Modeling the length of the care episode after hip fracture: does the type of fracture Matter?
|
|
|
- Amy Hutchinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 98: , 009 Modeling the length of the care episode after hip fracture: does the type of fracture Matter? r. sund 1, J. riihimäki, M. Mäkelä 1,3, a. Vehtari, p. lüthje 4, t. huusko 5, u. häkkinen 1 1 National Institute for Health and Welfare, Helsinki, Finland Department of Biomedical Engineering and Computational Science, Helsinki University of Technology, Helsinki, Finland 3 Services for the Aged and Disabled, City of Vantaa, Vantaa, Finland 4 Kuusankoski Regional Hospital, Kuusankoski, Finland 5 The Social Insurance Institution, Health Department/Rehabilitation Section, Helsinki, Finland abstract Background and Aims: hip fractures are common events that require intensive operative hospital care and alengthy rehabilitation. the effect of hip fracture type on successful rehabilitation is not well known. the aim of this study is to model and compare the length of the care episodes between intra- and extracapsular hip fractures in finland. Material and Methods: hip fracture patients living at home in finland were followed using register-based data. patient characteristics, outcomes, and length of stay (los) distributions were analyzed using a bayesian nonparametric multilayer perceptron (Mlp) network model. Results: Mortality was similar in intra- and extracapsular hip fractures. patients were more likely to need long-term care after extracapsular hip fracture. the average los at the surgical ward was similar for intra- and extracapsular fractures (1.7 weeks), but there was aconsiderable difference for the total inpatient los between the groups (5. weeks vs. 6.9 weeks). intracapsular fractures had asimple unimodal los distribution, whereas the los distribution for the extracapsular fractures was multimodal with two clear peaks. patients with more comorbidities required a longer los. Conclusions: the causes for differences in los between fracture types were most likely due to the different surgical methods and rehabilitation practices for the fracture types. as national guidelines suggest similar rehabilitation for all hip fracture patients, there is aneed for early and aggressive rehabilitation of patients with extracapsular fractures, including full-weight bearing for all but selected patients. Key words: Intracapsular/extracapsular hip fractures; care episodes; rehabilitation; length of stay; register-based data; Bayesian modeling Correspondence: Reijo Sund, D.Soc.Sc. National Institute for Health and Welfare (THL) P.O. Box 30 FI-0071 Helsinki Finland reijo.sund@thl.fi
2 170 R. Sund, J. Riihimäki, M. Mäkelä, A. Vehtari, P. Lüthje, T. Huusko, U. Häkkinen INTRODUCTION Among the ageing population, hip fractures are common events that can be devastating and costly (1). Besides having a high mortality rate, they also require intensive operative hospital care and alengthy rehabilitation (). In anumber of cases, rehabilitation is unsuccessful and the patient requires long term residential care, leading to even higher costs of care (3). As the incidence of hip fractures increases sharply with age, and as populations age, the outcome ofhip fracture care is critical for the health system and elderly care (1). Hip fracture events serve as an excellent model for studying the determinants of successful geriatric rehabilitation, as the diagnosis of hip fractures is usually straightforward, best practices are well established, and critical outcomes are readily defined. The success of rehabilitation after ahip fracture has been shown to depend on the comorbidity and cognitive impairment level of the patient (4, 5), but also on the way the rehabilitation care isprovided (6 8). The term hip fracture refers to a fracture of the upper end of the femur. Hip fractures are commonly classified into intra- and extracapsular according to their relationship to the capsular attachment of the hip. Patients with intracapsular fractures tend to be younger, more mobile, and are less likely to use walking aids or live in residential accommodation; they also have aconsiderably shorter length of hospital stay than those with extracapsular fractures (9 1). However, the effect of hip fracture type on successful rehabilitation is not well known. The aim of this study is to model and compare the length of the care episodes between intra- and extracapsular hip fractures in Finland. MATERIAL AND METHODS The total population of hip fracture patients in was identified in the Finnish Health Care Register using the 10 th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) diagnosis codes S7.0 (fracture of the neck of femur), S7.1 (trochantheric fracture) and S7. (subtrochanteric fracture). Data on the use of residential care and deaths for this hip fracture population were extracted from the Finnish Health Care Register and from the national Causes of Death Statistics using the unique personal identification number of each patient. Records in these registers include a lot of data: patient and provider ID-numbers, age, sex, area codes, and diagnosis and operation codes, as well as dates of admission, operation and discharge (or death). The validity of Finnish register-data for hip fracture follow-up studies is very good (13). The actual study population was restricted to patients aged 65 or older having their first hip fracture and living at home at the time of fracture (n=15544). Hip fractures were classified into intra-capsular (S7.0) and extracapsular fractures (S7.1, S7.), using diagnosis codes recorded for the primary operative care period. Other covariates included were age at the time of fracture, sex, operation type, hospital district, days of inpatient care during one year before the fracture, and the place from which the patient was admitted to the surgical ward (home, nursing home, primary care inpatient ward, hospital). Also certain preexisting comorbid conditions were identified from the data in a manner similar to that used in previous register-based hip fracture studies (14). There are three main outcomes for hip fracture treatment: 1) the patient is able to return home, ) the patient becomes along-term patient, or 3) the patient dies. Discharge home may take place directly from the surgical ward orafter some inpatient rehabilitation. The hip fracturecareepisode was defined as acontinuous episode of inpatient treatment, beginning with operative treatment on the surgical ward and ending with discharge to home. If the rehabilitation period exceeded four months, the patient was classified as along-term patient (15). The hip fracture care episode was considered successful if the patient was still staying at home two weeks after the discharge home. STATISTICAL METHODS ABayesian nonparametric multilayer perceptron (MLP) network model was used for the statistical modeling (16, 17). Bayesian formalism gives aprincipled approach to combine the MLP model description,prior information and the data. The MLP model allows flexible ways to present distributions without fixing the functional forms in advance, and makes it possible to deal with nonlinearities and complex interactions between covariates in the data. Modeling was formulated as aclassification task. For the length of stay (LOS) distributions each class corresponded to the length of stay at an accuracy of one week. The probability that a class target y had value j (out of k possible outputs) was computed using softmax likelihood exp( f j ( x, w)) p( y j x, w). exp( f ( x, w)) k k The latent function was modelled with an MLP function, corresponding to the network with one hidden layer of the form k m d k 0 wkj tanh( w j0 w ji xi) j1 i1 f ( x, w) w, where a d-dimensional input vector is denoted by x, and w represents weight parameters in the model. Indices i and j correspond to input and hidden layers, respectively. The prior was set indirectly via the network and weight priors toafunction space. The following hierarchical structure was used w ~ N( 0, ) ~ Inv gamma( i ji ave i ave, v ) ~ Inv gamma(, v 0,ave ), which favours smooth solutions since small weights produce smooth functions (16, 17). The separate prior variance i for each input automatically determines the relevance of various inputs. The variance hyperparameter i is controlled by the next level hyperparameters ave and v, that are determined by the third level hyperparameters 0 and v, ave.the suggested fixed values for the highest level hyperparameters were used (16). An integration of parameters posterior was made using stochastic Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulation techniques. The computations were made using the MCMC Methods for MLP and GP and Stuff (for Matlab) -toolbox V.1 ( The relative risks for the background characteristics and process variables between the intracapsular and extraca-
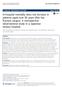
