Title. Lau, TW; Fang, CX; Leung, FKL. Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehabilitation, 2013, v. 4 n. 1, p Citation.
|
|
|
- Lewis Blankenship
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Title The Effectiveness of a Geriatric Hip Fracture Clinical Pathway in Reducing Hospital and Rehabilitation Length of Stay and Improving Short-Term Mortality Rates Author(s) Lau, TW; Fang, CX; Leung, FKL Citation Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehabilitation,, v. n., p. - Issued Date URL Rights Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation. Copyright Sage Publications, Inc.; This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives.0 International License.
2 Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation The Effectiveness of Geriatric Hip Fracture Clinical Pathway in Reducing Acute and Rehabilitation Hospital Stay with Improved Short Term Mortality Rates Journal: Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Manuscript ID: GOS--00.R Manuscript Type: Original Manuscript Keywords: Geriatric Trauma, Systems of Care, Trauma surgery, Fragility Fractures, Geriatric medicine Background: A geriatric hip fracture clinical pathway, led by an orthopedic surgeon, was developed in 0. This clinical pathway team is a multidisciplinary team consists of surgeons, physicians, anesthetists, nurses, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, medical social workers, dieticians as well as voluntary support groups. Methods: From early 0 onwards, all isolated acute geriatric hip fractures, age over, were included. During the whole in-patient treatment, all relevant data were captured prospectively. The data in 0, before the implementation of the clinical pathway, were collected retrospectively through computer record system. A study of the length of stay in acute and rehabilitation hospital and also the short term mortality rate is carried out to compare the difference before and after the implementation of the pathway. Abstract: Results: From 0 onwards, we treated more than 00 hip fracture patients. After the implementation of the pathway, the pre-operative length of stay was markedly shortened by days, from an average of. days in 0 to. days in, which is statistically significant (p<0.0). The post-op length of stay and the overall acute hospital length of stay also showed improvement with statistical significance. The length of stay in rehabilitation hospital is also significantly shorter in the last four years. Despite we operated more and more hip fractures with increasing age and increasing number of co-morbidities each year, the in-patient mortality rate showed a gradual decrease from.% in 0 to.% in 0. The 0 days mortality rate also showed a decrease from.% in 0 to.% in 0. Conclusion: Geriatric hip fracture clinical pathway is an excellent approach to the geriatric hip fracture service. The most significant improvement is the dramatic shortening of hospital stay. Our success in the last years has
3 Page of Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation proven its value and sustainability.
4 Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Page of The Effectiveness of Geriatric Hip Fracture Clinical Pathway in Reducing Acute and Rehabilitation Hospital Stay with Improved Short Term Mortality Rates Abstract: Background: A geriatric hip fracture clinical pathway, led by an orthopedic surgeon, was developed in 0. This clinical pathway team is a multidisciplinary team consists of surgeons, physicians, anesthetists, nurses, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, medical social workers, dieticians as well as voluntary support groups. Methods: From early 0 onwards, all isolated acute geriatric hip fractures, age over, were included. During the whole in-patient treatment, all relevant data were captured prospectively. The data in 0, before the implementation of the clinical pathway, were collected retrospectively through computer record system. A study of the length of stay in acute and rehabilitation hospital and also the short term mortality rate is carried out to compare the difference before and after the implementation of the pathway. Results: From 0 onwards, we treated more than 00 hip fracture patients. After the implementation of the pathway, the pre-operative length of stay was markedly shortened by days, from an average of. days in 0 to. days in, which is statistically significant (p<0.0). The post-op length of stay and the overall acute hospital length of stay also showed
5 Page of Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation improvement with statistical significance. The length of stay in rehabilitation hospital is also significantly shorter in the last four years. Despite we operated more and more hip fractures with increasing age and increasing number of co-morbidities each year, the in-patient mortality rate showed a gradual decrease from.% in 0 to.% in 0. The 0 days mortality rate also showed a decrease from.% in 0 to.% in 0. Conclusion: Geriatric hip fracture clinical pathway is an excellent approach to the geriatric hip fracture service. The most significant improvement is the dramatic shortening of hospital stay. Our success in the last years has proven its value and sustainability.
6 Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Page of Keywords: Geriatric hip fractures; Clinical pathway; Multidisciplinary; Length of hospital stay; Mortality rate
7 Page of Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Introduction: Geriatric hip fracture is probably one of the most common orthopedic problems. As the number of elderly population increases, the annual number of hip fractures globally is expected to exceed million in the next 0-0 years. In United Kingdom, the bed occupancy rate was more than. million days, which represent % of total orthopedic beds. Last year, in Hong Kong, in a population of million people, over 00 hip fractures were operated. The trend is increasing in the last years, which is also reflected in other parts of the world. Furthermore, these geriatric hip fractures are associated with many co-morbidities. Despite the fact that aggressive treatment is commenced during the pre-operative, peri-operative and postoperative period, morbidities and complications rate are still high comparing to other common surgeries. Most important of all, the mortality rate is relatively high. The 0 days mortality is around 0% and the year mortality rate can be up to 0%. Geriatric hip fracture is an increasing burden to our medical system which requires increasing health utilization in the first year of fracture. In our medical care system, our patients are operated in acute hospital and then transferred to rehabilitation hospital before they are discharged home. There were literatures supporting the use of clinical pathway to shorten the hospital stay and thus improve the clinical outcomes -. However, many of these clinical pathways only focused on the acute hospital stay and ignore the rehabilitation hospitals. These clinical pathways may not be able to apply to our medical system where the patients need to stay in the rehabilitation hospital before discharging back to home. Therefore, we feel that there is a need to develop a unique pathway tailor-made for the local medical system needs.
8 Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Page of Model of Care: Since early 0, we have started our geriatric hip fracture critical clinical pathway. Generally for hip fracture patients coming into our hospital, they will be admitted to the orthopedic ward in our hospital, which is a level I trauma centre having over one thousand acute beds. During the stay in admission ward, pre-operative work up and anesthetist assessment will be done. After the operation, they will be transferred back to the ward for post-operative care. When the patients are stable, usually in to days time, they will be transferred to a rehabilitation hospital. The Geriatric hip fracture clinical pathway team was first developed by a team of medical staff in the acute hospital, led by an orthopedic surgeon, named as the clinical champion. He/she is the one who develops and coordinates the running of the pathway. A case manager, who is a nurse, will be responsible for the monitoring of the whole pathway running on a day to day basis. In order to achieve a smoother and shorter pre-operative stay, the whole process of preoperative assessment is re-defined. It started with the communication with the emergency department. When a geriatric hip fracture patient is admitted, apart from the hip x-ray, a chest x-ray and a pelvic x-ray should be available before he/she is transferred to the orthopedic admission ward. Once the patient is in the ward, a general pre-operative work-up will be done immediately in a -hour basis so that the patient can be ready to be seen by anesthetist the next day morning. The pre-operative work-up includes complete blood count, liver and renal
9 Page of Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation function test, clotting profile, cross-matching of blood group and -leads electrocardiogram as well. Our pathway team, led by the clinical champion and the case manager, also includes surgeons and nurses that are responsible for the daily routine in the acute and rehabilitation ward. The other team members include a cardiologist, a respiratory physician and a senior anesthetist who are responsible for the guidelines of the indications of pre-operative cardiac, respiratory and other medical consultations. Close collaboration with cardiologist is a crucial step in eliminating last minute operation cancellation. After several meetings and discussions with several dedicated cardiologists and anesthetists, a consensus was made. Whenever there is any active cardiac problems, for example, active heart failure, uncontrolled arrhythmias, recent myocardial infarction, and/or previously undiagnosed severe ejection systolic murmur, a consultation will be arranged with the cardiologist the next day morning together with a -leads electrocardiogram faxed prior to the consultation. A proper pre-operative cardiac assessment, usually including an echocardiogram, will be performed. Senior representatives from allied health worker group include physiotherapists, occupational therapists, medical social workers, community nurse units and voluntary support groups are also involved in the development and running of the pathway. Besides the usual daily routine of the therapist in taking care of the patients, they also define which assessment scores, Mini- Mental State Examination (MMSE) and Modified Barthel Index (MBI), are used for the monitoring of the rehabilitation potential and the progress during the hospital stay. Social
10 Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Page of problem is also one of the difficult aspects in patient discharge. The medical social workers redefine their duty in geriatric hip fracture care by assessing all admitted patients and make a discharge plan with the patients and their family in the early phase of management. Outpatient therapists and community nurse units also extend their services to the post-discharge period in order to provide a better and comprehensive rehabilitation. During the stay in rehabilitation hospital, standard protocol of post-operative management helps to speed-up the rehabilitation process. During the first week, the patients are encouraged to mobilize in the ward with the help from the therapists. The wounds are inspected once they are transferred to the rehabilitation ward. Stitches are removed on day fourteen after operation. Pain control is very important and regular analgesics are usually prescribed. In the second week, x-ray will be taken to check for early problem. The physiotherapists will focus on strengthening of muscles and walking stability. The occupational therapists will look for potential home modifications and start planning early. During the third week, the patients should be ready to be discharged home or nursing home. The care providers or families are educated for home exercise. Any medication that has been changed during the hospital stay will be finalized. (Fig. ). Methodology: The clinical pathway first started running in February 0. All isolated hip fractures with age greater than were recruited into the clinical pathway. Prospective collection of demographics, including age, sex, original placement where the patients live before admission,
11 Page of Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation history of previous fractures, pre-morbid mobility and walking aids. Other data including number of co-morbidities, laterality of fractures, classification of fractures, surgery types, American Society of Anesthesiology (ASA) score, surgeons rank, pre-operative hemoglobin level, post-operative requirement of blood transfusion, number of days before patients start walking, number of days when drains are removed, financial assistance requirements and also re-arrangement of placement are all collected from 0 till the end of 0. The co-morbidities are defined by the previously diagnosed problems when the patient is admitted. These co-morbidities include six main categories, cardiovascular, respiratory, neurological, endocrine, psychiatric problems and neoplasm. Common cardiovascular problems include ischemic heart disease, history of myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure and arrhythmias. Respiratory problems include chronic obstructive airway disease, pulmonary tuberculosis and asthma. Neurological problems include history of cerebral vascular accident, transient ischemic attack, and Parkinsonism. The most common endocrine problems include diabetes and thyroid disease. Psychiatric problems include dementia, schizophrenia and other forms of psychosis. There are some other problems like renal impairment, chronic renal failure and liver problems which are also considered as co-morbidities. Pathological fractures, multiple fractures, and hip fractures that were transferred from other specialty were excluded from this pathway. The pre-operative, post-operative length of acute hospital stay and also the rehabilitation hospital stay were also recorded. Wound complications and medical complications are recorded. The in-patient mortality rate and the 0-days mortality rate were used as the clinical outcomes to evaluate the effectiveness of this pathway.
