NEGLECTED RESISTANT RECURRENT CTEV CORRECTION WITH JESS FIXATOR Muktevi Sreedhar 1
|
|
|
- Kimberly Watts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NEGLECTED RESISTANT RECURRENT CTEV CORRECTION WITH JESS FIXATOR Muktevi Sreedhar 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Muktevi Sreedhar. Neglected Resistant Recurrent CTEV Correction with Jess Fixator. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences 2014; Vol. 3, Issue 63, November 20; Page: , ABSTRACT: Idiopathic club foot and its management have been the topic of keen interest to the orthopaedics field ever since time immemorial and many techniques in the successful management of these have been advocated till date. This study discusses one such technique of management in children with the Jess fixator. KEYWORDS: Idiopathic club foot, Jess fixator. INTRODUCTION: Idiopathic clubfoot is one of the oldest and commonest deformities of mankind, ever since man has adopted the erect posture. 1 It occurs in variable severity and some of the mobile feet are corrected well with manipulation and stretching. Nearly half the feet are rigid and do not show full correction with conservative management. In developing countries, clubfoot remains a significant problem and yields an unpredictable outcome because of late presentation and ignorance of the parents. Neglected clubfoot usually presents the unyielding rigid deformities because of the extremely contracted skin, tendons, ligaments and capsules on the postero medial aspect of the foot. 2 In the earliest times there has been no limit to the indigenous devices that have been used to correct the clubfoot. The 20 th century has been marked by the classification of two concepts in management of clubfoot. The first is the general acceptance of the principles of manipulation, strapping and serial correction plaster cast advocated by Kite and Dennis Browne. An impressive assay of clinical evidence was accumulated in support of their methods. The goal of treatment for clubfoot deformities is to obtain full and lasting correction, so that the patient has a functional, painfree, plan tigrade foot with good mobility. 3 The treatment of relapsed, neglected and rigid varieties of club foot is based on corrective operation in the hind foot by posteromedial release and correction of varus heel by calcaneal osteotomy (Dwyer ) as in metatarsal region by extensive medial release and cuboid osteotomy (Evans 1961). However, none of the described methods can completely achieve the goal of functional, painless and cosmetically acceptable foot. This unsatisfactory situation prompted scientists to seek a method which does not involve soft tissue trauma, bony resection etc. The second concept is a simple versatile and light fixator system with tremendous potential was developed by Dr. B.B. Joshi 4 of Bombay (Mumbai) INDIA in the year This method proved successful in almost all age groups ranging from 4 months to 19 years. Dr. B. B. Joshi advocated a method of controlled, differential distraction which is semi invasive, more physiological in comparison to any other technique, using Prof. Ilizarov's principles. The intention of this discussion is to review the current thinking and address the changing spectrum of management as a poet has rightly said, "we are guilty of many errors and faults, but our worst crime is abandoning the children, neglecting the formation of life. Many of the things we need may wait, the child cannot, right now is the time his bones have been formed, his blood has been made and his senses are being developed. To him we cannot assure tomorrow, his need is today". J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 63/Nov 20, 2014 Page 13913
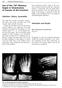
2 OBJECTIVES: 1. To assess the efficacy of controlled differential distraction as a method of treatment in resistant and recurrent CTEV and critically assess the results based on the clinical and radiological findings. 2. To evaluate various technical problems, complications of techniques and suggest ways to overcome them. MATERIALS AND METHODS: This study was conducted in VMMC Karaikal Pondicherry, study includes management of 20 feet in 14 patients with old neglected, recurrent or resistant cases of CTEV by JESS. INCLUSION CRITERIA: Age: Patients aged between 1 to 8 years. Both unilateral and bilateral cases. Neglected, recurrent and resistant cases of clubfoot. EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Age < 1 year and > 8 years. Patients who are unfit for surgery. Parents refusal for surgery. On admission of the patient a careful history was elicited from the parents/ attendants to reveal the duration and previous treatment of the deformed foot. The patients were then assessed clinically using Caroll assessment which Includes: 1. Calf atrophy. 2. Posterior displacement of the fibula. 3. Creases medial or posterior. 4. Curved lateral border. 5. Cavus. 6. Fixed equinus. 7. Navicular fixed to the medial malleolus. 8. OS calcis fixed to tibia. 9. No midtarsal mobility. 10. Fixed forefoot supination. Each feature scores one point when present and no point when absent. Thus the worst foot having all the features would score ten points whereas the normal or a fully corrected foot would score zero point. Radiological Evaluation: Radiologically evaluated with ankle and foot in AP and stress dorsiflexion views. J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 63/Nov 20, 2014 Page 13914
3 The following angles are Calculated: Talocalcaneal angle in AP and stress dorsiflexion views. Talus 1 st metatarsal angle in AP view. Tibiocalcaneal angle in lateral view. Talocalcaneal index. Normal values: Talocalcaneal: AP 30 to 550, lateral- 25 to 500. Tibiocalcaneal: stress lateral- 10 to 400. Talus 1stmetatarsal: AP -5 to 150. Talocalcaneal index: in AP and lateral, >40 0. The patient was taken up for surgery after investigations and making the patient medically fit for surgery. OPERATIVE PROCEDURE FOR JESS: The procedure is carried out under general anesthesia with the patient in supine position. A pneumatic cuff is applied on the thigh but, the tourniquet is inflated only if need arises intraoperatively. COMPONENTS: To suit the requirements for different age groups, three sets of assembly components are designed: small, medium and large. COMPONENTS OF JESS FIXATOR OPERATIVE PROCEDURE: TIBIAL WIRES: Two parallel transfixing wires are passed in the tibia, perpendicular to the longitudinal axis from lateral to medial. The length of the middle segment of the Z bar is marked below the first wire. The second wire is passed parallel to the first wire at this level. METATARSAL WIRES: While passing the metatarsal wires the surgeon should hold the foot with one hand and drill the wires with the other, using a power drill: One transfixing wire is passed from the fifth to the first metatarsal engaging at least the fifth and the first metatarasal at the level of the neck. Two separate wires, one from the medial and the other from the lateral aspects are inserted parallel to the first wire. These two wires engage two or three metatarsals on their respective side at the level of the proximal shaft. The distance between the transfixing wires and these wires should correspond with the distance between J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 63/Nov 20, 2014 Page 13915