3 Modeling LOS after hip fracture 171 psular groups were estimated using abinomial model for discrete variables, and anormal distribution for continuous variables. In both these cases a noninformative prior was chosen, and credible intervals were obtained using simulation samples from the posterior distributions. To analyze the differences between the binary valued outcome variables of intra- and extracapsular groups, the MLP model with a single output was used. In this case the probability that a binary class target y had value 1was computed using logistic transformation 1 p( y 1 x, w). 1 exp( f ( x, w)) This allowed us to obtain the relative risks, adjusted for background characteristics and process variables. To illustrate the effects of the covariates on the probability of discharge during certain weeks, we computed average predictive comparisons for the probability of discharge during these weeks for the variables of interest. The comparisons wereobtained for alarge simulation test group by observing the average difference in probability corresponding to aunit difference in each of the input covariates (18). For the two covariates (the place from which the patient was admitted to the surgical ward and operation type), the average difference was compared to the average value. RESULTS The basic characteristics of the hip fracture population are reported in Table 1. Intracapsular fractures were more common, accounting for about 63% of all hip fractures. Patients in both fracture groups had similar background characteristics.osteoarthritis was more common among the extracapsular patients. There were no differences in mortality figures between intra- and extracapsular hip fractures (Table 1). Ahigher proportion of patients with intracapsular hip fractures were discharged home directly from the surgical ward orduring the rehabilitation period. Thus, it was more likely that a patient with an extracapsular hip fracture required long-term care. The proportion of patients dying before returning home or becoming a long-term patient was 16.% and 16.6% for intra- and extracapsular patients, respectively. The proportion of patients at home one year after fracture did not differ between fracture types. The average LOS at the surgical ward was similar for both groups (1.7 weeks), but there was a significant difference in the length of total inpatient treatment between intra- and extracapsular fractures (5. weeks vs. 6.9 weeks). The mode class for the length of stay was 3 weeks for intracapsular fractures, while the LOS distribution had a typical right-skewed shape, where the mode is reached quite quickly and the probabilities for longer stays steadily decrease (Fig. 1A). For extracapsular hip fractures, the shape of the LOS distribution was non-standard, having no systematic decrease in probabilities after reaching a peak at weeks until the mode in the distribution seen at 7 8 weeks. The disparity between the shapes of the distributions for intracapsular and extracapsular fractures was clear (Fig. 1A). For both of the fracture types, the MLP model was also used to examine how the differences in the observed LOS and predicted LOS relate to the success of discharge home. The discharge was considered successful if the patient was staying at home two weeks after discharge. In Fig. 1B, the proportions of successful discharges home are shown as afunction of the residual (the difference in the observed LOS and expected LOS) for each fracture type. The result was computed using the MLP classifier to adjust for the effect of covariates and to obtain a smoothed result. For extracapsular fractures, a shorter than expected LOS was associated with aslightly higher proportion of successful discharges, while alonger than expected LOS resulted in alower proportion of successful discharges. In other words, there was no indication that shorter inpatient stay would lead to worse results among the patients with extracapsular fractures. The results for intracapsular fractures demonstrated that somewhat shorter than expected LOS was associated with ahigher proportion of successful discharges, indicating that the available registerbased data had not enabled the model to identify some early-discharge patients with aclearly better prognosis. The simulated effects of the covariates on the probability of an early discharge are presented in Fig. with corresponding 95% credible intervals. It seemed that patients with more frailties required longer LOS. DISCUSSION In this study, the length of stay until discharge home was found to be significantly longer for the extracapsular fractures. Asimilar pattern has been detected in previous studies (9, 11, 19). The novel finding in this study was the markedly different shape of LOS distributions for intra- and extracapsular fractures. The LOS distribution for the intracapsular fractures was shown to have a simple unimodal shape, whereas the shape of the LOS distribution for extracapsular fractures was found to be multimodal with two clear peaks, suggesting (at least) two separate subpopulations. Determining the total length of stay in inpatient institutions in a reliable way for all hip fracture patients required a reconstruction of the treatment chains, made possible by the comprehensive Finnish register-based data. Although the registers do not contain all clinically relevant variables, and certain comorbidity prevalences are probably underestimated because of missed diagnoses or underreporting (6, 0), the validity of the register data for follow-up purposes has been demonstrated to be even better than with separate audit data collection (13). The anomaly in the shapes of LOS distribution would probably have been missed without the use of ahierarchical nonparametric Bayesian model. The actual reasons for the detected differences in LOS are largely unknown. They were not due to differences in background characteristics, as the groups were very similar in this respect and there were no differences in mortality figures. Because operation techniques vary between the types of hip fractures,
4 17 R. Sund, J. Riihimäki, M. Mäkelä, A. Vehtari, P. Lüthje, T. Huusko, U. Häkkinen TABLE 1 Characteristics of and outcomes for hip fracture population by hip fracture type Intracapsular hip fracture Extracapsular hip fracture Relative risk between groups (95% CI) Number of hip fracture patients aged 65 or more living at home at the time of fracture Background characteristics: Age (SD) 80.5 (7.1) 81.0 (7.3) 1.01 ( ) Female sex, % ( ) Admitted from home, % ( ) Weeks of inpatient care during year preceding fracture (SD) 0.5 (4.5) 0.6 (4.6) 1.01 ( ) Malignancy, % ( ) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, % ( ) Ischemic heart disease, % ( ) Previous myocardial infarction, % ( ) Congestive heart failure, % ( ) Cerebrovascular disease, % ( ) Peripheral vascular disease, % ( ) Diabetes, % ( ) Osteoarthritis, % ( ) Parkinson s disease, % ( ) Dementia, % ( ) Alcoholism, % ( ) Process variables: Operation type, % Internal fixation ( ) Hemiarthoplasty ( ) Total hip arthoplasty ( ) Other ( ) No operation ( ) Outcomes*: 30 day mortality, % ( ) 10 day mortality, % ( ) 365 day mortality, % ( ) Proportion of patients at home one month after fracture ( ) Proportion of patients at home 4 months after fracture ( ) Proportion of patients at home one year after fracture ( ) Discharged home from surgical ward, % ( ) Discharged home during rehabilitation period, % ( ) Becomes a long term care patient, % ( ) Died during treatment, % ( ) Mean week of discharge from surgical ward (SD) 01.7 (1.6) 01.7 (1.6) 1.01 ( ) Mean week of discharge from total inpatient stay (SD) 05. (3.4) 06.9 (4.) 1.3 ( ) Mean week of readmission to hospital after discharge home (SD) 14.3 (13.4) 13.8 (1.7) 1.00 ( ) Mean weeks alive and out of inpatient care during 60 days following discharge home (SD) Proportion of patients staying at home two weeks after discharge home, % 08.1 (1.9) 08.1 (.0) 1.00 ( ) ( ) *adjusted for covariates listed in the table these may have an influence on the LOS. In Finland, hemiarthoplasty has been the primary mode of treatment for intracapsular fractures, and osteosynthesis has been used mainly for younger patients (1). Extracapsular fractures have been typically treated with a sliding hip screw or gamma nail (). Total hip arthoplasty is used only for patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or rheumatoid arthritis. As the femoral head is removed and the femoral stem is typically cemented in hemiarthoplasty, there may be less pain in ambulation and full-weight bearing may be easier than for patients who underwent internal fixation. This interpretation is supported by the fact that patients with trochanteric fractures are known to expe-
5 Modeling LOS after hip fracture 173 A) B) week of discharge Fig. 1 A) Distributions of lengths of stay in inpatient care by fracture type B) Proportion of successful discharges to home presented as a function of residual with corresponding 95% credible intervals by fracture type residual: observed minus expected LOS (weeks) Fig.. Simulated average predictive comparisons (95% credible intervals) for the probability of discharge during the weeks 1 5, for background characteristics and process variables average change in early discharge probability Background characteristics Intracapsular fracture Five years increase in mean age Female sex Admitted from home One week increase in mean weeks of preceding care Malignancy Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Ischemic heart disease Previous myocardial infarction Congestive heart failure Cerebrovascular disease Peripheral vascular disease Diabetes Osteoarthritis Parkinson s disease Dementia Alcoholism Process variables Operation type Internal fixation Hemiarthoplasty Total hip arthoplasty Other No operation
