SUPPLEMENTARY FEEDING OF GRAZING SHEEP - ITS EFFECT ON PASTURE INTAKE ByJ.M. HOLDER*
|
|
|
- Johnathan Ellis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY FEEDING OF GRAZING SHEEP - ITS EFFECT ON PASTURE INTAKE ByJ.M. HOLDER* Summary In three experiments conducted with Merino sheep grazing unimproved native pasture, feeding a grain supplement significantly depressed grazing time and pasture intake. An efficiency of supplementation coefficient is developed to. describe this substitution effect. If 100 per cent. efficiency indicates that the supplement does not act as a substitute for pasture, the highest efficiency of supplementation reached in these experiments was 43 per cent. The higher efficiency coefficients tended to occur when unsupplemented animals were losing weight on the pasture. The effect on grazing time and pasture intake of mixing supplemented with unsupplemented sheep varied. Generally the trend was towards lower grazing times and pasture intake of unsupplemented animals, but in one experiment there was a significant increase in the grazing time of the supplemented sheep. I. INTRODUCTION At the 1st Biennial Conference of the Australian Society of Animal Production it was pointed out by McClymont ( 1956) that while the feeding of supplements of conserved roughage or concentrates is widely recommended as a means of combating the effect of poor pasture on growth or milk production of stock... the responses have been most erratic and far less than would have been expected on the basis of feeding standards. Reports since then have tended to confirm this contention (Corbett 1958; Castle et al. 1960; Holder 1960). The data of these authors, all obtained with dairy cattle, suggest that the supplement fed acted as a substitute Although intake data were not presented, in the latter report there was decrease in the grazing time of the cows. Tribe ( 1950) also has reported that Scottish Blackface ewes supplement grazed for much shorter periods than did unsupplemented the two groups were mixed as one flock, however, the grazing times for pasture. a significant fed a meal ewes. When 1were similar and approached that of the unsupplemented animals when they had grazed alone. That is, the presence of presumably hungry animals appeared to stimulate the supplemented ewes to graze for a longer daily period, an effect described as, one of social facilitation. If Tribe s report of social interactions in the sheep used in his study holds for other breeds, and if grazing time is a reflection of pasture intake, then his findings are of considerable significance in relation to design and interpretation of grazing experiments and may have application in husbandry of the grazing animal. The present experiments were therefore designed to determine the social interactions, if any, between supplemented and unsupplemented Merino sheep as they might affect grazing time and pasture intake * N.S.W. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Station, Wollongbar. 154
2 II. METHODS AND MATERIALS The experiments were conducted on unimproved native pasture at Armidale, New South Wales. The total food intake of individual sheep was estimated by indirect techniques, with faecal output determined bv the chromic oxide method (Raymond and Mins& 1955), and ;he intake factor (Lancaster 1954) from the relationship: F = l-03 - Om2438 N N2 where F = intake factor (digestible organic matter) and N = faeca1 nitrogen percentage. This local regression was developed from analysis of digestibility experiments covering a wide range of pasture species, including those used in the present experiments (Lambourne, Reardon, and Holder, unpublished data). Total food intake was measured over lo- or 12-day collection periods. The supplement fed in each experiment was oat grain derived from the one supply. Animals receiving the supplement were yarded each morning and fed individually SO that the oats could be measured. The digestibility of organic matter in the oat grain was determined by standard methods, oat grain alone being fed to Merino wethers in metabolism crates. Pasture intake of the supplemented sheep was calculated by difference, total intake in grams of digestible organic matter (D.O.M.) minus D.O.M. intake in grams from the supplement. Grazing times of individual sheep were obtained bv direct observation over 24.hour periods, generally with two such periods in each collection period of 10 or 12 days. (i) Experiment 1. Winter Ten Merino wethers were offered 450 g grain once daily and were run as one group (S.A.), while another ten unsupplemented animals were run alone as one group (US.A. ). A third mixed group consisted of ten supplemented (S.M.) and ten unsupplemented animals (US.M.). The stocking rate was 2 sheep per acre and the duration of the experiment was two consecutive 1 O-day collection periods. (ii) Experiment 2. Spring Same treatments as for Experiment 1. The supplement offered was 340 g grain per day. Duration, two consecutive 12.day collection periods. (iii) Experiment 3. Autumn Same treatments as for Experiments 1 and 2. The supplement offered was 340 g grain daily. Duration, one 12-day collection period. The sheep used in Experiment 1 were not used again. The 60 sheep used in Experiment 2 were used again in Experiment 3 after spending the intervening period as one flock on native pasture without supplements.. The animals were allocated at random to treatments. Ten similarly treated sheep were added to each of the alone groups so that numbers in these groups equalled those in the mixed group. Data were not collected for these sheep. In all experiments, the groups were rotationally grazed round the three paddocks used at three- or four-day intervals to overcome the confounding of paddock effects. In each experiment a period of at least 7 days elapsed between allocation to treatments and t.he commencement of the collection periods. 155
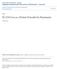
3 GRAZING TIME cvnin per 24 hrs) TOTAL WI1TAKE (D.o.M. g /day) z! 3 m
4 III. RESULTS The mean digestibility of organic matter in the oat grain used was 76.5 per cent. A summary of the grazing times, total food intake, and intake of supplement where appropriate, is given for all four experiments in Fig. 1. Intakes are recorded in grams D.O.M., and grazing time in minutes. In Experiment 2 two of the sheep allocated to the S.M. treatment group consistently refused to eat the supplement offered. In the same group one sheep was badly affected by pizzle rot over the experimental period. The data for these three sheep was excluded from calculations, so that the group mean was derived from seven sheep. In an endeavour to describe in quantitative terms the substitution effect of the supplement noted in these experiments, a coefficient of efficiency of supplementation has been developed: Efficiemy of su/+baetitation (per cc?) t.) z ( Intake of D.O.M. from supplement - ) ( Difference D.O.M. intake of.n&pletnelzted vs. unsupplemented animals ) (Intake of D.O.lK from szzpplewzent) x 100 Thus if supplementation were 100 per cent. efficient in this context it would be found that there was no difference in the pasture intakes of the supplemented and unsupplemented animals running alone. That is, the supplement could exert maximum productive effect without substituting for pasture. The efficiency coefficients are recorded in Table 1, together with the liveweight and the mean change in weight, over the period of each experiment, of the supplemented and unsupplemented animals. TABLE 1 EFFICIENCY OF SUPPLEMENTATION, LIVEWEIGHT AND LIVEWEIGHT CHANGE OF SUPPLEMENTED AND UNSUPPLEMENTED SHEEP Experiment Efficiency of Supplementation * S.A. compared with US.A Liveweight Liveweight Change -F (kg) (is Per day) S.A. US.A. S.A. US.A i * Efficiency of Supplementation-see text. *? Liveweight change as measured over the experimental period divided by the number of days in the period. 157
