Tao Lin, Baojun Xiao, Xiucai Ma, Dehao Fu * and Shuhua Yang
|
|
|
- Junior Hines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:206 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with a locking compression plate is superior to open reduction and internal fixation in the management of the proximal humerus fractures Tao Lin, Baojun Xiao, Xiucai Ma, Dehao Fu * and Shuhua Yang Abstract Background: The use of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) via anterolateral deltoid splitting has good outcomes in the management of proximal humerus fractures. While using this approach has several advantages, including minimal soft tissue disruption, preservation of natural biology and minimal blood loss, there is an increased risk for axillary nerve damage. This study compared the advantages and clinical and radiological outcomes of MIPO or open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) in patients with proximal humerus fractures. Methods: A matched-pair analysis was performed, and patient groups were matched according to age (±3 years), sex and fracture type. Forty-three pairs of patients (average age: MIPO, 63 and ORIF, 61) with a minimum follow-up of 12 months were enrolled in the study group. The patients were investigated radiographically and clinically using the Constant score. Results: The MIPO technique required less surgery time and caused less blood loss compared to ORIF (p < 0.01). In addition, MIPO required a smaller incision, resulted in less scarring, and was cosmetically more appealing and acceptable to female patients than ORIF. Following MIPO, patients had better functional results at 3 and 6 months, with better outcomes, less pain, higher satisfaction in activities of daily living, and a higher range of motion when compared to ORIF (p < 0.05). Fracture configuration, according to the AO/ASIF(Association for the Study of Internal Fixation) fracture classification, did not significantly influence the functional results. The complication rate was comparable between both groups. Conclusion: The use of MIPO with a locking compression plate in the management of proximal humerus fractures is a safe and superior option compared to ORIF. Keywords: Proximal humeral fractures, Minimally invasive, MIPO, Locking compression plate Background There are a variety of surgical options for the treatment proximal humerus fractures, including open reduction internal fixation (ORIF), intramedullary device fixation, external fixation and hemi arthroplasty. Of these, ORIF is the most commonly used technique for the majority of fractures [1-5]. However, there is much debate on * Correspondence: fudehao@qq.com Equal contributors Department of Orthopedics, Union Hospital of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan , Hubei Province, China what method or technique for ORIF is optimal, and the decision is often based on the fracture configuration and surgical experience [6-12]. Recent literature has indicated that intramedullary nailing is most suitable for managing two-part proximal humerus fractures. Most surgeons agree that ORIF with a plate is the ideal technique for managing comminuted and 3 or 4 part fractures [13]. This particular technique can also be performed with minimally invasive techniques, which is known as minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) Lin et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly credited. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Lin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:206 Page 2 of 7 Previous studies have shown that the traditional deltopectoral approach to the proximal humerus provides limited access to the posterolateral aspect of the shoulder and that the visualization and reduction of a large retracted greater tuberosity fragment may be difficult [11,14-18]. The deltopectoral approach requires extensive soft tissue dissection and muscle retraction to gain adequate exposure to the lateral aspect of the humerus [10,11,14,16,18-20]. This can cause further devascularization of fracture fragments during dissection and plating, leading to the disruption of critical blood supplies to the humeral head [10,18-20]. The deltoid splitting approach, which is an alternative method, provides good visualization of the posterolateral aspect of the shoulder without extensive soft tissue dissection or forcible retraction; however, there is an increased risk of injuring the axillar nerve as compared to the conventional deltopectoral approach [16,21,22]. Recently, many studies have demonstrated the superiority of MIPO techniques via anterolateral deltoid splitting combined with skin incisions for the management of proximal humerus fractures [15,17,19,21-28]. This method is a minimally invasive technique, leading to less soft tissue injury, decreased postoperative pain, and decreased functional loss. In addition, MIPO allows for the visualization of the axillary nerve [12,14,16,22]. Thus, MIPO is a safe and effective method for the treatment of proximal humerus fractures [14,19,20,22]. Despite these results, a consensus amongst orthopedic surgeons on the best treatment for proximal humerus fractures has not been determined [7,28]. Although many of the complications associated with MIPO are related to incorrect surgical technique, many surgeons still prefer to use the conventional ORIF with the deltopectoral approach [29]. The objective of this study was to compare MIPO using a locking compression plate and ORIF using a deltopectoral approach in the management of proximal humerus fractures. We compared surgical advantages of each technique, radiograph outcomes, the incidence of nerve injury, and functional deficits during a one year follow-up period. Methods Patient information This was a retrospective case control study including two groups. Between September 2007 and April 2012, 184 patients with displaced proximal humerus fractures were treated with LCP (Locking Compression Plate) according to Neer criteria in Union hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technologe. Of these, 118were treated with ORIF via a traditional deltopectoral approach between September 2007 and June 2010, while 66 were treated with MIPO via anterolateral deltoid splitting between June 2010 and April Patients with pathological fractures, head split fractures, open fractures, fractures with primary neurovascular damage and cases lost to follow-up were excluded from the study. After these exclusions, 158 patients remained in the study. Of these 158 patients, 86 (43 pairs) were selected for a retrospective matchedpaired analysis according to age (±3 years), gender, and fracture type with a minimum follow-up of 12 months (range, 12 17months). Thus, inclusion bias could be excluded. The median age of the MIPO group was 63 years compared to 61 years in the ORIF group. The distribution of age and sex by group was 27 (62%) women and 16 (38%) men in the MIPO group, and 31 (72%) women and 12 (28%) men in the ORIF group. According to the AO/ASIF classification system, the most frequent type of fracture was type B (n = 46; 53.5%), with 19 (22.1%) type A and 21 (24.4%) type C fractures. There were 10 type A, 24 type B and 9 type C fractures in the MIPO group, and there were 9 type A, 22 type B and 12 type C fractures in the ORIF group (Table 1). Implant The LCP plate (titanium; thickness: 4.2 mm; width: 12 mm; length: mm; Double Engine Medical Material Company, China) was anatomically pre-contoured with threeto ten holes on the plate shaft and nine holes for head screws. The proximal suture holes were applied to secure the tuberosity fragments and the plate. Surgical technique In both the MIPO and ORIF groups, the patients were positioned in the beach-chair or supine position to allow two plane intraoperative C-arm image intensifier views [8,11,12,16,18,19,30-32]. All of the procedures were performed under general anesthesia with administration of a broad-spectrum antibiotic prophylaxis [16,18,22,30]. In the ORIF group, ORIF was performed using a standard deltopectoral approach with a LCP. The cm incision started at the tip of the coracoid process and ran laterally Table 1 Patient demographics Characteristic Treatment P MIPO (n = 43) ORIF (n = 43) value Gender Female 27 (62%) 31 (72%) Male 16 (38%) 12 (28%) Age, years 63 ± ± AO classification type A 10 (23.2%) 9 (20.9%) type B 24 (55.8%) 22 (51.2%) type C 9 (20.9%) 12 (27.9%)
