Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion
|
|
|
- Ashlee Sharleen Crawford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion
2 Introduction to Digestion Read pages Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including: the six nutrients their building blocks (ie: the simple molecules that make them up, if any) their dietary sources their importance in the body Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (2 of 37)
3 Review Homework Fill in the Information for each of the essential nutrients: Carbohydrates Building blocks: Dietary sources: Importance in the body: Fats (lipids) Building blocks: Dietary sources: Importance in the body: Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (3 of 37)
4 Review Homework Fill in the Information for each of the essential nutrients: Cholesterol Building blocks: Dietary sources: Importance in the body: Proteins Building blocks: Dietary sources: Importance in the body: Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (4 of 37)
5 Review Homework Fill in the Information for each of the essential nutrients: Minerals Building blocks: Dietary sources: Importance in the body: Vitamins Building blocks: Dietary sources: Importance in the body: Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (5 of 37)
6 Review Homework And one more: Water Building blocks: Dietary sources: Importance in the body: Which of the items on this list is not really considered an essential nutrient? Why not? Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (6 of 37)
7 Title: Dec 17 10:23 AM (7 of 37)
8 Title: Dec 14 1:45 PM (8 of 37)
9 Group Work Individually, read pages Don't worry about trying to remember everything at this point, this is just an initial reading to get a general feel for the topic. Number off to form groups of up to three people Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (9 of 37)
10 Group Work In your group, use the markers and chart paper provided to complete an graphic outline showing all organs of the digestive system. You will keep and continue work on this chart later, so be sure to complete this carefully! Draw the organs food passes through in order, starting with the mouth Label each organ, using large capital letters Using smaller letters, briefly explain the organ's in digestion If the organ has multiple sections, such as the small intestine, label the sections Finally, draw any accessory organs, and label them with their function as well Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (10 of 37)
11 Group Work Note: Draw all organs so that they form a straight pathway; you don't need, for example, to draw the small intestine as a coiled mass. Accessory organs are ones that aid in digestion, but which the food doesn't actually pass through. (For example, saliva glands) Not all of the accessory organs are included in this section, so keep your chart in the classroom when you are done...we will be completing it later. Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (11 of 37)
12 Example: Getting Started Mouth Begins mechanical and chemical breakdown of food Saliva Glands Moistens and lubricates food, assists in chemical breakdown Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (12 of 37)
13 Title: Dec 18 8:46 AM (13 of 37)
14 Homework Read pages , stopping when you reach the section titled Health and the Digestive System. Create a concept map to show the major enzymes secreted by each organ of the digestive system, and their actions. Review on page 373 Digestive Enzymes Saliva Glands Salivary Amylase Secreted into the mouth Breaks starch into disaccharides Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (14 of 37)
15 Digestive System Diagram Add the remaining accessory organs to your digestive system diagrams. Add all enzymes and other secretions to the diagram. List each secretion with the organ of origin, and include its action in digestion. Digestive Enzymes Saliva Glands Salivary Amylase Secreted into the mouth Breaks starch into disaccharides Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (15 of 37)
16 Label Digestive System Saliva Glands Mouth Esophagus 12 Stomach Gallbladder Liver Large intestine Pancreas Small intestine Appendix Anus Rectum Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (16 of 37)
17 Modelling Digestion Use the models of large nutrients to model the stages of digestion in the various organs. Protein Polysaccharide Fat (triglyceride) Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (17 of 37)
18 Modelling Digestion Mouth Protein Polysaccharide Fat (triglyceride) Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (18 of 37)
19 Modelling Digestion Stomach Protein Polysaccharide Fat (triglyceride) Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (19 of 37)
20 Modelling Digestion Small Intestine Protein Polysaccharide Fat (triglyceride) Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (20 of 37)
21 Homework Study the digestive system summary sheet, and complete the questions (1 11) on the sheet. Come to class tomorrow prepared to review for your unit test. Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (21 of 37)
22 Homework Questions: Answers 1) What are the six essential nutrients, and why are they important in the human body? Of the six, which need to be digested before being absorbed into the bloodstream? Water lubrication, temperature control, chemical reactions are dissolved in water Minerals Many different roles in maintaining body function Vitamins Simple organic compounds, often needed as coenzymes Proteins Structure, transport, communication (hormones) control of chemical reactions (enzymes), antigens and antibodies Fats Insulation, structure of cell membrane, energy storage Carbohydrates Primary energy source for cell respiration Only proteins, fats, and carbohydrates need to be digested. Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (22 of 37)
