E XTRAVASATIONS from the pelvicalyceal
|
|
|
- Dominick Jordan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VOL. 112, No. 3 PELVICALYCEAL EXTRAVASATIONS* By FILEMON LOPEZ, M.D. BRONX, NEW YORK E XTRAVASATIONS from the pelvicalyceal system, previously considered rare, are being demonstrated with increasing frequency. Some of these extravasations are benign in nature, requiring only a conservative approach to management. However, a number of the conditions associated with pelvicalyceal extravasations may be life-threatening so that prompt diagnosis and treatment are absolutely necessary. The purpose of this paper is to acquaint the radiologist with some of the conditions associated with pelvicalyceal extravasations and to describe the salient roentgen characteristics of the different types of extravasation. Pelvicalyceal extravasations may be classified as follows: I. Spontaneous (renal backftow) A. Acute Obstruction i. Pyelosinus 2. Pyelotubular 3. Pyelolymphatic 4. Pyelointerstitial. Pyelovenous B. Chronic Obstruction i. Retroperitoneal 2. Intraperitoneal II. Post-traumatic extravasations i. Penetrating injury 2. Non-penetrating injury (a) Direct blunt injury (b) Lateral flexion injury 3. Surgical trauma REPORT OF CASES ACUTE URETERAL OBSTRUCTION CASE i. J. M., a 6s year old male, was admitted to the hospital because of sudden onset of right flank pain. Intravenous urography was performed a few hours after the onset of the pain. No radiopaque calculus was noted on the preliminary roentgenogram of the abdomen. The 30 minute urogram (Fig. I) showed indistinct calyces on the right, with extravasations presenting as horn-shaped opacifications adjacent to the calyces. The intrarenal portion of the renal pelvis was exquisitely outlined by contrast medium in the renal pelvis and hilum. The extravasated material was also seen in the periureteral tissues, outlining the wall of the proximal ureter. Dilatation of the right collecting system, with columnization of contrast material down to the ureterovesical junction was observed. A diagnosis of obstructive uropathy due to a calculus with extravasation was made. Twenty-four hours later, the patient was asymptomatic and a repeat urogram showed no abnormality. Comment. This case demonstrates the typical roentgenologic and clinical course of patients with spontaneous extravasation due to acute urinary tract obstruction. A mild degree of dilatation of the collecting system proximal to the level of obstruction is usually noted. Extravasation that occurs in cases of acute renal colic is a means of decompression so that the calyces and renal pelvis are never markedly dilated. Subcapsular collection of contrast material is not usually observed in these patients. The horn-shaped opacities adjacent to the calyces are typical. The differential diagnosis usually includes renal tuberculosis and papillary necrosis. CHRONIC OBSTRUCTION CASE II. J. M., a 68 year old male, was hospitalized because of an enlarging lump in the right groin which was subsequently found to be part of generalized lymphosarcoma. He also complained of a steady right flank pain of to 5 days duration. An enlarged prostate gland was found on physical examination. An intravenous urogram (Fig. 2A) demonstrated bilateral hydronephrosis with fish-hooking of both ureters. On the right, extravasation was noted in the renal sinus and retroperitoneal * Presented at the Seventy-first Annual Meeting of the American Roentgen Ray Society, Miami Beach, Florida, September 29- October 2, From the Departments of Radiology of the Montefiore Hospital and Medical Center, Morrisania Hospital Afliliate, and the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York. 593
2 594 Filemon Lopez Jr IY, 1971 PENETRATING INJURY VIG. I. Case I. Thirty minute urogram shows extravasations presenting as horn-shaped opacifications adjacent to the calyces. Extravasated material is also seen in the periureteral tissues. Dilatation of the right collecting system down to the ureterovesical junction is noted. space. An indentation was present at the base of tile bladder due to the enlarged prostate. The patient was placed on catheter drainage and a repeat urogram (Fig. 2B) 2 weeks later showed marked improvement in the upper tracts with no evidence of hydronephrosis or extravasation. l he patient subsequently died of generalized lymphosarcoma without urinary tract involvemen t. Comment. This case is similar to the previous case except for the presence of chronic urinary tract obstruction secondary to prostatic enlargement. The extravasation was retroperitoneal and the response to conservative management was dramatic. On occasion, in cases of chronic urinary tract obstruction, extravasation can occur in traperitoneally, producing urine ascites. 4 CASE III. L. R., an IS year old female, was hospitalized because of Ilematuria following a stab wound in the left flank. An intravenous urogram (Fig. 3) showed prompt bilateral renal excretion with a moderate degree of ureteropelvic junction obstruction on the right. Retroperitoneal extravasation was noted on tile left, outlining the entire renal pelvis except the inferomedial border, indicating that the laceration was in the renal pelvis close to the ureteropelvic junction. A radiolucent line was observed representing the thickness of the wall of the renal pelvis and proximal ureter. At surgery, the diagnosis of laceration of the left renal pelvis was confirmed. Comment. Penetrating injuries to the pelvicalyceal structures are usually easy to diagnose. The demonstration of a radiolucent stripe representing the wall of the pelvis and1/or ureter, outlined by contrast material both within and around these structures, is pathognomonic of retroperitoneal extravasation (Fig. 4A). The ureter occasionally can be seen in the early phase of the urogram (Fig. 4B) as a lucent tubular defect in the pooi of extravasated contrast medium, another pathognomonic sign of retroperitoneal extravasation. NON-PENETRATING INJURY CASE IV. P. B., a 12 year old girl, was hospitalized following a football injury to the abdomen. Urinalysis showed numerous red blood cells. Intravenous urography demonstrated a large filling defect in the left renal pelvis and ureter (Fig. ), conforming to the contour of these structures. No appreciable dilatation of the upper tracts was present. The mucosa of the renal pelvis and ureter was outlined by contrast medium surrounding the radiolucent filling defect. Intraparenchymal and perihilar extravasations were also noted. A diagnosis of renal injury with blood clots in the collecting system and extrarenal extravasation was made. The patient was treated conservatively and a follow-up examination 2 weeks later showed no extravasations or filling defects in the urinary tract. Comment. Non-penetrating injury to the kidney due to direct blunt trauma is frequently seen in the younger age group. The demonstration of a filling defect that conforms to the
3 OL. 112, No. 3 Pelvicalyceal Extravasations 595 FIG. 2. Case II. (A) Urogram shows bilateral hydronephrosis with fish-hooking of both ureters. Extravasation is seen in the right renal sinus and retroperitoneal space. An indentation at the base of the bladder is demonstrated. (B) Two weeks later, a repeat urogram shows no evidence of extravasation or hydronephrosis. contour of the pelvis, ureter and/or bladder, with a radiopaque mucosal outline giving a double contrast configuration, is pathognomonic of intravasation in the urinary system. Significant dilatation is usually absent in spite of the presence of massive intravasation. This roent- FIG. 3. Case III. Urogram demonstrates bilateral renal excretion with a moderate degree of ureteropelvic junction obstruction on the right. Extravasated contrast material is seen surrounding the renal pelvis except the inferomedial border, indicating that the laceration is in the pelvis close to the ureteropelvic junction. A lucent line is seen (arrow) representing the thickness of the wall of the renal pelvis. 7
