Nutrition Diagnosis (3 pts) Inadequate energy intake and limited food acceptance R/T poor appetite due to chemotherapy AEB 8.9% weight loss, BMI 18.
|
|
|
- Patricia Greene
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Taylor Zwimpfer Nutrition 302L 2/12/2014 Albumin Assessment Lab (NCP) Nutrition Assessment (3 pts) Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Nutrition-related PMH, treatments, surgeries: Chemotherapy, appetite affected Age, gender: 55 year old female Dietary intake: N/A Food preferences, allergies, intolerances: N/A Exercise habits: N/A Knowledge, readiness for change: Seeks aid in keeping down food due to chemotherapy Functional/behavioral factors: chemotherapy patient, bladder cancer Resources for obtaining, preparing food: N/A Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite Ht/wt: 5 5 /112lbs BMI: 18.6, IBW: 125lbs, %IBW: 89.6%, UBW: 123lbs, %UBW: 91.1%, %wt change: 8.9%, Weight Status: Mild depletion (Underweight), Degree of malnutrition/depletion: Mild Energy Needs: kcal/day Protein Needs: gm pro/d (based upon suggested protein for patient with a tumor and therapy) Fluid Needs: 30ml/kg/day Labs/tests Glucose: 83 mg/dl, BUN: 15mg/dl, Hgb: 12.2g/dl, Hct: 37%, Total Protein: 5.5g/dl, Albumin: 2.8 g/dl Medications/supplements: Chemotherapy Skin integrity: N/A Fluid intake/output (I/O): N/A Bowel movements (BM): N/A Nutrition Diagnosis (3 pts) Inadequate energy intake and limited food acceptance R/T poor appetite due to chemotherapy AEB 8.9% weight loss, BMI 18.6 Nutrition Intervention (3 pts) 1. Meals and snacks texture/fluid modified foods 2. Nutrition-related medication management REC appetite stimulant Goals 1. Dietary intake to meet >75% estimated energy needs. 2. Weight gain of 1#/week until pt reaches UBW/IBW. Nutrition Monitoring and Evaluation
2 Patient will consume a nutrient dense diet comprised of texture/fluid modified foods and drink plenty of fluids. Monitoring will include weekly weight measurements and nutrient intake analysis. If nutrition status is not improving, the patient s needs will be reassessed and new goals will be made for further intervention.
3 Taylor Zwimpfer NCP: Glucose Assessment 2/25/2014 Nutrition Assessment (3 pts) Diagnosis: Type 1 Diabetes Nutrition-related PMH: takes insulin injections Age, gender: 24 years old, male Dietary intake: infrequent meals with snacks in between, poor nutrition choices, high caloric meals, generally unhealthful diet Food preferences, allergies, intolerances: N/A Exercise habits: physically inactive Knowledge, readiness for change: not knowledgeable in nutrition choices, does not monitor glucose intake, not ready for diet/lifestyle change Functional/behavioral factors: does not monitor blood glucose well Resources for obtaining, preparing food: N/A Symptoms: frequent urination, excessive thirst and hunger Ht/wt: 5 10 (70 ), 165lbs (74.84kg) BMI: 23.7 (normal) IBW: 166lbs (ideal), %IBW: 99.40% (ideal), UBW: 165lbs, %UBW: 100%, %wt change : 0% Energy Needs: Abbreviated version for persons of normal height and weight o REE (male): 74.84kg x 1 kcal/kg x 24hr= kcal o Total energy needs: kcal x 1.3=2335 kcal (ambulatory, non-stressed state) Protein Needs: Non-stressed state ( gm protein/kg) o Weight in Kg x gm protein/kg=protein needs/d o 74.84kg x 0.8 gm protein/kg= gm protein o 74.84Kg x 1.0 gm protein/kg= gm protein o Range: gm protein (non-stressed state) Fluid Needs: o Adolescent: 40-60mL/kg/day x actual body weight (kg)= ml/day o ml/day (as an adolescent male) Labs/tests : Glycosylated hemoglobin: 9.4% Medications/supplements: insulin injections Skin integrity: N/A Fluid intake/output (I/O): N/A Bowel movements (BM): N/A Nutrition Diagnosis (3 pts) Behavioral-Environmental: Lack of nutritional knowledge, self-monitoring deficit R/T excessive thirst, CHO and fat intake AEB glycosylated hemoglobin of 9.4% (should not be above %, this is a marker for long term poor blood glucose control). Goal: Monitor blood glucose levels to reduce glycosylated hemoglobin levels. Nutrition Intervention (3 pts) Food and Nutrient Delivery REC multivitamin 1. To lessen appetite and thirst 2. To supplement for inadequate vitamin/healthful nutrient intake in diet. Nutrition Education
4 REC nutrition education classes and dietary log to be taken for four weeks 1. Improve eating habits and begin a general/healthful diet. 2. Reduce fluid loss, CHO, and fat intake. 3. Enforce healthy eating habits Coordination of Nutrition Care REC consultation with exercise physiologist for further evaluation of lab tests and overall physical activity habits 1. Further evaluation of nutritional/physical status. 2. To provide second opinion of suggested lifestyle changes Nutrition Monitoring and Evaluation Patient levels should be reassessed in 4 weeks, to monitor dietary changes (diet log), glycosylated hemoglobin, blood glucose, and ability to change lifestyle habits. If glycosylated hemoglobin levels are lowered or within the acceptable range of %, I can be identified that progress has been made and self-monitoring of diet should continue.
5 Taylor Zwimpfer NCP: Hemoglobin/Hematocrit Assessment 2/25/2014 Nutrition Assessment (3 pts) Diagnosis: Apparently healthy, breastfeeding mother Nutrition-related PMH: stopped taking vitamin/mineral supplement prescribed by doctor, vegetarian, fatigue, Hgb: 9.5g/dL, Hematocrit: 30% Age, gender: 22 year old, female Dietary intake: vegetarian, no meat Food preferences, allergies, intolerances: no meat Exercise habits: N/A Knowledge, readiness for change: not knowledgeable in nutrition choices, stopped taking vitamins prescribed by doctor, not ready for diet/lifestyle change Functional/behavioral factors: stopped taking vitamins prescribed by doctor Resources for obtaining, preparing food: N/A Symptoms: fatigue, worn out Ht/wt: 5 4 (162.56cm), 108lbs (48.99kg) BMI: 18.5 (normal) IBW: 120lbs, %IBW: 90% (mild malnutrition), UBW: 108lbs, %UBW: 100%, %wt change : 0% Energy Needs: Harris benedict formula to determine REE o REE (female): 655+ (9.6 x 48.99kg) + (1.8 x cm)- (4.7 x 22 years old)= kcal o Total energy needs: kcal x 1.3 (ambulatory) x (no injury factor)+ 500kcal (lactation)= kcal (ambulatory, non-stressed state) Protein Needs: Non-stressed state ( gm protein/kg) o Weight in Kg x gm protein/kg + 15 gm pro/d (lactation first 6 months)=protein needs/d o 48.99kg x 0.8 gm protein/kg + 15 gm pro/d= gm protein o 48.99Kg x 1.0 gm protein/kg + 15 gm pro/d= gm protein o Range: gm protein (non-stressed state, lactating) Fluid Needs: o Adolescent: 40-60mL/kg/day x actual body weight (kg)= ml/day o ml/day (as an adolescent female) Labs/tests : Hgb: 9.5g/dL, Hematocrit: 30% Medications/supplements: none Skin integrity: N/A Fluid intake/output (I/O): N/A Bowel movements (BM): N/A Nutrition Diagnosis (3 pts) Intake Increased nutrient/iron needs R/T discontinuation of taking vitamin/mineral supplements, vegetarianism AEB fatigue and tiredness of being a new mother, mild malnutrition, low hemoglobin and hematocrit levels (Hgb: 9.5 g/dl, hematocrit: 30%). Nutrition Intervention (3 pts) Food and Nutrient Delivery REC foods heavier in iron/not susceptible to phytochemicals that block iron absorption. Examples of such foods include dark leafy greens, eggs, dried fruit, beans/ legumes, artichokes, ironenriched cereals and grains.