3 Lin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:206 Page 3 of 7 in the direction of the insertion of the deltoid muscle (Figure 1F). Reduction was enabled with a K-wire under fluoroscopy according to the landmarks of the long head of biceps, the greater and lesser tubercles, and the intertubercular groove [26,30]. After the fracture was anatomically reduced, a LCP was placed 1 cm posterior to the intertubercular groove [11,30] and 1 cm distal to the tip of the greater tubercle [15,27]. In the MIPO group, the anterolateral deltoid splitting approach was utilized, and the tip of the acromion was palpated and used as a landmark [14,19]. A line perpendicular to the palpable shaft of the humerus was drawn 5 cm distal to the tip of the acromion. A second parallel line was drawn 2 cm further distal to thefirstline(figure1b).theareabetweenthesetwo lines contained the axillary nerve and was considered the unsafe zone. A longitudinal incision was made on the lateral side of the humerus starting from the lateral acromial border and ending distally 5 cm was to access the proximal humerus, the greater tuberosity and the humeral head (Figure 1E). To insert distal screws, a distal incision was made 7 cm distal to the acromion and was approximately cm long (Figure 1E). In most cases, good reduction was achieved by applying axial traction on the humerus and pulling the rotator cuff [6,8,22,23,33]. In some cases, indirect reduction techniques, such as ligamentotaxis, were used. Plate reduction was performed in cases of a valgus displaced fracture configuration [22,28]. The LCP was placed proximally below the apex of the greater tuberosity to maintain reduction. If non-absorbable sutures were used, they were secured to the suture wires holes in the LCP [6,11,16,19,21-23,26,28,33]. The plate was anchored proximally with multiple angled stable screws into the humeral head fragment. After removing the aiming arm, the non-absorbable sutures were tightened to the LCP [21-23]. Patients in both groups had individual patient-related postoperative management. In the majority of cases, the patients arm was placed in a sling for a maximum of two weeks. Passive and active range of motion exercises were started after surgery, depending on pain and activity level [6,11]. Ethics and consent This study has been performed in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration and has been granted an exemption from Hospital s Ethics Committee of Union Hospital of Tongji Medical College. The patients were informed and have written informed consent; all patients were over 18 years old. The classic cases in this article have been undertaken with the patient's consent. Data analysis We used SPSS 18 statistical software for Windows for all analyses. For normally distributed data (patient age, time between fracture and fixation, operative time, blood loss, hospital stay, and follow-up time), an independent sample t-test was used. For data that was not normally distributed data (AO classification and the Constant shoulder score), the Mann Whitney rank sum test was used. For categorical data (gender and fracture pattern), a chi-square test was used. A P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Figure 1 A, Preoperative radio-graph of a70-year-old man with a displaced 3-part fracture (AO 11-B1) of the humeral head. B, Two marker lines perpendicular to the palpable shaft of the humerus. The first line was5cm distal to the tip of the acromion and another line was2cm further distal to the first line. The area between these two lines was considered an unsafe zone. C and D, Postoperativeradiographshows proper placement of plate and screws. E, Theminimally invasive approach shows that two small incisions with a skin bridge over the palpated axillary nerve. F, Thedeltopectoral approachrequired an approximately 14cmin the ORIF group. Results Follow up We performed clinical and radiographic assessments 3, 6 and 12 months after surgery [6,11]. At each follow-up, the Constant score was used to assess shoulder function. Standardized X-rays were obtained in anteroposterior and transscapular views to evaluate fracture healing, avascular necrosis, placement of the plate, and quality of reduction. Complications were evaluated based on follow-up radiographs and a retrospective chart review of the patients medical records to determine the incidence of humeral head necrosis, delayed union, implant failure or a neurological deficit.
4 Lin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:206 Page 4 of 7 Table 2 Surgical and follow-up data Characteristic Treatment MIPO (n = 43) ORIF (n = 43) P value Average length of surgery in min 71 ± ± Average length of hospital stay in days 6.8 ± ± Average blood loss (ml) 126 ± ± Average duration between trauma 5.0 ± ± and surgery(day) Follow-up(months) 12.6 ± ± The rate of union (at 6 months) 93% 97.7% To perform the retrospective matched-paired analysis, we selected patients according to age (±3 years), gender and fracture types. The patient demographics of 86 patients are listed in Table 1. The analysis revealed no significant differences in group demographics, including AO/ASIF classification and mean age (p > 0.05). However, there was a higher female ratio in the ORIF group compared to the MIPO group (p > 0.05). The average duration between trauma and surgery in the MIPO group was 5 days and 6.3 days in the ORIF group. In addition, MIPO required less surgery time and resulted in less blood loss (both p < 0.01). The union rate at 6 months was 93% in the MIPO group and 97.7% in the ORIF group (Table 2). The Constant score was higher in the MIPO group at the 3 and 6 month follow-up time points compared to the ORIF group (P =0.033 and P = 0.043) (Figure 2). At the 12 month follow-up, the Constant score was not statistically significant (P = 0.065) (Figure 2). In addition, patients in the MIPO group experienced significantly less pain, higher satisfaction in activities of daily living, and greater range of motion at the 3 and 6 months follow-up time points (p < 0.05). The level of strength was not significantly different at these time points (p > 0.05). At the 12 month follow-up, there were no significant differences in both groups (Table 3). At the 12 month follow-up, type A fractures had the highest average Constant score in both groups (MIPO: 76.2 ± 7.1, ORIF: 75.6 ± 10.8), followed by type B fractures (MIPO: 71.7 ± 11.3, ORIF 69.0 ± 14.2; ORIF: 69. ±13.9) and type C fractures (MIPO: 69.4 ± 17.1, ORIF: 69.8 ± 13.2) (Figure 3). The type of fracture between groups was not significantly different (p = 0.205). In the MIPO group, 5/43 patients experienced complications and 4/43 patients experienced complications in the ORIF group (Table 4). No patients developed wound infection and nonunion after one year of follow-up in both groups. In 3 patients (group MIPO, 2 patients, type B and C; group ORIF, 1 patient, type B), the fracture collapsed after 3 months, leading to a varus malalignment. These patients developed loss of reduction and underwent reoperation either by reosteosynthesis combined with cancellous grafting or by joint replacement. One patient in the MIPO group presented with clinical signs of axillary injury, which was characterized by poorly localized posterior shoulder pain, parenthesis over the lateral aspect of the shoulder, and deltoid muscle weakness. Axillary nerve injury was confirmed on electromyography examination. However, there was no functional impairment when the patient was assessed at one year follow-up. One plate in the MIPO group and two plates in the ORIF group were removed due to subacromial impingement after radiographs confirmed fracture union at about 5 months. In the ORIF group, one patient underwent reoperation to change a perforated screw 3 months after the initial operation. Discussion The objective of this study was to compare MIPO and ORIF with a LCP plate to treat proximal humerus fracture. Our retrospective comparative study showed Figure 2 Mean value of Constant score at each follow up. Mean values of the Constant score for all patients (total), MIPO and ORIF at 3, 6, and 12 months (*p < 0.05).
