Sensory recovery of the reverse homodigital island flap in fingertip reconstruction: a review of 66 cases
|
|
|
- Basil Stewart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ACTA ORTHOPAEDICA et TRAUMATOLOGICA TURCICA Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2010;44(5): doi: /aott Sensory recovery of the reverse homodigital island flap in fingertip reconstruction: a review of 66 cases Memet YAZAR, Atakan AYDIN, Sevgi KURT YAZAR, Karaca BAfiARAN, Erdem GÜVEN stanbul University, stanbul Faculty of Medicine, Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, stanbul Objectives: The location of the fingertip entitles it to have significant cosmetic and functional values, but also places it at high risk for injury. During repair, finger length and function should be maintained, and stiffness and neuroma should be avoided. Various flaps have been described for reconstruction of distal finger defects with bone, tendon, or joint exposures, including reverse flow homodigital island flap. In this study, we present our experience of reverse flow homodigital island flap in terms of sensory recovery. Methods: Sixty-six patients (70 fingers) with fingertip amputations were included in the study. Patients were treated with homodigital island flaps. All patients underwent sensitivity assessment by 2-point discrimination and Semmes-Weinstein monofilament tests at 6, 12, and 18 months during follow-up, and complications were recorded. Results: Monofilament testing results were normal in 64 fingers (91.4%), and diminished light touch was found in six fingers. Two-point discrimination results were normal (<6 mm) in 40 fingers and fair (6-10 mm) in 30 fingers (mean 5.7 mm, range 4-9 mm). Complications included one partial flap necrosis, three flexion contractures, and two neuromas. Conclusion: In repair of injuries to areas in which sensory feedback is critical, such as the index finger, the homodigital flap may be the treatment of choice. Key words: Fingers; reconstructive surgical procedures; recovery of function; sensation; surgical flaps. Because of the highly specialized nature of the fingertip, pulp reconstruction may be challenging. The optimal treatment of the fingertip injuries is still arguable. Finger length and function should be preserved, and there should be no joint stiffness or neuroma formation. Cosmetically acceptable appearance is also required by patients. Fingertip sensation is particularly important for the thumb and the index finger, where pinch and grasp are crucial. Many options like V-Y advancement flap (Atasoy), lateral V-Y advancement flap (Kutler), thenar flap, and cross-finger flap have been defined in fingers with exposed bones, tendons, or joints. [1-5] One of these methods is the reverse flow homodigital island flap, first described by Lai et al. [6] and Kojima et al. [7] Different results have been reported concerning the outcomes of this flap in literature. In our series of 66 patients who referred to our emergency department for fingertip injury, we aimed to report the sensory recovery following reverse flow homodigital island flap. Correspondence: Sevgi Kurt Yazar, MD. stanbul Üniversitesi stanbul T p Fakültesi, Plastik ve Rekonstrüktif Cerrahi Anabilim Dal, stanbul, Turkey. Tel: svgkrt@gmail.com Submitted: September 24, 2009 Accepted: April 12, Turkish Association of Orthopaedics and Traumatology
2 346 Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc Patients and methods Sixty-six patients (70 fingers, 56 males, 10 females) with complex fingertip injuries between May 2006 and June 2008 were included in the study. Flap coverage was indicated for all injuries. Reverse flow homodigital island flap was chosen as the treatment method. Patients age ranged between 10 and 54 years (mean 31.5 years). Forty cases were workrelated accidents, 15 were home accidents, and the remaining 11 were classified as traffic accidents. Involved digits included the second finger in 36 cases, middle finger in 15 cases, fourth finger in 16 cases, and fifth finger in three cases (Table 1). All cases were regarded as group 1 by Tamai classification. Bone or tendon exposure with volar oblique or transverse amputations was found in all patients. Surgical technique All patients were operated by the same surgeon. A digital or axillary block was used. Antibiotic prophylaxis was done, and a pneumatic tourniquet was applied. A loupe with 4x magnification was used throughout the procedure. Debridement of the stump was done initially. The flap was designed from the mid-lateral portion of the non-dominant side of the proximal phalanx of the same finger (Fig. 1). During planning, flap size was determined in a standard fashion, where flap width did not cross the borders between midlateral line and the middle of the volar zone. Therefore all donor regions could be closed primarily without a need for a skin graft (Fig. 1). The length, in contrast, was planned according to the flap size. However, it was maximally planned between the levels of proximal interphalangeal (PIP) and the metacarpaphalangeal (MP) joints (Fig. 1). The flap was designed in a fusiform shape. This enabled us to close the defect easily together and get rid of dog ears. After the inital plan, we performed a straight 1-cm incision proximally towards the distal palmar crease and a zig-zag incision distally up to the defect. This incision was required to prevent contracture during healing. Flap incison was done later together with the dissection of the digital bundle proximally. After identification of the digital artery, it was ligated and cut (Fig. 2a). The distal end of the artery was ligated with 5/0 silk and left long where it was used for retraction during dissection. The identified proximal digital nerve was again ligated and cut proximally. To prevent a neuroma, the proximal stump of the nerve was buried in the soft tissues. Table 1 Demographic and clinical findings [number of patients or mean (range)] Gender Injured finger Male 56 Female 10 Index 36 Middle 15 Fourth 16 Fifth 13 Two-point discrimination test (mm) 5.7 (4-9) Semmes-Weinstein monofilament testing Normal 64 Diminished light touch 6
3 Yazar et al. The reverse homodigital island flap in fingertip reconstruction 347 After completion of the ipsilateral dissection, a contralateral mid-lateral incision was done where the digital nerve was identified and cut from an appropriate level. The flap inset was done later. The contralateral transected digital nerve was coapted to the recipient nerve in the flap (Fig. 3a). The donor region was closed primarily (Fig. 3b). Skin edges close to the pedicle were approximated only loosely in order to prevent pedicle constriction (Fig. 4). A dorsal splint was applied with the hand in an anatomical positon. The splint was removed 10 days later with the initiation of physiotherapy. Fig. 1. Finger-tip amputation. 1: View following debridement. Homodigital island flap design. 1: Flap skin island, 2: Contralateral incision for nerve coaptation, 3: Mid-volar line 6: Mid-lateral line (3 and 6 designate the flap width), 4: Flap length borders (between proximal interphalangeal and metacarpaphalangeal creases), 5. Zig-zag incision planned at region distal to the flap, 7: Proximal incision for the nerve transection. The flap was then dissected over the paratenon distally to 5 mm proximal to the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint with inclusion of the bundle (Fig. 2b). Fig. 3. Nerve coaptation. Final view of the finger. Fig. 2. Flap dissection. 1: Distal digital bundle, 2: Flap, 3: Proximal digital nerve, 4: Proximal digital artery. Flap harvesting over the paratenon. 1: Distal digital bundle, 2: Paratenon, 3: Proximal digital nerve, 4. Proximal digital artery. Results All of the patients were evaluated at 6, 12, and 18 months with Semmes-Weinstein monofilament and 2-point discrimination tests (Fig. 5, Table 1). In addition, cold intolerance, hypersensitivity at the donor and the recipient regions, cosmetic outcome, and patient satisfaction were evaluated (Fig. 6). On Semmes-Weinstein tests 64 fingers had normal sensation (value 2.83, corresponding to the green color), and 6 patients had decreased sensation (value 3.61, corresponding to the blue color); in average, 91.42% of the fingers had normal sensory recovery (Table 1). Tactile sensation was evaluated with the Disk- Criminator to assess 2-point discrimination. Forty
4 348 Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc (c) (d) Fig. 4. Homodigital island flap. Design of the reverse flow homodigital island flap at the non-dominant side of the finger following an amputation. Incision made on the distal palmar crease with demonstration of the proximal bundle dissection. (c) Inclusion of the digital bundle together with the elevation of the flap over paratenon. (d) Coaptation of the included nerve to the contralateral nerve. patients had normal values (<6 mm), and 30 patients had good-to-moderate values (6-10 mm). Values ranged between 4 and 9 mm, and the mean value was 5.7 mm (Table 1). In terms of complications, two patients had neuromas. They refused reoperation, so they had desensitization therapy. [8] Three patients had flexion contractures at the incision sites (Table 2). These contractures were released with Z-plasties (Fig. 7). One patient had a partial necrosis. Debridement was done, and the wound healed secondarily. All the patients had a full range of motion. Cold intolerance was seen in seven patients (Table 2). All of the patients were satisfied with the cosmetic outcome (Fig. 6). Discussion One of the mostly commonly used classifications of fingertip amputations is the Tamai classification, [9] in which the distal phalanx is divided into two regions. The region between the nail bed and distally to the Fig. 5. Semmes-Weinstein monofilament test. Two-point discrimination test.
