Food-borne zoonotic parasites: Recent developments
|
|
|
- Elfreda Howard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Food-borne zoonotic parasites: Recent developments Stig M. Thamsborg Department of Veterinary Disease Biology, Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Copenhagen, Denmark Nguyen Thi Lan Anh, Parasitology Department, National Institute of Veterinary Research, Hanoi, Vietnam Phan Thi Van, Research Institute for Aquaculture No 1, Bac Ninh, Vietnam D. Murrell, A. Dalsgaard & M.V. Johansen Department of Veterinary Disease Biology, Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Copenhagen, Denmark 1
2 My background Our division (Parasitology, Health and Development) is involved in research/teaching on parasites in domestic animals and humans with a strong focus on developing countries and hosts WHO/FAO Collaborating Centre for Training and Research on Neglected and other Parasitic Zoonoses and WHO Collaborating Centre for Integrated Control of Helminth Infections Own experience in clinical parasitology for 25 years, mainly in livestock and a strong emphasis on helminths we hosted the Danish Centre for Experimental Parasitology focusing on population dynamics of Trichinella, Toxocara, Schistosoma japonicum etc Merged in 2009 with DBL, former Danish Bilharziasis Laboratory 2
3 Synopsis Food-borne zoonotic parasites with emphasis on: Fish-borne zoonotic trematodes (= flukes) Etiology Potential impact Diagnostics Epidemiology Treatment Control Take home messages 3
4 Take-home messages Rapid expansion of aquaculture and increased consumption of raw fish have led to more infections with fish-borne zoonotic trematodes (FZT) in humans Large, underestimated food safety problem in many parts of Asia FZT cover both the highly pathogenic liver flukes and the very common intestinal flukes (but some studies do no discriminate!!!) We need to know more basic epidemiology!! We need more sensitive and specific diagnostic tools to differentiate specific infections, e.g. for control programs We need to define the pathogenic role of small intestinal flukes before treatment is directed to this group Control has to be integrated: education, treatment of humans and animal reservoir, sanitation, aquaculture management practices etc. In combination with control of fish products for parasites! 4
5 Neglected communicable diseases in poor populations 'Previously' neglected diseases Food/water borne diseases Human TB Salmonellosis Escherichia coli Campylobacter HIV/AIDS Anthrax Malaria ST Helminths Schistosomiasis L Filariasis Onchocerciasis Trachoma HAT, Leish, Bovine tuberculosis Fish-borne trematodes Cysticercosis Brucellosis Echinococcosis Neglected tropical diseases Rabies Zoonotic trypanosomiasis Neglected zoonoses (F. Meslin, Zoonoses Unit, FOS/WHO, 2007) 5
6 Food-borne zoonotic parasites Examples: Protozoa Giardia, Cryptosporidium, Cyclospora, Entamoeba histolytica, Toxoplasma gondii Cestodes Taenia saginata, T. solium, Diphyllobothrium spp. Trematodes Plant- and fish-borne zoonotic trematodes Nematode Anisakis simplex, Trichinella spp., (Toxocara spp.) 6
7 Plant-borne zoonotic trematodes Plantborne zoonotic trematodes Liver trematodes Fasciola hepatica: Europe, Northern Asia, Oceania ++ Intestinal trematodes Fasciolopsis buskii: Central and East Asia Fasciola gigantica: China, Japan, Korea, SE Asia, Pacific, Africa ++ 7
8 Fish-borne zoonotic parasites Fishborne zoonotic trematodes (FZT) Liver trematodes Small intestinal trematodes Lung flukes crustaceanborne Paragonimus spp. East and central Asia ++ 8
9 Life cycle of intestinal trematodes Vietnamese raw fish dish: Gỏi cá 9 Source:
10 FZT: species and pathogenicity (10-25 mm) Liver trematodes Opisthorchiidae: Clonorchis sinensis Opistorchis viverrini O. felineus Metorchis spp. Humans: depending on worm burden Acute infections: fever, anorexia, cutaneous rash abdominal discomfort, pain or pressure Chronic infections: fatigue, emaciation biliary cholic due to obstruction jaundice, fever cholelithiasis and cholangitis liver abscess cholangiocarcinoma (O. viverrini, esp. Khon Kaen, Thailand and C. sinensis) (WHO 2009) 10
11 FZT: species and pathogenicity Small intestinal worms Heterophyidae (1-2.5mm) Haplorchis pumilio H. taichui Centrocestus formosanus Heterophyes heterophyes Metagonimus spp. Echinostomatiidae Echinochasmus japonicus Plagiorchiidae Humans (+animals): depending on worm burden transitory malabsorption and diarrhoea, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, anorexia, nausea villi atrophy in small intestine but also mucosal erosion, ulcers and wall necrosis ectopic locations: significant pathology in the heart, brain, and spinal cord (5-15 mm) (Africa et al. 1940; WHO 1995; Chai et al. 2005a, Toledo et al. 2006) 11
12 FZT: worldwide distribution Estimated prevalences: C.sinensis: 35 million people (50% in China) O. viverrini: 10 million (80% in Thailand) O. felineus: 1 million 680 million people worldwide are at risk (WHO 2009) Intestinal flukes: unknown but believed to be high (millions) Distribution of Clonorchis and Opisthorchis 12
13 Clonorchiasis in China Increased >100% in a decade in Guangdong province Increased awareness? All wild caught Pseudoasbora parva fish infected (Lun et al., 2005) 13
14 FZT: impact Cyprinid freshwater fish (e.g. carps) main intermediate hosts of FZT Metacercaria survive in raw, undercooked, poorly cured, dried, pickled or salted fish meat Important food safety issue: human health and export Burden of human disease not yet estimated Animal health? Incidence increasing: more travel increased fish production and consumption 14
15 Example: Rising aquaculture in Asia Inland freshwater fish production, China (Kaiser & Utzinger 2009) Production rapidly increasing all over Asia - important for national economy, as protein source for domestic consumption and to generate foreign currency - Intake of raw fish increasing! Seafood export value in Vietnam from
16 FZT: diagnosis Presence of eggs in faeces Traditionally diagnosed by examination of stools (faeces) for eggs: Kato Katz a.o. DBL-method (sieving) Serious drawbacks: low specificity: can only discriminate small (<50 μm= FZT) & large (>130μm = Fasciola/Fasciolopsis) trematode eggs low sensitivity - only patent infections poor correlation with low worm burdens combine with diagnostic deworming Other means (some properly evaluated): circulating Ab/Ag faecal Ag faecal PCR (Johansen et al. 2010) 16
17 Egg Size Comparisons: small eggs length < 50 µm FZT: Liver flukes cannot be distinguished from small intestinal flukes 17
18 FZT: diagnosis in domestic animals Evaluation of the techniques in dogs, cats and pigs showed relatively similar sensitivities Techniques Amount of faeces Time for preparation and reading Toxic chemical Special equipment Transparency of the eggs DBL# 5g 45 min No No Clear KK 54.5mg 30 min No No Not clear FE 1g 40 min Ether, formalin Fume cupboard Clear # a method combining sedimentation and sieving (Willingham et al., 1996) 18
19 Vietnam: FIBOZOPA-project Fishborne Zoonotic Parasites project C. sinensis to determine FZT status, risk factors and control of FZT in Vietnam funded by DANIDA O. viverrini multi-disciplinary approach with several partners in Vietnam 19
20 Nam Dinh province study site NAM DINH PROVINCE High density of freshwater aquaculture households Endemic area for FZT high prevalence in fish and humans Characterized by a tropical rainy season with high rainfall in the summers Selected communes in Nam Dinh province 20
21 FZT: epidemiology questions? What is the role of other final hosts? How do humans get infected? When, where and which fish get infected? Dynamics in the snails? (Sources: Kaewkes, 2003; Lun và cs., 2005) 21
22 When, where and which fish get infected? PhD-thesis of Phan Thi Van (2010) Fish sampling scheme: Hatchery Fish fry N=10,500 Nursery 1 mth(++) Juveniles N=2,524 (overwintering) Grow-out ponds (partial harvesting: continuous production 1 year) Grow-out fish N=4,025 + Wild caught fish N=714 22
