Clinical Experience of Interlocking Nail Stabilization of Long Bone Fractures in Dogs A Retrospective Study of 26 Cases
|
|
|
- Cory Harmon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
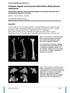
1 Clinical Experience of Interlocking Nail Stabilization of Long Bone Fractures in Dogs A Retrospective Study of 26 Cases Arican, M., 1 * Alkan, F., 1 Altan, S., 2 Parlak, K. 1 and Yavru, N. 1 1 University of Selcuk, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Department of Surgery, Konya, Turkey. 2 University of Dicle, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Department of Surgery, Diyarbakir, Turkey. * Corresponding Author: Mustafa Arican, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, The University of Selcuk, Campüs, Konya/ Turkey. Phone: , Fax: marican@selcuk.edu.tr ABSTRACT The aim of the study is to report the clinical and radiographic outcome after use of an interlocking nail (ILN) for stabilization of long bone fractures in dogs. Twenty-six dogs were evaluated. There were ten femoral fractures, 12 tibial fractures and four humeral fractures. The equipment was manufactured by Orthovet (Orthovet, Izmir, Turkey). Three ILN lengths with three different diameters (4, 6 and 8 mm) were used. Each ILN had a trocar tip on one end and four screw holes (two distal and two proximal). Ten fractures (four femoral, five tibial, one humeral) were associated with other orthopedic problems. Nine (39.1%) patients had aseptic nonunion and malunion fractures. A static fixation mode was used for nine fractures and a dynamic fixation mode was used in 17 (65.3%). The surgical time recorded was minutes. Three dogs had a major complication requiring surgical intervention. At 6 months, the functional outcome was excellent in 15 (57.6%) animals, good in seven (26.9%), fair in three (11.5%), and poor in one (3.8). In conclusion, the use of ILNs to repair diaphyseal fractures of the femur, tibia, and humerus in dogs resulted in a good or excellent functional outcome in most patients. Keywords: Dogs; Interlocking Nail Stabilization; Long Bone Fractures. INTRODUCTION Interlocking nails (ILNs) are a valuable tool for treating tibial, femoral, and humeral fractures in small animals, and especially comminuted fractures in dogs and cats (1, 2, 3, 4). ILNs have been used for more than a decade for the treatment of long-bone fractures in dogs and cats (5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11), and in birds (12). ILNs provide a viable option for minimally invasive fracture repair and may be an attractive alternative to the use of standard bone plates for the repair of comminuted diaphyseal fractures. However ILNs, like other fracture repair modalities, have associated complications. These include implant failure, including failure of the nail itself and failure of the locking bolt, misdirected locking bolts, joint penetration, delayed union, non-union and infection (13, 14). Nail failure has been reported in dogs (3, 8, 15) but not in cats (11, 15, 16). Screw failure is a less serious complication because bone healing is usually not affected (3, 8, 15). Screw bending has also been reported as a complication (1, 17, 18). In the current study, the clinical outcomes of femoral, tibial, and humeral diaphyseal fractures repaired by ILN in 26 dogs are reported. Long-term follow-up (> 6 months) was available for all patients. MATERIALS AND METHODS Dogs Twenty-six dogs weighing 15 to 50 kg (mean 28.5 kg) with diaphyseal fractures of the femur, tibia (Fig. 1) or humerus were used in the study. The fracture type (bone, degree of Israel Journal of Veterinary Medicine Vol. 72 (2) June 2017 Naıl Stabılızatıon of Fractures in Dogs 45
2 comminution, cause), use of ILN as method of application, complications that occurred during application, surgical time, and clinical outcome, including healing, function and complications, were assessed. Confirmation of the diagnosis was obtained by radiography of the involved bone in mediolateral and craniocaudal views, in order to assess the location and type of fracture. The dogs were followed up for 6 months. The study was performed with approval from and under the guidelines of the Institutional Laboratory Animal Care and use Committee of Selcuk University. Interlocking Nails Three generations of ILN and instrumentation were used in this study. The equipment was manufactured by Ortovet (Orto-vet, Izmir, Turkey, Seven ILN lengths (150, 160, 170, 180, 190, 210 and 230) with three different diameters (4, 6 and 8 mm) were available (Table 1). Each ILN had a trocar tip on one end, a negative thread on the other end to receive the jig used for cortical screw placement, and four screw holes (two distal and two proximal). The ILNs could be inserted with a Jacobs chuck in a retrograde direction (with use of a removable tip), and AO/ASIF cortical bone screws (2.7 mm diameter; 22, 24, 26, 28, 30 and 32 mm length) were used as interlocking screws. Figure 1: 3 year old, male, German Shepferd dog with diaphysis / oblique, middle 1/3rd of tibial fracture. Surgical Technique The surgical techniques followed published procedures (3). The dogs selected for this surgical approach had evidence on preoperative radiographs that the proximal and distal fragments were of sufficient length to tolerate insertion of an ILN, so that locking screws could be positioned on proximal and distal fragments sides of the fracture with interlocking screws positioned at least 10 mm distant from the fracture. Finally, the bone had to have a radiographic appearance that suggested it should be able to hold screws firmly. In addition, with the measurements performed on these radiographs, the relation between the fracture line and the screw holes to be opened was assessed. If the fracture site was short with an unstable fracture, the ILN dimensions were determined by measuring the silhouette of the contralateral unfractured bone. Implant diameter was selected to provide the best fit within the medullary canal. Food was withheld from each dog for 12 hours before anaesthesia. Preoperative flunixin meglumine (0.5-2 mg/ kg BW, Flumed inj., Alke, Istanbul, Turkey) was given IV before the operations. Anesthesia was induced with intravenous xylazine hydrochloride (Alfazyne 2% 20 mg/ ml, Egevet, Izmir) and ketamine hydrochloride (Alfamine 10%, 100 mg/ml Egevet, Izmir). After 10 minutes, anesthesia was maintained with isoflurane in oxygen (AErrane, Baxter, Mississauga (Ontario), 2%-4%). After open fracture reduction and following the exposition of fracture line (humerus, tibia and femur) medullary canal of the proximal fragment was drilled of the same diameter with the nail to be used. If necessary the ILN was inserted initially in the distal fragment to verify that the diameter was adequate and to prepare the medullary canal for implant seating. Interlocking nail was placed in the proximal fragment in retrograde direction and pulled out from the hole opened by the drill s tip. The nail was pulled until the fracture line proximally with the use of the drill. The ILN was pushed into the metaphysis, without penetration of the articular surface, to reduce exceptionally distal fractures and in order to avoid damage to the proximal end of the ILN, which might prevent attachment of the guide jig. Instead, when the ILN was inserted to three-quarters of its length, a handle used for guide jig attachment was attached to the proximal end of the ILN, then, with alternating rotational movements of the handle, the ILN was fully seated in the distal aspect of the diaphysis. With the ILN seated, the guide jig was positioned close to the bone and attached 46 Arıcan, M. Israel Journal of Veterinary Medicine Vol. 72 (2) June 2017
