Medial approach to treat humeral mid-shaft fractures: a retrospective study
|
|
|
- Dustin Long
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:32 DOI /s RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Medial approach to treat humeral mid-shaft fractures: a retrospective study Shun Lu 1, Junwei Wu 1, Shihong Xu 1, Baisheng Fu 1, Jinlei Dong 1, Yongliang Yang 1, Guodong Wang 1, Maoyuan Xin 1, Qinghu Li 1, Tong-Chuan He 2, Fu Wang 1* and Dongsheng Zhou 1* Abstract Background: Plate fixation is the gold standard for diaphyseal fracture management, and the anterolateral approach is widely used by reconstructive surgeons. However, the outcomes of humeral shaft fracture fixation using a medial approach are rarely reported. The aim of this study is to explore the management and outcomes of humeral mid-shaft fractures fixed through a medial incision. Methods: Thirty-four patients who sustained a humeral mid-shaft fracture and underwent an open-reduction internal fixation (ORIF) in our department between January 2010 and January 2013 were included in this study. Sixteen patients had an ORIF performed through a medial approach, while the remaining 18 were fixed through an anterolateral approach. Postoperative clinical and radiographic results were reviewed. Results: There were no significant differences in the blood loss and the range of motion of the shoulder and elbow between the anterolateral and medial fixation groups. One patient in the medial group and two patients in the anterolateral group had radial nerve dysfunction that improvedafter8,3and6weeks,respectively.allpatients healed radiographically except one from the anterolateral group who underwent grafting and re-fixation for a non-union. No vascular injuries, infections, malunions, broken plates or loose screws were noted in either group. Conclusions: The medial approach to the humerus had equivalent outcomes to anterolateral fixation. It is an available choice for humeral mid-shaft fracture fixation in cases where there is no need to expose the radial nerve. The medial approach does not require a pre-bent plate and creates a large operative exposure. A well-hidden incision can also be designed, improving cosmetic outcomes. However, the medial approach is not suitable to proximal or distal humerus fractures. Keywords: Humeral mid-shaft fractures, Medial approach, Plate fixation Background Plate fixation is the gold standard for the surgical management of humeral mid-shaft fractures [1 3], and the anterolateral approach is most commonly used [4 7]. However, the medial approach is rarely discussed for humeral shaft fracture management [8]. This is because of the complicated anatomy of the medial aspect of the upper arm. We believe that there are several merits to the medial approach for humeral mid-shaft fracture management, such as no need to expose the radial nerve and no need to * Correspondence: @qq.com; @qq.com Equal contributors 1 Department of Orthopedics, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong , China Full list of author information is available at the end of the article pre-bent the plate and a well-hidden incision. So the aim of this study is to explore the management and outcomes of humeral mid-shaft fracture fixation with a medial approach and evaluate the safety, efficacy and benefits of this approach. Methods Permission for this retrospective study was obtained from the medical ethics committee of Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University. A total of 34 patients who sustained a humeral midshaft fracture and underwent an open-reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) at our department between January 2010 and January 2013 were included in this study. There were 22 males and 12 females with ages ranging from Lu et al. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Lu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:32 Page 2 of 7 to 59 years. The initial injuries were traffic accidents in 19 cases, falls in nine cases and sport-related injuries in six cases. According to the AO/Orthopaedic Trauma Association classification, 18 fractures were type A, nine were type B and seven were type C fractures (Table 1). The medial approach was used on 16 patients, while 18 patients underwent anterolateral fixation. All procedures were performed by a senior trauma surgical team. Those injuries associated with an ipsilateral upper limb fracture or a neurovascular injury were excluded from this study. Data on clinical outcomes, operative time and operative complications were collected and reviewed. Postoperatively, patients were assessed radiographically 1, 2, 3, 6, 9 and 12 months after surgery, with annual imaging thereafter. The range of motion (ROM) of the shoulder and elbow joints was also assessed. Surgical technique Medial approach Patients were placed in the supine position with their injured limb in 90 of abduction. A medial incision was created over the fracture site along a line connecting the armpit with the medial condyle of the humerus. The median nerve and the brachial vessels were dissected. Unlike the radial nerve, which is directly attached to the humerus, in the medial approach, the ulnar nerve runs in a relatively superficial location and was therefore easy to dissect. The ulnar nerve also had a high degree of relaxation and was easy to retract away from the fracture site to create ample operative space. The biceps and the triceps were retracted with the neurovascular structures, allowing the triceps to protect the ulnar nerve and brachial artery. The brachialis was longitudinally incised to Table 1 The Characteristics of patients between the two groups Characteristics Medial incision group Anterolateral incision group Number of cases Gender (male/female) 10/5 12/7 Mean age, years (range) 33.6 (18 56) 35.2 (23 59) Standard deviation (SD) Mechanism of injury Traffic accident 9 10 Fall 5 4 Sport injury 2 4 Fracture type (AO/OTA Classification) Type A 8 10 Type B 5 4 Type C 3 4 create a clear fracture exposure. The plate was placed on the anteromedial aspect of the humerus after a satisfactory reduction was performed. X-ray imaging was used to verify proper plate placement (Fig. 1). Anterolateral approach We performed plate fixation through the anterolateral incision using a previously described technique [4 7]. However, the exploration and protection of the radial nerve through this approach is routinely performed in our department. Statistical analysis All results were evaluated using SPSS 19.0 for Windows (IBM, Chicago, IL, USA). Differences in patient characteristics between the medial and anterolateral approaches such as sex, mechanism of injury and fracture classification were compared along with clinical and radiographic outcomes using a chi-squared test. Patient age and blood loss were compared using Student s t test. Complications including the rates of nerve injury and fracture non-union were assessed using Fisher s exact test. In all cases, statistical significance was defined as p <0.05. Results The average age of patients who underwent a medial approach was 33.6 years (range 18 to 56 years), with a male/ female ratio of 2:1. The average age of patients who underwent an anterolateral approach was 35.2 years (range 23 to 59 years), with a similar male/female ratio to the medial group. There were no significant differences between the average age, gender composition, mechanism of injury and fracture type between the two surgical approach groups. Blood loss was ± ml in the medial group and ± ml in the anterolateral group. There was no significant difference in blood loss between the approaches (p > 0.05) (Table 2). Radiographic healing was observed 3 months after surgery in 14 of 16 patients in the medial approach group. The remaining two patients healed after a longer followup period. Radiographic healing was observed in 15 of 18 patients 3 months following surgery. Two patients healed after a longer follow-up. One patient required iliac bone grafting for a non-union 1 year after surgery and went on to good healing. Full range of motion (ROM) of the shoulder was restored in both groups postoperatively. All patients in the medial group had full ROM of their elbow joint without postoperative restriction. Two patients in the anterolateral group had slightly reduced elbow extension in the early postoperative period, although full elbow ROM was restored 1 to 2 months later (Fig. 2).
