Chapter 16 URINARY, SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE IMPAIRMENT
|
|
|
- Lora Knight
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 16 URINARY, SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE IMPAIRMENT Introduction This chapter provides criteria for assessing permanent impairment from entitled urinary, sexual and reproductive conditions. The chapter is divided into two sections. The first section provides criteria to rate impairment of upper and lower urinary tract conditions. The second section provides criteria to rate impairment of sexual and reproductive conditions. Impairment from rectovaginal fistula(e) is rated within Chapter 14, Gastrointestinal Impairment. Impairment from loss of a kidney due to tuberculosis is rated within Chapter 24, Tuberculosis Impairment. Impairment from malignant urinary, sexual and reproductive conditions is rated within Chapter 18, Malignant Impairment. Follow the steps contained within the Malignant Impairment chapter. Rating Tables This chapter contains four Loss of Function tables and two Other Impairment tables which may be used to rate entitled urinary, sexual and reproductive conditions. The tables within this chapter are: Table 16.1 Table 16.2 Table 16.3 Table 16.4 Loss of Function - Upper Urinary Tract Loss of Function - Lower Urinary Tract Loss of Function - Sexual and Reproductive - Male Loss of Function - Sexual and Reproductive - Female This table is used to rate impairment in the upper urinary tract. This table is used to rate impairment in the lower urinary tract. This table is used to rate impairment in male sexual and reproductive function. This table is used to rate impairment in female sexual and reproductive function. Table 16.5 Other Impairment - Breasts - Male Table 16.6 Other Impairment - Breasts - Female This table is used to rate impairment of the male breast. This table is used to rate impairment of the female breast. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 1
2 Section 1 Determining Impairment Assessment of Urinary Tract Function The tables that may be used to rate impairment from urinary tract conditions are: Table 16.1 Table 16.2 Loss of Function - Upper Urinary Tract Loss of Function - Lower Urinary Tract This table is used to rate impairment in the upper urinary tract. This table is used to rate impairment in the lower urinary tract. Loss of Function - Upper Urinary Tract Table 16.1 is used to rate impairment from conditions of the upper urinary tract (kidney and ureter). Only one rating may be selected for each entitled condition. If more than one rating is applicable for an entitled condition, the ratings are compared and the highest selected. Ratings in the upper urinary tract table take into account the presence of signs and symptoms and laboratory findings which may accompany the urinary tract impairment. Signs and symptoms include hypertension, chronic anemia, edema, headache, dyspnea, fatigue, fever, chills, back pain, dizziness, hematuria, anuria and recurrent urinary infections. The creatinine clearance test is used in routine practice to estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). The GFR is the single best indicator of overall renal function. Creatinine clearance may be estimated either by analysis of a 24 hour urine collection or from the serum creatinine level by applying the following modified Cockcroft-Gault formula: Males: b Creatinine clearance (ml/min) = 1.2 (140 - patient s age, years) (TBW, kg) (serum creatinine, µmol/l) Females: Multiply equation above by b To convert from ml/min to SI (ml/s) divide the ml/min value by 60. Abbreviation: TBW = Total Body Weight When entitled upper urinary tract conditions result in permanent impairment of other organ systems, a consequential entitlement decision is required. If awarded, the resulting impairment of that organ system(s) will be rated using the applicable body system specific table(s). Veterans Affairs Canada Page 2
3 If non-entitled conditions or conditions rated within another chapter/table of the Table of Disabilities are contributing to the overall impairment, then the Partially Contributing Table (PCT) must be applied to arrive at the rating which is due to the entitled condition(s) rated within this table. Loss of Function - Lower Urinary Tract Table 16.2 is used to rate impairment from conditions of the lower urinary tract (bladder and urethra), prostate and epididymis. Only one rating may be selected for each entitled condition. If more than one rating is applicable for an entitled condition, the ratings are compared and the highest selected. When entitled lower urinary tract conditions result in permanent impairment of other organ systems, a consequential entitlement decision is required. If awarded, the resulting impairment of that organ system(s) will be rated using the applicable body system specific table(s). If non-entitled conditions or conditions rated within another chapter/table of the Table of Disabilities are contributing to the overall impairment, then the Partially Contributing Table (PCT) must be applied to arrive at the rating which is due to the entitled condition(s) rated within this table. Table Loss of Function - Upper Urinary Tract Only one rating may be given for each entitled condition from Table If more than one rating is applicable for an entitled condition, the ratings are compared and the highest rating is selected. Each bullet ( ) represents one criterion. In order for a rating to be established for Table 16.1, follow the ands and ors. Table Loss of Function - Upper Urinary Tract Rating Criteria Nil Normal or mildly impaired renal function; and No clinical signs of renal disease. Four Pyelonephritis: up to 2 attacks per year; or Kidney stones: occasional attacks of renal colic. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 3
4 Rating Criteria Nine Diminution in renal function evidenced by creatinine clearance less than 63 ml/min (< than 90 L / 24hrs). Signs and symptoms and abnormal laboratory findings may be present; or Pyelonephritis: 3-4 attacks per year; or Kidney stones: yearly attacks of renal colic; or Chronic unilateral hydronephrosis with infection. Thirteen Pyelonephritis: more than 4 attacks per year; or Nephrectomy; or Chronic bilateral hydronephrosis with infection. Twenty-one Successful renal transplant (minimum value). Twenty-six Diminution in renal function evidenced by creatinine clearance of less than 53 ml/ min (< than 75 L /24 hrs). Signs and symptoms and abnormal laboratory findings may be present; or Permanent urinary diversion with ostomy of the skin (i.e. nephrostomy, ureterointestinal, ileal conduit, cutaneous ureterostomy). Forty-three Diminution in renal function evidenced by creatinine clearance of less than 43 ml/ min (< than 60 L /24 hrs). Signs and symptoms and abnormal laboratory findings may be present. Fifty-seven Eighty-one Diminution in renal function evidenced by creatinine clearance of less than 33 ml/ min (< than 48 L /24 hrs). Signs and symptoms and abnormal laboratory findings may be present. Diminution in renal function evidenced by creatinine clearance of less than 28 ml/ min (< than 40 L /24 hrs). Signs and symptoms and abnormal laboratory findings may be present; or Requiring constant peritoneal or hemodialysis. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 4
5 Steps to Determine Urinary Tract Assessment (Upper Tract) Step 1: Step 2: Step 3: Determine the rating from Table 16.1 (Loss of Function - Upper Urinary Tract). Does the Partially Contributing Table apply? If yes, then apply to rating at Step 1. Determine the Quality of Life rating. Step 4: Add the ratings at Step 2 and Step 3. Step 5: If partial entitlement exists, apply to the rating above. This is the Disability Assessment. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 5
