Simulation of upper-ocean biogeochemistry with a flexible-composition phytoplankton model: C, N and Si cycling in the western Sargasso Sea.
|
|
|
- Timothy Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Simulation of upper-ocean biogeochemistry with a flexible-composition phytoplankton model: C, N and Si cycling in the western Sargasso Sea. Mathieu Mongin 1,2, David M. Nelson 1, Philippe Pondaven 2, Mark A. Brzezinski 3 and Paul Tréguer 2. 1 College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences, Oregon State University 2 Institut Universitaire Européen de la Mer, Plouzané, France 3 Dept. of Ecology, Evolution & Marine Biology, University of California, Santa Barbara
2 Models of nutrient-limited primary production in the ocean 1. Nitrogen-based models (e.g. Fasham et al., 1990, Martin et al., 2001) Simulate the transformations of one potentially limiting element (N). Simulate light limitation by making rates of NO 3 and NH + 4 uptake light-dependent. Usually consider just one phytoplankton group, or at most two (large and small cells). Do not explicitly consider limitation by other nutrients (e.g. Si limitation for diatoms). 2. Multi-element models in which the phytoplankton has a fixed elemental composition (e.g. Walsh, 1975, Pondaven et al., 1998, Chai et al., 2002) Explicitly allow for limitation by light, and by one or more nutrients. Usually consider more than one phytoplankton group (e.g. diatoms and nonsiliceous forms). Require phytoplankton to grow with fixed (usually Redfield) C:N or C:N:P ratios. Require diatoms (if considered explicitly) to grow with a fixed Si:N or Si:C ratio. Assume that productivity is controlled by the most limiting resource (i.e. the one that causes phytoplankton biomass to be produced at the lowest rate).
3 Biogeochemically significant processes that no single-element or fixed-composition phytoplankton model can consider 1. Growth of phytoplankton with altered elemental composition under either nutrient limitation or light limitation For all phytoplankton: higher C/N ratios when N is limiting lower C/N ratios when light is limiting For diatoms: lower Si/C and Si/N ratios when Si is limiting higher Si/N ratios when N is limiting higher Si/C ratios when light is limiting higher Si/C and Si/N ratios when Fe is limiting 2. Differential light dependence of C, NO 3, NH 4 + and Si(OH) 4 uptake, resulting in different depth distributions, day/night timing and depth/time-integrated rates of uptake absolute light requirement for C uptake strong light dependence for NO 3 uptake little or no light dependence for NH 4 + or Si(OH) 4 uptake
4 Difference between kinetics of nutrient uptake and kinetics of nutrient-limited growth V max µ max 1 1 Specific uptake rate (V) V = V max S/(K S + S) Specific growth rate (µ) µ = µ max S / (K D + S) K S K D Nutrient concentration (S) 0 0 Nutrient 10 concentration (S) 40 For many species, and several different nutrients, K d << K s
5 Severity of Si uptake rate limitation and estimated severity of Si limitation of diatom growth rates, as a function of latitude and time (a): V a :V max calculated from [Si(OH) 4 ] a and K s for Si uptake. (b): estimated µ a /µ max calculated in the same manner, but assuming that K µ = 0.15 K s. Symbol as in Fig.3. the location of the southern boundary of the APF is also shown in both panel. This analysis include only those experiments in which V was measurably limited by [Si(OH) 4 ] a (i.e. where E>1.2); thus all V a /V max values in (a) are constrained to be <0.83.
6 "Cell quota" model for nutrient-limited growth 1.4 µ inf µ max µ =µ inf (Q Q O )/Q Q O Q max Amount of the limiting element per cell (Q)
7 Fraction of externally controlled uptake rate 1 0 No N uptake Low cellular Si limits growth and N uptake Si uptake and N uptake are independent N uptake Si uptake Low cellular N limits growth and Si uptake No Si uptake Si/N ratio of living diatoms (log scale)
8 Fraction of externally controlled uptake rate 1 No N uptake Low cellular C limits growth and N uptake C uptake and N uptake are independent N uptake C uptake Low cellular N limits growth and C uptake No C uptake C/N ratio of living diatoms or picoplankton
9 Mean seasonal depth profiles of nitrate and silicic acid A & B from BATS data: (A) [NO - 3 ]; (B) [Si(OH) 4 ] C & D from model output (C) [NO - 3 ]; (D) [Si(OH) 4 ]
10 Time course of simulated surface [NO - 3 ] and [NH + 4 ] (mmol N m -3 )
11 Contour plot of measured and simulated Chlorophyll-a, and simulated chlorophyll-a in picophytoplankton and Diatoms, (mg m -3 )
12 Measured and model-drived primary productivity at the BATS site, Primary productivity (mg C m -2 d -1 ) BATS Data Model results Time (year
13 Model derived C/N ratio of picophytoplankton and diatoms At the BATS site,
14 Mean C/N ratio in 25 m depth intervals at the BATS site (simulated and measured) Mean POC/PON (model outpu Depth range (m) Redfield ratio (6.6) Mean POC/PON (BATS dat Depth range (m) Redfield ratio ( Mean POC/PON (BATS dat Depth range (m) Redfield ratio (
FRCGC, JAMSTEC ECEM07,
 Comparing Optimal Uptake Kinetics and Michaelis-Menten by Assimilating Data from the SERIES Fe-Enrichment Experiment into a Marine Ecosystem Model S. Lan Smith, Naoki Yoshie 2 and Yasuhiro Yamanaka Ecosystem
Comparing Optimal Uptake Kinetics and Michaelis-Menten by Assimilating Data from the SERIES Fe-Enrichment Experiment into a Marine Ecosystem Model S. Lan Smith, Naoki Yoshie 2 and Yasuhiro Yamanaka Ecosystem
Nutrients. Classification of Elements or Nutrients (Wally Broecker):
 Nutrients Nutrients are generally considered to be elements or compounds (e.g. N is a nutrient, NO3 and NH4 are types of N compound that are also nutrients) that are needed for biological growth. Classification
Nutrients Nutrients are generally considered to be elements or compounds (e.g. N is a nutrient, NO3 and NH4 are types of N compound that are also nutrients) that are needed for biological growth. Classification
Macronutrients in the ocean
 Macronutrients in the ocean Philip Boyd NIWA/OTAGO, New Zealand September 2011 OUTLINE What is a macronutrient? Trends in nutrients & limitation The N cycle sources, sinks and recycling Silicate the body
Macronutrients in the ocean Philip Boyd NIWA/OTAGO, New Zealand September 2011 OUTLINE What is a macronutrient? Trends in nutrients & limitation The N cycle sources, sinks and recycling Silicate the body
Nutrients & iclicker Question Which is not a major ion? A) Sodium (Na + ) B) Potassium (K + ) C) Chloride (Cl - ) D) Silicon (Si) E) Sulfate (SO 4
 Nutrients & Tracers Non-conservative element: short residence time removed efficiently by biological or chemical processes Nutrients: used by living organisms Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorous, Iron, silicate,
Nutrients & Tracers Non-conservative element: short residence time removed efficiently by biological or chemical processes Nutrients: used by living organisms Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorous, Iron, silicate,
Multi-nutrient, multi-group model of present and future oceanic phytoplankton communities
 Biogeosciences, 3, 585 606, 2006 Author(s) 2006. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Biogeosciences Multi-nutrient, multi-group model of present and future oceanic phytoplankton communities
Biogeosciences, 3, 585 606, 2006 Author(s) 2006. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Biogeosciences Multi-nutrient, multi-group model of present and future oceanic phytoplankton communities
Nutrient- vs. Energy-Limitation in the Sea:
 Nutrient- vs. Energy-Limitation in the Sea: The Red Sea and the Antarctic Ocean as Extreme Case Studies Max M. Tilzer University of Constance, Germany ISEEQS-Meeting, 29 May 1 June 2005 Katsushika Hokusai:
Nutrient- vs. Energy-Limitation in the Sea: The Red Sea and the Antarctic Ocean as Extreme Case Studies Max M. Tilzer University of Constance, Germany ISEEQS-Meeting, 29 May 1 June 2005 Katsushika Hokusai:
Total organic carbon at BATS Remember that DOC = ~98% of the TOC.
