الله الر ح م ن الر ح يم مسب
|
|
|
- Barrie Watson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 بسم رلا هللارلا هللا This is the second histology lecture in the GI system. In this lecture, we will discuss the histology of the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine so prepare yourself.this sheet only covers what the doctor said in his lecture; so, refer to his slides as you read this sheet. thnx Histology of the Esophagus - Esophagus: it is a muscular tube, its length is about 25cm. - from the incisor to the cardia of the stomach it takes about 45cm. - this is important for the gastroscope. gastroscope is divided as 10,15,20,25.. ect cm. - so when the Dr. sees it s now 45cm at the incisors, he knows that it reached reached the cardia of the stomach. - Histologically, the layers of the esophagus are: mucosa, sub-mucosa, muscularis externa(muscular layer) and connective tissue (adventitia or serosa) - Serosa covers about 1.2 cm of ir, which is the only part of esophagus in the abdominal cavity, it mostly lies in neck and thorax. For the esophagus, these are: 1-Mucosa, which consist of: -lining epithelium: stratified squamous non-keratinized. -lamina propria :loose connective tissue, it contains lymphatics, blood vessels and the most important content is the glands,so called esophageal cardiac gland (called cardiac in relation to the 1 st part of the stomach; the cardia) and its very common in the lower third before the stomach which has gastric glands in its lamina propria also. - In histology they re no abrupt changes in the structure of connected tissues, that s why the histological structure of the lower third of esophagus is so similar to that of the stomach. -Muscularis mucosa: which is basically two ribbons of smooth muscle (outerlongitudinal, inner-circular) but because it's very thin, may not be visible... not really well-developed here as in other organs. 2- Submucosa: its significance in GI tract, contains lymphatics, blood vessels and in some organs like the esophagus it has glands. most of the sub-mucosa of the esophagus contains esophageal glands proper, we can find them in the upper, middle, and lower thirds (the lower third also contains cardiac gland in its lamina propria). 1
2 3-Muscularis externa: in the GI tract this layer is divided into outer longitudinal and inner circular, between them is the myenteric plexus or Auerbach's plexus (parasympathetic and sympathetic). In physiology they consider it a separate nervous system and depend on reflex, but here in anatomy the parasympathetic part is connected to the CNS, it s secretomotor for glands and stimulate smooth muscle peristaltic movement. while the sympathetic is vasomotor for blood vessels and cause vasoconstriction. 4- Adventitia: Connective tissue found in most of the esophagus (ex: neck, thorax and the small part in the abdomen after it pierces the diaphragm through an opening called esophageal orifices,that s located one inch to the left at the level of T10, carried with the esophagus through this opening the two vagi (right & left), but when they enter the diaphragm they become anterior & posterior. Now the Dr. gives a brief explanation about this pic. The type of secretion for esophageal gland is seromucous. The type of glands is tubular (may be straight or branched) In the esophagus, the upper third is voluntary ( with striated muscle), the middle third contains both smooth and striated muscle cells, while the lower third has only smooth muscle cells. therefore, histologically you can determine which area of the esophagus you're looking at (upper, middle,or lower third ) according to the type of muscle cells you identify. Stomach : divided into 4 parts : 1- fundus 2- cardia: which works as a physiological sphincter because it prevents regurgitation of the chyme, but NOT an anatomical one, because there is no thickening in the smooth muscle layer. 3-body 4-pylorus (pyloric canal & pyloric sphincter ). NOTE :Histologically,the fundus and body are identical but they are different from the cardia and pylorus. 2
3 - Mucosa of stomach contains 4 types of cells: 1- Parietal cells for secreting HCL and intrinsic factor ( required for absorption of vitamin B12 in the ileum. 2- Chief cells: secrete pepsinogen,which is converted into pepsin, and gastric lipase. 3- Mucous cells: secrete the mucous 4- Gastrin cells (endocrine cells) : secrete gastrin hormone. The layers of the stomach are the same, we have : 1-mucosa, 2- sub-mucosa, 3- muscularis externa, 4- serosa ( with simple squamous covering epithelium (mesothelium) ) We now turn back to the mucosa for a more detailed discussion of its layers: Mucosal layers: 1-lining epithelium or surface epithelium : The epithelium covering the surface and lining the pits is a simple columnar epithelium, which is different than that of esophagus. 