CONSTIPATION IN TODDLERS
|
|
|
- Caren Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 For Healthcare Professional use CONSTIPATION IN TODDLERS Learning points 1 Constipation is increasingly common in childhood, often causing misery and discomfort to toddlers and families 6 Behavioural intervention should include advice on toilet training 2 3 Healthcare professionals should take the condition seriously and show empathy towards the child and family Causes of constipation include pain on defaecation, fever and underhydration, poor or inadequate food, fibre and fluid intake, psychological problems and coercive toilet training 7 8 Laxatives should be used when other strategies have been shown not to work. They should be given in sufficient doses to be effective. Regular review of progress is vital If the bowel is loaded with faeces disimpaction of the bowel with laxatives is the essential first-line management 4 5 Treatment of constipation usually requires a combination of dietary, behavioural and medical interventions Diet and fluid management are important and can be a challenge. Parents need both practical and emotional support 9 Constipation can be prevented by attention to healthy eating, adequate fluid intake, exercise and sensible toilet training
2 WHAT IS CONSTIPATION? Constipation is a collection of symptoms and signs, not a disease. It may be defined as 'abnormally delayed or infrequent passage of dry, hardened faeces often accompanied by straining and/or pain' 1. However the stools may not always be hard, particularly if constipation is associated with soiling 2. Normally the rectum (lower large bowel) is empty. When a stool passes into the rectum the child experiences a sensation of fullness. If the child does not pass the stool, it accumulates and the rectum adapts to being stretched and the normal feeling of urgency to defaecate does not occur. If this happens frequently or for a long time the bowel may become loaded with faeces which may result in the retention of hard stools. Soft or liquid stools may then leak from the bowel at inopportune times. This is called soiling. Stool withholding for long periods can distend the rectum and reduce the sensation of the urge to go to the toilet. Soiling may prompt parents to seek help and the child may have had undiagnosed constipation for many months 3. Constipation Normal Bowel Constipated Bowel In constipation the large bowel (rectum and sometimes colon) becomes distended and full of large hard stools. WHAT IS NORMAL BOWEL HABIT? Normal stool frequency in infants and children in industrialised countries ranges from an average of four per day in the first week of life to two per day at one year of age 4,5,6. The average adult frequency of once a day (range of three per day to three per week) is usually attained by four years of age 4,5. Breast fed infants tend to pass stools which are softer and generally more frequent than formula-fed infants 6. % Every 4 days Times per day Frequency of bowel actions in cohort of 350 children aged between 1 and 4 years 4. Reproduced from reference 4, with kind permission from Archives of Disease in Childhood and the BMJ Publishing Group. PREVALENCE OF CONSTIPATION IN THE UK Constipation is one of the commonest medical conditions in wealthy, developed and industrialised nations. Although the precise prevalence is not known, it is currently estimated to be between 5 to 30 per cent of the general population 7. Constipation accounts for 25 per cent of visits to the doctor and can often require prolonged support from a multidisciplinary team 8. In about 25 per cent of cases, constipation starts when the child is a baby. Constipation is often first seen between the ages of two and four years when toddlers are potty training 9. There is a perception that constipation is a trivial complaint in childhood, rarely life-threatening and has little impact on health care provision. The reality is somewhat different. Many children require medical and nutritional treatment for this condition, it causes great misery and discomfort and may precipitate or aggravate other medical problems, particularly urinary tract infections and urinary continence. The management of constipation in adults and children incurs a high cost for the NHS, not only economically ( 43 million is spent annually on prescribed laxatives 10 ) but also in medical and nursing expertise. 02
3 CAUSES AND RISK FACTORS FOR CONSTIPATION The exact cause of constipation is not fully understood but it is generally viewed as due to a combination of factors. Pain from an anal fissure, fever and dehydration, poor dietary and fluid intake, psychological problems, coercive toilet training (e.g. when the child is forced to sit on the potty/toilet for a long period) and family history can all play a part. Constipation is usually referred to as 'idiopathic' when it cannot be explained by an anatomical, physiological, radiological or histological abnormality. The commonest cause of pain on defaecation is the passage of large hard stools which can sometimes result in an anal fissure. An anal fissure is a tear of the lining of the anal canal, which most commonly occurs during the passage of firm or hard stools 11,12. Anal fissures are common in infants and toddlers aged six to 24 months. The fissure causes pain on defaecation, which may result in the child withholding stools in an effort to avoid further pain 11,13,14. If it is not diagnosed and treated promptly, an anal fissure can set in motion a cycle of negativity towards stooling, constipation caused by withholding, and increasing pain with subsequent defaecation 12. Pyrexia, dehydration and immobility, as a result of an infection, may cause stools to become dry and hard. Weaning difficulties, inadequate dietary fibre or fluid intake, excessive milk intake and 'faddy' eating can also precipitate constipation in toddlers. Toilet Training The acquisition of toileting skills is an important milestone in child development. Mis-timed or inappropriate toilet training strategies can contribute to constipation in some children over two years of age 16,17,18,19. Parents and carers should provide their child with the right environment, motivation and encouragement for successful toilet training. The correct position for defaecation is important; knees should be higher than hips, spine should be straight, abdomen should be pushed out and elbows should be placed on knees 20. The toilet should be comfortable, clean, warm, private and inviting. The use of a child toilet seat and footstool, so that the toddler can sit with feet supported, may be appropriate. Successful toilet training requires children to be eating a healthy, balanced diet, with adequate fluid intake, and to be able to recognise and respond to the physical cues. They must learn to differentiate between appropriate and inappropriate places to defaecate, learn how to undress for the toilet, be able to push to initiate evacuation and know how to clean themselves afterwards. Causes of and Risk Factors for Constipation in Toddlers 15 Nutritional/ Dietary Social Psychological/ Emotional Physical Poor diet, overfeeding in infancy, insufficient dietary fibre or fluid intake, excessive milk intake, faddy eating Potty training difficulties, problems with nursery/ school toilets, changes in lifestyle and routine Lack of exercise Perceptions and beliefs about 'normal' bowel pattern Poor bowel habit - ignoring the urge to go, withholding stools Eating disorders Emotional abuse in general could impact on behaviour Anal fissure Mild pyrexia, dehydration, immobility Bad position for defaecation Weight - both underweight and overweight Children who have been sexually abused may present with pain on defaecation or rectal bleeding 03
