI falls under the purview of physicians: There s not much Nurses can do much to help. Fact: UI can be managed by non-pharmacologic treatments implemented by nursing staff. Thorough health histories, identification of risk factors and implementation of 3 day bladder diaries can provide the foundation for identifying the type of UI and implementing behavioral strategies.
15 Myth #5: UI is unmanageable in people with dementia. Fact: Although UI is often concurrent with dementia, cognitive impairment alone has not been shown to cause UI While impaired cognition may affect a patient s ability to find a bathroom or to recognize the urge to void, it doesn t necessarily affect bladder function Prompted voiding has been demonstrated to be effective in improving dryness in cognitively impaired and dependent nursing home residents Myth #6: Complete continence is the only indication of successful treatment. Fact: Until recently, continence and incontinence were viewed at opposite ends of the spectrum with nothing in between Successful treatment may include: dryness at night or during the day fewer episodes of UI a greater percentage of dry time an increase in the number of times a person urinates in the toilet. Any improvement can be seen as a significant success and caregivers should acknowledge both their own efforts and that of the patient.
16 Myth #7: Older adults don t mind being incontinent and wearing pads. Fact: Studies have found that UI represents a loss of control and made older adults feel angry They grieved the loss and were embarrassed, ashamed and depressed Many hid their UI fearing nursing home placement Incontinence pads are often referred to as diapers reinforcing the stereotype that a childlike loss of control and dignity accompanies aging Although, some adults wear pads to enhance a feeling of security, others do so because they haven t been presented with other options Routine use of incontinence pads by continent residents in the nursing home communicates the expectation that the resident will become incontinent and is considered a breech of nursing ethics
17 Myth #8: Indwelling catheters are the best intervention for intractable UI Fact: In an effort to keep patients dry and to protect their skin, particularly in the face of understaffing, indwelling catheters are too frequently used. Although the intentions may be good, these catheters are often used without consideration of the consequences. Continuous indwelling catheterization may be an appropriate management strategy for only a few patients and existing recommendations for care are based on short-term (less than 30 days) rather than long-term use. There are no recommendations for long-term indwelling catheters.
18 Myth #9: Prevention is impossible Fact: Continence should be fostered as the norm in all health care settings. Maintenance of the person s functional abilities is the first step in maintaining continence. Combining wheelchair use with exercise twice daily, visible bathrooms, toileting at regular intervals or according to individual voiding patterns, easy to manage clothing, and CNA involvement in the care plan are key to promoting continence. The availability of necessary equipment such as standing lifts and full mechanical lifts with hygiene slings increase continence as does effective staffing. Education of the patient and their families regarding prevention and management strategies is also key.
19 Educating Residents and Families Age-Related Bladder Changes Kidneys less able to concentrate urine during the day, bladder has less capacity resulting in frequency, urgency, nocturia Delayed sensation resulting in urgency and less time to get to the toilet Decreased muscle tone in the pelvic floor resulting in leaking or sudden loss of urine Self-Care Strategies Important to educate residents and their families Avoidance of bladder irritants - caffeine, alcohol, artificial sweeteners Maintain adequate fluid intake - water! Stop smoking - treat chronic cough Avoid constipation Pay attention to weight Dress comfortably - avoid restrictive clothing Consider ability to access the toilet - assistive devices, negotiating a proactive plan with caregivers Manage chronic health problems i.e. diabetes, COPD Maintain good genital hygiene - keep clean, wipe from front to back
20 What Nurses in LTC Can Do to Support Continence Identify Residents at Risk for Developing UI and Put Prevention Strategies in Place Lifestyle Factors diet/bladder irritants smoking, weight functional changes/mobility Constipation Female Childbirth Hypoestrogen State i.e. Menopause Pelvic surgery Prostate hypertrophy and/or surgery
21 Medications Cognitive Impairment Dementias Delirium Neurologic Disease CVA Parkinson s Disease MS Other co-morbidities Diabetes Heart Failure Arthritis Depression/anxiety Assess Continence Status Nursing Assessment on Admission Resident and family interview Adding evidence based questions to nursing assessment upon admission can encourage patients to report UI Are you having any problems with your bladder? Do you ever lose urine when you don t want to? Do you ever leak urine when you cough, laugh, sneeze or exercise? Do you wear pads to protect your clothes from urine leakage? Do you ever leak urine on your way to the bathroom? Hand off from setting from which they are being admitted Review of medical records
22 Weekly Nursing Summary Continence status documented in chart by the primary nurse Includes toileting plan Includes change of condition MDS Quarterly Review Section H on the MDS Assessment Tool Gather Objective Data Bladder Diaries Used to determine voiding patterns and frequency, # of incontinent episodes Complete in a timely and accurate way Wide variety of tools exist Implement for 3 days
23 Determine Bladder Emptying Bladder Scan - portable ultrasound that scans the bladder for void residual Straight cath Monitor for signs and symptoms of incomplete bladder emptying Review of Literature of Evidence Based Practice Any assessment of UI should include the availability of a bladder ultrasound scanner to determine post-void residual (PVR) urine amounts (CMS, 2006; Ehlman et al., 2012)
24 Polling Question 2 Do you have a bladder scanner in your facility? Studies looking at Bladder Scanners in LTC, show that about 1.3% of facilities purchased a bladder ultrasound scanner (Tubaro et al., 2010) Slow integration of technology into LTC as compared to acute and primary care (Singh, 2010) Cost (Altschuler & Diaz, 2006)