5 Yazar et al. The reverse homodigital island flap in fingertip reconstruction 349 Table 2 Complications following homodigital island flap application Number of patients Flap loss 1 (partial) Cold intolerance 7 Hypersensitivity 2 (at flap) Contracture 3 (at incision site) Neuroma 2 fingertip is classified as Zone 1, and the zone between the nail bed and proximally to the DIP joint is designated as Zone 2. Although replantation is the best treatment method, it may not always be possible. [10,11] Because of the importance of the fingertip for the general function of the hand, many options have been proposed for reconstruction. In cases of bone or tendon exposition, initial options might be local flaps, such as the V-Y flap of Kutler and the Atasoy volar V-Y flap. [1-3] In order to cover larger defects, cross-finger and thenar flaps have been proposed. Although these options seem to be logical, long-term immobilization of the hand may be a disadvantage for these flaps. [4,5] As understanding of the vascular anatomy of the fingers has advanced, the option of using pedicle-based neurovascular island flaps has developed. [12] It has been found that each palmar digital artery has deeper branches as well as superficial branches. Superficial branches mainly supply palmar subcutaneous tissues, and deep branches make anastomoses with the contralateral counterparts on proximal and middle phalanges. [13] (c) Fig. 6. Preoperative view of the finger. Long-term volar and (c) dorsal view of the same finger. (c) Fig. 7. (a-c) Release of the contracture following a homodigital island flap with Z-plasties.
6 350 Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc These anastomoses, particularly at the level between the nailbed and the distal phalanx enable the homodigital island flap to survive retrogradely. [14] Distal anastomosis is located between DIP joint and the fingertip. A retrotendinous vascular network is situated at the PIP joint and proximal to the DIP joint (Fig. 8). [13] In cadaver studies, these anastomoses were found to be at the proximal phalanx and at the middle part of middle phalanx. Therefore, these flaps are contraindicated in injuries located proximal to the distal phalanx. [14] These type of island flaps have certain advantages when compared to local flaps. [15] They have a larger axis of rotation, which enables transfer of healthy tissue distant from the injury zone. A single step surgery confined to the damaged finger is another advantage. It also enables early mobilization. Healthy vascular tissue is transferred to the relatively poorly nourished area, enabling good wound healing. Cold intolerance risk might be reduced, as well. In addition, tactile sensation can be transferred to an anesthetic region. [15] Transferred hairless palmar skin enables a better sensory recovery because of better alignment and greater numbers of myelinated fibers. Possible disadvantages are the sacrifice of the digital artery and the relative difficulty of the dissection and requirement of microsurgical skills. [16,17] Fig. 8. Vascular anatomy of the finger. 1: Transverse commissural artery, 2: Proper digital artery. Homodigital island flaps can be raised antegrade or retrograde. Antegrade flow homodigital island flap was first used by Kim et al. [13] in This flap was based on transverse branch of proper palmar digital artery. The main advantage of this flap is the achievement of flap harvesting without sacrifice of one of the digital arteries. A disadvantage is that requirement of graft placement on the volar donor region might cause a contracture. [17] The reverse flow homodigital island flap was first described by Lai et al. [6] in a study of 10 patients. Kojima et al. [7] also used the same flap in a study of 8 patients. Three transverse commissural branches between 2 proper palmar digital arteries enable these flaps to survive. These arteries maintain a back-flow when one of the main digital arteries has been ligated proximally. These arteries might be located proximally on phalanx condyle and dorsal to the flexor tendons. This flap can be harvested from any place on the non-dominant side of the proximal and middle phalanges. In addition, the size of the flap can be increased in either the volar or dorsal direction, according to the size of the defect. Sensory restoration can be obtained by two methods in island flaps. One method is increasing the dimension of the flap toward the dorsal side with inclusion of the dorsal digital nerve. [18] The other option is the harvesting of digital nerve together with the digital artery. Included digital nerve can be coapted to the contralateral transected nerve. In cases where a dorsal digital nerve is included in the flap, the flap is composed of dorsal skin. As mentioned above, it does not have the advantages of volar skin, which is thicker and hairless; this may cause aesthetic and functional problems postoperatively. In the literature, no significant differences have been observed when cases with nerve coaptation were compared with non-coapted ones in terms of 2-point discrimination. [19] However, in a study by Kaleli et al., [14] 2-point discrimination was found to be 5-7 mm in cases where nerve coaptation had been done; 2-point discrimination was 8-10 mm in cases
7 Yazar et al. The reverse homodigital island flap in fingertip reconstruction 351 where nerve repair had not been done. In cases where nerve repair had not been done and dorsal digital nerve had been included, 2-point discrimination test was 9-10 mm. [18] Sensory recovery, however, was observed to be worse when no digital nerve was included in the flap. [15,20] The result of 2-point discrimination testing was 6.5 mm in a study by Lai et al. [6] with 10 patients and also in a separate study by Alagöz et al. [21] with 14 patients. Digital nerve was included in all flaps in that study. In our study, the digital nerve was included and coapted together with the homodigital island flaps. The 2-point discrimination test value was 5.7 mm, which was similar to values of previous studies. In conclusion, sensation is indispensable for the hand. Therefore, sensory flaps should be used in reconstruction of fingertip injuries, where sensation is crucial. The reverse flow homodigital island flap may be an option for these cases. References 1. Goubier JN, Teboul F. Atasoy flap. Interact Surg Am 2007;2: Shepard GH. The use of lateral V-Y advancement flaps for fingertip reconstruction. J Hand Surg Am 1983;8: Venkataswami R, Subramanian N. Oblique triangular flap: a new method of repair for oblique amputations of the fingertip and thumb. Plast Reconstr Surg 1980;66: Tempest MN. Cross-finger flaps in the treatment of injuries to the finger tip. Plast Reconstr Surg 1952;9: Dellon A. The proximal inset thenar flap for fingertip reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 1983;72: Lai CS, Lin SD, Yang CC. The reverse digital artery island flap for fingertip reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 1989;22: Kojima T, Tsuchida Y, Hirasé Y, Endo T. Reverse vascular pedicle digital island flap. Br J Plast Surg 1990;43: Fisher GT, Boswick JA Jr. Neuroma formation following digital amputations. J Trauma 1983;23: Tamai S. Twenty years experience of limb replantation-- review of 293 upper extremity replants. J Hand Surg Am 1982;7: Dautel G, Barbary S. Mini replants: fingertip replant distal to the IP or DIP joint. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2007; 60: Özçelik B, Purisa H, Sezer, Mersa B, Ayd n A. The results of digital replantations et the level of the distal interphalangeal joint and the distal phalanx. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc [Article in Turkish] 2006;40: Smith KL, Elliot D. The extended Segmüller flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 2000;105: Kim KS, Yoo SI, Kim DY, Lee SY, Cho BH. Fingertip reconstruction using a volar flap based on the transverse palmar branch of the digital artery. Ann Plast Surg 2001;47: Kaleli T, Ersözlü S, Öztürk Ç. Double reverse-flow island flaps for two adjacent finger tissue defect. [Article in Turkish] Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2004;124: Han SK, Lee BI, Kim WK. The reverse digital artery island flap: clinical experience in 120 fingers. Plast Reconstr Surg 1998;101: Y ld r m S, Avc G, Akan M. Complications of the reverse homodigital island flap in fingertip reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 2002;48: Koshima I, Urushibara K, Fukuda N, Ohkochi M, Nagase T, Gonda K, et al. Digital artery perforator flaps for fingertip reconstructions. Plast Reconstr Surg 2006;118: Tan O. Reverse dorsolateral proximal phalangeal island flap: a new versatile technique for coverage of finger defects. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2010;63: Moschella F, Cordova A. Reverse homodigital dorsal radial flap of the thumb. Plast Reconstr Surg 2006;117: Orhun E, Öztürk K, Nuzumlal E. The results of reverse digital artery island flap for fingertip injuries. [Article in Turkish] Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2000;34: Alagöz M, Uysal CA, Kerem M, fiensöz O. Reverse homodigital artery flap coverage for bone and nailbed grafts in fingertip amputations. Ann Plast Surg 2006;56:
The homodigital neurovascular antegrade island flap. for fingertip reconstruction in children and
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 598-602 ORIGINAL STUDY The homodigital neurovascular antegrade island flap for fingertip reconstruction in children Bingqi WAng, Lei CHEn, Laijin LU, Zhigang LiU, Zhixin ZHAng,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 598-602 ORIGINAL STUDY The homodigital neurovascular antegrade island flap for fingertip reconstruction in children Bingqi WAng, Lei CHEn, Laijin LU, Zhigang LiU, Zhixin ZHAng,
What s New in Fingertip Injuries. Gordon A. Brody, MD SOAR Redwood City
 What s New in Fingertip Injuries Gordon A. Brody, MD SOAR Redwood City Goals of Treatment Durable Sensate Aesthetic Preserve Length Preserve Mobility Goals of Treatment Pain and Worker s Compensation are
What s New in Fingertip Injuries Gordon A. Brody, MD SOAR Redwood City Goals of Treatment Durable Sensate Aesthetic Preserve Length Preserve Mobility Goals of Treatment Pain and Worker s Compensation are
Propeller perforator flaps for finger reconstruction
 Technical Note Page 1 of 7 Propeller perforator flaps for finger reconstruction Alexandru Valentin Georgescu, Ileana Rodica Matei Department of Plastic Surgery, University of Medicine Iuliu Hatieganu Cluj
Technical Note Page 1 of 7 Propeller perforator flaps for finger reconstruction Alexandru Valentin Georgescu, Ileana Rodica Matei Department of Plastic Surgery, University of Medicine Iuliu Hatieganu Cluj
TRANSPOSITIONAL ADIPOFASCIAL FLAPS FOR COMPLICATED ACUTE FINGER INJURIES
 K.B. Poon, S.H. Chien, G.T. Lin, et al TRANSPSITINAL ADIPFASCIAL FLAPS FR CMPLICATED ACUTE FINGER INJURIES Kein Boon Poon, Song-Hsiung Chien, 1 Gau-Tyan Lin, 1 and Yin-Chih Fu 1 Department of rthopaedic
K.B. Poon, S.H. Chien, G.T. Lin, et al TRANSPSITINAL ADIPFASCIAL FLAPS FR CMPLICATED ACUTE FINGER INJURIES Kein Boon Poon, Song-Hsiung Chien, 1 Gau-Tyan Lin, 1 and Yin-Chih Fu 1 Department of rthopaedic
SURGERY OF THE HAND. Reverse Digital Island Flap with Skin Strip Retention to Prevent Flap Congestion INTRODUCTION ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 598-3889 eissn 34-998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 6;():7-76. http://dx.doi.org/.79/jkssh.6...7 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Reverse Digital Island Flap with Skin
ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 598-3889 eissn 34-998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 6;():7-76. http://dx.doi.org/.79/jkssh.6...7 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Reverse Digital Island Flap with Skin
Heterotopic replantations in mutilating hand injuries, presentation of three cases
 Eur Orthop Traumatol (2012) 3:89 93 DOI 10.1007/s12570-012-0086-x CASE REPORT Heterotopic replantations in mutilating hand injuries, presentation of three cases İsmail Bülent Özçelik & Samet Vasfi Kuvat
Eur Orthop Traumatol (2012) 3:89 93 DOI 10.1007/s12570-012-0086-x CASE REPORT Heterotopic replantations in mutilating hand injuries, presentation of three cases İsmail Bülent Özçelik & Samet Vasfi Kuvat
The Boomerang Flap in Managing Injuries of the Dorsum of the Distal Phalanx
 The Boomerang Flap in Managing Injuries of the Dorsum of the Distal Phalanx Shao-Liang Chen, M.D., Trong-Duo Chou, M.D., Shyi-Gen Chen, M.D., Tian-Yeu Cheng, M.D., Tim-Mo Chen, M.D., and Hsian-Jenn Wang,
The Boomerang Flap in Managing Injuries of the Dorsum of the Distal Phalanx Shao-Liang Chen, M.D., Trong-Duo Chou, M.D., Shyi-Gen Chen, M.D., Tian-Yeu Cheng, M.D., Tim-Mo Chen, M.D., and Hsian-Jenn Wang,
Sensate First Dorsal Metacarpal Artery Flap for Resurfacing Extensive Pulp Defects of the Thumb
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sensate First Dorsal Metacarpal Artery Flap for Resurfacing Extensive Pulp Defects of the Thumb Shun-Cheng Chang, MD, Shao-Liang Chen, MD, Tim-Mo Chen, MD, Chia-Jueng Chuang, MD, Tian-Yeu
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sensate First Dorsal Metacarpal Artery Flap for Resurfacing Extensive Pulp Defects of the Thumb Shun-Cheng Chang, MD, Shao-Liang Chen, MD, Tim-Mo Chen, MD, Chia-Jueng Chuang, MD, Tian-Yeu
Cross finger flap for reconstruction of complex finger defects
 Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2015; 17(1-2): 73-77 Cross finger flap for reconstruction of complex finger defects Bista N, Shrestha KM, Bhattachan CL Department of General Surgery, Nepal Medical College
Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2015; 17(1-2): 73-77 Cross finger flap for reconstruction of complex finger defects Bista N, Shrestha KM, Bhattachan CL Department of General Surgery, Nepal Medical College
Interesting Case Series. Traumatic Thumb Amputation: Case and Review
 Interesting Case Series Traumatic Thumb Amputation: Case and Review Ryan Engdahl, MD, a and Norman Morrison, MD b a Division of Plastic Surgery, New York Presbyterian Hospital, The University Hospital