3 Lu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:32 Page 3 of 7 Fig. 1 a Mark the incision before operation. b Expose the fracture region. c Fluoroscopy after fixation. d Place the plate and fixation Judet in 1968 [8]. Jupiter [9] later reported that it could be used in cases of complex non-unions of the humeral diaphysis. The main reason that the medial approach is not widely used may be the complicated anatomy of the medial aspect of the upper arm. Surgeons tend to choose an approach with fewer nerves and blood vessels, and the brachial vessels, median nerve and ulnar nerve are visible during a medial approach. The anterolateral approach is widely accepted for midshaft humeral fracture fixation [4 7]. However, in our evaluation of the medial approach, we found that there are no significant differences in the blood loss, fracture healing rate and postoperative function of patients treated with either approach. Moreover, there are several merits to the medial approach. We therefore have adopted the medial approach for diaphyseal humeral fractures at our institution. One patient in the medial approach group developed a radial nerve palsy after surgery. This may be owing to operative manipulation. Normal function returned 8 weeks after surgery. Two radial nerve palsies occurred in the anterolateral approach group, with a recovery in both patients following the use of neurotrophic drugs for 3 and 6 weeks after surgery. One patient in the anterolateral group developed a non-union after the ORIF, requiring refixation with autologous iliac bone graft using the same surgical approach to achieve a union. All patients in the medial approach group achieved a union after the operation. No vascular injury, infection, fracture displacement, plate fracture, screw extrusion, plate breakage or screw loosening was observed in either group. Discussion Plate fixation is considered the gold standard for humeral mid-shaft fracture fixation [1 3]. The anterolateral approach is widely accepted for the treatment of these injuries [4 7]. The medial approach is another choice for humeral shaft fracture fixation but has been rarely discussed. The medial approach was first reported by Operative site exposure The anterolateral approach is the classic approach for humeral shaft fracture fixation. It allows for excellent fracture exposure and fixation. In the medial approach, Table 2 The Blood loss and Complications between the two groups Operative records Medial incision group Anterolateral incision group t/χ2 value p value Blood loss (ml) ± ± Nerve disturbances Non-union Complications
4 Lu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:32 Page 4 of 7 Fig. 2 Female, 56 years, who was fall from a height, the fracture type: A, and she was taken ORIF by medial incision. a a The X-ray after injury and b the X-ray after ORIF. b The X-ray at 1 year after operation. c The ROM of shoulder and elbow joint the brachial vessels and the median nerve run in a relatively superficial location, making them easy to explore. It is also possible to create a clear exposure by splitting the brachialis after properly protecting the vessels and nerves. We found that the ulnar nerve is relaxed enough that it can be easily pulled away at least 3.5 cm from the fracture site (Fig. 3a), ensuring an ample operative space for reduction and fixation. In contrast, in the anterolateral approach, the radial nerve is strained and requires meticulous protection to reduce the incidence of nerve damage. Reports of radial nerve injury are common [9 12]. The biggest limitation of the medial approach is the reduced ability for the surgeon to extend the exposure compared to the anterolateral approach. It is therefore difficult to expose and manipulate both the proximal and distal humerus through the medial approach. We therefore only recommend the medial approach for mid-shaft fractures without proximal or distal humerus involvement. Nerve exploration and damage It is controversial whether or not the radial nerve needs to be exposed in humeral shaft fractures without clinical evidence of nerve palsy. It is reported that more than 80 % of radial nerve injuries recover spontaneously [10, 13], and early detection is advocated to reduce iatrogenic radial nerve injuries. However, despite radial nerve exploration, intraoperative traction, direct nerve contact with the plate, nerve compression by scar tissue and bony callus are still risk factors for radial nerve injury. In our study, there were two radial nerve palsies after fixation using the anterolateral approach that improved after conservative treatment with neurotrophic drugs for 3 and 6 weeks. No long-term radial nerve paralysis occurred. Among those who were fixed medially, one patient developed a radial nerve palsy that resolved in 8 weeks. This may be owing to operative manipulation. No ulnar nerve or other neurovascular injury occurred. We believe that the neurovascular structures on the medial arm are superficial and easily detected during the medial approach, and an ample operative space can be created because of the high degree of relaxation of the ulnar nerve. Compared with the anterolateral approach, it may also be possible to get better soft tissue coverage over the plate using the medial approach. Plate placement The cross-sectional shape of the humerus from the midshaft to the distal metaphysis is triangular. It has three aspects: anteromedial, anterolateral and posterior [14, 15]. In the anterolateral approach, the lateral aspect of the
5 Lu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:32 Page 5 of 7 Fig. 3 a The ulnar nerve is easy to pull away from the fracture site with at least 3.5 cm. b In the medial approach, the incision was secluded. c In the medial approach, the plate could be placed directly without being reshaped. d In the anterolateral approach, gap widen (indicated by the arrows) often occurs in the medial of fracture site when the fixation is undertaken humerus is uneven, often leading to medial gapping during fixation (Fig. 3c, d). The plate often needs to be prebent during placement. During the medial approach, the plate can be placed without being reshaped onto the smooth anteromedial humerus. Biomechanically, the plate should be placed on the tension side of the injury [16]. The implant should therefore be placed on either the anterolateral or the posterior aspects of the bone. Unlike the femur or tibia, whose primary stresses are weight-bearing, the major stresses on the humerus are rotational forces. The plate can therefore be placed on the medial aspect of the humerus [17]. The scars of the skin In the medial approach, the incision is partially hidden, which may result in an improved long-term cosmesis that is particularly beneficial for patients with particular cosmetic demands (Fig. 3d). Scars are difficult to find after surgery and can therefore meet patients aesthetic requirements. Fig. 4 The learning curve of applied ORIF through medial approach