23 When, where and which fish get infected? FZT metacercariae in fish Fish or fish fillets: Pepsin digestion method of WHO (1995) Mice confirmation for FZT identification Source: Murell et al.,
24 When, where and which fish get infected? FZT in hatcheries & nurseries FZT prevalence in fish fry from hatcheries: 0% FZT prevalence in fish from nurseries predominantly in grass carps % 24
25 When, where and which fish get infected? FZT: species distribution in fish in nurseries Fish FZT species species C. sinensis H. pumilio H. taichui C. formosanus n/n (%)* n/n(%) n/n(%) n/n(%) Overall 12/797 (1.5) 443/797 (55.6) 2/797 (0.3) 327/797 (41.0) Grass carp 6/313 (1.9) 213/313 (68.1) 1/313 (0.3) 186/313 (59.4) Rohu 1/208 (0.5) 92/208 (44.2) - 65/208 (31.3) Mrigal 0/55 (0) 17/55 (30.9) - 2/55 (3.6) Pacu 0/8(0) 6/8(75.0) - 5/8(62.5) Silver carp 5/213 (2.4) 115/213 (53.9) 1/313 (0.3) 69/213 (32.4) n: number of infected fish: N number of sampled fish 25
26 When, where and which fish get infected? FZT in grow-out ponds FZT prevalence in cultured species in grow-out ponds over a one year cycle % Again, grass and silver carp most infected Risk factors for FZT infections in grow-out fish farms: - culture time - presence of snails in ponds - feeding grass carp with vegetables originating from outside households 26
27 When, where and which fish get infected? FZT in cultured and wild-caught fish Prevalence (%) Predominantly H. pumilio >95% C. sinensis 1/829 (0.1%) By Nguyen viet Khue 27
28 When, where and which fish get infected? FZT density in cultured/wild fish By Tran Kim Chi
29 FZT: definitive (=final) hosts What is the role of other final hosts? 29
30 What is the role of other final hosts? Another study site introduced: Nghe An Nghe An province Low FZT infection levels in human (1%) (Olsen et al., 2006) Aquaculture: developed The rainy season starts from September and lasts until April. Floods during April and May What is the source of infection for fish? High FZT infection levels in fish (45%) (Chi et al, 2008) 30
31 What is the role of other final hosts? VAC system: Vegetable, pond and animals Common use of untreated manure Source: 31
32 What is the role of other final hosts? Design and methods 1 Nghe An 5 districts Questionnaires to fishfarming households Nam Dinh 2 communes: Nghia Lac/ Nghia Phu Faecal examination (dogs cats pigs) 83,36, ,94,168 Necropsy (dogs, cats, pigs) 38,25,16 25,29,4 PhD study by Lan Anh (2009) 32
33 What is the role of other final hosts? Design and methods 2 Total daily egg excretion (TDEE) was determined as: Number of each species x prevalence x intensity x amount of faeces excreted per day Relative Transmission Index (RTI) for each definitive host determined as: RTI = TDEE for each species x 100/ TDEE for all species Questionnaire: animal behaviour and animal husbandry practices in relation to FZT infection 33
34 What is the role of other final hosts? Prevalences in domestic animals Dogs Cats Pigs (Lan Anh et al., 2009 Acta Trop EID) Nghe An Nam Dinh Based on faecal examination Dogs and cats 5-8 times higher risk of being infected than pigs (p<0.001) 34
35 What is the role of other final hosts? Potential transmission from domestic animals Total daily egg excretion (TDEE) & relative transmission index (RTI) Host species Nghe An Total number Prevalence (%) Intensity (epg) ±sem TDEE (10 6 ) Humans % Dogs (8) % Cats (22) 91 10% Pigs (2) % Nam Dinh Dogs (516) % Cats (102) 4 2% Pigs (3) 38 21% (Data on humans: Olsen et al., 2006) RTI (%) 35
36 What is the role of other final hosts? Risk factors for animal infections Animal level, similar in both sites (n=229/448): Animal species Being fed raw fish Only pigs: OR 1 to 5 Nghe An OR 1 to 19 Nam Dinh (Free roaming) (Eating raw fish) Household level Infection in fish (p<0.05) (Nghe An, n=48) Being fed raw fish (p<0.05) (Nam Dinh, n=248) (Lan Anh et al., 2009 Acta Trop EID) 36
37 What is the role of other final hosts? FZT in domestic animals Liver flukes in domestic animals: 1 dog (4%) and 2 cats (7%) in Nam Dinh only Clonorchis sinensis Clonorchis-endemic regions in China: all cats infected (Lun et al., 2005) 37
38 What is the role of other final hosts? FZT in domestic animals 2 Most prevalent small intestinal trematodes recovered from dogs, cats and pigs in Ngha An/Nam Dinh Haplorchis pumilio (84-100% prev.) H. taichui (16-78% prev.) H. yokogawai (11-70% prev.) 38
39 What is the role of other final hosts? FZT in domestic animals 3 Echinochasmus japonicus (0-60% prevalence) E. perfoliatus (0-19% prev.) Echinostoma cinetorchis (only dogs 4-8%) 39
40 What is the role of other final hosts? FZT in domestic animals 4 Stellantchasmus falcatus (only Nam Dinh 25-44%) Stictodora manilensis Centrocestus formosanus 40
41 What is the role of other final hosts? FZT: typical transmission sites Fish intestine (Photos: Lan Anh) 41
42 FZT: Levels of human infections Nam Dinh province, 5000 fish-farming households 615 persons examined by Kato-Katz 14% had >1000 eggs per g faeces 33 of these were dewormed for species determination Trematodes Small eggs (<50 μm) Large eggs Species recovered from 33 high excretors: Clonorchis sinensis Haplorchis pumilio H. taichui H. yokogawai Stellantchasmus falcatus Fasciolopsis buskii Prevalence 65% 1% 52% 100% 70% 3% 6% 3% Worm burdens How do humans get infected? (Trung Dung et al., 2007 EID) 42
43 How do humans get infected? Raw fish dishes served in China, Japan, Korea and Vietnam Gỏi cá Zhang et al., 2007 Shenzhen, Guangdong httpen.wikipedia.orgwikihoe_(dish) Hoe dish httpwww.ethnicfoodsco.comjapandishes.htm Sashimi 43
44 How do humans get infected? Fish eating behaviour of household members % Study of Van Thi Phan et al (in press) (N=180; duplicate Kato-Katz) 44
45 How do humans get infected? Fish eating behaviour in Vietnam Many types of fish dishes using e.g. silver carp, grass carp and, rohu Usually >18 years before eating raw fish (and drinking rice vodka!) Men often clean and cut fish while women prepare the rest Metacercaria stay alive in water on chop boards Gathering to eat raw fish: at home, restaurant or with friends Lao: Women often taste during preparation! 45
46 Treatment of FZT infections Humans: Praziquantel (PZQ) is the only drug recommended by WHO to treat Clonorchis/Opisthorchis (>4 years): 25 mg/kg 3 times a day for 2 consecutive days, or 40 mg/kg single administration Single dose recommended for mass chemotherapy for people at risk in endemic areas Small intestinal flukes (Heterophyids): 25 mg PZQ/kg single adm. (WHO, 2009) Albendazole not recommended but high doses for 7 days in Clonorchis can perhaps be used (Lun et al, 2005) Animals: Few studies, e.g. opistorchids in dogs mg PZQ/kg as single dose for 1 day (Schuster et al., 2002) 46
47 Lessons learning from FIBOZOPA Metacercaria of small intestinal flukes extremely common in a variety of fish, especially Haplorchis pumilio and other heterophyids Nursery ponds are hot spots for infections (from 14% to 58%) Prevalence in wild-caught fish was not different from grow-out fish but higher density in the meat FZT infections were common in cats and dogs in fish farming household but less common in pigs In general, mixed infections in dogs, cats and pig of intestinal flukes species very similar to findings in fish but rarely liver fluke in this region (no bithynid snails in ponds!) Pigs may potentially be important in transmission if untreated pig faeces recycled The practice of feeding of raw fish was an important risk factor in pigs 47
48 Lessons learned from FIBOZOPA In Nam Dinh, 32-65% household members of fish farms were infected with FZT All infected persons hosted small intestinal flukes and some of them C. sinensis (prevalence unknown but in the range 3-33%) Farmed fish source of C. sinensis in humans in this area or other sources? Eating raw fish, especially raw fish from restaurants imposed a higher risk for FZT infection in humans. 26% people not eating raw fish were infected with FZT FZT can contaminate hands and utensils during fish processing and eating time and then infect humans 48
