Biochemistry lecturer Bio- chemical Eng. Zahraa Abdulhussein Mousa. Bio.Eng Zahraa A.A. Mousa
|
|
|
- Jonathan Pearson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biochemistry lecturer Bio- chemical Eng. Zahraa Abdulhussein Mousa
2 Overview Carbohydrates are the most abundant organic molecules in nature Wide range of functions e.g., a significant fraction of the energy in the diet, acting as storage form of energy in body, serving as memb. components that mediate some forms of intercellular communication Carbohydrates also serve as structural component of many organisms, including CW of bacteria, exoskeleton of many insects, & fibrous cellulose of plants The empiric formula for many of the simpler carbohydrates is (CH2O) n, hence the name hydrate of carbon
3 II. Classification and structure of carbohydrates - Monosacch (simple sugars) can be classified according to # of C atoms they contain. - CHO s with an aldehyde as their most oxidized functional group are called aldoses, whereas those with a keto group as their most oxidized functional group are ketoses e.g., glyceraldehyde is an aldose, whereas dihydroxyacetone is a ketose - CHO s that have a free carbonyl group have the suffix -ose Note: ketoses (with some exceptions e.g., fructose) have an additional 2 letters in their suffix; -ulose, e.g., xylulose - Monosacch can be linked by glycosidic bonds to create larger structures - Disacch contain 2 monosacch units - Oligosacch contain from 3 to about 12 monosacch units - Polysacch contain > 12 monosacch units, can be 100 s of sugar units
4 Examples of monosaccharides found in humans, classified according to the number of carbons they contain.
5 Examples of an aldose (A) and a ketose (B) sugar.
6 . A glycosidic bond between two hexoses producing a disaccharide.
7 A. Isomers and epimers - Cpds that have same chemical formula but have different structures = isomers e.g., fructose, glucose, mannose, & galactose are all isomers of each other, having same formula C 6 H 12 O 6 - If 2 monosacch differ in configuration around only one specific C atom (with exception of carbonyl C), they are defined as epimers of each other (of course they are also isomers) e.g., - glucose & galactose are C-4 epimers, their structures differ only in the position of OH group at C 4. - Glucose & mannose are C-2 epimers - however, galactose & mannose are not epimers, they differ in position of OH groups at two carbons, and defined only as isomers Note: carbons in sugars are numbered beginning at end containing the carbonyl C i.e., aldehyde or keto group
8 C-2 and C-4 epimers and an isomer of glucose.
9 B. Enantiomers - A special type of isomerism is found in the pairs of structures that are mirror images of each other. These mirror images = enantiomers, & the 2 members of the pair are designated as D- & L-sugar. Vast majority of sugars in humans are D-sugars Enantiomers (mirror images) of glucose.
10 C. Cyclization of monosaccharides - Less than 1% of each of the monosacch with 5 or more C s exist in the open-chain (acyclic) form. Rather, they are predominantly found in ring form, in which aldehyde (or ketone) group has reacted with an alcohol group on the same sugar 1. Anomeric carbon: - Formation of a ring results in creation of an anomeric C at carbon 1 of an aldose or at carbon 2 of a ketose - These structures are designated the α or β configurations of the sugar, e.g., α-d-glucose & β-d-glucose. They are both glucose, but are anomers of each other - Enz s are able to distinguish b/w the 2 structures & use one or the other preferentially e.g., glycogen is synthesized from α-d-glucopyranose. - The cyclic α & β anomers of a sugar in solution are in equil. with each other, & can be spontaneously interconverted (a process called mutarotation)
11 . The interconversion of the α and β anomeric forms of glucose (mutarotation).
12 2. Reducing sugars: - If the oxygen on the anomeric C (the carbonyl group) of a sugar is not attached to any other structure, that sugar is a reducing sugar. - A reducing sugar can react with chemical reagents e.g., Benedict s soln & reduce the reactive component, with the anomeric C becoming oxidized Note: only the state of the oxygen on the anomeric C determines if the sugar is reducing or non-reducing, the other hydroxyl groups on the molecule are not involved
13 D. Complex carbohydrates - CHO s can be attached by glycosidic bonds to non-cho structures e.g., purines & pyrimidines (found in nucleic acids), aromatic rings (such as those found in steroids & bilirubin), proteins (found in glycoproteins & glycosaminoglycans), and lipids (found in glycolipids) - The aldose (C1) or ketose (C2) participates in the glycosidic link, is called glycosyl residue. E.g., if anomeric C of glucose participates in such a bond, that sugar = glucosyl residue; thus the disacch lactose is galactosyl-glucose
14 1. O- & N-glycosides: - If the group of the non-cho molecule to which sugar is attached is OH group, the structure is O- glycoside. If the group is NH2, structure is N- glycoside. Note: all sugar-sugar glycosidic bonds are O-type
15 . Glycosides: examples of N- and O-glycosidic bond
16 2. Naming glycosidic bonds: - Glycosidic bonds b/w sugars are named according to numbers of connected C s, & also with regard to position of anomeric hydroxyl group of the sugar involved in the bond - If anomeric hydroxyl group is in α configuration, the linkage is α-bond. If it is in β β-bond. - Lactose e.g., is synthesized by forming a glycosidic bond b/w C-1 of β-galactose & C-4 of glucose. Linkage is = β (1 4) glycosidic bond. [note: anomeric end of glucose is not involved in glycosidic linkage, it (&, therefore lactose) remains a reducing sugar
17 A glycosidic bond between two hexoses producing a disaccharide.
18 Digestion of carbohydrates - The principal sites of dietary CHO digestion are mouth & intestinal lumen. This digestion is rapid & is generally completed by the time stomach contents reach the junction of duodenum & jejunum - There is little monosacch present in diets of mixed animal & plant origin. Therefore, enz s needed for degradation of most dietary CHO s are primarily disaccharidases & endoglycosidases (break oligo- & polysacch) - Hydrolysis of glycosidic bond is catalyzed by a family of glycosidases that degrade CHO s into their reducing sugar components - These enz s are usually specific for structure & config of glycosyl residue to be removed, as well as type of bond broken
19 . Hydrolysis of a glycosidic bond
20 A. Digestion of CHO s begins in the mouth - Major dietary polysacch are of animal (glycogen) & plant origin (starch, composed of amylose & amylopectin) - During mastication, salivary amylase acts briefly on dietary starch in a random manner, breaking some α(1 4) bonds Note: there are both α(1 4) & β(1 4)-endoglucosidases in nature, but human do not produce & secrete the latter in digestive juices, therefore, they are unable to digest cellulose: CHO of plant origin containing β(1 4)-glycosidic bonds b/w glucose residues. - Because branched amylopectin & glycogen also contain α(1 6) bonds, digest resulting from action of α-amylase contains a mixture of smaller, branched oligosacch molecules - CHO digestion halts temporarily in stomach, as high acidity inactivates α-amylase
