Fecal Incontinence. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse. What is fecal incontinence (FI)?
|
|
|
- Clara Terry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fecal Incontinence National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is fecal incontinence (FI)? Fecal incontinence, commonly referred to as bowel control problems, is the inability to hold a bowel movement until reaching a bathroom. FI also refers to the accidental leakage for example, while passing gas of solid or liquid stool. Feces is another name for stool. FI can be upsetting and embarrassing. Many people with FI feel ashamed and try to hide the problem. However, health care providers are experienced in talking about FI. People with FI should not be afraid or embarrassed to talk with their health care provider. FI is often caused by a medical problem and treatment is available. How does bowel control work? Bowel control relies on muscles and nerves of the rectum and anus working together to hold and release stool. The rectum, which is the lower end of the large bowel, also called the large intestine, stretches to hold stool. Stool is normally solid by the time it reaches the rectum. Circular muscles called sphincters close tightly like rubber bands around the opening at the end of the rectum, called the anus, until stool is ready to be released during a bowel movement. Pelvic floor muscles also help maintain bowel control. Who gets FI? Nearly 18 million U.S. adults about one in 12 have FI. 1 FI is not always a part of aging, but it is more common in older adults. FI is slightly more common among women. Having any of the following can increase the risk of FI: diarrhea a disease or injury that damages the nervous system poor overall health multiple chronic, or long-lasting, illnesses a difficult childbirth with injuries to the pelvic floor the muscles, ligaments, and tissues that support the uterus, vagina, bladder, and rectum 1 Whitehead WE, Borrud L, Goode PS, et al. Fecal incontinence in US adults: epidemiology and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 2009;137: Liver Appendix The digestive system Esophagus Stomach Pancreas Large intestine Small intestine Rectum Anus
2 Rectum External sphincter Internal sphincter The external and internal anal sphincter muscles What causes FI? Fecal incontinence has many causes, including diarrhea constipation muscle damage or weakness nerve damage loss of stretch in the rectum hemorrhoids pelvic floor dysfunction Diarrhea Anus External sphincter Internal sphincter Diarrhea can cause FI. Loose stools fill the rectum quickly and are more difficult to hold than solid stools. Diarrhea increases the chances of not reaching a toilet in time. Constipation Constipation, a condition in which a person has fewer than three bowel movements a week, can cause FI. Constipation can lead to large, hard stools that get stuck in the rectum. Watery stool builds up behind the hard stool and may leak out around the hard stool. Constipation can, over time, stretch and weaken sphincter muscles, reducing the rectum s ability to hold stool. Muscle Damage or Weakness Injury to one or both of the sphincter muscles can cause FI. If these muscles, called the external and internal anal sphincter muscles, are damaged or weakened, they may not be strong enough to keep the anus closed and prevent stool from leaking. Trauma, cancer surgery, and hemorrhoid surgery are possible causes of injury to the sphincters. Hemorrhoids are inflamed veins around the anus or in the lower rectum. Nerve Damage The anal sphincter muscles won t properly open and close if the nerves that control them are damaged. Likewise, if the nerves that sense stool in the rectum are damaged, a person may not feel the urge to go to the bathroom. Both types of nerve damage can lead to FI. Possible sources of nerve damage are giving birth, a long-term habit of straining to pass stool, stroke, injury, and diseases that affect the nerves, such as diabetes and multiple sclerosis. 2 Fecal Incontinence
3 Loss of Stretch in the Rectum Normally, the rectum stretches to hold stool until a person has a bowel movement. Rectal surgery, radiation treatment, and inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn s disease and ulcerative colitis, can cause scarring that stiffens the rectal walls. The rectum then can t stretch as much to hold stool, increasing the risk of FI. Hemorrhoids External hemorrhoids, which develop under the skin around the anus, can prevent the anal sphincter muscles from closing completely. Small amounts of mucus or liquid stool can then leak through the anus. Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Abnormalities of the pelvic floor muscles and nerves called pelvic floor dysfunction can lead to FI by impairing the ability to sense stool in the rectum decreasing the ability to contract muscles used during a bowel movement causing the rectum to drop down through the anus, a condition called rectal prolapse causing the rectum to protrude through the vagina, a condition called rectocele causing the pelvic floor to become weak and sag Giving birth sometimes causes pelvic floor dysfunction. Risk is greater if forceps are used to help deliver the baby or if an episiotomy a cut in the vaginal area to prevent the baby s head from tearing the vagina during birth is performed. FI related to childbirth can appear soon or many years after delivery. How is FI diagnosed? Health care providers diagnose FI based on a patient s medical history, physical exam, and medical test results. Diagnosis is key to treatment. People with concerns about FI should see a health care provider, who may ask the following questions: When did FI start? How often does FI occur? How much stool leaks? Does the stool just streak the underwear? Does just a little bit of solid or liquid stool leak out? Or does complete loss of bowel control occur? Does FI involve a strong urge to have a bowel movement or does it happen without warning? For people with hemorrhoids, do hemorrhoids bulge through the anus? How does FI affect daily life? Do certain foods seem to make FI worse? Can gas be controlled? Based on answers to these questions, a health care provider may refer the patient to a doctor who specializes in problems of the digestive system, such as a gastroenterologist, proctologist, or colorectal surgeon. The specialist will perform a physical exam and may suggest one or more of the following tests, which may be performed at a hospital or clinic: Anal manometry uses a pressuresensitive tube to check the sensitivity and function of the rectum. Anal manometry also checks the tightness of the anal sphincter muscles and their ability to respond to nerve signals. 3 Fecal Incontinence
