Clinical Policy Title: Knee Braces
|
|
|
- Gyles Rose
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clinical Policy Title: Knee Braces Clinical Policy Number: CCP.1392 Effective Date: August 1, 2018 Initial Review Date: June 5, 2018 Most Recent Review Date: July 3, 2018 Next Review Date: July 2019 Policy contains: Knee brace. Knee orthotics. Osteoarthritis. Related policies: None. ABOUT THIS POLICY: Select Health of South Carolina has developed clinical policies to assist with making coverage determinations. Select Health of South Carolina s clinical policies are based on guidelines from established industry sources, such as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), state regulatory agencies, the American Medical Association (AMA), medical specialty professional societies, and peerreviewed professional literature. These clinical policies along with other sources, such as plan benefits and state and federal laws and regulatory requirements, including any state- or plan-specific definition of medically necessary, and the specific facts of the particular situation are considered by Select Health of South Carolina when making coverage determinations. In the event of conflict between this clinical policy and plan benefits and/or state or federal laws and/or regulatory requirements, the plan benefits and/or state and federal laws and/or regulatory requirements shall control. Select Health of South Carolina s clinical policies are for informational purposes only and not intended as medical advice or to direct treatment. Physicians and other health care providers are solely responsible for the treatment decisions for their patients. Select Health of South Carolina s clinical policies are reflective of evidence-based medicine at the time of review. As medical science evolves, Select Health of South Carolina will update its clinical policies as necessary. Select Health of South Carolina s clinical policies are not guarantees of payment. Coverage policy Select Health of South Carolina considers the use of knee braces (orthoses) to be clinically proven, and therefore, medically necessary, for any of the following conditions: 1. Prefabricated braces. a. A flexion contracture (shortening of the muscles and/or tendons that limits knee extension to zero degrees extension) after injury, surgery, casting, or other immobilization. b. An extension contracture (shortening of the muscles and/or tendons that limits knee flexion to 80 degrees by passive range of motion) after injury, surgery, casting, or other immobilization. c. Weakness or deformity of the knee that requires stabilization. d. Flexion or extension contractures with movement on passive range of motion testing of at least 10 degrees (brace has locking knee joint). e. A recent injury or knee surgery (brace has a knee immobilizer without joints or with an adjustable flexion and extension joint that provides medial-lateral and rotation control). f. A congenital or acquired hyperextended knee causing instability in ambulatory members. 0
2 g. Painful arthritis in the medial compartment of the knee (unloader braces). 2. Custom fabricated braces. a. A documented physical characteristic requiring use of a custom fabricated orthosis. These include, but are not limited to, deformity of the leg or knee, size of thigh and calf, and minimal muscle mass upon which to suspend an orthosis. An adjustable flexion and extension joint may be required in some cases. b. Instability due to internal ligamentous disruption of the knee (derotation knee orthosis). c. Knee instability due to genu recurvatum/hyperextended knee for ambulatory members (custom fabricated knee orthosis with a modified supracondylar prosthetic socket) (CMS, L33018, 2015). Limitations: Select Health of South Carolina considers the use of knee braces (orthoses) to be investigational/experimental, and therefore not medically necessary, for: 1. Prefabricated braces for members with no documented criteria in (1) above. 2. Custom fabricated braces for members with no documented criteria in (2) above. 3. Molded-to-patient model braces. 4. Prophylactic knee braces. Alternative covered services: None. Background Knee braces are a type of durable medical equipment that are also known as orthotics. They are devices that range from a simple strap worn below the kneecap to an elaborate device that stretches from the thigh to the shin, with a hinge at the joint. Knee braces consist of a hinge centered around the knee s axis of motion, superstructure (shell that extends around the hinge), and strap system that secures the brace to the limb. The purpose of a knee brace is to support a weak or deformed body part or restrict motion in a damaged body part. Braces can reduce pain or other impairment and prevent further injury and/or improve range of motion without causing further harm or damage. Several types of knee braces are used for various reasons. 1. A prefabricated model is purchased over the counter and fitted to individual body contours. 2. A custom-made model is made for a specific individual by bending, cutting, sewing, or molding. 1
3 3. A molded-to-patient model is manufactured by first creating a plaster cast impression, and molding the brace on to the model (Personal Health Insurance, 2013). Knee braces are used for various purposes, including: 1. A functional brace stabilizes an unstable joint, often during elective activities, such as sports, and sometimes when osteoarthritis is present. 2. An unloader brace shifts some weight in an osteoarthritic knee, reducing pain; osteoarthritis affects 9.3 Americans older than age 45 in the United States (Gohal, 2018). 3. A rehabilitative brace moderates motion in a knee just after injury or surgery. 4. A prophylactic brace is used to prevent or reduce injury severity, such as ligament tears (Paluska, 2000). For years, guidelines have been developed for knee brace use. An early set of recommendations by the American Academy of Family Physicians found no conclusive evidence that prophylactic knee braces were effective to prevent knee damage; that patellofemoral braces offer moderate improvement to anterior knee disorders; and functional braces have demonstrated ability to stabilize knees during rotational and anteroposterior forces (Paluska, 2000). Many guidelines in the last decade address only single purposes of knee braces; osteoarthritis is a common topic. A guideline from the French Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Society found that while braces are not often prescribed for osteoarthritis of the knee, responses to valgus knee bracing remain inconsistent with considerable side effects (Beaudreuil, 2009). Unloading knee braces have been recommended to reduce knee pain, based on professional evidence (Rannou, 2010). The Osteoarthritis Research Society International guideline recommended bracing for persons with knee osteoarthritis and mild-to-moderate varus/valgus instability, based on findings that knee braces can reduce pain and increase stability of the joint (Zhang, 2008). The American College of Rheumatology did not make recommendations on wearing knee braces for osteoarthritis (Hochberg, 2012). The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (2013) could not recommend for or against the use of valgus directing force knee braces for persons with osteoarthritis. The Academy did state that a hinged knee brace and/or unloading brace may be appropriate for reducing pain and increasing range of motion in knee osteoarthritis (Yates, 2014). Searches Select Health of South Carolina searched PubMed and the databases of: UK National Health Services Centre for Reviews and Dissemination. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality s National Guideline Clearinghouse and other evidence-based practice centers. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. 2
4 We conducted searches on April 28, Search terms were: knee braces and orthotics. We included: Systematic reviews, which pool results from multiple studies to achieve larger sample sizes and greater precision of effect estimation than in smaller primary studies. Systematic reviews use predetermined transparent methods to minimize bias, effectively treating the review as a scientific endeavor, and are thus rated highest in evidence-grading hierarchies. Guidelines based on systematic reviews. Economic analyses, such as cost-effectiveness, and benefit or utility studies (but not simple cost studies), reporting both costs and outcomes sometimes referred to as efficiency studies which also rank near the top of evidence hierarchies. Findings Numerous systematic reviews and meta-analyses have been conducted on effectiveness of knee braces. Articles mentioned below are all systematic reviews, unless meta-analysis is indicated. Comparing types of braces 1. Studies (n = 24) of knee complications documented that static progressive stretch bracing (one to three sessions a day, seven to nine weeks) had a significantly greater increase in range of motion (31 degrees) than did dynamic braces (six to eight weeks). Patients who had static progressive stretch bracing also had a superior increase in mean flexion (22 degrees) compared with that of patients who had dynamic knee bracing (seven degrees), leading authors to recommend it as a first-line recommendation for persons with knee pathology (Sodhi, 2017). Sports injuries anterior cruciate ligament 1. Early studies showed no benefit of wearing knee braces to the anterior cruciate ligament. A review (seven studies) on effects of prophylactic use of knee braces among college football players found injury risk declined in three and increased in four studies (Pietrosimone, 2008). 2. A review of 70 randomized controlled trials determined that use of a knee brace, after reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament, does not affect the clinical outcome (Andersson, 2009). 3. A review of six studies of rehabilitation after anterior cruciate ligament surgery concluded bracing was ineffective and no recommendation was made for its use. However, the review did find that accelerated and home-based rehabilitation, neuromuscular training programs, hyaluronic acid injection, and single (uninjured) leg cycling may be beneficial (Grant, 2013). 3
