Urine a Quandary: Feline Idiopathic Cystitis Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN Cornell University Veterinary Specialists Stamford, CT
|
|
|
- Jasper Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
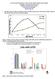
1 Urine a Quandary: Feline Idiopathic Cystitis Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN Cornell University Veterinary Specialists Stamford, CT Prevalence of lower urinary tract disease is more common in cats between 1 and 10 years of age; whereas in dogs, the prevalence increases with advancing age 12 Figure. Prevalence of lower urinary tract disease in dogs ( ) and cats ( ) reported through the Veterinary Medical Database In cats >10 years of age, bacterial urinary tract infection is most common In young cats, idiopathic lower urinary tract disease occurs most commonly Figure. Causes of lower urinary tract disease in cats from 3 studies Proportional Morbidity Dogs Cats 0 0 to 1 1 to 2 2 to 4 4 to 7 7 to 10 Age (years) 10 to 15 > % Kruger 1991 Buffington 1997 Bartges 1996 What is feline idiopathic cystitis (idiopathic feline lower urinary tract disease)? Currently, there are 2 hypotheses concerning FIC Viral hypothesis A gamma-herpesvirus, a calicivirus, and a retrovirus have been isolated from urine and tissues from cats with naturally occurring idiopathic lower urinary tract disease Reproducible clinical evidence that viruses cause naturally occurring disease is scarce Viral particles have been observed in plugs recovered from cats with matrix-crystalline urethral plugs Neurogenic inflammation hypothesis Similar in some respects to hypothesis for interstitial cystitis in women Cats with idiopathic lower urinary tract disease have decreased urinary glycosaminoglycan concentration and similar light microscopic changes to interstitial cystitis This may represent a central nervous system problem o In cats with FIC, there appears to be a dysregulation of the sympathetic nervous system o sans activation w/o activation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis for counter-regulation CRF release w/o appropriate cortisol (adrenocortical hypoplasia) tissue inflammatory response epithelial permeability Fluorescein studies neuron firing ->pain (nitric oxide?) flare-ups of signs with stress o Developmental disorder (Pandora Syndrome) Early age adverse experience (?) Queen stress -> cortisol suppression of adrenal development in kittens 1
2 Other organ system problems Clinical signs of feline lower urinary tract disease Causes of lower urinary tract disease in cats present with similar clinical signs including, but not limited to: o Pollakiuria o Hematuria o Stranguria o Dysuria o Inappropriate urination o +/- Urethral obstruction Diagnostic testing for cats with lower urinary tract signs CBC and biochemical analysis are normal unless urethral obstruction is present Urinalysis reveals hematuria o Pyuria and possibly bacteriuria present, if UTI o Crystalluria may be present with plugs or stones Urine culture is negative unless a UTI is present Abdominal radiography and ultrasonography may be normal o A large bladder may be found with urethral obstruction o Uroliths may be observed or sand o Urinary bladder wall may be thickened on ultrasound Cystoscopically, small pin-point hemorrhages (glomerulations) are found and occasionally larger mucosal ulceration o These can be found with other diseases of the lower urinary tract Bladder biopsy often reveals submucosal edema, mucosal ulceration, possible submucosal inflammation, possible fibrosis o May be observed with other diseases of the lower urinary tract o We routinely biopsy the bladder wall for histopathologic examination and aerobic and anaerobic bacterial culture Idiopathic disease is a diagnosis of exclusion Treatment of lower urinary tract disease Urethral obstruction Obstruction may occur from uroliths or from matrix-crystalline urethral plugs o Matrix-crystalline plugs have been found only in male cats o Approximately 84% of matrix-crystalline plugs contain a mineral component o Struvite is present in 80% of these o Urethral plugs have not been observed to occur in dogs o Uroliths occur in both dogs and cats (we will discuss in future lectures) Consequences of urethral obstruction Consequences of urethral obstruction o Early in course of urethral obstruction May not be clinically evident Stranguria, pollakiuria, and inability to urinate may be present Patient may appear uncomfortable and/or have behavior changes o As obstruction progresses, clinical signs increase in severity Cat may sit in liter box attempting to urinate or dog may attempt urination and pass only few drops; owners often mistake this sign as constipation As urine retention continues, post-renal azotemia and eventually uremia develops Depression, lethargy, moribund state Vomiting due to uremia Bradycardia and collapse due to hyperkalemia Halitosis due to uremia Death will occur in hours after complete obstruction o If urethral obstruction is relieved, cat is likely to recover The most common abnormalities associated with obstructive uropathy include: dehydration, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis, and post-renal azotemia 2
3 o Dehydration Fluid therapy is very important in obstructive uropathy because of dehydration and for circulatory support Remember the 3 components of fluid therapy Amount for rehydration o % dehydrated x BWkg = L for rehydration Maintenance o Typically 1 ml/lb/hour (2.2 ml/kg/hour) On-going losses o Measure or estimate o Some recommend ½ maintenance fluid requirements You should review types of fluid and routes of administration that are acceptable for managing patients with obstructive uropathy o Hyperkalemia Management of hyperkalemia with obstructive uropathy is similar to management of hyperkalemia occurring with acute renal failure Re-establishing urethral patency and fluid therapy is often all that is required as long as arrhythmias are not present Arrhythmias (bradycardia -> sinoatrial arrest -> ventricular escape beats) typically do not occur until the serum potassium is > 8 meq/l Death occurs with potassium concentration exceeds meq/l 3 ways to decrease plasma/blood potassium concentration o Dilute and excrete fluid therapy or dialysis o Transcellular shift Glucose Insulin Insulin and glucose Bicarbonate o Counteract effect of hyperkalemia at sino-atrial node Calcium gluconate Re-establishing urethral patency Male cats o Male cats may be obstructed with uroliths or matrix-crystalline urethral plugs o In male cats, heavy sedation or anesthesia is required o Position male cats in lateral or dorsal recumbency dorsal is best o Massage distal urethra while compressing the urinary bladder may dislodge the plug o Perform cystocentesis in order to obtain a diagnostic sample and to decompress the bladder. Do not remove all of the urine so that the bladder can be palpated. A potential complication is urine extravasation, which is uncommon if the procedure is performed correctly. o Urethral patency can be re-established by retrograde flushing the urethra Aftercare once urethral patency is re-established Re-establishing urethral patency is not the end point o Remove as much of the urine as possible once the cat is un-blocked o The bladder may need to be rinsed if there is a lot of particulate matter and/or mucous present in the urine Use sterile crystalloids or water; do not use glucose containing solutions Do not infuse antibiotics, anti-spasmodics, anesthetics, or acidifiers into the bladder o Glucocorticoids are not indicated as they increase risk of infection o Systemic antibiotics may be administered if an indwelling urinary catheter is not inserted o Anti-spasmodics (urethral relaxants) may help, but there is little data that they in fact do help In order to relax the urethra, an alpha-antagonist is administered Phenoxybenzamine or prazosin can be used Some people administered a skeletal muscle relaxant; however, diazepam has minimal effect on the urinary tract o An indwelling urethral catheter may be required 3