6 Lu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:32 Page 6 of 7 Plate removal In some cases, patients require plate removal. In these cases, the direct contact of the radial nerve with the plate and the increased local scar tissue and bony callus results in increased rates of radial nerve injuries. Running superficial to the radial nerve, the neurovascular structures of the medial arm can be explored easily. There were two patients at our institution who underwent plate removal, and no nerve injury resulted. The manipulation necessary to perform a medial approach requires a significant learning curve. Familiarity with the local anatomy is needed to avoid neurovascular injury. The time to complete the ORIF through a medial approach was recorded, and the learning curve of each surgeon was plotted (Fig. 4). In early cases, the ORIF took approximately 120 min. This time was decreased significantly in subsequent cases to a mean operative time of 90 min. As the brachial vessels, median nerve and ulnar nerve go through the medial aspect of the arm, surgeons tend to choose other approaches that manipulate fewer critical structures. However, we were able to create a clear exposure in our study. Neurovascular injury can be avoided through meticulous manipulation and cautious neurovascular protection. We therefore believe that a complex anatomy should not be the reason for avoiding a medial approach. When managing humeral mid-shaft fractures through the medial approach, there is no need to expose the radial nerve and no need to pre-bend the plate before fixation. An ample operative space could be created through a cosmetically occult incision. We therefore recommend that a medial approach be used in the following cases: (1) humeral mid-shaft fractures without a radial nerve injury; (2) humeral shaft fractures associated with a medial neurovascular injury that requires surgical exploration and repair; (3) a laceration or soft tissue disruption on the lateral arm and (4) patients with significant cosmetic requirements. Patients with distal and proximal humeral fractures or radial nerve injuries are not indicated for this approach. Conclusions The medial approach to the humerus is a possible choice for humeral mid-shaft fractures. However, humeral shaft fractures with radial nerve damage require nerve exploration, and a medial approach should not be performed. As this study was based on a small sample size and a retrospectively analysis of early results and short-term complications, a larger sample size and a longer followup period are required to fully study this approach. Consent statement Written informed consent was obtained from the patients for publication of this report and accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions FW and DZ drafted the manuscript. SL, JW, SX, BF, JD, YY, MX and QL contributed to the acquisition of the data, analysis and interpretation of the data. SL and MX helped to search literature and to draft the manuscript. SL, JW, GW and FW participated in the conception, design and coordination. TH, FW and DZ supervised the whole study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Authors information SL, JW, SX, BF, JD, YY, GW, XM, QL, FW and DZ they are all from the Department of Orthopedics, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China. TH is from the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University of Chicago Medical Center, Chicago, IL, USA. SL and JW contributed equally to the study, and FW and DZ are co-corresponding authors. Funding This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO ) Author details 1 Department of Orthopedics, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong , China. 2 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehabilitation Medicine, The University of Chicago Medical Center, Chicago, IL 60637, USA. Received: 30 November 2015 Accepted: 10 March 2016 References 1. Niall D, O Mahony J, McElwain J. Plating of humeral shaft fractures has the pendulum swung back? Injury. 2004;35(6): McCormack R, Brien D, Buckley R, McKee M, Powell J, Schemitsch E. Fixation of fractures of the shaft of the humerus by dynamic compression plate or intramedullary nail: a prospective, randomised trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(3): Lin J. Treatment of humeral shaft fractures with humeral locked nail and comparison with plate fixation. J Trauma-Injury Infect Critical Care. 1998; 44(5): Vander Griend R, Tomasin J, Ward EF. Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral shaft fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986;68: Mulier T, Seligson D, Sioen W, Van Den Bergh J, Reynaert P. Operative treatment of humeral shaft fractures. Acta Orthop Belg. 1997;63(3): Klenerman L. Fractures of the shaft of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1966;48(1): Blum J, Rommens P. Surgical approaches to the humeral shaft. Acta Chir Belg. 1997;97(5): Judet R, Patel A, Demeulenaere C. 3 approaches to the upper part of the humerus and the humeral diaphysis. Presse Med. 1968;76(41): Böstman O, Bakalim G, Vainionpää S, Wilppula E, Pätiälä H, Rokkanen P. Immediate radial nerve palsy complicating fracture of the shaft of the humerus: when is early exploration justified? Injury. 1985;16(7): DeFranco MJ, Lawton JN. Radial nerve injuries associated with humeral fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2006;31(4): Ekholm R, Ponzer S, Tornkvist H, Adami J, Tidermark J. Primary radial nerve palsy in patients with acute humeral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2008; 22(6): Pollock FH, Drake D, Bovill EG, Day L, Trafton PG. Treatment of radial neuropathy associated with fractures of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981;63(2): Lowe III JB, Sen SK, Mackinnon SE. Current approach to radial nerve paralysis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;110(4): Qu X. Morphological effects of mechanical forces on the human humerus. Br J Sports Med. 1992;26(1):51 3.