Interesting Case Series Traumatic Thumb Amputation: Case and Review Ryan Engdahl, MD, a and Norman Morrison, MD b a Division of Plastic Surgery, New York Presbyterian Hospital, The University Hospital
with cross-finger pedicle grafts
 Salvage of digits with cross-finger pedicle grafts Robert I. Horner, MD and Floyd B. Bralliar, MD Mechanization in home and industry has brought to our emergency rooms an increasing number of patients
Salvage of digits with cross-finger pedicle grafts Robert I. Horner, MD and Floyd B. Bralliar, MD Mechanization in home and industry has brought to our emergency rooms an increasing number of patients
DORSAL APPROACH FOR VASCULAR REPAIRS IN DISTAL FINGER REPLANTATIONS
 DORSAL APPROACH FOR VASCULAR REPAIRS IN DISTAL FINGER REPLANTATIONS FATIH KABAKAŞ, M.D.* Introduction: Distal finger replantations are technically difficult operations due to small vessel sizes and narrow
DORSAL APPROACH FOR VASCULAR REPAIRS IN DISTAL FINGER REPLANTATIONS FATIH KABAKAŞ, M.D.* Introduction: Distal finger replantations are technically difficult operations due to small vessel sizes and narrow
Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts
 Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts Ahmed Elshahat, MD Plastic Surgery Department, Ain Shams University,
Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts Ahmed Elshahat, MD Plastic Surgery Department, Ain Shams University,
Basics of Flap Design
 Basics of Flap Design Reconstructive Ladder (Mathes & Nahai 1982) Consider the defect, systematically Move from simple to complex Occam s Razor Sutton s Law Ladder is simple, emphasizes closure over form
Basics of Flap Design Reconstructive Ladder (Mathes & Nahai 1982) Consider the defect, systematically Move from simple to complex Occam s Razor Sutton s Law Ladder is simple, emphasizes closure over form
Second toe to index finger transfer
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery' (2000), 53, 324-330 9 2000 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2000.3345 BRITISH JOURNAL OF ~ PLASTIC SURGERY Second toe to index finger transfer
British Journal of Plastic Surgery' (2000), 53, 324-330 9 2000 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2000.3345 BRITISH JOURNAL OF ~ PLASTIC SURGERY Second toe to index finger transfer
PLASTIC SURGERY October-December 2018 / Volume 26 / Issue 4
 EISSN 2528-8644 TURKISH JOURNAL OF PLASTIC SURGERY October-December 2018 / Volume 26 / Issue 4 turkjplastsurg.org Original Article A New Technique in Fingertip Defects Including Nail Lost: Reverse Dorsal
EISSN 2528-8644 TURKISH JOURNAL OF PLASTIC SURGERY October-December 2018 / Volume 26 / Issue 4 turkjplastsurg.org Original Article A New Technique in Fingertip Defects Including Nail Lost: Reverse Dorsal
Repair and sensory reconstruction of the children s finger pulp defects with perforator pedicled propeller flap in proper digital artery
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3533-3537 Repair and sensory reconstruction of the children s finger pulp defects with perforator pedicled propeller flap in proper digital
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3533-3537 Repair and sensory reconstruction of the children s finger pulp defects with perforator pedicled propeller flap in proper digital
Hand and forearm reconstruction after skin cancer ablation
 Clin Plastic Surg 31 (2004) 113 119 Hand and forearm reconstruction after skin cancer ablation Patrick J. O Neill, MD a, *, Christopher Litts, MD b a Department of Surgery, Division of Plastic Surgery,
Clin Plastic Surg 31 (2004) 113 119 Hand and forearm reconstruction after skin cancer ablation Patrick J. O Neill, MD a, *, Christopher Litts, MD b a Department of Surgery, Division of Plastic Surgery,
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls??
 Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
The distally-based island ulnar artery perforator flap for wrist defects
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article The distally-based island ulnar artery perforator flap for wrist defects Durga Karki, A. K. Singh Post Graduate Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article The distally-based island ulnar artery perforator flap for wrist defects Durga Karki, A. K. Singh Post Graduate Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
Fingertip replantation (zone I) without venous anastomosis: clinical experience and outcome analysis
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3394-8 RESEARCH Open Access Fingertip replantation (zone I) without venous anastomosis: clinical experience and outcome analysis An shi Huan 1,2, Subhash Regmi 2, Jia xiang Gu 1*,
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3394-8 RESEARCH Open Access Fingertip replantation (zone I) without venous anastomosis: clinical experience and outcome analysis An shi Huan 1,2, Subhash Regmi 2, Jia xiang Gu 1*,
Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 258 262 CASE REPORTS Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects Kenji Yano*, Ko Hosokawa, Tateki Kubo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 258 262 CASE REPORTS Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects Kenji Yano*, Ko Hosokawa, Tateki Kubo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
Reverse Adipofascial Radial Forearm Flap Surgery for Soft-Tissue Reconstruction of Hand Defects
 Reverse Adipofascial Radial Forearm Flap Surgery for Soft-Tissue Reconstruction of Hand Defects Osman Akdag, MD, a Mehtap Karamese, MD, a Muhammed NebilSelimoglu, MD, a Ahmet Akatekin, MD, a Malik Abacı,
Reverse Adipofascial Radial Forearm Flap Surgery for Soft-Tissue Reconstruction of Hand Defects Osman Akdag, MD, a Mehtap Karamese, MD, a Muhammed NebilSelimoglu, MD, a Ahmet Akatekin, MD, a Malik Abacı,
Repair of complete syndactyly by tissue expansion and composite grafts
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (1995), 48. 396-400 1995 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons BRITISH JOURNAL OF / PLASTIC SURGERY I Repair of complete syndactyly by tissue expansion and composite
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (1995), 48. 396-400 1995 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons BRITISH JOURNAL OF / PLASTIC SURGERY I Repair of complete syndactyly by tissue expansion and composite
Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction
 180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
Johannesburg, South Africa
 NEUROVASCULAR ISLAND FLAP IN THE TREATMENT OF TROPHIC ULCERATION OF THE HEEL By ISIDORE KAPLAN, F.R.C.S., F.R.C.S.(Ed.) Johannesburg, South Africa THE transfer of skin and subcutaneous tissue on a neurovascular
NEUROVASCULAR ISLAND FLAP IN THE TREATMENT OF TROPHIC ULCERATION OF THE HEEL By ISIDORE KAPLAN, F.R.C.S., F.R.C.S.(Ed.) Johannesburg, South Africa THE transfer of skin and subcutaneous tissue on a neurovascular
Versatility of Reverse Sural Artery Flap for Heel Reconstruction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
Hand injuries. The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck.
 Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
Cooling Composite Graft for Distal Finger Amputation: A Reliable Alternative to Microsurgery Implantation
 Cooling Composite Graft for Distal Finger Amputation: A Reliable Alternative to Microsurgery Implantation FRANCESCO IDONE 1, ANDREA SISTI 2, JURI TASSINARI 2 and GIUSEPPE NISI 2 1 Jalisco Plastic and Reconstructive
Cooling Composite Graft for Distal Finger Amputation: A Reliable Alternative to Microsurgery Implantation FRANCESCO IDONE 1, ANDREA SISTI 2, JURI TASSINARI 2 and GIUSEPPE NISI 2 1 Jalisco Plastic and Reconstructive
Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist. Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury
 Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury Disclosures We have no disclosures that are pertinent to this presentation Terminology Ring Long Index Small Thumb
Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury Disclosures We have no disclosures that are pertinent to this presentation Terminology Ring Long Index Small Thumb
Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique
 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L. Zeineh, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine,
Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L. Zeineh, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine,
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure
 Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
Anatomic Basis of Dorsal Finger Skin Cover
 JOBNAME: tihues 9# 2005 PAGE: 1 OUTPUT: Fri June 24 00:02:15 2005 Prod#: BTH200002 Techniques in Hand and Upper Extremity Surgery 9():000 000, 2005 Ó 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia S
JOBNAME: tihues 9# 2005 PAGE: 1 OUTPUT: Fri June 24 00:02:15 2005 Prod#: BTH200002 Techniques in Hand and Upper Extremity Surgery 9():000 000, 2005 Ó 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia S
Fractures and dislocations of the fingers
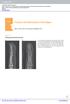 Chapter 1 Fractures and dislocations of the fingers Felix S. Chew, M.D., and Catherine Maldjian, M.D. Case 1 1 Phalangeal tuft avulsion fracture 31-year-old woman injured in a ground-level fall. Lateral
Chapter 1 Fractures and dislocations of the fingers Felix S. Chew, M.D., and Catherine Maldjian, M.D. Case 1 1 Phalangeal tuft avulsion fracture 31-year-old woman injured in a ground-level fall. Lateral
Interesting Case Series. Ring Avulsion Injuries
 Interesting Case Series Ring Avulsion Injuries Matt Jones BMBS, BSc, MRCS, and Sameer Gujral MBChB, BSc, MRCS Department of Plastic Surgery, Royal Devon & Exeter Hospital, Exeter, Devon, England Correspondence:
Interesting Case Series Ring Avulsion Injuries Matt Jones BMBS, BSc, MRCS, and Sameer Gujral MBChB, BSc, MRCS Department of Plastic Surgery, Royal Devon & Exeter Hospital, Exeter, Devon, England Correspondence:
FINGERTIP INJURIES ARE THEY REALLY THAT SIMPLE? SANJAY K SHARMA, MD, FACS INSTITUTE OF RECONSTRUCTIVE PLASTIC SURGERY
 FINGERTIP INJURIES ARE THEY REALLY THAT SIMPLE? SANJAY K SHARMA, MD, FACS INSTITUTE OF RECONSTRUCTIVE PLASTIC SURGERY Austin Trauma and Critical Care Conference 2018 May 31-June 1, 2018 Outline 1. Scope
FINGERTIP INJURIES ARE THEY REALLY THAT SIMPLE? SANJAY K SHARMA, MD, FACS INSTITUTE OF RECONSTRUCTIVE PLASTIC SURGERY Austin Trauma and Critical Care Conference 2018 May 31-June 1, 2018 Outline 1. Scope
Fig Fig Fig. 6-3
 CHAPTER 6 UPPER EXTREMITY The surgical treatment of hand problems is a specialized area of interest in plastic surgery. The hand is a unique organ which transmits sensations from the external environment
CHAPTER 6 UPPER EXTREMITY The surgical treatment of hand problems is a specialized area of interest in plastic surgery. The hand is a unique organ which transmits sensations from the external environment
Lower Extremity Reconstruction
 1 Chapter 21 Overview: Lower Extremity Reconstruction Louis Carter This subject is also partially covered in the chapters Flaps for Wound Coverage and Perforator Flaps. This chapter will deal with reconstruction
1 Chapter 21 Overview: Lower Extremity Reconstruction Louis Carter This subject is also partially covered in the chapters Flaps for Wound Coverage and Perforator Flaps. This chapter will deal with reconstruction
First dorsal metacarpal artery flap for thumb reconstruction: a retrospective clinical study
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2009) 4:27 33 DOI 10.1007/s11751-009-0056-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE First dorsal metacarpal artery flap for thumb reconstruction: a retrospective clinical study Thomas Muyldermans Æ Robert
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2009) 4:27 33 DOI 10.1007/s11751-009-0056-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE First dorsal metacarpal artery flap for thumb reconstruction: a retrospective clinical study Thomas Muyldermans Æ Robert
Evaluation of the Hand. Learning Objectives. Sitting down with the Client. Observation 2/16/2012
 Introduction to Hand & UE Rehabilitation Hand Evaluation Basics J. Robin Janson, MS, OTR, CHT Indiana University Department of Occupational Therapy Learning Objectives After actively engaging with this
Introduction to Hand & UE Rehabilitation Hand Evaluation Basics J. Robin Janson, MS, OTR, CHT Indiana University Department of Occupational Therapy Learning Objectives After actively engaging with this
Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report
 Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DISTALLY BASED PERONEUS BREVIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR DISTAL LEG DEFECTS
 DISTALLY BASED PERONEUS BREVIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR DISTAL LEG DEFECTS Peddi Manjunath 1, Ramesha K.T 2, Smitha S Segu 3, Jainath 4, Shankarappa M 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Peddi Manjunath, Ramesha KT, Smitha
DISTALLY BASED PERONEUS BREVIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR DISTAL LEG DEFECTS Peddi Manjunath 1, Ramesha K.T 2, Smitha S Segu 3, Jainath 4, Shankarappa M 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Peddi Manjunath, Ramesha KT, Smitha
Outcome of Thumb Reconstruction Using the First Dorsal Metacarpal Artery Island Flap
 Ghoraba et al. 1 Original Article Outcome of Thumb Reconstruction Using the First Dorsal Metacarpal Artery Island Flap Samir M Ghoraba, Wael H Mahmoud* Plastic, Reconstructive Surgery and Burns Department,
Ghoraba et al. 1 Original Article Outcome of Thumb Reconstruction Using the First Dorsal Metacarpal Artery Island Flap Samir M Ghoraba, Wael H Mahmoud* Plastic, Reconstructive Surgery and Burns Department,
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 01 Page January 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.36 Original Article A Study on the
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.36 Original Article A Study on the
Homodigital reconstruction of the digits: The perspective of one unit
 CME Homodigital reconstruction of the digits: The perspective of one unit D. Elliot The Hand Surgery Department, St. Andrew s Centre for Plastic Surgery, Broomfield Hospital, Chelmsford, Essex. Address