4 Indications for an indwelling urethral catheter include Difficulty in un-obstructing the patient A large amount of particulate matter and/or mucous despite flushing of the urinary bladder When there is a high likelihood of re-obstruction If detrusor atony is present Management of an indwelling urethral catheter An indwelling urethral catheter should be considered on an individual case basis o Severely ill patients o If difficult to catheterize o Poor urine stream post obstruction o Detrusor atony (atonic bladder) A urethral catheter should be connected to a closed collection system Management o Systemic antibiotics should not be administered unless given for some other reason The risk of bacterial urinary tract infection decreases with antibiotic administration However, when an infection occurs, the organism has a high degree of resistance Furthermore, the bacterial organism may invade the upper urinary tract resulting in chronic pyelonephritis o Anti-inflammatory agents such as an NSAID may be beneficial as long as renal function is good o With an indwelling catheter, a urethral relaxing agent (alpha blocker: prazosin: mg PO q12-24h; phenoxybenzamine: mg PO q12-24h) is administered to minimize catheter-induced urethral trauma and irritation o With bladder atony, a drug to stimulate bladder contraction, a parasympathomimetic (bethanechol: mg PO q8h; metoclopramide: mg/kg PO q8h), is administered Catheter-associated UTI o Occurs in 50-80% of catheterized patients o Prophylactic antibiotics decrease incidence, but increase likelihood of resistance or of an unusual organism o Prevention: Use as clean to aseptic technique as possible Physically separate patients with indwelling catheters from others Wear gloves and wash hands between patients Replace catheters when damaged or dirty Typically, an indwelling urinary catheter is maintained for 2 to 3 days o This is not a hard and fast rule, however o Decision to remove the catheter should be based on the progress of the patient, appearance of the urine, and likelihood that the tight junctions of the detrusor muscle have re-established o Remove if catheter is non-patent, damaged, or contaminated Post-obstructive diuresis must be addressed o Due to back pressure from the obstructive uropathy being transmitted to the upper urinary tract, a heavy diuresis may develop when the obstruction is relieved o This may be as much 2.4 L per day (most cats urinate ml per day) o It is important to adjust fluid intake to match urine output so that dehydration does not occur Cystostomy catheters may be inserted and used long term o These may be mushroom-tipped catheters or low-profile catheters o Allows for long term, indefinite use Non-obstructive idiopathic feline lower urinary tract disease There have been dozens of proposed treatments for cats with lower urinary tract disease; very few have undergone evaluation in a randomized controlled clinical trial Antimicrobial agents o Often administered o Bacterial urinary tract infection is an uncommon cause of lower urinary tract disease in cats <10 years of age occurring in <1% of such cats o If a bacterial infection was present, then the cat would have a diagnosis of bacterial cystitis and not idiopathic lower urinary tract disease 4
5 o Their use is not indicated in cats without a proven bacterial urinary tract infection Urinary tract antiseptics o Methenamine and methylene blue are not indicated in cats with idiopathic lower urinary tract disease o They may cause side effects such as metabolic acidosis (methenamine) or Heinz body anemia (methylene blue) o Since bacterial urinary tract infections are uncommon in young cats, they are not recommended Urinary tract analgesics o Phenazopyridine is an over the counter preparation available for use by women with recurrent vaginitis/cystitis o In cats, phenazopyridine causes Heinz body anemia and should not be used Smooth muscle and skeletal muscle relaxants o Many cats with idiopathic lower urinary tract disease have urge incontinence and inappropriate urination o Propantheline, an anticholinergic agent, minimizes force and frequency of uncontrolled detrusor contractions, but has negligible effect on urethral tone ( mg/kg PO q12h) It may be beneficial in some cats However, one study could not document a benefit o Phenoxybenzamine and prazosin are sympatholytic agents that decrease urethral tone and spasm Clinical data is lacking as to their efficacy with idiopathic feline lower urinary tract disease I use for a short time in some cats that strain frequently or that had a urethral obstruction especially if an indwelling urinary catheter was inserted prazosin: mg PO q12-24h; phenoxybenzamine: mg PO q12-24h o Diazepam and dantrolene are skeletal muscle relaxants that may decrease tone and spasm of the distal urethra Diazepam has minimal effect on urethral tone (2-5 mg PO q8h) Dantrolene is more effective ( mg/kg PO q8h) Clinical studies are lacking as to efficacy of these drugs in cats with idiopathic lower urinary tract disease I do not usually use Anti-inflammatory agents o Glucocorticoids Have been used historically to decrease inflammation Several studies have shown no benefit They are contraindicated in cats with urethral obstruction or those that have indwelling urinary catheters Risk of urinary tract infection increases in cats with indwelling urethral catheters that receive glucocorticoids Some cats develop pyelonephritis o Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents There are no clinical studies demonstrating safety or efficacy of use of these drugs in cats with idiopathic lower urinary tract disease o Amitriptyline A tricyclic antidepressant May have analgesic properties, stabilize mast cells, and decrease inflammation In one uncontrolled study, 9 of 15 cats with idiopathic lower urinary tract disease improved with amitriptyline One controlled study of cats with active lower urinary tract disease showed no benefit and cats receiving amitriptyline had a higher incidence of recurrence of lower urinary tract signs Goal is to find a dose that will have a calming effect on the cat (begin at 5 mg than increase slowly; most cats require mg) Glycosaminoglycans o Cats with idiopathic lower urinary tract disease have decreased concentrations of glycosaminoglycans in their urine o Glycosaminoglycans may have a protectant role at the mucosal-urine interface o Two controlled study\ies, failed to show a difference in clinical signs between a glycosaminoglycan and placebo in cats with idiopathic lower urinary tract disease o Pentosan polysulfate sodium, however, may still have effect (50 mg PO q12h) Dietary modification 5