4 SYMPTOMS & Signs OF CONSTIPATION The physical signs and symptoms of childhood idiopathic constipation include: irregular bowel motions foul smelling wind and stools, excessive flatus irregular stool texture, passing occasional enormous stools and/or frequent small pellets withholding or straining to stop passage of stools soiling or overflow of stool abdominal pain/distension/discomfort poor appetite lack of energy, unhappy/angry/irritable children and general malaise streaking of stool or toilet paper with blood (sign of anal fissure) Psychosocial problems that may contribute to or be an effect of constipation include: social isolation poor self-esteem bullying difficulties in family relationships 21 DIAGNOSIS In most cases, constipation is not caused by a specific disease. The diagnosis is generally made by medical history and physical examination. Investigations are rarely required. Abdominal X-ray can sometimes be useful to demonstrate the extent of the problem to parents, but is not carried out routinely. Constipation that occurs from or very soon after birth, which is associated with other symptoms or signs, or does not respond to the management outlined below, should prompt referral to a paediatrician. PREVENTION OF CONSTIPATION IN TODDLERS The bowel works properly (like the rest of the body) if it has a good combination of foods passing through it. Stools are composed of: the residue of components of food that are not digested and absorbed in the small intestine the normal bacteria of the colon water and normal intestinal secretions cells sloughed off from the intestine lining, which constantly renews itself. A large part of the food residue is made of plantderived materials - fruit, vegetables and cereals - known as dietary fibre or non-digestible carbohydrates (sometimes called non-digestible polysaccharide). Dietary fibre includes 'prebiotics', which are carbohydrates that are not digested in the small intestine and enhance the growth of 'healthy' bacteria in the colon. They may help to prevent constipation by creating a healthy environment in the large bowel. A mixed, balanced diet from the time of weaning should be encouraged and will protect against the development of constipation in toddlers. Fruits, vegetables, cereal based foods, meat, fish and pulses should be introduced during weaning and for the over ones a balanced diet will include a combination of foods from all five food groups. see Factsheet 1.2 There are no evidence-based recommendations for the ideal fibre content of a toddler's diet, but 5-7g/day is an average intake. see Factsheet 1.1i Because a high percentage of the stool weight is water, underhydration can lead to hard stools. Soft stools that are easy to pass require adequate fluid intake to keep them moist. Toddlers should have 6-8 drinks each day each drink being about 3-4 oz ( mls). However they may need more fluid in hot weather and after a lot of physical activity. All drinks count: e.g. water, well-diluted fruit juice and milk. However excessive whole milk intake is a risk factor for constipation because it limits the consumption of adequate quantities of other foods thereby limiting dietary fibre intake. Milk drinks should be limited to a maximum of 3 per day - for toddlers each drink should be no more than 120mls or 4oz. Large bottles of milk should have been phased out soon after their first birthday. 04
5 TREATMENT OF CONSTIPATION The management of idiopathic constipation often requires a combination of nutritional, medical and behavioural, and occasionally surgical interventions. Simple interventions such as making appropriate dietary changes and increasing fluid intake to soften the stool may be adequate and effective if constipation is recognised early. Faecal disimpaction of the bowel with laxatives is essential first-line management if the bowel is loaded with faeces. Faecal impaction is usually, although not always, signalled by the presence of overflow soiling. Examination of the abdomen (and sometimes rectum by a doctor) should be undertaken to determine the extent of the problem. Food, Fibre and Fluid Some toddlers are faddy eaters see Factsheets 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 and this can become a source of frustration and tension for parents who have been advised to ensure the fibre content of their child's diet is adequate. Children may be reluctant to eat sufficient fruit, vegetables and cereal based foods, and/or their parents may find it easier to give them sweet and high fat convenience foods and snacks. These usually contain negligible dietary fibre. Encouraging healthy eating with a balanced diet see Factsheet 1.1, 1.2 and promoting positive parenting for families requires time, patience and family support. This support can be provided through nurse specialists in nurse-led clinics, child and family mental health services, health visitors and community children's nursing services. Diet - Parents should aim to: Offer six to eight drinks per day - one with each meal and one in between meals or with a snack Include a fruit and a vegetable with the midday and evening meals Include a starchy or cereal based food with each meal - make it wholegrain sometimes Offer regular meals and only planned snacks - one snack halfway between meals Make sure there is always time in the mornings for breakfast - include some fruit or a wholegrain bread or cereal Laxatives The initial aim of medical treatment is to empty the bowel (disimpaction). Macrogols (e.g. Movicol Paediatric Plain) are now generally recommended as first line treatment for disimpaction 22. Although stimulant laxatives can also be used to disimpact the bowel, such as senna, sodium picosulfate and bisacodyl, they should be used only after the stools have been softened with either docusate sodium or lactulose. Following disimpaction, maintenance laxative therapy should be continued for at least six months until a regular bowel habit is established. This is usually achieved by giving a smaller dose of whatever was used successfully for disimpaction, such as Movicol Paediatric Plain or a combination of stimulant laxatives such as senna, sodium picosulphate and docusate sodium and softeners including lactulose. The drugs used and the doses required need to be titrated to a dose that is effective for the individual child. In some cases this may mean using high doses under medical supervision. Regular follow up and support is essential. Oral medication is the first treatment of choice. Rectal preparations, enemas and suppositories should rarely be necessary because they are invasive and distressing for the child. Families tend to eat together less than in the past. The experience of families eating together plays a role in teaching children to eat 'by example'. Toddlers watch others eating food that may be unfamiliar to them and will eventually copy what they see. see Factsheet 2.2 Constipation can suppress appetite and in some instances it may be necessary to use laxatives concurrently with diet change. 05
