Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR Arthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears
|
|
|
- Jody Nichols
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI: /JR Received December 8, 2014; accepted after revision May 6, NeuroSkeletal Imaging Institute (NSI), 255 North Sykes Creek Pkwy, Merritt Island, FL ddress correspondence to T. (tmageerad@cfl.rr.com). 2 Department of Radiology, University of Central Florida School of Medicine, Orlando, FL. JR 2015; 205: X/15/ merican Roentgen Ray Society Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears OJECTIVE. Shoulder surgeons commonly intervene to repair unstable labral tears (tears that displace with patient movement). Surgeons can detect unstable tears at surgery. It is difficult to be certain if a tear is unstable from a static MR image. This study reports the comparative benefits of using unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography together to detect unstable labral tears. MTERILS ND METHODS. One hundred fifty consecutive unenhanced shoulder MRI and MR arthrography examinations performed on the same patients were reviewed retrospectively by consensus reading of two musculoskeletal radiologists. oth unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography were performed on each patient on the same day. Labral tears were assessed. It was also determined if there was any difference in position of the labral tear between unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms. change in position of 4 mm or more between unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms was considered indicative of an unstable tear. ll patients proceeded to arthroscopy. RESULTS. Of these 150 patients, 94 had superior labral anterior-to-posterior (SLP) tears, 53 had posterior labral tears, and 42 had anterior labral tears on MRI. ll lesions described on MRI were described on arthroscopy. Twenty-three SLP tears, 16 posterior labral tears, and 17 anterior labral tears showed a change in the position of the labral tear when comparing unenhanced MR images versus MR arthrograms of 4 mm or more. ll of these labral tears were considered unstable by the surgeon, and all of these patients had surgical tacking performed. The other labral tears showed motion on unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms of less than 4 mm. ll of these tears except for three were considered stable on arthroscopic examination. There were five SLP tears, three anterior labral tears, and four posterior labral tears seen on arthroscopy that were not seen on unenhanced MRI or MR arthrography. The tears not seen on unenhanced MRI or MR arthrography were considered stable at arthroscopy. CONCLUSION. In this study, unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography of the shoulder was useful in diagnosing unstable labral tears in 23 patients with SLP tears, 16 patients with posterior labral tears, and 17 patients with anterior labral tears. This information was useful in surgical planning. Of 133 tears that moved less than 4 mm on unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms, 130 were considered stable on arthroscopy. L abral tears are common injuries that often require surgery. In our practice, labral tears are commonly seen on MRI examination. High-field-strength MRI as well as increased awareness of labral tears has resulted in labral tears being commonly reported on MRI examinations. Very high sensitivity for detection of labral tears has been reported on both 1.5- and 3-T MRI [1, 2]. Labral tears reported on MRI examinations are often found to be stable at arthroscopy [3, 4]. Some of these stable tears do not require surgical intervention. Unstable labral tears are more likely to require surgical in- tervention than are stable tears [3, 4]. It is difficult to determine if a labral tear is unstable on the basis of a static MR image. Preoperative determination of whether a labral tear is stable or unstable would be of great benefit to the surgeon. For this reason, I sought to determine if a change in position of a labral tear between an unenhanced MR image compared and an MR arthrogram would be useful in determining if a labral tear was stable or unstable preoperatively. Materials and Methods One hundred fifty consecutive unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography examinations of the 1056 JR:205, November 2015
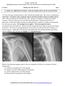
2 Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears C Fig year-old man with shoulder pain., T2-weighted axial MR image (TR/TE, 3250/55) shows anterior labral tear (arrow)., T1-weighted fat-saturated axial MR arthrogram (TR/TE, 677/12) shows anterior labral tear (arrow). There is motion of this anterior labral tear by more than 4 mm as compared with unenhanced MR image. This was found to be unstable tear at arthroscopy and was surgically tacked. C, Line on T1-weighted fat-saturated axial MR arthrogram (TR/TE, 677/12) shows how labral displacement, here due to anterior labral tear, was measured on PCS. shoulder performed between June 2013 and January 2014 on patients presenting with shoulder pain who subsequently underwent arthroscopy were retrospectively read in consensus by two musculoskeletal radiologists. ll patients were referred from one orthopedic group. The age range of the 150 patients was years (mean, 33 years). Postoperative shoulder patients were excluded from this study. One hundred thirty-one male patients and 19 female patients were included. ll patients underwent surgery within 51 days of the MRI examination (range, 1 51 days; mean time between MRI examination and surgery, 21 days). ll patients had prospective MR image and MR arthrogram readings performed by one of three musculoskeletal radiologists with more than 10 years experience. Institutional review board approval was obtained for this retrospective review and correlation with surgical records [5]. ll patients underwent shoulder MRI in oblique coronal, oblique sagittal, and axial planes on a 3.0-T scanner (Signa, GE Healthcare). Oblique coronal and sagittal fast spin-echo T1-weighted (TR/TE, 550/10; number of excitations, 2), oblique coronal and sagittal fast spinecho fat-saturated T2-weighted (TR/TE, 3850/55; number of excitations, 4), and fast spin-echo fatsaturated proton density weighted axial (TR/TE, 3250/55; number of excitations, 3) sequences were used, with an FOV of 12 cm on all images. Slice thickness was 4 mm with a 10% interslice gap on all sequences except for the fast spin-echo proton density weighted axial sequence, which had a 3-mm slice thickness. The echo-train length was 10 on all T2-weighted and proton density weighted sequences and 3 on the T1-weighted sequences. The bandwidth was khz on all sequences. The imaging time was 4 minutes 43 seconds for the oblique coronal and sagittal T2-weighted sequences; 3 minutes 26 seconds for the proton density axial sequences; and 2 minutes 28 seconds for the T1-weighted sequences. The matrix was for all T2-weighted sequences and for all T1-weighted sequences. 