5 4. A review of six analyses of prophylactic use of knee braces among U.S. football players showed a significant reduction in medial collateral ligament injuries in only one study, and thus authors did not recommend routine prophylactic use of braces (Salata, 2010). 5. A systematic review of biomechanical and clinical evidence suggests functional bracing does not sufficiently restore normal biomechanics to the anterior cruciate ligament-deficient knee, protect the reconstructed ligament, and improve long-term patient outcomes, and that further improvements are needed in bracing technology (Smith, 2014). 6. A review of 15 studies (only three randomized) of persons followed from three to 48 months after anterior cruciate ligament repair showed bracing significantly improved kinematics of the knee joint and improved gait kinetics, while decreasing quadriceps activation. Authors termed the effectiveness of this type of surgery to be elusive (Lowe, 2017), while another expert (after a review of 28 articles) declared that the literature does not support the use of braces after anterior cruciate ligament surgery (Rodriguez-Merchan, 2016). Osteoarthritis 1. In 25 studies of patients with varus and valgus knee osteoarthritis, Generation II knee braces, valgus knee braces, and functional off-loading knee braces were found to be effective in decreasing pain, joint stiffness, and drug dosage (Raja, 2011). 2. A Cochrane review of 13 studies (n = 1,356) of knee braces and other conservative methods of treating medial compartment knee osteoarthritis revealed inconclusive benefits of bracing for pain, stiffness, function, and quality of life (Duivenvoorden, 2015). 3. A meta-analysis of six studies documented persons with osteoarthritis using valgus braces to have a significant pain improvement (P = 0.001) and function (P = 0.03). Compared with a control group that did not use an orthosis, the valgus group had a significantly greater reduction in pain (P = 0.04) and function (P = 0.04) and a significant improvement (P = 0.01) in pain compared with patients using a control orthosis (Moyer, 2015a). 4. The same research team performed a meta-analysis of 17 studies, linking braces with a significant decrease in external knee adduction moment during walking, with a near-significant link to effect size and duration of brace use only, and with longer durations of brace use associated with smaller treatment effects (Moyer, 2015b). 5. A review of 12 studies of persons with knee osteoarthritis determined knee braces decreased pain, but improved function, improved range of motion, and increased speed of walking and step length, along with a reduction in the adduction moment applied to the knee (Mileki, 2016). 6. A review found 20 of 24 articles addressing medial osteoarthritis revealed that valgus unloader braces significantly decrease the knee adduction moment (Petersen, 2016). 4
6 7. A review of 31 studies (n = 619) typically found improved pain outcomes using valgus offloader braces, but variable results in functional outcomes and stiffness. Offloader bracing was more effective at reducing pain versus neutral braces or neoprene sleeves (Gohal, 2018). 8. A review of 11 studies (n = 284), six randomized, documented significant improvement in pain (P = 0.007) for persons with osteoarthritis wearing versus not wearing a soft brace. Those wearing a soft brace versus standard care showed significant improvements in pain reduction (P < 0.001) and self-reported physical function (P = 0.006) (Cudejko, 2018). 9. A review of 30 studies (four of which addressed bracing) compared several treatments for pain in knee osteoarthritis. Bracing had a significant reduction standardized mean difference in pain of 1.34 more effective than insoles (0.992) but less effective than transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (1.796) and neuromuscular electrical stimulation (1.924) (Cherian, 2016). 10. A review of seven Japanese-language randomized trials found no conclusive evidence on effectiveness of any braces for patients with medial knee osteoarthritis (Mine, 2017). Patellofemoral syndrome. 1. A Cochrane review of five trials (n = 368) failed to produce helpful evidence on effectiveness of knee orthoses for treating patellofemoral syndrome. Very-low-quality evidence suggested that knee braces did not reduce knee pain or improve knee function in under three months in adults who were also undergoing an exercise program for treating the disorder (Smith, 2015). 2. A meta-analysis of 37 trials on adults with patellofemoral pain found 80 percent did not show a clinically significant benefit. In the remaining seven studies, significant reductions in pain were documented for pulsed electromagnetic fields plus home exercise (-33.0), hip muscle strengthening (-65.0 and -32.0), weight-bearing exercise (-40.0), neuromuscular facilitation plus aerobic exercise and stretching (-60.1), postural stabilization (-24.4), and patellar bracing (-31.6) (Saltychev, 2018). Policy updates: None. Summary of clinical evidence: Citation Saltychev (2018) Content, Methods, Recommendations Key points: Systematic review and meta-analysis of adults with patellofemoral pain. 5
7 Citation Treatment of patellofemoral pain syndrome Cudejko (2018) Soft braces in knees with osteoarthritis Cherian (2016) Comparing effectiveness of nonoperative treatments for osteoarthritis of the knee Moyer (2015a) Valgus bracing for knee osteoarthritis Pietrosimone (2008) Content, Methods, Recommendations Various conservative treatments compared with placebo, sham, no treatment, or other conservative treatments. More than 80% of the 37 trials did not show a clinically significant benefit. Of the remaining seven trials, positive effects were documented (large change in pain severity). - Pulsed electromagnetic fields combined with home exercise, Hip muscle strengthening, and Weight-bearing exercise, Neuromuscular facilitation with aerobic exercise/stretching, Postural stabilization, Patellar bracing, Key points: Key points: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 11 studies (n = 284), six randomized trials of persons with osteoarthritis. Significant reduction in pain (P = 0.007) for persons wearing versus not wearing a soft brace. Persons wearing a soft brace versus standard care showed significant improvements in pain reduction (P < 0.001) and self-reported physical function (P = 0.006). Systematic review of 30 studies (four of which addressed bracing). Four treatments compared for ability to control pain in knee osteoarthritis. Bracing had a significant reduction standardized mean difference in pain of 1.34, more effective than insoles (0.992) but less effective than transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (1.796) and neuromuscular electrical stimulation (1.924). All four results are statistically significant. Key points: Meta-analysis of six studies of persons with osteoarthritis using valgus braces. Patients had significant pain improvement (P = 0.001) and function (P = 0.03). Valgus group had significantly greater pain reduction (P = 0.004) and function (P = 0.004) versus a control group that did not use an orthosis. Valgus group had significant improvement (P = 0.01) in pain compared with patients using a control orthosis. Key points: Prophylactic braces in preventing knee ligament injuries Systematic review of the benefit to the anterior cruciate ligament of wearing prophylactic knee braces. Seven studies in the review, among college football players. Injury risk declined in three studies. Injury risk increased in four studies. References 6
8 Professional society guidelines/other: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS). Guideline on the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee (non-arthroplasty). Rosemont IL: AAOS, Available at: Accessed April 26, Beaudreuil J, Bendaya S, Faucher, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for rest orthosis, knee sleeves, and unloading knee braces in knee osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2009;76(6): Hochberg MC, Altman RD, April KT, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2012 recommendations for the use of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies in osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64(4): Paluska S, McKeag D. Knee braces: Current evidence and clinical recommendations for their use. Am Fam Physician. 2000;61(2): Personal Health Insurance (PHI). Does health insurance cover knee braces? PHI, Accessed April 26, Rannou F, Poiraudeau S, Beaudreuil J. Role of bracing in the management of knee osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010;22(2): Yates AJ Jr, McGrory BJ, Starz TW, Vincent KR, McCardel B, Golightly YM. AAOS appropriate use criteria: optimizing the non-arthroplasty management of osteoarthritis of the knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014;22(4): Zhang W, Moskowitz RW, Nuki G, et al. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis, Part II: OARSI evidence-based, expert consensus guidelines. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16(2): Peer-reviewed references: Andersson D, Samuelsson K, Karlsson J. Treatment of anterior cruciate ligament injuries with special reference to surgical technique and rehabilitation: an assessment of randomized controlled trials. Arthroscopy. 2009;25(6): Cherian JJ, Jauregui JJ, Leichliter AK, Elmallah RK, Bhave A, Mont MA. The effects of various physical nonoperative modalities on the pain in osteoarthritis of the knee. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(1 Suppl A): Cudejko T, van der Esch M, van der Leeden M, et al. Effect of soft braces on pain and physical function in patients with knee osteoarthritis: Systematic review with meta-analyses. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;99(1):
9 Duivenvoorden T, Brouwer RW, van Raaji TM, Verhagen AP, Verhaar JA, Bierma-Zeinstra SM. Braces and orthoses for treating osteoarthritis of the knee. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(3):CD Doi: / CD pub3. Gohal C, Shanmugarai A, Tate P, et al. Effectiveness of valgus offloading knee braces in the treatment of medial compartment knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review. Sports Health. 2018: Doi: / Grant JA. Updating recommendations for rehabilitation after ACL reconstruction: a review. Clin J Sport Med. 2013;23(6): Lowe WR, Warth RJ, Davis EP, Bailey L. Functional bracing after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A systematic review. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25(3): Maleki M, Arazpour M, Joghtaei M, Hutchins SW, Aboutorabi A, Pouyan A. The effect of knee orthoses on gait parameters in medial knee compartment osteoarthritis: A literature review. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2016;40(20: Mine K, Nakayama T, Milanese S, Grimmer K. The effectiveness of braces and orthoses for patients with knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review of Japanese-language randomised controlled trials. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2017;41(2): Moyer RF, Birmingham TB, Bryant DM, Giffin JR, Marriott KA, Leitch KM. Valgus bracing for knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2015a;67(4): Moyer RF, Birmingham TB, Bryant DM, Giffin JR, Marriott KA, Leitch KM. Biomechanical effects of valgus knee bracing: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015b;23(2): Doi: /j.joca Petersen W, Ellermann A, Zantop T, et al. Biomechanical effect of unloader braces for medial osteoarthritis of the knee: a systematic review (CRD ). Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136(5): Pietrosimone BG, Grindstaff TL, Linens SW, Uczekai E, Hertel J. A systematic review of prophylactic braces in the prevention of knee ligament injuries in collegiate football players. J Athl Train. 2008;43(4): Raja K, Dewan N. Efficacy of knee braces and foot orthoses in conservative management of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2011;90(3): Rodriguez-Merchan EC. Knee Bracing after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Orthopedics Jul 1;39(4):e Doi: /