6 174 R. Sund, J. Riihimäki, M. Mäkelä, A. Vehtari, P. Lüthje, T. Huusko, U. Häkkinen rience more pain on walking during the first couple of postoperative weeks (3). Moreover, osteosynthesis was found to be a significant predictor for a longer LOS in this study. However, the multimodal shape of the LOS distribution for extracapsular fractures was unexpected, because similar postoperative rehabilitation practices, including immediate weight-bearing (7, 8), has been promoted in Finland for all patients regardless of the fracture type or operation performed (4). Certain subtrochanteric fractures are an exception, while multifragmented trochanteric fractures may sometimes result in an unstable osteosynthesis that makes immediate weight-bearing more difficult (19); it is unlikely however that these special cases would explain the multimodality. On the other hand, most hip fracture patients are referred to rehabilitation units or to a local health centre hospital for rehabilitation immediately after operative treatment in the surgical ward (5), and different local service structures and resources lead to variations in rehabilitation practices (). Amore plausible explanation for the multimodality is therefore that hospitals may be using outdated practices, such as instructing most of the patients with extracapsular fractures to start rehabilitation with partial weight-bearing. In fact, the examination of residuals in this study suggested that no harm would arise from shortening the LOS of patients with extracapsular fractures, and actually a somewhat shorter than expected LOS might result in better success of discharge to home, as was the case with the intracapsular fractures. In conclusion, the results confirmed that patients with extracapsular fractures require more health system resources during the hip fracture treatment process, since the rehabilitation is significantly slower than in the intracapsular group. As theredonot seem to be any obvious adverse effects in shortening the LOS for patients with extracapsular fractures, and as the recent Finnish clinical guideline suggests similar rehabilitation for all hip fracture patients (4), early and aggressive rehabilitation of patients with extracapsular fractures is needed, including full-weight bearing for all but selected patients. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The work of Jaakko Riihimäki was supported by Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation (project TERANA). The work of Aki Vehtari was supported by Academy of Finland (Academy Research Fellowship). The funding body played no role in the formulation of the design, methods, data analysis, or the preparation of this paper. REFERENCES 01. Marks R, Allegrante JP, Ronald MacKenzie C et al: Hip fractures among the elderly: causes, consequences and control. Ageing Res Rev 003;: Holmberg S,Thorngren KG: Rehabilitation after femoral neck fracture patients followed for 6 years. Acta Orthop Scand 1985;56: Nurmi I, Narinen A, Lüthje Pet al: Cost analysis of hip fracture treatment among the elderly for the public health services: a 1-year prospective study in 106 consecutive patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 003;13: Huusko TM, Karppi P, Avikainen V et al: Randomised, clinically controlled trial of intensive geriatric rehabilitation in patients with hip fracture: subgroup analysis of patients with dementia. Bmj 000;31: Rolland Y, Pillard F, Lauwers-Cances V et al: Rehabilitation outcome of elderly patients with hip fracture and cognitive impairment. Disabil Rehabil 004;6: Huusko TM, Karppi P, Avikainen V et al: Intensive geriatric rehabilitation of hip fracture patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Acta Orthop Scand 00;73: Raivio M, Korkala O, Pitkälä K et al: Rehabilitation outcome in hip-fracture: Impact of weight-bearing restriction Apreliminary investigation. Phys Occup Ther Geriatr 005;: Heinonen M, Karppi P, Huusko Tetal: Post-operative degree of mobilization at two weeks predicts one-year mortality after hip fracture. Aging Clin Exp Res 004;16: Parker MJ, Pryor GA, Anand JK et al: Acomparison of presenting characteristics of patients with intracapsular and extracapsular proximal femoral fractures. J R Soc Med 199;85: Cornwall R, Gilbert MS, Koval KJ et al: Functional outcomes and mortality vary among different types of hip fractures: a function of patient characteristics. Clin Orthop Relat Res 004: Thorngren KG, Norrman PO, Hommel Aetal: Influence of age, sex, fracture type and pre-fracture living on rehabilitation pattern after hip fracture in the elderly. Disabil Rehabil 005;7: Haentjens P, Autier P, Barette Metal: Survival and functional outcome according to hip fracture type: Aone-year prospective cohort study in elderly women with an intertrochanteric or femoral neck fracture. Bone 007;41: Sund R, Nurmi-Lüthje I, Lüthje Petal: Comparing properties of audit data and routinely collected register data in case of performance assessment of hip fracture treatment in Finland. Methods Inf Med 007;46: Sund R, Liski A: Quality effects of operative delay on mortality in hip fracture treatment. Qual Saf Health Care 005;14: Heikkinen T, Jalovaara P: Four or twelve months follow-up in the evaluation of functional outcome after hip fracture surgery? Scand J Surg 005;94: Lampinen J, Vehtari A: Bayesian approach for neural networks review and case studies. Neural Networks 001;14: Neal RM: Bayesian Learning for Neural Networks. Volume 118 of Lecture Notes in Statistics. Springer, New York, Gelman A, Hill J: Data Analysis Using Regression and Multilevel/Hierarchical Models. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, Jarnlo GB, Ceder L, Thorngren KG: Early rehabilitation at home of elderly patients with hip fractures and consumption of resources in primary care. Scand JPrim Health Care 1984; : Laurila JV, Pitkälä KH, Strandberg TEetal: Detection and documentation of dementia and delirium in acute geriatric wards. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 004;6: Heikkinen T, Parker M, Jalovaara P: Hip fractures in Finland and Great Britain--a comparison of patient characteristics and outcomes. Int Orthop 001;5: Heikkinen T, Willig R, Hänninen Aet al: Hip fractures in Finland--a comparison of patient characteristics and outcomes in six hospitals. Scand J Surg 004;93: Thorngren KG: Optimal treatment of hip fractures. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 1991;41: Duodecim Study Group, Finnish Orthopedic Society: [Care of patients with hip fractures]. Duodecim 006;1: Huusko T, Karppi P, Avikainen Vetal: Significant changes in the surgical methods and length of hospital stay of hip fracture patients occurring over 10 years in Central Finland. Ann Chir Gynaecol 1999;88:55 60 Received: May 30, 008 Accepted: March 5, 009
Peterborough Community Rehabilitation Schemes. Martyn Parker
 Peterborough Community Rehabilitation Schemes Martyn Parker Peterborough Hospital at Home Established 1987 Provided home care for patients Initially used by for hip fracture patients and after hysterectomy
Peterborough Community Rehabilitation Schemes Martyn Parker Peterborough Hospital at Home Established 1987 Provided home care for patients Initially used by for hip fracture patients and after hysterectomy
Outcome after surgery for fracture of the hip in patients aged over 95 years
 Outcome after surgery for fracture of the hip in patients aged over 95 years G. Holt, D. Macdonald, M. Fraser, A. T. Reece From Western Infirmary, Glasgow, Scotland Despite the increase in numbers of the
Outcome after surgery for fracture of the hip in patients aged over 95 years G. Holt, D. Macdonald, M. Fraser, A. T. Reece From Western Infirmary, Glasgow, Scotland Despite the increase in numbers of the
The Peterborough experience over the years with hip fractures. Martyn Parker Peterborough UK
 The Peterborough experience over the years with hip fractures Martyn Parker Peterborough UK PETERBOROUGH HIP FRACTURE PROJECT Avoid delays to surgery Minimally invasive surgery by experienced staff Unrestricted
The Peterborough experience over the years with hip fractures Martyn Parker Peterborough UK PETERBOROUGH HIP FRACTURE PROJECT Avoid delays to surgery Minimally invasive surgery by experienced staff Unrestricted
Management of Hip Fractures
 Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient David A. Brown MD COL U.S. Army Ret. The Center for Orthopedics and Neurosurgery Optimizing Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient Optimizing
Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient David A. Brown MD COL U.S. Army Ret. The Center for Orthopedics and Neurosurgery Optimizing Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient Optimizing
FOUR OR TWELVE MONTHS FOLLOW-UP IN THE EVALUATION OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME AFTER HIP FRACTURE SURGERY?
 Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 94: 59 66, 2005 FOUR OR TWELVE MONTHS FOLLOW-UP IN THE EVALUATION OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME AFTER HIP FRACTURE SURGERY? T. Heikkinen, P. Jalovaara University of Oulu University
Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 94: 59 66, 2005 FOUR OR TWELVE MONTHS FOLLOW-UP IN THE EVALUATION OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME AFTER HIP FRACTURE SURGERY? T. Heikkinen, P. Jalovaara University of Oulu University
Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
EUROHOPE: Hip fracture in Europe are slippery regions different?