3-channel phased-array shoulder coil was used [5]. ll 150 patients also underwent MR arthrography immediately after the unenhanced MRI examination. t our institution, my colleagues and I routinely perform both unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography. MR arthrography was performed with approximately 15 ml of a mixture of Mag nevist (ayer HealthCare) and saline, diluted to a concentration of 0.15 ml of Magnevist per 20 ml of normal saline. 22-gauge needle was placed in the glenohumeral joint via an anterior approach under fluoroscopic guidance. The injection was performed by one of three musculoskeletal radiologists. The shoulder was exercised after injection, and T1-weighted (TR/TE, 677/12) fat-saturated oblique coronal, oblique sagittal, and axial images were obtained. T1-weighted (TR/TE, 677/12) fat-saturated oblique coronal images were obtained before MR arthrography for direct comparison with images after MR arthrography. The imaging time for the T1-weighted sequences was 2 minutes 28 seconds. ll MR arthrograms were acquired with a 12-cm FOV and a 4-mm slice thickness (with a 10% interslice gap) [5]. ll 150 MRI examinations were retrospectively reviewed by consensus reading of two musculoskel- Fig year-old man with shoulder pain., T2-weighted coronal MR image (TR/TE, 3250/55) shows superior labral anterior-to-posterior (SLP) tear (arrow)., T1-weighted fat-saturated coronal MR arthrogram (TR/TE, 677/12) shows SLP tear (arrow). There is motion of this SLP tear by more than 4 mm as compared with unenhanced MR image. This was found to be unstable tear at arthroscopy and was surgically tacked. JR:205, November
3 Fig year-old woman with shoulder pain., T2-weighted axial MR image (TR/TE, 3250/55) shows posterior labral tear (arrow)., T1-weighted fat-saturated axial MR arthrogram (TR/TE, 677/12) shows posterior labral tear (arrow). There is motion of this posterior labral tear by more than 4 mm as compared with unenhanced MR image. This was found to be unstable tear at arthroscopy and was surgically tacked. etal radiologists, each with more than 10 years of experience reading musculoskeletal MR images. The readers were blinded to arthroscopic findings at the time of consensus review. Retrospective MR image readings were then correlated with arthroscopic results (n = 150). The surgeons were aware of prospective MR image interpretations before the patients underwent arthroscopy. There was no reporting of labral stability or instability on prospective MR image readings. The unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms were reviewed together. The examinations were read in two separate sessions with unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms for each patient compared directly. Reviewers were blinded to names of patients, prospective MRI reports, and arthroscopy results. Scans were assessed for superior labral anterior-to-posterior (SLP) tears and anterior or posterior labral tears. MRI criterion used for diagnosis of labral tear was a morphologic abnormality of the glenoid labrum, increased signal intensity, or both. Labral tears were diagnosed on MRI examinations when there was high signal intensity on T2-weighted images in the labrum, an irregular or detached labrum, or both. SLP tear was defined as superior labral irregularity, high signal intensity on T2-weighted images within the superior labrum, or both [6]. SLP tears that extended anteriorly were defined as SLP tears, not as anterior labral tears. n anterior or posterior labral tear was defined as an area of abnormal increased signal intensity on T2-weighted images in the labrum, an irregular or detached labrum, or both. MR arthrography criterion for a labral tear also included high signal intensity within the labrum owing to gadolinium extending into the labrum on T1 fat-saturated images. The images were reviewed for the presence or absence of anterior labral, posterior labral, or SLP tears and were not graded. That is, on retrospective review, images were not graded for highor low-grade SLP tears or detached or nondetached labral tears, but rather for whether the lesions were present or absent. It was also determined whether there was any difference in position of the labral tear between unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms. change in position of 4 mm or more between unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms was considered indicative of an unstable tear. The 4-mm cutoff was determined by a previous analysis of 20 patients who subsequently underwent surgery. Unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography examinations were correlated with arthroscopy results. In this pilot study, all patients who had labral displacement of 4 mm or more between unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms were found to have unstable labral tears at arthroscopy. The 4-mm measurement was acquired in either the axial or oblique coronal plane on a PCS workstation. The axial plane was used for anterior and posterior labral tears, and the oblique coronal plane was used for SLP tears. ll patients proceeded to arthroscopy. MR arthrograms alone were assessed in a separate reading session to determine if unenhanced MR images were needed to assess if a labral tear was unstable. MR arthrograms were assessed for displacement of 4 mm or more. Tears with displacement of 4 mm or more on MR arthrograms were then correlated with arthroscopy to determine if this criterion was useful in detection of unstable labral tears. Results Of these 150 patients, 94 had SLP tears, 53 had posterior labral tears, and 42 had anterior labral tears on MRI. ll lesions seen at MRI were seen at arthroscopy. Twentythree SLP tears, 16 posterior labral tears, and 17 anterior labral tears showed a change in the position of the labral tear when comparing unenhanced MR images versus MR arthrograms of 4 mm or more. ll of these labral tears were considered unstable by the surgeon, and all of these patients had surgical tacking performed. The other labral tears showed motion between unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms of less than 4 mm. ll of these tears except for three were Fig year-old man with shoulder pain., T2-weighted coronal MR image (TR/TE, 3250/55) shows superior labral anterior-to-posterior (SLP) tear (arrow)., T1-weighted fat-saturated coronal MR arthrogram (TR/TE, 677/12) shows SLP tear (arrow). There is no motion of this SLP tear when comparing unenhanced MR images versus MR arthrograms. This was found to be stable tear at arthroscopy and was débrided JR:205, November 2015