6 Behavioural Interventions Behavioural interventions can be used alone or more commonly in combination with medical management. They involve psychological approaches to encourage positive changes in behaviour that should be child-friendly and age-appropriate. These interventions include toilet training programmes to encourage regular bowel habit, and colouring and sticker charts that reward healthy eating and an adequate fluid intake. It is vital that time is given to explain constipation to the child and family so that they understand the reasons for a particular management approach. Wherever possible, children should be encouraged to take as much responsibility for their treatment as they are able. Interventions are more likely to succeed if the child is engaged and involved with the programme. Rewards can be used, but they must be discussed with individual children, as some do not like them. It is important to negotiate the right reward and the reward to effort ratio. Children will not work towards a reward if they feel that it is not worth it. Emphasis should always be placed on positive results rather than negative. Parents, other family members, friends and school or nursery teachers can contribute by providing ongoing support and motivation. However, it is essential to recognise the toddler's need for privacy when defecating. Need for Empathy Healthcare professionals need to be empathetic regarding the diagnosis of idiopathic constipation. They should explain the diagnosis and treatment options in appropriate, simple language, offer and provide ongoing support to reinforce knowledge. The management plan should be reviewed and evaluated within agreed timescales and the key healthcare professional should liaise with other appropriate colleagues for help as required. The child and family need to feel that they can ask questions and negotiate the support that they require. They need to participate in the management plan and maintain regular contact with their healthcare professional to ensure that any problems can be discussed and addressed as soon as they arise. Pitfalls in the treatment of constipation 15 Using stimulant laxatives before disimpacting, softening and evacuating stool Stopping or changing laxatives too soon or not prescribing sufficient dosage Not appreciating the role fear plays in toddlers' perception of constipation Being as disappointed and frustrated as the family and resorting to inconsistent management Insufficient support for families especially with complex treatment regimes Working in isolation without sharing and accepting expertise from other professionals 23 Missing other causes of constipation 06
7 References 1. Croffie JMB, Fitzgerald JF. Hypomotility disorders. In Walker A. (ed.) Pediatric Gastrointestinal Disease (3rd Edition.) Ontario; Decker Inc: Clayden G, Agnarsson U. Constipation in Childhood. Oxford; Oxford University Press: Benninga MA, Buller HA, Taminiau JA. Biofeedback training in chronic constipation. Arch Dis Child. 1993;68: Weaver LT, Steiner H. The bowel habit of young children. Arch Dis Child. 1984;59(7): Fontana M, Bianchi C, Cataldo F, Conti Nibali S, Cucchiara S, Gobio Casali L, et al. Bowel frequency in healthy children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1989;78(5): Weaver LT, Ewing G, Taylor LC. The bowel habit of milk-fed infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1988;7(1): Candelli M, Nista EC, Zocco MA, Gasbarrini A. Idiopathic chronic constipation: Pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Hepatol. 2001;48: Youssef NN, Di Lorenzo C. Childhood constipation: Evaluation and treatment. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001;33(3): Nelson R, Wagget J, Lennard-Jones J. Constipation and megacolon in children and adults. In Misiewicz JJ, Pounder RE, Venables CW (eds.) Diseases of the Gut and Pancreas (2nd Edition.) Oxford; Blackwell Scientific: Bush S. Fluids, fibre and constipation. Nurs Times. 2000;96(31 Suppl): Kenny SE, Irvine T, Driver CP, Nunn AT, Losty PD, Jones MO, et al. Double blind randomised controlled trial of topical glyceryl trinitrate in anal fissure. Arch Dis Child. 2001;85: Gillet BP, Paidas CN. Anal Fissure. Accessed 05/10/ Sutcliffe JR, King SK, Southwell BR, Hutson JM. Paediatric constipation for adult surgeons-article 1: Targeting the cause. ANZ J Surg. 2004;74(10): Rogers, J. Paediatric bowel problems. Gastrointestinal Nursing. 2004;2: Gillett P, Glendinning A, Gordon J, Mok J, Purves J, Reid P et al. 'Tough Going' Childhood Idiopathic Constipation Management Pathway. A Resource for Health Professionals. Edinburgh: Royal Hospital for Sick Children (RHSC); Bernard-Bonnin AC, Haley N, Belanger S, Nadeau D. Parental and patient perceptions about encopresis and its treatment. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 1993;14: Partin JC, Hamill SK, Fischel JE, Partin JS. Painful defecation and fecal soiling in children. Pediatrics. 1992;89(6 Pt 1): McGrath ML, Clawson E. The defecation anxiety scale for parents and children. Unpublished assessment instrument. Cited in McGrath ML, Mellon MW, Murphy L. Empirically supported treatments in pediatric psychology: constipation and encopresis. J Pediatr Psychol. 2000;25:225-54; discussion Loening-Baucke V. Assessment, diagnosis and treatment of constipation in childhood. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 1994;21(2): Addison R, Ness W. Correct position for opening your bowels. Norgine Ltd: Brazzelli M, Griffiths P. Behavioural and cognitive interventions with or without other treatments for defaecation disorders in children (Review). In The Cochrane Library (Issue 2.) Oxford; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Guest JF, Candy DCA, Clegg JP, Edwards D, Helter MT, Dale AK, et al. Clinical and economic impact of using Macrogol 3350 plus electrolytes in an outpatient setting compared to enemas and suppositories and manual evacuation to treat paediatric faecal impaction based on actual clinical practice in England and Wales. Current Medical Research and Opinion. 2007;23(9): Clayden G. A guide for good paediatric practice: childhood constipation. Ambulatory Child Health. 1996;1: Further Reading Pijpers MAM, Tabbers M, Benninga MA, Berger MY. Currently recommended treatments of childhood constipation are not evidence based. A systematic literature review on the effect of laxative treatment and dietary measures. Arch Dis Child. 2008;0:adc v1 Additional copies of this Factsheet can be downloaded from The information contained within this Factsheet represents the independent views of the members of the Forum and copyright rests with the Forum members. 07