2-lamina propria filled with gastric gland which have ducts called gastric pits which are invaginations of the gastric epithelium, gastric glands contain the four aforementioned types of secretory cells. ** NOTE : oblique sections don t show all the ducts, some of them are seen and others looks circular or oval. what are the comparisons between body, cardia and pylorus? depends on lamina propria and the size of the gland and the size of the ducts(gastric pits). pylorus: long ducts, small glands, tubular glands, simple or usually columnar, and coiled secretory portion. body: large glands, short ducts,the type of gland is tubular simple or usually branched. 3-muscularis mucosa (two rebounds of smooth muscle ). Mucus consists primarily of water (95%), lipids, and glycoproteins, which in combination form a hydrophobic protective gel. Bicarbonate secreted by the surface epithelial cells into the mucous gel, forms a ph gradient ranging from 1 at the gastric luminal surface to 7 along the epithelial cell surface. surface epithelial cells prevent autodigestion; bicarbonate and mucous decrease effects of HCl and protect the mucosa. 3
4 Cardia: **The cardia is a narrow circular band 1-2cm long, and1.5 3 cm in width. at the transition between the esophagus and the stomach. **Its mucosa contains simple or branched tubular cardiac glands. **The terminal portions of these glands are frequently coiled, often with large lumens.(we can see coiling in cardia and pylorus) **Most of the secretory cells produce mucus and lysozyme (an enzyme that attacks bacterial walls), but a few parietal cells secreting H+ and Cl (which will form HCl in the lumen) can be found. **These glands are similar in structure to the cardiac glands of the terminal portion of the esophagus. Fundus and body : the glands are large and take up a large part of the lamina propria, but the gastric pits are short,some books say 2/5-3/5 of the length. each gastric gland has three distinct regions: the isthmus, neck and base. especially in the body, majority of mucous cells are in the isthmus. parietal cells mostly in the neck but in other sites are also found. chief cells are found in the base where we also find enteroendocrine cells (gastrin cells) in the neck and isthmus: you also find stem cells that are responsible of mitosis and regeneration (in 4-6 days after damage in mucous cell)... stem cells move upwards or downwards to replace other degenerative cells. under the light microscope the most seen cells are : 1- mucous cells 2- parietal cells (find most between isthmus and neck) and the parietal cells are acidophilic which secrete HCL & appear pink in color. 3- chief cells are most common in the base which has chief cells with large amount of ribonucleic acids and RER are basophilic and appear dark in color. Now lets do a brief review : The isthmus : close to the gastric pit, mainly contains Mucous cells(in the body), also find stem cells. the neck: mainly contains parietal cells, also find stem cells. the base: mainly contains chief cells. 4
5 Stem Cells: Found in the isthmus and neck regions but few in number.gland has simple columnar cells but in different types of cells. Are there goblet cells in the stomach? no. these are unicellular glands that secrete mucus which start in small intestine and increase distally, but in stomach no goblet cell just simple columnar mucus cell. These cells have a high rate of mitosis; some of them move upward or downwards to replace the degenerative cells, which have a turnover time of 4-7 days. Mucous Neck cells : Mucous neck cells are present in clusters or as single cells between parietal cells in the necks of gastric glands. Their mucus secretion is quite different from that of the surface epithelial mucus cells. They are irregular in shape, with the nucleus at the base of the cell and the secretory granules near the apical surface. in preparation by eosin stain, has a foamy appearance after dissolving of mucous like a vacuoles (as all mucous secretary cells appear foamy). Parietal cells : parietal cells present in the surface epithelium at the neck of the gland, faint or acidphilic in appearance. While at the base of gland is dark basophilic chief cell. parietal cells have two stages : resting stage: no HCl production. These stage contains tubulovesicles, the common component of cell are tubules and vesicles. active stage: produce HCL and converted into intracellular canaliculus, contain HCl towards the apex of the cell. parietal cells are responsible for secretion of HCL through parasympathetic: a secertomotor system of myennetric plexus from the vagus nerve ( make the parasympathetic fibers) which synapses in myenteric ganglia. Postganglionic fibers : very very short in the wall and goes to smooth muscle and gland. 5