4 TLE 1: Sensitivity and Specificity of Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Detection of Unstable Labral Tears Versus MR rthrography Unenhanced Only MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Examination(s) True-Positives False-Positives True-Negatives False-Negatives Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) oth unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography MR arthrography only a a Displaced by 4 mm. considered stable at arthroscopy. Of 133 tears that moved less than 4 mm between unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography, 130 were considered stable at arthroscopy (see Figs. 1 5). There were five SLP tears, three anterior labral tears, and four posterior labral tears seen at arthroscopy that were not seen on unenhanced MR images or MR arthrograms. The tears not seen on unenhanced MR images or MR arthrograms were considered stable at arthroscopy. The sensitivity and specificity for detection of an unstable labral tear by using the criterion of displacement of 4 mm or more comparing unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms were 95% and 100%, respectively (Table 1). n additional review of MR arthrography only was performed to assess whether displacement of the labrum by 4 mm or more was accurate in determining if a labral tear was unstable. The 23 SLP tears, 16 posterior labral tears, and 17 anterior labral tears that showed displacement by 4 mm or more compared with unenhanced MRI examination were all found to be unstable at arthroscopy. n additional eight SLP tears, six posterior labral tears, and five anterior labral tears were displaced by 4 mm or more on MR arthrograms that showed minimal or no difference in position compared with the unenhanced MR images. One of these SLP tears and one of these anterior labral tears were found to be unstable at arthroscopy. The sensitivity and specificity for detection of an unstable labral tear by using the criterion of displacement of 4 mm or more on MR arthrography only were 98% and 88%, respectively (Table 1). Discussion There were a large number of labral tears in this study. Most of the labral tears were seen on both unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography. The main use of MR arthrography in this study was to determine if a tear was stable or unstable. Unstable tears are more likely to result in clinical symptoms for the patient and often require surgical tacking. Stable tears are less likely to cause clinical symptoms, usually do not require surgical tacking, and often warrant no surgical intervention at all [3, 4]. It is difficult for the surgeon to determine if a labral tear is stable or unstable just on physical examination. t arthroscopy, the surgeon can determine if the tear is unstable by probing the tear to see if it moves. Movement with probing is indicative of an unstable tear [3, 4]. In this study, very accurate prediction of unstable labral tears was achieved by using the criterion of a change in the position of the labral tear when comparing unenhanced MR images versus MR arthrograms of 4 mm or more. ll 23 SLP tears, 16 posterior labral tears, and 17 anterior labral tears that showed a change in the position of the labral tear when comparing unenhanced MR images versus MR arthrograms of 4 mm or more were considered unstable by the surgeon, and all of these patients had surgical tacking performed. Of the 133 labral tears that showed motion on unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography of less than 4 mm, 130 were considered stable at arthroscopy. The tears were either débrided or no surgical intervention was performed on them. Three of these 133 labral tears with motion of less than 4 mm when comparing unenhanced MR images versus MR arthrograms were considered unstable at arthroscopy, and surgical tacking was subsequently performed. previous study by Modi et al. [7] showed that abducted and externally rotated (ER) positioning after arthrography improved accuracy in diagnosis of labral tears. In Modi et al. s study, it was suggested that ER positioning be used routinely when ordering MR arthrography examinations to increase diagnostic accuracy for labral tears. This study did not address the use of ER positioning to determine if a tear was stable or unstable [7]. (ER positioning has elsewhere been shown to be useful in detection of some partial thickness supraspinatus tendon tears and some anterior labral tears [8, 9].) nother study, by Marcus et al. [10], showed that MRI examinations performed with the arm in internal rotation increased accuracy in diagnosis of anterior labral tears. Their study did not assess whether the tears were stable or unstable [10]. third study, by Chiavaras et al. [11], assessed use of flexion, adduction, and internal rotation positioning as an adjunct to unenhanced MR arthrography. Chiavaras et al. found that flexion, adduction, and internal rotation positioning was useful in detecting additional posteroinferior labral abnormalities as compared with unenhanced MR arthrographic sequences. Their study did not address whether the labral tears were stable or unstable [11]. The aforementioned three studies [7, 10, 11] made use of changing arm position to highlight labral tears. In the present study, I compared unenhanced MR versus MR arthrography to determine if labral tears would change position when the joint was distend- Fig year-old man with shoulder pain., T2-weighted axial MR image (TR/TE, 3250/55) shows posterior labral tear (arrow)., T1-weighted fat-saturated axial MR arthrogram (TR/TE, 677/12) shows posterior labral tear (arrow). There is motion of this posterior labral tear by less than 4 mm as compared with unenhanced MR image. This was found to be unstable tear at arthroscopy and was surgically tacked. JR:205, November
5 ed with intraarticular contrast. In our practice, my colleagues and I do not routinely use ER positioning because many of our patients do not feel comfortable in that position. In a previous surgical study by Hurley and nderson [3], one hundred shoulder arthroscopies were reviewed. In Hurley and nderson s study, most labral lesions found at arthroscopy were not associated with instability; many of these lesions were not treated surgically. In another surgical study by Glasgow et al. [4], 72% of labral injuries noted at arthroscopy were not associated with instability; again, many of these lesions were not treated surgically. The aforementioned studies [3, 4] in the surgical literature describe a large number of labral lesions seen at arthroscopy that were not felt to be associated with instability. In our practice, labral tears are commonly diagnosed at MRI. High-field-strength MRI allows very sensitive detection of such tears. Many of these tears are stable and may not be considered clinically significant to the surgeon [12]. In most cases, anterior labral tears were tacked surgically. nterior labral tears often occur secondary to anterior dislocations in a younger population. nterior labral tears are often unstable at arthroscopy [12]. Posterior labral tears and SLP tears are often degenerative in nature and stable at arthroscopy. These tears occur in all age groups. t our institution, the surgeons tack these lesions when they are found to be unstable at arthroscopy [12]. change in position of 4 mm or more of a labral tear on unenhanced MRI versus MR arthrography was used as