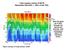 Total organic carbon at BATS Remember that DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Total organic carbon at BATS Remember that DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis!
 Factors Affecting Photosynthesis! Temperature Eppley (1972) Light Sverdrup s Critical Depth Model Nutrients Limitations Uptake Kinetics Temperature! The oceans vary much less than the land does, both seasonally
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis! Temperature Eppley (1972) Light Sverdrup s Critical Depth Model Nutrients Limitations Uptake Kinetics Temperature! The oceans vary much less than the land does, both seasonally
Iron and zinc effects on silicic acid and nitrate uptake kinetics in three high-nutrient, low-chlorophyll (HNLC) regions
 MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 252: 1533, 2003 Published April 30 Mar Ecol Prog Ser Iron and zinc effects on silicic acid and nitrate uptake kinetics in three high-nutrient, low-chlorophyll (HNLC)
MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 252: 1533, 2003 Published April 30 Mar Ecol Prog Ser Iron and zinc effects on silicic acid and nitrate uptake kinetics in three high-nutrient, low-chlorophyll (HNLC)
Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean
 Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean Michael Landry Integrative Oceanography Division Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego SIBER Workshop
Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean Michael Landry Integrative Oceanography Division Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego SIBER Workshop
Seasonal cycle of phytoplankton community structure and photophysiological state in the western subarctic gyre of the North Pacific
 PICES 2014 Annual Meeting Yeosu, Korea Seasonal cycle of phytoplankton community structure and photophysiological state in the western subarctic gyre of the North Pacific T. Fujiki 1, K. Matsumoto 1, Y.
PICES 2014 Annual Meeting Yeosu, Korea Seasonal cycle of phytoplankton community structure and photophysiological state in the western subarctic gyre of the North Pacific T. Fujiki 1, K. Matsumoto 1, Y.
One-dimensional ecosystem model of the equatorial Pacific upwelling system. Part I: model development and silicon and nitrogen cycle
 Deep-Sea Research II 49 (2002) 2713 2745 One-dimensional ecosystem model of the equatorial Pacific upwelling system. Part I: model development and silicon and nitrogen cycle F. Chai a, *, R.C. Dugdale
Deep-Sea Research II 49 (2002) 2713 2745 One-dimensional ecosystem model of the equatorial Pacific upwelling system. Part I: model development and silicon and nitrogen cycle F. Chai a, *, R.C. Dugdale
Sverdrup s Critical Depth Revisited
 Sverdrup s Critical Depth Revisited For Homework 2, question 4, you need some additional information. Sverdrup assumed that the Compensation Depth (Ec) includes respiration from both phytoplankton and
Sverdrup s Critical Depth Revisited For Homework 2, question 4, you need some additional information. Sverdrup assumed that the Compensation Depth (Ec) includes respiration from both phytoplankton and
The importance of trace metal nutrients for marine phytoplankton and bacteria along Line-P. Jay T. Cullen, Maite Maldonado (UBC), Erin Lane (UBC)
 The importance of trace metal nutrients for marine phytoplankton and bacteria along Line-P Jay T. Cullen, Maite Maldonado (UBC), Erin Lane (UBC) Outline Trace Metals and Marine Biogeochemical Cycles Iron
The importance of trace metal nutrients for marine phytoplankton and bacteria along Line-P Jay T. Cullen, Maite Maldonado (UBC), Erin Lane (UBC) Outline Trace Metals and Marine Biogeochemical Cycles Iron
Deep-Sea Research II
 Deep-Sea Research II 58 (2011) 493 511 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Deep-Sea Research II journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/dsr2 Co-limitation of diatoms by iron and silicic acid in
Deep-Sea Research II 58 (2011) 493 511 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Deep-Sea Research II journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/dsr2 Co-limitation of diatoms by iron and silicic acid in
Modeling the coupling of ocean ecology and biogeochemistry
 Click Here for Full Article GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 23,, doi:10.1029/2008gb003405, 2009 Modeling the coupling of ocean ecology and biogeochemistry S. Dutkiewicz, 1 M. J. Follows, 1 and J. G.
Click Here for Full Article GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 23,, doi:10.1029/2008gb003405, 2009 Modeling the coupling of ocean ecology and biogeochemistry S. Dutkiewicz, 1 M. J. Follows, 1 and J. G.