49 Prevention break the cycle Ultimate goal: produce fish free of FZT and safe to eat Toilets emptying into fish pond 49
50 Prevention of FZT infections in man/animals Control need to be integrated, applying several of the following: 1) Education campaigns Fish farmers on management next slide Other households on improved hygiene, e.g. Heating 70 deg C for 15 min; Freezing -20 deg C for 24 h Changing of feeding habits shown to be difficult! 2) Systematic treatment of people with PZQ (either mass or after diagnosis) 3) Continued monitoring of infection levels in humans in high endemic regions, in China e.g. clonorchiasis in Guangdong province! 4) Infected domestic animals must be treated and kept from ponds 5) Pigs (animals) should not be fed raw fish 6) Food safety control of fish by HACCP 7) More political awareness!! 50
51 Recommendations for fish farms 51
52 Perspectives/research needs Influences of water quality on FZT eggs, cercariae and population of snails? Age-related susceptibility in fish? Better diagnostics discrimination between liver and intestinal flukes What is clinical importance of small intestinal flukes in animals and man? (Danish PhD study on-going) Is there any side effect of treatments in man? Best treatment for animals? Role of rodents in transmission? Survival of metacercariae after different treatments of food Can eating behaviour be moderated if not changed? (e.g. frozen fish for raw fish dishes) 52
53 Take-home messages Rapid expansion of aquaculture and increased consumption of raw fish have led to more infections with fish-borne zoonotic trematodes (FZT) in humans Large, underestimated food safety problem in many parts of Asia FZT cover both the highly pathogenic liver flukes and the very common intestinal flukes (but some studies do no discriminate!!!) We need to know more basic epidemiology!! We need more sensitive and specific diagnostic tools to differentiate specific infections, e.g. for control programs We need to define the pathogenic role of small intestinal flukes before treatment is directed to this group Control has to be integrated: education, treatment of humans and animal reservoir, sanitation, aquaculture management practices etc. In combination with control of fish products for parasites! 53
54 Thank you for your attention! Visit FIBOZOPA-project www. I will stop eating raw fish. And you? 54
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
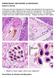 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 54-year-old man originally from Vietnam was admitted to the hospital for complaints of upper abdominal pain and liver enlargement. The bile
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 12 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 54-year-old man originally from Vietnam was admitted to the hospital for complaints of upper abdominal pain and liver enlargement. The bile
FOOD-BORNE TREMATODE INFECTIONS IN ASIA
 REPORT JOINT WHO/FAO WORKSHOP ON FOOD-BORNE TREMATODE INFECTIONS IN ASIA Ha Noi, Viet Nam 26-28 November 2002 World Health Organization Regional office for the Western Pacific (WP)MVP/ICP/MVP/1.2/001-E
REPORT JOINT WHO/FAO WORKSHOP ON FOOD-BORNE TREMATODE INFECTIONS IN ASIA Ha Noi, Viet Nam 26-28 November 2002 World Health Organization Regional office for the Western Pacific (WP)MVP/ICP/MVP/1.2/001-E
Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica.
 TREMATODES: INTRODUCTION: Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica. The life cycle of trematodes involves a sexual cycle in humans and asexual reproduction in freshwater snails (intermediate
TREMATODES: INTRODUCTION: Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica. The life cycle of trematodes involves a sexual cycle in humans and asexual reproduction in freshwater snails (intermediate
Intestinal Parasites. James Gaensbauer MD, MScPH Fellow, Pediatric Infectious Diseases University of Colorado School of Medicine November 12, 2012
 Intestinal Parasites James Gaensbauer MD, MScPH Fellow, Pediatric Infectious Diseases University of Colorado School of Medicine November 12, 2012 Outline Parasites 101 Global Burden of Disease An Evolutionary
Intestinal Parasites James Gaensbauer MD, MScPH Fellow, Pediatric Infectious Diseases University of Colorado School of Medicine November 12, 2012 Outline Parasites 101 Global Burden of Disease An Evolutionary
Parasitology Questions. Choose the best correct answer in the following statements
 Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 5, 2016,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 5, 2016, 2954 2958 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) Review Article FISH AND SHELL FISH BORNE PARASITIC INFECTIONS- A REVIEW A. Sangaran
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 5, 2016, 2954 2958 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) Review Article FISH AND SHELL FISH BORNE PARASITIC INFECTIONS- A REVIEW A. Sangaran
An Integrated Control Strategy Takes Clonorchis sinensis Under Control in an Endemic Area in South China
 VECTOR-BORNE AND ZOONOTIC DISEASES Volume XX, Number XX, 2017 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/vbz.2017.2133 ORIGINAL ARTICLE An Integrated Control Strategy Takes Clonorchis sinensis Under Control
VECTOR-BORNE AND ZOONOTIC DISEASES Volume XX, Number XX, 2017 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/vbz.2017.2133 ORIGINAL ARTICLE An Integrated Control Strategy Takes Clonorchis sinensis Under Control
Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia.
 Parasite II Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia. They are worm-like organisms that live and feed off living hosts, receiving nourishment
Parasite II Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia. They are worm-like organisms that live and feed off living hosts, receiving nourishment
Food-borne Parasitic disease in Aisa
 Food-borne Parasitic disease in Aisa Liu Mingyuan OIE Collaborating Centre for Food-Borne Parasite from the Asian-Pacific Region; Institute of Zoonosis, Jilin University, China Food-borne parasitic disease
Food-borne Parasitic disease in Aisa Liu Mingyuan OIE Collaborating Centre for Food-Borne Parasite from the Asian-Pacific Region; Institute of Zoonosis, Jilin University, China Food-borne parasitic disease
INTRODUCTION. Liver fluke infection, opisthorchiasis in humans, is a major public health problem in the Greater Mekong sub-region
 PREVLENCE AND RISK FACTORS FOR OPISTHORCHIS VIVERRINI INFECTION AMONG CATS AND DOGS IN SIX DISTRICTS SURROUNDING THE UBOLRATANA DAM, AN ENDEMIC AREA FOR HUMAN OPISTHORCHIASIS IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND Surasit
PREVLENCE AND RISK FACTORS FOR OPISTHORCHIS VIVERRINI INFECTION AMONG CATS AND DOGS IN SIX DISTRICTS SURROUNDING THE UBOLRATANA DAM, AN ENDEMIC AREA FOR HUMAN OPISTHORCHIASIS IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND Surasit
A new endemic focus of Heterophyes nocens and other heterophyid infections in a coastal area of Gangjin-gun, Jeollanam-do
 Korean Journal of Parasitology Vol. 45, No. 1: 33-38, March 2007 A new endemic focus of Heterophyes nocens and other heterophyid infections in a coastal area of Gangjin-gun, Jeollanam-do Jae-Hwan PARK
Korean Journal of Parasitology Vol. 45, No. 1: 33-38, March 2007 A new endemic focus of Heterophyes nocens and other heterophyid infections in a coastal area of Gangjin-gun, Jeollanam-do Jae-Hwan PARK
Simplified Techniques for Killing the Carcinogenic, Opisthorchis Viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinid Fish
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.6.1507 RESEARCH ARTICLE Simplified Techniques for Killing the Carcinogenic, Opisthorchis Viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinid Fish Panupan Sripan 1,2,3, Thidarut Boonmars 1,2,3
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.6.1507 RESEARCH ARTICLE Simplified Techniques for Killing the Carcinogenic, Opisthorchis Viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinid Fish Panupan Sripan 1,2,3, Thidarut Boonmars 1,2,3