10 Salata MJ, Gibbs AE, Sekiya JK. The effectiveness of prophylactic knee bracing in American football: a systematic review. Sports Health. 2010;2(5): Saltychev M, Dutton RA, Laimi K, Beaupre GS, Virolainen P, Fredericson M. Effectiveness of conservative treatment for patellofemoral pain syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Rehabil Med Jan 25. doi: / Smith SD, Laprade RF, Jansson KS, Aroen A, Wijdicks CA. Functional bracing of ACL injuries: current state and future directions. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(5): Smith TO, Drew BT, Meek TH, Clark AB. Knee orthoses for treating patellofemoral pain syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev Dec 8;(12):CD Doi: / CD pub2. Sodhi N, Yao B, Khlopas A, et al. A case for the brace: A critical, comprehensive, and up-to-date review of static progressive stretch, dynamic, and turnbuckle braces for the management of elbow, knee, and shoulder pathology. Surg Technol Int. 2017;31: CMS National Coverage Determinations (NCDs): No NCDs identified as of the writing of this policy. Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs): L33318 Knee orthoses. Effective date October 1, KeyWord=knee&KeyWordLookUp=Title&KeyWordSearchType=And&bc=gAAAACAAAAAA&. Accessed April 26, L33686 Ankle-Foot/Knee-Ankle-Foot Orthoses. Effective date October 1, Accessed July 6, Commonly submitted codes Below are the most commonly submitted codes for the service(s)/item(s) subject to this policy. This is not an exhaustive list of codes. Providers are expected to consult the appropriate coding manuals and bill accordingly. CPT Code Description Comments N/A Not Applicable 9
11 HCPCS Level II Code A4467 A9270 K0670 L1810 L1812 L1820 L1830 L1831 L1832 L1833 L1834 L1836 L1840 L1843 L1844 L1845 L1846 L1847 L1848 L1850 Description Belt, strap, sleeve, garment, or covering, any type Non-covered item or service Addition to lower extremity orthosis, removable soft interface, all components, replacement only, each Knee orthosis, elastic with joints, prefabricated item that has been trimmed, bent, molded, assembled, or otherwise customized to fit a specific patient by an individual with expertise Knee orthosis, elastic with joints, prefabricated, off-the-shelf Knee orthotic, elastic with condylar pads and joints, with or without patellar control, prefabricated, includes fitting and adjustment Knee orthosis, immobilizer, canvas longitudinal, prefabricated, off-the-shelf Knee orthotic, locking knee joint(s), positional orthotic, prefabricated, includes fitting and adjustment Knee orthosis, adjustable knee joints (unicentric or polycentric), positional orthosis, rigid support, prefabricated item that has been trimmed, bent, molded, assembled, or otherwise customized to fit a specific patient by an individual with expertise Knee orthosis, adjustable knee joints (unicentric or polycentric), positional orthosis, rigid support, prefabricated, off-the shelf Knee orthotic (KO), without knee joint, rigid, custom fabricated Knee orthosis, rigid, without joint(s), includes soft interface material, prefabricated, offthe-shelf Knee orthotic (KO), derotation, medial-lateral, anterior cruciate ligament, custom fabricated Knee orthosis, single upright, thigh and calf, with adjustable flexion and extension joint (unicentric or polycentric), medial-lateral and rotation control, with or without varus/valgus adjustment, prefabricated item that has been trimmed, bent, molded, assembled, or otherwise customized to fit a specific patient by an individual with expertise Knee orthotic (KO), single upright, thigh and calf, with adjustable flexion and extension joint (unicentric or polycentric), medial-lateral and rotation control, with or without varus/valgus adjustment, custom fabricated Knee orthosis, double upright, thigh and calf, with adjustable flexion and extension joint (unicentric or polycentric), medial-lateral and rotation control, with or without varus/valgus adjustment, prefabricated item that has been trimmed, bent, molded, assembled, or otherwise customized to fit a specific patient by an individual with expertise Knee orthotic, double upright, thigh and calf, with adjustable flexion and extension joint (unicentric or polycentric), medial-lateral and rotation control, with or without varus/valgus adjustment, custom fabricated Knee orthosis, double upright with adjustable joint, with inflatable air support chamber(s), prefabricated item that has been trimmed, bent, molded, assembled, or otherwise customized to fit a specific patient by an individual with expertise Knee orthosis, double upright with adjustable joint, with inflatable air support chamber(s), prefabricated, off-the-shelf Knee orthosis, swedish type, prefabricated, off-the-shelf Comments 10
12 HCPCS Level II Code L1851 L1852 L1860 L2000 L2005 L2010 L2020 L2030 L2034 L2035 L2036 L2037 L2038 L2126 L2128 L2132 L2134 L2136 L2182 L2184 L2186 L2320 L2330 L2380 Description Knee orthosis (KO), single upright, thigh and calf, with adjustable flexion and extension joint (unicentric or polycentric), medial-lateral and rotation control, with or without varus/valgus adjustment, prefabricated, off-the-shelf Knee orthosis (KO), double upright, thigh and calf, with adjustable flexion and extension joint (unicentric or polycentric), medial-lateral and rotation control, with or without varus/valgus adjustment, prefabricated, off-the-shelf Knee orthotic (KO), modification of supracondylar prosthetic socket, custom fabricated (SK) Knee ankle foot orthosis, single upright, free knee, free ankle, solid stirrup, thigh and calf bands/cuffs (single bar 'ak' orthosis), custom fabricated Knee ankle foot orthosis, any material, single or double upright, stance control, automatic lock and swing phase release, any type activation, includes ankle joint, any type, custom fabricated Knee ankle foot orthosis, single upright, free ankle, solid stirrup, thigh and calf bands/cuffs (single bar 'ak' orthosis), without knee joint, custom fabricated Knee ankle foot orthosis, double upright, free ankle, solid stirrup, thigh and calf bands/cuffs (double bar 'ak' orthosis), custom fabricated Knee ankle foot orthosis, double upright, free ankle, solid stirrup, thigh and calf bands/cuffs, (double bar 'ak' orthosis), without knee joint, custom fabricated Knee ankle foot orthosis, full plastic, single upright, with or without free motion knee, medial lateral rotation control, with or without free motion ankle, custom fabricated Knee ankle foot orthosis, full plastic, static (pediatric size), without free motion ankle, prefabricated, includes fitting and adjustment Knee ankle foot orthosis, full plastic, double upright, with or without free motion knee, with or without free motion ankle, custom fabricated Knee ankle foot orthosis, full plastic, single upright, with or without free motion knee, with or without free motion ankle, custom fabricated Knee ankle foot orthosis, full plastic, with or without free motion knee, multi-axis ankle, custom fabricated Knee ankle foot orthosis, fracture orthosis, femoral fracture cast orthosis, thermoplastic type casting material, custom fabricated Knee ankle foot orthosis, fracture orthosis, femoral fracture cast orthosis, custom fabricated Kafo, fracture orthosis, femoral fracture cast orthosis, soft, prefabricated, includes fitting and adjustment Kafo, fracture orthosis, femoral fracture cast orthosis, semi-rigid, prefabricated, includes fitting and adjustment Kafo, fracture orthosis, femoral fracture cast orthosis, rigid, prefabricated, includes fitting and adjustment Addition to lower extremity fracture orthosis, drop lock knee joint Addition to lower extremity fracture orthosis, limited motion knee joint Addition to lower extremity fracture orthosis, adjustable motion knee joint, lerman type Addition to lower extremity, non-molded lacer, for custom fabricated orthosis only Addition to lower extremity, lacer molded to patient model, for custom fabricated orthosis only Addition to lower extremity, torsion control, straight knee joint, each joint Comments 11
13 HCPCS Level II Code L2385 L2387 L2390 L2395 L2397 L2405 L2415 L2425 L2430 L2492 L2750 L2755 L2780 L2785 L2795 L2999 L2800 L2810 L2820 L2830 L4002 L4070 L4080 L4090 L4100 L4110 L4205 L4210 L9999 Description Addition to lower extremity, straight knee joint, heavy duty, each joint Addition to lower extremity, polycentric knee joint, for custom fabricated knee ankle foot orthosis, each joint Addition to lower extremity, offset knee joint, each joint Addition to lower extremity, offset knee joint, heavy duty, each joint Addition to lower extremity orthotic, suspension sleeve Addition to knee joint, drop lock, each Addition to knee lock with integrated release mechanism (bail, cable, or equal), any material, each joint Addition to knee joint, disc or dial lock for adjustable knee flexion, each joint Addition to knee joint, ratchet lock for active and progressive knee extension, each joint Addition to knee joint, lift loop for drop lock ring Addition to lower extremity orthosis, plating chrome or nickel, per bar Addition to lower extremity orthotic, high strength, lightweight material, all hybrid lamination/prepreg composite, per segment, for custom fabricated orthotic only Addition to lower extremity orthosis, non-corrosive finish, per bar Addition to lower extremity orthotic, drop lock retainer, each Addition to lower extremity orthotic, knee control, full kneecap Lower extremity orthoses, not otherwise specified Addition to lower extremity orthotic, knee control, knee cap, medial or lateral pull, for use with custom fabricated orthotic only Addition to lower extremity orthotic, knee control, condylar pad Addition to lower extremity orthosis, soft interface for molded plastic, below knee section Addition to lower extremity orthosis, soft interface for molded plastic, above knee section Replacement strap, any orthosis, includes all components, any length, any type Replace proximal and distal upright for kafo Replace metal bands kafo, proximal thigh Replace metal bands kafo-afo, calf or distal thigh Replace leather cuff kafo, proximal thigh Replace leather cuff kafo-afo, calf or distal thigh Repair of orthotic device, labor component, per 15 minutes Repair of orthotic device, repair or replace minor parts Orthotic and prosthetic supply, accessory, and/or service component of another HCPCS "l" code Comments M Felty's syndrome, right knee M Felty's syndrome, left knee M Rheumatoid vasculitis with rheumatoid arthritis of right knee M Rheumatoid vasculitis with rheumatoid arthritis of left knee M Rheumatoid heart disease with rheumatoid arthritis of right knee M Rheumatoid heart disease with rheumatoid arthritis of left knee M Rheumatoid myopathy with rheumatoid arthritis of right knee 12