6 o In cats with matrix-crystalline plugs or with struvite crystalluria, feeding a struvite preventative diet may have some benefit o In one study of cats with idiopathic lower urinary tract disease, cats fed a canned diet had fewer recurrences than those fed a dry diet However, there were more drop-outs in the canned group for unexplained reasons and if added back in no difference between diet groups o In another study, there was a dramatic decrease in recurrence of clinical signs when cats with idiopathic cystitis were fed a diet that contained higher levels of omega 3 fatty acids and anti-oxidants Clomipramine and Fluoxetine o Used for urine spraying / marking behavior o Modifies behavior may have some analgesic effects o Not studied for FIC Pheromones o Sprays and diffusers o May calm a cat down o 1 study of cats with FIC no benefit Multi-modal environmental modification (MEMO) o Cats do not respond to force o Cats are territorial and in control o Litter boxes and food should be away from noise and distractions o Cats like to climb, hide, scratch, and hunt vertical and horizontal space o Cats are clean and self-grooming o Cats are active at night o 1+1 rule 1 food dish, 1 water bowl, and 1 litter box per cat plus 1 extra o Indoor Cat Initiative: How do I treat cats with lower urinary tract disease? First episode, urethral obstruction, young cat Unobstruct Radiographs, UA (other lab work?) Indwelling catheter? Diet change (likely)? Antibiotics (peri-catheterizationenvironmental and behavioral modification? o If persists or recurs, do additional diagnosticsfirst episode, no urethral obstruction, young cat Urinalysis (minimum) Diet change (likely)? usually crystal-related disease (either stones or plugs) If persists or recurs o Do additional diagnostics o Consider Diet? Amitriptyline? Pentosan polysulfate? Environmental and behavior treatment First episode, urethral obstruction, older cat Unobstruct Radiographs, UA (other lab work?) Indwelling catheter? Diet change (likely) Stones? o Struvite: infection vs. non-infection o Calcium oxalate Matrix-crystalline plug? 6
7 Others? Antibiotics (peri-catheterization)first episode, no urethral obstruction, older cat Diagnostics Diet change? Most likely urolithiasis most likely cause (especially calcium oxalate) If persists or recurs o Torbugesic as needed o Diet? o Amitriptyline? o Pentosan polysulfate? o Environmental and behavior treatment 7
0 to 1 1 to 2 2 to 4 4 to 7 7 to to 15 > 15. Age (years)
 CAN YOU SHOW ME WHERE IT HURTS: FELINE LOWER URINARY TRACT DISEASE Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN Professor of Medicine and Nutrition The University of Georgia jbartges@uga.edu * Prevalence of lower
CAN YOU SHOW ME WHERE IT HURTS: FELINE LOWER URINARY TRACT DISEASE Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN Professor of Medicine and Nutrition The University of Georgia jbartges@uga.edu * Prevalence of lower
& FELINE LOWER URINARY TRACT DISEASE Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN
 URINE A MESS: MICTURITION DISORDERS & FELINE LOWER URINARY TRACT DISEASE Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN UROLOGY/NEPHROLOGY Micturition refers to the process of storing and periodically voiding urine.
URINE A MESS: MICTURITION DISORDERS & FELINE LOWER URINARY TRACT DISEASE Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN UROLOGY/NEPHROLOGY Micturition refers to the process of storing and periodically voiding urine.
Urine a Mess: Micturition Disorders Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN Cornell University Veterinary Specialists Stamford, CT
 Urine a Mess: Micturition Disorders Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN Cornell University Veterinary Specialists Stamford, CT 1. Micturition refers to the process of storing and periodically voiding
Urine a Mess: Micturition Disorders Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN Cornell University Veterinary Specialists Stamford, CT 1. Micturition refers to the process of storing and periodically voiding
Proceedings of the Congreso Ecuatoriano de Especialidades Veterinarias CEEV Nov , 2011 Quito, Ecuador
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Congreso Ecuatoriano de Especialidades Veterinarias CEEV 2011 Nov. 15-17, 2011 Quito, Ecuador Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Congreso Ecuatoriano de Especialidades Veterinarias CEEV 2011 Nov. 15-17, 2011 Quito, Ecuador Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of
Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats (Struvite Stones in the Urinary Tract of Cats) Basics
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats (Struvite Stones in the Urinary Tract of Cats) Basics
A Technician s Guide to Feline Urethral Obstruction. Jennie Schade, RVT November 5, 2017
 A Technician s Guide to Feline Urethral Obstruction Jennie Schade, RVT November 5, 2017 Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease A variety of conditions affecting the bladder and the urethra Symptoms Causes
A Technician s Guide to Feline Urethral Obstruction Jennie Schade, RVT November 5, 2017 Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease A variety of conditions affecting the bladder and the urethra Symptoms Causes
Approaches to dealing with FLUTD
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Approaches to dealing with FLUTD Author : Rachel Sant Categories : Vets Date : May 14, 2012 Rachel Sant discusses causes of
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Approaches to dealing with FLUTD Author : Rachel Sant Categories : Vets Date : May 14, 2012 Rachel Sant discusses causes of
The term feline lower urinary tract disease
 Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery (2003) 5, 133 138 doi:10.1016/s1098-612x(02)00129-8 PROCEEDINGS OF THE ESFM FELINE CONGRESS, STOCKHOLM, SEPTEMBER 2002 Feline lower urinary tract disease Danièlle
Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery (2003) 5, 133 138 doi:10.1016/s1098-612x(02)00129-8 PROCEEDINGS OF THE ESFM FELINE CONGRESS, STOCKHOLM, SEPTEMBER 2002 Feline lower urinary tract disease Danièlle
Asociación Mexicana de Médicos Veterinarios Especialistas en Pequeñas Especies
 Asociación Mexicana de Médicos Veterinarios Especialistas en Pequeñas Especies XXXI CONGRESO NACIONAL DE LA ASOCIACIÓN MEXICANA DE MÉDICOS VETERINARIOS ESPECIALISTAS EN PEQUEÑAS ESPECIES, A.C. DRA. IRENE
Asociación Mexicana de Médicos Veterinarios Especialistas en Pequeñas Especies XXXI CONGRESO NACIONAL DE LA ASOCIACIÓN MEXICANA DE MÉDICOS VETERINARIOS ESPECIALISTAS EN PEQUEÑAS ESPECIES, A.C. DRA. IRENE
Management of common uroliths through diet
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Management of common uroliths through diet Author : Marge Chandler Categories : Canine, Companion animal, Feline, Vets Date
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Management of common uroliths through diet Author : Marge Chandler Categories : Canine, Companion animal, Feline, Vets Date
TREATMENT METHODS FOR DISORDERS OF SMALL ANIMAL BLADDER FUNCTION
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk TREATMENT METHODS FOR DISORDERS OF SMALL ANIMAL BLADDER FUNCTION Author : SIMONA T RADAELLI Categories : Vets Date : July
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk TREATMENT METHODS FOR DISORDERS OF SMALL ANIMAL BLADDER FUNCTION Author : SIMONA T RADAELLI Categories : Vets Date : July
Lecture 7. The Urinary System
 Lecture 7 The Urinary System Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning The Urinary System The urinary system removes wastes from the body The urinary system also maintains homeostasis or a constant internal
Lecture 7 The Urinary System Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning The Urinary System The urinary system removes wastes from the body The urinary system also maintains homeostasis or a constant internal
Bacterial urinary tract infections
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Bacterial urinary tract infections Author : CATHERINE F LE BARS Categories : Vets Date : February 11, 2008 CATHERINE F LE
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Bacterial urinary tract infections Author : CATHERINE F LE BARS Categories : Vets Date : February 11, 2008 CATHERINE F LE
Associated Terms: Bladder Stones, Ureteral Stones, Kidney Stones, Cystotomy, Urolithiasis, Cystic Calculi
 Associated Terms: Bladder Stones, Ureteral Stones, Kidney Stones, Cystotomy, Urolithiasis, Cystic Calculi The term "ACVS Diplomate" refers to a veterinarian who has been board certified in veterinary surgery.
