found it difficult to express all the fluid from the loop. 32-2
|
|
|
- Bryce Peters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 487 J. Physiol. (I940) 98, I 6i2.364: THE ABSORPTION OF WATER FROM THE COLON OF THE RAT UNDER URETHANE ANAESTHESIA By B. L. ANDREW, J. N. DAVIDSON AND R. C. GARRY From the Physiology Department, University College, Dundee, The University of St Andrews (Received 20 June 1940) THE colon of the rat under urethane anaesthesia can absorb only negligible amounts of monosaccharides [Davidson & Garry, 1939]. In view of the rather unexpected nature of this result, we decided to investigate the powers of the colon to absorb other substances, in particular water. Moreover, we wished to make sure that the colonic loops in such rats had still an active circulation and that absorption was therefore possible. Three methods of attack were chosen. In the first place, since sugars are not absorbed from the colon, the variation of concentration of sugar in a closed loop of colon will give an indication of the movement of water into or out of the loop. Secondly, a non-absorbable indicator will reveal increase or decrease in the concentration of the contents of the loop in similar fashion. The indicator used was phenol red first recommended by Goreham in 1923, and subsequently used by a large number of investigators, e.g. Wilhelmj, Neigus & Hill [1933], Penner, Hollander & Saltzman [1938], as a dilution indicator in gastric analysis. The concentration of phenol red employed was too low to have any appreciable effect on the osmotic pressure of the solution. Thirdly, deuterium oxide may be used as an index of water exchange as has been done in the case of the small intestine by Hevesy & Hofer [1934], McDougall, Verzar, Erlenmeyer & Gaertner [1934] and by Peters & Visscher [1939]. Distilled water alone cannot be used since it damages the mucous membrane [Dennis, 1940]. We therefore introduced as solute either glucose or xylose in all experiments. No attempt was made to&measure the actual volume of solution in the colon at the end of 90 min., since we found it difficult to express all the fluid from the loop. 32-2
2 488 B. L. ANDREW, J. N. DAVIDSON AND R. C. GARRY METHODS Rats were given water but no food for 48 hr. and were then anaesthetized with urethane given subcutaneously in a dose of 1-6 mg./g. body weight. One hour later the abdomen was opened by a mid-line incision and the lower end of the ileum was tied off. An opening was made into the tip of the caecum and into the colon at its junction with the caecum. Colon and caecum were then washed out with Ringer's solution at 380 C. Thereafter a purse-string suture was inserted round the anus and tightened on a small glass cannula. A second cannula was inserted into the proximal end of the colon and all traces of Ringer's solution washed out of the colon with a stream of fluid containing hyper-, iso- or hypotonic sugar solution at 380 C. In the majority of experiments this sugar solution contained phenol red. The anal cannula was then withdrawn and the purse-string suture tightened. The colon was allowed to fill with solution, the upper cannula was withdrawn and the opening ligatured. In many cases the caecum was similarly washed out and filled with sugar solution. The abdomen was closed and the animal left in warm surroundings for 90 min. At the end of that tima the rat was killed, the colonic loop and the caecum were removed, opened and the contents drained out. Reducing sugar was estimated by the method of Hagedorn and Jensen and phenol red by the colorimetric method of Hollander, Penner & Saltzman [1937]. In the experiments with deuterium oxide the colon alone was used. After the colon had been washed out with Ringer the bulk of the residual liquid was removed with a few puffs of air. 5 ml. of a 4% solution of xylose in water containing approximately 20% D20 were then run repeatedly through the colon. The anal suture was tightened and about 3 ml. of the solution left in the colon which was then tied off as before. The remaining 2 ml. were preserved for control estimations of sugar and D20. At the end of a given time the animal was killed, the colonic loop removed, and the contents drained out. For the deuterium oxide estimations portions of about 1 ml. of the fluid under investigation were distilled in vacuo at 200 C. into a receiver cooled in a freezing mixture. When all the water had passed over, the distillate was allowed to come to room temperature and the D20 content was measured in a Pulfrich refractometer. Control experiments were carried out to ensure that no interfering substances were carried over in the distillation of fluid from colonic loops.
3 ABSORPTION OF WATER FROM THE COLON 489 RESULTS In all cases where the original solution was hypertonic (10.0%) the contents of the colon at the end of 90 min. were much less concentrated. Since passage of sugar out of the colon does not occur there must have been passage of water into the loop. When phenol red was present as well as glucose, the extent to which this indicator was diluted corresponded closely to the degree of dilution of the glucose (Table I). The opposite effect was seen where the initial glucose solution was hypotonic (2-7 %), the solution undergoing concentration during the 90 min. in the colon. The concentration of phenol red rose correspondingly (Table I). TABLE I. Variations in the concentration of the contents of colonic loops in rats under urethane anaesthesia in the course of 90 min. The figures given are average values obtained from several experiments. Glucose concentration Phenol red concentration g./100 ml. mg./100 ml. Initial Final Initial Final C, c2 c2/cl c, ' C2 c27/61 / * * *42 Where the initial glucose concentration was 5-4 %, the value usually considered to be isotonic with mammalian blood [Verzar & McDougall, 1936], the concentration within the colon after 90 min. was slightly lower, about 4-9 %. This was not due to loss of sugar since the phenol red concentration fell to a similar degree (Table I). Similar results were obtained with the caecum. In the experiments with heavy water, xylose was used as the nonabsorbable sugar. Xylose behaved in exactly the same way as glucose, and the strength of solution neither concentrated nor diluted was found to be 4 0 %. This, as in the case of glucose, is lower than the concentration (4.5%) said to be isotonic with blood. We therefore used a 40 % solution of xylose in water containing about 20-0% D20. The diminution in concentration of D20 due to exchange of deuterium atoms with the hydrogen atoms of the hydroxyl groups of xylose was negligible. Moreover any rapid exchange of deuterium atoms with hydrogen atoms present in the colon mucous membrane was allowed for by preliminary repeated passage of the solution through the loop. Although measurements of heavy water concentration by a refractometer are not particularly delicate, yet the 32-3
4 490 B. L. ANDREW, J. N. DAVIDSON AND R. C. GARRY concentration changes we observed were so gross that the method was perfectly adequate for the purpose. The xylose concentration, originally in the neighbourhood of 4-0%, remained at that level throughout the absorption period which varied from 5 to 90 min. We can therefore assume that the total amount of water in the colon remained constant. Deuterium oxide disappeared very rapidly from the colon; in 30 min. the bulk had gone, and even in as short a time as 5 min. a large proportion had disappeared (Fig. 1) Fig. 1. Min. Decrease in the concentration of heavy water in the contents of colonic loops in the anaesthetized rat. DISCUSSION There can be no doubt that the colonic mucous membrane in rats under the conditions of our experiments allows mass movement of water in both directions while remaining impermeable to monosaccharides. This latter property is lost when the colon is isolated in vitro [Davidson & Garry, 1939]. Even in the absence of an osmotic gradient, exchange of water molecules between the blood and the colonic contents was very rapid. The colonic mucous membrane seems to act as an extremely efficient semi-permeable membrane and there can no longer be any suspicion that the failure to absorb monosaccharides was due to experimental conditions interfering with the state of the colon.
