Accumulation of Copper, Zinc, Cadmium and Lead and Distribution within Organs of Cotton Cultivars, Grown in Metal -Contaminated Soil
|
|
|
- Allan Dorsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 43 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (2006), National Centre for Agrarian Sciences Accumulation of Copper, Zinc, Cadmium and Lead and Distribution within Organs of Cotton Cultivars, Grown in Metal -Contaminated Soil V. DELIBALTOVA and B. YANKOV Agricultural University, Agricultural Faculty, Department of Crop Science, BG-4000 Plovdiv, Bulgaria Abstract DELIBALTOVA, V. and B.YANKOV, Accumulation of copper, zinc, cadmium and lead and distribution within organs of cotton cultivars, grown in metal -contaminated soil. Bulg. J.Agric.Sci., 12: The purpose of the research was to establish the accumulation of five Bulgarian cotton cultivars to different concentrations of heavy metals in the soil, as well as the distribution of copper, zinc, cadmium and lead in the plants organs. In order to accomplish our purpose, we set pot experiments with the cultivars Beli izvor, Ogosta, Chirpan 603, Chirpan 539 and Avanguard. The trial was carried out in 6 variants with 3 replications. These concentrations of heavy metals were - 0, 1.5, 2.5, 3.5, 5 and 10 times above the maximum permissible concentrations. The results showed that, heavy metals concentrations in the soil, that were higher than 5 times above the maximum permissible concentrations, were lethal to some cotton cultivars. The main part of the absorbed quantities of heavy metals were fixed and accumulated in the root system of the cotton plants. In concentrations of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in the soil up to 3.5 times above the maximum permissible concentrations, the Bulgarian cotton cultivars did not exhibit tendency towards accumulation of high quantities of heavy metals in the fibre and the seeds. Key words: accumulation, cotton, cultivars, concentrations of heavy metals Introduction The heavy metal pollution of soils is a current environmental problem (Alntara et al., 2002). These metals are a potential risk for human health when transferred from plant products to the human diet. On entering from the soil into the plants, in higher doses the heavy metals cause changes in the running of the plants vegetative and generative processes, by reducing the agricultural plants productivity (Shilev et al., 2003b; Zheljazkov and Nielsen, 1996). The increase of the heavy metals contents above the maximum permissible concentrations in the agricultural produce strongly impedes and limits its
2 44 selling. Differences of species and cultivars were found on entrance and localization of the heavy metals in the plants organs (Angelova et al., 2004b; Andonov and Georgieva, 2001). Higher concentrations were ascertained in maize, leguminous and ethereal-oil crops (Angelova et al., 2004d). In general, the heavy metals distribution in the plants decreases in the following direction: roots > stems > leaves > fruits (Angelova et al., 2004c; Yankov and Tahsin, 2001; Shilev et al., 2003a). Watson et al. (1985) have found that the contents of Cd in the cotton leaves was higher compared to that in the seeds. According to Malewar and Dudde (1995), cotton was more resistant to increased contents of zinc in the soil than sorghum. Angelova et al. (2004a) ascertained high resistance of cotton to pollution. The purpose of the research was to establish the accumulation of 5 Bulgarian cotton cultivars to different concentrations of heavy metals in the soil, as well as the distribution of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in the plants organs. Material and Methods V. Delibaltova and B. Yankov In 1999 and 2000 pot experiments were conducted with the cotton cultivars Beli izvor, Ogosta, Chirpan 603, Chirpan 539 and Avanguard. The soil was taken from the arable layer of the experimental base of the Agricultural University in Plovdiv, Bulgaria. The experiment was held on a former meadow-swampy slightly saline soil, sandy-clayey. The soil reaction was neutral to alkaline (ph ) and the humus content was high (4-6%)The soil preparation included cleaning, sifting through a sieve with diameter of the openings 2 mm and treatment, by means of sprayer, with a working solution, containing nitrogen and the heavy metals - Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in the form of Cu(N0 3, Zn(N0 3, Cd(N0 3, Pb(N0 3. In all variants of the trial, together with the solution we introduced once 100 mg N in the form of Ca(N0 3, then the soil was homogenized and prepared for analysis by means of treatment with aqua regia, ensuring practically the complete extraction of the heavy metals. The trial was carried out in 6 variants with 3 replications. Variant 1 - control Variant 2 Cu 405 mg/kg ; Zn 540 mg/kg ; Cd 3 mg/kg and Pb 120 metals were 1.5 times above the maximum Variant 3 Cu 675 mg/kg ; Zn 900 mg/kg ; Cd 5 mg/kg and Pb 200 metals were 2.5 times above the maximum Variant 4 Cu 945 mg/kg ; Zn 1260 mg/kg ; Cd 7 mg/kg and Pb 280 metals were 3.5 times above the maximum Variant 5 Cu 1350 mg/kg; Zn 1800 mg/kg; Cd 10 mg/kg and Pb 400 metals were 5 times above the maximum Variant 6 Cu 2700 mg/kg; Zn 3600 mg/kg; Cd 20 mg/kg and Pb 800 metals were 10 times above the maximum 9000 g of absolutely dry soil at volume density 1.15 were introduced in vessels * Maximum permissible concentrations Cu mg/kg, Zn mg/kg, Cd - 2 mg/kg, Pb - 80 mg/kg.
3 Accumulation of Copper, Zinc, Cadmium and Lead and Distribution Within Organs with volume 10 liters, that were preliminarily weighed with drainage (sieved fine gravel). The moisture content was registered daily and 70±75% of the maximum water-holding capacity was maintained through the experiment by weighing each pot followed by adjustment with tap water. In order to achieve dynamic equilibrium of the heavy metals with the soil s absorbing complex, the sowing was carried out thirty days after the preparation of the vessels (Vassilev et al., 1998). After germination we left one plant in each vessel. Weeding, loosening and irrigation were carried out during the vegetation. The irrigation complied with the plants needs during the separate phenophases. In all variants of the studied cotton cultivars the heavy metals contents (Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb) in the roots, stems, leaves, fibres and seeds was determined after the method of the dry mineralization, described by Angelova (1998). For the purpose of determining the quantity dependence between the studied indicators, the experimental data was processed according to the Anova Method of dispersion analysis, and the differences between the variants were determined by means of the Dunkan s Multiple Range Test (1995). Results and Discussion The obtained results for the contents of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in the organs of cotton plants, grown at different levels of heavy metals in the soil, showed that soil concentrations of heavy metals 5 and 10 times above the maximum permissible concentrations did not allow the cotton seeds to germinate and to form plants, i.e. these doses were lethal for the cotton plants (data not shown). The increase of the quantity of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in the soil up to 3.5 times above the maximum permissible concentrations lead to an increase of their contents in the cotton plants organs. Most considerable changes occurred in the roots. The main part of the absorbed quantities were fixed and accumulated in them (Table 1). The considerably higher contents of heavy metals in the roots, compared to the other plants organs, was explained with the fact that, on penetration in the plasma, inactivation and precipitation of considerable quantities of heavy metals has taken place in result of the formation of little mobile compounds with the organic substance. Cultivar differences were found. The cultivar Beli izvor accumulated the highest quantity of Cu and Zn, and the cultivar Avanguard Pb. The lowest were the concentrations of Cu and Zn in the roots of cultivar Chirpan 539. The contents of heavy metals in the stems of the cotton plants (Table 2) was considerably different compared to that in the roots. On increasing their quantity in the soil times above the maximum permissible concentrations, the contents of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb was respectively 9, 2, 3 and 5 times lower in the stems, compared to the roots. The lowest quantity of Zn was accumulated in cultivar Chirpan 539, and the highest in cultivar Beli izvor. The leaves are a basic metabolic organ, in which all cells are active, while the stem is mainly a transportation organ. The higher quantity of heavy metals in the leaves of the plants from the control (V 1 ), compared to the stems, was due to the fact that the absorbed water and soluble nutritious substances were included in the synthesis of assimilative substances, necessary for formation of new biomass and for obtaining energy for maintaining the plants
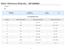
4 46 V. Delibaltova and B. Yankov Table 1 Contents of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb (mg/kg) in the roots of cotton cultivars Variants Cultivars Cu Zn Cd Pb V 1 (control) Beli izvor 0.5 a 2.1 b 0.05 b 0.7 c Cu mg/kg Ogosta 0.5 a 2.0 b 0.05 b 0.6 b Zn mg/kg Chirpan a b 2.1 b 0.04 a 0.5 a Cd mg/kg Chirpan b c 1.9 b 0.05 b 0.6 b Pb mg/kg Avanguard 0.8 c 1.4 a 0.04 a 0.6 b LSD 5 % V 2 Beli izvor 25.2 c 41.6 b 0.26 b 2.10 a Cu mg/kg Ogosta 20.3 a 35.1 a 0.21 a 2.13 a b Zn mg/kg Chirpan c 46.1 c 0.20 a 2.27 c Cd - 3 mg/kg Chirpan a 35.8 a 0.18 a 2.23 b c Pb mg/kg Avanguard 22.6 b 35.8 a 0.19 a 2.30 c LSD 5 % V 3 Beli izvor 45.4 c 116 d 0.88 d 21.7 a Cu mg/kg Ogosta 36.5 a 108 c 0.71 b 22.1 a Zn mg/kg Chirpan c 119 d 0.68 b 23.5 b Cd - 5 mg/kg Chirpan a 95 a 0.62 а 23.1 b Pb mg/kg Avanguard 40.7 b 100 b 0.75 c 23.8 b LSD 5 % V 4 Beli izvor 186 d 215 e 2.20 b c 36.1 d Cu mg/kg Ogosta 160 b 209 d 1.60 a 25.1 a Zn mg/kg Chirpan c 180 b 1.90 a b 31.9 c Cd - 7 mg/kg Chirpan a 169 a 1.60 a 28.3 b Pb mg/kg Avanguard 162 b 200 c 2.30 c 40.3 e LSD 5 % vital processes. A part of the heavy metals were fixed in the leaves. On increasing the contents of the heavy metals in the soil (the variants V 2, V 3 and V 4 ), their variation in the leaves was different compared to than in the cotton roots and stems. The contents of Cu varied within small limits and in variant V 4 was about times higher compared to the control. The variation of the quantity of Zn and Cd in the leaves was significantly higher compared to Cu. The values read in the variants V 2, V 3 and V 4 were higher in the leaves compared to the stems. In variant V 4 the quantity of Pb in the leaves was about 3-4 times higher compared to the control, and the read values were almost alike those in the stems.