21 Degradation of dietary glycogen by salivary or pancreatic α- amylase.
22 B. Further digestion of CHOs by pancreatic enz s occurs in the small intestine - When acidic stomach contents reach small intestine, they are neutralized by bicarbonates secreted by pancreas, & pancreatic α-amylase continues process of starch digestion
23 C. Final carbohydrate digestion by enzymes synthesized from the intestinal mucosal cells - Final digestion processes occur at mucosal lining of the upper jejunum, declining as they proceed down the small intestine, & include action of several disaccharidases & oligosaccharidases. - E.g., - isomaltase cleaves the α(1 6) bond in isomaltose and maltase cleaves maltose, both producing: glucose - Sucrase cleaves sucrose producing glucose & fructose - Lactase (β-galactosidase) cleaves lactose producing galactose & glucose. - These enz s are secreted through, & remain associated with, luminal side of the brush border memb s of intestinal mucosal cells
24 Digestion of carbohydrates.
25 D. Absorption of monosaccharides by intestinal mucosal cells - Duodenum & upper jejunum absorb the bulk of dietary sugars. - Insulin is not required for uptake of glucose by intestinal cells. - Different sugars have different mechanisms of absorption e.g., - galactose & glucose are transported into mucosal cells by an active, energy requiring process that involves a specific transport protein & requires a concurrent uptake of sodium ions. - Fructose uptake requires a sodium-independent monosaccharide transporter (GLUT-5) for its absorption - All 3 monosacch s are transported from intestinal mucosal cell into the portal circulation by yet another transporter, GLUT-2
26 The hexose transporters are large integral membrane proteins. They have 12 membrane-spanning regions with cytoplasmic C-terminal and N- terminal tails. Also, they all appear to be glycosylated on one of the extracellular loops.
27 E. Abnormal degradation of disaccharides - Overall process of CHO digestion & absorption is efficient in healthy individuals. Ordinarily all digestible dietary CHO is absorbed by time the ingested material reaches lower jejunum - Because predominantly monosacch s are absorbed, any defect in a specific disacch activity of intestinal mucosa causes the passage of undigested CHO into large intestine - As a consequence of presence of this osmotically active material, water is drawn from the mucosa into large intestine osmotic diarrhea. This is reinforced by the bacterial fermentation of remaining CHO to 2- & 3-C cpds (which are also osmotically active) plus large volumes of CO2 & H2 gas, causing abdominal cramps, diarrhea and flatulence
28 1. Digestive enzyme deficiencies: Hereditary deficiencies of the individual disaccharidases have been reported in infants & children with disaccharide intolerance Alterations in disaccharide degradation can also be caused by a variety of intestinal diseases, malnutrition, or drugs the injure mucosa of small intestine E.g., brush border enz s are rapidly lost in normal individuals with severe diarrhea causing a temporary acquired enz deficiency. Thus, patients suffering or recovering from such a disorder cannot drink or eat significant amount of dairy products or sucrose without exacerbating diarrhea
29 2. Lactose intolerance: - More than ½ of the world s adults are lactose intolerant. This is particularly manifested in certain races e.g., up to 90% of adults of African or Asian descent are lactase-deficient &, are less able to metabolize lactose than individuals of northern European origin - The mechanism by which enz is lost is not clear, but it is determined genetically and represents a reduction in amount of enz protein rather than a modified inactive enz. - Treatment for this disorder is simply to remove lactose from diet, or to take lactase in pill form prior to eating
30 Abnormal lactose metabolism.
31 4. diagnosis: - Identification of specific enz deficiency can be obtained by performing oral tolerance with individual disaccharides - Measurement of hydrogen gas in breath is a reliable test for determining the amount of ingested CHO not absorbed by the body, but which is metabolized instead by intestinal flora.
32 Summary Monosacch (simple sugars) containing aldehyde group = aldoses, those with keto = ketoses Disacch, oligosacch, & polysacch cosist of monosacch s linked by glycosidic bonds Compounds with same chemical formula = isomers. If 2 monosacch isomers differ in config around one specific C atom (with the exception of carbonyl C) are defined as epimers of each other If a pair of sugars are mirror images (= enantiomers) the 2 members of a pair are D- & L-sugars When a sugar cyclizes, an anomeric C is created from the aldehyde group of an ladose or keto group of a ketose. This C can have 2 configs α or β. If the oxygen on anomeric C is not attached to any other structure, the sugar is a reducing sugar A sugar with its anomeric C linked to another structure is called a glycosyl residue Sugars can be attached either to NH2 or OH group N- & O-glycosides
33 Salivary α-amylase acts on dietary starch (glycogen, amylose, amylopectin) oligosacch s Pancreatic α-amylase continues the process of starch digestion The final digestive processes occur at mucosal lining of small intestine. Several disaccharidases [e.g., lactas (β-galactosidase), sucrase, maltase, & isomaltase] monosacch s (glucose, galactose & fructose) These enz s secreted by & remain associated with luminal side of brush border memb s of intestinal mucosal cells Absorption of monosacch s requires specific transporters If CHO degradation is deficient (as result of heredity, intestinal disease, malnutrition, or drugs that injure mucosa of small intestine), undigested CHO will pass into large intestine osmotic diarrhea Bacterial fermentation of the cpds large volumes of CO2 & H2 gas abdominal cramps, diarrhea & flatulence Lactose intolerance, caused by lack of lactase, most common of these deficiencies
34
Carbohydrates. What are they? What do cells do with carbs? Where do carbs come from? O) n. Formula = (CH 2
 Carbohydrates What are they? Formula = (C 2 O) n where n > 3 Also called sugar Major biomolecule in body What do cells do with carbs? Oxidize them for energy Store them to oxidize later for energy Use
Carbohydrates What are they? Formula = (C 2 O) n where n > 3 Also called sugar Major biomolecule in body What do cells do with carbs? Oxidize them for energy Store them to oxidize later for energy Use
Carbohydrates. Learning Objective
 , one of the four major classes of biomolecules, are aldehyde or ketone compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups. They function as energy stores, metabolic intermediates and important fuels for the body.
, one of the four major classes of biomolecules, are aldehyde or ketone compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups. They function as energy stores, metabolic intermediates and important fuels for the body.
Digestion of Carbohydrates. BCH 340 Lecture 2
 Digestion of Carbohydrates BCH 340 Lecture 2 Carbohydrates are called carbohydrates because they are essentially hydrates of carbon (i.e. they are composed of carbon and water and have a composition of
Digestion of Carbohydrates BCH 340 Lecture 2 Carbohydrates are called carbohydrates because they are essentially hydrates of carbon (i.e. they are composed of carbon and water and have a composition of
Chapter 18. Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry. Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry page 1
 Chapter 18 Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry page 1 Introduction to Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Bioenergetics Metabolism and
Chapter 18 Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry page 1 Introduction to Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Bioenergetics Metabolism and
College of Science Department of Biochemistry
 Dr. Abir Alghanouchi College of Science Department of Biochemistry Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are called carbohydrates because they are essentially hydrates of carbon(i.e. they are composed of carbon
Dr. Abir Alghanouchi College of Science Department of Biochemistry Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are called carbohydrates because they are essentially hydrates of carbon(i.e. they are composed of carbon
Lecture 2 Carbohydrates
 Lecture 2 Carbohydrates Sources of CHOs Wholegrains major dietary intake Vegetables, legumes ad fruit contain dietary fibre Milk products provide lactose essential for infants Glycogen is a storage carbohydrate,
Lecture 2 Carbohydrates Sources of CHOs Wholegrains major dietary intake Vegetables, legumes ad fruit contain dietary fibre Milk products provide lactose essential for infants Glycogen is a storage carbohydrate,
Carbohydrates. Monosaccharides
 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (also called saccharides) are molecular compounds made from just three elements: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Monosaccharides (e.g. glucose) and disaccharides (e.g. sucrose)
Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (also called saccharides) are molecular compounds made from just three elements: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Monosaccharides (e.g. glucose) and disaccharides (e.g. sucrose)
24.1 Introduction to Carbohydrates
 24.1 Introduction to Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (sugars) are abundant in nature: They are high energy biomolecules. They provide structural rigidity for organisms (plants, crustaceans, etc.). The polymer
24.1 Introduction to Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (sugars) are abundant in nature: They are high energy biomolecules. They provide structural rigidity for organisms (plants, crustaceans, etc.). The polymer
A. Incorrect! No, this is not the description of this type of molecule. B. Incorrect! No, this is not the description of this type of molecule.