14 M Rheumatoid myopathy with rheumatoid arthritis of left knee M Rheumatoid polyneuropathy with rheumatoid arthritis of right knee M Rheumatoid polyneuropathy with rheumatoid arthritis of left knee M Rheumatoid arthritis of right knee with involvement of other organs and systems M Rheumatoid arthritis of left knee with involvement of other organs and systems M Rheumatoid arthritis with rheumatoid factor of right knee without organ or systems involvement M Rheumatoid arthritis with rheumatoid factor of left knee without organ or systems involvement M Other rheumatoid arthritis with rheumatoid factor of right knee M Other rheumatoid arthritis with rheumatoid factor of left knee M Rheumatoid arthritis without rheumatoid factor, right knee M Rheumatoid arthritis without rheumatoid factor, left knee M06.1 Adult-onset Still's disease M Rheumatoid bursitis, right knee M Rheumatoid bursitis, left knee M Rheumatoid nodule, right knee M Rheumatoid nodule, left knee M Other specified rheumatoid arthritis, right knee M Other specified rheumatoid arthritis, left knee M Unspecified juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, right knee M Unspecified juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, left knee M Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis with systemic onset, right knee M Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis with systemic onset, left knee M08.3 Juvenile rheumatoid polyarthritis (seronegative) M Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, right knee M Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, left knee M Other juvenile arthritis, right knee M Other juvenile arthritis, left knee M Juvenile arthritis, unspecified, right knee M Juvenile arthritis, unspecified, left knee M Chronic postrheumatic arthropathy [Jaccoud], right knee M Chronic postrheumatic arthropathy [Jaccoud], left knee M17.0 Bilateral primary osteoarthritis of knee M17.11 Unilateral primary osteoarthritis, right knee M17.12 Unilateral primary osteoarthritis, left knee M17.2 Bilateral post-traumatic osteoarthritis of knee M17.31 Unilateral post-traumatic osteoarthritis, right knee M17.32 Unilateral post-traumatic osteoarthritis, left knee M17.4 Other bilateral secondary osteoarthritis of knee M17.5 Other unilateral secondary osteoarthritis of knee M17.9 Osteoarthritis of knee, unspecified M22.2X1 Patellofemoral disorders, right knee M22.2X2 Patellofemoral disorders, left knee M22.3X1 Other derangements of patella, right knee M22.3X2 Other derangements of patella, left knee 13
15 M22.41 Chondromalacia patellae, right knee M22.42 Chondromalacia patellae, left knee M22.8X1 Other disorders of patella, right knee M22.8X2 Other disorders of patella, left knee M22.91 Unspecified disorder of patella, right knee M22.92 Unspecified disorder of patella, left knee M Cystic meniscus, unspecified lateral meniscus, right knee M Cystic meniscus, unspecified lateral meniscus, left knee M Cystic meniscus, unspecified medial meniscus, right knee M Cystic meniscus, unspecified medial meniscus, left knee M Cystic meniscus, unspecified meniscus, right knee M Cystic meniscus, unspecified meniscus, left knee M Cystic meniscus, anterior horn of medial meniscus, right knee M Cystic meniscus, anterior horn of medial meniscus, left knee M Cystic meniscus, posterior horn of medial meniscus, right knee M Cystic meniscus, posterior horn of medial meniscus, left knee M Cystic meniscus, other medial meniscus, right knee M Cystic meniscus, other medial meniscus, left knee M Cystic meniscus, anterior horn of lateral meniscus, right knee M Cystic meniscus, anterior horn of lateral meniscus, left knee M Cystic meniscus, posterior horn of lateral meniscus, right knee M Cystic meniscus, posterior horn of lateral meniscus, left knee M Cystic meniscus, other lateral meniscus, right knee M Cystic meniscus, other lateral meniscus, left knee M Derangement of unspecified lateral meniscus due to old tear or injury, right knee M Derangement of unspecified lateral meniscus due to old tear or injury, left knee M Derangement of unspecified medial meniscus due to old tear or injury, right knee M Derangement of unspecified medial meniscus due to old tear or injury, left knee M Derangement of unspecified meniscus due to old tear or injury, right knee M Derangement of unspecified meniscus due to old tear or injury, left knee M Derangement of anterior horn of medial meniscus due to old tear or injury, right knee M Derangement of anterior horn of medial meniscus due to old tear or injury, left knee M Derangement of posterior horn of medial meniscus due to old tear or injury, right knee M Derangement of posterior horn of medial meniscus due to old tear or injury, left knee M Derangement of other medial meniscus due to old tear or injury, right knee M Derangement of other medial meniscus due to old tear or injury, left knee M Derangement of anterior horn of lateral meniscus due to old tear or injury, right knee M Derangement of anterior horn of lateral meniscus due to old tear or injury, left knee M Derangement of posterior horn of lateral meniscus due to old tear or injury, right knee M Derangement of posterior horn of lateral meniscus due to old tear or injury, left knee M Derangement of other lateral meniscus due to old tear or injury, right knee M Derangement of other lateral meniscus due to old tear or injury, left knee M Other meniscus derangements, unspecified lateral meniscus, right knee M Other meniscus derangements, unspecified lateral meniscus, left knee M Other meniscus derangements, unspecified medial meniscus, right knee M Other meniscus derangements, unspecified medial meniscus, left knee 14
16 M Other meniscus derangements, unspecified meniscus, right knee M Other meniscus derangements, unspecified meniscus, left knee M Other meniscus derangements, anterior horn of medial meniscus, right knee M Other meniscus derangements, anterior horn of medial meniscus, left knee M Other meniscus derangements, posterior horn of medial meniscus, right knee M Other meniscus derangements, posterior horn of medial meniscus, left knee M Other meniscus derangements, other medial meniscus, right knee M Other meniscus derangements, other medial meniscus, left knee M Other meniscus derangements, anterior horn of lateral meniscus, right knee M Other meniscus derangements, anterior horn of lateral meniscus, left knee M Other meniscus derangements, posterior horn of lateral meniscus, right knee M Other meniscus derangements, posterior horn of lateral meniscus, left knee M Other meniscus derangements, other lateral meniscus, right knee M Other meniscus derangements, other lateral meniscus, left knee M23.51 Chronic instability of knee, right knee M23.52 Chronic instability of knee, left knee M Other spontaneous disruption of unspecified ligament of right knee M Other spontaneous disruption of unspecified ligament of left knee M Other spontaneous disruption of anterior cruciate ligament of right knee M Other spontaneous disruption of anterior cruciate ligament of left knee M Other spontaneous disruption of posterior cruciate ligament of right knee M Other spontaneous disruption of posterior cruciate ligament of left knee M Other spontaneous disruption of medial collateral ligament of right knee M Other spontaneous disruption of medial collateral ligament of left knee M Other spontaneous disruption of lateral collateral ligament of right knee M Other spontaneous disruption of lateral collateral ligament of left knee M Other spontaneous disruption of capsular ligament of right knee M Other spontaneous disruption of capsular ligament of left knee M23.8X1 Other internal derangements of right knee M23.8X2 Other internal derangements of left knee M23.91 Unspecified internal derangement of right knee M23.92 Unspecified internal derangement of left knee M Spontaneous rupture of extensor tendons, right thigh M Spontaneous rupture of extensor tendons, left thigh M Spontaneous rupture of extensor tendons, right lower leg M Spontaneous rupture of extensor tendons, left lower leg M80.051A - M80.052S M80.061A - M80.062S M80.851A - M80.852S Age-related osteoporosis with current pathological fracture, right femur, initial encounter for fracture - Age-related osteoporosis with current pathological fracture, left femur, Age-related osteoporosis with current pathological fracture, right lower leg, initial encounter for fracture - Age-related osteoporosis with current pathological fracture, left lower leg, Other osteoporosis with current pathological fracture, right femur, initial encounter for fracture - Other osteoporosis with current pathological fracture, left femur, 15
17 Other osteoporosis with current pathological fracture, right lower leg, initial encounter M80.851A - for fracture - Other osteoporosis with current pathological fracture, left lower leg, M80.852S M80.861A - M80.862S Other osteoporosis with current pathological fracture, right lower leg, initial encounter for fracture - Other osteoporosis with current pathological fracture, left lower leg, sequel M84.351A - M84.352S Stress fracture, right femur, initial encounter for fracture - Stress fracture, left femur, M84.361A - M84.364S - Stress fracture, right tibia, initial encounter for fracture - Stress fracture, left fibula, M84.451A - M84.452S Pathological fracture, right femur, initial encounter for fracture - Pathological fracture, left femur, M84.461A - M84.464S Pathological fracture, right tibia, initial encounter for fracture - Pathological fracture, left fibula, M84.551A - M84.552S Pathological fracture in neoplastic disease, right femur, initial encounter for fracture - Pathological fracture in neoplastic disease, left femur, M84.561A - M84.564S Pathological fracture in neoplastic disease, right tibia, initial encounter for fracture - Pathological fracture in neoplastic disease, left fibula, M84.651A - M84.652S Pathological fracture in other disease, right femur, initial encounter for fracture - Pathological fracture in other disease, left femur, M84.661A - M84.664S Pathological fracture in other disease, right tibia, initial encounter for fracture - Pathological fracture in other disease, left fibula, M Idiopathic aseptic necrosis of right tibia M Idiopathic aseptic necrosis of left tibia M Idiopathic aseptic necrosis of right fibula M Idiopathic aseptic necrosis of left fibula M Osteonecrosis due to drugs, right tibia M Osteonecrosis due to drugs, left tibia M Osteonecrosis due to drugs, right fibula M Osteonecrosis due to drugs, left fibula M Osteonecrosis due to previous trauma, right tibia M Osteonecrosis due to previous trauma, left tibia M Osteonecrosis due to previous trauma, right fibula M Osteonecrosis due to previous trauma, left fibula M Other secondary osteonecrosis, right tibia M Other secondary osteonecrosis, left tibia M Other secondary osteonecrosis, right fibula M Other secondary osteonecrosis, left fibula M Other osteonecrosis, right tibia M Other osteonecrosis, left tibia M Other osteonecrosis, right fibula M Other osteonecrosis, left fibula M Osteonecrosis in diseases classified elsewhere, right lower leg M Osteonecrosis in diseases classified elsewhere, left lower leg M Fracture of femur following insertion of orthopedic implant, joint prosthesis, or bone plate, right leg 16