5 Accumulation of Copper, Zinc, Cadmium and Lead and Distribution Within Organs Table 2 Contents of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb ( mg /kg ) in the stems and leaves of cotton cultivars Variants Cultivars Cu Zn Cd Pb stems leaves stems leaves stems leaves stems leaves V 1 (control) Beli izvor 0.7 a 6.0 d 2.5 b c 15.9 e 0.02 a 0.20 b 0.6 a 1.95 b Cu mg/kg Ogosta 0.9 a 5.6 c 2.8 d 13.7 c 0.03 a 0.16 a b 0.6 a 1.45 a Zn mg/kg Chirpan a 5.2 b 2.6 c d 15.1 d 0.03 a 0.16 a b 0.5 a 1.41 a Cd mg/kg Chirpan a 4.6 a 2.3 a b 12.1 a 0.03 a 0.11 a 0.5 a 1.42 a Pb mg/kg Avanguard 0.9 a 5.9 c d 2.1 a 13.1 b 0.03 a 0.15 a b 0.6 a 1.39 a LSD 5 % V 2 Beli izvor 8.20 c 7.0 b 30.3 c 47.1 a 0.14 c d 0.34 c d 1.40 c 2.06 a b Cu mg/kg Ogosta 6.85 a 6.4 a 27.1 b 60.4 c 0.11 a 0.31 b 1.20 b 2.30 c Zn mg/kg Chirpan b 6.8 b 36.2 d 46.1 a 0.12 a b 0.27 a 1.50 d 1.95 a Cd - 3 mg/kg Chirpan c 8.2 c 24.7 a 57.5 b 0.13 b c 0.31 b 0.95 a 2.15 b c Pb mg/kg Avanguard 9.11 d 8.5 d 26.6 b 66.6 d 0.15 d 0.36 d 1.45 c d 2.20 b c LSD 5 % V 3 Beli izvor 13.5 c 8.2 b 51.1 c 108 b 0.26 b 0.65 c 2.4 c 3.6 b Cu mg/kg Ogosta 11.3 a 7.5 a 46.5 b 114 c 0.21 a 0.59 b 2.1 a b 3.7 b c Zn mg/kg Chirpan b 7.9 b 58.3 d 107 a 0.21 a 0.52 a 2.5 c 3.4 a Cd - 5 mg/kg Chirpan b 9.2 c 43.2 a 104 a b 0.24 b 0.57 b 1.9 a 3.7 b c Pb mg/kg Avanguard 13.1 c 9.9 d 44.3 a 125 d 0.25 b 0.64 c 2.3 b c 3.8 c LSD 5 % V 4 Beli izvor 21.0 c 10.0 a 191 d. 262 d 0.87 b 1.28 b 6.50 b 6.2 b Cu mg/kg Ogosta 14.7 a 12.0 a b 171 c 257 c 0.60 a 0.99 a 5.40 a 5.7 a Zn mg/kg Chirpan c 13.4 b c 154 b 252 b 0.80 b 1.05 a 8.16 d 7.5 c Cd - 7 mg/kg Chirpan a b 10.1 a 145 a. 219 a a 0.96 a 5.20 a 5.9 a b Pb mg/kg Avanguard 17.4 b 14.8 c 172 c 286 e a 1.30 b 7.30 c 8.2 d. LSD 5 % Cultivar differences were observed. The highest quantities of Zn and Pb were accumulated in the leaves of cultivar Avanguard, and the lowest contents of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb was found in cultivar Chirpan 539. Comparatively the lowest variations in the contents of the heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb) were observed in seeds and fibre (Table 3), which showed that at high concentrations the cotton plants did not exhibit tendency towards accumulation of high quantities of heavy metals in these organs. We did not observe significant cultivar differences in the heavy metals accumulation in the plants reproductive organs. Conclusion On the grounds of the carried out vessel trial with cotton cultivars, grown on soils, polluted with different concentrations of heavy metals, we made the following more important conclusions: Heavy metals concentrations in the soil, that were higher than 5 times above
6 48 V. Delibaltova and B. Yankov Table 3 Contents of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb (mg /kg) in the seeds and figre of cotton cultivars Variants Cultivars Cu Zn Cd Pb seeds fibre seeds fibre seeds fibre seeds fibre V 1 (control) Beli izvor 7.0 a 1.8 a 32.4 a b 8.9 a 0.06 a b 0.05 a 0.35 a 1.25 a Cu mg/kg Ogosta 6.7 a 1.8 a 38.6 c 9.5 b 0.06 a b 0.10 b 0.45 b 1.20 a Zn mg/kg Chirpan b 1.7 a 29.7 a 9.7 b c 0.05 a 0.09 b 0.45 b 1.35 b Cd mg/kg Chirpan a 1.6 a 32.8 b 9.8 b c 0.05 a 0.09 b 0.55 c 1.57 c Pb mg/kg Avanguard 6.8 a 2.1 b 34.8 b 10.1 c 0.07 b 0.08 b 0.40 a b 1.52 c LSD 5 % V 2 Beli izvor 7.4 b 2.5 b 55.0 b 16.1 a 0.14 a b 0.20 a b 0.6 a 2.0 b Cu mg/kg Ogosta 7.6 b c 2.9 c 51.4 a 18.6 b c 0.14 a b 0.20 a b 0.8 b 2.0 b Zn mg/kg Chirpan a 1.9 a 58.8 c 19.7 c 0.13 a 0.22 b 0.6 a 1.8 a Cd - 3 mg/kg Chirpan c 2.2 a b 57.6 c 17.2 a b 0.15 b c 0.18 a 0.8 b 1.9 a b Pb mg/kg Avanguard 7.5 b c 2.4 b 54.6 b 19.9 c 0.16 a 0.19 a 0.7 a b 1.8 a LSD 5 % V 3 Beli izvor 8.9 b 2.7 b 64.7 b 22.2 a 0.24 b 0.31 b 0.76 a 2.1 a b Cu mg/kg Ogosta 8.8 b 3.1 c 62.5 a 25.9 b 0.24 b 0.32 b c 0.84 c 2.1 a b Zn mg/kg Chirpan a 2.2 a 67.2 c 27.6 c 0.22 a 0.33 c 0.78 a b 2.0 a Cd - 5 mg/kg Chirpan b 2.4 a b 65.8 b c 24.8 b 0.25 b 0.29 a 0.83 c 2.1 a b Pb mg/kg Avanguard 8.7 b 2.6 b 62.2 a 25.8 b 0.25 b 0.29 a 0.81 b c 2.2 b LSD 5 % V 4 Beli izvor 10.9 c 3.10 b c 79.3 c 32.3 a 0.40 c 0.38 b c 0.89 a 2.2 a Cu mg/kg Ogosta 11.2 d 3.30 c 72.3 a 34.8 b 0.40 c 0.37 b c 0.90 a 2.3 a Zn mg/kg Chirpan d 2.67 a 75.1 b 39.5 d 0.35 b 0.39 c 0.90 a 2.4 a Cd - 7 mg/kg Chirpan b 2.90 a b 74.6 b 37.0 c 0.30 a 0.36 a b 0.93 b 2.2 a Pb mg/kg Avanguard 10.2 a 2.80 a b 84.8 d 30.6 a 0.30 a 0.34 a 0.90 a 2.8 b LSD 5 % the maximum permissible concentrations, were lethal to cotton. They did not allow the seeds to germinate and to form plants. The main part of the absorbed quantities of heavy metals were fixed and accumulated in the root system of the cotton plants. In concentrations of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in the soil up to 3.5 times above the maximum permissible concentrations, the Bulgarian cotton cultivars did not exhibit tendency towards accumulation of high quantities of heavy metals in the fibre and the seeds. Cultivar differences were observed in the accumulation of heavy metals in the separate plant organs. Cultivar Avanguard accumulated higher quantities of Zn and Pb in the leaves of the plants, compared to the other cultivars. Cultivar Beli izvor exhibited stronger tendency towards accumulation of Cu and Zn in the roots and stems.