 Biochemistry - Problem Drill 08: Carbohydrates No. 1 of 10 1. have one aldehyde (-CHO) or one keto (-C=O) group and many hydroxyl (-OH) groups. (A) Amino acids (B) Proteins (C) Nucleic Acids (D) Carbohydrates
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 08: Carbohydrates No. 1 of 10 1. have one aldehyde (-CHO) or one keto (-C=O) group and many hydroxyl (-OH) groups. (A) Amino acids (B) Proteins (C) Nucleic Acids (D) Carbohydrates
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry. CHAPTER 6: Carbohydrates
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 6: Carbohydrates Carbohydrates
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 6: Carbohydrates Carbohydrates
Biochemistry: Macromolecules
 1 Biology: Macromolecules 2 Carbohydrates Carbohydrate organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Meaning: hydrated carbon ratio of h:0 is 2:1 (same as in water) Source: plants
1 Biology: Macromolecules 2 Carbohydrates Carbohydrate organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio Meaning: hydrated carbon ratio of h:0 is 2:1 (same as in water) Source: plants
Monosaccharides: Little amounts Don t need any digestion
 Slide 8 Digestion result in mono and disaccharides & alpha-dextrins (oligosaccharides) Alpha1-4 in sequences / alpha1-6 at branches Dietary carbohydrates: Polysaccharides: 1) Containing α(1,4)/ α(1,6)
Slide 8 Digestion result in mono and disaccharides & alpha-dextrins (oligosaccharides) Alpha1-4 in sequences / alpha1-6 at branches Dietary carbohydrates: Polysaccharides: 1) Containing α(1,4)/ α(1,6)
Ch13. Sugars. What biology does with monosaccharides disaccharides and polysaccharides. version 1.0
 Ch13 Sugars What biology does with monosaccharides disaccharides and polysaccharides. version 1.0 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2015 Ch13 Sugars Haworth Structures Saccharides can form rings. That creates a
Ch13 Sugars What biology does with monosaccharides disaccharides and polysaccharides. version 1.0 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2015 Ch13 Sugars Haworth Structures Saccharides can form rings. That creates a
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 10 Carbohydrates 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 10 Outline Monosaccharides are aldehydes or ketones that contain two or
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 10 Carbohydrates 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 10 Outline Monosaccharides are aldehydes or ketones that contain two or
Chapter 24: Carbohydrates
 Chapter 24: Carbohydrates [Sections: 24.1 24.10] 1. Carbohydrates definition naturally occuring compounds derived from carbon, oxygen and hydrogen the net molecular formula comes from each carbon having
Chapter 24: Carbohydrates [Sections: 24.1 24.10] 1. Carbohydrates definition naturally occuring compounds derived from carbon, oxygen and hydrogen the net molecular formula comes from each carbon having
Carbohydrates 1. Steven E. Massey, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Bioinformatics Department of Biology University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras
 Carbohydrates 1 Steven E. Massey, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Bioinformatics Department of Biology University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Office & Lab: NCN#343B Tel: 787-764-0000 ext. 7798 E-mail: stevenemassey@gmail.com
Carbohydrates 1 Steven E. Massey, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Bioinformatics Department of Biology University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Office & Lab: NCN#343B Tel: 787-764-0000 ext. 7798 E-mail: stevenemassey@gmail.com
CLASS 11th. Biomolecules
 CLASS 11th 01. Carbohydrates These are the compound of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen having hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as that of water, i.e. 2 : 1. They are among the most widely distributed
CLASS 11th 01. Carbohydrates These are the compound of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen having hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as that of water, i.e. 2 : 1. They are among the most widely distributed
Questions- Carbohydrates. A. The following structure is D-sorbose. (Questions 1 7) CH 2 OH C = O H C OH HO C H H C OH
 Questions- Carbohydrates A. The following structure is D-sorbose. (Questions 1 7) CH 2 C = O H C HO C H H C CH 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Which characteristic is different when comparing the open-chain forms of
Questions- Carbohydrates A. The following structure is D-sorbose. (Questions 1 7) CH 2 C = O H C HO C H H C CH 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Which characteristic is different when comparing the open-chain forms of
Dr. Entedhar Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are carbon compounds that have aldehyde (C-H=0) or ketone (C=O) moiety and comprises polyhyroxyl alcohol
 Dr. Entedhar Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are carbon compounds that have aldehyde (C-H=0) or ketone (C=O) moiety and comprises polyhyroxyl alcohol (polyhydroxyaldehyde or polyhyroxyketone); their polymers,which
Dr. Entedhar Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are carbon compounds that have aldehyde (C-H=0) or ketone (C=O) moiety and comprises polyhyroxyl alcohol (polyhydroxyaldehyde or polyhyroxyketone); their polymers,which
Carbohydrates. Chapter 12
 Carbohydrates Chapter 12 Educational Goals 1. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it as either aldoses or ketoses. 2. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it by
Carbohydrates Chapter 12 Educational Goals 1. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it as either aldoses or ketoses. 2. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it by
Chapter-8 Saccharide Chemistry
 Chapter-8 Saccharide Chemistry Page 217-228 Carbohydrates (Saccharides) are most abundant biological molecule, riginally produced through C 2 fixation during photosynthesis I (C 2 ) n or - C - I where
Chapter-8 Saccharide Chemistry Page 217-228 Carbohydrates (Saccharides) are most abundant biological molecule, riginally produced through C 2 fixation during photosynthesis I (C 2 ) n or - C - I where
!"#$%&'()*+(!,-./012-,345(
 (!"#$%&'()*+(!,-./012-,345( (!"#"$%&'()$*%#+,'(-(.+/&/*+,%&(01"2+34$5( 6%#+,"(!/$75#38+(92+41( CAPTER 20: Learning Objectives:! >
(!"#$%&'()*+(!,-./012-,345( (!"#"$%&'()$*%#+,'(-(.+/&/*+,%&(01"2+34$5( 6%#+,"(!/$75#38+(92+41( CAPTER 20: Learning Objectives:! >
BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 7 Lecture Notes
 BC 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 7 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 7 Carbohydrates 2 Carbohydrates: Nomenclature ydrates of carbon General formula (C 2 ) n (simple sugars) or C x ( 2 0) y Monosaccharides (simple sugars)
BC 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 7 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 7 Carbohydrates 2 Carbohydrates: Nomenclature ydrates of carbon General formula (C 2 ) n (simple sugars) or C x ( 2 0) y Monosaccharides (simple sugars)
Chem 263 Nov 22, Carbohydrates (also known as sugars or saccharides) See Handout