a cutoff to show movement of the labral tear. The reason for using 4 mm as a cutoff is that this degree of motion shows a definite change in labral tear position. Technologists at our institution are instructed to position the patient exactly the same for unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography; nevertheless, there remains a possibility that the patient could be slightly differently positioned. This cutoff of 4 mm allows some variation in position on unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms, therefore enabling a definitive diagnosis of motion. ll patients with motion of 4 mm or more between unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms had unstable labral tears at arthroscopy that required surgical tacking. In the present study, there were three patients with motion of labral tears when comparing unenhanced MR images versus MR arthrograms of less than 4 mm who had unstable labral tears at arthroscopy. Of 133 tears that moved less than 4 mm between unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms, 130 were considered stable at arthroscopy. The criterion of 4 mm or more displacement on MR arthrogram images only (i.e., without assessment of unenhanced MR images) yielded excellent sensitivity and good specificity for detection of unstable labral tears (sensitivity, 98%; specificity, 88%) (Table 1). The criterion of displacement of 4 mm or more when comparing unenhanced MR images versus MR arthrograms yielded excellent sensitivity and specificity for detection of unstable labral tears (sensitivity, 95%; specificity, 100%) (Table 1). Imaging times for performing both unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography versus MR arthrography only are the same because the same sequences are used. The total imaging time is approximately 21 minutes. The additional time needed for both unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography versus MR arthrography only is the time required in order to move the patient on and off the table. There is a slight additional cost to perform both unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography versus MR arthrography only. Current Medicare reimbursement rates in the United States are $ for only shoulder MR arthrography versus $ for both unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography of the shoulder. In our practice, my colleagues and I routinely perform both unenhanced MRI and MR arthrography because we believe that doing so allows better analysis of joint effusion and better analysis of labral tears. The unenhanced portion of the examination provides important diagnostic information for those patients who cannot complete the arthrogram portion of the examination. The unenhanced portion of the examination is also useful in postoperative patients to determine if there is significant metallic artifact on MRI. This can preclude MR arthrography in some cases. In those cases, we proceed to CT arthrography instead. There are limitations to this study. This study included only those patients who subsequently underwent surgery. This could have introduced bias with respect to the patient population. The criterion of 4 mm of labral displacement for instability has not been previously scientifically proved as a cutoff number in the literature. The use of 4 mm is based on a pilot study of 20 patients. The study design involved consensus reading rather than independent reading. In conclusion, comparison of unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms can be useful in determining if a labral tear is stable or unstable preoperatively. Labral tear motion of 4 mm or more at MR arthrography allowed detection of all but three unstable labral tears. There were no stable labral tears that showed motion of 4 mm or more when comparing unenhanced MRI versus MR arthrography. Use of unenhanced MR images and MR arthrograms together to determine if there is labral tear motion at MR arthrography helps the surgeon determine if a labral tear is stable or unstable preoperatively. This may aid presurgical planning. References 1. TH, Williams D. Sensitivity and specificity in detection of labral tears with 3.0 T MRI of the shoulder. JR 2006; 187: Gusmer P, Potter HG, Schatz J, et al. Labral injuries: accuracy of detection with unenhanced MR imaging of the shoulder. Radiology 1996; 200: Hurley J, nderson TE. Shoulder arthroscopy: its role in evaluating shoulder disorders in the athlete. m J Sports Med 1990; 18: Glasgow SG, ruce R, Yacibyccu GN, Torq JS. rthroscopic resection of glenoid labral tears in the athlete: a report of 29 cases. rthroscopy 1992; 8: T. 3-T MRI of the shoulder: is MR arthrography necessary? JR 2009; 192: Tuite MJ, Cirillo RL, DeSmet, et al. Superior labrum anterior-posterior (SLP) tears: evaluation of three MR signs on T2-weighted images. Radiology 2000; 215: Modi CS, Karthikeyan S, Marks, et al. ccuracy of abduction-external rotation MR versus standard MR in the diagnosis of intra-articular shoulder pathology. Orthopedics 2013; 36:e337 e Saleem M, Lee JK, Novak LM. Usefulness of the abduction and external rotation views in shoulder MR arthrography. JR 2008; 191: Cvitanic O, Tirman PF, Feller JF, et al. Using abduction and external rotation of the shoulder to increase the sensitivity of MR arthrography in revealing tears of the anterior glenoid labrum. JR 1997; 169: Marcus M, Malhotra, Peri M, et al. Kinematic shoulder MRI: the diagnostic value in acute shoulder dislocations. Eur Radiol 2013; 23: Chiavaras MM, Harish S, urr J. MR arthrographic assessment of suspected posteroinferior labral lesions using flexion, adduction, and internal rotation positioning of the arm: preliminary experience. Skeletal Radiol 2010; 39: T. How often do surgeons intervene on shoulder labral lesions detected at MR examination? retrospective review of MR examinations correlated with arthroscopy. r J Radiol 2014; 87: JR:205, November 2015
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast Necessary?
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Major et al. 3-T MRI of the Glenoid Labrum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Major et al. 3-T MRI of the Glenoid Labrum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations
 MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
Rotator Cable: MRI Study of Its Appearance in the Intact Rotator Cuff With Anatomic and Histologic Correlation
 Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Rotator Cable in Intact Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83
Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Rotator Cable in Intact Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research
 MR rthrography fter Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:237 241 0361 803X/06/1861 237 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y Sylvain R.
MR rthrography fter Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:237 241 0361 803X/06/1861 237 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y Sylvain R.