8 Page suitable for photocopying for healthcare professionals to give to parents CONSTIPATION IN TODDLERS GUIDANCE & TIPS FOR PARENTS If you think your child is constipated, do not be afraid to seek help - sooner is better than later. Constipation can show itself in different ways, the toddler: - having no bowel movement for three or more days - passing lots of small hard stools - holding on to stools: appearing to be pushing with signs such as face becoming red, when in fact holding on to stools using avoidance techniques such as dancing about or hiding soiling - loose stools that leak into pants, pyjamas and bedclothes. This happens when the bowel is full. Make sure your toddler is drinking enough fluid - six to eight drinks a day. Always give a drink with each meal and at least one in between meals or with a snack. Your toddler may need more fluid in hot weather and if he or she is taking a laxative. Water is the best drink between meals. You can give water or diluted fruit juices with meals. Limit milk to three small drinks per day - about 120mls or 4oz. Try to eat together as a family. Give your toddler small regular meals and snacks. Serve a variety of foods and concentrate on quality rather than quantity. Persevere with fruits, vegetables and cereals. Encourage your toddler to be physically active, to play outside, swim, walk, and join in team games. A consistent routine will help your toddler develop regular toilet habits. For example, sitting on the potty or toilet for a few minutes after meals. Hand washing afterwards can be fun! Listen and watch for signs that your toddler is ready to begin potty/toilet training. Take your time, don't rush it. - Give praise and positive encouragement. Minimise fuss over 'accidents' - Make sure your toddler can sit on the toilet, supported (using a child seat or foot stool for example) so that he or she feels safe. If these measures do not work your healthcare professional may suggest seeking medical advice. Practical help and information on nutrition and development Supported by an educational grant from Danone UK ITF134 - October 2008
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
Advice for Parents and Carers
 Advice for Parents and Carers 1 2 CONTENTS 4. What is constipation? 4. What is faecal impaction? 5. How common is constipation in children? 5. How to tell if your child may be constipated 6. How constipation
Advice for Parents and Carers 1 2 CONTENTS 4. What is constipation? 4. What is faecal impaction? 5. How common is constipation in children? 5. How to tell if your child may be constipated 6. How constipation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children
 Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
Constipation in children
 Search date August 2003 Gregory Rubin QUESTIONS Effects of treatments...397 395 INTERVENTIONS CONSTIPATION Trade off between benefits and harms Cisapride with or without magnesium oxide*...397 Unknown
Search date August 2003 Gregory Rubin QUESTIONS Effects of treatments...397 395 INTERVENTIONS CONSTIPATION Trade off between benefits and harms Cisapride with or without magnesium oxide*...397 Unknown
Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling
 Patient and Family Education Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling While it is normal for a child to be constipated now and then, ongoing problems are not. This handout gives a treatment
Patient and Family Education Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling While it is normal for a child to be constipated now and then, ongoing problems are not. This handout gives a treatment
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
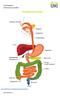 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery)
 Saint Mary s Hospital Newborn Intensive Care Unit Information for Parents A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery) Introduction This information leaflet is designed to help parents and families to care for
Saint Mary s Hospital Newborn Intensive Care Unit Information for Parents A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery) Introduction This information leaflet is designed to help parents and families to care for
A patient s guide to the. management of constipation following surgery
 A patient s guide to the management of constipation following surgery This leaflet has been designed to give you more information about using laxatives after your surgery. What is constipation? After your
A patient s guide to the management of constipation following surgery This leaflet has been designed to give you more information about using laxatives after your surgery. What is constipation? After your
Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up
 1400 Gut 1993; 34:1400-1404 Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up Department of Pediatrics, University of Iowa, USA V Loening-Baucke Correspondence
1400 Gut 1993; 34:1400-1404 Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up Department of Pediatrics, University of Iowa, USA V Loening-Baucke Correspondence
Human Anatomy rectum
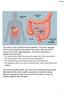 rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
Primary Care Constipation Guidelines. Version 1 November 2016
 Primary Care Constipation Guidelines Version 1 November 2016 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1 November 2016 New guideline Contents 1. Management of constipation in adults: acute and
Primary Care Constipation Guidelines Version 1 November 2016 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1 November 2016 New guideline Contents 1. Management of constipation in adults: acute and
Delorme s Operation For Rectal Prolapse
 Delorme s Operation For Rectal Prolapse Patient Information Colorectal Surgery Author ID: NM Leaflet Number: Surg 045 Version: 3.1 Name of Leaflet: Delorme s Operation for Rectal Prolapse Date Produced:
Delorme s Operation For Rectal Prolapse Patient Information Colorectal Surgery Author ID: NM Leaflet Number: Surg 045 Version: 3.1 Name of Leaflet: Delorme s Operation for Rectal Prolapse Date Produced:
Biofeedback Program. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
 Biofeedback Program GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Biofeedback Checklist Bristol Stool Form Scale Digestive process 4F s Fibre, Fluid, Fitness,
Biofeedback Program GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Biofeedback Checklist Bristol Stool Form Scale Digestive process 4F s Fibre, Fluid, Fitness,
DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION
 Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Constipation. AL amyloidosis Infosheet Series. Symptoms and complications. Infoline:
 Constipation This Infosheet explains what constipation is, what causes it in AL amyloidosis patients, the signs and symptoms, how it is treated and tips for self-management/prevention. What is constipation?
Constipation This Infosheet explains what constipation is, what causes it in AL amyloidosis patients, the signs and symptoms, how it is treated and tips for self-management/prevention. What is constipation?
About Parachoc. To Mum and Dad. Colour me in! Please take the time to read this book. Using the Parachoc training diary...
 Parachoc Training Diary About Parachoc Parachoc is a lubricating laxative containing liquid paraffin. It contains no bowel stimulant, so it is a gentle treatment for constipation. This diary is designed
Parachoc Training Diary About Parachoc Parachoc is a lubricating laxative containing liquid paraffin. It contains no bowel stimulant, so it is a gentle treatment for constipation. This diary is designed
Protocol to support reducing the use of and the effective use of laxatives. HaRD CCG employed Pharmacists and Medicines Optimisation Technicians.