CME Homodigital reconstruction of the digits: The perspective of one unit D. Elliot The Hand Surgery Department, St. Andrew s Centre for Plastic Surgery, Broomfield Hospital, Chelmsford, Essex. Address
Different modalities of soft tissue coverage of hand and wrist defects
 ifferent modalities of soft tissue coverage of hand and wrist defects Soft tissue defects of hand and wrist with exposed tendons, joints, nerves and bones represent a challenge to plastic surgeons. Such
ifferent modalities of soft tissue coverage of hand and wrist defects Soft tissue defects of hand and wrist with exposed tendons, joints, nerves and bones represent a challenge to plastic surgeons. Such
Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria
 TRANSPOSITION OF THE LATERAL SLIPS OF THE APONEUROSIS IN TREATMENT OF LONG-STANDING " BOUTONNIERE DEFORMITY " OF THE FINGERS By IVAN MATEV Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria RUPTURE of
TRANSPOSITION OF THE LATERAL SLIPS OF THE APONEUROSIS IN TREATMENT OF LONG-STANDING " BOUTONNIERE DEFORMITY " OF THE FINGERS By IVAN MATEV Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria RUPTURE of
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Microsurgery. Assessing the opinions of subjects with or without sustained hand injury about toe-to-thumb transfer
 Hand Microsurgery & Original Article Hand Microsurg 2015;4:58-62 doi:10.5455/handmicrosurg.188551 Assessing the opinions of subjects with or without sustained hand injury about toe-to-thumb transfer Ismail
Hand Microsurgery & Original Article Hand Microsurg 2015;4:58-62 doi:10.5455/handmicrosurg.188551 Assessing the opinions of subjects with or without sustained hand injury about toe-to-thumb transfer Ismail
The earlier clinic experience of the reverse-flow anterolateral thigh island flap
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 160 164 The earlier clinic experience of the reverse-flow anterolateral thigh island flap Gang Zhou, Qi-Xu Zhang*, Guang-Yu Chen Scar Multiple Treatment Centre,
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 160 164 The earlier clinic experience of the reverse-flow anterolateral thigh island flap Gang Zhou, Qi-Xu Zhang*, Guang-Yu Chen Scar Multiple Treatment Centre,
Management of Hand Palsies in Isolated C7 to T1 or C8, T1 Root Avulsions
 12(3):156 160, 2008 T E C H N I Q U E Management of Hand Palsies in Isolated C7 to T1 or C8, T1 Root Avulsions Jean-Noel Goubier, PhD and Frédéric Teboul, MD Centre International de Chirurgie de la Main
12(3):156 160, 2008 T E C H N I Q U E Management of Hand Palsies in Isolated C7 to T1 or C8, T1 Root Avulsions Jean-Noel Goubier, PhD and Frédéric Teboul, MD Centre International de Chirurgie de la Main
JPRAS Open 6 (2015) 44e48. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 6 (2015) 44e48 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report A novel technique: Subatmospheric pressure wound
JPRAS Open 6 (2015) 44e48 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report A novel technique: Subatmospheric pressure wound
Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
The lumbar artery perforator based island flap: anatomical study and case reports
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (1999), 52, 541 546 1999 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons The lumbar artery perforator based island flap: anatomical study and case reports H. Kato*, M. Hasegawa,
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (1999), 52, 541 546 1999 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons The lumbar artery perforator based island flap: anatomical study and case reports H. Kato*, M. Hasegawa,
eplasty: Vol. 8 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique
 eplasty: Vol. 8 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine, University of Louisville,
eplasty: Vol. 8 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine, University of Louisville,
THE MOST CHALLENGING RECONSTRUCTIVE PROCEDURE FOR GOD: FINGERTIP RECONSTRUCTION
 Original Article Plastic Surgery THE MOST CHALLENGING RECONSTRUCTIVE PROCEDURE FOR GOD: FINGERTIP RECONSTRUCTION MEHMET O. YENIDUNYA* SUMMARY: We presented 59 fingertip injury cases that we treated and
Original Article Plastic Surgery THE MOST CHALLENGING RECONSTRUCTIVE PROCEDURE FOR GOD: FINGERTIP RECONSTRUCTION MEHMET O. YENIDUNYA* SUMMARY: We presented 59 fingertip injury cases that we treated and
Modified Bilhaut-Cloquet Procedure for Wassel Type-II and III Polydactyly of the Thumb. Surgical Technique
 This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. Modified Bilhaut-Cloquet Procedure for Wassel Type-II and III Polydactyly
This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. Modified Bilhaut-Cloquet Procedure for Wassel Type-II and III Polydactyly
Distally Based Sural Artery Adipofascial Flap based on a Single Sural Nerve Branch: Anatomy and Clinical Applications
 Distally Based Sural Artery Adipofascial Flap based on a Single Sural Nerve Branch: Anatomy and Clinical Applications Wan Loong James Mok 1, Yong Chen Por 1, Bien Keem Tan 2 1 Department of Plastic, Reconstructive
Distally Based Sural Artery Adipofascial Flap based on a Single Sural Nerve Branch: Anatomy and Clinical Applications Wan Loong James Mok 1, Yong Chen Por 1, Bien Keem Tan 2 1 Department of Plastic, Reconstructive
Chapter 39. Volar surface incisions
 Chapter 39 EXPLORATION OF AN INJURED HAND OR FOREARM KEY FIGURES: Tourniquet Midlateral finger incisions Brunner zigzag incisions Volar surface incisions Dorsal incisions Proximal and distal extension
Chapter 39 EXPLORATION OF AN INJURED HAND OR FOREARM KEY FIGURES: Tourniquet Midlateral finger incisions Brunner zigzag incisions Volar surface incisions Dorsal incisions Proximal and distal extension
Hand Trauma Update: Outline. Hand Surgeon s Area of Expertise. Orthopaedic Update 2015
 Hand Trauma Update: 2015 Orthopaedic Update 2015 March 21, 2015 Peter Tang, MD, MPH Director Hand, Upper Extremity & Microvascular Surgery Fellowship Associate Professor Drexel University College of Medicine
Hand Trauma Update: 2015 Orthopaedic Update 2015 March 21, 2015 Peter Tang, MD, MPH Director Hand, Upper Extremity & Microvascular Surgery Fellowship Associate Professor Drexel University College of Medicine
Wound coverage of plantar metatarsal ulcers in leprosy using a toe web flap
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article Wound coverage of plantar metatarsal ulcers in leprosy using a toe web flap J. Joshua, V. Chakraborthy Premananda Memorial Leprosy Hospital, The Leprosy
Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article Wound coverage of plantar metatarsal ulcers in leprosy using a toe web flap J. Joshua, V. Chakraborthy Premananda Memorial Leprosy Hospital, The Leprosy
Case Report The posterior interosseous pedicle free flap in soft-tissue coverage for small-area tissue defects of the hand
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(11):15599-15605 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0047672 Case Report The posterior interosseous pedicle free flap in soft-tissue coverage for small-area tissue defects of the
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(11):15599-15605 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0047672 Case Report The posterior interosseous pedicle free flap in soft-tissue coverage for small-area tissue defects of the
