Improving tibial component coronal alignment using clearly defined anatomical structures in total knee arthroplasty
|
|
|
- Duane Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, ORIGINAL STUDY Improving tibial component coronal alignment using clearly defined anatomical structures in total knee arthroplasty Masahiko Ikeuchi, Masashi Izumi, Koji Aso, Natsuki Sugimura, Toshikazu Tani From Kochi Medical School, Kochi University, Nankoku, Kochi, Japan Several authors recently proposed to use clearly defined anatomical structures for extramedullary tibial alignment in total knee replacement, instead of using the intermalleolar center. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the benefits of using the dorsalis pedis artery and the anterior tibial crest as distal landmarks. Postoperative radiographs in 195 knees (98 in the control and 97 in the landmark group) were evaluated. The mean coronal alignment of the tibial component was 89.7 ± 2.1 in the control group and 90.0 ± 1.3 in the landmark group. Although there was no significant difference, the proportion of radiological outliers was significantly reduced in the landmark group compared to the control group (6.2% vs 27.6% in > 2 outliers ; p < , 1.0% vs 10.2% in > 3 outliers ; p = 0.01). In order to achieve accurate coronal alignment of the tibial component, it appears better to use multiple clear anatomical landmarks such as the dorsal pedis artery and the anterior tibial crest rather than using only the intermalleolar center. Keywords : knee, arthroplasty, landmark, coronal alignment. INTRODUCTION Proper alignment of the lower extremity is essential for the long-term success of total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Negative effects of component malalignment include poor clinical outcomes, excessive polyethylene wear, implant loosening, and early revision arthroplasty (18,6,20). It is commonly accepted that the position of 90 ± 3 to the long axis of the tibia in the coronal plane is ideal (3,14,11,20). Conventional techniques in cutting the proximal tibia are fairly effective for achieving proper coronal alignment of the tibial component. However, there are considerable outliers representing more than 3 of varus or valgus alignment even with computed navigation assistance (9). An extramedullary cutting guide is preferred rather than an intramedullary guide when determining tibial alignment (15). It is essential to accurately locate the ankle center for extramedullary tibial alignment. Although the traditional landmark for the ankle center is a point slightly medial to the intermalleolar center (7), it seems inappropriate to use this point as the sole landmark for determining the alignment (16,22). Recently, several authors proposed using more clearly defined anatomical structures for extramedullary tibial alignment, such as the extensor hallucis longus tendon (17), the anterior tibial n Masahiko Ikeuchi, MD, PhD, Associate Professor. n Masashi Izumi, MD, PhD, Orthopaedic Surgeon. n Koji Aso, MD, Orthopaedic Surgeon. n Natsuki Sugimura, MD, Orthopaedic Surgeon. n Toshikazu Tani, MD, PhD, Professor and Chairman. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kochi Medical School, Kochi University, Nankoku, Kochi, , Japan. Correspondence : Masahiko Ikeuchi, Department of Orthopaedics, Kochi Medical School, Kochi University Kohasu, Okocho, Nankoku, Kochi, Japan. ikeuchim@kochi-u.ac.jp 2013, Acta Orthopædica Belgica. No benefits or funds were received in support of this study. The authors report no conflict of interests.
2 improving tibial component coronal alignment 695 crest (10,23), and the dorsalis pedis artery (21). In actual practice, it is easy to locate these new landmarks except the extensor hallucis longus tendon during surgery. Because it is better to use multiple anatomical landmarks to reduce errors in component alignment, we recently started to use two of these new landmarks, i.e. the dorsalis pedis artery and the anterior tibial crest. The purpose of this retrospective study was to evaluate the benefits of using these new landmarks for extramedullay tibial alignment in TKA by comparing the accuracy of tibial component coronal alignment between the traditional technique and the new one. PATIENTS AND METHODS Between September 2009 and August 2012, primary TKAs were consecutively performed on 164 patients (200 knees) at our institution. There were 33 men and 131 women. The average age was 73 years (range : 52-89). The diagnosis was osteoarthritis in 166 knees, rheumatoid arthritis in 27 knees, osteonecrosis in 7 knees. Patients with osteoarthritis following high tibial osteotomy or fractures were excluded from this study. From September 2009 to March 2011 the intermalleolar center was used as a distal landmark in 100 knees (control group), and from April 2011 to August 2012 the dorsalis pedis artery and the anterior tibial crest were used in 100 knees (landmark group). Postoperative long-leg anteroposterior standing radiographs taken at 3 months were analyzed. Five radiographs were rejected because the ankle was not clearly visualized. A total of 98 radiographs in the control group and a total of 97 radiographs in the landmark group were analyzed. The measurement on the radiograph was made using image analysis software (CIS-Image/Viewer for Windows, version , IBM, Tokyo, Japan). For assessment of the coronal alignment of the tibial component, two lines were drawn on the computer monitor. The first line was the mechanical axis of the tibia ; a line connecting the center of the proximal tibia and the midpoint of the dome of the talus. The second line was drawn parallel to the undersurface of the tibial component. The medial angle formed between these two lines was measured semi-automatically as the coronal alignment of the tibial component. An angle less than 90 was classified as varus alignment, while an angle greater than 90 was classified as valgus alignment. Surgical outliers were graded as deviation greater than 2 or 3 from ideal alignment. All measured values were displayed to one decimal place (degree) on the computer monitor. The measurements were performed twice by two observers (MI and MI) with an interval of at least a week. Intraclass correlation coefficients were calculated for the inter- and intra-observer reliability of measurements. Surgical Procedures All surgeries were performed by or under supervision of the senior author (MI) through a medial parapatellar approach. An intramedullary jig was used for the femur while an extramedullary jig was used for the tibia. In order to clearly identify anatomical landmarks during surgery, the leg was wrapped with an adhesive transparent drape. Anatomical landmarks used in the landmark group (Fig. 1) were marked with surgical skin marker at the beginning of the surgery. The dorsalis pedis artery was carefully located approximately 1cm lateral to the tibialis anterior tendon at the level of the ankle joint (21). Prostheses used in this study were the Vanguard PS (Biomet, Warsaw, USA) in 148 knees and the Nexgen LPS (Zimmer, Warsaw, USA) in 47 knees. A measured resection technique was used to determine femoral component rotation (8). The posterior slope of the tibial cutting guide was 3 degrees for the Vanguard PS and 7 degrees for the Nexgen LPS. Identical tibial cutting jigs with 2 spikes and the ankle clamp were used in all patients. First, the proximal end of the jig was provisionally secured by impacting the longer spike of the cutting jig into a point where the postoperative mechanical axis intersected the tibial articular surface, which was determined at preoperative planning (13). At the same time, rotational orientation of the cutting jig was carefully assessed so that it aligned over the Akagi s line connecting the middle of the posterior cruciate ligament and the medial border of the patella tendon attachment (1). Its orientation in the coronal and sagittal planes was then determined by placing the arms of the alignment clamp around the ankle. In the control group, a point slightly medial to the intermalleolar center was used as a distal landmark for the extramedullary cutting jig. In the landmark group, the cutting jig was roughly aligned over the anterior tibial crest, specifically a line connecting the medial border of the patellar tendon attachment and the distal one-fourth of the anterior border (10), and then the coronal orientation was determined so that the distal end of the cutting jig pointed to the dorsal pedis artery at the level of the ankle joint. If the dorsalis pedis artery could not be located, the coronal orientation of the extramedullary jig was aligned over the anterior tibial crest. After reassessing the align-
3 696 m. ikeuchi, m. izumi, k. aso, n. sugimura, t. tani Fig. 1. Anatomical landmarks for extramedullary tibial alignment in the landmark group. Line A represents the anterior tibial crest ; a line connecting the medial border of the patellar attachment and the distal one-fourth of the anterior border. Point B represents the dorsal pedis artery at the level of the ankle joint. ment of the cutting jig, the shorter spike was impacted into the proximal tibia to finally secure the assembly. A tibial stylus was used to determine the exact bone resection thickness and the cutting block was secured with 3 pins. The proximal tibia was cut with a bone saw through the slit opening of the cutting block. After pre paration for the tibial stem and fin, all prostheses were implanted with cement. Statistical analysis Categorical data including coronal alignment of the tibia were compared between two groups using Fisher s exact test, while continuous variables were compared Fig. 2. Histogram illustrating the distribution of coronal alignment of the tibial component in the landmark and control group. using the Mann-Whitney U test. P < 0.05 was considered significant. All analyses were performed using SPSS ver (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL). RESULTS Patients demographic data are shown in Table I. No significant differences were found between the two groups regarding gender, age, body mass index (BMI), preoperative diagnosis, range of motion (ROM), or femorotibial angle (FTA) on the anteroposterior radiographs. Figure 2 shows the distribution of the coronal alignment of the tibial component for the landmark group and the control group. The mean coronal alignment of the tibial component was 89.7 (SD : 2.1 ) in the control group and 90.0 (SD : 1.3 ) in Table I. Demographic data of the two groups Landmark Control p value Female (%) n.s. Age (years) 75 (5) 73 (8) n.s. BMI (kg/m 2 ) 28 (4) 26 (8) n.s. Osteoarthritis (%) n.s. ROM (degrees) 111 (13) 109 (16) n.s. FTA (degrees) 186 (9) 184 (12) n.s. Values are means (SD). BMI = body mass index, ROM = range of motion, FTA = femorotibial angle.
4 improving tibial component coronal alignment 697 Table II. The number of surgical outliers in the landmark and control group Landmark Control p value > 2 outliers 6 (6.2%) 27 (27.6%) < > 3 outliers 1 (1.0%) 10 (10.2%) 0.01 the landmark group. There was no significant difference in the mean coronal alignment between the two groups (p = 0.29). However, the proportion of outliers in the landmark group was significantly smaller than in the control group (p < for > 2 outliers and p = 0.01 for > 3 outliers) (Table II). Intraclass correlation coefficient was 0.86 for the inter-observer reliability and 0.90 for the intraobserver reliability of measurements, giving good agreement. DISCUSSION The main finding of this study was that patients in the landmark group showed better coronal alignment of the tibial component compared to the control group. The only difference between the two groups was the use of anatomical landmarks for extramedullary tibial alignment. Although there was no significant difference in the mean coronal alignment, the proportion of radiological outliers (both > 2 and > 3 outliers) was significantly reduced in the landmark group. Because good placement within 3 of ideal alignment has been shown to reduce the risk of implants failure (3,14,11,20), the results obtained in the present study provide clinically important information on the anatomical landmarks for extramedullary alignment in TKA. Based on our results, it is better to use the dorsalis pedis artery and the anterior tibial crest rather than using only the intermalleolar center to achieve accurate coronal alignment of the tibial component. There are several possible reasons for improved accuracy of component alignment in the landmark group. One is that the dorsalis pedis artery and the anterior tibial crest are clear anatomical structures which can be easily located during surgery. On the other hand, the intermalleolar center is not an anatomical structure which can be determined by palpating the prominences of medial and lateral mal- leoli. In addition, although the ankle center is located at a point slightly medial to the intermalleolar center (8), it is unclear how much medial adjustment of the extramedullary guide should be done in each patient. These factors can negatively affect the accuracy in the control group. Another reason is that two landmarks were used in the landmark group, while the intermalleolar center was used as the sole landmark in the control group. Errors in landmark identification commonly occur during surgery. In addition, recently reported landmarks also have drawbacks similar to the intermalleolar center. Previous studies showed congenital absence (24) or absent pulse (12) of the dorsalis pedis artery, and wide variations among individuals (10) and gender differences (23) of the anterior tibial crest. Therefore, it is safer to use multiple landmarks to reduce errors in component alignment. Computer navigation is a recent advancement in joint replacement surgery. Computer assistance achieves more accurate postoperative alignment in TKA (2,4,5,9,19). A recent meta-analysis concluded that the proportion of > 2 outliers for coronal alignment of the tibial component was 6.0% in navigated TKAs and 19.7% in conventional TKAs, and the proportion of > 3 outliers was 2.8% and 9.9% respectively (9). Several studies have shown no significant difference between navigated and conventional TKAs. Our findings are comparable to the results reported with navigated TKA. If computed navigation is not available, it is thus possible to improve the accuracy of the tibial component coronal alignment similar to navigated TKA. We think that it is essential to use multiple clear anatomical structures for anatomical landmarks such as the dorsalis pedis artery and the anterior tibial crest. This study has some limitations. First, it was a retrospective case-control study. The results might