3 to the slot in the handle. Holes in the jig corresponded in alignment with the holes in the ILN and were used to insert of a drill guide (2.5 mm) against the bone and a gliding hole was drilled through both cortices. After drilling, the drill guide was replaced by a screw guide. Screw length was measured with a special gauge. A screw and the screwdriver were inserted into the screw guide and the screw was inserted through the ILN and both cortices. It is essential that the distal aspect of the bone is locked first to ensure good mechanical stability. After the nail was locked, the jig was removed. The ILN can be implanted in a static or dynamic fixation mode, depending on whether it is desirable to neutralize part or all of the rotational or compression stress. In the static mode, both proximal and distal screws are inserted, whereas, in the dynamic mode, only proximal or distal screws, but not both, are locked. Craniocaudal and mediolateral radiographs were taken postoperatively in order to view the results of the procedure, and 22,000 IU/kg of penicillin G (Devapen, Deva) and 2 days after surgery I.V flunixin meglumine (Flumed inj., Alke, Istanbul, Turkey) or 0.4cc/10 kg S.C Meloksikam 20 mg (Maksikam, Sanovel, Istanbul, Turkey) was administered postoperatively. Femur The femoral diaphysis was exposed through a lateral approach.when the femur and fracture line were exposed, the medullary canal of the proximal fragment was opened using a drill tip of the same diameter as the nail to be used. The ILN was inserted into the proximal fragment in a retrograde direction and pulled out through the hole made by the drill tip. The nail was pulled to the fracture line proximally with the use of the drill. When reduction of the fracture was complete, a handle used for guide jig attachment was attached to the proximal end of the ILN. With alternating rotational movements of the handle, the ILN was fully seated in the distal aspect of the diaphysis. Tibia A craniomedial skin incision was made along most of the tibial length. Dissection through the subcutaneous fascia exposed the tibial shaft, with the cranial tibial muscle forming the cranial margin and the long digital flexor muscle the caudal margin. The ILN was placed in the proximal fragment in a retrograde direction and pulled out through the hole opened by the drill tip. The nail was pulled proximally to the fracture line with the use of the drill. When reduction of the fracture was completed, the nail was then placed in the distal fragment by launching with the drill. Humerus The proximal aspect of the shaft was exposed by a lateral approach, and the distal portion of the shaft was also exposed laterally. ILNs were placed in a retrograde manner. Fracture Classification Fractures were classified by their location; whether closed or open; new or pre-existing (delayed union, non-union, implant failure); comminuted or non-comminuted. The severity of comminution was graded according to the modified Winquist Hansen criteria, which consider the stability and complexity of the fracture: class 0, non-comminuted fracture; classes I-V, comminuted fractures where class I has a small unimportant bone chip, class II has greater than 50% contact between proximal and distal fragments, class III has less than 50% contact between proximal and distal fragments, class IV has no contact between proximal and distal fragments, and class V has segmental fractures (19). Outcome Fracture healing and functional outcome were assessed 6 months after surgery. Assessment of Fracture Healing Radiographic assessment of fracture healing was made at 1, 3, and 6 months until there was radiographic evidence of healing and no pain could be noted during limb manipulation. Fracture healing was classified by use of a modified Meynard and Magnin method that assesses the quality of fracture reduction, the quality of healing of the interosseous space (size of this space, lack of bony substance, density of the callus), and periosteal callus volume (normal or exuberant) (3, 20). Functional Outcome The limb was scored as: 1, excellent (total absence of lameness); 2, good but favoring the limb after exercise); 3, fair (constant lameness); and 4, poor (no use of the limb for support). Intraoperative (technical errors during surgery or the incorrect choice of implants) and postoperative (implant failure, delayed healing, non-union) complications were recorded and Israel Journal of Veterinary Medicine Vol. 72 (2) June 2017 Naıl Stabılızatıon of Fractures in Dogs 47
4 analyzed (3). Delayed union was defined as a fracture that had not healed by 3 months and non-union as a fracture that had not healed by 5 months. Implant failure was defined either as the breakage of the nail before fracture union or removal of the ILN and replacement by another type of fixation. Statistical Analysis Outcome was assessed through recheck examinations by the primary surgeon at least until radiographic healing. Further follow-up was by re-examination or telephone interview by the primary author (M.A). The distribution of dogs with respect to fracture type, sex, age, fracture location in the involved bones, and outcome of treatment was reported as a percentage. RESULTS Twenty-six dogs were evaluated. Their ages ranged from 1 to 5 years (mean, 2.5 years) and they weighed kg (mean, 28.5 kg). There were ten femoral fractures, 12 tibial fractures (Fig. 2 and Fig. 3) and four humeral fractures. Fourteen fractures (53.8%) were acute. Twelve fractures (46.2 %) were old fractures. All fractures were closed. Ten fractures (four femoral, five tibial, one humeral) were associated with other orthopedic problems (such as cranial cruciate ligament rupture and arthritis). The fractures in nine (34.6%) patients showed aseptic non-union or malunion. The static fixation mode was used for nine fractures, and the dynamic fixation mode in 17 (65.3%). In six fractures (23.0%), cerclage wires were used in association with the ILN to stabilize the fragments. The surgical time recorded for the 26 fracture repairs was minutes since skin insicion start. Outcome Complete follow-up data were available for all cases (100%). Among all the animals, 23 (88.4%) showed fracture healing without complications. Three had a major complication requiring surgical intervention (one osteomyelitis, two nonunion with an incorrectly locked ILN). Figure 2: Post-operative, cranio-caudal position after interlocking nail fixation. Figure 3: Post-operative, medio-lateral position after interlocking nail fixation. 48 Arıcan, M. Israel Journal of Veterinary Medicine Vol. 72 (2) June 2017
