Journal of Applied Science and Agriculture
|
|
|
- Edgar Morton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AENSI Journals Journal of Applied Science and Agriculture ISSN Journal home page: Effect of Applying Plant Residues and Zinc Sulfate on Chemical Forms of Zinc in Rhizosphere and Bulk Soil and Its Relationship to Wheat Grain 1 Amir Kadkhodaie, 2 Mahmoud Kalbasi, 3 Mahmoud Solhi, 4 Habiballah Nadian, 5 Ali Gholami 1 Ph. D Student, Department of Soil Science, Khouzestan Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Ahvaz, Iran. 2 Professor, College of Agriculture, Department of Soil Science, Islamic Azad University, Khurasgan Branch, Esfahan, Iran. 3 Academic member of soil and water Agriculture and Natural Resource Research center, Esfahan, Iran. 4 Associate professor, Soil Science Department, Ramin University, Khuzestan, Iran. 5 Department of Soil Science, Khouzestan Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Ahvaz, Iran. A R T I C L E I N F O Article history: Received 8 January 2014 Received in revised form 20 February 2014 Accepted 23 February 2014 Available online 28 March 2014 Key words: Wheat, Zinc, plant residues, Rhizosphere, Zinc chemical forms A B S T R A C T Background: Zinc deficiency is considered as one of the major nutritional problems of people across the world, especially in areas where people's lives depend on cereal as a basic food. Several approaches have been proposed to deal with Zinc deficiency, of which the most common is the utilization of chemical fertilizers containing zinc. However, in calcareous soils which forms the majority of lands in Iran, most of these fertilizers will change shortly into non-absorbable form. A new strategy to deal with the shortage of micronutrient is bioenrichment of crops (crop enrichment). Objective: The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of plant residues on chemical forms of zinc in the solid phase of the soil in rhizosphere and bulk soil and its correlation with the amount of zinc in wheat grain. Result: The results showed that the application of plant residues to the chemical forms of zinc resulted in the increase in organic and carbonated forms of zinc in the soil. But, all forms of zinc particularly its oxidized and residual forms were increased by applying the zinc sulfate. The correlation between the wheat grain and the chemical forms of zinc in soil showed that there was a significant positive correlation between the concentration of zinc in wheat grain and the zinc forms (Exchangeable, Organic and Carbonated) in the rhizosphere and bulk Soil. Conclusion: Conducting this study, we can conclude that the plant can absorb zinc in exchangeable, organic and carbonated forms. The main part of the zinc added to the soil is converted to a non-available form for the plant by zinc sulfate. But the application of plant residues can increase the unavailable added zinc to the soil into the available forms of zinc for the plants through decreasing ph and increasing the dissolved organic carbon AENSI Publisher All rights reserved. To Cite This Article: Amir Kadkhodaie, Mahmoud Kalbasi, Mahmoud Solhi, Habiballah Nadian, Ali Gholami., Effect of Applying Plant Residues and Zinc Sulfate on Chemical Forms of Zinc in Rhizosphere and Bulk Soil and Its Relationship to Wheat Grain. J. Appl. Sci. & Agric., 9(3): , 2014 INTRODUCTION More than 80% of the cultivable lands suffer from zinc deficiency in various degrees and plants grown in these grounds may be zinc deficient, resulting in their reduced yield (Malakouti, 2005). Of the reasons for zinc deficiency in soils, it can be addressed to high ph, being calcareous soil, excessive utilization of phosphate fertilizers, high concentrations of bicarbonate in irrigation waters, all of which result in zinc deposit in the soil and thus its unavailability for plant to uptake. Therefore, it is necessary to add this element to the soil leading to high accumulation of the element in non-available form. Several strategies have been proposed to deal with the zinc deficiency in the soil such as crop rotation, adding sewage sludge to the land, and applying the plant residues to the soil. However, the application of plant residues to the soil is considered as a better method with fewer side-effects. Any element in the soil is found in different chemical forms which vary considerably in different soils. These differences lead to changes in the availability of elements for plant in different soils (Emst, 1996). Zinc is found in soluble and exchangeable forms, in bond with organic materials, carbonates, iron and aluminum oxides and as well as residues. But of all these forms, only the soluble and exchangeable forms, and in bond with organic materials are consumed by crops and they constitute only a minute percentage of the total zinc found in soil (Alloway, 2008). Khadivi (2003) studied the cumulative effects and the effect of compost residues, sewage sludge and manure on chemical forms and mobility factor of Pb, Ni, Cd, Zn, Cu and Fe in the soil. The results showed that the soluble, exchangeable, and carbonated forms, iron and aluminum oxides, and organic materials increased and the residues decreased by increasing the amount and frequency of fertilization. Nyamangara (1998) reported that application of sewage sludge and mineral salts increased the amount of Zinc Corresponding Author: Amir Kadkhodaie, Department of Soil Science, Khouzestan Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Ahvaz, Iran. Amir_kad2005@yahoo.com
2 943 Amir Kadkhodaie et al, 2014 in exchangeable part, while the major part of zinc was observed in the residual in the control treatment. Rhizosphere is the superficial layer of soil subject to the influence of plant roots and their associated microorganisms (Chen et al., 2006). Zinc forms such as deposited form by carbonates and phosphates, complex form with organic matter, iron oxides, and manganese oxides can be active and inactive depending on physical, chemical and biological properties of soil (Sposito, 1989). Change in the chemical form of metal and its bioavailability in the rhizosphere is the resultant of the biogeochemical concentration gradients of metal, ph, pco2, po2, the concentration of organic ligand, and microbial biomass (Hinsinger et al., 2009, Kidd et al., 2009). Wang & et al (2002) reported that the zinc bonded with iron and manganese oxides was decreased in wheat rhizosphere. They stated the reduction of iron and manganese oxides as the reason for the reduced zinc form in rhizosphere. In recent years, many researchers have based on adding different amounts of chemical fertilizers containing zinc and manure to the soil and not paid more attention to applying different plant residues in the soil and measuring the chemical forms of zinc in solid phase, as well as the correlation between these forms and the amount of zinc in wheat grain. This study will attempt to examine this issue in more accurate details. Methodology: This experiment was conducted in the form of a randomized complete block design with eight treatments (control, zinc sulfate, plant residues of alfalfa, bean and wheat and alfalfa plant residues, bean and wheat with zinc sulfate), in 3 replications in an Iranian farm at an altitude of 2059 m. of sea level, longitude of 51 degrees 39 minutes, and latitude of 31 degrees 56 minutes. At first, the studied land was plowed to a depth of 30 cm and after analyzing the soil (Table 1), it was added a required amount of macronutrients and micronutrients to all treatments, and to considered treatments zinc sulfate by 60 kg/ha and plant residues by 10 t/ha (ton per hectare) based on the mean of yield index of these plants (Malakooti & Nafissi, 1994). About two weeks after preparation of treatments, it was planted 350 kg/ha of wheat seeds in each treatment. During the growing season, the irrigation of crop was done based on plot, and the necessary agricultural cares such as eradicating weeds both mechanically and chemically. The soil was sampled in several locations at 0 to 30 cm depth from both the bulk soil and rhizosphere, and it was used the sequential extraction procedure to determine the various chemical forms of zinc in solid phase of soil. In this method, it was specified for each element 5 components, and the method was described in details in Table (2) (Tessier & et al, 1979). It was done the needed statistical calculations of the data by the software SAS, and the means of treatments were compared by Duncan test. Table 1: Some physicochemical properties of the tested soil ph EC OC CaCO 3 Texture P K Zn --- ds/m % % --- mg/kg mg/kg mg/kg Clay Loam Table 2: Measurement of Zinc Chemical forms to Tessier chemical form of Zn Extraction ph Method Exchangeable 20 ml 1 M NH 4OAc 7 30 min shaking and centrifuged Bound to Carbonates 20 ml 1 M NaOAc 5 5 hours shaking and centrifuged Bound to Iron and Manganese 20 ml 0.04 M NH 2OH.HCl 2 6 hours shaking on a 96 0 C Oxides in 25% w/v HOAc and centrifuged Bound to Organic Matter H2O2 30% 5 ml 0.1 M HNO3-30 hours shking on a 85 0 C / 10 ml+15 ml NH 4OAc 3.2 M Residual HNO 3+HClO 4+H 2SO 4-30 min shaking and centrifuged Results: Application of plant residues and zinc sulfate to zinc chemical forms in rhizosphere region and bulk soil: Applying plant residues in the soil increased significantly the organic and carbonated forms of zinc in rhizosphere region and bulk soil, but no change was observed in exchangeable, oxidized, and residual forms of zinc, compared to the control. Among the plant residues, alfalfa residues increased more the exchangeable and organic forms because of greater degradation (less C/N) and more chelating effect. The application of zinc sulfate to the soil causes a significant increase in all zinc forms in the rhizosphere and bulk soil. Also, in treatments to which was added the plant residues along with zinc sulfate, all zinc forms increased. But they had two differences compared to the treatment with zinc sulfate alone, that is, the organic form of zinc increased while the zinc residues decreased. It can be stated that the plant residues can prevent available zinc forms from converting into the zinc residues (Table 3).