6 Table Loss of Function - Lower Urinary Tract Only one rating may be given for each entitled condition from Table If more than one rating is applicable for an entitled condition, the ratings are compared and the highest selected. Each bullet ( ) represents one criterion. In order for a rating to be established for Table 16.2, only one criterion must be met at a level of impairment for that rating to be selected. Table Loss of Function - Lower Urinary Tract Rating Criteria Nil Voiding dysfunction: occasional symptoms of dysuria, urgency or frequency; or Prostatectomy. One Obstructed voiding: with hesitancy or diminished stream; or Lower urinary tract infection: occurring 1-2 times per year. Four Voiding dysfunction: symptoms of dysuria, urgency and/or frequency; daytime voiding every 3 hours and awakening once through the night; or 1-2 incontinent pads required daily; or Chronic epididymitis without urinary tract symptoms but with ongoing pain. Nine Obstructed voiding: requiring 2-4 dilatations per year; or Lower tract infection: occurring at least 4 times per year despite long term prophylactic antibiotic drug therapy. Thirteen Voiding dysfunction: symptoms of dysuria, urgency and frequency; daytime voiding every 2 hours and nocturia 2-3 times per night; or More than 2 incontinent pads required daily. Eighteen Twenty-six Voiding dysfunction: symptoms of dysuria, urgency and frequency; daytime voiding every 1 hour and nocturia 4-5 times per night; or Permanent use of condom catheter; or Obstructed voiding: with any one of the following: post-void residuals greater than 150 cc; uroflometry - markedly diminished peak flow rate (less than 10 cc/sec); stricture disease requiring more than 4 dilatations per year. Voiding dysfunction: symptoms of dysuria, urgency and frequency, with less than 30 minutes between voidings and voiding more than 5 times per night; or Obstructed voiding: with urinary retention requiring intermittent daily catheterization. Thirty-four Voiding dysfunction: no voluntary control of bladder; or Permanent indwelling catheter. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 6
7 Rating Criteria Forty-three Voiding dysfunction: with painful urinary frequency and voids every 15 minutes day and night; or Permanent suprapubic catheter. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 7
8 Steps to Determine Urinary Tract Assessment (Lower Tract) Step 1: Step 2: Step 3: Determine the rating from Table 16.2 (Loss of Function - Lower Urinary Tract). Does the Partially Contributing Table apply? If yes, then apply to rating at Step 1. Determine the Quality of Life rating. Step 4: Add the ratings at Step 2 and Step 3. Step 5: If partial entitlement exists, apply to the Step 4 rating. This is the Disability Assessment. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 8
9 Section 2 Determining Impairment Assessment of Sexual and Reproductive Function Selection of Tables The tables that may be used to rate impairment from sexual and reproductive conditions are: Table 16.3 Table 16.4 Loss of Function - Sexual and Reproductive - Male Loss of Function - Sexual and Reproductive - Female This table is used to rate impairment in male sexual and reproductive function. This table is used to rate impairment in female sexual and reproductive function. Table 16.5 Other Impairment - Breasts - Male This table is used to rate impairment of the male breast. Table 16.6 Other Impairment - Breasts - Female This table is used to rate impairment of the female breast. Loss of Function - Sexual and Reproductive - Male Table 16.3 is used to rate impairment from male sexual and reproductive conditions. Only one rating may be selected for each entitled condition. If more than one rating is applicable for an entitled condition, the ratings are compared and the highest selected. For Veterans Affairs Canada (VAC) purposes Sterility is defined as the complete inability to produce offspring despite medical intervention. When entitled male sexual and reproductive conditions result in permanent impairment of other organ systems, a consequential entitlement decision is required. If awarded, the resulting impairment of that organ system(s) will be rated using the applicable body system specific table(s). If non-entitled conditions or conditions rated within another chapter/table of the Table of Disabilities are contributing to the overall impairment, then the Partially Contributing Table (PCT) must be applied to arrive at the rating which is due to the entitled condition(s) rated within this table. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 9
10 Loss of Function - Sexual and Reproductive - Female Table 16.4 is used to rate impairment from female sexual and reproductive conditions. Only one rating may be selected for each entitled condition. If more than one rating is applicable for an entitled condition, the ratings are compared and the highest selected. For Veterans Affairs Canada (VAC) purposes Sterility is defined as the complete inability to produce offspring despite medical intervention. When entitled female sexual and reproductive conditions result in permanent impairment of other organ systems, a consequential entitlement decision is required. If awarded, the resulting impairment of that organ system(s) will be rated using the applicable body system specific table(s). If non-entitled conditions or conditions rated within another chapter/table of the Table of Disabilities are contributing to the overall impairment, then the Partially Contributing Table (PCT) must be applied to arrive at the rating which is due to the entitled condition(s) rated within this table. Other Impairment - Breasts - Male Table 16.5 is used to rate impairment from male breast conditions. Only one rating may be selected for each entitled condition. If more than one rating is applicable for an entitled condition, the ratings are compared and the highest selected. When entitled male breast conditions result in permanent impairment of other organ systems, a consequential entitlement decision is required. If awarded, the resulting impairment of that organ system(s) will be rated using the applicable body system specific table(s). If non-entitled conditions or conditions rated within another chapter/table of the Table of Disabilities are contributing to the overall impairment, then the Partially Contributing Table (PCT) must be applied to arrive at the rating which is due to the entitled condition(s) rated within this table. Other Impairment - Breasts - Female Table 16.6 is used to rate impairment from female breast conditions. Only one rating may be selected for each entitled condition. If more than one rating is applicable for an entitled condition, the ratings are compared and the highest selected. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 10
11 When entitled female breast conditions result in permanent impairment of other organ systems, a consequential entitlement decision is required. If awarded, the resulting impairment of that organ system(s) will be rated using the applicable body system specific table(s). If non-entitled conditions or conditions rated within another chapter/table of the Table of Disabilities are contributing to the overall impairment, then the Partially Contributing Table (PCT) must be applied to arrive at the rating which is due to the entitled condition(s) rated within this table. Table Loss of Function - Sexual and Reproductive - Male Only one rating may be given for each entitled condition from Table If more than one rating is applicable for an entitled condition, the ratings are compared and the highest selected. Each bullet ( ) represents one criterion. In order for a rating to be established for Table 16.3, only one criterion must be met at a level of impairment for that rating to be selected. Table Loss of Function - Sexual and Reproductive - Male Rating Criteria Nil Circumcision; or Varicocele, hydrocele or spermatocele asymptomatic; or Vasectomy*. One Unilateral atrophy of the testicle. Four Loss of one testicle; or Peyronie s disease; still capable of intercourse; or Varicocele, hydrocele or spermatocele symptomatic; or Erectile dysfunction responsive to treatment; or Bilateral atrophy of the testicles*. Nine Permanent sterility. Eighteen Severe post-ejaculatory pain sufficient to cause total avoidance of intercourse*; or Peyronie s disease; incapable of intercourse*; or Erectile dysfunction unresponsive to treatment*; or Loss of up to one-half of the penis*. Twenty-six Loss of more than one-half of the penis*; or Bilateral loss of testicles*. *A separate rating for permanent sterility is not given for these conditions. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 11