25 Polling Question 3 Have you received training on how and when to use a bladder scanner? Barriers to Bladder Ultrasound Use Lack of clear policies and procedures regarding indications for the use of bladder scanners Limited staff knowledge levels pertaining to UI Education and Training is Key
26 Polling Question 4 Do you feel confident in using a bladder scanner to assess bladder emptying? The adoption of bladder scanners in LTC has the potential to: Improve UI assessment Change knowledge and attitudes related to UI among skilled nursing facility staff Ehlman, et al., 2012
27 Physical Exam In addition to cognition, mobility and function also Abdominal exam Uro-Genital Exam Skin changes consistent with Incontinence Associated Dermatitis (IAD) In women inspect for: Signs of hypoestrogenemia (i.e. pale, thin, fragile tissues) Structural changes (i.e. pelvic organ prolapse, urethral caruncle) Loss of Pelvic floor tone (i.e. observable urine loss with position change or coughing) Rectal exam Bulbocavernous Reflex Presence of Stool Rectal Tone Neuro Exam Lower extremity reflexes Sensation
28 Assessment: Determining Type of UI Predicated on: Subjective (History): Bladder symptoms (Stress, Urge, Mixed, Functional, Overflow) Chronic Illnesses/Risk factors Social and cognitive status Medication review Objective (PE): Collected data Bladder Diary Bladder emptying Focused physical exam Mobility & Function Abdominal Urogenital Rectal Putting an Individualized Continence Plan of Care in Place Includes Continence Goals: Maintaining dignity and quality of life Individualizing continence plan of care Reducing the risk of UTIs Reducing the risk of falls Maintaining skin integrity
29 Nursing Toolbox for Continence Management Partnering with resident (and family) to put plan in place Interventions to treat and manage contributing factors that put continence at risk Fluid management Bowel plan to address constipation Environment/clothing Assistive toileting devices Appropriate absorbent product use Behavioral Interventions Toileting regimes Bladder urge inhibition/retraining Preservation of Mobility and Function Walking/toileting/core strength Pelvic muscle exercises Consultation/Referral for: Further evaluation Vaginal Estrogen Replacement Incontinence Devices i.e. pessaries Pharmacologic Treatments for Urge UI and BPH
30 Partnering with Residents to Achieve Continence Talk with cognitively able residents to find out what would be helpful to them in staying dry Reassure them that you will do what you can to help them stay dry Follow through Involved CNAs Communication shift to shift Identify and address lifestyle factors/health habits that put continence at risk: Fluid management Reduce Bladder irritants (caffeine, alcohol, NutraSweet) Smoking cessation/chronic cough management Weight loss/management Support function and mobility
31 Toileting Understand the different approaches that can be used In addition to ambulating to the bathroom and sitting on the toilet, toileting regimes can also be used with bedside commodes and bedpans Recognize that daytime and night time toileting plans may not be the same Help residents choose clothing that will be easy to manage when toileting (i.e. avoiding zippers, buttons, etc.). Based on Bladder Diaries Determine a Toileting Regime Independent Scheduled Prompted Social Continence
32 Independent Able to toilet themselves Manage clothing Confident in social situations Scheduled Toileting (Habit) Goal: To find a schedule that works for dryness Keep a record, go by the clock Every 2-3 hours is usual Should reflect the resident s routine and activities rather than the NH i.e. upon rising, after meals, after rest, before bed
33 Prompted Voiding Supports voiding habits + positive reinforcement for continence behavior Effective in mild dementia/cognitive impairment Relationship of the caregiver to the patient very important Steps: 1. Remind on a schedule 2. Assist as needed to the toilet 3. Positive reinforcement (praise) for success 4. Remind when you will be back Bladder Retraining Helpful in controlling urgency and frequency Key to urge control is to not respond by rushing to the bathroom Involves techniques for postponing urge to void Slow, deep breaths Distraction Self-statements I can wait or It s not time yet Quick Flicks Improvement is gradual but will occur
34 Social Continence Appropriate for those with intractable UI More than check and change avoid this language! Move thinking to focus on dignity social continence Utilizes an absorbent product Goals: Keep dry Odor free Skin in good condition About Absorbent Products Avoid using absorbent products with patients who are continent In those patients that need a product, match the right size and type of absorbent product with the amount of urine typically lost Maintain good genital hygiene by providing regular pericare after wet episodes Change as soon as they are wet Consider other collection devices
35 Support Function and Mobility Assist residents in ways that support their function and mobility Work with patients to maintain core strength through daily ambulation and getting up and down from a chair In Residents who are cognitively able and personally motivated offer pelvic muscle exercises Pelvic Muscle Exercises A series of 10 squeeze/relax repetitions using the pelvic floor muscles Can be taught and reinforced by the nurse Can be incorporated into Restorative Nursing Activities Focus is on: Isolation of correct muscles Strengthening of muscles Goal is to: Prevent UI Improve bladder symptoms/continence
36 Provide ongoing nursing assessment to identify changes in: continence status bowel function cognitive function mobility skin integrity MDS Quarterly Review Repeat bladder diary Adjust care plan Resident/CNA Report Repeat bladder diary Adjust care plan In Summary Nurses Have a Key Role in Supporting Continence in LTC that includes: Acknowledging the impact of UI on quality of life Identifying residents at risk for developing UI and put prevention strategies in place Identifying residents with changes in bladder function/continence status and providing nursing assessment to determine contributing factors/type of UI Implementing individualized plans of care to preserve and restore continence/bladder status Engaging residents and families in education and health behavior change strategies to support continence Providing information about further evaluation and treatment options. Making referrals as needed