5 ABSORPTION OF WATER FROM THE COLON 491 SUMMARY The colon of the rat under urethane anaesthesia, although impermeable to monosaccharides, is freely permeable in both directions to water molecules. We wish to express our thanks to Prof. W. F. K. Wynne-Jones for supplying the deuterium oxide and to the Carnegie Trust for the Universities of Scotland for an expenses grant for this work. REFERENCES Davidson, J. N. & Garry, R. C. [1939]. J. Phy8iol. 96, 172. Dennis, C. [1940]. Amer. J. Phy8iol. 129, 171. Goreham, F. D. [1923]. J. Amer. med. A88. 81, Hevesy, G. & Hofer, E. [1934]. Nature, Lond., 134, 879. Hollander, F., Penner, A. & Saltzman, M. [1937]. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol., N.Y., 36, 568. McDougall, E. J., Verzar, F. Erlenmeyer, H. & Gaertner, H. [1934]. Nature, Lond., i34, Penner, A., Hollander, F. & Saltzman, M. [1938]. Amer. J. dige. Diw. 5, 657. Peters, H. G. & Visscher, M. B. [1939]. J. ce. comp. Phy8iol. 13, 51. Verz4r, F. & McDougall, E. J. [1936]. Absorptionfrom the Intedtine. London: Longmans, Green and Co. Wilhelmj, C. M., Neigus, I. & Hill, F. C. [1933]. Amer. J. Physiol. 106, 381.
Surprisingly enough, McDougall & Verzar [1935] statethat "in Katzendarm. (Received 14 October 1939)
![Surprisingly enough, McDougall & Verzar [1935] statethat in Katzendarm. (Received 14 October 1939) Surprisingly enough, McDougall & Verzar [1935] statethat in Katzendarm. (Received 14 October 1939)](/thumbs/94/119530412.jpg) 509 J. Physiol. (I940) 97, 509-5I6 612.332*72 THE ABSORPTION OF MONOSACCHARIDES FROM S THE DISTAL SMALL INTESTINE OF ANAESTHETIZED CATS L j BY J. N. DAVIDSON AND R. C. GARRY From the Physiology Department,
509 J. Physiol. (I940) 97, 509-5I6 612.332*72 THE ABSORPTION OF MONOSACCHARIDES FROM S THE DISTAL SMALL INTESTINE OF ANAESTHETIZED CATS L j BY J. N. DAVIDSON AND R. C. GARRY From the Physiology Department,
below. METHODS GALACTOSE ABSORPTION FROM THE SURVIVING SMALL INTESTINE OF THE RAT
 224 J. Physiol. (I953) II9, 224-232 GALACTOSE ABSORPTION FROM THE SURVIVING SMALL INTESTINE OF THE RAT BY R. B. FISHER AND D. S. PARSONS From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Oxford (Received
224 J. Physiol. (I953) II9, 224-232 GALACTOSE ABSORPTION FROM THE SURVIVING SMALL INTESTINE OF THE RAT BY R. B. FISHER AND D. S. PARSONS From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Oxford (Received
Chapter MEMBRANE TRANSPORT
 Chapter 3 I MEMBRANE TRANSPORT The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is the outermost layer of the cell. It completely surrounds the protoplasm or living portion of the cell, separating the cell s interior
Chapter 3 I MEMBRANE TRANSPORT The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is the outermost layer of the cell. It completely surrounds the protoplasm or living portion of the cell, separating the cell s interior
estimates were made of the normal rate of increase in plasma urea over periods in skin and in plasma, hypertonic sodium chloride solution was
 482 J. Physiol. (I95I) II5, 482-487 THE STTE OF BODY WTER IN THE CT BY M. GRCE EGGLETON From the Department of Physiology, University College, London (Received 5 July 1951) In the course of an investigation
482 J. Physiol. (I95I) II5, 482-487 THE STTE OF BODY WTER IN THE CT BY M. GRCE EGGLETON From the Department of Physiology, University College, London (Received 5 July 1951) In the course of an investigation
Using a technique by which it is possible to study gastro-intestinal absorption
 531 J. Physiol. (I956) I34, 53I-537 THE ABSORPTION OF GLUCOSE BY THE INTACT RAT BY P. C. REYNELL AND G. H. SPRAY From the Nuffield Department of Clinical Medicine, University of Oxford (Received 30 May
531 J. Physiol. (I956) I34, 53I-537 THE ABSORPTION OF GLUCOSE BY THE INTACT RAT BY P. C. REYNELL AND G. H. SPRAY From the Nuffield Department of Clinical Medicine, University of Oxford (Received 30 May
College of Medicine, Newcastle-upon-Tyne.)
 GLUCOSE ABSORPTION IN THE RENAL TUBULES OF THE FROG. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory of the University of Durham College of Medicine, Newcastle-upon-Tyne.) OPINION is divided on the
GLUCOSE ABSORPTION IN THE RENAL TUBULES OF THE FROG. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory of the University of Durham College of Medicine, Newcastle-upon-Tyne.) OPINION is divided on the
The absorption of water from the whole stomach. or one of its parts has not been demonstrated. Many years ago Pavlov showed that water was a
 GASTRIC SECRETION. III. THE ABSORPTION OF HEAVY WATER FROM POUCHES OF THE BODY AND ANTRUM OF THE STOMACH OF THE DOG By OLIVER COPE, HESTER BLATT, AND MARGARET R. BALL (From the Surgical Research Laboratories
GASTRIC SECRETION. III. THE ABSORPTION OF HEAVY WATER FROM POUCHES OF THE BODY AND ANTRUM OF THE STOMACH OF THE DOG By OLIVER COPE, HESTER BLATT, AND MARGARET R. BALL (From the Surgical Research Laboratories
I:6I (Rowett Research Institute, Aberdeen.) angiostomized dogs. Lang [1928] criticized Charit's methods, and
![I:6I (Rowett Research Institute, Aberdeen.) angiostomized dogs. Lang [1928] criticized Charit's methods, and I:6I (Rowett Research Institute, Aberdeen.) angiostomized dogs. Lang [1928] criticized Charit's methods, and](/thumbs/92/110970246.jpg) 288 GLYCOGEN SYNTHESIS IN THE SMALL INTESTINE. BY E. A. HORNE AND H. E. MAGEE. (Rowett Research Institute, Aberdeen.) 612.352.I:6I2.332.72 IT has been claimed that the glycogen content of the portal blood
288 GLYCOGEN SYNTHESIS IN THE SMALL INTESTINE. BY E. A. HORNE AND H. E. MAGEE. (Rowett Research Institute, Aberdeen.) 612.352.I:6I2.332.72 IT has been claimed that the glycogen content of the portal blood
investigated. According to the current hypothesis fat is completely hydrolysed
 306 J. Physiol. (I943) I02, 3o6-3I2 6i2. 322 73 DIFFERENTIATION IN THE ABSORPTION OF OLIVE OIL *0 AND OLEIC ACID IN THE. RAT By A. C. FRAZER,* From the Physiology Department, St Mary's Hospital Medical
306 J. Physiol. (I943) I02, 3o6-3I2 6i2. 322 73 DIFFERENTIATION IN THE ABSORPTION OF OLIVE OIL *0 AND OLEIC ACID IN THE. RAT By A. C. FRAZER,* From the Physiology Department, St Mary's Hospital Medical
epithelium occluded by folding cannot participate in absorptive activity. In
 655 J. Physiol. (I955) I30, 655-664 THE ABSORPTION OF WATER AND OF SOME SMALL SOLUTE MOLECULES FROM THE ISOLATED SMALL INTESTINE OF THE RAT By R. B. FISHER From the Department of Biochemistry, University
655 J. Physiol. (I955) I30, 655-664 THE ABSORPTION OF WATER AND OF SOME SMALL SOLUTE MOLECULES FROM THE ISOLATED SMALL INTESTINE OF THE RAT By R. B. FISHER From the Department of Biochemistry, University
GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which
 ON THE ACTION OF PHLORHIZIN ON THE KIDNEY. By E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which is completely held back