3 944 Amir Kadkhodaie et al, 2014 Table 3: Application of plant residues and zinc sulfate to zinc chemical forms bulk soil )mg/kg( Treatments Exchangeable Organic Carbonate Oxide Residual Control 0.10 b 0.74 e 1.32 d 7.60 c c Zinc Solfate 0.22 a 1.42 b 2.02 ab b a Wheat residue 0.11 b 1.03 d 1.63 c 7.66 c c Bean residue 0.12 b 0.91 c 1.60 c 7.56 c c Alfalfa residue 0.11 b 1.26 c 1.83 b 7.46 c c Wheat residue + Zinc Solfate 0.20 a 1.76 a 2.10 a 3.36 a ab Bean residue + Zinc Solfate 0.19 a 1.46 b 2.03 ab b ab Alfalfa residue + Zinc Solfate 0.19 a 1.55 b 2.16 a b b Rhizosphere)mg/kg) Control 0.14 b 1.13 d 2.45 d 6.93 b b Zinc Solfate 0.24 a 1.92 bc 3.46 b 9.46 a a Wheat residue 0.15 b 1.63 c 2.83 c 6.72 b b Bean residue 0.14 b 1.83 ab 3.00 c 6.53 b b Alfalfa residue 0.14 b 1.80 bc 2.9 c 5.46 b b Wheat residue + Zinc Solfa 0.27 a 2.41 a 4.00 a a a Bean residue + Zinc Solfate 0.27 a 2.26 a 3.90 a a a Alfalfa residue + Zinc Solfat 0.27 a 2.26 a 3.86 a a a Means with the same letter are not significantly different at 5% level. Correlation between some soil properties and available zinc and chemical forms of zinc: Table (4) shows the correlation coefficients between some soil properties in rhizosphere and bulk soil and zinc forms. The results in Table (4) showed that there was a significant negative correlation between ph in bulk soil and zinc in available, exchangeable, carbonate and organic forms. But in the rhizosphere region, it was not observed a significant correlation between ph and chemical forms of zinc. A significant positive correlation was found between dissolved organic carbons in soil and the available zinc in rhizosphere and bulk soil. Based on other results, it can be addressed to the significant positive correlation between the available zinc and the exchangeable, organic, and carbonated zinc forms. But there was no significant correlation between the available zinc and oxidized and residual zinc forms. Table 4: Correlation between soil properties and chemical forms of zinc Bulk soil )mg/kg( Soil properties Available Exchangeable Organic Crbonate Oxide Residual ph * EC Soil organic carbon Dissolved organic carbon 0.6* Available zinc * 0.9 ** 0.9 ** Zinc amount in grain 0.9 ** 0.7 * 0.9 ** 0.9 ** Rhizosphere )mg/kg( ph EC Soil organic carbon Dissolved organic carbon 0.6 * Available zinc ** ** ** Zinc amount in grain ** ** ** ** Concentration of zinc in wheat grain: As seen in Fig (1), the application of plant residues to the soil led to the increase in zinc concentration in the wheat grain, compared to the control (no residue). This increase varied in treatments of different plant residues, and the most increase in the zinc concentration in wheat grain was found in the treatment of alfalfa plant residues. Also, the application of zinc sulfate to the soil resulted in the increase of zinc concentration in the grains and its impact was greater than the application of plant residues to the soil. Habibi (2010) reported in a greenhouse experiment that the addition of plant residues to the soil increases the organic carbons dissolved in the soil and consequently increases the absorption of zinc by the wheat grain.
4 945 Amir Kadkhodaie et al, 2014 Fig. 1: Application of plant residues and zinc sulfate to zinc concentration of wheat grain Means with the same letter are not significantly different at 5% level. Correlation between zinc concentration in wheat grain and chemical forms of zinc: The correlation between the wheat grain and the chemical forms of zinc in rhizosphere and bulk soil is shown in Table (4). The results showed that there was a significant positive correlation between the concentration zinc in the wheat grain and the exchangeable, organic, and carbonated forms of zinc in the rhizosphere and bulk soil, but no significant correlation was observed between it and the oxidized and residual forms of zinc. It seems that these two forms play no role in zinc absorbed by the plant. It can be expressed that the plant absorbs zinc in exchangeable, organic and carbonated forms. The correlation between the available zinc and its carbonated form indicates that zinc in carbonated form doesn t affect only the availability of zinc negatively, but can serve also as potential source for zinc available to plants in calcareous soil. Discussion: As stated in the results, the application of plant residues to the soil increases the organic and carbonated forms of zinc in rhizosphere and bulk soil. Khadivi (2003) studied the cumulative effects and the effect of compost residues, sewage sludge and cow manure on chemical forms and mobility factor of Pb, Ni, Cd, Zn, Cu and Fe in the soil. The results showed that the soluble, exchangeable, and carbonated forms, iron and aluminum oxides, and organic form increased and the residual form decreased by increasing the amount and frequency of fertilization. The comparison between rhizosphere and bulk soil showed that the exchangeable, organic, and carbonated forms are more in the rhizosphere than that in the bulk soil. It could be because of lower ph, root exudates, and microbial activities in the rhizosphere region. A study by Golestanifar (2012) showed that the soluble and exchangeable zinc increased in the rhizosphere soil of oilseed rape and maize, compared to the bulk soil. It may indicate the effective role of rhizosphere processes in the increased bioavailability of zinc. Also Cattani & et al (2006) has reported that the more dissolved organic carbon is found in the rhizosphere than the bulk soil, and this enhanced the organic form of zinc in the rhizosphere. Wang & et al (2009) reported that the zinc bonded with iron and manganese oxides was decreased in wheat rhizosphere. They expressed the reduction of iron and manganese oxides as the reason for the reduced zinc form in rhizosphere. The results of correlation coefficients shows that there was a significant negative correlation between ph and available zinc in bulk soil. As a significant positive correlation was found between dissolved organic carbons in soil and the available zinc in rhizosphere and bulk soil. Iyengar & et al. (1981) reported that there was a significant negative correlation between ph and available zinc in their 19 studied samples of soil. Studying several sample of acid soils of Canada, Neilson & et al. (1986) reported also a direct relationship between the amounts of organic matter in these soil samples and available zinc. The application of plant residues to the soil led to the increase in zinc concentration in the wheat grain, compared to the control. Yilmaz et al. (1997) showed in a study that applying various methods of Zinc consumption in different wheat cultivars increased not only the yield significantly, but also the concentration of this element in the grain and resulted in enriched grains. Concentrations of copper and zinc in wheat grain increased through applying organic matter in the soil regardless of the type of organic matter. This increase could be implying that these metals would be carried easily from stem to seed when they were absorbed by the roots (Narwal and Singh, 1998). Release of organic acids from decomposing plant residues of alfalfa is considered as a major part of several mechanisms which improves zinc absorption by plants (Singh et al., 2005). The results of correlation between the zinc concentration in wheat grain and the chemical forms of zinc indicated that there was a significant positive correlation between the zinc concentration in wheat grain and the exchangeable, organic and carbonated forms of zinc. It was reported in many studies a significant correlation between the plant response and the exchangeable zinc (Youssef & Chino,1989 ; Rupa & Shukla,