4 596 Filemon Lopez JULY, 1971 FIG... This 51 ear old male presented with an acute onset of right flank pain. Urinalysis showed microscopic hematuria. (A) Excretory urogram demonstrates a radiolucent tubular structure in the pool of extravasated contrast medium, indicating retroperitoneal extravasation. An opaque calculus is seen within the ureter causing obstructive uropathv. (B) A 15 minute roentgenogram shows a lucent stripe representing the walls of the pelvis and ureter, outlined by contrast material both within and around these structures. This is another pathognomonic sign of retroperitoneal extravasation. genologic appearance differs from that of penpelvic and peniureteral extravasation, in which the walls of these structures are demonstrated as a radiolucent line.9 LATERAL FLEXION INJURY CASE v. A. L., a io year old boy, was struck on the left flank by a car. Urinalysis was normal. An intravenous urogram (Fig. 6A) revealed a normal left kidney and ureter. On the right, a slight fullness of the collecting system was noted with a cut-off at the level of the ureteropelvic junction. The ureter beyond this point was never visualized. A diagnosis of lateral flexion injury with rupture of the right ureteropelvic junction was made. Right retrograde pvelography (Fig. 6B) was performed on the same day, demonstrating complete laceration of tile ureteropelvic junction with retropenitoneal extravasation. The patient was operated upon and an endto-end anastomosis performed. Follow-up urograms showed no abnormality except for a deformity at the ureteropelvic junction presumably due to the surgical procedure. Comment. This type of kidney injury is very deceiving and can easily be missed if the physician is not alert. Trauma to the flank may cause sudden marked lateral flexion of the body, resulting in stretching of the contralateral ureter and impingement against the transverse process of the upper lumbar vertebrae.7 In these cases, the ureter distal to the laceration is usually not visualized. This type of injury demands immediate surgical intervention. SURGICAL TRAUMA CASE VI. H. H., a 70 year old hypertensive male, was hospitalized after an episode of chest pain, diaphoresis and headache followed by unconsciousness. Intravenous urography was performed to rule out a renal cause for the hypertension. A cyst in the lower pole of the left kidney was found and surgical unroofing of the
5 VoL. 112, No. 3 Pelvicalyceal Extravasations 597.i I cyst was accomplished. A few days postoperatively the patient complained of left flank pain, and another urogram (l ig. 7) was obtained. At this time, extravasation from tile lower pole calyx of the left kidney was observed. The ureter was normal. File patient was treated conservatively and i week later a follow-up urogram demonstrated no extravasation. The patient was discharged very much improved. Comment. Extravasations are not infrequent after renal surgery and are particularly cornl IG. 5. Case IV. The intravenous urogram shows a long filling defect in the left renal pelvis and ureter conforming to the contour of these structures. No appreciable dilatation of the upper tracts is apparent. Intraparenchymal and perihilar extravasation is also demonstrated. 11G. 6. Case v. (4) 1. rogram shows a cut-off at the level of the ureteropelvic junction, and moderate fullness of the collecting system is apparent on the right. The ureter beyond the ureteropelvic juncti()n was never seen. There is minimal retroperitoneal extravasation noted. The left kidney and ureter were normal. (B) Retrograde urogram confirms the presence of ureteropelvic rupture with retropenitoneal extravasation. I FIG. 7. Case vi. Urogram demonstrates extravasation from the lower pole calyx into the retroperitoneal space. No dilatation of the ureter_is apparent.
6 598 Filemon Lopez JULY, 1971 mon after ureteropelvic surgery. As long as the ureter is not obstructed, the extravasation usually terminates spontaneously. In the presence of obstruction, even of the mildest degree, extravasation will continue and an urinoma may develop. DISCUSSION The phenomenon of spontaneous extravasation, formerly considered rare, is seen with increasing frequency as techniques and contrast media improve and the radiologist s awareness increases. Numerous case reports and discussions have appeared in the literature; however, only a few have met with the strict criteria of the diagnosis of spontaneous extravasation as outlined by Schwartz et al. #{176}These include absence of the following : (i ) recent instrumentation; ( 2) a previous surgery; () external trauma; (4) a destructive kidney lesion; () external compression; and (6) pressure necrosis produced by a stone in the pelvis or ureter. Renal backflow or spontaneous extravasation demonstrated du ring intravenous urography refers generally to the escape of contrast material outside the pelvicalyceal system. Spontaneous extravasation may be found in cases ofacute and chronic obstructive uropathy, although it is more frequently observed with acute obstruction. The mechanism of spontaneous extravasation due to acute ureteral obstruction is a sudden increase in intrapelvic pressure, causing rupture ofthe fornix ofone or more calyces.8 The contrast medium mixed with urine then escapes into the renal sinuses and collects in the peripelvic and periureteral areas. Pyelosinus extravasation is the most common type of spontaneous extravasation. The mechanism of pyelovenous backflow, the least common type of spontaneous extravasation, has been demonstrated by Green a al.3 Using microradiologic techniques and cadaver kidneys, they concluded that pyelovenous backflow takes place through rupture of a fornix. The hydronephrotic kidney allows pyelovenous backflow to occur at a much reduced pressure, when compared to a normal kidney. According to these authors, preferential pyelovenous backflow in hydronephrotic kidneys serves as a protective mechanism and may explain induced bacteremia seen in retrograde studies in patients with ureteral obstruction. The disti nction between spontaneous forniceal rupture and an acute rent of the pelvis or ureter, due to trauma, is important because the patients with spontaneous extravasation due to acute obstruction are not as ill as those with acute rent of the pelvis and ureter. Also, conservative management is usually indicated in most cases of spontaneous extravasation, while in cases of acute rent of the pelvis or ureter, surgical intervention is usually required. During intravenous urographv, the ureter is usually demonstrated down to the level of obstruction in cases of spontaneous extravasation. In cases ofacute rent, however, the ureter distal to the rupture is frequently not demonstrated. The relatively benign nature of spontaneous extravasation associated with renal colic is to be differentiated from extravasation due to rupture of the kidney following trauma. In the latter, renal function may be decreased or absent. A 30 second nephrogram may show a peripheral radiolucent line in the kidney due to blood bisecting the cortex.5 Dilatation of the upper tract is uncommon and the extravasation is predomina ntly subcapsular or intraparenchymal. Surgical intervention may be required, whereas it is never necessary in spontaneous extravasation. It should be noted, however, that spontaneous extravasation is not without complications. Hanrow4 described a perinephric abscess secondary to spontaneous urine extravasation associated with renal colic. Other reported complications include peripelvic urine granuloma, fibrolipomatosis, localized retroperitoneal fibrosis, and strictures of the upper ureter and calyceal infundibula. Spontaneous extravasation associated with chronic obstructive uropathy is not common. Urine may leak into the retro-