ON THE ACTION OF PHLORHIZIN ON THE KIDNEY. By E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which is completely held back
INSULIN AND THE SUPRARENAL GLAND OF THE RABBIT
 Brit. J. Phawmacol. (1951), 6, 289. INSULIN AND THE SUPRARENAL GLAND OF THE RABBIT BY From the Pharmacological Laboratory, University of St. Andrews, Medical School, Dundee (Received February 2, 1951)
Brit. J. Phawmacol. (1951), 6, 289. INSULIN AND THE SUPRARENAL GLAND OF THE RABBIT BY From the Pharmacological Laboratory, University of St. Andrews, Medical School, Dundee (Received February 2, 1951)
There are mainly two types of transport :
 There are mainly two types of transport : # Type one: Passive diffusion 1- which does not require additional energy and occurs down the concentration gradient (high low concentration) " Down Hill" (^_^
There are mainly two types of transport : # Type one: Passive diffusion 1- which does not require additional energy and occurs down the concentration gradient (high low concentration) " Down Hill" (^_^
Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with
![Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with](/thumbs/91/106294335.jpg) 381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
THE ABSORPTION OF VOLATILE FATTY ACIDS FROM THE RUMEN
 VOL. 24, Nos. 1 & 2 SEPTEMBER 1947 THE ABSORPTION OF VOLATILE FATTY ACIDS FROM THE RUMEN BY F. V. GRAY From the Division of Biochemistry and General Nutrition of the Council for Scientific and Industrial
VOL. 24, Nos. 1 & 2 SEPTEMBER 1947 THE ABSORPTION OF VOLATILE FATTY ACIDS FROM THE RUMEN BY F. V. GRAY From the Division of Biochemistry and General Nutrition of the Council for Scientific and Industrial
Lab 4: Osmosis and Diffusion
 Page 4.1 Lab 4: Osmosis and Diffusion Cells need to obtain water and other particles from the fluids that surround them. Water and other particles also move out of cells. Osmosis (for water) and diffusion
Page 4.1 Lab 4: Osmosis and Diffusion Cells need to obtain water and other particles from the fluids that surround them. Water and other particles also move out of cells. Osmosis (for water) and diffusion
1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
 Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Directions: Questions 2 and 3 refer to
Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Directions: Questions 2 and 3 refer to
INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION BIOLOGY HANDOUT OSMOSIS, DIFFUSION AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT CLASS 9
 INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL 2014 2015 ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION BIOLOGY HANDOUT OSMOSIS, DIFFUSION AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT CLASS 9 Name :... Date:... d) Movement of substances into and
INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL 2014 2015 ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION BIOLOGY HANDOUT OSMOSIS, DIFFUSION AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT CLASS 9 Name :... Date:... d) Movement of substances into and
establishing perfusion and of collecting and analysing the effluent fluid 1934]. Comparable increases in serum potassium were obtained when
![establishing perfusion and of collecting and analysing the effluent fluid 1934]. Comparable increases in serum potassium were obtained when establishing perfusion and of collecting and analysing the effluent fluid 1934]. Comparable increases in serum potassium were obtained when](/thumbs/95/123294922.jpg) 303 577.I74.5:612.I26 ACTION OF ADRENALINE ON THE SERUM POTASSIUM BY J. L. D'SILVA From the Department of Physiology, King's College, London (Received 24 March 1937) IN a previous communication it was
303 577.I74.5:612.I26 ACTION OF ADRENALINE ON THE SERUM POTASSIUM BY J. L. D'SILVA From the Department of Physiology, King's College, London (Received 24 March 1937) IN a previous communication it was
Cushny(4) has shown, however, that the amount of urea in the kidney. by some vital process, retain those diflusible substances which are of
 THE FUNCTION OF THE TUBULES IN KIDNEY EXCRETION. BY E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) IT is becoming generally recognised that filtration through the glomeruli and some degree
THE FUNCTION OF THE TUBULES IN KIDNEY EXCRETION. BY E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) IT is becoming generally recognised that filtration through the glomeruli and some degree
CXII. THE EXCRETION OF CALCIUM BY THE LARGE INTESTINE OF THE RABBIT
 CXII. THE EXCRETION OF CALCIUM BY THE LARGE INTESTINE OF THE RABBIT BY STUART JASPER COWELL From St Thomas's Hospital Medical School and the Medical Unit, University College Hospital, London (Received
CXII. THE EXCRETION OF CALCIUM BY THE LARGE INTESTINE OF THE RABBIT BY STUART JASPER COWELL From St Thomas's Hospital Medical School and the Medical Unit, University College Hospital, London (Received
McSwiney and Wadge [1930] described the effects on the stomach of
![McSwiney and Wadge [1930] described the effects on the stomach of McSwiney and Wadge [1930] described the effects on the stomach of](/thumbs/83/87976616.jpg) 6I2.328:6I2.898 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. II. The effect of stimulation of the peri-arterial nerves on the stomach and small intestine. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND J. M. ROBSON. (Department
6I2.328:6I2.898 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. II. The effect of stimulation of the peri-arterial nerves on the stomach and small intestine. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND J. M. ROBSON. (Department
ADRENALECTOMIZED rats drink less than normal rats when 2 per cent saline. daily by stomach tube and water to drink freely, died quickly but such
 THE EFFECT OF PROLONGED INTRAGASTRIC INFUSIONS OF ISOTONIC AND HYPERTONIC SALINE ON WATER AND SODIUM EXCRETION AND ON EXCHANGEABLE BODY SODIUM IN NORMAL AND ADRENALECTOMIZED RATS. By C. J. EDMONDS. From
THE EFFECT OF PROLONGED INTRAGASTRIC INFUSIONS OF ISOTONIC AND HYPERTONIC SALINE ON WATER AND SODIUM EXCRETION AND ON EXCHANGEABLE BODY SODIUM IN NORMAL AND ADRENALECTOMIZED RATS. By C. J. EDMONDS. From
possibility of a secretion of adrenaline from the suprarenal glands resulting
 355 J Physiol. (I942) IOI, 355-36I 6i2.014.465:577 I74.5 THE EFFECT OF ANAESTHESIA ON THE ADRENALINE CONTENT OF THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS BY P. C. ELMES AND A. A. JEFFERSON From the Department of Pharmacology,
355 J Physiol. (I942) IOI, 355-36I 6i2.014.465:577 I74.5 THE EFFECT OF ANAESTHESIA ON THE ADRENALINE CONTENT OF THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS BY P. C. ELMES AND A. A. JEFFERSON From the Department of Pharmacology,
normally observed after insulin to the action of bacterial contamination.