5 946 Amir Kadkhodaie et al, ). Bansal & et al. (1990) reported a significant correlation between the amount of available zinc in the soil and the amount of zinc in the wheat grain. Yasrebi (1991) observed in his studies on calcareous soils that there was a significant correlation between the concentration of carbonated zinc and the concentration of zinc in plant. Also, Stanton & Burger (1967) stated in their study that iron oxide has a high affinity to absorb zinc. But the zinc absorbed by iron oxides in the soil is useless for the plant is. Conclusion: Conducting this study, we can conclude that the chemical forms of zinc play important role in its absorption by plants, and plants Can absorb the exchangeable, organic and carbonate forms of zinc. The application of zinc sulfate to the soil resulted in the increase in all forms of zinc, particularly its oxidized and residual forms. That is, the major part of zinc added to soil will turn into non-available form for the plant, but the application of plant residues can change the unavailable added zinc to the soil into the absorbable forms of zinc to be absorbed into the plant through decreasing ph and increasing the dissolved organic carbon. Also the application of zinc along with the plant residues can increase the absorbable forms of zinc (exchangeable, organic and carbonate) and reduce the non-absorbable forms of zinc (oxidized and residual), compared to the application of zinc sulfate alone, and also the zinc concentration is increased further in grain. REFRENCE A Book : Alloway, B.J., Zinc in Soils and Crop Nutrition. IZA and IFA, Brussels, Belgium and Paris. Journal Articles: Bansal, R.L., P.N. Taklear, A.l. Bhandari and D.S. Rana,1990. Critical levels of DTPA extractable Zn for wheat in alkaline soils of semiarid region of Punjab, India, Fer. Res., 21(3): Journal Articles: Cattani, I., G. Fragoulis, R. Boccelli and E. Capri, Copper bioavailability in the rhizosphere of maize (Zeamays L.) grown in two Italian soils. Chemosphere, 64: Journal Articles: Chen, Y.M., M.K. Wang, S.Y. Zhuang and P.N. Chiang, Chemical and physical properties of rhizosphere and bulk soils of three tea plants cultivated in Ultisols. Geoderma, 36: Journal Articles: Ernst, W.H.O., Bioavailability of heavy metal and decontamination of soil by plants.appl. Geochem, 11: Journal Articles: Golestanifar, A., Evaluation of different chemical forms of lead and zinc in oilseed rape and maize rhizosphere. Journal of Soil and Water., 26(6): A Thesis: Habibi, H., Effect of cultivation on some soil chemical properties and growth, yield and zinc concentration in wheat grain. M.S. thesis, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Technology, Isfahan,Iran. Journal Articles: Hinsinger, P., C. Plassard and B. Jaillard, Rhizosphere: A new frontier for soil biogeochemistry. J. Geochem. Explor., 88: Journal Articles: Iyengar, S.S., D.C. Martens and W.P. Miller,1981. Distribution and plant availabiliy of soil zinc fractions. Soil. Sci. Soc. Ame. J. 45: A Thesis: Khadivi, A., Effect of organic fertilizers and chemical forms of heavy metals in soil and uptake of its by wheat. M.S. thesis, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Technology, Isfahan, Iran. Journal Articles: Kidd, P., J. Barcelo, M.P. Bernal, F. Navari-Izzo, C. Poschenrider, S. Shilev, R. Clemente, and C. Monterroso, Trace element behavior at the root-soil interface: Implication in photoremediation. Enviro. Exp. Bot., 67: Journal Articles: Malakouti, M.J., Important role of zinc in enhancing crop yeild and improving human health. General Meeting of Third world academey of Science. TWAS 16 th. Alexandria, Egypt. A Book: Malakooti, M.J., and M. Nafissi, Fertilizer use in irrigated and rainfed lands (translator), Tarbiat Modarres University Press, Tehran. Iran. Journal Articles: Narwal, R. P., and B.R. Singh, Effect of organic materials on partitioning, extractability and plant uptake of metals in an alum shale soil. Water Air Soil Poll., 103: Journal Articles: Neilson, D., P.B. Hoyt and F. Mackenzie, Distribution of soil Zn fractions in British Columbia interior orchard soils. Can. J. Soil Sci., 66: Journal Articles: Nyamangara, J., Use of sequential extraction to evaluate zinc and copper in a soil amended with sewage sludge and inorganic metal salts. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment. 69: Journal Articles: Rupa, T.R. and L.M. Shukla, Comparison of four extractants and chemical fractions for assessing available zinc and copper in soils of India. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal., 30: Journal Articles: Stanton, D.A. and R.T. Burger, Availability to plants of zinc absorbed by soil and hydrous iron oxides. Geoderma., 1: Journal Articles: Singh. G., S.K.A. Natesan, B.K. Singh and K. Usha, Improving Zinc efficiency of cereals under zinc deficiency. Curr. Sci., 88: Journal Articles: Sposito. G., L.J. lund and A.C. Chang, Trace metal chemistry in arid- zone field soils amended with sewage sludge, fraction of Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb in solid phases. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 46:
6 947 Amir Kadkhodaie et al, 2014 Journal Articles: Tessier A., P.G.C. Campbell and M. Bisson, Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem., 51: Journal Articles: Wang, J., C.B. Zhang and Z.X. Jin, The distribution and phytoavailability of heavy metal fractions in rhizosphere soils of Paulowniu fortunei (Seem) Hems near a Pb/Zn smelter in Guangdong, PR China. Geoderma. 148: A Thesis: Yasrebi, J., Effects of zinc on the remaining forms in calcareous soils of Fars and relationships with growth and Zn in maize. M.S. thesis, Soil Science, Faculty Agriculture, Shiraz, Iran. Journal Articles: Youssef, R.A. and M. Chino, Root-induced changes in the rhizosphere of plants. II. Distribution of heavy metals across the rhizosphere in soils. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr., 35:
The 1 th International and The 4 th National Congress on Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture April 2012 in Isfahan, Iran
 PERIODIC MUNICIPAL COMPOST AND SEWAGE SLUDGE APPLICATION ON ACCUMULATION OF HEAVY METALS IN SOIL AND PLANTS Ali R. Marjovvi 1,* and Moslehedin Rezaei 1 1 Soil and Water Department, Isfahan Agricultural
PERIODIC MUNICIPAL COMPOST AND SEWAGE SLUDGE APPLICATION ON ACCUMULATION OF HEAVY METALS IN SOIL AND PLANTS Ali R. Marjovvi 1,* and Moslehedin Rezaei 1 1 Soil and Water Department, Isfahan Agricultural
Received: 4 th April-2014 Revised: 24 th May-2014 Accepted: 26 th May-2014 Research article
 Received: 4 th April-2014 Revised: 24 th May-2014 Accepted: 26 th May-2014 Research article BIOCHAR EFFECTS ON COPPER AVAILABILITY AND UPTAKE BY SUNFLOWER IN A COPPER CONTAMINATED CALCAREOUS SOIL Mina
Received: 4 th April-2014 Revised: 24 th May-2014 Accepted: 26 th May-2014 Research article BIOCHAR EFFECTS ON COPPER AVAILABILITY AND UPTAKE BY SUNFLOWER IN A COPPER CONTAMINATED CALCAREOUS SOIL Mina
Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability
 Symposium no. 33 Paper no. 08 Presentation: poster Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability KHOSHGOFTARMENSH A.H., JAAFARI B. and SHARIATMADARI H. Department of Soil Science, College of Agriculture,
Symposium no. 33 Paper no. 08 Presentation: poster Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability KHOSHGOFTARMENSH A.H., JAAFARI B. and SHARIATMADARI H. Department of Soil Science, College of Agriculture,
COMPARISON THE EFFECTS OF SPRAYING DIFFERENT AMOUNTS OF NANO ZINCOXIDE AND ZINC OXIDE ON, WHEAT
 Received: 05 th May-201 Revised: 27 th June-201 Accepted: 29 th June-201 Research article COMPARISON THE EFFECTS OF SPRAYING DIFFERENT AMOUNTS OF NANO ZINCOXIDE AND ZINC OXIDE ON, WHEAT Isa Afshar 1, Akbar
Received: 05 th May-201 Revised: 27 th June-201 Accepted: 29 th June-201 Research article COMPARISON THE EFFECTS OF SPRAYING DIFFERENT AMOUNTS OF NANO ZINCOXIDE AND ZINC OXIDE ON, WHEAT Isa Afshar 1, Akbar
VOL. 5, NO. 6, June 2015 ISSN ARPN Journal of Science and Technology All rights reserved.
 VOL. 5, NO. 6, June 2015 ISSN 22-7217 Impact of Cumulative Sediment Deposition by Irrigation Water on Soil and Sugarcane in Savannah Sugar Company Limited; Numan, Adamawa State Nigeria 1 R.P. Ali, 2 H.M.