6 In the past they used to consider the hyperacidity is the cause of peptic ulcers. so, The surgery focused on the vagus nerve and cut it, to prevent the acidity and gastric ulcer. but, nowadays it been discovered that a bacterial called helicobacter pylori is responsible of peptic ulcer. Chief (zymogenic) cells: above (in the gland) you see parietal cells which are acidophilic, rounded with nucleous and are very clear. but chief cells have zymogenic granules towards the apex while the base is basophilic which has mitochondria and ribonucleic acids, and secrete pepsinogen and gastric lipase. Enteroendocrine cells: In the stomach they re G-cells or gastric cells (a type of enteroendocrine cells), secreting gastrin hormone. It appears the lumen in the middle with nucleus and other structures. NOW we finished the body and fundus, we give a huge explanation about body& fundus cause they take a large part of the whole stomach. Pylorus: - Consist of pyloric canal and pyloric sphincter, sphincter means thickening of circular smooth muscle which is different than cardia (cardia is a physiological sphincter only, no thickening of smooth muscle). - The difference between pylorus and body is that gastric pits are very long but gastric glands are thin. Because, most of the digestion occurs in the body and in the pylorus the digestion decreases. pylorus functions to passes the chyme to the duodenum, and most of the digestion occurs in the body. - The type of gland is: tubular coiled glands, may be branched or simple. The lamina propria it contains lymphatic nodules. lymphocytes when scattered has no significance. but, when it gathered it appears like lymphatic nodule and this indicates an effect (an action). lymphatic system helps in immunity because it s possible that the food we eat contains bacteria, viruses, dusts etc. so, the lymphatic nodules in pylorus engulf these foreign bodies. 6
7 important note: pylorus cell, does it have parietal or chief cells? No it doesn t, what distinguishes it that it has a few parietal cells (some books say no parietal cells). when we see a section in the lab, we don t see parietal nor chief cells.mostly we see mucus cells whether in glands or at the surface. we find mucus cells to balance the body's acidity and the chyme as it passes to the duodenum ( although the duodenum rich in bicarbonate and mucous to balance the acidity to prevent duodenal ulcer in the first inch). Briefly about the other layers : The submucosa is composed of dense connective tissue containing blood and lymph vessels; it is infiltrated by lymphoid cells, macrophages, and mast cells. for pylorus and body: muscularis externa in stomach have 3 layers, (usually we have outer longitudinal and inner circular) but here you find: the internal layer is oblique The middle layer is circular, and you should know that at pylorus the pyloric sphincter comes from thickening in the middle circular smooth muscle. The external layer is longitudinal The stomach is covered by a thin serosa, which is simple squamous epithelium. Histology of the small intestine - Consists of three parts: *duodenum *jejunum *ileum the difference between them that duodenum its retroperitoneal ; while, jejunum and ileum are intraperitoneal and have mesentery (two layers of peritoneum surrounding the jejunum and ileum). The length of the small intestine is between 5-6 m. The function mainly if for digestion and absorption especially the duodenum which receives the bile salts from gall bladder and liver, and also the secretions of pancreas which, both open in the second part of duodenum in pancreatic duct and common bile duct. In the small intestine the mucosa has finger-like projections called intestinal villi between mm to increase surface area. Plicae circularis (Kerckring's valves): projection from lamina propria which enter through the mucosa to increase surface area. 7
8 The layers of small intestine are also the same: mucosa which has lamina propria and muscularis mucosa. lamina propria also filled with glands called crypts of Lieberkühn, it has different cells the same as the stomach. The distinguishing factor of small intestine : it has goblet cells and every time we go distally it increases (increase gradually). They are most numerous in the large intestine for lubrication. the submucosa: duodenum is the second organ which contains gland, called Brunner's glands, secrete alkaline secretion for neutralization of the acidity of the stomach. muscularis externa: inner circular, outer longitudinal, and also myennetric plexus for secretion and motility of the small intestine (peristaltic movement). Duodenum has leaf-shaped projections while in jejenum and ileum: finger-like projection. Intestinal glands (crypts of lieberkuhn) with the villi have a continuation (the lower half is glands, upper is villi ), An indication of this is that lining epithelium for gland and surface are simple columnar epithelium cells and goblet cells. look at the Diagram: The villi of small intestine extend from the surface. In the villi : o you find cells (simple columnar epithelium cells) and goblet cells o lymphatic capillary (lacteals): blind-ended lymphatic capillary: for absorption of lymph or fat. o also blood vessels: capillaries in villi o villi's inside has lamina propria, rich in lymphatic&blood capillaries o scattered lymphocytes and goblet cells o surface is striated because of microvili extruding on the surface. o as for the gland (bottom left): also has goblet cells 8