 NY&AWC Medicines Management Team Protocol to support reducing the use of and the effective use of laxatives Applies to HaRD CCG employed Pharmacists and Medicines Optimisation Technicians. These protocols
NY&AWC Medicines Management Team Protocol to support reducing the use of and the effective use of laxatives Applies to HaRD CCG employed Pharmacists and Medicines Optimisation Technicians. These protocols
Bowel Health in Adults
 Bowel Health in Adults Patient Information Contact Details: Bladder and Bowel Specialist Nurse Service First Floor New Alderley House Macclesfield District General Hospital Victoria Road Macclesfield SK10
Bowel Health in Adults Patient Information Contact Details: Bladder and Bowel Specialist Nurse Service First Floor New Alderley House Macclesfield District General Hospital Victoria Road Macclesfield SK10
AL amyloidosis Infosheet
 AL amyloidosis Infosheet Myeloma UK Broughton House 31 Dunedin Street Edinburgh EH7 4JG Tel: 0131 557 3332 Myeloma Infoline 0800 980 3332 www.myeloma.org.uk/amyloidosis Myeloma Awareness Week 21 28 June
AL amyloidosis Infosheet Myeloma UK Broughton House 31 Dunedin Street Edinburgh EH7 4JG Tel: 0131 557 3332 Myeloma Infoline 0800 980 3332 www.myeloma.org.uk/amyloidosis Myeloma Awareness Week 21 28 June
Constipation in Children
 Page 1 of 7 Constipation in Children Constipation is a very common problem for children. For most children, constipation means passing hard stools, with difficulty, less frequently than normal. Regular
Page 1 of 7 Constipation in Children Constipation is a very common problem for children. For most children, constipation means passing hard stools, with difficulty, less frequently than normal. Regular
BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS
 BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS BI-PED PROJECT (BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: PEDIATRICS) Emotional Health Committee Maryland Chapter American Academy of Pediatrics David Bromberg M.D. Overview: Encopresis is diagnosed
BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS BI-PED PROJECT (BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: PEDIATRICS) Emotional Health Committee Maryland Chapter American Academy of Pediatrics David Bromberg M.D. Overview: Encopresis is diagnosed
Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care
 Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care Slide Presentation Supporting Implementation of the RNAO BPGs: Promoting Continence Using Prompted Voiding and Prevention of Constipation in the
Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care Slide Presentation Supporting Implementation of the RNAO BPGs: Promoting Continence Using Prompted Voiding and Prevention of Constipation in the
15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications
 15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing
15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing
Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate.
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy
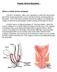 Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
HELPING SCHOOLS MANAGE CONTINENCE PROBLEMS. The Right to
 HELPING SCHOOLS MANAGE CONTINENCE PROBLEMS The Right to Go Continence problems in childhood are common and as a result it is not unusual for schools to have at least one child with a wetting or soiling
HELPING SCHOOLS MANAGE CONTINENCE PROBLEMS The Right to Go Continence problems in childhood are common and as a result it is not unusual for schools to have at least one child with a wetting or soiling
Constipation. What are the signs and symptoms of constipation? Less than three bowel movements per week. Pain or discomfort when opening your bowels
 Infosheet Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is usually diagnosed when your bowels are moving less than three times per week. When you are constipated your bowel movements may be dry, hard
Infosheet Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is usually diagnosed when your bowels are moving less than three times per week. When you are constipated your bowel movements may be dry, hard
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
MANAGING CONSTIPATION
 MANAGING CONSTIPATION INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Constipation is. The Symptoms of Constipation. How to Help Manage Constipation. WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
MANAGING CONSTIPATION INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Constipation is. The Symptoms of Constipation. How to Help Manage Constipation. WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
Anal sphincter exercises. Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals
 Anal sphincter exercises Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Anal sphincter exercises to help lessen leakage from the bowel Sphincter exercises, when practiced correctly, can build up
Anal sphincter exercises Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Anal sphincter exercises to help lessen leakage from the bowel Sphincter exercises, when practiced correctly, can build up
Obstructive Defaecation
 Oxford Pelvic Floor Service Obstructive Defaecation Information for patients page 2 What is obstructive defaecation? Obstructive defaecation is the inability to pass stools (open your bowels). This is
Oxford Pelvic Floor Service Obstructive Defaecation Information for patients page 2 What is obstructive defaecation? Obstructive defaecation is the inability to pass stools (open your bowels). This is
Diverticular Disease Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.
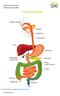 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
CONSTIPATION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS
 ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT CONSTIPATION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS THIS FACTSHEET IS ABOUT CONSTIPATION Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different
ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT CONSTIPATION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS THIS FACTSHEET IS ABOUT CONSTIPATION Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different
Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included.
 Urology Clinic Hospital for Sick Children Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included. Information on bladder retraining, urinary tract infections
Urology Clinic Hospital for Sick Children Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included. Information on bladder retraining, urinary tract infections
Faecal Incontinence Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
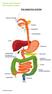 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
Stool softeners are medicines like (ducolox - pericolace - senokot). You want the stool to remain soft so it is easier to empty the bowel.