Trace metals in the ocean Lecture January 23, 2006
 Trace metals in the ocean 12.097 Lecture January 23, 2006 Metals of interest Required for metabolic functions Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn Deficiency limits production (photosynthetic ability) Excess limits
Trace metals in the ocean 12.097 Lecture January 23, 2006 Metals of interest Required for metabolic functions Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn Deficiency limits production (photosynthetic ability) Excess limits
In steady state, new production = carbon export
 In steady state, new production = carbon export Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority
In steady state, new production = carbon export Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority
Recovery of Thalassiosira weissflogii from nitrogen and silicon starvation
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 49(1), 2004, 245 255 2004, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Recovery of Thalassiosira weissflogii from nitrogen and silicon starvation Christina L. De La Rocha
Limnol. Oceanogr., 49(1), 2004, 245 255 2004, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Recovery of Thalassiosira weissflogii from nitrogen and silicon starvation Christina L. De La Rocha
Seasonal cycle of phytoplankton community structure and photophysiological state in the western subarctic gyre of the North Pacific.
 Seasonal cycle of phytoplankton community structure and photophysiological state in the western subarctic gyre of the North Pacific Tetsuichi Fujiki Introduction Subarctic North Pacific: High Nutrient
Seasonal cycle of phytoplankton community structure and photophysiological state in the western subarctic gyre of the North Pacific Tetsuichi Fujiki Introduction Subarctic North Pacific: High Nutrient
Lab 3: Inorganic Plant Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Silicate
 Introduction Lab 3: Inorganic Plant Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Silicate Compounds of nitrogen and phosphorus are major cellular components of organisms. Since the availability of these elements may
Introduction Lab 3: Inorganic Plant Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Silicate Compounds of nitrogen and phosphorus are major cellular components of organisms. Since the availability of these elements may
Michael J. Behrenfeld Oregon State University
 Michael J. Behrenfeld Oregon State University global > 15 o C Tidbits Based on Vertically Generalized Production Model (VGPM) Initial increase = 1,930 TgC/yr Subsequent decrease = 190 TgC/yr Global trends
Michael J. Behrenfeld Oregon State University global > 15 o C Tidbits Based on Vertically Generalized Production Model (VGPM) Initial increase = 1,930 TgC/yr Subsequent decrease = 190 TgC/yr Global trends
Growth responses of Ulva prolifera to inorganic and organic. nutrients: Implications for macroalgal blooms in the
 1 2 3 Growth responses of Ulva prolifera to inorganic and organic nutrients: Implications for macroalgal blooms in the southern Yellow Sea, China 4 5 Hongmei Li a, Yongyu Zhang a *, Xiurong Han b, Xiaoyong
1 2 3 Growth responses of Ulva prolifera to inorganic and organic nutrients: Implications for macroalgal blooms in the southern Yellow Sea, China 4 5 Hongmei Li a, Yongyu Zhang a *, Xiurong Han b, Xiaoyong
Annual boom bust cycles of polar phytoplankton biomass revealed by space-based lidar
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NGEO2861 Annual boom bust cycles of polar phytoplankton biomass revealed by space-based lidar Michael J. Behrenfeld,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NGEO2861 Annual boom bust cycles of polar phytoplankton biomass revealed by space-based lidar Michael J. Behrenfeld,
A dynamic model of oceanic sulfur (DMOS) applied to the Sargasso Sea: Simulating the dimethylsulfide (DMS) summer paradox
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jg000415, 2008 A dynamic model of oceanic sulfur (DMOS) applied to the Sargasso Sea: Simulating the dimethylsulfide
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jg000415, 2008 A dynamic model of oceanic sulfur (DMOS) applied to the Sargasso Sea: Simulating the dimethylsulfide
LONG-TERM GOALS OBJECTIVES
 Trace Metal Speciation: Equilibrium and Kinetic Considerations on Biological Effects, Phytoplankton Uptake and Sorption Processes in Coastal Waters (Field and Laboratory Studies) Kenneth W. Bruland University
Trace Metal Speciation: Equilibrium and Kinetic Considerations on Biological Effects, Phytoplankton Uptake and Sorption Processes in Coastal Waters (Field and Laboratory Studies) Kenneth W. Bruland University
N/P ratio of nutrient uptake in the Baltic Sea
 Ocean Sci., 7, 693 704, 2011 doi:10.5194/os-7-693-2011 Author(s) 2011. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Ocean Science N/P ratio of nutrient uptake in the Baltic Sea Z. Wan 1, L. Jonasson 1, and H. Bi 2 1 Centre
Ocean Sci., 7, 693 704, 2011 doi:10.5194/os-7-693-2011 Author(s) 2011. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Ocean Science N/P ratio of nutrient uptake in the Baltic Sea Z. Wan 1, L. Jonasson 1, and H. Bi 2 1 Centre
Dynamics of the decline of a phytoplankton bloom after an upwelling event
 Vol. 16: 121-126, 1984 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Published February 29 Dynamics of the decline of a phytoplankton bloom after an upwelling event R. G. Barlow Sea Fisheries
Vol. 16: 121-126, 1984 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Published February 29 Dynamics of the decline of a phytoplankton bloom after an upwelling event R. G. Barlow Sea Fisheries
Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea
 The following supplement accompanies the article Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea Eva Sintes 1, 2, *, Karen Stoderegger 1, Veronica Parada 1,
The following supplement accompanies the article Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea Eva Sintes 1, 2, *, Karen Stoderegger 1, Veronica Parada 1,
Coupled physical biological modelling study of the East Australian Current with idealised wind forcing: Part II. Biological dynamical analysis
 Journal of Marine Systems 59 (2006) 271 291 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmarsys Coupled physical biological modelling study of the East Australian Current with idealised wind forcing: Part II. Biological dynamical
Journal of Marine Systems 59 (2006) 271 291 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmarsys Coupled physical biological modelling study of the East Australian Current with idealised wind forcing: Part II. Biological dynamical
Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea
 Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea DOC distributions in the Atlantic Marine Microplankton Ecology OCN 626 Matthew Church Figures from Dennis Hansell DOC distributions in the Pacific Basin scale
Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea DOC distributions in the Atlantic Marine Microplankton Ecology OCN 626 Matthew Church Figures from Dennis Hansell DOC distributions in the Pacific Basin scale
Supplementary data. Dissolved extracellular polymeric substance (deps) dynamics and bacterial growth
 Polar Biology Supplementary data Dissolved extracellular polymeric substance (deps) dynamics and bacterial growth during sea ice formation in an ice tank study Shazia N Aslam 1*, Graham J.C. Underwood
Polar Biology Supplementary data Dissolved extracellular polymeric substance (deps) dynamics and bacterial growth during sea ice formation in an ice tank study Shazia N Aslam 1*, Graham J.C. Underwood
VERIFICATION OF THE PREDICTED SHIFT FROM DIATOMS TO FLAGELLATES IN COASTAL SEAS USING LARGE SCALE MESOCOSM DATA
 International Journal of Latest Research in Science and Technology Volume, Issue 1: Page No.11-1, January-February 15 http://www.mnkjournals.com/ijlrst.htm ISSN (Online):7-599 VERIFICATION OF THE PREDICTED
International Journal of Latest Research in Science and Technology Volume, Issue 1: Page No.11-1, January-February 15 http://www.mnkjournals.com/ijlrst.htm ISSN (Online):7-599 VERIFICATION OF THE PREDICTED
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Growth rates, half-saturation constants, and silicate, nitrate, and phosphate depletion in relation to iron availability of four large, open-ocean diatoms from the Southern Ocean
University of Groningen Growth rates, half-saturation constants, and silicate, nitrate, and phosphate depletion in relation to iron availability of four large, open-ocean diatoms from the Southern Ocean
Effect of Zn, Mn, and Fe on Cd accumulation in phytoplankton: Implications for oceanic Cd cycling
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(7), 2000, 1501 1516 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Effect of Zn, Mn, and Fe on Cd accumulation in phytoplankton: Implications for oceanic Cd cycling
Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(7), 2000, 1501 1516 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Effect of Zn, Mn, and Fe on Cd accumulation in phytoplankton: Implications for oceanic Cd cycling
Regional, seasonal and lagged influences of the Amundsen Sea Low on Antarctic Sea Ice
 Regional, seasonal and lagged influences of the Amundsen Sea Low on Antarctic Sea Ice Laura Landrum 1, Marika Holland 1, and Marilyn Raphael 2 1 National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), Boulder,
Regional, seasonal and lagged influences of the Amundsen Sea Low on Antarctic Sea Ice Laura Landrum 1, Marika Holland 1, and Marilyn Raphael 2 1 National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), Boulder,
BIOGEOCHEMISTRY OF NUTRIENTS, TRACE METALS AND ORGANIC MICROPOLLUTANTS IN THE NORTH SEA.