12 Steps to Determine Sexual and Reproductive Assessment (Male) Step 1: Step 2: Step 3: Determine the rating from Table 16.3 (Loss of Function - Sexual and Reproductive - Male). Does the Partially Contributing Table apply? If yes, then apply to rating at Step 1. Determine the Quality of Life rating. Step 4: Add the ratings at Step 2 and Step 3. Step 5: If partial entitlement exists, apply to the rating at Step 4. This is the Disability Assessment. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 12
13 Table 16.4 Loss of Function - Sexual and Reproductive - Female Only one rating may be given for each entitled condition from Table If more than one rating is applicable for an entitled condition, the ratings are compared and the highest selected. Each bullet ( ) represents one criterion. In order for a rating to be established for Table 16.4, only one criterion must be met at a level of impairment for that rating to be selected. Table Loss of Function - Sexual and Reproductive - Female Rating Criteria Nil Tubal ligation*; elective; or Permanent sterility; onset at or after natural menopause; or Hysterectomy*; elective, postmenopausal. One Dysmenorrhea. Four Unilateral oophrectomy; premenopausal. Nine Chronic, pelvic pain and/or heavy irregular bleeding requiring continuous treatment to control; or Permanent sterility; premenopausal; or Bilateral loss of tubal patency*; premenopausal; or Bilateral salpingectomy* (not carried out for contraceptive purposes); premenopausal; or Hysterectomy*; premenopausal. Thirteen Chronic pelvic pain not controlled by treatment. Eighteen Dyspareunia, with persistent inability to participate in vaginal intercourse. Twenty-six Vulvectomy; or Clitoridectomy; or Bilateral oophrectomy*; premenopausal; or Severe vaginal stenosis. *A separate rating for permanent sterility is not given for these conditions. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 13
14 Steps to Determine Sexual and Reproductive Assessment (Female) Step 1: Step 2: Step 3: Determine the rating from Table 16.4 (Loss of Function - Sexual and Reproductive - Female). Does the Partially Contributing Table apply? If yes, then apply to rating at Step 1. Determine the Quality of Life rating. Step 4: Add the ratings at Step 2 and Step 3. Step 5: If partial entitlement exists, apply to the rating at Step 4. This is the Disability Assessment. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 14
15 Table Other Impairment - Breasts - Male Only one rating may be given for each entitled condition from Table If more than one rating is applicable for an entitled condition, the ratings are compared and the highest selected. Each bullet ( ) represents one criterion. In order for a rating to be established for Table 16.5, only one criterion must be met at a level of impairment for that rating to be selected. Table Other Impairment - Breasts - Male Rating Criteria Nil Lumpectomy with no sequella; or Gynaecomastia, operated, no sequella. One Gynaecomastia; or Unilateral mastectomy. Four Bilateral mastectomy; or Persistent mammary discharge. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 15
16 Steps to Determine Assessment (Male Breast) Step 1: Step 2: Step 3: Determine the rating from Table 16.5 (Other Impairment - Breasts - Male). Does the Partially Contributing Table apply? If yes, then apply to rating at Step 1. Determine the Quality of Life rating. Step 4: Add the ratings at Step 2 and Step 3. Step 5: If partial entitlement exists, apply to the rating at Step 4. This is the Disability Assessment. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 16
17 Table Other Impairment - Breasts - Female Only one rating may be given for each entitled condition from Table If more than one rating is applicable for an entitled condition, the ratings are compared and the highest selected. Each bullet ( ) represents one criterion. In order for a rating to be established for Table 16.6, only one criterion must be met at a level of impairment for that rating to be selected. Table Other Impairment - Breasts - Female Rating Criteria Nil Lumpectomy with no sequella. Four Partial unilateral mastectomy or segmental resection; or Unilateral mastectomy with reconstructive surgery; or Persistent mammary discharge. Nine Unilateral mastectomy without reconstructive surgery; or Bilateral mastectomy with reconstructive surgery. Thirteen Radical unilateral mastectomy; or Simple bilateral mastectomy without reconstructive surgery. Twenty-six Radical bilateral mastectomy without reconstruction. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 17
18 Steps to Determine Assessment (Female Breast) Step 1: Step 2: Step 3: Determine the rating from Table 16.6 (Other Impairment - Breasts -Female). Does the Partially Contributing Table apply? If yes, then apply to rating at Step 1. Determine the Quality of Life rating. Step 4: Add the ratings at Step 2 and Step 3. Step 5: If partial entitlement exists, apply to the Step 4 rating. This is the Disability Assessment. Veterans Affairs Canada Page 18
Chapter 14 GASTROINTESTINAL IMPAIRMENT
 Chapter 14 GASTROINTESTINAL IMPAIRMENT Introduction This chapter provides criteria for assessing permanent impairment from entitled conditions of the gastrointestinal tract and the accessory organs of
Chapter 14 GASTROINTESTINAL IMPAIRMENT Introduction This chapter provides criteria for assessing permanent impairment from entitled conditions of the gastrointestinal tract and the accessory organs of
Chapter 15 ENDOCRINE AND METABOLIC IMPAIRMENT
 Chapter 15 ENDOCRINE AND METABOLIC IMPAIRMENT Introduction This chapter provides criteria used to rate permanent impairment resulting from endocrine disorders and disorders of metabolism. The endocrine
Chapter 15 ENDOCRINE AND METABOLIC IMPAIRMENT Introduction This chapter provides criteria used to rate permanent impairment resulting from endocrine disorders and disorders of metabolism. The endocrine
HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases
 HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases Urine production Core elements: Glomerulus, proximal and distal convoluted tube, loop of Henle, collecting tubules, ureters, bladder, sphincter, uretra, and out
HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases Urine production Core elements: Glomerulus, proximal and distal convoluted tube, loop of Henle, collecting tubules, ureters, bladder, sphincter, uretra, and out
LENT SOMA SCALE FOR CERVIX CARCINOMA RADIOTHERAPY Lent Soma V5 15/05/01 OBJECTIVE CRITERIA - PART 3
 Hospital Number_ Date of Assessment_ Initials of Researcher_ Uterus/Cervix Pyometria 0 = No pyometria 1 = Asymptomatic Haematometria 0 = No haematometria 1 = Asymptomatic Necrosis 0 = No necrosis 1 = Asymptomatic
Hospital Number_ Date of Assessment_ Initials of Researcher_ Uterus/Cervix Pyometria 0 = No pyometria 1 = Asymptomatic Haematometria 0 = No haematometria 1 = Asymptomatic Necrosis 0 = No necrosis 1 = Asymptomatic
Dr. Aso Urinary Symptoms
 Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
RATIONALE: The organs making up the urinary system consist of the kidneys, bladder, urethra, and ureters.