6 3. Reach ideal body weight 4. Increase lab values to healthy levels (Hemoglobin: g/dl, Hematocrit: 37-47%) REC Supplementation of iron, vitamin B12, and folate. 5. Reach ideal body weight 6. To begin taking recommended vitamin and mineral supplements again 7. To supplement for inadequate vitamin/healthful nutrient intake in diet. Nutrition Education REC nutrition education classes through WIC to be taken for four weeks 1. Improve eating habits and begin a general/healthful diet. 2. Gain knowledge about the importance of eating a healthful diet when lactating as a new mother 3. Gain confidence in being a new mother to overcome worn out feelings Coordination of Nutrition Care REC Albumin and total protein lab tests 1. To find out the status of protein needs/deficiency 2. Determine if additional protein is necessary in the diet Nutrition Monitoring and Evaluation Patient levels should be reassessed in four weeks, to monitor Hemoglobin and Hematocrit levels have increased to normal, measure overall fatigue/ tiredness level, assess diet and iron levels. Outcomes will be evaluated based on new findings. Should hematocrit and hemoglobin levels be in the proper ranges (Hemoglobin: g/dl, Hematocrit: 37-47%) it can be evaluated that dietary changes were successful and should be continued to be followed. If fatigue continues, referral to alternative specialists may be necessary.
7 Taylor Zwimpfer NCP: Triglyceride Assessment 3/4/2014 Nutrition Assessment (3 pts) Diagnosis: Type II Diabetes Mellitus Nutrition-related PMH: Albumin: 4.2 g/dl, Hgb: 13.4 g/dl, Hct: 41%, Glucose:145mg/dL, Triglycerides: 205 mg/dl, Type II Diabetes Mellitus Age, gender: 37 year old, female Dietary intake: N/A Food preferences, allergies, intolerances: N/A Exercise habits: N/A Knowledge, readiness for change: N/A Functional/behavioral factors: N/A Resources for obtaining, preparing food: N/A Symptoms: elevated glucose levels (above the normal range of mg/dL), elevated triglycerides (above the recommended (<150mg/dL) Ht/wt: 5 1 (154.94cm), 152lbs (69.09kg) BMI: 28.7 (overweight) IBW: 105lbs, %IBW: 144.8%, UBW: 152lbs, %UBW: 100%, %wt change : 0% Energy Needs: Harris benedict formula to determine REE o REE (female): 655+ (9.6 x 69.09kg) + (1.8 x cm)- (4.7 x 37 years old)= kcal o Total energy needs: kcal x 1.3 (ambulatory) x (no injury factor)= kcal (ambulatory, non-stressed state) Protein Needs: Non-stressed state ( gm protein/kg) o Weight in Kg x gm protein/kg=protein needs/d o 69.09kg x 0.8 gm protein/kg= 55.27gm protein o 69.09Kg x 1.0 gm protein/kg= 69.09gm protein o Range: gm protein (non-stressed state) Fluid Needs: o Adult (25-55years): 35mL/kg/day x actual body weight (kg)= ml/day o ml/day (as an adult female) Labs/tests : Albumin: 4.2 g/dl, Hgb: 13.4 g/dl, Hct: 41%, Glucose:145mg/dL, Triglycerides: 205 mg/dl Medications/supplements: N/A Skin integrity: N/A Fluid intake/output (I/O): N/A Bowel movements (BM): N/A Nutrition Diagnosis (3 pts) Behavioral-Environmental Self-monitoring deficit R/T apparent excessive fat and nutrient intake affecting Type II Diabetes AEB elevated triglyceride levels of 205mg/dL (above the recommended <150mg/dL), elevated glucose levels of 145mg/dL (above the recommended mg/dL) and BMI of 28.7 (overweight). Nutrition Intervention (3 pts) Nutrition Education REC participation in nutrition courses related to Type II Diabetes Mellitus for further dietary changes.
8 8. To reduce dietary energy and fat intake (approximately 30% of total energy) 9. Frequent participation to produce long term weight loss of at least 5-7% usual body weight. 10. To achieve normal or near normal levels of blood glucose (70-110mg/dL). Nutrition Monitoring and Evaluation Patient levels should be reassessed in 4 weeks, to reevaluate lab tests of glucose and triglycerides and determine is progress has been made. If triglycerides show a decrease from 205 mg/dl, dietary changes should remain and nutrition counseling will be continued until near normal levels are reached (<150mg/dL). Blood glucose levels will be monitored continuously to ensure that they decline from the elevated state. Nutrition behavioral modifications will likely need to remain in place indefinitely in order to manage Type II Diabetes mellitus in patient.
9 Taylor Zwimpfer Nutrition 302L March 13, 2014 Case Study 5: Diet Plan Results of 24hr. recall: computrition (DRIs/Diet Analysis Plus). Calories: (2346kcals/d). Macronutrients: CHO: 236.5g ( ) Fiber: 29.85g (25g) Sugar: 79.52g (no recommendation) Protein: 84.79g (61.69g) Fat: 70.54g ( g) Saturated fat: 29.75g (<23.0g) Trans fat: 0.3g (no recommendation) Vitamins: A: ug (700ug) C: mg (75mg) D: 1.36ug (15ug) Iron: 42.2mg (18mg) Calcium: mg (1,000mg) Potassium: mg (4,700mg) Sodium: mg (1500mg) In order to analyze my 24-hour food recall, all data was input into the Diet Analysis Plus program. According to Diet Analysis Plus, it was calculated that a person of my height and weight should be
10 consuming 2346kcals/d. My caloric intake during the 24 hour recall was about 80% of this amount ( kcals). Total fat was within the recommended range established by the DRI s. Carbohydrate intake was less than the recommended intake and protein exceeded the recommended amount. Vitamin intake for this particular recall was not ideal. Vitamin A, iron, and sodium appeared to exceed the recommended values, however, my diet was lacking in sufficient Vitamin C, D, calcium, and potassium. The MyPlate Analysis provided through Diet Analysis Plus gave recommendations for nutrient intake goals in among the different food group categories. The goal for grain consumption was 8.0 oz, of which I met 90.2% of that goal by consuming 7.2oz. Vegetable intake on this particular day was more than twice the recommended amount of 3 cups. Consumption of fruits and dairy for this day was seriously lacking however. It was recommended that I consume 2 cups of fruits daily and during the period of this recall 0.2 cups where consumed. Another interesting addition to the data provided demonstrated that 717.3kcals for this day were a result of empty calories, providing no nutritional benefit to my diet, this number far exceeded the recommended allotment of 330kcal/day. Overall the recommendations and calculated nutrient content for the foods I ate appear to be accurate; there are a few areas that could be improved when using this method of analysis however. The database did not have all of the exact foods that I ate during that day, so I was forced to find different ingredients of similar content but still not containing the same nutritional value. Also, it is difficult to measure the nutritional content of a meal if it is eaten out because portions are not always measured the same and added ingredients are unknown. These meals are also not likely to be found exactly as they come in real life when searching for them in the Diet Analysis database. In addition, this was not a normal day of eating for me, so it would not be considered an accurate estimation of the foods that I consume and the changes that need to be made. Based on this 24 hour recall, a diet plan is able to be made for future consumption. It is clear that there is a lack of essential recommended Vitamins in my diet. These vitamins could easily be taken in supplemental form or through eating proper foods. Considering I was deficient in recommended fruits, I would be wise to attempt to eat the recommended 2 cups to gain the beneficial vitamins, minerals and carbohydrates that fruits provide. Dairy intake also should be increased to meet the recommended 3 cups. This could easily be done through drinking milk with a meal or snacking on cheese instead of the other sources of empty calories that were found to be in my diet.
11 Taylor Zwimpfer HDL-C and LDL-C Assessment Lab 3/25/2014 Nutrition Assessment (3 pts) Diagnosis: Coronary Artery Bypass graft, female patient Nutrition-related PMH: coronary artery bypass graft surgery, heart complications, family history of heart disease Age, gender: 54 year old female Dietary intake: smokes 2 packs of cigarettes a day, no other dietary information Food preferences, allergies, intolerances: smoker Exercise habits: N/A Knowledge, readiness for change: lack of knowledge of healthful practices, continues to smoke after enduring major surgery Functional/behavioral factors: smoker Resources for obtaining, preparing food: N/A Symptoms: AST: 76 UI/L, ALT:31 U/L, LDH: 322 U/L, CPK:268 U/L, Bilirubin (total): 0.5 mg/dl, Billiruben (direct): 0.1 mg/dl, Triglycerides: 188mg/dl (abnormal:high), Total Cholesterol:216mg/dl (abnormal: high), HDL: 37mg/dl (abnormal: low), LDL: 141mg/dl (abnormal: high) Ht/wt: 5 4 (162.56cm), 148lbs (67.13kg) BMI: 25.4 (overweight) IBW: 120lbs, %IBW: %, obese Energy Needs: Harris benedict formula to determine REE o REE (female): 655+ (9.6 x 67.13kg) + (1.8 x cm)- (4.7 x 54 years old)= kcal o Total energy needs: kcal x 1.3 (ambulatory) x (surgery)= kcal (ambulatory, post surgery) Protein Needs: Major surgery ( gm protein/kg) o Weight in Kg x gm protein/kg=protein needs/d o 67.13kg x 1.25 gm protein/kg= 83.91gm protein o 67.13Kg x 1.5 gm protein/kg= gm protein o Range: gm protein (non-stressed state) Fluid Needs: o Adult (25-55years): 35mL/kg/day x actual body weight (kg)= ml/day o ml/day (as an adult female) Labs/tests : Albumin: AST: 76 UI/L, ALT:31 U/L, LDH: 322 U/L, CPK:268 U/L, Bilirubin (total): 0.5 mg/dl, Billiruben (direct): 0.1 mg/dl, Triglycerides: 188mg/dl, Total Cholesterol:216 mg/dl, HDL: 37mg/dl, LDL: 141mg/dl Medications/supplements: N/A Skin integrity: N/A Fluid intake/output (I/O): N/A Bowel movements (BM): N/A Nutrition Diagnosis (3 pts) Behavioral-Environmental Self-monitoring deficit R/T less than optimal intake of healthy fats (MUFA s and PUFA s) AEB elevated total cholesterol levels of 216mg/dL (above the recommended <200mg/dL), low levels of HDL cholesterol at 37mg/dl (recommended: >40mg/dl), high levels of LDL cholesterol at 141mg/dl (recommended <130mg/dl)and BMI of 25.4 (overweight).