37 CNAs have an important role in directly supporting continence Hydration Accurate completion of bladder diaries Toileting regimes Talking with residents about continence Appropriate use of absorbent products Assisting with good genital hygiene after toileting Assisting residents with clothing selection that will support continence Supporting mobility and function Learn bladder emptying techniques Learn how to do pelvic muscle exercises and encourage residents to do also Observe for and report changes in health status: continence, bowel function, cognition, mobility and skin integrity
38 Benefits of Continence Care Respects resident dignity and quality of life Addresses issues related to quality, safety and cost of care Family feels supported and confident in your care Reduces CNA workload and improves job satisfaction Thank You for all you do! Kelly Kruse RN APRN-BC MS Continence Consultant UroGyn Consultations LLC Office: (608)
39 Q & A To ask a question: Use *2 to unmute your line Use the chat function to the right of your screen GPQIN State Nursing Home Contacts Kansas Brenda Groves, LPN brenda.groves@area-a.hcqis.org Johnathan Reeves, BA johnathan.reeves@area-a.hcqis.org Kansas Foundation for Medical Care 2947 SW Wanamaker Drive Topeka, KS P: 785/ Nebraska Krystal Hays, RN, MSN, RAC-CT krystal.hays@area-a.hcqis.org CIMRO of Nebraska 1200 Libra Drive, Suite 102 Lincoln, NE P: 402/ , Ext. 522 South Dakota Lori Hintz, RN lori.hintz@area-a.hcqis.org South Dakota Foundation for Medical Care 2600 West 49th Street, Suite 300 Sioux Falls, SD P: 605/ North Dakota Michelle Lauckner, RN, BA, RAC-CT michelle.lauckner@area-a.hcqis.org Quality Health Associates of North Dakota 3520 North Broadway Minot, ND P: 701/ This material was prepared by the Great Plains Quality Innovation Network, the Medicare Quality Improvement Organization for Kansas, Nebraska, North Dakota and South Dakota, under contract with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), an agency of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The contents presented do not necessarily reflect CMS policy. 11SOW-GPQIN-NE-C2-138/
Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care
 Welcome To Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care Presented by Kamal Masaki, MD Professor and Chair Department of Geriatric Medicine John A. Burns School of Medicine, UH Manoa September 5, 2018 10:00 11:00
Welcome To Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care Presented by Kamal Masaki, MD Professor and Chair Department of Geriatric Medicine John A. Burns School of Medicine, UH Manoa September 5, 2018 10:00 11:00
Appendix F: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation. Audience: For Front-line Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010
 Appendix F: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation Audience: For Front-line Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010 Objectives Address individual needs and preferences with respect
Appendix F: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation Audience: For Front-line Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010 Objectives Address individual needs and preferences with respect
When Laughing is No Longer Funny Managing Transient Urinary Incontinence in Hospitalized Elderly Women
 When Laughing is No Longer Funny Managing Transient Urinary Incontinence in Hospitalized Elderly Women Grace Umejei, BSN, RN, CWOC. Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital Dallas NICHE Online Connect Webinars
When Laughing is No Longer Funny Managing Transient Urinary Incontinence in Hospitalized Elderly Women Grace Umejei, BSN, RN, CWOC. Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital Dallas NICHE Online Connect Webinars
DIAPPERS: Transient Causes of Urinary Incontinence and other contributing factors
 DIAPPERS: Transient Causes of Urinary Incontinence and other contributing factors D Delirium Acute confusion alters one s ability to anticipate and meet own needs. Delirium may occur from drugs, surgery,
DIAPPERS: Transient Causes of Urinary Incontinence and other contributing factors D Delirium Acute confusion alters one s ability to anticipate and meet own needs. Delirium may occur from drugs, surgery,
Appendix E: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation. Audience: For Registered Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010
 Appendix E: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation Audience: For Registered Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010 Objectives Address individual needs and preferences with respect
Appendix E: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation Audience: For Registered Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010 Objectives Address individual needs and preferences with respect
Diane K. Newman DNP, ANP-BC, PCB-PMD, FAAN
 Diane K. Newman DNP, ANP-BC, PCB-PMD, FAAN Diane K. Newman, DNP is a Biofeedback Certified Continence Specialist. With over 35-years experience, she is an expert in the assessment and management of pelvic-floor
Diane K. Newman DNP, ANP-BC, PCB-PMD, FAAN Diane K. Newman, DNP is a Biofeedback Certified Continence Specialist. With over 35-years experience, she is an expert in the assessment and management of pelvic-floor
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women
 Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
Chapter 18. Assisting With Urinary Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 18 Assisting With Urinary Elimination The urinary system: The Urinary System Removes waste products from the blood Maintains the body s water balance 2 Normal Urination The healthy adult produces
Chapter 18 Assisting With Urinary Elimination The urinary system: The Urinary System Removes waste products from the blood Maintains the body s water balance 2 Normal Urination The healthy adult produces
Various Types. Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG
 Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE
 IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
Clinical Model for IC 5
 Clinical Model for IC 5 The WHAT What is ideal clinical care for urinary incontinence? SELF-ASSESSMENT What components of ideal continence care is the hospital currently following? The HOW How can you
Clinical Model for IC 5 The WHAT What is ideal clinical care for urinary incontinence? SELF-ASSESSMENT What components of ideal continence care is the hospital currently following? The HOW How can you
Management of Female Stress Incontinence
 Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Coping with urges and leaks?