VOL. 5, NO. 6, June 2015 ISSN 22-7217 Impact of Cumulative Sediment Deposition by Irrigation Water on Soil and Sugarcane in Savannah Sugar Company Limited; Numan, Adamawa State Nigeria 1 R.P. Ali, 2 H.M.
AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 9, No 3, pp 195-200, 2007 Copyright 2007 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA TH.
Global NEST Journal, Vol 9, No 3, pp 195-200, 2007 Copyright 2007 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA TH.
UPTAKE OF MAJOR AND TRACE ELEMENTS BY GRASS BIOMASS AFTER AMELIORATION OF DEGRADED SOIL
 General and Applied Plant Physiology 2010, Volume 36 (1 2), pp. 12 16 2010 ISSN 1312-8183 Published by the Institute of Plant Physiology Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Available online at http://www.bio21.bas.bg/ipp/
General and Applied Plant Physiology 2010, Volume 36 (1 2), pp. 12 16 2010 ISSN 1312-8183 Published by the Institute of Plant Physiology Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Available online at http://www.bio21.bas.bg/ipp/
Discuss the importance of healthy soils Soil properties, physical, chemical and biological that one can manage for soil health How organics play a
 Andrew Ristvey The University of Maryland Extension programs are open to any person and will not discriminate against anyone because of race, age, sex, color, sexual orientation, physical or mental disability,
Andrew Ristvey The University of Maryland Extension programs are open to any person and will not discriminate against anyone because of race, age, sex, color, sexual orientation, physical or mental disability,
Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils
 The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
Trace Elements in Manure
 Trace Elements in Manure Purpose: Whenever soil profiles are examined for nutrient trace elements, it has been demonstrated that the metals tend to accumulate in the topsoil. Soil properties affect plant
Trace Elements in Manure Purpose: Whenever soil profiles are examined for nutrient trace elements, it has been demonstrated that the metals tend to accumulate in the topsoil. Soil properties affect plant
The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient Soil
 387 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (2006), 387-392 National Centre for Agrarian Sciences The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient
387 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (2006), 387-392 National Centre for Agrarian Sciences The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient
Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in
 Vol. 28, pp. 39-43, /979 Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in Relation to Heavy Metal Content of Sludge-Amended Soil by Frank T. Bingham* Results of greenhouse and laboratory experiments on factors influencing
Vol. 28, pp. 39-43, /979 Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in Relation to Heavy Metal Content of Sludge-Amended Soil by Frank T. Bingham* Results of greenhouse and laboratory experiments on factors influencing
BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION. MACRONUTRIENTS Found in air and water carbon C oxygen hydrogen
 BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION Segment One Nutrient Listing Plants need 17 elements for normal growth. Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are found in air and water. Nitrogen, phosphorus,
BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION Segment One Nutrient Listing Plants need 17 elements for normal growth. Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are found in air and water. Nitrogen, phosphorus,
EFFECTS OF ZINC AND BORON ON YIELD, NUTRIENT UPTAKE AND ECONOMICS OF MUSTARD (BRASSICA JUNCEA L.) IN MUSTARD-MAIZE CROPPING SEQUENCE
 Bangladesh J. Bot. 46(2): 817-821, 2017 (June) - Short communication EFFECTS OF ZINC AND BORON ON YIELD, NUTRIENT UPTAKE AND ECONOMICS OF MUSTARD (BRASSICA JUNCEA L.) IN MUSTARD-MAIZE CROPPING SEQUENCE
Bangladesh J. Bot. 46(2): 817-821, 2017 (June) - Short communication EFFECTS OF ZINC AND BORON ON YIELD, NUTRIENT UPTAKE AND ECONOMICS OF MUSTARD (BRASSICA JUNCEA L.) IN MUSTARD-MAIZE CROPPING SEQUENCE
Soil Fertility and Nutrient Management. Hailin Zhang. Department of Plant and Soil Sciences
 Soil Fertility and Nutrient Management Hailin Zhang Department of Plant and Soil Sciences C H O P N K 16 ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS Ca S Mg B Cl Cu Fe Mn Mo B NON-MINERAL NUTRIENTS Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Oxygen
Soil Fertility and Nutrient Management Hailin Zhang Department of Plant and Soil Sciences C H O P N K 16 ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS Ca S Mg B Cl Cu Fe Mn Mo B NON-MINERAL NUTRIENTS Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Oxygen
Total zinc was determined by digesting the soil ZnSO 4
 ADVANCE RESEARCH JOURNAL OF CROP IMPROVEMENT Volume 2 Issue 2 (December, 2011) Page : 203-207 Received : September, 2011; Revised : October, 2011; Accepted : November, 2011 Research Paper See end of the
ADVANCE RESEARCH JOURNAL OF CROP IMPROVEMENT Volume 2 Issue 2 (December, 2011) Page : 203-207 Received : September, 2011; Revised : October, 2011; Accepted : November, 2011 Research Paper See end of the
Estimating Micronutrient Status and their Relationship with Other Soil Properties of Rewa District in Fiji
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.335
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.335
Downloaded from jstnar.iut.ac.ir at 21:58 IRDT on Monday May 14th 2018
 / / / *...... (// : // : ).. ( ) ( ) (P ()... ... / / / /..
/ / / *...... (// : // : ).. ( ) ( ) (P ()... ... / / / /..
Effect of Fly Ash application on Microbial Population in Acid Soil
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 12 (2017) pp. 888-894 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.612.096
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 12 (2017) pp. 888-894 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.612.096
ANALYSIS OF RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT CHELATED ZINC SOURCES ON MICRO AND MACRO NUTRIENTS UPTAKE IN MOONG PLANT AND SEED (VIGNA RADIATA)
 ANALYSIS OF RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT CHELATED ZINC SOURCES ON MICRO AND MACRO NUTRIENTS UPTAKE IN MOONG PLANT AND SEED (VIGNA RADIATA) Jilani A A 1 1 Department of Chemistry, St. John s College, Agra-282003
ANALYSIS OF RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT CHELATED ZINC SOURCES ON MICRO AND MACRO NUTRIENTS UPTAKE IN MOONG PLANT AND SEED (VIGNA RADIATA) Jilani A A 1 1 Department of Chemistry, St. John s College, Agra-282003
Soil Composition. Air
 Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
ABSTRACT. Keywords: Added Zn, Significant increase, Exchangeable Zn, Aerobic and Anaerobic Condition INTRODUCTION
 J. Sci. Foundation, 9(1&): 9-14, June-December 11 ISSN 178-7855 INCUBATION STUDIES ON EXCHANGEABLE Zn FOR VARYING LEVELS OF ADDED Zn UNDER AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC CONDITIONS IN GREY TERRACE SOILS, NON CALCARIOUS
J. Sci. Foundation, 9(1&): 9-14, June-December 11 ISSN 178-7855 INCUBATION STUDIES ON EXCHANGEABLE Zn FOR VARYING LEVELS OF ADDED Zn UNDER AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC CONDITIONS IN GREY TERRACE SOILS, NON CALCARIOUS
Understanding a Soil Report
 Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
Assessment of Secondary and Micro Nutrient Status under Long-Term Fertilizer Experiment on Vertisol
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Joga Rao et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (4): 328-339 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.3068 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Available online at www.ijpab.com Joga Rao et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (4): 328-339 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.3068 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Micro Nutrient Evaluation in Soils of Jhabua District of Madhya Pradesh
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Patidar et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (1): 918-926 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.2508 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Available online at www.ijpab.com Patidar et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (1): 918-926 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.2508 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Study of Zinc effects on quantitative and qualitative traits of winter wheat in saline soil condition
 Study of Zinc effects on quantitative and qualitative traits of winter wheat in saline soil condition M. Seilsepour * Academic Member of Varamin Agricultural Research (Received 12 Jan. 2006, Accepted 3
Study of Zinc effects on quantitative and qualitative traits of winter wheat in saline soil condition M. Seilsepour * Academic Member of Varamin Agricultural Research (Received 12 Jan. 2006, Accepted 3
Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001
 Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001 K.A. Kelling and P.E. Speth Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison Why micronutrients now: Higher yield, therefore
Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001 K.A. Kelling and P.E. Speth Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison Why micronutrients now: Higher yield, therefore
Bio-accessibility of Trace Metals Using Chemical Fractionation and In Vitro Extraction Methods
 Bio-accessibility of Trace Metals Using Chemical Fractionation and In Vitro Extraction Methods Naomi Waissman Assadian 1 and Juan Pedro Flores Margez 2 Abstract Rural and urban border communities at Paso
Bio-accessibility of Trace Metals Using Chemical Fractionation and In Vitro Extraction Methods Naomi Waissman Assadian 1 and Juan Pedro Flores Margez 2 Abstract Rural and urban border communities at Paso
Welcome. Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories
 Welcome Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories Discussion Soil test levels Dropping P,K Organic matter levels dropping Cost of Fertilizer Increasing due to Global Demand Environmental
Welcome Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories Discussion Soil test levels Dropping P,K Organic matter levels dropping Cost of Fertilizer Increasing due to Global Demand Environmental
Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients. Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients. Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops
 Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops Yield K 2 O taken up Crop level/ac in total crop, lb Alfalfa 8 tons
Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops Yield K 2 O taken up Crop level/ac in total crop, lb Alfalfa 8 tons
Distribution of Micronutrients in Soil of Garhi Tehsil, Banswara District of Rajasthan, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 3765-3772 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.455
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 3765-3772 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.455
The Effect of Composted and Un-Composted Date-Palm Waste as a Media on Some Microelements of Tomato Fruit
 Research Journal of Recent Sciences ISSN 2277-2502 Res.J.Recent Sci. The Effect of Composted and Un-Composted Date-Palm Waste as a Media on Some Microelements of Tomato Fruit Abstract Shirani M. 1 and
Research Journal of Recent Sciences ISSN 2277-2502 Res.J.Recent Sci. The Effect of Composted and Un-Composted Date-Palm Waste as a Media on Some Microelements of Tomato Fruit Abstract Shirani M. 1 and
Interpretation of Soil Tests for Environmental Considerations
 Interpretation of Soil Tests for Environmental Considerations Ray Ward Ward Laboratories, Inc Kearney, NE www.wardlab.com Guiding Producers Today to Feed the World Tomorrow www.wardlab.com Saline County
Interpretation of Soil Tests for Environmental Considerations Ray Ward Ward Laboratories, Inc Kearney, NE www.wardlab.com Guiding Producers Today to Feed the World Tomorrow www.wardlab.com Saline County
Effect of Micronutrients Application on Availability of Zn, Fe and B of Sunflower (Helianthus annus L.) in Inceptisol
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 438-442 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.051
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 438-442 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.051
Interpreting Soils Report. Beyond N P K
 Interpreting Soils Report Beyond N P K What we will cover We will not discuss Macro Nutrients Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium. We will touch on Secondary Nutrients Magnesium, Calcium and Sulfur. We
Interpreting Soils Report Beyond N P K What we will cover We will not discuss Macro Nutrients Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium. We will touch on Secondary Nutrients Magnesium, Calcium and Sulfur. We
Yield and quality of cumin as influenced by FYM enriched micronutrients
 International J. Seed Spices 6(1), Jan 2016: 17-24 Abstract Yield and quality of cumin as influenced by FYM enriched micronutrients S. M. Patel, A. U. Amin, S. P. Patel and B. T. Patel Center for Research
International J. Seed Spices 6(1), Jan 2016: 17-24 Abstract Yield and quality of cumin as influenced by FYM enriched micronutrients S. M. Patel, A. U. Amin, S. P. Patel and B. T. Patel Center for Research
Micronutrient Management. Dorivar Ruiz Diaz Soil Fertility and Nutrient Management
 Micronutrient Management Dorivar Ruiz Diaz Soil Fertility and Nutrient Management Essential Nutrients Thirteen essential nutrients Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur Iron, manganese,
Micronutrient Management Dorivar Ruiz Diaz Soil Fertility and Nutrient Management Essential Nutrients Thirteen essential nutrients Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur Iron, manganese,
26 27 April 2012 in Isfahan, Iran. Hamid Reza Rahmani. Scientific Member of Soil and Water Institute of Iran.
 The 1 th International and The 4 th National Congress on Effect of Industrial Recycling and Municipal of Organic Effluent Waste On in Agriculture Soil, Water, and Plants in Isfahan Hamid Reza Rahmani Scientific
The 1 th International and The 4 th National Congress on Effect of Industrial Recycling and Municipal of Organic Effluent Waste On in Agriculture Soil, Water, and Plants in Isfahan Hamid Reza Rahmani Scientific
May 2008 AG/Soils/ pr Understanding Your Soil Test Report Grant E. Cardon Jan Kotuby-Amacher Pam Hole Rich Koenig General Information
 May 2008 AG/Soils/2008-01pr Understanding Your Soil Test Report Grant E. Cardon, USU Extension Soil Specialist Jan Kotuby-Amacher, Coordinator for North American Proficiency Testing Program Pam Hole, Supervisor
May 2008 AG/Soils/2008-01pr Understanding Your Soil Test Report Grant E. Cardon, USU Extension Soil Specialist Jan Kotuby-Amacher, Coordinator for North American Proficiency Testing Program Pam Hole, Supervisor
Soil Organic Matter. Unit 2. Forms of Soil Organic Matter: OM OC x (assumes 30% C) (1.72 typically used as a conversion factor)
 Unit 2 Soil Organic Matter OM OC x 1.7-2.0 (assumes 30% C) (1.72 typically used as a conversion factor) Histosol Alfisol Spodosol Forms of Soil Organic Matter: - dissolved (soil solution): DOM Nonliving
Unit 2 Soil Organic Matter OM OC x 1.7-2.0 (assumes 30% C) (1.72 typically used as a conversion factor) Histosol Alfisol Spodosol Forms of Soil Organic Matter: - dissolved (soil solution): DOM Nonliving
Zinc Deficiency in Soil of Rajasthan and its Management
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Nagar et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (3): 154-158 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.6548 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6
Available online at www.ijpab.com Nagar et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (3): 154-158 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.6548 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6
Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs. Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison
 Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison Sources of nutrients available for plant uptake Nutrients in the soil solution are: In ionic form At low concentration
Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison Sources of nutrients available for plant uptake Nutrients in the soil solution are: In ionic form At low concentration
Use of A Multi-ionic Extractant to Determine Available P, K, Na, Ca, and Mg in Acid Soils of Sri Lanka
 , 152-158 Use of A Multi-ionic Extractant to Determine Available P, K, Na, Ca, and Mg in Acid Soils of Sri Lanka W.S. Madurapperuma and D. Kumaragamage 1 Postgraduate Institute of Agriculture University
, 152-158 Use of A Multi-ionic Extractant to Determine Available P, K, Na, Ca, and Mg in Acid Soils of Sri Lanka W.S. Madurapperuma and D. Kumaragamage 1 Postgraduate Institute of Agriculture University
Understanding ph management and plant nutrition Part 3: Fertilizers
 Understanding ph management and plant nutrition Part 3: Fertilizers Bill Argo, Ph.D. Blackmore Company, Tel: 800-874-8660, Intl 734-483-8661, E-mail: bargo@blackmoreco.com Originally printed in 2003 in
Understanding ph management and plant nutrition Part 3: Fertilizers Bill Argo, Ph.D. Blackmore Company, Tel: 800-874-8660, Intl 734-483-8661, E-mail: bargo@blackmoreco.com Originally printed in 2003 in
By Andrew & Erin Oxford, Bethel
 Chemistry in Plant Nutrition & Growth Objectives Review elements of chemistry and apply them to plant nutrition and growth in an agricultural context. Suggested grade levels 9-12 Alaska Content Standards
Chemistry in Plant Nutrition & Growth Objectives Review elements of chemistry and apply them to plant nutrition and growth in an agricultural context. Suggested grade levels 9-12 Alaska Content Standards
JORIND 9(2) December, ISSN
 SEQUENTIAL EXTRACTION OF Cu, Cd, Pb AND Zn FROM SOIL AROUND INDUSTRIAL WASTE DUMP SITES IN KADUNA ENVIRON USING SIMPLE AND SEQUENTIAL PROCEDURES. H.A Zakari, D.D. Adams, M Shimbayev, P. Nyam Department
SEQUENTIAL EXTRACTION OF Cu, Cd, Pb AND Zn FROM SOIL AROUND INDUSTRIAL WASTE DUMP SITES IN KADUNA ENVIRON USING SIMPLE AND SEQUENTIAL PROCEDURES. H.A Zakari, D.D. Adams, M Shimbayev, P. Nyam Department
Supplying Nutrients to Crops
 Supplying Nutrients to Crops What is Plant Nutrition? Plants need nutrients for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on
Supplying Nutrients to Crops What is Plant Nutrition? Plants need nutrients for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on
DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA
 DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA www.domogran.de DOMOGRAN 45 nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer for positive nutrient dynamics Because of its attraction
DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA www.domogran.de DOMOGRAN 45 nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer for positive nutrient dynamics Because of its attraction
DETERMINATION OF SUITABLE CHEMICAL EXTRACTION METHODS FOR AVAILABLE IRON CONTENT OF THE SOILS FROM EDIRNE PROVINCE IN TURKEY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DETERMINATION OF SUITABLE CHEMICAL EXTRACTION METHODS FOR AVAILABLE IRON CONTENT OF THE SOILS FROM EDIRNE PROVINCE IN TURKEY ADILOGLU A. ABSTRACT The aim of this research was to determine
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DETERMINATION OF SUITABLE CHEMICAL EXTRACTION METHODS FOR AVAILABLE IRON CONTENT OF THE SOILS FROM EDIRNE PROVINCE IN TURKEY ADILOGLU A. ABSTRACT The aim of this research was to determine
Nutrient Use Strategies for Coconut Based Cropping System in Onattukara Sandy Tract, Kerala
 IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-issn: 2319-2380, p-issn: 2319-2372. Volume 8, Issue 3 Ver. I (Mar. 2015), PP 11-15 www.iosrjournals.org Nutrient Use Strategies for Coconut
IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-issn: 2319-2380, p-issn: 2319-2372. Volume 8, Issue 3 Ver. I (Mar. 2015), PP 11-15 www.iosrjournals.org Nutrient Use Strategies for Coconut
FACTORS AFFECTING WATER QUALITY
 TECHNICAL PAPER WATER QUALITY PLANT HEALTH FACTORS Water quality is one of the most important factors affecting plant growth, as unwanted components in water can interfere with nutrient availability and
TECHNICAL PAPER WATER QUALITY PLANT HEALTH FACTORS Water quality is one of the most important factors affecting plant growth, as unwanted components in water can interfere with nutrient availability and
What s new with micronutrients in our part of the world?