12 Nutrition Intervention (3 pts) Meals and Snacks for a fat and fiber modified diet. Replace saturated fats with polyunsaturated fats and monounsaturated fats: fish, avocado, fruits, vegetables, walnuts, flax, beans, whole grains etc. Supplementation of omega 3, niacin, CoQ10 to aid in lowering LDL and increasing HDL. 11. To reduce dietary energy and fat intake (approximately 30% of total energy) 12. To reduce LDL cholesterol and triglycerides and increase HDL cholesterol. 13. Limit saturated fat intake to <7% of energy and trans fat <1%. Refer to a nutrition professional for recommendation of new diet, exercise, and health plan. Smoking should be eliminated from daily life, and exercise should be incorporated to promote HDL cholesterol production. 1. Healthy recovery from coronary artery bypass graft surgery 2. Overall healthful lifestyle behaviors 3. Weight loss to decrease overweight BMI and alleviate arterial stress/damage. Nutrition Monitoring and Evaluation Patient levels should be reassessed in 3 weeks, to reevaluate cholesterol and triglyceride levels to determine if progress has been made. If total cholesterol level shows a decrease from 216 mg/dl, dietary changes should remain until normal levels are reached (<200mg/dL). HDL and LDL levels should be reassessed to determine if dietary changes are effectual. If levels remain the same, more severe dietary restrictions will be implemented. Other lab tests and BMI will be reevaluated as well to assess the overall change in health. Nutrition behavioral modifications will likely need to remain in place in order to maintain weight loss and promote recovery from previous arterial damage.
13 Taylor Zwimpfer Nutrition 302L 4/12/2014 Calcium Assessment Lab (NCP) Nutrition Assessment (3 pts) Diagnosis: Excessive calcium intake Nutrition-related PMH, treatments, surgeries: N/A Age, gender: 67 year old male Dietary intake: N/A Food preferences, allergies, intolerances: N/A Exercise habits: N/A Knowledge, readiness for change: concern for general health, no specific issue with lifestyle Functional/behavioral factors: N/A Resources for obtaining, preparing food: N/A Symptoms: Serum Calcium: 9.5 mg/dl (low, normal: mg/dl), urinary Calcium: 300mg/dl (high, normal: mg/dl) Ht/wt: 5 8 /166lbs BMI:25.2 (overweight), IBW: 154lbs, %IBW: %, Weight Status: Overweight Energy Needs: Harris benedict formula to determine REE o REE (male): 66+ (13.7 x 75.3kg) + (5 x cm)- (6.8 x 67 years old)= o Total energy needs: kcal x 1.3 (ambulatory) x (no injury factor)= kcal Protein Needs: Non-stressed state ( gm protein/kg) o Weight in Kg x gm protein/kg=protein needs/d o 75.3kg x 0.8 gm protein/kg= 60.24gm protein o 75.3Kg x 1.0 gm protein/kg= 75.3gm protein o Range: gm protein (non-stressed state) Fluid Needs: o Adult (>65years): 25mL/kg/day x actual body weight (kg)= ml/day o ml/day (as an adult male) Labs/tests : Albumin: 3.8g/dl, Glucose: 112 mg/dl, Triglycerides: 89mg/dl, Cholesterol:188 mg/dl, Serum Calcium: 9.5 mg/dl Medications/supplements: N/A Skin integrity: N/A Fluid intake/output (I/O): N/A Bowel movements (BM): N/A Nutrition Diagnosis (3 pts) Behavioral-Environmental Self-monitoring deficit R/T excessive intake of Calcium AEB elevated urinary Calcium levels of 300mg/dL (above the recommended mg/dL). Nutrition Intervention (3 pts) Meals and Snacks for a Calcium modified diet. Limit consumption of Calcium rich food intake: milk, cheese, salmon, cereals, broccoli, and almonds).
14 14. To reduce dietary Calcium intake to recommended DRI of 1,000 mg/day. 15. To ensure that Calcium intake does not exceed Upper Level intake recommendations of 2,500mg/day. 16. Maintain consumption of food containing Calcium but decrease portion sizes. 17. To decrease decrease Urinary Calcium levels to normal range ( mg/dL). Increase fluid intake to meet fluid needs ( ml/day or 64 oz/day). 1. Increase urine production to at least 2 L per day. 2. Prevent production of kidney stones due to excessive Calcium intake. Nutrition Monitoring and Evaluation Patient levels should be reassessed in 3 weeks, to reevaluate Serum Calcium and Urinary Calcium levels. A 24 hour recall should be utilized to ensure that patient is implementing the advised nutritional intervention. If a change is not seen, referral to a specialized dietitian may be necessary for an additional opinion of the necessary actions to be taken in order to decrease Calcium levels. Bone density should be measured using DEXA or Ultrasound densitometry.
3/17/2017. What is Fiber? Fiber and Protein in Your Diet. Fiber Intake Recommendations. Fiber, Satiety, and Weight Relationships.
 What is Fiber? Dietary Fiber consists of nondigestible carbohydrates. Fiber has many roles such as delaying gastric emptying and reducing blood cholesterol concentrations. Fiber and Protein in Your Diet
What is Fiber? Dietary Fiber consists of nondigestible carbohydrates. Fiber has many roles such as delaying gastric emptying and reducing blood cholesterol concentrations. Fiber and Protein in Your Diet
Chapter 2. Planning a Healthy Diet
 Chapter 2 Planning a Healthy Diet Principles and Guidelines Diet Planning Principles Adequacy Sufficient energy Adequate nutrients for healthy people Balance Enough but not too much kcalorie (energy) control
Chapter 2 Planning a Healthy Diet Principles and Guidelines Diet Planning Principles Adequacy Sufficient energy Adequate nutrients for healthy people Balance Enough but not too much kcalorie (energy) control
Esophageal Cancer Treated with Surgery and Radiation Case Study (Evaluation and ADIME Note)
 Esophageal Cancer Treated with Surgery and Radiation Case Study (Evaluation and ADIME Note) Nutritional care plan: N.S. is a 58 yr old male. His serum albumin is below normal with a value of 3.1L (9/5)
Esophageal Cancer Treated with Surgery and Radiation Case Study (Evaluation and ADIME Note) Nutritional care plan: N.S. is a 58 yr old male. His serum albumin is below normal with a value of 3.1L (9/5)
Nutritional Recommendations for the Diabetes Managements
 In the name of God Nutritional for the Diabetes Managements Zohreh Mazloom. PhD Shiraz University of Medical Sciences School of Nutrition and Food Sciences Department of Clinical Nutrition OVERVIEW Healthful
In the name of God Nutritional for the Diabetes Managements Zohreh Mazloom. PhD Shiraz University of Medical Sciences School of Nutrition and Food Sciences Department of Clinical Nutrition OVERVIEW Healthful
BCH 445 Biochemistry of nutrition Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 BCH 445 Biochemistry of nutrition Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 1 Energy Needs & Requirements Food is the only source of body which undergoes Metabolism and liberate / Generates Energy required for vital activities
BCH 445 Biochemistry of nutrition Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 1 Energy Needs & Requirements Food is the only source of body which undergoes Metabolism and liberate / Generates Energy required for vital activities
Dietary Guidelines for Americans & Planning a Healthy Diet. Lesson Objectives. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2010
 Dietary Guidelines for Americans & Planning a Healthy Diet NUTR 2050 NUTRITION FOR NURSING PROFESSIONALS MRS. DEBORAH A. HUTCHEON, MS, RD, LD Lesson Objectives At the end of the lesson, the student will
Dietary Guidelines for Americans & Planning a Healthy Diet NUTR 2050 NUTRITION FOR NURSING PROFESSIONALS MRS. DEBORAH A. HUTCHEON, MS, RD, LD Lesson Objectives At the end of the lesson, the student will
Dietary Fat Guidance from The Role of Lean Beef in Achieving Current Dietary Recommendations
 Dietary Fat Guidance from 1980-2006 The Role of Lean Beef in Achieving Current Dietary Recommendations Penny Kris-Etherton, Ph.D., R.D. Department of Nutritional Sciences Pennsylvania State University
Dietary Fat Guidance from 1980-2006 The Role of Lean Beef in Achieving Current Dietary Recommendations Penny Kris-Etherton, Ph.D., R.D. Department of Nutritional Sciences Pennsylvania State University
The Food Guide Pyramid
 The Food Guide Pyramid In this lesson, you will Learn About n What influences a person s food choices. n How to use the Food Guide Pyramid to make healthful food choices. The Foods You Choose The foods
The Food Guide Pyramid In this lesson, you will Learn About n What influences a person s food choices. n How to use the Food Guide Pyramid to make healthful food choices. The Foods You Choose The foods
Chapter 1: Food, Nutrition, and Health Test Bank
 Chapter 1: Food, Nutrition, and Health Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Promoting a health care service that improves diabetes management for the elderly in a community would assist in which of the following?