9 o type of cells: simple columnar epithelium o also has mucous cells and enteroendocrine cells o the base: paneth's cells whose base is clear with a nucleus and apical granules found especially in jejenum and maybe in the ileum. the apex of villi: striated or brush border come from the microvilli: Each absorptive cell is estimated to have an average of 3000 microvilli, and 1-2 mm of mucosa contains about 200 million of these structures. The presence of plicae, villi, and microvilli greatly increases the surface of the intestinal lining. It has been calculated that plicae increase the intestinal surface 3-fold, the villi increase it 10-fold, and the microvilli increase it 20-fold. Together, these processes are responsible for a 600-fold increase in the intestinal surface, resulting in a total area of 200 m2 Goblet cells: Goblet cells find in the surface and in the gland, begins in the duodenum and increases in number as they approach the ileum. Goblet cells function to protection and lubrication. Paneth's Cells: Find in the basal portion of the gland, has secretory granules at the apex of the cytoplasm whose function is secreting lysozyme which is antibacterial and protect the flora of the intestine. The end Please forgive me for any mistakes. Best of luck سر من أسرار النجاح) 5 دقائق( DONE BY: Malak Shbeta 9
Dana Alrafaiah. Dareen Abu Shalbak. Mohammad Almuhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Dana Alrafaiah Dareen Abu Shalbak Mohammad Almuhtaseb 1 P a g e Esophagus: A muscular tube that is 25 cm long, but if measured from the incisors it would be 45cm long. Extends from C6 of cervical vertebra,
2 Dana Alrafaiah Dareen Abu Shalbak Mohammad Almuhtaseb 1 P a g e Esophagus: A muscular tube that is 25 cm long, but if measured from the incisors it would be 45cm long. Extends from C6 of cervical vertebra,
The doctor mentioned a few things about the esophagus from the previous lecture:
 السالم عليكم [HISOLOGY 2] April 27, 2014 The doctor mentioned a few things about the esophagus from the previous lecture: Esophagus - It is about 25 cm in length (from the incisor it is 45 cm) Histological
السالم عليكم [HISOLOGY 2] April 27, 2014 The doctor mentioned a few things about the esophagus from the previous lecture: Esophagus - It is about 25 cm in length (from the incisor it is 45 cm) Histological
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
HISTOLOGY. GIT Block 432 Histology Team. Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih
 HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
DIGESTIVE TRACT ESOPHAGUS
 DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine
 Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
Digestive system L 2. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel
 Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
Esophagus. Transport is achieved by peristaltic contractions and relaxation of the esophageal sphincters (upper and lower)
 GI Histology 2 Esophagus is a muscular tube whose function is to transport foodstuffs from the mouth to the stomach and to prevent the retrograde flow of gastric contents Transport is achieved by peristaltic
GI Histology 2 Esophagus is a muscular tube whose function is to transport foodstuffs from the mouth to the stomach and to prevent the retrograde flow of gastric contents Transport is achieved by peristaltic
The Digestive System Laboratory
 The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B
 Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system. Lab activity 1: esophagus stomach - small intestines
 Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
Histology Lab. looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira book and you can use BlueHistolgy website
 Done By: Aseel Twaijer & Laith Sorour Histology Lab *These notes help in differentiating tissues and you must read them while looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira
Done By: Aseel Twaijer & Laith Sorour Histology Lab *These notes help in differentiating tissues and you must read them while looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
Tissues and organs PART 1
 Tissues and organs PART 1 Animals and plants are multicellular (made of many cells). Cells become specialised according to their function Tissues: Many cells that perform one or several functions; they
Tissues and organs PART 1 Animals and plants are multicellular (made of many cells). Cells become specialised according to their function Tissues: Many cells that perform one or several functions; they
Connective tissue The Digestive System
 Connective tissue The Digestive System Part 1 Structure of digestive system Functions Basic Structure of the Alimentary Canal Wall Tube is made up of four layers: 1. Mucosa 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis externa
Connective tissue The Digestive System Part 1 Structure of digestive system Functions Basic Structure of the Alimentary Canal Wall Tube is made up of four layers: 1. Mucosa 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis externa
consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs FUNCTION Individual parts function in: ingestion mechanical digestion chemical and enzymatic digestion
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs FUNCTION Individual parts function in: ingestion mechanical digestion chemical and enzymatic digestion
Gastrointestinal System!