 2006 Integrated Crop Management Conference - Iowa State University 181 What s new with micronutrients in our part of the world? George Rehm, Professor, Soil, Water and Climate, University of Minnesota
2006 Integrated Crop Management Conference - Iowa State University 181 What s new with micronutrients in our part of the world? George Rehm, Professor, Soil, Water and Climate, University of Minnesota
NUTRIENT AND HEAVY METAL CONTENTS OF HOG MANURE - EFFECT ON SOIL QUALITY AND PRODUCTIVITY
 NUTRIENT AND HEAVY METAL CONTENTS OF HOG MANURE - EFFECT ON SOIL QUALITY AND PRODUCTIVITY G.J. Racz and M.M. Fitzgerald Professor and Research Associate, respectively, Department of Soil Science, University
NUTRIENT AND HEAVY METAL CONTENTS OF HOG MANURE - EFFECT ON SOIL QUALITY AND PRODUCTIVITY G.J. Racz and M.M. Fitzgerald Professor and Research Associate, respectively, Department of Soil Science, University
Effect of FYM, biofertilizers and zinc on phosphorus uptake by maize
 An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 10 Issue 1 June, 2015 87-92 e ISSN 0976 7231 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in Research Article DOI : 10.15740/HAS/AJSS/10.1/87-92 Effect of FYM, biofertilizers
An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 10 Issue 1 June, 2015 87-92 e ISSN 0976 7231 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in Research Article DOI : 10.15740/HAS/AJSS/10.1/87-92 Effect of FYM, biofertilizers
Evaluation of AB - DTPA Extractant for Multinutrients Extraction in Soils
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 3 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/1.2546/ijcmas.218.73.141
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 3 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/1.2546/ijcmas.218.73.141
Nutrient level (EC) in a pot is like a bank
 Dirt, Fert and Squirt (1) Supplying Essential Nutrients What are the most common nutritional problems? Too much fertilizer Not enough fertilizer Paul Fisher pfisher@ufl.edu 1 ph too high ph too low 2 Nutrient
Dirt, Fert and Squirt (1) Supplying Essential Nutrients What are the most common nutritional problems? Too much fertilizer Not enough fertilizer Paul Fisher pfisher@ufl.edu 1 ph too high ph too low 2 Nutrient
Soil research in Europe with special reference to that in Finland A Review
 Soil research in Europe with special reference to that in Finland A Review Jouko Sippola MTT Agrifood Research Finland, Environmental Research, FIN-31600 Jokioinen, Finland jouko.sippola@surffi.net Abstract
Soil research in Europe with special reference to that in Finland A Review Jouko Sippola MTT Agrifood Research Finland, Environmental Research, FIN-31600 Jokioinen, Finland jouko.sippola@surffi.net Abstract
Scientific registration n o : 2303 Symposium : 25 Presentation : poster
 Scientific registration n o : 2303 Symposium : 25 Presentation : poster Evaluation of nutrients availability and metals toxicity by different universal extractants in brazilian soils 1 Evaluation de la
Scientific registration n o : 2303 Symposium : 25 Presentation : poster Evaluation of nutrients availability and metals toxicity by different universal extractants in brazilian soils 1 Evaluation de la
CONCENTRATION AND SPECIATION OF Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn IN CULTIVATED AND UNCULTIVATED SOILS
 129 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 15 (No 2) 2009, 129-134 Agricultural Academy CONCENTRATION AND SPECIATION OF Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn IN CULTIVATED AND UNCULTIVATED SOILS C. AYDINALP Uludag University,
129 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 15 (No 2) 2009, 129-134 Agricultural Academy CONCENTRATION AND SPECIATION OF Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn IN CULTIVATED AND UNCULTIVATED SOILS C. AYDINALP Uludag University,
Table 1. Plant Nutrients. Nutrients From Air & Water Primary Macronutrients
 WHITEPAPER THE GREAT DEBATE SYNTHETIC VS. ORGANIC PLANT NUTRIENTS RX GREEN Plant nutrients are inorganic elements such as zinc or magnesium that are absorbed by plant roots in order to fuel growth and
WHITEPAPER THE GREAT DEBATE SYNTHETIC VS. ORGANIC PLANT NUTRIENTS RX GREEN Plant nutrients are inorganic elements such as zinc or magnesium that are absorbed by plant roots in order to fuel growth and
Micronutrient status in soils of Shirpur tehsil of Dhule district (M.S.) India
 An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 11 Issue 2 December, 2016 e ISS 0976 7231 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in A Case Study DOI : 10.15740/HAS/AJSS/11.2/ Micronutrient status in soils of Shirpur
An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 11 Issue 2 December, 2016 e ISS 0976 7231 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in A Case Study DOI : 10.15740/HAS/AJSS/11.2/ Micronutrient status in soils of Shirpur
Chapter 1: Overview of soil fertility, plant nutrition, and nutrient management
 Chapter 1: Overview of soil fertility, plant nutrition, and nutrient management Agustin Pagani, John E. Sawyer, and Antonio P. Mallarino / Department of Agronomy, Iowa State University Developed in cooperation
Chapter 1: Overview of soil fertility, plant nutrition, and nutrient management Agustin Pagani, John E. Sawyer, and Antonio P. Mallarino / Department of Agronomy, Iowa State University Developed in cooperation
Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs
 Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs Kelly T. Morgan Soil and Water Science Department Southwest Florida Research and Education Center Immokalee 239 658 3400 conserv@ufl.edu
Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs Kelly T. Morgan Soil and Water Science Department Southwest Florida Research and Education Center Immokalee 239 658 3400 conserv@ufl.edu
Influence of sewage sludge and organic composts on different soils under incubation periods: I. Zinc and copper releases
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.10 No.15, pp 108-114, 2017 Influence of sewage sludge and organic composts on different soils
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.10 No.15, pp 108-114, 2017 Influence of sewage sludge and organic composts on different soils
Figure 1. Location of 43 benchmark sites across Alberta.