 Chapter 12 Section Review 12.1 1. A. Kidneys RATIONALE: The renal pelvis receives urine from the kidney, travels through the ureters on the way to the bladder, but urine is formed in the kidney. 2. C.
Chapter 12 Section Review 12.1 1. A. Kidneys RATIONALE: The renal pelvis receives urine from the kidney, travels through the ureters on the way to the bladder, but urine is formed in the kidney. 2. C.
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Learning Objectives Identify signs and symptoms that may indicate presence of UTI (both complicated and uncomplicated) List common causative organisms and risk factors for UTIs
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Learning Objectives Identify signs and symptoms that may indicate presence of UTI (both complicated and uncomplicated) List common causative organisms and risk factors for UTIs
Chapter 47 1/8/2018. Urinary System Disorders. Urinary Tract Infections. Treatment
 Chapter 47 Urinary System Disorders Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common Infection in one area can involve the entire system Microbes enter through the urethra. Catheterization,
Chapter 47 Urinary System Disorders Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common Infection in one area can involve the entire system Microbes enter through the urethra. Catheterization,
Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela
 Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela Microbiology Department Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela Microbiology Department Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia Urinary Tract Infection
BACTERIAL CULTURE, URINE
 789.00-789.09 ABDOMINAL PAIN 789.60-789.69 ABDOMINAL TENDERNESS 276.2 ACIDOSIS 570 ACUTE AND SUBACUTE NECROSIS OF LIVER 580.0-580.9 ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 780.97 ALTERED MENTAL STATUS V44.50-V44.6 ARTIFICIAL
789.00-789.09 ABDOMINAL PAIN 789.60-789.69 ABDOMINAL TENDERNESS 276.2 ACIDOSIS 570 ACUTE AND SUBACUTE NECROSIS OF LIVER 580.0-580.9 ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 780.97 ALTERED MENTAL STATUS V44.50-V44.6 ARTIFICIAL
RECTUM/SIGMOID COLON/BOWEL,
 EMBRACE Follow-up Patient ID: Day Month Year Physician (initials) RECTUM/SIGMOID COLON/BOWEL, morbidity scoring CTC v3.0 1. Diarrhea 1: Increase of
EMBRACE Follow-up Patient ID: Day Month Year Physician (initials) RECTUM/SIGMOID COLON/BOWEL, morbidity scoring CTC v3.0 1. Diarrhea 1: Increase of
University Medical Center Brackenridge Specialty Clinics. Urology Clinic Worksheet
 Urology Clinic Worksheet Distal Stone Thank you for the consult. Please make sure patient is staying well hydrated by drinking at least 2 liters of water/fluids per day, pain is controlled with ibuprofen
Urology Clinic Worksheet Distal Stone Thank you for the consult. Please make sure patient is staying well hydrated by drinking at least 2 liters of water/fluids per day, pain is controlled with ibuprofen
PAINFUL URINATION CAUSES & NATURAL REMEDY. Dr. Bestman Anyatonwu
 LIBRACIN NATURAL MEDICINE IND. LTD PAINFUL URINATION CAUSES & NATURAL REMEDY Dr. Bestman Anyatonwu MEANING Painful urination is a broad term that describes discomfort during urination. This pain may originate
LIBRACIN NATURAL MEDICINE IND. LTD PAINFUL URINATION CAUSES & NATURAL REMEDY Dr. Bestman Anyatonwu MEANING Painful urination is a broad term that describes discomfort during urination. This pain may originate
UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys.
 UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys. 1-3% of Below 1 yr. male: female ratio is 4:1 especially among uncircumcised males,
UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys. 1-3% of Below 1 yr. male: female ratio is 4:1 especially among uncircumcised males,
THE UROLOGY GROUP
 THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
MALE GENITAL SURGICAL PROCEDURES
 Male Genital Surgical ProceduresDecember 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) PENIS Slit of prepuce (complete care) S5 - newborn... 14.35 S58 - infant... 21.50 S59 - adult or child... 30.25 EXCISION Circumcision
Male Genital Surgical ProceduresDecember 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) PENIS Slit of prepuce (complete care) S5 - newborn... 14.35 S58 - infant... 21.50 S59 - adult or child... 30.25 EXCISION Circumcision
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
Section H Bladder and Bowel
 Instructor Guide Section H Bladder and Bowel Objectives State the intent of Section H Bladder and Bowel. Describe how to conduct the assessment for urinary incontinence. Describe how to conduct the assessment
Instructor Guide Section H Bladder and Bowel Objectives State the intent of Section H Bladder and Bowel. Describe how to conduct the assessment for urinary incontinence. Describe how to conduct the assessment
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 9 Urinary Tract and Perineum Key Points 2 9.1 Urinary Bladder & Urinary Retention Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 9 Urinary Tract and Perineum Key Points 2 9.1 Urinary Bladder & Urinary Retention Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder
FISTULA CARE. FISTULA TREATMENT COMPLICATIONS: Reporting Guidelines. Updated 12/12/12
 FISTULA CARE FISTULA TREATMENT COMPLICATIONS: Reporting Guidelines Updated 12/12/12 EngenderHealth, 440 Ninth Avenue, New York, NY 10001, USA Telephone: 212-561-8000; Fax: 212-561-8067; E-mail: fistulacare@engenderhealth.org
FISTULA CARE FISTULA TREATMENT COMPLICATIONS: Reporting Guidelines Updated 12/12/12 EngenderHealth, 440 Ninth Avenue, New York, NY 10001, USA Telephone: 212-561-8000; Fax: 212-561-8067; E-mail: fistulacare@engenderhealth.org
PROSTATIC ARTERY EMBOLISATION (PAE) FOR BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA. A Minimally Invasive Innovative Treatment
 PROSTATIC ARTERY EMBOLISATION (PAE) FOR BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA A Minimally Invasive Innovative Treatment What is the prostate? The prostate is an accessory organ of the male reproductive system.
PROSTATIC ARTERY EMBOLISATION (PAE) FOR BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA A Minimally Invasive Innovative Treatment What is the prostate? The prostate is an accessory organ of the male reproductive system.