5 Lin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:206 Page 5 of 7 Table 3 Subjective parameters of the constant score Score 3 months 6 months 12 months MIPO (n = 43) ORIF (n = 43) P value MIPO (n = 43) ORIF (n = 43) P value MIPO (n = 43) ORIF (n = 43) P value Pain 8.8 ± ± ± ± ± ± ADL 14.5 ± ± ± ± ± ± ROM 25.6 ± ± ± ± ± ± Strength 8.23 ± ± ± ± ± ± Total 57.1 ± ± ± ± ± ± ADL activities of daily living; ROM range of motion. that the MIPO technique was superior to ORIF in the management of proximal humerus fractures. First, the MIPO group required less surgery time, resulted in less blood loss, and the patients required a relatively shorter hospital stay. Second, the MIPO group had better shoulder function at 3 and 6 months, with less pain, higher satisfaction in activities of daily living and greater range of motion (p < 0.05). The complication rate was comparable between both groups (MIPO:11.6%;ORIF:9.3%). The MIPO technique provides good visualization of the posterolateral aspect of the shoulder via a small incision without extensive soft-tissue dissection or forcible retraction. Thus, it is relatively easy to perform a reduction of a large greater tuberosity fragment under direct vision and significantly reduces the intra-operative time. These findings were in accordance to previous reports [11,19,23,28]. In this study, Constant scores based on fracture type were similarly distributed in both groups. In general, type A fractures had the highest average Constant score, followed by type B and C fractures. However, when subgroup analysis was carried out, the Constant scores were higher for type A and B fractures treated with MIPO. This was in contrast with previous reports by Hepp et al. [11]. In this study, the technique (MIPO/ORIF) employed had no significant influence on the final functional muscle weakness and shoulder range of motion. In addition, these findings were independent of an axillary nerve injury. These findings are not consistent with the findings from Hepp et al. [11]. Their study suggested that the ORIF technique had a higher deltoid muscle level at 3 and 6 months follow up. In addition, there was less soft tissue disruption in the MIPO group, most likely leading to a greater range of movement when compared to the ORIF group. Taken together, these findings indicate that the MIPO technique is safe and has a low risk of axillary nerve injury for treating proximal humerus fractures. Previous anatomical studies have revealed that axillary nerve lesions occur between 5.58 cm to 6.66 cm distal to the lateral acromion [14,34,35]. In this study, to prevent the axillary nerve damage, we split the deltoid no more than 5 cm distal to the mid-acromion in any given vertically neutral position [16,35]. For the second incision to place distal screws, we recommend a starting deltoid split point at least 7 cm distal to the acromion, while Cheung [35] suggests 9 cm. In our study, none of the patients required an extension of the incision. Axillary nerve palsy in one patient was most likely due to sliding of the LCP plate. A study by Visser et al. [36,37] showed that axillary nerve lesions were more frequent in proximal humeral fractures, with an Figure 3 Average scores for the fracture types based on the AO/ASIF fracture classification after12months of follow-up. Type Afractures had the highest average Constant score in both groups, followed by type B and C fractures. There were no significant differences toward the type of fracture and each type between groups (p = 0.205).
6 Lin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:206 Page 6 of 7 Table 4 Complications after one year of follow-up Complications MIPO (n = 43) ORIF (n = 43) Complications rate 5 (11.6%) 4 (9.3%) Reoperations (%) 2 (4.6%) 2 (4.6%) Varus displacement 1 Second loss of reduction 2 1 Nerve lesions 1 Impingement rates 1 2 Screw perforation 1 overall incidence of 58% and 62%. It should be noted that clinical exam is not reliable in detecting nerve injuries, and an electromyography investigation is recommended for an accurate diagnosis [36,37]. Moreover, this study revealed that the surgical approach did not influence the complication rate and/or radiological outcomes. The complication rate of the MIPO group was less than 12%, which is comparable to previous reports [21,23,30,31,38]. In the literature, the main complications with LCP are implant-related, including impingement, intra-articular screw perforation and the proximal screw loosening [21,22,31,33,38]. In our study, the major complication was secondary loss of reduction following a varus collapse of the fracture. This also resulted in subacromial impingement due to a reduced acromio-humeral distance. In these three patients, there was loss of medial hinge integrity due to impaction and osteoporosis, causing the fractures to be unstable. Recent studies have demonstrated a direct association between medial support and subsequent reduction loss [30,38]. In the MIPO group in this study, wound healing occurred faster and there was minimal scaring following surgery. Thus, patients might have engaged in early full weight bearing activities and functional exercises, leading to delayed healing. The second major complication was subacromial impingement, which occurred in one plate in the MIPO group and two plates in the ORIF group. The plates were removed after radiograph confirmation of the fracture union at about 5 months. At the last follow-up, the patients achieved optimal functional outcomes with good range of motion. In our study, the most frequent type of fracture was type B in both groups. The mean Constant score of type B fractures was more than in type A and type C fractures. These findings are similar to the report by Röderer and Brorson et al. [32,39], although our overall complication rate was much lower. There are some limitations in our study. First, our study was retrospective in design. However, our study provided long-term results and outcomes of patients undergoing MIPO compared to ORIF. Second, the study was conducted at a single center with different surgeons. The surgeons were experienced and had expertise in MIPO and ORIF. Third, patients treated with MIPO underwent surgery 1 3 years later than the patients who were treated with ORIF. All the other parameters were similar between the two groups. Conclusion This study shows that MIPO with LCP requires less surgery time, causes less blood loss, shortens hospital stay,results in less scarring, and is cosmetically more appealing and acceptable to female patients compared to ORIF with LCP. Further, MIPO with LCP provides good functional results and has less morbidity at one year follow-up. MIPO with LCP for proximal humerus fractures isasafeandfavorableoptioncomparedtoorifwithlcp. Abbreviations LCP: Locking compression plate; MIPO: Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis; ORIF: Open reduction and internal fixation; ADL: Activities of daily living; ROM: Range of motion. Competing interests The authors have declared that no competing interest exists. Authors contributions All authors have made substantial contributions to design, acquisition of data, and analysis and interpretation of data. DF and SY conceived the study. TL, XM and DF were responsible for the design and the statistical analysis. TL and BX were involved in drafting the manuscript or revising it critically for important intellectual content. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript. DF and SY have given final approval of the version to be published. Acknowledgments We thank Medjaden Biosciences Ltd. for proofreading the manuscript. Received: 15 October 2013 Accepted: 12 June 2014 Published: 16 June 2014 References 1. Helmy N, Hintermann B: New trends in the treatment of proximal humerus fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2006, 442: Wijgman AJ, Roolker W, Patt TW, Raaymakers EL, Marti RK: Open reduction and internal fixation of three and four-part fractures of the proximal part of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2002, 84: Lill H, Hepp P, Rose T, König K, Josten C: The angle stable Locking-Proximal- Humerus-Plate (LPHP) for proximal humeral fractures using a small anterior-lateral-deltoid-splitting-approach-technique and first results. Zentralbl Chir 2004, 129: Lill H, Josten C: Conservative or operative treatment of humeral head fractures in the elderly? Chirurg 2001, 72: Plecko M, Kraus A: Internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures using the locking proximal humerus plate. Oper Orthop Traumatol 2005, 17: Gradl G, Dietze A, Kääb M, Hopfenmüller W, Mittlmeier T: Is locking nailing of humeral head fractures superior to locking plate fixation? Clin Orthop Relat Res 2009, 467(11): Matziolis D, Kaeaeb M, Zandi SS, Perka C, Greiner S: Surgical treatment of two-part fractures of the proximal humerus: comparison of fixed-angle plate osteosynthesis and Zifkonails. Injury 2010, 41(10): Wachtl SW, Marti CB, Hoogewoud HM, Jakob RP, Gautier E: Treatment of proximal humerus fracture using multiple intramedullary flexible nails. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2000, 120(3 4): Gardner MJ, Griffith MH, Lorich DG: Helical plating of the proximal humerus. Injury 2005, 36:
7 Lin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:206 Page 7 of Smith J, Berry G, Laflamme Y, Blain-Pare E, Reindl R, Harvey E: Percutaneous insertion of a proximal humeral locking plate: an anatomic study. Injury 2007, 38(2): Hepp P, Theopold J, Voigt C, Engel T, Josten C, Lill H: The surgical approach for locking plate osteosynthesis of displaced proximal humeral fractures influences the functional outcome. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2008, 17: Gardner MJ, Boraiah S, Helfet DL, Lorich DG: The anterolateral acromial approach for fractures of the proximal humerus. J Orthop Trauma 2008, 22(2): Gerber C, Werner CM, Vienne P: Internal fixation of complex fractures of the proximal humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2004, 86: Gardner MJ, Griffith MH, Dines JS, Briggs SM, Weiland AJ, Lorich DG: The extended anterolateral acromial approach allows minimally invasive access to the proximal humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2005, 434: Gardner MJ, Voos JE, Wanich T, Helfet DL, Lorich DG: Vascular implications of minimally invasive plating of proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Trauma 2006, 20(9): Robinson CM, Khan L, Akhtar A, Whittaker R: The extended deltoid-splitting approach to the proximal humerus. J Orthop Trauma 2007, 21(9): Saran N, Bergeron SG, Benoit B, Reindl R, Harvey EJ, Berry GK: Risk of axillary nerve injury during percutaneous proximal humerus locking plateinsertionusinganexternalaimingguide.injury 2010, 41(10): Khan LA, Robinson CM, Will E, Whittaker R: Assessment of axillary nerve function and functional outcome after fixation of complex proximal humeral fractures using the extended deltoid-splitting approach. Injury 2009, 40(2): Rouleau DM, Laflamme GY, Berry GK, Harvey EJ, Delisle J, Girard J: Proximal humerus fractures treated by percutaneous locking plate internal fixation. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2009, 95(1): Karataglis D, Stavridis SI, Petsatodis G, Papadopoulos P, Christodoulou A: New trends in fixation of proximal humeral fractures: a review. Injury 2011, 42(4): Röderer G, Erhardt J, Graf M, Kinzl L, Gebhard F: Clinical results for minimally invasive locked plating of proximal humerusfractures. J Orthop Trauma 2010, 24(7): Acklin YP, Sommer C: Plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures using the minimally invasive anterolateral delta split approach. O Acklin per Orthop Traumatol 2012, 24(1): Gavaskar AS, Muthukumar S, Chowdary N: Biological osteosynthesis of complex proximal humerus fractures: surgical technique and results from a prospective single center trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2010, 130(5): Röderer G, Sperfeld AD, Hansen P, Krischak G, Gebhard F, Kassubek J: Electrophysiological assessment of the deltoid muscle after minimally invasive treatment of proximal humerus fractures - a clinical observation. Open Orthop J 2011, 5: Tan SL, Balogh ZJ: Indications and limitations of locked plating. Injury 2009, 40(7): Röderer G, Abouelsoud M, Gebhard F, Böckers TM, Kinzl L: Minimally invasive application of the non-contact-bridging (NCB) plate to the proximal humerus: an anatomical study. J Orthop Trauma 2007, 21(9): Brunner A, Thormann S, Babst R: Minimally invasive percutaneous plating of proximal humeral shaft fractures with the Proximal Humerus Internal Locking System (PHILOS). J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2012, 21(8): Ruchholtz S, Hauk C, Lewan U, Franz D, Kühne C, Zettl R: Minimally invasive polyaxial locking plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures: a prospective study. J Trauma 2011, 71(6): Südkamp N, Bayer J, Hepp P, Voigt C, Oestern H, Kääb M, Luo C, Plecko M, Wendt K, Köstler W, Konrad G: Open reduction and internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with use of the locking proximal humerus plate. Results of a prospective, multicenter, observational study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2009, 91(6): Zhang L, Zheng J, Wang W, Lin G, Huang Y, Zheng J, Edem Prince GA, Yang G: The clinical benefit of medial support screws in locking plating of proximal humerus fractures: a prospective randomized study. Int Orthop 2011, 35(11): Geiger EV, Maier M, Kelm A, Wutzler S, Seebach C, Marzi I: Functional outcome and complications following PHILOS plate fixation in proximal humeral fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2010, 44(1): Röderer G, Erhardt J, Kuster M, Vegt P, Bahrs C, Kinzl L, Gebhard F: Second generation locked plating of proximal humerus fractures a prospective multicentre observational study. Int Orthop 2011, 35(3): Erhardt JB, Roderer G, Grob K, Forster TN, Stoffel K, Kuster MS: Early results in the treatment of proximal humeral fractures with a polyaxial locking plate. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2009, 129(10): Apaydin N, Tubbs RS, Loukas M, Duparc F: Review of the surgical anatomy of the axillary nerve and the anatomic basis of its iatrogenic and traumatic injury. Surg Radiol Anat 2010, 32(3): Cheung S, Fitzpatrick M, Lee TQ: Effects of shoulder position on axillary nerve positions during the split lateral deltoid approach. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2009, 18(5): Visser CP, Coene LN, Brand R, Tavy DL: Nerve lesions in proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2001, 10(5): Visser CP, Tavy DL, Coene LN, Brand R: Electromyographic findings in shoulder dislocations and fractures of the proximal humerus: comparison with clinical neurological examination. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 1999, 101(2): Osterhoff G, Ossendorf C, Wanner GA, Simmen HP, Werner CM: The calcar screw in angular stable plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures a case study. J Orthop Surg Res 2011, 6: Brorson S, Frich LH, Winther A, Hróbjartsson A: Locking plate osteosynthesis in displaced 4-part fractures of the proximal humerus. Acta Ortho 2011, 82(4): doi: / Cite this article as: Lin et al.: Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with a locking compression plate is superior to open reduction and internal fixation in the management of the proximal humerus fractures. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders :206. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1811.001 Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study Kongcharoensombat W, MD, Wattananon P, MD Department of Orthopaedics,
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1811.001 Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study Kongcharoensombat W, MD, Wattananon P, MD Department of Orthopaedics,
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Index. B Backslap technique depth assessment, 82, 83 diaphysis distal trocar, 82 83
 Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
LCP Percutaneous Aiming System 3.5 for PHILOS. For less invasive surgery at the proximal humerus.