7 Lu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:32 Page 7 of Apivatthakakul T, Arpornchayanon O, Bavornratanavech S. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) of the humeral shaft fracture: is it possible? A cadaveric study and preliminary report. Injury. 2005;36(4): Müller ME. Treatment of nonunions by compression. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1965;43: Ambrósio J, Quental C, Pilarczyk B, Folgado J, Monteiro J. Multibody biomechanical models of the upper limb. Procedia IUTAM. 2011;2:4 17. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and we will help you at every step: We accept pre-submission inquiries Our selector tool helps you to find the most relevant journal We provide round the clock customer support Convenient online submission Thorough peer review Inclusion in PubMed and all major indexing services Maximum visibility for your research Submit your manuscript at
Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures. OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD
 Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do?
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
Minimally Invasive Helical Plating for Shaft of Humerus Fractures: Technique and Outcome
 184 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, 184-188 Open Access Minimally Invasive Helical Plating for Shaft of Humerus Fractures: Technique and Outcome James Chung Hui Tan *,1,2, Fareed Husain Yusuf Kagda
184 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, 184-188 Open Access Minimally Invasive Helical Plating for Shaft of Humerus Fractures: Technique and Outcome James Chung Hui Tan *,1,2, Fareed Husain Yusuf Kagda
Complex fractures of the humeral shaft. Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden
 Complex fractures of the humeral shaft Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Kopenhagen 2018 Complex fracture Changes in the AO/OTA classification system Complex Multifragmentary
Complex fractures of the humeral shaft Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Kopenhagen 2018 Complex fracture Changes in the AO/OTA classification system Complex Multifragmentary
Dr. Raja Rathnam Korani
 2018; 2(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(1): 06-10 Received: 12-11-2017 Accepted: 15-12-2017 Civil Surgeon Specialist, District
2018; 2(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(1): 06-10 Received: 12-11-2017 Accepted: 15-12-2017 Civil Surgeon Specialist, District
Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Screw Compression Method for Treatment of Humeral Shaft Fractures
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:506-513 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.506 Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Screw Compression Method for Treatment of Humeral
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:506-513 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.506 Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Screw Compression Method for Treatment of Humeral
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Effectiveness of the surgical torque limiter: a model comparing drill- and hand-based screw insertion into locking plates
 Ioannou et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:118 DOI 10.1186/s13018-016-0458-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Effectiveness of the surgical torque limiter: a model comparing drill- and hand-based
Ioannou et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:118 DOI 10.1186/s13018-016-0458-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Effectiveness of the surgical torque limiter: a model comparing drill- and hand-based
Comparison of Complication Rates of Intramedullary Pin Fixation Versus Plating of Midshaft Clavicle Fractures in an Active Duty Military Population
 Comparison of Complication Rates of Intramedullary Pin Fixation Versus Plating of Midshaft Clavicle Fractures in an Active Duty Military Population Jerome J. Wenninger Jr., PA-C; Joseph H. Dannenbaum,
Comparison of Complication Rates of Intramedullary Pin Fixation Versus Plating of Midshaft Clavicle Fractures in an Active Duty Military Population Jerome J. Wenninger Jr., PA-C; Joseph H. Dannenbaum,
CiSE. PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal Fractures of the Distal Humerus through an Anterolateral Approach. Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 18, No. 3, September, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2015.18.3.128 CiSE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 18, No. 3, September, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2015.18.3.128 CiSE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal
AcUMEDr. LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM
 AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral non-unions : Radiological and functional results
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 299-303 ORIGINAL STUDY Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral non-unions : Radiological and functional results Anani ABALO, Ekoué D. DOSSEh, Komlan ADABRA, Atsi WALLA,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 299-303 ORIGINAL STUDY Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral non-unions : Radiological and functional results Anani ABALO, Ekoué D. DOSSEh, Komlan ADABRA, Atsi WALLA,
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing
 Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
A Patient s Guide to Adult Forearm Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Forearm Fractures Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this
A Patient s Guide to Adult Forearm Fractures Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6251-6255 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Comparison study of the clinical effect and biomechanics between locking compression plate and interlocking intramedullary
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6251-6255 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Comparison study of the clinical effect and biomechanics between locking compression plate and interlocking intramedullary
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) of the humeral shaft fracture Is it possible? A cadaveric study and preliminary report
 Injury, Int. J. Care Injured (2005) 36, 530 538 www.elsevier.com/locate/injury Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) of the humeral shaft fracture Is it possible? A cadaveric study and preliminary
Injury, Int. J. Care Injured (2005) 36, 530 538 www.elsevier.com/locate/injury Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) of the humeral shaft fracture Is it possible? A cadaveric study and preliminary