Chapter 1: Food, Nutrition, and Health Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Promoting a health care service that improves diabetes management for the elderly in a community would assist in which of the following?
Following Dietary Guidelines
 LESSON 26 Following Dietary Guidelines Before You Read List some things you know and would like to know about recommended diet choices. What You ll Learn the different food groups in MyPyramid the Dietary
LESSON 26 Following Dietary Guidelines Before You Read List some things you know and would like to know about recommended diet choices. What You ll Learn the different food groups in MyPyramid the Dietary
PREGNANCY PROJECT RACHEL CRAWFORD
 PART I (I-V): PREGNANCY PROJECT RACHEL CRAWFORD I. Identifying data A. First name: Aija B. Description of the individual: Aija is the wife of a gamer who works at Blizzard entertainment in the customer
PART I (I-V): PREGNANCY PROJECT RACHEL CRAWFORD I. Identifying data A. First name: Aija B. Description of the individual: Aija is the wife of a gamer who works at Blizzard entertainment in the customer
Test Bank For Williams' Essentials of Nutrition and Diet Therapy 10th edittion by Schlenker and Roth
 Test Bank For Williams' Essentials of Nutrition and Diet Therapy 10th edittion by Schlenker and Roth Chapter 01: Nutrition and Health Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major focus of nutritional recommendations
Test Bank For Williams' Essentials of Nutrition and Diet Therapy 10th edittion by Schlenker and Roth Chapter 01: Nutrition and Health Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major focus of nutritional recommendations
PREGNANCY PROJECT. Brianne Squires 2/28/14 NDFS 424. PART I (Complete Sections I V): I. Identifying data (1 point)
 PREGNANCY PROJECT Brianne Squires 2/28/14 NDFS 424 PART I (Complete Sections I V): I. Identifying data (1 point) A. Chelsea B. Chelsea is attending BYU, majoring in elementary education. She is working
PREGNANCY PROJECT Brianne Squires 2/28/14 NDFS 424 PART I (Complete Sections I V): I. Identifying data (1 point) A. Chelsea B. Chelsea is attending BYU, majoring in elementary education. She is working
Food Labels: Becoming a Healthier Educated Consumer
 Food Labels: Becoming a Healthier Educated Consumer Steven Rudner, BS Nutrition & Dietetics Dietetic Intern, Sodexo Allentown www.dieteticintern.com www.sodexo.com Reading and understanding food labels
Food Labels: Becoming a Healthier Educated Consumer Steven Rudner, BS Nutrition & Dietetics Dietetic Intern, Sodexo Allentown www.dieteticintern.com www.sodexo.com Reading and understanding food labels
NUTRITION IN CHILDHOOD
 NUTRITION IN CHILDHOOD Nutrient requirement Children growing & developing need more nutritious food May be at risk for malnutrition if : - poor appetite for a long period - eat a limited number of food
NUTRITION IN CHILDHOOD Nutrient requirement Children growing & developing need more nutritious food May be at risk for malnutrition if : - poor appetite for a long period - eat a limited number of food
NUTRITION: THE STUDY OF HOW THE BODY UTILIZES THE FOOD WE EAT
 NUTRITION: THE STUDY OF HOW THE BODY UTILIZES THE FOOD WE EAT NUTRIENT: a chemical found in food that is needed for life and growth, & the building blocks to make your body function correctly! WHAT DO
NUTRITION: THE STUDY OF HOW THE BODY UTILIZES THE FOOD WE EAT NUTRIENT: a chemical found in food that is needed for life and growth, & the building blocks to make your body function correctly! WHAT DO
Chapter 4: Nutrition. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 4: Nutrition ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction SCAN group of dieticians who practice in sports and cardiovascular nutrition [SCAN]; locate local SCAN dieticians by contacting
Chapter 4: Nutrition ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction SCAN group of dieticians who practice in sports and cardiovascular nutrition [SCAN]; locate local SCAN dieticians by contacting
Facts that you need to know
 NUTRITION This article explores the basic concepts of nutrition and provides useful tips on healthy diet My neighbor walks up to me asking whether I am aware of the nutritional value of a new food product
NUTRITION This article explores the basic concepts of nutrition and provides useful tips on healthy diet My neighbor walks up to me asking whether I am aware of the nutritional value of a new food product
Foundations of Personal Fitness. Chapter 4 Nutrition and Your Personal Fitness
 Foundations of Personal Fitness Chapter 4 Nutrition and Your Personal Fitness Lesson 1: The Importance of Nutrition Healthful Eating Taking in the proper amount of nutrients each day Nutrients substances
Foundations of Personal Fitness Chapter 4 Nutrition and Your Personal Fitness Lesson 1: The Importance of Nutrition Healthful Eating Taking in the proper amount of nutrients each day Nutrients substances
Hemoglobin. What is it? Why is iron important? What food sources contain iron?
 Hemoglobin What is it? Why is iron important? What food sources contain iron? Poor Diet Lack of Iron and B12 vitamins in the diet Blood Loss Pregnancy Genetics Fatigue due to cells and tissues not being
Hemoglobin What is it? Why is iron important? What food sources contain iron? Poor Diet Lack of Iron and B12 vitamins in the diet Blood Loss Pregnancy Genetics Fatigue due to cells and tissues not being
Case Study #1: General Nutritional Assessment Matthew Thomas
 Fall 13 Case Study #1: General Nutritional Assessment Matthew Thomas September 17, 2013 Professor Dray DIE 3213 2 1. Convert her height and weight to centimeters and kilograms. Calculate her % IBW, % UBW,
Fall 13 Case Study #1: General Nutritional Assessment Matthew Thomas September 17, 2013 Professor Dray DIE 3213 2 1. Convert her height and weight to centimeters and kilograms. Calculate her % IBW, % UBW,
Classes of Nutrients A Diet
 Ch. 7 Notes Section 1: What is Nutrition? is the science or study of food and the ways the body uses food. are substances in food that provide energy or help form body tissues and are necessary for life
Ch. 7 Notes Section 1: What is Nutrition? is the science or study of food and the ways the body uses food. are substances in food that provide energy or help form body tissues and are necessary for life
THE SAME EFFECT WAS NOT FOUND WITH SPIRITS 3-5 DRINKS OF SPIRITS PER DAY WAS ASSOCIATED WITH INCREASED MORTALITY
 ALCOHOL NEGATIVE CORRELATION BETWEEN 1-2 DRINKS PER DAY AND THE INCIDENCE OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE SOME HAVE SHOWN THAT EVEN 3-4 DRINKS PER DAY CAN BE BENEFICIAL - WHILE OTHERS HAVE FOUND IT TO BE HARMFUL
ALCOHOL NEGATIVE CORRELATION BETWEEN 1-2 DRINKS PER DAY AND THE INCIDENCE OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE SOME HAVE SHOWN THAT EVEN 3-4 DRINKS PER DAY CAN BE BENEFICIAL - WHILE OTHERS HAVE FOUND IT TO BE HARMFUL
Reserve the computer lab. You will need one computer for each student. Earphones are recommended.