12 Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Page 0 of The in-patient mortality is defined as the patient s death occurs either in the acute or the rehabilitation hospital stay. The 0-days mortality is defined as the patient s death occurs within 0 days after his/her admission to the acute hospital, regardless of the fact that whether he/she is staying in or discharged from the hospital system. The data from 0 were then collected retrospectively through the computer medical system. These two sets of data were then compared and analyzed. Results: Demographics: From 0 till 0, we treated hip fracture patients. The female to male ratio was kept relatively constant at around.: each year. The average age was from in 0 increasing to in 0. The youngest age of the hip fracture was which corresponded to the lowest limit of our hip fracture clinical pathway. The oldest patient operated was a female patient age 0. Regarding the number of hip fractures operated each year, there was a steady increase annually, reaching more than 00 cases a year in 0. Among all these fractures, (0%) were neck of femur fractures, (%) were intertrochanteric fractures and (%) were subtrochanteric fractures. (%) patients received cannulated screws fixation. (%) patients received hemiarthroplasty replacement. (%) patients had dynamic hip screws done and (%) patients received cephalomedullary nail fixation. Among these patients, majority of them has ASA score and, comprising % and % respectively (Table ). The number of co-morbidities also increased gradually in last years (Fig.
13 Page of Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation ). Moreover, % of them had more than co-morbidities when they were admitted. The three most common problems were hypertension, diabetes and dementia. Regarding the community we serve, about 0% of these hip fractures lived in their home and the remaining 0% were already institutionalized before admission. In 0, when we did not have this clinical pathway, we have treated hip fracture patients. The average age was. All other parameters including male to female ratio, hip fracture types, number of co-morbidities and ASA score were comparable to those of the following years. However, one point worth noticing is that there was a three times increase in the use of cephalomedullary device for fixing the intertrochanteric fractures from 0 to 0 despite the fracture patterns were comparable in these periods. Length of hospital stay: After the implementation of the clinical pathway since 0, there was a mark decrease in the pre-operative length of stay as well as the total length of stay in acute hospital. Besides, the length of stay in rehabilitation hospital also markedly decreased. In year 0, the average preoperative length of stay was. days. It was dramatically decreased to an average of. days in 0. Upon the subsequent years with the clinical pathway fully operational, there was a steady and gradual improvement of the pre-operative length of stay. Our most recent data showed that the average pre-operative length of stay was. days in 0. This improvement was significant when compared with that of the year 0 (p<0.0). The post-op length of stay also showed a decrease from. days in 0 to. days in 0. This improvement was also statistically significant (p<0.0). Since both pre-operative and post-operative stay were 0
14 Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Page of significantly shorter, the total length of stay also showed a significant improvement from.0 days in 0 to. days in 0 (Fig. ). Although there was a gradual increase in the number of geriatric hip fractures each year, a total of 0% reduction in the total acute hospital stay demonstrated the tremendous effectiveness of the clinical pathway. One of the uniqueness of our clinical pathway when comparing with the other pathways in the world - is that ours starts from the emergency department of the acute hospital when the patient is admitted, and continues all the way to another rehabilitation hospital until the patient is discharged home. This ensures a smooth running of the whole chain of care. Our statistics showed that in 0, the average length of stay in rehabilitation hospital was 0 days. This was greatly reduced to. days in 0 (Fig. ). The decrease was statistically significant as well (p<0.0). The reduction was more than 0%. Despite this dramatic improvement, over 0% of the patients were still able to be discharged back to their original placements during the study period. Complication rates: Wound infection rate is one of the parameters we monitor after the implementation of the clinical pathway. There is no obvious improvement in the infection rate in both fixation group and hemiarthroplasty group. The fixation group includes cannulated screws fixation, dynamic hip screws and cephalomedullary devices. The hemiarthroplasty group includes bipolar hemiarthroplasty, cemented and non-cemented ones and also Austin Moore hemiarthroplasty. In fact, there is a slight increase in the infection rate in the data of 0 (Table ). Postoperative pneumonia was another parameter we monitored. Post-operative pneumonia is
15 Page of Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation defined as the patients with clinical signs of chest infection together with positive sputum culture. There is a slight decrease in the rate of pneumonia (Table ). Mortality rates: Our results showed that despite we operated more and more hip fractures with advancing age and increasing number of co-morbidities every year, the inpatient mortality rate showed a decrease from.% in 0 to.% in 0 (Fig.). The 0-day-mortality rate also showed a decrease from.% in 0 to.% in 0 (Fig. ). However, the decrease in both mortality rates showed no statistical significance which is likely due to the relative small number of deceased patients. Discussion: Geriatric hip fractures used to be less attended in the old days because these patients were considered as less urgent when compared to the younger patients. These fractures are also traditionally considered simple fracture to treat. Therefore they were considered to be fractures that were suitable for beginners to learn. However, this traditional approach was changing rapidly in the last decade. More and more evidence showed that these osteoporotic fractures should be managed with aggressive medical and surgical support which achieved excellent results with good clinical outcomes. Among all the different stages during the hospital stay, the pre-operative length of stay is one of the most important factors that affect clinical outcomes. In many clinical studies, the shorter the pre-operative waiting time, the fewer the complications and the lower the mortality rate
16 Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Page of Therefore, the significant reduction of the pre-operative waiting time is considered one of the major accomplishments in the clinical pathway. Besides, the post-operative length of stay and thus the total length of stay were both improved accordingly. Geriatric trauma service cannot achieve success without the support of the hospital administration itself. The availability of a dedicated day-time trauma operating room is certainly a big help to the efficient running of the whole management process. This trauma list caters for all patients that need fracture care. There are several advantages of a day-time trauma list that contribute to the significant reduction in hospital stay. First is the flexibility of the trauma cases allocated for operation. When there is a dedicated day time list caters for trauma only, the more difficult cases, in terms of anesthesia or surgical technical difficulty, can be allocated to the time when more experienced surgeons or anesthetists are available. Second is the availability of the operating room staff. The operating room for trauma cases will have a team of nurses and supporting staff always ready for trauma care and fracture fixation. This helps to shorten the operating time and the transit time between cases. Third is the readiness of the anesthetists for geriatric trauma patients. These anesthetists, when they are allocated for the trauma list, are prepared psychologically and knowledge wise to take care of the fragile and patients approaching extreme age. Finally is the group of the dedicated trauma surgeons in the trauma list. These surgeons understand the philosophy of the geriatric hip fracture care. Their common goal is to help these patients safely and efficiently, managing their hip fractures with the appropriate implants or prosthesis. All the XR of the hip fractures are audited weekly with the senior surgeons. All these factors work together resulting in a significant decrease in the
17 Page of Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation hospital length of stay because of much improved efficacy. The pain and suffering caused by the unfixed unstable fracture is reduced and the complications due to prolong immobilization are also kept to the minimum. In rehabilitation hospital, rehabilitation doctors, nurses, therapists and medical social workers all work together to speed up the whole rehabilitation process. Early active walking exercise and post-discharge rehabilitation by community nurses and therapists play a great role in shortening the need of in-patient treatment. The overall shortened rehabilitation hospital stay reflects the effectiveness and cooperation with this multidisciplinary approach 0. Behind all the managing process in the clinical pathway, it is led by an experience clinical champion, whom should be familiar with all the details of managing the geriatric fractures and the related issues. He is responsible for the development of the prototype of the pathway, the recruitment of the related clinical staff, the coordination of the pathway and negotiation with the stake holders, especially the hospital administration. A case manager, who is preferably a full-time nurse, is a major key to success of the smooth running of the pathway. He/she is usually responsible for not just one pathway in the hospital but may be few. His/her main duty is daily monitoring and the collection of the data. He/she is also the one who communicates most with all the different clinical departments to understand the needs and the difficulties. If there is any problem arises in any part of the pathway, the case manager is the first to know. The problem should then be solved as soon as possible, usually through the communication and discussion with the clinical champion, case manager and the involved clinical department.