 OAB AND YOU Coping with urges and leaks? Let me help you learn more about overactive bladder (OAB) symptoms and ways to help manage them 1 HOW DOES THE BLADDER WORK? Within the urinary tract, the kidneys
OAB AND YOU Coping with urges and leaks? Let me help you learn more about overactive bladder (OAB) symptoms and ways to help manage them 1 HOW DOES THE BLADDER WORK? Within the urinary tract, the kidneys
Management of Incontinence and Pelvic Floor Disorders
 Management of Incontinence and Pelvic Floor Disorders Dear Colleague: Multiple studies demonstrate that pelvic floor disorders urinary or fecal leakage occurring at an inappropriate time or place has a
Management of Incontinence and Pelvic Floor Disorders Dear Colleague: Multiple studies demonstrate that pelvic floor disorders urinary or fecal leakage occurring at an inappropriate time or place has a
Continence Promotion in
 Everybody s Business- Continence Promotion in Aged Care Melissa O Grady Clinical Nurse Consultant Continence Warning Some graphic images are contained in this presentation Objectives What is Old Age? What
Everybody s Business- Continence Promotion in Aged Care Melissa O Grady Clinical Nurse Consultant Continence Warning Some graphic images are contained in this presentation Objectives What is Old Age? What
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
SECTION H: BLADDER AND BOWEL. H0100: Appliances. Item Rationale Health-related Quality of Life. Planning for Care
 SECTION H: BLADDER AND BOWEL Intent: The intent of the items in this section is to gather information on the use of bowel and bladder appliances, the use of and response to urinary toileting programs,
SECTION H: BLADDER AND BOWEL Intent: The intent of the items in this section is to gather information on the use of bowel and bladder appliances, the use of and response to urinary toileting programs,
Section H Bladder and Bowel
 Instructor Guide Section H Bladder and Bowel Objectives State the intent of Section H Bladder and Bowel. Describe how to conduct the assessment for urinary incontinence. Describe how to conduct the assessment
Instructor Guide Section H Bladder and Bowel Objectives State the intent of Section H Bladder and Bowel. Describe how to conduct the assessment for urinary incontinence. Describe how to conduct the assessment
The Urinary System. 1. Define important words in this chapter. 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system
 109 16 The Urinary System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system 3. Discuss changes in the urinary system due to aging 4. List normal qualities
109 16 The Urinary System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system 3. Discuss changes in the urinary system due to aging 4. List normal qualities
Urinary Continence & Management Post Stroke
 Urinary Continence & Management Post Stroke Incontinence and Stroke occurs in greater than 50% of acute stroke patients despite the personal, economic and psychosocial impact treatment evidence specific
Urinary Continence & Management Post Stroke Incontinence and Stroke occurs in greater than 50% of acute stroke patients despite the personal, economic and psychosocial impact treatment evidence specific
Incontinence. Anatomy The human body has two kidneys. The kidneys continuously filter the blood and make urine.
 Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
IF YOU VE GOT TO GO, WE VE GOT SOLUTIONS.
 IF YOU VE GOT TO GO, WE VE GOT SOLUTIONS. Get the facts about urinary incontinence and get real solutions. HENRY FORD PELVIC HEALTH & CONTINENCE CENTER HENRY FORD WOMEN S HEALTH SERVICES INCONVENIENCE?
IF YOU VE GOT TO GO, WE VE GOT SOLUTIONS. Get the facts about urinary incontinence and get real solutions. HENRY FORD PELVIC HEALTH & CONTINENCE CENTER HENRY FORD WOMEN S HEALTH SERVICES INCONVENIENCE?
Delaware Valley Geriatric Education Center 1
 Welcome to the second of our two modules, Continence: A Matter of Dignity, Care of Chronic and Complex UI. We are here today to discuss a topic which, every day, affects our jobs and lives of those we
Welcome to the second of our two modules, Continence: A Matter of Dignity, Care of Chronic and Complex UI. We are here today to discuss a topic which, every day, affects our jobs and lives of those we
INCONTINENCE. Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation TYPES OF INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE 11/08/2015
 INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
URINARY INCONTINENCE. Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
Urinary incontinence. Urology Department. Patient Information Leaflet
 Urinary incontinence Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with urinary incontinence. It contains information about the bladder,
Urinary incontinence Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with urinary incontinence. It contains information about the bladder,
Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider.
 Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider. To begin the diary, please choose two days when you will be at home. The two
Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider. To begin the diary, please choose two days when you will be at home. The two
Information to Help You Live Life to the Fullest
 Information to Help You Live Life to the Fullest For more information and to join the conversation visit: Prevail.com/LOBC 800-227-3551 CONSUMER EDUCATION 2015 First Quality Products, Inc. All rights reserved.