18 M Fracture of femur following insertion of orthopedic implant, joint prosthesis, or bone plate, left leg M Fracture of tibia or fibula following insertion of orthopedic implant, joint prosthesis, or bone plate, right leg M Fracture of tibia or fibula following insertion of orthopedic implant, joint prosthesis, or bone plate, left leg Q68.2 Congenital deformity of knee Q68.6 Discoid meniscus Q74.1 Congenital malformation of knee S72.001A - S72.002S Fracture of unspecified part of neck of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Fracture of unspecified part of neck of left femur, S72.011A - S72.012S Unspecified intracapsular fracture of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Unspecified intracapsular fracture of left femur, Displaced fracture of epiphysis (separation) (upper) of right femur, initial encounter for S72.021A - closed fracture - Displaced fracture of epiphysis (separation) (upper) of left femur, S72.022S S72.024A - S72.025S S72.031A - S72.032S S72.034A - S72.035S S72.041A - S72.042S S72.044A - S72.045S S72.051A - S72.052S S72.061A - S72.062S S72.064A - S72.065S S72.091A - S72.092S S72.101A - S72.102S S72.111A - S72.112S S72.114A - S72.115S S72.121A - S72.122S S72.124A - S72.125S S72.131A - S72.132S Nondisplaced fracture of epiphysis (separation) (upper) of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced fracture of epiphysis (separation) (upper) of left femur, Displaced midcervical fracture of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Displaced midcervical fracture of left femur, Nondisplaced midcervical fracture of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced midcervical fracture of left femur, Displaced fracture of base of neck of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Displaced fracture of base of neck of left femur, Nondisplaced fracture of base of neck of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced fracture of base of neck of left femur, Unspecified fracture of head of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Unspecified fracture of head of left femur, Displaced articular fracture of head of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Displaced articular fracture of head of left femur, Nondisplaced articular fracture of head of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced articular fracture of head of left femur, Other fracture of head and neck of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Other fracture of head and neck of left femur, Unspecified trochanteric fracture of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Unspecified trochanteric fracture of left femur, Displaced fracture of greater trochanter of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Displaced fracture of greater trochanter of left femur, Nondisplaced fracture of greater trochanter of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced fracture of greater trochanter of left femur, Displaced fracture of lesser trochanter of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Displaced fracture of lesser trochanter of left femur, Nondisplaced fracture of lesser trochanter of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced fracture of lesser trochanter of left femur, Displaced apophyseal fracture of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Displaced apophyseal fracture of left femur, 17
19 S72.134A - S72.135S Nondisplaced apophyseal fracture of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced apophyseal fracture of left femur, S72.141A - S72.142S Displaced intertrochanteric fracture of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Displaced intertrochanteric fracture of left femur, S72.144A - S72.145S Nondisplaced intertrochanteric fracture of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced intertrochanteric fracture of left femur, S72.21XA - S72.22XS Displaced subtrochanteric fracture of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Displaced subtrochanteric fracture of left femur, S72.24XA - S72.25XS Nondisplaced subtrochanteric fracture of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced subtrochanteric fracture of left femur, S72.301A - S72.302S Unspecified fracture of shaft of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Unspecified fracture of shaft of left femur, S72.321A - S72.322S Displaced transverse fracture of shaft of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Displaced transverse fracture of shaft of left femur, S72.324A - S72.325S Nondisplaced transverse fracture of shaft of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced transverse fracture of shaft of left femur, S72.331A - S72.332S Displaced oblique fracture of shaft of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Displaced oblique fracture of shaft of left femur, S72.334A - S72.335S Nondisplaced oblique fracture of shaft of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced oblique fracture of shaft of left femur, S72.341A - S72.342S Displaced spiral fracture of shaft of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Displaced spiral fracture of shaft of left femur, S72.344A - S72.345S Nondisplaced spiral fracture of shaft of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced spiral fracture of shaft of left femur, S72.351A - S72.352S Displaced comminuted fracture of shaft of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Displaced comminuted fracture of shaft of left femur, S72.354A - S72.355S Nondisplaced comminuted fracture of shaft of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced comminuted fracture of shaft of left femur, S72.361A - S72.362S Displaced segmental fracture of shaft of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Displaced segmental fracture of shaft of left femur, S72.364A - S72.365S Nondisplaced segmental fracture of shaft of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced segmental fracture of shaft of left femur, S72.391A - S72.392S Other fracture of shaft of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Other fracture of shaft of left femur, S72.401A - S72.402S Unspecified fracture of lower end of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Unspecified fracture of lower end of left femur, Displaced unspecified condyle fracture of lower end of right femur, initial encounter for S72.411A - closed fracture - Displaced unspecified condyle fracture of lower end of left femur, S72.412S S72.414A - S72.415S S72.421A - S72.422S S72.424A - S72.425S Nondisplaced unspecified condyle fracture of lower end of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced unspecified condyle fracture of lower end of left femur, Displaced fracture of lateral condyle of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Displaced fracture of lateral condyle of left femur, Nondisplaced fracture of lateral condyle of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture - Nondisplaced fracture of lateral condyle of left femur, 18
Original Policy Date
 MP 1.03.02 Knee Braces Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical Policy
MP 1.03.02 Knee Braces Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical Policy
V-VAS ORTHOSIS: A NEW CONCEPT IN UNLOADER KNEE ORTHOSIS DESIGN
 V-VAS ORTHOSIS: A NEW CONCEPT IN UNLOADER KNEE ORTHOSIS DESIGN Joseph W. Whiteside CO/LO 1399 E. Western Reserve Road, Poland, OH 44514-3250 (800) 837-3888 www.anatomicalconceptsinc.com Page 1 of 5 The
V-VAS ORTHOSIS: A NEW CONCEPT IN UNLOADER KNEE ORTHOSIS DESIGN Joseph W. Whiteside CO/LO 1399 E. Western Reserve Road, Poland, OH 44514-3250 (800) 837-3888 www.anatomicalconceptsinc.com Page 1 of 5 The
A Single-Bar Above-Knee Orthosis
 A Single-Bar Above-Knee Orthosis Robert O. Nitschke,* C.P.O. I would like to present a different approach to the design of aboveknee, or "long leg", orthoses. When weight-bearing is not necessary, I have
A Single-Bar Above-Knee Orthosis Robert O. Nitschke,* C.P.O. I would like to present a different approach to the design of aboveknee, or "long leg", orthoses. When weight-bearing is not necessary, I have
ORTHOTIC REFERENCE GUIDE. srtprosthetics.com
 ORTHOTIC REFERENCE GUIDE srtprosthetics.com 1.866.633.3961 AFO, Ankle Foot Orthosis, Articulated (Custom-Molded) Provides adjustable control of the ankle and foot Designed with an articulated ankle and
ORTHOTIC REFERENCE GUIDE srtprosthetics.com 1.866.633.3961 AFO, Ankle Foot Orthosis, Articulated (Custom-Molded) Provides adjustable control of the ankle and foot Designed with an articulated ankle and
Biomechanics of. Knee Replacement. Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm
 Biomechanics of Knee Replacement Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm 1 Table of contents Knee Anatomy Movements of the Knee Knee conditions leading to knee replacement Materials Alignment and Joint Loading Knee
Biomechanics of Knee Replacement Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm 1 Table of contents Knee Anatomy Movements of the Knee Knee conditions leading to knee replacement Materials Alignment and Joint Loading Knee
AFO Designs You Should Use
 AFO Designs You Should Use Josh White, DPM, Cped Founder, SafeStep Commonly Seen Biomechanical Disorders Ankle Sprain Gait Instability Posterior Tibial Tendon Rupture Achilles Tendonitis, Rupture Charcot,
AFO Designs You Should Use Josh White, DPM, Cped Founder, SafeStep Commonly Seen Biomechanical Disorders Ankle Sprain Gait Instability Posterior Tibial Tendon Rupture Achilles Tendonitis, Rupture Charcot,
A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES
 A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES THE KNEE in movement! Climbing stairs, walking and running are everyday actions that we can perform thanks to our knees. The knee joint is one of the most exposed and
A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES THE KNEE in movement! Climbing stairs, walking and running are everyday actions that we can perform thanks to our knees. The knee joint is one of the most exposed and
ORTHOTIC REFERENCE GUIDE. srtprosthetics.com
 ORTHOTIC REFERENCE GUIDE srtprosthetics.com 1.866.633.3961 AFO, Ankle Foot Orthosis, Articulated (Custom-Molded) Purpose of the Device Provides adjustable control of the ankle and foot Designed with an
ORTHOTIC REFERENCE GUIDE srtprosthetics.com 1.866.633.3961 AFO, Ankle Foot Orthosis, Articulated (Custom-Molded) Purpose of the Device Provides adjustable control of the ankle and foot Designed with an
PLAY PLAY. Hard. Smart. Knee Product Guide
 PLAY Hard. PLAY Smart. Knee Product Guide Osteoarthritis/Ligament Bracing M.4 OA Knee Brace Provides exact and effective valgus and varus pressure adjustment exerted close to the knee joint Physioglide
PLAY Hard. PLAY Smart. Knee Product Guide Osteoarthritis/Ligament Bracing M.4 OA Knee Brace Provides exact and effective valgus and varus pressure adjustment exerted close to the knee joint Physioglide
SUBJECT: LIMB PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION EFFECTIVE DATE: 06/27/13 DEVICES FOR VENOUS REVISED DATE: 06/26/14 THROMBOEMBOLISM PROPHYLAXIS
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: LIMB PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: LIMB PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
Clinical Policy Title: Genicular nerve block
 Clinical Policy Title: Genicular nerve block Clinical Policy Number: 14.01.10 Effective Date: October 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: September 21, 2017 Most Recent Review Date: October 19, 2017 Next Review