Original Article Remove orthopedic fracture implant with minimal invasive surgery is good for the patient s early rehabilitation
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(12):22377-22381 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0016560 Original Article Remove orthopedic fracture implant with minimal invasive surgery is good for the patient s early rehabilitation
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(12):22377-22381 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0016560 Original Article Remove orthopedic fracture implant with minimal invasive surgery is good for the patient s early rehabilitation
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures:
 Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Humerus shaft - Reduction & Fixation - Compression plate - AO Surgery Reference. Compression plating
 Humerus shaft 12-A3 ORIF 1. Principles Compression plating Authors Compression plate Compression plating provides fixation with absolute stability for two-part fracture patterns, where the bone fragments
Humerus shaft 12-A3 ORIF 1. Principles Compression plating Authors Compression plate Compression plating provides fixation with absolute stability for two-part fracture patterns, where the bone fragments
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty
 Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
A clinical study of minimal invasive anterior bridge plating for humerus shaft fractures
 2018; 4(2): 01-05 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(2): 01-05 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-02-2018 Accepted: 02-03-2018 Mohammed Ibrahim Dr. Vijay H Rathod A clinical study of minimal invasive
2018; 4(2): 01-05 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(2): 01-05 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-02-2018 Accepted: 02-03-2018 Mohammed Ibrahim Dr. Vijay H Rathod A clinical study of minimal invasive
E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus
 Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus Alexander A. Weening, Kim M. Brouwer, Margaritha Adams & David Ring Orthopaedic Hand
Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus Alexander A. Weening, Kim M. Brouwer, Margaritha Adams & David Ring Orthopaedic Hand
Upper Extremity Fractures
 Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Case Presentation: Comminuted Fractures of the Proximal Ulna 11/28/2017. Disclosures. Surgical Strategy. Implant Choice. Melvin P.
 Current Solutions in Orthopaedic Trauma Case Presentation: Comminuted Fracture of the Proximal Ulna Melvin P. Rosenwasser, MD Robert E. Carroll Professor of Surgery of the Hand Chief, Orthopaedic Hand
Current Solutions in Orthopaedic Trauma Case Presentation: Comminuted Fracture of the Proximal Ulna Melvin P. Rosenwasser, MD Robert E. Carroll Professor of Surgery of the Hand Chief, Orthopaedic Hand
EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE
 EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE Orthofix approach to Evidence Based Medicine: For years, clinical decision-making was based primarily on physician knowledge and expert opinion. Now, the medical community
EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE Orthofix approach to Evidence Based Medicine: For years, clinical decision-making was based primarily on physician knowledge and expert opinion. Now, the medical community
97% UNION. Humeral Nonunions: Issues and Strategies? Disclosure. Humeral Shaft Fractures 5/3/2016. Cory Collinge, MD
 Humeral Nonunions: Issues and Strategies? Cory Collinge, MD Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN 15 minutes Disclosure Consultant Biomet Smith and Nephew Royalties Biomet Smith & Nephew Advanced Orthopedic
Humeral Nonunions: Issues and Strategies? Cory Collinge, MD Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN 15 minutes Disclosure Consultant Biomet Smith and Nephew Royalties Biomet Smith & Nephew Advanced Orthopedic
Open reduction; plate fixation 1 Principles
 Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Functional outcome of open reduction and internal fixation of clavicle fracture
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Pillai MG. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Aug;4(8):3205-3210 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20162255
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Pillai MG. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Aug;4(8):3205-3210 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20162255
Minimally Invasive Plating Osteosynthesis for Mid-distal Third Humeral Shaft Fractures
 Minimally Invasive Plating Osteosynthesis for Mid-distal Third Humeral Shaft Fractures Kejian Lian, MD; Lei Wang, MD; Dasheng Lin, MD; Zhiwen Chen, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics.
Minimally Invasive Plating Osteosynthesis for Mid-distal Third Humeral Shaft Fractures Kejian Lian, MD; Lei Wang, MD; Dasheng Lin, MD; Zhiwen Chen, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics.
Qiuke Wang 1, Jian Hu 2, Junjie Guan 1, Yunfeng Chen 1* and Lei Wang 1*
 Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:203 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0908-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Proximal third humeral shaft fractures fixed with long helical
Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:203 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0908-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Proximal third humeral shaft fractures fixed with long helical
Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y.
 Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y. YANAGIHARA 2 1 Department of 2nd Orthopaedic
Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y. YANAGIHARA 2 1 Department of 2nd Orthopaedic
Fractures of the shaft of the humerus
 Trauma Fractures of the shaft of the humerus AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY OF 401 FRACTURES R. Ekholm, J. Adami, J. Tidermark, K. Hansson, H. Törnkvist, S. Ponzer From the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
Trauma Fractures of the shaft of the humerus AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY OF 401 FRACTURES R. Ekholm, J. Adami, J. Tidermark, K. Hansson, H. Törnkvist, S. Ponzer From the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 02 Page February 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Comparative Study of Functional Outcome of Compression Plating and Interlocking Nailing For Fracture Shaft Humerus in Adults Authors Dr.
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Comparative Study of Functional Outcome of Compression Plating and Interlocking Nailing For Fracture Shaft Humerus in Adults Authors Dr.