5 698 m. ikeuchi, m. izumi, k. aso, n. sugimura, t. tani have been confounded by other factors related to the study design, such as the different periods involved and different prostheses used. Second, only radiological alignment of the tibial component was evaluated in this study. It is unclear whether good placement of the tibial component improves the clinical outcomes. Third, although we noted that arterial pulse of the dorsalis pedis artery was not palpable in a few patients, the exact number of such patients is unknown. Only the anterior tibial crest was used in these patients. Despite these limitations, this study provides important information on the value of using anatomical landmarks for extramedullary alignment in TKA. REFERENCES 1. Akagi M, Oh M, Nonaka T et al. An anteroposterior axis of the tibia for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2004 : 420 : Bathis H, Perlick L, Tingart M et al. Alignment in total knee arthroplasty. A comparison of computer-assisted surgery with the conventional technique. J Bone Joint Surg 2004 ; 86-B : Berend ME, Ritter MA, Meding JB et al. Tibial component failure mechanisms in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2004 ; 428 : Chauhan SK, Scott RG, Breidahl W et al. Computerassisted knee arthroplasty versus a conventional jig-based technique. A randomised, prospective trial. J Bone Joint Surg 2004 ; 86-B : Chin PL, Yang KY, Yeo SJ et al. Randomized control trial comparing radiographic total knee arthroplasty implant placement using computer navigation versus conventional technique. J Arthroplasty 2005 ; 20 : Collier MB, Engh CA, Jr., McAuley JP et al. Factors associated with the loss of thickness of polyethylene tibial bearings after knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 2007 ; 89-A : Dennis DA, Channer M, Susman MH et al. Intramedullary versus extramedullary tibial alignment systems in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 1993 ; 8 : Dennis DA, Komistek RD, Kim RH et al. Gap balancing versus measured resection technique for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010 ; 468 : Fu Y, Wang M, Liu Y et al. Alignment outcomes in navigated total knee arthroplasty : a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2012 ; 20 : Fukagawa S, Matsuda S, Mitsuyasu H et al. Anterior border of the tibia as a landmark for extramedullary alignment guide in total knee arthroplasty for varus knees. J Orthop Res 2011 ; 29 : Huang NF, Dowsey MM, Ee E et al. Coronal alignment correlates with outcome after total knee arthroplasty : fiveyear follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. J Arthroplasty 2012 ; 27 : Ludbrook J, Clarke AM, Mc KJ. Significance of absent ankle pulse. Br Med J 1962 ; 1 : Matsuda S, Mizu-uchi H, Miura H et al. Tibial shaft axis does not always serve as a correct coronal landmark in total knee arthroplasty for varus knees. J Arthroplasty 2003 ; 18 : Patil S, D Lima DD, Fait JM et al. Improving tibial component coronal alignment during total knee arthroplasty with use of a tibial planing device. J Bone Joint Surg 2007 ; 89-A : Phillips AM, Goddard NJ, Tomlinson JE. Current techniques in total knee replacement : results of a national survey. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 1996 ; 78 : Reed MR, Bliss W, Sher JL et al. Extramedullary or intramedullary tibial alignment guides : a randomised, prospective trial of radiological alignment. J Bone Joint Surg 2002 ; 84-B : Schneider M, Heisel C, Aldinger PR et al. Use of palpable tendons for extramedullary tibial alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2007 ; 22 : Sharkey PF, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH et al. Insall Award paper. Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today? Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002 ; 404 : Sparmann M, Wolke B, Czupalla H et al. Positioning of total knee arthroplasty with and without navigation support. A prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg 2003 ; 85-B : Srivastava A, Lee GY, Steklov N et al. Effect of tibial component varus on wear in total knee arthroplasty. Knee 2012 ; 19 : Sugimura N, Ikeuchi M, Izumi M et al. The dorsal pedis artery as a new distal landmark for extramedullary tibial alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2013 Jan 11. [Epub ahead of print] 22. Teter KE, Bregman D,Colwell CW, Jr. Accuracy of intra medullary versus extramedullary tibial alignment cutting systems in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1995 ; 321 : Tsukeoka T, Lee TH, Tsuneizumi Y, Suzuki M. The tibial crest as a practical useful landmark in total knee arthroplasty. Knee 2012 Nov 12. [Epub ahead of print] 24. Yamada T, Gloviczki P, Bower TC, Naessens JM, Carmichael SW. Variations of the arterial anatomy of the foot. Am J Surg 1993 ; 166 :
Clinical Study Accuracy of Implant Placement Utilizing Customized Patient Instrumentation in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 891210, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891210 Clinical Study Accuracy of Implant Placement Utilizing Customized Patient
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 891210, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891210 Clinical Study Accuracy of Implant Placement Utilizing Customized Patient
Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
Lateralization of Tibial Plateau Reference Point Improves Accuracy of Tibial Resection in Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients with Proximal Tibia Vara
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:458-464 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.458 Lateralization of Tibial Plateau Reference Point Improves Accuracy of Tibial Resection in Total Knee
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:458-464 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.458 Lateralization of Tibial Plateau Reference Point Improves Accuracy of Tibial Resection in Total Knee
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: COMPUTER ASSISTED NAVIGATION FOR KNEE AND HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
Extramedullary Tibial Preparation
 Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: COMPUTER ASSISTED NAVIGATION FOR KNEE AND HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: COMPUTER ASSISTED PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including an
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: COMPUTER ASSISTED PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including an
No radiographic difference between patient-specific guiding and conventional Oxford UKA surgery
 DOI 10.1007/s00167-014-2849-0 KNEE No radiographic difference between patient-specific guiding and conventional Oxford UKA surgery Bart Kerens Martijn G. M. Schotanus Bert Boonen Nanne P. Kort Received:
DOI 10.1007/s00167-014-2849-0 KNEE No radiographic difference between patient-specific guiding and conventional Oxford UKA surgery Bart Kerens Martijn G. M. Schotanus Bert Boonen Nanne P. Kort Received:
Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON. Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD
 CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique
 Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Intramedullary Tibial Preparation
 Surgical Technique Intramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Intramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 IM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Surgical Technique Intramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Intramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 IM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
ORTHOPAEDICS. Component position alignment with patient-specific jigs in total knee arthroplasty. Introduction. ANZJSurg.com
 ORTHOPAEDICS ANZJSurg.com Component position alignment with patient-specific jigs in total knee arthroplasty Terence R. Moopanar,* Jeevaka E. Amaranath* and Rami M. Sorial *Department of Orthopaedics,
ORTHOPAEDICS ANZJSurg.com Component position alignment with patient-specific jigs in total knee arthroplasty Terence R. Moopanar,* Jeevaka E. Amaranath* and Rami M. Sorial *Department of Orthopaedics,
Accelerometer-Based, Portable Navigation vs Imageless, Large-Console Computer-Assisted Navigation in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2012 Accelerometer-Based, Portable Navigation vs Imageless, Large-Console Computer-Assisted Navigation in Total Knee Arthroplasty A Comparison of Radiographic
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2012 Accelerometer-Based, Portable Navigation vs Imageless, Large-Console Computer-Assisted Navigation in Total Knee Arthroplasty A Comparison of Radiographic
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
JOINT RULER. Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement
 JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
POSTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION. Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Posterior Reference Surgical Technique
 POSTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Posterior Reference Surgical Technique For NexGen Cruciate Retaining & Legacy Posterior Stabilized Knees
POSTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Posterior Reference Surgical Technique For NexGen Cruciate Retaining & Legacy Posterior Stabilized Knees
ANTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION. Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Anterior Reference Surgical Technique
 ANTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Anterior Reference Surgical Technique For NexGen Cruciate Retaining & Legacy Posterior Stabilized Knees INTRODUCTION
ANTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Anterior Reference Surgical Technique For NexGen Cruciate Retaining & Legacy Posterior Stabilized Knees INTRODUCTION
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 22 No
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 22 No. 8 2007 Interobserver and Intra-observer Errors in Obtaining Visually Selected Anatomical Landmarks During Registration Process in Non Image-Based Navigation-Assisted
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 22 No. 8 2007 Interobserver and Intra-observer Errors in Obtaining Visually Selected Anatomical Landmarks During Registration Process in Non Image-Based Navigation-Assisted
Coronal Instability after Total Knee Arthroplasty using Bi-Surface type 3 : An Averaged 10 Year Follow-up Study
 51 2018; 65: 51-58 M. Kim et al. Original Article Coronal Instability after Total Knee Arthroplasty using Bi-Surface type 3 : An Averaged 10 Year Follow-up Study Kim Mindae, Toshifumi Watanabe, Takeshi
51 2018; 65: 51-58 M. Kim et al. Original Article Coronal Instability after Total Knee Arthroplasty using Bi-Surface type 3 : An Averaged 10 Year Follow-up Study Kim Mindae, Toshifumi Watanabe, Takeshi
Revolution. Unicompartmental Knee System
 Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference?
 Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
The Journal of Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty 28 (213) 82 86 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect The Journal of Arthroplasty journal homepage: www.arthroplastyjournal.org Accuracy of Image-Free Computer Navigated
The Journal of Arthroplasty 28 (213) 82 86 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect The Journal of Arthroplasty journal homepage: www.arthroplastyjournal.org Accuracy of Image-Free Computer Navigated
Reliability of patient specific instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 0, 8, 668-67 ORIGINAL STUDY Reliability of patient specific instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty Harold Jennart, Marie-Ange Ngo Yamben, Theofylaktos Kyriakidis, David Zorman Department
Acta Orthop. Belg., 0, 8, 668-67 ORIGINAL STUDY Reliability of patient specific instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty Harold Jennart, Marie-Ange Ngo Yamben, Theofylaktos Kyriakidis, David Zorman Department
High flexion knee arthroplasty: the relationship between rotational angles and flexion angle after total knee arthroplasty
 Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med (2014) 7:103 107 DOI 10.1007/s12178-014-9215-1 TKA SYMPOSIUM (P SANCHETI, SECTION EDITOR) High flexion knee arthroplasty: the relationship between rotational angles and flexion
Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med (2014) 7:103 107 DOI 10.1007/s12178-014-9215-1 TKA SYMPOSIUM (P SANCHETI, SECTION EDITOR) High flexion knee arthroplasty: the relationship between rotational angles and flexion
Simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty with robotic and conventional techniques: a prospective, randomized study
 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2011) 19:1069 1076 DOI 10.1007/s00167-011-1400-9 KNEE Simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty with robotic and conventional techniques: a prospective, randomized
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2011) 19:1069 1076 DOI 10.1007/s00167-011-1400-9 KNEE Simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty with robotic and conventional techniques: a prospective, randomized
Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p.
 Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
A Non-CT Based Total Knee Arthroplasty System Featuring Complete Soft-Tissue Balancing
 A Non-CT Based Total Knee Arthroplasty System Featuring Complete Soft-Tissue Balancing Manuela Kunz 1, Matthias Strauss 2, Frank Langlotz 1, Georg Deuretzbacher 2, Wolfgang Rüther 2, and Lutz-Peter Nolte
A Non-CT Based Total Knee Arthroplasty System Featuring Complete Soft-Tissue Balancing Manuela Kunz 1, Matthias Strauss 2, Frank Langlotz 1, Georg Deuretzbacher 2, Wolfgang Rüther 2, and Lutz-Peter Nolte
Is patella eversion during total knee arthroplasty crucial for gap adjustment and soft-tissue balancing?
