APPLICATION OF HAZARD ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP) AS A POSSIBLE CONTROL MEASURE FOR OPISTHORCHIS
|
|
|
- Alexis Gilbert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 APPLICATION OF HAZARD ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP) AS A POSSIBLE CONTROL MEASURE FOR OPISTHORCHIS VIVERRINIINFECTION IN CULTURED CARP (PUNT/US GONIONOTUS) Khamboonruang Cl, Keawvichit RI, Wongworapat KI, Suwanrangsi S2, Hongpromyart M 3, Sukhawat K 4, Tonguthai K5 and Lima dos Santos CAM6 'Research Institute of Health Sciences, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand; 2Fish Inspection and Quality Control Division, Department of Fisheries, Bangkok, Thailand; 3Provincial Fisheries, Chiang Mai, Thailand; "Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand; 5Aquatic Animal Health Research Institute, Department of Fisheries, Bangkok, Thailand; "Fish Utilization and Marketing Service, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), Rome, Italy Abstract, Opisthorchiasis due to Opisthorchis viverini and transmitted through infected freshwater cyprinoid fish (carps) affects more than 8 million people in Thailand, People's Democratic Republic of Lao, and Vietnam. The Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) -concept has been recommended by FAO and WHO to be included in programs to control foodborne trematode infections (FBT). HACCP is a multifactorial approach to control food hazards through surveillance of diseases. foods, and operations and education. This study describes the first attempt to apply HACCP to the prevention and control of Opisthorchis viverrini in culture carp (Puntius gonionotus). The experiment was designed and carried out by a multidisciplinary "HACCP team" including experts in the field of pulic health. parasitology, epidemiology, aquaculture, fisheries extension and fish inspection. The investigation was performed in two fish s in the District of Sun Pa Tong. Chiang Mai, Thailand. In the experimental. fish was cultured according to HACCP principles and compared with the control. which followed conventional aquaculture practices. Water supply to the, fish fry, fish feed and conditions during the growing period were identified as critical control points (CCPs). Hazards were identified and analyzed, as well as control measures. critical limits, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, and record keeping developed for each one of the above CCPs. Complete preparation. particularly aiming to eliminate contamination of water with O. viverrini eggs, fish infected with parasite meacercariae and the first intermediate host tbithynia spp). was conducted. After the was filled with water, O. viverrini metacercaria-free fry were released into the. The preliminary results obtained indicate that HACCP-based principles applied to carp culture could be used as a strategy to prevent and control O. viverrini. Further studies should be undertaken aiming to confirm these preliminary results. INTRODUCTION Thailand is the most highly endemic country for opisthorchiasis due to Opisthorchis viverrini (WHO, 1995). According to the epidemiological survey carried out in 1991 by the Department of Communicable Diseases, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand, the overall prevalence of opisthorchiasis in the country was 15.2%.11 was found that the prevalence was 24.0% in the northeast, 22.8% in the north, 7.3% in the center and only 0.3% in the south. According to the rates among different subpopulation groups and geographical areas, it is currently estimated that the approximate infected population throughout the country would be up to 8.6 million (Jongsuksuntigul and Imsomboon, 1993). In Chiang Mai area, in the northern part of Thailand, the disease has shown a high prevalence rate of 26.78% (Khamboonruang, 1993). Other studies carried in four districts (Sankampang, Sanpatong, Hang Dong and Mae Wong) in the Chiang Mai Area have reported a prevalence as high as 54% (Kaewvichit et ai, 1993). The northerners are believed to acquire the infection from eating raw-fish dishes call "lahbpia" and "pla-som" prepared from wild caught fish (WHO, 1995). 65
2 Since 1988, a national opisthorchiasis control program has been organized. The approaches used in the large pilot project carried out in seven provinces in the northeast Thailand included health education, introduction of community participation by employing health care approaches aimed at community selfreliance, annual selective treatment, and improvement of sanitation and nutritional status. The program has been implemented in all provinces in the northeast and is currently being extended to the northern provinces of Thailand. The program was centrally planned, with the participation of the provincial chief medical officers, local health authorities and individual members of the community (WHO, 1995). Food control measures are particularly important in the struggle to control opisthorchiasis since the disease is definitely related to fish and fishery products being eaten raw or undercooked. In fact, despite the positive overall results of the National Opisthorchiasis Control Program which claimed that frequent consumption of uncooked fish dishes in northeast Thailand has decreased from 14% in 1990 to 7% in 1994, occasional consumption of raw fish dishes in the same region remains as high as 42% (Jongsuksuntigul and Imsomboon, 1995). The prevention of fish becoming infected with O. viverrini depends on environmental control of surface waters where fish is caught or harvested (cultured fish) and the control of the first intermediate hosts (snails). There are many potential difficulties in the implementation of these measures. For example, monitoring and control of large bodies of surface waters (rivers, lakes, reservoirs) may be impracticable in Thailand. However, the improvement of aquaculture practices, widely spread in Thailand to exclude O. viverrini, may be possible with the cooperation and participation of the people involved. Prevention and control of opisthorchiasis could be reinforced by food safety procedures based on the principles of the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP)- system, which offers a systematic and sequential approach to the control of food hazards, including food (fish)-borne trematodes. This invol ves a complete new strategy of food-borne trematode control based on the comprehensive coverage of the origin of the fish up to its consumption. The proposed strategy is based on the assumption that the fish farmer must design and apply a HACCP plan for the production and marketing of fish safe from O. viverrini infection. The farmer would be assisted by local public health officers, fisheries officers and fish inspection officers. The whole process should involve the local commu- nity and reach village and retail markets, processing plants, restaurants, housewives and have the support of a well-coordinated health education and public information program (Lima dos Santos, 1995). The National Opisthorchiasis Control Program in Thailand has sufficient data to convincingly demonstrate the public health importance of this food (fish)-borne disease, and to justify the priority for the intervention of other government institutions. However, control of opisthorchiasis and other fish-borne parasitic zoonoses has not been given priority by the areas of aquaculture and fish inspection and quality control of the Department of Fisheries of the Ministry of Agriculture. This Department plays a key role in the development of aquaculture and in the control of safety and quality of fishery products exported by the country. The safety of fishery products sold within the national market is the responsibility of the Ministry of Public Health. However, in regions of high prevalence of opisthorchiasis such as the north and northeast provinces of the country, the involvement of aquaculturists and fish inspectors, side by side with medicaupublic health officers is crucial. Furthermore, the increased production of cultured fish and shellfish has opened new domestic and international markets. International travels and increasing availability and interest in ethnic foods also contribute to spread the risk of infection with food-borne trematode infections (Dixon and Flohr, 1995). The potential economic losses that would result from banning the export of fish products from endemic areas need to be taken into account in economic planning and in deciding what priority should be given to the control of fish-borne trematode infections, in particular opisthorchiasis, by the Department of Fisheries. The objective of the study was to assess the possibilities of successfully apply HACCP principles to prevent and control the infection of cultured fish with O. viverrini metacercariae. The work was planned and carried out by a rnultidisciplinary group of experts from different government institutions in Thailand in close collaboration with the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). HACCP MATERIALS AND METHODS The HACCP system is based on the recognition that hazards to health exist at various points in the food 66