Iatrogenic Radial Nerve Palsy After Humeral Shaft Nonunion Repair: More Common Than You Think
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Iatrogenic Radial Nerve Palsy After Humeral Shaft Nonunion Repair: More Common Than You Think Rafael Kakazu, MD, Steven K. Dailey, MD, Amanda J. Schroeder, MD, John D. Wyrick, MD, and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Iatrogenic Radial Nerve Palsy After Humeral Shaft Nonunion Repair: More Common Than You Think Rafael Kakazu, MD, Steven K. Dailey, MD, Amanda J. Schroeder, MD, John D. Wyrick, MD, and
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus. H. Sithebe 2012
 Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Section: Orthopaedics. Original Article INTRODUCTION
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.5.OR7 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Comparative Analysis of Results of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPPO) and Intramedullary
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.5.OR7 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Comparative Analysis of Results of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPPO) and Intramedullary
A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The
A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The
Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique
 Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique Percutaneous Pinning Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Closed reduction followed by percutaneous fixation reduces risk from soft tissue dissection
Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique Percutaneous Pinning Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Closed reduction followed by percutaneous fixation reduces risk from soft tissue dissection
FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF PROXIMAL TIBIA EXTR-ARTICULAR FRACTURES TREATED WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATING
 FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF PROXIMAL TIBIA EXTR-ARTICULAR FRACTURES TREATED WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATING Original Article Orthopaedics Pradip B. Patil 1, Dhanish V. Mehendiratta 2, S.A. Lad 3, Rishi K. Doshi
FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF PROXIMAL TIBIA EXTR-ARTICULAR FRACTURES TREATED WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATING Original Article Orthopaedics Pradip B. Patil 1, Dhanish V. Mehendiratta 2, S.A. Lad 3, Rishi K. Doshi
Functional Outcome of Plating versus Nailing in Adult Midshaft Radius-Ulna Fractures
 ORIGINAL ARTICALE Functional Outcome of Plating versus Nailing in Adult Midshaft Radius-Ulna Fractures Ashish Agarwal 1, Prashant N. Gedam 2, Hiren B Patel 3, Rajendra Phunde 4, Anuj Bharuka 5 1- Professor,
ORIGINAL ARTICALE Functional Outcome of Plating versus Nailing in Adult Midshaft Radius-Ulna Fractures Ashish Agarwal 1, Prashant N. Gedam 2, Hiren B Patel 3, Rajendra Phunde 4, Anuj Bharuka 5 1- Professor,
Humeral shaft fractures: retrospective results of non-operative and operative. treatment of 186 patients
 1 2 3 4 Humeral shaft fractures: retrospective results of non-operative and operative treatment of 186 patients Kiran C. Mahabier, MD 1, Lucas M.M. Vogels, MD 1, Bas J. Punt, MD 2, Gert R. Roukema, MD
1 2 3 4 Humeral shaft fractures: retrospective results of non-operative and operative treatment of 186 patients Kiran C. Mahabier, MD 1, Lucas M.M. Vogels, MD 1, Bas J. Punt, MD 2, Gert R. Roukema, MD
Approximately 3% to 18% of humeral shaft fractures
 An Original Study Humeral Shaft Fractures and Radial Nerve Palsy: To Explore or Not to Explore That Is the Question Matthew W. Heckler, DO, and H. Brent Bamberger, DO Abstract Humeral shaft fracture with
An Original Study Humeral Shaft Fractures and Radial Nerve Palsy: To Explore or Not to Explore That Is the Question Matthew W. Heckler, DO, and H. Brent Bamberger, DO Abstract Humeral shaft fracture with
recovery. Many methods of treatment for fractures of the clavicle had been IJMDS January 2016; 5(1) 991
 Original article A clinical study on role of different types of plates in surgical management of middle one third clavicle fracture in adults Garg V 1, Agarwal A 2 ABSTRACT Background: Fractures of the
Original article A clinical study on role of different types of plates in surgical management of middle one third clavicle fracture in adults Garg V 1, Agarwal A 2 ABSTRACT Background: Fractures of the
Fractures Healing & Management. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4
 Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4)
 AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
A Patient s Guide to Adult Olecranon (Elbow) Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Olecranon (Elbow) Fractures 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Adult Olecranon (Elbow) Fractures 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF OPERATIVE AND NON-OPERATIVE TREATMENT IN MIDSHAFT CLAVICLE FRACTURES
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF OPERATIVE AND NON-OPERATIVE TREATMENT IN MIDSHAFT CLAVICLE FRACTURES R. Sahaya Jose 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Mookambika Institute
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF OPERATIVE AND NON-OPERATIVE TREATMENT IN MIDSHAFT CLAVICLE FRACTURES R. Sahaya Jose 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Mookambika Institute
Clinico-radiological outcome of closed reduction and percutaneous fixation of proximal humerus fractures
 2018; 4(1): 614-618 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 614-618 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-11-2017 Accepted: 11-12-2017 Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Assistant Professor, KGMU, Lucknow, Dr. Neerav Anand
2018; 4(1): 614-618 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 614-618 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-11-2017 Accepted: 11-12-2017 Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Assistant Professor, KGMU, Lucknow, Dr. Neerav Anand
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES. Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures
 REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Technical Note Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:
 Technical Note Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:327-333 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.4.327 Biologic Fixation through Bridge Plating for Comminuted Shaft Fracture of the Clavicle: Technical
Technical Note Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:327-333 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.4.327 Biologic Fixation through Bridge Plating for Comminuted Shaft Fracture of the Clavicle: Technical
A Patient s Guide to Adult Humerus Shaft Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Humerus Shaft Fractures Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult Humerus Shaft Fractures Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Distal Humerus Fractures: How should they be fixed?