7 VOL. 112, No. Pelvicalyceal Extravasations 599 peritoneal region, in which instance correction of the obstruction is all that is required to produce relief. Leakage may occur into the peritoneal cavity, producing urine ascites. Spontaneous intraperi toneal extravasation is a potentially lethal condition producing signs ofperitonitis, but seldom causing signs or symptoms to implicate the urinary tract. Emergency laparotomy is frequently required as a therapeutic measure. Most of the reported cases have been in the neonatal age group;4 i i adult cases are also described in the literature.2 SUMMARY The characteristic roentgen features of the different types of pelvicalyceal extravasation are discussed and illustrated. The demonstration of a linear lucent tubular structure or a linear radiolucent stripe during intravenous urography is pathogno-. monic of retroperitoneal extravasation. Spontaneous extravasations due to acute urinary tract obstruction usually are benign and require conservative management. Chronic obstruction associated with intraperitoneal extravasation (urine ascites) and lateral flexion injury to the kidney may be life threatening so that prompt recognition and emergency treatment are mandatory. Other types of post-traumatic extravasation present a fairly characteristic clinicoradiologic picture and management should be individualized. Department of Radiology Montefiore Hospital and Medical Center Bronx, New York RE FERENCES I. BRAUN, W. T. Peripelvic extravasations during intravenous urography. AM. J. ROENTGENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1966, 98, GLEN, S. E. Spontaneous intraperitoneal rupture of hydronephrosis. Brit. 7. Urol., 1969, 4!, GREEN, N., 1INGERHUT, A., and FRENCH, S. Mechanism of renovascular backflow. Radiology, 1969, 92, HARROW, R. B. Urinary extravasation associated with renal colic causing perinephric abscess. AM. J. ROENTGENOL., RAD. THERAPY & Nu- CLEAR MED., 1966, 98, LOPEZ, F. A., STERN, W. Z., SIEGELMAN, S. S., and JACOBSON, H. G. Nephrogram: valuable indicator ofrenal abnormalities. AM. J. ROENT- GENOL., RAD. 1HERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1969, io#{243}, MONCADA, R., WANG, J., and LOVE L. Neonatal ascites associated with urinary outlet obstruction (urines ascites). Radiology, 1968, 9 o, i i NEY, C., and 1 RI EDEN BERG, R. Trauma of ureter. In: Radiographic Atlas of the Genito-Uri. nary System. J. B. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, 1966, pp OLssoN, 0. Studies on backflow in excretion urography. Ada radiol., 1948, Suppl RABINOWITZ, J. A., KELTER, R. J., and WOLF, B. S. Benign peripelvic extravasation associated with renal colic. Radiology, 1966, 86, SCHWARTZ, A., CAINE, M., HERMANN, G., and BI I-FERMANN, W. Spontaneous renal extravasation during intravenous urography. AM. J. ROENTGENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1966, 98,
8 This article has been cited by: 1. Haopeng Pang, Xuefei Dang, Zhenwei Yao, Xiaoyuan Feng, Guangyao Wu Bilateral spontaneous urinary extravasation shown by computed tomography urography in a patient with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Radiology Case Reports 10:4, [CrossRef]
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging
 Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Acute renal colic Radiological investigation in patients with renal colic
 Acute renal colic Radiological investigation in patients with renal colic Mikael Hellström Professor Department of Radiology Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg University 0.9-1.8/1.000 inhabitants
Acute renal colic Radiological investigation in patients with renal colic Mikael Hellström Professor Department of Radiology Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg University 0.9-1.8/1.000 inhabitants
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
An Unexpected Cause Of Spontaneous Perinephric Urinoma: A Case Report. L Chandrasekharan, T Abdl Ghaffar, M Venkatramana, K Mammigatty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 4 Number 1 An Unexpected Cause Of Spontaneous Perinephric Urinoma: A Case Report L Chandrasekharan, T Abdl Ghaffar, M Venkatramana, K Mammigatty Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 4 Number 1 An Unexpected Cause Of Spontaneous Perinephric Urinoma: A Case Report L Chandrasekharan, T Abdl Ghaffar, M Venkatramana, K Mammigatty Citation
Outline. Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system. Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract
 Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning
Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning
Outline. Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system. Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract
 Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract Diagnostic Investigations in Urinary System PLAIN KUB EXCRETORY UROGRAPHY RETROGRADE
Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract Diagnostic Investigations in Urinary System PLAIN KUB EXCRETORY UROGRAPHY RETROGRADE
What s Your Diagnosis??? Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012
 Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012 What s Your Diagnosis??? Signalment Emma, a 9 year old, Female, Spayed, Domestic Short Haired Feline Presenting Complaint Weight loss, vomited the morning of her visit,
Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012 What s Your Diagnosis??? Signalment Emma, a 9 year old, Female, Spayed, Domestic Short Haired Feline Presenting Complaint Weight loss, vomited the morning of her visit,
Pediatric Ure-Radiology*
 Pediatric Ure-Radiology* HERMAN GROSSMAN, M.D. Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina "Routine" radiologic studies do not, often enough, concentrate
Pediatric Ure-Radiology* HERMAN GROSSMAN, M.D. Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina "Routine" radiologic studies do not, often enough, concentrate
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys II. Nephron Unit and Urine Formation
 URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
Uroradiology For Medical Students
 Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 4: Cystography & Urethrography - Part 2 American Urological Association Review Cystography is useful in evaluating the bladder, the urethra and the competence of
Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 4: Cystography & Urethrography - Part 2 American Urological Association Review Cystography is useful in evaluating the bladder, the urethra and the competence of
Role of imaging in evaluation of genitourinary i trauma Spectrum of GU injuries Relevance of imaging findings in determining management Focus on MDCT
 Genitourinary Tract Injuries 6 th Nordic Course Scott D. Steenburg, MD Assistant Professor University of Maryland Department of Radiology Division of Trauma and Emergency Radiology R Adams Cowley Shock
Genitourinary Tract Injuries 6 th Nordic Course Scott D. Steenburg, MD Assistant Professor University of Maryland Department of Radiology Division of Trauma and Emergency Radiology R Adams Cowley Shock
A Case of Calcified Ureteritis Cystica: An Indiscernible Condition from Ureterolithiasis
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 110 (2009) No. 3, p. 245 249 245) A Case of Calcified Ureteritis Cystica: An Indiscernible Condition from Ureterolithiasis Alicioglu B. 1, Kaplan M. 2, Aktoz T. 3, Atakan I.
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 110 (2009) No. 3, p. 245 249 245) A Case of Calcified Ureteritis Cystica: An Indiscernible Condition from Ureterolithiasis Alicioglu B. 1, Kaplan M. 2, Aktoz T. 3, Atakan I.