23 Homework Questions: Answers 2) Compare mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. In what ways are they similar and different? Mechanical digestion involves physically breaking down food into smaller pieces. This includes chewing, emulsifying fats (by bile from the liver), churning of the stomach, etc. Chemical digestion is the separation of large molecules into their components by chemical reactions (hydrolysis). This is controlled by digestive enzymes. Both involve breaking food into smaller parts, but only chemical digestion involves enzyme controlled reactions; in mechanical digestion, the molecules themselves are not changed. Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (23 of 37)
24 Homework Questions: Answers 3) How would digestion be affected if mechanical digestion did not occur? What is one secretion into the digestive system which acts to break down a nutrient mechanically, but not chemically? If mechanical digestion did not occur, chemical digestion would still happen, but it would be much slower. Why? Because if the food isn't broken into smaller pieces, the surface area is much smaller, meaning the enzymes cannot act on as many molecules at once. One secretion which helps with mechanical digestion but not chemical digestion is bile, which emulsifies fats (breaks them apart into little bubbles) but doesn't break apart the fat molecule.) Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (24 of 37)
25 Homework Questions: Answers 4) What triggers the glands in the stomach? What do these secretions act on? The stomach secretes hydrochloric acid and the proteinase pepsin. This begins the breakdown of proteins into polypeptide chains. Stomach secretions are triggered by the hormone gastrin, which is released when a person sees, smells, or even thinks of food, or when food entering the stomach touches or stretches the stomach wall. The stomach also releases a mucus coating which lines the stomach and protects it. Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (25 of 37)
26 Homework Questions: Answers 5) What is an ulcer, and how does it develop? (see pgs ) An ulcer occurs when the acids in the stomach penetrate the mucus lining, and begin to eat at the wall of the stomach itself. (So an ulcer is really an acid burn on the inside of the stomach!) Most ulcers are caused by bacteria which attach to the stomach wall and remove the mucus layer; smoking, alcohol, and caffeine can also contribute to ulcers. They can often be controlled by diet and other behavior changes (such as quitting smoking), and in severe cases can be surgically repaired. Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (26 of 37)
27 Homework Questions: Answers 6) What are three major functions of the liver? Note: ( only one is directly related to digestion) The liver's role in digestion is the production of bile salts, which dissolve in water to form bile. This is stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine, where it emulsifies fats. The liver also detoxifies blood, removing harmful chemicals and converting them into harmless forms which are removed from the body by excretion. Finally, the liver controls several nutrient levels in the blood, most importantly glucose (which it stores as glycogen) but also other chemicals, such as some fatsoluble vitamins. Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (27 of 37)
28 Homework Questions: Answers 7) Describe the structure of villi and microvilli. What is their function in digestion? Villi are small, finger like projections on the inside lining of the small intestine. The are covered with cells which have brush like membranes, forming even smaller projections called microvilli. They increase surface area in the small intestine to increase the absorption of nutrients. Villi contain capillaries, which absorb most of the products of digestion, and lacteals small lymph vessels which absorb the larger fat particles which cannot enter the capillaries. Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (28 of 37)
29 Homework Questions: Answers 8) What is a lacteal? Why is it important in digestion? Lacteals are small lymph vessels which absorb the larger fat particles which cannot enter the capillaries. These flow into the lymph vessels, which carry fluid and return it to the circulatory system near the base of the throat (the subclavian veins). Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (29 of 37)
30 Homework Questions: Answers 9) What four purposes does peristalsis serve in the small intestine? Peristalsis: 1) moves food through the small intestine 2) helps mechanically digest food with muscular contractions 3) mixes food with enzymes to aid in chemical digestions 4) pushes food past villi to aid in absorption of nutrients Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (30 of 37)
31 Homework Questions: Answers 10) What is the appendix? What condition can develop if the appendix becomes infected? The appendix is a small projection of the large intestine, near where it joins the smal intestine. It serves no function in humans, although there is speculation that it may b related to the immune system. If it becomes infected, this is called appendicitis. Without treatment, the bacteria could cause the appendix to rupture, leaking toxins into the abdominal cavity. This condition is potentially fatal, but routine surgery can remove the appendix. Since th appendix plays no real role in maintaining homeostasis, if it is removed, most people suffer no long term effects. Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (31 of 37)
32 Homework Questions: Answers 11) Give two examples of vitamins produced by bacteria in the large intestine. Why are these vitamins important? (see pg. 371) Vitamin B12(which is important for metabolism, maintaining a healthy nervous system, and red blood cell development) and Vitamin K (needed for blood clotting) are both formed by bacteria in the large intestine. Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (32 of 37)