 "Bowel Management" How the Body Works The food you eat and drink provides your body with many nutrients. These nutrients give you energy and help you stay healthy. As food moves through your body it breaks
"Bowel Management" How the Body Works The food you eat and drink provides your body with many nutrients. These nutrients give you energy and help you stay healthy. As food moves through your body it breaks
Constipation. Self-study course
 Constipation Self-study course 2 Course objectives: At the end of this course you will be able to: 1. Define the term constipation 2. Explain three reasons why older adults are at greater risk for constipation
Constipation Self-study course 2 Course objectives: At the end of this course you will be able to: 1. Define the term constipation 2. Explain three reasons why older adults are at greater risk for constipation
Constipation. Myeloma Infosheet Series. Symptoms and complications. Infoline:
 Constipation This Infosheet explains what constipation is, what causes it in myeloma patients, what the symptoms of it are, how it is treated and some tips for self-management. What is constipation? Constipation
Constipation This Infosheet explains what constipation is, what causes it in myeloma patients, what the symptoms of it are, how it is treated and some tips for self-management. What is constipation? Constipation
Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse
 Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse Your Questions Answered What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the rectum become weakened, allowing the muscle of the rectum
Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse Your Questions Answered What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the rectum become weakened, allowing the muscle of the rectum
Authors and Disclosures
 Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education January Home Economics Assessment Unit AS 2. assessing. Priority Health Issues
 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education January 2013 Home Economics Assessment Unit AS 2 assessing Priority Health Issues [AN121] TUESDAY 22 JANUARY, MORNING MARK SCHEME 7896.01 1 (a)
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education January 2013 Home Economics Assessment Unit AS 2 assessing Priority Health Issues [AN121] TUESDAY 22 JANUARY, MORNING MARK SCHEME 7896.01 1 (a)
Foreword. Bowel Management
 2 Bowel Management Foreword The section on is very similar to that of Bladder Care and Management section, as there are many issues to be addressed. You should always remember that what works for one individual
2 Bowel Management Foreword The section on is very similar to that of Bladder Care and Management section, as there are many issues to be addressed. You should always remember that what works for one individual
Constipation- more than Movicol? PATRICK NEARNEY GPSI PAEDIATIRICS
 Constipation- more than Movicol? PATRICK NEARNEY GPSI PAEDIATIRICS Learning Points How to rule out an underlying cause for constipation How to diagnose and treat faecal impaction How to manage encopresis
Constipation- more than Movicol? PATRICK NEARNEY GPSI PAEDIATIRICS Learning Points How to rule out an underlying cause for constipation How to diagnose and treat faecal impaction How to manage encopresis
Patient Information Leaflet. Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation
 Patient Information Leaflet Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation Treating Rectal Prolapse - Delormes operation What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the
Patient Information Leaflet Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation Treating Rectal Prolapse - Delormes operation What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the
Clinical guideline Published: 26 May 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg99
 Constipation in children and young people: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 26 May 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg99 NICE 2019. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Constipation in children and young people: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 26 May 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg99 NICE 2019. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Constipation usually is not a cause for concern, and easy to avoid by adopting healthy eating and exercise habits.
 From the Health Clinic Mrs. Maureen Earner (mearner@stambroseschool.org Constipation Constipation is a very common problem in children. A child is considered constipated when he or she has fewer than three
From the Health Clinic Mrs. Maureen Earner (mearner@stambroseschool.org Constipation Constipation is a very common problem in children. A child is considered constipated when he or she has fewer than three
Talk about Constipation
 This booklet is part of a series for children with bowel and/or bladder problems. The booklets give a simple explanation of the problems the child is having. They give practical advice about how to help.
This booklet is part of a series for children with bowel and/or bladder problems. The booklets give a simple explanation of the problems the child is having. They give practical advice about how to help.
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized intermediate
 GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized intermediate 1. Introduction In some forms of EB formation of blisters on the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus can occur. This causes various problems;
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized intermediate 1. Introduction In some forms of EB formation of blisters on the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus can occur. This causes various problems;
Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin
 Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin Co-Management Guidelines To support collaborative care, we have developed guidelines for our community providers to utilize when referring to, and managing patients with,
Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin Co-Management Guidelines To support collaborative care, we have developed guidelines for our community providers to utilize when referring to, and managing patients with,
Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy
 A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
Irritable Bowel. Syndrome. Health Promotion Service
 The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
Chapter 19. Assisting With Bowel Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Rotavirus. Children s Ward Macclesfield District General Hospital.
 Rotavirus Children s Ward 01625 661080 Macclesfield District General Hospital www.eastcheshire.nhs.uk Leaflet Ref: 10941 Published: 07/15 Review: 07/18 Page 1 Rotavirus is a viral infection that can cause
Rotavirus Children s Ward 01625 661080 Macclesfield District General Hospital www.eastcheshire.nhs.uk Leaflet Ref: 10941 Published: 07/15 Review: 07/18 Page 1 Rotavirus is a viral infection that can cause
Nutrition & Food Safety Policy
 Nutrition & Food Safety Policy National Quality Standards (NQS) Our Service recognises the importance of healthy eating to the growth and development of young children and is committed to supporting the
Nutrition & Food Safety Policy National Quality Standards (NQS) Our Service recognises the importance of healthy eating to the growth and development of young children and is committed to supporting the
Chapter 22. Bowel Needs. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces
 Rationale Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces These guidelines are to provide the required information for designated registered nurses, health care assistants and bank support workers to perform
Rationale Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces These guidelines are to provide the required information for designated registered nurses, health care assistants and bank support workers to perform
Physiotherapy advice following your third or fourth degree perineal tear
 Further sources of information NHS Choices: www.nhs.uk/conditions Our website: www.sfh-tr.nhs.uk INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Patient Experience Team (PET) PET is available to help with any of your compliments,
Further sources of information NHS Choices: www.nhs.uk/conditions Our website: www.sfh-tr.nhs.uk INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Patient Experience Team (PET) PET is available to help with any of your compliments,
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet Your Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal
Patient Information Leaflet Your Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal
CT colonography. Information for patients Radiology
 CT colonography Information for patients Radiology This information booklet has been provided to help answer some of the questions you may have about having a CT colonography. What is computed tomography
CT colonography Information for patients Radiology This information booklet has been provided to help answer some of the questions you may have about having a CT colonography. What is computed tomography
Are you aware there are many different reasons for having irregular bowels? This chart is to help you get back into balance during and post detox.