4 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses radio waves and magnets to produce detailed pictures of the body s internal organs and soft tissues without using x rays. MRI can be used to create images of the anal sphincter muscles. Anorectal ultrasonography, an ultrasound procedure specific to the anus and rectum, uses a device, called a transducer, that bounces safe, painless sound waves off organs to create an image of their structure. Anorectal ultrasonography can be used to evaluate the structure of the anal sphincter muscles. Proctography, also known as defecography, is an x-ray test that shows how much stool the rectum can hold, how well the rectum can hold stool, and how well the rectum can eliminate stool. Proctosigmoidoscopy uses a lighted, flexible tube to see inside the rectum and the lower large intestine to look for potential FI-related problems such as inflammation, tumors, or scar tissue. How is FI treated? Successful FI treatment relies on correctly diagnosing the underlying problem. Treatment may include one or more of the following: eating, diet, and nutrition medication pelvic floor exercises bowel training surgery electrical stimulation Eating, Diet, and Nutrition Food affects stool consistency and how quickly it passes through the digestive system. If stools are hard to control because they are loose, high-fiber foods may add bulk and make stool easier to control. However, some people find that high-fiber foods loosen stool and make FI worse. Foods and drinks that contain caffeine, such as coffee, tea, or chocolate, may relax the internal anal sphincter muscles and worsen FI. Anal electromyography tests for pelvic floor and rectal muscle nerve damage. 4 Fecal Incontinence
5 Keeping a Food Diary A food diary can help identify foods that cause diarrhea and FI. A food diary should list foods eaten, portion size, and when FI occurs. After a few days, the diary may show a link between certain foods and FI. Eating less of foods linked to FI may improve symptoms. A food diary can also be helpful to a health care provider treating a patient with FI. Common foods and drinks linked to diarrhea and FI include dairy products such as milk, cheese, and ice cream drinks and foods containing caffeine cured or smoked meat such as sausage, ham, and turkey spicy foods Dietary changes that may improve FI include Eating the right amount of fiber. For many people, fiber adds bulk to their stool and makes it softer and easier to control. Fiber can help with diarrhea and constipation. Fiber is found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and beans. Fiber supplements sold in a pharmacy or in a health food store are another common source of fiber to treat FI. A normal diet should include 20 to 30 grams of fiber a day. Fiber should be added to the diet slowly to avoid bloating. Getting plenty to drink. Eight, 8-ounce glasses of liquid a day may help prevent constipation. Water is a good choice. Drinks with caffeine, alcohol, milk, or carbonation should be avoided if they trigger diarrhea. alcoholic beverages fruits such as apples, peaches, and pears fatty and greasy foods sweeteners in diet drinks and sugarless gum and candy, including sorbitol, xylitol, mannitol, and fructose 5 Fecal Incontinence
6 What foods have fiber? Examples of foods that have fiber include Beans, cereals, and breads Fiber 1/2 cup of beans (navy, pinto, grams kidney, etc.), cooked 1/2 cup of shredded wheat, grams ready-to-eat cereal 1/3 cup of 100% bran, 9.1 grams ready-to-eat cereal 1 small oat bran muffin 3.0 grams 1 whole-wheat English muffin 4.4 grams Fruits 1 small apple, with skin 3.6 grams 1 medium pear, with skin 5.5 grams 1/2 cup of raspberries 4.0 grams 1/2 cup of stewed prunes 3.8 grams Vegetables 1/2 cup of winter squash, cooked 2.9 grams 1 medium sweet potato, baked in skin 3.8 grams 1/2 cup of green peas, cooked grams 1 small potato, baked, with skin 3.0 grams 1/2 cup of mixed vegetables, cooked 4.0 grams 1/2 cup of broccoli, cooked grams 1/2 cup of greens (spinach, collards, grams turnip greens), cooked Source: U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Dietary Guidelines for Americans, Fecal Incontinence
7 Over time, diarrhea can prevent a person s body from obtaining enough vitamins and minerals. Health care providers can recommend vitamin supplements to help correct this problem and can give information about how changes in eating, diet, or nutrition could help with treatment. Medication If diarrhea is causing FI, medication may help. Health care providers sometimes recommend using bulk laxatives, such as Citrucel and Metamucil, to develop more regular bowel patterns. Antidiarrheal medicines such as loperamide or diphenoxylate may be recommended to slow down the bowels and help control the problem. Pelvic Floor Exercises Exercises that strengthen the pelvic floor muscles may improve bowel control. Pelvic floor exercises involve squeezing and relaxing pelvic floor muscles 50 to 100 times a day. A health care provider can help with proper technique. Biofeedback therapy may also help. Biofeedback therapy uses sensors to tell patients if they are exercising the right muscles. Success with pelvic floor exercises depends on the cause of FI, its severity, and a person s ability to perform the exercises. Bowel Training Developing a regular bowel movement pattern can help improve FI, especially FI due to constipation. Bowel training involves attempting to have bowel movements at specific times of the day, such as after every meal. Over time, the body becomes accustomed to a regular bowel movement pattern, thus reducing constipation and related FI. Persistence is key to successful bowel training. Achieving a regular bowel control pattern can take weeks to months. Surgery Surgery may be an option for FI that fails to improve with other treatments or for FI caused by pelvic floor or anal sphincter muscle injuries. Sphincteroplasty, the most common FI surgery, reconnects the separated ends of a sphincter muscle torn by childbirth or another injury. Sphincteroplasty is performed at a hospital by a colorectal, gynecological, or general surgeon. Another surgery involves placing an inflatable cuff, called an artificial sphincter, around the anus and implanting a small pump beneath the skin that the patient activates to inflate or deflate the cuff. This surgery is much less common and is performed at a hospital by specially trained colorectal surgeons. Electrical Stimulation Electrical stimulation, also called sacral nerve stimulation or neuromodulation, involves placing electrodes in the nerves to the anal canal and rectum and continuously stimulating these nerves with electrical pulses. This procedure requires a batteryoperated stimulator placed beneath the skin. 7 Fecal Incontinence