Clinical Policy Title: Genicular nerve block Clinical Policy Number: 14.01.10 Effective Date: October 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: September 21, 2017 Most Recent Review Date: October 19, 2017 Next Review
Clinical Policy Title: Arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament surgery skeletally immature
 Clinical Policy Title: Arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament surgery skeletally immature Clinical Policy Number: 14.03.08 Effective Date: May 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: April 19, 2017 Most Recent Review
Clinical Policy Title: Arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament surgery skeletally immature Clinical Policy Number: 14.03.08 Effective Date: May 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: April 19, 2017 Most Recent Review
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Orthotics File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: orthotics 6/1990 2/2017 2/2018 2/2017 Description of Procedure or Service An orthotic (orthosis)
Corporate Medical Policy Orthotics File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: orthotics 6/1990 2/2017 2/2018 2/2017 Description of Procedure or Service An orthotic (orthosis)
Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures
 Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures Roy Snelson, C.P.O.*, George Irons, C.P.O.**, and Vert Mooney, M.D.*** The fracture cast brace is designed to allow early ambulation
Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures Roy Snelson, C.P.O.*, George Irons, C.P.O.**, and Vert Mooney, M.D.*** The fracture cast brace is designed to allow early ambulation
Lower Limb Biomechanical Examination
 Lower Limb Biomechanical Examination Click here for completion instructions. Patient Name: Chief Complaint: History of problem: Nature of discomfort/pain Location (anatomic) Duration Onset Course Aggravating
Lower Limb Biomechanical Examination Click here for completion instructions. Patient Name: Chief Complaint: History of problem: Nature of discomfort/pain Location (anatomic) Duration Onset Course Aggravating
Insurance Guideline Summary
 Insurance Guideline Summary Foot/Ankle: Soft Goods- Ankle lace-up, Velocity, PTTD $83.00 Had an injury, surgery, or chronic instability (will not be covered for osteoarthritis unless you document instability
Insurance Guideline Summary Foot/Ankle: Soft Goods- Ankle lace-up, Velocity, PTTD $83.00 Had an injury, surgery, or chronic instability (will not be covered for osteoarthritis unless you document instability
Clinical Policy Title: Arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament surgery skeletally immature
 Clinical Policy Title: Arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament surgery skeletally immature Clinical Policy Number: 14.03.08 Effective Date: May 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: April 19, 2017 Most Recent Review
Clinical Policy Title: Arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament surgery skeletally immature Clinical Policy Number: 14.03.08 Effective Date: May 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: April 19, 2017 Most Recent Review
Freedom and safety in treatment
 medi GmbH & Co. KG Medicusstraße 1 95448 Bayreuth Germany T +49 921 912-0 F +49 921 912 780 ortho@medi.de www.medi.de 97E37/09.2012 Freedom and safety in treatment An informative brochure with an individual
medi GmbH & Co. KG Medicusstraße 1 95448 Bayreuth Germany T +49 921 912-0 F +49 921 912 780 ortho@medi.de www.medi.de 97E37/09.2012 Freedom and safety in treatment An informative brochure with an individual
CLINICAL CONCEPTS FOR ORTHOPEDICS. CMS Clinical Concepts
 CLINICAL CONCEPTS FOR ORTHOPEDICS CMS Clinical Concepts ICD 10 LESSONS FROM OFFICE DOCUMENTATION Presented by Dr. Frankeny OUR CHALLENGE: CHANGING OUR DOCUMENTATION ICD 10 Learn the nomenclature Documenting
CLINICAL CONCEPTS FOR ORTHOPEDICS CMS Clinical Concepts ICD 10 LESSONS FROM OFFICE DOCUMENTATION Presented by Dr. Frankeny OUR CHALLENGE: CHANGING OUR DOCUMENTATION ICD 10 Learn the nomenclature Documenting
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Clinical Policy Title: Cardiac rehabilitation
 Clinical Policy Title: Cardiac rehabilitation Clinical Policy Number: 04.02.02 Effective Date: September 1, 2013 Initial Review Date: February 19, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: February 6, 2018 Next Review
Clinical Policy Title: Cardiac rehabilitation Clinical Policy Number: 04.02.02 Effective Date: September 1, 2013 Initial Review Date: February 19, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: February 6, 2018 Next Review
Lower Limb Biomechanical Examination
 Lower Limb Biomechanical Examination Click here for completion instructions. Patient Name: Chief Complaint: History of problem: Nature of discomfort/pain Location (anatomic) Duration Onset Course Aggravating
Lower Limb Biomechanical Examination Click here for completion instructions. Patient Name: Chief Complaint: History of problem: Nature of discomfort/pain Location (anatomic) Duration Onset Course Aggravating
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
Common Knee Injuries
 Common Knee Injuries In 2010, there were roughly 10.4 million patient visits to doctors' offices because of common knee injuries such as fractures, dislocations, sprains, and ligament tears. Knee injury
Common Knee Injuries In 2010, there were roughly 10.4 million patient visits to doctors' offices because of common knee injuries such as fractures, dislocations, sprains, and ligament tears. Knee injury
YOU MAY NEED A KNEE REPLACEMENT
 Knee pain? YOU MAY NEED A KNEE REPLACEMENT Introduction If you re reading this brochure, you or a loved one is likely suffering from a severe knee problem. Serious knee joint conditions can cause pain,
Knee pain? YOU MAY NEED A KNEE REPLACEMENT Introduction If you re reading this brochure, you or a loved one is likely suffering from a severe knee problem. Serious knee joint conditions can cause pain,
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity
 Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Fig. 1. Lateral view of the patient showing stockinet in place and indelible pencil marks indicating areas where modification of the positive model wi
 Femoral Immobilizer CHARLES H. PRITHAM 1 MELVIN L. STILLS 2 During the past ten years orthotics has come to play a role in the treatment of selected patients with fractures of the femur. Fundamentally,
Femoral Immobilizer CHARLES H. PRITHAM 1 MELVIN L. STILLS 2 During the past ten years orthotics has come to play a role in the treatment of selected patients with fractures of the femur. Fundamentally,
Bracing for Acute Injury, Functional Activity, and Osteoarthritis of the Knee
 Bracing for Acute Injury, Functional Activity, and Osteoarthritis of the Knee UCSF Osher Mini-Medical School for the Public Tim Baldwin, ATC, CFo Amber Pryor, ATC, CFo Andrew Simpkins, ATC, CFo 3/15/18
Bracing for Acute Injury, Functional Activity, and Osteoarthritis of the Knee UCSF Osher Mini-Medical School for the Public Tim Baldwin, ATC, CFo Amber Pryor, ATC, CFo Andrew Simpkins, ATC, CFo 3/15/18
Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus
 Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide a recommended syllabus for medical students in Trauma & Orthopaedics (T&0). It should help students on
Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide a recommended syllabus for medical students in Trauma & Orthopaedics (T&0). It should help students on
Knee Capsular Disorder. ICD-9-CM: Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified
 1 Knee Capsular Disorder "Knee Capsulitis" ICD-9-CM: 719.56 Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified Diagnostic Criteria History: Physical Exam: Stiffness Aching with prolonged weight
1 Knee Capsular Disorder "Knee Capsulitis" ICD-9-CM: 719.56 Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified Diagnostic Criteria History: Physical Exam: Stiffness Aching with prolonged weight
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
SUBJECT: LIMB PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION EFFECTIVE DATE: 06/27/13 DEVICES FOR VENOUS REVISED DATE: 06/26/14, 09/15/15,09/21/17. THROMBOEMBOLISM PROPHYLAXIS
 MEDICAL POLICY REVISED DATE: 06/26/14, 09/15/15,09/21/17. PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases,
MEDICAL POLICY REVISED DATE: 06/26/14, 09/15/15,09/21/17. PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases,
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Orthopedic Casts, Braces and Splints
 Clinical Policy Bulletin: Orthopedic Casts, Braces and Splints Number: 0009 Policy *Pleasesee amendment forpennsylvaniamedicaidattheendofthiscpb. Policy History Last Review: 03/29/2018 Effective: 07/21/1995
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Orthopedic Casts, Braces and Splints Number: 0009 Policy *Pleasesee amendment forpennsylvaniamedicaidattheendofthiscpb. Policy History Last Review: 03/29/2018 Effective: 07/21/1995
Clinical Policy Title: Subtalar arthroereisis (implant)
 Clinical Policy Title: Subtalar arthroereisis (implant) Clinical Policy Number: 14.03.05 Effective Date: April 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: August 17, 2016 Most Recent Review Date: September 21, 2017 Next
Clinical Policy Title: Subtalar arthroereisis (implant) Clinical Policy Number: 14.03.05 Effective Date: April 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: August 17, 2016 Most Recent Review Date: September 21, 2017 Next
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: LIMB PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION DEVICES FOR VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM PROPHYLAXIS
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: LIMB PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION REVISED DATE: 06/26/14, 10/15/15, 06/16/16, PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: LIMB PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION REVISED DATE: 06/26/14, 10/15/15, 06/16/16, PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria
Patellofemoral Instability
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
For Commercial products, please refer to the following policy: Preauthorization via Web-Based Tool for Procedures
 Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the
 The Arthritic Knee The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the medial compartment of the knee, and
The Arthritic Knee The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the medial compartment of the knee, and
Kineto. Orthopaedics & Rehabilitation Products
 Member of Vincent Medical Holdings Limited Kineto Orthopaedics & Rehabilitation Products Our orthopaedic and rehabilitation products comprise of a variety of adjustable rehabilitation braces for support,
Member of Vincent Medical Holdings Limited Kineto Orthopaedics & Rehabilitation Products Our orthopaedic and rehabilitation products comprise of a variety of adjustable rehabilitation braces for support,
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA)
 TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
Anterior knee pain.