Disease and Environment: Implications of Clonorchiasis Infection in Taiwan and Mainland China
 Disease and Environment: Implications of Clonorchiasis Infection in Taiwan and Mainland China Ts ui-jung Liu with Maps charted by Yu-ting Lee Institute of Taiwan History Academia Sinica Paper prepared
Disease and Environment: Implications of Clonorchiasis Infection in Taiwan and Mainland China Ts ui-jung Liu with Maps charted by Yu-ting Lee Institute of Taiwan History Academia Sinica Paper prepared
1. Parasitology Protozoa 4
 Contents 1. Parasitology 1 Host Parasite Relationship 2 Mode of Transmission 2 2. Protozoa 4 Classification 4 Reproduction 5 Immunity 5 Pathogenesis 6 Laboratory Diagnosis 6 Treatment 8 Entamoeba 8 Classification
Contents 1. Parasitology 1 Host Parasite Relationship 2 Mode of Transmission 2 2. Protozoa 4 Classification 4 Reproduction 5 Immunity 5 Pathogenesis 6 Laboratory Diagnosis 6 Treatment 8 Entamoeba 8 Classification
Brief Survey of Common Intestinal Parasites in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area. Tsukasa NOZAKI1), Kouichi NAGAKURA2)*, Hisae FUSEGAWA3)
 Brief Survey of Common Intestinal Parasites in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area Tsukasa NOZAKI1), Kouichi NAGAKURA2)*, Hisae FUSEGAWA3) and Yasuhiko AND01),3) 1) Central Clinical Laboratoly, Tokai University
Brief Survey of Common Intestinal Parasites in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area Tsukasa NOZAKI1), Kouichi NAGAKURA2)*, Hisae FUSEGAWA3) and Yasuhiko AND01),3) 1) Central Clinical Laboratoly, Tokai University
Food-Borne Trematodiases
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, July 2009, p. 466 483 Vol. 22, No. 3 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00012-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Food-Borne Trematodiases
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, July 2009, p. 466 483 Vol. 22, No. 3 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00012-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Food-Borne Trematodiases
Report of the WHO Expert Consultation on Foodborne Trematode Infections and Taeniasis/Cysticercosis
 Report of the WHO Expert Consultation on Foodborne Trematode Infections and Taeniasis/Cysticercosis Vientiane, Lao People's Democratic Republic 12-16 October 2009 World Health Organization 2011 All rights
Report of the WHO Expert Consultation on Foodborne Trematode Infections and Taeniasis/Cysticercosis Vientiane, Lao People's Democratic Republic 12-16 October 2009 World Health Organization 2011 All rights
Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Helminthic Parasites of Humans Helminths are macroscopic, multicellular, eukaryotic
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Helminthic Parasites of Humans Helminths are macroscopic, multicellular, eukaryotic
Sushi Worms Diagnostic Challenges
 Department Medicine Diagnostic Centre Swiss TPH Winter Symposium 2017 Helminth Infection from Transmission to Control Sushi Worms Diagnostic Challenges Beatrice Nickel Fish-borne helminth infections Consumption
Department Medicine Diagnostic Centre Swiss TPH Winter Symposium 2017 Helminth Infection from Transmission to Control Sushi Worms Diagnostic Challenges Beatrice Nickel Fish-borne helminth infections Consumption
APPLICATION OF HAZARD ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP) AS A POSSIBLE CONTROL MEASURE FOR OPISTHORCHIS
 APPLICATION OF HAZARD ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP) AS A POSSIBLE CONTROL MEASURE FOR OPISTHORCHIS VIVERRINIINFECTION IN CULTURED CARP (PUNT/US GONIONOTUS) Khamboonruang Cl, Keawvichit RI, Wongworapat
APPLICATION OF HAZARD ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP) AS A POSSIBLE CONTROL MEASURE FOR OPISTHORCHIS VIVERRINIINFECTION IN CULTURED CARP (PUNT/US GONIONOTUS) Khamboonruang Cl, Keawvichit RI, Wongworapat
FOOD BORNE INFECTIONS
 Food Poisoning Food poisoning Advisory commitee on Microbiological safety of food (ACMSF, UK) has defined food poisoning as : An acute illness with gastrointestinal or neurological manifestation affecting
Food Poisoning Food poisoning Advisory commitee on Microbiological safety of food (ACMSF, UK) has defined food poisoning as : An acute illness with gastrointestinal or neurological manifestation affecting
COPRO-DIAGNOSIS OF HAPLORCHIS TAICHUI INFECTION USING SEDIMENTATION AND PCR-BASED METHODS
 COPRO-DIAGNOSIS OF HAPLORCHIS TAICHUI INFECTION USING SEDIMENTATION AND PCR-BASED METHODS Chalobol Wongsawad, Pheravut Wongsawad, Suksan Chuboon and Somboon Anuntalabhochai Department of Biology, Faculty
COPRO-DIAGNOSIS OF HAPLORCHIS TAICHUI INFECTION USING SEDIMENTATION AND PCR-BASED METHODS Chalobol Wongsawad, Pheravut Wongsawad, Suksan Chuboon and Somboon Anuntalabhochai Department of Biology, Faculty
RVC OPEN ACCESS REPOSITORY COPYRIGHT NOTICE
 RVC OPEN ACCESS REPOSITORY COPYRIGHT NOTICE This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced version of an article accepted for publication in Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene
RVC OPEN ACCESS REPOSITORY COPYRIGHT NOTICE This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced version of an article accepted for publication in Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene
Estimates of the global and regional burden of foodborne parasites as determined by the World Health Organization
 Estimates of the global and regional burden of foodborne parasites as determined by the World Health Organization Brecht Devleesschauwer IAFWP International Symposium Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 06/09/2017
Estimates of the global and regional burden of foodborne parasites as determined by the World Health Organization Brecht Devleesschauwer IAFWP International Symposium Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 06/09/2017
Opisthorchis viverrini infection in minute intestinal fluke endemic areas of Chiang Mai Province, Thailand
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 3 No. 2 April 2009;187-191 Brief communication (original) Opisthorchis viverrini infection in minute intestinal fluke endemic areas of Chiang Mai Province, Thailand Choosak Nithikathkul
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 3 No. 2 April 2009;187-191 Brief communication (original) Opisthorchis viverrini infection in minute intestinal fluke endemic areas of Chiang Mai Province, Thailand Choosak Nithikathkul
Class Digenea (Trematoda) - The Flukes
 Class Digenea (Trematoda) - The Flukes A. The information on the Platyhelminthes provided in the previous section should be reviewed, as it still applies. B. Adult trematodes are parasites of vertebrates.
Class Digenea (Trematoda) - The Flukes A. The information on the Platyhelminthes provided in the previous section should be reviewed, as it still applies. B. Adult trematodes are parasites of vertebrates.
Protozoans and Helminthes
 Protozoans and Helminthes 1 Protozoans 2 3 4 5 6 Worm: Leishmania donovani General Family: Trypanosomes (Blood/tissue flagellates) Larvae or Adult Sketch of dermal, post-visceral kala-azar Life Cycle:
Protozoans and Helminthes 1 Protozoans 2 3 4 5 6 Worm: Leishmania donovani General Family: Trypanosomes (Blood/tissue flagellates) Larvae or Adult Sketch of dermal, post-visceral kala-azar Life Cycle:
Population dynamics and host reactions in young foxes following experimental infection with the minute intestinal fluke, Haplorchis pumilio
 Nissen et al. Parasites & Vectors 2013, 6:4 RESEARCH Open Access Population dynamics and host reactions in young foxes following experimental infection with the minute intestinal fluke, Haplorchis pumilio
Nissen et al. Parasites & Vectors 2013, 6:4 RESEARCH Open Access Population dynamics and host reactions in young foxes following experimental infection with the minute intestinal fluke, Haplorchis pumilio
Organisms of Concern. Roundworms (nematodes) Anisakis spp., Pseudoterranova spp., Eustrongylides spp. and Gnathostoma spp.