 Section 4 Purpose Section 4 explains macronutrients and how they are broken down through the process of digestion. Students will have a chance to practice reading labels and figuring out calories from
Section 4 Purpose Section 4 explains macronutrients and how they are broken down through the process of digestion. Students will have a chance to practice reading labels and figuring out calories from
Case Study #4: Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease
 Helen Jang Tara Hooley John K Rhee Case Study #4: Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease 7. What risk factors does Mrs. Sanders currently have? The risk factors that Mrs. Sanders has are high blood pressure
Helen Jang Tara Hooley John K Rhee Case Study #4: Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease 7. What risk factors does Mrs. Sanders currently have? The risk factors that Mrs. Sanders has are high blood pressure
KEY INDICATORS OF NUTRITION RISK
 NUTRITION TOOLS KEY INDICATORS OF Consumes fewer than 2 servings of fruit or fruit juice per day. Consumes fewer than 3 servings of vegetables per day. Food Choices Fruits and vegetables provide dietary
NUTRITION TOOLS KEY INDICATORS OF Consumes fewer than 2 servings of fruit or fruit juice per day. Consumes fewer than 3 servings of vegetables per day. Food Choices Fruits and vegetables provide dietary
Diet Analysis Assignment KNH 102 Sections B, C, D Spring 2011
 Diet Analysis Assignment KNH 102 Sections B, C, D Spring 2011 Name: Kathryn Davis 1. Collect the following demographic information from your client. Age 19 Sex Female Ethnicity White Vegetarian? Specify
Diet Analysis Assignment KNH 102 Sections B, C, D Spring 2011 Name: Kathryn Davis 1. Collect the following demographic information from your client. Age 19 Sex Female Ethnicity White Vegetarian? Specify
BASIC NUTRITION NUTRITION /17/2017. Agenda
 BASIC NUTRITION Haley Quade, M A, RD, CD Tarrah M ccreary, M S, RD, SNS Agenda Gain a basic understanding of general nutrition Become familiar with the Dietary Guidelines for Americans current standards
BASIC NUTRITION Haley Quade, M A, RD, CD Tarrah M ccreary, M S, RD, SNS Agenda Gain a basic understanding of general nutrition Become familiar with the Dietary Guidelines for Americans current standards
Meal Menu Approximate Amount Eaten
 Meal Menu Approximate Amount Eaten Myself 16 Year Old Active Male Teen 3 Year Old Female Child ¼ cup 1 slice 70 Year Old Female Breakfast Special K Cereal(red berries) 1 cup 1 Banana (slices) ¼ cup ¾ cup
Meal Menu Approximate Amount Eaten Myself 16 Year Old Active Male Teen 3 Year Old Female Child ¼ cup 1 slice 70 Year Old Female Breakfast Special K Cereal(red berries) 1 cup 1 Banana (slices) ¼ cup ¾ cup
Nutrition Basics. Chapter McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
 Nutrition Basics Chapter 12 1 The Body s Nutritional Requirements Essential nutrients The Six Essential Nutrients: Proteins, Fats, Carbohydrates, Vitamins, Minerals, Water Defined as : Nutrients one must
Nutrition Basics Chapter 12 1 The Body s Nutritional Requirements Essential nutrients The Six Essential Nutrients: Proteins, Fats, Carbohydrates, Vitamins, Minerals, Water Defined as : Nutrients one must
Chapter 02 Tools of a Healthy Diet
 Chapter 02 Tools of a Healthy Diet Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which is true about the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)? A. They apply to people in Canada and the U.S. B. They differ by age group. C.
Chapter 02 Tools of a Healthy Diet Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which is true about the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)? A. They apply to people in Canada and the U.S. B. They differ by age group. C.
NAME/ID: SAMPLE PATIENT SEX: FEMALE ACC #: F DATE: NOV 12, 2015 IMPORTANT INFORMATION
 Personal Details Name: SAMPLE PATIENT DOB: Jan 1, 19XX Gender: Female Ethnicity: Caucasian Report Date: Nov 12, 2015 Received Date: Nov 2, 2015 IMPORTANT INFORMATION PAGE 3 Test Performed / Method Genotyping
Personal Details Name: SAMPLE PATIENT DOB: Jan 1, 19XX Gender: Female Ethnicity: Caucasian Report Date: Nov 12, 2015 Received Date: Nov 2, 2015 IMPORTANT INFORMATION PAGE 3 Test Performed / Method Genotyping
Nutrition BCH 445 L e c t u r e s : 1-3
 Nutrition BCH 445 L e c t u r e s : 1-3 Biochemistry department Sciences college Course description This course is designed to study nutrition via biochemical concepts with emphasis on biochemical and
Nutrition BCH 445 L e c t u r e s : 1-3 Biochemistry department Sciences college Course description This course is designed to study nutrition via biochemical concepts with emphasis on biochemical and
Nutrition and Cancer. Prof. Suhad Bahijri
 Nutrition and Cancer Objectives 1. Discuss current knowledge regarding nutritional prevention of cancer 2. Discuss goals for the cancer patient 3. Explain how cancer treatment affects nutritional needs
Nutrition and Cancer Objectives 1. Discuss current knowledge regarding nutritional prevention of cancer 2. Discuss goals for the cancer patient 3. Explain how cancer treatment affects nutritional needs
[MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION]
![[MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION] [MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION]](/thumbs/89/98489114.jpg) Case 7 By: Emily Lancaster October 19, 2012 Medical Nutrition Therapy Case Study #3 [MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION] I HAVE NOT GIVEN, RECIVED OR USED ANY UNAUTHORIZED ASSISTANCE ON THIS ASSIGNMENT. X 1. Mr. Klosterman
Case 7 By: Emily Lancaster October 19, 2012 Medical Nutrition Therapy Case Study #3 [MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION] I HAVE NOT GIVEN, RECIVED OR USED ANY UNAUTHORIZED ASSISTANCE ON THIS ASSIGNMENT. X 1. Mr. Klosterman
Assignment Overview. NOTE: Make sure you save your graded version of Part I because you will need to submit it (the graded version) with your Part II.
 PREGNANCY PROJECT (55 POINTS) The purpose of this project is to provide you with a real-life experience to enhance your skills in assessing the nutritional status of a pregnant woman and in providing appropriate
PREGNANCY PROJECT (55 POINTS) The purpose of this project is to provide you with a real-life experience to enhance your skills in assessing the nutritional status of a pregnant woman and in providing appropriate
Appendix G. U.S. Nutrition Recommendations and Guidelines. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, Balancing Calories to Manage Weight
 Appendix G U.S. Nutrition Recommendations and Guidelines Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2010 Balancing Calories to Manage Weight Prevent and/or reduce overweight and obesity through improved eating
Appendix G U.S. Nutrition Recommendations and Guidelines Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2010 Balancing Calories to Manage Weight Prevent and/or reduce overweight and obesity through improved eating
Maintain Cholesterol
 Maintain Cholesterol What is Cholesterol? Cholesterol is a Lipid Molecule that has a waxy appearance and is found in every cell of the body and has some important natural functions. It is manufactured
Maintain Cholesterol What is Cholesterol? Cholesterol is a Lipid Molecule that has a waxy appearance and is found in every cell of the body and has some important natural functions. It is manufactured
Disorders of Lipid Metabolism Toolkit Table of Contents
 American Dietetic Association Table of Contents 1. Acknowledgements 2. Overview of 3. Medical Nutrition Therapy Protocol Forms for Implementing Disorders of Lipid Metabolism Evidence-Based Guideline a.
American Dietetic Association Table of Contents 1. Acknowledgements 2. Overview of 3. Medical Nutrition Therapy Protocol Forms for Implementing Disorders of Lipid Metabolism Evidence-Based Guideline a.
You Bet Your Weight. Karah Mechlowitz
 You Bet Your Weight Karah Mechlowitz What to Expect for Today n Introduction to macronutrients n Breakdown of each macronutrient n Ways to track macronutrients n Wrap up What are the macronutrients? Carbohydrates
You Bet Your Weight Karah Mechlowitz What to Expect for Today n Introduction to macronutrients n Breakdown of each macronutrient n Ways to track macronutrients n Wrap up What are the macronutrients? Carbohydrates
The Nutritional Information Panel is a pretty technical looking piece of artwork and the main question people ask about it WHAT DOES IT ALL MEAN?
 The Nutritional Information Panel is a pretty technical looking piece of artwork and the main question people ask about it is WHAT DOES IT ALL MEAN? Well, we want you to understand it as well as we do.
The Nutritional Information Panel is a pretty technical looking piece of artwork and the main question people ask about it is WHAT DOES IT ALL MEAN? Well, we want you to understand it as well as we do.