 BIOGEOCHEMISTRY OF NUTRIENTS, TRACE METALS AND ORGANIC MICROPOLLUTANTS IN THE NORTH SEA. SUBPROJECT:BIOGEOCHEMISTRY OF NUTRIENTS AND TRACE METALS IN THE NORTH SEA. Vrije Universiteit Brussel Dienst analytische
BIOGEOCHEMISTRY OF NUTRIENTS, TRACE METALS AND ORGANIC MICROPOLLUTANTS IN THE NORTH SEA. SUBPROJECT:BIOGEOCHEMISTRY OF NUTRIENTS AND TRACE METALS IN THE NORTH SEA. Vrije Universiteit Brussel Dienst analytische
Danish Institute for Fisheries Research, Kavalergården 6, DK-2920 Charlottenlund, Denmark
 Seasonal changes in food quantity and quality for the development and egg production of the common North Sea copepods Temora longicornis and Pseudocalanus elongatus 1) Marja Koski, 1) Jörg Dutz and ) Wim
Seasonal changes in food quantity and quality for the development and egg production of the common North Sea copepods Temora longicornis and Pseudocalanus elongatus 1) Marja Koski, 1) Jörg Dutz and ) Wim
Size Fractionated Chlorophyll a Response from an Open. Ocean Ecosystem Iron Addition Experiment
 Size Fractionated Chlorophyll a Response from an Open Ocean Ecosystem Iron Addition Experiment by Zackary I. Johnson Submitted to the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering in partial fulfillment
Size Fractionated Chlorophyll a Response from an Open Ocean Ecosystem Iron Addition Experiment by Zackary I. Johnson Submitted to the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering in partial fulfillment
PUBLICATIONS. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: A new ecosystem model with nitrogen and phosphorus limitation was developed The effect of phosphorus limitation on a plume
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: A new ecosystem model with nitrogen and phosphorus limitation was developed The effect of phosphorus limitation on a plume
Modeling the Coupling of Ocean Ecology and Biogeochemistry
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Modeling the Coupling of Ocean Ecology and Biogeochemistry S. Dutkiewicz Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, Massachusetts Institute
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Modeling the Coupling of Ocean Ecology and Biogeochemistry S. Dutkiewicz Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, Massachusetts Institute
Recovery of nutrients from biomass for nutrient recycling
 Recovery of nutrients from biomass for nutrient recycling John Hewson, Ryan Davis, Todd Lane, Nicholas Wyatt Sandia National Laboratories Anthony Siccardi, Zachary Fuqua Texas A&M University 2013 Algae
Recovery of nutrients from biomass for nutrient recycling John Hewson, Ryan Davis, Todd Lane, Nicholas Wyatt Sandia National Laboratories Anthony Siccardi, Zachary Fuqua Texas A&M University 2013 Algae
IS THE CONDITION AND GROWTH OF EARLY LIFE STAGES OF NORTHERN ANCHOVY RELATED TO THE BIOCHEMICAL CLIMATOLOGY OF THE NORTHERN CALIFORNIA CURRENT?