 hem 263 Nov 22, 2016 arbohydrates (also known as sugars or saccharides) See andout Approximately 0.02% of the sun s energy is used on this planet for photosynthesis in which organisms convert carbon dioxide
hem 263 Nov 22, 2016 arbohydrates (also known as sugars or saccharides) See andout Approximately 0.02% of the sun s energy is used on this planet for photosynthesis in which organisms convert carbon dioxide
Carbohydrates. Lecture2
 Carbohydrates Lecture2 Disaccharides Consist of two monosaccharides covalently bound to each other. All of which are isomers with the molecular formula C 12 22 O 11. The differences in these disaccharides
Carbohydrates Lecture2 Disaccharides Consist of two monosaccharides covalently bound to each other. All of which are isomers with the molecular formula C 12 22 O 11. The differences in these disaccharides
Farah Al-Khaled. Razi Kittaneh. Mohammad Omari
 7 Farah Al-Khaled Razi Kittaneh Mohammad Omari Dr. Mamoun Ahram In this lecture we are going to talk about modified sugars. Remember: The Fischer projection can be turned into a ring structure (which is
7 Farah Al-Khaled Razi Kittaneh Mohammad Omari Dr. Mamoun Ahram In this lecture we are going to talk about modified sugars. Remember: The Fischer projection can be turned into a ring structure (which is
Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids. Carbohydrates
 Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Synthesized by plants using sunlight to convert CO 2 and H 2 O to glucose and O 2. Polymers include starch and cellulose. Starch is storage unit
Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Synthesized by plants using sunlight to convert CO 2 and H 2 O to glucose and O 2. Polymers include starch and cellulose. Starch is storage unit
CARBOHYDRATES (SUGARS)
 ARBYDRATES (SUGARS) ARBYDRATES: 1. Most Abundant Molecules on Earth: (100 MILLIN METRI TNS f 2 And 2 0 onverted To ellulose and ther Plant Products/Year) 2. FUNTINS: Diet, Energy, Structural, Signalling
ARBYDRATES (SUGARS) ARBYDRATES: 1. Most Abundant Molecules on Earth: (100 MILLIN METRI TNS f 2 And 2 0 onverted To ellulose and ther Plant Products/Year) 2. FUNTINS: Diet, Energy, Structural, Signalling
2/25/2015. Chapter 6. Carbohydrates. Outline. 6.1 Classes of Carbohydrates. 6.1 Classes of Carbohydrates. 6.1 Classes of Carbohydrates
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Carbohydrates Julie Klare Fortis College Smyrna, GA Outline 6.7 Carbohydrates and Blood The simplest carbohydrates are monosaccharides (mono is Greek for one, sakkhari is
Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Carbohydrates Julie Klare Fortis College Smyrna, GA Outline 6.7 Carbohydrates and Blood The simplest carbohydrates are monosaccharides (mono is Greek for one, sakkhari is
Topic 4 - #2 Carbohydrates Topic 2
 Topic 4 - #2 Carbohydrates Topic 2 Biologically Important Monosaccharide Derivatives There are a large number of monosaccharide derivatives. A variety of chemical and enzymatic reactions produce these
Topic 4 - #2 Carbohydrates Topic 2 Biologically Important Monosaccharide Derivatives There are a large number of monosaccharide derivatives. A variety of chemical and enzymatic reactions produce these
Chemistry B11 Chapters 13 Esters, amides and carbohydrates
 Chapters 13 Esters, amides and carbohydrates Esters: esters are derived from carboxylic acids (the hydrogen atom in the carboxyl group of carboxylic acid is replaced by an alkyl group). The functional
Chapters 13 Esters, amides and carbohydrates Esters: esters are derived from carboxylic acids (the hydrogen atom in the carboxyl group of carboxylic acid is replaced by an alkyl group). The functional
Chapter 11. Learning objectives: Structure and function of monosaccharides, polysaccharide, glycoproteins lectins.
 Chapter 11 Learning objectives: Structure and function of monosaccharides, polysaccharide, glycoproteins lectins. Carbohydrates Fuels Structural components Coating of cells Part of extracellular matrix
Chapter 11 Learning objectives: Structure and function of monosaccharides, polysaccharide, glycoproteins lectins. Carbohydrates Fuels Structural components Coating of cells Part of extracellular matrix
Chapter 22 Carbohydrates
 Chapter 22 Carbohydrates Introduction Classification of Carbohydrates Carbohydrates have the general formula C x (H 2 O) y Carbohydrates are defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or substances that
Chapter 22 Carbohydrates Introduction Classification of Carbohydrates Carbohydrates have the general formula C x (H 2 O) y Carbohydrates are defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or substances that
Carbohydrates. Green plants turn H 2 O, CO 2, and sunlight into carbohydrates.
 Chapter 27 Carbohydrates Green plants turn 2 O, CO 2, and sunlight into carbohydrates. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris ein, Scott Pattison, and Susan
Chapter 27 Carbohydrates Green plants turn 2 O, CO 2, and sunlight into carbohydrates. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris ein, Scott Pattison, and Susan
CHAPTER 27 CARBOHYDRATES SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 27 09/17/2013 11:12:35 Page 397 APTER 27 ARBYDRATES SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. In general, the carbohydrate carbon oxidation state determines the carbon s metabolic energy content. The more oxidized
27 09/17/2013 11:12:35 Page 397 APTER 27 ARBYDRATES SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. In general, the carbohydrate carbon oxidation state determines the carbon s metabolic energy content. The more oxidized
You know from previous lectures that carbonyl react with all kinds of nucleophiles. Hydration and hemiacetal formation are typical examples.
 hem 263 Nov 17, 2009 D,L onfiguration of Sugars Glyceraldehyde has only one stereogenic center and therefore has two enantiomers (mirror image) forms. A D-sugar is defined as one that has configuration
hem 263 Nov 17, 2009 D,L onfiguration of Sugars Glyceraldehyde has only one stereogenic center and therefore has two enantiomers (mirror image) forms. A D-sugar is defined as one that has configuration
MahaAbuAjamieh. BahaaNajjar. MamoonAhram
 7 MahaAbuAjamieh BahaaNajjar MamoonAhram Carbohydrates (saccharides) can be classified into these main categories: 1. Monosaccharides, they are simplesugars (the simplest units), such as glucose, galactose
7 MahaAbuAjamieh BahaaNajjar MamoonAhram Carbohydrates (saccharides) can be classified into these main categories: 1. Monosaccharides, they are simplesugars (the simplest units), such as glucose, galactose
Chapter 16: Carbohydrates
 Vocabulary Aldose: a sugar that contains an aldehyde group as part of its structure Amylopectin: a form of starch; a branched chain polymer of glucose Amylose: a form of starch; a linear polymer of glucose
Vocabulary Aldose: a sugar that contains an aldehyde group as part of its structure Amylopectin: a form of starch; a branched chain polymer of glucose Amylose: a form of starch; a linear polymer of glucose
Anomeric carbon Erythritol is achiral because of a mirror plane in the molecule and therefore, the product is optically inactive.