Screening Results. Juniata College. Juniata College. Screening Results. October 11, October 12, 2016
 Juniata College Screening Results Juniata College Screening Results October 11, 2016 & October 12, 2016 JUNIATA COLLEGE The J.C. Blair Hospital CARES team screened 55 Juniata College employees on October
Juniata College Screening Results Juniata College Screening Results October 11, 2016 & October 12, 2016 JUNIATA COLLEGE The J.C. Blair Hospital CARES team screened 55 Juniata College employees on October
Children, Adolescents and Teen Athlete
 Children, Adolescents and Teen Athlete General Nutritional Needs Across the Life Cycle Many health problems are linked to Nutrition It would be wise to know and follow the guidelines of the Food Pyramid
Children, Adolescents and Teen Athlete General Nutritional Needs Across the Life Cycle Many health problems are linked to Nutrition It would be wise to know and follow the guidelines of the Food Pyramid
Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing: 8 Edition Test Bank Ladewig
 Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing: 8 Edition Test Bank Ladewig Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-contemporarymaternal-newborn-nursing-care-8th-edition/ Chapter 12 Question
Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing: 8 Edition Test Bank Ladewig Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-contemporarymaternal-newborn-nursing-care-8th-edition/ Chapter 12 Question
Chapter 2. Tools for Designing a Healthy Diet
 Chapter 2 Tools for Designing a Healthy Diet Fig. 2.p035 Philosophy That Works Consume a variety of foods balanced by a moderate intake of each food Variety choose different foods Balanced do not overeat
Chapter 2 Tools for Designing a Healthy Diet Fig. 2.p035 Philosophy That Works Consume a variety of foods balanced by a moderate intake of each food Variety choose different foods Balanced do not overeat
ABLE TO READ THE LABEL?
 ARE ABLE TO READ THE LABEL? A Consumer s Guide to Navigating Food Labels Food and Drug Safety Program Consumer and Environmental Health Services Phone: 609-826-4935 Fax: 609-826-4990 http://nj.gov/health/eoh/foodweb/
ARE ABLE TO READ THE LABEL? A Consumer s Guide to Navigating Food Labels Food and Drug Safety Program Consumer and Environmental Health Services Phone: 609-826-4935 Fax: 609-826-4990 http://nj.gov/health/eoh/foodweb/
HEÆRT HEÆLTH. Cardiovascular disease is
 Cardiovascular disease is the term for several diseases which include high blood pressure, stroke, Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) and others. For this lesson we will address CHD, the leading cause of death
Cardiovascular disease is the term for several diseases which include high blood pressure, stroke, Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) and others. For this lesson we will address CHD, the leading cause of death
Nutrition Analysis Project. Robin Hernandez. California State University, San Bernardino. HSCL Dr. Chen-Maynard
 Nutrition Analysis Project Robin Hernandez California State University, San Bernardino HSCL 365 - Dr. Chen-Maynard March 15, 2012 1. A) Personal Background: Summary of Findings Name: Pregnancy: Robin S.
Nutrition Analysis Project Robin Hernandez California State University, San Bernardino HSCL 365 - Dr. Chen-Maynard March 15, 2012 1. A) Personal Background: Summary of Findings Name: Pregnancy: Robin S.
HEALTHY EATING. What you need to know for a long and healthy life. March National Nutrition Month
 HEALTHY EATING What you need to know for a long and healthy life March National Nutrition Month 890246 This presentation is for informational purposes only. Material within this presentation should not
HEALTHY EATING What you need to know for a long and healthy life March National Nutrition Month 890246 This presentation is for informational purposes only. Material within this presentation should not
Study Exercises: 1. What special dietary needs do children <1 yr of age have and why?
 Exam 3 Review: Lectures 21+ Nutrition 150 Winter 2007 Exam: Monday, March 19, 8-10am in regular classroom Strategies for Studying: 1) Go over all lectures including those given by fellow students 2) Read
Exam 3 Review: Lectures 21+ Nutrition 150 Winter 2007 Exam: Monday, March 19, 8-10am in regular classroom Strategies for Studying: 1) Go over all lectures including those given by fellow students 2) Read
Chapter 2 Nutrition Tools Standards and Guidelines
 Chapter 2 Nutrition Tools Standards and Guidelines MULTICHOICE 1. Which of the following statements best describes the recommended dietary allowances (RDA)? (A) they are average nutrient intake goals that
Chapter 2 Nutrition Tools Standards and Guidelines MULTICHOICE 1. Which of the following statements best describes the recommended dietary allowances (RDA)? (A) they are average nutrient intake goals that
Nutrition Competency Framework (NCF) March 2016
 K1 SCIENCES understanding of the basic sciences in relation to nutrition Framework (NCF) March 2016 1. Describe the functions of essential nutrients, and the basis for the biochemical demand for energy
K1 SCIENCES understanding of the basic sciences in relation to nutrition Framework (NCF) March 2016 1. Describe the functions of essential nutrients, and the basis for the biochemical demand for energy
Nutrition. Chapter 45. Reada Almashagba
 Nutrition Chapter 45 1 Nutrition: - Nutrient are organic substances found in food and are required for body function - No one food provide all essential nutrient Major function of nutrition: providing
Nutrition Chapter 45 1 Nutrition: - Nutrient are organic substances found in food and are required for body function - No one food provide all essential nutrient Major function of nutrition: providing
Nutrition Basics. Health, Wellness & Fitness. Brenda Brown
 Nutrition Basics Health, Wellness & Fitness Brenda Brown bbrown9@asu.edu Why do we eat? Building blocks to fuel our bodies Hunger Don t want to starve Socialization Emotional eating or not eating when
Nutrition Basics Health, Wellness & Fitness Brenda Brown bbrown9@asu.edu Why do we eat? Building blocks to fuel our bodies Hunger Don t want to starve Socialization Emotional eating or not eating when
Session 21: Heart Health
 Session 21: Heart Health Heart disease and stroke are the leading causes of death in the world for both men and women. People with pre-diabetes, diabetes, and/or the metabolic syndrome are at higher risk
Session 21: Heart Health Heart disease and stroke are the leading causes of death in the world for both men and women. People with pre-diabetes, diabetes, and/or the metabolic syndrome are at higher risk
Part 1: Cronometer Food Diary. Date. Add Food. Part 2: Cronometer Nutrition Report
 This assignment has 3 parts: 1) Food Diary: Cronometer (https://cronometer.com) is a free diet analysis tool. You will record your food & beverage intake for 3-5 days. Entering your exercise is optional.
This assignment has 3 parts: 1) Food Diary: Cronometer (https://cronometer.com) is a free diet analysis tool. You will record your food & beverage intake for 3-5 days. Entering your exercise is optional.
Nutrition. For the young athlete. Georgia Bevan Accredited Practicing Dietitian. Georgia Bevan APD -Eclipsefuel.com
 Nutrition For the young athlete Georgia Bevan Accredited Practicing Dietitian What will be covered? Different energy sources in food Impact of nutrients on sports performance and health Target nutrients
Nutrition For the young athlete Georgia Bevan Accredited Practicing Dietitian What will be covered? Different energy sources in food Impact of nutrients on sports performance and health Target nutrients
Macronutrients and Dietary Patterns for Glucose Control
 제 20 회대한당뇨병학회춘계학술대회 Macronutrients and Dietary Patterns for Glucose Control 2017.5.13 서울대학교병원임정현 Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Contents Review of Nutrition Recommendation
제 20 회대한당뇨병학회춘계학술대회 Macronutrients and Dietary Patterns for Glucose Control 2017.5.13 서울대학교병원임정현 Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Contents Review of Nutrition Recommendation
Prevent and/or reduce overweight and obesity through improved eating and physical activity.
 A summary of the key recommendations to healthier living for Americans of the 2010 Dietary Guidelines and a weight-loss guide to combat obesity are offered by the May 2011 issue of the Tufts Health & Nutrition
A summary of the key recommendations to healthier living for Americans of the 2010 Dietary Guidelines and a weight-loss guide to combat obesity are offered by the May 2011 issue of the Tufts Health & Nutrition
Note-Taking Strategy. You will receive another guided note sheet to record all notes. Anything that is green should be recorded.