 THE ACTION OF INSULIN ON THE ASEPTICALLY PERFUSED HEART. BY R. BODO AND H. P. MARKS. (From the National Institute for Medical Research, London.) Cousy (1), of Noyon's laboratory, has recently repeated
THE ACTION OF INSULIN ON THE ASEPTICALLY PERFUSED HEART. BY R. BODO AND H. P. MARKS. (From the National Institute for Medical Research, London.) Cousy (1), of Noyon's laboratory, has recently repeated
Overton,1 who has worked exhaustively at the subject, looked upon. considered by some to be due to the state of the fluid originally in the
 THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON THE OSMOTIC PROPER- TIES OF MUSCLE. By D. H. DE SOUZA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Sheffield.) (With six diagrams in the text.) (Received for publication
THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON THE OSMOTIC PROPER- TIES OF MUSCLE. By D. H. DE SOUZA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Sheffield.) (With six diagrams in the text.) (Received for publication
Lesson Overview. 7.3 Cell Transport
 7.3 THINK ABOUT IT When thinking about how cells move materials in and out, it can be helpful to think of a cell as a nation. The boundaries of a nation are its borders, and nearly every country tries
7.3 THINK ABOUT IT When thinking about how cells move materials in and out, it can be helpful to think of a cell as a nation. The boundaries of a nation are its borders, and nearly every country tries
University College, London.)
 6I2.I2I:547.472*3 LACTIC ACID FORMATION AND REMOVAL WITH CHANGE OF BLOOD REACTION. BY M. GRACE EGGLETON1 AND C. LOVATT EVANS. (From the Department of Physiology and Biochemistry, University College, London.)
6I2.I2I:547.472*3 LACTIC ACID FORMATION AND REMOVAL WITH CHANGE OF BLOOD REACTION. BY M. GRACE EGGLETON1 AND C. LOVATT EVANS. (From the Department of Physiology and Biochemistry, University College, London.)
Westenbrink, 1936 a). (Donhofler, 1935) or ingested (Mackay & Clark, 1941), and by making
 276 J. Physiol. (I95') II3, 276-282 THE ABSORPTION OF GLUCOSE AND XYLOSE BY ADULT AND NEWBORN RATS BY PHILIP E. H. JONES From the Medical Research Council Department of Experimental Medicine, University
276 J. Physiol. (I95') II3, 276-282 THE ABSORPTION OF GLUCOSE AND XYLOSE BY ADULT AND NEWBORN RATS BY PHILIP E. H. JONES From the Medical Research Council Department of Experimental Medicine, University
Ch. 7 Diffusion, Osmosis, and Movement across a Membrane
 Ch. 7 Diffusion, Osmosis, and Movement across a Membrane Diffusion Spontaneous movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Does not require energy (exergonic)
Ch. 7 Diffusion, Osmosis, and Movement across a Membrane Diffusion Spontaneous movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Does not require energy (exergonic)
POLAR COVALENT BOND 1 P
 POLAR COVALENT BOND 1 P HP OXYGEN HIGHER ELECTRO- O WATER MOLECULE HYDROGEN LOWER ELECTRO- H BOND BOND H ELECTRO- = 3.5 ELECTRO- = 2.1 ELECTRO- = 2.1 = E- POLAR COVALENT BOND +/- - 1 P? CHARGE OXYGEN HIGHER
POLAR COVALENT BOND 1 P HP OXYGEN HIGHER ELECTRO- O WATER MOLECULE HYDROGEN LOWER ELECTRO- H BOND BOND H ELECTRO- = 3.5 ELECTRO- = 2.1 ELECTRO- = 2.1 = E- POLAR COVALENT BOND +/- - 1 P? CHARGE OXYGEN HIGHER
Slide 2 of 47. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall. End Show
 2 of 47 7-3 Cell Boundaries All cells are surrounded by a thin, flexible barrier known as the cell membrane. Many cells also produce a strong supporting layer around the membrane known as a cell wall.
2 of 47 7-3 Cell Boundaries All cells are surrounded by a thin, flexible barrier known as the cell membrane. Many cells also produce a strong supporting layer around the membrane known as a cell wall.
J. Physiol. (I956) I33,
 626 J. Physiol. (I956) I33, 626-630 ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF AMINO ACIDS BY SACS OF EVERTED SMALL INTESTINE OF THE GOLDEN HAMSTER (MESOCRICETUS AURATUS) BY G. WISEMAN From the Department of Physiology, University
626 J. Physiol. (I956) I33, 626-630 ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF AMINO ACIDS BY SACS OF EVERTED SMALL INTESTINE OF THE GOLDEN HAMSTER (MESOCRICETUS AURATUS) BY G. WISEMAN From the Department of Physiology, University
University College, London.)
 236 57.979.8:62.353 THE FATE OF CAROTENE INJECTED INTO THE CIRCULATION OF THE RAT. BY J. C. DRUMMOND AND R. J. MACWALTER. (From the Department of Physiology, Pharmacology and Biochemistry, University College,
236 57.979.8:62.353 THE FATE OF CAROTENE INJECTED INTO THE CIRCULATION OF THE RAT. BY J. C. DRUMMOND AND R. J. MACWALTER. (From the Department of Physiology, Pharmacology and Biochemistry, University College,
Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in distilled water.