33 Unit Test Tomorrow! You may use the remainder of the class to study for the unit test, or to ask questions. Remember, this test covers: Circulatory system Immune system (and the other defenses) Respiratory (or gas exchange) system Digestive system Title: Dec 12 8:43 AM (33 of 37)
34 Title: Dec 12 1:37 PM (34 of 37)
35 Title: Dec 12 1:37 PM (35 of 37)
36 Title: Dec 12 10:02 AM (36 of 37)
37 Title: Dec 13 3:45 PM (37 of 37)
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Nutrients and Digestion
 Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
The Digestive System CP Biology
 The Digestive System CP Biology Objectives Explain how food provides energy. Identify the 6 forms of nutrients your body needs and describe their use in the body. Identify the organs of the digestive system;
The Digestive System CP Biology Objectives Explain how food provides energy. Identify the 6 forms of nutrients your body needs and describe their use in the body. Identify the organs of the digestive system;
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
The Digestive Process Begins
 Name Date Class The Digestive Process Begins This section explains what the digestive system does and describes the functions of the mouth, the esophagus, and the stomach. Use Target Reading Skills Before
Name Date Class The Digestive Process Begins This section explains what the digestive system does and describes the functions of the mouth, the esophagus, and the stomach. Use Target Reading Skills Before
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
Digestive System. Science 7 HMS 2015
 Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2015 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2015 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
Nutrition and Digestion
 Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System Practice Test
 Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Digestive System Notes. Biology - Mrs. Kaye
 Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs 6/1/2015. The Wall of the Digestive Tract
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages )
 Name Class Date Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971-977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy (page 971) 1. Cells convert
Name Class Date Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971-977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy (page 971) 1. Cells convert
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages )
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
Digestive System. Science 7 HMS 2016
 Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2016 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2016 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals a) Suspension feeders i) (1) Humpback whales b) Substrate feeders i)
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract
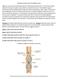 Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
The Human Digestive Tract
 The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body
 Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that
 PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM THE FOUR STEPS OF DIGESTION
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM WHAT IS THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM? the digestive system is a long, muscular tube The entire system is approximately 9m in length and is usually a one way tract WHY DO WE NEED A DIGESTIVE
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM WHAT IS THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM? the digestive system is a long, muscular tube The entire system is approximately 9m in length and is usually a one way tract WHY DO WE NEED A DIGESTIVE
Digestion Review V1 /36
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Digestion Review V1 /36 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the above parts of the digestive system would be
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Digestion Review V1 /36 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the above parts of the digestive system would be
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM There are three primary functions for the digestive system 1. Break down food into molecules the body can use 2. The molecules are absorbed into the
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM There are three primary functions for the digestive system 1. Break down food into molecules the body can use 2. The molecules are absorbed into the
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
Digestion and Nutrition. Chapter 40
 Digestion and Nutrition Chapter 40 Impacts, Issues Hormones and Hunger Fat cells secrete leptin, which reduces appetite; an empty stomach secretes ghrelin, which makes you hungry the goal is healthy nutrition
Digestion and Nutrition Chapter 40 Impacts, Issues Hormones and Hunger Fat cells secrete leptin, which reduces appetite; an empty stomach secretes ghrelin, which makes you hungry the goal is healthy nutrition
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Student Exploration: Digestive System
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Digestive System Vocabulary: absorption, amino acid, carbohydrate, chemical digestion, chyme, complex carbohydrate, digestion, digestive system, elimination, enzyme, fat,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Digestive System Vocabulary: absorption, amino acid, carbohydrate, chemical digestion, chyme, complex carbohydrate, digestion, digestive system, elimination, enzyme, fat,
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes
 Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
This section identifies the nutrients your body needs and explains why water is such an important nutrient.