Information to Help You Live Life to the Fullest For more information and to join the conversation visit: Prevail.com/LOBC 800-227-3551 CONSUMER EDUCATION 2015 First Quality Products, Inc. All rights reserved.
Module 3 Causes Of Urinary Incontinence
 Causes Of Urinary Incontinence V4: Last Reviewed September 2017 Learning Outcomes Appreciate the numerous requirements and skills necessary for the person to achieve and maintain urinary continence Discuss
Causes Of Urinary Incontinence V4: Last Reviewed September 2017 Learning Outcomes Appreciate the numerous requirements and skills necessary for the person to achieve and maintain urinary continence Discuss
Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy
 A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Objectives. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
 URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
Incontinence. Urinary. In Adults. THIS PUBLICATION IS OUT OF DATE. For most current information:
 Urinary Incontinence In Adults A Patient's Guide r I When you eat and drink, your body absorbs the liquid. The kidneys filter out waste products from the body fluids and make urine. Urine travels down
Urinary Incontinence In Adults A Patient's Guide r I When you eat and drink, your body absorbs the liquid. The kidneys filter out waste products from the body fluids and make urine. Urine travels down
Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS
 Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS OhioHealth, Columbus Ohio Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the role of a pelvic floor therapist in
Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS OhioHealth, Columbus Ohio Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the role of a pelvic floor therapist in
Hydration Practices and Urinary Incontinence Care Planning
 AHRQ Safety Program for Long term Long-term Care: HAIs/CAUTI Hydration Practices and Urinary Incontinence Care Planning National Content Series for Facility Team Leads and Core Team Members September 17,
AHRQ Safety Program for Long term Long-term Care: HAIs/CAUTI Hydration Practices and Urinary Incontinence Care Planning National Content Series for Facility Team Leads and Core Team Members September 17,
Incontinence Patient Information Form
 Incontinence Patient Information Form (To be completed by patient) Before talking with you, the doctor would like some information about your urine leakage. These questions are important for finding out
Incontinence Patient Information Form (To be completed by patient) Before talking with you, the doctor would like some information about your urine leakage. These questions are important for finding out
Overactive bladder can result from one or more of the following causes:
 Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC)
 Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
URINARY INCONTINENCE FOR FALLS PREVENTION. by Susan Elms P.T. Elms Physiotherapy
 URINARY INCONTINENCE PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGEMENT FOR FALLS PREVENTION by Susan Elms P.T. Elms Physiotherapy OR How to avoid the mad dash to the bathroom! INCONTINENCE INFORMATION TALK What is incontinence?
URINARY INCONTINENCE PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGEMENT FOR FALLS PREVENTION by Susan Elms P.T. Elms Physiotherapy OR How to avoid the mad dash to the bathroom! INCONTINENCE INFORMATION TALK What is incontinence?
Module 5 Management Of Urinary Incontinence
 Management Of Urinary Incontinence V3: Last Reviewed September 2017 Learning Outcomes Outline conservative management options Discover the options available to manage the different types of incontinence
Management Of Urinary Incontinence V3: Last Reviewed September 2017 Learning Outcomes Outline conservative management options Discover the options available to manage the different types of incontinence
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence and what causes it? A: When you are not able to hold your urine until you can get to a bathroom, you have what s called urinary incontinence (also called
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence and what causes it? A: When you are not able to hold your urine until you can get to a bathroom, you have what s called urinary incontinence (also called
FreshRN Podcast Season 4, Episode 6. All Things Urinary Catheters
 FreshRN Podcast Season 4, Episode 6 All Things Urinary Catheters Key Focus: Catheters can lead to infections, which can be fatal. CAUTI - Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection CAUTI is a type of
FreshRN Podcast Season 4, Episode 6 All Things Urinary Catheters Key Focus: Catheters can lead to infections, which can be fatal. CAUTI - Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection CAUTI is a type of
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Dementia Support Across the Care Continuum
 Dementia Support Across the Care Continuum Michelle Niedens, L.S.C.S.W. Director of Education, Programs and Public Policy Alzheimer's Association - Heart of America Chapter July 16, 2015 DEMENTIA SUPPORT
Dementia Support Across the Care Continuum Michelle Niedens, L.S.C.S.W. Director of Education, Programs and Public Policy Alzheimer's Association - Heart of America Chapter July 16, 2015 DEMENTIA SUPPORT
AgePage. Urinary Incontinence
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
Table 1. International Consultation on Incontinence recommendations for frail older adults
 Table 1. International Consultation on Incontinence recommendations for frail older adults Clinicians need to assess and manage co-existing co morbid conditions which are known to have an impact on continence
Table 1. International Consultation on Incontinence recommendations for frail older adults Clinicians need to assess and manage co-existing co morbid conditions which are known to have an impact on continence
Patient Information. Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms. pubic bone. urethra. scrotum. bladder. vaginal canal
 Patient Information English Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is the bladder? pubic bone bladder seminal vesicles prostate rectum The
Patient Information English Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is the bladder? pubic bone bladder seminal vesicles prostate rectum The
AgePage. Urinary Incontinence
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
Portable Bladder Ultrasound. OHTAC Recommendation. Portable Bladder Ultrasound
 OHTAC Recommendation Portable Bladder Ultrasound April 18, 2006 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee (OHTAC) met on April 18, 2006 to review the utility of portable bladder ultrasound for
OHTAC Recommendation Portable Bladder Ultrasound April 18, 2006 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee (OHTAC) met on April 18, 2006 to review the utility of portable bladder ultrasound for
Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (care home)
 Addressograph label CHI:... Name:... Address:...... Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (care home) Past medical history: Is the patient on medications which can affect bladder function? If, please list
Addressograph label CHI:... Name:... Address:...... Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (care home) Past medical history: Is the patient on medications which can affect bladder function? If, please list
Disease Management. Incontinence Care. Chan Sau Kuen Continence Nurse Consultant United Christian Hospital 14/11/09