 APTER 22 Practice Exercises 22.1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 D-Ribulose L-Ribulose D-Xyulose L-Xyulose (one pair of enantiomers) (a second pair of enantiomers) 22.3 2 Anomeric carbon Glycosidic bond 3 () Methyl -D-mannopyranoside
APTER 22 Practice Exercises 22.1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 D-Ribulose L-Ribulose D-Xyulose L-Xyulose (one pair of enantiomers) (a second pair of enantiomers) 22.3 2 Anomeric carbon Glycosidic bond 3 () Methyl -D-mannopyranoside
Chapter 1. Chemistry of Life - Advanced TABLE 1.2: title
 Condensation and Hydrolysis Condensation reactions are the chemical processes by which large organic compounds are synthesized from their monomeric units. Hydrolysis reactions are the reverse process.
Condensation and Hydrolysis Condensation reactions are the chemical processes by which large organic compounds are synthesized from their monomeric units. Hydrolysis reactions are the reverse process.
Carbohydrates: structure and Function. Important. 436 Notes Original slides. 438 notes Extra information
 Carbohydrates: structure and Function Important. 436 Notes Original slides. 438 notes Extra information Objectives: To understand: 1- The structure of carbohydrates of physiological significance. 2- The
Carbohydrates: structure and Function Important. 436 Notes Original slides. 438 notes Extra information Objectives: To understand: 1- The structure of carbohydrates of physiological significance. 2- The
Chapter 27 Carbohydrates
 Chapter 27 Carbohydrates Green plants turn 2 O, CO 2, and sunlight into carbohydrates. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris ein, Scott Pattison, and Susan
Chapter 27 Carbohydrates Green plants turn 2 O, CO 2, and sunlight into carbohydrates. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris ein, Scott Pattison, and Susan
May 21 st, 2008 Biochemistry Recitation
 May 21 st, 2008 Biochemistry Recitation MBioS 303 Summer 2008 Outline Carbohydrate basics Aldoses vs. ketoses L and D configurations and anomers Glycosidic bonds, disaccharides Polysaccharides Storage:
May 21 st, 2008 Biochemistry Recitation MBioS 303 Summer 2008 Outline Carbohydrate basics Aldoses vs. ketoses L and D configurations and anomers Glycosidic bonds, disaccharides Polysaccharides Storage:
Carbohydrates are aldehyde or ketone compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups Have multiple roles in all forms of life
 Carbohydrates 1 Carbohydrates are aldehyde or ketone compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups Have multiple roles in all forms of life Classification Serve as energy stores, fuels, and metabolic intermediates
Carbohydrates 1 Carbohydrates are aldehyde or ketone compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups Have multiple roles in all forms of life Classification Serve as energy stores, fuels, and metabolic intermediates
Dr. Basima Sadiq Ahmed PhD. Clinical biochemist
 Dr. Basima Sadiq Ahmed PhD. Clinical biochemist MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. major source of energy for man. e.g, glucose is used in the human body for energy production. 2. serve as reserve food
Dr. Basima Sadiq Ahmed PhD. Clinical biochemist MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. major source of energy for man. e.g, glucose is used in the human body for energy production. 2. serve as reserve food
I. Carbohydrates Overview A. Carbohydrates are a class of biomolecules which have a variety of functions. 1. energy
 Chapter 22 Carbohydrates Chem 306 Roper I. Carbohydrates Overview A. Carbohydrates are a class of biomolecules which have a variety of functions. 1. energy 2. energy storage 3. structure 4. other functions!
Chapter 22 Carbohydrates Chem 306 Roper I. Carbohydrates Overview A. Carbohydrates are a class of biomolecules which have a variety of functions. 1. energy 2. energy storage 3. structure 4. other functions!
Long time ago, people who sacrifice their sleep, family, food, laughter, and other joys of life were called SAINTS. But now, they are called STUDENTS!
 Long time ago, people who sacrifice their sleep, family, food, laughter, and other joys of life were called SAINTS. But now, they are called STUDENTS! Monosaccharaides Q. Can hydrolysis occur at anytime
Long time ago, people who sacrifice their sleep, family, food, laughter, and other joys of life were called SAINTS. But now, they are called STUDENTS! Monosaccharaides Q. Can hydrolysis occur at anytime
I (CH 2 O) n or H - C - OH I
 V. ARBYDRATE arbohydrates (glycans) have the following basic composition: I ( ) n or - - I Many carbohydrates are soluble in water. The usual chemical test for the simpler carbohydrates is heating with
V. ARBYDRATE arbohydrates (glycans) have the following basic composition: I ( ) n or - - I Many carbohydrates are soluble in water. The usual chemical test for the simpler carbohydrates is heating with
Carbohydrates. Organic compounds which comprise of only C, H and O. C x (H 2 O) y
 Carbohydrates Organic compounds which comprise of only C, H and O C x (H 2 O) y Carbohydrates Monosaccharides Simple sugar Soluble in water Precursors in synthesis triose sugars of other (C3) molecules
Carbohydrates Organic compounds which comprise of only C, H and O C x (H 2 O) y Carbohydrates Monosaccharides Simple sugar Soluble in water Precursors in synthesis triose sugars of other (C3) molecules
Chem 263 Apr 11, 2017
 hem 263 Apr 11, 2017 arbohydrates- emiacetal Formation You know from previous lectures that carbonyl compounds react with all kinds of nucleophiles. ydration and hemiacetal formation are typical examples.
hem 263 Apr 11, 2017 arbohydrates- emiacetal Formation You know from previous lectures that carbonyl compounds react with all kinds of nucleophiles. ydration and hemiacetal formation are typical examples.
Waseem Abu Obeida. Salsabeel Fleifal. Mamoon Ahram
 8 Waseem Abu Obeida Salsabeel Fleifal Mamoon Ahram Anomers Anomers cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers, they differ from each other in the configuration of C-1 if they are aldoses or
8 Waseem Abu Obeida Salsabeel Fleifal Mamoon Ahram Anomers Anomers cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers, they differ from each other in the configuration of C-1 if they are aldoses or
CARBOHYDRATES. By: SHAMSUL AZAHARI ZAINAL BADARI Department of Resource Management And Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM
 CARBOHYDRATES By: SHAMSUL AZAHARI ZAINAL BADARI Department of Resource Management And Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM OBJECTIVES OF THE LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define
CARBOHYDRATES By: SHAMSUL AZAHARI ZAINAL BADARI Department of Resource Management And Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM OBJECTIVES OF THE LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define
For more info visit
 Carbohydrates Classification of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides: Polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones which cannot be decomposed by hydrolysis to give simpler carbohydrates.examples: Glucose, Fructose,
Carbohydrates Classification of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides: Polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones which cannot be decomposed by hydrolysis to give simpler carbohydrates.examples: Glucose, Fructose,
Chem 60 Takehome Test 2 Student Section
 Multiple choice: 1 point each. Mark only one answer for each question. 1. are composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen, but may also include oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, and a few other elements.