 Parasites in Fish Parasites are a natural occurrence The parasites do not make the fish sick Thorough cooking of fish will make parasites harmless to humans Organisms of Concern Roundworms (nematodes)
Parasites in Fish Parasites are a natural occurrence The parasites do not make the fish sick Thorough cooking of fish will make parasites harmless to humans Organisms of Concern Roundworms (nematodes)
Specific and common antigens of Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini (Opisthorchidae, Trematoda)
 The Korean Journal of Parasitology Vol. 41, No. 3. 155-163, September 2003 Specific and common antigens of Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini (Opisthorchidae, Trematoda) Min-Ho CHOI 1), Jin-Sook
The Korean Journal of Parasitology Vol. 41, No. 3. 155-163, September 2003 Specific and common antigens of Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini (Opisthorchidae, Trematoda) Min-Ho CHOI 1), Jin-Sook
CONFIRMATION STATUS OF HELMINTHIASIS IN LOW RISK AREAS IN CENTRAL THAILAND
 CONFIRMATION STATUS OF HELMINTHIASIS IN LOW RISK AREAS IN CENTRAL THAILAND Ampas Wisetmora *1,2, Duangduen Krailas 2, Choosak Nithikethkul 3,Wanchai Phatihattakorn 4, Opart Karnkawinpong 1, Thitima Wongsaroj
CONFIRMATION STATUS OF HELMINTHIASIS IN LOW RISK AREAS IN CENTRAL THAILAND Ampas Wisetmora *1,2, Duangduen Krailas 2, Choosak Nithikethkul 3,Wanchai Phatihattakorn 4, Opart Karnkawinpong 1, Thitima Wongsaroj
European Union comments
 15/10/2015 General comments FINAL European Union comments CODEX COMMITTEE ON FOOD HYGIENE Forty-seventh Session Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America, 9 13 November 2015 Agenda Item 5: Proposed
15/10/2015 General comments FINAL European Union comments CODEX COMMITTEE ON FOOD HYGIENE Forty-seventh Session Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America, 9 13 November 2015 Agenda Item 5: Proposed
The Vicious Worm An electronic health education tool assessed in Tanzania
 Evaluation of the learning outcome in Tanzania when using an online learning platform (The Vicious Worm) created for information sharing and learning about cysticercosis in developing countries The Vicious
Evaluation of the learning outcome in Tanzania when using an online learning platform (The Vicious Worm) created for information sharing and learning about cysticercosis in developing countries The Vicious
PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN
 PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN OUTLINE Intruduction Important terms classification of hosts Mode of parasitic infections General Classification of parasites Specific Classification of parasites Protozoa
PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN OUTLINE Intruduction Important terms classification of hosts Mode of parasitic infections General Classification of parasites Specific Classification of parasites Protozoa
IV. Important trematodes (Chapters 16 18)
 IV. Important trematodes (Chapters 16 18) A. Placed in the subclass Digenea 1. Flukes 2. Digenea refers to having an alternation of hosts in the life cycle B. Characteristics 1. Cuplike suckers without
IV. Important trematodes (Chapters 16 18) A. Placed in the subclass Digenea 1. Flukes 2. Digenea refers to having an alternation of hosts in the life cycle B. Characteristics 1. Cuplike suckers without
Social determinants of Taeniasoliumcysticercosis
 Social determinants of Taeniasoliumcysticercosis Maria Vang Johansen Dept. of Veterinary Disease Biology Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences University of Copenhagen, Denmark Slide 1 Once upon a time
Social determinants of Taeniasoliumcysticercosis Maria Vang Johansen Dept. of Veterinary Disease Biology Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences University of Copenhagen, Denmark Slide 1 Once upon a time
Title. Author(s)OOI, Hong Kean; CHEN, Ching-I; OKU, Yuzaburo. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 50(1): 3-7. Issue Date DOI
 Title Excystation of Haplorchis taichui metacercariae coul Author(s)OOI, Hong Kean; CHEN, Ching-I; OKU, Yuzaburo CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 50(1): 3-7 Issue Date 2002-05-31 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.50.1.3
Title Excystation of Haplorchis taichui metacercariae coul Author(s)OOI, Hong Kean; CHEN, Ching-I; OKU, Yuzaburo CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 50(1): 3-7 Issue Date 2002-05-31 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.50.1.3
Parasites in food chains
 Parasites in food chains Kristina Roesel and Delia Grace Microsporidia in the Animal to Human Food Chain: An International Symposium to Address Chronic Epizootic Disease 9 August 2015 at University of
Parasites in food chains Kristina Roesel and Delia Grace Microsporidia in the Animal to Human Food Chain: An International Symposium to Address Chronic Epizootic Disease 9 August 2015 at University of
Platyhelminthes (flat worms) as parasites of medical interest
 Platyhelminthes (flat worms) as parasites of medical interest Type of parasites Protozoa Helminths Arthropods Nematodes Trematodes Cestodes Platyhelminthes A simplified classification of flat worms Platyhelminthes
Platyhelminthes (flat worms) as parasites of medical interest Type of parasites Protozoa Helminths Arthropods Nematodes Trematodes Cestodes Platyhelminthes A simplified classification of flat worms Platyhelminthes
Helminths in tropical regions
 Helminths in tropical regions Schistosoma spp. Blood flukes Schistosomiasis is one of the most widespread parasitic infections in humans Humans are the principal hosts for: Schistosoma mansoni, Schistosoma
Helminths in tropical regions Schistosoma spp. Blood flukes Schistosomiasis is one of the most widespread parasitic infections in humans Humans are the principal hosts for: Schistosoma mansoni, Schistosoma
A new endemic focus of Gymnophalloides seoi infection on Aphae Island, Shinan-gun, Jeollanam-do
 Korean Journal of Parasitology Vol. 45, No. 1: 39-44, March 2007 A new endemic focus of Gymnophalloides seoi infection on Aphae Island, Shinan-gun, Jeollanam-do Jae-Hwan PARK 1), Sang-Mee GUK 1), Eun-Hee
Korean Journal of Parasitology Vol. 45, No. 1: 39-44, March 2007 A new endemic focus of Gymnophalloides seoi infection on Aphae Island, Shinan-gun, Jeollanam-do Jae-Hwan PARK 1), Sang-Mee GUK 1), Eun-Hee
Parasite Life Cycles. Dickson D. Despommier John W Karapelou. Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo
 Parasite Life Cycles Dickson D. Despommier John W Karapelou Parasite Life Cycles With 49 Life Cycle Drawings Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Dickson D. Despommier, Ph.D. Professor
Parasite Life Cycles Dickson D. Despommier John W Karapelou Parasite Life Cycles With 49 Life Cycle Drawings Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Dickson D. Despommier, Ph.D. Professor
L:7, L:8 Parasitology
 L:7, L:8 Parasitology 2.Fasciola hepatica Adult The adult Fasciola hepatica worm is flattened, leaf like shape, equipped with shoulders, somewhat oblong. Adult Fasciola hepatica measuring 3cm by 1cm in
L:7, L:8 Parasitology 2.Fasciola hepatica Adult The adult Fasciola hepatica worm is flattened, leaf like shape, equipped with shoulders, somewhat oblong. Adult Fasciola hepatica measuring 3cm by 1cm in
Foodborne Disease in the Region of Peel
 Foodborne Disease in the Region of Peel HIGHLIGHTS The incidence of selected foodborne diseases was generally higher in Peel than in Ontario between 1993 and 22. A higher incidence was observed in Peel
Foodborne Disease in the Region of Peel HIGHLIGHTS The incidence of selected foodborne diseases was generally higher in Peel than in Ontario between 1993 and 22. A higher incidence was observed in Peel
Introduction. Causes. Roundworms. Worms. Flatworms. How Flatworms are transmitted. Fast fact. Fast fact
 Module 5 Worms MODULE 5 INTRODUCTION Introduction Worms Worms or helminths are parasites that live on or in human or animal hosts and draw nutrients from their host 1. Worms are multi-cellular, have complex
Module 5 Worms MODULE 5 INTRODUCTION Introduction Worms Worms or helminths are parasites that live on or in human or animal hosts and draw nutrients from their host 1. Worms are multi-cellular, have complex
Diversity of human intestinal helminthiasis in Lao PDR
 Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (2009) 103, 247 254 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevierhealth.com/journals/trst Diversity of human intestinal
Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (2009) 103, 247 254 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevierhealth.com/journals/trst Diversity of human intestinal
Schistosomiasis. Li Qian Department of Infectious Diseases, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University
 Schistosomiasis Li Qian Department of Infectious Diseases, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University Topics Definition The Pathogen Epidemiology Etiology and Life Cycle Pathobiology Clinical manifestations Diagnosis
Schistosomiasis Li Qian Department of Infectious Diseases, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University Topics Definition The Pathogen Epidemiology Etiology and Life Cycle Pathobiology Clinical manifestations Diagnosis
REVISED PROPOSED DRAFT GUIDELINES ON THE APPLICATION OF GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF FOOD HYGIENE TO THE CONTROL OF FOODBORNE PARASITES
 E Agenda Item 5 FH/47 CRD/2 JOINT FAO/WHO FOOD STANDARDS PROGRAMME CODEX COMMITTEE ON FOOD HYGIENE Forty-seventh Session Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America, 9 13 November 2015 REVISED PROPOSED