 1.0 INTRODUCTION This report describes the micronutrient and trace element status of the AESA (Alberta Environmentally Sustainable Agriculture) Soil Quality Benchmark Sites. Previous reports completed
1.0 INTRODUCTION This report describes the micronutrient and trace element status of the AESA (Alberta Environmentally Sustainable Agriculture) Soil Quality Benchmark Sites. Previous reports completed
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.37 - SOIL.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Plants produce sugars from photosynthesis, but still have many nutritional requirements C, H, and O account for ~95% of a plant s dry weight, and are obtained from CO2 and H2O Vascular
!! www.clutchprep.com Plants produce sugars from photosynthesis, but still have many nutritional requirements C, H, and O account for ~95% of a plant s dry weight, and are obtained from CO2 and H2O Vascular
RESPONSE OF BIO FERTILIZERS IN CONJUNCTION WITH INORGANIC FERTILIZERS IN KHARIF PADDY
 RESPONSE OF BIO FERTILIZERS IN CONJUNCTION WITH INORGANIC FERTILIZERS IN KHARIF PADDY TANDEL, B. B., PATEL, D. D., THANKI, J. D., ARVADIA, M. K. AND JAT, R. A. NAVSARI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY NAVSARI-396
RESPONSE OF BIO FERTILIZERS IN CONJUNCTION WITH INORGANIC FERTILIZERS IN KHARIF PADDY TANDEL, B. B., PATEL, D. D., THANKI, J. D., ARVADIA, M. K. AND JAT, R. A. NAVSARI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY NAVSARI-396
Barley and Sugarbeet Symposium
 MICRONUTRIENT TESTING & MANAGEMENT IN BARLEY, CORN & PULSES Barley and Sugarbeet Symposium Billings, MT January 10, 2017 Clain Jones clainj@montana.edu 994-6076 MSU Soil Fertility Extension Goals Today
MICRONUTRIENT TESTING & MANAGEMENT IN BARLEY, CORN & PULSES Barley and Sugarbeet Symposium Billings, MT January 10, 2017 Clain Jones clainj@montana.edu 994-6076 MSU Soil Fertility Extension Goals Today
Nutrient Content of Vegetable Amaranth (Amaranths cruentus L.) At Different Harvesting Stages
 World Journal of Agricultural Sciences 6 (3): 85-89, ISSN 87-347 IDOSI Publications, Nutrient Content of Vegetable Amaranth (Amaranths cruentus L.) At Different Harvesting Stages N.D. Makobo, M.D. Shoko
World Journal of Agricultural Sciences 6 (3): 85-89, ISSN 87-347 IDOSI Publications, Nutrient Content of Vegetable Amaranth (Amaranths cruentus L.) At Different Harvesting Stages N.D. Makobo, M.D. Shoko
The effectiveness of different application methods of zinc sulfate on nutritional conditions of apple in calcareous soils of Iran
 Symposium no. 15 Paper no. 2151 Presentation: poster The effectiveness of different application methods of zinc sulfate on nutritional conditions of apple in calcareous soils of Iran RASOULI SADAGHIANI
Symposium no. 15 Paper no. 2151 Presentation: poster The effectiveness of different application methods of zinc sulfate on nutritional conditions of apple in calcareous soils of Iran RASOULI SADAGHIANI
ABREU Cleide Aparecida de (1), BERTON Ronaldo Severiano (1), KOEKKOEK Edwin Peter Josef (2)
 Scientific registration number: 2207 Symposium number: 25 Presentation : poster Validation of annual and total cumulative loading limits stipulated by USEPA for Zn on oxisol. Validation des apports-limites
Scientific registration number: 2207 Symposium number: 25 Presentation : poster Validation of annual and total cumulative loading limits stipulated by USEPA for Zn on oxisol. Validation des apports-limites
Evaluation of Quality and Nutrient Status of Enriched Compost
 IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-issn: 2319-2380, p-issn: 2319-2372. Volume 6, Issue 2 (Nov. - Dec. 2013), PP 19-23 Evaluation of Quality and Nutrient Status of Enriched
IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS) e-issn: 2319-2380, p-issn: 2319-2372. Volume 6, Issue 2 (Nov. - Dec. 2013), PP 19-23 Evaluation of Quality and Nutrient Status of Enriched
The uptake of nutrients occurs at both the roots and the leaves.
 CHAPTER 37: WHAT DO PLANTS NEED TO LIVE AND HOW DO THEY GET IT? Elemental Composition of Living Organisms WHAT ARE ORGANISMS MADE OF? Element Human Alfalfa Bacterium Carbon 19.37% 11.34% 12.14% Hydrogen
CHAPTER 37: WHAT DO PLANTS NEED TO LIVE AND HOW DO THEY GET IT? Elemental Composition of Living Organisms WHAT ARE ORGANISMS MADE OF? Element Human Alfalfa Bacterium Carbon 19.37% 11.34% 12.14% Hydrogen
Fertilization Programming
 Fertilization Plant Composition Water composes 90% of plant weight (fresh weight) Dry weight is composed of 17 essential elements: Non-fertilizer elements: Carbon (C) -- 41% of dry weight (DW) Hydrogen
Fertilization Plant Composition Water composes 90% of plant weight (fresh weight) Dry weight is composed of 17 essential elements: Non-fertilizer elements: Carbon (C) -- 41% of dry weight (DW) Hydrogen
Micronutrients Distribution in Soybean Plant with Zn, Fe, and Mn Application
 Annual Review & Research in Biology 3(2): 83-91, 2013 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Micronutrients Distribution in Soybean Plant with Zn, Fe, and Mn Application Soheil Kobraee 1*, Ghorban
Annual Review & Research in Biology 3(2): 83-91, 2013 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Micronutrients Distribution in Soybean Plant with Zn, Fe, and Mn Application Soheil Kobraee 1*, Ghorban
Importance of Water Quality: ph, buffering, and effects on nutrient availability
 Importance of Water Quality: ph, buffering, and effects on nutrient availability Andrew G. Ristvey The University of Maryland Extension programs are open to any person and will not discriminate against
Importance of Water Quality: ph, buffering, and effects on nutrient availability Andrew G. Ristvey The University of Maryland Extension programs are open to any person and will not discriminate against
IRON. AGRITOPIC August INTRODUCTION 2. IRON IN THE SOIL
 AGRITOPIC August 2015 IRON 1. INTRODUCTION Of all the elements plants derive from the soil, iron (Fe) is the most abundant. Yet, as far as plant nutrition is concerned, it is classified as a micronutrient,
AGRITOPIC August 2015 IRON 1. INTRODUCTION Of all the elements plants derive from the soil, iron (Fe) is the most abundant. Yet, as far as plant nutrition is concerned, it is classified as a micronutrient,
Delineation of Areas Deficient for Micronutrients in Soils of Chittoor District, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 23197706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 512520 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.066
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 23197706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 512520 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.066
Correction of Zinc Deficiency in Avocado
 1997 California Avocado Research Symposium pages 9-12 California Avocado Society and University of California, Riverside Correction of Zinc Deficiency in Avocado Final Report for Project Year 4 of 4 Cooperating
1997 California Avocado Research Symposium pages 9-12 California Avocado Society and University of California, Riverside Correction of Zinc Deficiency in Avocado Final Report for Project Year 4 of 4 Cooperating
Soil fertility status and nutrient recommendations based on soil analysis of Jaisalmer district of western Rajasthan
 An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 12 Issue 1 June, 2017 103-107 e ISSN 0976 7231 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in Research Article DOI : 10.15740/HAS/AJSS/12.1/103-107 Soil fertility status and
An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 12 Issue 1 June, 2017 103-107 e ISSN 0976 7231 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in Research Article DOI : 10.15740/HAS/AJSS/12.1/103-107 Soil fertility status and
Speciation Analysis and Removal of Heavy Metals Zn, Cu, Cd from Sludge by Organic Acid
 5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Speciation Analysis and Removal of Heavy Metals Zn, Cu, Cd from Sludge by Organic Acid S.W. SONG 1*, L. WANG
5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Speciation Analysis and Removal of Heavy Metals Zn, Cu, Cd from Sludge by Organic Acid S.W. SONG 1*, L. WANG
TNPSC Chemistry Study Material Fertilizers
 TNPSC Chemistry Study Material A fertilizer is any material of natural or synthetic origin (other than liming materials) that is applied to soils or to plant tissues to supply one or more plant nutrients
TNPSC Chemistry Study Material A fertilizer is any material of natural or synthetic origin (other than liming materials) that is applied to soils or to plant tissues to supply one or more plant nutrients