Associated Terms: Bladder Stones, Ureteral Stones, Kidney Stones, Cystotomy, Urolithiasis, Cystic Calculi The term "ACVS Diplomate" refers to a veterinarian who has been board certified in veterinary surgery.
Urolithiasis in Small Ruminants
 Urolithiasis in Small Ruminants From an article by the American College of Veterinary Surgeons Overview The urinary tract includes the kidneys, ureters (small tubes that drain urine from the kidneys to
Urolithiasis in Small Ruminants From an article by the American College of Veterinary Surgeons Overview The urinary tract includes the kidneys, ureters (small tubes that drain urine from the kidneys to
Feline idiopathic cystitis management
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Feline idiopathic cystitis management Author : Stephanie Jayson, Mayank Seth Categories : Vets Date : September 23, 2013 STEPHANIE
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Feline idiopathic cystitis management Author : Stephanie Jayson, Mayank Seth Categories : Vets Date : September 23, 2013 STEPHANIE
Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis (Calcium Oxalate Stones in the Urinary Tract) Basics
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis (Calcium Oxalate Stones in the Urinary Tract) Basics
AND URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN
 URINE PAIN: UROLITHIASIS AND URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN UROLOGY/NEPHROLOGY Urolithiasis occurs commonly in dogs and cats, and approximately 98% occur in the lower urinary
URINE PAIN: UROLITHIASIS AND URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN UROLOGY/NEPHROLOGY Urolithiasis occurs commonly in dogs and cats, and approximately 98% occur in the lower urinary
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
 Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Steve Garnett, DVM, DACVS-SA Dogs and Cats Veterinary Referral and Emergency April 30, 2017
 Steve Garnett, DVM, DACVS-SA Dogs and Cats Veterinary Referral and Emergency April 30, 2017 Overview Anatomy review Cystotomy Urethrotomy Urethrostomy What s New! Anatomy Anatomy Cystotomy Indications
Steve Garnett, DVM, DACVS-SA Dogs and Cats Veterinary Referral and Emergency April 30, 2017 Overview Anatomy review Cystotomy Urethrotomy Urethrostomy What s New! Anatomy Anatomy Cystotomy Indications
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urinalysis (UA) provides information about the urinary
 Today s TeChniCian PEER REVIEWED URINALYSIS IN COMPANION ANIMALS Part 1: Collection, Sample Handling, & Initial Evaluation Theresa E Rizzi, DVM, Diplomate ACVP (Clinical Pathology) Oklahoma State University
Today s TeChniCian PEER REVIEWED URINALYSIS IN COMPANION ANIMALS Part 1: Collection, Sample Handling, & Initial Evaluation Theresa E Rizzi, DVM, Diplomate ACVP (Clinical Pathology) Oklahoma State University
Urinary tract disorders
 Urinary tract disorders Medicines Formulary Contents: 1. Urinary retention 1 2. Urinary incontinence 2 3. Urethral pain prevention during catheterisation 3 4. Indwelling catheters maintenance of patency
Urinary tract disorders Medicines Formulary Contents: 1. Urinary retention 1 2. Urinary incontinence 2 3. Urethral pain prevention during catheterisation 3 4. Indwelling catheters maintenance of patency
UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys.
 UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys. 1-3% of Below 1 yr. male: female ratio is 4:1 especially among uncircumcised males,
UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys. 1-3% of Below 1 yr. male: female ratio is 4:1 especially among uncircumcised males,
A multimodal approach to feline and canine cystitis management
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk A multimodal approach to feline and canine cystitis management Author : Kit Sturgess Categories : Companion animal, Vets Date
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk A multimodal approach to feline and canine cystitis management Author : Kit Sturgess Categories : Companion animal, Vets Date
Acute Kidney Injury. Eleanor Haskey BSc(hons) RVN VTS(ECC) VPAC A1
 Acute Kidney Injury Eleanor Haskey BSc(hons) RVN VTS(ECC) VPAC A1 Anatomy and Physiology The role of the kidneys is to filter the blood through the glomerulus to form filtrate. The filtrate is then reabsorbed
Acute Kidney Injury Eleanor Haskey BSc(hons) RVN VTS(ECC) VPAC A1 Anatomy and Physiology The role of the kidneys is to filter the blood through the glomerulus to form filtrate. The filtrate is then reabsorbed
URETERAL OBSTRUCTION IN SMALL ANIMALS. Courtney Ikuta, DVM Department of Surgery VCA West Coast Specialty and Emergency Animal Hospital
 URETERAL OBSTRUCTION IN SMALL ANIMALS Courtney Ikuta, DVM Department of Surgery VCA West Coast Specialty and Emergency Animal Hospital URETERAL OBSTRUCTION Vague history and clinical signs Difficult diagnosis
URETERAL OBSTRUCTION IN SMALL ANIMALS Courtney Ikuta, DVM Department of Surgery VCA West Coast Specialty and Emergency Animal Hospital URETERAL OBSTRUCTION Vague history and clinical signs Difficult diagnosis
An informational newsletter
 Pacific Tide An informational newsletter Pacific Veterinary Specialists & Emergency Service 1980 41 st Avenue Capitola, CA 95010 Specialty 831-476-2584 ~Emergency 831-476-0667 August 2014 Volume 8, Issue
Pacific Tide An informational newsletter Pacific Veterinary Specialists & Emergency Service 1980 41 st Avenue Capitola, CA 95010 Specialty 831-476-2584 ~Emergency 831-476-0667 August 2014 Volume 8, Issue
Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I
 Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I 1 Assessment of renal function Clinical manifestations Laboratory tests Urinalysis Urine culture and sensitivity Renal/bladder ultrasound Testicular
Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I 1 Assessment of renal function Clinical manifestations Laboratory tests Urinalysis Urine culture and sensitivity Renal/bladder ultrasound Testicular
Interstitial Cystitis
 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers HOW
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers HOW
VOIDING UROHYDROPROPULSION
 CANINE UROLITHIASIS 0195-5616/99 $8.00 +.00 VOIDING UROHYDROPROPULSION Lessons From 5 Years of Experience Jody P. Lulich, DVM, PhD, Carl A. Osborne, DVM, PhD, Sherry L. Sanderson, DVM, Lisa K. Ulrich,
CANINE UROLITHIASIS 0195-5616/99 $8.00 +.00 VOIDING UROHYDROPROPULSION Lessons From 5 Years of Experience Jody P. Lulich, DVM, PhD, Carl A. Osborne, DVM, PhD, Sherry L. Sanderson, DVM, Lisa K. Ulrich,
Urine Heaven Page 2. D o g s C a t s
 Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN Professor of Medicine and Nutrition The Acree Endowed Chair of Small Animal Research Department of Small Animal Clinical Sciences College of Veterinary Medicine The
Joe Bartges, DVM, PhD, DACVIM, DACVN Professor of Medicine and Nutrition The Acree Endowed Chair of Small Animal Research Department of Small Animal Clinical Sciences College of Veterinary Medicine The
Dr. Liz O Brien s Top 10 Tips
 Dr. Liz O Brien s Top 10 Tips 1. Do your feline patients carry ID? In Canada, only about 3% of lost cats are returned to their owners. Microchip both indoor & outdoor cats, and ensure their contact information
Dr. Liz O Brien s Top 10 Tips 1. Do your feline patients carry ID? In Canada, only about 3% of lost cats are returned to their owners. Microchip both indoor & outdoor cats, and ensure their contact information
NATURAL MEDICINES - ANIMAL HOMEOPATHIC DOSING APPLICATION:
 Product Code AN015 Bladder Blockages-Infections 7 Pages Suitability For all species & ages. Related Products: Last Updated: 11-01-18 NATURAL MEDICINES - ANIMAL HOMEOPATHIC DOSING APPLICATION: HAMPL BladderClear
Product Code AN015 Bladder Blockages-Infections 7 Pages Suitability For all species & ages. Related Products: Last Updated: 11-01-18 NATURAL MEDICINES - ANIMAL HOMEOPATHIC DOSING APPLICATION: HAMPL BladderClear
Chapter 23. Micturition and Renal Insufficiency
 Chapter 23 Micturition and Renal Insufficiency Voiding Urine Between acts of urination, the bladder is filling. detrusor muscle relaxes urethral sphincters are tightly closed accomplished by sympathetic
Chapter 23 Micturition and Renal Insufficiency Voiding Urine Between acts of urination, the bladder is filling. detrusor muscle relaxes urethral sphincters are tightly closed accomplished by sympathetic
FELINE URETHRAL OBSTRUCTION: DIAGNOSIS & MANAGEMENT
 Peer Reviewed FELINE URETHRAL OBSTRUCTION: DIAGNOSIS & MANAGEMENT FELINE URETHRAL OBSTRUCTION: DIAGNOSIS & MANAGEMENT Christopher M. George, DVM, and Gregory F. Grauer, DVM, MS, Diplomate ACVIM (Small
Peer Reviewed FELINE URETHRAL OBSTRUCTION: DIAGNOSIS & MANAGEMENT FELINE URETHRAL OBSTRUCTION: DIAGNOSIS & MANAGEMENT Christopher M. George, DVM, and Gregory F. Grauer, DVM, MS, Diplomate ACVIM (Small
M E D I C A L T E R M I N O L O G Y
 URINARY SYSTEM M E D I C A L T E R M I N O L O G Y Is the organ system which produces, stores and eliminates waste. Is responsible for waste excretion in the form of urine Fluid Intake Is necessary in
URINARY SYSTEM M E D I C A L T E R M I N O L O G Y Is the organ system which produces, stores and eliminates waste. Is responsible for waste excretion in the form of urine Fluid Intake Is necessary in
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Chronic kidney disease in cats
 Chronic kidney disease in cats What is chronic kidney disease (CKD)? Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the name now used to refer to cats with kidney failure (or chronic kidney failure). CKD is one of the
Chronic kidney disease in cats What is chronic kidney disease (CKD)? Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the name now used to refer to cats with kidney failure (or chronic kidney failure). CKD is one of the
Urinary. Smooth, collapsible, muscular sac stores urine. Figure Slide 15.21a