18 Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Page of Regular yearly audit of the performance and the clinical outcomes is another important aspect leading to the early success and the sustainability of this clinical pathway for the last five years. All the data were analyzed and presented during the half yearly meeting. Everyone has the opportunity to review what has been achieved and what was not done well. Any setback of any clinical outcome is discussed during the meeting, even to the case by case level, in order to seek for the solutions and revision of the clinical pathway if needed. Extra resources in the form of better communication, dedicated altitude and eliminate inadvertent wastage have achieved excellent clinical outcomes in the last years in terms of short term mortality rate. Our 0 days mortality rate were generally much lower than the commonly quoted figures, ranging from.% to % -. It probably just reflected the difference in general health of the local population. Although there is no statistical significance in the mortality rate before and after the clinical pathway, it definitely showed a general decreasing trend. Most important is that despite we operate more and more hip fractures with increasing number of co-morbidities, the mortality rate was kept low. Moreover, it also proved that despite the patients were operated as short as days, these patients were operated in a safe and well prepared clinical situation. The shortened hospital length of stay is not a result of administrative pressure but a better preparation and coordination of all the involved clinical staff. Yet, the substantial shorter length of stay in both acute and rehabilitation hospitals can lead to significant decrease in cost of care. Conclusion
19 Page of Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Our geriatric hip fracture clinical pathway was introduced years ago to improve our fragility fracture service as well as to face the ever growing challenge from the elderly population. This was proven to be successful in terms of both clinical and administrative point of view. The principle of using a clinical pathway to provide multidisciplinary approach to the geriatric fracture problem is also proven to be very effective as well.
20 Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Page of References:. Parker M, Johansen A. Hip fracture. BMJ 0;():-0.. Royal College of Physicians. Osteoporosis. Clinical Guidelines for prevention and treatment. London: Royal College of Physicians of London,.. Clague JE, Craddock E, Andrew G, Horan MA, Pendleton N. Predictors of outcome following hip fracture. Admission time predicts length of stay and in-hospital mortality. Injury 0;():-.. Kates SL, Kates OS, Mendelson DA. Advances in the medical management of osteoporosis. Injury 0; Suppl :S-.. Kenzora JE, McCarthy RE, Lowell JD, Sledge CB. Hip fracture mortality. Relation to age, treatment, preoperative illness, time of surgery, and complications. Clinical orthopaedics and related research ():-.. Roche JJ, Wenn RT, Sahota O, Moran CG. Effect of comorbidities and postoperative complications on mortality after hip fracture in elderly people: prospective observational cohort study. BMJ 0;():.. Brainsky A, Glick H, Lydick E, Epstein R, Fox KM, Hawkes W, et al. The economic cost of hip fractures in community-dwelling older adults: a prospective study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society ;():-.
21 Page of Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Johnell O, Kanis J. Epidemiology of osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporosis international : a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 0; Suppl :S-.. Gholve PA, Kosygan KP, Sturdee SW, Faraj AA. Multidisciplinary integrated care pathway for fractured neck of femur. A prospective trial with improved outcome. Injury 0;():-; discussion. 0. Friedman SM, Mendelson DA, Kates SL, McCann RM. Geriatric co-management of proximal femur fractures: total quality management and protocol-driven care result in better outcomes for a frail patient population. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 0;():-.. Choong PF, Langford AK, Dowsey MM, Santamaria NM. Clinical pathway for fractured neck of femur: a prospective, controlled study. The Medical journal of Australia 00;():-.. Lau TW, Leung F, Siu D, Wong G, Luk KD. Geriatric hip fracture clinical pathway: the Hong Kong experience. Osteoporosis international : a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 0;(Suppl ):S-.. Beaupre LA, Cinats JG, Senthilselvan A, Lier D, Jones CA, Scharfenberger A, et al. Reduced morbidity for elderly patients with a hip fracture after implementation of a perioperative evidence-based clinical pathway. Quality & safety in health care 0;():-.
22 Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Page of Roberts HC, Pickering RM, Onslow E, Clancy M, Powell J, Roberts A, et al. The effectiveness of implementing a care pathway for femoral neck fracture in older people: a prospective controlled before and after study. Age and ageing 0;():-.. British Orthopaedic Association. The Care of Fragility Fracture Patients. London: British Orthopaedic Association, 0. Bottle A, Aylin P. Mortality associated with delay in operation after hip fracture: observational study. BMJ 0;():-.. Wixted JJ, Reed M, Eskander MS, Millar B, Anderson RC, Bagchi K, et al. The effect of an orthopedic trauma room on after-hours surgery at a level one trauma center. Journal of orthopaedic trauma 0;():-.. Moran CG, Wenn RT, Sikand M, Taylor AM. Early mortality after hip fracture: is delay before surgery important? The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume 0;():-.. Leung AH, Lam TP, Cheung WH, Chan T, Sze PC, Lau T, et al. An orthogeriatric collaborative intervention program for fragility fractures: a retrospective cohort study. The Journal of trauma ;():0-.. Neuman MD, Archan S, Karlawish JH, Schwartz JS, Fleisher LA. The relationship between short-term mortality and quality of care for hip fracture: a meta-analysis of clinical pathways for hip fracture. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 0;():-.
23 Page of Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Conflict of Interest: The authors certify that there are no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence (bias) their work.
24 Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Page of Table Table : ASA score trend from year 0-0 Table : Wound infection rate of hip fracture surgeries 0-0 Table : Post-operative pneumonia rate 0-0
25 Page of Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Figure caption Fig. The model of geriatric hip fracture clinical pathway Fig. The number of co-morbidities for hip fracture patients in the years 0-0 Fig. The average preoperative length of stay in terms of days during the period 0-0 Fig. The average length of stay in the rehabilitation hospital in terms of days during the period 0-0 Fig. The in-patient mortality rate during the period 0-0 Fig. The 0 days mortality rate during the period 0-0
26 Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Page of Fig.. Emergency room doctors Orthopaedic surgeons Nurses Physiotherapists Occupational therapists Orthopaedic surgeons Anaesthetists OT Nurses Orthopaedic surgeons Nurses Physiotherapists Occupational therapists Medical social workers Orthopaedic surgeons Nurses Physiotherapists Occupational therapists Medical social workers Community nurse support Geriatric hip fracture patient A&E Department: Hip and Pelvic XR Chest XR Admission ward: Pain control hour routine blood tests ECG Fit for surgery Operating theatre: Fixation of fracture/ Hip replacement Optimization Post-op ward: Pain control Prevent complications Rehabilitation assessment mental and physical Rehabilitation ward: Physical therapy and training Social support Medical support Discharge preparation Discharge home Not fit for surgery Physician assessment special investigations Anaesthetist s assessment
27 Page of Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Fig. Fig.
28 Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Page of Fig. Fig.