E Agenda Item 5 FH/47 CRD/2 JOINT FAO/WHO FOOD STANDARDS PROGRAMME CODEX COMMITTEE ON FOOD HYGIENE Forty-seventh Session Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America, 9 13 November 2015 REVISED PROPOSED
Foodborne diseases: an ongoing global challenge
 Foodborne diseases: an ongoing global challenge Arie Havelaar GLOBALG.A.P. Summit 2016 Amsterdam, September 27-28, 2016 Outline WHO estimates of the global burden of foodborne disease Regional differences
Foodborne diseases: an ongoing global challenge Arie Havelaar GLOBALG.A.P. Summit 2016 Amsterdam, September 27-28, 2016 Outline WHO estimates of the global burden of foodborne disease Regional differences
Intestinal Helminths Recovered from Humans in Xieng Khouang Province, Lao PDR with a Particular Note on Haplorchis pumilio Infection
 ISSN (Print) 0023-4001 ISSN (Online) 1738-0006 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Parasitol Vol. 53, No. 4: 439-445, August 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2015.53.4.439 Intestinal Helminths Recovered from Humans
ISSN (Print) 0023-4001 ISSN (Online) 1738-0006 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Parasitol Vol. 53, No. 4: 439-445, August 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2015.53.4.439 Intestinal Helminths Recovered from Humans
HUMAN PARASITOLOGY. lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura, hookworm. Human Parasitology (Code: ) Guideline
 HUMAN PARASITOLOGY Human Parasitology (Code:1001021) Guideline I. Course Introduction 128 classes comprise 72 for lecturing, 54 for lab practice, and 2 for self-study. 6.0 credits; 5 th semester II. Lecturing
HUMAN PARASITOLOGY Human Parasitology (Code:1001021) Guideline I. Course Introduction 128 classes comprise 72 for lecturing, 54 for lab practice, and 2 for self-study. 6.0 credits; 5 th semester II. Lecturing
Overview IMPORTANCE CLASSIFICATION SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROTOZOA WORMS BLOOD PARASITES ARTHROPODS DELUSIONAL PARASITOSIS QUIZZES GROSS
 IMPORTANCE Overview CLASSIFICATION SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROTOZOA WORMS BLOOD PARASITES ARTHROPODS DELUSIONAL PARASITOSIS QUIZZES GROSS - Of 6.6 billion people on Earth, 2.7 billion live on
IMPORTANCE Overview CLASSIFICATION SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROTOZOA WORMS BLOOD PARASITES ARTHROPODS DELUSIONAL PARASITOSIS QUIZZES GROSS - Of 6.6 billion people on Earth, 2.7 billion live on
Tantrawatpan et al. Parasites & Vectors 2014, 7:88
 Tantrawatpan et al. Parasites & Vectors 2014, 7:88 RESEARCH Open Access Development of a PCR assay and pyrosequencing for identification of important human fish-borne trematodes and its potential use for
Tantrawatpan et al. Parasites & Vectors 2014, 7:88 RESEARCH Open Access Development of a PCR assay and pyrosequencing for identification of important human fish-borne trematodes and its potential use for
Current Status of Taeniasis and Cysticercosis in Vietnam
 ISSN (Print) 0023-4001 ISSN (Online) 1738-0006 MINI-REVIEW Korean J Parasitol Vol. 52, No. 2: 125-129, April 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2014.52.2.125 Current Status of Taeniasis and Cysticercosis
ISSN (Print) 0023-4001 ISSN (Online) 1738-0006 MINI-REVIEW Korean J Parasitol Vol. 52, No. 2: 125-129, April 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2014.52.2.125 Current Status of Taeniasis and Cysticercosis
Stitaya Sirisinha, Runglawan Chawengkirttikul.and. Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University, Bangkok 10400, Thailand.
 Stitaya Sirisinha, Runglawan Chawengkirttikul.and Rasana Sennswan Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University, Bangkok 10400, Thailand. Abstract. Monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked
Stitaya Sirisinha, Runglawan Chawengkirttikul.and Rasana Sennswan Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University, Bangkok 10400, Thailand. Abstract. Monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked
Introduction to Parasitic Helminths
 Introduction to Parasitic Helminths Lecture 4 Medical Parasitology Course (MLAB 362) Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 1 Parasitic Helminths Eukaryotic, multicellular animals that usually have digestive, circulatory,
Introduction to Parasitic Helminths Lecture 4 Medical Parasitology Course (MLAB 362) Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 1 Parasitic Helminths Eukaryotic, multicellular animals that usually have digestive, circulatory,
DEVELOPMENT OF HAPLORCHIS TAICHUI (TREMATODA: HETEROPHYIDAE) IN MUS MUSCULUS MICE
 DEVELOPMENT OF HAPLORCHIS TAICHUI (TREMATODA: HETEROPHYIDAE) IN MUS MUSCULUS MICE Kom Sukontason, Kabkaew L Sukontason, Nares Boonsriwong, Udom Chaithong, Somsak Piangjai and Wej Choochote Department of
DEVELOPMENT OF HAPLORCHIS TAICHUI (TREMATODA: HETEROPHYIDAE) IN MUS MUSCULUS MICE Kom Sukontason, Kabkaew L Sukontason, Nares Boonsriwong, Udom Chaithong, Somsak Piangjai and Wej Choochote Department of
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION. Control of neurocysticercosis
 WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION FIFTY-SIXTH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A56/10 Provisional agenda item 14.2 6 March 2003 Control of neurocysticercosis Report by the Secretariat BACKGROUND 1. Cysticercosis of the central
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION FIFTY-SIXTH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A56/10 Provisional agenda item 14.2 6 March 2003 Control of neurocysticercosis Report by the Secretariat BACKGROUND 1. Cysticercosis of the central
Opisthorchis viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinoid Fish from Three Rivers in Khammouane Province, Lao PDR
 J Trop Med Parasitol. 2009;32:23-9. Original Article Available online at www.ptat.thaigov.net Opisthorchis viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinoid Fish from Three Rivers in Khammouane Province, Lao PDR Khemphavanh
J Trop Med Parasitol. 2009;32:23-9. Original Article Available online at www.ptat.thaigov.net Opisthorchis viverrini Metacercariae in Cyprinoid Fish from Three Rivers in Khammouane Province, Lao PDR Khemphavanh
Trematodes General characteristics:-
 Trematodes General characteristics:- 1- They are commonly referred to as flukes. 2- Life cycle have 3 morphologica form:- a- Egg b- Multiple larval stage c- Adult worm 3- The eggs, which are the primary
Trematodes General characteristics:- 1- They are commonly referred to as flukes. 2- Life cycle have 3 morphologica form:- a- Egg b- Multiple larval stage c- Adult worm 3- The eggs, which are the primary
(Data from the Travel Health Surveillance Section of the Health Protection Agency Communicable Disease Surveillance Centre)
 Travellers Diarrhoea Introduction Travellers diarrhoea (TD) is a syndrome that commonly affects travellers caused by one of several different organisms, the most common being enterotoxigenic Escherichia
Travellers Diarrhoea Introduction Travellers diarrhoea (TD) is a syndrome that commonly affects travellers caused by one of several different organisms, the most common being enterotoxigenic Escherichia
Many of you asked about this topic
 Many of you asked about this topic Water borne disease: The largest water quality problem in developing countries. CEE 3510 Environmental Quality Engineering According to: Chemical and Engineering News
Many of you asked about this topic Water borne disease: The largest water quality problem in developing countries. CEE 3510 Environmental Quality Engineering According to: Chemical and Engineering News
EGGSHELL MORPHOLOGY OF THE SMALL EGGS OF HUMAN TREMATODES IN THAILAND
 EGGSHELL MORPHOLOGY OF THE SMALL EGGS OF HUMAN TREMATODES IN THAILAND Smam Tesana l, Tuanchai Srisawangwonk l, Sasithom.Kaewkes l, Paiboon Sithithawom l, Pipatphong Kanla2 and Channarong Arunyanart2 IDepartment
EGGSHELL MORPHOLOGY OF THE SMALL EGGS OF HUMAN TREMATODES IN THAILAND Smam Tesana l, Tuanchai Srisawangwonk l, Sasithom.Kaewkes l, Paiboon Sithithawom l, Pipatphong Kanla2 and Channarong Arunyanart2 IDepartment
Gut parasites in general practice
 Gut parasites in general practice A biased account Dr. Samson Wong Department of Microbiology The University of Hong Kong Classification of parasites Protozoa Helminths Arthropods Nematodes (roundworms)
Gut parasites in general practice A biased account Dr. Samson Wong Department of Microbiology The University of Hong Kong Classification of parasites Protozoa Helminths Arthropods Nematodes (roundworms)
RISK-BASED SURVEILLANCE FOR FOOD-BORNE PARASITES Advantages, requirements and limitations
 RISK-BASED SURVEILLANCE FOR FOOD-BORNE PARASITES Advantages, requirements and limitations Lis Alban DVM, PhD., DipECVPH Chief Scientist, Danish Agriculture & Food Council Adjunct Professor, University
RISK-BASED SURVEILLANCE FOR FOOD-BORNE PARASITES Advantages, requirements and limitations Lis Alban DVM, PhD., DipECVPH Chief Scientist, Danish Agriculture & Food Council Adjunct Professor, University
Epidemiology, diagnosis and control of Toxoplasma gondii in animals and food stuff
 Epidemiology, diagnosis and control of Toxoplasma gondii in animals and food stuff Aize Kijlstra Rome 2009 Toxoplasmosis is a neglected disease entity Disease burden is similar to salmonellosis and campylobacteriosis
Epidemiology, diagnosis and control of Toxoplasma gondii in animals and food stuff Aize Kijlstra Rome 2009 Toxoplasmosis is a neglected disease entity Disease burden is similar to salmonellosis and campylobacteriosis
Giardiasis. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Case Definition... Error! Bookmark not defined. Reporting Requirements... 2 Etiology... Error! Bookmark not defined. Clinical Presentation... Error! Bookmark not defined. Diagnosis...