7 Accumulation of Copper, Zinc, Cadmium and Lead and Distribution Within Organs References Alntara, E.,R. Barra, M. Benlloch, A. Ginhas, J.V. Jorrнn, A. Lora, M. A. Ojeda, M. Puig, A. Pujadas, R. Requejo, J. Romera, E.D. Sancho, S.Shilev and M. Tena Fitorremediaciуn de suelos contaminados del Бrea de Aznalcуllar. M. Benlloch, E. Sancho and M. Tena (eds.). Universidad de Cordoba. Spain. ISBN (ES) Andonov, A. and T. Georgieva, Growth and photosynthesis responses of young oats (Avena sativa) plants to excess of cadmium and copper. Journal of Environmental. Protection and Ecology, 2 (Nо1): Angelova, V., R. Ivanova, V. Delibaltova and Kr. Ivanov, 2004a. Bio-accumulation and distribution of heavy metals in fibre crops (flax, cotton and hemp). Industrial Crops and Products, 19 (3): Angelova, V., R. Ivanova and Kr. Ivanov, 2004b. Effect of chemical forms of lead, cadmium and zinc in polluted soils on their uptake by tobacco. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 27 (5): Angelova, V., R. Ivanova and Kr. Ivanov, 2004c. Accumulation of lead, cadmium and zinc from contaminated soils to various plants. Journal of Balkan Ecology, 7 (1): Angelova, V., R. Ivanova and Kr. Ivanov, 2004d. Heavy metal accumulation and distribution in oil crops. Commun. Soil and Plant Analysis, 35. Dunkan, D. V., Multiple range and multiple F test. Biometrics. Malewar, G and K. Dudde, Evaluation of critical limits of DTPA zinc for sorghum Received February, 16, 2005; accepted December, 19, and cotton in Chromusters of Parbhane (Maharachtra). Journal-of - Maharachtra- Agricultural-Universities. pp Shilev, S., M. Benlloch and E. Sancho, 2003a. Utilization of rhizobacteria Pseudomonas fluorescens in phytoremediation strategies, p. 39. In: Vanek, T. and J. P. Schwitzguebel (eds.). Phytoremediation Inventory COST Action 837 view. Published by VOCHB AVИR. Czech Republic. Shilev, S., M. Benlloch and E. D. Sancho, 2003b. Pseudomonas fluorescens promotes water and arsenic transport to shoots in sunflower (Helianthusannuus L.) plants. In: Risk assessment and sustainable land management using plants in trace elementcontained soils, Mench M. and B. Mocquot (eds). pp , COST Action 837,4th WG2, Workshop, Bordeaux France Vassilev, A., I. Yordanov and T. Tsonev, Physiological responses of two barley cultivars to soil pollution with cadmium. Environmental Pollution, 100: 1-7. Watson, J., I. Pepper, M. Unger and W. Fuller, Yields and leaf elemental composition of cotton grown on sludgeamended soil. J.Environ. Qual.,14 ( 2): Yankov, B. and N. Tahsin, Accumulation and distribution of Pb, Cu, Zn and Cd in sunflower (Helianthus annus L.) grown in an industrially polluted region. Helia, 24 (No. 34): Zheljazkov, V. and N. Nielsen, Studies on the effect of heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Cu, Mn, Zn and Fe) upon the growth, productivity and quality of lavender production. J. Essential oil Research, 8:
HEAVY METAL ACCUMULATION IN SOLANACEAE-PLANTS GROWN AT CONTAMINATED AREA
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 452 460) HEAVY METAL ACCUMULATION IN
PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 452 460) HEAVY METAL ACCUMULATION IN
UPTAKE OF MAJOR AND TRACE ELEMENTS BY GRASS BIOMASS AFTER AMELIORATION OF DEGRADED SOIL
 General and Applied Plant Physiology 2010, Volume 36 (1 2), pp. 12 16 2010 ISSN 1312-8183 Published by the Institute of Plant Physiology Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Available online at http://www.bio21.bas.bg/ipp/
General and Applied Plant Physiology 2010, Volume 36 (1 2), pp. 12 16 2010 ISSN 1312-8183 Published by the Institute of Plant Physiology Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Available online at http://www.bio21.bas.bg/ipp/
AUTHORS MWANSA MUKUKA DR. CHISHALA BENSON H. DR. MUTITI SAMUEL DR. UCHIDA YOSHITAKA APPSA CONFERENCE 6 TH NOVEMBER, 2017
 EVALUATION OF THE PHYTOREMEDIATION POTENTIAL OF LEMON GRASS (Cymbopogon citratus) AND VETIVER GRASS (Chrysopogon zizanioides) IN LEAD CONTAMINATED SOILS AUTHORS MWANSA MUKUKA DR. CHISHALA BENSON H. DR.
EVALUATION OF THE PHYTOREMEDIATION POTENTIAL OF LEMON GRASS (Cymbopogon citratus) AND VETIVER GRASS (Chrysopogon zizanioides) IN LEAD CONTAMINATED SOILS AUTHORS MWANSA MUKUKA DR. CHISHALA BENSON H. DR.
Uptake Potential of Some Heavy Metals by Vetiver Grass
 asetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 35 : 46-5 (21) Uptake Potential of Some Heavy Metals by Vetiver Grass Nualchavee Roongtanakiat 1 and Prapai Chairoj 2 ABSTRACT The uptake potential of upland vetiver grass (Vetiveria
asetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 35 : 46-5 (21) Uptake Potential of Some Heavy Metals by Vetiver Grass Nualchavee Roongtanakiat 1 and Prapai Chairoj 2 ABSTRACT The uptake potential of upland vetiver grass (Vetiveria
Acad. M. Popov Institute of Plant Physiology, Acad. G. Bonchev Str., Bl. 21, 1113 Sofia, Bulgaria 2
 12 BULG. J. PLANT PHYSIOL., 1997, 23(1 2), 12 23 GROWTH, YIELD, LEAD, ZINC AND CADMIUM CONTENT OF RADISH, PEA AND PEPPER PLANTS AS INFLUENCED BY LEVEL OF SINGLE AND MULTIPLE CONTAMINATION OF SOIL. III.
12 BULG. J. PLANT PHYSIOL., 1997, 23(1 2), 12 23 GROWTH, YIELD, LEAD, ZINC AND CADMIUM CONTENT OF RADISH, PEA AND PEPPER PLANTS AS INFLUENCED BY LEVEL OF SINGLE AND MULTIPLE CONTAMINATION OF SOIL. III.