Imaging the Urogenital System
 maging the Urogenital System Tony Pease, DVM, MS, DACVR Assistant Professor of Radiology North Carolina State University Reading Thrall Chapters 42-46 Prostate Gland Not visible radiographically in normal
maging the Urogenital System Tony Pease, DVM, MS, DACVR Assistant Professor of Radiology North Carolina State University Reading Thrall Chapters 42-46 Prostate Gland Not visible radiographically in normal
URINOMA: A POTENTIAL UROLOGIC EMERGENCY
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 3 SURGERY ORIGINAL PAPERS URINOMA: A POTENTIAL UROLOGIC EMERGENCY Adelina Miron 1,2, D. Puia 1,2, C. Pricop 1,2* Grigore T. Popa University of Medicine
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 3 SURGERY ORIGINAL PAPERS URINOMA: A POTENTIAL UROLOGIC EMERGENCY Adelina Miron 1,2, D. Puia 1,2, C. Pricop 1,2* Grigore T. Popa University of Medicine
CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION
 CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION DR ANAND AARTI 1, DR CHANDAK PRIYA 2,DR SURESH PARVATHY 3 1. PROF AND HOD, DEPARTMENT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS, GOVERNMENT
CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION DR ANAND AARTI 1, DR CHANDAK PRIYA 2,DR SURESH PARVATHY 3 1. PROF AND HOD, DEPARTMENT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS, GOVERNMENT
Uroradiology Tutorial For Medical Students
 Uroradiology Tutorial For Medical Students Lesson 3: Cystography & Urethrography Part 1 American Urological Association Introduction Conventional radiography of the urinary tract includes several diagnostic
Uroradiology Tutorial For Medical Students Lesson 3: Cystography & Urethrography Part 1 American Urological Association Introduction Conventional radiography of the urinary tract includes several diagnostic
R adio logical investigations of urinary system
 R adio logical investigations of urinary system There are 4 main radiological Ix: 1 IVU: Intravenous urography. 2- U/S 3-CT scan 4-Radioisotope scan. Others (not frequently used): MRI, arteriography, antegrade
R adio logical investigations of urinary system There are 4 main radiological Ix: 1 IVU: Intravenous urography. 2- U/S 3-CT scan 4-Radioisotope scan. Others (not frequently used): MRI, arteriography, antegrade
A Giant Hydronephrotic Kidney with Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction with Blunt Renal Trauma in a Boy
 A Giant Hydronephrotic Kidney with Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction with Blunt Renal Trauma in a Boy BY JUNYA TSURUKIRI, HIDEFUMI SANO, YOSUKE TANAKA, TAKAO SATO, HIROKAZU TAGUCHI Abstract An 18-year-old
A Giant Hydronephrotic Kidney with Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction with Blunt Renal Trauma in a Boy BY JUNYA TSURUKIRI, HIDEFUMI SANO, YOSUKE TANAKA, TAKAO SATO, HIROKAZU TAGUCHI Abstract An 18-year-old
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers IMAGING
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers IMAGING
Case Report Spontaneous Ureteral Rupture Diagnosis and Treatment
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2013, Article ID 851859, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/851859 Case Report Spontaneous Ureteral Rupture Diagnosis and Treatment E. Pampana, S. Altobelli, M. Morini,
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2013, Article ID 851859, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/851859 Case Report Spontaneous Ureteral Rupture Diagnosis and Treatment E. Pampana, S. Altobelli, M. Morini,
Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet
 Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet If there was no traumatic injury with PENETRATION of the bladder DO NOT proceed Date of injury: / / Time of injury: Date of hospital arrival: / / Time of hospital arrival:
Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet If there was no traumatic injury with PENETRATION of the bladder DO NOT proceed Date of injury: / / Time of injury: Date of hospital arrival: / / Time of hospital arrival:
Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka. Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1991, 36
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Large Periureteral Lipoma Associa Hydronephrosis. Hayashi, Tomayoshi; Imamura, Atushi Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Large Periureteral Lipoma Associa Hydronephrosis. Hayashi, Tomayoshi; Imamura, Atushi Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA
 Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA Outline I. Introduction highlighting normal renal enhancement physiology including normal
Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA Outline I. Introduction highlighting normal renal enhancement physiology including normal
Lecture 56 Kidney and Urinary System
 Lecture 56 Kidney and Urinary System The adrenal glands are located on the superomedial aspect of the kidney The right diagram shows a picture of the kidney with the abdominal walls and organs removed
Lecture 56 Kidney and Urinary System The adrenal glands are located on the superomedial aspect of the kidney The right diagram shows a picture of the kidney with the abdominal walls and organs removed
D URING the past i8 months at this institution, infusion urography has been
 SEPTEMBER, 1975 ABSTRACT: EVALUATION OF PELVIC MASSES DURING INFUSION EXCRETORY UROGRAPHY* By THOMAS J. IMRAY, M.D. MILWAUKEE, WISCONSIN Infusion excretory urography not only clearly delineates the urinary
SEPTEMBER, 1975 ABSTRACT: EVALUATION OF PELVIC MASSES DURING INFUSION EXCRETORY UROGRAPHY* By THOMAS J. IMRAY, M.D. MILWAUKEE, WISCONSIN Infusion excretory urography not only clearly delineates the urinary
Obstructive Uropathy. PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO. Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta
 Obstructive Uropathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta INTRODUCTION Obstructive uropathy refers to the functional or anatomic obstruction
Obstructive Uropathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta INTRODUCTION Obstructive uropathy refers to the functional or anatomic obstruction
Intrarenal reflux and the scarred kidney
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1974, 49, 531. Intrarenal reflux and the scarred kidney G. L. ROLLESTON, T. M. J. MALING, and C. J. HODSON* From the Department of Radiology, Christchurch Hospital and
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1974, 49, 531. Intrarenal reflux and the scarred kidney G. L. ROLLESTON, T. M. J. MALING, and C. J. HODSON* From the Department of Radiology, Christchurch Hospital and
Jerne Kaz Niels B. Paber, MD* and Michael U. Abutazil, MD**
 Case Report Case Report: Page Kidney Secondary to Severe Ureterohydronephrosis and Perinephric Urinoma with Rupture of Renal Fornix Secondary to a Rare Complication of Ureteral Calculi Jerne Kaz Niels