 The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
CHAPTER. Movement Across Plasma Membrane. Chapter 6 Outline. Diffusion Osmosis. Membrane Potential Cell Signaling
 CHAPTER 6 Interaction Between Cells and the Extracellular Environment Chapter 6 Outline Extracellular Environment Diffusion Osmosis Carrier-Mediated Carrier Mediated Transport Membrane Potential Cell Signaling
CHAPTER 6 Interaction Between Cells and the Extracellular Environment Chapter 6 Outline Extracellular Environment Diffusion Osmosis Carrier-Mediated Carrier Mediated Transport Membrane Potential Cell Signaling
J. Physiol. (I953) 3121,
 452 J. Physiol. (I953) 3121, 452-469 THE MOVEMENT OF POTASSIUM, SODIUM, CHLORIDE AND WATER ACROSS THE RUMEN EPITHELIUM OF SHEEP BY D. PARTHASARATHY AND A. T. PHILLIPSON From the Rowett Research Institute,
452 J. Physiol. (I953) 3121, 452-469 THE MOVEMENT OF POTASSIUM, SODIUM, CHLORIDE AND WATER ACROSS THE RUMEN EPITHELIUM OF SHEEP BY D. PARTHASARATHY AND A. T. PHILLIPSON From the Rowett Research Institute,
Vpyl.=volume passing pylorus and Vabs.= volume absorbed. The volume. sulphaguanidine. This substance has been shown (Hunt, 1947) only to be
 134 J Physiol. (1949) I09, I34-I4I 6I2.322.7:6I2.0I4.46I THE SIMULTANEOUS ESTIMATION OF THE ABSORPTION OF WATER AND SULPHAGUANIDINE FROM THE STOMACH OF MAN BY J. N. HUNT From Guy's Hospital Medical School,
134 J Physiol. (1949) I09, I34-I4I 6I2.322.7:6I2.0I4.46I THE SIMULTANEOUS ESTIMATION OF THE ABSORPTION OF WATER AND SULPHAGUANIDINE FROM THE STOMACH OF MAN BY J. N. HUNT From Guy's Hospital Medical School,
STATION 4: TONICITY due to OSMOSIS / Turgor Pressure in Plants
 STATION 4: TONICITY due to OSMOSIS / Turgor Pressure in Plants Tonicity is the concentration of solutions that determines the direction water will move across a semi-permeable membrane. A solution is a
STATION 4: TONICITY due to OSMOSIS / Turgor Pressure in Plants Tonicity is the concentration of solutions that determines the direction water will move across a semi-permeable membrane. A solution is a
(Received 22 July 1957) It is now generally accepted that the unequal distribution of ions between cells
 190 J. Physiol. (I958) I40, I90-200 THE EFFECT OF ALTERATIONS OF PLASMA SODIUM ON THE SODIUM AND POTASSIUM CONTENT OF MUSCLE IN THE RAT By F. 0. DOSEKUN AND D. MENDEL From the Department of Physiology,
190 J. Physiol. (I958) I40, I90-200 THE EFFECT OF ALTERATIONS OF PLASMA SODIUM ON THE SODIUM AND POTASSIUM CONTENT OF MUSCLE IN THE RAT By F. 0. DOSEKUN AND D. MENDEL From the Department of Physiology,
To understand osmosis, we must focus on the behavior of the solvent, not the solute.
 GCC CHM 130LL Osmosis and Dialysis Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to observe the closely related phenomena of osmosis and diffusion as it relates to dialysis. It is hoped that you will be able
GCC CHM 130LL Osmosis and Dialysis Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to observe the closely related phenomena of osmosis and diffusion as it relates to dialysis. It is hoped that you will be able
Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membranes. Chapter 5
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membranes. Chapter 5
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membranes
 Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
AN EXPERIMENTAL TUBE PEDICLE LINED WITH SMALL BOWEL. By J. H. GOLDIN, F.R.C.S.(Edin.) Plastic Surgery Unit, St Thomas' Hospital, London
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (I972), 25, 388-39z AN EXPERIMENTAL TUBE PEDICLE LINED WITH SMALL BOWEL By J. H. GOLDIN, F.R.C.S.(Edin.) Plastic Surgery Unit, St Thomas' Hospital, London ONE of the
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (I972), 25, 388-39z AN EXPERIMENTAL TUBE PEDICLE LINED WITH SMALL BOWEL By J. H. GOLDIN, F.R.C.S.(Edin.) Plastic Surgery Unit, St Thomas' Hospital, London ONE of the
Lab #2: Osmosis Pre-Lab Exercise
 Lab #2: Osmosis Pre-Lab Exercise Name 1. Using your own words, define the following terms: a. Osmosis b. Concentration gradient: c. Hypertonic solution: d. Isotonic solution: e. Hypotonic solution: 2.
Lab #2: Osmosis Pre-Lab Exercise Name 1. Using your own words, define the following terms: a. Osmosis b. Concentration gradient: c. Hypertonic solution: d. Isotonic solution: e. Hypotonic solution: 2.
Unit 7: Topic 7.4 Cellular Transport
 Unit 7: Topic 7.4 Cellular Transport Name: Class key Period: Page 1 of 39 Topic 7.4 assignments Pages/Sections Date Assigned Date Due Page 2 of 39 Topic: Membrane Channels Objective: Why do molecules move
Unit 7: Topic 7.4 Cellular Transport Name: Class key Period: Page 1 of 39 Topic 7.4 assignments Pages/Sections Date Assigned Date Due Page 2 of 39 Topic: Membrane Channels Objective: Why do molecules move
little or no regard has been paid to the analysis of the movements of (maximal relaxation) manifests itself during the height of antral
 6I2.327.3 THE REGULATION OF THE PYLORIC SPHINCTER. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND L. N. PYRAH. (From the Department of Physiology, The University of Leeds.) CONSIDERABLE discussion has taken place as to the mechanism
6I2.327.3 THE REGULATION OF THE PYLORIC SPHINCTER. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND L. N. PYRAH. (From the Department of Physiology, The University of Leeds.) CONSIDERABLE discussion has taken place as to the mechanism
Histologically the pyloric glands and the glands of Brunner in the. Ivy(7) and his co-workers seem to believe, at the present time, in the
 6I2.323[6I2.33 6I2.OI5.2I THE SMALL INTESTINE AND GASTRIC SECRETION. (With special reference to Brunner's Glands.) BY MARGARET M. MURRAY. (From the Department of Physiology, Bedford College.) EVIDENCE
6I2.323[6I2.33 6I2.OI5.2I THE SMALL INTESTINE AND GASTRIC SECRETION. (With special reference to Brunner's Glands.) BY MARGARET M. MURRAY. (From the Department of Physiology, Bedford College.) EVIDENCE
TRANSPORT ACROSS THE CELL MEMBRANE. Example of a Cell Receptor The target cell has receptors that match the hormone.
 TRANSPORT ACROSS THE CELL MEMBRANE Name I. Structure of the Cell Membrane 2 layers (bi-layer) of with imbedded known as the (molecules are in motion) II. The Functions of the Cell Membrane 1. between the
TRANSPORT ACROSS THE CELL MEMBRANE Name I. Structure of the Cell Membrane 2 layers (bi-layer) of with imbedded known as the (molecules are in motion) II. The Functions of the Cell Membrane 1. between the
Section 4: Cellular Transport. Cellular transport moves substances within the cell and moves substances into and out of the cell.
 Section 4: Cellular transport moves substances within the cell and moves substances into and out of the cell. Essential Questions What are the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active
Section 4: Cellular transport moves substances within the cell and moves substances into and out of the cell. Essential Questions What are the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active
(From the Physiological Laboratories of University College, London and Cambridge University.) extracts2, etc.). dilation of the vessels.