4 the holes in the block in the distractor to be used. The distractor can be used as a jig. It is essential to be sure that all the metatarsals have been inserted by at least one of the wires. Calcaneal wires: Two transfixing parallel wires are passed into the tuberosity of the calcaneum from the medial side avoiding the posterior tibial artery. These wires should be perpendicular to the long axis of the calcaneum. The distance between these two wires should again be equidistant between the holes in the blocks in the distractor to be used. AXIAL CALCANEAL WIRE: The axial calcaneal wire is passed posterior to anterior. The point of entry is just distal to the insertion to the achillis tendon. The wire is directed medially and distally to mimic J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 63/Nov 20, 2014 Page 13916
5 the equinus and the varus of the calcaneum. This wire is passed under image intensifier control when available or should lie in the long axis of the calcaneum. Attachments of the 'Z' and 'L' rods: Tibial attachment- the tibial k wires are attached to the middle segment of the Z rods by link joints on the medial and the lateral aspects. The wires are prestressed by bringing them forwards each other by few millimeters while tightening the joint. The limbs of the Z rods now lie perpendicular to the axis of the tibia. One connecting rod is used to span the anterior limbs of Z rods and the other span the posterior limbs. Maintain a finger breadth clearance between the skin and the Z rods and all subsequent connections to the k wires. METATARSAL ATTACHMENTS: Two small L rods are attached to the metatarsal wires on medial and lateral aspect of the foot with one limb projecting plantar wards and the angle of L is placed distally. CALCANEAL ATTACHMENTS: Two large L rods are attached to the transfixing calcaneal wires on either side of the heel. Behind the foot these rods are connected to each other by a connecting rod to which the axial calcaneal wire is clamped. CONNECTING THE SEGMENTAL HOLD: a. Calcaneal- metatarsal connection: A pair of appropriately sized distractors is attached to the calcaneal and metatarsal wires on either side of the foot keeping the distractor knobs interiorly for easy handling during the distraction. b. Tibiocalcaneal connection: Posterior limbs of the Z rods are attached to the L rods of the calcaneal hold by a distractor on either side. Distractors are attached near the transfixing pins (lateral and medial aspect of the calcaneum). c. Tibiometatarsal connection: The anterior limbs of the Z rods are connected by a pair of rods to the small L rods anterior to the attachment of the metatarsal wires. POST OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT: 1. Pin site care: the dressings are performed twice a week with savlon, spirit and betadine lotion. Pin sites are covered with dry gauge and protective dressings are applied. 2. Distraction: in all hospitalized patients fractional distraction at the rate of 0.25 mm/hrs is applied. Differential distraction on the medial side is performed twice the rate than that on the lateral side. Distraction on the lateral side not only prevents crushing of the articular cartilage but also permits normal growth of epiphyseal plate on lateral side which may be affected if compression is done on the lateral side. In non-hospitalized patients parents do the distraction at the rate of 1mm/day on the medial side and ½ mm/day on the lateral side. On the 3 rd postoperative day the distraction is started as Follows: The calcaneometatarsal Distraction: Medial mm every 6 hours. Lateral mm every 12 hours. The tibiocalcaneal distraction is carried out in two Positions: J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 63/Nov 20, 2014 Page 13917
6 1. The distractors are mounted between the inferior limbs of the Z rods and posterior limbs of the calcaneal L rods. The distractors lie parallel to the leg and just posterior to the transfixing calcaneal wires. Distraction in this position corrects varus of the hindfoot and the equinus. Medial mm every 6 hours. Lateral mm every 12 hours. End point - (judged clinically). 2. The tibiocalcaneal distractors are now shifted posteriorly and connected above to the transverse bar connecting the posterior limbs of Z rods and below to the posterior calcaneal bars connecting the posterior limbs of L rods and axial calcaneal pin. The distractors lie on either side of the axial calcaneal pin. Distraction in this position provides thrust force to stretch posterior structures and corrects hind foot equinus at the ankle and subtalar joints. Both distractors mm every 6 hours. End point - assessed clinically and radiologically. Approximately 2-3 weeks of distraction (end of 6 th postoperative week) 3. Clinical and radiological assessment: Visual correction of the deformities is noted during the distraction phase. Full correction is achieved, usually at the end of 5-6 weeks. X ray was taken finally after the removal of the fixator. The roentgenogram correlates well with the clinical picture. 4. The static phase: Following the correction, the assembly is held in static position for further three to six weeks to allow soft tissue maturation in elongation position. 5. Removal of the fixator: Single stage removal of the whole assembly was done under general anaesthesia and a plaster cast is given as follows 6. After removal of the assembly, a well moulded above knee plaster cast is applied in maximum correction for two weeks. Once the pin tracts heel completely, a below knee cast is applied with polyurethane bandage and the patient is asked to ambulate with full weight bearing in plaster. Below knee cast is removed after 4-6 weeks. 7. Orthotic device: Appropriate orthotic devices are absolutely essential for maintenance of correction and prevention of recurrence in long term follow up. OBSERVATIONS AND RESULTS: The present study includes treatment of 20 feet in 14 patients with old neglected, relapsed and rigid clubfoot treated with JESS application. The following observations were made from the data collected in our study: Type No. of feet percentage Neglected 4 20 Pop drop out Recurrent/relapsed 5 25 Total TABLE SHOWING TYPE OF CLUB FOOT J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 63/Nov 20, 2014 Page 13918
7 COMPLICATIONS: Temporary edema noted in 15 feet which was treated by elevation of foot and temporary stoppage of distraction. 1. Superficial pin tract infection noted in 17 feet which was treated with regular dressing and antibiotics. 2. Skin necrosis noted in 1 foot (on the lateral border of the foot) was treated with dressing and temporary cessation of distraction. 3. Flexion contracture of toes was noted in 1 patient which was treated with passive stretching and foot plate application. 4. No incidence of loosening of pins or hematoma formation or osteomyelitis. The average follow up period was 8 months with ranging from 4 to 12 months. RESULTS: Of the 20 feet treated by JESS 7 (35%) were excellent, 11 (55%) were good, 1 (5%) was fair and 1 (5%) was poor. WE GRADE RESULTS AS FOLLOWS EXCELLENT: The foot was normal in appearance and shape, equal to the other side (in unilateral cases) t with well-maintained arches. The child could actively dorsiflex and evert the foot. The range of movements were full. The child could comfortably squat. There were no permanent residual complications osteomyelitis or skin necrosis due to over permanent flexion deformities of toes needing some corrective procedure. The foot could be used for routine physical activities without any disability. GOOD: Same as above except that the range of movements of the foot was more than 50% but not full. The child parents were fully satisfied with the result. J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 63/Nov 20, 2014 Page 13919