 Gastrointestinal System! Assoc. Prof. Prasit Suwannalert, Ph.D. (Email: prasit.suw@mahidol.ac.th)! Objectives: After learning, student should be able to describe and discuss in topics of! 1. Anatomical
Gastrointestinal System! Assoc. Prof. Prasit Suwannalert, Ph.D. (Email: prasit.suw@mahidol.ac.th)! Objectives: After learning, student should be able to describe and discuss in topics of! 1. Anatomical
Digestive System II - Lower tract Revised
 ANAT D502 Basic Histology Digestive System II - Lower tract Revised 10.12.12 Outline: I. Small intestine II. Enterocyte digestion II. Hepatic portal system IV. Large intestine V. Enteric nervous system
ANAT D502 Basic Histology Digestive System II - Lower tract Revised 10.12.12 Outline: I. Small intestine II. Enterocyte digestion II. Hepatic portal system IV. Large intestine V. Enteric nervous system
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Week 12 - Outline. Outline. Digestive System I Major Organs. Overview of Digestive System
 Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Practical Histology o
 Practical Histology o 1.. Contents: Histology of the : Stomach Esophagus Small intestine Large intestine Liver Gallbladder Exocrine pancreas Spleen GNT Block Things you need to know before the exam : o
Practical Histology o 1.. Contents: Histology of the : Stomach Esophagus Small intestine Large intestine Liver Gallbladder Exocrine pancreas Spleen GNT Block Things you need to know before the exam : o
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Histology 3. We will continue talking about a few things from last lecture, starting with M cells:
 Histology 3 This is the last Histology lecture in the GI system. Enjoy! There are some extra notes listed as footnotes. We will continue talking about a few things from last lecture, starting with M cells:
Histology 3 This is the last Histology lecture in the GI system. Enjoy! There are some extra notes listed as footnotes. We will continue talking about a few things from last lecture, starting with M cells:
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Digestive System and Body Digestion Metabolism Breakdown of ingested
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Digestive System and Body Digestion Metabolism Breakdown of ingested
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
GI Histology Lab 1. Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji
 GI Histology Lab 1 Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji Lip ORAL MUCOSA -Arrow shows labial salivary glands in the submucosa. VERMILLION transitional zone. SKIN Stratified Squamous epithelium, keratinized -Arrow
GI Histology Lab 1 Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji Lip ORAL MUCOSA -Arrow shows labial salivary glands in the submucosa. VERMILLION transitional zone. SKIN Stratified Squamous epithelium, keratinized -Arrow
Done by: Dina Sawadha & Mohammad Abukabeer
 Done by: Dina Sawadha & Mohammad Abukabeer The stomach *the stomach is a dilated part of the gastro intestinal tract, it's "J" shape. *the lower surface of the stomach ( the greater curvature ) reaches
Done by: Dina Sawadha & Mohammad Abukabeer The stomach *the stomach is a dilated part of the gastro intestinal tract, it's "J" shape. *the lower surface of the stomach ( the greater curvature ) reaches
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
Chapter 9. The digestive system. Glossary. Louise McErlean
 Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Lab 8: Digestive System
 BIOL 221 A&P II Lab 8: Digestive System Become familiar with the gross anatomy of the digestive system (Exercise 38) using the models, Fig. 38.1 (Activity 1), and the rat. Recognize and know the functions
BIOL 221 A&P II Lab 8: Digestive System Become familiar with the gross anatomy of the digestive system (Exercise 38) using the models, Fig. 38.1 (Activity 1), and the rat. Recognize and know the functions
MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS
 MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES, FORM, FUNCTION, MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE: A hollow
MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES, FORM, FUNCTION, MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE: A hollow
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Digestive Anatomy Lab
 Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
The Digestive System 1
 The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
(A) Diarrhea. (B) Stomach cramps. (C) Dehydration due to excess fluid loss. (D) A, B, and C are correct. (E) Only answer B is correct.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
The Digestive System. What is the advantage of a one-way gut? If you swallow something, is it really inside you?