 BRISTOL POOP CHART The Bristol Poop Chart was created in the United Kingdom by a group of gastroenterologists at the University of Bristol. This chart is designed to help you determine the health of your
BRISTOL POOP CHART The Bristol Poop Chart was created in the United Kingdom by a group of gastroenterologists at the University of Bristol. This chart is designed to help you determine the health of your
PATIENT INFORMATION Anterior Resection After Care
 PATIENT INFORMATION Anterior Resection After Care Anatomy of your bowel Transverse colon Ascending colon Descending colon Sigmoid colon Rectum Anus Your bowel before your operation The large bowel or colon
PATIENT INFORMATION Anterior Resection After Care Anatomy of your bowel Transverse colon Ascending colon Descending colon Sigmoid colon Rectum Anus Your bowel before your operation The large bowel or colon
Managing your Bowels. Below is a diagram of the different parts of the digestive system and what they do. The Digestive System:
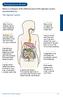 Managing your Bowels Below is a diagram of the different parts of the digestive system and what they do. The Digestive System: 1. Mouth When food is chewed, saliva starts digesting carbohydrates. 2. Oesophagus
Managing your Bowels Below is a diagram of the different parts of the digestive system and what they do. The Digestive System: 1. Mouth When food is chewed, saliva starts digesting carbohydrates. 2. Oesophagus
What Is Constipation?
 CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized severe
 GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized severe 1. Introduction In some forms of EB formation of blisters on the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus can occur. This causes various problems; the
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN EBS generalized severe 1. Introduction In some forms of EB formation of blisters on the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus can occur. This causes various problems; the
Stoma Care Policy and Procedures
 Stoma Care Policy and Procedures Policy number 19.09 Approved by :CEO Version 1 Scheduled review date 28/3/2018 Created on 28/3/2017 POLICY STATEMENT Clients requiring management with the stoma will be
Stoma Care Policy and Procedures Policy number 19.09 Approved by :CEO Version 1 Scheduled review date 28/3/2018 Created on 28/3/2017 POLICY STATEMENT Clients requiring management with the stoma will be
Healthy bladder and bowel habits. Continence Foundation of Australia
 Healthy bladder and bowel habits Continence Foundation of Australia Easy English 2016 Healthy bladder and bowel habits This factsheet is about how to keep your bladder and bowel healthy. This factsheet
Healthy bladder and bowel habits Continence Foundation of Australia Easy English 2016 Healthy bladder and bowel habits This factsheet is about how to keep your bladder and bowel healthy. This factsheet
A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence
 Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2000, 279- A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence Christine Norton, MA, RN, and Sonya Chelvanayagam, MSc, RN Abstract Fecal incontinence
Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2000, 279- A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence Christine Norton, MA, RN, and Sonya Chelvanayagam, MSc, RN Abstract Fecal incontinence
Constipation An Overview. Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment
 CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
Managing dietary problems in pancreatic cancer Contents
 13 11 20 Information and support Managing dietary problems in pancreatic cancer Contents Eating after a Whipple procedure Vomiting Diabetes Pancreatic enzyme replacement supplements Nutritional supplements
13 11 20 Information and support Managing dietary problems in pancreatic cancer Contents Eating after a Whipple procedure Vomiting Diabetes Pancreatic enzyme replacement supplements Nutritional supplements
MOVICOL HALF PI December MOVICOL-Half. Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Potassium 5.4 mmol/l. Bicarbonate 17 mmol/l
 MOVICOL -Half Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Product Name: Product Description: MOVICOL-Half Each sachet of MOVICOL-Half contains: Macrogol 3350 6.563 g Sodium chloride 175.4 mg Sodium bicarbonate
MOVICOL -Half Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Product Name: Product Description: MOVICOL-Half Each sachet of MOVICOL-Half contains: Macrogol 3350 6.563 g Sodium chloride 175.4 mg Sodium bicarbonate
Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (community)
 Addressograph label CHI:... Name:... Address:...... Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (community) Past medical history: Is the patient on medications which can affect bladder function? If, please list
Addressograph label CHI:... Name:... Address:...... Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (community) Past medical history: Is the patient on medications which can affect bladder function? If, please list
Had enough? to turn tears into smiles, a drink of water might be all that s needed
 Had enough? to turn tears into smiles, a drink of water might be all that s needed Did you know that children are at greater risk from dehydration than adults? 1 Not drinking enough can make children confused,
Had enough? to turn tears into smiles, a drink of water might be all that s needed Did you know that children are at greater risk from dehydration than adults? 1 Not drinking enough can make children confused,
Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know. A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury
 Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about bowel movements After SCI, you may need more
Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about bowel movements After SCI, you may need more
Level One Paediatric Continence Assessment
 Level One Paediatric Continence Assessment Paediatric Continence Assessment Form LEVEL 1. Completed by... Date:... Designation... Contact no... Abbreviations used in this document to be listed here with
Level One Paediatric Continence Assessment Paediatric Continence Assessment Form LEVEL 1. Completed by... Date:... Designation... Contact no... Abbreviations used in this document to be listed here with
Pelvic organ prolapse. Information for patients Continence Service
 Pelvic organ prolapse Information for patients Continence Service What is a pelvic organ prolapse? A pelvic organ prolapse occurs when the uterus (womb), vagina, bladder or bowel slips out of place, resulting
Pelvic organ prolapse Information for patients Continence Service What is a pelvic organ prolapse? A pelvic organ prolapse occurs when the uterus (womb), vagina, bladder or bowel slips out of place, resulting
Perineal Tears. Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women & Children s Group
 Perineal Tears Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women & Children s Group This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that
Perineal Tears Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women & Children s Group This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that
Uterus (Womb) Rectum. Another problem could be the sensation of something coming down at the birth canal or back passage (prolapse).
 Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
CONSTIPATION. Atan Baas Sinuhaji
 CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception
 Scan for mobile link. Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception Therapeutic enema is used to help identify and diagnose intussusception, a serious disorder in which one part of the intestine slides into another
Scan for mobile link. Therapeutic Enema for Intussusception Therapeutic enema is used to help identify and diagnose intussusception, a serious disorder in which one part of the intestine slides into another
Foreword. Dr Hilary Jones. debilitating digestive health conditions.