Case Report Case Report: Page Kidney Secondary to Severe Ureterohydronephrosis and Perinephric Urinoma with Rupture of Renal Fornix Secondary to a Rare Complication of Ureteral Calculi Jerne Kaz Niels
THE operation of reimplantation of the ureter into the bladder has undergone
 REIMPLANTATION OF THE URETER INTO THE BLADDER J. G. WARDEN, M.D., and C. C. HIGGINS, M.D. Department of Urology THE operation of reimplantation of the ureter into the bladder has undergone a stormy course
REIMPLANTATION OF THE URETER INTO THE BLADDER J. G. WARDEN, M.D., and C. C. HIGGINS, M.D. Department of Urology THE operation of reimplantation of the ureter into the bladder has undergone a stormy course
Different successful management strategies for obstructing renal parapelvic cysts
 Title Page Different successful management strategies for obstructing renal parapelvic cysts Sabrina H Rossi 1, Brendan Koo 2, Antony Riddick 1, Nimish Shah 1, Grant D Stewart 1 1 Urology Department, Addenbrooke's
Title Page Different successful management strategies for obstructing renal parapelvic cysts Sabrina H Rossi 1, Brendan Koo 2, Antony Riddick 1, Nimish Shah 1, Grant D Stewart 1 1 Urology Department, Addenbrooke's
Diagnosis & Management of Kidney Trauma. LAU - Urology Residency Program LOP Urology Residents Meeting
 Diagnosis & Management of Kidney Trauma LAU - Urology Residency Program LOP Urology Residents Meeting Outline Introduction Investigation Staging Treatment Introduction The kidneys are the most common genitourinary
Diagnosis & Management of Kidney Trauma LAU - Urology Residency Program LOP Urology Residents Meeting Outline Introduction Investigation Staging Treatment Introduction The kidneys are the most common genitourinary
Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان
 4th stage Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان 11/10/2015 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ureteric, Vesical, & urethral stones Ureteric Calculus Epidemiology like renal stones Etiology like renal stones Risk factors like
4th stage Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان 11/10/2015 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ureteric, Vesical, & urethral stones Ureteric Calculus Epidemiology like renal stones Etiology like renal stones Risk factors like
Sonographic Features of Necrosed Renal Papillae Causing Hydronephrosis
 Case Series Sonographic Features of Necrosed Renal Papillae Causing Hydronephrosis S. Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, MD, DMRD, Sangampalayam Vedhanayagam Kandasamy, MS, MCh, Mylsamy Arul, MS, DNB (Uro), Muniappan
Case Series Sonographic Features of Necrosed Renal Papillae Causing Hydronephrosis S. Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, MD, DMRD, Sangampalayam Vedhanayagam Kandasamy, MS, MCh, Mylsamy Arul, MS, DNB (Uro), Muniappan
이학종분당서울대학교병원. Ultrasound in Urinary Colic
 이학종분당서울대학교병원 Ultrasound in Urinary Colic U l t r a s o u n d i n U r i n a US: Normal Kidney r y C o l i c Contents 1. 1. Definition and clinical consideration 2. 2. Pathophysiology 3. 3. US in in obstructive
이학종분당서울대학교병원 Ultrasound in Urinary Colic U l t r a s o u n d i n U r i n a US: Normal Kidney r y C o l i c Contents 1. 1. Definition and clinical consideration 2. 2. Pathophysiology 3. 3. US in in obstructive
P RIMARY carcinoma of the ureter, once considered rare, makes up about I per
 JANUARY, 1973 TUMORS OF THE URETER PROBLEMS IN DIAGNOSIS By J. J. CANCELMO, JR., M.D., R. C. UHLMAN, M.D., J. L. ESHLEMAN, M.D., andn. F. V1EK, M.D. WAYNE, P RIMARY carcinoma of the ureter, once considered
JANUARY, 1973 TUMORS OF THE URETER PROBLEMS IN DIAGNOSIS By J. J. CANCELMO, JR., M.D., R. C. UHLMAN, M.D., J. L. ESHLEMAN, M.D., andn. F. V1EK, M.D. WAYNE, P RIMARY carcinoma of the ureter, once considered
Radiological changes of renal papillary necrosis
 Kidney International, Vol. 13 (1978), pp. 93-1 06 Radiological changes of renal papillary necrosis NILs LINDVALL Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Karolinska Sjukhuset, Stockholm, Sweden Necrosis of
Kidney International, Vol. 13 (1978), pp. 93-1 06 Radiological changes of renal papillary necrosis NILs LINDVALL Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Karolinska Sjukhuset, Stockholm, Sweden Necrosis of
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations
 Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
 Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Clinical aspects in urogenital injuries
 Clinical aspects in urogenital injuries Rolf Wahlqvist Oslo Urological University Clinic Aker University Hospital Nordic Rad.2008 1 Urogenital injuries in trauma patients Renal injury Ureteral injury (infrequent/iatrogenic)
Clinical aspects in urogenital injuries Rolf Wahlqvist Oslo Urological University Clinic Aker University Hospital Nordic Rad.2008 1 Urogenital injuries in trauma patients Renal injury Ureteral injury (infrequent/iatrogenic)
Canadian Undergraduate Urology Curriculum (CanUUC): Genitourinary Trauma. Last reviewed June 2014
 Canadian Undergraduate Urology Curriculum (CanUUC): Genitourinary Trauma Last reviewed June 2014 Session Objectives 1. Recognize hematuria as the cardinal symptom of urinary tract trauma. 1. Outline the
Canadian Undergraduate Urology Curriculum (CanUUC): Genitourinary Trauma Last reviewed June 2014 Session Objectives 1. Recognize hematuria as the cardinal symptom of urinary tract trauma. 1. Outline the
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY
 RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
Pelvic lipomatosis. Case report
 Pelvic lipomatosis Case report Sebastian A. Cook, M.D.* Kuniaki Hayashi, M.D.f Anthony F. Lalli, M.D. Division of Radiology * Fellow, Division of Radiology. t Special Fellow, Division of Radiology. Since
Pelvic lipomatosis Case report Sebastian A. Cook, M.D.* Kuniaki Hayashi, M.D.f Anthony F. Lalli, M.D. Division of Radiology * Fellow, Division of Radiology. t Special Fellow, Division of Radiology. Since
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93
 Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Scintiphotography Transplants
 Scintiphotography Transplants In Evaluation of Renal HALCOTT T. HADEN, M.D. Associate Professor of Radiology and Medicine, Chief. Nuclear Medicine Section, McGuire VA Hospital, Richmond. Virginia Renal
Scintiphotography Transplants In Evaluation of Renal HALCOTT T. HADEN, M.D. Associate Professor of Radiology and Medicine, Chief. Nuclear Medicine Section, McGuire VA Hospital, Richmond. Virginia Renal
Traumatic Renocaval Fistula With Pseudoaneurysm Leading To Renal Atrophy
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 6 Number 2 Traumatic Renocaval Fistula With Pseudoaneurysm Leading To Renal Atrophy M Kukkady, A Deena, S Raj, Ramachandra Citation M Kukkady, A Deena,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 6 Number 2 Traumatic Renocaval Fistula With Pseudoaneurysm Leading To Renal Atrophy M Kukkady, A Deena, S Raj, Ramachandra Citation M Kukkady, A Deena,