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
FACTORS INFLUENCING THE MANAGEMENT OF THE FLEXOR TENDON INJURIES IN THE HAND
 Basrah Journal of Surgery FACTORS INFLUENCING THE MANAGEMENT OF THE FLEXOR TENDON INJURIES IN THE HAND Avadis F.I.C.M.S. Lecturer in Orthopaedic, Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, and specialist
Basrah Journal of Surgery FACTORS INFLUENCING THE MANAGEMENT OF THE FLEXOR TENDON INJURIES IN THE HAND Avadis F.I.C.M.S. Lecturer in Orthopaedic, Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, and specialist
Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger Flaps and Vigorous Postoperative Exercises
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.4.574 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(4):574-578, 2010 Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.4.574 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(4):574-578, 2010 Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger
Evaluation of the Posterior Interosseous Artery Flap in Reconstructing Hand Defects
 POSTERIOR THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE INTEROSSEOUS MEDICAL ARTERY JOURNAL FLAP Evaluation of the Posterior Interosseous Artery Flap in Reconstructing Hand Defects Osam Ahmed Ibraheem, Mahdi Hameed Abood, Heider
POSTERIOR THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE INTEROSSEOUS MEDICAL ARTERY JOURNAL FLAP Evaluation of the Posterior Interosseous Artery Flap in Reconstructing Hand Defects Osam Ahmed Ibraheem, Mahdi Hameed Abood, Heider
Canine metacarpal pad trauma salvage and reconstruction case
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Canine metacarpal pad trauma salvage and reconstruction case Author : Nigel Dougherty Categories : Companion animal, Vets
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Canine metacarpal pad trauma salvage and reconstruction case Author : Nigel Dougherty Categories : Companion animal, Vets
Wrist and Hand Complaints
 Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Squamous cell carcinoma of the nail bed: Three case reports
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2004:12(2):248 252 Squamous cell carcinoma of the nail bed: Three case reports TC Wong, FK Ip, WC Wu Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Pamela Youde Nethersole
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2004:12(2):248 252 Squamous cell carcinoma of the nail bed: Three case reports TC Wong, FK Ip, WC Wu Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Pamela Youde Nethersole
THE FIRST PERCUTANEOUS LOCKED FLEXIBLE INTRAMEDULARY NAIL SYSTEM FOR HAND FRACTURES
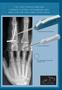 THE FIRST PERCUTANEOUS LOCKED FLEXIBLE INTRAMEDULARY NAIL SYSTEM FOR HAND FRACTURES Intramedullary Nail & Slotted Awl Proximal Locking Device New Radio Opaque Soft Tissue Protection Cap Pre Operative Post
THE FIRST PERCUTANEOUS LOCKED FLEXIBLE INTRAMEDULARY NAIL SYSTEM FOR HAND FRACTURES Intramedullary Nail & Slotted Awl Proximal Locking Device New Radio Opaque Soft Tissue Protection Cap Pre Operative Post
HAND & MICROSURGERY PROCEDURE A ( RM RM 4800 ) PROCEDURE B ( RM RM 4400 ) PROCEDURE C ( RM RM 3600 )
 HAND & MICROSURGERY PROCEDURE A ( RM 4401 - RM 4800 ) 1 Brachial plexus Exploration with nerve graft 2 Brachial plexus Exploration with neurotisation 3 Brachial plexus Free functioning muscle transfer
HAND & MICROSURGERY PROCEDURE A ( RM 4401 - RM 4800 ) 1 Brachial plexus Exploration with nerve graft 2 Brachial plexus Exploration with neurotisation 3 Brachial plexus Free functioning muscle transfer
Safe Treatment of Trigger Thumb With Longitudinal Anatomic Landmarks
 Safe Treatment of Trigger Thumb With Longitudinal Anatomic Landmarks Ron Hazani, MD, Josh Elston, BS, Ryan D. Whitney, BS, Jeremiah Redstone, MD, Saeed Chowdhry, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division
Safe Treatment of Trigger Thumb With Longitudinal Anatomic Landmarks Ron Hazani, MD, Josh Elston, BS, Ryan D. Whitney, BS, Jeremiah Redstone, MD, Saeed Chowdhry, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
The gastrocnemius with soleus bi-muscle flap
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 77 82 The gastrocnemius with soleus bi-muscle flap Ikuo Hyodo a, *, Bin Nakayama b, Mitsuru Takahashi c, Kazuhiro Toriyama d, Yuzuru Kamei d, Shuhei
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 77 82 The gastrocnemius with soleus bi-muscle flap Ikuo Hyodo a, *, Bin Nakayama b, Mitsuru Takahashi c, Kazuhiro Toriyama d, Yuzuru Kamei d, Shuhei
Anonfunctional digit that is limited
 Review Article Ray Resections of the Fingers: Indications, Techniques, and Outcomes Philip E. Blazar, MD Mark T. Garon, MD Abstract Ray resection, which was pioneered by Bunnell in the 1920s, was initially
Review Article Ray Resections of the Fingers: Indications, Techniques, and Outcomes Philip E. Blazar, MD Mark T. Garon, MD Abstract Ray resection, which was pioneered by Bunnell in the 1920s, was initially
DISTANT FLAPS KEY FIGURES:
 Chapter 14 DISTANT FLAPS KEY FIGURES: Chest flap Cross arm flap Cross leg flap Design of groin flap Examples of groin flap Examples of free flaps A distant flap involves moving tissue (skin, fascia, muscle,
Chapter 14 DISTANT FLAPS KEY FIGURES: Chest flap Cross arm flap Cross leg flap Design of groin flap Examples of groin flap Examples of free flaps A distant flap involves moving tissue (skin, fascia, muscle,
Mentosternal Contracture Treated With an Occipito-Scapular Flap in a 5-year-old Boy: A Case Report
 Mentosternal Contracture Treated With an Occipito-Scapular Flap in a 5-year-old Boy: A Case Report Armin Kraus, MD, Hans-Eberhard Schaller, MD, and Hans-Oliver Rennekampff, MD Department for Hand, Plastic,
Mentosternal Contracture Treated With an Occipito-Scapular Flap in a 5-year-old Boy: A Case Report Armin Kraus, MD, Hans-Eberhard Schaller, MD, and Hans-Oliver Rennekampff, MD Department for Hand, Plastic,
Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 552 556 Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q N. Imanishi a, *, H. Nakajima b, T. Minabe c, H. Chang d,
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 552 556 Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q N. Imanishi a, *, H. Nakajima b, T. Minabe c, H. Chang d,
TIE-IN. trapezium IMPLANT. surgical technique. presented by by James H. Calandruccio, MD and Mark T. Jobe, MD
 TRAPEZIUM IMPLANT TIE-IN trapezium IMPLANT surgical technique presented by by James H. Calandruccio, MD and Mark T. Jobe, MD TIE-IN TRAPEZIUM IMPLANT as described by James H. Calandruccio, MD and Mark
TRAPEZIUM IMPLANT TIE-IN trapezium IMPLANT surgical technique presented by by James H. Calandruccio, MD and Mark T. Jobe, MD TIE-IN TRAPEZIUM IMPLANT as described by James H. Calandruccio, MD and Mark
Reconstruction of axillary scar contractures retrospective study of 124 cases over 25 years
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 100 105 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00035-3 Reconstruction
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 100 105 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00035-3 Reconstruction
From the Orthopaedic Department, St. George's Hospital Medical School, London S.W.I.