29 Page of Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Fig.
Geriatric hip fracture clinical pathway: the Hong Kong experience
 Osteoporos Int (2010) 21 (Suppl 4):S627 S636 DOI 10.1007/s00198-010-1387-y REVIEW Geriatric hip fracture clinical pathway: the Hong Kong experience T. W. Lau & F. Leung & D. Siu & G. Wong & K. D. K. Luk
Osteoporos Int (2010) 21 (Suppl 4):S627 S636 DOI 10.1007/s00198-010-1387-y REVIEW Geriatric hip fracture clinical pathway: the Hong Kong experience T. W. Lau & F. Leung & D. Siu & G. Wong & K. D. K. Luk
Management of Hip Fractures
 Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient David A. Brown MD COL U.S. Army Ret. The Center for Orthopedics and Neurosurgery Optimizing Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient Optimizing
Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient David A. Brown MD COL U.S. Army Ret. The Center for Orthopedics and Neurosurgery Optimizing Management of Hip Fractures in the Elderly Patient Optimizing
Audit of perioperative management of patients with fracture neck of femur
 Audit of perioperative management of patients with fracture neck of femur *M Dissanayake 1, N Wijesuriya 2 Registrar in Anaesthesia 1, Consultant Anaesthetist 2, North Colombo Teaching Hospital, Ragama,
Audit of perioperative management of patients with fracture neck of femur *M Dissanayake 1, N Wijesuriya 2 Registrar in Anaesthesia 1, Consultant Anaesthetist 2, North Colombo Teaching Hospital, Ragama,
The Experience in Exeter with. hip fracture care. Data For Change
 The Experience in Exeter with hip fracture care Data For Change John Charity Associate Specialist in T&O, Lead NHFD Clinician, Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Respond Deliver & Enable People
The Experience in Exeter with hip fracture care Data For Change John Charity Associate Specialist in T&O, Lead NHFD Clinician, Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Respond Deliver & Enable People
My hip fracture care: 12 questions to ask A guide for patients, their families and carers
 My hip fracture care: 12 questions to ask A guide for patients, their families and carers About this guide This guide is aimed at patients who have a hip fracture, and their families and carers. It explains
My hip fracture care: 12 questions to ask A guide for patients, their families and carers About this guide This guide is aimed at patients who have a hip fracture, and their families and carers. It explains
Effect of age, sex, co morbidities, delay in surgery and complications on outcome in elderly with proximal femur fractures
 2018; 4(3): 498-506 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 498-506 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 27-05-2018 Accepted: 28-06-2018 P Venu Gopala Reddy Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
2018; 4(3): 498-506 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 498-506 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 27-05-2018 Accepted: 28-06-2018 P Venu Gopala Reddy Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
The Peterborough experience over the years with hip fractures. Martyn Parker Peterborough UK
 The Peterborough experience over the years with hip fractures Martyn Parker Peterborough UK PETERBOROUGH HIP FRACTURE PROJECT Avoid delays to surgery Minimally invasive surgery by experienced staff Unrestricted
The Peterborough experience over the years with hip fractures Martyn Parker Peterborough UK PETERBOROUGH HIP FRACTURE PROJECT Avoid delays to surgery Minimally invasive surgery by experienced staff Unrestricted
Inpatient cost for hip fracture patients managed with an orthogeriatric care model in Singapore
 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 139-144 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2016065 Inpatient cost for hip fracture patients managed with an orthogeriatric care model in Singapore Lester Teong Jin Tan 1, MBBS, MRCS, Seng
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 139-144 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2016065 Inpatient cost for hip fracture patients managed with an orthogeriatric care model in Singapore Lester Teong Jin Tan 1, MBBS, MRCS, Seng
EUROHOPE: Hip fracture in Europe are slippery regions different?
 EUROHOPE: Hip fracture in Europe are slippery regions different? 25 Sep, 2012 Emma Medin Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Hip fracture is the most common fracture and associated with increased
EUROHOPE: Hip fracture in Europe are slippery regions different? 25 Sep, 2012 Emma Medin Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Hip fracture is the most common fracture and associated with increased
Evolutions in Geriatric Fracture Care Preparing for the Silver Tsunami
 Evolutions in Geriatric Fracture Care Preparing for the Silver Tsunami James Holstine, DO Medical Director for the Joint Replacement Center, Geriatric Fracture Center, Orthopedic Surgeon PeaceHealth Whatcom
Evolutions in Geriatric Fracture Care Preparing for the Silver Tsunami James Holstine, DO Medical Director for the Joint Replacement Center, Geriatric Fracture Center, Orthopedic Surgeon PeaceHealth Whatcom
FRAGILITY FRACTURE REGISTRY IN HONG KONG. Dr. WK NGAI COC (O&T), Hospital Authority
 FRAGILITY FRACTURE REGISTRY IN HONG KONG Dr. WK NGAI COC (O&T), Hospital Authority Osteoporosis - Silent Epidemic Every year, 2 million fractures occur in USA that no accident, but signs of osteoporosis
FRAGILITY FRACTURE REGISTRY IN HONG KONG Dr. WK NGAI COC (O&T), Hospital Authority Osteoporosis - Silent Epidemic Every year, 2 million fractures occur in USA that no accident, but signs of osteoporosis
Perso An. Geri-O. Objectives: fragility fracture. AL SUPPORT. presentation.
 10 th Annual Spring Conference Arizona Geriatrics Society Perso on-centered Care: An Interprofessional Panel Ana Sanguineti, MD Geri-O Ortho Hip Fracture Consult Service Banner Univer rsity Medical Center
10 th Annual Spring Conference Arizona Geriatrics Society Perso on-centered Care: An Interprofessional Panel Ana Sanguineti, MD Geri-O Ortho Hip Fracture Consult Service Banner Univer rsity Medical Center
Effect of Ortho-Geriatric Co-Management on Hip Fractures
 Effect of Ortho-Geriatric Co-Management on Hip Fractures Kenji Shigemoto Takeshi Sawaguchi Daigo Sakagoshi Kenichi Goshima Yu Hatsuchi Dept. Orthop. Surg. Toyama Municipal Hospital, Toyama, Japan Purpose
Effect of Ortho-Geriatric Co-Management on Hip Fractures Kenji Shigemoto Takeshi Sawaguchi Daigo Sakagoshi Kenichi Goshima Yu Hatsuchi Dept. Orthop. Surg. Toyama Municipal Hospital, Toyama, Japan Purpose
Accompanied to walk Yes No Accompanied to walk Yes No Side of Fracture
 Fracture Neck Of Femur / Fast Track Criteria: Admission where femoral neck fracture is the primary diagnosis Accident & Emergency Assessment (To be completed by A/E Nurse and/or A/E doctor) Patient label
Fracture Neck Of Femur / Fast Track Criteria: Admission where femoral neck fracture is the primary diagnosis Accident & Emergency Assessment (To be completed by A/E Nurse and/or A/E doctor) Patient label
Introduction. Peripheral arterial disease. Hospital inpatient data - 5,498 FCE (2009/10), & 530 deaths in England alone
 1 Introduction 2 Introduction Peripheral arterial disease Affects 20% adults in Europe and North America In the UK 500-1000/million PAD, 1-2% require amputation LLA 8-15% in people with diabetes with up
1 Introduction 2 Introduction Peripheral arterial disease Affects 20% adults in Europe and North America In the UK 500-1000/million PAD, 1-2% require amputation LLA 8-15% in people with diabetes with up
Dr Ben Edwards Consultant Anaesthetist Sheffield Teaching Hospitals
 Dr Ben Edwards Consultant Anaesthetist Sheffield Teaching Hospitals 70-75,000 #NOF per annum (costs 2 billion) 10% die within 1 month 33% die within 1 year Operative delays >48hs more than doubles risk
Dr Ben Edwards Consultant Anaesthetist Sheffield Teaching Hospitals 70-75,000 #NOF per annum (costs 2 billion) 10% die within 1 month 33% die within 1 year Operative delays >48hs more than doubles risk
Hip Fracture (HFR) Measures Document
 Hip Fracture (HFR) Measures Document HFR Version: 2 - covering patients discharged between 01/10/2017 and present. Programme Lead: Sam Doddridge Clinical Leads: Ms Phil Thorpe Dr John Tsang Number of Measures
Hip Fracture (HFR) Measures Document HFR Version: 2 - covering patients discharged between 01/10/2017 and present. Programme Lead: Sam Doddridge Clinical Leads: Ms Phil Thorpe Dr John Tsang Number of Measures
SAFE HIP FRACTURES. Dr Karthik Kayan MD FRCP Consultant Physician and Orthogeriatrician Stockport NHS Foundation Trust
 SAFE HIP FRACTURES Dr Karthik Kayan MD FRCP Consultant Physician and Orthogeriatrician Stockport NHS Foundation Trust Why hip fracture? Common in older adult (~84 years) UK current incidence : 70000 (Stockport
SAFE HIP FRACTURES Dr Karthik Kayan MD FRCP Consultant Physician and Orthogeriatrician Stockport NHS Foundation Trust Why hip fracture? Common in older adult (~84 years) UK current incidence : 70000 (Stockport
Preoperative Cardiac Evaluation of Patients With Acute Hip Fracture
 An Original Study Preoperative Cardiac Evaluation of Patients With Acute Hip Fracture Jonathan Cluett, MD, Jill Caplan, MD, and Warren Yu, MD Abstract The goals of the present study were to assess if there
An Original Study Preoperative Cardiac Evaluation of Patients With Acute Hip Fracture Jonathan Cluett, MD, Jill Caplan, MD, and Warren Yu, MD Abstract The goals of the present study were to assess if there
Integrated Care Pathway for Hip Fractures in a Subacute Rehabilitation Setting
 Original Article 579 Integrated Care Pathway for Hip Fractures in a Subacute Rehabilitation Setting Tsung Wei Chong, 1 MMed, FCFP, Gribson Chan, 2 MSc, Liang Feng, 3 PhD, Susie Goh, 4 BSN, Agnes Hew, 2