 LCP Percutaneous Aiming System 3.5 for PHILOS. For less invasive surgery at the proximal humerus. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants
LCP Percutaneous Aiming System 3.5 for PHILOS. For less invasive surgery at the proximal humerus. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2018 Vol 12 No 2
 Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2018 Vol 12 No 2 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1807.004 Complex Proximal Humeral Fracture Fixation with PHILOS Plate using Minimal Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis
Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2018 Vol 12 No 2 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1807.004 Complex Proximal Humeral Fracture Fixation with PHILOS Plate using Minimal Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus Plate
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 643-650, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 643-650, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus
Open reduction; plate fixation 1 Principles
 Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures. OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD
 Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
To Detect the Outcome of Proximal Humerus Fractures Treated With a Locking Proximal Humerus Plate
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE To Detect the Outcome of Proximal Humerus Fractures Treated With a Locking Proximal Humerus Plate NASIR AHMED 1, TARIQUE ALI KHAN 2, MUHAMMAD ABSAR ANWAR 3, AHMED ALI 4 ABSTRACT Aim: To
ORIGINAL ARTICLE To Detect the Outcome of Proximal Humerus Fractures Treated With a Locking Proximal Humerus Plate NASIR AHMED 1, TARIQUE ALI KHAN 2, MUHAMMAD ABSAR ANWAR 3, AHMED ALI 4 ABSTRACT Aim: To
3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 8. DISTAL GUIDED LOCKING FOR PROXIMAL NAIL PROXIMAL LOCKING FOR LONG NAIL 13
 Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL NAIL INSERTION 6-7 7. PROXIMAL LOCKING
Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL NAIL INSERTION 6-7 7. PROXIMAL LOCKING
PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE TSHT 2017
 PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE TSHT 2017 ANIL DUTTA, M.D. ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Displacement > 1 cm Angulation > 45 degree SHOULDER AND ELBOW SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER SAN ANTONIO DISCLOSURE
PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE TSHT 2017 ANIL DUTTA, M.D. ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Displacement > 1 cm Angulation > 45 degree SHOULDER AND ELBOW SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER SAN ANTONIO DISCLOSURE
MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATE Shivananda S 1, Radhakrishna A. M 2, Kumar M 3
 MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATE Shivananda S 1, Radhakrishna A. M 2, Kumar M 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Shivananda S, Radhakrishna A. M, Kumar M. Management of Proximal
MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATE Shivananda S 1, Radhakrishna A. M 2, Kumar M 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Shivananda S, Radhakrishna A. M, Kumar M. Management of Proximal
P.R.C.T II FIXATION PLATE FOR ARTICULAR FRACTURE OF THE PROXIMAL HUMERUS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 P.R.C.T II FIXATION PLATE FOR ARTICULAR FRACTURE OF THE PROXIMAL HUMERUS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE INDICATIONS - Surgical technique...page 0 - Mini invasive approach...page 04 - Diaphyseal plates...page 05 -
P.R.C.T II FIXATION PLATE FOR ARTICULAR FRACTURE OF THE PROXIMAL HUMERUS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE INDICATIONS - Surgical technique...page 0 - Mini invasive approach...page 04 - Diaphyseal plates...page 05 -
Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique
 Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique Percutaneous Pinning Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Closed reduction followed by percutaneous fixation reduces risk from soft tissue dissection
Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique Percutaneous Pinning Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Closed reduction followed by percutaneous fixation reduces risk from soft tissue dissection
System. Humeral Nail. Surgical Technique
 System Humeral Nail Surgical Technique Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL
System Humeral Nail Surgical Technique Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL
Incidence of traumatic axillary nerve injury after glenohumeral dislocation and fractures of the proximal humerus in Mansoura Emergency Hospital
 Incidence of traumatic axillary nerve injury after glenohumeral dislocation, El Sllab and Selim MD. 93 Incidence of traumatic axillary nerve injury after glenohumeral dislocation and fractures of the proximal
Incidence of traumatic axillary nerve injury after glenohumeral dislocation, El Sllab and Selim MD. 93 Incidence of traumatic axillary nerve injury after glenohumeral dislocation and fractures of the proximal
Humerus Block. Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) Surgical Technique. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA.
 Humerus Block Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Contents
Humerus Block Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Contents
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do?
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
The Surgical And Functional Outcome In Two Part And Three Part Fracture Of The Proximal Humerus Using Proximal Humerus Locking Plate (Philos Plate).
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 10 Ver. 2 (October. 2018), PP 01-06 www.iosrjournals.org The Surgical And Functional Outcome
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 10 Ver. 2 (October. 2018), PP 01-06 www.iosrjournals.org The Surgical And Functional Outcome
Proximal Humerus Fractures
 Proximal Humerus Fractures Trafford General Hospital, June 2010 Nehmat Singh, Jawad Sultan Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus Consists of four parts: humeral head, surgical neck and greater and lesser tubercles
Proximal Humerus Fractures Trafford General Hospital, June 2010 Nehmat Singh, Jawad Sultan Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus Consists of four parts: humeral head, surgical neck and greater and lesser tubercles
Fixation of the greater tuberosity in proximal humeral fractures : FiberWire or wire cerclage?
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 9-16 ORIGINAL STUDY Fixation of the greater tuberosity in proximal humeral fractures : FiberWire or wire cerclage? Benjamin Bockmann, Benjamin Buecking, Daphne Asimenia Eschbach,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 9-16 ORIGINAL STUDY Fixation of the greater tuberosity in proximal humeral fractures : FiberWire or wire cerclage? Benjamin Bockmann, Benjamin Buecking, Daphne Asimenia Eschbach,
Technique Guide. PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus.