8 FAIR: The shape of the foot was not normal, some residual deformity persisting or mild pes planus deformity. Though active dorsiflexion and eversion was possible the foot could only be brought to plantigrade position. Further dorsiflexion or eversion was not possible. POOR: There was incomplete correction or there was over correction giving rise to flat foot; difficulty in squatting. Some residual permanent complication. NEGLECTED CLUB FOOT PRE OPERATIVE PHOTOGRAPHS DISCUSSION: Functional improvement concerns patients more than just deformity correction. The goal of any club foot surgery is to obtain a cosmetically acceptable foot, pliable, functional, painless, plant grade foot and to spare the parent and the child from frequent hospitalization and years of treatment with casts and braces. 4 The treatment for relapsed clubfoot is usually based on corrective operations on either side of the central deformity in the form of posteromedial release, calcanealosteotomy, medial release and cuboid osteotomy. 5 No treatment for relapsed clubfeet can achieve normal foot function. The goal of any club foot surgery is to obtain a cosmetically acceptable, pliable, functional, painless, plantigrade foot. Differential distraction using JESS enables long-term maintenance of correction and good function. Nonetheless, the need for the JESS procedure is likely to decline because of the worldwide shift to the Ponseti method for primary treatment. Further follow-up is needed to determine whether any degenerative changes occur and affect function in adulthood. 6,7 This fixator has many theoretical advantages like avoiding fibrous tissue formation, prevention of further shortening of foot as against the bony procedures and proper control of all components of corrections, with actual lengthening and histioneogenesis of the soft tissues. 8 J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 63/Nov 20, 2014 Page 13920
9 POST OPERATIVE PHOTOGRAPHS CONCLUSION: JESS technique plays an excellent role in the treatment of neglected, recurrent and resistant cases of CTEV to obtain a cosmetically acceptable, pliable, functional, painless and plantigrade foot and spares the parent and the child from the ordeal of frequent hospitalization and years of treatment with casts and braces. The main advantages of JESS being gain in length of soft tissues as that of normal foot, actual lengthening of the musculotendinous units and the soft tissues by the method of distraction histogenesis without any loss of muscle power, absence of further shortening unlike bony procedures, maintenance of normal size and shape of foot and proper control of all the components of correction including repositioning of the bones. JESS frame is superior to Ilizarov fixator because of its easier application, lighter weight, less cumbersome, shorter learning curve, less inventory and lower cost. JESS procedure is easy to perform, semi invasive blood less surgery avoiding postoperative complications and fibrous tissue / scar formation and doesn t require any sophisticated instrumentation or image intensification. The chief complications of JESS technique are temporary edema, pin tract infection, skin necrosis and flexion contracture of toes which can be successfully managed by foot elevation, regular dressing and antibiotics, temporary cessation of distraction and passive stretching of toes respectively. The drawbacks of this procedure are that it cannot be applied in a grown up child with rigid bony and soft tissue deformities and in patients previously treated with JESS and having residual deformities, it requires regular and frequent out-patient visits with long term follow up to assess the complications, correction and recurrence. In our study the length of foot was not lost, the deformity of the foot was nearly fully corrected and the strength of the muscle was retained to normal. However long term studies are necessary to accurately assess the functional outcome of the treatment of club foot by JESS. J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 63/Nov 20, 2014 Page 13921
10 REFERENCES: 1. Ajai Singh. Evaluation of Neglected Idiopathic CTEV Managed by Ligamentotaxis Using Jess: A Long-Term Follow up SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics 2011: , Ramesh Chandra Meena, Devi Sahai Meena, Purnima Patni, Narendra Saini, Ankit Chauhan. Jess and Illizarov in Neglected /Relapsed CTEV: A Prospective Comparative Study. IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences; Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. VII (Sep. 2014), PP K. Ikeda. Conservative treatment of idiopathic clubfoot. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics, vol. 12, no. 2, pp , Joshi BB, Laud NS, Warrier S, Kanaji BG, Joshi AP, Dabake H. Treatment of CTEV by Joshi s External Stabilization System (JESS). In: Kulkarni GS, editor. Textbook of Orthopaedics and Trauma. 1 st ed. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers; Graham GP, Dent CM. Dillwyn Evans operation for relapsed club foot. Long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1992; 74: Turco VJ. Surgical correction of the resistant club foot. One stage postero medial release with internal fixation: A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1971; 53: Khan SA, Kumar A. Ponseti s manipulation in neglected club foot in children more than 7 years of age: A prospective evaluation of 25 feet with long term follow up. J Pediatr Orthop B 2010; 19: Suresh S, Ahmed A, Sharma VK. Role of Joshi s external stabilisation system fixator in the management of idiopathic clubfoot. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2003; 11: AUTHORS: 1. Muktevi Sreedhar PARTICULARS OF CONTRIBUTORS: 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Karaikal, Pondicherry. NAME ADDRESS ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Dr. Muktevi Sreedhar, # 8-133, J. P. Colony, Patancheru , Medak District, Telangana. drmuktevi@gmail.com Date of Submission: 05/11/2014. Date of Peer Review: 06/11/2014. Date of Acceptance: 14/11/2014. Date of Publishing: 19/11/2014. J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 63/Nov 20, 2014 Page 13922
Joshi s External Stablization System (JESS) Application For Correction Of Resistant Club-Foot
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 18 Number 1 Joshi s External Stablization System (JESS) Application For Correction Of Resistant Club-Foot M CN Citation M CN. Joshi s External
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 18 Number 1 Joshi s External Stablization System (JESS) Application For Correction Of Resistant Club-Foot M CN Citation M CN. Joshi s External
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 77/ Sept 24, 2015 Page 13430