5 Mean grazing times of the treatment groups followed the same pattern in each experiment with S.A. < S.M. < US.M. < US.A. The percentage increase in grazing time of each group over the previous group in the series is given in Table 2. TABLE 2 RELATIVE GRAZING TIMES-EXPERIMENTS 1 TO 3 Increase in Grazing Time ( % ) Experiment S.M. compared with US.M. compared with US.A. compared with S.A. S.M. US.M. - :I- Difference significant at P < O O * +12*5 * +4*0 N.S. +2*5 +2*5 +12*0 * +6*0 +8-O +16*0 * IV. DISCUSSION The use may well be questioned of a regression equation, to estimate intake factor, developed from digestibility experiments with pasture species and not including a grain similar to that used in these experiments. Unpublished data (Holder 1959), however, have shown that the addition of oat grain to a diet of natural pasture fed to penned sheep did not improve the digestibility of the pasture portion of the diet. That is, the digestibility of organic matter in the mixed diet (native pasture and grain to the proportion 1 to l-5), viz per cent., was closer to that of oat grain (76.5 per cent.) than that of the pasture only (42 5 per cent.) in proportion to the grain fed. Although it may reasonably be argued that the inclusion of oat grain in the diet could lead to a higher faecal nitrogen percentage, particularly in the faeces of sheep grazing the winter pasture, this could only lead to the use of a higher intake factor in calculation of total intake than is actually warranted. Thus there may be an overestimate of the total intake of the supplemented animals, but this would not invalidate the conclusions drawn from these experiments. In all three experiments the marked substitution effect of the grain supplement was recorded, differences in pasture intake of the two groups running alone being highly significant. Even in Experiment 1, when the supplement alone group was losing weight and when the time was apparently available to increase daily grazing activity, the efficiency of supplementation wash only 43 per cent. The depression of pasture intake by the S.A. groups was paralleled by the marked depression of the grazing time of this group when compared with the USA. group in Experiments 1 to 3. Social interactions appear to have played a most important, though variable, role in the grazing behaviour and pasture intake of the sheep used in the 158
6 experiments. While the effect reported by Tribe ( 1950) was recorded in Experiment 1, there being a significant increase in the grazing time of S.M. sheep compared with those in the S.A. group, the trend in these experiments generally appears to be toward a reduction in the grazing time of the US.M. sheep, that is, a social inhibition effect appeared to be at work. It would appear, therefore, that it is only in special circumstances, under practical farming conditions, that any beneficial effect on pasture intake of supplemented sheep may be obtained by running decoy unsupplemented sheep with them. However, it is felt that the data presented should serve at least as a warning to workers designing experiments dealing with supplementary feeding of grazing sheep. Due recognition must obviously be paid to the social interactions which may be at work in a mixed group of supplemented and unsupplemented animals, and which could well affect interpretation of the data gained. V. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Special thanks are due to Professor G. L. McClymont and to Mr. L. J. Lambourne of C.S.I.R.O. Pastoral Research Laboratory, Armidale, for encouragement and advice. Appreciation is expressed to C.S.I.R.O. for provision of most of the facilities used in this work. Messrs. R. L. Rocks and D. J. Brett provided valuable technical assistance. VI. REFERENCES CASTLE, M. E., DRYSDALE, A. D., and WATSON, J. N. (1960).-The effect of feed supplements on the yield and composition of milk from cows grazing good pasture. J. Dairy Res. 27: 419. CORBETT, J. L. (1958).-Effects of low protein supplements on the yield and composition of milk from grazing dairy cows. Proc. Brit. Soc. Anim. Prod. 1: HOLDER, J. M. (1960).-Observations on the grazing behaviour of lactating dairy cattle in a subtropical environment. J. Agric. Sci. 55: 261. LANCASTER, R. J. ( 1954).- Measurement of feed intake of grazing cattle and sheep. V. The estimation of the feed to faeces ratio from the nitrogen content of the faeces of pasturefed cattle. N.Z. J. Sci. Tech. A36: 15. MCCLYMONT, G. L. (1956).-Response of stock to supplementary feeding on pastures. Proc. Aust. Soc. Anim. Prod. 1: 63. R AYMOND, W. F., and M INSON, D, J. (1955).-The use of chromic oxide for estimating the faecal production of grazing animals. J. Brit. Grassl. Soc. 10: 282. TRIBE, D. E. ( 1950).-Social facilitation in grazing sheep. Nature 166:
The Efficiency of Wool Growth
 The Efficiency of Wool Growth By K. A. FERGUSON* IN the present paper, efficiency of wool growth is defined as the percentage of the food crude protein which is converted into wool. Efficiency is discussed
The Efficiency of Wool Growth By K. A. FERGUSON* IN the present paper, efficiency of wool growth is defined as the percentage of the food crude protein which is converted into wool. Efficiency is discussed
ESTIMATION OF THE ENERGY VALUE OF EWE MILK
 Proc. Aust. Soc. Anim. Prod. (1972) 9: 286 ESTIMATION OF THE ENERGY VALUE OF EWE MILK D. J. BRETT*, J. L. CORBETT and M. W. INSKIP Summary Energy, fat, protein, and lactose were determined in 68 samples
Proc. Aust. Soc. Anim. Prod. (1972) 9: 286 ESTIMATION OF THE ENERGY VALUE OF EWE MILK D. J. BRETT*, J. L. CORBETT and M. W. INSKIP Summary Energy, fat, protein, and lactose were determined in 68 samples
THE EFFECT OF UREA BLOCK SUPPLEMENTATION ON THE UTILISATION OF ROUGHAGE BY SHEEP
 THE EFFECT OF UREA BLOCK SUPPLEMENTATION ON THE UTILISATION OF ROUGHAGE BY SHEEP P. McINNES* and N. W. MANGELSDORF Summary Blocks containing urea were provided to groups of penned sheep fed ad libitum
THE EFFECT OF UREA BLOCK SUPPLEMENTATION ON THE UTILISATION OF ROUGHAGE BY SHEEP P. McINNES* and N. W. MANGELSDORF Summary Blocks containing urea were provided to groups of penned sheep fed ad libitum
Forage Intake of Range Cows as Mfected Breed and Level of Winter Supplement
 Forage Intake of Range Cows as Mfected Breed and Level of Winter Supplement by K.S. Lusby, D.F. Stephens, Leon Knori and Robert Totusek Story in Brief The effects of breed and level of winter supplement
Forage Intake of Range Cows as Mfected Breed and Level of Winter Supplement by K.S. Lusby, D.F. Stephens, Leon Knori and Robert Totusek Story in Brief The effects of breed and level of winter supplement
THE EFFECT OF PLANE OF NUTRITION ON CRIMP FREQUENCY AND FIBRE DIMENSIONS IN MEDIUM-WOOLED MERINO SHEEP. H. IRAZOQUI* and M. K.
 THE EFFECT OF PLANE OF NUTRITION ON CRIMP FREQUENCY AND FIBRE DIMENSIONS IN MEDIUM-WOOLED MERINO SHEEP H. IRAZOQUI* and M. K. HILL* Sixteen medium-wooled Merino wethers similar in body-weight, fibre diameter,
THE EFFECT OF PLANE OF NUTRITION ON CRIMP FREQUENCY AND FIBRE DIMENSIONS IN MEDIUM-WOOLED MERINO SHEEP H. IRAZOQUI* and M. K. HILL* Sixteen medium-wooled Merino wethers similar in body-weight, fibre diameter,
EFFECT OF WATER, NITROGEN AND POTASSIUM LOADING ON SODIUM RETENTION BY CATTLE ON A LOW SODIUM INTAKE. D. W. HENNESSY and G. L.
 EFFECT OF WATER, NITROGEN AND POTASSIUM LOADING ON SODIUM RETENTION BY CATTLE ON A LOW SODIUM INTAKE D. W. HENNESSY and G. L. McCLYMONT* Summary Steers grew- at 0.25 kg per day for over a year on a ration
EFFECT OF WATER, NITROGEN AND POTASSIUM LOADING ON SODIUM RETENTION BY CATTLE ON A LOW SODIUM INTAKE D. W. HENNESSY and G. L. McCLYMONT* Summary Steers grew- at 0.25 kg per day for over a year on a ration
Growth and Wool Production of Merino Hoggets Related to Grazing Intake in a South Australian Environment
 Growth and Wool Production of Merino Hoggets Related to Grazing Intake in a South Australian Environment K. J. H UTCHINSON* AND R. B. P ORTER* Summary The growth of young sheep grazing mature summer pasture
Growth and Wool Production of Merino Hoggets Related to Grazing Intake in a South Australian Environment K. J. H UTCHINSON* AND R. B. P ORTER* Summary The growth of young sheep grazing mature summer pasture
EFFECTS OF DAILY OR WEEKLY FEEDING OF WHEAT ON WOOL PRODUCTION. M. K. HILL*, M. J. WATSON and G. L. McCLYMONT
 EFFECTS OF DAILY OR WEEKLY FEEDING OF WHEAT ON WOOL PRODUCTION M. K. HILL*, M. J. WATSON and G. L. McCLYMONT Summary Non pregnant Merino ewes were fed for survival on isocaloric wheat rations given either
EFFECTS OF DAILY OR WEEKLY FEEDING OF WHEAT ON WOOL PRODUCTION M. K. HILL*, M. J. WATSON and G. L. McCLYMONT Summary Non pregnant Merino ewes were fed for survival on isocaloric wheat rations given either
PREDICTION OF BODY COMPOSITION IN LIVE ANIMALS
 PREDICTION OF BODY COMPOSITION IN LIVE ANIMALS H. R. GHARAYBEH*, G. W. ARNOLD, W. R. McMANUS* and M. L. DUDZINSKI Summary Merino and Border Leicester x Merino ewe and wether weaners within the bodyweight
PREDICTION OF BODY COMPOSITION IN LIVE ANIMALS H. R. GHARAYBEH*, G. W. ARNOLD, W. R. McMANUS* and M. L. DUDZINSKI Summary Merino and Border Leicester x Merino ewe and wether weaners within the bodyweight
INTAKEANDDIGESTIBiliTY
 EFFECTS OF LACTATION TYPE OF SUPPLEMENTS ON FORAGE INTAKEANDDIGESTIBiliTY T.T. Marston1 and K. S. Lusby2 Story In Brief Spring-calving beef cows were used in two consecutive years, (n=32, year 1; n=42,
EFFECTS OF LACTATION TYPE OF SUPPLEMENTS ON FORAGE INTAKEANDDIGESTIBiliTY T.T. Marston1 and K. S. Lusby2 Story In Brief Spring-calving beef cows were used in two consecutive years, (n=32, year 1; n=42,
A COMPARISON OF PROTEIN CONCENTRATES FOR WOOL GROWTH. W. F. COLEBROOK*, K. A. FERGUSON*, J. A. HEMSLEY,* J. P. HOGAN*, P. J. REIS* and R. H.