Genitourinary Trauma Introduction GU Trauma overlooked
 Genitourinary Trauma Introduction GU Trauma overlooked 10-20% of all injured patients Long term morbidity Impotence Incontinence Life-threatening injuries first Urethral Injury Plan Bladder Injury Kidney
Genitourinary Trauma Introduction GU Trauma overlooked 10-20% of all injured patients Long term morbidity Impotence Incontinence Life-threatening injuries first Urethral Injury Plan Bladder Injury Kidney
already in the operating room.(0 Ultrasonography (US) has also been found to be very useful in the early evaluation
 Pictorial Essay Singapore Med J 2010, 51(6) 68 CME Article Computed tomography of blunt renal trauma Razali M R, Azian A A, Am ran A R, Azlin S ABSTRACT Renal injury is observed in 10 percent of cases
Pictorial Essay Singapore Med J 2010, 51(6) 68 CME Article Computed tomography of blunt renal trauma Razali M R, Azian A A, Am ran A R, Azlin S ABSTRACT Renal injury is observed in 10 percent of cases
Contents. Review anatomy of the urinary tract Imaging modalities
 Contents Review anatomy of the urinary tract Imaging modalities The Urinary Tract Kidneys ตาแหน งไต (position) อย ใน retroperitoneum ระด บ T12-L3 โดยไต ขวาจะม ระด บตากว าไตซ ายเล กน อย ร ปร าง (shape)
Contents Review anatomy of the urinary tract Imaging modalities The Urinary Tract Kidneys ตาแหน งไต (position) อย ใน retroperitoneum ระด บ T12-L3 โดยไต ขวาจะม ระด บตากว าไตซ ายเล กน อย ร ปร าง (shape)
Urogenital Injuries The role of radiology
 Urogenital Injuries The role of radiology NORDTER 7 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course Helsinki, Finland May 21-24, 2012 Johann Baptist Dormagen, MD, PhD Oslo University Hospital, Norway Kidney injuries
Urogenital Injuries The role of radiology NORDTER 7 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course Helsinki, Finland May 21-24, 2012 Johann Baptist Dormagen, MD, PhD Oslo University Hospital, Norway Kidney injuries
Imaging spectrum of genitourinary tuberculosis: Our experience at a tertiary care centre of a third world country
 Imaging spectrum of genitourinary tuberculosis: Our experience at a tertiary care centre of a third world country Poster No.: C-361 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary Authors:
Imaging spectrum of genitourinary tuberculosis: Our experience at a tertiary care centre of a third world country Poster No.: C-361 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary Authors:
IMAGING OF THE UROGENITAL TRACT
 IMAGING OF THE UROGENITAL TRACT 1 A) URINARY TRACT There are many methods of imaging the urinary tract but plain abdominal X-ray and ultrasound scan are usually done first in most cases, especially in
IMAGING OF THE UROGENITAL TRACT 1 A) URINARY TRACT There are many methods of imaging the urinary tract but plain abdominal X-ray and ultrasound scan are usually done first in most cases, especially in
Functions of the kidney:
 Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Excretory Cystograms After Voiding
 July, 1947 17 Excretory Cystograms After Voiding JAMES R. DILLON,* M.D., Sani Franicisco Y ANY pathological conditions of the upper urinary tract and bladder can be diagnosed and differentiated by excretory
July, 1947 17 Excretory Cystograms After Voiding JAMES R. DILLON,* M.D., Sani Franicisco Y ANY pathological conditions of the upper urinary tract and bladder can be diagnosed and differentiated by excretory
Chapter IV. Angionephrography in Simple Renal Cysts
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Chapter IV. Angionephrography in Simple Renal Cysts To cite this article: (1957) Chapter IV. Angionephrography
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Chapter IV. Angionephrography in Simple Renal Cysts To cite this article: (1957) Chapter IV. Angionephrography
ISPUB.COM. Traumatic Uretero-Pelvic Junction Disruption. G Kraushaar, S Harder, K Visvanathan INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 4 Number 1 Traumatic Uretero-Pelvic Junction Disruption G Kraushaar, S Harder, K Visvanathan Citation G Kraushaar, S Harder, K Visvanathan. Traumatic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 4 Number 1 Traumatic Uretero-Pelvic Junction Disruption G Kraushaar, S Harder, K Visvanathan Citation G Kraushaar, S Harder, K Visvanathan. Traumatic
SciFed Journal of Public Health. Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature
 SciFed Journal of Public Health Case Report Open Access Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature * Yasin Idweini * Chairperson of Urology Department
SciFed Journal of Public Health Case Report Open Access Endoscopic Management of Obstetrical Uretero-Uterine Fistula. Case Report and Review of Literature * Yasin Idweini * Chairperson of Urology Department
Question 2. What percentage of abdominal trauma involve the kidney? a) 5 % b) 10% c) 15 % d) 20 %
 Quiz Question 1 After injecting 2ml/kg of contrast for a patient needing a single-shot IVP before kidney exploration, What is the best turnaround time to take the X-ray? a) 3 minutes b) 5 minutes c) 10
Quiz Question 1 After injecting 2ml/kg of contrast for a patient needing a single-shot IVP before kidney exploration, What is the best turnaround time to take the X-ray? a) 3 minutes b) 5 minutes c) 10
Hydronephrosis. Nephrosis. Refers to the kidney
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydro Nephrosis Refers to water or fluid Refers to the kidney A build-up of fluid (urine) in the kidney is the medical term for a build-up of urine in the kidney. As the urine builds
What is hydronephrosis? Hydro Nephrosis Refers to water or fluid Refers to the kidney A build-up of fluid (urine) in the kidney is the medical term for a build-up of urine in the kidney. As the urine builds
Obstructive Nephropathy
 Obstructive Nephropathy Liza A. Lucero RN, FNP-C, MSN Renal Medicine Associates Conflicts No conflict of interests Obstructive Nephropathy Objectives Definition of Obstructive Nephropathy Causes Clinical
Obstructive Nephropathy Liza A. Lucero RN, FNP-C, MSN Renal Medicine Associates Conflicts No conflict of interests Obstructive Nephropathy Objectives Definition of Obstructive Nephropathy Causes Clinical
UROLOGIC TRAUMA. Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 UROLOGIC TRAUMA Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara UROLOGIC TRAUMA Renal trauma Ureteral injury Bladder injury Urethral injury Injury to external genitalia
UROLOGIC TRAUMA Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara UROLOGIC TRAUMA Renal trauma Ureteral injury Bladder injury Urethral injury Injury to external genitalia
A Z OF ABDOMINAL RADIOLOGY