8 Anal Discomfort The skin around the anus is delicate and sensitive. Constipation and diarrhea or contact between skin and stool can cause pain or itching. The following steps can help relieve anal discomfort: Washing the anal area after a bowel movement. Washing with water, but not soap, can help prevent discomfort. Soap can dry out the skin, making discomfort worse. Ideally, the anal area should be washed in the shower with lukewarm water or in a sitz bath a special plastic tub that allows a person to sit in a few inches of warm water. No-rinse skin cleansers, such as Cavilon, are a good alternative. Wiping with toilet paper further irritates the skin and should be avoided. Premoistened, alcohol-free towelettes are a better choice. Keeping the anal area dry. The anal area should be allowed to air dry after washing. If time doesn t permit air drying, the anal area can be gently patted dry with a lint-free cloth. Creating a moisture barrier. A moisture barrier cream that contains ingredients such as dimethicone a type of silicone can help form a barrier between skin and stool. The anal area should be cleaned before applying barrier cream. Patients, however, should talk with their health care provider before using anal creams and ointments. Some can irritate the anus. Using nonmedicated powders. Nonmedicated talcum powder or cornstarch can also relieve anal discomfort. As when moisture barrier creams are used, the anal area should be clean and dry before use. Using wicking pads or disposable underwear. Pads and disposable underwear with a wicking layer can pull moisture away from the skin. Wearing breathable clothes and underwear. Clothes and underwear should allow air to flow and keep skin dry. Tight clothes or plastic or rubber underwear that blocks air can worsen skin problems. Changing soiled underwear as soon as possible. 8 Fecal Incontinence
9 What are some practical tips for coping with FI? Because FI can cause embarrassment, fear, and loneliness, taking steps to deal with it is important. Treatment can dramatically improve quality of life and help people with FI feel better about themselves. The first step is to contact a health care provider. The organizations listed at the end of this fact sheet can provide information, support, and resources to help find FI treatment specialists. The following tips can help people cope with FI: carrying a bag with cleanup supplies and a change of clothes when leaving the house finding public restrooms before one is needed using the toilet before leaving home wearing disposable underwear if loss of bowel control is suspected using fecal deodorants pills that reduce the smell of stool and gas; although fecal deodorants are available over the counter, a health care provider can help patients find them What if a child has FI? A child with FI who is toilet trained should see a health care provider, who can determine the cause and recommend treatment. FI can occur in children because of a birth defect or disease, but in most cases it occurs because of constipation. Children often develop constipation as a result of stool withholding. They may withhold stool because they are stressed about toilet training, embarrassed to use a public bathroom, do not want to interrupt playtime, or are fearful of having a painful or unpleasant bowel movement. Similarly to adults, constipation in children can cause large, hard stools that get stuck in the rectum. Watery stool builds up behind the hard stool and may unexpectedly leak out, soiling a child s underwear. Parents often mistake this soiling as a sign of diarrhea. 9 Fecal Incontinence
10 Points to Remember Fecal incontinence (FI), commonly referred to as bowel control problems, is the inability to hold a bowel movement until reaching a bathroom. Nearly 18 million U.S. adults about one in 12 have FI. People with FI should not be afraid or embarrassed to talk with their health care provider. FI is often caused by a medical problem. Bowel control relies on muscles and nerves of the rectum and anus working together to hold and release stool. Circular muscles called sphincters close tightly like rubber bands around the opening at the end of the rectum, called the anus, until stool is ready to be released during a bowel movement. The pelvic floor the muscles, ligaments, and tissues that support the uterus, vagina, bladder, and rectum helps maintain bowel control. FI has many causes, including diarrhea, constipation, muscle damage or weakness, nerve damage, loss of stretch in the rectum, hemorrhoids, and pelvic floor dysfunction. Health care providers diagnose FI based on the patient s medical history, a physical examination, and medical tests. Successful FI treatment relies on correctly diagnosing the underlying problem. Treatment may include eating, diet, and nutrition; medication; pelvic floor exercises; bowel training; surgery; or electrical stimulation. A food diary can help identify foods that cause diarrhea and FI. Steps that can help relieve anal discomfort include washing the anal area after a bowel movement, keeping the anal area dry, wearing breathable clothes and underwear, and changing soiled underwear as soon as possible. Treatment for FI is available. The first step is to contact a health care provider. FI can occur in children because of a birth defect or disease, but in most cases it occurs because of constipation. Hope through Research The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) conducts and supports research into many kinds of digestive disorders, including FI. The NIDDK is researching ways to create new anal sphincter muscles from patients own cells or tissues. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is currently reviewing sacral nerve stimulation, a technique used in Europe to treat FI. Sacral nerve stimulation involves implanting a small electronic device to stimulate the sacral nerves, which run from the spinal cord to the anal sphincter muscles. Participants in clinical trials can play a more active role in their own health care, gain access to new research treatments before they are widely available, and help others by contributing to medical research. For information about current studies, visit 10 Fecal Incontinence