Received: 4 th April-2014 Revised: 24 th May-2014 Accepted: 26 th May-2014 Research article
 Received: 4 th April-2014 Revised: 24 th May-2014 Accepted: 26 th May-2014 Research article BIOCHAR EFFECTS ON COPPER AVAILABILITY AND UPTAKE BY SUNFLOWER IN A COPPER CONTAMINATED CALCAREOUS SOIL Mina
Received: 4 th April-2014 Revised: 24 th May-2014 Accepted: 26 th May-2014 Research article BIOCHAR EFFECTS ON COPPER AVAILABILITY AND UPTAKE BY SUNFLOWER IN A COPPER CONTAMINATED CALCAREOUS SOIL Mina
Lead Influence on the Main Properties of Bradyrhizobium Japonicum
 683 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (26), 683-687 National Centre for Agrarian Sciences Lead Influence on the Main Properties of Bradyrhizobium Japonicum R. DONKOVA "N.Poushkarov" Institute
683 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (26), 683-687 National Centre for Agrarian Sciences Lead Influence on the Main Properties of Bradyrhizobium Japonicum R. DONKOVA "N.Poushkarov" Institute
THE EFFECT OF RENI PRODUCTS ON ENZYMATIC ACTIVITY OF NITROGEN METABOLISM IN GARDEN PEAS
 69 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 16 (No 5) 21, 69-614 Agricultural Academy THE EFFECT OF RENI PRODUCTS ON ENZYMATIC ACTIVITY OF NITROGEN METABOLISM IN GARDEN PEAS N. POPOV 1, A. DZIMOTUDIS
69 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 16 (No 5) 21, 69-614 Agricultural Academy THE EFFECT OF RENI PRODUCTS ON ENZYMATIC ACTIVITY OF NITROGEN METABOLISM IN GARDEN PEAS N. POPOV 1, A. DZIMOTUDIS
The 1 th International and The 4 th National Congress on Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture April 2012 in Isfahan, Iran
 PERIODIC MUNICIPAL COMPOST AND SEWAGE SLUDGE APPLICATION ON ACCUMULATION OF HEAVY METALS IN SOIL AND PLANTS Ali R. Marjovvi 1,* and Moslehedin Rezaei 1 1 Soil and Water Department, Isfahan Agricultural
PERIODIC MUNICIPAL COMPOST AND SEWAGE SLUDGE APPLICATION ON ACCUMULATION OF HEAVY METALS IN SOIL AND PLANTS Ali R. Marjovvi 1,* and Moslehedin Rezaei 1 1 Soil and Water Department, Isfahan Agricultural
Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs
 Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs Kelly T. Morgan Soil and Water Science Department Southwest Florida Research and Education Center Immokalee 239 658 3400 conserv@ufl.edu
Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs Kelly T. Morgan Soil and Water Science Department Southwest Florida Research and Education Center Immokalee 239 658 3400 conserv@ufl.edu
INTRODUCTION TO VISCOFOL. Revolutionary high viscosity foliar feeds
 INTRODUCTION TO VISCOFOL Revolutionary high viscosity foliar feeds Contents Page 1 Page 2 Pages 3-5 Page 6 Page 7 Pages 8 27 GCiC launches VISCOFOL Why choose VISCOFOL? VISCOFOL formulation technology
INTRODUCTION TO VISCOFOL Revolutionary high viscosity foliar feeds Contents Page 1 Page 2 Pages 3-5 Page 6 Page 7 Pages 8 27 GCiC launches VISCOFOL Why choose VISCOFOL? VISCOFOL formulation technology
Understanding a Soil Report
 Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
RemovalofToxicMetalsContaminatedSoilusingDifferentAmendmentsandSunflowerSpeciesHelianthusAnnuus
 Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: H Environment & Earth Science Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: H Environment & Earth Science Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient Soil
 387 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (2006), 387-392 National Centre for Agrarian Sciences The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient
387 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (2006), 387-392 National Centre for Agrarian Sciences The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient
Interpreting Plant Tissue and Soil Sample Analysis
 Interpreting Plant Tissue and Soil Sample Analysis Dan Fromme Associate Professor-Cotton, Corn, & Grain Sorghum Specialist LSU AgCenter Dean Lee Research & Extension Center Alexandria, Louisiana Fertilization
Interpreting Plant Tissue and Soil Sample Analysis Dan Fromme Associate Professor-Cotton, Corn, & Grain Sorghum Specialist LSU AgCenter Dean Lee Research & Extension Center Alexandria, Louisiana Fertilization
RESPONSE OF TOMATO AND CORN PLANTS TO INCREASING Cd LEVELS IN NUTRIENT CULTURE
 Pak. J. Bot., 37(3): 593--599, 2005. RESPONSE OF TOMATO AND CORN PLANTS TO INCREASING Cd LEVELS IN NUTRIENT CULTURE * NESRIN YILDIZ Department of Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, Faculty of Agriculture,
Pak. J. Bot., 37(3): 593--599, 2005. RESPONSE OF TOMATO AND CORN PLANTS TO INCREASING Cd LEVELS IN NUTRIENT CULTURE * NESRIN YILDIZ Department of Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, Faculty of Agriculture,
MICRO NUTRIENTS AND SECONDARY NUTRIENTS
 BR Global, LLC. P.O. Box 8164 Rocky Mount, NC 27804 Tel: 252-442-0700 / Fax: 252-442-0787 Sales@BRGLimited.com www.brglimited.com MICRO NUTRIENTS AND SECONDARY NUTRIENTS Trace elements or micronutrients
BR Global, LLC. P.O. Box 8164 Rocky Mount, NC 27804 Tel: 252-442-0700 / Fax: 252-442-0787 Sales@BRGLimited.com www.brglimited.com MICRO NUTRIENTS AND SECONDARY NUTRIENTS Trace elements or micronutrients
Thresholds of copper toxicity to lettuce in field-collected agricultural soils exposed to copper mining activities in Chile
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Thresholds of copper toxicity to lettuce in field-collected agricultural soils exposed to copper mining activities in Chile J. Verdejo 1, R. Ginocchio 2,3, S. Sauvé 4, P. Mondaca 1, A.
RESEARCH ARTICLE Thresholds of copper toxicity to lettuce in field-collected agricultural soils exposed to copper mining activities in Chile J. Verdejo 1, R. Ginocchio 2,3, S. Sauvé 4, P. Mondaca 1, A.
TYPE: ORGANIC NUTRIENTS CODE: BF4 - GRANULE (JAIVIZYME)
 TYPE: ORGANIC NUTRIENTS CODE: BF4 GRANULE (JAIVIZYME) AVAILABLE: BULK, PRIVATE LABEL & BRANDS Composition Ingredient % Potassium Humate 5.00% w/w Min. Carrier Granules 95.00% w/w Max. Advantages Mode of
TYPE: ORGANIC NUTRIENTS CODE: BF4 GRANULE (JAIVIZYME) AVAILABLE: BULK, PRIVATE LABEL & BRANDS Composition Ingredient % Potassium Humate 5.00% w/w Min. Carrier Granules 95.00% w/w Max. Advantages Mode of
DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA
 DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA www.domogran.de DOMOGRAN 45 nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer for positive nutrient dynamics Because of its attraction
DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA www.domogran.de DOMOGRAN 45 nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer for positive nutrient dynamics Because of its attraction
Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in
 Vol. 28, pp. 39-43, /979 Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in Relation to Heavy Metal Content of Sludge-Amended Soil by Frank T. Bingham* Results of greenhouse and laboratory experiments on factors influencing
Vol. 28, pp. 39-43, /979 Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in Relation to Heavy Metal Content of Sludge-Amended Soil by Frank T. Bingham* Results of greenhouse and laboratory experiments on factors influencing
Efficiency of Arsenic Removal from Soil by Vetiveria zizanioides and Vetiveria nemoralis
 Efficiency of Arsenic Removal from Soil by Vetiveria zizanioides and Vetiveria nemoralis Thares Srisatit 1, Tuearnjai Kosakul 2, and Dusaluk Dhitivara 3 1 Department of Environmental Engineering, Faculty
Efficiency of Arsenic Removal from Soil by Vetiveria zizanioides and Vetiveria nemoralis Thares Srisatit 1, Tuearnjai Kosakul 2, and Dusaluk Dhitivara 3 1 Department of Environmental Engineering, Faculty
Product Name : Fish s Amino Nutrients
 Product Name : Fish s Amino Nutrients Bio Organic Fertilizer Provides Quality Nitrogen, Among with Other Nutrients to Plants Fish Hydrolysate Fertilizer is an excellent source of many nutrients. As natural,
Product Name : Fish s Amino Nutrients Bio Organic Fertilizer Provides Quality Nitrogen, Among with Other Nutrients to Plants Fish Hydrolysate Fertilizer is an excellent source of many nutrients. As natural,
Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability
 Symposium no. 33 Paper no. 08 Presentation: poster Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability KHOSHGOFTARMENSH A.H., JAAFARI B. and SHARIATMADARI H. Department of Soil Science, College of Agriculture,
Symposium no. 33 Paper no. 08 Presentation: poster Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability KHOSHGOFTARMENSH A.H., JAAFARI B. and SHARIATMADARI H. Department of Soil Science, College of Agriculture,
FROM SOIL ELEMENTS TO FOOD NUTRIENTS: Joyce Kinabo Dept. of Food Science and Technology, Sokoine University, Tanzania
 FROM SOIL ELEMENTS TO FOOD NUTRIENTS: Joyce Kinabo Dept. of Food Science and Technology, Sokoine University, Tanzania All forms of life are directly dependent on plants for food Plant foods contain almost
FROM SOIL ELEMENTS TO FOOD NUTRIENTS: Joyce Kinabo Dept. of Food Science and Technology, Sokoine University, Tanzania All forms of life are directly dependent on plants for food Plant foods contain almost
ELEGANT AGRO ELEGANT AGRO
 Head Office: Elegant Fashion Fiber Chemicals Ltd. (Agro Division) 75B, Christopher Road. Kolkata - 700046, WestBengal, India Ph.: (033) 23282043/2045, Fax: (033) 23295358 E-mail: elegant@efcl-india.com
Head Office: Elegant Fashion Fiber Chemicals Ltd. (Agro Division) 75B, Christopher Road. Kolkata - 700046, WestBengal, India Ph.: (033) 23282043/2045, Fax: (033) 23295358 E-mail: elegant@efcl-india.com
Basafer Plus/Fetrilon / Zitrilon /Mantrilon
 Basafer Plus/Fetrilon / Zitrilon /Mantrilon Chelated Single Micronutrient Fertilizer Fully chelated single micronutrients Rapid nutrient uptake Preventive and curative use Correction of Fe-, Mn- and Zn-deficiencies
Basafer Plus/Fetrilon / Zitrilon /Mantrilon Chelated Single Micronutrient Fertilizer Fully chelated single micronutrients Rapid nutrient uptake Preventive and curative use Correction of Fe-, Mn- and Zn-deficiencies
HEAVY METAL CONCENTRATIONS IN SOIL AND TOBACCO PLANTS FOLLOWING LONG-TERM PHOSPHORUS FERTILIZATION
 16 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 22 (No 1) 2016, 16-20 Agricultural Academy HEAVY METAL CONCENTRATIONS IN SOIL AND TOBACCO PLANTS FOLLOWING LONG-TERM PHOSPHORUS FERTILIZATION R. BOZHINOVA
16 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 22 (No 1) 2016, 16-20 Agricultural Academy HEAVY METAL CONCENTRATIONS IN SOIL AND TOBACCO PLANTS FOLLOWING LONG-TERM PHOSPHORUS FERTILIZATION R. BOZHINOVA
Soil research in Europe with special reference to that in Finland A Review
 Soil research in Europe with special reference to that in Finland A Review Jouko Sippola MTT Agrifood Research Finland, Environmental Research, FIN-31600 Jokioinen, Finland jouko.sippola@surffi.net Abstract
Soil research in Europe with special reference to that in Finland A Review Jouko Sippola MTT Agrifood Research Finland, Environmental Research, FIN-31600 Jokioinen, Finland jouko.sippola@surffi.net Abstract
Care Chemicals & Formulators. Librel BMX. Technical Information. = Registered trademark of BASF group Multi-Micronutrient EDTA Chelate.