 STUDY OF SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF NEGLECTED CONGENITAL TALIPES EQUINO VARUS IN CHILDREN Chinta Shyam Kumar 1, D. Venkateswara Rao 2, Vijay Sreenivas 3, Anvesh Sangepu 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Chinta Shyam
STUDY OF SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF NEGLECTED CONGENITAL TALIPES EQUINO VARUS IN CHILDREN Chinta Shyam Kumar 1, D. Venkateswara Rao 2, Vijay Sreenivas 3, Anvesh Sangepu 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Chinta Shyam
Role of Jess in Management of Neglected, Relapsed And Resistant Ctev
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. V (October. 2016), PP 15-19 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Jess in Management of Neglected,
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. V (October. 2016), PP 15-19 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Jess in Management of Neglected,
Management of Congenital Talipes Equinovarus by Joshi s External Stabilizing System
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/555 Management of Congenital Talipes Equinovarus by Joshi s External Stabilizing System G B S Varun 1, N Muralidhar 2, Kavya Bharathidasan 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/555 Management of Congenital Talipes Equinovarus by Joshi s External Stabilizing System G B S Varun 1, N Muralidhar 2, Kavya Bharathidasan 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Jess and Illizarov in Neglected /Relapsed Ctev: A Prospective Comparative Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. VII (Sep. 2014), PP 20-26 Jess and Illizarov in Neglected /Relapsed Ctev: A Prospective
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. VII (Sep. 2014), PP 20-26 Jess and Illizarov in Neglected /Relapsed Ctev: A Prospective
Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 586-590 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities Hani EL-MOWAFI From Mansoura
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 586-590 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities Hani EL-MOWAFI From Mansoura
Radiological Outcomes of Management of Congenital Clubfoot Using JESS
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/284 Radiological Outcomes of Management of Congenital Clubfoot Using JESS G B S Varun 1, N Muralidhar 2, Kavya Bharathidasan 3 1 Assistant Professor, Department
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/284 Radiological Outcomes of Management of Congenital Clubfoot Using JESS G B S Varun 1, N Muralidhar 2, Kavya Bharathidasan 3 1 Assistant Professor, Department
We present the results of the management of 17
 The Ilizarov method in the management of relapsed club feet C. F. Bradish, S. Noor From the Royal Orthopaedic Hospital NHS Trust, Birmingham, England We present the results of the management of 17 relapsed
The Ilizarov method in the management of relapsed club feet C. F. Bradish, S. Noor From the Royal Orthopaedic Hospital NHS Trust, Birmingham, England We present the results of the management of 17 relapsed
Conservative management of idiopathic clubfoot: Kite versus Ponseti method
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2009;17(1):67-71 Conservative management of idiopathic clubfoot: Kite versus Ponseti method AV Sanghvi, 1 VK Mittal 2 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Government Medical College
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2009;17(1):67-71 Conservative management of idiopathic clubfoot: Kite versus Ponseti method AV Sanghvi, 1 VK Mittal 2 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Government Medical College
International Journal of Biological & Medical Research
 Int J Biol Med Res. 2013; 4(1): 2986-2990 Int J Biol Med Res Volume 3, Issue 1, Jan 2012 www.biomedscidirect.com BioMedSciDirect Publications Contents lists available at BioMedSciDirect Publications International
Int J Biol Med Res. 2013; 4(1): 2986-2990 Int J Biol Med Res Volume 3, Issue 1, Jan 2012 www.biomedscidirect.com BioMedSciDirect Publications Contents lists available at BioMedSciDirect Publications International
K. Sundaresh 1, E. Venkateshulu 2, Bellara Raghavendra 3*, M Venkata Subba Reddy 4, Shaikh Mohammad Imran 5
 e - ISSN - 2349-8005 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN CASE REPORTS Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ijacr A STUDY OF OUTCOME OF B.B.JOSHI S EXTERNAL FIXATOR FOR MANAGEMENT OF NEGLECTED AND RELAPSED
e - ISSN - 2349-8005 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN CASE REPORTS Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ijacr A STUDY OF OUTCOME OF B.B.JOSHI S EXTERNAL FIXATOR FOR MANAGEMENT OF NEGLECTED AND RELAPSED
Copyright 2004, Yoshiyuki Shiratori. All right reserved.
 Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
COMPARISION OF RESULTS OF TWO DIFFERENT INCISIONS IN POSTERO MEDIAL SOFT TISSUE RELEASE IN IDIOPATHIC CLUB FOOT D. Ramkishann 1, S. Y.
 COMPARISION OF RESULTS OF TWO DIFFERENT INCISIONS IN POSTERO MEDIAL SOFT TISSUE RELEASE IN IDIOPATHIC CLUB FOOT D. Ramkishann 1, S. Y. Narsimulu 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: D. Ramkishann, S. Y. Narsimulu.
COMPARISION OF RESULTS OF TWO DIFFERENT INCISIONS IN POSTERO MEDIAL SOFT TISSUE RELEASE IN IDIOPATHIC CLUB FOOT D. Ramkishann 1, S. Y. Narsimulu 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: D. Ramkishann, S. Y. Narsimulu.
FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]
![FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test] FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]](/thumbs/83/88335212.jpg) FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
Mid-term results of ponseti method for the treatment of congenital idiopathic clubfoot - (A study of 67 clubfeet with mean five year follow-up)
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Mid-term results of ponseti method for the treatment of congenital idiopathic clubfoot - (A study of 67 clubfeet with mean five year follow-up) Milind M Porecha 1*, Dipak S
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Mid-term results of ponseti method for the treatment of congenital idiopathic clubfoot - (A study of 67 clubfeet with mean five year follow-up) Milind M Porecha 1*, Dipak S
Clinical Study Evaluation of Neglected Idiopathic Ctev Managed by Ligamentotaxis Using Jess: A Long-Term Followup
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 218489, 6 pages doi:10.4061/2011/218489 Clinical Study Evaluation of Neglected Idiopathic Ctev Managed by Ligamentotaxis
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 218489, 6 pages doi:10.4061/2011/218489 Clinical Study Evaluation of Neglected Idiopathic Ctev Managed by Ligamentotaxis
EVALUATION OF THREE DIFFERENT SURGICAL PROCEDURES FOR CONGENITAL TALIPES EQUINOVARUS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF THREE DIFFERENT SURGICAL PROCEDURES FOR CONGENITAL TALIPES EQUINOVARUS Ismatullah Department of Casualty, Postgraduate Medical Institute, Lady Reading Hospital, Peshawar
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF THREE DIFFERENT SURGICAL PROCEDURES FOR CONGENITAL TALIPES EQUINOVARUS Ismatullah Department of Casualty, Postgraduate Medical Institute, Lady Reading Hospital, Peshawar
Financial Disclosure. The authors have not received any financial support for the preparation of this work.