 Distal Humerus Fractures: How should they be fixed? Dr. Emil Schemitsch, MD, FRCS(C) Richard Ivey Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery, Western University Chief of Surgery London Health Sciences
Distal Humerus Fractures: How should they be fixed? Dr. Emil Schemitsch, MD, FRCS(C) Richard Ivey Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery, Western University Chief of Surgery London Health Sciences
Pediatric Fractures. Objectives. Epiphyseal Complex. Anatomy and Physiology. Ligaments. Bony matrix
 1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF DIAPHYSEAL FEMUR FRACTURE WITH INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL AND K. NAIL
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 3 Apr. 2016, pp. 560-564 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ COMPARATIVE
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 3 Apr. 2016, pp. 560-564 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ COMPARATIVE
Case Report An Undescribed Monteggia Type 3 Equivalent Lesion: Lateral Dislocation of Radial Head with Both-Bone Forearm Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 8598139, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8598139 Case Report An Undescribed Monteggia Type 3 Equivalent Lesion: Lateral Dislocation of Radial
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 8598139, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8598139 Case Report An Undescribed Monteggia Type 3 Equivalent Lesion: Lateral Dislocation of Radial
Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1811.001 Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study Kongcharoensombat W, MD, Wattananon P, MD Department of Orthopaedics,
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1811.001 Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study Kongcharoensombat W, MD, Wattananon P, MD Department of Orthopaedics,
Index. B Backslap technique depth assessment, 82, 83 diaphysis distal trocar, 82 83
 Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation
 A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Intramedullary fibular fixation in the operative management of fractures of the distal tibia and fibula
 Royal Liverpool & Broadgreen University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Intramedullary fibular fixation in the operative management of fractures of the distal tibia and fibula Michael Smith MBChB, Zuned
Royal Liverpool & Broadgreen University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Intramedullary fibular fixation in the operative management of fractures of the distal tibia and fibula Michael Smith MBChB, Zuned
Technology and Health Care 21 (2013) DOI /THC IOS Press
 Technology and Health Care 21 (2013) 143 147 143 DOI 10.3233/THC-130714 IOS Press Comparison between conservative and surgical treatment of midshaft clavicle fractures: Outcome of 151 cases Kiriakos Daniilidis
Technology and Health Care 21 (2013) 143 147 143 DOI 10.3233/THC-130714 IOS Press Comparison between conservative and surgical treatment of midshaft clavicle fractures: Outcome of 151 cases Kiriakos Daniilidis
Operative treatment of clavicle midshaft fractures using a locking compression plate: Comparison between mini-invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO)
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 666 671 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative treatment of clavicle midshaft fractures using a locking compression
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 666 671 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative treatment of clavicle midshaft fractures using a locking compression
COMPRESSION HUMERUS INTERLOCK NAILING : A STUDY TO UNDERSTAND &
 COMPRESSION HUMERUS INTERLOCK NAILING : A STUDY TO UNDERSTAND & OVERCOME THE DRAWBACKS OF INTERLOCK NAIL SYSTEM DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO UNIVERSITY OF SEYCHELLES AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE IN PARTIAL
COMPRESSION HUMERUS INTERLOCK NAILING : A STUDY TO UNDERSTAND & OVERCOME THE DRAWBACKS OF INTERLOCK NAIL SYSTEM DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO UNIVERSITY OF SEYCHELLES AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE IN PARTIAL
Mark VanDer Kaag 1, Ajmal Ikram 2. Hand Unit, Tygerberg Hospital University of Stellenbosch
 A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
CASE REPORT. Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
AcUMEDr. Locking Proximal Humeral Plate. PoLARUSr PHPt
 AcUMEDr Locking Proximal Humeral Plate PoLARUSr PHPt PoLARUSr PHPt LOCKING PROXIMAL HUMERAL PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons,
AcUMEDr Locking Proximal Humeral Plate PoLARUSr PHPt PoLARUSr PHPt LOCKING PROXIMAL HUMERAL PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons,
Radial Nerve Palsy Following Fractures of the Humerus
 Radial Nerve Palsy Following Fractures of the Humerus Mike Starecki, MD Atlanta Trauma Symposium April 21 st, 2018 No Disclosures Humeral Shaft and Radial Nerve 237,000 humeral shaft fractures in the US
Radial Nerve Palsy Following Fractures of the Humerus Mike Starecki, MD Atlanta Trauma Symposium April 21 st, 2018 No Disclosures Humeral Shaft and Radial Nerve 237,000 humeral shaft fractures in the US
Anterior Plating of Displaced Middle Third Fractures of Clavicle An Effective Alternate Method
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.8 March. (2018), PP 24-28 www.iosrjournals.org Anterior Plating of Displaced Middle Third
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.8 March. (2018), PP 24-28 www.iosrjournals.org Anterior Plating of Displaced Middle Third
Fractures of the Radial and Ulnar Shafts In the Pediatric Patient
 Fractures of the Radial and Ulnar Shafts In the Pediatric Patient Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas Health Science
Fractures of the Radial and Ulnar Shafts In the Pediatric Patient Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas Health Science
AcUMEDr. FoREARM ROD SYSTEM
 AcUMEDr FoREARM ROD SYSTEM FoREARM ROD SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been
AcUMEDr FoREARM ROD SYSTEM FoREARM ROD SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been