5 Functional Assessment At 6 months, the functional outcome was excellent in 15 (57.6%) animals, good in seven (26.9%), fair in three (11.5%), and poor in one (3.8%) (Table 2). The ILNs were removed from one dog with osteomyelitis in tibia. The case was a malunion. Implant Failure There were no nail failures associated with bending or fractures of locking screws in this study. Locking Mistakes Six ILNs were not locked correctly because of misdirected distal screws that failed to engage the ILN holes. In three of them only one screw was inserted distal to the implant but in the other three all distal screws were misdirected. There were not misdirected proximal screws. Other Complications Metal cerclage wires used in an one case showed evidence of aseptic necrosis on the tension surface of the femur and osteoporosis associated with stabilization that was caused by disruption of blood supply to bone fragments caused by micro-movement of the wires. The wires were removed, and healing was achieved 6 weeks after replacement. A slight lameness was noted after walking, and therefore functional outcome was classified as fair or good. Excessive callus production were seen in six cases. DISCUSSION Interlocking nail fixation (ILN) supports bone stabilization with or without minimal surgical intervention (2, 5, 9, 15, 21). ILN repairs offer several biomechanical advantages when compared with other fixation devices (17, 22). The method reduces blood loss during the procedure, it speeds up healing time and the recovery of limb function, and it minimizes the risk of complications, such as infections or incomplete bone union (8). Fracture repair involving intramedullary nails is a shorter procedure than plate osteosynthesis (23). As a biological osteosynthesis method, the ILN technique minimizes disturbance to blood supply at the fracture site (15). An ability to lock the cortices of each fracture segment to the nail by use of screws or bolts increases resistance to torsional, compressive, and shear forces when compared with intramedullary pins about the implant going through the neutral axis (24). In this study, ILNs were used to stabilize diaphyseal fractures of the femur, tibia, and humerus of dogs, with a high likelihood of an good and excellent functional outcome. In the study, 22 (84.6%) of 26 dogs with fractures healed with a good or excellent functional outcome. Twenty-two (84.6%) healed without complications, the outcome was considered excellent in 15 patients (57.6%), good in seven patients (26.9%), and fair in three patients. Sixteen patients (14%) required more than 6 weeks to achieve a functional outcome of good or excellent for periodic examination after surgery. Interlocking nails, like other fracture repair modalities, have associated complications. Previously described complications include implant failure, including failure of the nail itself and failure of the locking bolt, misdirected locking bolts, joint penetration, delayed union, non-union and infection. In this study, no nail failures were associated with bending or fracture of locking screws. A relatively large retrospective study of 121 ILN fracture repairs documented problems with healing in 10%-12% of cases and a 4% incidence of stabilization failure (3, 15, 25). ILNs have better resistance to torsion, bending, and shearing than bone plates or external fixators (3, 26, 27). These advantages are especially important in the treatment of comminuted fractures. Likewise, superficial bone deformation, and bone demineralization occurs less with ILNs than with plate fixation (3, 20, 22). From a technical perspective, an ILN does not need to be contoured like a bone plate that must be altered to fit the bone surface. This can be difficult when bone segments are deformed in three dimensions (e.g., the humerus and distal femur of chondrodystrophic dogs). Cerclage wires were used in six cases with multiple fractures for secure and anatomic reconstruction of the bone segments. In this study, surgical time was recorded at around 50 minutes, which should minimize the risk of postoperative infection. However, six ILNs were not locked correctly because of misdirected distal screws that failed to engage the ILN holes. In three cases only one screw was inserted distal to the implant, and but in the other three all distal screws were misdirected. This technical error was related to a failure to align the jig and the ILN accurately. Typically, this occurred if the fixation screw between the ILN and the jig was not applied tightly, if the slide of the jig was not controlled and supported by the muscle, or if the jig moved between locking screw insertions. In conclusion, the use of ILNs to repair diaphyseal fractures of the femur, tibia, and humerus in dogs resulted in a good or excellent functional outcome in most patients. Israel Journal of Veterinary Medicine Vol. 72 (2) June 2017 Naıl Stabılızatıon of Fractures in Dogs 49
6 CONFLICT OF INTERESTS STATEMENT: The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in this research. REFERENCES 1. Basinger, R.R. and Suber, J.T.: Two techniques for supplementing interlocking nail repair of fractures of the humerus, femur, and tibia: results in 12 dogs and cats. Vet. Surg. 33: , Déjardin, L.M., Guiot, L.P. and von Pfeil, D.J.: Interlocking nails and minimally invasive osteosynthesis.vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 42: , Duhautois, B.: Use of veterinary interlocking nails for diaphyseal fractures in dogs and cats: 121 cases. Vet. Surg. 32: 8-20, Nanai, B. and Basinger, R.R.: Use of a new investigational interlocking nail supplement in the repair of comminuted diaphyseal tibia fractures in two dogs. JAVMA. 