Lecture 14. More Soil chemistry and nutrients in soils
 Lecture 14 More Soil chemistry and nutrients in soils SOIL INORGANIC SOLIDS saprolite development elemental changes that occur during weathering The gain or loss of chemical constituents in saprolite records
Lecture 14 More Soil chemistry and nutrients in soils SOIL INORGANIC SOLIDS saprolite development elemental changes that occur during weathering The gain or loss of chemical constituents in saprolite records
Inorganic Contaminants
 Inorganic Contaminants Dr Stephen R Smith Dept Civil & Environmental Engineering Page 1 Scope of Presentation Sources and concentrations Qualifying environmental limits Phytotoxicity Dietary intake Grain
Inorganic Contaminants Dr Stephen R Smith Dept Civil & Environmental Engineering Page 1 Scope of Presentation Sources and concentrations Qualifying environmental limits Phytotoxicity Dietary intake Grain
ANIMAL, PLANT & SOIL SCIENCE D3-6 CHARACTERISTICS AND SOURCES OF PHOSPHORUS AND POTASSIUM
 ANIMAL, PLANT & SOIL SCIENCE D3-6 CHARACTERISTICS AND SOURCES OF PHOSPHORUS AND POTASSIUM INTEREST APPROACH Show images of plants suffering from phosphorus and potassium deficiencies. Ask students if they
ANIMAL, PLANT & SOIL SCIENCE D3-6 CHARACTERISTICS AND SOURCES OF PHOSPHORUS AND POTASSIUM INTEREST APPROACH Show images of plants suffering from phosphorus and potassium deficiencies. Ask students if they
TSADILAS Christos, SAMARAS Vasilios, SIMONIS Asterios, SETATOU Helen
 Scientific registration n o : 776 Symposium n o : 6 Presentation : poster Changes in DTPA-extractable iron, zinc, manganese and copper after liming Modification de la teneur du sol en fer, zinc, manganèse,
Scientific registration n o : 776 Symposium n o : 6 Presentation : poster Changes in DTPA-extractable iron, zinc, manganese and copper after liming Modification de la teneur du sol en fer, zinc, manganèse,
Correlation between soil physico-chemical properties and available micronutrients in salt affected soils
 Symposium no. 33 Paper no. 2220 Presentation: poster Correlation between soil physico-chemical properties and available micronutrients in salt affected soils MALI V.S., ZENDE N.A. and VERMA U.K. Vasantdada
Symposium no. 33 Paper no. 2220 Presentation: poster Correlation between soil physico-chemical properties and available micronutrients in salt affected soils MALI V.S., ZENDE N.A. and VERMA U.K. Vasantdada
EFFECT OF BORON AND ZINC FERTILIZERS ON LEAF ZINC AND BORON CONTENTS OF MAIZE IN A CALCAREOUS SOIL
 Agric. Sci. Digest, 32 (1) : 1-6, 2012 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.ar.arccjour ccjournals.com / indianjournals.com nals.com EFFECT OF BORON AND ZINC FERTILIZERS ON LEAF ZINC AND BORON
Agric. Sci. Digest, 32 (1) : 1-6, 2012 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.ar.arccjour ccjournals.com / indianjournals.com nals.com EFFECT OF BORON AND ZINC FERTILIZERS ON LEAF ZINC AND BORON
Long term effect of cropping systems on the chemical fractions of zinc and copper in alluvial soils of north-west India
 An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 7 Issue June, 202 Research Article Long term effect of cropping systems on the chemical fractions of zinc and copper in alluvial soils of north-west India MEMBERS
An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 7 Issue June, 202 Research Article Long term effect of cropping systems on the chemical fractions of zinc and copper in alluvial soils of north-west India MEMBERS
Bioavailability based approaches for soil risk assessment of metals: Regional differences arising from distributions of soil chemical properties
 Bioavailability based approaches for soil risk assessment of metals: Regional differences arising from distributions of soil chemical properties EFSA/ECHA Soil Risk Assessment Workshop Wednesday, October
Bioavailability based approaches for soil risk assessment of metals: Regional differences arising from distributions of soil chemical properties EFSA/ECHA Soil Risk Assessment Workshop Wednesday, October
Care Chemicals & Formulators. Librel BMX. Technical Information. = Registered trademark of BASF group Multi-Micronutrient EDTA Chelate.
 Technical Information Librel BMX April 2010 08_100206e-00/Page 1 of 6 = Registered trademark of BASF group Multi-Micronutrient EDTA Chelate Care Chemicals & Formulators 08_100206e-00 April 2010 Page 2
Technical Information Librel BMX April 2010 08_100206e-00/Page 1 of 6 = Registered trademark of BASF group Multi-Micronutrient EDTA Chelate Care Chemicals & Formulators 08_100206e-00 April 2010 Page 2
Investigation the quality and quantity of Melissa officinalis L. under chemical and bio-fertilizers of sulfur
 International Journal of Biosciences IJB ISSN: 2220-6655 (Print) 2222-5234 (Online) http://www.innspub.net Vol. 4, No. 4, p. 92-96, 2014 RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Investigation the quality and quantity
International Journal of Biosciences IJB ISSN: 2220-6655 (Print) 2222-5234 (Online) http://www.innspub.net Vol. 4, No. 4, p. 92-96, 2014 RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Investigation the quality and quantity
RemovalofToxicMetalsContaminatedSoilusingDifferentAmendmentsandSunflowerSpeciesHelianthusAnnuus
 Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: H Environment & Earth Science Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: H Environment & Earth Science Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Matrix Reference Materials - SCP SCIENCE
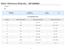 EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
Soil Program Recommendation
 Soil Program Recommendation Grower: G.C. Wynne Consultant: Bill Munton Doyle St Quirindi NSW 2343 Soil Test No: K6930ABC These comments and suggestions are based on our interpretation of soil analysis
Soil Program Recommendation Grower: G.C. Wynne Consultant: Bill Munton Doyle St Quirindi NSW 2343 Soil Test No: K6930ABC These comments and suggestions are based on our interpretation of soil analysis
Kinetics of decomposition of wheat straw and mineralisation of micronutrients in zinc-treated rice field
 Ag ropedology 2010, 20 (l), 60-66 Kinetics of decomposition of wheat straw and mineralisation of micronutrients in zinc-treated rice field R. K. PRASAD l, VIPIN KUMAR, B. PRASAD AND A. P. SINGH Depanment
Ag ropedology 2010, 20 (l), 60-66 Kinetics of decomposition of wheat straw and mineralisation of micronutrients in zinc-treated rice field R. K. PRASAD l, VIPIN KUMAR, B. PRASAD AND A. P. SINGH Depanment
Effect of organics and inorganic phosphorus on inorganic P-fractions in soil of soy bean (Glycine max L.) crop
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Annals of Biological Research, 2015, 6 (11):11-16 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0976-1233 CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Effect of organics
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Annals of Biological Research, 2015, 6 (11):11-16 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0976-1233 CODEN (USA): ABRNBW Effect of organics
Trends in Micro-Nutrient Soil Test Levels in Saskatchewan Pat Flaten, PAg 1, Brandon Green, PAg 2, Paul Routledge, PAg 3
 Trends in Micro-Nutrient Soil Test Levels in Saskatchewan Pat Flaten, PAg 1, Brandon Green, PAg 2, Paul Routledge, PAg 3 1 Enviro-Test Laboratories, 124 Veterinary Road, Saskatoon, SK, S7N 5E3 2 Enviro-Test
Trends in Micro-Nutrient Soil Test Levels in Saskatchewan Pat Flaten, PAg 1, Brandon Green, PAg 2, Paul Routledge, PAg 3 1 Enviro-Test Laboratories, 124 Veterinary Road, Saskatoon, SK, S7N 5E3 2 Enviro-Test
Understanding Your Soil Report. Michael Cook 2018
 Understanding Your Soil Report Michael Cook 2018 Soil Sampling Advantage gives nutrient concentrations may shed light on soil issues baseline so look for trends can be done pre-plant timing not as critical
Understanding Your Soil Report Michael Cook 2018 Soil Sampling Advantage gives nutrient concentrations may shed light on soil issues baseline so look for trends can be done pre-plant timing not as critical
Biosolids Nutrien Management an Soil Testing. Craig Cogger, Soil Scientis WSU Puyallup
 Biosolids Nutrien Management an Soil Testing Craig Cogger, Soil Scientis WSU Puyallup Nutrient Manageme Meet crop nutrient needs Maintain soil quality Conserve resources Protect water quality -- reduc
Biosolids Nutrien Management an Soil Testing Craig Cogger, Soil Scientis WSU Puyallup Nutrient Manageme Meet crop nutrient needs Maintain soil quality Conserve resources Protect water quality -- reduc