3 chain (in the case of fish from catching or harvesting to the consumer), but that measures can be taken to control these hazards. Once the system is established, the main control efforts are directed towards the critical control points. The HACCP system comprises the following sequential steps: 1. Identify hazards and assess the severity and risk. 2. Determine critical control points (CCPs). 3. Establish critical control limits and tolerances at each CCP. 4. Monitor CCPs. 5. Take corrective action when monitoring indicates that criteria are not met. 6. Recording and record keeping. 7. Verify that the system is functioning as planned. In the case of fish, the application of the HACCP concept to the control of opisthorchiasis would start with the assessment of the risk that certain species of fish ( particularly those members of the Cyprinidae family, ie carps) caught or harvested in endemic areas are infected. A risk will exist if fish from endemic areas are consumed raw or inadequately processed. The HACCP concept is unique for every product and for every production unit: in each case a detailed study of the food producing/processing/marketing/ preparation flow is necessary to identify hazards and the critical control points. Designing and implementation of HACCP plan The formulation of the specific HACCP plan for the present study was based on the CODEX Guidelines for the Application of the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point System ( Codex Alimentarius Commission, 1993). The work was carried out by a multidisciplinary "HACCP team" including experts in public health, parasitology, epidemiology, aquaculture, fish biology, fisheries extension, and fish inspection and HACCP-based quality assurance programs. The initial work included the selection of two appropriate fish s, one experimental and one control, to conduct the experiment. Members of the HACCP team have visited a number of fish s located within Chiang Mai districts recognized as endemic for O. viverrini and selected two fish s of the San Pa Tong Experimental Rice Farm of the Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives located in Sun Pa Tong district, Chaing Mai. The final selection was made taking into account of the following factors: confirmation of local endemic human opisthorchiasis; traditional fish farming practices in place; better possibility of efficient application of HACCP strategy; and proximity with RIHES laboratory facilities. To confirm the prevalence of opisthorchiasis in the area where the selected s were located, feces were collected from all villagers and examined for helminthic eggs using the formalin-ether concentration technic (Richie, 1948). The HACCP team decided to use a small carp called "Pia Ta Pien Kao" (Puntius gonionotus) in the experiment due to its reported incrimination as second intermediate hosts of O. viverrini (SEAMEO- TROPMED, 1988; WHO, 1995), as well as its common use as food fish in Chiang Mai area from local fish farms. The experimental dimensions were 250 x 10m while the control was smaller, measuring only 40 x 4m. The s had a muddy bottom and had not been used for fish culturing for a considerable period of time prior to the experiment. Four CCPs were identified in the experimental by the HACCP team, namely: water supply, fish fry, fish feed, conditions during growing. For each one of the above CCPs the following hazards were identified and appropriate control measures established: a) Water quality: Three significant hazards were identified by the HACCP team at this CCP, namely: (I) presence of O. viverrini eggs as a result of human and/or animal fecal contamination; (2) presence of fish infected with O. viverrini rnetacercariae: and, presence of infected or non-infected first hosts snails (Bithynia spp ) with O. viverrini sporocysts. Control measures were taken against each of the above hazards. The first step consisted in draining the existing water from the experimental, which could not be completely done due to the prevailing raining season. Due to a moderately dense population of snails (Bithynia spp ), a combination of molluscicides, including niclosamide (Bayluscide), copper sulfate and calcium oxide was sprayed at the bottom (base) and banks. Since the experiment was initiated during the raining season, the spontaneously refilled with permeated water from the surrounding environment. Three days after the treatment, approximately half the volume of the water 67
4 was evacuated by a water pump regularly used by the farmers. The water level again was allowed to refill with permeated water. Dried animal manure was added to the s twice, aiming at fertilizing the. Random samples of the dried manure were collected and analyzed for the presence of eggs of O. viverrini according to the formalin-ether concentration technic (Beaver, 1984). b) Fish fry: The hazard of releasing fish fry infected with O. viverrini metacercariae in the was controlled by assuring that the fish fry supply was free from infection. Fry were randomly collected from the breeding place and inspected for metacercariae by the compression technic recommended by WHO (1995) for freshwater fish hosts of fishbome trematodes. c) Fish feed: In the case of the fish feed, the presence of O. viverrini eggs as a result of human or animal fecal contamination was identified as a hazard. The feed consisted of "Charern Phokaphan" (CP) pellets which were packed in plastic bags and kept within the farmer's house. Fish was fed daily at 04:30 pm. Random feed samples were taken and analyzed for the presence of O. viverrini eggs by simple sedimentation technic. d) Pond condition during culturing period: The HACCP team identified the contamination of water with O. viverrini eggs from human and/or animal sources, as well as the invasion of the experimental by infected snails as significant hazards at this CCP. Feces were collected from the farmer and its family members (3 persons in total) and examined for helminthic eggs using the formalin-ether concentration technic. The farmer's family had no pets (dogs, cats), therefore, it was not necessary to apply a similar control procedure. However, since loose dogs were present in the area, fencing was constructed around the experimental to prevent intrusion of animal reservoir hosts and, if flooding ever occurred, it would help to prevent contamination of water with possibly infected wild fish. Aquatic vegetation overgrowth on the experimental banks were constantly removed since leaves can serve as the best breeding place for intermediate snail hosts. The farmer's house had a proper latrine and a second proper latrine was available close by the farmer's house for the use of personnel harvesting rice fields nearby. Monitoring procedures In the specific conditions of this study, since the water supply and the fisb fry were added to the s only once, ie at the beginning of the experiment, monitoring procedures of established control criteria were limited to the third and fourth CCP. Some parameters of water quality were monthly recorded in the experimental, aiming at controlling environment. The measurements included temperature of air and water, ox ygen, ph, turbidity and conductivity. These measurements were done using a Water Quality CheckerTOA-WQC-20A. The criteria (critical limit) established for the control of presence of O. viverrini eggs in the water (absence of viable eggs) were monitored monthly by the modified WHO recommended method for the determination of trematode eggs in waste water used in agriculture and aquaculture (WHO, 1989). The possibility of fecal contamination from human and/ or animal sources was also checked monthly through bacteriological analyzes (determination of coliform and fecal coliform bacteria) and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) measurements according to Greenberg et al (1992). The monitoring of the presence of infected and/or non-infected Bithynia spp snails in the s during the fish culturing period was performed by monthly collection of snails in the s, morphological selection of Bithynia spp specimens and examining the snails for the presence of O. viverrini sporocysts, according to Malek (1962). The monitoring of the presence of metacercariae of O. viverrini in the fish during the culturing period was carried out by monthly sampling and inspection according to WHO recommended procedures for the determination of metacercariae in freshwater fish (WHO, 1995). Fish weight and length in both s were also recorded monthly. RESULTS Table I shows the results of the stool examination survey of the villagers living near the s carried out before the experiment. It shows that 13.9% of the villagers were infected with O. viverrini, confirming the endemic character of the parasite in the selected area. Table 2 indicates the monthly records of water quality parameters relevant to proper fish culture. Table 3 gives the results of the monthly water analysis carried out to monitor the presence of O. viverrini eggs. The results were all negative. Table 4 also relates to the monitoring of water 68
5 quality for the possible fecal contamination from human and/or animal origin: it gives the monthly results of microbiological analysis for the determination of coliforms and fecal coli forms in the water, as well as BOO monthly records. The results are all lower than the normal values for surface water according to National Requirements (Ministry of Health, 1989) and the WHO (1989) recommended coliform concentrations of less than 1000 per 100 ml for wastewater used for agriculture and aquaculture. Table 5 gives the monthly results of the monitoring inspection conducted to determine the presence of infected and/or non-infected Bithynia spp snails in both boundaries. Results indicate that the snails were able to survive the molluscicide initial treatment and/or to invade the s. However, no inspected snail showed the presence of O. viverrini sporocysts. Table 6 shows the negative results with the monthly sampling and inspection of fish to monitor the presence of O. viverrini metacercariae. Table 7 indicates, instead, the increasing infection of fish with Haplorchis spp. metacercariae observed during the monthly fish sampling and analysis. Table 8 indicates the monthly records taken of fish length and weight at both s. Table 1 Stool examination of the villagers living near the s. Parasite Male Number positive (%) Female Children Total Opisthorchis spp 18 (20.5) S. stercoralis 20 (25.0) Teania spp I (1.1 ) Hookworm 1 (1.1) G.lamblia I (1.1) 50 (56.8) 3 (6.5) 3 (6.5) 41 (89.1) 17 (loo) 21 (13.9) 23 ( (15.2) 1(0.7) I (0.7) I (0.7) 108 (71.5) Table 2 Measurements of water quality in the experimental. Collection time (Month after fry releasing) Air Temperature Water 2 ph Turbidity Conductivity o I Table 3 Examination of water for the presence of O. viverrini eggs. Collection time (Month after fry releasing) 6 days I 2 3 Control Experimental 69
6 Table 4 Determination of water quality. Collection time (month after fry releasing) Coliform MPNllOO ml Control Fecal coliform MPNIlOOml Experimental Control Experimental Control BOO mg/i Experimental Before fry releasing I 2 >240 > > > IS >7 4.7 Normal value for surface water Coliform bacilli (MPN/lOO ml) 5,000 Fecal coliform (MPN/lOO ml) 1,000 BOO (mg/i) 1.5 From Laws and Standards on Pollution Control in Thailand, 2nd ed, Table 5 Examination of Bithynia intermediate host snails for the presence of O. viverrini sporocysts. Collection time (Month after fry releasing) -7 days 2 3 Control (N = 57) (N = 82) (N = 48) (N =7) Pond boundary Experimental Control Experimental * (N = 59) (N= 8) (N = 51) (N =42) (N = 120) (N = 2(0) (N = 25) (N = 76) (N = 62) (N =6) (N = 182) (N = 26) Table 6 Table 7 Examination of cultured fish for O. viverrini metacercariae. Haplorchis spp metacercariae found in cultured fish. Collection time (Month after fry releasing) Control Experimental Collection time (Month after fry releasing) Control Experimental (N = 48) (N = 50) 2 (N = 50) (N = 50) 3 (N = 30) (N = 30) 25% 12% (N = 12/48) (N = 6150) 2 28% 10% (N = 14/50) (N = 5150) 3 60% 17% (N = 18/30) (N = 6130) 70