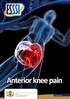 Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
Clinical Policy Title: Strep testing
 Clinical Policy Title: Strep testing Clinical Policy Number: 07.01.09 Effective Date: December 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: October 19, 2017 Most Recent Review Date: November 16, 2017 Next Review Date:
Clinical Policy Title: Strep testing Clinical Policy Number: 07.01.09 Effective Date: December 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: October 19, 2017 Most Recent Review Date: November 16, 2017 Next Review Date:
2/28/2017. Learning Objectives. Hip Joint: Anatomy and Kinesiology
 Regional Pain Syndromes: Hip and Knee Srinivas Nalamachu, MD Clinical Assistant Professor, KU School of Medicine President and Medical Director, Pain Management Institute Overland Park, KS Learning Objectives
Regional Pain Syndromes: Hip and Knee Srinivas Nalamachu, MD Clinical Assistant Professor, KU School of Medicine President and Medical Director, Pain Management Institute Overland Park, KS Learning Objectives
Clinical Policy Title: Platelet rich plasma
 Clinical Policy Title: Platelet rich plasma Clinical Policy Number: 05.02.10 Effective Date: February 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: November 16, 2016 Most Recent Review Date: November 16, 2017 Next Review
Clinical Policy Title: Platelet rich plasma Clinical Policy Number: 05.02.10 Effective Date: February 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: November 16, 2016 Most Recent Review Date: November 16, 2017 Next Review
ACL Athletic Career. ACL Rupture - Warning Features Intensive pain Immediate swelling Locking Feel a Pop Dead leg Cannot continue to play
 FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
Treatment of congenital subluxation and dislocation of the hip by knee splint harness
 Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 1994,18, 34-39 Treatment of congenital subluxation and dislocation of the hip by knee splint harness M. FUKUSHIMA Fukushima Orthopaedic Clinic, Hiroshima City,
Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 1994,18, 34-39 Treatment of congenital subluxation and dislocation of the hip by knee splint harness M. FUKUSHIMA Fukushima Orthopaedic Clinic, Hiroshima City,
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY
 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
Payment Policy. Chiropractic Care. Policy Specific Section: September 10, 2012 November 10, 2012
 Payment Policy Chiropractic Care Type: Payment Policy Policy Specific Section: Payment Original Policy Date: Effective Date: September 10, 2012 November 10, 2012 Description Chiropractic is a branch of
Payment Policy Chiropractic Care Type: Payment Policy Policy Specific Section: Payment Original Policy Date: Effective Date: September 10, 2012 November 10, 2012 Description Chiropractic is a branch of
What is an ACL Tear?...2. Treatment Options...3. Surgical Techniques...4. Preoperative Care...5. Preoperative Requirements...6
 Table of Contents What is an ACL Tear?....2 Treatment Options...3 Surgical Techniques...4 Preoperative Care...5 Preoperative Requirements...6 Postoperative Care...................... 7 Crutch use...8 Initial
Table of Contents What is an ACL Tear?....2 Treatment Options...3 Surgical Techniques...4 Preoperative Care...5 Preoperative Requirements...6 Postoperative Care...................... 7 Crutch use...8 Initial
Jennifer L. Cook, MD
 Jennifer L. Cook, MD Florida Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Center 5243 Hanff Lane New Port Richey, FL 34652 Phone: (727)848-4249 Fax: (727) 841-8934 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE
Jennifer L. Cook, MD Florida Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Center 5243 Hanff Lane New Port Richey, FL 34652 Phone: (727)848-4249 Fax: (727) 841-8934 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE
OSCELL MICROFRACTURE OR DRILLING OPERATION (FEMORAL CONDYLE SITES) PATIENT ADVICE.
 OSCELL MICROFRACTURE OR DRILLING OPERATION ( SITES) PATIENT ADVICE. Anatomy of the Right Knee example of a femoral condyle articular defect site Knee Straight Knee Bent KEY: Patella Kneecap Trochlea Groove
OSCELL MICROFRACTURE OR DRILLING OPERATION ( SITES) PATIENT ADVICE. Anatomy of the Right Knee example of a femoral condyle articular defect site Knee Straight Knee Bent KEY: Patella Kneecap Trochlea Groove
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
Metha Short Hip Stem System
 Metha Short Hip Stem System Accuracy That Stands Alone Aesculap Orthopaedics Metha Short Hip Stem System Designed For Anatomic Accuracy The Metha Short Hip Stem is designed for anatomic accuracy to restore
Metha Short Hip Stem System Accuracy That Stands Alone Aesculap Orthopaedics Metha Short Hip Stem System Designed For Anatomic Accuracy The Metha Short Hip Stem is designed for anatomic accuracy to restore
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers
 CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Continuous Passive Motion in the Home Setting File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: continuous_passive_motion_in_the_home_setting 9/1993 6/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Continuous Passive Motion in the Home Setting File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: continuous_passive_motion_in_the_home_setting 9/1993 6/2018
40 th Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine. Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete. Disclosure
 40 th Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine Travis Murray, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete Disclosure Dr. Travis Murray
40 th Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine Travis Murray, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete Disclosure Dr. Travis Murray
K n e e b r a f o r l a t e p a t e l l a r r e t i n a c u
 K n e e b r a f o r l a t e p a t e l l a r r e t i n a c u 20-11-2012 Retinaculum Knee Catherine Blake. Loading. Anatomy Of The Patellar Tendon. Arthroscopic Lateral Release and Medial Imbrication. What
K n e e b r a f o r l a t e p a t e l l a r r e t i n a c u 20-11-2012 Retinaculum Knee Catherine Blake. Loading. Anatomy Of The Patellar Tendon. Arthroscopic Lateral Release and Medial Imbrication. What
Clinical Policy Title: Computerized gait analysis
 Clinical Policy Title: Computerized gait analysis Clinical Policy Number: 15.01.01 Effective Date: October 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: May 21, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: May 1, 2018 Next Review Date:
Clinical Policy Title: Computerized gait analysis Clinical Policy Number: 15.01.01 Effective Date: October 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: May 21, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: May 1, 2018 Next Review Date:
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT
 ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
The KineSpring Knee Implant System Product Information
 The KineSpring Knee Implant System Product Information The Treatment Gap Increasing numbers of young, active OA patients with longer life expectancy and higher activity demands. 1 Large increase in arthroplasty
The KineSpring Knee Implant System Product Information The Treatment Gap Increasing numbers of young, active OA patients with longer life expectancy and higher activity demands. 1 Large increase in arthroplasty
Clinical Policy Title: Computerized gait analysis
 Clinical Policy Title: Computerized gait analysis Clinical Policy Number: 15.01.01 Effective Date: October 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: May 21, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: June 22, 2017 Next Review Date:
Clinical Policy Title: Computerized gait analysis Clinical Policy Number: 15.01.01 Effective Date: October 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: May 21, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: June 22, 2017 Next Review Date:
Y: Orthopedic Specialty
 Y: Orthopedic Specialty Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 253 Major Competency Area: Y Priority: One Competency: Y-1 HPA Authorization and Standards Date: September 1, 2005 Y-1-1 Demonstrate
Y: Orthopedic Specialty Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 253 Major Competency Area: Y Priority: One Competency: Y-1 HPA Authorization and Standards Date: September 1, 2005 Y-1-1 Demonstrate
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
PEDIATRIC KNEE SUPPORTS Indications:
 PEDIATRIC KNEE SUPPORTS Indications: ANTERIOR CRUCIATE INSTABILITY POSTERIOR CRUCIATE INSTABILITY CHONDROMALACIA LATERAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INSTABILITY MEDIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INSTABILITY PATELLAR
PEDIATRIC KNEE SUPPORTS Indications: ANTERIOR CRUCIATE INSTABILITY POSTERIOR CRUCIATE INSTABILITY CHONDROMALACIA LATERAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INSTABILITY MEDIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INSTABILITY PATELLAR
Contents SECTION 1: GENERAL TRAUMA AND RECONSTRUCTIVE HIP SURGERY
 SECTION 1: GENERAL TRAUMA AND RECONSTRUCTIVE HIP SURGERY 1. Acetabular and Pelvic Fractures...3 2. Acetabular Orientation (Total Hips)...6 3. Acetabular Osteotomy...7 4. Achilles Tendon Ruptures...9 5.