 IS THE CONDITION AND GROWTH OF EARLY LIFE STAGES OF NORTHERN ANCHOVY RELATED TO THE BIOCHEMICAL CLIMATOLOGY OF THE NORTHERN CALIFORNIA CURRENT? Jessica A. Miller 1, William T. Peterson 2, Louise Copeman
IS THE CONDITION AND GROWTH OF EARLY LIFE STAGES OF NORTHERN ANCHOVY RELATED TO THE BIOCHEMICAL CLIMATOLOGY OF THE NORTHERN CALIFORNIA CURRENT? Jessica A. Miller 1, William T. Peterson 2, Louise Copeman
The role of unchelated Fe in the iron nutrition of phytoplankton
 400 Notes Limnol. Oceanogr., 53(1), 2008, 400 404 E 2008, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. The role of unchelated Fe in the iron nutrition of phytoplankton Abstract The important
400 Notes Limnol. Oceanogr., 53(1), 2008, 400 404 E 2008, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. The role of unchelated Fe in the iron nutrition of phytoplankton Abstract The important
Modelling carbon overconsumption and the formation of extracellular particulate organic carbon
 Biogeosciences, 4, 433 454, 27 www.biogeosciences.net/4/433/27/ Author(s) 27. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Biogeosciences Modelling carbon overconsumption and the formation of
Biogeosciences, 4, 433 454, 27 www.biogeosciences.net/4/433/27/ Author(s) 27. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Biogeosciences Modelling carbon overconsumption and the formation of
Human Impacts on ecosystem health and resources of Lake Edward (HIPE): the phytoplankton study
 Human Impacts on ecosystem health and resources of Lake Edward (HIPE): the phytoplankton study M.P. Stoyneva-Gärtner 2,J.-P. Descy 1, C. Morana 3, S. Bouillon 3, Lambert T. 4 & A.V. Borges 1 1 University
Human Impacts on ecosystem health and resources of Lake Edward (HIPE): the phytoplankton study M.P. Stoyneva-Gärtner 2,J.-P. Descy 1, C. Morana 3, S. Bouillon 3, Lambert T. 4 & A.V. Borges 1 1 University
Southern Ocean MBL CCN Budget: Contribution from Primary Sea Spray Aerosol Organics. Trish Quinn NOAA PMEL
 Southern Ocean MBL CCN Budget: Contribution from Primary Sea Spray Aerosol Organics Trish Quinn NOAA PMEL patricia.k.quinn@noaa.gov Marine Biota Climate Feedback Loop Charlson et al., Nature, 1987. Aerosol
Southern Ocean MBL CCN Budget: Contribution from Primary Sea Spray Aerosol Organics Trish Quinn NOAA PMEL patricia.k.quinn@noaa.gov Marine Biota Climate Feedback Loop Charlson et al., Nature, 1987. Aerosol
Experiments on nutrient limitation in bottles
 Journal of Plankton Research Vol.20 no.8 pp.1527-1538, 1998 Experiments on nutrient limitation in bottles D.H.Cushing and J.W.Horwood 1 198 Yarmouth Road, Lowestoft, Suffolk NR32 4AB and * Centre for Environment,
Journal of Plankton Research Vol.20 no.8 pp.1527-1538, 1998 Experiments on nutrient limitation in bottles D.H.Cushing and J.W.Horwood 1 198 Yarmouth Road, Lowestoft, Suffolk NR32 4AB and * Centre for Environment,
Effects of increasing nutrient loads on the competition and succession between two predominant red tide algae of East China Sea
 Effects of increasing nutrient loads on the competition and succession between two predominant red tide algae of East China Sea Reporter:Yuping Zhou The Tutor:Jiangtao Wang Contents Background Experiments
Effects of increasing nutrient loads on the competition and succession between two predominant red tide algae of East China Sea Reporter:Yuping Zhou The Tutor:Jiangtao Wang Contents Background Experiments
Global diversity patterns of marine phytoplankton and zooplankton
 AIV presentation 14/10/05 Claude Loverdo Sakina Ayata Global diversity patterns of marine phytoplankton and zooplankton X.Irigoien, J.Huisman and R.P.Harris Nature 429, 863-867 (2004) Presentation's overview
AIV presentation 14/10/05 Claude Loverdo Sakina Ayata Global diversity patterns of marine phytoplankton and zooplankton X.Irigoien, J.Huisman and R.P.Harris Nature 429, 863-867 (2004) Presentation's overview
Variations in Synechococcus Cell Quotas of Phosphorus, Sulfur, Manganese, Iron, Nickel, and Zinc within Mesoscale Eddies in the Sargasso Sea
 Old Dominion University ODU Digital Commons OEAS Faculty Publications Ocean, Earth & Atmospheric Sciences 2010 Variations in Synechococcus Cell Quotas of Phosphorus, Sulfur, Manganese, Iron, Nickel, and
Old Dominion University ODU Digital Commons OEAS Faculty Publications Ocean, Earth & Atmospheric Sciences 2010 Variations in Synechococcus Cell Quotas of Phosphorus, Sulfur, Manganese, Iron, Nickel, and
Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling
 Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling Monika Winder Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences Stockholm University What does a more acidic
Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling Monika Winder Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences Stockholm University What does a more acidic
Some thoughts on the concept of colimitation: Three definitions and the importance of bioavailability
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 53(1), 2008, 276 290 E 2008, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Some thoughts on the concept of colimitation: Three definitions and the importance of bioavailability
Limnol. Oceanogr., 53(1), 2008, 276 290 E 2008, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Some thoughts on the concept of colimitation: Three definitions and the importance of bioavailability
Iron limitation and the cyanobacterium Synechococcus in equatorial Pacific waters
 Notes 48 spatial distribution pattern and biomass estimate of TALLING, J. F. 957. Some observations on the stratithe major demersal fishes in Lake Victoria. Afr. J. fication of Lake Victoria. Limnol. Oceanogr.
Notes 48 spatial distribution pattern and biomass estimate of TALLING, J. F. 957. Some observations on the stratithe major demersal fishes in Lake Victoria. Afr. J. fication of Lake Victoria. Limnol. Oceanogr.
Redfield revisited: variability of C:N:P in marine microalgae and its biochemical basis
 European Journal of Phycology ISSN: 0967-0262 (Print) 1469-4433 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tejp20 Redfield revisited: variability of C:N:P in marine microalgae and its biochemical
European Journal of Phycology ISSN: 0967-0262 (Print) 1469-4433 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tejp20 Redfield revisited: variability of C:N:P in marine microalgae and its biochemical
Ammonium uptake and growth limitation in marine phytoplankton
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 52(6), 2007, 2496 2506 E 2007, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Ammonium uptake and growth limitation in marine phytoplankton William G. Sunda and D. Ransom
Limnol. Oceanogr., 52(6), 2007, 2496 2506 E 2007, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Ammonium uptake and growth limitation in marine phytoplankton William G. Sunda and D. Ransom
Phytoplankton community structure and dynamics in the North
 1 1 2 Phytoplankton community structure and dynamics in the North Atlantic subtropical gyre 3 Carlos Cáceres 1,2, Antonella Rivera 1, Sonia González 1,3, Ricardo Anadón 1 4 5 6 1 Área de Ecología. Departamento