41: , Durall, I. and Diaz, M.C.: Early experience with the use of an interlocking nail for the repair of canine femoral shaft fractures. Vet. Surg. 25: , Durall, I., Falcón, C., Díaz-Bertrana, M.C. and Franch, J.: Effects of static fixation and dynamization after interlocking femoral nailing locked with an external fixator: an experimental study in dogs. Vet. Surg. 33: , Gatineau, M. and Planté, J.: Ulnar interlocking intramedullary nail stabilization of a proximal radio-ulnar fracture in a dog. Vet. Surg. 39: , Horstman, C.L. and Beale, B.S.: Long fracture repair using the interlocking nail in a minimally invasive surgical procedure in cats and dogs: 65 cases ( ). Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 15: A6, Kürüm, B.: Interlocking Nail Stabilization of Canine Femoral Fractures; Clinical Experience and Results of the Nineteen Cases. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 18, , Dueland, R.T., Berglund, L., Vanderby, Jr. R. and Chao, E.Y.S.: Structural properties of interlocking nails, canine femora, and femur-interlocking nail constructs. Vet. Surg. 25: , Larin, A., Eich, C.S., Parker, R. and Stubbs, W.P.: Repair of diaphyseal femoral fractures in cats using interlocking intramedullary nails: 12 cases ( ). JAVMA. 219: , Langley-Hobbs, S.J. and Friend, E.: Interlocking nail repair of a fractured femur in a turkey. Vet. Rec. 150: , Burns, C.G., Litsky, A.S., Allen, M.J. and Johnson, K.A.; Influence of locking bolt location on the mechanical properties of an interlocking nail in the canine femur. Vet. Surg. 40: , Nunamaker, D.M.: Methods of in internal fixation, in Newton CD, Nunamaker DM (eds): Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, Philadelphia, PA, Lippincott, pp Dueland, R.T., Johnson, K.A., Roe, S.C., Engen, M.H. and Lesser, A.S.: Interlocking nail treatment of diaphyseal long-bone fractures. JAVMA. 214: 59-66, Endo, K., Nakamura, K., Maeda, H. and Matsushita, T.: Interlocking intramedullary nail method for the treatment of femoral and tibial fractures in cats and small dogs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 60: , Durall, I., Diaz-Bertrana, M.C. and Puchol, J.L.: Radiographic findings related to interlocking nailing: windshield wiper effect, and locking screw failure. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 16; , Suber, J.T., Basinger, R.R. and Keller, W.G.: Two unreported modes of interlocking nail failure: breakout and screw bending. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 15: , Winquist, R.A. and Hansen, S.T. Jr.: Comminuted fractures of the femoral shaft treated by intramedullary nailing. Orthop. Clin. North Am. 11, , Meynard, J.A. and Magnin, G.: Clinical callus computerization Proc. World Small Animal Veterinary Association XIX World Congress, Durban, p Patil, D.B., Adamiak, Z. and Piórek, A.: Veterinary interlocking nailing and its augmentation for fracture repair. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 11: , Bernarde, A., Diop, A., Maurel, N. and Viguer, E.: An in vitro biomechanical study of bone plate and interlocking nail in a canine diaphyseal femoral fracture model. Vet. Surg. 30: , Im, G.I. and Tae, S.K.: Distal metaphyseal fractures of tibia: a prospective randomized trial of closed reduction and intramedullary nail versus open reduction and plate and screws fixation. J. Trauma. 59: , Nieves, M.A.: Fracture management using the interlocking nail. Proceedings of the 30th Annual American College of Veterinary Surgeons Forum, San Diego CA, Piórek, A., Adamiak, Z., Jaskólska, M. and Zhalniarovich, Y.: Treatment of comminuted tibial shaft fractures in four dogs with the use of interlocking nailconnected with type I external fixator. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 15: , Schrader, S.C.: Complications associated with the use of Steinmann intramedullary pins and cerclage wires for fixation of long-bone fractures. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 21: , Vasseur, P.B., Paul, H.A. and Crumley, L.: Evaluation of fixation devices for prevention of rotation in transverse fractures of the canine femoral shaft: an in vitro study. Am J Vet Res, 45: , Arıcan, M. Israel Journal of Veterinary Medicine Vol. 72 (2) June 2017
InternationalJournalofAgricultural
 www.ijasvm.com IJASVM InternationalJournalofAgricultural SciencesandVeterinaryMedicine ISSN:2320-3730 Vol.5,No.2,May2017 E-Mail:editorijasvm@gmail.com oreditor@ijasvm.comm@gmail.com Int. J. Agric.Sc &
www.ijasvm.com IJASVM InternationalJournalofAgricultural SciencesandVeterinaryMedicine ISSN:2320-3730 Vol.5,No.2,May2017 E-Mail:editorijasvm@gmail.com oreditor@ijasvm.comm@gmail.com Int. J. Agric.Sc &
Interlocking nails are cylindrical implants designed for intramedullary stabilization
 Article #2 CE Now Online: CE Testing at VetLearn.com An In-Depth Look: INTERLOCKING NAIL FIXATION Intramedullary Interlocking Nail Fixation in Dogs and Cats: Biomechanics and Instrumentation* Jason L.
Article #2 CE Now Online: CE Testing at VetLearn.com An In-Depth Look: INTERLOCKING NAIL FIXATION Intramedullary Interlocking Nail Fixation in Dogs and Cats: Biomechanics and Instrumentation* Jason L.
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery. Zimmer NCB Plating System
 A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
Surgical Technique. Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90
 Surgical Technique Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Table of contents Indications/Contraindications 2 Implants 3 Surgical technique 5 Implant
Surgical Technique Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Table of contents Indications/Contraindications 2 Implants 3 Surgical technique 5 Implant
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery. Zimmer NCB Plating System
 A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90.
 Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Table of Contents Introduction
Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Table of Contents Introduction
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System. Surgical Technique
 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System 1 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System 1 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
EVOS MINI with IM Nailing
 Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
WVJ World's Veterinary Journal
 WVJ World's Veterinary Journal World's Vet. J. 4(1): 06-10, 2014 2014, Scienceline Publication Osteo-synthesis Use in Dogs Femur Surgical Fractures Repair: An Experimental and Comparative Study Bouknine
WVJ World's Veterinary Journal World's Vet. J. 4(1): 06-10, 2014 2014, Scienceline Publication Osteo-synthesis Use in Dogs Femur Surgical Fractures Repair: An Experimental and Comparative Study Bouknine
AcUMEDr. FoREARM ROD SYSTEM
 AcUMEDr FoREARM ROD SYSTEM FoREARM ROD SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been
AcUMEDr FoREARM ROD SYSTEM FoREARM ROD SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been
Technique Guide. LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System.