 A COMPARISON OF PROTEIN CONCENTRATES FOR WOOL GROWTH W. F. COLEBROOK*, K. A. FERGUSON*, J. A. HEMSLEY,* J. P. HOGAN*, P. J. REIS* and R. H. WESTON* Summary The value of 14 protein concentrates for wool
A COMPARISON OF PROTEIN CONCENTRATES FOR WOOL GROWTH W. F. COLEBROOK*, K. A. FERGUSON*, J. A. HEMSLEY,* J. P. HOGAN*, P. J. REIS* and R. H. WESTON* Summary The value of 14 protein concentrates for wool
Phosphorus nutrition & management overcoming constraints to wider adoption
 Phosphorus nutrition & management overcoming constraints to wider adoption Rob Dixon, David Coates, Bill Holmes, Bernie English & Joe Rolfe & with thanks to other members of the team preparing the new
Phosphorus nutrition & management overcoming constraints to wider adoption Rob Dixon, David Coates, Bill Holmes, Bernie English & Joe Rolfe & with thanks to other members of the team preparing the new
The use of n-alkanes to estimate supplementary grass silage intake in grazing dairy cows
 Journal of Agricultural Science, Cambridge (1998), 131, 205 209. 1998 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom 205 The use of n-alkanes to estimate supplementary grass silage intake in
Journal of Agricultural Science, Cambridge (1998), 131, 205 209. 1998 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom 205 The use of n-alkanes to estimate supplementary grass silage intake in
DIFFERENCES IN MUSCLE : BONE RATIOS BETWEEN ZEBU CROSS AND BRITISH BREED STEERS
 DIFFERENCES IN MUSCLE : BONE RATIOS BETWEEN ZEBU CROSS AND BRITISH BREED STEERS R. W. HEWETSON* Summary Differences- were found in the ratio of the weight of four large muscles to the weight of total side
DIFFERENCES IN MUSCLE : BONE RATIOS BETWEEN ZEBU CROSS AND BRITISH BREED STEERS R. W. HEWETSON* Summary Differences- were found in the ratio of the weight of four large muscles to the weight of total side
Beef Cattle Handbook
 Beef Cattle Handbook BCH-5450 Product of Extension Beef Cattle Resource Committee Adapted from the Cattle Producer s Library Formulating Supplements Roger Brownson, Extension Beef Cattle Specialist, Montana
Beef Cattle Handbook BCH-5450 Product of Extension Beef Cattle Resource Committee Adapted from the Cattle Producer s Library Formulating Supplements Roger Brownson, Extension Beef Cattle Specialist, Montana
RESPONSES OF YOUNG SHEEP TO SUPPLEMENTS SUMMARY
 1 RESPONSES OF YOUNG SHEEP TO SUPPLEMENTS R.M. DIXON* **, R. THOMAS*, A. THALEN* AND A.R. EGAN* SUMMARY Three pen experiments were undertaken to investigate growth responses of young BL x M wether lambs
1 RESPONSES OF YOUNG SHEEP TO SUPPLEMENTS R.M. DIXON* **, R. THOMAS*, A. THALEN* AND A.R. EGAN* SUMMARY Three pen experiments were undertaken to investigate growth responses of young BL x M wether lambs
Potash Development Association FERTILISERS AND HYPOMAGNESAEMIA: AN HISTORIC EXAGGERATION?
 Potash Development Association FERTILISERS AND HYPOMAGNESAEMIA: AN HISTORIC EXAGGERATION? by Professor Gordon Hemingway Glasgow University Veterinary School, Bearsden Glasgow G61 1QH, UK Potash Development
Potash Development Association FERTILISERS AND HYPOMAGNESAEMIA: AN HISTORIC EXAGGERATION? by Professor Gordon Hemingway Glasgow University Veterinary School, Bearsden Glasgow G61 1QH, UK Potash Development
INTAKE AND GROWTH OF STEERS OFFERED DIFFERENT ALLOWANCES OF AUTUMN GRASS AND CONCENTRATES. E.G. O Riordan, P. French, P. O Kiely and A.P.
 ID # 19-16 INTAKE AND GROWTH OF STEERS OFFERED DIFFERENT ALLOWANCES OF AUTUMN GRASS AND CONCENTRATES. E.G. O Riordan, P. French, P. O Kiely and A.P. Moloney Teagasc, Grange Research Centre, Dunsany, Co.
ID # 19-16 INTAKE AND GROWTH OF STEERS OFFERED DIFFERENT ALLOWANCES OF AUTUMN GRASS AND CONCENTRATES. E.G. O Riordan, P. French, P. O Kiely and A.P. Moloney Teagasc, Grange Research Centre, Dunsany, Co.
THE EFFECT UPON THE FATTY ACID COMPOSITION OF MILK OF FEEDING TROPICAL PASTURES TO JERSEY COWS
 Proc. Aust. Soc. Anim. Prod. (1972) 9: 297 THE EFFECT UPON THE FATTY ACID COMPOSITION OF MILK OF FEEDING TROPICAL PASTURES TO JERSEY COWS T. H. STOBBS* and D. J. BRETT** Summary The fatty acid composition
Proc. Aust. Soc. Anim. Prod. (1972) 9: 297 THE EFFECT UPON THE FATTY ACID COMPOSITION OF MILK OF FEEDING TROPICAL PASTURES TO JERSEY COWS T. H. STOBBS* and D. J. BRETT** Summary The fatty acid composition
M. C. FRANKLIN MEMORIAL SYMPOSIUM DROUGHT FEEDING OF SHEEP
 M. C. FRANKLIN MEMORIAL SYMPOSIUM DROUGHT FEEDING OF SHEEP P. K. BRIGGS* I. INTRODUCTION Drought may be regarded as an extended period of nutritional deficiency, that is a period during which the rate
M. C. FRANKLIN MEMORIAL SYMPOSIUM DROUGHT FEEDING OF SHEEP P. K. BRIGGS* I. INTRODUCTION Drought may be regarded as an extended period of nutritional deficiency, that is a period during which the rate
56 Trop Anim Prod :1
 56 Trop Anim Prod 977 2: INVESTIGATION OF DIETARY LIMITATIONS ON SUGAR CANE BASED DIETS 2 3 4 H M Ferreiro, T R Preston, and T M Sutherland Centro de Investigación y Experimentación Ganadera Chetumal,
56 Trop Anim Prod 977 2: INVESTIGATION OF DIETARY LIMITATIONS ON SUGAR CANE BASED DIETS 2 3 4 H M Ferreiro, T R Preston, and T M Sutherland Centro de Investigación y Experimentación Ganadera Chetumal,
Quick Start. Cornell Net Carbohydrate and Protein System for Sheep
 Quick Start Cornell Net Carbohydrate and Protein System for Sheep The Cornell Net Carbohydrate and Protein System (CNCPS) for Sheep is a feeding system derived from the CNCPS for cattle (Fox et al., 2003).
Quick Start Cornell Net Carbohydrate and Protein System for Sheep The Cornell Net Carbohydrate and Protein System (CNCPS) for Sheep is a feeding system derived from the CNCPS for cattle (Fox et al., 2003).