11 For More Information Fact sheets and easy-to-read booklets about FI and related conditions are available from the National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse at including Bowel Control: What You Need to Know Constipation Constipation in Children Diarrhea What I need to know about Bowel Control (Easy-to-Read) What I need to know about Constipation (Easy-to-Read) What I need to know about Diarrhea (Easy-to-Read) American Academy of Family Physicians P.O. Box Shawnee Mission, KS Phone: or Fax: fp@aafp.org Internet: American College of Gastroenterology P.O. Box Bethesda, MD Phone: Internet: American Neurogastroenterology and Motility Society Harmony Lane Belleville, MI Phone: Fax: admin@motilitysociety.org Internet: International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders P.O. Box Milwaukee, WI Phone: or Fax: iffgd@iffgd.org Internet: The Simon Foundation for Continence P.O. Box 815 Wilmette, IL Phone: SIMON ( ) or Fax: Internet: 11 Fecal Incontinence
12 Acknowledgments Publications produced by the Clearinghouse are carefully reviewed by both NIDDK scientists and outside experts. This publication was originally reviewed by Arnold Wald, M.D., University of Pittsburgh Medical Center; Paul Hyman, M.D., University of Kansas Medical Center; and Diane Darrell, A.P.R.N., B.C., Research College of Nursing, Kansas City, MO. The Bowel Control Awareness Campaign The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) Bowel Control Awareness Campaign provides current, science-based information about the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of bowel control problems, also known as fecal incontinence. The Awareness Campaign is an initiative of the National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse, a service of the NIDDK. Download this publication and learn more about the Awareness Campaign at You may also find additional information about this topic by visiting MedlinePlus at This publication may contain information about medications. When prepared, this publication included the most current information available. For updates or for questions about any medications, contact the U.S. Food and Drug Administration tollfree at INFO FDA ( ) or visit Consult your health care provider for more information. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse 2 Information Way Bethesda, MD Phone: TTY: Fax: nddic@info.niddk.nih.gov Internet: The National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse (NDDIC) is a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). The NIDDK is part of the National Institutes of Health of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Established in 1980, the Clearinghouse provides information about digestive diseases to people with digestive disorders and to their families, health care professionals, and the public. The NDDIC answers inquiries, develops and distributes publications, and works closely with professional and patient organizations and Government agencies to coordinate resources about digestive diseases. This publication is not copyrighted. The Clearinghouse encourages users of this publication to duplicate and distribute as many copies as desired. This publication is available at The U.S. Government does not endorse or favor any specific commercial product or company. Trade, proprietary, or company names appearing in this document are used only because they are considered necessary in the context of the information provided. If a product is not mentioned, the omission does not mean or imply that the product is unsatisfactory. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health NIH Publication No April 2011 The NIDDK prints on recycled paper with bio-based ink.
Saratoga Schenectady Endoscopy Center, LLC Burnt Hills, N.Y Hemorrhoids. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Hemorrhoids National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What are hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids are swollen and inflamed veins
Hemorrhoids National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What are hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids are swollen and inflamed veins
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 What I need to know about Irritable Bowel Syndrome NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know
What I need to know about Irritable Bowel Syndrome NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know
Treatments for Fecal Incontinence A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treatments for Fecal Incontinence A Review of the Research for Adults e Is This Information Right for Me? This information is right for you if: Your health care professional* said you or your loved one
Treatments for Fecal Incontinence A Review of the Research for Adults e Is This Information Right for Me? This information is right for you if: Your health care professional* said you or your loved one
Colonoscopy. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Colonoscopy National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is colonoscopy? Colonoscopy is a procedure used to see
Colonoscopy National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is colonoscopy? Colonoscopy is a procedure used to see
Virtual Colonoscopy. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Virtual Colonoscopy National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is virtual colonoscopy? Virtual colonoscopy is
Virtual Colonoscopy National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is virtual colonoscopy? Virtual colonoscopy is
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Flexible Sigmoidoscopy
 Flexible Sigmoidoscopy National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is flexible sigmoidoscopy? Flexible sigmoidoscopy
Flexible Sigmoidoscopy National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is flexible sigmoidoscopy? Flexible sigmoidoscopy
Lower GI Series. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Lower GI Series National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is a lower gastrointestinal (GI) series? A lower GI
Lower GI Series National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is a lower gastrointestinal (GI) series? A lower GI
Hemorrhoids. What are hemorrhoids? What is the cause? What are the symptoms?