 Technical Information Librel BMX April 2010 08_100206e-00/Page 1 of 6 = Registered trademark of BASF group Multi-Micronutrient EDTA Chelate Care Chemicals & Formulators 08_100206e-00 April 2010 Page 2
Technical Information Librel BMX April 2010 08_100206e-00/Page 1 of 6 = Registered trademark of BASF group Multi-Micronutrient EDTA Chelate Care Chemicals & Formulators 08_100206e-00 April 2010 Page 2
Effect of Micronutrients Application on Availability of Zn, Fe and B of Sunflower (Helianthus annus L.) in Inceptisol
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 438-442 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.051
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 438-442 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.051
Sulphur Fertilizer Effect on Crop Development & Quality
 Sulphur Fertilizer Effect on Crop Development & Quality Sulphur Play a key role in: Chlorophyll (Photosynthesis) a key ingredient in the formation and sulphur deficient plants can be 40% lower in chlorophyll.
Sulphur Fertilizer Effect on Crop Development & Quality Sulphur Play a key role in: Chlorophyll (Photosynthesis) a key ingredient in the formation and sulphur deficient plants can be 40% lower in chlorophyll.
Foliar Micronutrients for Broad Acre Crops Higher yield and better quality Balanced trace element supply for healthy crops Insurance against
 B S Zn Mn Mo Foliar Micronutrients for Broad Acre Crops Higher yield and better quality Balanced trace element supply for healthy crops Insurance against deficiencies of micronutrients Crop adapted nutrient
B S Zn Mn Mo Foliar Micronutrients for Broad Acre Crops Higher yield and better quality Balanced trace element supply for healthy crops Insurance against deficiencies of micronutrients Crop adapted nutrient
TOXIC HEAVY METALS ACCUMULATION IN TOMATO PLANT (Solanum lycopersicum)
 TOXIC HEAVY METALS ACCUMULATION IN TOMATO PLANT (Solanum lycopersicum) Nidá M. Salem 1, Luma S. Albanna 1 and Akl M. Awwad 2 1 Department of Plant Protection, Faculty of Agriculture, the University of
TOXIC HEAVY METALS ACCUMULATION IN TOMATO PLANT (Solanum lycopersicum) Nidá M. Salem 1, Luma S. Albanna 1 and Akl M. Awwad 2 1 Department of Plant Protection, Faculty of Agriculture, the University of
Università Degli Studi Di Napoli Federico II
 Università Degli Studi Di Napoli Federico II SCUOLA POLITECNICA E DELLE SCIENZE DI BASE DIPARTIMENTO DI INGEGNERIA CIVILE EDILE E AMBIENTALE CZECH UNIVERSITY OF LIFE SCIENCES PRAGUE FACULTY OF ENVIRONMENTAL
Università Degli Studi Di Napoli Federico II SCUOLA POLITECNICA E DELLE SCIENZE DI BASE DIPARTIMENTO DI INGEGNERIA CIVILE EDILE E AMBIENTALE CZECH UNIVERSITY OF LIFE SCIENCES PRAGUE FACULTY OF ENVIRONMENTAL
Bio-accessibility of Trace Metals Using Chemical Fractionation and In Vitro Extraction Methods
 Bio-accessibility of Trace Metals Using Chemical Fractionation and In Vitro Extraction Methods Naomi Waissman Assadian 1 and Juan Pedro Flores Margez 2 Abstract Rural and urban border communities at Paso
Bio-accessibility of Trace Metals Using Chemical Fractionation and In Vitro Extraction Methods Naomi Waissman Assadian 1 and Juan Pedro Flores Margez 2 Abstract Rural and urban border communities at Paso
Immobilizing Arsenic in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates
 Immobilizing in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates Alexander I.Shulgin 1 and D. Joseph Hagerty 2, F. ASCE, PE 1. Research Professor, Chemical Engineering Dept., U. Louisville, Louisville,
Immobilizing in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates Alexander I.Shulgin 1 and D. Joseph Hagerty 2, F. ASCE, PE 1. Research Professor, Chemical Engineering Dept., U. Louisville, Louisville,
Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients. Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients. Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops
 Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops Yield K 2 O taken up Crop level/ac in total crop, lb Alfalfa 8 tons
Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops Yield K 2 O taken up Crop level/ac in total crop, lb Alfalfa 8 tons
Supplying Nutrients to Crops
 Supplying Nutrients to Crops What is Plant Nutrition? Plants need nutrients for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on
Supplying Nutrients to Crops What is Plant Nutrition? Plants need nutrients for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on
Effects of Soil Copper Concentration on Growth, Development and Yield Formation of Rice (Oryza sativa)
 Rice Science, 05, 12(2): 125-132 125 http://www.ricescience.org Effects of Soil Copper Concentration on Growth, Development and Yield Formation of Rice (Oryza sativa) XU Jia-kuan 1, 2, YANG Lian-xin 1,
Rice Science, 05, 12(2): 125-132 125 http://www.ricescience.org Effects of Soil Copper Concentration on Growth, Development and Yield Formation of Rice (Oryza sativa) XU Jia-kuan 1, 2, YANG Lian-xin 1,
How to Develop a Balanced Program for Pecan and Chili. Robert R Smith
 Essential Plant Nutrients How to Develop a Balanced Program for Pecan and Chili Robert R Smith Nutrition Management Involves Knowledge of: Site/Soil characteristics and chemistry Plant requirements Cropping
Essential Plant Nutrients How to Develop a Balanced Program for Pecan and Chili Robert R Smith Nutrition Management Involves Knowledge of: Site/Soil characteristics and chemistry Plant requirements Cropping
Teff Compendium Nutrient deficiency symptoms SINCE
 Teff Compendium Nutrient deficiency symptoms SINCE Experimental design The experiment was conducted in a green house in 3 liter pots, filled with perlite. Each nutrient was tested in three levels: zero,
Teff Compendium Nutrient deficiency symptoms SINCE Experimental design The experiment was conducted in a green house in 3 liter pots, filled with perlite. Each nutrient was tested in three levels: zero,
Fetrilon Combi 1/ Fetrilon Combi 2/ Hortrilon
 Combi 1/ Combi 2/ Hortrilon Chelated Multi Micronutrient Fertilizers Fully chelated Micronutrients Highly efficient Uptake of chelated Nutrients Containing all Vital Trace Elements Preventive and Curative
Combi 1/ Combi 2/ Hortrilon Chelated Multi Micronutrient Fertilizers Fully chelated Micronutrients Highly efficient Uptake of chelated Nutrients Containing all Vital Trace Elements Preventive and Curative
BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION. MACRONUTRIENTS Found in air and water carbon C oxygen hydrogen
 BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION Segment One Nutrient Listing Plants need 17 elements for normal growth. Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are found in air and water. Nitrogen, phosphorus,
BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION Segment One Nutrient Listing Plants need 17 elements for normal growth. Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are found in air and water. Nitrogen, phosphorus,
Terry Richmond s Fertilizer Package mentioned in the panel discussion March 14, 2013.