 THE OXYGEN EXCHANGE OF THE PANCREAS. BY J. BARCROFT AND E. H. STARLING. (From the Physiological Laboratories of University College, London and Cambridge University.) THE interest of the investigations,
THE OXYGEN EXCHANGE OF THE PANCREAS. BY J. BARCROFT AND E. H. STARLING. (From the Physiological Laboratories of University College, London and Cambridge University.) THE interest of the investigations,
THE TOXICITY OF THE DOUBLE CHLORIDES OF MERCURY AND SODIUM
 325 THE TOXICITY OF THE DOUBLE CHLORIDES OF MERCURY AND SODIUM I. EXPERIMENTS WITH THE MINNOW PHOXINUS PHOXINUS (L.) BY J. R. ERICHSEN JONES Department of Zoology, University College of Wales, Aberystwyth
325 THE TOXICITY OF THE DOUBLE CHLORIDES OF MERCURY AND SODIUM I. EXPERIMENTS WITH THE MINNOW PHOXINUS PHOXINUS (L.) BY J. R. ERICHSEN JONES Department of Zoology, University College of Wales, Aberystwyth
DIFFUSON AND OSMOSIS INTRODUCTION diffusion concentration gradient. net osmosis water potential active transport
 DIFFUSON AND OSMOSIS NAME DATE INTRODUCTION The life of a cell is dependent on efficiently moving material into and out of the cell across the cell membrane. Raw materials such as oxygen and sugars needed
DIFFUSON AND OSMOSIS NAME DATE INTRODUCTION The life of a cell is dependent on efficiently moving material into and out of the cell across the cell membrane. Raw materials such as oxygen and sugars needed
What is the function of the cell membrane?
 What is the function of the cell membrane? 1. DIFFUSION: The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. Why do molecules move from high concentration to
What is the function of the cell membrane? 1. DIFFUSION: The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. Why do molecules move from high concentration to
Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes
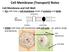 Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells
Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells
Outline. Membrane Structure and Function. Membrane Models Fluid-Mosaic. Chapter 5
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Membrane Models Fluid-Mosaic Outline Plasma Membrane Structure and Function Protein Functions Plasma Membrane Permeability! Diffusion! Osmosis! Transport Via Carrier
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Membrane Models Fluid-Mosaic Outline Plasma Membrane Structure and Function Protein Functions Plasma Membrane Permeability! Diffusion! Osmosis! Transport Via Carrier
s. J. RUNE, M.D., AND F. W. HENRIKSEN, M.D.
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 56, No.4 Printed in U.S.A. CARBON DOXDE TENSONS N TlE PROXMAL PART OF THE CANNE GASTRONTESTNAL TRACT s. J. RUNE, M.D., AND F. W. HENRKSEN,
GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 56, No.4 Printed in U.S.A. CARBON DOXDE TENSONS N TlE PROXMAL PART OF THE CANNE GASTRONTESTNAL TRACT s. J. RUNE, M.D., AND F. W. HENRKSEN,
Diffusion and Osmosis
 Diffusion and Osmosis Introduction: In this exercise you will measure diffusion of small molecules through dialysis tubing, an example of a semi permeable membrane. The movement of a solute through a semi
Diffusion and Osmosis Introduction: In this exercise you will measure diffusion of small molecules through dialysis tubing, an example of a semi permeable membrane. The movement of a solute through a semi
substances (Chain, Frank, Pocchiari, Rossi, Ugolini & Ugolini, 19.56) has
 J. Physiol. (196), 154, pp. 39-51 39 With 4 text-ftgurew Printed in Great Britain THE ABSORPTIO OF SUCROSE, MALTOSE AD HIGHER OLIGOSACCHARIDES FROM THE ISOLATED RAT SMALL ITESTIE BY E. B. CHAI, K. R. L.
J. Physiol. (196), 154, pp. 39-51 39 With 4 text-ftgurew Printed in Great Britain THE ABSORPTIO OF SUCROSE, MALTOSE AD HIGHER OLIGOSACCHARIDES FROM THE ISOLATED RAT SMALL ITESTIE BY E. B. CHAI, K. R. L.
Passive Transport. Does not expend cellular energy for the movement to take place. Ex-rolling down a hill
 Passive Transport Fluid Mosaic Model Passive Transport Does not expend cellular energy for the movement to take place Ex-rolling down a hill Parts of a Solution Solute: what gets dissolved Solvent: What
Passive Transport Fluid Mosaic Model Passive Transport Does not expend cellular energy for the movement to take place Ex-rolling down a hill Parts of a Solution Solute: what gets dissolved Solvent: What
5.6 Diffusion, Membranes, and Metabolism
 5.6 Diffusion, Membranes, and Metabolism Concentration of a substance Number of atoms or molecules in a given volume Concentration gradient of a substance A difference in concentration between two regions
5.6 Diffusion, Membranes, and Metabolism Concentration of a substance Number of atoms or molecules in a given volume Concentration gradient of a substance A difference in concentration between two regions
Membranes. Chapter 5. Membrane Structure
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
Cell Boundaries Section 7-3
 Cell Boundaries Section 7-3 The most important parts of a cell are its borders, which separate the cell from its surroundings. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells. The
Cell Boundaries Section 7-3 The most important parts of a cell are its borders, which separate the cell from its surroundings. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells. The
Cellular Transport Notes
 Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes All cells have a cell membrane Functions: a. Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b. Provides protection
Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes All cells have a cell membrane Functions: a. Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b. Provides protection
AGENDA for 01/09/14 AGENDA: HOMEWORK: Due end of period OBJECTIVES:
 AGENDA for 01/09/14 AGENDA: 1. 2.3.2: Diabetic Emergency! Blood Glucose Effects on Simulated Cellular Models Egg Demo Day 3 OBJECTIVES: 1. Design an experiment to simulate osmosis in body cells 2. Relate
AGENDA for 01/09/14 AGENDA: 1. 2.3.2: Diabetic Emergency! Blood Glucose Effects on Simulated Cellular Models Egg Demo Day 3 OBJECTIVES: 1. Design an experiment to simulate osmosis in body cells 2. Relate
Name: Bio A.P. Lab Diffusion & Osmosis
 Name: Bio A.P. Lab Diffusion & Osmosis BACKGROUND: Many aspects of the life of a cell depend on the fact that atoms and molecules are constantly in motion (kinetic energy). This kinetic energy results
Name: Bio A.P. Lab Diffusion & Osmosis BACKGROUND: Many aspects of the life of a cell depend on the fact that atoms and molecules are constantly in motion (kinetic energy). This kinetic energy results
Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT
 Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Cell (plasma) membrane Thin, flexible barrier Membranes also organize the interior of a cell. Cell organelles are defined by
Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Cell (plasma) membrane Thin, flexible barrier Membranes also organize the interior of a cell. Cell organelles are defined by