 What are hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower end of your intestine (rectum) or the anus. The anus is the opening where bowel movements pass out of your body. Hemorrhoids
What are hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower end of your intestine (rectum) or the anus. The anus is the opening where bowel movements pass out of your body. Hemorrhoids
from Bowel Control Problems twitter.com/voicesforpfd
 BREAK FREE from Bowel Control Problems POP Quiz THE NUMBER OF PEOPLE IN THE UNITED STATES WITH BOWEL CONTROL PROBLEMS: A. 6 million B. 12 million C. 18 million BOWEL CONTROL PROBLEMS Nearly 18 million
BREAK FREE from Bowel Control Problems POP Quiz THE NUMBER OF PEOPLE IN THE UNITED STATES WITH BOWEL CONTROL PROBLEMS: A. 6 million B. 12 million C. 18 million BOWEL CONTROL PROBLEMS Nearly 18 million
Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis
 Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What are diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What are diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
Constipation. What I need to know about. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
 What I need to know about Constipation U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Constipation
What I need to know about Constipation U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What I need to know about Constipation
National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Urodynamic Testing National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the urinary tract? The urinary tract
Urodynamic Testing National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the urinary tract? The urinary tract
Gas. What I need to know about. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
 What I need to know about Gas NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know about Gas NATIONAL INSTITUTES
What I need to know about Gas NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know about Gas NATIONAL INSTITUTES
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Upper GI Endoscopy National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy? Upper
Upper GI Endoscopy National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy? Upper
Gas in the Digestive Tract
 Gas in the Digestive Tract National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Everyone has gas and eliminates it by burping
Gas in the Digestive Tract National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Everyone has gas and eliminates it by burping
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Bowel Problems after Radiation
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Bowel Problems after Radiation If you have bowel problems after radiation, you may feel embarrassed. Don t let this stop you from asking for help. Sometimes, radiation
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Bowel Problems after Radiation If you have bowel problems after radiation, you may feel embarrassed. Don t let this stop you from asking for help. Sometimes, radiation
Stool softeners are medicines like (ducolox - pericolace - senokot). You want the stool to remain soft so it is easier to empty the bowel.
 "Bowel Management" How the Body Works The food you eat and drink provides your body with many nutrients. These nutrients give you energy and help you stay healthy. As food moves through your body it breaks
"Bowel Management" How the Body Works The food you eat and drink provides your body with many nutrients. These nutrients give you energy and help you stay healthy. As food moves through your body it breaks
Managing bowel problems after cancer treatment
 Managing bowel problems after cancer treatment Information for cancer survivors Read this pamphlet to learn: What bowel problems are What causes bowel problems What you can do to manage your bowel problems
Managing bowel problems after cancer treatment Information for cancer survivors Read this pamphlet to learn: What bowel problems are What causes bowel problems What you can do to manage your bowel problems
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
Faecal Incontinence Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
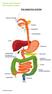 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea
 Patient & Family Guide 2018 Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea www.nscancercare.ca What is diarrhea? Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea Diarrhea
Patient & Family Guide 2018 Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea www.nscancercare.ca What is diarrhea? Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea Diarrhea
Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence)
 Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence) What is Accidental Bowel Leakage (ABL)? Accidental bowel leakage is the inability to control solid or liquid stool. This is the inability to control gas and
Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence) What is Accidental Bowel Leakage (ABL)? Accidental bowel leakage is the inability to control solid or liquid stool. This is the inability to control gas and
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Diarrhea National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Diarrhea National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Bleeding in the Digestive Tract
 Bleeding in the Digestive Tract National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health
Bleeding in the Digestive Tract National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence and what causes it? A: When you are not able to hold your urine until you can get to a bathroom, you have what s called urinary incontinence (also called
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence and what causes it? A: When you are not able to hold your urine until you can get to a bathroom, you have what s called urinary incontinence (also called
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) has a variety of symptoms, most commonly cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Symptoms can vary from person to person,
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) has a variety of symptoms, most commonly cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Symptoms can vary from person to person,
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Barrett s Esophagus National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is
Barrett s Esophagus National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is
Urodynamic Testing National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Urodynamic Testing National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health
Urodynamic Testing National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health
Bowel Health in Adults
 Bowel Health in Adults Patient Information Contact Details: Bladder and Bowel Specialist Nurse Service First Floor New Alderley House Macclesfield District General Hospital Victoria Road Macclesfield SK10
Bowel Health in Adults Patient Information Contact Details: Bladder and Bowel Specialist Nurse Service First Floor New Alderley House Macclesfield District General Hospital Victoria Road Macclesfield SK10
General Surgery. Haemorrhoids
 General Surgery Haemorrhoids Hemorrhoids_PRINT.indd 1 5/9/2016 5:50:45 PM A painful problem Haemorrhoids, cushions of swollen veins in the anal canal, are often a source of embarrassment. They shouldn
General Surgery Haemorrhoids Hemorrhoids_PRINT.indd 1 5/9/2016 5:50:45 PM A painful problem Haemorrhoids, cushions of swollen veins in the anal canal, are often a source of embarrassment. They shouldn
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
 Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (ZES)? ZES
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (ZES)? ZES
Lactose Intolerance National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Lactose Intolerance National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is lactose intolerance? Lactose
Lactose Intolerance National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is lactose intolerance? Lactose
Incontinence. Anatomy The human body has two kidneys. The kidneys continuously filter the blood and make urine.
 Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
Suggestions for Perianal Care in patients with itching or irritation:
 Suggestions for Perianal Care in patients with itching or irritation: Itching (and sometimes pain, even intense pain) in the anal area is termed pruritis ani (proo-rii-tus a-ni) and is in essence adult
Suggestions for Perianal Care in patients with itching or irritation: Itching (and sometimes pain, even intense pain) in the anal area is termed pruritis ani (proo-rii-tus a-ni) and is in essence adult
ONE IN THREE WOMEN WHO EVER HAD A BABY WET THEMSELVES EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD DO PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING.
 08 EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD Women who have even just one baby are nearly three times more likely to leak urine and wet themselves, than women who have not had a baby. The more babies you have,
08 EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD Women who have even just one baby are nearly three times more likely to leak urine and wet themselves, than women who have not had a baby. The more babies you have,
What is ulcerative colitis?