PROTEIN LIMITS TO PRODUCTION IN RUMINANTS
 PROTEIN LIMITS TO PRODUCTION IN RUMINANTS J. P. HOGAN* Summary Although the extent of protein synthesis in non-ruminants depends on the total amounts of nutrients available, the efficiency of protein synthesis
PROTEIN LIMITS TO PRODUCTION IN RUMINANTS J. P. HOGAN* Summary Although the extent of protein synthesis in non-ruminants depends on the total amounts of nutrients available, the efficiency of protein synthesis
Balanced nutritional solutions for optimal animal performance
 Balanced nutritional solutions for optimal animal performance Maxcare ruminant mineral range Add performance to nutrition Introduction The Maxcare mineral range has been formulated to help meet the requirements
Balanced nutritional solutions for optimal animal performance Maxcare ruminant mineral range Add performance to nutrition Introduction The Maxcare mineral range has been formulated to help meet the requirements
NITROGEN AND ENERGY SUPPLEMENTS FOR LOW QUALITY ROUGHAGES INTRODUCTION JANE LEIBHOLZ*
 NITROGEN AND ENERGY SUPPLEMENTS FOR LOW QUALITY ROUGHAGES INTRODUCTION JANE LEIBHOLZ* Edibility and the digestible energy content of low quality roughages may be increased by:- (i) treatment of the forages
NITROGEN AND ENERGY SUPPLEMENTS FOR LOW QUALITY ROUGHAGES INTRODUCTION JANE LEIBHOLZ* Edibility and the digestible energy content of low quality roughages may be increased by:- (i) treatment of the forages
Evaluation of Models to Estimate Urinary Nitrogen and Expected Milk Urea Nitrogen 1
 J. Dairy Sci. 85:227 233 American Dairy Science Association, 2002. Evaluation of Models to Estimate Urinary Nitrogen and Expected Milk Urea Nitrogen 1 R. A. Kohn, K. F. Kalscheur, 2 and E. Russek-Cohen
J. Dairy Sci. 85:227 233 American Dairy Science Association, 2002. Evaluation of Models to Estimate Urinary Nitrogen and Expected Milk Urea Nitrogen 1 R. A. Kohn, K. F. Kalscheur, 2 and E. Russek-Cohen
104 Trop Anim Prod :2
 04 Trop Anim Prod 977 : SUGAR CANE FOR BEEF PRODUCTION: DERINDED SUGAR CANE AND CHOPPED CANE COMPARED WITH HAY AND CITRUS PULP F M Dixon Bodles Agricultural Station Old Harbour, Jamaica In two separate
04 Trop Anim Prod 977 : SUGAR CANE FOR BEEF PRODUCTION: DERINDED SUGAR CANE AND CHOPPED CANE COMPARED WITH HAY AND CITRUS PULP F M Dixon Bodles Agricultural Station Old Harbour, Jamaica In two separate
THE EFFECT OF BROWSE SPECIES WHEN FED AS A SUPPLEMENT TO LOW QUALITY NATIVE GRASS HAY ON ANIMAL PERFORMANCE. Abstract
 ID # 19-18 THE EFFECT OF BROWSE SPECIES WHEN FED AS A SUPPLEMENT TO LOW QUALITY NATIVE GRASS HAY ON ANIMAL PERFORMANCE A. Elgersma 2, J.F. Oerlemans 1,2 and D.B. Coates 1 1 CSIRO Davies Laboratory, Private
ID # 19-18 THE EFFECT OF BROWSE SPECIES WHEN FED AS A SUPPLEMENT TO LOW QUALITY NATIVE GRASS HAY ON ANIMAL PERFORMANCE A. Elgersma 2, J.F. Oerlemans 1,2 and D.B. Coates 1 1 CSIRO Davies Laboratory, Private
Effect of supplementary concentrate type on milk yield and composition in early lactation dairy cows offered perennial ryegrass based pasture
 Session 30 Presentation 8, authors email: stephen.c.whelan@ucd.ie Effect of supplementary concentrate type on milk yield and composition in early lactation dairy cows offered perennial ryegrass based pasture
Session 30 Presentation 8, authors email: stephen.c.whelan@ucd.ie Effect of supplementary concentrate type on milk yield and composition in early lactation dairy cows offered perennial ryegrass based pasture
Supplementation for the Cow-Calf Calf Producer
 Supplementation for the Cow-Calf Calf Producer Jason Cleere Assistant Professor Extension Beef Cattle Specialist Department of Animal Science Texas A&M University Why is nutrition important??? Animal Nutrition
Supplementation for the Cow-Calf Calf Producer Jason Cleere Assistant Professor Extension Beef Cattle Specialist Department of Animal Science Texas A&M University Why is nutrition important??? Animal Nutrition
Free access minerals
 Free access minerals At W.E. Jameson we supply a full range of minerals & vitamin supplements for feeding to cattle and sheep. Some are suitable for only feeding to cattle and some can be used for both.
Free access minerals At W.E. Jameson we supply a full range of minerals & vitamin supplements for feeding to cattle and sheep. Some are suitable for only feeding to cattle and some can be used for both.
Supplementary crude protein and phosphorus levels: effect on spring milk production in dairy cows Michael Reid 1,2
 Supplementary crude protein and phosphorus levels: effect on spring milk production in dairy cows Michael Reid 1,2 Dr M O Donovan 1, Prof C Elliot 2, Dr J Bailey 3, Dr C Watson 3, S Lalor 4 and Dr E Lewis
Supplementary crude protein and phosphorus levels: effect on spring milk production in dairy cows Michael Reid 1,2 Dr M O Donovan 1, Prof C Elliot 2, Dr J Bailey 3, Dr C Watson 3, S Lalor 4 and Dr E Lewis
{A number of conditions
 Need to Know How to adjust sheep feed requirements Things you need to know about livestock production practices. LINK The information on this Need to Know card is from Virtual Apprentice 2040: Livestock1.
Need to Know How to adjust sheep feed requirements Things you need to know about livestock production practices. LINK The information on this Need to Know card is from Virtual Apprentice 2040: Livestock1.
Guidelines for Feeding Broiler Litter to Beef Cattle
 Guidelines for Feeding Broiler Litter to Beef Cattle Prepared by: Roger G. Crickenberger Extension Animal Husbandry Specialist Lemuel Goode Professor Department of Animal Science Published by North Carolina
Guidelines for Feeding Broiler Litter to Beef Cattle Prepared by: Roger G. Crickenberger Extension Animal Husbandry Specialist Lemuel Goode Professor Department of Animal Science Published by North Carolina
HIGH FIBRE CONCENTRATES FOR COWS ON PASTURE
 AFMA Symposium, Pretoria 30 October 2018 HIGH FIBRE CONCENTRATES FOR COWS ON PASTURE Robin Meeske, Outeniqua Research Farm, Cell no :0829084110 Outeniqua Research Farm at George Annual rainfall: 728 mm
AFMA Symposium, Pretoria 30 October 2018 HIGH FIBRE CONCENTRATES FOR COWS ON PASTURE Robin Meeske, Outeniqua Research Farm, Cell no :0829084110 Outeniqua Research Farm at George Annual rainfall: 728 mm
Beef Cattle Nutrient Requirements
 Beef Cattle Nutrient Requirements Nutrients Required by Beef Cattle Beef cattle require nutrients to support body maintenance, reproduction, lactation, and growth. The nutritional needs of beef cattle
Beef Cattle Nutrient Requirements Nutrients Required by Beef Cattle Beef cattle require nutrients to support body maintenance, reproduction, lactation, and growth. The nutritional needs of beef cattle
RATE AND MUSCLE BONE RATIO IN CATTLE
 Proc. Aust. Soc. Anim. Prod. (1972) 9: 360 GROWTH RATE AND MUSCLE BONE RATIO IN CATTLE D. M. MURRAY*, N. M. TULLOH* and W. H. WINTER* Summary The effect of growing Angus steers from 300 to 440 kg along
Proc. Aust. Soc. Anim. Prod. (1972) 9: 360 GROWTH RATE AND MUSCLE BONE RATIO IN CATTLE D. M. MURRAY*, N. M. TULLOH* and W. H. WINTER* Summary The effect of growing Angus steers from 300 to 440 kg along
SUPPLEMENTS FOR LIGHT WEIGHT CALVES RECEIVED AND GROWN ON NATIVE GRASS HAY. Story in Brief
 SUPPLEMENTS FOR LIGHT WEIGHT CALVES RECEIVED AND GROWN ON NATIVE GRASS HAY M.A. Kaill and K.S. Lusby2 Story in Brief Fifty-eight 3- to 4-month old Hereford and Hereford X Angus calves (240 lb) were used