Multiple choice: 1 point each. Mark only one answer for each question. 1. are composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen, but may also include oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, and a few other elements.
Structural Polysaccharides
 Carbohydrates & ATP Carbohydrates include both sugars and polymers of sugars. The simplest carbohydrates are the monosaccharides, or simple sugars; these are the monomers from which more complex carbohydrates
Carbohydrates & ATP Carbohydrates include both sugars and polymers of sugars. The simplest carbohydrates are the monosaccharides, or simple sugars; these are the monomers from which more complex carbohydrates
Carbohydrates- Disaccharides. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Carbohydrates- Disaccharides By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Disaccharides ofbiological importance: Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages. They are crystalline, water-soluble
Carbohydrates- Disaccharides By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Disaccharides ofbiological importance: Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages. They are crystalline, water-soluble
Disaccharides. Three Important Disaccharides Maltose, Lactose, and Sucrose. The formation of these three common disaccharides are:
 DISACCHARIDES Disaccharides Three Important Disaccharides Maltose, Lactose, and Sucrose The formation of these three common disaccharides are: 2 Disaccharides Maltose (Malt Sugar) Maltose is known as malt
DISACCHARIDES Disaccharides Three Important Disaccharides Maltose, Lactose, and Sucrose The formation of these three common disaccharides are: 2 Disaccharides Maltose (Malt Sugar) Maltose is known as malt
CHAPTER 23. Carbohydrates
 CAPTER 23 Carbohydrates 1 Introduction Carbohydrates are naturally occurring compounds of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Carbohydrates have the empirical formula C 2. Carbohydrates have the general formula
CAPTER 23 Carbohydrates 1 Introduction Carbohydrates are naturally occurring compounds of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Carbohydrates have the empirical formula C 2. Carbohydrates have the general formula
2.2: Sugars and Polysaccharides François Baneyx Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Washington
 2.2: Sugars and Polysaccharides François Baneyx Department of hemical Engineering, University of Washington baneyx@u.washington.edu arbohydrates or saccharides are abundant compounds that play regulatory
2.2: Sugars and Polysaccharides François Baneyx Department of hemical Engineering, University of Washington baneyx@u.washington.edu arbohydrates or saccharides are abundant compounds that play regulatory
Review from last lecture
 eview from last lecture D-glucose has the structure shown below (you are responsible for its structure on the exam). It is an aldohexose ( aldo since it contains aldehyde functionality and hexose since
eview from last lecture D-glucose has the structure shown below (you are responsible for its structure on the exam). It is an aldohexose ( aldo since it contains aldehyde functionality and hexose since
Definition of a Carbohydrate
 * Atoms held together by covalent bonds Definition of a Carbohydrate * Organic macromolecules * Consist of C, H, & O atoms * Usually in a 1:2:1 ratio of C:H : O Functions Performed by Carbohydrates Used
* Atoms held together by covalent bonds Definition of a Carbohydrate * Organic macromolecules * Consist of C, H, & O atoms * Usually in a 1:2:1 ratio of C:H : O Functions Performed by Carbohydrates Used
Chapter 20 Carbohydrates Chapter 20
 Chapter 20 Carbohydrates Chapter 20 1 Carbohydrates Carbohydrate: A polyhydroxyaldehyde or polyhydroxyketone, or a substance that gives these compounds on hydrolysis. Monosaccharide: A carbohydrate that
Chapter 20 Carbohydrates Chapter 20 1 Carbohydrates Carbohydrate: A polyhydroxyaldehyde or polyhydroxyketone, or a substance that gives these compounds on hydrolysis. Monosaccharide: A carbohydrate that
A Getting-It-On Review and Self-Test. . Carbohydrates are
 A Getting-It-n Review and Self-Test arbohydrates arbohydrates, one of the three principal classes of foods, contain only three elements: (1), (2), and (3). The name carbohydrate is derived from the French
A Getting-It-n Review and Self-Test arbohydrates arbohydrates, one of the three principal classes of foods, contain only three elements: (1), (2), and (3). The name carbohydrate is derived from the French
Carbohydrates are a large group of organic compounds occurring in and including,, and. They contain hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as (2:1).
 Carbohydrates are a large group of organic compounds occurring in and and including,, and. They contain hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as (2:1). Why we study carbohydrates 1) carbohydrates are the
Carbohydrates are a large group of organic compounds occurring in and and including,, and. They contain hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as (2:1). Why we study carbohydrates 1) carbohydrates are the
among the most important organic compounds in the living organisms;
 CARBOHYDRATES Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" CARBOHYDRATESare among the most
CARBOHYDRATES Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" CARBOHYDRATESare among the most
Downloaded from
 Biomolecules Section A (One Mark Question) 1. Name the sugar present in milk. A: Lactose, 2. How many monosaccharide units are present in it? A: two monosaccharide units are present. 3.What are such oligosaccharides
Biomolecules Section A (One Mark Question) 1. Name the sugar present in milk. A: Lactose, 2. How many monosaccharide units are present in it? A: two monosaccharide units are present. 3.What are such oligosaccharides
BIOMOLECULES & SPECTROSCOPY TABLE OF CONTENTS S.NO. TOPIC PAGE NO. i) Carbohydrates B3. ii) Proteins & Nucleic Acids.