 Disease Management in Incontinence Care Chan Sau Kuen Continence Nurse Consultant United Christian Hospital 14/11/09 What is incontinence? Definition of Incontinence - Is the compliant of any involuntary
Disease Management in Incontinence Care Chan Sau Kuen Continence Nurse Consultant United Christian Hospital 14/11/09 What is incontinence? Definition of Incontinence - Is the compliant of any involuntary
December Objectives. Housekeeping Announcements
 Comprehensive Review of Regulations & Interpretive Guidance for Top F-Tags Bowel/Bladder Incontinence, Catheter, & UTI Requirements F690 Objectives 1. Identify the regulatory requirements related to Bowel/Bladder
Comprehensive Review of Regulations & Interpretive Guidance for Top F-Tags Bowel/Bladder Incontinence, Catheter, & UTI Requirements F690 Objectives 1. Identify the regulatory requirements related to Bowel/Bladder
Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (community)
 Addressograph label CHI:... Name:... Address:...... Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (community) Past medical history: Is the patient on medications which can affect bladder function? If, please list
Addressograph label CHI:... Name:... Address:...... Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (community) Past medical history: Is the patient on medications which can affect bladder function? If, please list
Continence Management
 Dear Learner, This training guide was designed for you to complete as a selfstudy activity. Please do the following in order to ensure successful completion: First, read through EVERYTHING. There is a
Dear Learner, This training guide was designed for you to complete as a selfstudy activity. Please do the following in order to ensure successful completion: First, read through EVERYTHING. There is a
Faecal Incontinence Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
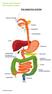 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
Y0028_2726_0 File&Use Bladder Control Does Matter
 Y0028_2726_0 File&Use 04092012 Bladder Control Does Matter If you suffer from urinary incontinence, you re not alone Don t be afraid to raise your hand if you ve been struggling with the embarrassment
Y0028_2726_0 File&Use 04092012 Bladder Control Does Matter If you suffer from urinary incontinence, you re not alone Don t be afraid to raise your hand if you ve been struggling with the embarrassment
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
PREVENTING URINARY INCONTINENCE through PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION in DISABLED ELDERLY
 PREVENTING URINARY INCONTINENCE through PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION in DISABLED ELDERLY Paolo DI BENEDETTO Lecturer, Tor Vergata University, Rome, Italy Former Director of Rehabilitation Department Institute
PREVENTING URINARY INCONTINENCE through PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION in DISABLED ELDERLY Paolo DI BENEDETTO Lecturer, Tor Vergata University, Rome, Italy Former Director of Rehabilitation Department Institute
Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence
 Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence This leaflet explains what urge incontinence is and how we can help to reduce and relieve your symptoms. If you have any questions or concerns,
Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence This leaflet explains what urge incontinence is and how we can help to reduce and relieve your symptoms. If you have any questions or concerns,
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment
 Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Urogynecology Associates of Philadelphia URODYNAMIC TESTING
 URODYNAMIC TESTING Urogynecology Associates of Philadelphia Most women with urinary incontinence will need to complete a few simple tests, performed in the office, to help your doctor assess your symptoms
URODYNAMIC TESTING Urogynecology Associates of Philadelphia Most women with urinary incontinence will need to complete a few simple tests, performed in the office, to help your doctor assess your symptoms
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence. Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa
 Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
CNA Training Advisor
 CNA Training Advisor Volume 12 Issue No. 2 February 2014 Bowel and bladder management Although the likelihood of incontinence the loss of bladder or bowel control increases as an individual gets older,
CNA Training Advisor Volume 12 Issue No. 2 February 2014 Bowel and bladder management Although the likelihood of incontinence the loss of bladder or bowel control increases as an individual gets older,
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Not a Laughing Matter
 Not a Laughing Matter How to Incorporate Pelvic Health Rehabilitation into your STAR program Nancy Corvigno MSPT PRPC Certified Star Clinician STAR Program at Griffin Hospital Survivorship Training and
Not a Laughing Matter How to Incorporate Pelvic Health Rehabilitation into your STAR program Nancy Corvigno MSPT PRPC Certified Star Clinician STAR Program at Griffin Hospital Survivorship Training and
Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider
 Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider Diana J Scott FNP-BC https://youtu.be/gmzaue1ojn4 1 Assessment of Urinary Incontinence Urge Stress Mixed Other overflow, postural, continuous, insensible,
Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider Diana J Scott FNP-BC https://youtu.be/gmzaue1ojn4 1 Assessment of Urinary Incontinence Urge Stress Mixed Other overflow, postural, continuous, insensible,
Information for Patients. Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) English
 Information for Patients Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) English Table of contents What is the bladder?... 3 What are overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 What causes overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 Diagnosis
Information for Patients Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) English Table of contents What is the bladder?... 3 What are overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 What causes overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 Diagnosis
The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women
 The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women This booklet is supported by WWWWW Wellbeing of Women Registered Charity No. 239281 www.wellbeingofwomen.org.uk Introduction Up to a third of all women experience
The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women This booklet is supported by WWWWW Wellbeing of Women Registered Charity No. 239281 www.wellbeingofwomen.org.uk Introduction Up to a third of all women experience
Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz
 Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz 54 year old female presenting with: Dragging sensation Urinary incontinence Some faecal incontinence HPC Since May 14 had noticed a mass protruding from the vagina when going
Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz 54 year old female presenting with: Dragging sensation Urinary incontinence Some faecal incontinence HPC Since May 14 had noticed a mass protruding from the vagina when going
Incontinence: The silent scourge of the young and old. The International Continence Society has. In this article:
 Focus on CME at the University of Toronto Incontinence: The silent scourge of the young and old By Sender Herschorn, BSc, MDCM, FRCSC In this article: 1. What is the workup for urinary incontinence? 2.