 Technique Guide PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction PHILOS and PHILOS Long 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction PHILOS and PHILOS Long 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
Proximal Humerus Fractures: contemporary perspectives
 Proximal Humerus Fractures: contemporary perspectives Diego L Fernandez M.D Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lindenhof Hospital, Berne, Switzerland www.diegofernandez.ch
Proximal Humerus Fractures: contemporary perspectives Diego L Fernandez M.D Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lindenhof Hospital, Berne, Switzerland www.diegofernandez.ch
Clinico-radiological outcome of closed reduction and percutaneous fixation of proximal humerus fractures
 2018; 4(1): 614-618 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 614-618 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-11-2017 Accepted: 11-12-2017 Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Assistant Professor, KGMU, Lucknow, Dr. Neerav Anand
2018; 4(1): 614-618 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 614-618 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-11-2017 Accepted: 11-12-2017 Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Assistant Professor, KGMU, Lucknow, Dr. Neerav Anand
TABLE OF CONTENTS. 2 (8144 Rev 2)
 1 (8144 Rev 2) TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Conventus CAGE TM - Proximal Humerus...3 Indications and Contraindications...4 Surgical Summary...5 Patient Positioning & Approach...6 Surgical Technique Plate
1 (8144 Rev 2) TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Conventus CAGE TM - Proximal Humerus...3 Indications and Contraindications...4 Surgical Summary...5 Patient Positioning & Approach...6 Surgical Technique Plate
NCB Proximal Humerus Plating System
 NCB Proximal Humerus Plating System Surgical Technique The right locking option for tough fractures Disclaimer This document is intended exclusively for experts in the field, i.e. physicians in particular,
NCB Proximal Humerus Plating System Surgical Technique The right locking option for tough fractures Disclaimer This document is intended exclusively for experts in the field, i.e. physicians in particular,
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate 3.5. The anatomic fixation system with anterolateral shaft placement.
 LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate 3.5. The anatomic fixation system with anterolateral shaft placement. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate 3.5. The anatomic fixation system with anterolateral shaft placement. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
Integra. Proximal Humeral Fracture Plate CASE STUDY
 Integra CASE STUDY Integra Physician Profile Galen Kam, MD The Bronstein Hand Center, Las Vegas, NV Board Certification: Upper Extremity, American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical School: Creighton
Integra CASE STUDY Integra Physician Profile Galen Kam, MD The Bronstein Hand Center, Las Vegas, NV Board Certification: Upper Extremity, American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical School: Creighton
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques
 Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Humeral SuturePlate. Surgical Technique
 Humeral SuturePlate Surgical Technique The humeral SuturePlate is an anatomically designed, low profile, titanium polyaxial locking plate and screw system. Multiple chamfered suture eyelets along the margin
Humeral SuturePlate Surgical Technique The humeral SuturePlate is an anatomically designed, low profile, titanium polyaxial locking plate and screw system. Multiple chamfered suture eyelets along the margin
Surgical Technique. Proximal Humerus Locking Plate
 Surgical Technique Proximal Humerus Locking Plate PERI-LOC Upper Extremity Locked Plating System 3.5mm & 4.5mm Proximal Humerus Locking PlatesCatalog Infor Table of Contents Introduction.........................................................2
Surgical Technique Proximal Humerus Locking Plate PERI-LOC Upper Extremity Locked Plating System 3.5mm & 4.5mm Proximal Humerus Locking PlatesCatalog Infor Table of Contents Introduction.........................................................2
AcUMEDr. LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM
 AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE
 EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE Orthofix approach to Evidence Based Medicine: For years, clinical decision-making was based primarily on physician knowledge and expert opinion. Now, the medical community
EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE Orthofix approach to Evidence Based Medicine: For years, clinical decision-making was based primarily on physician knowledge and expert opinion. Now, the medical community
AcUMEDr. Locking Proximal Humeral Plate. PoLARUSr PHPt
 AcUMEDr Locking Proximal Humeral Plate PoLARUSr PHPt PoLARUSr PHPt LOCKING PROXIMAL HUMERAL PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons,
AcUMEDr Locking Proximal Humeral Plate PoLARUSr PHPt PoLARUSr PHPt LOCKING PROXIMAL HUMERAL PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons,
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Proximal humerus fractures operated with PHILOS plate: 4 year prospective study
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni S et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):304-309 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170790
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni S et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):304-309 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170790
Locking Proximal Humerus Plate. For complex and unstable fractures.
 Locking Proximal Humerus Plate. For complex and unstable fractures. Features and Benefits Anatomic design & low profile (2.2mm) 95 No bending required Minimised soft tissue irritation Low risk of subacromial
Locking Proximal Humerus Plate. For complex and unstable fractures. Features and Benefits Anatomic design & low profile (2.2mm) 95 No bending required Minimised soft tissue irritation Low risk of subacromial
Review Article Meta-analysis comparing deltoid-splitting approach with deltopectoral approach for treatment of proximal humeral fractures
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2019;12(1):58-66 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0073587 Review Article Meta-analysis comparing deltoid-splitting approach with deltopectoral approach for treatment of proximal humeral
Int J Clin Exp Med 2019;12(1):58-66 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0073587 Review Article Meta-analysis comparing deltoid-splitting approach with deltopectoral approach for treatment of proximal humeral
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty
 Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
Comparison Study of Different Approach (Deltoid Splitting Approach and Delto-pectoral Interval Approach) for Proximal Humeral Fractures
 Original Article Comparison Study of Different Approach (Deltoid Splitting Approach and Delto-pectoral Interval Approach) for Proximal Humeral Fractures Seung-Hee Kim, M.D., Jinmyoung Dan, M.D., Byoung-Kook
Original Article Comparison Study of Different Approach (Deltoid Splitting Approach and Delto-pectoral Interval Approach) for Proximal Humeral Fractures Seung-Hee Kim, M.D., Jinmyoung Dan, M.D., Byoung-Kook
Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR. Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR. Introduction
 Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Xavier A. Duralde, MD Peachtree Orthopaedic Clinic Atlanta, GA Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Consultant: Smith+Nephew Board of Directors: CORR Introduction Incidence
Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Xavier A. Duralde, MD Peachtree Orthopaedic Clinic Atlanta, GA Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Consultant: Smith+Nephew Board of Directors: CORR Introduction Incidence
Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture Dislocation of the Elbow in an Adult
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
URSA HEMI-SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY B I O T E K
 URSA HEMI-SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE B I O T E K 2 Surgical Position Once general anesthesia has been satisfactorily induced, or a supraclavicular nerve block has been given, the patient
URSA HEMI-SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE B I O T E K 2 Surgical Position Once general anesthesia has been satisfactorily induced, or a supraclavicular nerve block has been given, the patient
Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Humeral Locking Plate
 Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Humeral Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Humeral Locking Plate 1 Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Humeral Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Humeral Locking Plate 1 Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture.
 Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Alvin Chao-Yu Chen *, Chih-Hao Chiu, Kuo-Yau Hsu and Yi-Sheng Chan
 Chen et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:495 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1840-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Influence of age, gender, and radiographic features on the deltoid splitting approach
Chen et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:495 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1840-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Influence of age, gender, and radiographic features on the deltoid splitting approach
Proximal fractures of the humerus in patients older than 75 years of age: should we consider operative treatment?
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2014) 15:111 115 DOI 10.1007/s10195-013-0273-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proximal fractures of the humerus in patients older than 75 years of age: should we consider operative treatment?