 What is ulcerative colitis? Ulcerative colitis is a disease that causes inflammation and sores, called ulcers, in the lining of the rectum and colon. Ulcers form where inflammation has killed the cells
What is ulcerative colitis? Ulcerative colitis is a disease that causes inflammation and sores, called ulcers, in the lining of the rectum and colon. Ulcers form where inflammation has killed the cells
DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION
 Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Pelvic Support Problems
 AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
Bowel Problems and Radiation Therapy
 Bowel Problems and Radiation Therapy (The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different.) 1 Table of Contents What Will I
Bowel Problems and Radiation Therapy (The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different.) 1 Table of Contents What Will I
Unconsciously gulping air as they talk, especially when they are upset, excited or nervous
 Topic Page: Flatulence Definition: flatulence from Stedman's Medical Dictionary (flat yū-lents). Presence of an excessive amount of gas in the stomach and intestines. [Mod. L. flatulentus, fr. L. flatus,
Topic Page: Flatulence Definition: flatulence from Stedman's Medical Dictionary (flat yū-lents). Presence of an excessive amount of gas in the stomach and intestines. [Mod. L. flatulentus, fr. L. flatus,
A painful problem. Symptoms of haemorrhoids. Causes of haemorrhoids. Your evaluation
 A painful problem Haemorrhoids, cushions of swollen veins in the anal canal, are often a source of embarrassment. They shouldn t be they re a very common problem that affects all kinds of people, including
A painful problem Haemorrhoids, cushions of swollen veins in the anal canal, are often a source of embarrassment. They shouldn t be they re a very common problem that affects all kinds of people, including
Dietary advice for people with colostomies
 Dietary advice for people with colostomies Introduction During your surgery, you have had a colostomy formed. Colostomies are formed due to problems in the colon (large bowel). This leaflet is designed
Dietary advice for people with colostomies Introduction During your surgery, you have had a colostomy formed. Colostomies are formed due to problems in the colon (large bowel). This leaflet is designed
Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling
 Patient and Family Education Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling While it is normal for a child to be constipated now and then, ongoing problems are not. This handout gives a treatment
Patient and Family Education Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling While it is normal for a child to be constipated now and then, ongoing problems are not. This handout gives a treatment
Anal sphincter exercises. Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals
 Anal sphincter exercises Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Anal sphincter exercises to help lessen leakage from the bowel Sphincter exercises, when practiced correctly, can build up
Anal sphincter exercises Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Anal sphincter exercises to help lessen leakage from the bowel Sphincter exercises, when practiced correctly, can build up
Information to Help You Live Life to the Fullest
 Information to Help You Live Life to the Fullest For more information and to join the conversation visit: Prevail.com/LOBC 800-227-3551 CONSUMER EDUCATION 2015 First Quality Products, Inc. All rights reserved.
Information to Help You Live Life to the Fullest For more information and to join the conversation visit: Prevail.com/LOBC 800-227-3551 CONSUMER EDUCATION 2015 First Quality Products, Inc. All rights reserved.
Constipation usually is not a cause for concern, and easy to avoid by adopting healthy eating and exercise habits.
 From the Health Clinic Mrs. Maureen Earner (mearner@stambroseschool.org Constipation Constipation is a very common problem in children. A child is considered constipated when he or she has fewer than three
From the Health Clinic Mrs. Maureen Earner (mearner@stambroseschool.org Constipation Constipation is a very common problem in children. A child is considered constipated when he or she has fewer than three
Advice for Parents and Carers
 Advice for Parents and Carers 1 2 CONTENTS 4. What is constipation? 4. What is faecal impaction? 5. How common is constipation in children? 5. How to tell if your child may be constipated 6. How constipation
Advice for Parents and Carers 1 2 CONTENTS 4. What is constipation? 4. What is faecal impaction? 5. How common is constipation in children? 5. How to tell if your child may be constipated 6. How constipation
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
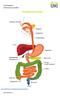 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury
 Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury A resource for individuals with SCI and their supporters This presentation is based on SCI Model Systems research and was developed with support from the National
Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury A resource for individuals with SCI and their supporters This presentation is based on SCI Model Systems research and was developed with support from the National
Liver Biopsy. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Liver Biopsy National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is a liver biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure to remove
Liver Biopsy National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is a liver biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure to remove
Anorectal physiology test
 Anorectal physiology test We hope this factsheet will help to answer some of your questions about having an anorectal physiology test. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don t hesitate
Anorectal physiology test We hope this factsheet will help to answer some of your questions about having an anorectal physiology test. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don t hesitate
Symptom Management. How to Manage Your Diarrhea
 Symptom Management How to Manage Your Diarrhea This patient guide will help you understand: A What is cancer-related diarrhea?...3 B What causes cancer-related diarrhea?...4 C What can I do to manage diarrhea?...5
Symptom Management How to Manage Your Diarrhea This patient guide will help you understand: A What is cancer-related diarrhea?...3 B What causes cancer-related diarrhea?...4 C What can I do to manage diarrhea?...5
AgePage. Urinary Incontinence
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
AgePage. Urinary Incontinence
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
CT: Virtual Colonoscopy
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION CT: Virtual Colonoscopy How to prepare and what to expect This handout explains how a virtual colonoscopy CT works, how to prepare, how it is done, what to expect, and how
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION CT: Virtual Colonoscopy How to prepare and what to expect This handout explains how a virtual colonoscopy CT works, how to prepare, how it is done, what to expect, and how
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
 Page 1 of 7 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate Patient education: High-fiber diet (The Basics) Written by the doctors and editors at UpToDate What is fiber? Fiber is a substance
Page 1 of 7 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate Patient education: High-fiber diet (The Basics) Written by the doctors and editors at UpToDate What is fiber? Fiber is a substance
Getting Ready for Your Colonoscopy
 Getting Ready for Your Colonoscopy One and Done Let s do this once and let s do it right! Inside you will find: How to prepare for your colonoscopy Information about your colonoscopy Answers to commonly
Getting Ready for Your Colonoscopy One and Done Let s do this once and let s do it right! Inside you will find: How to prepare for your colonoscopy Information about your colonoscopy Answers to commonly
WHAT IS ULCERATIVE COLITIS?