1 1 2 Phytoplankton community structure and dynamics in the North Atlantic subtropical gyre 3 Carlos Cáceres 1,2, Antonella Rivera 1, Sonia González 1,3, Ricardo Anadón 1 4 5 6 1 Área de Ecología. Departamento
Modelling alkaline phosphatase activity in microalgae under orthophosphate limitation: the case of Phaeocystis globosa
 Journal of lankton Research plankt.oxfordjournals.org J. lankton Res. (2015) 37(5): 869 885. First published online August 6, 2015 doi:10.1093/plankt/fbv062 Modelling alkaline phosphatase activity in microalgae
Journal of lankton Research plankt.oxfordjournals.org J. lankton Res. (2015) 37(5): 869 885. First published online August 6, 2015 doi:10.1093/plankt/fbv062 Modelling alkaline phosphatase activity in microalgae
Sequential nutrient uptake as a potential mechanism for phytoplankton to maintain high primary productivity and balanced nutrient stoichiometry
 Biogeosciences, 1, 269 280, 2017 www.biogeosciences.net/1/269/2017/ doi:10.519/bg-1-269-2017 Author(s) 2017. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Sequential nutrient uptake as a potential mechanism for phytoplankton
Biogeosciences, 1, 269 280, 2017 www.biogeosciences.net/1/269/2017/ doi:10.519/bg-1-269-2017 Author(s) 2017. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Sequential nutrient uptake as a potential mechanism for phytoplankton
Nutrient Enrichment Experiment to Establish Relationship between Chlorophyll and Phosphate
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Earth Science and Engineering 2014, Volume 3, Issue 1, pp. 211-224, Article ID Sci-252 ISSN: 2320 3609 Research Article Open Access Nutrient Enrichment
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Earth Science and Engineering 2014, Volume 3, Issue 1, pp. 211-224, Article ID Sci-252 ISSN: 2320 3609 Research Article Open Access Nutrient Enrichment
The interaction between zinc deficiency and copper toxicity as it affects the silicic acid uptake mechanisms in Thalassiosira pseudonana l
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 26(l), 1981, 67-73 The interaction between zinc deficiency and copper toxicity as it affects the silicic acid uptake mechanisms in Thalassiosira pseudonana l John G. Rueter, Jr.,2 and
Limnol. Oceanogr., 26(l), 1981, 67-73 The interaction between zinc deficiency and copper toxicity as it affects the silicic acid uptake mechanisms in Thalassiosira pseudonana l John G. Rueter, Jr.,2 and
The Influence of Iron on the Cellular Quota of Prochlorococcus
 The Influence of Iron on the Cellular Quota of Prochlorococcus Mak Saito Department of Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole MA 02543 phone: (508) 289-2393 fax:
The Influence of Iron on the Cellular Quota of Prochlorococcus Mak Saito Department of Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole MA 02543 phone: (508) 289-2393 fax:
Zackary Johnson Department of Oceanography
 Zackary Johnson Department of Oceanography http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/oceanography/zij/education/ocn621 Application of Bioenergetics to Biological Oceanography Biochemical parameters indicative of stock
Zackary Johnson Department of Oceanography http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/oceanography/zij/education/ocn621 Application of Bioenergetics to Biological Oceanography Biochemical parameters indicative of stock
Journal of Great Lakes Research
 Journal of Great Lakes Research 38 (212) 54 513 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Journal of Great Lakes Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jglr Causal mechanisms of the
Journal of Great Lakes Research 38 (212) 54 513 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Journal of Great Lakes Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jglr Causal mechanisms of the
Accounting for grazing dynamics in nitrogen-phytoplankton-zooplankton models
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 52(2), 2007, 649 661 E 2007, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Accounting for grazing dynamics in nitrogen-phytoplankton-zooplankton models Aditee Mitra and
Limnol. Oceanogr., 52(2), 2007, 649 661 E 2007, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Accounting for grazing dynamics in nitrogen-phytoplankton-zooplankton models Aditee Mitra and
Carbon versus iron limitation of bacterial growth in the California upwelling regime
 December 2000 Volume 45 Number 8 Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(8), 2000, 1681 1688 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Carbon versus iron limitation of bacterial growth in the California
December 2000 Volume 45 Number 8 Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(8), 2000, 1681 1688 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Carbon versus iron limitation of bacterial growth in the California
Iron requirements of the pennate diatom Pseudo-nitzschia: Comparison of oceanic (high-nitrate, low-chlorophyll waters) and coastal species
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 51(5), 2006, 2092 2101 E 2006, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Iron requirements of the pennate diatom Pseudo-nitzschia: Comparison of oceanic (high-nitrate,
Limnol. Oceanogr., 51(5), 2006, 2092 2101 E 2006, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Iron requirements of the pennate diatom Pseudo-nitzschia: Comparison of oceanic (high-nitrate,
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC.
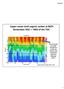 Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Plants, soil, and nutrients. Created in partnership with Alex Lindsey, Ph.D., The Ohio State University
 Plants, soil, and nutrients Created in partnership with Alex Lindsey, Ph.D., The Ohio State University Where do plants get their nutrients? Atmospheric deposition (N, S) Irrigation water Shallow groundwater
Plants, soil, and nutrients Created in partnership with Alex Lindsey, Ph.D., The Ohio State University Where do plants get their nutrients? Atmospheric deposition (N, S) Irrigation water Shallow groundwater
Limnol. Oceanogr., 40(l), 1995, , by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc.
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 40(l), 1995, 132-137 0 1995, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Regulation of copper concentration in the oceanic nutricline by phytoplankton uptake and regeneration
Limnol. Oceanogr., 40(l), 1995, 132-137 0 1995, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Regulation of copper concentration in the oceanic nutricline by phytoplankton uptake and regeneration
Remote Sensing of phytoplankton photosynthetic rates
 June-Aug Fv/Fm 998 Remote Sensing of phytoplankton photosynthetic rates and production from measurements of ocean colour. Jim Aiken, Gerald Moore, James Fishwick, Claudia Omachi, Tim Smyth, Plymouth Marine
June-Aug Fv/Fm 998 Remote Sensing of phytoplankton photosynthetic rates and production from measurements of ocean colour. Jim Aiken, Gerald Moore, James Fishwick, Claudia Omachi, Tim Smyth, Plymouth Marine
Lesson: Plankton. We will use each of these three categories in our investigations of plankton.