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971-977) 44P TEKS FOCUS: 9A Structure and function of biomolecules; 11 C Importance of nutrition on health This section
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971-977) 44P TEKS FOCUS: 9A Structure and function of biomolecules; 11 C Importance of nutrition on health This section
UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food
 UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food Introduction to the Digestive System PART ONE Systems of the Body The Digestive System Also referred to as alimentary system, the gut, gastrointestinal
UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food Introduction to the Digestive System PART ONE Systems of the Body The Digestive System Also referred to as alimentary system, the gut, gastrointestinal
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
Chapter 3 Reading Guide Be sure to use the many figures and tables provided by the book to help answer these questions.
 Chapter 3 Reading Guide Be sure to use the many figures and tables provided by the book to help answer these questions. 1. What is digestion? What is the difference between mechanical and enzymatic digestion?
Chapter 3 Reading Guide Be sure to use the many figures and tables provided by the book to help answer these questions. 1. What is digestion? What is the difference between mechanical and enzymatic digestion?
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1. Digestion 101 & H.O.P.E.
 Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Name Date Class. 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Food is required for the body to. maintain homeostasis, keeping a steady internal state.
 CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Monday, October Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page.
 1. Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page. 2. Answer the following question on the same page: How do proteins, lipids and carbs impact
1. Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page. 2. Answer the following question on the same page: How do proteins, lipids and carbs impact
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
The Digestive System. 1. The Mouth. 2. Epiglottis and Esophagus. 3. The Stomach. 4. The Small Intestine
 The Digestive System Name: The digestive system has 3 main functions. First, it breaks down food into smaller nutrients that the body can use. Secondly, these nutrients are absorbed into the blood. Thirdly,
The Digestive System Name: The digestive system has 3 main functions. First, it breaks down food into smaller nutrients that the body can use. Secondly, these nutrients are absorbed into the blood. Thirdly,
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. Materials: Markers Ruler 1,000 cm string Map Pencils Digestive Organ Mouth 11 Esophagus 25
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. Materials: Markers Ruler 1,000 cm string Map Pencils Digestive Organ Mouth 11 Esophagus 25
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Digestive and Excretory Systems
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) This section identifies the nutrients your body needs and explains why water is such an important nutrient Food
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) This section identifies the nutrients your body needs and explains why water is such an important nutrient Food
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
Student Exploration: Digestive System
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Digestive System Vocabulary: absorption, amino acid, carbohydrate, chemical digestion, chyme, complex carbohydrate, digestion, digestive system, elimination, enzyme, fat,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Digestive System Vocabulary: absorption, amino acid, carbohydrate, chemical digestion, chyme, complex carbohydrate, digestion, digestive system, elimination, enzyme, fat,
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by. broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Station One: Nutrition
 Station One: Nutrition Name that thing! 1. Chemical substances, found in foods, which are used in the human body. 2. Nutrient in human diet where foods are the only possible source of the nutrient. 3.
Station One: Nutrition Name that thing! 1. Chemical substances, found in foods, which are used in the human body. 2. Nutrient in human diet where foods are the only possible source of the nutrient. 3.
SNC4M The Digestive System
 SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
Human Digestion. Junior Science
 Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Primary Function. 1. Ingestion: food enters the system
 Digestive System Primary Function 1. Ingestion: food enters the system - Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins 2. Digestion: Further breakdown - Chemical/enzymatic 3. Absorption: Nutrients enter circulatory
Digestive System Primary Function 1. Ingestion: food enters the system - Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins 2. Digestion: Further breakdown - Chemical/enzymatic 3. Absorption: Nutrients enter circulatory
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Harvesting energy from food. Digestion: A Closer Look. Where digestion begins. Salivary Glands 4/17/13. Or how food gets from
 Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Digestive System. What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning?
 Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Lesson 1. Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
What are you made of????
 What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014
 HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014 In this lesson, we: Absorption Lesson Description Examine and understand absorption Define absorption and describe where it occurs Study the structure
HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014 In this lesson, we: Absorption Lesson Description Examine and understand absorption Define absorption and describe where it occurs Study the structure
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Digestive System. Physical and breakdown begins. : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic
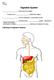 SBI 3C Digestive System : food enters the system Physical and breakdown begins : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic : Nutrients enter system, delivered to tissues of the body Elimination of Waste (
SBI 3C Digestive System : food enters the system Physical and breakdown begins : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic : Nutrients enter system, delivered to tissues of the body Elimination of Waste (
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 The Digestive System
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Figure Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore
 Figure 41.1 Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore Essential Nutrients: Amino acids Fatty acids Vitamins Minerals Figure 41.2 Complete vs incomplete Omnivore vs herbivore (vegetarian) Table 41.1 Table
Figure 41.1 Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore Essential Nutrients: Amino acids Fatty acids Vitamins Minerals Figure 41.2 Complete vs incomplete Omnivore vs herbivore (vegetarian) Table 41.1 Table
7.4 Digestion. Highlight the definition of mechanical digestion.
 7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The Human Digestive System We will divide the Human Digestive System into two main topics: 1. Nutrition and what our body needs 2. How the human body breaks down food and makes
THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The Human Digestive System We will divide the Human Digestive System into two main topics: 1. Nutrition and what our body needs 2. How the human body breaks down food and makes
4/8/16. Digestive System. When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy
 When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy Section 1 Digestive System A group of organs that work together to digest food so that it can be used
When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy Section 1 Digestive System A group of organs that work together to digest food so that it can be used
Homework: Finish BrainPop Worksheet(pg. 23a)
 As the Stomach Churns Tuesday January 12, 2016 Objective: You will examine the different organs of the digestive system and investigate the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion. Homework:
As the Stomach Churns Tuesday January 12, 2016 Objective: You will examine the different organs of the digestive system and investigate the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion. Homework:
Chapter 6, Part Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99.
 Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99. 2. Your body is made up of,,,, and many other materials.
Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99. 2. Your body is made up of,,,, and many other materials.
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy
 The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology W: www.wsbht.co.uk E: holistics@wsbht.co.uk T: 07824 337333 Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology
The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology W: www.wsbht.co.uk E: holistics@wsbht.co.uk T: 07824 337333 Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology
Nutrition, Digestive System & Enzyme Review Packet
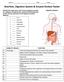 Name: Date: Class: Nutrition, Digestive System & Enzyme Review Packet Identify the major parts of the human digestive system on a diagram. Using the key, match the following parts to their correct structure
Name: Date: Class: Nutrition, Digestive System & Enzyme Review Packet Identify the major parts of the human digestive system on a diagram. Using the key, match the following parts to their correct structure
Sphincters heartburn diaphragm The Stomach gastric glands pepsin, chyme The Small Intestine 1-Digestion Is Completed in the Small Intestine duodenum
 Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Big Idea/Questions/Notes:
 Ch 38: Digestive and Excrery Systems 38-1 Food and Nutrition A. Food and Energy 1. One calorie is equal the amount of energy needed raise the temperature of. 2. The energy in food is measured. 3. One Calorie
Ch 38: Digestive and Excrery Systems 38-1 Food and Nutrition A. Food and Energy 1. One calorie is equal the amount of energy needed raise the temperature of. 2. The energy in food is measured. 3. One Calorie
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium I Topic: Human Digestive System Page 1 of 13. The Chemical Foundation of Digestion
 Page 1 of 13 The Chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms, regardless of size or complexity, have some method to obtain the essential nutrients they need for survival. Heterotrophs: Organisms that
Page 1 of 13 The Chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms, regardless of size or complexity, have some method to obtain the essential nutrients they need for survival. Heterotrophs: Organisms that
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption. Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs
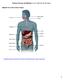 Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