 235 60th Street, West New York, NJ 07093 T: (201) 854-4646 F: (201) 854-4647 810 Main Street, Hackensack, NJ 07601 T: (201) 488-0095 Ulcerative Colitis WHAT IS ULCERATIVE COLITIS? Ulcerative colitis is
235 60th Street, West New York, NJ 07093 T: (201) 854-4646 F: (201) 854-4647 810 Main Street, Hackensack, NJ 07601 T: (201) 488-0095 Ulcerative Colitis WHAT IS ULCERATIVE COLITIS? Ulcerative colitis is
What is Crohn's disease?
 What is Crohn's disease? Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area
What is Crohn's disease? Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area
What Is Constipation?
 CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
Constipation. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Constipation National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Constipation is defined as having a bowel
Constipation National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Constipation is defined as having a bowel
Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma
 Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma Dr. Shamaila Butt Gastroenterology Research Registrar GI Physiology unit University College Hospital London GI manifestations in Scleroderma Oesophagus
Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma Dr. Shamaila Butt Gastroenterology Research Registrar GI Physiology unit University College Hospital London GI manifestations in Scleroderma Oesophagus
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE
 IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
Patient Information Leaflet. Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation
 Patient Information Leaflet Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation Treating Rectal Prolapse - Delormes operation What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the
Patient Information Leaflet Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation Treating Rectal Prolapse - Delormes operation What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the
Uterus (Womb) Rectum. Another problem could be the sensation of something coming down at the birth canal or back passage (prolapse).
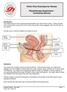 Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
How Is Scleroderma Treated?
 Lab tests What Is Scleroderma? A skin biopsy. Scleroderma can be hard to diagnose. Other diseases can have similar symptoms. It is easier to diagnose if you have: Common symptoms Skin that gets thick fast.
Lab tests What Is Scleroderma? A skin biopsy. Scleroderma can be hard to diagnose. Other diseases can have similar symptoms. It is easier to diagnose if you have: Common symptoms Skin that gets thick fast.
Biofeedback Program. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
 Biofeedback Program GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Biofeedback Checklist Bristol Stool Form Scale Digestive process 4F s Fibre, Fluid, Fitness,
Biofeedback Program GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Biofeedback Checklist Bristol Stool Form Scale Digestive process 4F s Fibre, Fluid, Fitness,
Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse
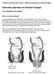 Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse Your Questions Answered What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the rectum become weakened, allowing the muscle of the rectum
Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse Your Questions Answered What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the rectum become weakened, allowing the muscle of the rectum
Foreword. Bowel Management
 2 Bowel Management Foreword The section on is very similar to that of Bladder Care and Management section, as there are many issues to be addressed. You should always remember that what works for one individual
2 Bowel Management Foreword The section on is very similar to that of Bladder Care and Management section, as there are many issues to be addressed. You should always remember that what works for one individual
Y0028_2726_0 File&Use Bladder Control Does Matter
 Y0028_2726_0 File&Use 04092012 Bladder Control Does Matter If you suffer from urinary incontinence, you re not alone Don t be afraid to raise your hand if you ve been struggling with the embarrassment
Y0028_2726_0 File&Use 04092012 Bladder Control Does Matter If you suffer from urinary incontinence, you re not alone Don t be afraid to raise your hand if you ve been struggling with the embarrassment
Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It
 Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It Urogynecology Patient Information Sheet What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for example,
Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It Urogynecology Patient Information Sheet What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for example,
SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health
 SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health 1 Heart Health If you re like most Americans, heart health might be something you don t think about very often. You should. The risk of heart disease increases with age and
SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health 1 Heart Health If you re like most Americans, heart health might be something you don t think about very often. You should. The risk of heart disease increases with age and
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e. For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries
 B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy
 A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists
 Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists Disclosures none Outline Definition Etiologies Exam findings Additional testing Medical management Surgical options What is fecal incontinence? Recurrent
Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists Disclosures none Outline Definition Etiologies Exam findings Additional testing Medical management Surgical options What is fecal incontinence? Recurrent
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Directorate of Women, Children and Surgical Services Burton and District Urogynaecology Centre A Nationally Accredited Urogynaecology Unit Pelvic Floor Exercises You have been given this leaflet because
Directorate of Women, Children and Surgical Services Burton and District Urogynaecology Centre A Nationally Accredited Urogynaecology Unit Pelvic Floor Exercises You have been given this leaflet because
Chronic Constipation. written by Harvard Medical School.