7 Table 8 Comparison of the size of fish in both s. Collection time Control Experimental (Month after fry releasing) Length Weight Length Weight DISCUSSION The experiment is the first attempt to apply the HACCP-concept for the prevention and control of fish-borne trematodes. It is also the first collaborative investigation in the field involving the participation of a multi-disciplinary group of experts and institutions outside the public health sector. The exercise is a follow-up of specific recommendations made by the WHO Study Group on the Control of Foodbome Trematode Infections, held in Manila, Philippines, October Results presented in the paper are not final, since the experiment is still in evolution. However, they confirm the positive contribution that the application of the HACCP concept can make for the control of opisthorchiasis and other fishbome trematode infections. If this approach is properly applied, no other system or method can provide such a degree of food safety. Its great advantage is that it is a systematic, multi disciplinary strategy that is both adaptable and cost-effective. It provides a comprehensive coverage of the fish-chain, from the origin of the fish (farm, river, lake, fish-) to consumption, and requires.producers (fishermen, fish-farmers, fish processing plant owners) and traders to accept greater responsibility for food fish through their integration into a national plan of action (WHO,1995). The prevailing satisfactory sanitary conditions in the farm where both s were located have substantially contributed to the positive introduction of HACCP principles, confirming that through appropriate aquaeulture practices, contamination of the cultured fish and the risk of these infections can efficiently be reduced or eliminated. However, due to the originality of the study and the inexperience of those involved with the practical application of HACCP to aquaculture, the investigations have required considerable improvization and adaptation to the specific conditions faced in the selected s. At each CCP identified by the HACCP team it was possible to successfully apply control measures to the hazards identified by the team with two exceptions: snail control and reservoir animal control. In fact, despite the control measures applied in the experimental, the snails were back one month after the chemical and physical control measures. However, no infected snail was found (when trematode eggs are not present in the s, the presence of the first intermediate host does not constitute a hazard "per se"). In the case of reservoir, a regular visual inspection monitoring visit showed the existence of holes in the experimental probably made by large size wild rats. These rats may not only contaminate the with parasite eggs but also facilitate the penetration of infected snails in the. The corrective measure taken included the physical obstruction of the rat holes, the use of chemical rat poison, rat-traps and hunting. The investigation is scheduled to proceed until the moment when the -fish is considered ready for harvesting and marketing. Therefore, a number of monitoring procedures will be performed to assure that all criteria (critical limits) are under proper control. A parallel research will be carried out to confirm the susceptibility of the raised crap (Puntius gonionotus) as an intermediate host for O. viverrini. The infection of fish with Haplorchis spp metacercariae was an unexpected result but it demonstrates 71
8 the value of the application of HACCP for the control of food safety hazards in aquaculture: 1. The HACCP plan was specifically designed and implemented aiming to produce fish free from O. viverrini metacercariae. No attempt was originally made to control the fish infection with other fishbome trematode. 2. The finding of fish infected with Haplorchis spp metacercariae through the application of HACCP principles has led to the identification of a new fishborne safety hazard in Chiang Mai area which must be further investigated. Efforts should be made to determine the first and second intermediate hosts in order to clarify the evolutive cycle of the parasite and to prevent human infection. REFERENCES Beaver PC Jung RC Cupp EW. Clinical Parasitology. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 1984: 740 pp. Codex Alimentarius Commission Guidelines for the Application of the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point System. Alinorm 93113,Joint FAOIWHO Food Standards Programme, Rome, Dixon BR, Flohr RB. Fish-and shellfish-borne trematode infections in Canada. Paper presented at the Second Seminar on Food-borne Parasitic Zoonoses: Current Problems, Epidemiology, Food Safety and Control, Khon, Kaen, Thailand, 6-9 December, Greenberg AE, Clesent LS, Eaton AD. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 18th ed, Jongsuksuntigul P, Imsomboon T. The impact of a decade long opisthorchiasis control program in Northeast Thailand. Paper presented at the "2nd Seminar on Food-borne Parasitic Zoonoses: Current problems, epidemiology, food safety and control. Khon Kaen, Thailand, 6-9 Dec, Jongsuksuntigul P, Imsomboon T. Epidemiology and control of opisthorchiasis in Thailand. Working paper prepared for the WHO Study Group on the Control of Food-Borne Trematode Infections, WHO, Manila, Philippines, October, Kaewvichit R, Wongworapat K, Kobayashi J, Sato Y, Khamboonruang C. Prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Cooperative study on seroepidemiology and pathogenesis of viral and parasitical diseases in Okinawa, Japan and Thailand. Project N , Research Institute on Health Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, University of Chiang Mai, Chiang Mai, Thailand 1993; (Unpulished). Khamboonruang C. Present status of food-borne trematode infections in Thailand. Working paper prepared for the WHO Study Group on the Control of Food-Borne Trematode Infections, WHO, Manila, Philippines, October, Lima dos Santos CAM. The possible use of HACCP for the prevention and control of food-borne trematodes in cultured fish. INFOFlSH Int, No. 2/95: Malek EA. Medical Malacology. Burgess Publishing Co, Minneapolis, USA 1962: 106 pp. Richie LS. An ether sedimentation technique for routine stool examination. Bull. US Army Med Dept 1948; N 8: 326 SEAMEO- TROPMED. Liver fluke infection (Thailand). Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Bangkok (1988). WHO Control of Foodbome Trematode Infections. Report of a WHO Study Group. WHO Technical Report Ser 1995; 849: 157pp. WHO Health guidelines for the use of wastewater in agriculture and aquaculture. Report of a WHO Scientific Group. WHO Tech Rep Ser 1989;
Opisthorchis viverrini infection in minute intestinal fluke endemic areas of Chiang Mai Province, Thailand
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 3 No. 2 April 2009;187-191 Brief communication (original) Opisthorchis viverrini infection in minute intestinal fluke endemic areas of Chiang Mai Province, Thailand Choosak Nithikathkul
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 3 No. 2 April 2009;187-191 Brief communication (original) Opisthorchis viverrini infection in minute intestinal fluke endemic areas of Chiang Mai Province, Thailand Choosak Nithikathkul
INTRODUCTION. Liver fluke infection, opisthorchiasis in humans, is a major public health problem in the Greater Mekong sub-region
 PREVLENCE AND RISK FACTORS FOR OPISTHORCHIS VIVERRINI INFECTION AMONG CATS AND DOGS IN SIX DISTRICTS SURROUNDING THE UBOLRATANA DAM, AN ENDEMIC AREA FOR HUMAN OPISTHORCHIASIS IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND Surasit
PREVLENCE AND RISK FACTORS FOR OPISTHORCHIS VIVERRINI INFECTION AMONG CATS AND DOGS IN SIX DISTRICTS SURROUNDING THE UBOLRATANA DAM, AN ENDEMIC AREA FOR HUMAN OPISTHORCHIASIS IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND Surasit
COPRO-DIAGNOSIS OF HAPLORCHIS TAICHUI INFECTION USING SEDIMENTATION AND PCR-BASED METHODS
 COPRO-DIAGNOSIS OF HAPLORCHIS TAICHUI INFECTION USING SEDIMENTATION AND PCR-BASED METHODS Chalobol Wongsawad, Pheravut Wongsawad, Suksan Chuboon and Somboon Anuntalabhochai Department of Biology, Faculty
COPRO-DIAGNOSIS OF HAPLORCHIS TAICHUI INFECTION USING SEDIMENTATION AND PCR-BASED METHODS Chalobol Wongsawad, Pheravut Wongsawad, Suksan Chuboon and Somboon Anuntalabhochai Department of Biology, Faculty
CONFIRMATION STATUS OF HELMINTHIASIS IN LOW RISK AREAS IN CENTRAL THAILAND
 CONFIRMATION STATUS OF HELMINTHIASIS IN LOW RISK AREAS IN CENTRAL THAILAND Ampas Wisetmora *1,2, Duangduen Krailas 2, Choosak Nithikethkul 3,Wanchai Phatihattakorn 4, Opart Karnkawinpong 1, Thitima Wongsaroj
CONFIRMATION STATUS OF HELMINTHIASIS IN LOW RISK AREAS IN CENTRAL THAILAND Ampas Wisetmora *1,2, Duangduen Krailas 2, Choosak Nithikethkul 3,Wanchai Phatihattakorn 4, Opart Karnkawinpong 1, Thitima Wongsaroj
Opisthorchis viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinoid Fish from Three Rivers in Khammouane Province, Lao PDR
 J Trop Med Parasitol. 2009;32:23-9. Original Article Available online at www.ptat.thaigov.net Opisthorchis viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinoid Fish from Three Rivers in Khammouane Province, Lao PDR Khemphavanh
J Trop Med Parasitol. 2009;32:23-9. Original Article Available online at www.ptat.thaigov.net Opisthorchis viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinoid Fish from Three Rivers in Khammouane Province, Lao PDR Khemphavanh
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
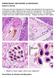 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 54-year-old man originally from Vietnam was admitted to the hospital for complaints of upper abdominal pain and liver enlargement. The bile
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 54-year-old man originally from Vietnam was admitted to the hospital for complaints of upper abdominal pain and liver enlargement. The bile
Stitaya Sirisinha, Runglawan Chawengkirttikul.and. Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University, Bangkok 10400, Thailand.
 Stitaya Sirisinha, Runglawan Chawengkirttikul.and Rasana Sennswan Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University, Bangkok 10400, Thailand. Abstract. Monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked
Stitaya Sirisinha, Runglawan Chawengkirttikul.and Rasana Sennswan Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University, Bangkok 10400, Thailand. Abstract. Monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked
European Union comments
 15/10/2015 General comments FINAL European Union comments CODEX COMMITTEE ON FOOD HYGIENE Forty-seventh Session Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America, 9 13 November 2015 Agenda Item 5: Proposed
15/10/2015 General comments FINAL European Union comments CODEX COMMITTEE ON FOOD HYGIENE Forty-seventh Session Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America, 9 13 November 2015 Agenda Item 5: Proposed
Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica.