 Note-Taking Strategy You will receive another guided note sheet to record all notes. Anything that is green should be recorded. Giving Your Body What It Needs Each of the six nutrients has a specific job
Note-Taking Strategy You will receive another guided note sheet to record all notes. Anything that is green should be recorded. Giving Your Body What It Needs Each of the six nutrients has a specific job
Nutrition Glossary for Healthy Food & Special Diet
 Nutrition Glossary for Healthy Food & Special Diet The nutrition glossary is a tool to help you understand the basics of nutrition through an understanding of the key terminology used throughout the food
Nutrition Glossary for Healthy Food & Special Diet The nutrition glossary is a tool to help you understand the basics of nutrition through an understanding of the key terminology used throughout the food
Nutrients are: water carbohydrates lipids proteins. minerals vitamins fiber
 Nutrients are: water carbohydrates lipids proteins minerals vitamins fiber WATER Essential nutrient 55-65% body weight Body loses water through evaporation, excretion, and respiration The only nutrient
Nutrients are: water carbohydrates lipids proteins minerals vitamins fiber WATER Essential nutrient 55-65% body weight Body loses water through evaporation, excretion, and respiration The only nutrient
Coach on Call. Thank you for your interest in Lifestyle Changes as a Treatment Option. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful.
 It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
MyPlate.gov Assignment
 Name: Class Hour: MyPlate.gov Assignment Directions: In 2011 the USDA came out with MyPlate.gov, a way to help Americans live a more healthy life. In this assignment you will explore the site and see how
Name: Class Hour: MyPlate.gov Assignment Directions: In 2011 the USDA came out with MyPlate.gov, a way to help Americans live a more healthy life. In this assignment you will explore the site and see how
For Growing Bones Which Milk?
 For Growing Bones Which Milk? Why Milk? Check the Nutrition Facts label on milk cartons. You will see several nutrients that everyone in your family needs. Calcium and vitamin D for your child s growing
For Growing Bones Which Milk? Why Milk? Check the Nutrition Facts label on milk cartons. You will see several nutrients that everyone in your family needs. Calcium and vitamin D for your child s growing
OM s Health Corner Cholesterol & Heart Disease!!
 Cholesterol & Heart Disease!! We may associate cholesterol with fatty foods, but most of the waxy substance is made by our own bodies. The liver produces 75% of the cholesterol that circulates in our blood.
Cholesterol & Heart Disease!! We may associate cholesterol with fatty foods, but most of the waxy substance is made by our own bodies. The liver produces 75% of the cholesterol that circulates in our blood.
Estimated mean cholestero intake. (mg/day) NHANES survey cycle
 320 Estimated mean cholestero intake (mg/day) 300 280 260 240 220 200 2001-02 2003-04 2005-06 2007-08 2009-10 2011-12 2013-14 NHANES survey cycle Figure S1. Estimated mean 1 (95% confidence intervals)
320 Estimated mean cholestero intake (mg/day) 300 280 260 240 220 200 2001-02 2003-04 2005-06 2007-08 2009-10 2011-12 2013-14 NHANES survey cycle Figure S1. Estimated mean 1 (95% confidence intervals)
To see a description of the Academy Recommendation Rating Scheme (Strong, Fair, Weak, Consensus, Insufficient Evidence), click here.
 Gestational Diabetes Gestational Diabetes (GDM) Guideline (2016) Gestational Diabetes GDM: Executive Summary of Recommendations (2016) Executive Summary of Recommendations Below are the major recommendations
Gestational Diabetes Gestational Diabetes (GDM) Guideline (2016) Gestational Diabetes GDM: Executive Summary of Recommendations (2016) Executive Summary of Recommendations Below are the major recommendations
STAYING HEART HEALTHY PAVAN PATEL, MD CONSULTANT CARDIOLOGIST FLORIDA HEART GROUP
 STAYING HEART HEALTHY PAVAN PATEL, MD CONSULTANT CARDIOLOGIST FLORIDA HEART GROUP What is Heart Disease Cardiovascular Disease (CVD): Heart or Blood vessels are not working properly. Most common reason
STAYING HEART HEALTHY PAVAN PATEL, MD CONSULTANT CARDIOLOGIST FLORIDA HEART GROUP What is Heart Disease Cardiovascular Disease (CVD): Heart or Blood vessels are not working properly. Most common reason
Study of how your body takes in and uses food
 Chapter 10 Lesson 1 Study of how your body takes in and uses food Nutrients substances in food that your body needs to grow, repair, and supply energy Calorie unit of heat used to measure the energy your
Chapter 10 Lesson 1 Study of how your body takes in and uses food Nutrients substances in food that your body needs to grow, repair, and supply energy Calorie unit of heat used to measure the energy your
Lecture 4 Nutrition Part 2 Nutrition 1. Healthy Diet 2. Sugar 3. Consumer Concerns
 Lecture 4 Nutrition Part 2 1 Nutrition 1. Healthy Diet 2. Sugar 3. Consumer Concerns 2 1 Healthy Diet! 3 Four basic behaviors that constitute a "healthy lifestyle" 1. A good diet, 2. Moderate Exercise,
Lecture 4 Nutrition Part 2 1 Nutrition 1. Healthy Diet 2. Sugar 3. Consumer Concerns 2 1 Healthy Diet! 3 Four basic behaviors that constitute a "healthy lifestyle" 1. A good diet, 2. Moderate Exercise,
DFM 253 Nutrition Project
 DFM 253 Nutrition Project Sonia Malhotra March 7, 2009 Issue 1= Consumed 241 % of Sodium vs. Goal Report Problem Statement= At Risk for Hypertension Pg 410, Section: Sodium Recommendations, High Sodium
DFM 253 Nutrition Project Sonia Malhotra March 7, 2009 Issue 1= Consumed 241 % of Sodium vs. Goal Report Problem Statement= At Risk for Hypertension Pg 410, Section: Sodium Recommendations, High Sodium
ENERGY NUTRIENTS: THE BIG PICTURE WHY WE EAT FUNCTIONS FATS FAT, CARBS, PROTEIN
 ENERGY NUTRIENTS: FAT, CARBS, PROTEIN Angeline B. David, DRPH, MHS NAD Health Summit March 14, 2013 The science of cooking is not a small matter.... This art should be regarded as the most valuable of
ENERGY NUTRIENTS: FAT, CARBS, PROTEIN Angeline B. David, DRPH, MHS NAD Health Summit March 14, 2013 The science of cooking is not a small matter.... This art should be regarded as the most valuable of
Topic 12-2 Making Daily Food Choices
 Topic 12-2 Making Daily Food Choices In this topic, you will learn how to choose foods that will supply nutrients, as well as Influences on food choices MyPyramid The Dietary Guidelines for Americans Making
Topic 12-2 Making Daily Food Choices In this topic, you will learn how to choose foods that will supply nutrients, as well as Influences on food choices MyPyramid The Dietary Guidelines for Americans Making
EAT GOOD FATS TO MEET YOUR HEALTH GOALS!