 EUROHOPE: Hip fracture in Europe are slippery regions different? 25 Sep, 2012 Emma Medin Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Hip fracture is the most common fracture and associated with increased
EUROHOPE: Hip fracture in Europe are slippery regions different? 25 Sep, 2012 Emma Medin Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Hip fracture is the most common fracture and associated with increased
More than half of hip fracture patients do not regain mobility in the first postoperative yearggi_
 bs_bs_banner Geriatr Gerontol Int 2013; 13: 334 341 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: EPIDEMIOLOGY, CLINICAL PRACTICE AND HEALTH More than half of hip fracture patients do not regain mobility in the first postoperative
bs_bs_banner Geriatr Gerontol Int 2013; 13: 334 341 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: EPIDEMIOLOGY, CLINICAL PRACTICE AND HEALTH More than half of hip fracture patients do not regain mobility in the first postoperative
Poor Prognosis in Elderly Patients Receiving Nonoperative Treatment for Hip Fracture: A Study of 224 Cases at Kofu National Hospital
 Yamanashi Med. J. (2, 37 ~, 5 Clinical Study Poor Prognosis in Elderly Patients Receiving Nonoperative Treatment for Hip Fracture: A Study of 22 Cases at Kofu National Hospital Tetsuo HAGINO, Eiichi SATO,
Yamanashi Med. J. (2, 37 ~, 5 Clinical Study Poor Prognosis in Elderly Patients Receiving Nonoperative Treatment for Hip Fracture: A Study of 22 Cases at Kofu National Hospital Tetsuo HAGINO, Eiichi SATO,
The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
The Experience in Exeter with. hip fracture care. Data For Change
 The Experience in Exeter with hip fracture care Data For Change John Charity Associate Specialist in T&O, Lead NHFD Clinician, Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Respond Deliver & Enable People
The Experience in Exeter with hip fracture care Data For Change John Charity Associate Specialist in T&O, Lead NHFD Clinician, Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Respond Deliver & Enable People
One-year health and care costs after hip fracture for home-dwelling elderly in Norway. Results from the Trondheim Hip Fracture Trial
 One-year health and care costs after hip fracture for home-dwelling elderly in Norway. Results from the Trondheim Hip Fracture Trial Liv Faksvåg Hektoen 1, Ingvild Saltvedt 2,3, Olav Sletvold 2, 3, Jorunn
One-year health and care costs after hip fracture for home-dwelling elderly in Norway. Results from the Trondheim Hip Fracture Trial Liv Faksvåg Hektoen 1, Ingvild Saltvedt 2,3, Olav Sletvold 2, 3, Jorunn
The Geriatrician in the Trauma Service. Trauma Quality Improvement Program (TQIP) Annual Scientific Meeting and Training 2013
 The Geriatrician in the Trauma Service Trauma Quality Improvement Program (TQIP) Annual Scientific Meeting and Training 2013 Challenges of the Geriatric Trauma Patient Challenges of the Geriatric Patient
The Geriatrician in the Trauma Service Trauma Quality Improvement Program (TQIP) Annual Scientific Meeting and Training 2013 Challenges of the Geriatric Trauma Patient Challenges of the Geriatric Patient
Rehabilitation - Reducing costs and hospital stay. Dr Elizabeth Aitken Consultant Physician
 Rehabilitation - Reducing costs and hospital stay Dr Elizabeth Aitken Consultant Physician What factors affect outcome? Comorbidities Cardiac Respiratory Neurological Nutritional issues Diabetes Anaemia
Rehabilitation - Reducing costs and hospital stay Dr Elizabeth Aitken Consultant Physician What factors affect outcome? Comorbidities Cardiac Respiratory Neurological Nutritional issues Diabetes Anaemia
Cognitive Impairment and 1-Year Outcome in Elderly Patients with Hip Fracture
 e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.892304 Received: 2014.08.23 Accepted: 2014.09.15 Published: 2014.10.17 Cognitive Impairment and 1-Year Outcome in Elderly Patients with Hip Fracture Authors Contribution:
e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.892304 Received: 2014.08.23 Accepted: 2014.09.15 Published: 2014.10.17 Cognitive Impairment and 1-Year Outcome in Elderly Patients with Hip Fracture Authors Contribution:
Geriatric Hip Fracture Co-Management. Pannida Wattanapanom, M.D., FACP.
 Geriatric Hip Fracture Co-Management Pannida Wattanapanom, M.D., FACP. An 80 year old man with a hip fracture The General Medicine approach: Medical clearance for surgery Role of Geriatrician Assess caused
Geriatric Hip Fracture Co-Management Pannida Wattanapanom, M.D., FACP. An 80 year old man with a hip fracture The General Medicine approach: Medical clearance for surgery Role of Geriatrician Assess caused
Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER. undisplaced, but as a consequence of the delay in diagnosis displacement occurred SUMMARY
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 23-27 Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER Peterborough District Hospital, SUMMARY Thorpe Road, Peterborough From a series of 825 consecutive admissions with a hip
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 23-27 Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER Peterborough District Hospital, SUMMARY Thorpe Road, Peterborough From a series of 825 consecutive admissions with a hip
Geriatric Hip Fractures: Pearls for the Hospitalist. Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Speakers Bureau-Synthes
 Geriatric Hip Fractures: Pearls for the Hospitalist Jason W. Stoneback, MD Assistant Professor, Univ. of Colorado SOM Director, Orthopedic Trauma and Fracture Surgery Service Director, Orthopedic Inpatient
Geriatric Hip Fractures: Pearls for the Hospitalist Jason W. Stoneback, MD Assistant Professor, Univ. of Colorado SOM Director, Orthopedic Trauma and Fracture Surgery Service Director, Orthopedic Inpatient
National Registration of Hip Fractures in Sweden
 Preface This is the 9th volume of the European Instructional Lectures, which contains more new material, which will be presented during the 1th EFORT Congress in Vienna by distinguished authors from across
Preface This is the 9th volume of the European Instructional Lectures, which contains more new material, which will be presented during the 1th EFORT Congress in Vienna by distinguished authors from across
Predicting discharge location of hip fracture patients; the new discharge of hip fracture patients score
 International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2012) 36:1709 1714 DOI 10.1007/s00264-012-1526-5 ORIGINAL PAPER Predicting discharge location of hip fracture patients; the new discharge of hip fracture patients score
International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2012) 36:1709 1714 DOI 10.1007/s00264-012-1526-5 ORIGINAL PAPER Predicting discharge location of hip fracture patients; the new discharge of hip fracture patients score
Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients
 Original article Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients 1Dr. Vipin Garg, 2 Dr. Anjul Agarwal 1MS Orhtopaedics, Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics,
Original article Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients 1Dr. Vipin Garg, 2 Dr. Anjul Agarwal 1MS Orhtopaedics, Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics,
Effect of age, sex, co morbidities, delay in surgery and complications on outcome in elderly with proximal femur fractures
 2018; 4(3): 498-506 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 498-506 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 27-05-2018 Accepted: 28-06-2018 P Venu Gopala Reddy Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
2018; 4(3): 498-506 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 498-506 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 27-05-2018 Accepted: 28-06-2018 P Venu Gopala Reddy Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Clinical Care Team approach to management of key conditions
 Clinical Care Team approach to management of key conditions BJD Ho Chi Minh City Nov 30, 2012 Kristina Åkesson, MD, PhD Dept of Orthopedics Malmö University Hospital Lund University Malmö, Sweden Multidisciplinary
Clinical Care Team approach to management of key conditions BJD Ho Chi Minh City Nov 30, 2012 Kristina Åkesson, MD, PhD Dept of Orthopedics Malmö University Hospital Lund University Malmö, Sweden Multidisciplinary
Quality of life after primary hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fracture: 6-year follow-up of 185 patients
 Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 000-0 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://wwwtandfonlinecom/loi/iort9 Quality of life after primary hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fracture: -year follow-up
Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 000-0 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://wwwtandfonlinecom/loi/iort9 Quality of life after primary hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fracture: -year follow-up
The Long-term Prognosis of Delirium
 The Long-term Prognosis of Jane McCusker, MD, DrPH, Professor, Epidemiology and Biostatistics, McGill University; Head, Clinical Epidemiology and Community Studies, St. Mary s Hospital, Montreal, QC. Nine
The Long-term Prognosis of Jane McCusker, MD, DrPH, Professor, Epidemiology and Biostatistics, McGill University; Head, Clinical Epidemiology and Community Studies, St. Mary s Hospital, Montreal, QC. Nine
The Risks of Hip Fracture in Older People from Private Homes and Institutions
 Age and Ageing 1996:25:381-385 The Risks of Hip Fracture in Older People from Private Homes and Institutions MEG BUTLER, ROBYN NORTON, TREVOR LEE-JOE, ADA CHENG, A. JOHN CAMPBELL Summary This study aimed
Age and Ageing 1996:25:381-385 The Risks of Hip Fracture in Older People from Private Homes and Institutions MEG BUTLER, ROBYN NORTON, TREVOR LEE-JOE, ADA CHENG, A. JOHN CAMPBELL Summary This study aimed
Appendix E : Evidence table 9 Rehabilitation: Other Key Documents
 Appendix E : Evidence table 9 Rehabilitation: Other Key Documents 1. Cameron et al. Geriatric rehabilitation following following fractures in older people: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment
Appendix E : Evidence table 9 Rehabilitation: Other Key Documents 1. Cameron et al. Geriatric rehabilitation following following fractures in older people: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment
Misdiagnosis of occult hip fracture is more likely in patients with poor mobility and cognitive impairment
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 341-346 ORIGINAL STUDY Misdiagnosis of occult hip fracture is more likely in patients with poor mobility and cognitive impairment Munier HOSSAIN, Syed A. AKBAR, Glynne ANDREW
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 341-346 ORIGINAL STUDY Misdiagnosis of occult hip fracture is more likely in patients with poor mobility and cognitive impairment Munier HOSSAIN, Syed A. AKBAR, Glynne ANDREW
Decision Making and Outcomes of a Hospice Patient Hospitalized With a Hip Fracture
 458 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management Vol. 44 No. 3 September 2012 Brief Report Decision Making and Outcomes of a Hospice Patient Hospitalized With a Hip Fracture Natalie E. Leland, PhD, OTR/L, Joan
458 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management Vol. 44 No. 3 September 2012 Brief Report Decision Making and Outcomes of a Hospice Patient Hospitalized With a Hip Fracture Natalie E. Leland, PhD, OTR/L, Joan
Technical Appendix for Outcome Measures
 Study Overview Technical Appendix for Outcome Measures This is a report on data used, and analyses done, by MPA Healthcare Solutions (MPA, formerly Michael Pine and Associates) for Consumers CHECKBOOK/Center
Study Overview Technical Appendix for Outcome Measures This is a report on data used, and analyses done, by MPA Healthcare Solutions (MPA, formerly Michael Pine and Associates) for Consumers CHECKBOOK/Center
AO Debate Controversies in Management
 46 AODIALOGUE 2 07 Jan Tidermark and Hans Törnqvist AO Debate Controversies in Management Case 1 A 72-year-old active lady (Fig 1). Sustained a displaced femoral neck fracture (Fig 2) after a simple fall.