 TREMATODES: INTRODUCTION: Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica. The life cycle of trematodes involves a sexual cycle in humans and asexual reproduction in freshwater snails (intermediate
TREMATODES: INTRODUCTION: Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica. The life cycle of trematodes involves a sexual cycle in humans and asexual reproduction in freshwater snails (intermediate
OVERVIEW OF FOOD SAFETY REGULATION IN THE UNITED STATES. Presented By William C. Balek International Sanitary Supply Association March 30, 2001
 OVERVIEW OF FOOD SAFETY REGULATION IN THE UNITED STATES Presented By William C. Balek International Sanitary Supply Association March 30, 2001 I INTRODUCTION The regulation of food safety in the United
OVERVIEW OF FOOD SAFETY REGULATION IN THE UNITED STATES Presented By William C. Balek International Sanitary Supply Association March 30, 2001 I INTRODUCTION The regulation of food safety in the United
BIOTECHNOLOGY Vol. IX - Molecular Tools for Improving Seafood Safety - Karunasagar, Iddya MOLECULAR TOOLS FOR IMPROVING SEAFOOD SAFETY
 MOLECULAR TOOLS FOR IMPROVING SEAFOOD SAFETY Karunasagar, Iddya University of Agricultural Sciences, College of Fisheries, Mangalore, India Keywords: Seafood, aquaculture, pathogens, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio
MOLECULAR TOOLS FOR IMPROVING SEAFOOD SAFETY Karunasagar, Iddya University of Agricultural Sciences, College of Fisheries, Mangalore, India Keywords: Seafood, aquaculture, pathogens, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio
FDA Foodborne Illness Risk Factor Study Data Collection Form
 APPENDIX O 2105 Data Collection Wake County Facility ID# Sample # QA FDA Foodborne Illness Risk Factor Study Data Collection Form Date: Time In: Time Out: Inspector: Establishment: Manager: Physical Address:
APPENDIX O 2105 Data Collection Wake County Facility ID# Sample # QA FDA Foodborne Illness Risk Factor Study Data Collection Form Date: Time In: Time Out: Inspector: Establishment: Manager: Physical Address:
INTESTINAL HELMINTHIC INFECTIONS IN SCHOOLCHILDREN IN CAMBODIA
 INTESTINAL HELMINTHIC INFECTIONS IN SCHOOLCHILDREN IN CAMBODIA Muth Sinuon 1, Malinee T Anantaphruti 2 and Doung Socheat 1 1 National Center for Parasitology, Entomology and Malaria Control, Pnom Penh,
INTESTINAL HELMINTHIC INFECTIONS IN SCHOOLCHILDREN IN CAMBODIA Muth Sinuon 1, Malinee T Anantaphruti 2 and Doung Socheat 1 1 National Center for Parasitology, Entomology and Malaria Control, Pnom Penh,
A COLLABORATIVE NATIONAL STRATEGY TO MANAGE FERAL SWINE IMPACTS IN THE U.S.
 A COLLABORATIVE NATIONAL STRATEGY TO MANAGE FERAL SWINE IMPACTS IN THE U.S. National Association of Conservation Districts Annual Meeting January 31, 2017 USDA APHIS National Feral Swine Program Wendy
A COLLABORATIVE NATIONAL STRATEGY TO MANAGE FERAL SWINE IMPACTS IN THE U.S. National Association of Conservation Districts Annual Meeting January 31, 2017 USDA APHIS National Feral Swine Program Wendy
Paragonimiasis in Kasy District Vientiane Province, Lao PDR
 Paragonimiasis in Kasy District Vientiane Province, Lao PDR Present by: Youthanavanh VONGHACHACK, MD ( MSc. TropMed student ) Department of Helminthology, Faculty of Tropical Medicine Mahidol University
Paragonimiasis in Kasy District Vientiane Province, Lao PDR Present by: Youthanavanh VONGHACHACK, MD ( MSc. TropMed student ) Department of Helminthology, Faculty of Tropical Medicine Mahidol University
TECHNICAL REPORT ECDC SCIENTIFIC ADVICE
 TECHNICAL REPORT ECDC SCIENTIFIC ADVICE Health advice for people living in or travelling to countries where the A/H5N1 virus has been detected Version April 2006 www.ecdc.eu.int Health advice for people
TECHNICAL REPORT ECDC SCIENTIFIC ADVICE Health advice for people living in or travelling to countries where the A/H5N1 virus has been detected Version April 2006 www.ecdc.eu.int Health advice for people
HOUSEFLIES WITH HELMINTHIC OBJECTS, GOOD INDICATOR OF AN UNSANITARY ENVIRONMENT
 HOUSEFLIES WITH HELMINTHIC OBJECTS, GOOD INDICATOR OF AN UNSANITARY ENVIRONMENT Wanna Maipanich, Paron Dekumyoy, Surapol Sa-nguankiat, Somchit Pubampen, Akkarin Poodeepiyasawat, Teera Kusolsuk, Urusa Thaenkham,
HOUSEFLIES WITH HELMINTHIC OBJECTS, GOOD INDICATOR OF AN UNSANITARY ENVIRONMENT Wanna Maipanich, Paron Dekumyoy, Surapol Sa-nguankiat, Somchit Pubampen, Akkarin Poodeepiyasawat, Teera Kusolsuk, Urusa Thaenkham,
Disease and Environment: Implications of Clonorchiasis Infection in Taiwan and Mainland China
 Disease and Environment: Implications of Clonorchiasis Infection in Taiwan and Mainland China Ts ui-jung Liu with Maps charted by Yu-ting Lee Institute of Taiwan History Academia Sinica Paper prepared
Disease and Environment: Implications of Clonorchiasis Infection in Taiwan and Mainland China Ts ui-jung Liu with Maps charted by Yu-ting Lee Institute of Taiwan History Academia Sinica Paper prepared
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 5, May ISSN Parasitological contamination
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 5, May-2016 885 Parasitological Contamination of Some Common Consumable Farm Produce in Dekina Kogi State, Nigeria Omowaye,.
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 5, May-2016 885 Parasitological Contamination of Some Common Consumable Farm Produce in Dekina Kogi State, Nigeria Omowaye,.
Simplified Techniques for Killing the Carcinogenic, Opisthorchis Viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinid Fish
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.6.1507 RESEARCH ARTICLE Simplified Techniques for Killing the Carcinogenic, Opisthorchis Viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinid Fish Panupan Sripan 1,2,3, Thidarut Boonmars 1,2,3
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.6.1507 RESEARCH ARTICLE Simplified Techniques for Killing the Carcinogenic, Opisthorchis Viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinid Fish Panupan Sripan 1,2,3, Thidarut Boonmars 1,2,3
21 Oct F. Kasuga
 Risk Assessment & Risk Management Activities in Japan Fumiko Kasuga National Institute of Health Sciences, Japan Today s topics Risk management activities for food safety in Japan Risk analysis framework
Risk Assessment & Risk Management Activities in Japan Fumiko Kasuga National Institute of Health Sciences, Japan Today s topics Risk management activities for food safety in Japan Risk analysis framework
How to prevent transmission to/from domestic pigs
 Workshop on African swine fever management in wild boar surveillance and prevention of transmission to/from domestic pigs How to prevent transmission to/from domestic pigs Marius Masiulis FAO international
Workshop on African swine fever management in wild boar surveillance and prevention of transmission to/from domestic pigs How to prevent transmission to/from domestic pigs Marius Masiulis FAO international
Introduction. Future U.S. initiatives regarding the food safety for fresh produce. FoodNet Partners. FoodNet Partners
 Introduction Future U.S. initiatives regarding the food safety for fresh produce This presentation is based upon FDA s testimony about the E. coli outbreaks to the U.S. Congress delivered on November 15,
Introduction Future U.S. initiatives regarding the food safety for fresh produce This presentation is based upon FDA s testimony about the E. coli outbreaks to the U.S. Congress delivered on November 15,
Essential Medicines. WHO
 12 Health Technology and Pharmaceuticals Participants to the Workshop on Pharmaceutical Policies and Access to Good Quality Essential Medicines for Pacific Island Countries observing pharmaceutical services
12 Health Technology and Pharmaceuticals Participants to the Workshop on Pharmaceutical Policies and Access to Good Quality Essential Medicines for Pacific Island Countries observing pharmaceutical services
ACCESS TO EC MARKET REQUIREMENTS TO FACILITIES BLATERAL NEGOTIATIONS ON ISSUES OF SANITARY AND PHYTO-SANITARY MEASURES
 ACCESS TO EC MARKET REQUIREMENTS TO FACILITIES BLATERAL NEGOTIATIONS ON ISSUES OF SANITARY AND PHYTO-SANITARY MEASURES BASHINSKY VITALY BISHKEK 2016 WHY COUNTRIES APPLY RESTRICTIVE AND PROTECTION MEASURES?
ACCESS TO EC MARKET REQUIREMENTS TO FACILITIES BLATERAL NEGOTIATIONS ON ISSUES OF SANITARY AND PHYTO-SANITARY MEASURES BASHINSKY VITALY BISHKEK 2016 WHY COUNTRIES APPLY RESTRICTIVE AND PROTECTION MEASURES?