Focus on CME at the University of Toronto Incontinence: The silent scourge of the young and old By Sender Herschorn, BSc, MDCM, FRCSC In this article: 1. What is the workup for urinary incontinence? 2.
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME
 CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
Training a Wayward Bladder
 D. James Ballard, PT, DPT, GCS The University of Utah, Dept. of Physical Therapy Training a Wayward Bladder Agenda 1. Discuss urinary incontinence 2. Review pelvic floor and lower urinary tract functional
D. James Ballard, PT, DPT, GCS The University of Utah, Dept. of Physical Therapy Training a Wayward Bladder Agenda 1. Discuss urinary incontinence 2. Review pelvic floor and lower urinary tract functional
Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help
 Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help Urogynaecology Introduction This leaflet is produced as a self-help guide for women of East and North Herts that are experiencing issues with continence.
Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help Urogynaecology Introduction This leaflet is produced as a self-help guide for women of East and North Herts that are experiencing issues with continence.
Geriatric Urinary Incontinence
 Geriatric Urinary Incontinence Neil M. Resnick, MD Thomas Detre Professor of Medicine Chief, Division of Geriatric Medicine University of Pittsburgh/UPMC UI: The Problem Prevalence in elderly 33% Morbidity
Geriatric Urinary Incontinence Neil M. Resnick, MD Thomas Detre Professor of Medicine Chief, Division of Geriatric Medicine University of Pittsburgh/UPMC UI: The Problem Prevalence in elderly 33% Morbidity
Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence
 Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI Family Physiotherapy Centre of London
 Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI blandry@fpclondon.com Family Physiotherapy Centre of London Objectives To describe the scope of post-prostatectomy incontinence To describe what s been done To provide
Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI blandry@fpclondon.com Family Physiotherapy Centre of London Objectives To describe the scope of post-prostatectomy incontinence To describe what s been done To provide
Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for women
 Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for women Introduction Many women suffer from weakness of their pelvic floor muscles. Common symptoms include: leaking urine
Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for women Introduction Many women suffer from weakness of their pelvic floor muscles. Common symptoms include: leaking urine
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN
 Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles. Information for men
 Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for men Introduction Many men suffer from weakness of their pelvic floor muscles. Common symptoms include: leaking urine with
Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for men Introduction Many men suffer from weakness of their pelvic floor muscles. Common symptoms include: leaking urine with
Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care
 Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care Slide Presentation Supporting Implementation of the RNAO BPGs: Promoting Continence Using Prompted Voiding and Prevention of Constipation in the
Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care Slide Presentation Supporting Implementation of the RNAO BPGs: Promoting Continence Using Prompted Voiding and Prevention of Constipation in the
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Directorate of Women, Children and Surgical Services Burton and District Urogynaecology Centre A Nationally Accredited Urogynaecology Unit Pelvic Floor Exercises You have been given this leaflet because
Directorate of Women, Children and Surgical Services Burton and District Urogynaecology Centre A Nationally Accredited Urogynaecology Unit Pelvic Floor Exercises You have been given this leaflet because
Overactive Bladder. When to see a doctor. Normal bladder function
 Overactive Bladder Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder-storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to stop, and overactive bladder may lead to the involuntary
Overactive Bladder Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder-storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to stop, and overactive bladder may lead to the involuntary
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Managing Female Urinary Incontinence Within Primary Care
 Managing Female Urinary Incontinence Within Primary Care Angela Patterson Lead Clinical Nurse Specialist in Bladder and Bowel Dysfunction. South Eastern HSCT Background More than 14 million in the UK affected
Managing Female Urinary Incontinence Within Primary Care Angela Patterson Lead Clinical Nurse Specialist in Bladder and Bowel Dysfunction. South Eastern HSCT Background More than 14 million in the UK affected
encathopedia Volume 7 PARKINSON S AND THE BLADDER
 encathopedia Volume 7 PARKINSON S AND THE BLADDER Parkinson s disease Parkinson s is a progressive neurological condition. In people with Parkinson s, some of the brain cells that create the chemical dopamine
encathopedia Volume 7 PARKINSON S AND THE BLADDER Parkinson s disease Parkinson s is a progressive neurological condition. In people with Parkinson s, some of the brain cells that create the chemical dopamine
Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Incontinence. Urinary Incontinence