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Sensitivity of MR Arthrography in the Evaluation of Acetabular Labral Tears
 MR Arthrography of Acetabular Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Glen A. Toomayan 1 W. Russell Holman 1 Nancy M. Major 1 Shannon M. Kozlowicz
MR Arthrography of Acetabular Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Glen A. Toomayan 1 W. Russell Holman 1 Nancy M. Major 1 Shannon M. Kozlowicz
Meniscal Tears: Role of Axial MRI Alone and in Combination with Other Imaging Planes
 Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging
 MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
MR Arthrography in the Differential Diagnosis of Type II Superior Labral Anteroposterior Lesion and Sublabral Recess
 Jin et al. MR rthrography of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C D E M N E U T R Y L I M C I G O F I N G Wook Jin 1 Kyung Nam Ryu 2 Se Hwan Kwon 2 Yong Girl Rhee 3 Dal Mo Yang 1 Jin
Jin et al. MR rthrography of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C D E M N E U T R Y L I M C I G O F I N G Wook Jin 1 Kyung Nam Ryu 2 Se Hwan Kwon 2 Yong Girl Rhee 3 Dal Mo Yang 1 Jin
Intramuscular Rotator Cuff Cysts: Association with Tendon Tears on MRI and Arthroscopy
 Kassarjian et al. MRI of Rotator Cuff Cysts and Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Ara Kassarjian 1 Martin Torriani Hugue Ouellette William E. Palmer Kassarjian A, Torriani M, Ouellette
Kassarjian et al. MRI of Rotator Cuff Cysts and Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Ara Kassarjian 1 Martin Torriani Hugue Ouellette William E. Palmer Kassarjian A, Torriani M, Ouellette
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography. Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System
 Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
MRI Shoulder - Slap tear
 MRI Shoulder - Slap tear Poster No.: C-1149 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. Abubacker Sulaiman, R. Ravi; Chennai/IN Keywords: Musculoskeletal joint, Musculoskeletal soft tissue,
MRI Shoulder - Slap tear Poster No.: C-1149 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. Abubacker Sulaiman, R. Ravi; Chennai/IN Keywords: Musculoskeletal joint, Musculoskeletal soft tissue,
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP MR arthrography
 Skeletal Radiol (2010) 39:473 480 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0844-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP
Skeletal Radiol (2010) 39:473 480 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0844-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 9/22/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 91 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 9/22/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 91 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder
 Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery 6(4):21&279 Published by Raven Press, Ltd. Q 1990 Arthroscopy Association of North America SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder Stephen J. Snyder, M.D.,
Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery 6(4):21&279 Published by Raven Press, Ltd. Q 1990 Arthroscopy Association of North America SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder Stephen J. Snyder, M.D.,
Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR Arthrography and Arthroscopic Correlation
 Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR rthrography and rthroscopic Correlation Kyung h Chun, MD Min Sung Kim, MD Young Joo Kim, MD Index terms: Shoulder MR arthrography
Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR rthrography and rthroscopic Correlation Kyung h Chun, MD Min Sung Kim, MD Young Joo Kim, MD Index terms: Shoulder MR arthrography
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, Davis
 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, Davis Lloyd W. Taylor Resident Award: Diagnostic Accuracy of MRI in SLAP Tears: A Retrospective Review of 444 Patients Utilizing Musculoskeletal
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, Davis Lloyd W. Taylor Resident Award: Diagnostic Accuracy of MRI in SLAP Tears: A Retrospective Review of 444 Patients Utilizing Musculoskeletal
Lawrence Gulotta Gillian Lieberman, MD October Gillian Lieberman, MD. Shoulder Imaging. Lawrence V. Gulotta, HMS IV 10/16/02
 October 2002 Shoulder Imaging Lawrence V. Gulotta, HMS IV 10/16/02 Goals Review Anatomy of the Shoulder -Dynamic Stabilizers -> Rotator Cuff -Static Stabilizers -> Labrum and Capsule Systematic Approach
October 2002 Shoulder Imaging Lawrence V. Gulotta, HMS IV 10/16/02 Goals Review Anatomy of the Shoulder -Dynamic Stabilizers -> Rotator Cuff -Static Stabilizers -> Labrum and Capsule Systematic Approach
Demystifying ABER (ABduction and External Rotation) sequence in shoulder MR arthrography
 Demystifying ABER (ABduction and External Rotation) sequence in shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-1016 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit Z. Maras Ozdemir 1, F. B. Ergen 2, U. Aydingoz
Demystifying ABER (ABduction and External Rotation) sequence in shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-1016 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit Z. Maras Ozdemir 1, F. B. Ergen 2, U. Aydingoz
Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff: Prevalence, Characteristics, and Diagnostic Accuracy Using Indirect MR Arthrography
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. MR Arthrography of Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Jung-Han Kim 2 Dong
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. MR Arthrography of Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Jung-Han Kim 2 Dong
Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography.
 Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography. Poster No.: C-2407 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Lord, I. Katsimilis, N. Purohit, V. T. Skiadas; Southampton/UK
Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography. Poster No.: C-2407 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Lord, I. Katsimilis, N. Purohit, V. T. Skiadas; Southampton/UK
Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1017 Ankur M Manvar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ankur M Manvar BS, Sheetal M
10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1017 Ankur M Manvar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ankur M Manvar BS, Sheetal M
MRI Findings of 26 Patients with
 MRI of Patients with Parsonage-Turner Syndrome Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Richard E. Scalf 1 Doris E. Wenger 1 Matthew. Frick 1 Jayawant N. Mandrekar 2 Mark C. dkins 1 Scalf RE, Wenger
MRI of Patients with Parsonage-Turner Syndrome Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Richard E. Scalf 1 Doris E. Wenger 1 Matthew. Frick 1 Jayawant N. Mandrekar 2 Mark C. dkins 1 Scalf RE, Wenger
Increased Risk of Posterior Glenoid Labrum Tears in Football Players
 Escobedo et al. Posterior Labral Tears in Football Players Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations 193.FM 11/30/06 A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G Eva M. Escobedo 1,2 Michael L. Richardson
Escobedo et al. Posterior Labral Tears in Football Players Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations 193.FM 11/30/06 A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G Eva M. Escobedo 1,2 Michael L. Richardson
Introduction & Question 1
 Page 1 of 7 www.medscape.com To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/424981 Case Q & A Shoulder Pain, Part
Page 1 of 7 www.medscape.com To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/424981 Case Q & A Shoulder Pain, Part
Diagnostic Utility of MRI and MR Arthrography for Detection of Ligamentum Teres Tears: A Retrospective Analysis of 187 Patients With Hip Pain
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Datir et al. MRI and MR for Ligamentum Teres Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research bhijit Datir 1 Minzhi Xing 1 Jian Kang 2 Paul Harkey 1 parna Kakarala
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Datir et al. MRI and MR for Ligamentum Teres Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research bhijit Datir 1 Minzhi Xing 1 Jian Kang 2 Paul Harkey 1 parna Kakarala
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Peripheral Tear of the Triangular Fibrocartilage: Depiction with MR Arthrography of the Distal Radioulnar Joint
 Rüegger et al. MR rthrography of the Wrist Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research 187.fm 11/30/06 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.195.206 on 02/13/18 from IP address 37.44.195.206. Copyright
Rüegger et al. MR rthrography of the Wrist Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research 187.fm 11/30/06 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.195.206 on 02/13/18 from IP address 37.44.195.206. Copyright
Diagnosis of SLAP lesions with Grashey-view arthrography
 Skeletal Radiol (2003) 32:388 395 DOI 10.1007/s00256-003-0642-0 ARTICLE J. H. Edmund Lee Vanessa van Raalte Vartan Malian Diagnosis of SLAP lesions with Grashey-view arthrography Received: 19 November
Skeletal Radiol (2003) 32:388 395 DOI 10.1007/s00256-003-0642-0 ARTICLE J. H. Edmund Lee Vanessa van Raalte Vartan Malian Diagnosis of SLAP lesions with Grashey-view arthrography Received: 19 November
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging
 Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED
 81 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED The Use of Magnetic Resonance Arthrography to Detect Partial-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears BY WILLIAM B. STETSON, MD, THOMAS PHILLIPS,
81 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED The Use of Magnetic Resonance Arthrography to Detect Partial-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears BY WILLIAM B. STETSON, MD, THOMAS PHILLIPS,
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
MRI Evaluation of Bipolar Bone Loss Using the On-Track Off-Track Method: A Feasibility Study
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Bipolar Bone Loss Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Soterios Gyftopoulos 1 Luis S. Beltran 1 Jared Bookman 2 Andrew Rokito 3
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Bipolar Bone Loss Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Soterios Gyftopoulos 1 Luis S. Beltran 1 Jared Bookman 2 Andrew Rokito 3
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP?
 CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
Body Planes. (A) Transverse Superior Inferior (B) Sagittal Medial Lateral (C) Coronal Anterior Posterior Extremity Proximal Distal
 Body Planes (A) Transverse Superior Inferior (B) Sagittal Medial Lateral (C) Coronal Anterior Posterior Extremity Proximal Distal C B A Range of Motion Flexion Extension ADDUCTION ABDUCTION Range of Motion
Body Planes (A) Transverse Superior Inferior (B) Sagittal Medial Lateral (C) Coronal Anterior Posterior Extremity Proximal Distal C B A Range of Motion Flexion Extension ADDUCTION ABDUCTION Range of Motion
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols
 Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder
 MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder Poster No.: C-1482 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Bartocci, C. Dell'atti, E. Federici, D. Beomonte Zobel, V. Martinelli,
MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder Poster No.: C-1482 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Bartocci, C. Dell'atti, E. Federici, D. Beomonte Zobel, V. Martinelli,
MR Arthrography of the Labral Capsular Ligamentous Complex in the Shoulder: Imaging Variations and Pitfalls
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.194.143 on 12/31/17 from IP address 37.44.194.143. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Yang Hee Park 1 Ji Yeon Lee 2 Sung Hee Moon 1 Jong
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.194.143 on 12/31/17 from IP address 37.44.194.143. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Yang Hee Park 1 Ji Yeon Lee 2 Sung Hee Moon 1 Jong
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD
 Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD my background: 1994 University of Illinois 1998 MD University of Illinois College of Medicine 1999-2003 Diagnostic Radiology Mayo Clinic 2004 Fellowship
Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD my background: 1994 University of Illinois 1998 MD University of Illinois College of Medicine 1999-2003 Diagnostic Radiology Mayo Clinic 2004 Fellowship
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference. Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16
 Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Use of 3D SPCE Sequences for ssessment of nkle Syndesmosis Injury Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Minchul Kim 1 Yun Sun Choi 1 Min Sun Jeong 1 Mira Park
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Use of 3D SPCE Sequences for ssessment of nkle Syndesmosis Injury Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Minchul Kim 1 Yun Sun Choi 1 Min Sun Jeong 1 Mira Park
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder
 Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
MR Arthrography of Shoulder
 MR Arthrography of UNIT A22.2 The glenohumeral joint boasts the greatest range of motion of any peripheral joint in the body, but not without cost; it is also the most frequently dislocated joint in the
MR Arthrography of UNIT A22.2 The glenohumeral joint boasts the greatest range of motion of any peripheral joint in the body, but not without cost; it is also the most frequently dislocated joint in the
A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1
 A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1 Joo Yeon Ji, M.D. Purpose: To assess the feasibility of ultrasound-guided shoulder
A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1 Joo Yeon Ji, M.D. Purpose: To assess the feasibility of ultrasound-guided shoulder
Posterosuperior glenoid internal impingement of the shoulder in the overhead athlete: Pathogenesis, clinical features and MR imaging findings
 bs_bs_banner Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 59 (2015) 182 187 RADIOLOGY PICTORIAL ESSAY Posterosuperior glenoid internal impingement of the shoulder in the overhead athlete: Pathogenesis,
bs_bs_banner Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 59 (2015) 182 187 RADIOLOGY PICTORIAL ESSAY Posterosuperior glenoid internal impingement of the shoulder in the overhead athlete: Pathogenesis,
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures
 Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
HAGL lesion of the shoulder
 HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
significant increase of glenohumeral translation at middle and lower elevation angles [6].
![significant increase of glenohumeral translation at middle and lower elevation angles [6]. significant increase of glenohumeral translation at middle and lower elevation angles [6].](/thumbs/94/120620199.jpg) significant increase of glenohumeral translation at middle and lower elevation angles [6]. Two types of injury mechanisms have been postulated for superior labral tears. 1. Traction injury : Chronic repetitive
significant increase of glenohumeral translation at middle and lower elevation angles [6]. Two types of injury mechanisms have been postulated for superior labral tears. 1. Traction injury : Chronic repetitive
Elbow Effusions in Trauma in Adults and Children: Is There an Occult Fracture?
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.193.109 on 01/20/18 from IP address 46.3.193.109. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Nancy M. Major 1 Steven T. Crawford 1,2 Received July
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.193.109 on 01/20/18 from IP address 46.3.193.109. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Nancy M. Major 1 Steven T. Crawford 1,2 Received July
Shoulder Instability. Fig 1: Intact labrum and biceps tendon
 Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE
 MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know.
 Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
MRI of Bucket-Handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1
 MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the
 CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the Magnet Kirkland W. Davis, M.D. University of Wisconsin Department of Radiology Disclosures Financial FDA IA Gd! What Is CT Arthrography? (CTR) Arthrogram: imaging
CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the Magnet Kirkland W. Davis, M.D. University of Wisconsin Department of Radiology Disclosures Financial FDA IA Gd! What Is CT Arthrography? (CTR) Arthrogram: imaging
Original Report. Sonography of Tears of the Distal Biceps Tendon. Theodore T. Miller 1,2 Ronald S. Adler 3
 Theodore T. Miller 1,2 Ronald S. dler 3 Received October 15, 1999; accepted after revision March 21, 2000. Presented at the annual meeting of the merican Roentgen Ray Society, Washington, DC, May 2000.
Theodore T. Miller 1,2 Ronald S. dler 3 Received October 15, 1999; accepted after revision March 21, 2000. Presented at the annual meeting of the merican Roentgen Ray Society, Washington, DC, May 2000.
Type II SLAP lesions are created when the biceps anchor has pulled away from the glenoid attachment.
 Arthroscopic Superior Labral (SLAP) Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the post-operative rehabilitation course of
Arthroscopic Superior Labral (SLAP) Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the post-operative rehabilitation course of
The mandibular condyle fracture is a common mandibular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
Comparison of Three-dimensional Isotropic T1-weighted Fast Spin-Echo MR Arthrography with Two-dimensional MR Arthrography of the Shoulder 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Hye Jung Choo, MD
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Hye Jung Choo, MD
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
4 MR and MR Arthrography
 MR and MR Arthrography 35 4 MR and MR Arthrography J. Hodler CONTENTS 4.1 Introduction 35 4.2 Hardware Requirements 35 4.2.1 Field Strength 35 4.2.2 Coil Selection 36 4.3 The Patient 36 4.3.1 Patient Screening
MR and MR Arthrography 35 4 MR and MR Arthrography J. Hodler CONTENTS 4.1 Introduction 35 4.2 Hardware Requirements 35 4.2.1 Field Strength 35 4.2.2 Coil Selection 36 4.3 The Patient 36 4.3.1 Patient Screening
Comparison of radiation doses of various approaches of MR arthrograms with fluoroscopic guided contrast injection
 Comparison of radiation doses of various approaches of MR arthrograms with fluoroscopic guided contrast injection Poster No.: C-1294 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: H. M. Cheng, C.
Comparison of radiation doses of various approaches of MR arthrograms with fluoroscopic guided contrast injection Poster No.: C-1294 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: H. M. Cheng, C.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Anastasia Fotiadou & Antonios Drevelegas & Michelangelo Nasuto & Giuseppe Guglielmi
 Insights Imaging (2013) 4:157 162 DOI 10.1007/s13244-013-0225-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance arthrography of the shoulder in the evaluation of anteroinferior labrum abnormalities:
Insights Imaging (2013) 4:157 162 DOI 10.1007/s13244-013-0225-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance arthrography of the shoulder in the evaluation of anteroinferior labrum abnormalities:
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
 October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
Lesions of the Menisci of the Knee: Value of MR Imaging Criteria for Recognition of Unstable Lesions
 B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Cliniques
B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Cliniques
MR arthrography of glenohumeral lesions with arthroscopic correlation, using PD and T2 sequences in addition to standard fat saturated sequences
 MR arthrography of glenohumeral lesions with arthroscopic correlation, using PD and T2 sequences in addition to standard fat saturated sequences Poster No.: C-2217 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational
MR arthrography of glenohumeral lesions with arthroscopic correlation, using PD and T2 sequences in addition to standard fat saturated sequences Poster No.: C-2217 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational
Patient Presentation and Selection
 Patient Presentation and Selection Joshua Harris, MD August 7, 2016 Disclosures Research support: Smith & Nephew, Depuy Synthes, Ossur; Consultant: Smith & Nephew, NIA Magellan; Royalties: SLACK, Inc.;
Patient Presentation and Selection Joshua Harris, MD August 7, 2016 Disclosures Research support: Smith & Nephew, Depuy Synthes, Ossur; Consultant: Smith & Nephew, NIA Magellan; Royalties: SLACK, Inc.;
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries
 What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
Labral Tears. Fig 1: Intact labrum and biceps tendon
 Labral Tears What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone that is
Labral Tears What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone that is
Icd 10 code for tear labrum
 Icd 10 code for tear labrum Free, official coding info for 2018 ICD - 10 -CM S43.43 - includes detailed rules, notes, synonyms, ICD -9-CM conversion, index and annotation crosswalks, DRG grouping. guidance.
Icd 10 code for tear labrum Free, official coding info for 2018 ICD - 10 -CM S43.43 - includes detailed rules, notes, synonyms, ICD -9-CM conversion, index and annotation crosswalks, DRG grouping. guidance.
11/15/2017. Biceps Lesions. Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS Trust) E: LHB Anatomy.