 Chronic Constipation written by Harvard Medical School www.patientedu.org What is Constipation? Although estimates vary widely, up to 28% of adult Americans may suffer from constipation. The problem is
Chronic Constipation written by Harvard Medical School www.patientedu.org What is Constipation? Although estimates vary widely, up to 28% of adult Americans may suffer from constipation. The problem is
POST-OPERATIVE INSTRUCTIONS FOLLOWING RECTAL OFFICE SURGERY
 POST-OPERATIVE INSTRUCTIONS FOLLOWING RECTAL OFFICE SURGERY 1. KEEP THE RECTAL AREA CLEAN AND DRY. After a bowel movement, clean your bottom with peri-anal cleansing pads (i.e. Tucks or baby-wipes), followed
POST-OPERATIVE INSTRUCTIONS FOLLOWING RECTAL OFFICE SURGERY 1. KEEP THE RECTAL AREA CLEAN AND DRY. After a bowel movement, clean your bottom with peri-anal cleansing pads (i.e. Tucks or baby-wipes), followed
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Diarrhea National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is diarrhea? Diarrhea is loose, watery stools. Having diarrhea
Diarrhea National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is diarrhea? Diarrhea is loose, watery stools. Having diarrhea
Colorectal Cancer How to reduce your risk
 Prevention Series Colorectal Cancer How to reduce your risk Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Colorectal Cancer How to reduce your risk Colorectal cancer is the third most commonly diagnosed
Prevention Series Colorectal Cancer How to reduce your risk Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Colorectal Cancer How to reduce your risk Colorectal cancer is the third most commonly diagnosed
 Page 1 of 7 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Page 1 of 7 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate
 TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
What I need to know about Diabetes Medicines
 What I need to know about Diabetes Medicines What do diabetes medicines do? Over time, high levels of blood glucose, also called blood sugar, can can cause health problems. These problems include heart
What I need to know about Diabetes Medicines What do diabetes medicines do? Over time, high levels of blood glucose, also called blood sugar, can can cause health problems. These problems include heart
Incontinence. Urinary. In Adults. THIS PUBLICATION IS OUT OF DATE. For most current information:
 Urinary Incontinence In Adults A Patient's Guide r I When you eat and drink, your body absorbs the liquid. The kidneys filter out waste products from the body fluids and make urine. Urine travels down
Urinary Incontinence In Adults A Patient's Guide r I When you eat and drink, your body absorbs the liquid. The kidneys filter out waste products from the body fluids and make urine. Urine travels down
Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included.
 Urology Clinic Hospital for Sick Children Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included. Information on bladder retraining, urinary tract infections
Urology Clinic Hospital for Sick Children Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included. Information on bladder retraining, urinary tract infections
Infections of the Urine System 366 What causes bladder and kidney infections? 366 Signs and treatment 367
 364 Problems of the Urine System Chapter 23 In this chapter: Infections of the Urine System 366 What causes bladder and kidney infections? 366 Signs and treatment 367 Other Problems of the Urine System
364 Problems of the Urine System Chapter 23 In this chapter: Infections of the Urine System 366 What causes bladder and kidney infections? 366 Signs and treatment 367 Other Problems of the Urine System
What do diabetes medicines do?
 What do diabetes medicines do? Over time, high levels of blood glucose, also called blood sugar, can cause health problems. These problems include heart disease, heart attacks, strokes, kidney disease,
What do diabetes medicines do? Over time, high levels of blood glucose, also called blood sugar, can cause health problems. These problems include heart disease, heart attacks, strokes, kidney disease,
235 60th Street, West New York, NJ T: (201) F: (201) Main Street, Hackensack, NJ T: (201)
 235 60th Street, West New York, NJ 07093 T: (201) 854-4646 F: (201) 854-4647 810 Main Street, Hackensack, NJ 07601 T: (201) 488-0095 Barrett's Esophagus WHAT IS BARRETTT'S ESOPHAGUS? Barrett's esophagus
235 60th Street, West New York, NJ 07093 T: (201) 854-4646 F: (201) 854-4647 810 Main Street, Hackensack, NJ 07601 T: (201) 488-0095 Barrett's Esophagus WHAT IS BARRETTT'S ESOPHAGUS? Barrett's esophagus
The Infant/Child with a Bowel Ostomy
 The Infant/Child with a Bowel Ostomy Thank you for choosing the Medical College of Georgia Hospitals and Clinics for your child s health care needs. This information is to help answer some of the questions
The Infant/Child with a Bowel Ostomy Thank you for choosing the Medical College of Georgia Hospitals and Clinics for your child s health care needs. This information is to help answer some of the questions
What to do when getting radiation therapy to the pelvis (rectal or anal cancers)
 What to do when getting radiation therapy to the pelvis (rectal or anal cancers) Princess Margaret Information for patients who are having radiation therapy Read this pamphlet to learn about: Your radiation
What to do when getting radiation therapy to the pelvis (rectal or anal cancers) Princess Margaret Information for patients who are having radiation therapy Read this pamphlet to learn about: Your radiation
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet Your Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal
Patient Information Leaflet Your Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal
Patients First. Preventing Constipation. Often, constipation is relieved by choosing highfiber. increasing fluids, and exercising.
 Patient Education HEALTH AND WELLNESS Often, constipation is relieved by choosing highfiber foods, increasing fluids, and exercising. Preventing Constipation Signs of constipation are bowel movements that
Patient Education HEALTH AND WELLNESS Often, constipation is relieved by choosing highfiber foods, increasing fluids, and exercising. Preventing Constipation Signs of constipation are bowel movements that
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal act like
Patient Information Leaflet Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal act like
Pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis
 Pancreatitis Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach and close to the duodenum. The duodenum is the upper part of the small intestine. The pancreas
Pancreatitis Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach and close to the duodenum. The duodenum is the upper part of the small intestine. The pancreas