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Urology Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Urology Revised: 11/2013 10 questions on this outline on Exam 7 Urinary System performs: Maintains
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Urology Revised: 11/2013 10 questions on this outline on Exam 7 Urinary System performs: Maintains
Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان
 4th stage Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان 11/10/2015 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ureteric, Vesical, & urethral stones Ureteric Calculus Epidemiology like renal stones Etiology like renal stones Risk factors like
4th stage Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان 11/10/2015 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ureteric, Vesical, & urethral stones Ureteric Calculus Epidemiology like renal stones Etiology like renal stones Risk factors like
UTI IN ELDERLY. Zeinab Naderpour
 UTI IN ELDERLY Zeinab Naderpour Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most frequent bacterial infection in elderly populations. While urinary infection in the elderly person is usually asymptomatic, symptomatic
UTI IN ELDERLY Zeinab Naderpour Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most frequent bacterial infection in elderly populations. While urinary infection in the elderly person is usually asymptomatic, symptomatic
Reproductive System: Male
 Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Dr. Syah Mirsya Warli, SpU Dr. Bungaran Sihombing,SpU Div. of Urology, Surgery Dept. Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 Emergency Room Urology Dr. Syah Mirsya Warli, SpU Dr. Bungaran Sihombing,SpU Div. of Urology, Surgery Dept. Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Ref : Clinical Manual of Urology, (Philip M. Hanno
Emergency Room Urology Dr. Syah Mirsya Warli, SpU Dr. Bungaran Sihombing,SpU Div. of Urology, Surgery Dept. Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Ref : Clinical Manual of Urology, (Philip M. Hanno
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
University Gynecologic Oncology Associates
 University Gynecologic Oncology Associates Medical History Form Date: Name: Date of Birth: / / GYNE HISTORY Age of first period? If you no longer have periods, at what age did they stop? Are you pregnant
University Gynecologic Oncology Associates Medical History Form Date: Name: Date of Birth: / / GYNE HISTORY Age of first period? If you no longer have periods, at what age did they stop? Are you pregnant
PRIVILEGE APPLICATION FORM - [Mercy Medical Center]
![PRIVILEGE APPLICATION FORM - [Mercy Medical Center] PRIVILEGE APPLICATION FORM - [Mercy Medical Center]](/thumbs/78/77615248.jpg) Current Privilege Status Key Practitioner's Current Privilege status is signified in ( ) preceding each privilege. G = W = Withdrawn T = Temporary P = With Proctor A = Assist with C = With Consult E =
Current Privilege Status Key Practitioner's Current Privilege status is signified in ( ) preceding each privilege. G = W = Withdrawn T = Temporary P = With Proctor A = Assist with C = With Consult E =
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males
 Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
BCAN Fall Series: Survivorship
 BCAN Fall Series: Survivorship The New Normal after Bladder Removal and Urinary Diversion Vashti Livingston RN, MS, CNS, CWOCN Ambulatory Urology MSKCC NYC livingsv@mskcc.org Disclosure None BCAN Volunteer
BCAN Fall Series: Survivorship The New Normal after Bladder Removal and Urinary Diversion Vashti Livingston RN, MS, CNS, CWOCN Ambulatory Urology MSKCC NYC livingsv@mskcc.org Disclosure None BCAN Volunteer
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation
 Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation Chris Freise, MD Professor of Surgery UCSF Transplant Division Urologic Complications Review of Bladder Anastomosis Complications and Management
Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation Chris Freise, MD Professor of Surgery UCSF Transplant Division Urologic Complications Review of Bladder Anastomosis Complications and Management
SECTION R: UROLOGICAL SURGERY. Class Anae. Visits
 Visits Fee Class Anae 5R Initial Assessment $111.00 -- of a specific condition includes: pertinent family history, patient history, history of presenting complaint, functional enquiry, examination of affected
Visits Fee Class Anae 5R Initial Assessment $111.00 -- of a specific condition includes: pertinent family history, patient history, history of presenting complaint, functional enquiry, examination of affected
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 1/22/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 4 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 1/22/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 4 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Michelle Eslami, M.D., FACP Professor of Medicine Division of Geriatrics David Geffen SOM at UCLA Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) One of most common infections in outpatient and
Urinary Tract Infections Michelle Eslami, M.D., FACP Professor of Medicine Division of Geriatrics David Geffen SOM at UCLA Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) One of most common infections in outpatient and
The Neurogenic Bladder
 The Neurogenic Bladder Outline Brandon Haynes, MD Resident Physician Department of Urology Jelena Svircev, MD Assistant Professor Department of Rehabilitation Medicine Anatomy and Bladder Physiology Bladder
The Neurogenic Bladder Outline Brandon Haynes, MD Resident Physician Department of Urology Jelena Svircev, MD Assistant Professor Department of Rehabilitation Medicine Anatomy and Bladder Physiology Bladder
List of Core and Specialised Procedures for Urology
 List of Core and Specialised Procedures for Urology Appendix 5 The list below of privileges for core and specialised procedures is subject to periodic review by Farrer Park Hospital and/or Farrer Park
List of Core and Specialised Procedures for Urology Appendix 5 The list below of privileges for core and specialised procedures is subject to periodic review by Farrer Park Hospital and/or Farrer Park
1. Spell and define the key terms 2. List and describe the disorders of the. the urinary system and the male reproductive
 CHAPTER 34 Urology Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define the key terms 2. List and describe the disorders of the urinary system and the male reproductive system 3. Describe and explain
CHAPTER 34 Urology Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define the key terms 2. List and describe the disorders of the urinary system and the male reproductive system 3. Describe and explain
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called benign prostatic hypertrophy or benign prostatic obstruction, is a condition in
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called benign prostatic hypertrophy or benign prostatic obstruction, is a condition in
SHABNAM TEHRANI M.D., MPH ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF INFECTIOUS DISEASESE &TROPICAL MEDICINE RESEARCH CENTER, SHAHID BEHESHTI UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL
 URINARY TRACT INFECTION SHABNAM TEHRANI M.D., MPH ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF INFECTIOUS DISEASESE &TROPICAL MEDICINE RESEARCH CENTER, SHAHID BEHESHTI UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES Definition inflammatory
URINARY TRACT INFECTION SHABNAM TEHRANI M.D., MPH ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF INFECTIOUS DISEASESE &TROPICAL MEDICINE RESEARCH CENTER, SHAHID BEHESHTI UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES Definition inflammatory
Urinary System. Dr. Thorson
 Urinary System Dr. Thorson Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, students should be able to Define and spell the terms to learn for this chapter. Describe the purpose and function of the urinary
Urinary System Dr. Thorson Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, students should be able to Define and spell the terms to learn for this chapter. Describe the purpose and function of the urinary
Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring
 Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring Yaacov Frishberg, MD Division of Pediatric Nephrology Shaare Zedek Medical Center Jerusalem, ISRAEL UTI - definitions UTI = growth of bacteria
Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring Yaacov Frishberg, MD Division of Pediatric Nephrology Shaare Zedek Medical Center Jerusalem, ISRAEL UTI - definitions UTI = growth of bacteria
LOGBOOK EBU ORAL EXAM 2015
 LOGBOOK EBU ORAL EXAM 2015 Surname First Name Date of Birth (daymonthyear) MEDICAL DEGREE (MD) UROLOGIST TRAINING: - Training in urology - Training in surgery (as part of the urology training) - Other
LOGBOOK EBU ORAL EXAM 2015 Surname First Name Date of Birth (daymonthyear) MEDICAL DEGREE (MD) UROLOGIST TRAINING: - Training in urology - Training in surgery (as part of the urology training) - Other
4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007)
 4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007) I. Genitourinary Trauma: 1. Goal: The student will be able to demonstrate a basic clinical approach to the management & diagnosis of
4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007) I. Genitourinary Trauma: 1. Goal: The student will be able to demonstrate a basic clinical approach to the management & diagnosis of
Prostate surgery. What is the prostate? What is a TURP? Why is a TURP operation necessary? Deciding to have a TURP operation.