Agenda Item 14 CX/FFP 12/32/14
 E Agenda Item 14 CX/FFP 12/32/14 JOINT FAO/WHO FOOD STANDARDS PROGRAMME CODEX COMMITTEE ON FISH AND FISHERY PRODUCTS Thirty-Second Session Bali, Indonesia 1 5 October 2012 DISCUSSION PAPER HISTAMINE Prepared
E Agenda Item 14 CX/FFP 12/32/14 JOINT FAO/WHO FOOD STANDARDS PROGRAMME CODEX COMMITTEE ON FISH AND FISHERY PRODUCTS Thirty-Second Session Bali, Indonesia 1 5 October 2012 DISCUSSION PAPER HISTAMINE Prepared
Draft of the Rome Declaration on Nutrition
 Draft of the Rome Declaration on Nutrition 1. We, Ministers and Plenipotentiaries of the Members of the World Health Organization and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, assembled
Draft of the Rome Declaration on Nutrition 1. We, Ministers and Plenipotentiaries of the Members of the World Health Organization and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, assembled
TIP SHEET 17 ALLERGEN MANAGEMENT APPLICABLE CODE ELEMENT(S) LEARNING OBJECTIVES O CONTROL AND PREVENT THE SOURCES OF ALLERGENS O 2.8.
 ALLERGEN MANAGEMENT Food allergies affect a small but growing proportion of the population. They are most common in children, although some can be life-long, and can cause mild to severe and sometimes
ALLERGEN MANAGEMENT Food allergies affect a small but growing proportion of the population. They are most common in children, although some can be life-long, and can cause mild to severe and sometimes
CODEX and the European Union s food safety policy
 CODEX and the European Union s food safety policy Mike van Schothorst ABRAPA 1 Purpose of lecture introduce the Risk Analysis framework show its importance for international trade make the link with Codex
CODEX and the European Union s food safety policy Mike van Schothorst ABRAPA 1 Purpose of lecture introduce the Risk Analysis framework show its importance for international trade make the link with Codex
Why Bio Security is Essential in the Ornamental Fish Industry, and How to Implement it Danny Benjamin Hazorea Aquatics Kibbutz Hazorea, Israel
 Why Bio Security is Essential in the Ornamental Fish Industry, and How to Implement it Danny Benjamin Hazorea Aquatics Kibbutz Hazorea, Israel 2 nd International Ornamental Fish Trade and Technical Conference
Why Bio Security is Essential in the Ornamental Fish Industry, and How to Implement it Danny Benjamin Hazorea Aquatics Kibbutz Hazorea, Israel 2 nd International Ornamental Fish Trade and Technical Conference
Brief Survey of Common Intestinal Parasites in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area. Tsukasa NOZAKI1), Kouichi NAGAKURA2)*, Hisae FUSEGAWA3)
 Brief Survey of Common Intestinal Parasites in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area Tsukasa NOZAKI1), Kouichi NAGAKURA2)*, Hisae FUSEGAWA3) and Yasuhiko AND01),3) 1) Central Clinical Laboratoly, Tokai University
Brief Survey of Common Intestinal Parasites in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area Tsukasa NOZAKI1), Kouichi NAGAKURA2)*, Hisae FUSEGAWA3) and Yasuhiko AND01),3) 1) Central Clinical Laboratoly, Tokai University
Final Rules Preventive Controls for Human Food Preventive Controls for Animal Food
 Final Rules Preventive Controls for Human Food Preventive Controls for Animal Food http://www.fda.gov/fsma THE FUTURE IS NOW 1 Current Good Manufacturing Practice, Hazard Analysis, and Risk-Based Preventive
Final Rules Preventive Controls for Human Food Preventive Controls for Animal Food http://www.fda.gov/fsma THE FUTURE IS NOW 1 Current Good Manufacturing Practice, Hazard Analysis, and Risk-Based Preventive
Giardiasis Surveillance Protocol
 Provider Responsibilities 1. Report all cases to your local health department by completing the provider section of the WVEDSS form within the timeframe indicated: Sporadic case of - should be reported
Provider Responsibilities 1. Report all cases to your local health department by completing the provider section of the WVEDSS form within the timeframe indicated: Sporadic case of - should be reported
Implementation of indicators for biological hazards by meat inspection of poultry
 Implementation of indicators for biological hazards by meat inspection of poultry Ellerbroek, L. Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR), Diedersdorfer Weg 1, D-12277 Berlin, Germany. *Corresponding
Implementation of indicators for biological hazards by meat inspection of poultry Ellerbroek, L. Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR), Diedersdorfer Weg 1, D-12277 Berlin, Germany. *Corresponding
Appendix A: Disease-Specific Chapters
 Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix A: Disease-Specific Chapters Chapter: Giardiasis Revised Giardiasis Communicable Virulent Health Protection and Promotion Act: Ontario Regulation 558/91 Specification
Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix A: Disease-Specific Chapters Chapter: Giardiasis Revised Giardiasis Communicable Virulent Health Protection and Promotion Act: Ontario Regulation 558/91 Specification
A COLLABORATIVE NATIONAL STRATEGY TO MANAGE FERAL SWINE IMPACTS IN THE U.S.
 A COLLABORATIVE NATIONAL STRATEGY TO MANAGE FERAL SWINE IMPACTS IN THE U.S. Restore America s Estuaries Summit Invasive Species Workshop December 15, 2016 USDA APHIS National Feral Swine Program Wendy
A COLLABORATIVE NATIONAL STRATEGY TO MANAGE FERAL SWINE IMPACTS IN THE U.S. Restore America s Estuaries Summit Invasive Species Workshop December 15, 2016 USDA APHIS National Feral Swine Program Wendy
Report of the WHO Expert Consultation on Foodborne Trematode Infections and Taeniasis/Cysticercosis
 Report of the WHO Expert Consultation on Foodborne Trematode Infections and Taeniasis/Cysticercosis Vientiane, Lao People's Democratic Republic 12-16 October 2009 World Health Organization 2011 All rights
Report of the WHO Expert Consultation on Foodborne Trematode Infections and Taeniasis/Cysticercosis Vientiane, Lao People's Democratic Republic 12-16 October 2009 World Health Organization 2011 All rights
Action Plan of China Malaria Elimination ( ) Page 2
 http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/att/att/site1/20100526/001e3741a2cc0d67233801.doc Action Plan of China Malaria Elimination (2010 2020) Malaria is a major parasitic disease, which imposes serious threat to people
http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/att/att/site1/20100526/001e3741a2cc0d67233801.doc Action Plan of China Malaria Elimination (2010 2020) Malaria is a major parasitic disease, which imposes serious threat to people
ISPM No. 9 GUIDELINES FOR PEST ERADICATION PROGRAMMES (1998)
 ISPM No. 9 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES ISPM No. 9 GUIDELINES FOR PEST ERADICATION PROGRAMMES (1998) Produced by the Secretariat of the International Plant Protection Convention FAO
ISPM No. 9 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES ISPM No. 9 GUIDELINES FOR PEST ERADICATION PROGRAMMES (1998) Produced by the Secretariat of the International Plant Protection Convention FAO
Alberta Food Banks Together We Are Stronger
 FOOD SAFETY GUIDELINES Each year millions of dollars of donated food is distributed by Food Banks 1 across Alberta. Food Banks have become an essential service by providing nutritional food to people in
FOOD SAFETY GUIDELINES Each year millions of dollars of donated food is distributed by Food Banks 1 across Alberta. Food Banks have become an essential service by providing nutritional food to people in
Food Consumption Data in Microbiological Risk Assessment
 1972 Journal of Food Protection, Vol. 67, No. 9, 2004, Pages 1972 1976 Copyright, International Association for Food Protection Food Consumption Data in Microbiological Risk Assessment LEILA M. BARRAJ*
1972 Journal of Food Protection, Vol. 67, No. 9, 2004, Pages 1972 1976 Copyright, International Association for Food Protection Food Consumption Data in Microbiological Risk Assessment LEILA M. BARRAJ*
APEC Ministerial Meeting on Avian and Influenza Pandemics Da Nang, Viet Nam, 4-6 May 2006
 APEC Ministerial Meeting on Avian and Influenza Pandemics Da Nang, Viet Nam, 4-6 May 2006 APEC Action Plan on the Prevention and Response to Avian and Influenza Pandemics 1. Many APEC economies have been
APEC Ministerial Meeting on Avian and Influenza Pandemics Da Nang, Viet Nam, 4-6 May 2006 APEC Action Plan on the Prevention and Response to Avian and Influenza Pandemics 1. Many APEC economies have been
HALAL FOOD AND SAFETY COMPLIANCE AGROASIA 2011 HALAL INDUSTRY RESEARCH CENTRE
 HALAL FOOD AND SAFETY COMPLIANCE AGROASIA 2011 July 2010 Page 1 Revolutionizing Assistance in the disposal Industry of in Prime a Shariah Liquid Compliant Emulsion way Industries! Halal Industry Research