 Persistent Clubfoot Deformity Following Treatment by the Ponseti Method W.B. Lehman, M.D. Alice Chu, M.D. New York Ponseti Clubfoot Center Department of Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Financial Disclosure
Persistent Clubfoot Deformity Following Treatment by the Ponseti Method W.B. Lehman, M.D. Alice Chu, M.D. New York Ponseti Clubfoot Center Department of Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Financial Disclosure
The effect of two different plastering techniques on the rate of major surgery in idiopathic clubfoot
 Page 28 SA Orthopaedic Journal Summer 2013 Vol 12 No 4 The effect of two different plastering techniques on the rate of major surgery in idiopathic clubfoot A Horn, MBChB(Pret) Registrar, Department of
Page 28 SA Orthopaedic Journal Summer 2013 Vol 12 No 4 The effect of two different plastering techniques on the rate of major surgery in idiopathic clubfoot A Horn, MBChB(Pret) Registrar, Department of
Evidence-Based Examination of the Foot Presented by Alexis Wright, PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check-offs
 Evidence-Based Examination of the Foot Presented by Alexis Wright, PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check-offs Module Five: Movement Assessment of the Foot/Ankle (1 hour CEU Time) Skilled
Evidence-Based Examination of the Foot Presented by Alexis Wright, PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check-offs Module Five: Movement Assessment of the Foot/Ankle (1 hour CEU Time) Skilled
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
V osteotomy and Ilizarov technique for residual idiopathic or neurogenic clubfeet
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2008;16(2):215-9 V osteotomy and Ilizarov technique for residual idiopathic or neurogenic clubfeet E Segev, E Ezra, M Yaniv, S Wientroub, Y Hemo Department of Pediatric Orthopaedics,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2008;16(2):215-9 V osteotomy and Ilizarov technique for residual idiopathic or neurogenic clubfeet E Segev, E Ezra, M Yaniv, S Wientroub, Y Hemo Department of Pediatric Orthopaedics,
Workshop Outline. Pre-operative planning
 Workshop Objective To build and apply the True/Lok TM circular external fixator frame for correction of the Charcot forefoot deformity (Lisfranc fracture dislocation) Workshop Outline Pre-operative planning
Workshop Objective To build and apply the True/Lok TM circular external fixator frame for correction of the Charcot forefoot deformity (Lisfranc fracture dislocation) Workshop Outline Pre-operative planning
Pathology & Primary Treatment of Clubfoot
 Pathology & Primary Treatment of Clubfoot Hyun-Dae Shin, MD, PhD. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea Introduction The affected foot Restricted
Pathology & Primary Treatment of Clubfoot Hyun-Dae Shin, MD, PhD. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea Introduction The affected foot Restricted
Foot Injuries. Dr R B Kalia
 Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Metatarsus adductus, Skew foot, Club foot 성균관대학교삼성창원병원 장현정
 Metatarsus adductus, Skew foot, Club foot 성균관대학교삼성창원병원 장현정 Metatarsus adductus Epidemiology and Etiology 0.1-12% with higher number for multiple birth Deformation and compression from intrauterine crowding
Metatarsus adductus, Skew foot, Club foot 성균관대학교삼성창원병원 장현정 Metatarsus adductus Epidemiology and Etiology 0.1-12% with higher number for multiple birth Deformation and compression from intrauterine crowding
Scar Engorged veins. Size of the foot [In clubfoot, small foot]
![Scar Engorged veins. Size of the foot [In clubfoot, small foot] Scar Engorged veins. Size of the foot [In clubfoot, small foot]](/thumbs/78/77722241.jpg) 6. FOOT HISTORY Pain: Walking, Running Foot wear problem Swelling; tingly feeling Deformity Stiffness Disability: At work; recreation; night; walk; ADL, Sports Previous Rx Comorbidities Smoke, Sugar, Steroid
6. FOOT HISTORY Pain: Walking, Running Foot wear problem Swelling; tingly feeling Deformity Stiffness Disability: At work; recreation; night; walk; ADL, Sports Previous Rx Comorbidities Smoke, Sugar, Steroid
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE. Arthrodiatasis. Articulated Joint Distraction
 4 Arthrodiatasis Articulated Joint Distraction ARTHRODIATASIS OF THE HIP To prepare the assembly, remove the female component and replace it with the ProCallus articulated body for the hip. Remove cam
4 Arthrodiatasis Articulated Joint Distraction ARTHRODIATASIS OF THE HIP To prepare the assembly, remove the female component and replace it with the ProCallus articulated body for the hip. Remove cam
Analysis of Correlation of Foot Bimalleolar Angle and Pirani Scoring for its Predictive value in the management of Idiopathic CTEV by Ponseti Method
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 12 Number 1 Analysis of Correlation of Foot Bimalleolar Angle and Pirani Scoring for its Predictive value in the management of Idiopathic CTEV
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 12 Number 1 Analysis of Correlation of Foot Bimalleolar Angle and Pirani Scoring for its Predictive value in the management of Idiopathic CTEV
The Valgus Foot in Cerebral Palsy Equinovalgus not Plano-Valgus. Alfred D. Grant, M.D. David Feldman, M.D.
 The Valgus Foot in Cerebral Palsy Equinovalgus not Plano-Valgus Alfred D. Grant, M.D. David Feldman, M.D. Norman Otsuka, MD M.D. THE PURPOSE OF THIS PRESENTATION IS TO STATE CLEARLY THAT THE VALGUS FOOT
The Valgus Foot in Cerebral Palsy Equinovalgus not Plano-Valgus Alfred D. Grant, M.D. David Feldman, M.D. Norman Otsuka, MD M.D. THE PURPOSE OF THIS PRESENTATION IS TO STATE CLEARLY THAT THE VALGUS FOOT
Orthopaedics. Current concepts Common errors in the treatment of congenital clubfoot. International. I. V. Ponseti
 International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (1997) 21: 137 141 Orthopaedics International Springer-Verlag 1997 Current concepts Common errors in the treatment of congenital clubfoot I. V. Ponseti Department of
International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (1997) 21: 137 141 Orthopaedics International Springer-Verlag 1997 Current concepts Common errors in the treatment of congenital clubfoot I. V. Ponseti Department of
Physical Examination of the Foot & Ankle
 Inspection Standing, feet straight forward facing toward examiner Swelling Deformity Flatfoot (pes planus and hindfoot valgus) High arch (pes cavus and hindfoot varus) Peek-a-boo heel Varus Too many toes
Inspection Standing, feet straight forward facing toward examiner Swelling Deformity Flatfoot (pes planus and hindfoot valgus) High arch (pes cavus and hindfoot varus) Peek-a-boo heel Varus Too many toes
What Happens to the Paediatric Flat Foot? Peter J Briggs Freeman Hospital Newcastle upon Tyne
 What Happens to the Paediatric Flat Foot? Peter J Briggs Freeman Hospital Newcastle upon Tyne We don t know!! Population Studies 2300 children aged 4-13 years Shoe wearers Flat foot 8.6% Non-shoe wearers
What Happens to the Paediatric Flat Foot? Peter J Briggs Freeman Hospital Newcastle upon Tyne We don t know!! Population Studies 2300 children aged 4-13 years Shoe wearers Flat foot 8.6% Non-shoe wearers
Management of congenital talipes equino varus by ponseti method: Our experience
 Management of congenital talipes equino varus by ponseti method: Our experience Sreeranga Nagaraj 1*, Shankara K 2, Lakshmeesha T 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Hassan Institute of
Management of congenital talipes equino varus by ponseti method: Our experience Sreeranga Nagaraj 1*, Shankara K 2, Lakshmeesha T 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Hassan Institute of
Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries
 Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published April 1, 2015 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Tibialis posterior is the deepest, strongest, and most central muscle of the
Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published April 1, 2015 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Tibialis posterior is the deepest, strongest, and most central muscle of the
Correlation of Pirani score and Foot bimalleolar angle in the treatment of idiopathic congenital talipes equino varus by Ponseti method in infants
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2016, 82, 861-865 ORIGINAL STUDY Correlation of Pirani score and Foot bimalleolar angle in the treatment of idiopathic congenital talipes equino varus by Ponseti method in infants Rahul
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2016, 82, 861-865 ORIGINAL STUDY Correlation of Pirani score and Foot bimalleolar angle in the treatment of idiopathic congenital talipes equino varus by Ponseti method in infants Rahul
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program
 Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Results of Using Reversed Ponseti Technique in Treatment of Congenital Vertical Talus