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2011) 97, 287 291 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is patella eversion during total knee arthroplasty crucial for gap adjustment and soft-tissue balancing? G. Kamei a,,
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2011) 97, 287 291 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is patella eversion during total knee arthroplasty crucial for gap adjustment and soft-tissue balancing? G. Kamei a,,
)116( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
 )116( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Analysis of the Geometry of the Distal Femur and Proximal Tibia in the Osteoarthritic Knee: A 3D Reconstruction CT Scan Based
)116( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Analysis of the Geometry of the Distal Femur and Proximal Tibia in the Osteoarthritic Knee: A 3D Reconstruction CT Scan Based
Zimmer NexGen MIS Tibial Component. Cemented Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME
 Zimmer NexGen MIS Tibial Component Cemented Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME Zimmer NexGen MIS Tibial Component Cemented Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer NexGen MIS Tibial Component Cemented Surgical Technique
Zimmer NexGen MIS Tibial Component Cemented Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME Zimmer NexGen MIS Tibial Component Cemented Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer NexGen MIS Tibial Component Cemented Surgical Technique
Alignment in total knee arthroplasty
 Alignment in total knee arthroplasty A COMPARISON OF COMPUTER-ASSISTED SURGERY WITH THE CONVENTIONAL TECHNIQUE H. Bäthis, L. Perlick, M. Tingart, C. Lüring, D. Zurakowski, J. Grifka From the University
Alignment in total knee arthroplasty A COMPARISON OF COMPUTER-ASSISTED SURGERY WITH THE CONVENTIONAL TECHNIQUE H. Bäthis, L. Perlick, M. Tingart, C. Lüring, D. Zurakowski, J. Grifka From the University
Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick
 Dr Andreas Loefler www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Dr Andreas Loefler Joint Replacement & Spine Surgery CAS or Navigation in TKA New Software for a Full
Dr Andreas Loefler www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Dr Andreas Loefler Joint Replacement & Spine Surgery CAS or Navigation in TKA New Software for a Full
MIS Cemented Tibial Component
 MIS Cemented Tibial Component NexGen Complete Knee Solution Surgical Technique Table of Contents Surgical Exposure... 2 Finish the Tibia... 2 Position Based on Anatomic Landmarks... 3 Lateral Posterior
MIS Cemented Tibial Component NexGen Complete Knee Solution Surgical Technique Table of Contents Surgical Exposure... 2 Finish the Tibia... 2 Position Based on Anatomic Landmarks... 3 Lateral Posterior
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology
 PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM 90-SRK-700000 B.0 0 Contents 1. Implant Sizing 2. Surgical Technique a. Incision and Exposure b. Distal Femoral Resection c. Tibial Resection d. Femoral
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM 90-SRK-700000 B.0 0 Contents 1. Implant Sizing 2. Surgical Technique a. Incision and Exposure b. Distal Femoral Resection c. Tibial Resection d. Femoral
TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments
 TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments Resection Guide System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RESECTION GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the SIGMA
TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments Resection Guide System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RESECTION GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the SIGMA
Distal Cut First Femoral Preparation
 Surgical Technique Distal Cut First Femoral Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Femoral preparation Contents Introduction...3 DCF femoral highlights...4 Preoperative planning...6
Surgical Technique Distal Cut First Femoral Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Femoral preparation Contents Introduction...3 DCF femoral highlights...4 Preoperative planning...6
Computer Navigation in TKA The role of Robotic Surgery. Christos Yiannakopoulos, M.D., Ph.D.
 Computer Navigation in TKA The role of Robotic Surgery Christos Yiannakopoulos, M.D., Ph.D. Why are TKA failing? 11.8% Sharkley, CORR, 2005 55.6% of revision occurred early (< 2 years) 32% of patients
Computer Navigation in TKA The role of Robotic Surgery Christos Yiannakopoulos, M.D., Ph.D. Why are TKA failing? 11.8% Sharkley, CORR, 2005 55.6% of revision occurred early (< 2 years) 32% of patients
PROPHECY INBONE. Preoperative Navigation Guides
 PROPHECY INBONE Preoperative Navigation Guides Simple. Fast. Accurate. Simple. Fast. Accurate. Prophecy Envision the Results PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Guides have ushered in a new era of total ankle
PROPHECY INBONE Preoperative Navigation Guides Simple. Fast. Accurate. Simple. Fast. Accurate. Prophecy Envision the Results PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Guides have ushered in a new era of total ankle
Presented By Dr Vincent VG An MD BSc (Adv) MPhil Dr Murilo Leie MD Mr Joshua Twiggs BEng Dr Brett A Fritsch MBBS FRACS (Orth) FAOrthA.
 A comparison of kinematic and mechanical alignment with regards to bony resection, soft tissue release, and deformity correction in total knee replacement Presented By Dr Vincent VG An MD BSc (Adv) MPhil
A comparison of kinematic and mechanical alignment with regards to bony resection, soft tissue release, and deformity correction in total knee replacement Presented By Dr Vincent VG An MD BSc (Adv) MPhil
Sasaki E 1,2, Otsuka H 2, Sasaki N 2, and Ishibashi Y 1
 Influence of osteophyte resection of the posterior femoral condyle on extension range of motion and gap balance in cruciate retaining type total knee arthroplasty. - Intraoperative evaluation using navigation
Influence of osteophyte resection of the posterior femoral condyle on extension range of motion and gap balance in cruciate retaining type total knee arthroplasty. - Intraoperative evaluation using navigation
Duration of Follow-up (mo)
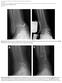 Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
Aesculap Orthopaedics Columbus MIOS
 Aesculap Orthopaedics Columbus MIOS Minimally Invasive Orthopaedic Solutions Manual TKA Surgical Technique MIOS 4-in-1 Cutting Block MIOS Distal Femoral Cutting Block MIOS Tibial Left and Right Cutting
Aesculap Orthopaedics Columbus MIOS Minimally Invasive Orthopaedic Solutions Manual TKA Surgical Technique MIOS 4-in-1 Cutting Block MIOS Distal Femoral Cutting Block MIOS Tibial Left and Right Cutting
TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments
 TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments Pin Guide System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE PIN GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the SIGMA High Performance
TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments Pin Guide System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE PIN GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the SIGMA High Performance
Total knee replacement in patients with significant femoral bowing in the coronal plane
 KNEE Total knee replacement in patients with significant femoral bowing in the coronal plane A COMPARISON OF CONVENTIONAL AND COMPUTER-ASSISTED SURGERY IN AN ASIAN POPULATION T.-W. Huang, W.-H. Hsu, K.-T.
KNEE Total knee replacement in patients with significant femoral bowing in the coronal plane A COMPARISON OF CONVENTIONAL AND COMPUTER-ASSISTED SURGERY IN AN ASIAN POPULATION T.-W. Huang, W.-H. Hsu, K.-T.
Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W.