 Technique Guide LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Technique Guide LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques
 Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Principles of intramedullary nailing. Management for ORP
 Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
Zimmer ITST Intertrochanteric/ Subtrochanteric Fixation System. Abbreviated Surgical Technique
 Zimmer ITST Intertrochanteric/ Subtrochanteric Fixation System Abbreviated Surgical Technique ITST System Abbreviated Surgical Technique Indications The ITST Intramedullary Nail is indicated for use in
Zimmer ITST Intertrochanteric/ Subtrochanteric Fixation System Abbreviated Surgical Technique ITST System Abbreviated Surgical Technique Indications The ITST Intramedullary Nail is indicated for use in
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL
 LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
Zimmer MIS Periarticular Distal Femoral Locking Plate
 For Clinical Evaluations Zimmer MIS Periarticular Distal Femoral Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer MIS Periarticular Distal Femoral Locking Plate Surgical Technique
For Clinical Evaluations Zimmer MIS Periarticular Distal Femoral Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer MIS Periarticular Distal Femoral Locking Plate Surgical Technique
LCP Distal Tibia Plate
 Surgical Technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF Table of contents Indications 3 Implants/Instruments 5 Surgical
Surgical Technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF Table of contents Indications 3 Implants/Instruments 5 Surgical
System. Humeral Nail. Surgical Technique
 System Humeral Nail Surgical Technique Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL
System Humeral Nail Surgical Technique Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL
Fracture and Dislocation of Metacarpal Bones, Metacarpophalangeal Joints, Phalanges, and Interphalangeal Joints ( 1-Jan-1985 )
 In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
The Titanium Tibial Nail System
 The Titanium Tibial Nail System Solid Tibial Nails (UTN) and Cannulated Tibial Nails (CTN) Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
The Titanium Tibial Nail System Solid Tibial Nails (UTN) and Cannulated Tibial Nails (CTN) Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments. Part of the 3.5 mm LCP Percutaneous Instrument System.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments. Part of the 3.5 mm LCP Percutaneous Instrument System. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments. Part of the 3.5 mm LCP Percutaneous Instrument System. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal
Zimmer Natural Nail System
 Zimmer Natural Nail System Antegrade Femoral Nail Surgical Technique (Piriformis Fossa & Greater Trochanteric Approaches) Zimmer Natural Nail System Antegrade Femoral Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer Natural
Zimmer Natural Nail System Antegrade Femoral Nail Surgical Technique (Piriformis Fossa & Greater Trochanteric Approaches) Zimmer Natural Nail System Antegrade Femoral Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer Natural
Pakistan Veterinary Journal
 REVIEW ARTICLE Pakistan Veterinary Journal ISSN: 0253-8318 (PRINT), 2074-7764 (ONLINE) Accessible at: www.pvj.com.pk Stabilization of Fractures with the Use of Veterinary Interlocking Nails Adam Piórek*,
REVIEW ARTICLE Pakistan Veterinary Journal ISSN: 0253-8318 (PRINT), 2074-7764 (ONLINE) Accessible at: www.pvj.com.pk Stabilization of Fractures with the Use of Veterinary Interlocking Nails Adam Piórek*,
TITANIUM TIBIAL NAIL SySTEM
 TITANIUM TIBIAL NAIL SySTEM Solid and Cannulated Nails SURGICAL TEChNIqUE Table of contents Introduction Indications 2 Preoperative Implant Selection 6 Surgical Technique Instruments for Opening the Tibia
TITANIUM TIBIAL NAIL SySTEM Solid and Cannulated Nails SURGICAL TEChNIqUE Table of contents Introduction Indications 2 Preoperative Implant Selection 6 Surgical Technique Instruments for Opening the Tibia
Techique. Results. Discussion. Materials & Methods. Vol. 2 - Year 1 - December 2005
 to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
Surgical Technique. Targeter Systems Overview
 Surgical Technique Targeter Systems Overview PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Targeter Systems Overview Table of contents Product overview... 2 Introduction... 2 Indications... 2 Design features and benefits...
Surgical Technique Targeter Systems Overview PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Targeter Systems Overview Table of contents Product overview... 2 Introduction... 2 Indications... 2 Design features and benefits...
3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM
 3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm VA-LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 2 AO
3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm VA-LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 2 AO
Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate
 Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer MIS
Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer MIS
Surgical Technique. Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates
 Surgical Technique Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates PERI-LOC Periarticular Locked Plating System Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates Surgical Technique Contents Product
Surgical Technique Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates PERI-LOC Periarticular Locked Plating System Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates Surgical Technique Contents Product
3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 8. DISTAL GUIDED LOCKING FOR PROXIMAL NAIL PROXIMAL LOCKING FOR LONG NAIL 13
 Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL NAIL INSERTION 6-7 7. PROXIMAL LOCKING
Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL NAIL INSERTION 6-7 7. PROXIMAL LOCKING
A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of The Tibia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual
 Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual Note: The surgical procedures should be performed under the guidance of qualified skilled orthopedic surgeons, and this surgical
Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual Note: The surgical procedures should be performed under the guidance of qualified skilled orthopedic surgeons, and this surgical
Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia
 Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: DCP Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia 1. Undercut adjacent to the holes low contact: less stress shield 2. Undercut at the undersurface
Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: DCP Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia 1. Undercut adjacent to the holes low contact: less stress shield 2. Undercut at the undersurface
Small Fragment Plating System. Securing optimal fixation through locked and compression plating technology
 Small Fragment Plating System Securing optimal fixation through locked and compression plating technology Contents Design Rationale Introduction Interfragmentary Fixation Insertion of a 3.5 mm Cortical
Small Fragment Plating System Securing optimal fixation through locked and compression plating technology Contents Design Rationale Introduction Interfragmentary Fixation Insertion of a 3.5 mm Cortical
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications 3 Clinical
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications 3 Clinical
Fracture fixation. Types. Mechanical considerations. Biomechanics of fracture fixation. External fixation. Internal fixation
 Fracture fixation Biomechanics of fracture fixation Types External fixation Mechanical considerations Internal fixation Mechanical considerations in treatment of 1. In the external fixation: fracture When
Fracture fixation Biomechanics of fracture fixation Types External fixation Mechanical considerations Internal fixation Mechanical considerations in treatment of 1. In the external fixation: fracture When
LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
 LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia. LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia. LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the Synthes LCP periarticular plating system.
 LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the Synthes LCP periarticular plating system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the Synthes LCP periarticular plating system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates
2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP Elbow System DJ9257-B 1
 2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP Elbow System DJ9257-B 1 System overview Simply complete: A comprehensive system, consisting of five (5) distal humerus plates and three (3) types of olecranon plates Implant
2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP Elbow System DJ9257-B 1 System overview Simply complete: A comprehensive system, consisting of five (5) distal humerus plates and three (3) types of olecranon plates Implant
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System
 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Flexibility and compatibility in one system Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Flexibility and compatibility in one system Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System
Provision of Rotational Stability: Prevention of Collapse: Closed Fracture Reduction: Minimally Invasive Surgery with no Exposure of the Fracture:
 INTRODUCTION Percutaneous Compression Plating was developed by considering each of the stages in the surgical procedure for pertrochanteric fractures and the ways in which these might be improved. Primary
INTRODUCTION Percutaneous Compression Plating was developed by considering each of the stages in the surgical procedure for pertrochanteric fractures and the ways in which these might be improved. Primary
Technique Guide. SureLock Distal Targeting Device. C-arm guided targeting for trochanteric fixation nail.
 Technique Guide SureLock Distal Targeting Device. C-arm guided targeting for trochanteric fixation nail. Table of Contents Introduction SureLock Distal Targeting Device 2 Surgical Technique Preoperative
Technique Guide SureLock Distal Targeting Device. C-arm guided targeting for trochanteric fixation nail. Table of Contents Introduction SureLock Distal Targeting Device 2 Surgical Technique Preoperative
NeoGen Femoral Nail System
 NeoGen Femoral Nail System LESS IS MORE TE-2070-04 Surgical Technique BLE OF CONTENT Preface Standard Femoral Mode Recon Mode Post-Operative Management Appendix Products Information Indication Patient
NeoGen Femoral Nail System LESS IS MORE TE-2070-04 Surgical Technique BLE OF CONTENT Preface Standard Femoral Mode Recon Mode Post-Operative Management Appendix Products Information Indication Patient
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation.
 LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions)
 Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
NeoGen Tibia Nail System
 NeoGen Tibia Nail System LESS IS MORE TE-2070-03 Surgical Technique BLE OF CONTENT Preface Surgical Technique Appendix Products Information Patient Preparation Entry Portal Fracture Reduction Canal Preparation
NeoGen Tibia Nail System LESS IS MORE TE-2070-03 Surgical Technique BLE OF CONTENT Preface Surgical Technique Appendix Products Information Patient Preparation Entry Portal Fracture Reduction Canal Preparation
The Vilex FUZETM. Dual Thread Screw & Intramedullary Nail in One Implant. The Ultimate TTC Arthrodesis Internal Fixator
 The Vilex FUZETM Dual Thread Screw & Intramedullary Nail in One Implant The Ultimate TTC Arthrodesis Internal Fixator Introduction The Vilex FUZE TM TTC Arthrodesis Compression Nail combines the attributes
The Vilex FUZETM Dual Thread Screw & Intramedullary Nail in One Implant The Ultimate TTC Arthrodesis Internal Fixator Introduction The Vilex FUZE TM TTC Arthrodesis Compression Nail combines the attributes
Surgical Technique. Intramedullary locked Nailing With Screws for Humerus Fractures Solid/Cannulated. Humeral Interlocking Nail.
 Screws for Humerus Fractures Surgical Technique Humeral Interlocking Nail Approved by Humerus Nail Kit Code 08050001 Contents Introduction Implant design Indications Pre-operative planning Patient positioning
Screws for Humerus Fractures Surgical Technique Humeral Interlocking Nail Approved by Humerus Nail Kit Code 08050001 Contents Introduction Implant design Indications Pre-operative planning Patient positioning
Small Fragment Plating System
 Small Fragment Plating System Securing optimal fixation through locked and compression plating technology SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RECOVERY FUNCTION SURVIVORSHIP DePuy believes in an approach to trauma surgery
Small Fragment Plating System Securing optimal fixation through locked and compression plating technology SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RECOVERY FUNCTION SURVIVORSHIP DePuy believes in an approach to trauma surgery
Olecranon Osteotomy Nail. For simple fractures and osteotomies of the olecranon.
 Olecranon Osteotomy Nail. For simple fractures and osteotomies of the olecranon. Technique Guide Discontinued June 2016; AVAILABLE FOR IMPLANT REMOVAL PURPOSES ONLY DSEM/TRM/0517/0843 Table of Contents
Olecranon Osteotomy Nail. For simple fractures and osteotomies of the olecranon. Technique Guide Discontinued June 2016; AVAILABLE FOR IMPLANT REMOVAL PURPOSES ONLY DSEM/TRM/0517/0843 Table of Contents
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
2016 SIGN Conference: Treatment of Difficult Fractures Around The World
 2016 SIGN Conference: Treatment of Difficult Fractures Around The World September 21-24, 2016 Long Bone Osteosynthesis Failure DUONG BUNN Trauma-Orthopedique ward Preah Kossamak Preah Sihaknouk Ville Beach
2016 SIGN Conference: Treatment of Difficult Fractures Around The World September 21-24, 2016 Long Bone Osteosynthesis Failure DUONG BUNN Trauma-Orthopedique ward Preah Kossamak Preah Sihaknouk Ville Beach
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation
 Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
TIBIAL NAILING SYSTEM OPTIONS MADE EASY
 S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E TIBIAL NAILING SYSTEM OPTIONS MADE EASY TABLE OF CONTENTS DESIGN SUMMARY INSTRUMENT OVERVIEW AND JIG OPTIONS 1 2 ENTRY AND CANAL PREP NAIL INSERTION LOCKING NAIL REMOVAL
S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E TIBIAL NAILING SYSTEM OPTIONS MADE EASY TABLE OF CONTENTS DESIGN SUMMARY INSTRUMENT OVERVIEW AND JIG OPTIONS 1 2 ENTRY AND CANAL PREP NAIL INSERTION LOCKING NAIL REMOVAL
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system.
 LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
Large Distractor Femur
 Fracture Reduction and Provisional Stabilization Large Distractor Femur Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Standard Femoral Distraction 2 Large Distractor System 4 Surgical Technique Prepare
Fracture Reduction and Provisional Stabilization Large Distractor Femur Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Standard Femoral Distraction 2 Large Distractor System 4 Surgical Technique Prepare
Surgical Technique. Proximal Humerus Locking Plate
 Surgical Technique Proximal Humerus Locking Plate PERI-LOC Upper Extremity Locked Plating System 3.5mm & 4.5mm Proximal Humerus Locking PlatesCatalog Infor Table of Contents Introduction.........................................................2
Surgical Technique Proximal Humerus Locking Plate PERI-LOC Upper Extremity Locked Plating System 3.5mm & 4.5mm Proximal Humerus Locking PlatesCatalog Infor Table of Contents Introduction.........................................................2
OPERATING MANUAL AND TECHNIQUE GUIDE FOR TITANIUM FEMORAL AND TIBIAL NAILING SYSTEMS
 OPERATING MANUAL AND TECHNIQUE GUIDE FOR TITANIUM FEMORAL AND TIBIAL NAILING SYSTEMS ORTHO-MEDICAL GMBH TITANIUM FEMORAL NAIL OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE Introduction: Why a new type of femoral nail? The latest
OPERATING MANUAL AND TECHNIQUE GUIDE FOR TITANIUM FEMORAL AND TIBIAL NAILING SYSTEMS ORTHO-MEDICAL GMBH TITANIUM FEMORAL NAIL OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE Introduction: Why a new type of femoral nail? The latest
GREENS SURGICALS. Redefining Excellence INSTRUMENT SYSTEM PREPARED BY: DR. VINAY KUMAR
 GREENS SURGICALS Redefining Excellence TIBIA AND FEMUR INSTRUMENT SYSTEM PREPARED BY: DR. VINAY KUMAR OPERATIVE TECHNIQUES INDEX SR.NO CONTENTS 1 LIST OF INSTRUMENT FOR TIBIA AND FEMUR. 2 RADIO GRAPH OF
GREENS SURGICALS Redefining Excellence TIBIA AND FEMUR INSTRUMENT SYSTEM PREPARED BY: DR. VINAY KUMAR OPERATIVE TECHNIQUES INDEX SR.NO CONTENTS 1 LIST OF INSTRUMENT FOR TIBIA AND FEMUR. 2 RADIO GRAPH OF
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF DIAPHYSEAL FEMUR FRACTURE WITH INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL AND K. NAIL
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 3 Apr. 2016, pp. 560-564 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ COMPARATIVE
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 3 Apr. 2016, pp. 560-564 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ COMPARATIVE
OptiLock Periarticular Plating System For Distal Femoral Fractures. Pre-Launch Surgical Technique
 OptiLock Periarticular Plating System For Distal Femoral Fractures Pre-Launch Surgical Technique Contents Introduction... Page 1 Indications And Fracture Classification... Page 6 Design Features... Page
OptiLock Periarticular Plating System For Distal Femoral Fractures Pre-Launch Surgical Technique Contents Introduction... Page 1 Indications And Fracture Classification... Page 6 Design Features... Page
Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture
 Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture HT Ling, MBBS (UM), WM Ng, MS Ortho (UM), MK Kwan, MS Ortho (UM), LK Fathi Aizuddeen, MBBS (UM), PCM Tay, MBBS
Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture HT Ling, MBBS (UM), WM Ng, MS Ortho (UM), MK Kwan, MS Ortho (UM), LK Fathi Aizuddeen, MBBS (UM), PCM Tay, MBBS
Surgical Technique. CONQUEST FN Femoral Neck Fracture System
 Surgical Technique CONQUEST FN Femoral Neck Fracture System Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Indications... 3 Product Overview... 4 Surgical Technique... 5 Patient Positioning... 5 Reduce the Fracture...