Original Article 579 Integrated Care Pathway for Hip Fractures in a Subacute Rehabilitation Setting Tsung Wei Chong, 1 MMed, FCFP, Gribson Chan, 2 MSc, Liang Feng, 3 PhD, Susie Goh, 4 BSN, Agnes Hew, 2
Guidelines to standards. Orthogeriatrics How The UK Care For Fragility Fractures
 Guidelines to standards Orthogeriatrics How The UK Care For Fragility Fractures Karen Hertz-SOTN Advanced Nurse Practitioner The NHFD Project - jointly led by BOA and BGS with the involvement of the RCN
Guidelines to standards Orthogeriatrics How The UK Care For Fragility Fractures Karen Hertz-SOTN Advanced Nurse Practitioner The NHFD Project - jointly led by BOA and BGS with the involvement of the RCN
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/22306 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Vochteloo, Anne Jochem Hendrik Title: Determinants of outcome in hip fracture
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/22306 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Vochteloo, Anne Jochem Hendrik Title: Determinants of outcome in hip fracture
Aged Care and Health Services Research. A/Prof Kwang Lim Sep 2016
 Aged Care and Health Services Research A/Prof Kwang Lim Sep 2016 Accumulating evidence 20% of health care interventions is based on hard evidence. Feasibility of doing randomised controlled trials on all
Aged Care and Health Services Research A/Prof Kwang Lim Sep 2016 Accumulating evidence 20% of health care interventions is based on hard evidence. Feasibility of doing randomised controlled trials on all
Fragility Fracture Network - FFN
 Fragility Fracture Network - FFN A Global Multidisciplinary Network to Improve Fragility Fracture Management and Prevention Ami Hommel RN, CNS, PhD, Associate Professor Lund University & Skane university
Fragility Fracture Network - FFN A Global Multidisciplinary Network to Improve Fragility Fracture Management and Prevention Ami Hommel RN, CNS, PhD, Associate Professor Lund University & Skane university
Appendix E : Evidence table 9 Rehabilitation: Other Key Documents
 Appendix E : Evidence table 9 Rehabilitation: Other Key Documents 1. Cameron et al. Geriatric rehabilitation following following fractures in older people: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment
Appendix E : Evidence table 9 Rehabilitation: Other Key Documents 1. Cameron et al. Geriatric rehabilitation following following fractures in older people: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment
National Hip Fracture Data Base
 National Hip Fracture Data Base National Hip Fracture Data Base Spring Meeting Chester 3 February 2010 Hip Fracture Best Practice: Multidisciplinary Approach (Evidence Based Medicine) Atef Michael Consultant
National Hip Fracture Data Base National Hip Fracture Data Base Spring Meeting Chester 3 February 2010 Hip Fracture Best Practice: Multidisciplinary Approach (Evidence Based Medicine) Atef Michael Consultant
Scottish Standards of Care for Hip Fracture Patients
 Scottish Standards of Care for Hip Fracture Patients This document has been prepared in collaboration with Healthcare Improvement Scotland to align with the forthcoming updated Older People in Hospitals
Scottish Standards of Care for Hip Fracture Patients This document has been prepared in collaboration with Healthcare Improvement Scotland to align with the forthcoming updated Older People in Hospitals
Hip Fractures. Anatomy. Causes. Symptoms
 Hip Fractures A hip fracture is a break in the upper quarter of the femur (thigh) bone. The extent of the break depends on the forces that are involved. The type of surgery used to treat a hip fracture
Hip Fractures A hip fracture is a break in the upper quarter of the femur (thigh) bone. The extent of the break depends on the forces that are involved. The type of surgery used to treat a hip fracture
Rehabilitation - Reducing costs and hospital stay. Dr Elizabeth Aitken Consultant Physician
 Rehabilitation - Reducing costs and hospital stay Dr Elizabeth Aitken Consultant Physician What factors affect outcome? Comorbidities Cardiac Respiratory Neurological Nutritional issues Diabetes Anaemia
Rehabilitation - Reducing costs and hospital stay Dr Elizabeth Aitken Consultant Physician What factors affect outcome? Comorbidities Cardiac Respiratory Neurological Nutritional issues Diabetes Anaemia
Komorbiditet og ortopædkirugi - erfaringer og viden. Benn Rønnow Duus, Ledende overlæge, Ortopædkirurgisk afdeling Bispebjerg Hospital
 Komorbiditet og ortopædkirugi - erfaringer og viden Benn Rønnow Duus, Ledende overlæge, Ortopædkirurgisk afdeling Bispebjerg Hospital Kræft og komorbiditet alle skal have del i de gode resultater 1 Kræftens
Komorbiditet og ortopædkirugi - erfaringer og viden Benn Rønnow Duus, Ledende overlæge, Ortopædkirurgisk afdeling Bispebjerg Hospital Kræft og komorbiditet alle skal have del i de gode resultater 1 Kræftens
Our Experience as Mortality Outliers. Calderdale and Huddersfield NHS Foundation Trust Chris Ramsdale Sudhi Ankarath
 Our Experience as Mortality Outliers Calderdale and Huddersfield NHS Foundation Trust Chris Ramsdale Sudhi Ankarath Where were we? 2 orthopaedic wards 61 beds Patients admitted wherever the empty bed was
Our Experience as Mortality Outliers Calderdale and Huddersfield NHS Foundation Trust Chris Ramsdale Sudhi Ankarath Where were we? 2 orthopaedic wards 61 beds Patients admitted wherever the empty bed was
Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing and Dynamic Hip Screw in Intertrochanteric Fracture of Femur *
 Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 291-295 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.37053 291 Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing
Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 291-295 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.37053 291 Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing
Hip Fracture Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet
 riginator: Anne Flavall Professional Development Lead, Mr Marsh and Mr Quraishi Orthopaedic Consultant Surgeons Date: March 2012 Version: 2 Date for Review: March 2015 DGOH Ref No: DGOH/PIL/00611 Hip Fracture
riginator: Anne Flavall Professional Development Lead, Mr Marsh and Mr Quraishi Orthopaedic Consultant Surgeons Date: March 2012 Version: 2 Date for Review: March 2015 DGOH Ref No: DGOH/PIL/00611 Hip Fracture
Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
Striving to improve hip fracture care
 Striving to improve hip fracture care The UHL experience 2008-2015 Mr F. Condon, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Ms Jude Ryan, Consultant Ortho-Geriatrician (Mat Leave) & A. Butler Orthopaedic CNS (Mat
Striving to improve hip fracture care The UHL experience 2008-2015 Mr F. Condon, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Ms Jude Ryan, Consultant Ortho-Geriatrician (Mat Leave) & A. Butler Orthopaedic CNS (Mat
Evaluation of the functional independence for stroke survivors in the community
 Asian J Gerontol Geriatr 2009; 4: 24 9 Evaluation of the functional independence for stroke survivors in the community ORIGINAL ARTICLE CKC Chan Bsc, DWC Chan Msc, SKM Wong MBA, MAIS, BA, PDOT ABSTRACT
Asian J Gerontol Geriatr 2009; 4: 24 9 Evaluation of the functional independence for stroke survivors in the community ORIGINAL ARTICLE CKC Chan Bsc, DWC Chan Msc, SKM Wong MBA, MAIS, BA, PDOT ABSTRACT
Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2011 Vol 5 No 1 doi: /MOJ
 doi: 10.57704/MOJ.1103.001 Is there a Significant Difference in Surgery and Outcomes between Unipolar and Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty? A Retrospective Study of a Single Institution in Singapore WL Loo,
doi: 10.57704/MOJ.1103.001 Is there a Significant Difference in Surgery and Outcomes between Unipolar and Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty? A Retrospective Study of a Single Institution in Singapore WL Loo,
Internal fixation of a hip fracture. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Internal fixation of a hip fracture Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained
Internal fixation of a hip fracture Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained
Accelero Identifies Opportunities to Provide Greater Value in Hip Fracture Care
 Accelero Health Partners, 2015 WHITE PAPER Accelero Identifies Opportunities to Provide Greater Value in Hip Fracture Care Jason Pry, Senior Director ABSTRACT Every year more than a quarter of a million
Accelero Health Partners, 2015 WHITE PAPER Accelero Identifies Opportunities to Provide Greater Value in Hip Fracture Care Jason Pry, Senior Director ABSTRACT Every year more than a quarter of a million
Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients
 Original article Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients 1Dr. Vipin Garg, 2 Dr. Anjul Agarwal 1MS Orhtopaedics, Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics,
Original article Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients 1Dr. Vipin Garg, 2 Dr. Anjul Agarwal 1MS Orhtopaedics, Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics,
The Geriatrician in the Trauma Service. Trauma Quality Improvement Program (TQIP) Annual Scientific Meeting and Training 2013
 The Geriatrician in the Trauma Service Trauma Quality Improvement Program (TQIP) Annual Scientific Meeting and Training 2013 Challenges of the Geriatric Trauma Patient Challenges of the Geriatric Patient
The Geriatrician in the Trauma Service Trauma Quality Improvement Program (TQIP) Annual Scientific Meeting and Training 2013 Challenges of the Geriatric Trauma Patient Challenges of the Geriatric Patient