 What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows
What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows
CASES FOR TRAINING OF THE INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY LOWER URINARY TRACT FUNCTION BASIC DATA SET CASE 1
 1 CASES FOR TRAINING OF THE INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY LOWER URINARY TRACT FUNCTION BASIC DATA SET CASE 1 35 years old man, who previously has been completely healthy, was shot twice in the neck
1 CASES FOR TRAINING OF THE INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY LOWER URINARY TRACT FUNCTION BASIC DATA SET CASE 1 35 years old man, who previously has been completely healthy, was shot twice in the neck
Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. ISK
 Urinary Tract Infections Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. ISK 07 08 2009. Getting Clear on the Terminology UTI Cystitis Urosepsis Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Asymptomatic UTI Pyuria Symptomatic UTI Pylonephritis
Urinary Tract Infections Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. ISK 07 08 2009. Getting Clear on the Terminology UTI Cystitis Urosepsis Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Asymptomatic UTI Pyuria Symptomatic UTI Pylonephritis
EMPIRICAL TREATMENT OF SELECT INFECTIONS ADULT GUIDELINES. Refer to VIHA Algorithm for the empiric treatment of Urinary Tract Infection
 URINARY TRACT Refer to VIHA Algorithm for the empiric treatment of Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria on the VIHA Intranet: https://intranet.viha.ca/departments/pharmacy/clinical_pharmacy/pages/infec
URINARY TRACT Refer to VIHA Algorithm for the empiric treatment of Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria on the VIHA Intranet: https://intranet.viha.ca/departments/pharmacy/clinical_pharmacy/pages/infec
Functions of the kidney:
 Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Day 1 Bell Work We will be discussing one of FIVE excretory organs in the human body. We have already studied four of them. The kidneys are considered
 URINARY SYSTEM 1 Day 1 Bell Work We will be discussing one of FIVE excretory organs in the human body. We have already studied four of them. The kidneys are considered the main organ in the excretory system.
URINARY SYSTEM 1 Day 1 Bell Work We will be discussing one of FIVE excretory organs in the human body. We have already studied four of them. The kidneys are considered the main organ in the excretory system.
SECTION H: BLADDER AND BOWEL. H0100: Appliances. Item Rationale Health-related Quality of Life. Planning for Care
 SECTION H: BLADDER AND BOWEL Intent: The intent of the items in this section is to gather information on the use of bowel and bladder appliances, the use of and response to urinary toileting programs,
SECTION H: BLADDER AND BOWEL Intent: The intent of the items in this section is to gather information on the use of bowel and bladder appliances, the use of and response to urinary toileting programs,
Asyntomatic bacteriuria, Urinary Tract Infection
 Asyntomatic bacteriuria, Urinary Tract Infection C. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asyntomatic Bacteriuria in Adults (2005) Pyuria accompanying asymptomatic
Asyntomatic bacteriuria, Urinary Tract Infection C. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asyntomatic Bacteriuria in Adults (2005) Pyuria accompanying asymptomatic
Urinary Adverse Events after Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Urinary Adverse Events after Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Sexual Medicine Society of North America Scottsdale, Arizona 2016 Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial Sloan
Urinary Adverse Events after Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Sexual Medicine Society of North America Scottsdale, Arizona 2016 Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial Sloan
Dr.Nahid Osman Ahmed 1
 1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
Urinary Schistosomiasis: Urological manifestations &complications. Dr MJ Engelbrecht Department of Urology
 Urinary Schistosomiasis: Urological manifestations &complications Dr MJ Engelbrecht Department of Urology Clinical presentation Three clinical stages Swimmer s itch Acute schistosomiasis Chronic schistosomiasis
Urinary Schistosomiasis: Urological manifestations &complications Dr MJ Engelbrecht Department of Urology Clinical presentation Three clinical stages Swimmer s itch Acute schistosomiasis Chronic schistosomiasis
LDR prostate brachytherapy
 LDR prostate brachytherapy Introduction Low dose rate (LDR) prostate brachytherapy is a modern, effective minimally invasive treatment appropriate for many men with early prostate cancer. I perform this
LDR prostate brachytherapy Introduction Low dose rate (LDR) prostate brachytherapy is a modern, effective minimally invasive treatment appropriate for many men with early prostate cancer. I perform this
The Urinary System. Maintenance Systems Unit 5
 The Urinary System Maintenance Systems Unit 5 Basic Functions of the Urinary System Regulates the composition and volume of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of water and solutes. Eliminates
The Urinary System Maintenance Systems Unit 5 Basic Functions of the Urinary System Regulates the composition and volume of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of water and solutes. Eliminates
11/15/2010. Asymptomatic Bacteriuria UTI. Symptomatic UTI. Asymptomatic UTI. Cystitis. Pylonephritis. Pyuria. Urosepsis
 Urinary Tract Infections Renal vein Inferior vena cava Urinary bladder Urethra Renal artery Kidney Aorta Ureter Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. 06 08 2010. (a) Sherwood Fig. 12-6a, p.530 An introduction
Urinary Tract Infections Renal vein Inferior vena cava Urinary bladder Urethra Renal artery Kidney Aorta Ureter Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. 06 08 2010. (a) Sherwood Fig. 12-6a, p.530 An introduction
Patient Expectations Following Greenlight XPS
 Patient Expectations Following Greenlight XPS 1. Hematuria it is common for men to have light pink to cherry red urine following the procedure. This small amount of blood in the urine usually resolves
Patient Expectations Following Greenlight XPS 1. Hematuria it is common for men to have light pink to cherry red urine following the procedure. This small amount of blood in the urine usually resolves
16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children
 16. UTI prognosis 16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children Key question: What is the risk of recurrent UTI in children with no known structural or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract with a first
16. UTI prognosis 16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children Key question: What is the risk of recurrent UTI in children with no known structural or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract with a first
Kimberley A. Schroeder, D.O. 115 Baker Drive Tomball, TX
 Kimberley A. Schroeder, D.O. 115 Baker Drive Tomball, TX 77375 281.290.0531 www.feelwellagain.com FEMALE MEDICAL QUESTIONNAIRE (POSTMENOPAUSAL) NAME: DATE OF BIRTH: CHIEF COMPLAINT What is your primary
Kimberley A. Schroeder, D.O. 115 Baker Drive Tomball, TX 77375 281.290.0531 www.feelwellagain.com FEMALE MEDICAL QUESTIONNAIRE (POSTMENOPAUSAL) NAME: DATE OF BIRTH: CHIEF COMPLAINT What is your primary