 Z OF BDOMINL RDIOLOGY bdominal trauma to Z of bdominal Radiology Clinical characteristics general discussion, followed by organ-specific summaries, is given below. bdominal trauma is managed as part of
Z OF BDOMINL RDIOLOGY bdominal trauma to Z of bdominal Radiology Clinical characteristics general discussion, followed by organ-specific summaries, is given below. bdominal trauma is managed as part of
THE NATURAL HISTORY OF THE UPPER RENAL TRACTS IN ADULTS FOLLOWING URETERO- ILEAL DIVERSION (BRICKER PROCEDURE)*
 DECEMBER, 1975 THE NATURAL HISTORY OF THE UPPER RENAL TRACTS IN ADULTS FOLLOWING URETERO- ILEAL DIVERSION (BRICKER PROCEDURE)* By PHILIP STANLEY, M.R.C.P., F.R.C.R.,f J. DUNCAN CRAVEN, M.R.C.P., F.R.C.R.,
DECEMBER, 1975 THE NATURAL HISTORY OF THE UPPER RENAL TRACTS IN ADULTS FOLLOWING URETERO- ILEAL DIVERSION (BRICKER PROCEDURE)* By PHILIP STANLEY, M.R.C.P., F.R.C.R.,f J. DUNCAN CRAVEN, M.R.C.P., F.R.C.R.,
Radiographic Procedures III (RAD 228)
 Radiographic Procedures III (RAD 228) Urinary System RADIOGRAPHIC EXAMINATIONS Urinary System Antegrade Exam IVU Functional test Hypertensive evaluation as per protocol Retrograde Exams Retrograde Urography
Radiographic Procedures III (RAD 228) Urinary System RADIOGRAPHIC EXAMINATIONS Urinary System Antegrade Exam IVU Functional test Hypertensive evaluation as per protocol Retrograde Exams Retrograde Urography
Case Report Spontaneous Pelvic Rupture as a Result of Renal Colic in a Patient with Klinefelter Syndrome
 Volume 2013, Article ID 374973, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/374973 Case Report Spontaneous Pelvic Rupture as a Result of Renal Colic in a Patient with Klinefelter Syndrome Sergey Reva and Yuri
Volume 2013, Article ID 374973, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/374973 Case Report Spontaneous Pelvic Rupture as a Result of Renal Colic in a Patient with Klinefelter Syndrome Sergey Reva and Yuri
By GEORGE E. NELIGAN, M.C., M.A., B.M,, B.Ch. (Oxon.), F.R.C.S. (Swrgeon with charge of Out-patients and Surgeon in charge of the Genito-Urinary
 426 POST-GRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL November, 1935 RENAL TUMOURS. By GEORGE E. NELIGAN, M.C., M.A., B.M,, B.Ch. (Oxon.), F.R.C.S. (Swrgeon with charge of Out-patients and Surgeon in charge of the Genito-Urinary
426 POST-GRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL November, 1935 RENAL TUMOURS. By GEORGE E. NELIGAN, M.C., M.A., B.M,, B.Ch. (Oxon.), F.R.C.S. (Swrgeon with charge of Out-patients and Surgeon in charge of the Genito-Urinary
Five Views of Transitional Cell Carcinoma: One Man s Journey
 September 2006 Five Views of Transitional Cell Carcinoma: One Man s Journey Amsalu Dabela, Harvard Medical School III Outline Overview: Renal Anatomy Our Patient s Story Diagnostic Imaging Studies Appearance
September 2006 Five Views of Transitional Cell Carcinoma: One Man s Journey Amsalu Dabela, Harvard Medical School III Outline Overview: Renal Anatomy Our Patient s Story Diagnostic Imaging Studies Appearance
Case MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve
 Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
Interventional management of postoperative ureteric complications after pelvic surgery
 Interventional management of postoperative ureteric complications after pelvic surgery Poster No.: C-0169 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Tabashy, A. Hamed, S. El-Sebai; Cairo/EG
Interventional management of postoperative ureteric complications after pelvic surgery Poster No.: C-0169 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Tabashy, A. Hamed, S. El-Sebai; Cairo/EG
Separating and Distorted Nephroliths Signs of Renal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 203-208 203 Separating and Distorted Nephroliths Signs of Renal Squamous Cell Carcinoma TZE-YU LEE SHEUNG-FAT KO CHUNG-CHENG HUANG YU-FENG CHENG Department of Radiology, Chang Gung
Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 203-208 203 Separating and Distorted Nephroliths Signs of Renal Squamous Cell Carcinoma TZE-YU LEE SHEUNG-FAT KO CHUNG-CHENG HUANG YU-FENG CHENG Department of Radiology, Chang Gung
Abdominal ultrasound:
 Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
L. Alexandre Frigini MD; Aaron Thomas, MD; Veronica Lenge de Rosen, MD
 Computed Tomography Urography (CTU) for Evaluation of Asymptomatic microscopic hematuria. Is intravenous contrast administration warranted for all patients? A retrospective evaluation utilizing ACR s Appropriateness
Computed Tomography Urography (CTU) for Evaluation of Asymptomatic microscopic hematuria. Is intravenous contrast administration warranted for all patients? A retrospective evaluation utilizing ACR s Appropriateness
Unenhanced Spiral CT in Acute Ureteral Colic: A Replacement for Excretory Urography?
 Unenhanced Spiral CT in cute Ureteral Colic: Replacement for Excretory Urography? Jeong-h Ryu, MD 1 ohyun Kim, MD 1 Yong Hwan Jeon, MD 1 Jongmee Lee, MD 1 Jin-Wook Lee, MD 1 Seong Soo Jeon, MD 2 Kwan Hyun
Unenhanced Spiral CT in cute Ureteral Colic: Replacement for Excretory Urography? Jeong-h Ryu, MD 1 ohyun Kim, MD 1 Yong Hwan Jeon, MD 1 Jongmee Lee, MD 1 Jin-Wook Lee, MD 1 Seong Soo Jeon, MD 2 Kwan Hyun
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 1/22/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 4 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 1/22/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 4 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Cystic Ureteritis: a very rare condition
 Cystic Ureteritis: a very rare condition Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit V. Vallini, N. Armillotta, D. Caramella, C. Bartolozzi; Pisa/IT Infection,
Cystic Ureteritis: a very rare condition Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit V. Vallini, N. Armillotta, D. Caramella, C. Bartolozzi; Pisa/IT Infection,
Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1
 Contributions Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1 Gregory P. Borkowski, M.D. Craig R. George, M.D. Peter B. O'Donovan, M.D. While excretory urography has been useful in the evaluation
Contributions Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1 Gregory P. Borkowski, M.D. Craig R. George, M.D. Peter B. O'Donovan, M.D. While excretory urography has been useful in the evaluation
CODING COMPANION. Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement. Sample page
 Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2020 CODING COANION Power up your coding optum360coding.com Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Resequencing
Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2020 CODING COANION Power up your coding optum360coding.com Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Resequencing
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY
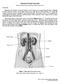 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan.