factors. directly. There are many, however, who regard the hydrochloric acid degree of stimulation of the stomach cells [Roseman, 1927; Katsch &
 308 J. Physiol. (I940) 97, 308-3I5 6I2.323.3 ON THE PRIMARY ACIDITY OF THE GASTRIC JUICE BY TORSTEN TEORELL From the Department of Medical Chemistry, University of Uppsala, Sweden (Received 10 July 1939)
308 J. Physiol. (I940) 97, 308-3I5 6I2.323.3 ON THE PRIMARY ACIDITY OF THE GASTRIC JUICE BY TORSTEN TEORELL From the Department of Medical Chemistry, University of Uppsala, Sweden (Received 10 July 1939)
Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane
 Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. What is/are the role(s) of structure A? (1) For cell recognition. (2) For carrying water-soluble substances across cell membrane. (3) For supporting
Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. What is/are the role(s) of structure A? (1) For cell recognition. (2) For carrying water-soluble substances across cell membrane. (3) For supporting
ABSORPTION AND SECRETION IN THE LARGE INTESTINE
 POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1965), 41, 435 ABSORPTION AND SECRETION IN THE LARGE INTESTINE Department of Surgery, THE ABSORPTIVE function of the colon is confined to transforming the fluid chyme, received from
POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1965), 41, 435 ABSORPTION AND SECRETION IN THE LARGE INTESTINE Department of Surgery, THE ABSORPTIVE function of the colon is confined to transforming the fluid chyme, received from
THE WATER AND ELECTROLYTE EXCHANGE OF NEREIS DIVERSICOLOR (MULLER)
 34 THE WATER AND ELECTROLYTE EXCHANGE OF NEREIS DIVERSICOLOR (MULLER) BY W. G. ELLIS Zoology Department, University College of North Wales, Bangor {Received g December 1936) (With Nine Text-figures) IT
34 THE WATER AND ELECTROLYTE EXCHANGE OF NEREIS DIVERSICOLOR (MULLER) BY W. G. ELLIS Zoology Department, University College of North Wales, Bangor {Received g December 1936) (With Nine Text-figures) IT
Measuring Osmotic Potential
 Measuring Osmotic Potential INTRODUCTION All cells require essential materials to ensure their survival. Chemical, physical, and biological processes are used to move these materials inside of cells. Similar
Measuring Osmotic Potential INTRODUCTION All cells require essential materials to ensure their survival. Chemical, physical, and biological processes are used to move these materials inside of cells. Similar
Ch. 5 Homeostasis & Cell Transport
 Ch. 5 Homeostasis & Cell Transport 5.1 Homeostasis & Permeability Homeostasis ability of cell to maintain balance needed for life To maintain balance: cells must transport needed materials into cells &
Ch. 5 Homeostasis & Cell Transport 5.1 Homeostasis & Permeability Homeostasis ability of cell to maintain balance needed for life To maintain balance: cells must transport needed materials into cells &
LAB 4: OSMOSIS AND DIFFUSION
 Page 4.1 LAB 4: OSMOSIS AND DIFFUSION Cells need to obtain water and other particles from the fluids that surround them. Water and other particles also move out of cells. Osmosis (for water) and diffusion
Page 4.1 LAB 4: OSMOSIS AND DIFFUSION Cells need to obtain water and other particles from the fluids that surround them. Water and other particles also move out of cells. Osmosis (for water) and diffusion
6I2.744.I5: e3. sufficiently high'. There exists in such cases a certain concentration of the. by direct analysis.
 194 THE DIFFUSION OF ACTATE INTO AND FROM MUSCE. BY S. C. DEVADATTA. 6I2.744.I5:547.472e3 (From the Department of Physiology, Edinburgh University.) CERTAIN constituents of the voluntary muscles of the
194 THE DIFFUSION OF ACTATE INTO AND FROM MUSCE. BY S. C. DEVADATTA. 6I2.744.I5:547.472e3 (From the Department of Physiology, Edinburgh University.) CERTAIN constituents of the voluntary muscles of the
Efflux of Red Cell Water into Buffered Hypertonic Solutions
 Efflux of Red Cell Water into Buffered Hypertonic Solutions EDWIN G. OLMSTEAD From the School of Medicine, University of North Dakota, Grand Forks ABSTRACT Buffered NaCI solutions hypertonic to rabbit
Efflux of Red Cell Water into Buffered Hypertonic Solutions EDWIN G. OLMSTEAD From the School of Medicine, University of North Dakota, Grand Forks ABSTRACT Buffered NaCI solutions hypertonic to rabbit
Transport Across a Membrane SEPT. 22, 2017
 Transport Across a Membrane SEPT. 22, 2017 Function (1) Passive Transport (2) Active Transport (3) Endocytosis/Exocytosis TOPICS Function Function Maintains internal cell environment at a steady state,
Transport Across a Membrane SEPT. 22, 2017 Function (1) Passive Transport (2) Active Transport (3) Endocytosis/Exocytosis TOPICS Function Function Maintains internal cell environment at a steady state,
Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function
 Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function Overview/Objectives 4.1 Plasma Membrane Structure & Function o Structure and Function of the PM o Major functions of proteins 4.2- Permeability of
Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function Overview/Objectives 4.1 Plasma Membrane Structure & Function o Structure and Function of the PM o Major functions of proteins 4.2- Permeability of
destroyed, or removed from the body. The experiments to be described intravenously injected insulin was observed in normal animals, in
 417 J. Physiol. (I940) 97, 4I7-428 6I5.361.37:6I2.I29.I ON THE DISAPPEARANCE FROM THE BLOOD OF INTRAVENOUSLY INJECTED INSULIN BY H. K. GOADBY1 AND J. S. RICHARDSON From the Medical Unit Laboratories, St
417 J. Physiol. (I940) 97, 4I7-428 6I5.361.37:6I2.I29.I ON THE DISAPPEARANCE FROM THE BLOOD OF INTRAVENOUSLY INJECTED INSULIN BY H. K. GOADBY1 AND J. S. RICHARDSON From the Medical Unit Laboratories, St
16. Excitability o f Squid Giant Axons in Hypertonic and Hypotonic Solutions
 68 Proc. Japan Acad., 51 (1975) [Vol. 51, 16. Excitability o f Squid Giant Axons in Hypertonic and Hypotonic Solutions By Fumio KUKITA*> and Shunichi YAMAGISHI**) (Comm. by Yasuj i KATSUKI, M. J. A., Jan.
68 Proc. Japan Acad., 51 (1975) [Vol. 51, 16. Excitability o f Squid Giant Axons in Hypertonic and Hypotonic Solutions By Fumio KUKITA*> and Shunichi YAMAGISHI**) (Comm. by Yasuj i KATSUKI, M. J. A., Jan.
Passive Transport: Practice Problems PAP BIOLOGY
 Passive Transport: Practice Problems PAP BIOLOGY #1 Draw a diagram where the cell has low concentration of salt molecules and the environment it is in has a high concentration of salt molecules in a water
Passive Transport: Practice Problems PAP BIOLOGY #1 Draw a diagram where the cell has low concentration of salt molecules and the environment it is in has a high concentration of salt molecules in a water
What location in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract has tight, or impermeable, junctions between the epithelial cells?