 Urinary Smooth, collapsible, muscular sac stores urine Figure 15.6 Slide 15.21a Urinary Bladder Wall Walls are and folded in an empty bladder Bladder can significantly without increasing internal pressure
Urinary Smooth, collapsible, muscular sac stores urine Figure 15.6 Slide 15.21a Urinary Bladder Wall Walls are and folded in an empty bladder Bladder can significantly without increasing internal pressure
The Urinary System 15PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
FELINE URETHRAL OBSTRUCTION: UPDATES AND CONTROVERSIES
 FELINE URETHRAL OBSTRUCTION: UPDATES AND CONTROVERSIES Marc Seitz, DVM, DABVP (Canine and Feline Practice) Assistant Clinical Professor of Emergency Medicine Mississippi State University College of Veterinary
FELINE URETHRAL OBSTRUCTION: UPDATES AND CONTROVERSIES Marc Seitz, DVM, DABVP (Canine and Feline Practice) Assistant Clinical Professor of Emergency Medicine Mississippi State University College of Veterinary
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS. Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >60%
 DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers. Workbook 13 The digestive system
 NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 13 The digestive system Contents Workbook 13 The digestive system 1 13.1 Aim 3 13.2 Learning outcomes 3 13.3 Digestive system 4 13.4 The endocrine
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 13 The digestive system Contents Workbook 13 The digestive system 1 13.1 Aim 3 13.2 Learning outcomes 3 13.3 Digestive system 4 13.4 The endocrine
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA LEARNING OBJECTIVES DEFINITION. KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer
 MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases
 HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases Urine production Core elements: Glomerulus, proximal and distal convoluted tube, loop of Henle, collecting tubules, ureters, bladder, sphincter, uretra, and out
HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases Urine production Core elements: Glomerulus, proximal and distal convoluted tube, loop of Henle, collecting tubules, ureters, bladder, sphincter, uretra, and out
Surgical Diseases of the Urinary Bladder Urinary Bladder Injury Surgical Diseases of the Urinary Bladder Urinary Bladder Injury Incidence frequent bot
 Surgical Anatomy ( ) Surgery of the Urinary Bladder Dr. T. Németh, DVM, PhD,CertSACS Assoc. Professor of Surgery Surgical Anatomy ( ) Surgical Anatomy Surgical Anatomy ( ) Surgical Anatomy of the Urinary
Surgical Anatomy ( ) Surgery of the Urinary Bladder Dr. T. Németh, DVM, PhD,CertSACS Assoc. Professor of Surgery Surgical Anatomy ( ) Surgical Anatomy Surgical Anatomy ( ) Surgical Anatomy of the Urinary
Chapter 47 1/8/2018. Urinary System Disorders. Urinary Tract Infections. Treatment
 Chapter 47 Urinary System Disorders Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common Infection in one area can involve the entire system Microbes enter through the urethra. Catheterization,
Chapter 47 Urinary System Disorders Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common Infection in one area can involve the entire system Microbes enter through the urethra. Catheterization,
Bladder Issues. HAMPL TinkleLess 50ml Contains homeopathic complex.
 Product Code AN080 Bladder Issues 5 Pages Last Updated: 11-10-18 HAMPL TinkleLess 50ml Contains homeopathic complex. The Incontinence formula is best used in conjunction with a natural diet and supplements,
Product Code AN080 Bladder Issues 5 Pages Last Updated: 11-10-18 HAMPL TinkleLess 50ml Contains homeopathic complex. The Incontinence formula is best used in conjunction with a natural diet and supplements,
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics. Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital 01/02/2018 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms LUTS - one of
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital 01/02/2018 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms LUTS - one of
Mysterious Interventional Cases. October 30 th 2011 Dr Marilyn Dunn DMV, MVSc, ACVIM, Fellow IR Vancouver, BC
 Mysterious Interventional Cases October 30 th 2011 Dr Marilyn Dunn DMV, MVSc, ACVIM, Fellow IR Vancouver, BC Molly FS Labrador 10 mths 6 months: pollakiuria, dysuria Urinalysis: bacterial cystitis, treated
Mysterious Interventional Cases October 30 th 2011 Dr Marilyn Dunn DMV, MVSc, ACVIM, Fellow IR Vancouver, BC Molly FS Labrador 10 mths 6 months: pollakiuria, dysuria Urinalysis: bacterial cystitis, treated
EMPIRICAL TREATMENT OF SELECT INFECTIONS ADULT GUIDELINES. Refer to VIHA Algorithm for the empiric treatment of Urinary Tract Infection
 URINARY TRACT Refer to VIHA Algorithm for the empiric treatment of Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria on the VIHA Intranet: https://intranet.viha.ca/departments/pharmacy/clinical_pharmacy/pages/infec
URINARY TRACT Refer to VIHA Algorithm for the empiric treatment of Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria on the VIHA Intranet: https://intranet.viha.ca/departments/pharmacy/clinical_pharmacy/pages/infec
Part I: On-line web-based survey of Dalmatian owners GENERAL INFORMATION
 Dr. Bartges' final report on the Dal stone survey: Commissioned by the Dalmatian Club of America Foundation (DCAF) Published in the DCA magazine, The Spotter, Summer 2006 Part I: On-line web-based survey
Dr. Bartges' final report on the Dal stone survey: Commissioned by the Dalmatian Club of America Foundation (DCAF) Published in the DCA magazine, The Spotter, Summer 2006 Part I: On-line web-based survey
Pediatric urinary tract infection. Dr. Nariman Fahmi Pediatrics/2013
 Pediatric urinary tract infection Dr. Nariman Fahmi Pediatrics/2013 objectives EPIDEMIOLOGY CAUSATIVE PATHOGENS PATHOGENESIS CATEGORIES OF URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN pediatrics
Pediatric urinary tract infection Dr. Nariman Fahmi Pediatrics/2013 objectives EPIDEMIOLOGY CAUSATIVE PATHOGENS PATHOGENESIS CATEGORIES OF URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN pediatrics
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment
 Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Angry Bladder Tumors: Practical Diagnosis and Management India Lane, DVM, MS, Ed. D, DACVIM University of Tennessee Knoxville, TN
 Angry Bladder Tumors: Practical Diagnosis and Management India Lane, DVM, MS, Ed. D, DACVIM University of Tennessee Knoxville, TN Neoplasms of the urinary tract are a rare overall tumor type in dogs and