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Incontinence Leslee L. Subak, MD Professor Obstetrics, Gynecology & RS Epidemiology, Urology University of California, San Francisco Urinary Incontinence Common - 25%
Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Incontinence Leslee L. Subak, MD Professor Obstetrics, Gynecology & RS Epidemiology, Urology University of California, San Francisco Urinary Incontinence Common - 25%
Pelvic floor weakness
 Information leaflet for patients Pelvic floor weakness Physiotherapy department You have been referred to this department for treatment and advice because you have one or more of the following symptoms:
Information leaflet for patients Pelvic floor weakness Physiotherapy department You have been referred to this department for treatment and advice because you have one or more of the following symptoms:
Integrated Continence Service Policy. January SafeCare Council January Carol Giffin, Continence Advisor
 Policy No: OP51 Version: 1.0 Name of Policy: Integrated Continence Service Policy Effective From: January 2008 Approved by: SafeCare Council January 2008 Next Review Date: January 2010 Reviewed by: Carol
Policy No: OP51 Version: 1.0 Name of Policy: Integrated Continence Service Policy Effective From: January 2008 Approved by: SafeCare Council January 2008 Next Review Date: January 2010 Reviewed by: Carol
CONTINENCE BEHAVIORAL REHABILITATION PROGRAM
 CONTINENCE BEHAVIORAL REHABILITATION PROGRAM PHYLLIS A. HEINTZ, PHD, RN, CTN-B NURSING, CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, BAKERSFIELD AUDREY COCHRAN, MSN, RN, GCNS-BC HEALTH CARE PLANNING AND EDUCATION FOR
CONTINENCE BEHAVIORAL REHABILITATION PROGRAM PHYLLIS A. HEINTZ, PHD, RN, CTN-B NURSING, CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, BAKERSFIELD AUDREY COCHRAN, MSN, RN, GCNS-BC HEALTH CARE PLANNING AND EDUCATION FOR
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Bladder Management and Preventing CAUTI. Bladder management CAUTI prevention standards
 Slide 1 Bladder Management and Preventing CAUTI Diana Weinel, MS RN James A. Haley Veterans Hospital & Clinics Tampa, FL Florida State Association of Rehabilitation Nurses Conference May, 2018 Slide 2
Slide 1 Bladder Management and Preventing CAUTI Diana Weinel, MS RN James A. Haley Veterans Hospital & Clinics Tampa, FL Florida State Association of Rehabilitation Nurses Conference May, 2018 Slide 2
Bladder Matters. Peggy P. Francis DNP, RN, MSN, CS, FNP-BC
 Bladder Matters Peggy P. Francis DNP, RN, MSN, CS, FNP-BC Disclosures Please be advised that I am on the following speaker bureaus: Astellas/GlaxoSmithKline Ortho Women s Health/Bayer Healthcare Pfizer
Bladder Matters Peggy P. Francis DNP, RN, MSN, CS, FNP-BC Disclosures Please be advised that I am on the following speaker bureaus: Astellas/GlaxoSmithKline Ortho Women s Health/Bayer Healthcare Pfizer
Management of Urinary Incontinence in Older Women. Dr. Cecilia Cheon Department of Obs. & Gyn. Queen Elizabeth Hospital
 Management of Urinary Incontinence in Older Women Dr. Cecilia Cheon Department of Obs. & Gyn. Queen Elizabeth Hospital Epidemiology Causes Investigation Treatment Conclusion Elderly Women High prevalence
Management of Urinary Incontinence in Older Women Dr. Cecilia Cheon Department of Obs. & Gyn. Queen Elizabeth Hospital Epidemiology Causes Investigation Treatment Conclusion Elderly Women High prevalence
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics. Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital 01/02/2018 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms LUTS - one of
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital 01/02/2018 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms LUTS - one of
Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME
 Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME Introductions Amelia Samuels, Physiotherapist, Active Rehabilitation Physiotherapy Supporting the Continence Foundation of Australia Continence Foundation of Australia
Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME Introductions Amelia Samuels, Physiotherapist, Active Rehabilitation Physiotherapy Supporting the Continence Foundation of Australia Continence Foundation of Australia
Are you frustrated because you can t always control
 Chapter 1 Understanding Incontinence Are you frustrated because you can t always control when you urinate? When you cough or sneeze, are you worried that urine might leak out? When you feel the urge to
Chapter 1 Understanding Incontinence Are you frustrated because you can t always control when you urinate? When you cough or sneeze, are you worried that urine might leak out? When you feel the urge to
Intermittent self-catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Spinal Injuries
 Intermittent self-catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Spinal Injuries page 2 of 12 What is clean intermittent self-catheterisation (CISC)? Urinary catheterisation is a procedure used to drain
Intermittent self-catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Spinal Injuries page 2 of 12 What is clean intermittent self-catheterisation (CISC)? Urinary catheterisation is a procedure used to drain
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises
 INFORMATION FOR WOMEN OF ALL AGES Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises How to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles ASSOCIATION OF CHARTERED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS IN WOMEN S HEALTH This leaflet is supported
INFORMATION FOR WOMEN OF ALL AGES Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises How to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles ASSOCIATION OF CHARTERED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS IN WOMEN S HEALTH This leaflet is supported