46 AODIALOGUE 2 07 Jan Tidermark and Hans Törnqvist AO Debate Controversies in Management Case 1 A 72-year-old active lady (Fig 1). Sustained a displaced femoral neck fracture (Fig 2) after a simple fall.
Technique Guide. DHS Blade. For osteoporotic bone.
 Technique Guide DHS Blade. For osteoporotic bone. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 Indications and Contraindications 4 Clinical Cases 5 Surgical Technique Implantation 6 Implant
Technique Guide DHS Blade. For osteoporotic bone. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 Indications and Contraindications 4 Clinical Cases 5 Surgical Technique Implantation 6 Implant
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Pincus D, Ravi B, Wasserstein D. Association between wait time and 30-day mortality in adults undergoing hip fracture surgery. JAMA. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.17606 eappendix
Supplementary Online Content Pincus D, Ravi B, Wasserstein D. Association between wait time and 30-day mortality in adults undergoing hip fracture surgery. JAMA. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.17606 eappendix
Research Report. Key Words: Functional status; Orthopedics, general; Treatment outcomes. Neva J Kirk-Sanchez. Kathryn E Roach
 Research Report Relationship Between Duration of Therapy Services in a Comprehensive Rehabilitation Program and Mobility at Discharge in Patients With Orthopedic Problems Background and Purpose. The purpose
Research Report Relationship Between Duration of Therapy Services in a Comprehensive Rehabilitation Program and Mobility at Discharge in Patients With Orthopedic Problems Background and Purpose. The purpose
A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral
 Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Effect of Ortho-Geriatric Co-Management on Hip Fractures
 Effect of Ortho-Geriatric Co-Management on Hip Fractures Kenji Shigemoto Takeshi Sawaguchi Daigo Sakagoshi Kenichi Goshima Yu Hatsuchi Dept. Orthop. Surg. Toyama Municipal Hospital, Toyama, Japan Purpose
Effect of Ortho-Geriatric Co-Management on Hip Fractures Kenji Shigemoto Takeshi Sawaguchi Daigo Sakagoshi Kenichi Goshima Yu Hatsuchi Dept. Orthop. Surg. Toyama Municipal Hospital, Toyama, Japan Purpose
Age as a Predictor of Functional Outcome in Anoxic Brain Injury
 Age as a Predictor of Functional Outcome in Anoxic Brain Injury Mrugeshkumar K. Shah, MD, MPH, MS Samir Al-Adawi, PhD David T. Burke, MD, MA Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Spaulding
Age as a Predictor of Functional Outcome in Anoxic Brain Injury Mrugeshkumar K. Shah, MD, MPH, MS Samir Al-Adawi, PhD David T. Burke, MD, MA Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Spaulding
Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement
 Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement Subcapital hip fractures The use of THR Historical data RCT outcomes 3 groups of patients Displaced subcapital fractures Which method is best? Arthroplasty
Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement Subcapital hip fractures The use of THR Historical data RCT outcomes 3 groups of patients Displaced subcapital fractures Which method is best? Arthroplasty
Ordinal Data Modeling
 Valen E. Johnson James H. Albert Ordinal Data Modeling With 73 illustrations I ". Springer Contents Preface v 1 Review of Classical and Bayesian Inference 1 1.1 Learning about a binomial proportion 1 1.1.1
Valen E. Johnson James H. Albert Ordinal Data Modeling With 73 illustrations I ". Springer Contents Preface v 1 Review of Classical and Bayesian Inference 1 1.1 Learning about a binomial proportion 1 1.1.1
H ip fractures are common injuries among older people
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Quality effects of operative delay on mortality in hip fracture treatment R Sund, A Liski... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: R Sund, STAKES, P O Box 220,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Quality effects of operative delay on mortality in hip fracture treatment R Sund, A Liski... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: R Sund, STAKES, P O Box 220,
Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study
 Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
The choice of internal fixator for fractures around the femoral trochanter depends on area classification
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3206-1 RESEARCH Open Access The choice of internal fixator for fractures around the femoral trochanter depends on area classification Hiroaki Kijima 1,2*, Shin Yamada 1,2, Natsuo
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3206-1 RESEARCH Open Access The choice of internal fixator for fractures around the femoral trochanter depends on area classification Hiroaki Kijima 1,2*, Shin Yamada 1,2, Natsuo
ISSUES FROM AN ORTHOPEDIC PERSPECTIVE
 ISSUES FROM AN ORTHOPEDIC PERSPECTIVE John Brown, MD The Core Institute Objectives: Understand the common orthopedic problems of the geriatric population. Describe the standard treatment algorithms for
ISSUES FROM AN ORTHOPEDIC PERSPECTIVE John Brown, MD The Core Institute Objectives: Understand the common orthopedic problems of the geriatric population. Describe the standard treatment algorithms for
Femoral Neck (Hip) Fracture
 Patient Information Leaflet Femoral Neck (Hip) Fracture Produced By: Orthopaedic Department September 2013 Review due September 2016 1 If you require this leaflet in another language, large print or another
Patient Information Leaflet Femoral Neck (Hip) Fracture Produced By: Orthopaedic Department September 2013 Review due September 2016 1 If you require this leaflet in another language, large print or another
8. OLDER PEOPLE Falls
 8. OLDER PEOPLE 8.2.1 Falls Falls and the fear of falling can seriously impact on the quality of life of older people. In addition to physical injury, they can lead to social isolation, reductions in mobility
8. OLDER PEOPLE 8.2.1 Falls Falls and the fear of falling can seriously impact on the quality of life of older people. In addition to physical injury, they can lead to social isolation, reductions in mobility
EMU A NEW MODEL OF EMERGENCY CARE FOR THE FRAIL & ELDERLY
 EMU A NEW MODEL OF EMERGENCY CARE FOR THE FRAIL & ELDERLY Geriatrics, General practice, Emergency medicine, Interface medicine SUMMARY An integrated, community emergency service specifically designed for
EMU A NEW MODEL OF EMERGENCY CARE FOR THE FRAIL & ELDERLY Geriatrics, General practice, Emergency medicine, Interface medicine SUMMARY An integrated, community emergency service specifically designed for
Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
 M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME BETWEEN DYNAMIC HIP SCREW AND PROXIMAL FEMORAL NAIL IN SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF PER-TROCHANTERIC FRACTURES Umesh M. Shivanna 1, Girish H. Rudrappa 2 HOW TO CITE
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME BETWEEN DYNAMIC HIP SCREW AND PROXIMAL FEMORAL NAIL IN SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF PER-TROCHANTERIC FRACTURES Umesh M. Shivanna 1, Girish H. Rudrappa 2 HOW TO CITE
How do we combine two treatment arm trials with multiple arms trials in IPD metaanalysis? An Illustration with College Drinking Interventions
 1/29 How do we combine two treatment arm trials with multiple arms trials in IPD metaanalysis? An Illustration with College Drinking Interventions David Huh, PhD 1, Eun-Young Mun, PhD 2, & David C. Atkins,
1/29 How do we combine two treatment arm trials with multiple arms trials in IPD metaanalysis? An Illustration with College Drinking Interventions David Huh, PhD 1, Eun-Young Mun, PhD 2, & David C. Atkins,
R Jagdeesh Kanan* et al. International Journal of Pharmacy & Technology
 ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com NEURAL NETWORK BASED FEATURE ANALYSIS OF MORTALITY RISK BY HEART FAILURE Apurva Waghmare, Neetika Verma, Astha
ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com NEURAL NETWORK BASED FEATURE ANALYSIS OF MORTALITY RISK BY HEART FAILURE Apurva Waghmare, Neetika Verma, Astha
Preoperative Cardiac Evaluation of Patients With Acute Hip Fracture
 An Original Study Preoperative Cardiac Evaluation of Patients With Acute Hip Fracture Jonathan Cluett, MD, Jill Caplan, MD, and Warren Yu, MD Abstract The goals of the present study were to assess if there