SUPPLEMENTS FOR LIGHT WEIGHT CALVES RECEIVED AND GROWN ON NATIVE GRASS HAY M.A. Kaill and K.S. Lusby2 Story in Brief Fifty-eight 3- to 4-month old Hereford and Hereford X Angus calves (240 lb) were used
University of California, Davis
 EFFECT OF VITAMIN D AND OF SHEARING ON EWE LAMBS D G. M. SPURLOCK, D. T. TORELL, B. McGowAN, W. C. WEIR AND G. E. BRADFORD University of California, Davis URING the usual winter in the Coast Range of California
EFFECT OF VITAMIN D AND OF SHEARING ON EWE LAMBS D G. M. SPURLOCK, D. T. TORELL, B. McGowAN, W. C. WEIR AND G. E. BRADFORD University of California, Davis URING the usual winter in the Coast Range of California
T.N. Bodine, H.T. Purvis II and D.A. Cox. Pages Animal Science Research Report
 T.N. Bodine, H.T. Purvis II and D.A. Cox 2000 Animal Science Research Report Pages 33-39 Effects of supplemental energy and Degradable Intake Protein on grazing behavior, forage intake, digestion and performance
T.N. Bodine, H.T. Purvis II and D.A. Cox 2000 Animal Science Research Report Pages 33-39 Effects of supplemental energy and Degradable Intake Protein on grazing behavior, forage intake, digestion and performance
186 Trop Anim Prod :3
 186 Trop Anim Prod 1977 3:3 CASSAVA OR SWEET POTATO FORAGE AS COMBINED SOURCES OF PROTEIN AND ROUGHAGE IN MOLASSES BASED DIETS: EFFECT OF SUPPLEMENTATION WITH SOYBEAN MEAL 1 D Ffoulkes and T R Preston
186 Trop Anim Prod 1977 3:3 CASSAVA OR SWEET POTATO FORAGE AS COMBINED SOURCES OF PROTEIN AND ROUGHAGE IN MOLASSES BASED DIETS: EFFECT OF SUPPLEMENTATION WITH SOYBEAN MEAL 1 D Ffoulkes and T R Preston
Beef Cattle Nutrient Requirements
 Beef Cattle Nutrient Requirements Nutrients Required by Beef Cattle Beef cattle require nutrients to support body maintenance, reproduction, lactation, and growth. The nutritional needs of beef cattle
Beef Cattle Nutrient Requirements Nutrients Required by Beef Cattle Beef cattle require nutrients to support body maintenance, reproduction, lactation, and growth. The nutritional needs of beef cattle
Feeding the Suckler Cow by Siobhan Kavanagh, Mark McGee, Liam Fitzgerald
 Section 6 by Siobhan Kavanagh, Mark McGee, Liam Fitzgerald Introduction Suckler herds produce the majority of stock destined for beef production (though weaned animals are also sourced from dairy herds).
Section 6 by Siobhan Kavanagh, Mark McGee, Liam Fitzgerald Introduction Suckler herds produce the majority of stock destined for beef production (though weaned animals are also sourced from dairy herds).
Feeding the Doe Herd. Lyle W. McNichol PAg. Lyle McNichol Livestock Consulting Services
 Feeding the Doe Herd Lyle W. McNichol PAg. Lyle McNichol Livestock Consulting Services Goals for the Doe Herd Maximize conception rate Minimize embryo and fetal mortality Birth of viable kids capable of
Feeding the Doe Herd Lyle W. McNichol PAg. Lyle McNichol Livestock Consulting Services Goals for the Doe Herd Maximize conception rate Minimize embryo and fetal mortality Birth of viable kids capable of
Product Purpose Statement for Commercial Feed Eli Miller University of Kentucky Lexington, KY May 15, 1997
 Product Purpose Statement for Commercial Feed Eli Miller University of Kentucky Lexington, KY May 15, 1997 The AAFCO Model Feed Regulations requires the label for most livestock feeds to include a product
Product Purpose Statement for Commercial Feed Eli Miller University of Kentucky Lexington, KY May 15, 1997 The AAFCO Model Feed Regulations requires the label for most livestock feeds to include a product
N-Alkanes: A technique to measure herbage intake in dairy cows
 N-Alkanes: A technique to measure herbage intake in dairy cows Mary McEvoy Grassland Science Research Dept., Animal & Grassland Research and Innovation Centre, Teagasc, Ireland Background Herbage intake
N-Alkanes: A technique to measure herbage intake in dairy cows Mary McEvoy Grassland Science Research Dept., Animal & Grassland Research and Innovation Centre, Teagasc, Ireland Background Herbage intake
THE INTAKE AND DIGESTIBILITY OF SILAGES MADE FROM DOLICHOS LABLAB L. ALONE AND WITH SORGHUM CV. SUGARDRIP
 THE INTAKE AND DIGESTIBILITY OF SILAGES MADE FROM DOLICHOS LABLAB L. ALONE AND WITH SORGHUM CV. SUGARDRIP By J. G. MORRIS* and M. S. LEVITT* Summary The digestibility was determined of silages made in
THE INTAKE AND DIGESTIBILITY OF SILAGES MADE FROM DOLICHOS LABLAB L. ALONE AND WITH SORGHUM CV. SUGARDRIP By J. G. MORRIS* and M. S. LEVITT* Summary The digestibility was determined of silages made in
Phosphorus and nitrogen excretion of Finnhorse mares with typical Finnish diets
 Phosphorus and nitrogen excretion of Finnhorse mares with typical Finnish diets S. Särkijärvi and M. Saastamoinen MTT Equine Research Finland Background Environmental sustainability has been an important
Phosphorus and nitrogen excretion of Finnhorse mares with typical Finnish diets S. Särkijärvi and M. Saastamoinen MTT Equine Research Finland Background Environmental sustainability has been an important
Effects of Vitamin A Supplementation on Plasma Retinol Concentrations, Fertility and Milk Yield of Dairy Cows
 Effects of Vitamin A Supplementation on Plasma Retinol Concentrations, Fertility and Milk Yield of Dairy Cows Graduate School for International Development and Cooperation, Hiroshima University, Higashihiroshima-shi
Effects of Vitamin A Supplementation on Plasma Retinol Concentrations, Fertility and Milk Yield of Dairy Cows Graduate School for International Development and Cooperation, Hiroshima University, Higashihiroshima-shi
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN THE RUMEN OF BULLS GIVEN DIFFERENT LEVELS OF MOLASSES AND CASSAVA ROOT. J B Rowe, F Bordas and T R Preston
 Trop Anim Prod 1980 5:1 57 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN THE RUMEN OF BULLS GIVEN DIFFERENT LEVELS OF MOLASSES AND CASSAVA ROOT 1 2 J B Rowe, F Bordas and T R Preston CEDIPCA, CEAGANA, Apartado 1256, Santo Domingo,
Trop Anim Prod 1980 5:1 57 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN THE RUMEN OF BULLS GIVEN DIFFERENT LEVELS OF MOLASSES AND CASSAVA ROOT 1 2 J B Rowe, F Bordas and T R Preston CEDIPCA, CEAGANA, Apartado 1256, Santo Domingo,
RECENT experiments (Prentice, 1933) 1
 The Balance of Laying Pullets A. J. MACDONALD National Institute of Poultry Husbandry, Newport, Shropshire, England RECENT experiments (Prentice, 19) 1 concerning the protein requirements of laying pullets
The Balance of Laying Pullets A. J. MACDONALD National Institute of Poultry Husbandry, Newport, Shropshire, England RECENT experiments (Prentice, 19) 1 concerning the protein requirements of laying pullets
Know Your Feed What to feed when and why. Ian Williams, Forage Specialist, Pioneer Brand Products
 Know Your Feed What to feed when and why Ian Williams, Forage Specialist, Pioneer Brand Products 3 Basic Truths Truth 1: NZ nutrition is not that complicated Truth 2: Most NZ cows lack 1 thing Truth 3:
Know Your Feed What to feed when and why Ian Williams, Forage Specialist, Pioneer Brand Products 3 Basic Truths Truth 1: NZ nutrition is not that complicated Truth 2: Most NZ cows lack 1 thing Truth 3:
The data was used to determine which of the relative yield of a range of cultivars.