 CONGENITAL SEMINAL VESICLE CYST ASSOCIATED WITH IPSILATERAL RENAL AGENESIS MIMICKING BLADDER OUTLET OBSTRUCTION: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Chien-Chang Kao, 1 Ching-Jiunn Wu, 2 Guang-Huan
CONGENITAL SEMINAL VESICLE CYST ASSOCIATED WITH IPSILATERAL RENAL AGENESIS MIMICKING BLADDER OUTLET OBSTRUCTION: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Chien-Chang Kao, 1 Ching-Jiunn Wu, 2 Guang-Huan
Renal trauma: What the radiologist needs to know
 Renal trauma: What the radiologist needs to know Poster No.: C-1519 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Roriz, I. Abreu, P. Belo Soares, F. Caseiro Alves ; 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 Guimarães/PT,
Renal trauma: What the radiologist needs to know Poster No.: C-1519 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Roriz, I. Abreu, P. Belo Soares, F. Caseiro Alves ; 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 Guimarães/PT,
EVALUATION OF SUSPECTED RENAL COLIC PATIENTS WITH UNENHANCED LOW-DOSE MULTI-DETECTOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
 190 EAST AFRICAN MEDICAL JOURNAL April 2009 East African Medical Journal Vol. 85 No. 4 April 2009 EVALUATION OF SUSPECTED RENAL COLIC PATIENTS WITH UNENHANCED LOW-DOSE MULTI-DETECTOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
190 EAST AFRICAN MEDICAL JOURNAL April 2009 East African Medical Journal Vol. 85 No. 4 April 2009 EVALUATION OF SUSPECTED RENAL COLIC PATIENTS WITH UNENHANCED LOW-DOSE MULTI-DETECTOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
 1 2 Infertile women are seven to ten times more likely to have endometriosis than their fertile 3 The mechanism by which endometriosis develops is unknown Theories for the histogenesis of endometriosis
1 2 Infertile women are seven to ten times more likely to have endometriosis than their fertile 3 The mechanism by which endometriosis develops is unknown Theories for the histogenesis of endometriosis
A Case Report of Acute Renal Artery Occlusion Mimicking Acute Appendicitis
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 7 Number 1 A Case Report of Acute Renal Artery Occlusion Mimicking Acute Appendicitis S Abouel-Enin, A Douglas, R Morgan Citation S Abouel-Enin, A Douglas,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 7 Number 1 A Case Report of Acute Renal Artery Occlusion Mimicking Acute Appendicitis S Abouel-Enin, A Douglas, R Morgan Citation S Abouel-Enin, A Douglas,
I N A previous paper3 extensive forms of renal papillary necrosis from analgesic
 VoL. No. 2 EARLY FORMS OF RENAL PAPILLARY NECROSIS* By BENEDICT R. HARROW, M.D. MIAMI, I N A previous paper3 extensive forms of renal papillary necrosis from analgesic abuse and from diabetes were described
VoL. No. 2 EARLY FORMS OF RENAL PAPILLARY NECROSIS* By BENEDICT R. HARROW, M.D. MIAMI, I N A previous paper3 extensive forms of renal papillary necrosis from analgesic abuse and from diabetes were described
Nephrographic and Pyelographic Analysis of CT Urography: Principles, Patterns, and Pathophysiology
 Genitourinary Imaging Review Wolin et al. CT Urography Principles, Patterns, and Genitourinary Imaging Review FOCUS ON: Ely A. Wolin 1 David S. Hartman J. Ryan Olson Wolin EA, Hartman DS, Olson JR Keywords:
Genitourinary Imaging Review Wolin et al. CT Urography Principles, Patterns, and Genitourinary Imaging Review FOCUS ON: Ely A. Wolin 1 David S. Hartman J. Ryan Olson Wolin EA, Hartman DS, Olson JR Keywords:
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL), as primary. Subcapsular Kidney Urinoma After Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy. Case Report
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY CASE REPORTS Volume 3.1, 2017 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 52 56 DOI: 10.1089/cren.2017.0011 Case Report Subcapsular Kidney Urinoma After Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy Eugenio Di Grazia,
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY CASE REPORTS Volume 3.1, 2017 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 52 56 DOI: 10.1089/cren.2017.0011 Case Report Subcapsular Kidney Urinoma After Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy Eugenio Di Grazia,
Title with transitional cell carcinoma: a. Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1992), 38(6):
 Title Primary localized amyloidosis of th with transitional cell carcinoma: a Author(s) Shiramizu, Miki; Nakamura, Kaoru; B Yoji; Kinoshita, Hidechika Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1992), 38(6): 699-702 Issue Date
Title Primary localized amyloidosis of th with transitional cell carcinoma: a Author(s) Shiramizu, Miki; Nakamura, Kaoru; B Yoji; Kinoshita, Hidechika Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1992), 38(6): 699-702 Issue Date
Spectrum of High-Resolution Sonographic Features of Urinary Tuberculosis
 Article Spectrum of High-Resolution Sonographic Features of Urinary Tuberculosis S. Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, MD, DMRD, Sangampalayam V. Kandasamy, MS, MCh, Mylsamy Arul, MS, DNB, Muniappan Prabhakar, MS,
Article Spectrum of High-Resolution Sonographic Features of Urinary Tuberculosis S. Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, MD, DMRD, Sangampalayam V. Kandasamy, MS, MCh, Mylsamy Arul, MS, DNB, Muniappan Prabhakar, MS,
Forms: Etiology ureter-occlusion! Ureter-occlusion
 Surgical anatomy Surgery of the Kidney Dr. T. Németh, DVM, Ph.D Surgical Diseases of the Kidney Hydronephrosis Renal injuries Surgical Diseases of the Kidney Hydronephrosis Renal injuries Hydronephrosis
Surgical anatomy Surgery of the Kidney Dr. T. Németh, DVM, Ph.D Surgical Diseases of the Kidney Hydronephrosis Renal injuries Surgical Diseases of the Kidney Hydronephrosis Renal injuries Hydronephrosis
PICTORIAL ESSAY. Experiences of using a single post-contrast CT scan of the urinary tract after triphasic contrast injection
 Experiences of using a single post-contrast CT scan of the urinary tract after triphasic contrast injection P C Pretorius, FCRad (Diag) SA Drs Visser, Erasmus, Vawda & Partners, Port Elizabeth Corresponding
Experiences of using a single post-contrast CT scan of the urinary tract after triphasic contrast injection P C Pretorius, FCRad (Diag) SA Drs Visser, Erasmus, Vawda & Partners, Port Elizabeth Corresponding
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
The Kidneys. (L., ren; Gk, nephros; hence the adjectives renal and nephric) & Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands. Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MBChB
 The Kidneys (L., ren; Gk, nephros; hence the adjectives renal and nephric) & Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MBChB Functions of Urinary System Regulate electrolytes (K+, Na+, etc) Regulate
The Kidneys (L., ren; Gk, nephros; hence the adjectives renal and nephric) & Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MBChB Functions of Urinary System Regulate electrolytes (K+, Na+, etc) Regulate
Latrogenic Injuries of Renal Pelvis and Ureter Following Open Surgery for Urolithiasis
 Latrogenic Injuries of Renal Pelvis and Ureter Following Open Surgery for Urolithiasis Abstract M. Naeem,K. Anwar ( Department of Urology, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Objective:
Latrogenic Injuries of Renal Pelvis and Ureter Following Open Surgery for Urolithiasis Abstract M. Naeem,K. Anwar ( Department of Urology, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Objective:
Urinary system Ultrasound (Renal & Urinary bladder)
 Urinary system Ultrasound (Renal & Urinary bladder) Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc.Phd ISRRT Associate Member Lecturer (National university) Reporting Sonographer (PHC) Objective By
Urinary system Ultrasound (Renal & Urinary bladder) Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc.Phd ISRRT Associate Member Lecturer (National university) Reporting Sonographer (PHC) Objective By
2. Blunt abdominal Trauma
 Abdominal Trauma 1. Evaluation and management depends on: a. Mechanism (Blunt versus Penetrating) b. Injury complex in addition to abdomen c. Haemodynamic stability assessment: i. Classically patient s
Abdominal Trauma 1. Evaluation and management depends on: a. Mechanism (Blunt versus Penetrating) b. Injury complex in addition to abdomen c. Haemodynamic stability assessment: i. Classically patient s
Cystitis cystica is a rare chronic reactive inflammatory
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY CASE REPORTS Volume 3.1, 2017 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 34 38 DOI: 10.1089/cren.2017.0010 Case Report Cystitis Cystica as a Large Solitary Bladder Cyst Stephanie Potts, MBChB and
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY CASE REPORTS Volume 3.1, 2017 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 34 38 DOI: 10.1089/cren.2017.0010 Case Report Cystitis Cystica as a Large Solitary Bladder Cyst Stephanie Potts, MBChB and
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen. Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university
 US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols
 Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