 BIOMOLECULES & SPECTROSCOPY TABLE OF CONTENTS S.NO. TOPIC PAGE NO. 1. Biomolecules i) Carbohydrates B3 ii) Proteins & Nucleic Acids iii) Steroids iv) Terpenes & Cartenoids B27 B61 B65 2. Spectroscopy v)
BIOMOLECULES & SPECTROSCOPY TABLE OF CONTENTS S.NO. TOPIC PAGE NO. 1. Biomolecules i) Carbohydrates B3 ii) Proteins & Nucleic Acids iii) Steroids iv) Terpenes & Cartenoids B27 B61 B65 2. Spectroscopy v)
The Structure and Func.on of Macromolecules: GRU1L4 Carbohydrates
 The Structure and Func.on of Macromolecules: GRU1L4 Carbohydrates Do Now: WHAT IS TABLE SUGAR MADE UP OF? Sucrose (table sugar) Composed of a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule Please draw the structure
The Structure and Func.on of Macromolecules: GRU1L4 Carbohydrates Do Now: WHAT IS TABLE SUGAR MADE UP OF? Sucrose (table sugar) Composed of a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule Please draw the structure
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2009 Examination #5 ANSWER KEY For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2009 Examination #5 ANSWER KEY For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush. Rana N. Talj
 2 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 19 th 2013 Rana N. Talj Review: Fischer suggested a projection in which the horizontal bonds are projecting towards the viewer and the vertical ones project away from the
2 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 19 th 2013 Rana N. Talj Review: Fischer suggested a projection in which the horizontal bonds are projecting towards the viewer and the vertical ones project away from the
BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT 2 Part 4 ACTIVITY #4 (Chapter 5) CARBOHYDRATES
 AP BIOLOGY BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT 2 Part 4 ACTIVITY #4 (Chapter 5) NAME DATE PERIOD CARBOHYDRATES GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS: Polymers of simple sugars Classified according to number of simple sugars Sugars 3
AP BIOLOGY BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT 2 Part 4 ACTIVITY #4 (Chapter 5) NAME DATE PERIOD CARBOHYDRATES GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS: Polymers of simple sugars Classified according to number of simple sugars Sugars 3
Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis Reactions. ne_content/animations/reaction_types.ht ml
 Glucose Molecule Macromolecules Carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids are polymers Polymers long molecules made from building blocks linked by covalent bonds Monomers the building blocks to polymers
Glucose Molecule Macromolecules Carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids are polymers Polymers long molecules made from building blocks linked by covalent bonds Monomers the building blocks to polymers
Section 2.1: Enzymes and Digestion
 Section 2.1: Enzymes and Digestion Glands produce enzymes that are used to break down large molecules into smaller ones that are ready for abortion. The digestive system provides an interface between the
Section 2.1: Enzymes and Digestion Glands produce enzymes that are used to break down large molecules into smaller ones that are ready for abortion. The digestive system provides an interface between the
L1, 2 : Biochemical Aspects of Digestion of Lipids, Proteins, and Carbohydrates
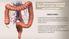 L1, 2 : Biochemical Aspects of Digestion of Lipids, Proteins, and Carbohydrates OBJECTIVES: Understand the process of digestion of dietary lipids, protein and carbohydrates including, the organs involved,
L1, 2 : Biochemical Aspects of Digestion of Lipids, Proteins, and Carbohydrates OBJECTIVES: Understand the process of digestion of dietary lipids, protein and carbohydrates including, the organs involved,
Carbohydrates. Haworth Projections
 Carbohydrates There are, for all intents and purposes, 2 classes of carbohydrates: pyranoses and furanoses ( ose is the suffix for a sugar). These two classes are so called because their carbon skeletons
Carbohydrates There are, for all intents and purposes, 2 classes of carbohydrates: pyranoses and furanoses ( ose is the suffix for a sugar). These two classes are so called because their carbon skeletons
Number of Carbohydrate Units
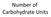 Number of Carbohydrate Units Monosaccharides = single unit Disaccharides = two units Oligiosaccharide = 3 10 units Polysaccharide = 11+ units Bonus: Can you name the most common Mono (4), Di(3), and Poly(4)
Number of Carbohydrate Units Monosaccharides = single unit Disaccharides = two units Oligiosaccharide = 3 10 units Polysaccharide = 11+ units Bonus: Can you name the most common Mono (4), Di(3), and Poly(4)
Topic 3: Molecular Biology
 Topic 3: Molecular Biology 3.2 Carbohydrates and Lipids Essen=al Understanding: Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen are used to supply and store energy. Carbohydrates CARBOHYDRATES CHO sugars Primarily consist
Topic 3: Molecular Biology 3.2 Carbohydrates and Lipids Essen=al Understanding: Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen are used to supply and store energy. Carbohydrates CARBOHYDRATES CHO sugars Primarily consist
Carbohydrates. 1. Using the terms provided below, complete the concept map showing the characteristics of organic compounds.
 Name: Class: Date: Grade 10 Science Related Reading/Biology Carbohydrates Biology Gr10 1. Using the terms provided below, complete the concept map showing the characteristics of organic compounds. maltose
Name: Class: Date: Grade 10 Science Related Reading/Biology Carbohydrates Biology Gr10 1. Using the terms provided below, complete the concept map showing the characteristics of organic compounds. maltose
BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURES BY RASAQ, N.O
 BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURES BY RASAQ, N.O LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION POLYSACCHARIDES STRUCTURAL POLYSACCHARIDES: CELLULOSE AND CHITIN BACTERIA CELL WALLS PEPTIDOGLYCAN PENICILLIN AND β-lactam ANTIBIOTICS AND
BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURES BY RASAQ, N.O LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION POLYSACCHARIDES STRUCTURAL POLYSACCHARIDES: CELLULOSE AND CHITIN BACTERIA CELL WALLS PEPTIDOGLYCAN PENICILLIN AND β-lactam ANTIBIOTICS AND
Wallington County Grammar School
 Wallington County Grammar School Y11 to Lower Sixth Bridging Work Subject: Subject Leader to direct questions to (email enquiries@wcgs.org.uk): Estimated hours of work needed to complete this work successfully:
Wallington County Grammar School Y11 to Lower Sixth Bridging Work Subject: Subject Leader to direct questions to (email enquiries@wcgs.org.uk): Estimated hours of work needed to complete this work successfully:
The addition of sugar moiety determines the blood group
 The addition of sugar moiety determines the blood group Sugars attached to glycoproteins and glycolipids on the surfaces of red blood cells determine the blood group termed A, B, and O. The A and B antigens
The addition of sugar moiety determines the blood group Sugars attached to glycoproteins and glycolipids on the surfaces of red blood cells determine the blood group termed A, B, and O. The A and B antigens
1 C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 C 6 C 7 C 8 C
 I. Carbon atoms form an enormous variety of structures A. Carbon has 4 valence electrons in the outer shell and therefore may form up to 4 covalent bonds B. Carbon tends to bond to C, H, O, N, S, and P
I. Carbon atoms form an enormous variety of structures A. Carbon has 4 valence electrons in the outer shell and therefore may form up to 4 covalent bonds B. Carbon tends to bond to C, H, O, N, S, and P
CONTENTS. Digestion of carbohydrates. Absorption of carbohydrates. Clinical significance
 CONTENTS Digestion of carbohydrates Absorption of carbohydrates Clinical significance Carbohydrates present in the diet Polysaccharides Disaccharides Monosaccharides Starch Glycogen Lactose Maltose Sucrose
CONTENTS Digestion of carbohydrates Absorption of carbohydrates Clinical significance Carbohydrates present in the diet Polysaccharides Disaccharides Monosaccharides Starch Glycogen Lactose Maltose Sucrose
HW #9: 21.36, 21.52, 21.54, 21.56, 21.62, 21.68, 21.70, 21.76, 21.82, 21.88, 21.94, Carbohydrates
 Chemistry 131 Lectures 16 & 17: Carbohydrates Chapter 21 in McMurry, Ballantine, et. al. 7 th edition 05/24/18, 05/25/18 W #9: 21.36, 21.52, 21.54, 21.56, 21.62, 21.68, 21.70, 21.76, 21.82, 21.88, 21.94,
Chemistry 131 Lectures 16 & 17: Carbohydrates Chapter 21 in McMurry, Ballantine, et. al. 7 th edition 05/24/18, 05/25/18 W #9: 21.36, 21.52, 21.54, 21.56, 21.62, 21.68, 21.70, 21.76, 21.82, 21.88, 21.94,
Carbohydrates CHAPTER SUMMARY
 14 2 cellulose 2 2 arbohydrates 2 amylose APTER SUMMARY 14.1 hemical Nature of arbohydrates - Polyhydroxy Aldehydes and Ketones arbohydrates are a class of organic biopolymers which consist of polyhydroxy
14 2 cellulose 2 2 arbohydrates 2 amylose APTER SUMMARY 14.1 hemical Nature of arbohydrates - Polyhydroxy Aldehydes and Ketones arbohydrates are a class of organic biopolymers which consist of polyhydroxy
Biomolecules are organic molecules produced by living organisms which consists mainly of the following elements:
 Biomolecules are organic molecules produced by living organisms which consists mainly of the following elements: These elements are non-metals which combine in various ways to form biomolecules through
Biomolecules are organic molecules produced by living organisms which consists mainly of the following elements: These elements are non-metals which combine in various ways to form biomolecules through
Welcome to Class 7. Class 7: Outline and Objectives. Introductory Biochemistry
 Welcome to Class 7 Introductory Biochemistry Class 7: Outline and Objectives l Monosaccharides l Aldoses, ketoses; hemiacetals; epimers l Pyranoses, furanoses l Mutarotation, anomers l Disaccharides and
Welcome to Class 7 Introductory Biochemistry Class 7: Outline and Objectives l Monosaccharides l Aldoses, ketoses; hemiacetals; epimers l Pyranoses, furanoses l Mutarotation, anomers l Disaccharides and
UNIT 4. CARBOHYDRATES
 UNIT 4. CARBOHYDRATES OUTLINE 4.1. Introduction. 4.2. Classification. 4.3. Monosaccharides. Classification. Stereoisomers. Cyclic structures. Reducing sugars. Sugar derivatives 4.4. Oligosaccharides. Disaccharides.