HALAL FOOD AND SAFETY COMPLIANCE AGROASIA 2011 July 2010 Page 1 Revolutionizing Assistance in the disposal Industry of in Prime a Shariah Liquid Compliant Emulsion way Industries! Halal Industry Research
Food Safety Modernization Act - Impacts on the Grain and Feed Industry
 Food Safety Modernization Act - Impacts on the Grain and Feed Industry NGFA 117th Annual Meeting and Convention March 17, 2013 San Francisco, California David Fairfield, NGFA Vice President of Feed Services
Food Safety Modernization Act - Impacts on the Grain and Feed Industry NGFA 117th Annual Meeting and Convention March 17, 2013 San Francisco, California David Fairfield, NGFA Vice President of Feed Services
HAZARD ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP) SYSTEM
 The HACCP Inspection/Food Audit HAZARD ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP) SYSTEM The HACCP system was originally designed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and is used by
The HACCP Inspection/Food Audit HAZARD ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP) SYSTEM The HACCP system was originally designed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and is used by
A CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY OF INTESTINAL PARASITIC INFECTIONS AMONG SCHOOLCHILDREN IN NAN PROVINCE, NORTHERN THAILAND
 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH A CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY OF INTESTINAL PARASITIC INFECTIONS AMONG SCHOOLCHILDREN IN NAN PROVINCE, NORTHERN THAILAND J Waikagul 1, S Krudsood 2, P Radomyos 3, B Radomyos
SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH A CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY OF INTESTINAL PARASITIC INFECTIONS AMONG SCHOOLCHILDREN IN NAN PROVINCE, NORTHERN THAILAND J Waikagul 1, S Krudsood 2, P Radomyos 3, B Radomyos
Editorial Process: Submission:06/22/2018 Acceptance:08/13/2018
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.9.2673 Health Behavior Modification Program for Liver Fluke Prevention among the Risk Group RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:06/22/2018 Acceptance:08/13/2018 The
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.9.2673 Health Behavior Modification Program for Liver Fluke Prevention among the Risk Group RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:06/22/2018 Acceptance:08/13/2018 The
Many of you asked about this topic
 Many of you asked about this topic Water borne disease: The largest water quality problem in developing countries. CEE 3510 Environmental Quality Engineering According to: Chemical and Engineering News
Many of you asked about this topic Water borne disease: The largest water quality problem in developing countries. CEE 3510 Environmental Quality Engineering According to: Chemical and Engineering News
Surveillance and early warning systems for climate sensitive diseases in Vietnam and Laos
 Surveillance and early warning systems for climate sensitive diseases in Vietnam and Laos Hu Suk Lee Workshop on climate change and health Hanoi, Vietnam, 23 November 2015 Outline Introduction of Pestforecast
Surveillance and early warning systems for climate sensitive diseases in Vietnam and Laos Hu Suk Lee Workshop on climate change and health Hanoi, Vietnam, 23 November 2015 Outline Introduction of Pestforecast
OIE/FAO International Scientific Conference on Avian Influenza OIE Paris, France, 7 8 April 2005 RECOMMENDATIONS
 CONSIDERING THAT: 1. Preventing the spread of pathogens through international trade in animals and animal products is one of the primary missions of the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE). This
CONSIDERING THAT: 1. Preventing the spread of pathogens through international trade in animals and animal products is one of the primary missions of the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE). This
FOOD-BORNE TREMATODE INFECTIONS IN ASIA
 REPORT JOINT WHO/FAO WORKSHOP ON FOOD-BORNE TREMATODE INFECTIONS IN ASIA Ha Noi, Viet Nam 26-28 November 2002 World Health Organization Regional office for the Western Pacific (WP)MVP/ICP/MVP/1.2/001-E
REPORT JOINT WHO/FAO WORKSHOP ON FOOD-BORNE TREMATODE INFECTIONS IN ASIA Ha Noi, Viet Nam 26-28 November 2002 World Health Organization Regional office for the Western Pacific (WP)MVP/ICP/MVP/1.2/001-E
Foodborne diseases: an ongoing global challenge
 Foodborne diseases: an ongoing global challenge Arie Havelaar GLOBALG.A.P. Summit 2016 Amsterdam, September 27-28, 2016 Outline WHO estimates of the global burden of foodborne disease Regional differences
Foodborne diseases: an ongoing global challenge Arie Havelaar GLOBALG.A.P. Summit 2016 Amsterdam, September 27-28, 2016 Outline WHO estimates of the global burden of foodborne disease Regional differences
White Spot Disease in Mozambique
 White Spot Disease in Mozambique Experiences and lessons learned A.P. BALOI (1), M. LE GROUMELLEC (2) (1) Ministry of Fisheries, National Institute for Fish Inspection, Mozambique. (2) OIE Consultant on
White Spot Disease in Mozambique Experiences and lessons learned A.P. BALOI (1), M. LE GROUMELLEC (2) (1) Ministry of Fisheries, National Institute for Fish Inspection, Mozambique. (2) OIE Consultant on
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #82 (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #82 (Lynne S. Garcia) ***Reminder: Slides are copyrighted and cannot be copied for publication. A 57 year old male was seen at a local clinic with a year-long history of productive
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #82 (Lynne S. Garcia) ***Reminder: Slides are copyrighted and cannot be copied for publication. A 57 year old male was seen at a local clinic with a year-long history of productive
PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION
 PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Parasite means : one who eats at the table of another. Differs from bacteria and viruses in their complex life cycles, intermediate hosts and chronicity. Evolved to
PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Parasite means : one who eats at the table of another. Differs from bacteria and viruses in their complex life cycles, intermediate hosts and chronicity. Evolved to
Commercial Processing Example: Pickled Herring
 Commercial Processing Example: Pickled Herring National Seafood HACCP Alliance for Training and Education Example: For Illustrative Purposes Only. Models are based in current guidance contained in FDA
Commercial Processing Example: Pickled Herring National Seafood HACCP Alliance for Training and Education Example: For Illustrative Purposes Only. Models are based in current guidance contained in FDA
Availability of safe drinking-water: the answer to cholera outbreak? Nabua, Camarines Sur, Philippines, 2012
 Outbreak Investigation Report Availability of safe drinking-water: the answer to cholera outbreak? Nabua, Camarines Sur, Philippines, 2012 Alethea De Guzman, ab Vikki Carr de los Reyes, b Ma Nemia Sucaldito
Outbreak Investigation Report Availability of safe drinking-water: the answer to cholera outbreak? Nabua, Camarines Sur, Philippines, 2012 Alethea De Guzman, ab Vikki Carr de los Reyes, b Ma Nemia Sucaldito
Measures to control Avian Influenza and Pandemic Preparedness in Vietnam
 Measures to control Avian Influenza and Pandemic Preparedness in Vietnam MEETING ON AVIAN INFLUENZA & HUMAN PANDEMIC INFLUENZA Geneva, 7-9 November 2005 Dr. Bui Ba Bong Vice-Minister Ministry of Agriculture
Measures to control Avian Influenza and Pandemic Preparedness in Vietnam MEETING ON AVIAN INFLUENZA & HUMAN PANDEMIC INFLUENZA Geneva, 7-9 November 2005 Dr. Bui Ba Bong Vice-Minister Ministry of Agriculture
Giardiasis. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Case Definition... Error! Bookmark not defined. Reporting Requirements... 2 Etiology... Error! Bookmark not defined. Clinical Presentation... Error! Bookmark not defined. Diagnosis...
Table of Contents Case Definition... Error! Bookmark not defined. Reporting Requirements... 2 Etiology... Error! Bookmark not defined. Clinical Presentation... Error! Bookmark not defined. Diagnosis...
Avian Influenza situation in Cambodia
 General Directorate of Animal Health and Production Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Avian Influenza situation in Cambodia Avian Health Workshop July 17-19, 2018, University of Japan Dr.
General Directorate of Animal Health and Production Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Avian Influenza situation in Cambodia Avian Health Workshop July 17-19, 2018, University of Japan Dr.