Sara Schaenzer Grand Rounds January 24 th, 2018
 Sara Schaenzer Grand Rounds January 24 th, 2018 Bladder Anatomy Ureter Anatomy Areas of Injury Bladder: Posterior bladder wall above trigone Ureter Crosses beneath uterine vessels At pelvic brim when ligating
Sara Schaenzer Grand Rounds January 24 th, 2018 Bladder Anatomy Ureter Anatomy Areas of Injury Bladder: Posterior bladder wall above trigone Ureter Crosses beneath uterine vessels At pelvic brim when ligating
Pediatric Urology. Access Center 24/7 access for referring physicians (866) 353-KIDS (5437)
 Pediatric Urology The Urology practice at Valley Children s provides specialized care for infants, children and adolescents with genital and urological problems. In addition to pediatric urologists, the
Pediatric Urology The Urology practice at Valley Children s provides specialized care for infants, children and adolescents with genital and urological problems. In addition to pediatric urologists, the
AUCKLAND REGIONAL UROLOGY GUIDELINES AND REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS
 AUCKLAND REGIONAL UROLOGY GUIDELINES AND REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS This document outlines the urological conditions currently funded at Auckland District Health Board (ADHB), Counties Manukau District Health
AUCKLAND REGIONAL UROLOGY GUIDELINES AND REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS This document outlines the urological conditions currently funded at Auckland District Health Board (ADHB), Counties Manukau District Health
Bladder replacement in men and women: when and when not? Outline. Continent Diversion History
 1 Bladder replacement in men and women: when and when not? Eila C. Skinner, MD Professor of Clinical Urology Keck USC School of Medicine Outline 1) Selection criteria for orthotopic diversion: Tumor-related
1 Bladder replacement in men and women: when and when not? Eila C. Skinner, MD Professor of Clinical Urology Keck USC School of Medicine Outline 1) Selection criteria for orthotopic diversion: Tumor-related
The number following the procedure code is the TRICARE payment group. KIDNEY
 TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M JUNE 25, 1999 S POLICY CHAPTER 13 SECTION 9.1 ADDENDUM 1, SECTION 8 TRICARE-APPROVED AMBULATORY SURGERY S - URINARY SYSTEM The number following the procedure code
TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M JUNE 25, 1999 S POLICY CHAPTER 13 SECTION 9.1 ADDENDUM 1, SECTION 8 TRICARE-APPROVED AMBULATORY SURGERY S - URINARY SYSTEM The number following the procedure code
Tools for Evaluation. Urodynamics Case Studies. Case 1. Evaluation. Case 1. Bladder Diary SUI 19/01/2018
 Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome.
 Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
PATIENT INFORMATION (Please Print) Patient First Middle Initial Last. Birthdate: / / Patient Financially Responsible Yes No
 PATIENT INFORMATION (Please Print) Date: Patient First Middle Initial Last Birthdate: / / Patient Financially Responsible Yes No Marital Status: Address: City: State: Zip Code: Primary Phone: ( ) (Circle
PATIENT INFORMATION (Please Print) Date: Patient First Middle Initial Last Birthdate: / / Patient Financially Responsible Yes No Marital Status: Address: City: State: Zip Code: Primary Phone: ( ) (Circle
ereferral QUICK REFERENCE: Advice Request Reasons for Referral
 ereferral QUICK REFERENCE: Advice Request Reasons for Referral The following is a list of specialties and reasons for referral that can be used to help you complete the Reason For Referral field when you
ereferral QUICK REFERENCE: Advice Request Reasons for Referral The following is a list of specialties and reasons for referral that can be used to help you complete the Reason For Referral field when you
PATIENT HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE Radiation Oncology
 REVIEWED DATE / INITIALS Safety: Are you at risk for falls? Do you have a Pacemaker? Females; Is there a possibility you may be pregnant? Allergies: If YES, please list medication allergies: Do you have
REVIEWED DATE / INITIALS Safety: Are you at risk for falls? Do you have a Pacemaker? Females; Is there a possibility you may be pregnant? Allergies: If YES, please list medication allergies: Do you have
WJ UROGENITAL SYSTEM. UROLOGY
 WJ UROGENITAL SYSTEM. UROLOGY 1 Societies 11 History Include all aspects 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible 15 Classification.
WJ UROGENITAL SYSTEM. UROLOGY 1 Societies 11 History Include all aspects 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible 15 Classification.
PATIENT HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE Radiation Oncology
 REVIEWED DATE / INITIALS Safety: Yes No Are you at risk for falls? Do you have a Pacemaker? Females; Is there a possibility you may be pregnant? Allergies: Yes No If YES, please list medication allergies:
REVIEWED DATE / INITIALS Safety: Yes No Are you at risk for falls? Do you have a Pacemaker? Females; Is there a possibility you may be pregnant? Allergies: Yes No If YES, please list medication allergies:
Incontinence Patient Information Form
 Incontinence Patient Information Form (To be completed by patient) Before talking with you, the doctor would like some information about your urine leakage. These questions are important for finding out
Incontinence Patient Information Form (To be completed by patient) Before talking with you, the doctor would like some information about your urine leakage. These questions are important for finding out
Urinary System. Unit 6.12 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.12 (7 th Edition)
 Urinary System Unit 6.12 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.12 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the urinary system and their functions. Explain the major functions of the kidneys.
Urinary System Unit 6.12 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.12 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the urinary system and their functions. Explain the major functions of the kidneys.
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE
 TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE A discussion of the operation and the pre and post operative care You and your doctor have considered the possibility that you have a transurethral resection of
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE A discussion of the operation and the pre and post operative care You and your doctor have considered the possibility that you have a transurethral resection of
9/13/2017. Highgate Private Hospital & Whittington Health NHS Trust. London Cancer Urology Guidelines for Target Referrals. Urological Cancer Groups
 London Cancer Urology Guidelines for Target Referrals Mr Paul Erotocritou MBBS BSc MSc, MRCS, FRCS (Urol)Eng Highgate Private Hospital & Whittington Health NHS Trust Urological Cancer Groups 5 groups:
London Cancer Urology Guidelines for Target Referrals Mr Paul Erotocritou MBBS BSc MSc, MRCS, FRCS (Urol)Eng Highgate Private Hospital & Whittington Health NHS Trust Urological Cancer Groups 5 groups:
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System
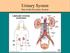 Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
Northeast Ohio Urogynecology Patient History Intake Form. Last Name First Name Age. Date of Birth Race Referring Physician.