Angry Bladder Tumors: Practical Diagnosis and Management India Lane, DVM, MS, Ed. D, DACVIM University of Tennessee Knoxville, TN Neoplasms of the urinary tract are a rare overall tumor type in dogs and
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis
 Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Urolithiasis. Ali Kasraeian, MD, FACS Kasraeian Urology Advanced Laparoscopic, Robotic & Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery
 Urolithiasis Ali Kasraeian, MD, FACS Kasraeian Urology Advanced Laparoscopic, Robotic & Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery Urolithiasis: Why should we care? Affects 5% of US men and women Men twice as
Urolithiasis Ali Kasraeian, MD, FACS Kasraeian Urology Advanced Laparoscopic, Robotic & Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery Urolithiasis: Why should we care? Affects 5% of US men and women Men twice as
Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela
 Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela Microbiology Department Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela Microbiology Department Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia Urinary Tract Infection
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective. Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado
 Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
URINARY TRACT NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS: DRUG THERAPY REVIEW
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk URINARY TRACT NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS: DRUG THERAPY REVIEW Author : Ian Battersby Categories : Vets Date : August 3, 2009
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk URINARY TRACT NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS: DRUG THERAPY REVIEW Author : Ian Battersby Categories : Vets Date : August 3, 2009
FELINE PERINEAL URETHROSTOMY Howard B. Seim III, DVM, DACVS Colorado State University
 FELINE PERINEAL URETHROSTOMY Howard B. Seim III, DVM, DACVS Colorado State University! Key Points Patients with cystic and urethral calculi present with stranguria Retropulsion of urethral calculi into
FELINE PERINEAL URETHROSTOMY Howard B. Seim III, DVM, DACVS Colorado State University! Key Points Patients with cystic and urethral calculi present with stranguria Retropulsion of urethral calculi into
Proceedings of the European Veterinary Conference Voorjaarsdagen
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the European Veterinary Conference Voorjaarsdagen Amsterdam, the Netherlands Apr. 5-7, 2012 Next Meeting: Apr. 18 20, 2013 - Amsterdam, the
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the European Veterinary Conference Voorjaarsdagen Amsterdam, the Netherlands Apr. 5-7, 2012 Next Meeting: Apr. 18 20, 2013 - Amsterdam, the
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
You have been booked for a. Flexible Cystoscopy. Under Local Anaesthetic
 You have been booked for a Flexible Cystoscopy Under Local Anaesthetic 1 WHAT IS A FLEXIBLE CYSTOSCOPY A flexible cystoscopy is a test to examine the uretha (waterpipe) and bladder using a thin, lighted
You have been booked for a Flexible Cystoscopy Under Local Anaesthetic 1 WHAT IS A FLEXIBLE CYSTOSCOPY A flexible cystoscopy is a test to examine the uretha (waterpipe) and bladder using a thin, lighted
Sub Flush Kit A Special Flush Kit with T-FloLoc TM for use with the SUB System
 NORFOLK VET PRODUCTS Specialty Medical Devices For The Veterinary Community the Sub Flush Kit A Special Flush Kit with T-FloLoc TM for use with the SUB System Instructions For Use provided by Drs. Allyson
NORFOLK VET PRODUCTS Specialty Medical Devices For The Veterinary Community the Sub Flush Kit A Special Flush Kit with T-FloLoc TM for use with the SUB System Instructions For Use provided by Drs. Allyson
Excretory System. Biology 2201
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System. Excretory System
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
UTI IN ELDERLY. Zeinab Naderpour
 UTI IN ELDERLY Zeinab Naderpour Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most frequent bacterial infection in elderly populations. While urinary infection in the elderly person is usually asymptomatic, symptomatic
UTI IN ELDERLY Zeinab Naderpour Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most frequent bacterial infection in elderly populations. While urinary infection in the elderly person is usually asymptomatic, symptomatic
NON-Neurogenic Chronic Urinary Retention AUA White Paper
 NON-Neurogenic Chronic Urinary Retention AUA White Paper Great Lakes SUNA Inside Urology March 16, 2018 Michelle J. Lajiness FNP-BC Nurse Practitioner DMC Urology Incidence Really unknown Lack consensus
NON-Neurogenic Chronic Urinary Retention AUA White Paper Great Lakes SUNA Inside Urology March 16, 2018 Michelle J. Lajiness FNP-BC Nurse Practitioner DMC Urology Incidence Really unknown Lack consensus
The Urinary System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN
 Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Updates on Managing Male Cats with Urethral Obstruction Dennis Chew, DVM, DACVIM The Ohio State University Columbus, OH
 Updates on Managing Male Cats with Urethral Obstruction Dennis Chew, DVM, DACVIM The Ohio State University Columbus, OH Pathophysiology of urethral obstruction (UO) Thrity-nine % to 67% of male cats evaluated
Updates on Managing Male Cats with Urethral Obstruction Dennis Chew, DVM, DACVIM The Ohio State University Columbus, OH Pathophysiology of urethral obstruction (UO) Thrity-nine % to 67% of male cats evaluated
Canine and Feline Urolithiasis Updates and Challenges
 Canine and Feline Urolithiasis Updates and Challenges India F. Lane, DVM, MS, EdD, DACVIM Elizabeth M. Lennon, DVM, PhD, DACVIM The University of Tennessee College of Veterinary Medicine Urolithiasis -
Canine and Feline Urolithiasis Updates and Challenges India F. Lane, DVM, MS, EdD, DACVIM Elizabeth M. Lennon, DVM, PhD, DACVIM The University of Tennessee College of Veterinary Medicine Urolithiasis -
It is an infection affecting any of the following parts like kidney,ureter,bladder or urethra
 UTI Dr jayaprakash.k.p,asst prof,ich,govt.medical college,kottayam What is UTI? It is an infection affecting any of the following parts like kidney,ureter,bladder or urethra What is prevalence of UTI?
UTI Dr jayaprakash.k.p,asst prof,ich,govt.medical college,kottayam What is UTI? It is an infection affecting any of the following parts like kidney,ureter,bladder or urethra What is prevalence of UTI?