Surgical Technique CONQUEST FN Femoral Neck Fracture System Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Indications... 3 Product Overview... 4 Surgical Technique... 5 Patient Positioning... 5 Reduce the Fracture...
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
Technique Guide. 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology.
 Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
Locked Plating: Clinical Indications
 Techniques in Orthopaedics 22(3):181 185 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Locked Plating: Clinical Indications Kyle F. Dickson, M.D., M.B.A., John Munz, M.D. Summary: As shown in the previous article,
Techniques in Orthopaedics 22(3):181 185 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Locked Plating: Clinical Indications Kyle F. Dickson, M.D., M.B.A., John Munz, M.D. Summary: As shown in the previous article,
IMPORTANT MEDICAL INFORMATION Advanced Orthopaedic Solutions INTRAMEDULLARY NAILS Warnings and Precautions (SINGLE USE ONLY)
 IMPORTANT MEDICAL INFORMATION Advanced Orthopaedic Solutions INTRAMEDULLARY NAILS Warnings and Precautions (SINGLE USE ONLY) IMPORTANT NOTE Intramedullary nails provide an alternative to open reduction
IMPORTANT MEDICAL INFORMATION Advanced Orthopaedic Solutions INTRAMEDULLARY NAILS Warnings and Precautions (SINGLE USE ONLY) IMPORTANT NOTE Intramedullary nails provide an alternative to open reduction
Arthrodesis of the Ankle
 TM Arthrodesis of the Ankle Plantar View of the Foot 1. Make a lateral incision to expose the tibia-talus joint and the talo-calcaneal joint. Prepare the arthrodesis sites surgically with a rasp or an
TM Arthrodesis of the Ankle Plantar View of the Foot 1. Make a lateral incision to expose the tibia-talus joint and the talo-calcaneal joint. Prepare the arthrodesis sites surgically with a rasp or an
Failed Subtrochanteric Fracture How I Decide What to Do?
 Failed Subtrochanteric Fracture How I Decide What to Do? Gerald E. Wozasek Thomas M. Tiefenboeck 5 October 2016, Washington Medical University of Vienna, Department of Trauma Surgery ordination @wozasek.at
Failed Subtrochanteric Fracture How I Decide What to Do? Gerald E. Wozasek Thomas M. Tiefenboeck 5 October 2016, Washington Medical University of Vienna, Department of Trauma Surgery ordination @wozasek.at
Femur Condylar Plate System Procedural Steps.
 Femur Condylar Plate System Procedural Steps www.carbo-fix.com 1 Table of Contents Introduction..3 Instrumentation Set... 8 Procedural Steps:...... 12 Ordering Information 19 2 Introduction The CarboFix
Femur Condylar Plate System Procedural Steps www.carbo-fix.com 1 Table of Contents Introduction..3 Instrumentation Set... 8 Procedural Steps:...... 12 Ordering Information 19 2 Introduction The CarboFix
S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E David A. McQueen, MD Return to Menu
 S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E David A. McQueen, MD TOTAL KNEE INSTRUMENTS Wichita Fusion Nail Introduction...1 Preoperative Planning...2 Surgical Technique...3-8 Wichita Fusion Nail Surgical Technique
S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E David A. McQueen, MD TOTAL KNEE INSTRUMENTS Wichita Fusion Nail Introduction...1 Preoperative Planning...2 Surgical Technique...3-8 Wichita Fusion Nail Surgical Technique
Surgical Technique.