 Northeast Ohio Urogynecology Patient History Intake Form Last Name _First Name Age_ Date of Birth Race Referring Physician Reason for Visit: _ Allergies: Preferred Lab (circle): QUEST LABCARE PLUS LABCORP
Northeast Ohio Urogynecology Patient History Intake Form Last Name _First Name Age_ Date of Birth Race Referring Physician Reason for Visit: _ Allergies: Preferred Lab (circle): QUEST LABCARE PLUS LABCORP
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are the nurse providing care for a client reporting symptoms of bloating, irritability,
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are the nurse providing care for a client reporting symptoms of bloating, irritability,
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Event
 Device-associated Events Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: The urinary tract is the most common site of healthcare-associated infection, accounting for more than 30% of
Device-associated Events Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: The urinary tract is the most common site of healthcare-associated infection, accounting for more than 30% of
Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks
 1100 Wayne Ave, Suite 825 Silver Spring, MD 20910 301.273.0570 Fax 301.273.0778 info@augs.org www.augs.org Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks ICD 9 ICD 9 Description ICD 10 Code ICD 10 Description
1100 Wayne Ave, Suite 825 Silver Spring, MD 20910 301.273.0570 Fax 301.273.0778 info@augs.org www.augs.org Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks ICD 9 ICD 9 Description ICD 10 Code ICD 10 Description
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics. Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital 01/02/2018 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms LUTS - one of
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital 01/02/2018 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms LUTS - one of
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
 Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Pelvic Prolapse. A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction
 Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Morbidity Audit and Logbook Tool SNOMED Board Reporting Terms for SET and IMG Urology ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT
 ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT Cystolitholapaxy Cystoscopic removal of foreign body from bladder Cystoscopic removal of ureteric stent Cystoscopy and cystodiathermy Cystoscopy and transurethral biopsy
ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT Cystolitholapaxy Cystoscopic removal of foreign body from bladder Cystoscopic removal of ureteric stent Cystoscopy and cystodiathermy Cystoscopy and transurethral biopsy
Bladder Cancer in Primary Care. Dr Penny Kehagioglou Consultant Clinical Oncologist
 Bladder Cancer in Primary Care Dr Penny Kehagioglou Consultant Clinical Oncologist Objectives Patient presentation in primary care Investigating bladder cancer Management of bladder cancer Differential
Bladder Cancer in Primary Care Dr Penny Kehagioglou Consultant Clinical Oncologist Objectives Patient presentation in primary care Investigating bladder cancer Management of bladder cancer Differential
MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
 MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH INTRODUCTION (1) Part of male sexual reproductive organ Size
MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH INTRODUCTION (1) Part of male sexual reproductive organ Size
NON-Neurogenic Chronic Urinary Retention AUA White Paper
 NON-Neurogenic Chronic Urinary Retention AUA White Paper Great Lakes SUNA Inside Urology March 16, 2018 Michelle J. Lajiness FNP-BC Nurse Practitioner DMC Urology Incidence Really unknown Lack consensus
NON-Neurogenic Chronic Urinary Retention AUA White Paper Great Lakes SUNA Inside Urology March 16, 2018 Michelle J. Lajiness FNP-BC Nurse Practitioner DMC Urology Incidence Really unknown Lack consensus
PROSTATIC EMBOLIZATION FOR BENIGN HYPERPLASIA
 St. Louis Hospital PROSTATIC EMBOLIZATION FOR BENIGN HYPERPLASIA INITIAL CLINICAL RESULTS Faculty of Medical Sciences New University of Lisbon JOÃO PISCO LUÍS CAMPOS PINHEIRO TIAGO BILHIM HUGO RIO TINTO
St. Louis Hospital PROSTATIC EMBOLIZATION FOR BENIGN HYPERPLASIA INITIAL CLINICAL RESULTS Faculty of Medical Sciences New University of Lisbon JOÃO PISCO LUÍS CAMPOS PINHEIRO TIAGO BILHIM HUGO RIO TINTO
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
 KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers. Workbook 13 The digestive system
 NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 13 The digestive system Contents Workbook 13 The digestive system 1 13.1 Aim 3 13.2 Learning outcomes 3 13.3 Digestive system 4 13.4 The endocrine
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 13 The digestive system Contents Workbook 13 The digestive system 1 13.1 Aim 3 13.2 Learning outcomes 3 13.3 Digestive system 4 13.4 The endocrine
CYSTOSCOPY & TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE
 Associates: Dr Kim Pese Dr Kym Horsell Dr Michael Chong Dr Jason Lee The Tennyson Centre Suite 19, First Floor 520 South Road Kurralta Park SA 5037 Appointments: 08 8292 2399 Fax: 08 8292 2388 admin@urologicalsolutions.com.au
Associates: Dr Kim Pese Dr Kym Horsell Dr Michael Chong Dr Jason Lee The Tennyson Centre Suite 19, First Floor 520 South Road Kurralta Park SA 5037 Appointments: 08 8292 2399 Fax: 08 8292 2388 admin@urologicalsolutions.com.au
Anatomy kidney ureters bladder urethra upper lower
 Urinary tract Anatomy The urinary tract consists of the kidney, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Urinary tract infections can be either: upper or lower based primarily on the anatomic location of the infection.
Urinary tract Anatomy The urinary tract consists of the kidney, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Urinary tract infections can be either: upper or lower based primarily on the anatomic location of the infection.
1 Urological evaluation
 Chap01.qxd 6/7/06 9:06 PM Page 1 1 Urological evaluation Hugh N Whitfield Urological complaints The most common urological complaints that trigger the need for referral to a primary care doctor or urological
Chap01.qxd 6/7/06 9:06 PM Page 1 1 Urological evaluation Hugh N Whitfield Urological complaints The most common urological complaints that trigger the need for referral to a primary care doctor or urological
BPH: a present and future perspective on health impact
 BPH: a present and future perspective on health impact Burden of disease in men with moderate LUTS Dalibor Pacík This presentation is financially supported by GlaxoSmithKline. CZ/DUTT/0019/12 Men with
BPH: a present and future perspective on health impact Burden of disease in men with moderate LUTS Dalibor Pacík This presentation is financially supported by GlaxoSmithKline. CZ/DUTT/0019/12 Men with
Medical Management of childhood UTI and VUR. Dr Patrina HY Caldwell Paediatric Continence Education, CFA 15 th November 2013
 Medical Management of childhood UTI and VUR Dr Patrina HY Caldwell Paediatric Continence Education, CFA 15 th November 2013 Terminology According to the current ICCS terminology guidelines Bladder and
Medical Management of childhood UTI and VUR Dr Patrina HY Caldwell Paediatric Continence Education, CFA 15 th November 2013 Terminology According to the current ICCS terminology guidelines Bladder and