 The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
Connective tissue The Digestive System
 Connective tissue The Digestive System Part 1 Structure of digestive system Functions Basic Structure of the Alimentary Canal Wall Tube is made up of four layers: 1. Mucosa 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis externa
Connective tissue The Digestive System Part 1 Structure of digestive system Functions Basic Structure of the Alimentary Canal Wall Tube is made up of four layers: 1. Mucosa 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis externa
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Today, we will leave all hormones and start with another topic which is GI system This lecture is talking about general histology of Gastrointestinal system.. The gastrointestinal
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Today, we will leave all hormones and start with another topic which is GI system This lecture is talking about general histology of Gastrointestinal system.. The gastrointestinal
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1. Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Digestive System. - Food is ingested
 11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
Human Structure and Function GI Tract Exercises
 GI Tract Exercises Study Exercises. Review of the Elements of the Alimentary Tube. On the following two pages is a chart or matrix of blank spaces. Each space is the intersection of a horizontal row and
GI Tract Exercises Study Exercises. Review of the Elements of the Alimentary Tube. On the following two pages is a chart or matrix of blank spaces. Each space is the intersection of a horizontal row and
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The stomach is formed of three parts: -
 The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
THE ORAL CAVITY
 THE ORAL CAVITY WALL OF ABDOMEN (ANTERIOR) The paraumbilical vein drains into the portal vein and then through the liver. This is an important clinical connection. THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA The small
THE ORAL CAVITY WALL OF ABDOMEN (ANTERIOR) The paraumbilical vein drains into the portal vein and then through the liver. This is an important clinical connection. THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA The small
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA
 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA Anatomy of the GI Tract The GI tract is essentially a hollow tube connecting the mouth to the anus.
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA Anatomy of the GI Tract The GI tract is essentially a hollow tube connecting the mouth to the anus.
458 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology
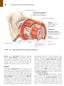 458 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology Visceral peritoneum Intrinsic nerve plexuses: Myenteric nerve plexus Submucosal nerve plexus Submucosal glands Mucosa: Surface epithelium Lamina propria Muscle
458 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology Visceral peritoneum Intrinsic nerve plexuses: Myenteric nerve plexus Submucosal nerve plexus Submucosal glands Mucosa: Surface epithelium Lamina propria Muscle
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Overview of the Digestive
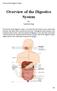 Overview of the Digestive System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The function of the digestive system is to break down the foods you eat, release their nutrients, and absorb those nutrients into the body. Although
Overview of the Digestive System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The function of the digestive system is to break down the foods you eat, release their nutrients, and absorb those nutrients into the body. Although
I. The Alimentary Canal (GI track)
 A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Gastrointestinal Tract
 CTO Lab #5 GI TRACT & GLANDS; ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Page 1 Gastrointestinal Tract Slide 126 This section through the esophagus shows the characteristic layers of the gastrointestinal tract. Examine the non-keratinized
CTO Lab #5 GI TRACT & GLANDS; ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Page 1 Gastrointestinal Tract Slide 126 This section through the esophagus shows the characteristic layers of the gastrointestinal tract. Examine the non-keratinized
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4
 Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Alimentary Canal (I) Salivatory Glands. (Esophagus and Stomach) Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra..
 Alimentary Canal (I) (Esophagus and Stomach) Salivatory Glands Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra.. Objectives: 1. By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic
Alimentary Canal (I) (Esophagus and Stomach) Salivatory Glands Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra.. Objectives: 1. By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function. Histology = study of tissues
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove.