Vibrio Cholerae (non-o1, non-o139)
 August 2011 Vibrio Cholerae (non-o1, non-o139) Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011
August 2011 Vibrio Cholerae (non-o1, non-o139) Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011
Escherichia coli Verotoxigenic Infections
 Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Epidemiology/Public Health Management March 2011 May 2018 March 2011 Includes O157:H7 Case Definition Confirmed Case Laboratory confirmation of infection
Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Epidemiology/Public Health Management March 2011 May 2018 March 2011 Includes O157:H7 Case Definition Confirmed Case Laboratory confirmation of infection
RISKS ASSESSMENT IN ROMANIAN FOOD SAFETY SYSTEMS: OPPORTUNITIES AND CONSTRAINS. Abstract
 N. Sava, et all. Journal of Agroalimentary Processes and Technologies, Volume XIII, No.1 (2007), 69-76 Review Food Control RISKS ASSESSMENT IN ROMANIAN FOOD SAFETY SYSTEMS: OPPORTUNITIES AND CONSTRAINS
N. Sava, et all. Journal of Agroalimentary Processes and Technologies, Volume XIII, No.1 (2007), 69-76 Review Food Control RISKS ASSESSMENT IN ROMANIAN FOOD SAFETY SYSTEMS: OPPORTUNITIES AND CONSTRAINS
Guangzhou Pond Feeding Trial Demonstrates Channel Catfish Production with Soy-Based Feed
 Guangzhou Pond Feeding Trial Demonstrates Channel Catfish Production with Soy-Based Feed INTRODUCTION Michael C. Cremer, Zhou Enhua and Zhang Jian ASA-IM/China Aquaculture Program A feeding trial was conducted
Guangzhou Pond Feeding Trial Demonstrates Channel Catfish Production with Soy-Based Feed INTRODUCTION Michael C. Cremer, Zhou Enhua and Zhang Jian ASA-IM/China Aquaculture Program A feeding trial was conducted
Parasitology Questions. Choose the best correct answer in the following statements
 Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
European Community comments ON PROPOSED DRAFT CCFFP STANDARDS AND CODE (OTHER SECTIONS) AT STEP 3 - (CL 2005/14-FFP)
 20 December 2005 European Community comments ON PROPOSED DRAFT CCFFP STANDARDS AND CODE (OTHER SECTIONS) AT STEP 3 - (CL 2005/14-FFP) Point 6: Proposed Draft Standard for Quick Frozen Scallop Adductor
20 December 2005 European Community comments ON PROPOSED DRAFT CCFFP STANDARDS AND CODE (OTHER SECTIONS) AT STEP 3 - (CL 2005/14-FFP) Point 6: Proposed Draft Standard for Quick Frozen Scallop Adductor
Q Fever among Dairy Cattle in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand, 2012: A Preliminary Study
 Q Fever among Dairy Cattle in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand, 2012: A Preliminary Study Pranee Rodtian 1, *, Nuamjit M 1, Srijan M 2, Opaschaitat P 3, Ekgatat M 3 1 Fifth Regional Livestock Office, Chiang
Q Fever among Dairy Cattle in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand, 2012: A Preliminary Study Pranee Rodtian 1, *, Nuamjit M 1, Srijan M 2, Opaschaitat P 3, Ekgatat M 3 1 Fifth Regional Livestock Office, Chiang
IUF Briefing Paper: Avian Influenza (H5N1) and Agricultural Workers October 2005
 IUF Briefing Paper: Avian Influenza (H5N1) and Agricultural Workers October 2005 I believe that the momentum that is now building up will give us a chance to change the course of history and head off a
IUF Briefing Paper: Avian Influenza (H5N1) and Agricultural Workers October 2005 I believe that the momentum that is now building up will give us a chance to change the course of history and head off a
Listeria monocytogenes in Food Plants with emphasis on Cold-Smoked Salmon Plants & Dairies. Presented by Rebecca Robertson January 19, 2009
 Listeria monocytogenes in Food Plants with emphasis on Cold-Smoked Salmon Plants & Dairies Presented by Rebecca Robertson January 19, 2009 Introduction Why are we so concerned with Listeria monocytogenes?
Listeria monocytogenes in Food Plants with emphasis on Cold-Smoked Salmon Plants & Dairies Presented by Rebecca Robertson January 19, 2009 Introduction Why are we so concerned with Listeria monocytogenes?
SECOND FAO/OIE REGIONAL MEETING ON AVIAN INFLUENZA CONTROL IN ASIA Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, February 2005
 SECOND FAO/OIE REGIONAL MEETING ON AVIAN INFLUENZA CONTROL IN ASIA Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 23-25 February 2005 OIE Address for the Opening Session (Dr T. Fujita, OIE Representative, OIE Regional Representation
SECOND FAO/OIE REGIONAL MEETING ON AVIAN INFLUENZA CONTROL IN ASIA Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 23-25 February 2005 OIE Address for the Opening Session (Dr T. Fujita, OIE Representative, OIE Regional Representation
THE HYGIENE PACKAGE A NEW APPROACH TO FOOD SAFETY
 24 THE HYGIENE PACKAGE A NEW APPROACH TO FOOD SAFETY Dwinger, R. H., Golden, T. E., Hatakka, M. and Daelman, W. European Commission, Health and Consumer Protection Directorate-General (DG SANCO), Unit
24 THE HYGIENE PACKAGE A NEW APPROACH TO FOOD SAFETY Dwinger, R. H., Golden, T. E., Hatakka, M. and Daelman, W. European Commission, Health and Consumer Protection Directorate-General (DG SANCO), Unit
Risk Analysis Activity APPENDIX 19. Consumer. Since 2003, Food Safety Policy and implementation have been campaigned in Thailand
 Since 2003, Safety Policy and implementation have been campaigned Mr. Mongkol Chenchittikul Director of Bureau of Quality and Safety of Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Pubic Health, Thailand
Since 2003, Safety Policy and implementation have been campaigned Mr. Mongkol Chenchittikul Director of Bureau of Quality and Safety of Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Pubic Health, Thailand
ASF cases and outbreaks in Poland
 ASF cases and outbreaks in Poland Since SGE1 meeting 13 cases (22-34) of ASF in wild boar and 1 outbreak (3 rd ) of ASF in pigs have been detected in Poland. Those events occurred in the same area as previous
ASF cases and outbreaks in Poland Since SGE1 meeting 13 cases (22-34) of ASF in wild boar and 1 outbreak (3 rd ) of ASF in pigs have been detected in Poland. Those events occurred in the same area as previous
CHAPTER 4: DISEASES SPREAD BY FOOD AND WATER
 CHAPTER 4: DISEASES SPREAD BY FOOD AND WATER Highlights The incidence of diseases spread by food and water was generally higher in Peel than Ontario with the exceptions of hepatitis A and verotoxinproducing
CHAPTER 4: DISEASES SPREAD BY FOOD AND WATER Highlights The incidence of diseases spread by food and water was generally higher in Peel than Ontario with the exceptions of hepatitis A and verotoxinproducing
The power of information to prevent foodborne illness
 The power of information to prevent foodborne illness Craig Hedberg, PhD University of Minnesota, School of Public Health Decrease the burden of foodborne illness using improved techniques in detection,
The power of information to prevent foodborne illness Craig Hedberg, PhD University of Minnesota, School of Public Health Decrease the burden of foodborne illness using improved techniques in detection,
Inspection Report Item 29: Compliance with Variance, Specialized Process, Reduced Oxygen Packaging Criteria, and HACCP Plan
 Inspection Report Item 29: Compliance with Variance, Specialized Process, Reduced Oxygen Packaging Criteria, and HACCP Plan FDA Food Code References: 3-502.11, 3-502.12, 8-201.13, 8-201.14 Special Processes
Inspection Report Item 29: Compliance with Variance, Specialized Process, Reduced Oxygen Packaging Criteria, and HACCP Plan FDA Food Code References: 3-502.11, 3-502.12, 8-201.13, 8-201.14 Special Processes
Intestinal Helminthiases in Two Communities of Phitsanulok Province, Northern Thailand
 J Trop Med Parasitol. 2012;35:1-5. Original Article Available online at www.ptat.thaigov.net Intestinal Helminthiases in Two Communities of Phitsanulok Province, Northern Thailand Apichat Vitta, Raxsina
J Trop Med Parasitol. 2012;35:1-5. Original Article Available online at www.ptat.thaigov.net Intestinal Helminthiases in Two Communities of Phitsanulok Province, Northern Thailand Apichat Vitta, Raxsina
Food-borne zoonotic parasites: Recent developments
 Food-borne zoonotic parasites: Recent developments Stig M. Thamsborg Department of Veterinary Disease Biology, Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Copenhagen, Denmark Nguyen Thi Lan Anh, Parasitology
Food-borne zoonotic parasites: Recent developments Stig M. Thamsborg Department of Veterinary Disease Biology, Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Copenhagen, Denmark Nguyen Thi Lan Anh, Parasitology
An Integrated Control Strategy Takes Clonorchis sinensis Under Control in an Endemic Area in South China
 VECTOR-BORNE AND ZOONOTIC DISEASES Volume XX, Number XX, 2017 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/vbz.2017.2133 ORIGINAL ARTICLE An Integrated Control Strategy Takes Clonorchis sinensis Under Control
VECTOR-BORNE AND ZOONOTIC DISEASES Volume XX, Number XX, 2017 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/vbz.2017.2133 ORIGINAL ARTICLE An Integrated Control Strategy Takes Clonorchis sinensis Under Control
Blastocystosis. Blastocystis Research Foundation 5060 SW Philomath Blvd, #202 Corvallis, OR
 Blastocystosis Blastocystis Research Foundation 5060 SW Philomath Blvd, #202 Corvallis, OR 97333 851-572-9701 www.bhomcenter.org Blastocystosis (Blastocystis Infection) What is Blastocystosis? Blastocystosis
Blastocystosis Blastocystis Research Foundation 5060 SW Philomath Blvd, #202 Corvallis, OR 97333 851-572-9701 www.bhomcenter.org Blastocystosis (Blastocystis Infection) What is Blastocystosis? Blastocystosis
Dr. Tipvon Parinyasiri
 Dr. Tipvon Parinyasiri Director, Bureau of Food Thai Food and Drug Administration 28 January 2014, Faculty of Medicine Guideline Content of Presentation Roles and Responsibility of Thai FDA From Research
Dr. Tipvon Parinyasiri Director, Bureau of Food Thai Food and Drug Administration 28 January 2014, Faculty of Medicine Guideline Content of Presentation Roles and Responsibility of Thai FDA From Research
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Nopparat Songserm 1,2, Supannee Promthet 1 *, Surapon Wiangnon 3,4, Paiboon Sithithaworn 5,6. Abstract.