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2014) 15:111 115 DOI 10.1007/s10195-013-0273-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proximal fractures of the humerus in patients older than 75 years of age: should we consider operative treatment?
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE GALAXY FIXATION SHOULDER
 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE GALAXY FIXATION SHOULDER cop2 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION 1 FEATURES OF SHOULDER COMPONENTS 2 EQUIPMENT REQUIRED 5 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING 6 SURGICAL PROCEDURE 8 POST OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE GALAXY FIXATION SHOULDER cop2 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION 1 FEATURES OF SHOULDER COMPONENTS 2 EQUIPMENT REQUIRED 5 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING 6 SURGICAL PROCEDURE 8 POST OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures:
 Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
A new nail with a locking blade for complex proximal humeral fractures
 Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2016) 26:831 836 DOI 10.1007/s00590-016-1817-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SHOULDER - FRACTURES A new nail with a locking blade for complex proximal humeral fractures F. R. Hashmi 1 Edgar
Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2016) 26:831 836 DOI 10.1007/s00590-016-1817-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SHOULDER - FRACTURES A new nail with a locking blade for complex proximal humeral fractures F. R. Hashmi 1 Edgar
What s New in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures?
 NHMI Winter Meeting Stowe, VT January 2015 What s New in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures? John Bell, M.D., M.S. Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
NHMI Winter Meeting Stowe, VT January 2015 What s New in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures? John Bell, M.D., M.S. Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
Surgical Technique Guide PANTERA. Proximal Humerus Fracture Fixation Plate System
 Surgical Technique Guide PANTERA Proximal Humerus Fracture Fixation Plate System Installing the PANTERA is a 4-Step Process: The following technique is designed to optimize the surgical exercise. Step
Surgical Technique Guide PANTERA Proximal Humerus Fracture Fixation Plate System Installing the PANTERA is a 4-Step Process: The following technique is designed to optimize the surgical exercise. Step
Proximal Humerus Plating System. Surgical Technique TRAUMA
 Proximal Humerus Plating System Surgical Technique TRAUMA S 3 Proximal Humerus Plating System Contents Introduction... 3 S 3 Proximal Humerus Plating System... 4 Deltopectoral Approach... 6 Surgical Technique...
Proximal Humerus Plating System Surgical Technique TRAUMA S 3 Proximal Humerus Plating System Contents Introduction... 3 S 3 Proximal Humerus Plating System... 4 Deltopectoral Approach... 6 Surgical Technique...
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus. H. Sithebe 2012
 Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
AO / Synthes Proximal Posterior Medial Tibia Plate. Tibial Plateau Fx. Osteosynthesis
 Tibial Plateau Fx. Osteosynthesis Articular Fractures Osteosynthesis Characteristics of the LCP system LCP 3.5 system LCP 4.5 system Many different traditional plates (small, large) Lag screws Rafting
Tibial Plateau Fx. Osteosynthesis Articular Fractures Osteosynthesis Characteristics of the LCP system LCP 3.5 system LCP 4.5 system Many different traditional plates (small, large) Lag screws Rafting
Section: Orthopaedics. Original Article INTRODUCTION
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.5.OR6 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Transdeltoid Approach in Proximal Humerus Fractures: Outcome in 35 Cases and Review of Literature. Sarabjeet Kohli
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.5.OR6 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Transdeltoid Approach in Proximal Humerus Fractures: Outcome in 35 Cases and Review of Literature. Sarabjeet Kohli
A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral
 Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
TORNIER AEQUALIS FX. Shoulder System SYSTEM OVERVIEW
 TORNIER AEQUALIS FX Shoulder System SYSTEM OVERVIEW Simple in design, but used for the most complex fractures Each year, approximately 4 million people in the United States seek medical care for shoulder
TORNIER AEQUALIS FX Shoulder System SYSTEM OVERVIEW Simple in design, but used for the most complex fractures Each year, approximately 4 million people in the United States seek medical care for shoulder
Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct
 Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct Tak-Wing Lau Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Singapore Trauma 2015 Trauma Through the
Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct Tak-Wing Lau Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Singapore Trauma 2015 Trauma Through the
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system.
 LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
Upper extremity. Part I
 Part I Upper extremity 1 Fractures of the clavicle Peter V. Giannoudis 1.1 OPEN REDUCTION AND INTERNAL FIXATION (ORIF) OF MIDSHAFT FRACTURES Indications (a) Open fractures. (b) Painful non-union. (c) Associated
Part I Upper extremity 1 Fractures of the clavicle Peter V. Giannoudis 1.1 OPEN REDUCTION AND INTERNAL FIXATION (ORIF) OF MIDSHAFT FRACTURES Indications (a) Open fractures. (b) Painful non-union. (c) Associated
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation.
 LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Locked Plating of 3- and 4-Part Proximal Humerus Fractures in Older Patients: The Effect of Initial Fracture Pattern on Outcome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Locked Plating of 3- and 4-Part Proximal Humerus Fractures in Older Patients: The Effect of Initial Fracture Pattern on Outcome Brian D. Solberg, MD,* Charles N. Moon, MD, Dennis P. Franco,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Locked Plating of 3- and 4-Part Proximal Humerus Fractures in Older Patients: The Effect of Initial Fracture Pattern on Outcome Brian D. Solberg, MD,* Charles N. Moon, MD, Dennis P. Franco,
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Surgical Technique. Clavicle Locking Plate
 Surgical Technique Clavicle Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Clavicle Locking Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient Positioning...4
Surgical Technique Clavicle Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Clavicle Locking Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient Positioning...4
Minimal Invasive Approach to Proximal Humerus. Fractures with Diaphysis Extension in Elderly
 Clinical and Experimental Medical Sciences, Vol. 1, 2013, no. 2, 59 68 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Minimal Invasive Approach to Proximal Humerus Fractures with Diaphysis Extension in Elderly Gazi Huri
Clinical and Experimental Medical Sciences, Vol. 1, 2013, no. 2, 59 68 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Minimal Invasive Approach to Proximal Humerus Fractures with Diaphysis Extension in Elderly Gazi Huri
Technology and Health Care 21 (2013) DOI /THC IOS Press
 Technology and Health Care 21 (2013) 143 147 143 DOI 10.3233/THC-130714 IOS Press Comparison between conservative and surgical treatment of midshaft clavicle fractures: Outcome of 151 cases Kiriakos Daniilidis
Technology and Health Care 21 (2013) 143 147 143 DOI 10.3233/THC-130714 IOS Press Comparison between conservative and surgical treatment of midshaft clavicle fractures: Outcome of 151 cases Kiriakos Daniilidis
STUDY OF OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR COMPLEX FRACTURE OF UPPER END OF HUMERUS
 STUDY OF OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR COMPLEX FRACTURE OF UPPER END OF HUMERUS Archit Gandhi, Parimal Patel, Bhavik Dalal, Rohit Shah Department of Orthopaedics, SCL Municipal Hospital, Smt. NHL Municipal
STUDY OF OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR COMPLEX FRACTURE OF UPPER END OF HUMERUS Archit Gandhi, Parimal Patel, Bhavik Dalal, Rohit Shah Department of Orthopaedics, SCL Municipal Hospital, Smt. NHL Municipal
Outcome of proximal humerus fractures treated by PHILOS plate internal fixation Experience of a District General Hospital
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 602-608 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of proximal humerus fractures treated by PHILOS plate internal fixation Experience of a District General Hospital Rizwan SHAHID, Abid MUSHTAQ,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 602-608 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of proximal humerus fractures treated by PHILOS plate internal fixation Experience of a District General Hospital Rizwan SHAHID, Abid MUSHTAQ,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus.
 PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the
PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the
WINSTA-C. Clavicle Plating System
 Clavicle Plating System Clinical Advisor Michael Kurer FRCS FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic and Shoulder Surgeon North Middlesex University Hospital NHS Trust Table of Contents Introduction Indication
Clavicle Plating System Clinical Advisor Michael Kurer FRCS FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic and Shoulder Surgeon North Middlesex University Hospital NHS Trust Table of Contents Introduction Indication
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES. Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures
 REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
Surgical Technique. CONQUEST FN Femoral Neck Fracture System
 Surgical Technique CONQUEST FN Femoral Neck Fracture System Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Indications... 3 Product Overview... 4 Surgical Technique... 5 Patient Positioning... 5 Reduce the Fracture...
Surgical Technique CONQUEST FN Femoral Neck Fracture System Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Indications... 3 Product Overview... 4 Surgical Technique... 5 Patient Positioning... 5 Reduce the Fracture...
Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments.
 CAPITELLAR FRACTURE Vasu Pai Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments. Nonsurgical management is fraught with complications including chronic pain, mechanical
CAPITELLAR FRACTURE Vasu Pai Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments. Nonsurgical management is fraught with complications including chronic pain, mechanical
Technique Guide. 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology.
 Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
A clinical study of minimal invasive anterior bridge plating for humerus shaft fractures
 2018; 4(2): 01-05 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(2): 01-05 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-02-2018 Accepted: 02-03-2018 Mohammed Ibrahim Dr. Vijay H Rathod A clinical study of minimal invasive
2018; 4(2): 01-05 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(2): 01-05 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-02-2018 Accepted: 02-03-2018 Mohammed Ibrahim Dr. Vijay H Rathod A clinical study of minimal invasive
LCP Distal Humerus Plates
 The anatomic fixation system for the distal humerus with angular stability Surgical technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Contents Indications and contraindications 2 Implants 3 Instruments 5 Preparation
The anatomic fixation system for the distal humerus with angular stability Surgical technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Contents Indications and contraindications 2 Implants 3 Instruments 5 Preparation
Aesculap Targon FN. Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures. Aesculap Orthopaedics
 Aesculap Targon FN Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures Aesculap Orthopaedics Targon FN Operating Technique Indications for Targon FN AO 3 B. AO 3 B.2 AO 3 B.3 Undisplaced intracapsular
Aesculap Targon FN Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures Aesculap Orthopaedics Targon FN Operating Technique Indications for Targon FN AO 3 B. AO 3 B.2 AO 3 B.3 Undisplaced intracapsular
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
I have no relevant disclosures pertaining to this talk.
 Bryan Houseman, D.O., ATC Orthopaedic Trauma and Fracture Surgeon New Hampshire Orthopaedic Center September 10, 2016 I have no relevant disclosures pertaining to this talk. From Rockwood & Green, 8 th
Bryan Houseman, D.O., ATC Orthopaedic Trauma and Fracture Surgeon New Hampshire Orthopaedic Center September 10, 2016 I have no relevant disclosures pertaining to this talk. From Rockwood & Green, 8 th
Shoulder hemiarthroplasty in the management of humeral head fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 214-218 ORIGINAL STUDY Shoulder hemiarthroplasty in the management of humeral head fractures Joseph J. CHRISTOFORAKIS, George M. KONTAKIS, Pavlos G. KATONIS, Konstantinos
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 214-218 ORIGINAL STUDY Shoulder hemiarthroplasty in the management of humeral head fractures Joseph J. CHRISTOFORAKIS, George M. KONTAKIS, Pavlos G. KATONIS, Konstantinos
MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y.
 Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y. YANAGIHARA 2 1 Department of 2nd Orthopaedic
Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y. YANAGIHARA 2 1 Department of 2nd Orthopaedic
Shoulder Arthroplasty for Proximal Humerus Fracture
 Arthroplasty in Upper Limb Trauma AADO/HKSSH Conjoint Scientific Meeting 2012 Shoulder Arthroplasty for Proximal Humerus Fracture Dr TSE Lung Fung Department of O&T, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese
Arthroplasty in Upper Limb Trauma AADO/HKSSH Conjoint Scientific Meeting 2012 Shoulder Arthroplasty for Proximal Humerus Fracture Dr TSE Lung Fung Department of O&T, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese
THE HUMERUS 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW
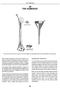 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM
 3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm VA-LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 2 AO
3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm VA-LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 2 AO
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
Does medial support decrease major complications of unstable proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plate?
 Jung et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:102 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Does medial support decrease major complications of unstable proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plate? Woo-Bin
Jung et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:102 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Does medial support decrease major complications of unstable proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plate? Woo-Bin
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications 3 Clinical
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications 3 Clinical
Lateral femoral traction pin entry: risk to the. femoral artery and other medial neurovascular structures
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Lateral femoral traction pin entry: risk to the femoral artery and other medial neurovascular structures John Y Kwon 1*, Catherine E Johnson 1, Paul Appleton 2, Edward K Rodriguez
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Lateral femoral traction pin entry: risk to the femoral artery and other medial neurovascular structures John Y Kwon 1*, Catherine E Johnson 1, Paul Appleton 2, Edward K Rodriguez
Complex fractures of the humeral shaft. Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden
 Complex fractures of the humeral shaft Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Kopenhagen 2018 Complex fracture Changes in the AO/OTA classification system Complex Multifragmentary
Complex fractures of the humeral shaft Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Kopenhagen 2018 Complex fracture Changes in the AO/OTA classification system Complex Multifragmentary
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6251-6255 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Comparison study of the clinical effect and biomechanics between locking compression plate and interlocking intramedullary
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6251-6255 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Comparison study of the clinical effect and biomechanics between locking compression plate and interlocking intramedullary
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability.
 LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Surgical Technique. Targeter Systems Overview
 Surgical Technique Targeter Systems Overview PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Targeter Systems Overview Table of contents Product overview... 2 Introduction... 2 Indications... 2 Design features and benefits...
Surgical Technique Targeter Systems Overview PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Targeter Systems Overview Table of contents Product overview... 2 Introduction... 2 Indications... 2 Design features and benefits...