 Terry Richmond s Fertilizer Package mentioned in the panel discussion March 14, 2013. Roles of the 16 essential nutrients in plant development Sixteen plant food nutrients are essential for proper crop
Terry Richmond s Fertilizer Package mentioned in the panel discussion March 14, 2013. Roles of the 16 essential nutrients in plant development Sixteen plant food nutrients are essential for proper crop
Plant-soil interactions of sludge-borne heavy metals and the effect on maize (Zea mays L.) seedling growth
 Plant-soil interactions of sludge-borne heavy metals and the effect on maize (Zea mays L.) seedling growth J Henning, HG Snyman * and TAS Aveling 3 Department of otany, University of Pretoria, Pretoria,
Plant-soil interactions of sludge-borne heavy metals and the effect on maize (Zea mays L.) seedling growth J Henning, HG Snyman * and TAS Aveling 3 Department of otany, University of Pretoria, Pretoria,
INTRODUCTION TO GCiC
 INTRODUCTION TO GCiC Contents Who are GCiC? Product Range Approach, features and benefits Who are GCiC? Incorporated on 26 March 2014. GCiC invests in: product research novel formulations registration
INTRODUCTION TO GCiC Contents Who are GCiC? Product Range Approach, features and benefits Who are GCiC? Incorporated on 26 March 2014. GCiC invests in: product research novel formulations registration
AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 9, No 3, pp 195-200, 2007 Copyright 2007 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA TH.
Global NEST Journal, Vol 9, No 3, pp 195-200, 2007 Copyright 2007 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA TH.
26 27 April 2012 in Isfahan, Iran. Hamid Reza Rahmani. Scientific Member of Soil and Water Institute of Iran.
 The 1 th International and The 4 th National Congress on Effect of Industrial Recycling and Municipal of Organic Effluent Waste On in Agriculture Soil, Water, and Plants in Isfahan Hamid Reza Rahmani Scientific
The 1 th International and The 4 th National Congress on Effect of Industrial Recycling and Municipal of Organic Effluent Waste On in Agriculture Soil, Water, and Plants in Isfahan Hamid Reza Rahmani Scientific
Greenhouse Horticulture
 Managing Nutrients in Greenhouse Horticulture Original content by Domenic Cavallaro Stoller Australia Pty Ltd Plant HORMONE PRODUCTION follows approx. cycles with changing NUTRIENT requirements Source:
Managing Nutrients in Greenhouse Horticulture Original content by Domenic Cavallaro Stoller Australia Pty Ltd Plant HORMONE PRODUCTION follows approx. cycles with changing NUTRIENT requirements Source:
Essential Soil Nutrients for Plant Growth and Development
 Essential Soil Nutrients for Plant Growth and Development Essential nutrients required by plants Role of nutrients within the plant Symptoms of deficiencies/toxicities 2 The basic soil components are:
Essential Soil Nutrients for Plant Growth and Development Essential nutrients required by plants Role of nutrients within the plant Symptoms of deficiencies/toxicities 2 The basic soil components are:
Mineral Nutrients and their functions in plants
 Mineral Nutrients and their functions in plants PLANT NUTRITION The term "nutrition" refers to the interrelated steps by which a living organism assimilates food and uses it for growth and replacement
Mineral Nutrients and their functions in plants PLANT NUTRITION The term "nutrition" refers to the interrelated steps by which a living organism assimilates food and uses it for growth and replacement
Plant Food. Nitrogen (N)
 Plant Food Nitrogen (N) Functions: Promote plant growth Increase protein content of crops Improves quality of crop Makes plant more efficient with water Helps for stay green and dry down Plants take up
Plant Food Nitrogen (N) Functions: Promote plant growth Increase protein content of crops Improves quality of crop Makes plant more efficient with water Helps for stay green and dry down Plants take up
An innovative remediation for metal polluted soils combined chemical and phytostabilisation
 An innovative remediation for metal polluted soils combined chemical and phytostabilisation Viktória Feigl 1, Katalin Gruiz 1, Attila Anton 2 1 Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department
An innovative remediation for metal polluted soils combined chemical and phytostabilisation Viktória Feigl 1, Katalin Gruiz 1, Attila Anton 2 1 Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department
Utilization of Slop Ash as a Source of Potassium for Corn Grown on the Pakchong Soil Series
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 17-23 (2010) Utilization of Slop Ash as a Source of Potassium for Corn Grown on the Pakchong Soil Series Pimolsiri Supasatienchai 1, Jongruk Chanchareoook 1 * and Ed Sarobol
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 17-23 (2010) Utilization of Slop Ash as a Source of Potassium for Corn Grown on the Pakchong Soil Series Pimolsiri Supasatienchai 1, Jongruk Chanchareoook 1 * and Ed Sarobol
DESERTNET MONITORING AND ACTIONS TO COMBAT DESERTIFICATION IN THE MEDITERRANEAN EUROPEAN REGION. Región de Murcia. Spain. Dra. Carmen Pérez Sirvent
 DESERTNET INTERREG III B ESPACIO MEDOC FEDER MONITORING AND ACTIONS TO COMBAT DESERTIFICATION IN THE MEDITERRANEAN EUROPEAN REGION Región de Murcia Spain Dra. Carmen Pérez Sirvent Comunidad Autónoma de
DESERTNET INTERREG III B ESPACIO MEDOC FEDER MONITORING AND ACTIONS TO COMBAT DESERTIFICATION IN THE MEDITERRANEAN EUROPEAN REGION Región de Murcia Spain Dra. Carmen Pérez Sirvent Comunidad Autónoma de
ANALYSIS OF RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT CHELATED ZINC SOURCES ON MICRO AND MACRO NUTRIENTS UPTAKE IN MOONG PLANT AND SEED (VIGNA RADIATA)
 ANALYSIS OF RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT CHELATED ZINC SOURCES ON MICRO AND MACRO NUTRIENTS UPTAKE IN MOONG PLANT AND SEED (VIGNA RADIATA) Jilani A A 1 1 Department of Chemistry, St. John s College, Agra-282003
ANALYSIS OF RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT CHELATED ZINC SOURCES ON MICRO AND MACRO NUTRIENTS UPTAKE IN MOONG PLANT AND SEED (VIGNA RADIATA) Jilani A A 1 1 Department of Chemistry, St. John s College, Agra-282003
Soil Composition. Air
 Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
EconovaPlus Fertiliser
 EconovaPlus Fertiliser The complete plant growth fertiliser, bio-stimulater & carbon control solution. A bio-fertiliser based on the need for organic mineral complexes in the soil. Manufactured by building
EconovaPlus Fertiliser The complete plant growth fertiliser, bio-stimulater & carbon control solution. A bio-fertiliser based on the need for organic mineral complexes in the soil. Manufactured by building
YaraTera KRISTALON. Premium water soluble NPK fertilizer. Growth stage based formulas. Top grade Crop Nutrition
 YaraTera KRISTALON Premium water soluble NPK fertilizer Top grade Crop Nutrition Growth stage based formulas YaraTera KRISTALON The best nutrient solutions is a growth stage based, fully water soluble
YaraTera KRISTALON Premium water soluble NPK fertilizer Top grade Crop Nutrition Growth stage based formulas YaraTera KRISTALON The best nutrient solutions is a growth stage based, fully water soluble
Specialists In Soil Fertility, Plant Nutrition and Irrigation Water Quality Management.