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Prevalence and Co-infection of Intestinal Parasites among Thai Rural Residents at High-risk of Developing Cholangiocarcinoma: A Cross-sectional Study in a Prospective Cohort Study Nopparat
RESEARCH ARTICLE Prevalence and Co-infection of Intestinal Parasites among Thai Rural Residents at High-risk of Developing Cholangiocarcinoma: A Cross-sectional Study in a Prospective Cohort Study Nopparat
Maintaining Food Safety and Quality to ensure Consumer Safety
 Maintaining Food Safety and Quality to ensure Consumer Safety Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) Masami Takeuchi, Ph.D. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
Maintaining Food Safety and Quality to ensure Consumer Safety Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) Masami Takeuchi, Ph.D. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
Frequently Asked Questions on Avian Influenza
 Frequently Asked Questions on Avian Influenza What is bird flu (avian influenza) and how does it differ from seasonal flu and pandemic influenza? Avian influenza or bird flu is a disease of birds caused
Frequently Asked Questions on Avian Influenza What is bird flu (avian influenza) and how does it differ from seasonal flu and pandemic influenza? Avian influenza or bird flu is a disease of birds caused
ProStart Chapter 2 Year One. Preparing and Serving Safe Food
 ProStart Chapter 2 Year One Preparing and Serving Safe Food Impact on Restaurant Loss of customers and sales Loss of prestige and reputation Legal suits resulting in lawyer and court costs Increased insurance
ProStart Chapter 2 Year One Preparing and Serving Safe Food Impact on Restaurant Loss of customers and sales Loss of prestige and reputation Legal suits resulting in lawyer and court costs Increased insurance
Summary and Recommendations - APEC Dialogue on Avian Influenza Risks in the Live Bird Market System (LBMS)
 2008/ATCWG12/031 Agenda Item: XII Summary and Recommendations - APEC Dialogue on Avian Influenza Risks in the Live Bird Market System (LBMS) Purpose: Information Submitted by: United States 12 th Agricultural
2008/ATCWG12/031 Agenda Item: XII Summary and Recommendations - APEC Dialogue on Avian Influenza Risks in the Live Bird Market System (LBMS) Purpose: Information Submitted by: United States 12 th Agricultural
THIAMINE DEFICIENCY AND PARASITIC INFECTION IN RURAL THAI CHILDREN
 THIAMINE DEFICIENCY AND PARASITIC INFECTION IN RURAL THAI CHILDREN Tueanjit Khampitak 1, Jacqueline Knowles 1, Puangrat Yongvanit 1, Paiboon Sithithaworn 2, Roongpet Tangrassameeprasert 1, Patcharee Boonsiri
THIAMINE DEFICIENCY AND PARASITIC INFECTION IN RURAL THAI CHILDREN Tueanjit Khampitak 1, Jacqueline Knowles 1, Puangrat Yongvanit 1, Paiboon Sithithaworn 2, Roongpet Tangrassameeprasert 1, Patcharee Boonsiri
New LEAP 2025 Science Grades 3-8 & Biology Assessments Overview
 New LEAP 2025 Science Grades 3-8 & Biology Assessments Overview Objectives and Agenda Objectives: 1. Teachers will learn about and be able to communicate key features of the new LEAP 2025 science assessments.
New LEAP 2025 Science Grades 3-8 & Biology Assessments Overview Objectives and Agenda Objectives: 1. Teachers will learn about and be able to communicate key features of the new LEAP 2025 science assessments.
Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia.
 Parasite II Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia. They are worm-like organisms that live and feed off living hosts, receiving nourishment
Parasite II Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia. They are worm-like organisms that live and feed off living hosts, receiving nourishment
Food Purchasing & Receiving Review
 Food Purchasing & Receiving Review Food Purchasing and Receiving 1. The first step in maintaining the safety of the food you prepare and serve, is to ensure that the food is safe as it enters your establishment.
Food Purchasing & Receiving Review Food Purchasing and Receiving 1. The first step in maintaining the safety of the food you prepare and serve, is to ensure that the food is safe as it enters your establishment.
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences
 Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 11. Epidemiology and Public Health Chapter 11 Outline Epidemiology Interactions Among Pathogens, Hosts and the Environment Chain of Infection Reservoirs
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 11. Epidemiology and Public Health Chapter 11 Outline Epidemiology Interactions Among Pathogens, Hosts and the Environment Chain of Infection Reservoirs
SETTING THE STAGE. News in Review November 2012 Teacher Resource Guide E. COLI HEALTH HAZARD
 News in Review November 2012 Teacher Resource Guide E. COLI HEALTH HAZARD SETTING THE STAGE In September 2012, the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) issued a notice informing Canadians not to eat
News in Review November 2012 Teacher Resource Guide E. COLI HEALTH HAZARD SETTING THE STAGE In September 2012, the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) issued a notice informing Canadians not to eat
Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever in Thailand
 By Wiwat Rojanapithayakorn Office of Dengue Control, Department of Communicable Diseases Control, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand Abstract Dengue haemorrhagic fever was first reported in Thailand in
By Wiwat Rojanapithayakorn Office of Dengue Control, Department of Communicable Diseases Control, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand Abstract Dengue haemorrhagic fever was first reported in Thailand in
Media centre. Dioxins and their effects on human health. Key Facts. 1 of 7 1/7/11 1:31 PM
 Media centre Dioxins and their effects on human health Fact sheet N 225 May 2010 Key Facts Dioxins are a group of chemically-related compounds that are persistent environmental pollutants. Dioxins are
Media centre Dioxins and their effects on human health Fact sheet N 225 May 2010 Key Facts Dioxins are a group of chemically-related compounds that are persistent environmental pollutants. Dioxins are
Joint FAO/WHO evaluation of the work of the Codex Alimentarius Commission
 FIFTY-SIXTH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY WHA56.23 Agenda item 14.19 28 May 2003 Joint FAO/WHO evaluation of the work of the Codex Alimentarius Commission The Fifty-sixth World Health Assembly, Recalling resolution
FIFTY-SIXTH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY WHA56.23 Agenda item 14.19 28 May 2003 Joint FAO/WHO evaluation of the work of the Codex Alimentarius Commission The Fifty-sixth World Health Assembly, Recalling resolution
This section provides some overall conclusions from each section of this review.
 95 8. Conclusions This section provides some overall conclusions from each section of this review. 8.1 Algae From the studies conducted to date it may be concluded that: Only about 10-15 percent of dietary
95 8. Conclusions This section provides some overall conclusions from each section of this review. 8.1 Algae From the studies conducted to date it may be concluded that: Only about 10-15 percent of dietary
PRELIMINARY ESTIMATES OF ECONOMIC IMPACT OF LIVER FLUKE INFECTION IN THAILAND AND THE FEASIBILITY OF IRRADIATION AS A CONTROL MEASURE
 PRELIMINARY ESTIMATES OF ECONOMIC IMPACT OF LIVER FLUKE INFECTION IN THAILAND AND THE FEASIBILITY OF IRRADIATION AS A CONTROL MEASURE Paisan Loaharanu' and Santasiri Sornmanf IHead, Food Preservation Section,
PRELIMINARY ESTIMATES OF ECONOMIC IMPACT OF LIVER FLUKE INFECTION IN THAILAND AND THE FEASIBILITY OF IRRADIATION AS A CONTROL MEASURE Paisan Loaharanu' and Santasiri Sornmanf IHead, Food Preservation Section,
questions and answers
 about influenza A (H7N9) What is avian influenza (AI)? Avian influenza (AI) is a bird disease, caused by Type A influenza viruses, which can affect several species of domestic poultry, such as chickens,
about influenza A (H7N9) What is avian influenza (AI)? Avian influenza (AI) is a bird disease, caused by Type A influenza viruses, which can affect several species of domestic poultry, such as chickens,
M E E T I N G R E P O R T. Expert Group Meeting on Swine Influenza in Asia Pacific Region
 Summary M E E T I N G R E P O R T Expert Group Meeting on Swine Influenza in Asia Pacific Region Tokyo, Japan, 23 April 2013 Reported by the Regional Representation for Asia and the Pacific The captioned
Summary M E E T I N G R E P O R T Expert Group Meeting on Swine Influenza in Asia Pacific Region Tokyo, Japan, 23 April 2013 Reported by the Regional Representation for Asia and the Pacific The captioned
REPORT ON ANIMAL HEALTH AND WELFARE ISSUES
 REPORT ON ANIMAL HEALTH AND WELFARE ISSUES PRESENTATION TO THE PORTFOLIO COMMITTEE ON AGRICULTURE, FORESTRY AD FISHERIES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, FORESTRY AND FISHERIES - 28 OCTOBER 2014 PRESENTATION
REPORT ON ANIMAL HEALTH AND WELFARE ISSUES PRESENTATION TO THE PORTFOLIO COMMITTEE ON AGRICULTURE, FORESTRY AD FISHERIES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, FORESTRY AND FISHERIES - 28 OCTOBER 2014 PRESENTATION