Accelero Identifies Opportunities to Provide Greater Value in Hip Fracture Care
 Accelero Identifies Opportunities to Provide Greater Value in Hip Fracture Care Every year more than a quarter of a million people over the age of 65 are admitted to a hospital with a hip fracture. Mortality
Accelero Identifies Opportunities to Provide Greater Value in Hip Fracture Care Every year more than a quarter of a million people over the age of 65 are admitted to a hospital with a hip fracture. Mortality
Poor Prognosis in Elderly Patients Receiving Nonoperative Treatment for Hip Fracture: A Study of 224 Cases at Kofu National Hospital
 Yamanashi Med. J. (2, 37 ~, 5 Clinical Study Poor Prognosis in Elderly Patients Receiving Nonoperative Treatment for Hip Fracture: A Study of 22 Cases at Kofu National Hospital Tetsuo HAGINO, Eiichi SATO,
Yamanashi Med. J. (2, 37 ~, 5 Clinical Study Poor Prognosis in Elderly Patients Receiving Nonoperative Treatment for Hip Fracture: A Study of 22 Cases at Kofu National Hospital Tetsuo HAGINO, Eiichi SATO,
IAEM Clinical Guideline 11 Management of Patients with Suspected Hip Fracture in the Emergency Department
 IAEM Clinical Guideline 11 Management of Patients with Suspected Hip Fracture in the Emergency Department Version 1 September 2018 Authors: Dr Mary Moore, Ms Marianne Walsh, Dr Termizi Hassan Guideline
IAEM Clinical Guideline 11 Management of Patients with Suspected Hip Fracture in the Emergency Department Version 1 September 2018 Authors: Dr Mary Moore, Ms Marianne Walsh, Dr Termizi Hassan Guideline
Mr Maulik J Gandhi (ST6 T&O) Mr Jan Herman Kuiper Ms Swati Bhasin Mr David J Ford Mr Alastair Marsh Mr Sohail Quraishi
 The Dudley Grid: An evidence-based audit/research tool to investigate mortality risk following a displaced intracapsular hip fracture. How can it be applied in practice? Mr Maulik J Gandhi (ST6 T&O) Mr
The Dudley Grid: An evidence-based audit/research tool to investigate mortality risk following a displaced intracapsular hip fracture. How can it be applied in practice? Mr Maulik J Gandhi (ST6 T&O) Mr
Geriatric screening in acute care wards a novel method of providing care to elderly patients
 Geriatric screening in acute care wards a novel method of providing care to elderly patients JKH Luk, T Kwok, J Woo Objective. To assess a nurse-implemented geriatric screening system. Design. Descriptive
Geriatric screening in acute care wards a novel method of providing care to elderly patients JKH Luk, T Kwok, J Woo Objective. To assess a nurse-implemented geriatric screening system. Design. Descriptive
Outcome Following Surgery for Proximal Femur Fractures in Centenarians
 American Research Journal of Orthopedics and Traumatology (ARJOT), 7 Pages Research Article Outcome Following Surgery for Proximal Femur Fractures in Centenarians Donald Buchanan 1, Neil Shastri-Hurst
American Research Journal of Orthopedics and Traumatology (ARJOT), 7 Pages Research Article Outcome Following Surgery for Proximal Femur Fractures in Centenarians Donald Buchanan 1, Neil Shastri-Hurst
Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study
 Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
COUNTRY REPORT OF VIET NAM AT THE 12 TH ASEAN & JAPAN HIGH LEVEL OFFICIALS MEETING ON CARING SOCIETIES
 COUNTRY REPORT OF VIET NAM AT THE 12 TH ASEAN & JAPAN HIGH LEVEL OFFICIALS MEETING ON CARING SOCIETIES 21-23 OCTOBER 2014 I. AGEING POPULATION IN VIETNAM 1. Vietnam is one of 10 countries with the world
COUNTRY REPORT OF VIET NAM AT THE 12 TH ASEAN & JAPAN HIGH LEVEL OFFICIALS MEETING ON CARING SOCIETIES 21-23 OCTOBER 2014 I. AGEING POPULATION IN VIETNAM 1. Vietnam is one of 10 countries with the world
MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL FEMORAL FRACTURES IN THE ELDERLY: FIXATION VS HEMIARTHROPLASTY VS BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY VS TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL FEMORAL FRACTURES IN THE ELDERLY: FIXATION VS HEMIARTHROPLASTY VS BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY VS TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Sławomir Dudko, Damian Kusz, Karolina Godyń, Marcin Kusz Department
MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL FEMORAL FRACTURES IN THE ELDERLY: FIXATION VS HEMIARTHROPLASTY VS BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY VS TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Sławomir Dudko, Damian Kusz, Karolina Godyń, Marcin Kusz Department
Fractured neck of femur
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is a fractured neck of femur? A healthy hip joint is vital to normal walking
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is a fractured neck of femur? A healthy hip joint is vital to normal walking
NCAP NATIONAL CARDIAC AUDIT PROGR AMME NATIONAL HEART FAILURE AUDIT 2016/17 SUMMARY REPORT
 NCAP NATIONAL CARDIAC AUDIT PROGR AMME NATIONAL HEART FAILURE AUDIT 2016/17 SUMMARY REPORT CONTENTS PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH HEART FAILURE...4 Demographics... 4 Trends in Symptoms... 4 Causes and Comorbidities
NCAP NATIONAL CARDIAC AUDIT PROGR AMME NATIONAL HEART FAILURE AUDIT 2016/17 SUMMARY REPORT CONTENTS PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH HEART FAILURE...4 Demographics... 4 Trends in Symptoms... 4 Causes and Comorbidities
SCHEDULE 2 THE SERVICES. A. Service Specifications
 SCHEDULE 2 THE SERVICES A. Service Specifications Service Specification No. 04/MSKT/0013 Service PAN DORSET FRACTURE LIAISON SERVICE Commissioner Lead CCP for Musculoskeletal & Trauma Provider Lead Deputy
SCHEDULE 2 THE SERVICES A. Service Specifications Service Specification No. 04/MSKT/0013 Service PAN DORSET FRACTURE LIAISON SERVICE Commissioner Lead CCP for Musculoskeletal & Trauma Provider Lead Deputy
A & E Protocol: Suspected Neck of Femur # Patient sticker:
 Proforma for Fractured Neck of Femur Audit: FAST TRACK 1 of 10 A & E Protocol: Suspected Neck of Femur # Date: / / Time of Arrival: Name of triage nurse: Time of triage : A& E member of staff: Resuscitate
Proforma for Fractured Neck of Femur Audit: FAST TRACK 1 of 10 A & E Protocol: Suspected Neck of Femur # Date: / / Time of Arrival: Name of triage nurse: Time of triage : A& E member of staff: Resuscitate
9 Diabetes care. Back to contents
 Back to contents Diabetes is a major risk factor for the development of peripheral vascular disease and 349/628 (55.6%) of the patients in this study had diabetes. Hospital inpatients with diabetes are
Back to contents Diabetes is a major risk factor for the development of peripheral vascular disease and 349/628 (55.6%) of the patients in this study had diabetes. Hospital inpatients with diabetes are
Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
Subcapital hip fracture surgery. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Subcapital hip fracture surgery Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the
Subcapital hip fracture surgery Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the
GRADE Tables and Summary of Findings for the recommendations of Rehabilitation in health systems
 GRADE Tables and Summary of Findings for the recommendations of Rehabilitation in health systems REHABILITATION SERVICE DELIVERY For the following PICO questions, Population includes any person who requires
GRADE Tables and Summary of Findings for the recommendations of Rehabilitation in health systems REHABILITATION SERVICE DELIVERY For the following PICO questions, Population includes any person who requires
Clinical Care Team approach to management of key conditions
 Clinical Care Team approach to management of key conditions BJD Ho Chi Minh City Nov 30, 2012 Kristina Åkesson, MD, PhD Dept of Orthopedics Malmö University Hospital Lund University Malmö, Sweden Multidisciplinary
Clinical Care Team approach to management of key conditions BJD Ho Chi Minh City Nov 30, 2012 Kristina Åkesson, MD, PhD Dept of Orthopedics Malmö University Hospital Lund University Malmö, Sweden Multidisciplinary
Geriatric Hip Fractures: Pearls for the Hospitalist. Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Speakers Bureau-Synthes
 Geriatric Hip Fractures: Pearls for the Hospitalist Jason W. Stoneback, MD Assistant Professor, Univ. of Colorado SOM Director, Orthopedic Trauma and Fracture Surgery Service Director, Orthopedic Inpatient
Geriatric Hip Fractures: Pearls for the Hospitalist Jason W. Stoneback, MD Assistant Professor, Univ. of Colorado SOM Director, Orthopedic Trauma and Fracture Surgery Service Director, Orthopedic Inpatient
Misdiagnosis of occult hip fracture is more likely in patients with poor mobility and cognitive impairment
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 341-346 ORIGINAL STUDY Misdiagnosis of occult hip fracture is more likely in patients with poor mobility and cognitive impairment Munier HOSSAIN, Syed A. AKBAR, Glynne ANDREW
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 341-346 ORIGINAL STUDY Misdiagnosis of occult hip fracture is more likely in patients with poor mobility and cognitive impairment Munier HOSSAIN, Syed A. AKBAR, Glynne ANDREW
Cite this article as: BMJ, doi: /bmj (published 18 November 2005)
 Cite this article as: BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.38643.663843.55 (published 18 November 2005) Effect of comorbidities and postoperative complications on mortality after hip fracture in elderly people: prospective
Cite this article as: BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.38643.663843.55 (published 18 November 2005) Effect of comorbidities and postoperative complications on mortality after hip fracture in elderly people: prospective
The Perioperative Care Chain is Only as Strong as its weakest link