Table of Contents Case Definition... Error! Bookmark not defined. Reporting Requirements... 2 Etiology... Error! Bookmark not defined. Clinical Presentation... Error! Bookmark not defined. Diagnosis...
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 5, May ISSN Parasitological contamination
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 5, May-2016 885 Parasitological Contamination of Some Common Consumable Farm Produce in Dekina Kogi State, Nigeria Omowaye,.
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 5, May-2016 885 Parasitological Contamination of Some Common Consumable Farm Produce in Dekina Kogi State, Nigeria Omowaye,.
The Global Burden of Foodborne Disease: Overview and Implications. Arie Havelaar on behalf of FERG
 The Global Burden of Foodborne Disease: Overview and Implications Arie Havelaar on behalf of FERG Summary FERG: why, what, how? Global overview of burden of foodborne disease Regional differences Policy
The Global Burden of Foodborne Disease: Overview and Implications Arie Havelaar on behalf of FERG Summary FERG: why, what, how? Global overview of burden of foodborne disease Regional differences Policy
INTRODUCTION TO PARASITOLOGY OBJECTIVES/RATIONALE
 INTRODUCTION TO PARASITOLOGY OBJECTIVES/RATIONALE Parasitology is the study of organisms that derive their nourishment from other living things and cause damage. The student will identify the morphology
INTRODUCTION TO PARASITOLOGY OBJECTIVES/RATIONALE Parasitology is the study of organisms that derive their nourishment from other living things and cause damage. The student will identify the morphology
CHAPTER 4: DISEASES SPREAD BY FOOD AND WATER
 CHAPTER 4: DISEASES SPREAD BY FOOD AND WATER Highlights The incidence of diseases spread by food and water was generally higher in Peel than Ontario with the exceptions of hepatitis A and verotoxinproducing
CHAPTER 4: DISEASES SPREAD BY FOOD AND WATER Highlights The incidence of diseases spread by food and water was generally higher in Peel than Ontario with the exceptions of hepatitis A and verotoxinproducing
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO MD (MEDICAL PARASITOLOGY) EXAMINATION JANUARY, 2001 PAPER 1
 JANUARY, 2001 Date: 15 th January 2001 Time: 2.00 p.m. -500 p.m. PAPER 1 Answer all five (5) questions Answer each question in a separate book 1. Discuss the underlying principles relating to the use of
JANUARY, 2001 Date: 15 th January 2001 Time: 2.00 p.m. -500 p.m. PAPER 1 Answer all five (5) questions Answer each question in a separate book 1. Discuss the underlying principles relating to the use of
NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE OF MITOCHONDRIAL CO I AND RIBOSOMAL ITS II GENES OF OPISTHORCHIS VIVERRINI IN NORTHEAST THAILAND
 NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE OF MITOCHONDRIAL CO I AND RIBOSOMAL ITS II GENES OF OPISTHORCHIS VIVERRINI IN NORTHEAST THAILAND Katsuhiko Ando 1, Paiboon Sithithaworn 2, Chadaporn Nuchjungreed 2, Smarn Tesana 2,
NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE OF MITOCHONDRIAL CO I AND RIBOSOMAL ITS II GENES OF OPISTHORCHIS VIVERRINI IN NORTHEAST THAILAND Katsuhiko Ando 1, Paiboon Sithithaworn 2, Chadaporn Nuchjungreed 2, Smarn Tesana 2,
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #82 (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #82 (Lynne S. Garcia) ***Reminder: Slides are copyrighted and cannot be copied for publication. A 57 year old male was seen at a local clinic with a year-long history of productive
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #82 (Lynne S. Garcia) ***Reminder: Slides are copyrighted and cannot be copied for publication. A 57 year old male was seen at a local clinic with a year-long history of productive
Trichinella Transmission and Control
 Trichinella Transmission and Control David Jenkins School of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, Charles Sturt University, Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia djjenkins@csu.edu.au The generosity of Dr K Darwin Murelle
Trichinella Transmission and Control David Jenkins School of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, Charles Sturt University, Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia djjenkins@csu.edu.au The generosity of Dr K Darwin Murelle
Enteric infections and common food borne diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, protozoa and parasites TYPICAL
 APPENDIX 9.1 Enteric infections and common food borne diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, protozoa and parasites COMMON FOODBORNE S CAUSED BY BACTERIA Bacillus cereus food poisoning diarrheal Bacillus
APPENDIX 9.1 Enteric infections and common food borne diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, protozoa and parasites COMMON FOODBORNE S CAUSED BY BACTERIA Bacillus cereus food poisoning diarrheal Bacillus
Section One: Background Material
 Section One: Background Material What is the problem? Every day people all over the world get sick from the food they eat. This sickness is called foodborne disease and is caused by dangerous microorganisms
Section One: Background Material What is the problem? Every day people all over the world get sick from the food they eat. This sickness is called foodborne disease and is caused by dangerous microorganisms
Hepatitis E FAQs for Health Professionals
 Hepatitis E FAQs for Health Professionals Index of Questions ± Overview and Statistics What is Hepatitis E? How common is Hepatitis E in the United States? Where is Hepatitis E most common? Are there different
Hepatitis E FAQs for Health Professionals Index of Questions ± Overview and Statistics What is Hepatitis E? How common is Hepatitis E in the United States? Where is Hepatitis E most common? Are there different
Giardiasis Surveillance Protocol
 Provider Responsibilities 1. Report all cases to your local health department by completing the provider section of the WVEDSS form within the timeframe indicated: Sporadic case of - should be reported
Provider Responsibilities 1. Report all cases to your local health department by completing the provider section of the WVEDSS form within the timeframe indicated: Sporadic case of - should be reported
Recent State of Parasitoses in Japan
 Parasitoses Recent State of Parasitoses in Japan Epidemiology for clinicians JMAJ 48(3): 148 154, 2005 Yoshiya SATO Professor, University of the Ryukyus Abstract: The recent profile of parasitic diseases
Parasitoses Recent State of Parasitoses in Japan Epidemiology for clinicians JMAJ 48(3): 148 154, 2005 Yoshiya SATO Professor, University of the Ryukyus Abstract: The recent profile of parasitic diseases
Parasitology lab. ü interdiction
 Parasitology lab ü interdiction "Humans are hosts to nearly 300 species of parasitic worms and over 70 species of protozoa, some derived from our primate ancestors and some acquired from the animals we
Parasitology lab ü interdiction "Humans are hosts to nearly 300 species of parasitic worms and over 70 species of protozoa, some derived from our primate ancestors and some acquired from the animals we
Western Pacific Region Neglected Tropical Diseases News
 Western Pacific Region Neglected Tropical Diseases News 2015 Issue 1 Welcome to Western Pacific NTD News! This newsletter, to be published quarterly by the WHO Regional Office for the Western Pacific,
Western Pacific Region Neglected Tropical Diseases News 2015 Issue 1 Welcome to Western Pacific NTD News! This newsletter, to be published quarterly by the WHO Regional Office for the Western Pacific,
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines August 2011
 August 2011 Trichinosis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 October 2005 Case Definition
August 2011 Trichinosis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 October 2005 Case Definition
Addis Ababa Institute of Technology Department of Civil Engineering. Zerihun Alemayehu