 Lesson: Plankton Plankton Most of the living organisms in the oceans we never see and rarely hear about. They are the plankton that float at or near the surface in ocean and freshwater environments. Plankton
Lesson: Plankton Plankton Most of the living organisms in the oceans we never see and rarely hear about. They are the plankton that float at or near the surface in ocean and freshwater environments. Plankton
ID # NUTRIENT DYNAMICS AND INVENTORY IN TROPICAL GRASSLAND ECOSYSTEM IN SOUTHERN INDIA. K. Karunaichamy 1 and K. Paliwal 2
 ID # 04-15 NUTRIENT DYNAMICS AND INVENTORY IN TROPICAL GRASSLAND ECOSYSTEM IN SOUTHERN INDIA K. Karunaichamy 1 and K. Paliwal 2 1 Scientist (Exploitation Studies), Rubber Research Institute of India, Kottayam
ID # 04-15 NUTRIENT DYNAMICS AND INVENTORY IN TROPICAL GRASSLAND ECOSYSTEM IN SOUTHERN INDIA K. Karunaichamy 1 and K. Paliwal 2 1 Scientist (Exploitation Studies), Rubber Research Institute of India, Kottayam
Silicon and zinc biogeochemical cycles coupled through the Southern Ocean
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2890 Silicon and zinc biogeochemical cycles coupled through the Southern Ocean Derek Vance, Susan H. Little,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2890 Silicon and zinc biogeochemical cycles coupled through the Southern Ocean Derek Vance, Susan H. Little,
Plant, Soil, and Nutrients
 Plant, Soil, and Nutrients 1 Where do plants get their nutrients? - Atmospheric Deposition (N, S) - Irrigation water - Shallow groundwater 2 What is surface exchange? Soil has an overall charge Overall
Plant, Soil, and Nutrients 1 Where do plants get their nutrients? - Atmospheric Deposition (N, S) - Irrigation water - Shallow groundwater 2 What is surface exchange? Soil has an overall charge Overall
Phytoplankton Climate Regulation in Positive and Negative Feedback Systems: The CLAW and anti-claw hypotheses
 Phytoplankton Climate Regulation in Positive and Negative Feedback Systems: The CLAW and anti-claw hypotheses Adam Stoer, Undergraduate Student, Dalhousie University Abstract The global climate crisis
Phytoplankton Climate Regulation in Positive and Negative Feedback Systems: The CLAW and anti-claw hypotheses Adam Stoer, Undergraduate Student, Dalhousie University Abstract The global climate crisis
The interaction between inorganic iron and cadmium uptake in the marine diatom Thalassiosira oceanica
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 53(5), 2008, 178 1789 E 2008, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. The interaction between inorganic iron and cadmium uptake in the marine diatom Thalassiosira
Limnol. Oceanogr., 53(5), 2008, 178 1789 E 2008, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. The interaction between inorganic iron and cadmium uptake in the marine diatom Thalassiosira
Modeling phytoplankton growth rates
 Journal of Plankton Research Vol.18 no.l pp.63-85,1996 Modeling phytoplankton growth rates Jeffrey D.Haney and George A Jackson 1 Department of Oceanography, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77843,
Journal of Plankton Research Vol.18 no.l pp.63-85,1996 Modeling phytoplankton growth rates Jeffrey D.Haney and George A Jackson 1 Department of Oceanography, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77843,
How well have can we answer our primary goal? Key questions/processes/issues to discuss include- (not in any order)
 AGENDA VERTIGO Workshop October 1-4, 2006 J. Erik Jonsson Woods Hole Center of the National Academy of Sciences, 314 Quissett Avenue, Woods Hole, and the last morning in room 509 in the Clark Building
AGENDA VERTIGO Workshop October 1-4, 2006 J. Erik Jonsson Woods Hole Center of the National Academy of Sciences, 314 Quissett Avenue, Woods Hole, and the last morning in room 509 in the Clark Building
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-III
 OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-III Guangyi Wang POST 103B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/oceanography/zij/education/ocn621/ dc 1 /dt = growth Standing Stock C 1 Overview
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-III Guangyi Wang POST 103B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/oceanography/zij/education/ocn621/ dc 1 /dt = growth Standing Stock C 1 Overview
Nitrate, phosphate, and ammonium uptake: a nutrient addition experiment in an East African stream
 Nitrate, phosphate, and ammonium uptake: a nutrient addition experiment in an East African stream Student: Mer Mietzelfeld Mentor: Catherine O Reilly Introduction Nitrogen and phosphorus are two nutrients
Nitrate, phosphate, and ammonium uptake: a nutrient addition experiment in an East African stream Student: Mer Mietzelfeld Mentor: Catherine O Reilly Introduction Nitrogen and phosphorus are two nutrients
Sources of nutrients to the surface mixed layer of the ocean
 Sources of nutrients to the surface mixed layer of the ocean What are nutrients anyway? (to a chemist that is.) Where do they come from? Preformed (recycled, delivered from elsewhere) Biosynthesized Nutrient
Sources of nutrients to the surface mixed layer of the ocean What are nutrients anyway? (to a chemist that is.) Where do they come from? Preformed (recycled, delivered from elsewhere) Biosynthesized Nutrient
Effect of Acartia grazing on the size distribution of phytoplankton in Academy Bay, Galapagos
 Effect of Acartia grazing on the size distribution of phytoplankton in Academy Bay, Galapagos Jonathan Herzog University of Washington School of Oceanography 1 NON-TECHNICAL SUMMARY The goal of this experiment
Effect of Acartia grazing on the size distribution of phytoplankton in Academy Bay, Galapagos Jonathan Herzog University of Washington School of Oceanography 1 NON-TECHNICAL SUMMARY The goal of this experiment
EOSC Biology 3. Zooplankton Measurements
 EOSC 473-573 Biology 3 Zooplankton Measurements Zooplankton Biomass and Abundance Two Quantitative Procedures: Biomass Determination (mg C per m 3 or per m 2 ) Abundance (# individuals per m 3 or per m
EOSC 473-573 Biology 3 Zooplankton Measurements Zooplankton Biomass and Abundance Two Quantitative Procedures: Biomass Determination (mg C per m 3 or per m 2 ) Abundance (# individuals per m 3 or per m
Grazing limitation and nutrient limitation in marine ecosystems: Steady state solutions of an ecosystem model with multiple food chains
 . Limnol. Oceanogr., 39(3), 1994, 597-608 0 1994, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Grazing limitation and nutrient limitation in marine ecosystems: Steady state solutions of
. Limnol. Oceanogr., 39(3), 1994, 597-608 0 1994, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Grazing limitation and nutrient limitation in marine ecosystems: Steady state solutions of
An Analysis of Diatom Growth Rate and the Implications for the Biodiesel Industry
 Occam's Razor Volume 5 (2015) Article 6 2015 An Analysis of Diatom Growth Rate and the Implications for the Biodiesel Industry Sara Spitzer Western Washington University, sara.spitzer@wwu.edu Follow this
Occam's Razor Volume 5 (2015) Article 6 2015 An Analysis of Diatom Growth Rate and the Implications for the Biodiesel Industry Sara Spitzer Western Washington University, sara.spitzer@wwu.edu Follow this
Stoichiometry of mesopelagic zooplankton and carbon sequestration in the ocean
 Stoichiometry of mesopelagic zooplankton and carbon sequestration in the ocean Tom Anderson National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, UK Ocean Carbon & Biogeochemistry workshop, Woods Hole, 28 June 2017
Stoichiometry of mesopelagic zooplankton and carbon sequestration in the ocean Tom Anderson National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, UK Ocean Carbon & Biogeochemistry workshop, Woods Hole, 28 June 2017
Temperature effects on phytoplankton growth in continuous culture1
 932 Notes lation of marine phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17 : 37 l-382. MACISAAC, J. J., AND R. C. DUGDALE. 1972. Interactions of light and inorganic nitrogen in controlling nitrogen uptake in the sea.