 Main Factors Determining the Dry Matter Production of Dryland Lucerne J. M. van Heerden Agricultural Research Council: Animal Production Institute, Matieland Email: jmvh@sun.ac.za in the Overberg area
Main Factors Determining the Dry Matter Production of Dryland Lucerne J. M. van Heerden Agricultural Research Council: Animal Production Institute, Matieland Email: jmvh@sun.ac.za in the Overberg area
DIGESTIBILITY AND CRUDE PROTEIN CHANGES IN TEN MATURING PASTURE SPECIES
 DIGESTIBILITY AND CRUDE PROTEIN CHANGES IN TEN MATURING PASTURE SPECIES J. C. RADCLIFFE* and M. J. COCHRANE* Summary Pure stands of Festuca arundinacea, Phalaris tuberosa, Bromus mollis, Lolium rigidum,
DIGESTIBILITY AND CRUDE PROTEIN CHANGES IN TEN MATURING PASTURE SPECIES J. C. RADCLIFFE* and M. J. COCHRANE* Summary Pure stands of Festuca arundinacea, Phalaris tuberosa, Bromus mollis, Lolium rigidum,
2. Digestible and Metabolisable Energy
 Module 1 The Theory and Practice of Animal Nutrition 2. Digestible and Metabolisable Energy John Nolan and Darryl Savage Learning objectives On completion of this topic you should be able to: Describe
Module 1 The Theory and Practice of Animal Nutrition 2. Digestible and Metabolisable Energy John Nolan and Darryl Savage Learning objectives On completion of this topic you should be able to: Describe
FACTORS AFFECTING MANURE EXCRETION BY DAIRY COWS 1
 FACTORS AFFECTING MANURE EXCRETION BY DAIRY COWS 1 W. P. Weiss Department of Animal Sciences Ohio Agricultural Research and Development Center The Ohio State University Manure in an inevitable byproduct
FACTORS AFFECTING MANURE EXCRETION BY DAIRY COWS 1 W. P. Weiss Department of Animal Sciences Ohio Agricultural Research and Development Center The Ohio State University Manure in an inevitable byproduct
Medical Definition of GEELDIKKOP
 Medical Definition of GEELDIKKOP A serious photodynamic disease of southern African sheep due to sensitization to light following the ingestion of some plants and characterized by intense jaundice and
Medical Definition of GEELDIKKOP A serious photodynamic disease of southern African sheep due to sensitization to light following the ingestion of some plants and characterized by intense jaundice and
THE COMPARATIVE COMPOSITION & DIGESTIBILITY OF GREEN CORN AND ENSILAGE. - BY - Linklater.
 THE COMPARATIVE COMPOSITION & DIGESTIBILITY OF GREEN CORN AND ENSILAGE. - BY - Linklater. Department of Chemistry 1000 In countries where the climate and of or conditions are suitable for its maturing
THE COMPARATIVE COMPOSITION & DIGESTIBILITY OF GREEN CORN AND ENSILAGE. - BY - Linklater. Department of Chemistry 1000 In countries where the climate and of or conditions are suitable for its maturing
Influenze ed effetti di CRYSTALYX sul metabolismo ruminale. Gerald Krabbe, Product Manager CRYSTALYX Products GmbH
 Influenze ed effetti di CRYSTALYX sul metabolismo ruminale Gerald Krabbe, Product Manager CRYSTALYX Products GmbH Contents What is CRYSTALYX? Successful international brand Mode of production Mode
Influenze ed effetti di CRYSTALYX sul metabolismo ruminale Gerald Krabbe, Product Manager CRYSTALYX Products GmbH Contents What is CRYSTALYX? Successful international brand Mode of production Mode
4.COW FEED REQUIREMENTS
 4.COW FEED REQUIREMENTS Determine what energy is required for different scenarios. Allocate just enough feed, not too much or too little, from using information in the following pages. 4. COW FEED REQUIREMENTS
4.COW FEED REQUIREMENTS Determine what energy is required for different scenarios. Allocate just enough feed, not too much or too little, from using information in the following pages. 4. COW FEED REQUIREMENTS
Milk Urea Nitrogen Evaluation in Louisiana Dairy Herds
 Milk Urea Nitrogen Evaluation in Louisiana Dairy Herds Michael E. McCormick, Associate Professor, Southeast Research Station, Franklinton, La Angelica M. Chapa, Graduate Assistant, Animal Science Department,
Milk Urea Nitrogen Evaluation in Louisiana Dairy Herds Michael E. McCormick, Associate Professor, Southeast Research Station, Franklinton, La Angelica M. Chapa, Graduate Assistant, Animal Science Department,
INTAKE AND QUALITATIVE ASPECTS OF GUINEA GRASS GRAZED BY SHEEP OVER THREE DIFFERENT SEASONS. W.A. van Niekerk. Africa
 INTAKE AND QUALITATIVE ASPECTS OF GUINEA GRASS GRAZED BY SHEEP OVER THREE DIFFERENT SEASONS ID # 09-40 W.A. van Niekerk Department of Animal & Wildlife Sciences, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, 0002,
INTAKE AND QUALITATIVE ASPECTS OF GUINEA GRASS GRAZED BY SHEEP OVER THREE DIFFERENT SEASONS ID # 09-40 W.A. van Niekerk Department of Animal & Wildlife Sciences, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, 0002,
Optimizing Intake Through Management: What to Expect?
 Optimizing Intake Through Management: What to Expect? Intake = time grazed X bites/min X bite size University of Missouri Pasture based Dairy Team: W. Prewitt; T. Probert; T. Rickard; S. Poock; R. Kallenbach;
Optimizing Intake Through Management: What to Expect? Intake = time grazed X bites/min X bite size University of Missouri Pasture based Dairy Team: W. Prewitt; T. Probert; T. Rickard; S. Poock; R. Kallenbach;
Effect of the Frequency of Corn Supplementation on a High Quality Alfalfa Hay Utilization by Cattle
 Effect of the Frequency of Corn Supplementation on a High Quality Alfalfa Hay Utilization by Cattle A.F. La Manna, H.T. Purvis II, T.N. Bodine, G.W. Horn, and F.N. Owens Story in Brief Two trials were
Effect of the Frequency of Corn Supplementation on a High Quality Alfalfa Hay Utilization by Cattle A.F. La Manna, H.T. Purvis II, T.N. Bodine, G.W. Horn, and F.N. Owens Story in Brief Two trials were
The effect of excessive iron intake upon the health and production of dairy cows
 New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research SSN: 0028-8233 (Print) 1175-8775 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tnza20 The effect of excessive iron intake upon the health and production
New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research SSN: 0028-8233 (Print) 1175-8775 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tnza20 The effect of excessive iron intake upon the health and production
Product Guide. Nutritional supplements for all your livestock needs
 Product Guide Nutritional supplements for all your livestock needs About Downland Downland is a UK wide network of independently owned agricultural retailers who work together to share knowledge and expertise
Product Guide Nutritional supplements for all your livestock needs About Downland Downland is a UK wide network of independently owned agricultural retailers who work together to share knowledge and expertise
The efficiency of utilization of energy and nitrogen in young sambar (Cervus unicolor) and red deer
 Journal of Agricultural Science, Cambridge (1998), 130, 193 198. 1998 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom 193 The efficiency of utilization of energy and nitrogen in young sambar (Cervus
Journal of Agricultural Science, Cambridge (1998), 130, 193 198. 1998 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom 193 The efficiency of utilization of energy and nitrogen in young sambar (Cervus
CHAPTER 1: ANIMAL ECOLOGY AND FORAGING BEHAVIOR... 1
 Table of Contents About the Authors... xii Acknowledgments... xiv CHAPTER 1: ANIMAL ECOLOGY AND FORAGING BEHAVIOR... 1 Introduction... 1 The Ecological Context... 1 Herbivore Adaptation and Foraging Habits...
Table of Contents About the Authors... xii Acknowledgments... xiv CHAPTER 1: ANIMAL ECOLOGY AND FORAGING BEHAVIOR... 1 Introduction... 1 The Ecological Context... 1 Herbivore Adaptation and Foraging Habits...
INCREASING PERFORMANCE OF GROWING CATTLE AFTER WEANING USING COTTONSEED AND COTTONSEED MEAL SUPPLEMENTS
 INCREASING PERFORMANCE OF GROWING CATTLE AFTER WEANING USING COTTONSEED AND COTTONSEED MEAL SUPPLEMENTS G. M. Hill, J. F. Baker, B.C. Hand, G. W. Stone, M. Keeler and T. Ingram Univ. of Georgia, Dept.