UNIT 4. CARBOHYDRATES OUTLINE 4.1. Introduction. 4.2. Classification. 4.3. Monosaccharides. Classification. Stereoisomers. Cyclic structures. Reducing sugars. Sugar derivatives 4.4. Oligosaccharides. Disaccharides.
Sheet #8 Dr. Nafeth Abu-Tarboush
 1 arbohydrates There are two topic goals in our study of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides: to recognize their structure, properties, & their stereochemistry. The nature of di-, oligo- & polysaccharides.
1 arbohydrates There are two topic goals in our study of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides: to recognize their structure, properties, & their stereochemistry. The nature of di-, oligo- & polysaccharides.
Dr. Mahendra P. Bhatt (BMLT, MS-Ph.D., Post-doctorate) Associate Professor Clinical Biochemistry
 Dr. Mahendra P. Bhatt (BMLT, MS-Ph.D., Post-doctorate) Associate Professor Clinical Biochemistry mahendramlt@gmail.com Students will be able to describe: Biochemical organization of the cell Transport
Dr. Mahendra P. Bhatt (BMLT, MS-Ph.D., Post-doctorate) Associate Professor Clinical Biochemistry mahendramlt@gmail.com Students will be able to describe: Biochemical organization of the cell Transport
Chem 263 Nov 21, 2013
 hem 263 Nov 21, 2013 arbohydrates- emiacetal Formation You know from previous lectures that carbonyl compounds react with all kinds of nucleophiles. ydration and hemiacetal formation are typical examples.
hem 263 Nov 21, 2013 arbohydrates- emiacetal Formation You know from previous lectures that carbonyl compounds react with all kinds of nucleophiles. ydration and hemiacetal formation are typical examples.
Chapter 11 Lecture Notes: Carbohydrates
 Educational Goals Chapter 11 Lecture Notes: Carbohydrates 1. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it as either aldoses or ketoses. 2. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide,
Educational Goals Chapter 11 Lecture Notes: Carbohydrates 1. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it as either aldoses or ketoses. 2. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide,
Sheet #10 Dr. Mamoun Ahram Sec 1,2,3 15/07/2014. Carbohydrates 2
 Carbohydrates 2 A study Guide: Kindly,refer to the slide number,look at the structures and read the sheet notes well,most of the slides content besides all what the doctor said are mentioned here,good
Carbohydrates 2 A study Guide: Kindly,refer to the slide number,look at the structures and read the sheet notes well,most of the slides content besides all what the doctor said are mentioned here,good
Carbohydrates Dr. Ameerah M. Zarzoor
 Carbohydrates Dr. Ameerah M. Zarzoor What Are Carbohydrates? Carbohydrates are the most abundant biomolecules on Earth Produced by plants during photosynthesis Carbohydrates are polyhydroxyl aldehydes
Carbohydrates Dr. Ameerah M. Zarzoor What Are Carbohydrates? Carbohydrates are the most abundant biomolecules on Earth Produced by plants during photosynthesis Carbohydrates are polyhydroxyl aldehydes
An aldose contains an aldehyde functionality A ketose contains a ketone functionality
 RCT Chapter 7 Aldoses and Ketoses; Representative monosaccharides. (a)two trioses, an aldose and a ketose. The carbonyl group in each is shaded. An aldose contains an aldehyde functionality A ketose contains
RCT Chapter 7 Aldoses and Ketoses; Representative monosaccharides. (a)two trioses, an aldose and a ketose. The carbonyl group in each is shaded. An aldose contains an aldehyde functionality A ketose contains
Lec 3a- BPK 110 Human Nutr.:Current Iss.
 Lec 3a- BPK 110 Human Nutr.:Current Iss. 1. Overview Carbohydrates (CHO) 2. Types of Carbohydrates 3. Why to Include Carbohydrates in Your Diet? 4. Digestion, Absorption and Transport of Carbohydrates
Lec 3a- BPK 110 Human Nutr.:Current Iss. 1. Overview Carbohydrates (CHO) 2. Types of Carbohydrates 3. Why to Include Carbohydrates in Your Diet? 4. Digestion, Absorption and Transport of Carbohydrates
Chemistry of Carbon. Building Blocks of Life
 Chemistry of Carbon Building Blocks of Life 2007-2008 Why study Carbon? All of life is built on carbon Cells ~72% 2 O ~25% carbon compounds carbohydrates lipids proteins nucleic acids ~3% salts Na, Cl,
Chemistry of Carbon Building Blocks of Life 2007-2008 Why study Carbon? All of life is built on carbon Cells ~72% 2 O ~25% carbon compounds carbohydrates lipids proteins nucleic acids ~3% salts Na, Cl,
Chapter 7 Overview. Carbohydrates
 Chapter 7 Overview n Carbohydrates main ingredient for energy production Most abundant biomolecule in nature Direct link between solar energy & chemical energy Glucose our main energy source Carbohydrates
Chapter 7 Overview n Carbohydrates main ingredient for energy production Most abundant biomolecule in nature Direct link between solar energy & chemical energy Glucose our main energy source Carbohydrates
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush. Tarek Khrisat
 1 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 18 th 2013 Tarek Khrisat 1 Lecture Outline: Aldoses and Ketoses Optical isomers -Fischer projection -Enantiomers, Diastereomers, and Epimers Isomers: Compounds with the same
1 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 18 th 2013 Tarek Khrisat 1 Lecture Outline: Aldoses and Ketoses Optical isomers -Fischer projection -Enantiomers, Diastereomers, and Epimers Isomers: Compounds with the same
Carbohydrates. Chapter 18
 Carbohydrates Chapter 18 Biochemistry an overview Biochemistry is the study of chemical substances in living organisms and the chemical interactions of these substances with each other. Biochemical substances
Carbohydrates Chapter 18 Biochemistry an overview Biochemistry is the study of chemical substances in living organisms and the chemical interactions of these substances with each other. Biochemical substances