An Original Study Preoperative Cardiac Evaluation of Patients With Acute Hip Fracture Jonathan Cluett, MD, Jill Caplan, MD, and Warren Yu, MD Abstract The goals of the present study were to assess if there
Inpatient cost for hip fracture patients managed with an orthogeriatric care model in Singapore
 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 139-144 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2016065 Inpatient cost for hip fracture patients managed with an orthogeriatric care model in Singapore Lester Teong Jin Tan 1, MBBS, MRCS, Seng
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 139-144 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2016065 Inpatient cost for hip fracture patients managed with an orthogeriatric care model in Singapore Lester Teong Jin Tan 1, MBBS, MRCS, Seng
NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE. Measure Information Form Collected For: CMS Outcome Measures (Claims Based)
 Last Updated: Version 4.3 NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Information Form Collected For: CMS Outcome Measures (Claims Based) Measure Set: CMS Mortality Measures Set
Last Updated: Version 4.3 NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Information Form Collected For: CMS Outcome Measures (Claims Based) Measure Set: CMS Mortality Measures Set
Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing and Dynamic Hip Screw in Intertrochanteric Fracture of Femur *
 Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 291-295 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.37053 291 Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing
Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 291-295 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.37053 291 Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing
MAINTAINING GOOD HEALTH FOR OLDER PEOPLE WITH DEMENTIA WHO EXPERIENCE FRACTURED NECK OF FEMUR: REPORT FOR PHASE 2
 MAINTAINING GOOD HEALTH FOR OLDER PEOPLE WITH DEMENTIA WHO EXPERIENCE FRACTURED NECK OF FEMUR: REPORT FOR PHASE 2 Catherine Henderson, Juliette Malley and Martin Knapp 1 Personal Social Services Research
MAINTAINING GOOD HEALTH FOR OLDER PEOPLE WITH DEMENTIA WHO EXPERIENCE FRACTURED NECK OF FEMUR: REPORT FOR PHASE 2 Catherine Henderson, Juliette Malley and Martin Knapp 1 Personal Social Services Research
Effects of age on functional independence measure score gain in stroke patients in kaifukuki rehabilitation ward
 32 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2012) Original Article Effects of age on functional independence measure score gain in stroke patients in kaifukuki rehabilitation ward Makoto
32 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2012) Original Article Effects of age on functional independence measure score gain in stroke patients in kaifukuki rehabilitation ward Makoto
Norwegian health services in comparative perspective. Terje P. Hagen Department of Health Management and Health Economics
 Norwegian health services in comparative perspective Terje P. Hagen Department of Health Management and Health Economics 1) What are the values and the pitfalls of international comparisons? Values Identify
Norwegian health services in comparative perspective Terje P. Hagen Department of Health Management and Health Economics 1) What are the values and the pitfalls of international comparisons? Values Identify
Outcome of Surgery for Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures in Octogenarians
 Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2014 Vol 8 No 1 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1403.014 MV Valera, et al Outcome of Surgery for Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures in Octogenarians MV Valera, MD, L
Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2014 Vol 8 No 1 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1403.014 MV Valera, et al Outcome of Surgery for Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures in Octogenarians MV Valera, MD, L
Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2011 Vol 5 No 1 doi: /MOJ
 doi: 10.57704/MOJ.1103.001 Is there a Significant Difference in Surgery and Outcomes between Unipolar and Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty? A Retrospective Study of a Single Institution in Singapore WL Loo,
doi: 10.57704/MOJ.1103.001 Is there a Significant Difference in Surgery and Outcomes between Unipolar and Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty? A Retrospective Study of a Single Institution in Singapore WL Loo,
)151( COPYRIGHT 2014 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE
 )151( COPYRIGHT 2014 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE In-Hospital Outcomes after Hemiarthroplasty versus Total Hip Arthroplasty for Isolated Femoral Neck Fractures Timothy Voskuijl,
)151( COPYRIGHT 2014 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE In-Hospital Outcomes after Hemiarthroplasty versus Total Hip Arthroplasty for Isolated Femoral Neck Fractures Timothy Voskuijl,
DIRECT SUPERIOR HIP APPROACH IN TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY. Anil Thomas, MD Adult Reconstruction Peachtree Orthopedics Atlanta, GA
 DIRECT SUPERIOR HIP APPROACH IN TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY Anil Thomas, MD Adult Reconstruction Peachtree Orthopedics Atlanta, GA Disclosures None Direct Superior Approach History and development of the approach
DIRECT SUPERIOR HIP APPROACH IN TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY Anil Thomas, MD Adult Reconstruction Peachtree Orthopedics Atlanta, GA Disclosures None Direct Superior Approach History and development of the approach
As the proportion of the elderly in the
 CANCER When the cancer patient is elderly, how do you weigh the risks of surgery? Marguerite Palisoul, MD Dr. Palisoul is Fellow in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Gynecologic
CANCER When the cancer patient is elderly, how do you weigh the risks of surgery? Marguerite Palisoul, MD Dr. Palisoul is Fellow in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Gynecologic
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/38039 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Embden, Daphne van Title: Facts and fiction in hip fracture treatment Issue Date:
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/38039 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Embden, Daphne van Title: Facts and fiction in hip fracture treatment Issue Date:
Comparative Study of Fixation Devices for Intertrochanteric Fractures
 Comparative Study of Fixation Devices for Intertrochanteric Fractures C. Sticlaru * A. Davidescu Politehnica University of Timişoara Politehnica University of Timişoara Timişoara, România Timişoara, România
Comparative Study of Fixation Devices for Intertrochanteric Fractures C. Sticlaru * A. Davidescu Politehnica University of Timişoara Politehnica University of Timişoara Timişoara, România Timişoara, România
INDIVIDUALS who sustain hip fractures exhibit high
 Journal of Gerontology: MEDICAL SCIENCES 2005, Vol. 60A, No. 10, 1285 1291 Copyright 2005 by The Gerontological Society of America Review Article A Critical Review of Literature Regarding the Effectiveness
Journal of Gerontology: MEDICAL SCIENCES 2005, Vol. 60A, No. 10, 1285 1291 Copyright 2005 by The Gerontological Society of America Review Article A Critical Review of Literature Regarding the Effectiveness
Outcomes of elderly hip fracture patients in the Swiss healthcare system
 Published 24 August 2010, doi:10.4414/smw.2010.13086 Cite this as: Outcomes of elderly hip fracture patients in the Swiss healthcare system A survey prior to the implementation of DRGs and prior to the
Published 24 August 2010, doi:10.4414/smw.2010.13086 Cite this as: Outcomes of elderly hip fracture patients in the Swiss healthcare system A survey prior to the implementation of DRGs and prior to the
Traumatic injuries of knee and hip
 Traumatic injuries of knee and hip Martin W. Korn, MD The United States secretary of transportation recently announced that highway deaths had risen from the previously announced 56,000 for 1969 to a new
Traumatic injuries of knee and hip Martin W. Korn, MD The United States secretary of transportation recently announced that highway deaths had risen from the previously announced 56,000 for 1969 to a new
The Relationship between Multimorbidity and Concordant and Discordant Causes of Hospital Readmission at 30 Days and One Year