 Specialists In Soil Fertility, Plant Nutrition and Irrigation Water Quality Management. TOMATOES T PLANT NUTRITION & SAMPLING NOTES - 1 Noel Garcia, CCA he most important aspect of tomato production (field,
Specialists In Soil Fertility, Plant Nutrition and Irrigation Water Quality Management. TOMATOES T PLANT NUTRITION & SAMPLING NOTES - 1 Noel Garcia, CCA he most important aspect of tomato production (field,
By Andrew & Erin Oxford, Bethel
 Chemistry in Plant Nutrition & Growth Objectives Review elements of chemistry and apply them to plant nutrition and growth in an agricultural context. Suggested grade levels 9-12 Alaska Content Standards
Chemistry in Plant Nutrition & Growth Objectives Review elements of chemistry and apply them to plant nutrition and growth in an agricultural context. Suggested grade levels 9-12 Alaska Content Standards
Scientific registration number: 2271 Symposium n o : 25 Presentation : poster. OLIVEIRA Fernando Carvalho (2) ; MATTIAZZO Maria Emilia (2)
 Scientific registration number: 2271 Symposium n o : 25 Presentation : poster Copper, Nickel and Zinc availability to corn plants in acid soils amended with sewage sludge (1) Disponibilité en cuivre, en
Scientific registration number: 2271 Symposium n o : 25 Presentation : poster Copper, Nickel and Zinc availability to corn plants in acid soils amended with sewage sludge (1) Disponibilité en cuivre, en
Animal, Plant & Soil Science. D3-7 Characteristics and Sources of Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients
 Animal, Plant & Soil Science D3-7 Characteristics and Sources of Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Interest Approach Obtain samples of minerals that serve as sources of calcium, magnesium, and sulfur
Animal, Plant & Soil Science D3-7 Characteristics and Sources of Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Interest Approach Obtain samples of minerals that serve as sources of calcium, magnesium, and sulfur
5. Plant Physiology/Chemistry Section
 5. Plant Physiology/Chemistry Section The research work/experiments conducted during the year 2014-15 are summarized is under: 1. Influence of potassium fertilizer on the incidence of CLCuV disease and
5. Plant Physiology/Chemistry Section The research work/experiments conducted during the year 2014-15 are summarized is under: 1. Influence of potassium fertilizer on the incidence of CLCuV disease and
Correction of Zinc Deficiency in Avocado
 1997 California Avocado Research Symposium pages 9-12 California Avocado Society and University of California, Riverside Correction of Zinc Deficiency in Avocado Final Report for Project Year 4 of 4 Cooperating
1997 California Avocado Research Symposium pages 9-12 California Avocado Society and University of California, Riverside Correction of Zinc Deficiency in Avocado Final Report for Project Year 4 of 4 Cooperating
Principles of Orchard Nutrition. Kevin Manning and Ross Wilson AgFirst
 Principles of Orchard Nutrition Kevin Manning and Ross Wilson AgFirst General Principles Nutrition is generally a very small proportion of production costs ( < 2%). Poor nutrition management can severely
Principles of Orchard Nutrition Kevin Manning and Ross Wilson AgFirst General Principles Nutrition is generally a very small proportion of production costs ( < 2%). Poor nutrition management can severely
Markus Braaten. Elston D. Solberg. Director of Agri-Knowledge Agri-Trend. US Director of Agri-Knowledge Agri-Trend USA
 Water Drives Everything!! So Make Every Drop Count Elston D. Solberg Director of Agri-Knowledge Agri-Trend Markus Braaten US Director of Agri-Knowledge Agri-Trend USA Food, Fibre and Fuel Uptake (lbs/a)
Water Drives Everything!! So Make Every Drop Count Elston D. Solberg Director of Agri-Knowledge Agri-Trend Markus Braaten US Director of Agri-Knowledge Agri-Trend USA Food, Fibre and Fuel Uptake (lbs/a)
VOL. 5, NO. 6, June 2015 ISSN ARPN Journal of Science and Technology All rights reserved.
 VOL. 5, NO. 6, June 2015 ISSN 22-7217 Impact of Cumulative Sediment Deposition by Irrigation Water on Soil and Sugarcane in Savannah Sugar Company Limited; Numan, Adamawa State Nigeria 1 R.P. Ali, 2 H.M.
VOL. 5, NO. 6, June 2015 ISSN 22-7217 Impact of Cumulative Sediment Deposition by Irrigation Water on Soil and Sugarcane in Savannah Sugar Company Limited; Numan, Adamawa State Nigeria 1 R.P. Ali, 2 H.M.
Using Plant Sap Analysis to Optimize Nutrient Use Efficiency
 Using Plant Sap Analysis to Optimize Nutrient Use Efficiency October 7, 2015 Lorne King Agenda How we got started Available tools Nutrient uptake Nutrient movement in plant Conversion of N to Protein Sugars/pH/EC
Using Plant Sap Analysis to Optimize Nutrient Use Efficiency October 7, 2015 Lorne King Agenda How we got started Available tools Nutrient uptake Nutrient movement in plant Conversion of N to Protein Sugars/pH/EC
Nitrophoska. Cereals, fodder beet, horticulture, maize and vegetables. Precise nutrition for superior plant performance
 Nitrophoska Cereals, fodder beet, horticulture, maize and vegetables Precise nutrition for superior plant performance Nitrophoska - The same composition of high-grade plant available nutrients in every
Nitrophoska Cereals, fodder beet, horticulture, maize and vegetables Precise nutrition for superior plant performance Nitrophoska - The same composition of high-grade plant available nutrients in every
ELEMENTS WITH MORE TOXIC EFFECTS
 BIOL 695 ELEMENTS WITH MORE TOXIC EFFECTS Chapter 20 MENGEL et al, 5th Ed IODINE Not shown to be essential, stimulating effects reported for some crops at 0.1 µg g -1 Toxic effects at 0.5-1.0 µg g -1 in
BIOL 695 ELEMENTS WITH MORE TOXIC EFFECTS Chapter 20 MENGEL et al, 5th Ed IODINE Not shown to be essential, stimulating effects reported for some crops at 0.1 µg g -1 Toxic effects at 0.5-1.0 µg g -1 in
3.0 Supplying Nutrients to Crops
 3.0 Supplying Nutrients to Crops Plants need for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on, often referred to as nutrients.
3.0 Supplying Nutrients to Crops Plants need for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on, often referred to as nutrients.
Zinc Toxicity in Tomato Plants
 World Applied Sciences Journal 24 (5): 649-653, 203 ISSN 88-4952 IDOSI Publications, 203 DOI: 0.5829/idosi.wasj.203.24.05.2249 Zinc Toxicity in Tomato Plants P.Vijayarengan and G.Mahalakshmi Department
World Applied Sciences Journal 24 (5): 649-653, 203 ISSN 88-4952 IDOSI Publications, 203 DOI: 0.5829/idosi.wasj.203.24.05.2249 Zinc Toxicity in Tomato Plants P.Vijayarengan and G.Mahalakshmi Department
Matrix Reference Materials - SCP SCIENCE
 EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
SOIL AND PLANT NUTRITION
 SOIL AND PLANT NUTRITION 1.0 Introduction Plants need at least 16 elements for normal growth to be able to produce well. Some of the elements are needed in large quantities. Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
SOIL AND PLANT NUTRITION 1.0 Introduction Plants need at least 16 elements for normal growth to be able to produce well. Some of the elements are needed in large quantities. Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
Çukurova Research Enstitü, Forage Crops Department, Adana, Turkey 2. Çukurova University, Agriculture Faculty Field Crops Department, Adana, Turkey
 www.biodicon.com Biological Diversity and Conservation ISSN 1308-8084 Online; ISSN 1308-5301 Print 3/3 (2010) 26-30 An investigation on determining the effects of different nitrogen and zinc fertilizer
www.biodicon.com Biological Diversity and Conservation ISSN 1308-8084 Online; ISSN 1308-5301 Print 3/3 (2010) 26-30 An investigation on determining the effects of different nitrogen and zinc fertilizer
Chromium Contaminated Soil
 Chelate Assisted Chromium Uptake by Indian Mustard in Tannery Sludge Contaminated Soil 一 Weimin You, Tianduo Li School of Light Chemistry and Environmental Engineering, Shandong Institute of Light Industry,
Chelate Assisted Chromium Uptake by Indian Mustard in Tannery Sludge Contaminated Soil 一 Weimin You, Tianduo Li School of Light Chemistry and Environmental Engineering, Shandong Institute of Light Industry,
Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils
 The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
CATION-EXCHANGE CHARACTERISTICS OF WHEAT, BARLEY AND PEA DEPENDING ON THE OSMOTIC PRESSURE IN NUTRIENT SOLUTIONS OF LOW ph
 BULG. J. PLANT PHYSIOL., 2002, 28(3 4), 35 45 35 CATION-EXCHANGE CHARACTERISTICS OF WHEAT, BARLEY AND PEA DEPENDING ON THE OSMOTIC PRESSURE IN NUTRIENT SOLUTIONS OF LOW ph Antoaneta Arsova * N. Pushkarov
BULG. J. PLANT PHYSIOL., 2002, 28(3 4), 35 45 35 CATION-EXCHANGE CHARACTERISTICS OF WHEAT, BARLEY AND PEA DEPENDING ON THE OSMOTIC PRESSURE IN NUTRIENT SOLUTIONS OF LOW ph Antoaneta Arsova * N. Pushkarov
COMPLETE FEEDS: ALL INGREDIENTS ARE NOT CREATED EQUAL!
 COMPLETE FEEDS: ALL INGREDIENTS ARE NOT CREATED EQUAL! When selecting or purchasing a feed, it is important to ask for the ingredient list from the manufacturer because, the guaranteed analysis on the
COMPLETE FEEDS: ALL INGREDIENTS ARE NOT CREATED EQUAL! When selecting or purchasing a feed, it is important to ask for the ingredient list from the manufacturer because, the guaranteed analysis on the
The uptake of nutrients occurs at both the roots and the leaves.