 By Dr. Raja Ali A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove. The flow of fluid from these glands serves to wash
By Dr. Raja Ali A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove. The flow of fluid from these glands serves to wash
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Glandular Epithelium Groups of surface cells differentiate, proliferate, and penetrate underlying connective tissue. Their main
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Glandular Epithelium Groups of surface cells differentiate, proliferate, and penetrate underlying connective tissue. Their main
Stomach. Stomach. Nerve supply. Blood supply. Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system
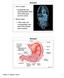 Stomach Nerve supply Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system Blood supply Celiac trunk, and corresponding veins (part of the hepa0c portal system) Stomach Figure 23.14a Chapter
Stomach Nerve supply Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system Blood supply Celiac trunk, and corresponding veins (part of the hepa0c portal system) Stomach Figure 23.14a Chapter
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
1. Approximately 21 ft. long: duodenum (one ft.), jejunum (eight ft.), and ileum (twelve ft.)
 IV. Small Intestines A. General features and functions 1. Approximately 21 ft. long: duodenum (one ft.), jejunum (eight ft.), and ileum (twelve ft.) 2. Functions: move forward chyme, continue digestion,
IV. Small Intestines A. General features and functions 1. Approximately 21 ft. long: duodenum (one ft.), jejunum (eight ft.), and ileum (twelve ft.) 2. Functions: move forward chyme, continue digestion,
The Stomach. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
General functions of digestive system. Ch. 15 The Digestive System. General histology of the wall of the digestive tract. Overview of digestive organs
 Overall idea: obtain nutrients from food (for energy and raw materials for synthesis), and defecate the leftover waste 2 types of organs involved: 1. Parts of the digestive tract (= a long muscular tube
Overall idea: obtain nutrients from food (for energy and raw materials for synthesis), and defecate the leftover waste 2 types of organs involved: 1. Parts of the digestive tract (= a long muscular tube
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Digestive System
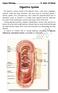 Digestive System The digestive system consists of the digestive tract oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, and anus and its associated glands salivary glands, liver, and pancreas.
Digestive System The digestive system consists of the digestive tract oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, and anus and its associated glands salivary glands, liver, and pancreas.
Omar Sami --- Muhammad Al-Muhatasib
 8 Omar Sami --- Muhammad Al-Muhatasib This sheet is a remake from 2015 s sheet for the same lecture; I have checked the record, added, omitted, edited & illustrated all what the Professor mentioned in
8 Omar Sami --- Muhammad Al-Muhatasib This sheet is a remake from 2015 s sheet for the same lecture; I have checked the record, added, omitted, edited & illustrated all what the Professor mentioned in
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A& M University Objectives Distinguish between the parotid and submandibular salivary glands. Understand and identify the structural
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A& M University Objectives Distinguish between the parotid and submandibular salivary glands. Understand and identify the structural
Digestive System. Presented by: Dr M. Arianmanesh PhD in Reproductive and Developmental Biology Dept. of Anatomical Sciences
 Digestive System Presented by: Dr M. Arianmanesh PhD in Reproductive and Developmental Biology Dept. of Anatomical Sciences Today we will discuss: Histological layers of alimentary canal Oral cavity Lip
Digestive System Presented by: Dr M. Arianmanesh PhD in Reproductive and Developmental Biology Dept. of Anatomical Sciences Today we will discuss: Histological layers of alimentary canal Oral cavity Lip
Digestive Tract. Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. stomach small intestine large intestine - anus
 Digestive Tract Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract Mouth pharynxepiglottis- esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine - anus Digestive Tract Digestion: The mechanical and chemical
Digestive Tract Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract Mouth pharynxepiglottis- esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine - anus Digestive Tract Digestion: The mechanical and chemical
Exercise. Digestive System. Digestive system function. 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc.
 Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Objectives. Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract
 GI Histology 1 Objectives Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function Describe the histological features of each part of the GI tract. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract Appreciate
GI Histology 1 Objectives Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function Describe the histological features of each part of the GI tract. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract Appreciate
BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number. Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet.
 BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. The homeostatic value of a particular controlled variable in the body
BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. The homeostatic value of a particular controlled variable in the body