 Surgical Technique www.biomet.co.uk INTRODUCTION design principals Recent advances in imaging technology have enabled orthopaedic surgeons to extend closed treatment of femoral fractures to include more
Surgical Technique www.biomet.co.uk INTRODUCTION design principals Recent advances in imaging technology have enabled orthopaedic surgeons to extend closed treatment of femoral fractures to include more
Fractures of the Humerus ( 1-Jan-1985 )
 In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fractures of the Humerus
In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fractures of the Humerus
2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP. Ankle Trauma System
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Locking Compression Plate (VA LCP ) System 2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP Ankle Trauma System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm
Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Locking Compression Plate (VA LCP ) System 2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP Ankle Trauma System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm
TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS
 TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS ANATOMICAL LOCATIONS FOR EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS Humeral Dynamic Axial Fixator Elbow Fixator Pelvic Dynamic Axial Fixator Pennig Wrist Fixator Hand Fixator Finger Fixator
TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS ANATOMICAL LOCATIONS FOR EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS Humeral Dynamic Axial Fixator Elbow Fixator Pelvic Dynamic Axial Fixator Pennig Wrist Fixator Hand Fixator Finger Fixator
Wichita Fusion Nail Surgical Technique. David A. McQueen, MD
 Wichita Fusion Nail Surgical Technique David A. McQueen, MD The patented design with a dual advantage Generates compression intraoperatively Innovative compression screw (a) locks femoral and tibial components
Wichita Fusion Nail Surgical Technique David A. McQueen, MD The patented design with a dual advantage Generates compression intraoperatively Innovative compression screw (a) locks femoral and tibial components
NEW INSTRUMENTS FOR INTERNAL FIXATION OF FRACTURES USING MINIMALLY INVASIVE TECHNIQUES
 NEW INSTRUMENTS FOR INTERNAL FIXATION OF FRACTURES USING MINIMALLY INVASIVE TECHNIQUES Dr.eng. Comşa Stanca, sing. Gheorghiu Doina, eng. Ciobota Dan National Institute of Research & Development for fine
NEW INSTRUMENTS FOR INTERNAL FIXATION OF FRACTURES USING MINIMALLY INVASIVE TECHNIQUES Dr.eng. Comşa Stanca, sing. Gheorghiu Doina, eng. Ciobota Dan National Institute of Research & Development for fine
Open reduction; plate fixation 1 Principles
 Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
 Copyright 2016 NGD. All rights reserved Neil Embleton, B.Sc., DVM and Veronica Barkowski, DVM Helivet Mobile Surgical Services, Sundre, AB, Canada July 2016 SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
Copyright 2016 NGD. All rights reserved Neil Embleton, B.Sc., DVM and Veronica Barkowski, DVM Helivet Mobile Surgical Services, Sundre, AB, Canada July 2016 SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
TABLE OF CONTENTS. 2 (8144 Rev 2)
 1 (8144 Rev 2) TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Conventus CAGE TM - Proximal Humerus...3 Indications and Contraindications...4 Surgical Summary...5 Patient Positioning & Approach...6 Surgical Technique Plate
1 (8144 Rev 2) TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Conventus CAGE TM - Proximal Humerus...3 Indications and Contraindications...4 Surgical Summary...5 Patient Positioning & Approach...6 Surgical Technique Plate
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System. Table of Contents AO ASIF Principles of Internal Fixation 4 Indications/Contraindications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System. Table of Contents AO ASIF Principles of Internal Fixation 4 Indications/Contraindications 5 Surgical Technique
Distal Ulnar Locking Plate
 INDEX Indications Patient Position Surgical Technique - Step 1 Approach - Step 2 Plate Contouring - Step 3 Fracture Reduction - Step 4 Distal Plate Fixation - Step 5 Confirm Proper Reconstruction - Step
INDEX Indications Patient Position Surgical Technique - Step 1 Approach - Step 2 Plate Contouring - Step 3 Fracture Reduction - Step 4 Distal Plate Fixation - Step 5 Confirm Proper Reconstruction - Step
SMV Scientific Bone Plate and Screw System Surgical Technique
 SMV Scientific Bone Plate and Screw System Surgical Technique Description: The SMV Scientific Bone Plate and Screw System consists of non-locking plates and bone screw fasteners in a variety of lengths,
SMV Scientific Bone Plate and Screw System Surgical Technique Description: The SMV Scientific Bone Plate and Screw System consists of non-locking plates and bone screw fasteners in a variety of lengths,
AcUMEDr. Locking Proximal Humeral Plate. PoLARUSr PHPt
 AcUMEDr Locking Proximal Humeral Plate PoLARUSr PHPt PoLARUSr PHPt LOCKING PROXIMAL HUMERAL PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons,
AcUMEDr Locking Proximal Humeral Plate PoLARUSr PHPt PoLARUSr PHPt LOCKING PROXIMAL HUMERAL PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons,
Surgical Technique. Distal Humerus Locking Plate
 Surgical Technique Distal Humerus Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Distal Humerus Locking Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
Surgical Technique Distal Humerus Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Distal Humerus Locking Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
AcUMEDr. LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM
 AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
Aesculap Targon FN. Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures. Aesculap Orthopaedics
 Aesculap Targon FN Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures Aesculap Orthopaedics Targon FN Operating Technique Indications for Targon FN AO 3 B. AO 3 B.2 AO 3 B.3 Undisplaced intracapsular
Aesculap Targon FN Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures Aesculap Orthopaedics Targon FN Operating Technique Indications for Targon FN AO 3 B. AO 3 B.2 AO 3 B.3 Undisplaced intracapsular
A Locking IM Rod that won't back out. Simple and straight to the point! SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 A Locking IM Rod that won't back out. Simple and straight to the point! SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The SLIM (Simple Locking IntraMedullary) System is a new generation of pediatric orthopedic nails specifically
A Locking IM Rod that won't back out. Simple and straight to the point! SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The SLIM (Simple Locking IntraMedullary) System is a new generation of pediatric orthopedic nails specifically
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE. The XCaliber Meta-Diaphyseal Fixator
 17 The XCaliber Meta-Diaphyseal Fixator GENERAL POINTS The XCaliber Fixator is made of radiolucent material for unobstructed X-ray visualization. The metallic bolts and the cam and bush of each ball-joint,
17 The XCaliber Meta-Diaphyseal Fixator GENERAL POINTS The XCaliber Fixator is made of radiolucent material for unobstructed X-ray visualization. The metallic bolts and the cam and bush of each ball-joint,
LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures.
 LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the
LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the
Surgical Technique. 3.5mm and 4.5mm Lateral Proximal Tibia Locking Plates
 Surgical Technique 3.5mm and 4.5mm Lateral Proximal Tibia Locking Plates PERI-LOC Periarticular Locked Plating System 3.5mm and 4.5mm Lateral Proximal Tibia Locking Plate Surgical Technique Contents Product
Surgical Technique 3.5mm and 4.5mm Lateral Proximal Tibia Locking Plates PERI-LOC Periarticular Locked Plating System 3.5mm and 4.5mm Lateral Proximal Tibia Locking Plate Surgical Technique Contents Product
THE NANCY NAIL. The End Caps ADVANTAGES OF NANCY NAIL
 NANCY NAIL THE NANCY NAIL Nancy nails are manufactured from a specific titanyum alloy with proprietary surface treatment, which provides increased fatigue resistance. Six nail diameters (1.5 mm 2.0 mm
NANCY NAIL THE NANCY NAIL Nancy nails are manufactured from a specific titanyum alloy with proprietary surface treatment, which provides increased fatigue resistance. Six nail diameters (1.5 mm 2.0 mm
Technique Guide. TomoFix Osteotomy System. A comprehensive plating system for stable fixation of osteotomies around the knee.
 Technique Guide TomoFix Osteotomy System. A comprehensive plating system for stable fixation of osteotomies around the knee. Table of Contents Introduction TomoFix Osteotomy System 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Technique Guide TomoFix Osteotomy System. A comprehensive plating system for stable fixation of osteotomies around the knee. Table of Contents Introduction TomoFix Osteotomy System 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate
 For Treatment of Periprosthetic Fractures 3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate 2 Indications 4 Surgical Technique Preparation
For Treatment of Periprosthetic Fractures 3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate 2 Indications 4 Surgical Technique Preparation