 University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
NexGen Cruciate Retaining (CR) and Revision Instrumentation. Surgical Technique
 NexGen Cruciate Retaining (CR) and Revision Instrumentation Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction... 4 Revision Arthroplasty... 4 Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Instrumentation System MICRO-MILL Instrumentation
NexGen Cruciate Retaining (CR) and Revision Instrumentation Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction... 4 Revision Arthroplasty... 4 Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Instrumentation System MICRO-MILL Instrumentation
S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E David A. McQueen, MD Return to Menu
 S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E David A. McQueen, MD TOTAL KNEE INSTRUMENTS Wichita Fusion Nail Introduction...1 Preoperative Planning...2 Surgical Technique...3-8 Wichita Fusion Nail Surgical Technique
S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E David A. McQueen, MD TOTAL KNEE INSTRUMENTS Wichita Fusion Nail Introduction...1 Preoperative Planning...2 Surgical Technique...3-8 Wichita Fusion Nail Surgical Technique
Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty for Patients with Extra-Articular Deformity
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2013;25(4):194-201 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2013.25.4.194 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2013;25(4):194-201 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2013.25.4.194 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty
Clinical evaluation of 292 Genesis II posterior stabilized high-flexion total knee arthroplasty: range of motion and predictors
 DOI 10.1007/s00590-014-1467-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical evaluation of 292 Genesis II posterior stabilized high-flexion total knee arthroplasty: range of motion and predictors Mathijs C. H. W. Fuchs Rob
DOI 10.1007/s00590-014-1467-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical evaluation of 292 Genesis II posterior stabilized high-flexion total knee arthroplasty: range of motion and predictors Mathijs C. H. W. Fuchs Rob
NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION S A. Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical. ATechnique
 NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION ATechnique Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical INTRODUCTION The NexGen Complete Knee Solution Intramedullary Tibial Instruments have been designed to provide an
NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION ATechnique Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical INTRODUCTION The NexGen Complete Knee Solution Intramedullary Tibial Instruments have been designed to provide an
Clinical Results of Genesis-I Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Acta Medica et Biologica Vol. 49, No.2, 47-52, 2001 Clinical Results of Genesis-I Total Knee Arthroplasty for Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Five-year Longitudinal Study H aojiang Kuanyu LIU1, Go
Acta Medica et Biologica Vol. 49, No.2, 47-52, 2001 Clinical Results of Genesis-I Total Knee Arthroplasty for Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Five-year Longitudinal Study H aojiang Kuanyu LIU1, Go
Ye-Ran Li, Yu-Hang Gao, Xin Qi *, Jian-Guo Liu, Lu Ding, Chen Yang, Zheng Zhang and Shu-Qiang Li
 Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:92 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0588-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Analysis of factors that affect the precision of the radiographic lateral femoral
Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:92 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0588-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Analysis of factors that affect the precision of the radiographic lateral femoral
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP
 THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER 16 LONG-TERM FAILURE MECHANISMS AND SURVIVORSHIP Long-Term Failure Mechanisms and Survivorship Presented by: Michael A. Mont, MD, Assem A. Sultan, MD, and Michael
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER 16 LONG-TERM FAILURE MECHANISMS AND SURVIVORSHIP Long-Term Failure Mechanisms and Survivorship Presented by: Michael A. Mont, MD, Assem A. Sultan, MD, and Michael
Case Report Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis with Extra-Articular Femoral Deformity and/or Retained Hardware
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 174384, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/174384 Case Report Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis with Extra-Articular
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 174384, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/174384 Case Report Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis with Extra-Articular
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
unicompartmental knee SURGICAL TECHNIQUE limacorporate.com
 unicompartmental knee SURGICAL TECHNIQUE limacorporate.com Index INTRAMEDULLARY (IM) SURGICAL PROCEDURE Introduction Page >> 04 Rationale Page >> 05 Preoperative Planning Page >> 07 Patient Preparation
unicompartmental knee SURGICAL TECHNIQUE limacorporate.com Index INTRAMEDULLARY (IM) SURGICAL PROCEDURE Introduction Page >> 04 Rationale Page >> 05 Preoperative Planning Page >> 07 Patient Preparation
Zimmer Unicompartmental High Flex Knee. Intramedullary, Spacer Block Option and Extramedullary Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Zimmer Unicompartmental High Flex Knee Intramedullary, Spacer Block Option and Extramedullary Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques ZIMMER UNICOMPARTMENTAL HIGH FLEX KNEE INTRAMEDULLARY, SPACER BLOCK
Zimmer Unicompartmental High Flex Knee Intramedullary, Spacer Block Option and Extramedullary Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques ZIMMER UNICOMPARTMENTAL HIGH FLEX KNEE INTRAMEDULLARY, SPACER BLOCK
Midterm outcomes of electromagnetic computer-assisted navigation in minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty
 Thiengwittayaporn et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2013, 8:37 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Midterm outcomes of electromagnetic computer-assisted navigation in minimally invasive total
Thiengwittayaporn et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2013, 8:37 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Midterm outcomes of electromagnetic computer-assisted navigation in minimally invasive total
Evaluation of soft-tissue balance during total knee arthroplasty
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2010;18(1):26-30 Evaluation of soft-tissue balance during total knee arthroplasty Hideyuki Sasanuma, Hitoshi Sekiya, Kenzo Takatoku, Hisashi Takada, Naoya Sugimoto Department
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2010;18(1):26-30 Evaluation of soft-tissue balance during total knee arthroplasty Hideyuki Sasanuma, Hitoshi Sekiya, Kenzo Takatoku, Hisashi Takada, Naoya Sugimoto Department
Clinical Results of Lateral Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Minimum 2-Year Follow-up
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:386-392 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.386 Clinical Results of Lateral Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Minimum 2-Year Follow-up Kyung Tae
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:386-392 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.386 Clinical Results of Lateral Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Minimum 2-Year Follow-up Kyung Tae
PIN GUIDE SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments System. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA.