 CHAPTER 37: WHAT DO PLANTS NEED TO LIVE AND HOW DO THEY GET IT? Elemental Composition of Living Organisms WHAT ARE ORGANISMS MADE OF? Element Human Alfalfa Bacterium Carbon 19.37% 11.34% 12.14% Hydrogen
CHAPTER 37: WHAT DO PLANTS NEED TO LIVE AND HOW DO THEY GET IT? Elemental Composition of Living Organisms WHAT ARE ORGANISMS MADE OF? Element Human Alfalfa Bacterium Carbon 19.37% 11.34% 12.14% Hydrogen
Effects of Bicarbonate and High ph Conditions on Zinc and Other Nutrients Absorption in Rice
 290 Rice Science, 2004, 11(56): 290 296 http://www.ricescience.org Effects of Bicarbonate and High ph Conditions on Zinc and Other Nutrients Absorption in Rice MENG Fanhua, WEI Youzhang, YANG Xiaoe, LIN
290 Rice Science, 2004, 11(56): 290 296 http://www.ricescience.org Effects of Bicarbonate and High ph Conditions on Zinc and Other Nutrients Absorption in Rice MENG Fanhua, WEI Youzhang, YANG Xiaoe, LIN
YaraVita PROCOTE. The colors of yield.
 YaraVita PROCOTE The colors of yield. Micronutrient Coating YaraVita PROCOTE is an innovative liquid technology developed by Yara for coating prilled and granular fertilizers with micronutrients. It allows
YaraVita PROCOTE The colors of yield. Micronutrient Coating YaraVita PROCOTE is an innovative liquid technology developed by Yara for coating prilled and granular fertilizers with micronutrients. It allows
Inorganic Contaminants
 Inorganic Contaminants Dr Stephen R Smith Dept Civil & Environmental Engineering Page 1 Scope of Presentation Sources and concentrations Qualifying environmental limits Phytotoxicity Dietary intake Grain
Inorganic Contaminants Dr Stephen R Smith Dept Civil & Environmental Engineering Page 1 Scope of Presentation Sources and concentrations Qualifying environmental limits Phytotoxicity Dietary intake Grain
Environmental Impacts of Compost Application on Construction Sites
 Environmental Impacts of Compost Application on Construction Sites Tom Glanville Agricultural & Biosystems Engineering Department by Dr. Tom Glanville, Agricultural & Biosystems Engineering, Iowa State
Environmental Impacts of Compost Application on Construction Sites Tom Glanville Agricultural & Biosystems Engineering Department by Dr. Tom Glanville, Agricultural & Biosystems Engineering, Iowa State
THE EFFECT OF ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION, ACIDIC RAINS, ALUMINIUM CONTAINING PACKAGING ON THE GROWTH OF WHEAT
 Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula Protecţia Mediului Vol. XXV, 2015 THE EFFECT OF ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION, ACIDIC RAINS, ALUMINIUM CONTAINING PACKAGING ON THE GROWTH OF WHEAT Szabó-Nagy Andrea*,
Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula Protecţia Mediului Vol. XXV, 2015 THE EFFECT OF ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION, ACIDIC RAINS, ALUMINIUM CONTAINING PACKAGING ON THE GROWTH OF WHEAT Szabó-Nagy Andrea*,
DETERMINATION OF SOME HEAVY METALS IN SPINACH AND LETTUCE FROM SELECTED MARKETS IN KADUNA METROPOLIS Z. N.
 DETERMINATION OF SOME HEAVY METALS IN SPINACH AND LETTUCE FROM SELECTED MARKETS IN KADUNA METROPOLIS Z. N. Ali, F.M. Abdulkadir and M. M. Imam Department of Applied Science, College of Science and Technology,
DETERMINATION OF SOME HEAVY METALS IN SPINACH AND LETTUCE FROM SELECTED MARKETS IN KADUNA METROPOLIS Z. N. Ali, F.M. Abdulkadir and M. M. Imam Department of Applied Science, College of Science and Technology,
Unit B: Seed Germination, Growth, and Development. Lesson 4: Determining Nutrient Functions and Utilization
 Unit B: Seed Germination, Growth, and Development Lesson 4: Determining Nutrient Functions and Utilization 1 Terms Denitrification Leach Macronutrient Micronutrient Nitrification Nitrogen cycle Nitrogen
Unit B: Seed Germination, Growth, and Development Lesson 4: Determining Nutrient Functions and Utilization 1 Terms Denitrification Leach Macronutrient Micronutrient Nitrification Nitrogen cycle Nitrogen
Upper Tolerances for Micronutrients in Fertilizers
 2017 Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada (Canadian Food Inspection Agency), all rights reserved. Use without permission is prohibited. Upper Tolerances for Micronutrients in Fertilizers Program Objectives
2017 Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada (Canadian Food Inspection Agency), all rights reserved. Use without permission is prohibited. Upper Tolerances for Micronutrients in Fertilizers Program Objectives
Water-Soluble Fertilizer Fertigation and Foliar Application. The Authority in Potassium and Magnesium
 Water-Soluble Fertilizer Fertigation and Foliar Application The Authority in Potassium and Magnesium Fertigation and Foliar Application In modern agriculture great improvements can be made in terms of
Water-Soluble Fertilizer Fertigation and Foliar Application The Authority in Potassium and Magnesium Fertigation and Foliar Application In modern agriculture great improvements can be made in terms of
COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT
 Analysis Report For: Copy To: Greg Gelewski OCRRA LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY Jamesville 1/2" C06659 9/27/2013 Screened Compost Finished Compost Windrow
Analysis Report For: Copy To: Greg Gelewski OCRRA LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY Jamesville 1/2" C06659 9/27/2013 Screened Compost Finished Compost Windrow
Nutrient Content of Vegetable Amaranth (Amaranths cruentus L.) At Different Harvesting Stages
 World Journal of Agricultural Sciences 6 (3): 85-89, ISSN 87-347 IDOSI Publications, Nutrient Content of Vegetable Amaranth (Amaranths cruentus L.) At Different Harvesting Stages N.D. Makobo, M.D. Shoko
World Journal of Agricultural Sciences 6 (3): 85-89, ISSN 87-347 IDOSI Publications, Nutrient Content of Vegetable Amaranth (Amaranths cruentus L.) At Different Harvesting Stages N.D. Makobo, M.D. Shoko
Organic Vegetables: High Levels of Heavy Metals!
 Organic Vegetables: High Levels of Heavy Metals! Organic vegetables fare no better than non-organic ones in tests 2 out of 9 organic samples had pesticide residues and 5 contaminated by heavy metals Organic
Organic Vegetables: High Levels of Heavy Metals! Organic vegetables fare no better than non-organic ones in tests 2 out of 9 organic samples had pesticide residues and 5 contaminated by heavy metals Organic
Trace Elements in Manure
 Trace Elements in Manure Purpose: Whenever soil profiles are examined for nutrient trace elements, it has been demonstrated that the metals tend to accumulate in the topsoil. Soil properties affect plant
Trace Elements in Manure Purpose: Whenever soil profiles are examined for nutrient trace elements, it has been demonstrated that the metals tend to accumulate in the topsoil. Soil properties affect plant
Innovation. Quality. Solutions.
 the cost-effective foliar safeguard against micronutrient deficiency in crops Innovation. Quality. Solutions. Micronutrient fertilisers Insufficient micronutrient supply limits crop yield in exactly the
the cost-effective foliar safeguard against micronutrient deficiency in crops Innovation. Quality. Solutions. Micronutrient fertilisers Insufficient micronutrient supply limits crop yield in exactly the
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(2):397-402 Analysis of heavy metals in citrus juice from
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(2):397-402 Analysis of heavy metals in citrus juice from
Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium deficiency on the uptake and mobilization of ions in Bengal gram (Cicer arietinum)
 J. Biosci., Vol. 3 Number 3, September 1981, pp. 249-257. Printed in India, Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium deficiency on the uptake and mobilization of ions in Bengal gram (Cicer arietinum)
J. Biosci., Vol. 3 Number 3, September 1981, pp. 249-257. Printed in India, Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium deficiency on the uptake and mobilization of ions in Bengal gram (Cicer arietinum)
COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT
 LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY C10462 04/27/2018 Analyte COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT (As is basis) Compost Test 3A (Dry weight basis) ph Soluble Salts Solids
LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY C10462 04/27/2018 Analyte COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT (As is basis) Compost Test 3A (Dry weight basis) ph Soluble Salts Solids
AGNES KTS (0-0-25)+SO3 42% Liquid T.C. Ministry of Agriculture License No.: 588 / Registration No.: 14627
 AGNES KTS (0-0-25)+SO3 42% Liquid Registration No.: 14627 Characteristics: AGNES should be used fruit form of plant period until harvest period. It stimulates photosynthesis, colouring and quality of the
AGNES KTS (0-0-25)+SO3 42% Liquid Registration No.: 14627 Characteristics: AGNES should be used fruit form of plant period until harvest period. It stimulates photosynthesis, colouring and quality of the