INCREASING PERFORMANCE OF GROWING CATTLE AFTER WEANING USING COTTONSEED AND COTTONSEED MEAL SUPPLEMENTS G. M. Hill, J. F. Baker, B.C. Hand, G. W. Stone, M. Keeler and T. Ingram Univ. of Georgia, Dept.
optimal protein level for broilers the response to dietary protein level Ross Tech GENOTYPE: Rate of response and optimal level of
 Protein accounts for a significant part of total feed cost and affects many aspects of bird performance and profitability. How much protein to use in broiler feeds is a challenging decision that must be
Protein accounts for a significant part of total feed cost and affects many aspects of bird performance and profitability. How much protein to use in broiler feeds is a challenging decision that must be
Understanding Forage Intake in Range Animals
 L-5152 1-99 Understanding Forage Intake in Range Animals Robert K. Lyons, Rick Machen, and T.D.A. Forbes* Forage quality influences the performance of range livestock and wildlife, and it is often assumed
L-5152 1-99 Understanding Forage Intake in Range Animals Robert K. Lyons, Rick Machen, and T.D.A. Forbes* Forage quality influences the performance of range livestock and wildlife, and it is often assumed
EC256 Urea as a Protein Extender for Ruminants
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1953 EC256 Urea as a Protein Extender for
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1953 EC256 Urea as a Protein Extender for
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Membership Examination. Animal Nutrition (Ruminant) Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2017 Animal Nutrition (Ruminant) Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2017 Animal Nutrition (Ruminant) Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal
A comparison of digestibility of some concentrate feed ingredients in cattle and sheep
 Animal Feed Science and Technology 81 (1999) 167±174 Short communication A comparison of digestibility of some concentrate feed ingredients in cattle and sheep F.P. O'Mara a,*, J.E. Coyle a, M.J. Drennan
Animal Feed Science and Technology 81 (1999) 167±174 Short communication A comparison of digestibility of some concentrate feed ingredients in cattle and sheep F.P. O'Mara a,*, J.E. Coyle a, M.J. Drennan
Supplement Types - Energy. ME Fixed? What is Metabolisable Energy? Feeding Supplements & Practical Ration Balancing. Dr Julian Waters 3/1/16
 Key Nutritional Principles for Profitable Dairy Farming Feeding Supplements & Practical Ration Balancing 14 13 12 11 Supplement Types - Energy ME (MJ/kg DM) Dr Julian Waters Protected Fats 32-37 MJ Expeller
Key Nutritional Principles for Profitable Dairy Farming Feeding Supplements & Practical Ration Balancing 14 13 12 11 Supplement Types - Energy ME (MJ/kg DM) Dr Julian Waters Protected Fats 32-37 MJ Expeller
Supplementation of High Corn Silage Diets for Dairy Cows. R. D. Shaver Professor and Extension Dairy Nutritionist
 INTRODUCTION Supplementation of High Corn Silage Diets for Dairy Cows R. D. Shaver Professor and Extension Dairy Nutritionist Department of Dairy Science College of Agricultural and Life Sciences University
INTRODUCTION Supplementation of High Corn Silage Diets for Dairy Cows R. D. Shaver Professor and Extension Dairy Nutritionist Department of Dairy Science College of Agricultural and Life Sciences University
The Value of Peanuts and Peanut Meal in Rations for Chickens
 i) CIRCULAR 80 NOVEMBER 1937 The Value of Peanuts and Peanut Meal in Rations for Chickens By D. F. KING and G. J. COTTIER AGRICULTURAL EXPERIMENT STATION OF THE ALABAMA POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE M. J. FUNCHESS,
i) CIRCULAR 80 NOVEMBER 1937 The Value of Peanuts and Peanut Meal in Rations for Chickens By D. F. KING and G. J. COTTIER AGRICULTURAL EXPERIMENT STATION OF THE ALABAMA POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE M. J. FUNCHESS,
Title. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information THE RUMEN DEGRADABILITY OF PROTEIN FOR VARIOUS FEEDS.
 Title THE RUMEN DEGRADABILITY OF PROTEIN FOR VARIOUS FEEDS Author(s)OKUBO, Masahiko; HANADA, Masaaki; SEKINE, Junjiro; M CitationJournal of the Faculty of Agriculture, Hokkaido Univ Issue Date 1986-12
Title THE RUMEN DEGRADABILITY OF PROTEIN FOR VARIOUS FEEDS Author(s)OKUBO, Masahiko; HANADA, Masaaki; SEKINE, Junjiro; M CitationJournal of the Faculty of Agriculture, Hokkaido Univ Issue Date 1986-12
Approaches for 100 percent organic feed to organic poultry in Sweden
 Approaches for 100 percent organic feed to organic poultry in Sweden Organic poultry production in Sweden is increasing rapidly. Researchers, advisers and farmers are working hard to find organic protein
Approaches for 100 percent organic feed to organic poultry in Sweden Organic poultry production in Sweden is increasing rapidly. Researchers, advisers and farmers are working hard to find organic protein
The University of Queensland. Nutrient requirement tables for Nutrition EDGE manual
 final report Project code: Prepared by: B.NBP.0799 Dr Stuart McLennan The University of Queensland Date published: 27 July 2015 ISBN: 9781741919325 PUBLISHED BY Meat and Livestock Australia Limited Locked
final report Project code: Prepared by: B.NBP.0799 Dr Stuart McLennan The University of Queensland Date published: 27 July 2015 ISBN: 9781741919325 PUBLISHED BY Meat and Livestock Australia Limited Locked
CEREAL OR LEGUME GRAINS AS SUPPLEMENTS FOR ANIMALS GRAZING STUBBLE OR DRY PASTURE SUMMARY
 72 CEREAL OR LEGUME GRAINS AS SUPPLEMENTS FOR ANIMALS GRAZING STUBBLE OR DRY PASTURE J B Rowe *, GD Tudor**, RM Dixon t and AR Egan SUMMARY A principal role of supplements for grazing sheep and cattle
72 CEREAL OR LEGUME GRAINS AS SUPPLEMENTS FOR ANIMALS GRAZING STUBBLE OR DRY PASTURE J B Rowe *, GD Tudor**, RM Dixon t and AR Egan SUMMARY A principal role of supplements for grazing sheep and cattle
VARIABILITY IN GASTROINTESTINAL PARASITE RESISTANCE AND PRODUCTIVITY IN ANGORA GOATS
 VARIABILITY IN GASTROINTESTINAL PARASITE RESISTANCE AND PRODUCTIVITY IN ANGORA GOATS M. E. Olayemi 1, S. W. Walkden-Brown 1, J. H. J. van der Werf 1 and L. F. Le Jambre 2 1 Animal Science, University of
VARIABILITY IN GASTROINTESTINAL PARASITE RESISTANCE AND PRODUCTIVITY IN ANGORA GOATS M. E. Olayemi 1, S. W. Walkden-Brown 1, J. H. J. van der Werf 1 and L. F. Le Jambre 2 1 Animal Science, University of
Why Graze? Supplementing Lactating Cows Requires Different Thinking. Grazing when grazing wasn t cool!! WHY? Good Pasture WVU Circular 379 Early 50s
 Supplementing Lactating Cows Requires Different Thinking Why Graze? Low cost feed source for seasonal dairy Least cost way to begin dairying Protein source for conventional dairy Carl E. Polan, Virginia
Supplementing Lactating Cows Requires Different Thinking Why Graze? Low cost feed source for seasonal dairy Least cost way to begin dairying Protein source for conventional dairy Carl E. Polan, Virginia
Basic Requirements. Meeting the basic nutrient requirements
 Basic Requirements It is imperative that cattle producers have an adequate understanding of the basic nutrient requirements of the cow herd to make informed and effective nutrition-related decisions. Meeting
Basic Requirements It is imperative that cattle producers have an adequate understanding of the basic nutrient requirements of the cow herd to make informed and effective nutrition-related decisions. Meeting
THE INFLUENCE OF CORN SILAGE HYBRID VARIETY ON BEEF STEER GROWTH PERFORMANCE. Department of Animal and Poultry Science, University of Guelph
 THE INFLUENCE OF CORN SILAGE HYBRID VARIETY ON BEEF STEER GROWTH PERFORMANCE P.L. McEwen 1 and J.G. Buchanan-Smith 2 1 Animal and Poultry Science Department, Ridgetown College of Agricultural Technology