SECTION 1: GENERAL TRAUMA AND RECONSTRUCTIVE HIP SURGERY 1. Acetabular and Pelvic Fractures...3 2. Acetabular Orientation (Total Hips)...6 3. Acetabular Osteotomy...7 4. Achilles Tendon Ruptures...9 5.
Full Function, Faster Medial-Pivot
 Full Function, Faster Medial-Pivot Total Knee Replacement Patient Brochure Does your knee prevent you from performing and enjoying everyday activities? Osteoarthritis affects nearly 350 million people
Full Function, Faster Medial-Pivot Total Knee Replacement Patient Brochure Does your knee prevent you from performing and enjoying everyday activities? Osteoarthritis affects nearly 350 million people
Case. 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds
 Case 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds Exam I: Swelling over entire tibia extending to foot P: Tenderness
Case 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds Exam I: Swelling over entire tibia extending to foot P: Tenderness
OSCELL ARTICULAR CARTILAGE CELL IMPLANTATION (FEMORAL CONDYLE SITES) PATIENT ADVICE.
 OSCELL ARTICULAR CARTILAGE CELL IMPLANTATION ( SITES) PATIENT ADVICE. Anatomy of the Right Knee example of a femoral articular defect site Knee Straight Knee Bent KEY: Patella Kneecap Trochlea Groove on
OSCELL ARTICULAR CARTILAGE CELL IMPLANTATION ( SITES) PATIENT ADVICE. Anatomy of the Right Knee example of a femoral articular defect site Knee Straight Knee Bent KEY: Patella Kneecap Trochlea Groove on
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: Revised Date: 07/26/17 Page 1 of 9
 Page 1 of 9 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination/ Clinical Indications Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on
Page 1 of 9 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination/ Clinical Indications Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on
Bledsoe Extender Brace Application Instructions CP Rev D 03/07
 Bledsoe Extender Brace Application Instructions CP020193 Rev D 03/07 Council Directive 93/2/EEC of 1 June 1993 concerning Medical devices Fast adjustment- Fast Hinge- Fast Straps- Fast Application This
Bledsoe Extender Brace Application Instructions CP020193 Rev D 03/07 Council Directive 93/2/EEC of 1 June 1993 concerning Medical devices Fast adjustment- Fast Hinge- Fast Straps- Fast Application This
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries Mark L. Wood, MD The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the most commonly injured ligaments of the knee. The incidence of ACL injuries is currently estimated
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries Mark L. Wood, MD The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the most commonly injured ligaments of the knee. The incidence of ACL injuries is currently estimated
W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco
 Knee Pain And Injuries In Adults W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco Pain Control Overview Narcotics rarely necessary after 1 st 1-2
Knee Pain And Injuries In Adults W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco Pain Control Overview Narcotics rarely necessary after 1 st 1-2
Fractures of Lower extremity
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Fractures of Lower extremity FRACTURES OF FEMORAL NECK Anatomy Neck-Shaft Angle: In the anteroposterior roentgenogram, it is the angle between the long axis of the femoral neck
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Fractures of Lower extremity FRACTURES OF FEMORAL NECK Anatomy Neck-Shaft Angle: In the anteroposterior roentgenogram, it is the angle between the long axis of the femoral neck
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
Knee Injuries. PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS. Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain
 Knee Injuries PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain Result from either a direct blow from the lateral side in a medial direction or a severe outward twist Greater injury
Knee Injuries PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain Result from either a direct blow from the lateral side in a medial direction or a severe outward twist Greater injury
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Original Date: December 2015 Page 1 of 8 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
ICD-10 CM Training. Orthopaedic
 ICD-10 CM Training Orthopaedic ICD-10-CM Compliance Dates ICD-10-CM will be valid for dates of service on or after October 1, 2015 Outpatient dates of service of October 1, 2015 and beyond. Inpatient hospital
ICD-10 CM Training Orthopaedic ICD-10-CM Compliance Dates ICD-10-CM will be valid for dates of service on or after October 1, 2015 Outpatient dates of service of October 1, 2015 and beyond. Inpatient hospital
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
Knee Braces. Medical Coverage Policy. Table of Contents. Related Coverage Resources. Coverage Policy. Fracture Knee Brace/Rehabilitative Brace
 Medical Coverage Policy Effective Date...06/15/2017 Next Review Date...06/15/2018 Coverage Policy Number... 0362 Knee Braces Table of Contents Coverage Policy... 1 Overview... 3 General Background... 3
Medical Coverage Policy Effective Date...06/15/2017 Next Review Date...06/15/2018 Coverage Policy Number... 0362 Knee Braces Table of Contents Coverage Policy... 1 Overview... 3 General Background... 3
ACL RECONSTRUCTION HAMSTRING METHOD. Presents ACL RECONSTRUCTION HAMSTRING METHOD. Multimedia Health Education
 HAMSTRING METHOD Presents HAMSTRING METHOD Multimedia Health Education Disclaimer Stephen J. Incavo MD This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Anterior Cruciate
HAMSTRING METHOD Presents HAMSTRING METHOD Multimedia Health Education Disclaimer Stephen J. Incavo MD This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Anterior Cruciate
Knee Surgical Technique
 Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
42 nd Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine. Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete. Disclosure
 42 nd Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine Travis Murray, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio January 23, 2015 Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete Disclosure
42 nd Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine Travis Murray, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio January 23, 2015 Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete Disclosure
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Repair and Reconstruction
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Repair and Reconstruction The knee consists of four bones that form three joints. The femur is the large bone
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Repair and Reconstruction The knee consists of four bones that form three joints. The femur is the large bone
Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
SAMPLE ONLY. NOT FOR DISTRIBUTION. The Knee
 SAMPLE ONLY. NOT FOR DISTRIBUTION. 1 The Knee 2 CHAPTER 1 SAMPLE ONLY. NOT FOR DISTRIBUTION. THEY ARE NOT CUSHIONS! I can t tell you how many times I ve heard it said that the meniscus cartilages are the
SAMPLE ONLY. NOT FOR DISTRIBUTION. 1 The Knee 2 CHAPTER 1 SAMPLE ONLY. NOT FOR DISTRIBUTION. THEY ARE NOT CUSHIONS! I can t tell you how many times I ve heard it said that the meniscus cartilages are the
Femoral Shaft Fracture
 Femoral Shaft Fracture The femoral shaft is well padded with muscles(an advantage in protecting the bone from all but the most powerful forces)but the disadvantage is that fractures are often severely
Femoral Shaft Fracture The femoral shaft is well padded with muscles(an advantage in protecting the bone from all but the most powerful forces)but the disadvantage is that fractures are often severely
Tyler P. Fawcett, Justin W. Hall, Travis F. Mulloy, Daniel J. Caporal Effect of Knee Brace Use on Healthy Gait
 Tyler P. Fawcett, Justin W. Hall, Travis F. Mulloy, Daniel J. Caporal Effect of Knee Brace Use on Healthy Gait Aquila The FGCU Student Research Journal Volume 3 Issue 2 (17) DOI.2449/aq.3.2.6 17 Fawcett
Tyler P. Fawcett, Justin W. Hall, Travis F. Mulloy, Daniel J. Caporal Effect of Knee Brace Use on Healthy Gait Aquila The FGCU Student Research Journal Volume 3 Issue 2 (17) DOI.2449/aq.3.2.6 17 Fawcett
Physical Examination of the Knee
 History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic? Acute vs Chronic Previous procedures done on the knee? Swelling, catching, instability General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate gait Examine hip
History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic? Acute vs Chronic Previous procedures done on the knee? Swelling, catching, instability General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate gait Examine hip
OSCELL ARTICULAR CARTILAGE CELL IMPLANTATION (PATELLOFEMORAL SITES) PATIENT ADVICE.
 OSCELL ARTICULAR CARTILAGE CELL IMPLANTATION ( SITES) PATIENT ADVICE. Anatomy of the Right Knee example of a trochlea articular defect site Knee Straight Knee Bent KEY: Patella Kneecap Trochlea Groove
OSCELL ARTICULAR CARTILAGE CELL IMPLANTATION ( SITES) PATIENT ADVICE. Anatomy of the Right Knee example of a trochlea articular defect site Knee Straight Knee Bent KEY: Patella Kneecap Trochlea Groove