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 4, June: 1447-1453, 217 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Results of Using Reversed Ponseti Technique in Treatment of Congenital Vertical Talus MOHAMED F. EL-KHOSOUSY,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 4, June: 1447-1453, 217 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Results of Using Reversed Ponseti Technique in Treatment of Congenital Vertical Talus MOHAMED F. EL-KHOSOUSY,
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Recurrent club-foot deformity following previous soft-tissue release
 Recurrent club-foot deformity following previous soft-tissue release MID-TERM OUTCOME AFTER REVISION SURGERY M. Mehrafshan, V. Rampal, R. Seringe, P. Wicart From Saint-Vincent de Paul Hospital, Paris,
Recurrent club-foot deformity following previous soft-tissue release MID-TERM OUTCOME AFTER REVISION SURGERY M. Mehrafshan, V. Rampal, R. Seringe, P. Wicart From Saint-Vincent de Paul Hospital, Paris,
ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION
 ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION Evaluation and Measurements By Isabelle Devreux 1 Ankle Plantar Flexion: Gastrocnemius and Soleus ROM: 0 to 40-45 A. Soleus: Origin: Posterior of head of fibula and proximal1/3 of
ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION Evaluation and Measurements By Isabelle Devreux 1 Ankle Plantar Flexion: Gastrocnemius and Soleus ROM: 0 to 40-45 A. Soleus: Origin: Posterior of head of fibula and proximal1/3 of
My Technique for Adjusting the Excessively Pronated Foot
 My Technique for Adjusting the Excessively Pronated Foot by Mark N. Charrette, DC One can think of Chiropractic in terms of science, art, and philosophy. The art or application of Chiropractic technique
My Technique for Adjusting the Excessively Pronated Foot by Mark N. Charrette, DC One can think of Chiropractic in terms of science, art, and philosophy. The art or application of Chiropractic technique
Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot
 168 Forefoot Reconstruction Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot Definition, History, Generalities This staple first provides a permanent compression both in the prongs
168 Forefoot Reconstruction Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot Definition, History, Generalities This staple first provides a permanent compression both in the prongs
Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module
 1.5 CME AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module Mahesh M. Thapa 1,2, Sumit Pruthi 1,2, Felix S. Chew 2 ABSTRACT
1.5 CME AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module Mahesh M. Thapa 1,2, Sumit Pruthi 1,2, Felix S. Chew 2 ABSTRACT
ISSN (Online) ISSN (Print) Hospital, 7, Works Road, Chromepet, Chennai(Tamilnadu) Pin , India
 Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2016; 4(3A):211-217 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2016; 4(3A):211-217 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Ponseti Treatment Method for Idiopathic Clubfoot Continuing Education Module
 Ponseti Treatment Method for Idiopathic Clubfoot Continuing Education Module Michelle J. Hall, CPO, BSE 1 Ignacio V. Ponseti, MD 2 1. Certified Prosthetist Orthotist at American Prosthetics & Orthotics,
Ponseti Treatment Method for Idiopathic Clubfoot Continuing Education Module Michelle J. Hall, CPO, BSE 1 Ignacio V. Ponseti, MD 2 1. Certified Prosthetist Orthotist at American Prosthetics & Orthotics,
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY
 BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY B.Resseque, D.P.M. ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing a ruler from the heel to the first metatarsal head Compare arch
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY B.Resseque, D.P.M. ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing a ruler from the heel to the first metatarsal head Compare arch
Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle AOFAS Resident Review Course September 28, 2013
 Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle Course September 28, 2013 Matthew M. Roberts, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Co-Chief, Foot and Ankle Service Hospital for Special Surgery Disclosure
Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle Course September 28, 2013 Matthew M. Roberts, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Co-Chief, Foot and Ankle Service Hospital for Special Surgery Disclosure
Knee spanning solutions
 Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY 3. TALRSALS = (FOOT BONES) Fibula. Frances Daly MSc 1 CALCANEUS 2. TALUS 3. NAVICULAR 4. CUBOID 5.
 ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
Dorsal surface-the upper area or top of the foot. Terminology
 It is important to learn the terminology as it relates to feet to properly communicate with referring physicians when necessary and to identify the relationship between the anatomical structure of the
It is important to learn the terminology as it relates to feet to properly communicate with referring physicians when necessary and to identify the relationship between the anatomical structure of the
2014 International Journal of Medical Science Research and Practice available on
 214 International Journal of Medical Science Research and Practice available on www.ijmsrp.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCE RESEARCH AND PRACTICE Print ISSN: 2349-3178 Online ISSN: 2349-3186
214 International Journal of Medical Science Research and Practice available on www.ijmsrp.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCE RESEARCH AND PRACTICE Print ISSN: 2349-3178 Online ISSN: 2349-3186
A novel surgical option for the operative treatment of clubfoot
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 155-161 A novel surgical option for the operative treatment of clubfoot Vasilios A. PAPAVASILIOU, Athanasios V. PAPAVASILIOU Clubfoot (talipes equinovarus) is a condition
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 155-161 A novel surgical option for the operative treatment of clubfoot Vasilios A. PAPAVASILIOU, Athanasios V. PAPAVASILIOU Clubfoot (talipes equinovarus) is a condition
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO)
 PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot)
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2007) 2:105 110 DOI 10.1007/s11751-007-0023-7 REVIEW Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot) Selvadurai Nayagam Received: 9 August
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2007) 2:105 110 DOI 10.1007/s11751-007-0023-7 REVIEW Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot) Selvadurai Nayagam Received: 9 August
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique. Description of Plate
 Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Functional outcome of tendoachilles following Ponseti s tenotomy for treatment of congenital talipes equino varus in children older than two years
 International Journal Research in Orthopaedics Agarwal S et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Sep;3(5):1057-1061 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20173941
International Journal Research in Orthopaedics Agarwal S et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Sep;3(5):1057-1061 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20173941
Functional outcome of idiopathic congenital talipes equinovarus treated by Ponseti method: a midterm study
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Madhuchandra P et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):296-301 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180683
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Madhuchandra P et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):296-301 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180683
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Ankle joint Synovial, hinge joint Allow movement of the foot in the sagittal plane only (1 degree of freedom): dorsiflexion:
The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Ankle joint Synovial, hinge joint Allow movement of the foot in the sagittal plane only (1 degree of freedom): dorsiflexion:
Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction & Repair
 1 Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction & Repair Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: The posterior tibialis muscle arises from the interosseous membrane and the adjacent
1 Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction & Repair Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: The posterior tibialis muscle arises from the interosseous membrane and the adjacent
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle
 Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics
 MEFiSTO Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics Surgical Technique Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF MEFiSTO Table
MEFiSTO Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics Surgical Technique Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF MEFiSTO Table
OTM Lecture Gait and Somatic Dysfunction of the Lower Extremity
 OTM Lecture Gait and Somatic Dysfunction of the Lower Extremity Somatic Dysfunction Tenderness Asymmetry Range of Motion Tissue Texture Changes Any one of which must be present to diagnosis somatic dysfunction.