 The Perioperative Care Chain is Only as Strong as its weakest link Associate Professor Kerin Fielding The University of Notre Dame, Australia School of Medicine, Sydney Outline The perioperative chain
The Perioperative Care Chain is Only as Strong as its weakest link Associate Professor Kerin Fielding The University of Notre Dame, Australia School of Medicine, Sydney Outline The perioperative chain
Dedicated orthogeriatric service reduces hip fracture mortality
 DOI 10.1007/s11845-016-1453-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dedicated orthogeriatric service reduces hip fracture mortality C. Y. Henderson 1 E. Shanahan 2 A. Butler 3 B. Lenehan 3 M. O Connor 2 D. Lyons 2 J. P. Ryan
DOI 10.1007/s11845-016-1453-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dedicated orthogeriatric service reduces hip fracture mortality C. Y. Henderson 1 E. Shanahan 2 A. Butler 3 B. Lenehan 3 M. O Connor 2 D. Lyons 2 J. P. Ryan
MSK Rehab Definitions Framework - hip fractures Self assessment Survey Outpatient Rehab
 MSK Rehab Definitions Framework - hip fractures Self assessment Survey Outpatient Rehab In response to a changing rehab landscape in which rehabilitation is offered in many different settings with variations
MSK Rehab Definitions Framework - hip fractures Self assessment Survey Outpatient Rehab In response to a changing rehab landscape in which rehabilitation is offered in many different settings with variations
Registry Highlights. Dale Daniel Symposium Hip Fracture Registry. Overall Volume by Year and Region 3/7/2014
 Dale Daniel Symposium 2014 Registry Highlights Overview: Updated Volume NCAL/SCAL Snapshot Hip Fracture Registry Update Gary Zohman, MD SCAL Regional Lead Anaheim, CA Quarterly Quality Report Review Future
Dale Daniel Symposium 2014 Registry Highlights Overview: Updated Volume NCAL/SCAL Snapshot Hip Fracture Registry Update Gary Zohman, MD SCAL Regional Lead Anaheim, CA Quarterly Quality Report Review Future
Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement
 Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement Subcapital hip fractures The use of THR Historical data RCT outcomes 3 groups of patients Displaced subcapital fractures Which method is best? Arthroplasty
Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement Subcapital hip fractures The use of THR Historical data RCT outcomes 3 groups of patients Displaced subcapital fractures Which method is best? Arthroplasty
Information for patients (and their families) waiting for liver transplantation
 Information for patients (and their families) waiting for liver transplantation Waiting list? What is liver transplant? Postoperative conditions? Ver.: 5/2017 1 What is a liver transplant? Liver transplantation
Information for patients (and their families) waiting for liver transplantation Waiting list? What is liver transplant? Postoperative conditions? Ver.: 5/2017 1 What is a liver transplant? Liver transplantation
Identifying patients at risk of delirium: a project for patients undergoing elective orthopedic surgery. The next steps in orthogeriatrics
 Identifying patients at risk of delirium: a project for patients undergoing elective orthopedic surgery Dr. John Joanisse, Chantal Chabot NP The next steps in orthogeriatrics Background More than 8 years
Identifying patients at risk of delirium: a project for patients undergoing elective orthopedic surgery Dr. John Joanisse, Chantal Chabot NP The next steps in orthogeriatrics Background More than 8 years
Hemiarthroplasty (half hip replacement)
 Hemiarthroplasty (half hip replacement) Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about an operation called a half hip replacement. It gives information about the
Hemiarthroplasty (half hip replacement) Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about an operation called a half hip replacement. It gives information about the
Care of the Elderly 1
 Care of the Elderly 1 Contents Summary... 3 Introduction... 4 National Trends 4 Older people's Care in Dumfries & Galloway... 6 Professional Body Recommendation 11 Experience from elsewhere..12 Models
Care of the Elderly 1 Contents Summary... 3 Introduction... 4 National Trends 4 Older people's Care in Dumfries & Galloway... 6 Professional Body Recommendation 11 Experience from elsewhere..12 Models
EMU A NEW MODEL OF EMERGENCY CARE FOR THE FRAIL & ELDERLY
 EMU A NEW MODEL OF EMERGENCY CARE FOR THE FRAIL & ELDERLY Geriatrics, General practice, Emergency medicine, Interface medicine SUMMARY An integrated, community emergency service specifically designed for
EMU A NEW MODEL OF EMERGENCY CARE FOR THE FRAIL & ELDERLY Geriatrics, General practice, Emergency medicine, Interface medicine SUMMARY An integrated, community emergency service specifically designed for
THE VALUE OF JOINT REPLACEMENT IN TREATING PATIENTS WITH OSTEOARTHRITIS
 THE VALUE OF JOINT REPLACEMENT IN TREATING PATIENTS WITH OSTEOARTHRITIS Total Joint Replacement is a valuable treatment option for many of the 27 million Americans who suffer from Osteoarthritis, a disease
THE VALUE OF JOINT REPLACEMENT IN TREATING PATIENTS WITH OSTEOARTHRITIS Total Joint Replacement is a valuable treatment option for many of the 27 million Americans who suffer from Osteoarthritis, a disease
Therapy following a neck of femur fracture
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Therapy following a neck of femur fracture Name of patient: ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff Procedure: ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff Consultant:
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Therapy following a neck of femur fracture Name of patient: ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff Procedure: ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff Consultant:
A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries. Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital
 A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital Cheung KK Wong CY Chan Andrew Tse Alfred Chow YY Department of Orthopaedics
A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital Cheung KK Wong CY Chan Andrew Tse Alfred Chow YY Department of Orthopaedics
Introduction. Femoral neck fracture in the elderly
 Fll Fellow: 姜智偉 Introduction Femoral neck fracture in the elderly 14 50 % mortality tlit rate in the first year Highest in the first 6 months, then gradually reduced Affect mortality: Age, gender, comitant
Fll Fellow: 姜智偉 Introduction Femoral neck fracture in the elderly 14 50 % mortality tlit rate in the first year Highest in the first 6 months, then gradually reduced Affect mortality: Age, gender, comitant
BED BLOCKERS: A STUDY ON THE ELDERLY PATIENTS IN A TEACHING HOSPITAL IN INDIA
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 11 Number 1 BED BLOCKERS: A STUDY ON THE ELDERLY PATIENTS IN A TEACHING HOSPITAL IN INDIA P N., N Shinge, P S. Citation P N., N Shinge, P S.. BED BLOCKERS:
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 11 Number 1 BED BLOCKERS: A STUDY ON THE ELDERLY PATIENTS IN A TEACHING HOSPITAL IN INDIA P N., N Shinge, P S. Citation P N., N Shinge, P S.. BED BLOCKERS:
THE WHITE PAPER Associate Professor Peter Lipski
 A0 NEW DIRECTION FOR GERIATRIC MEDICAL SERVICES ON THE NSW CENTRAL COAST 2007 THE WHITE PAPER Associate Professor Peter Lipski 1. Traditional Acute Geriatric Medicine Models of Hospital Care. 2. Acute
A0 NEW DIRECTION FOR GERIATRIC MEDICAL SERVICES ON THE NSW CENTRAL COAST 2007 THE WHITE PAPER Associate Professor Peter Lipski 1. Traditional Acute Geriatric Medicine Models of Hospital Care. 2. Acute
Comprehensive Assessment of the Frail Older Patient
 Comprehensive Assessment of the Frail Older Patient Executive Summary Comprehensive geriatric assessment (CGA) is a multidimensional and usually interdisciplinary diagnostic process designed to determine
Comprehensive Assessment of the Frail Older Patient Executive Summary Comprehensive geriatric assessment (CGA) is a multidimensional and usually interdisciplinary diagnostic process designed to determine
Outcome after surgery for fracture of the hip in patients aged over 95 years
 Outcome after surgery for fracture of the hip in patients aged over 95 years G. Holt, D. Macdonald, M. Fraser, A. T. Reece From Western Infirmary, Glasgow, Scotland Despite the increase in numbers of the
Outcome after surgery for fracture of the hip in patients aged over 95 years G. Holt, D. Macdonald, M. Fraser, A. T. Reece From Western Infirmary, Glasgow, Scotland Despite the increase in numbers of the
CHN Loong 1, YC Woo 1, WK Chau 2, JKY Lam 1, MMA Yuen 1, CH Lee 2, ACH Lee 1, ELY Leung 1, KSL Lam 2, KCB Tan 2 1
 CHN Loong 1, YC Woo 1, WK Chau 2, JKY Lam 1, MMA Yuen 1, CH Lee 2, ACH Lee 1, ELY Leung 1, KSL Lam 2, KCB Tan 2 1 Department of Medicine, Queen Mary Hospital, HK 2 Department of Medicine, The University
CHN Loong 1, YC Woo 1, WK Chau 2, JKY Lam 1, MMA Yuen 1, CH Lee 2, ACH Lee 1, ELY Leung 1, KSL Lam 2, KCB Tan 2 1 Department of Medicine, Queen Mary Hospital, HK 2 Department of Medicine, The University
*GERIATRIC FELLOWSHIP COMPETENCY CHECKLIST EDUCATIONAL GOALS:
 *GERIATRIC FELLOWSHIP COMPETENCY CHECKLIST EDUCATIONAL GOALS: The goal of geriatric fellowship training is to prepare fellows for competency in the following core areas: Check and record date completed
*GERIATRIC FELLOWSHIP COMPETENCY CHECKLIST EDUCATIONAL GOALS: The goal of geriatric fellowship training is to prepare fellows for competency in the following core areas: Check and record date completed
When You re Having Surgery for a Fractured Hip
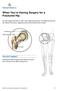 When You re Having Surgery for a Fractured Hip The hip includes the head or ball of the thigh bone (femur). The thigh bone fits into the socket of the pelvis. Ligaments and muscles hold the joint in place.