 EAT GOOD FATS TO MEET YOUR HEALTH GOALS! THE POWER OF GOOD FATS Did you know healthy fats provide a wealth of health benefits? At almost any age, replacing saturated fats* with polyunsaturated fats (omega-3,
EAT GOOD FATS TO MEET YOUR HEALTH GOALS! THE POWER OF GOOD FATS Did you know healthy fats provide a wealth of health benefits? At almost any age, replacing saturated fats* with polyunsaturated fats (omega-3,
Chapter 6 Notes Lesson 1
 Chapter 6 Notes Lesson 1 Maintaining a Healthy Weight 1) What is body image? The way you see your body 2) What factors affect your body image? Media images Attitudes of family and friends The Weight-Calorie
Chapter 6 Notes Lesson 1 Maintaining a Healthy Weight 1) What is body image? The way you see your body 2) What factors affect your body image? Media images Attitudes of family and friends The Weight-Calorie
25* or higher Underweight. 240 mg/dl and above High (More than twice the risk as desirable level.) OK, but higher is better
 Biometrics Screening Biometric Health Indicators The charts below provide a summary of the ranges for each of the biometric screening tests. Be sure to check with your doctor if your results are outside
Biometrics Screening Biometric Health Indicators The charts below provide a summary of the ranges for each of the biometric screening tests. Be sure to check with your doctor if your results are outside
Optimizing Nutrition for Bone Health
 Virtual Education Forum Optimizing Nutrition for Bone Health Presented by: Andrea Miller MHSc, RD 1 Outline: Optimizing Nutrition for Principles of Healthy Eating Bone Health Canada s Food Guide- A Review
Virtual Education Forum Optimizing Nutrition for Bone Health Presented by: Andrea Miller MHSc, RD 1 Outline: Optimizing Nutrition for Principles of Healthy Eating Bone Health Canada s Food Guide- A Review
Tools for Healthy Eating
 Chapter 2 Tools for Healthy Eating Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is not a key principle of healthy eating? A. availability B. balance C. variety D. moderation REF: 38 2. A diet consisting of
Chapter 2 Tools for Healthy Eating Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is not a key principle of healthy eating? A. availability B. balance C. variety D. moderation REF: 38 2. A diet consisting of
Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies
 Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies Introduction Nutrients Components of food required for the body s functioning Roles: Provide energy Building material Maintenance
Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies Introduction Nutrients Components of food required for the body s functioning Roles: Provide energy Building material Maintenance
Dietitians of Canada Recommendations for School Food and Nutrition for Ontario Ministry of Education
 Dietitians of Canada Recommendations for School Food and Nutrition for Ontario Ministry of Education Role of Schools in Promoting Healthy Eating Schools are uniquely positioned to provide knowledge on
Dietitians of Canada Recommendations for School Food and Nutrition for Ontario Ministry of Education Role of Schools in Promoting Healthy Eating Schools are uniquely positioned to provide knowledge on
Six Nutrients. Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy. Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water
 Nutrients Six Nutrients Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water Water Function: most essential nutrient Helps digest and absorb
Nutrients Six Nutrients Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water Water Function: most essential nutrient Helps digest and absorb
3 Day Diet Analysis for Nutrition 219
 Name 3 Day Diet Analysis for Nutrition 219 Keep a record of everything you eat and drink for 3 days. Be specific. Was it white or wheat bread, 1% or 2% milk, 1 cup or 1½ cups, did you fry it in oil or
Name 3 Day Diet Analysis for Nutrition 219 Keep a record of everything you eat and drink for 3 days. Be specific. Was it white or wheat bread, 1% or 2% milk, 1 cup or 1½ cups, did you fry it in oil or
DIETARY GUIDELINES FOR AMERICANS, ,
 DIETARY GUIDELINES FOR AMERICANS, 2015-2020, AND THE STATE OF THE AMERICAN DIET Vanessa da Silva, PhD, RD Assistant Professor and Nutrition Specialist University of Arizona DIETARY GUIDELINES FOR AMERICANS
DIETARY GUIDELINES FOR AMERICANS, 2015-2020, AND THE STATE OF THE AMERICAN DIET Vanessa da Silva, PhD, RD Assistant Professor and Nutrition Specialist University of Arizona DIETARY GUIDELINES FOR AMERICANS
The 6 Essential Nutrients for Proper Nutrition. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3. Protein 4. Vitamins 5. Minerals 6. Water
 Activity Level Inactive (little to no regular exercise) Moderately Active (20-30 minutes of exercise3-4 times per week Very Active (30-40 minutes of vigorous, sustained exercise 5-7 times weekly How Active
Activity Level Inactive (little to no regular exercise) Moderately Active (20-30 minutes of exercise3-4 times per week Very Active (30-40 minutes of vigorous, sustained exercise 5-7 times weekly How Active
Got Heart? Nutrition for Cardiovascular Health
 Objectives Got Heart? Nutrition for Cardiovascular Health 1. Achieve a basic understanding of the evidencebased dietary and lifestyle guidelines for reducing cardiovascular risk 2. Recognize potential
Objectives Got Heart? Nutrition for Cardiovascular Health 1. Achieve a basic understanding of the evidencebased dietary and lifestyle guidelines for reducing cardiovascular risk 2. Recognize potential
Basic Nutrition. The Basics of Nutrition. The Six Basic Nutrients. calories. How it Works. How it works 10/5/16
 Basic Nutrition The Basics of Nutrition Nutrition: The study of how your body uses the food that you eat Nutrient: a chemical substance in food that helps maintain the body The Six Basic Nutrients Carbohydrates
Basic Nutrition The Basics of Nutrition Nutrition: The study of how your body uses the food that you eat Nutrient: a chemical substance in food that helps maintain the body The Six Basic Nutrients Carbohydrates
Test Bank 1 for Nutrition: Your Life Science 1e Module 2 Tools to Plan, Manage, and Evaluate Diets. Exam A
 Module 2 Test Bank ~ 1 Test Bank 1 for Nutrition: Your Life Science 1e Module 2 Tools to Plan, Manage, and Evaluate Diets Question Information Key ANS = correct answer REF = page reference TOP = module
Module 2 Test Bank ~ 1 Test Bank 1 for Nutrition: Your Life Science 1e Module 2 Tools to Plan, Manage, and Evaluate Diets Question Information Key ANS = correct answer REF = page reference TOP = module
10/3/2016. SUPERSIZE YOUR KNOWLEDGE OF the CARDIAC DIET. What is a cardiac diet. If it tastes good, spit it out!!
 SUPERSIZE YOUR KNOWLEDGE OF the CARDIAC DIET What is a cardiac diet If it tastes good, spit it out!! 2 1 Heart healthy diet includes: Limiting saturated fat Including unsaturated fats Including omega 3
SUPERSIZE YOUR KNOWLEDGE OF the CARDIAC DIET What is a cardiac diet If it tastes good, spit it out!! 2 1 Heart healthy diet includes: Limiting saturated fat Including unsaturated fats Including omega 3
Coach on Call. Thank you for your interest in understanding the new Nutrition Facts labels. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful.
 Coach on Call It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in understanding the new labels. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about
Coach on Call It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in understanding the new labels. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter
 Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Nutrition for My Health:
 Nutrition for My Health: Balancing Protein in My Diet Richard Solomon, M.D. and Laurinda Solomon, R.N. (Adapted from a chapter in a program called PEAK [People Educated and Aware about Kidney Disease]
Nutrition for My Health: Balancing Protein in My Diet Richard Solomon, M.D. and Laurinda Solomon, R.N. (Adapted from a chapter in a program called PEAK [People Educated and Aware about Kidney Disease]
Health Score SM Member Guide
 Health Score SM Member Guide Health Score Your Health Score is a unique, scientifically based assessment of seven critical health indicators gathered during your health screening. This number is where
Health Score SM Member Guide Health Score Your Health Score is a unique, scientifically based assessment of seven critical health indicators gathered during your health screening. This number is where
'Eat Smart' - Nutrition for a Healthy Heart
 Definitions - Fats & Cholesterol Found in Blood LDL HDL 'low density lipoprotein' also known as 'bad cholesterol' major cholesterol-carrying molecule in blood delivers cholesterol to the arterial walls
Definitions - Fats & Cholesterol Found in Blood LDL HDL 'low density lipoprotein' also known as 'bad cholesterol' major cholesterol-carrying molecule in blood delivers cholesterol to the arterial walls
Section 3. Diets for Diabetics. Objectives. Vocabulary vegetarian vegan food allergy food intolerance. Dear Advice Line,
 Section 3 ~ Dear Advice Line, 've recently become a vegetarian, and it has my parents worried. They think 'm not getting enough nutrients, and they keep telling me that have to eat meat to be healthy.
Section 3 ~ Dear Advice Line, 've recently become a vegetarian, and it has my parents worried. They think 'm not getting enough nutrients, and they keep telling me that have to eat meat to be healthy.
American Diabetes Association: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2015
 American Diabetes Association: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2015 Synopsis of ADA standards relevant to the 11 th Scope of Work under Task B.2 ASSESSMENT OF GLYCEMIC CONTROL Recommendations: Perform
American Diabetes Association: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2015 Synopsis of ADA standards relevant to the 11 th Scope of Work under Task B.2 ASSESSMENT OF GLYCEMIC CONTROL Recommendations: Perform
Instructions for 3 Day Diet Analysis for Nutrition 219
 Name Instructions for 3 Day Diet Analysis for Nutrition 219 1. Keep a record of everything you eat and drink for 3 days. Be specific. Was it white or wheat bread, 1% or 2% milk, 1 cup or 1½ cups, did you
Name Instructions for 3 Day Diet Analysis for Nutrition 219 1. Keep a record of everything you eat and drink for 3 days. Be specific. Was it white or wheat bread, 1% or 2% milk, 1 cup or 1½ cups, did you
Cholesterol Levels -- What They Mean, Diet and Treatment
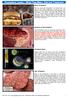 Cholesterol Levels -- What They Mean, Diet and Treatment What Is Cholesterol? We may associate cholesterol with fatty foods, but most of the waxy substance is made by our own bodies. The liver produces
Cholesterol Levels -- What They Mean, Diet and Treatment What Is Cholesterol? We may associate cholesterol with fatty foods, but most of the waxy substance is made by our own bodies. The liver produces
Module 1 An Overview of Nutrition. Module 2. Basics of Nutrition. Main Topics
 Module 1 An Overview of Nutrition Module 2 What is Nutrition? What Are Nutrients? Units of Energy Why we need energy? Maintaining energy balance Daily energy requirements Calorie Requirements for Different
Module 1 An Overview of Nutrition Module 2 What is Nutrition? What Are Nutrients? Units of Energy Why we need energy? Maintaining energy balance Daily energy requirements Calorie Requirements for Different