OTM Lecture Gait and Somatic Dysfunction of the Lower Extremity Somatic Dysfunction Tenderness Asymmetry Range of Motion Tissue Texture Changes Any one of which must be present to diagnosis somatic dysfunction.
Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures
 Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures Roy Snelson, C.P.O.*, George Irons, C.P.O.**, and Vert Mooney, M.D.*** The fracture cast brace is designed to allow early ambulation
Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures Roy Snelson, C.P.O.*, George Irons, C.P.O.**, and Vert Mooney, M.D.*** The fracture cast brace is designed to allow early ambulation
Are you suffering from heel pain? We can help you!
 Are you suffering from heel pain? We can help you! STOP THE PAIN! Heel pain can be effectively combated with the proven Body Armor Night Splint. Heel spurs and heel pain Why? Heel pain is among the most
Are you suffering from heel pain? We can help you! STOP THE PAIN! Heel pain can be effectively combated with the proven Body Armor Night Splint. Heel spurs and heel pain Why? Heel pain is among the most
Comparative Study of Management of CTEV by Turco s Procedure & Ponsetti s Technique. Dr. Bhasakr Rao M.B.B.S., D.
 Comparative Study of Management of CTEV by Turco s Procedure & Ponsetti s Technique. Dr. Bhasakr Rao M.B.B.S., D.Ortho, DNB (Ortho) 1 ABSTRACT A prospective study was undertaken in the field of management
Comparative Study of Management of CTEV by Turco s Procedure & Ponsetti s Technique. Dr. Bhasakr Rao M.B.B.S., D.Ortho, DNB (Ortho) 1 ABSTRACT A prospective study was undertaken in the field of management
A multifactorial study of application of Joshi s External Stabilizing System indisplaced Distal End Radius Fractures.
 Original article: A multifactorial study of application of Joshi s External Stabilizing System indisplaced Distal End Radius Fractures. Rajeev Shukla*, Ravi Kant Jain*, Neeraj K Sharma*, Ravindra Kumar
Original article: A multifactorial study of application of Joshi s External Stabilizing System indisplaced Distal End Radius Fractures. Rajeev Shukla*, Ravi Kant Jain*, Neeraj K Sharma*, Ravindra Kumar
Original Article. Usman Zafar Dar 1, Ayesha Saeed 2, Abdul Latif Sami 3, Syed Muhammad Awais 4
 Original Article A COMPARATIVE STUDY TO DETERMINE THE EFFECTIVENESS OF THREE SURGICAL TECHNIQUES USED IN THE TREATMENT OF SEVERE CONGENITAL IDIOPATHIC CLUB FOOT USING THE DIMIGLIO SCORING SYSTEM. Usman
Original Article A COMPARATIVE STUDY TO DETERMINE THE EFFECTIVENESS OF THREE SURGICAL TECHNIQUES USED IN THE TREATMENT OF SEVERE CONGENITAL IDIOPATHIC CLUB FOOT USING THE DIMIGLIO SCORING SYSTEM. Usman
Anterior Transfer of Tibialis Posterior through the Interosseous Membranes in Post Injection Drop Foot: The Expirence at CORU.
 Anterior Transfer of Tibialis Posterior through the Interosseous Membranes in Post Injection Drop Foot: The Expirence at CORU. J Okello,F Franceschi, A Loro, D Kintu, I Otim. CORU Mengo Hospital, Kampala,
Anterior Transfer of Tibialis Posterior through the Interosseous Membranes in Post Injection Drop Foot: The Expirence at CORU. J Okello,F Franceschi, A Loro, D Kintu, I Otim. CORU Mengo Hospital, Kampala,
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Zenith. Total Ankle Replacement Surgical technique
 Total Ankle Replacement Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning and templating 6 Patient positioning 6 Exposure 6 Saw blades 7 Joint line definition 7 Tibial alignment jig
Total Ankle Replacement Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning and templating 6 Patient positioning 6 Exposure 6 Saw blades 7 Joint line definition 7 Tibial alignment jig
Midfoot - Reduction & Fixation - ORIF - screw fixation - AO Surgery Reference. ORIF - screw fixation
 Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
Index. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) 309 314 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abductor digiti minimi muscle, myectomy of, for tailor s bunionette, 243 Achilles tendon, lengthening
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) 309 314 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abductor digiti minimi muscle, myectomy of, for tailor s bunionette, 243 Achilles tendon, lengthening
Other Congenital and Developmental Diseases of the Foot. Department of Orthopedic Surgery St. Vincent s s Hospital, The Catholic University
 Other Congenital and Developmental Diseases of the Foot Department of Orthopedic Surgery St. Vincent s s Hospital, The Catholic University Contents Metatarsus Adductus Skewfoot Hallux Valgus Hallux Valgus
Other Congenital and Developmental Diseases of the Foot Department of Orthopedic Surgery St. Vincent s s Hospital, The Catholic University Contents Metatarsus Adductus Skewfoot Hallux Valgus Hallux Valgus
Correction Of Resistant / Neglected Club Foot By Joshi External Stabilization System Fixator
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. XII (Feb. 2016), PP 37-41 www.iosrjournals.org Correction Of Resistant / Neglected Club
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. XII (Feb. 2016), PP 37-41 www.iosrjournals.org Correction Of Resistant / Neglected Club
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE GALAXY UNYCO ANKLE BRIDGING DELTA FRAME UNILATERAL FRAME
 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE GALAXY UNYCO ANKLE BRIDGING DELTA FRAME UNILATERAL FRAME CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3 GALAXY UNYCO ANKLE DELTA APPROACH 4 GALAXY UNYCO ANKLE UNILATERAL APPROACH 12 Operative Technique Contributing
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE GALAXY UNYCO ANKLE BRIDGING DELTA FRAME UNILATERAL FRAME CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3 GALAXY UNYCO ANKLE DELTA APPROACH 4 GALAXY UNYCO ANKLE UNILATERAL APPROACH 12 Operative Technique Contributing
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
Foot and Ankle Natalie Stork, MD
 Foot and Ankle Natalie Stork, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics Children s Mercy Kansas City,
Foot and Ankle Natalie Stork, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics Children s Mercy Kansas City,
Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique
 Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy
 Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
 COMPARISON OF PERCUTANEOUS TENOTOMY TECHNIQUES FOR CORRECTION OF EQUINUS DEFORMITY IN CONGENITAL TALIPES EQUINO VARUS (CTEV) IN CHILDREN: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL Raghvendra Choubey 1, Ashish Jain 2
COMPARISON OF PERCUTANEOUS TENOTOMY TECHNIQUES FOR CORRECTION OF EQUINUS DEFORMITY IN CONGENITAL TALIPES EQUINO VARUS (CTEV) IN CHILDREN: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL Raghvendra Choubey 1, Ashish Jain 2
Knee Surgical Technique
 Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. For staged fixation of the distal tibia.
 Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. For staged fixation of the distal tibia. Technique Guide Part of the Large External Fixation System Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge Technique
Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. For staged fixation of the distal tibia. Technique Guide Part of the Large External Fixation System Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge Technique
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System.
 LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY 2017
 BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY 2017 B. RESSEQUE, D.P.M., D.A.B.P.O. Professor, N.Y. College of Podiatric Medicine ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY 2017 B. RESSEQUE, D.P.M., D.A.B.P.O. Professor, N.Y. College of Podiatric Medicine ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing
Title. Issue Date Right.
 NOSITE: Nagasaki University's c Title uthor(s) Dynamic supination and hindfoot var tendons of both peroneus longus and Matsubayashi, Shohei; Tsujimoto, i Citation cta medica Nagasakiensia, 61(2), p Issue
NOSITE: Nagasaki University's c Title uthor(s) Dynamic supination and hindfoot var tendons of both peroneus longus and Matsubayashi, Shohei; Tsujimoto, i Citation cta medica Nagasakiensia, 61(2), p Issue
Study of the principles of ponseti technique in the management of idiopathic congenital talipes equinovarus
 2018; 4(2): 584-589 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(2): 584-589 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 14-02-2018 Accepted: 17-03-2018 Dr. Shaik Ajaz Department of Orthopaedics, Associate Professor, Deccan
2018; 4(2): 584-589 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(2): 584-589 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 14-02-2018 Accepted: 17-03-2018 Dr. Shaik Ajaz Department of Orthopaedics, Associate Professor, Deccan
Leg. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Jerald Cunningham, CPO, Lorna W. McHattie, PhD
 An Innovative design for the treatment of Talipes equinovarus utilizing dynamic tri-planar stretching rather than static positioning: a call to researchers Jerald Cunningham, CPO, Lorna W. McHattie, PhD
An Innovative design for the treatment of Talipes equinovarus utilizing dynamic tri-planar stretching rather than static positioning: a call to researchers Jerald Cunningham, CPO, Lorna W. McHattie, PhD
The Complete Subtalar Release In Ctev Correction; Does It Address All Deformities?
 Article ID: WMC001607 2046-1690 The Complete Subtalar Release In Ctev Correction; Does It Address All Deformities? Corresponding Author: Dr. Nasir Muzaffar, Registrar, Bone & Joint Surgery Hospital, 190005
Article ID: WMC001607 2046-1690 The Complete Subtalar Release In Ctev Correction; Does It Address All Deformities? Corresponding Author: Dr. Nasir Muzaffar, Registrar, Bone & Joint Surgery Hospital, 190005
TENDON TRANSFER IN CAVUS FOOT
 TENDON TRANSFER IN CAVUS FOOT Cavovarus deformity is defined by fixed equinus of the forefoot on the hindfoot, resulting in a pathologic elevation of the longitudinal arch, with either a fixed or flexible
TENDON TRANSFER IN CAVUS FOOT Cavovarus deformity is defined by fixed equinus of the forefoot on the hindfoot, resulting in a pathologic elevation of the longitudinal arch, with either a fixed or flexible
Surgical Technique. Customer Service:
 Patent and Patent Pending CAUTION: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. INDICATIONS FOR USE The Axis Charcot Fixation System in diameters of 5.5, 6.5 and 7.5mm
Patent and Patent Pending CAUTION: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. INDICATIONS FOR USE The Axis Charcot Fixation System in diameters of 5.5, 6.5 and 7.5mm
EVALUATION OF PONSETI S TECHNIQUE FOR CONGENITAL TALIPES EQUINO- VARUS BY DIMEGLIO CLASSIFICATION
 EVALUATION OF PONSETI S TECHNIQUE FOR CONGENITAL TALIPES EQUINO- VARUS BY DIMEGLIO CLASSIFICATION Nitin Kiradiya 1, Sameer Gupta 2, Utkarsh Pal 3 1 - Assistant Professor, Department Of Orthopaedics, B.
EVALUATION OF PONSETI S TECHNIQUE FOR CONGENITAL TALIPES EQUINO- VARUS BY DIMEGLIO CLASSIFICATION Nitin Kiradiya 1, Sameer Gupta 2, Utkarsh Pal 3 1 - Assistant Professor, Department Of Orthopaedics, B.
Evaluation of Gait Mechanics Using Computerized Plantar Surface Pressure Analysis and it s Relation to Common Musculoskeletal Problems
 Evaluation of Gait Mechanics Using Computerized Plantar Surface Pressure Analysis and it s Relation to Common Musculoskeletal Problems Laws of Physics effecting gait Ground Reaction Forces Friction Stored
Evaluation of Gait Mechanics Using Computerized Plantar Surface Pressure Analysis and it s Relation to Common Musculoskeletal Problems Laws of Physics effecting gait Ground Reaction Forces Friction Stored
RESIDUAL ADDUCTION OF THE FOREFOOT IN TREATED CONGENITAL
 RESIDUAL ADDUCTION OF THE FOREFOOT IN TREATED CONGENITAL CLUB FOOT L. W. LOWE and M. A. HANNON, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Hospitalfor Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London Adduction of the forefoot
RESIDUAL ADDUCTION OF THE FOREFOOT IN TREATED CONGENITAL CLUB FOOT L. W. LOWE and M. A. HANNON, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Hospitalfor Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London Adduction of the forefoot