 TRANSPLANTATION OF THE NAIL: A CASE REPORT By NICHOLAS P. PAPAVASSlI.IOU, M.D. 1 From the Orthopaedic Department, St. George's Hospital Medical School, London S.W.I. THE loss of a finger nail may be of
TRANSPLANTATION OF THE NAIL: A CASE REPORT By NICHOLAS P. PAPAVASSlI.IOU, M.D. 1 From the Orthopaedic Department, St. George's Hospital Medical School, London S.W.I. THE loss of a finger nail may be of
Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
Anatomical study. Clinical study. R. Ogawa, H. Hyakusoku, M. Murakami, R. Aoki, K. Tanuma* and D. G. Pennington?
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2002) 55, 396-40 I 9 2002 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3877 PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical and clinical study of the dorsal intercostal
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2002) 55, 396-40 I 9 2002 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3877 PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical and clinical study of the dorsal intercostal
A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report
 CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
Pedicled medial sural perforator flap for the reconstruction of knee defects
 International Wound Journal ISSN 1742-4801 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pedicled medial sural perforator flap for the reconstruction of knee defects I-Han Chiang 1, Chia-Chun Wu 2, Shyi-Gen Chen 1 & Chih-Hsin Wang
International Wound Journal ISSN 1742-4801 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pedicled medial sural perforator flap for the reconstruction of knee defects I-Han Chiang 1, Chia-Chun Wu 2, Shyi-Gen Chen 1 & Chih-Hsin Wang
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE HAND, FINGERS & THUMB
 RADIOGRAPHY OF THE HAND, FINGERS & THUMB FINGERS (2nd 5th) - PA Projection Patient Position: Seated; hand ; elbow on IR table top Part Position: Fingers centered to IR unless protocol is Central Ray: Perpendicular
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE HAND, FINGERS & THUMB FINGERS (2nd 5th) - PA Projection Patient Position: Seated; hand ; elbow on IR table top Part Position: Fingers centered to IR unless protocol is Central Ray: Perpendicular
CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY. Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS
 CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS The plastic and reconstructive surgeon is often called upon to treat many wound problems of the lower extremity. These include
CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS The plastic and reconstructive surgeon is often called upon to treat many wound problems of the lower extremity. These include
THE OPEN PALM TECHNIQUE IN DUPUYTREN'S CONTRACTURE. By CHARLES R. MCCASH, Ch.M., F.R.C.S.E. Roehampton Plastic Surgery Centre, London
 THE OPEN PALM TECHNIQUE IN DUPUYTREN'S CONTRACTURE By CHARLES R. MCCASH, Ch.M., F.R.C.S.E. Roehampton Plastic Surgery Centre, London IN 1833 Baron Dupuytren laid down the essential principles in the operative
THE OPEN PALM TECHNIQUE IN DUPUYTREN'S CONTRACTURE By CHARLES R. MCCASH, Ch.M., F.R.C.S.E. Roehampton Plastic Surgery Centre, London IN 1833 Baron Dupuytren laid down the essential principles in the operative
Use of Low-profile Palmar Internal Fixation in Digital Replantation
 TECHNIQUE Use of Low-profile Palmar Internal Fixation in Digital Replantation Mark Ross, MBBS, FRACS(Orth),*wz Christof Bollman, MBBS,*wy and Gregory B. Couzens, MBBS, FRACS(Orth)*8 Abstract: There are
TECHNIQUE Use of Low-profile Palmar Internal Fixation in Digital Replantation Mark Ross, MBBS, FRACS(Orth),*wz Christof Bollman, MBBS,*wy and Gregory B. Couzens, MBBS, FRACS(Orth)*8 Abstract: There are
NEUFLEX MCP/PIP FINGER JOINT IMPLANT SYSTEMS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA.
 NEUFLEX MCP/PIP FINGER JOINT IMPLANT SYSTEMS This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE MCP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Summary provided by designing surgeon Arnold-Peter C.
NEUFLEX MCP/PIP FINGER JOINT IMPLANT SYSTEMS This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE MCP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Summary provided by designing surgeon Arnold-Peter C.
Use of Dorsal Metacarpal Artery Flaps in Post Burn Reconstruction Two Cases Report
 Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011 Jun 15; 4(2):180-184. doi:10.3889/mjms.1857-5773.2011.0164 Case Report OPEN ACCESS Use of Dorsal Metacarpal Artery Flaps in Post Burn Reconstruction Two Cases
Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011 Jun 15; 4(2):180-184. doi:10.3889/mjms.1857-5773.2011.0164 Case Report OPEN ACCESS Use of Dorsal Metacarpal Artery Flaps in Post Burn Reconstruction Two Cases
New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description)
 New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description) 14301 Adjacent tissue transfer or rearrangement, any area; defect 30.1 sq cm to 60.0 sq cm 14302 each additional 30.0 sq cm,
New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description) 14301 Adjacent tissue transfer or rearrangement, any area; defect 30.1 sq cm to 60.0 sq cm 14302 each additional 30.0 sq cm,
Injuries to the Hands and Feet
 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect of Upper and Middle Third Leg
 Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Interesting Case Series. Reconstruction of Dorsal Wrist Defects
 Interesting Case Series Reconstruction of Dorsal Wrist Defects Maelee Yang, BS, and Joseph Meyerson, MD The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus Correspondence: maelee.yang@osumc.edu Keywords:
Interesting Case Series Reconstruction of Dorsal Wrist Defects Maelee Yang, BS, and Joseph Meyerson, MD The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus Correspondence: maelee.yang@osumc.edu Keywords:
Surgical Management of wounds, flaps, grafts, and scars
 Disclosures Surgical Management of wounds, flaps, grafts, and scars I have no financial disclosures Cherrie Heinrich, MD, FACS Department of Plastic Surgery Regions Hospital Assistant Professor University
Disclosures Surgical Management of wounds, flaps, grafts, and scars I have no financial disclosures Cherrie Heinrich, MD, FACS Department of Plastic Surgery Regions Hospital Assistant Professor University
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release ECTR
 Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release ECTR Christophe MATHOULIN Paris, France Historics Paget, 1854 Putnam, 1893 Hunt, 1909 Marie et Foix, 1913 Recommanded surgical release Learmonth, 1933 First reported release
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release ECTR Christophe MATHOULIN Paris, France Historics Paget, 1854 Putnam, 1893 Hunt, 1909 Marie et Foix, 1913 Recommanded surgical release Learmonth, 1933 First reported release
Initial experience with endoscopic carpal tunnel release surgery
 Initial experience with endoscopic carpal tunnel release surgery Craig H. Rabb, M.D., and Todd Kuether, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Oregon Health Sciences University, Portland, Oregon; and Portland
Initial experience with endoscopic carpal tunnel release surgery Craig H. Rabb, M.D., and Todd Kuether, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Oregon Health Sciences University, Portland, Oregon; and Portland
FINGER FINGER STRIPS BEDFORD FINGER SPLINTS MALLET FINGER SPLINT STATIC FINGER EXTENSION SPLINT
 BEDFORD FINGER SPLINTS Made from elasticated latex free stockinette, they provide firm support for injured fingers and give a small amount of protection. Minimum order of 20 per size. Width Length HBEDC
BEDFORD FINGER SPLINTS Made from elasticated latex free stockinette, they provide firm support for injured fingers and give a small amount of protection. Minimum order of 20 per size. Width Length HBEDC