Outcome of male cats managed for urethral obstruction with decompressive cystocentesis and urinary catheterization: 47 cats ( )
 Retrospective Study Journal of Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care 25(2) 2015, pp 256 262 doi: 10.1111/vec.12254 Outcome of male cats managed for urethral obstruction with decompressive cystocentesis
Retrospective Study Journal of Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care 25(2) 2015, pp 256 262 doi: 10.1111/vec.12254 Outcome of male cats managed for urethral obstruction with decompressive cystocentesis
Renal Disease. Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs
 Renal Disease Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs 1 Renal Embryology 2 Lab Tests UA CBC Enzymes Creatinine Creatinine clearance Ammonia Abs C Bx 3 BUN Creatinine Creatinine Clearance
Renal Disease Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs 1 Renal Embryology 2 Lab Tests UA CBC Enzymes Creatinine Creatinine clearance Ammonia Abs C Bx 3 BUN Creatinine Creatinine Clearance
MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
 MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH INTRODUCTION (1) Part of male sexual reproductive organ Size
MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH INTRODUCTION (1) Part of male sexual reproductive organ Size
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Acute tumor lysis syndrome (ATLS), although
 ACUTE TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME Michele Cohen, DVM, DACVIM (Oncology) College of Veterinary Medicine Auburn University Auburn, Alabama Acute tumor lysis syndrome (ATLS), although uncommon, can be a serious
ACUTE TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME Michele Cohen, DVM, DACVIM (Oncology) College of Veterinary Medicine Auburn University Auburn, Alabama Acute tumor lysis syndrome (ATLS), although uncommon, can be a serious
Mrs Maya Harris Consultant Urologist INDWELLING CATHETERS: COMPLICATIONS AND SOLUTIONS
 Mrs Maya Harris Consultant Urologist INDWELLING CATHETERS: COMPLICATIONS AND SOLUTIONS AIMS OF PRESENTATION Discuss what can go wrong Discuss reducing risks Discuss managing troublesome problems and when
Mrs Maya Harris Consultant Urologist INDWELLING CATHETERS: COMPLICATIONS AND SOLUTIONS AIMS OF PRESENTATION Discuss what can go wrong Discuss reducing risks Discuss managing troublesome problems and when
The Neurogenic Bladder
 The Neurogenic Bladder Outline Brandon Haynes, MD Resident Physician Department of Urology Jelena Svircev, MD Assistant Professor Department of Rehabilitation Medicine Anatomy and Bladder Physiology Bladder
The Neurogenic Bladder Outline Brandon Haynes, MD Resident Physician Department of Urology Jelena Svircev, MD Assistant Professor Department of Rehabilitation Medicine Anatomy and Bladder Physiology Bladder
Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome
 page 1 Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome Q: What is interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS)? A: Interstitial cystitis (int-uhr-stishuhl siss-tyt-uhss) (IC), is a chronic pain condition
page 1 Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome Q: What is interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS)? A: Interstitial cystitis (int-uhr-stishuhl siss-tyt-uhss) (IC), is a chronic pain condition
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers STAGED
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers STAGED
The Urinary System. Maintenance Systems Unit 5
 The Urinary System Maintenance Systems Unit 5 Basic Functions of the Urinary System Regulates the composition and volume of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of water and solutes. Eliminates
The Urinary System Maintenance Systems Unit 5 Basic Functions of the Urinary System Regulates the composition and volume of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of water and solutes. Eliminates
CAUTI CONFERENCE CAUTI Prevention and Appropriate Use of Indwelling Urinary Catheters in the Hospital Setting
 CAUTI CONFERENCE CAUTI Prevention and Appropriate Use of Indwelling Urinary Catheters in the Hospital Setting James T. Fields, MD Carolinas Center for Medical Excellence Columbia, South Carolina February
CAUTI CONFERENCE CAUTI Prevention and Appropriate Use of Indwelling Urinary Catheters in the Hospital Setting James T. Fields, MD Carolinas Center for Medical Excellence Columbia, South Carolina February
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University
 RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
Appendix E: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation. Audience: For Registered Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010
 Appendix E: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation Audience: For Registered Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010 Objectives Address individual needs and preferences with respect
Appendix E: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation Audience: For Registered Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010 Objectives Address individual needs and preferences with respect
SASKPIC April 16, 2014
 SASKPIC April 16, 2014 1 Why do we need a Continuing Care guideline? Most current guidelines and tools for UTI prevention focus on acute care Age related changes to the urinary tract predispose older adults
SASKPIC April 16, 2014 1 Why do we need a Continuing Care guideline? Most current guidelines and tools for UTI prevention focus on acute care Age related changes to the urinary tract predispose older adults
CATS AND KIDNEY DISEASE
 CATS AND KIDNEY DISEASE Kidney structure and function Like all mammals, cats have 2 kidneys located in the abdomen just below the lumbar spinal region. Each is normally similar in size and shape to a small
CATS AND KIDNEY DISEASE Kidney structure and function Like all mammals, cats have 2 kidneys located in the abdomen just below the lumbar spinal region. Each is normally similar in size and shape to a small
Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring
 Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring Yaacov Frishberg, MD Division of Pediatric Nephrology Shaare Zedek Medical Center Jerusalem, ISRAEL UTI - definitions UTI = growth of bacteria
Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring Yaacov Frishberg, MD Division of Pediatric Nephrology Shaare Zedek Medical Center Jerusalem, ISRAEL UTI - definitions UTI = growth of bacteria
Urine dilution: a key factor in the prevention of struvite and calcium oxalate uroliths
 Published in IVIS with the permission of the editor Close window to return to IVIS ROYAL CANIN VIEWPOINT Urine dilution: a key factor in the prevention of struvite and calcium oxalate uroliths KEY POINTS
Published in IVIS with the permission of the editor Close window to return to IVIS ROYAL CANIN VIEWPOINT Urine dilution: a key factor in the prevention of struvite and calcium oxalate uroliths KEY POINTS
EMR template and postprocedure notes
 EMR template and postprocedure notes Sample autopopulated text to create a BOTOX injection procedure report Information gathered from market research. These considerations are for reference only and should
EMR template and postprocedure notes Sample autopopulated text to create a BOTOX injection procedure report Information gathered from market research. These considerations are for reference only and should
Pediatric GU Dysfunction
 Pediatric GU Dysfunction Assessment of pediatric renal function Signs and symptoms Laboratory tests Radiological tests Nursing considerations Psychosocial and developmental considerations GU Disorders
Pediatric GU Dysfunction Assessment of pediatric renal function Signs and symptoms Laboratory tests Radiological tests Nursing considerations Psychosocial and developmental considerations GU Disorders
NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant Sterile (neomycin sulfate polymyxin B sulfate solution for irrigation)
 NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant Sterile (neomycin sulfate polymyxin B sulfate solution for irrigation) NEOSPORIN G.U.SOLUTION NOT FOR INJECTION DESCRIPTION NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant is a concentrated sterile antibiotic
NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant Sterile (neomycin sulfate polymyxin B sulfate solution for irrigation) NEOSPORIN G.U.SOLUTION NOT FOR INJECTION DESCRIPTION NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant is a concentrated sterile antibiotic
London Strategic Clinical Networks. My AKI. Guidance for patients with, or recovering from, acute kidney injury
 London Strategic Clinical Networks My AKI Guidance for patients with, or recovering from, acute kidney injury Supporting the delivery of equitable, high quality AKI care through collaboration www.londonaki.net
London Strategic Clinical Networks My AKI Guidance for patients with, or recovering from, acute kidney injury Supporting the delivery of equitable, high quality AKI care through collaboration www.londonaki.net