 PIN GUIDE SYSTEM with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments System This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Pin Guide Surgical Technique The following steps are
PIN GUIDE SYSTEM with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments System This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Pin Guide Surgical Technique The following steps are
Bicruciate-Retaining or Medial Pivot Total Knee Prosthesis Pritchett 225 Fig. 3. The MP total knee prosthesis. Fig. 1. An anteroposterior radiograph o
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 26 No. 2 2011 Patients Prefer A Bicruciate-Retaining or the Medial Pivot Total Knee Prosthesis James W. Pritchett, MD, FACS Abstract: Four-hundred forty patients underwent
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 26 No. 2 2011 Patients Prefer A Bicruciate-Retaining or the Medial Pivot Total Knee Prosthesis James W. Pritchett, MD, FACS Abstract: Four-hundred forty patients underwent
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up
 Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray
 Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique Give Bone A Solid Hold Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique
Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique Give Bone A Solid Hold Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique
Zimmer Unicompartmental High Flex Knee. Spacer Block Surgical Technique
 Zimmer Unicompartmental High Flex Knee Spacer Block Surgical Technique INTRO Zimmer Unicompartmental High Flex Knee Spacer Block Surgical Technique Introduction Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA)
Zimmer Unicompartmental High Flex Knee Spacer Block Surgical Technique INTRO Zimmer Unicompartmental High Flex Knee Spacer Block Surgical Technique Introduction Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA)
EXPERIENCE GPS FOR TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY DETERMINE YOUR OWN COURSE.
 EXPERIENCE GPS FOR TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY DETERMINE YOUR OWN COURSE. The year 2010 marked Exactech s silver aiversary and 25 years of mobility. As a company founded by an orthopaedic surgeon and a biomedical
EXPERIENCE GPS FOR TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY DETERMINE YOUR OWN COURSE. The year 2010 marked Exactech s silver aiversary and 25 years of mobility. As a company founded by an orthopaedic surgeon and a biomedical
RESECTION GUIDE SYSTEM. TRUMATCH Personalized Solutions Surgical Technique with ATTUNE Knee INTUITION Instruments
 RESECTION GUIDE SYSTEM TRUMATCH Personalized Solutions Surgical Technique with ATTUNE Knee INTUITION Instruments RESECTION GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the ATTUNE Knee
RESECTION GUIDE SYSTEM TRUMATCH Personalized Solutions Surgical Technique with ATTUNE Knee INTUITION Instruments RESECTION GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the ATTUNE Knee
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Influence of patellar subluxation on ligament balancing in total knee arthroplasty through a subvastus approach. An in vivo study
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 00, 76, 799-805 ORIGINAL STUDY Influence of patellar subluxation on ligament balancing in total knee arthroplasty through a subvastus approach. An in vivo study Wouter DE KEySER, Leo
Acta Orthop. Belg., 00, 76, 799-805 ORIGINAL STUDY Influence of patellar subluxation on ligament balancing in total knee arthroplasty through a subvastus approach. An in vivo study Wouter DE KEySER, Leo
STIFFNESS AFTER TKA PRE, PER AND POST OPERATIVE CAUSING FACTORS
 STIFFNESS AFTER TKA PRE, PER AND POST OPERATIVE CAUSING FACTORS Patrick DJIAN INTRODUCTION Stiffness is one of the most common complications following TKR, causing frustration to both the surgeon and the
STIFFNESS AFTER TKA PRE, PER AND POST OPERATIVE CAUSING FACTORS Patrick DJIAN INTRODUCTION Stiffness is one of the most common complications following TKR, causing frustration to both the surgeon and the
ANATOMIC SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. 5 in 1. Conventional instrumentation 07/11/2013
 ANATOMIC SURGICAL TECHNIQUE 5 in 1 Conventional instrumentation PRO.GB.933/1.0 Octobre 2013 2 Tibial step 3 Intramedullary technique - Based on the preoperative plan, drill the medullary canal with the
ANATOMIC SURGICAL TECHNIQUE 5 in 1 Conventional instrumentation PRO.GB.933/1.0 Octobre 2013 2 Tibial step 3 Intramedullary technique - Based on the preoperative plan, drill the medullary canal with the
Uniglide. Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Mk III surgical technique
 Uniglide Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Mk III surgical technique Uniglide Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative assessment 6 Preparation 7 Incision 7 Approach 7 Medial procedure 8 Tibial preparation
Uniglide Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Mk III surgical technique Uniglide Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative assessment 6 Preparation 7 Incision 7 Approach 7 Medial procedure 8 Tibial preparation
Clinical Performance of the Optetrak Total Knee Prosthesis: A 11-year Follow-up Study
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Journal of Clinical & Experimental Orthopaedics DOI: 10.4172/2471-8416.100045 Clinical Performance of the Optetrak Total Knee Prosthesis: A 11-year
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Journal of Clinical & Experimental Orthopaedics DOI: 10.4172/2471-8416.100045 Clinical Performance of the Optetrak Total Knee Prosthesis: A 11-year
Midterm results of cemented Press Fit Condylar Sigma total knee arthroplasty system
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005:13(3):280-284 Midterm results of cemented Press Fit Condylar Sigma total knee arthroplasty system S Asif, DSK Choon Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005:13(3):280-284 Midterm results of cemented Press Fit Condylar Sigma total knee arthroplasty system S Asif, DSK Choon Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of
Total knee arthroplasty using computer-assisted navigation in patients with deformities of the femur and tibia: A report of 5 cases
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery July 2005 Total knee arthroplasty using computer-assisted navigation
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery July 2005 Total knee arthroplasty using computer-assisted navigation
Zimmer NexGen Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation. Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME. Stem Extensions and Augments
 Zimmer NexGen Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME Stem Extensions and Augments Zimmer NexGen Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer NexGen Tibial
Zimmer NexGen Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME Stem Extensions and Augments Zimmer NexGen Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer NexGen Tibial
Surgical Technique. VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System
 Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE FastPak for LEGION Instrument Technique* Nota Bene The technique description herein is made available to the
Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE FastPak for LEGION Instrument Technique* Nota Bene The technique description herein is made available to the
Metal block augmentation for bone defects of the medial tibia during primary total knee arthroplasty
 Tsukada et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2013, 8:36 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Metal block augmentation for bone defects of the medial tibia during primary total knee arthroplasty Sachiyuki
Tsukada et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2013, 8:36 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Metal block augmentation for bone defects of the medial tibia during primary total knee arthroplasty Sachiyuki
ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT
 ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT Douglas A. Dennis, MD Medical Director at Porter Center for Joint Replacement Denver, Colorado Historically, sagittal plane instability following Total Knee Arthroplasty
ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT Douglas A. Dennis, MD Medical Director at Porter Center for Joint Replacement Denver, Colorado Historically, sagittal plane instability following Total Knee Arthroplasty
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete
 Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Triathlon Knee System
 Triathlon Knee System Express Instruments Surgical Protocol Posterior Stabilized & Cruciate Retaining TriathlonKneeSystem Express Instruments Surgical Protocol Acknowledgments..........................................................2
Triathlon Knee System Express Instruments Surgical Protocol Posterior Stabilized & Cruciate Retaining TriathlonKneeSystem Express Instruments Surgical Protocol Acknowledgments..........................................................2
ANATOMIC. Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0
 ANATOMIC Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0 SCREEN LAYOUT Take screenshot Surgical step Dynamic navigation zone Information area and buttons 2 SCREEN LAYOUT Indicates action when yellow
ANATOMIC Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0 SCREEN LAYOUT Take screenshot Surgical step Dynamic navigation zone Information area and buttons 2 SCREEN LAYOUT Indicates action when yellow
Anterior Cut First Surgical Technique
 Anterior Cut First Surgical Technique GENESIS II Anterior Cut First Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction....................................... 2 Preop Planning....................................