When You re Having Surgery for a Fractured Hip The hip includes the head or ball of the thigh bone (femur). The thigh bone fits into the socket of the pelvis. Ligaments and muscles hold the joint in place.
Femoral Neck (Hip) Fracture
 Patient Information Leaflet Femoral Neck (Hip) Fracture Produced By: Orthopaedic Department September 2013 Review due September 2016 1 If you require this leaflet in another language, large print or another
Patient Information Leaflet Femoral Neck (Hip) Fracture Produced By: Orthopaedic Department September 2013 Review due September 2016 1 If you require this leaflet in another language, large print or another
Geriatric Hip Fracture Co-Management. Pannida Wattanapanom, M.D., FACP.
 Geriatric Hip Fracture Co-Management Pannida Wattanapanom, M.D., FACP. An 80 year old man with a hip fracture The General Medicine approach: Medical clearance for surgery Role of Geriatrician Assess caused
Geriatric Hip Fracture Co-Management Pannida Wattanapanom, M.D., FACP. An 80 year old man with a hip fracture The General Medicine approach: Medical clearance for surgery Role of Geriatrician Assess caused
The in-hospital management of COPD-exacerbation includes three core processes:
 Appendix 1A. Process flow for in-hospital management of COPDexacerbation The in-hospital management of COPD-exacerbation includes three core processes: 1. Diagnostic assessment 2. Pharmacological management
Appendix 1A. Process flow for in-hospital management of COPDexacerbation The in-hospital management of COPD-exacerbation includes three core processes: 1. Diagnostic assessment 2. Pharmacological management
2010 National Audit of Dementia (Care in General Hospitals) North West London Hospitals NHS Trust
 Royal College of Psychiatrists 2010 National Audit of Dementia (Care in General Hospitals) Organisational checklist results and commentary for: rth West London Hospitals NHS Trust The 2010 national audit
Royal College of Psychiatrists 2010 National Audit of Dementia (Care in General Hospitals) Organisational checklist results and commentary for: rth West London Hospitals NHS Trust The 2010 national audit
Carolinas HealthCare System Fragility Fracture Program
 Carolinas HealthCare System Fragility Fracture Program Presented By: Monica C. Mowry, MSN, RN, NE-BC, ONC Director, Clinical Program Development Carolinas HealthCare System Charlotte, NC Objectives Expand
Carolinas HealthCare System Fragility Fracture Program Presented By: Monica C. Mowry, MSN, RN, NE-BC, ONC Director, Clinical Program Development Carolinas HealthCare System Charlotte, NC Objectives Expand
THE NATIONAL QUALITY FORUM
 THE NATIONAL QUALITY FORUM National Voluntary Consensus Standards for Patient Outcomes Table of Measures Submitted-Phase 1 As of March 5, 2010 Note: This information is for personal and noncommercial use
THE NATIONAL QUALITY FORUM National Voluntary Consensus Standards for Patient Outcomes Table of Measures Submitted-Phase 1 As of March 5, 2010 Note: This information is for personal and noncommercial use
PMH HKU PWH HKPU QMH. Tong HK, A&E Dept. Chu MLM, OT Dept. Fung KKH, OT Dept. Chan MTE, OT Dept. Wong CM, Com Med Dept.
 HKU Wong CM, Com Med Dept. PMH Lit CHA, A&E Dept. Cheng WCS, OT Dept. Wong D, OT Dept. Fong NKK, Rehab Sc Dept. HKPU A Community OT Falls Reduction Program Reducing Falls in Six Months for Elderly Attending
HKU Wong CM, Com Med Dept. PMH Lit CHA, A&E Dept. Cheng WCS, OT Dept. Wong D, OT Dept. Fong NKK, Rehab Sc Dept. HKPU A Community OT Falls Reduction Program Reducing Falls in Six Months for Elderly Attending
AOTrauma Course Fragility Fractures and Orthogeriatrics
 Course program AOTrauma Course Fragility Fractures and Orthogeriatrics November, 14-16, 2014, Conference and Cultural Center, University of Patras, Greece Chairpersons Minos Tyllianakis Greece Steve Schelkun
Course program AOTrauma Course Fragility Fractures and Orthogeriatrics November, 14-16, 2014, Conference and Cultural Center, University of Patras, Greece Chairpersons Minos Tyllianakis Greece Steve Schelkun
Integrating Medical and Social Support for Elderly System & Technology Enabled Service Innovations. Dr Christina MAW Hospital Authority, Hong Kong
 Integrating Medical and Social Support for Elderly System & Technology Enabled Service Innovations Dr Christina MAW Hospital Authority, Hong Kong Hospital Authority (HA) of Hong Kong A statutory body responsible
Integrating Medical and Social Support for Elderly System & Technology Enabled Service Innovations Dr Christina MAW Hospital Authority, Hong Kong Hospital Authority (HA) of Hong Kong A statutory body responsible
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Procedure (TAVI)
 Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Role and impact of orthogeriatric service in the hip fracture care pathway: 15-year experience
 Role and impact of orthogeriatric service in the hip fracture care pathway: 15-year experience AA Fisher, MW Davis Department of Geriatric Medicine, The Canberra Hospital, and Australian National University
Role and impact of orthogeriatric service in the hip fracture care pathway: 15-year experience AA Fisher, MW Davis Department of Geriatric Medicine, The Canberra Hospital, and Australian National University
Prevention and Management of Hip Fracture in Older People
 Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network 56 Prevention and Management of Hip Fracture in Older People A national clinical guideline 1 Introduction 1 2 Prevention of hip fracture 4 3 Pre-hospital management
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network 56 Prevention and Management of Hip Fracture in Older People A national clinical guideline 1 Introduction 1 2 Prevention of hip fracture 4 3 Pre-hospital management
Orthopaedic Therapy Service inpatient guide. Information for patients MSK Orthopaedic Inpatients (Therapy)
 Orthopaedic Therapy Service inpatient guide Information for patients MSK Orthopaedic Inpatients (Therapy) This leaflet is designed to answer any queries you may have about the Orthopaedic Therapy Service.
Orthopaedic Therapy Service inpatient guide Information for patients MSK Orthopaedic Inpatients (Therapy) This leaflet is designed to answer any queries you may have about the Orthopaedic Therapy Service.
Hip Fracture from audit into action
 Hip Fracture from audit into action Antony Johansen Orthogeriatrician Trauma Unit University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff National Hip Fracture Database Royal College of Physicians, London Global projections
Hip Fracture from audit into action Antony Johansen Orthogeriatrician Trauma Unit University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff National Hip Fracture Database Royal College of Physicians, London Global projections
AOTrauma Course Fragility Fractures and Orthogeriatrics
 Thursday, 22 Oct 2015 (Day 1) 09:00 09:30 Other REGISTATION AND WELCOME COFFEE Sokos Hotel Viru, Bolero venue 30 09:30 12:25 Module 1: The Geriatric Patient and Fracture 175 09:30 09:50 Lecture The Morbidity
Thursday, 22 Oct 2015 (Day 1) 09:00 09:30 Other REGISTATION AND WELCOME COFFEE Sokos Hotel Viru, Bolero venue 30 09:30 12:25 Module 1: The Geriatric Patient and Fracture 175 09:30 09:50 Lecture The Morbidity
Dynamic hip screw (sliding hip screw)
 Dynamic hip screw (sliding hip screw) Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about an operation called a dynamic hip screw, sometimes also known as a sliding hip
Dynamic hip screw (sliding hip screw) Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about an operation called a dynamic hip screw, sometimes also known as a sliding hip
Tamer Mettyas 1* and Clare Carpenter 2
 Mettyas and Carpenter Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2013, 8:44 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Secondary prevention of osteoporosis in non-neck of femur fragility : is it value for money? A
Mettyas and Carpenter Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2013, 8:44 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Secondary prevention of osteoporosis in non-neck of femur fragility : is it value for money? A