 CHAPTER 2 WATER QUALITY AND HEALTH Addis Ababa Institute of Technology Department of Civil Engineering Water Treatment Zerihun Alemayehu Some Water Facts Body composition Body, 65% water; blood, 83%; bones,
CHAPTER 2 WATER QUALITY AND HEALTH Addis Ababa Institute of Technology Department of Civil Engineering Water Treatment Zerihun Alemayehu Some Water Facts Body composition Body, 65% water; blood, 83%; bones,
Future Challenges in Diagnostic Medical Parasitology
 LYNNE S. GARCIA, MS, CLS, FAAM Lynnegarcia2@verizon.net CAPHLD 65 th Institute Future Challenges in Diagnostic Medical Parasitology SPONSOR: MEDICAL CHEMICAL CORPORATION 1 UNIVERSAL FIXATIVES OPTIONS:
LYNNE S. GARCIA, MS, CLS, FAAM Lynnegarcia2@verizon.net CAPHLD 65 th Institute Future Challenges in Diagnostic Medical Parasitology SPONSOR: MEDICAL CHEMICAL CORPORATION 1 UNIVERSAL FIXATIVES OPTIONS:
Original article. Chalobol Wongsawad a, b, Pheravut Wongsawad a, Somboon Anuntalabhochai a, Jong-Yil Chai c, Kom Sukontason d a
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 7 No. 1 February 2013; 97-104 DOI: 10.5372/1905-7415.0701.155 Original article Occurrence and molecular identification of liver and minute intestinal flukes metacercariae in freshwater
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 7 No. 1 February 2013; 97-104 DOI: 10.5372/1905-7415.0701.155 Original article Occurrence and molecular identification of liver and minute intestinal flukes metacercariae in freshwater
HOUSEFLIES WITH HELMINTHIC OBJECTS, GOOD INDICATOR OF AN UNSANITARY ENVIRONMENT
 HOUSEFLIES WITH HELMINTHIC OBJECTS, GOOD INDICATOR OF AN UNSANITARY ENVIRONMENT Wanna Maipanich, Paron Dekumyoy, Surapol Sa-nguankiat, Somchit Pubampen, Akkarin Poodeepiyasawat, Teera Kusolsuk, Urusa Thaenkham,
HOUSEFLIES WITH HELMINTHIC OBJECTS, GOOD INDICATOR OF AN UNSANITARY ENVIRONMENT Wanna Maipanich, Paron Dekumyoy, Surapol Sa-nguankiat, Somchit Pubampen, Akkarin Poodeepiyasawat, Teera Kusolsuk, Urusa Thaenkham,
Surveillance and early warning systems for climate sensitive diseases in Vietnam and Laos
 Surveillance and early warning systems for climate sensitive diseases in Vietnam and Laos Hu Suk Lee Workshop on climate change and health Hanoi, Vietnam, 23 November 2015 Outline Introduction of Pestforecast
Surveillance and early warning systems for climate sensitive diseases in Vietnam and Laos Hu Suk Lee Workshop on climate change and health Hanoi, Vietnam, 23 November 2015 Outline Introduction of Pestforecast
Human African Trypanosomiasis
 Human African Trypanosomiasis Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense Trypanosomoa brucei gambiense Acute -- can cause death in weeks or months Chronic --lasts years 100% Fatal if left untreated cardiac failure
Human African Trypanosomiasis Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense Trypanosomoa brucei gambiense Acute -- can cause death in weeks or months Chronic --lasts years 100% Fatal if left untreated cardiac failure
Developmental and Phylogenetic Characteristics of Stellantchasmus falcatus (Trematoda: Heterophyidae) from Thailand
 ISSN (Print) 2341 ISSN (Online) 17386 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Parasitol Vol. 53, No. 2: 2127, April 215 http://dx.doi.org/1.3347/kjp.215.53.2.21 Developmental and Phylogenetic Characteristics of Stellantchasmus
ISSN (Print) 2341 ISSN (Online) 17386 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Parasitol Vol. 53, No. 2: 2127, April 215 http://dx.doi.org/1.3347/kjp.215.53.2.21 Developmental and Phylogenetic Characteristics of Stellantchasmus
Correspondence should be addressed to Xing-Quan Zhu;
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation e Scientific World Journal Volume 2014, Article ID 893981, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/893981 Research Article Rapid Detection and Differentiation of Clonorchis
Hindawi Publishing Corporation e Scientific World Journal Volume 2014, Article ID 893981, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/893981 Research Article Rapid Detection and Differentiation of Clonorchis
Parasites List of Pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis) Giardia ( Giardia lamblia Coccidia ( Cryptosporidium
 Parasites List of Pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis) Pinworm, also known as seatworm or threadworm, is one of the most prevalent intestinal parasites in the United States, with approximately 40 million
Parasites List of Pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis) Pinworm, also known as seatworm or threadworm, is one of the most prevalent intestinal parasites in the United States, with approximately 40 million
ESCHERICHIA COLI. Pet Health Council Escherichia coli Updated November
 ESCHERICHIA COLI Introduction Escherichia coli 0157:H7 (E. coli 0157) is a cause of food borne illness. Infection may result in sickness and diarrhoea, which can often be severe and with blood. Complications
ESCHERICHIA COLI Introduction Escherichia coli 0157:H7 (E. coli 0157) is a cause of food borne illness. Infection may result in sickness and diarrhoea, which can often be severe and with blood. Complications
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE. 1. Type of cell. 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION TO THE KINGDOM FUNGI DOMAIN EUKARYA A. General Characteristics 1. Type of cell 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION TO THE KINGDOM FUNGI DOMAIN EUKARYA A. General Characteristics 1. Type of cell 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
Infection Status of Estuarine Fish and Oysters with Intestinal Fluke Metacercariae in Muan-gun, Jeollanam-do, Korea
 ISSN (Print) 0023-4001 ISSN (Online) 1738-0006 Korean J Parasitol Vol. 50, No. 3: 215-220, September 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2012.50.3.215 Infection Status of Estuarine Fish and Oysters with
ISSN (Print) 0023-4001 ISSN (Online) 1738-0006 Korean J Parasitol Vol. 50, No. 3: 215-220, September 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2012.50.3.215 Infection Status of Estuarine Fish and Oysters with
Overview of 2014 Zoonoses Data
 1 Overview of 2014 Zoonoses Data Introduction Zoonoses are diseases and infections naturally transmissible between animals and humans. Transmission may occur via direct contact with an animal or indirect
1 Overview of 2014 Zoonoses Data Introduction Zoonoses are diseases and infections naturally transmissible between animals and humans. Transmission may occur via direct contact with an animal or indirect
Trichinosis Table of Contents
 Subsection: Trichinosis Page 1 of 9 Trichinosis Table of Contents Trichinosis Trichinosis (Trichinellosis) Fact Sheet Investigation of Trichinosis Surveillance Case Report (CDC 54.7) Subsection: Trichinosis
Subsection: Trichinosis Page 1 of 9 Trichinosis Table of Contents Trichinosis Trichinosis (Trichinellosis) Fact Sheet Investigation of Trichinosis Surveillance Case Report (CDC 54.7) Subsection: Trichinosis
PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION
 PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Parasite means : one who eats at the table of another. Differs from bacteria and viruses in their complex life cycles, intermediate hosts and chronicity. Evolved to
PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Parasite means : one who eats at the table of another. Differs from bacteria and viruses in their complex life cycles, intermediate hosts and chronicity. Evolved to
World Health Day April. Food safety
 World Health Day 2015 7 April Food safety 1 FAO/WHO World Declaration on Nutrition (1992) access to nutritionally adequate and safe food is a right of each individual. 2 Food safety is a hidden, and often
World Health Day 2015 7 April Food safety 1 FAO/WHO World Declaration on Nutrition (1992) access to nutritionally adequate and safe food is a right of each individual. 2 Food safety is a hidden, and often