 Biceps Lesions Mr Omar Haddo (Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) ) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS Trust) E: admin@denovomedic.co.uk LHB Anatomy Arise from superior
Biceps Lesions Mr Omar Haddo (Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) ) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS Trust) E: admin@denovomedic.co.uk LHB Anatomy Arise from superior
Direct MR Arthrography of the Shoulder at 3 Tesla: Optimization of Gadolinium Concentration
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 30:229 235 (2009) Technical Note Direct MR Arthrography of the Shoulder at 3 Tesla: Optimization of Gadolinium Concentration Yao Shang, MD, Zhuo-zhao Zheng, MD,* and
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 30:229 235 (2009) Technical Note Direct MR Arthrography of the Shoulder at 3 Tesla: Optimization of Gadolinium Concentration Yao Shang, MD, Zhuo-zhao Zheng, MD,* and
Patient ID. Case Conference. Physical Examination. Image examination. Treatment 2011/6/16
 Patient ID Case Conference R3 高逢駿 VS 徐郭堯 55 y/o female C.C.: recurrent right shoulder dislocation noted since falling down injury 2 years ago Came to ER because of dislocation for many times due to minor
Patient ID Case Conference R3 高逢駿 VS 徐郭堯 55 y/o female C.C.: recurrent right shoulder dislocation noted since falling down injury 2 years ago Came to ER because of dislocation for many times due to minor
Glenohumeral Joint Instability. Static Stabilizers of the GHJ. Static Stabilizers of the GHJ. Static Stabilizers of the GHJ
 1 Glenohumeral Joint Instability GHJ Joint Stability: Or Lack Thereof! Christine B. Chung, M.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Static Stabilizers
1 Glenohumeral Joint Instability GHJ Joint Stability: Or Lack Thereof! Christine B. Chung, M.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Static Stabilizers
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound. Technical Guidelines SHOULDER
 Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines SHOULDER 1 Although patient s positioning for shoulder US varies widely across different Countries and Institutions reflecting multifaceted opinions and
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines SHOULDER 1 Although patient s positioning for shoulder US varies widely across different Countries and Institutions reflecting multifaceted opinions and
Hip pain rating after preforming MRI with gadolinium arthrography and intra-articular lidocaine
 Hip pain rating after preforming MRI with gadolinium arthrography and intra-articular lidocaine Poster No.: C-1352 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. García Yavar, J. Cabezudo, S.
Hip pain rating after preforming MRI with gadolinium arthrography and intra-articular lidocaine Poster No.: C-1352 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. García Yavar, J. Cabezudo, S.
The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy
 The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy Craig M. Capeci, MD Mohaned Al-Humadi, MD Malachy P. McHugh, PhD Alexis Chiang-Colvin,
The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy Craig M. Capeci, MD Mohaned Al-Humadi, MD Malachy P. McHugh, PhD Alexis Chiang-Colvin,
Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of lateral ankle ligaments and peroneal tendons in a group of asymptomatic patients
 Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of lateral ankle ligaments and peroneal tendons in a group of asymptomatic patients Abstract: Background: The role of magnetic resonance (MR) imaging in patients with
Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of lateral ankle ligaments and peroneal tendons in a group of asymptomatic patients Abstract: Background: The role of magnetic resonance (MR) imaging in patients with
Intern Arthroscopy Course 2015 Shoulder Arthroscopy Cases
 Intern Arthroscopy Course 2015 Shoulder Arthroscopy Cases Mary Lloyd Ireland, M.D. University of Kentucky Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery & Sports Medicine Lexington, KY Broken screw s/p Bristow procedure
Intern Arthroscopy Course 2015 Shoulder Arthroscopy Cases Mary Lloyd Ireland, M.D. University of Kentucky Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery & Sports Medicine Lexington, KY Broken screw s/p Bristow procedure
Arthroscopic Labral Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears:
 Arthroscopic Labral Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears: The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the postoperative rehabilitation course of a patient that
Arthroscopic Labral Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears: The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the postoperative rehabilitation course of a patient that
DK7215-Levine-ch12_R2_211106
 12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology
 Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX Tel#
 Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX 78240 www.saspine.com Tel# 210-487-7463 PATIENT GUIDE TO SHOULDER INSTABILITY LABRAL (BANKART) REPAIR / CAPSULAR SHIFT WHAT IS
Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX 78240 www.saspine.com Tel# 210-487-7463 PATIENT GUIDE TO SHOULDER INSTABILITY LABRAL (BANKART) REPAIR / CAPSULAR SHIFT WHAT IS
Hugo C. van der Veen James P. M. Collins Paul C. Rijk
 DOI 10.1007/s00402-011-1423-1 ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Value of magnetic resonance arthrography in post-traumatic anterior shoulder instability prior to arthroscopy: a prospective evaluation of
DOI 10.1007/s00402-011-1423-1 ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Value of magnetic resonance arthrography in post-traumatic anterior shoulder instability prior to arthroscopy: a prospective evaluation of
Complex Fractures and Hip Dislocations
 IMAGING OF HIP PAIN Patients may present with acute (< 2 weeks) or chronic hip pain. Acute pain may be related or not related to an acute traumatic event such as fall or trauma from a motor vehicle accident.
IMAGING OF HIP PAIN Patients may present with acute (< 2 weeks) or chronic hip pain. Acute pain may be related or not related to an acute traumatic event such as fall or trauma from a motor vehicle accident.
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process
 ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
Snapping Hip and Impingement
 Snapping Hip and Impingement Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE,
Snapping Hip and Impingement Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE,
Current Controversies in Shoulder Surgery:
 Current Controversies in Shoulder Surgery: Shoulder Instability Rotator Cuff Injury and Repair Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Brian Feeley, MD UC San Francisco Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery Disclosures
Current Controversies in Shoulder Surgery: Shoulder Instability Rotator Cuff Injury and Repair Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Brian Feeley, MD UC San Francisco Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery Disclosures
Shoulder MR arthrography
 Shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-2273 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: E. E. Martin, J. Cadena Berecoechea, A. Cadena Berecochea, D. Sarroca,
Shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-2273 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: E. E. Martin, J. Cadena Berecoechea, A. Cadena Berecochea, D. Sarroca,
MRI of Osteochondral Defects of the Lateral Femoral Condyle: Incidence and Pattern of Injury After Transient Lateral Dislocation of the Patella
 Sanders et al. MRI of Osteochond ral Defects of the Lateral Femoral Condyle Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 187:1332 1337 0361 803X/06/1875
Sanders et al. MRI of Osteochond ral Defects of the Lateral Femoral Condyle Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 187:1332 1337 0361 803X/06/1875
Superior Labral Anteroposterior Lesions of the Shoulder: Part 1, Anatomy and Anatomic Variants
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Modarresi et al. SLP Lesions of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Review CME SM SLP Lesions of the Shoulder FOCUS ON: Shahla Modarresi 1 Daria Motamedi 2 Cecilia Matilda
Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Modarresi et al. SLP Lesions of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Review CME SM SLP Lesions of the Shoulder FOCUS ON: Shahla Modarresi 1 Daria Motamedi 2 Cecilia Matilda