932 Notes lation of marine phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17 : 37 l-382. MACISAAC, J. J., AND R. C. DUGDALE. 1972. Interactions of light and inorganic nitrogen in controlling nitrogen uptake in the sea.
Iron limitation? Section 5. The case for iron
 Section 5 Iron limitation?!,imnol. Oceanogr., 36(8), 1991, 1793-1802 D 1991, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. The case for iron lohn H. Martin, R. Michael Gordon, and Steve E.
Section 5 Iron limitation?!,imnol. Oceanogr., 36(8), 1991, 1793-1802 D 1991, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. The case for iron lohn H. Martin, R. Michael Gordon, and Steve E.
Role of Trichodestnium spp. in the
 Chapter 4 Role of Trichodestnium spp. in the organic production and nitrogen fixation in the Arabian Sea 4.1. Introduction The planktonic marine diazotroph, Trichodesmium spp. is considered to be an important
Chapter 4 Role of Trichodestnium spp. in the organic production and nitrogen fixation in the Arabian Sea 4.1. Introduction The planktonic marine diazotroph, Trichodesmium spp. is considered to be an important
Award Number: N
 Trace Metal Speciation: Equilibrium and Kinetic Considerations on Biological Effects, Phytoplankton Uptake and Sorption Processes in Coastal Waters (Field and Laboratory Studies) Kenneth W. Bruland University
Trace Metal Speciation: Equilibrium and Kinetic Considerations on Biological Effects, Phytoplankton Uptake and Sorption Processes in Coastal Waters (Field and Laboratory Studies) Kenneth W. Bruland University
Response of Sargasso Sea phytoplankton biomass, growth rates and primary production to seasonally varying physical forcing
 Journal of Plankton Research Vol.20 no.12 pp.2223-2249, 1998 Response of Sargasso Sea phytoplankton biomass, growth rates and primary production to seasonally varying physical forcing Ralf Goericke and
Journal of Plankton Research Vol.20 no.12 pp.2223-2249, 1998 Response of Sargasso Sea phytoplankton biomass, growth rates and primary production to seasonally varying physical forcing Ralf Goericke and
TYPE: ORGANIC NUTRIENTS CODE: BF4 - GRANULE (JAIVIZYME)
 TYPE: ORGANIC NUTRIENTS CODE: BF4 GRANULE (JAIVIZYME) AVAILABLE: BULK, PRIVATE LABEL & BRANDS Composition Ingredient % Potassium Humate 5.00% w/w Min. Carrier Granules 95.00% w/w Max. Advantages Mode of
TYPE: ORGANIC NUTRIENTS CODE: BF4 GRANULE (JAIVIZYME) AVAILABLE: BULK, PRIVATE LABEL & BRANDS Composition Ingredient % Potassium Humate 5.00% w/w Min. Carrier Granules 95.00% w/w Max. Advantages Mode of
GROWTH RESPONSE OF ANTARCTIC PHYTOPLANKTON TO IRON ENRICHMENT. and Kentaro WATANABE~
 Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar Biol., 1, 14-24, 1997 GROWTH RESPONSE OF ANTARCTIC PHYTOPLANKTON TO IRON ENRICHMENT Shigenobu TAKEDA' and Kentaro WATANABE~ Central Research Institute of Electric Poer Industry,
Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar Biol., 1, 14-24, 1997 GROWTH RESPONSE OF ANTARCTIC PHYTOPLANKTON TO IRON ENRICHMENT Shigenobu TAKEDA' and Kentaro WATANABE~ Central Research Institute of Electric Poer Industry,
The impact of fine-scale turbulence on phytoplankton community structure
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The impact of fine-scale turbulence on phytoplankton community structure Andrew D. Barton, 1, Ben A. Ward, Richard G. Williams, 4 and Michael J. Follows 1 1 Department of Earth, Atmospheric,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The impact of fine-scale turbulence on phytoplankton community structure Andrew D. Barton, 1, Ben A. Ward, Richard G. Williams, 4 and Michael J. Follows 1 1 Department of Earth, Atmospheric,
Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils
 The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
Biosolids Nutrien Management an Soil Testing. Craig Cogger, Soil Scientis WSU Puyallup
 Biosolids Nutrien Management an Soil Testing Craig Cogger, Soil Scientis WSU Puyallup Nutrient Manageme Meet crop nutrient needs Maintain soil quality Conserve resources Protect water quality -- reduc
Biosolids Nutrien Management an Soil Testing Craig Cogger, Soil Scientis WSU Puyallup Nutrient Manageme Meet crop nutrient needs Maintain soil quality Conserve resources Protect water quality -- reduc
Commercial culture of 3 marine diatoms in raceways
 Commercial culture of 3 marine diatoms in raceways or A 37 years story (1976-2013, still going..) J.P. BRAUD - Innovalg Brief history of tank culture 1976-1982: Preliminary studies (22 Pleubian) 1982-1992:
Commercial culture of 3 marine diatoms in raceways or A 37 years story (1976-2013, still going..) J.P. BRAUD - Innovalg Brief history of tank culture 1976-1982: Preliminary studies (22 Pleubian) 1982-1992:
TNPSC Chemistry Study Material Fertilizers
 TNPSC Chemistry Study Material A fertilizer is any material of natural or synthetic origin (other than liming materials) that is applied to soils or to plant tissues to supply one or more plant nutrients
TNPSC Chemistry Study Material A fertilizer is any material of natural or synthetic origin (other than liming materials) that is applied to soils or to plant tissues to supply one or more plant nutrients
Effect of Ocean Iron Fertilization on the Phytoplankton Biological Carbon Pump
 Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics Adv. Appl. Math. Mech., Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 52-64 DOI: 128/aamm.1-m123 February 211 Effect of Ocean Iron Fertilization on the Phytoplankton Biological Carbon
Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics Adv. Appl. Math. Mech., Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 52-64 DOI: 128/aamm.1-m123 February 211 Effect of Ocean Iron Fertilization on the Phytoplankton Biological Carbon