THE INFLUENCE OF CORN SILAGE HYBRID VARIETY ON BEEF STEER GROWTH PERFORMANCE P.L. McEwen 1 and J.G. Buchanan-Smith 2 1 Animal and Poultry Science Department, Ridgetown College of Agricultural Technology
The use of polyethylene glycol as a marker for measuring rumen water volume and the rate of flow of water from the rumen of grazing sheep
 New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research ISSN: 0028-8233 (Print) 1175-8775 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tnza20 The use of polyethylene glycol as a marker for measuring
New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research ISSN: 0028-8233 (Print) 1175-8775 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tnza20 The use of polyethylene glycol as a marker for measuring
Feeding silage to dairy cows
 Chapter 13 Feeding silage to dairy cows 13.0 Introduction 336 13.1 Milk production potential of silage 337 13.2 Factors affecting milk production from silage 338 13.3 Response by grazing cows to silage
Chapter 13 Feeding silage to dairy cows 13.0 Introduction 336 13.1 Milk production potential of silage 337 13.2 Factors affecting milk production from silage 338 13.3 Response by grazing cows to silage
THE IN VIVO DETERMINATION OF BODY WATER SPACE IN CATTLE USING THE TRITIUM DILUTION TECHNIQUE. A. B. CARNEGIE* and N. M. TULLOH*
 THE IN VIVO DETERMINATION OF BODY WATER SPACE IN CATTLE USING THE TRITIUM DILUTION TECHNIQUE A. B. CARNEGIE* and N. M. TULLOH* Summary Tritiated water (TOH) space was determined in 26 steers (13 Angus,
THE IN VIVO DETERMINATION OF BODY WATER SPACE IN CATTLE USING THE TRITIUM DILUTION TECHNIQUE A. B. CARNEGIE* and N. M. TULLOH* Summary Tritiated water (TOH) space was determined in 26 steers (13 Angus,
THE APPLICATION OF NEW TECHNOLOGY FOR THE PROTECTION OF AMINO ACIDS TO IMPROVE WOOL PRODUCTION AND BODY GROWTH IN SHEEP
 22 THE APPLICATION OF NEW TECHNOLOGY FOR THE PROTECTION OF AMINO ACIDS TO IMPROVE WOOL PRODUCTION AND BODY GROWTH IN SHEEP L.D. STAPLES*, S.R.MCPHEE*, A.H. WILLIAMS**, AND R.J. JOHNSON*** SUMMARY Microspheres
22 THE APPLICATION OF NEW TECHNOLOGY FOR THE PROTECTION OF AMINO ACIDS TO IMPROVE WOOL PRODUCTION AND BODY GROWTH IN SHEEP L.D. STAPLES*, S.R.MCPHEE*, A.H. WILLIAMS**, AND R.J. JOHNSON*** SUMMARY Microspheres
P R O D U C T R A N G E
 DAIRY & BEEF P R O D U C T R A N G E Drinagh Drinagh manufactures a wide range of high quality feeds under the well known Score Drinagh Feeds brand. Accredited to the UFAS scheme our milling operation
DAIRY & BEEF P R O D U C T R A N G E Drinagh Drinagh manufactures a wide range of high quality feeds under the well known Score Drinagh Feeds brand. Accredited to the UFAS scheme our milling operation
24/10/2011. Hillcrest Pastoral Company. (Avenue Range)
 Hillcrest Pastoral Company (Avenue Range) We aim to improve soil, pasture and stock health through a 1. Balanced nutrition program 2. Incorporating biological properties into the system 1 Analysis of the
Hillcrest Pastoral Company (Avenue Range) We aim to improve soil, pasture and stock health through a 1. Balanced nutrition program 2. Incorporating biological properties into the system 1 Analysis of the
*Getenesh Teshome and Ashenafi Mengistu Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research, Holetta Agricultural Research Center *Author for Correspondence
 EFFECTS OF FEEDING MAIZE SILAGE AS A SOLE DIET AND PROTEIN SOURCES ON FEED INTAKE, MILK YIELD, MILK COMPOSITION, BODY WEIGHT CHANGE AND PRODUCT QUALITY *Getenesh Teshome and Ashenafi Mengistu Ethiopian
EFFECTS OF FEEDING MAIZE SILAGE AS A SOLE DIET AND PROTEIN SOURCES ON FEED INTAKE, MILK YIELD, MILK COMPOSITION, BODY WEIGHT CHANGE AND PRODUCT QUALITY *Getenesh Teshome and Ashenafi Mengistu Ethiopian
DIET DIGESTIBILITY AND RUMEN TRAITS IN RESPONSE TO FEEDING WET CORN GLUTEN FEED AND A PELLET CONSISTING OF RAW SOYBEAN HULLS AND CORN STEEP LIQUOR
 Dairy Day 2002 DIET DIGESTIBILITY AND RUMEN TRAITS IN RESPONSE TO FEEDING WET CORN GLUTEN FEED AND A PELLET CONSISTING OF RAW SOYBEAN HULLS AND CORN STEEP LIQUOR E. E. Ferdinand, J. E. Shirley, E. C. Titgemeyer,
Dairy Day 2002 DIET DIGESTIBILITY AND RUMEN TRAITS IN RESPONSE TO FEEDING WET CORN GLUTEN FEED AND A PELLET CONSISTING OF RAW SOYBEAN HULLS AND CORN STEEP LIQUOR E. E. Ferdinand, J. E. Shirley, E. C. Titgemeyer,
THE NATIONAL ACADEMIES
 THE NATIONAL ACADEMIES NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF ENGINEERING NATIONAL RESEARCH COUNCIL DIVISION ON EARTH AND LIFE STUDIES BOARD ON AGRICULTURE AND NATURAL RESOURCES
THE NATIONAL ACADEMIES NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF ENGINEERING NATIONAL RESEARCH COUNCIL DIVISION ON EARTH AND LIFE STUDIES BOARD ON AGRICULTURE AND NATURAL RESOURCES
Drenching dairy calves
 Drenching dairy calves There are many drenches available, many drenching regimes advertised, and many parasites a drench may (or may not) be effective against. Finding the best drenching management practice
Drenching dairy calves There are many drenches available, many drenching regimes advertised, and many parasites a drench may (or may not) be effective against. Finding the best drenching management practice
LIKE HUMANS, animals must consume
 Meeting the Nutritional Needs of Animals LIKE HUMANS, animals must consume food to survive, grow, and reproduce. Food provides nutrition to meet the varying needs of different animals. Some animals require
Meeting the Nutritional Needs of Animals LIKE HUMANS, animals must consume food to survive, grow, and reproduce. Food provides nutrition to meet the varying needs of different animals. Some animals require
Controlling Acidosis in the Equine Hindgut
 136 Controlling Acidosis in the Equine Hindgut J.B. Rowe, D.W. Pethick* and K.G. Johnson* Department of Animal Science, University of New England, Armidale, NSW 2350 Australia **School of Veterinary Studies,
136 Controlling Acidosis in the Equine Hindgut J.B. Rowe, D.W. Pethick* and K.G. Johnson* Department of Animal Science, University of New England, Armidale, NSW 2350 Australia **School of Veterinary Studies,
PIONEER FEEDS DAIRY CATTLE AND CALF FEEDING TECHNICAL INFORMATION.
 PIONEER FEEDS DAIRY CATTLE AND CALF FEEDING TECHNICAL INFORMATION. 1. STAGES IN LACTATION PERIOD IN DAIRY COWS The lactation period is divided into four phases based on the cow s physiological cycle and
PIONEER FEEDS DAIRY CATTLE AND CALF FEEDING TECHNICAL INFORMATION. 1. STAGES IN LACTATION PERIOD IN DAIRY COWS The lactation period is divided into four phases based on the cow s physiological cycle and
FEEDING and MANAGEMENT OF DAMASCUS GOATS CYPRUS EXPERIENCE By Miltiades Hadjipanayiotou
 DAMASCUS GOAT FEEDING and MANAGEMENT OF DAMASCUS GOATS CYPRUS EXPERIENCE By Miltiades Hadjipanayiotou Damascus goat is a breed originating from Syria, and is found as pure breed in many M.E. & N. African
DAMASCUS GOAT FEEDING and MANAGEMENT OF DAMASCUS GOATS CYPRUS EXPERIENCE By Miltiades Hadjipanayiotou Damascus goat is a breed originating from Syria, and is found as pure breed in many M.E. & N. African
Dry matter intake and digestibility of temperate pastures supplemented with sorghum grain in wethers and heifers
 251 Dry matter intake and digestibility of temperate pastures supplemented with sorghum grain in wethers and heifers M. Aguerre 1#, C. Cajarville 2, V. Machado 1, G. Persak 2, S. Bambillasca 2 and J.L.
251 Dry matter intake and digestibility of temperate pastures supplemented with sorghum grain in wethers and heifers M. Aguerre 1#, C. Cajarville 2, V. Machado 1, G. Persak 2, S. Bambillasca 2 and J.L.