 Foreword Research suggests that the number of people suffering from digestive health issues such as IBS is higher than first thought. Yet talking about bowel health is still a taboo subject for many people.
Foreword Research suggests that the number of people suffering from digestive health issues such as IBS is higher than first thought. Yet talking about bowel health is still a taboo subject for many people.
The Children s Hospital, Tom s Ward. Hirschsprung Disease. Information for parents
 The Children s Hospital, Tom s Ward Hirschsprung Disease Information for parents What is Hirschsprung disease? Hirschsprung disease is a rare disorder of the bowels, most commonly the large bowel (colon).
The Children s Hospital, Tom s Ward Hirschsprung Disease Information for parents What is Hirschsprung disease? Hirschsprung disease is a rare disorder of the bowels, most commonly the large bowel (colon).
Bowel Cancer Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
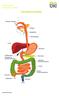 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about bowel cancer Throughout our lives, the lining of the bowel constantly renews itself. This lining contains many millions of tiny cells, which grow, serve their
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about bowel cancer Throughout our lives, the lining of the bowel constantly renews itself. This lining contains many millions of tiny cells, which grow, serve their
Straight Talk on. Women s GI Health. By Judith Reichman, MD, women s health specialist. A new nationwide health campaign for women over age 40
 Straight Talk on Women s GI Health By Judith Reichman, MD, women s health specialist A new nationwide health campaign for women over age 40 welcome! As a gynecologist for more than 25 years, I have seen
Straight Talk on Women s GI Health By Judith Reichman, MD, women s health specialist A new nationwide health campaign for women over age 40 welcome! As a gynecologist for more than 25 years, I have seen
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus.
 The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
Constipation in Children
 Lanarkshire Acute Hospitals Constipation in Children Information for patients What is constipation? Constipation refers to bowel movements which are infrequent, hard and difficult to pass. There are a
Lanarkshire Acute Hospitals Constipation in Children Information for patients What is constipation? Constipation refers to bowel movements which are infrequent, hard and difficult to pass. There are a
Management of the Neurogenic Bowel. June st National SBAA Conference Bloomington, Minnesota
 Management of the Neurogenic Bowel June 2016 41st National SBAA Conference Bloomington, Minnesota DEPARTMENT OF NURSING Rhonda Bolin, BSN, RN, CPN Spina Bifida Nurse Texas Children s Hospital Spina Bifida
Management of the Neurogenic Bowel June 2016 41st National SBAA Conference Bloomington, Minnesota DEPARTMENT OF NURSING Rhonda Bolin, BSN, RN, CPN Spina Bifida Nurse Texas Children s Hospital Spina Bifida
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal act like
Patient Information Leaflet Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal act like
YOUR OPERATION EXPLAINED
 RIGHT HEMICOLECTOMY This leaflet is produced by the Department of Colorectal Surgery at Beaumont Hospital supported by an unrestricted grant to better Beaumont from the Beaumont Hospital Cancer Research
RIGHT HEMICOLECTOMY This leaflet is produced by the Department of Colorectal Surgery at Beaumont Hospital supported by an unrestricted grant to better Beaumont from the Beaumont Hospital Cancer Research
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE The management of faecal incontinence in adults 1.1 Short title Faecal incontinence 2 Background (a) (b) (c) The National Institute
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE The management of faecal incontinence in adults 1.1 Short title Faecal incontinence 2 Background (a) (b) (c) The National Institute
The Infant/Child with a Bowel Ostomy
 The Infant/Child with a Bowel Ostomy Thank you for choosing the Medical College of Georgia Hospitals and Clinics for your child s health care needs. This information is to help answer some of the questions
The Infant/Child with a Bowel Ostomy Thank you for choosing the Medical College of Georgia Hospitals and Clinics for your child s health care needs. This information is to help answer some of the questions
Bowel Management for Children with Anorectal Malformations by Kathleen Guardino, RN, MSN
 Bowel Management for Children with Anorectal Malformations by Kathleen Guardino, RN, MSN Dr. Alberto Peña, Chief of Surgery at Schneider Children's Hospital created the posterior sagittal anorectoplasty
Bowel Management for Children with Anorectal Malformations by Kathleen Guardino, RN, MSN Dr. Alberto Peña, Chief of Surgery at Schneider Children's Hospital created the posterior sagittal anorectoplasty
Haemorrhoidectomy. Colorectal Surgery. Patient Information
 Haemorrhoidectomy Colorectal Surgery Patient Information What are haemorrhoids? Haemorrhoids, also know as piles, are soft fleshy lumps just inside the back passage (anus). They have a rich blood supply
Haemorrhoidectomy Colorectal Surgery Patient Information What are haemorrhoids? Haemorrhoids, also know as piles, are soft fleshy lumps just inside the back passage (anus). They have a rich blood supply
Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (care home)
 Addressograph label CHI:... Name:... Address:...... Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (care home) Past medical history: Is the patient on medications which can affect bladder function? If, please list
Addressograph label CHI:... Name:... Address:...... Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (care home) Past medical history: Is the patient on medications which can affect bladder function? If, please list
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
EATING WELL AND CANCER
 EATING WELL AND CANCER 2 Why is it important for people with cancer to eat well? If the person you care for has cancer, it is more important than ever that they eat well. Unfortunately, it is often at
EATING WELL AND CANCER 2 Why is it important for people with cancer to eat well? If the person you care for has cancer, it is more important than ever that they eat well. Unfortunately, it is often at
SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health
 SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health 1 Heart Health If you re like most Americans, heart health might be something you don t think about very often. You should. The risk of heart disease increases with age and
SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health 1 Heart Health If you re like most Americans, heart health might be something you don t think about very often. You should. The risk of heart disease increases with age and
Anterior Sphincter Repair Operation
 Anterior Sphincter Repair Operation How will the operation help me? The investigations that you have had indicate that your anal sphincter is damaged or very weak, and this is why you are having trouble
Anterior Sphincter Repair Operation How will the operation help me? The investigations that you have had indicate that your anal sphincter is damaged or very weak, and this is why you are having trouble