 The Relationship between Multimorbidity and Concordant and Discordant Causes of Hospital Readmission at 30 Days and One Year Arlene S. Bierman, M.D., M.S Professor, University of Toronto and Scientist,
The Relationship between Multimorbidity and Concordant and Discordant Causes of Hospital Readmission at 30 Days and One Year Arlene S. Bierman, M.D., M.S Professor, University of Toronto and Scientist,
Alcohol Abusing Patients that experience Delirium Tremens during admission for hip fractures experience higher morbidity
 Alcohol Abusing Patients that experience Delirium Tremens during admission for hip fractures experience higher morbidity Cory Couch, MD Regis L. Renard, MD, MS, FACS, FAAOS University of Arkansas of for
Alcohol Abusing Patients that experience Delirium Tremens during admission for hip fractures experience higher morbidity Cory Couch, MD Regis L. Renard, MD, MS, FACS, FAAOS University of Arkansas of for
A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing
 Original Article A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing Jaswinder Pal Singh Walia *, Himanshu Tailor**, H S Mann ***,
Original Article A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing Jaswinder Pal Singh Walia *, Himanshu Tailor**, H S Mann ***,
NCAP NATIONAL CARDIAC AUDIT PROGR AMME NATIONAL HEART FAILURE AUDIT 2016/17 SUMMARY REPORT
 NCAP NATIONAL CARDIAC AUDIT PROGR AMME NATIONAL HEART FAILURE AUDIT 2016/17 SUMMARY REPORT CONTENTS PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH HEART FAILURE...4 Demographics... 4 Trends in Symptoms... 4 Causes and Comorbidities
NCAP NATIONAL CARDIAC AUDIT PROGR AMME NATIONAL HEART FAILURE AUDIT 2016/17 SUMMARY REPORT CONTENTS PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH HEART FAILURE...4 Demographics... 4 Trends in Symptoms... 4 Causes and Comorbidities
Ankle fractures are one of
 Elevated Risks of Ankle Fracture Surgery in Patients With Diabetes Nelson F. SooHoo, MD, Lucie Krenek, MD, Michael Eagan, MD, and David S. Zingmond, MD, PhD Ankle fractures are one of the most common types
Elevated Risks of Ankle Fracture Surgery in Patients With Diabetes Nelson F. SooHoo, MD, Lucie Krenek, MD, Michael Eagan, MD, and David S. Zingmond, MD, PhD Ankle fractures are one of the most common types
Prevention and Management of Hip Fracture in Older People
 Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network 56 Prevention and Management of Hip Fracture in Older People A national clinical guideline 1 Introduction 1 2 Prevention of hip fracture 4 3 Pre-hospital management
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network 56 Prevention and Management of Hip Fracture in Older People A national clinical guideline 1 Introduction 1 2 Prevention of hip fracture 4 3 Pre-hospital management
Bayesian Approach for Neural Networks Review and Case Studies. Abstract
 Neural Networks, 4(3):7-24, April 2 (Invited article) Bayesian Approach for Neural Networks Review and Case Studies Jouko Lampinen and Aki Vehtari Laboratory of Computational Engineering, Helsinki University
Neural Networks, 4(3):7-24, April 2 (Invited article) Bayesian Approach for Neural Networks Review and Case Studies Jouko Lampinen and Aki Vehtari Laboratory of Computational Engineering, Helsinki University
Morbidity and Mortality in Jeju Residents over 50-Years of Age with Hip Fracture with Mean 6-Year Follow-Up: A Prospective Cohort Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Musculoskeletal Disorders http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.7.1089 J Korean Med Sci 2013; 28: 1089-1094 Morbidity and Mortality in Jeju Residents over 50-Years of Age with Hip Fracture
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Musculoskeletal Disorders http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.7.1089 J Korean Med Sci 2013; 28: 1089-1094 Morbidity and Mortality in Jeju Residents over 50-Years of Age with Hip Fracture
How to prevent early & unplanned hospital readmission?
 How to prevent early & unplanned hospital readmission? - after subacute care K. Singler 21th September 2017 CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURE I have no potential conflict of interest to report. K. Singler
How to prevent early & unplanned hospital readmission? - after subacute care K. Singler 21th September 2017 CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURE I have no potential conflict of interest to report. K. Singler
Internal fixation of femoral neck fractures
 Acta Orthop Scand 55, 423-429, 1984 Internal fixation of femoral neck fractures Compression screw compared with nail plate fixation In a prospective, randomized study of femoral neck fracture operations,
Acta Orthop Scand 55, 423-429, 1984 Internal fixation of femoral neck fractures Compression screw compared with nail plate fixation In a prospective, randomized study of femoral neck fracture operations,
TOTAL HIP AND KNEE REPLACEMENTS. FISCAL YEAR 2002 DATA July 1, 2001 through June 30, 2002 TECHNICAL NOTES
 TOTAL HIP AND KNEE REPLACEMENTS FISCAL YEAR 2002 DATA July 1, 2001 through June 30, 2002 TECHNICAL NOTES The Pennsylvania Health Care Cost Containment Council April 2005 Preface This document serves as
TOTAL HIP AND KNEE REPLACEMENTS FISCAL YEAR 2002 DATA July 1, 2001 through June 30, 2002 TECHNICAL NOTES The Pennsylvania Health Care Cost Containment Council April 2005 Preface This document serves as
In each hospital-year, we calculated a 30-day unplanned. readmission rate among patients who survived at least 30 days
 Romley JA, Goldman DP, Sood N. US hospitals experienced substantial productivity growth during 2002 11. Health Aff (Millwood). 2015;34(3). Published online February 11, 2015. Appendix Adjusting hospital
Romley JA, Goldman DP, Sood N. US hospitals experienced substantial productivity growth during 2002 11. Health Aff (Millwood). 2015;34(3). Published online February 11, 2015. Appendix Adjusting hospital
The Mechanical Properties Of Fixing Greater Trochanter Or Lesser Trochanter In Complex Four Part Intertrochanteric Fractures
 The Mechanical Properties Of Fixing Greater Trochanter Or Lesser Trochanter In Complex Four Part Intertrochanteric Fractures Chih-Hui Chen 1, Kui-Chou Huang 2, Cheng-Kung Cheng, PhD 3, Hung-Chan Kao 4.
The Mechanical Properties Of Fixing Greater Trochanter Or Lesser Trochanter In Complex Four Part Intertrochanteric Fractures Chih-Hui Chen 1, Kui-Chou Huang 2, Cheng-Kung Cheng, PhD 3, Hung-Chan Kao 4.
Healthcare, hospitals and the challenges of an ageing population
 Healthcare, hospitals and the challenges of an ageing population Prof David Oliver Vice President, RCP, London Past President, British Geriatrics Society Senior Visiting Fellow, King s Fund Consultant
Healthcare, hospitals and the challenges of an ageing population Prof David Oliver Vice President, RCP, London Past President, British Geriatrics Society Senior Visiting Fellow, King s Fund Consultant
Outcome Following Surgery for Proximal Femur Fractures in Centenarians
 American Research Journal of Orthopedics and Traumatology (ARJOT), 7 Pages Research Article Outcome Following Surgery for Proximal Femur Fractures in Centenarians Donald Buchanan 1, Neil Shastri-Hurst
American Research Journal of Orthopedics and Traumatology (ARJOT), 7 Pages Research Article Outcome Following Surgery for Proximal Femur Fractures in Centenarians Donald Buchanan 1, Neil Shastri-Hurst
Sanjit R. Konda, MD; Hesham Saleh, BS; Jordan Gales, BS; Loveita Raymond, MD; Kenneth A. Egol, MD
 The Capacity of the Score for Trauma Triage in the Geriatric and Middle Aged (STTGMA) to Predict Mortality Up to One Year Following Index Hospitalization Sanjit R. Konda, MD; Hesham Saleh, BS; Jordan Gales,
The Capacity of the Score for Trauma Triage in the Geriatric and Middle Aged (STTGMA) to Predict Mortality Up to One Year Following Index Hospitalization Sanjit R. Konda, MD; Hesham Saleh, BS; Jordan Gales,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. INTER TROCHANTERIC # NECK FEMUR FIXATION WITH TFN 250 CASES. Prasad Vijaykumar Joshi, Chandrashekar Yadav.
 INTER TROCHANTERIC # NECK FEMUR FIXATION WITH TFN 250 CASES. Prasad Vijaykumar Joshi, Chandrashekar Yadav. 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Orthopaedics, Joshi Hospital Pvt. Ltd. Phaltan, Maharashtra.
INTER TROCHANTERIC # NECK FEMUR FIXATION WITH TFN 250 CASES. Prasad Vijaykumar Joshi, Chandrashekar Yadav. 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Orthopaedics, Joshi Hospital Pvt. Ltd. Phaltan, Maharashtra.