Young Bones. Characteristics. Klaus Hindsø
 Young Bones Characteristics Klaus Hindsø What s so special Periostium Elasticity Growth The envelope Periostium Elasticity Growth Connects displaced fragments building a bridge during healing Interposed
Young Bones Characteristics Klaus Hindsø What s so special Periostium Elasticity Growth The envelope Periostium Elasticity Growth Connects displaced fragments building a bridge during healing Interposed
Or thopaedic Surger y
 Article Treatment of displaced flexion-type pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures in the prone position Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery Volume: 25(1) 1 6 ª Journal of
Article Treatment of displaced flexion-type pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures in the prone position Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery Volume: 25(1) 1 6 ª Journal of
A Patient s Guide to Adult Radial Head (Elbow) Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Radial Head (Elbow) Fractures 2321 Coronado Idaho Falls, ID 83404 Phone: 208-227-1100 jpond@summitortho.net 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Adult Radial Head (Elbow) Fractures 2321 Coronado Idaho Falls, ID 83404 Phone: 208-227-1100 jpond@summitortho.net 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Results Of Antegrade Humeral Interlocking Nailing In Adults A Prospective Study. S Rawa, M Farooq, S Singh, M Wani, M Bhat, A Hussain, M Mussa
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 24 Number 2 Results Of Antegrade Humeral Interlocking Nailing In Adults A Prospective Study S Rawa, M Farooq, S Singh, M Wani, M Bhat, A Hussain, M Mussa
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 24 Number 2 Results Of Antegrade Humeral Interlocking Nailing In Adults A Prospective Study S Rawa, M Farooq, S Singh, M Wani, M Bhat, A Hussain, M Mussa
Case Report Intra-Articular Osteotomy for Distal Humerus Malunion
 Volume 2009, Article ID 631306, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/631306 Case Report Intra-Articular Osteotomy for Distal Humerus Malunion RenéK.Marti 1 and Job Doornberg 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Volume 2009, Article ID 631306, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/631306 Case Report Intra-Articular Osteotomy for Distal Humerus Malunion RenéK.Marti 1 and Job Doornberg 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Diaphyseal fractures of humerus are commonly. Evaluation of Results of Different Treatment Modalities in Management of Diaphyseal Fractures of Humerus
 Evaluation of Results of Different Treatment Modalities in Management of Diaphyseal Fractures of Humerus Vipin Sharma*, Bhanu Awasthi, SM Mehta, RS Yadav #, Sudhir Babhulkar $ Abstract Introduction: This
Evaluation of Results of Different Treatment Modalities in Management of Diaphyseal Fractures of Humerus Vipin Sharma*, Bhanu Awasthi, SM Mehta, RS Yadav #, Sudhir Babhulkar $ Abstract Introduction: This
Proximal radioulnar translocation associated with elbow dislocation and radial neck fracture in child: a case report and review of literature
 DOI 10.1007/s00402-013-1820-8 TRAUMA SURGERY Proximal radioulnar translocation associated with elbow dislocation and radial neck fracture in child: a case report and review of literature Hong Kee Yoon
DOI 10.1007/s00402-013-1820-8 TRAUMA SURGERY Proximal radioulnar translocation associated with elbow dislocation and radial neck fracture in child: a case report and review of literature Hong Kee Yoon
THE HUMERUS 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW
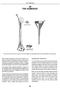 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
A Patient s Guide to Adult Proximal Humerus (Shoulder) Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Proximal Humerus (Shoulder) Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER:
A Patient s Guide to Adult Proximal Humerus (Shoulder) Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER:
Terrible Triad: Tricks for Dealing with the Unstable Elbow
 Terrible Triad: Tricks for Dealing with the Unstable Elbow Mark A. Mighell, MD Kaitlyn N. Christmas, BS Disclosure Paid Consultation Research Support Speakers Bureau Paid Consultation Speakers Bureau The
Terrible Triad: Tricks for Dealing with the Unstable Elbow Mark A. Mighell, MD Kaitlyn N. Christmas, BS Disclosure Paid Consultation Research Support Speakers Bureau Paid Consultation Speakers Bureau The
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
Olecranon fracture. Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital
 Olecranon fracture Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital 20% of forearm fracture 12 per 100.000 persons per year Low-energy fall Increased risk >50 years 90% AO 21.B1.1
Olecranon fracture Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital 20% of forearm fracture 12 per 100.000 persons per year Low-energy fall Increased risk >50 years 90% AO 21.B1.1
Forearm Fracture Solutions. Product Overview
 Forearm Fracture Solutions Product Overview Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions includes plating and rodding systems with a range of diaphyseal radius and ulna fracture
Forearm Fracture Solutions Product Overview Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions includes plating and rodding systems with a range of diaphyseal radius and ulna fracture
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES R. Sahaya Jose 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Mookambika
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES R. Sahaya Jose 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Mookambika
陳書佑 / 吳基銓副部長
 陳書佑 / 吳基銓副部長 2012-12-25 1 30 y/o male, TA no radial nerve injury 2 s/p splint arrange functional brace 3 1 month 4 2 months 5 3 months 6 4 months 7 One year 8 Conservative Treatment of Humeral Shaft Fractures
陳書佑 / 吳基銓副部長 2012-12-25 1 30 y/o male, TA no radial nerve injury 2 s/p splint arrange functional brace 3 1 month 4 2 months 5 3 months 6 4 months 7 One year 8 Conservative Treatment of Humeral Shaft Fractures
Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and
 Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