Anterior Cut First Surgical Technique GENESIS II Anterior Cut First Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction....................................... 2 Preop Planning....................................
Constrained Posterior Stabilized (CPS)
 Constrained Posterior Stabilized (CPS) Persona The Personalized Knee Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Constraint Options Initial Knee Assessment... 3 Femoral Box Cut CPS Tibial Bearing
Constrained Posterior Stabilized (CPS) Persona The Personalized Knee Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Constraint Options Initial Knee Assessment... 3 Femoral Box Cut CPS Tibial Bearing
Limb alignment in computer-assisted minimally-invasive unicompartmental knee replacement
 Limb alignment in computer-assisted minimally-invasive unicompartmental knee replacement G. Keene, D. Simpson, Y. Kalairajah From Sportsmed-SA Orthopaedic Clinic, Adelaide, South Australia Twenty patients
Limb alignment in computer-assisted minimally-invasive unicompartmental knee replacement G. Keene, D. Simpson, Y. Kalairajah From Sportsmed-SA Orthopaedic Clinic, Adelaide, South Australia Twenty patients
Triathlon Knee System. Universal Baseplate Surgical Protocol
 Triathlon Knee System Universal Baseplate Surgical Protocol Table of Contents Acknowledgments..........................................................2 Introduction...............................................................2
Triathlon Knee System Universal Baseplate Surgical Protocol Table of Contents Acknowledgments..........................................................2 Introduction...............................................................2
Table of Contents. Step One: Locate Medullary Canal 4 Step Two: Prepare Femur 4. Step Three: Size Femur 5. Step Four: Prepare Tibia 5
 Zimmer Natural-Knee Unicompartmental MIS Intramedullary Surgical Technique Zimmer MIS Surgical Technique for Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Developed in conjunction with Aaron A. Hofmann, MD Professor
Zimmer Natural-Knee Unicompartmental MIS Intramedullary Surgical Technique Zimmer MIS Surgical Technique for Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Developed in conjunction with Aaron A. Hofmann, MD Professor
FOREWORD PRESERVATION UNICOMPARTMENTAL KNEE SYSTEM
 Surgical Technique FOREWORD PRESERVATION UNICOMPARTMENTAL KNEE SYSTEM Our surgeon design team first implanted the Preservation Unicompartmental Knee System in 2001. The system was developed with over
Surgical Technique FOREWORD PRESERVATION UNICOMPARTMENTAL KNEE SYSTEM Our surgeon design team first implanted the Preservation Unicompartmental Knee System in 2001. The system was developed with over
)289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE
 )289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Different References for Valgus Cut Angle in Total Knee Arthroplasty Hamidreza Yazdi, MD; Ara Nazarian, DrSc; Jim S Wu, MD;
)289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Different References for Valgus Cut Angle in Total Knee Arthroplasty Hamidreza Yazdi, MD; Ara Nazarian, DrSc; Jim S Wu, MD;
Development of a Pneumatic Tensioning Device for Gap Measurement during Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:188-192 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.188 Development of a Pneumatic Tensioning Device for Gap Measurement during Total Knee Arthroplasty
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:188-192 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.188 Development of a Pneumatic Tensioning Device for Gap Measurement during Total Knee Arthroplasty
Unicondylar Surgical Technique
 Unicondylar Surgical Technique Contents Indications, Contra-indications and X-ray Templating 2 Approach and Exposure 3 Proximal Tibial Resection 4 Tibial Jig Alignment 6 Tibial Sizing 9 Balancing 10 Distal
Unicondylar Surgical Technique Contents Indications, Contra-indications and X-ray Templating 2 Approach and Exposure 3 Proximal Tibial Resection 4 Tibial Jig Alignment 6 Tibial Sizing 9 Balancing 10 Distal
Zimmer NexGen Rotating Hinge Knee Primary/ Revision
 Zimmer NexGen Rotating Hinge Knee Primary/ Revision Surgical Technique Designed for use in revision and difficult primary surgeries 1 INTRODUCTION The NexGen Rotating Hinge Knee Components are designed
Zimmer NexGen Rotating Hinge Knee Primary/ Revision Surgical Technique Designed for use in revision and difficult primary surgeries 1 INTRODUCTION The NexGen Rotating Hinge Knee Components are designed
Distal femoral condyle is more internally rotated to the patellar tendon at 90 of flexion in normal knees
 Kawahara et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:54 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0197-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Distal femoral condyle is more internally rotated to the patellar tendon
Kawahara et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:54 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0197-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Distal femoral condyle is more internally rotated to the patellar tendon
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART)
 CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
Pin Guide System. Surgical Technique
 Pin Guide System Surgical Technique Pin Guide Surgical Technique The following steps are an addendum to the SIGMA High Performance (HP) Instruments, Fixed Reference Surgical Technique (Cat. No. 0612-87-510
Pin Guide System Surgical Technique Pin Guide Surgical Technique The following steps are an addendum to the SIGMA High Performance (HP) Instruments, Fixed Reference Surgical Technique (Cat. No. 0612-87-510