 CASE 32 A 17-year-old boy presents to his primary care physician with complaints of diarrhea for the last 2 days. The patient states that he just returned to the United States after visiting relatives
CASE 32 A 17-year-old boy presents to his primary care physician with complaints of diarrhea for the last 2 days. The patient states that he just returned to the United States after visiting relatives
Equilibrium when two areas have the same concentration or are filled evenly
 Aim: How does the cell membrane function to maintain homeostasis? Do Now: Describe what homeostasis is. Homework: Vocab: Homeostasis, equilibrium, concentration gradient, diffusion, carrier protein, osmosis,
Aim: How does the cell membrane function to maintain homeostasis? Do Now: Describe what homeostasis is. Homework: Vocab: Homeostasis, equilibrium, concentration gradient, diffusion, carrier protein, osmosis,
(From Washington Square College, New York University.)
 6I2.III.22 THE MEASUREMENT OF RED CELL VOLUME. II. Alterations in cell volume in solutions of various tonicities. BY ERIC PONDER AND GEORGE SASLOW. (From Washington Square College, New York University.)
6I2.III.22 THE MEASUREMENT OF RED CELL VOLUME. II. Alterations in cell volume in solutions of various tonicities. BY ERIC PONDER AND GEORGE SASLOW. (From Washington Square College, New York University.)
Diffusion & Osmosis - Exercise 4
 Diffusion & Osmosis - Exercise 4 Objectives -Define: Solvent, Solute, and Solution -Define: Diffusion, Selectively permeable membrane, Osmosis, and Dialysis -Understand rule of thumb: Concentration will
Diffusion & Osmosis - Exercise 4 Objectives -Define: Solvent, Solute, and Solution -Define: Diffusion, Selectively permeable membrane, Osmosis, and Dialysis -Understand rule of thumb: Concentration will
Ch 3 Membrane Transports
 Ch 3 Membrane Transports what's so dynamic about cell membranes? living things get nutrients and energy from the envrionment this is true of the entire organism and each cell this requires transport in/out
Ch 3 Membrane Transports what's so dynamic about cell membranes? living things get nutrients and energy from the envrionment this is true of the entire organism and each cell this requires transport in/out
Studies on the site of fat absorption
 Studies on the site of fat absorption 1. The sites of absorption of increasing doses of 3'I-labelled triolein in the rat C. C. BOOTH, A. E. READ, AND E. JONES From the Department of Medicine, Postgraduate
Studies on the site of fat absorption 1. The sites of absorption of increasing doses of 3'I-labelled triolein in the rat C. C. BOOTH, A. E. READ, AND E. JONES From the Department of Medicine, Postgraduate
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 The Digestive System
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells
 Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells Why do cells need to control what enters and exits? Plasma membrane boundary between the cell and its environment Homeostasis maintaining the cells environment
Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells Why do cells need to control what enters and exits? Plasma membrane boundary between the cell and its environment Homeostasis maintaining the cells environment
Cell Biology. The Plasma Membrane
 Cell Biology The Plasma Membrane recall Fluid Mosiac Model S.J. Singer Semipermeable membrane fluid portion is double layer of phospholipids (=phospholipid bilayer) mosaic portion is the proteins and carbohydrates
Cell Biology The Plasma Membrane recall Fluid Mosiac Model S.J. Singer Semipermeable membrane fluid portion is double layer of phospholipids (=phospholipid bilayer) mosaic portion is the proteins and carbohydrates
preliminary account of some of the findings has been given [Parsons and
 FLUID AND SOLUTE TRANSPORT ACROSS RAT COLONIC MUCOSA. By D. S. PARSONS and C. R. PATERSON.* From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Oxford, South Parks Road, Oxford, Great Britain. (Received
FLUID AND SOLUTE TRANSPORT ACROSS RAT COLONIC MUCOSA. By D. S. PARSONS and C. R. PATERSON.* From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Oxford, South Parks Road, Oxford, Great Britain. (Received
(1933) suggest this to be due to the greater affinity of the sucrose particle for
 RELATIVE INHIBITION OF MICROORGANISMS BY GLUCOSE AND SUCROSE SIRUPS1 Massachusetts Agricultural Experiment Station, Amherst, Mass. Received for publication, December 29, 1941 In concentrations above 30
RELATIVE INHIBITION OF MICROORGANISMS BY GLUCOSE AND SUCROSE SIRUPS1 Massachusetts Agricultural Experiment Station, Amherst, Mass. Received for publication, December 29, 1941 In concentrations above 30
What is the major site of digestion? If you answered stomach, you missed it! The correct answer is small intestine.
 DIGESTION SIMULATION LAB PAP CLASS SET BACKGROUND INFORMATION What is digestion and where does it begin? Digestion is the breaking down of food into forms that our bodies can use. Your digestive system
DIGESTION SIMULATION LAB PAP CLASS SET BACKGROUND INFORMATION What is digestion and where does it begin? Digestion is the breaking down of food into forms that our bodies can use. Your digestive system
Kidney Physiology. Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed
 Kidney Physiology Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed The purpose of tubular secrection To dispose of certain substances that are bound to plasma proteins. To
Kidney Physiology Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed The purpose of tubular secrection To dispose of certain substances that are bound to plasma proteins. To
slowing of the muscle. Bronk [1933] has given a striking
![slowing of the muscle. Bronk [1933] has given a striking slowing of the muscle. Bronk [1933] has given a striking](/thumbs/89/99616855.jpg) 106 6I2.74I.I2 THE EFFECT OF ACTIVITY ON THE FORM OF THE MUSCLE TWITCH. BY J. L. PARKINSON. (From the Department of Physiology and Biochemistry, University College, London.) IT has been found by various
106 6I2.74I.I2 THE EFFECT OF ACTIVITY ON THE FORM OF THE MUSCLE TWITCH. BY J. L. PARKINSON. (From the Department of Physiology and Biochemistry, University College, London.) IT has been found by various
EXPERIMENT 4 DETERMINATION OF REDUCING SUGARS, TOTAL REDUCING SUGARS, SUCROSE AND STARCH
 Practical Manual Food Chemistry and Physiology EXPERIMENT 4 DETERMINATION OF REDUCING SUGARS, TOTAL REDUCING SUGARS, SUCROSE AND STARCH Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4.2 Experiment 4a: Reducing
Practical Manual Food Chemistry and Physiology EXPERIMENT 4 DETERMINATION OF REDUCING SUGARS, TOTAL REDUCING SUGARS, SUCROSE AND STARCH Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4.2 Experiment 4a: Reducing
Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell
 CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
What do you remember about the cell membrane?
 Cell Membrane What do you remember about the cell membrane? Cell (Plasma) Membrane Separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment All cells have a cell membrane Selectively
Cell Membrane What do you remember about the cell membrane? Cell (Plasma) Membrane Separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment All cells have a cell membrane Selectively
Constant Motion of Molecules. Kinetic Theory of Matter Molecules move randomly and bump into each other and other barriers
 CELL TRANSPORT Constant Motion of Molecules Kinetic Theory of Matter Molecules move randomly and bump into each other and other barriers Solution homogenous liquid throughout which two or more substances
CELL TRANSPORT Constant Motion of Molecules Kinetic Theory of Matter Molecules move randomly and bump into each other and other barriers Solution homogenous liquid throughout which two or more substances