Bundled Payments in Orthopedic Trauma: How to Succeed
 SE 87 Bundled Payments in Orthopedic Trauma: How to Succeed Sanjit R. Konda MD Ariana Lott BA Kurtis Carlock BS Kenneth A. Egol MD Department of Orthopedic Surgery NYU Langone Orthopedic Hospital, New
SE 87 Bundled Payments in Orthopedic Trauma: How to Succeed Sanjit R. Konda MD Ariana Lott BA Kurtis Carlock BS Kenneth A. Egol MD Department of Orthopedic Surgery NYU Langone Orthopedic Hospital, New
Study on the Efficiency of Fractures Treated With Proximal Femoral Locking Compression Plate
 Original Research Article Study on the Efficiency of Fractures Treated With Proximal Femoral Locking Compression Plate Ravi G.O 1, Shaik Hussain Saheb * 2. 1 Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedics,
Original Research Article Study on the Efficiency of Fractures Treated With Proximal Femoral Locking Compression Plate Ravi G.O 1, Shaik Hussain Saheb * 2. 1 Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedics,
Bayesian Logistic Regression Modelling via Markov Chain Monte Carlo Algorithm
 Journal of Social and Development Sciences Vol. 4, No. 4, pp. 93-97, Apr 203 (ISSN 222-52) Bayesian Logistic Regression Modelling via Markov Chain Monte Carlo Algorithm Henry De-Graft Acquah University
Journal of Social and Development Sciences Vol. 4, No. 4, pp. 93-97, Apr 203 (ISSN 222-52) Bayesian Logistic Regression Modelling via Markov Chain Monte Carlo Algorithm Henry De-Graft Acquah University
Evolutions in Geriatric Fracture Care Preparing for the Silver Tsunami
 Evolutions in Geriatric Fracture Care Preparing for the Silver Tsunami James Holstine, DO Medical Director for the Joint Replacement Center, Geriatric Fracture Center, Orthopedic Surgeon PeaceHealth Whatcom
Evolutions in Geriatric Fracture Care Preparing for the Silver Tsunami James Holstine, DO Medical Director for the Joint Replacement Center, Geriatric Fracture Center, Orthopedic Surgeon PeaceHealth Whatcom
Title. Lau, TW; Fang, CX; Leung, FKL. Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehabilitation, 2013, v. 4 n. 1, p Citation.
 Title The Effectiveness of a Geriatric Hip Fracture Clinical Pathway in Reducing Hospital and Rehabilitation Length of Stay and Improving Short-Term Mortality Rates Author(s) Lau, TW; Fang, CX; Leung,
Title The Effectiveness of a Geriatric Hip Fracture Clinical Pathway in Reducing Hospital and Rehabilitation Length of Stay and Improving Short-Term Mortality Rates Author(s) Lau, TW; Fang, CX; Leung,
Quality improvement for patients with hip fracture: experience from a multi-site audit
 QUALITY IMPROVEMENT REPORT Quality improvement for patients with hip fracture: experience from a multi-site audit C Freeman, C Todd, C Camilleri-Ferrante, C Laxton, P Murrell, C R Palmer, M Parker, B Payne,
QUALITY IMPROVEMENT REPORT Quality improvement for patients with hip fracture: experience from a multi-site audit C Freeman, C Todd, C Camilleri-Ferrante, C Laxton, P Murrell, C R Palmer, M Parker, B Payne,
Costs of internal fixation and arthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: a randomized study of 68 patients.
 Costs of internal fixation and arthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: a randomized study of 68 patients. Rogmark, Cecilia; Carlsson, Åke; Johnell, Olof; Sembo, Ingemar Published in: Acta Orthopaedica
Costs of internal fixation and arthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: a randomized study of 68 patients. Rogmark, Cecilia; Carlsson, Åke; Johnell, Olof; Sembo, Ingemar Published in: Acta Orthopaedica
The relationship between quality of care and hospital costs in Europe. Unto Häkkinen and EuroDRG teams in Finland, France, Germany, Spain and Sweden
 The relationship between quality of care and hospital costs in Europe Unto Häkkinen and EuroDRG teams in Finland, France, Germany, Spain and Sweden 1 Aims and data Motivation: Does introduction of cost
The relationship between quality of care and hospital costs in Europe Unto Häkkinen and EuroDRG teams in Finland, France, Germany, Spain and Sweden 1 Aims and data Motivation: Does introduction of cost
The Clinical Frailty Scale predicts inpatient mortality in older hospitalised patients with idiopathic Parkinson s disease.
 J R Coll Physicians Edinb 2018; 48: 103 7 doi: 10.4997/JRCPE.2018.201 PAPER The Clinical Frailty Scale predicts inpatient mortality in older hospitalised patients with idiopathic Parkinson s disease Clinical
J R Coll Physicians Edinb 2018; 48: 103 7 doi: 10.4997/JRCPE.2018.201 PAPER The Clinical Frailty Scale predicts inpatient mortality in older hospitalised patients with idiopathic Parkinson s disease Clinical
Hip Fractures. Anatomy. Causes. Symptoms
 Hip Fractures A hip fracture is a break in the upper quarter of the femur (thigh) bone. The extent of the break depends on the forces that are involved. The type of surgery used to treat a hip fracture
Hip Fractures A hip fracture is a break in the upper quarter of the femur (thigh) bone. The extent of the break depends on the forces that are involved. The type of surgery used to treat a hip fracture
Quality Outcomes and Financial Benefits of Nutrition Intervention. Tracy R. Smith, PhD, RD, LD Senior Clinical Manager, Abbott Nutrition
 Quality Outcomes and Financial Benefits of Nutrition Intervention Tracy R. Smith, PhD, RD, LD Senior Clinical Manager, Abbott Nutrition January 28, 2016 SHIFTING MARKET DYNAMICS PROVIDE AN OPPORTUNITY
Quality Outcomes and Financial Benefits of Nutrition Intervention Tracy R. Smith, PhD, RD, LD Senior Clinical Manager, Abbott Nutrition January 28, 2016 SHIFTING MARKET DYNAMICS PROVIDE AN OPPORTUNITY
Hip arthroplasty after failed fixation of trochanteric and subtrochanteric
 Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (5): 493 498 493 Hip arthroplasty after failed fixation of trochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures A cohort study with 5 11 year follow-up of 88 consecutive patients Anders
Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (5): 493 498 493 Hip arthroplasty after failed fixation of trochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures A cohort study with 5 11 year follow-up of 88 consecutive patients Anders
Yoshihisa Fujita 1*, Kumi Shimada 1, Tomohiko Sato 1, Masahiko Akatsu 1, Koichi Nishikawa 2, Atsuko Kanno 3 and Toshitake Aizawa 3
 Fujita et al. JA Clinical Reports (2018) 4:36 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40981-018-0172-3 CLINICAL RESEARCH LETTER Open Access In-hospital mortality does not increase in patients aged over 85 years after
Fujita et al. JA Clinical Reports (2018) 4:36 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40981-018-0172-3 CLINICAL RESEARCH LETTER Open Access In-hospital mortality does not increase in patients aged over 85 years after
DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP. Dr Károly Fekete
 DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP Dr Károly Fekete 1 OUTLINE Epidemiology Incidence Anatomy Patient s examination, clinical symptons Diagnosis Classification Management Special complications 2 EPIDEMIOLOGY,
DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP Dr Károly Fekete 1 OUTLINE Epidemiology Incidence Anatomy Patient s examination, clinical symptons Diagnosis Classification Management Special complications 2 EPIDEMIOLOGY,
The effect of early surgery after hip fracture on 1-year mortality
 Colais et al. BMC Geriatrics (2015) 15:141 DOI 10.1186/s12877-015-0140-y RESEARCH ARTICLE The effect of early surgery after hip fracture on 1-year mortality Paola Colais 1*, Mirko Di Martino 1, Danilo
Colais et al. BMC Geriatrics (2015) 15:141 DOI 10.1186/s12877-015-0140-y RESEARCH ARTICLE The effect of early surgery after hip fracture on 1-year mortality Paola Colais 1*, Mirko Di Martino 1, Danilo
Anaemia impedes functional mobility after hip fracture surgery
 Age and Ageing 2008; 37: 173 178 doi:10.1093/ageing/afm161 The Author 2008. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Geriatrics Society. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please
Age and Ageing 2008; 37: 173 178 doi:10.1093/ageing/afm161 The Author 2008. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Geriatrics Society. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please
