location, namely the deep peroneal nerve within the first intermetatarsal space, which, based on magnetic resonance image (MRI) findings, arose from t
|
|
|
- Ursula Norris
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of a Deep Peroneal Intraneural Ganglion Cyst Originating from the Second Metatarsophalangeal Joint: A Pattern of Propagation Supporting the Unified Articular (Synovial) Theory for the Formation of Intraneural Ganglia Neal M. Blitz, DPM, FACFAS, 1 Kimberly K. Amrami, MD, 2,3 and Robert J. Spinner, MD 3,4 A deep peroneal intraneural cyst of the first web space of the foot is presented. Analysis of the magnetic resonance image scans revealed not only a connection with the medial aspect of the second metatarsophalangeal joint, but also the presence of an interconnected cyst within the lateral digital branch of the hallux. These characteristic magnetic resonance image findings are consistent with those previously described for a peroneal intraneural ganglion cyst that arose from the superior tibiofibular joint, and include (1) origin (ascent) from the second metatarsophalangeal joint with propagation along the articular branch and into the dorsal digital branch of the second toe, (2) cross-over within the shared epineurial sheath of the deep peroneal nerve, and (3) further propagation (descent) within the dorsal digital branch of the hallux. The analogous features between intraneural ganglion cysts affecting small and large-caliber nerves support the fundamental principles of the unified articular (synovial) theory for the formation of intraneural ganglia, including (1) a connection to a synovial joint, (2) dissection of joint fluid through a capsular rent along the articular branch into the parent nerve, and (3) intra-epineurial, pressure-dependent propagation of cyst fluid along paths of least resistance. Level of Clinical Evidence: 4 ( The Journal of Foot & Ankle Surgery 48(1):80 84, 2009) Key Words: articular (synovial) theory, deep peroneal nerve, ganglia, intermetatarsal space, intraneural ganglion cyst Intraneural ganglion cysts are mucinous, non-neoplastic lesions that can be identified within the epineurium of peripheral nerves. They have been described in the foot and ankle region within tibial, medial plantar, superficial peroneal, and sural nerves (1 5). Origins from adjacent joints have rarely been demonstrated in cases in these locations (4, Address correspondence to: Robert J. Spinner, MD, Mayo Clinic, Gonda 8S-214, Rochester, MN spinner.robert@mayo.edu. 1 Chief of Foot Surgery, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Bronx- Lebanon Hospital Center, Bronx, NY. 2 Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic School of Medicine, Rochester, MN. 3 Professor, Department of Neurologic Surgery and Orthopedics, Mayo Clinic School of Medicine, Rochester, MN. 4 Department of Orthopedics, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN. Financial Disclosure: None reported. Conflict of Interest: None reported. Copyright 2009 by the American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons /09/ $36.00/0 doi: /j.jfas ), encouraging many authors to support the theory that intraneural ganglion cysts arise de novo. Recent literature dealing with intraneural ganglion cysts affecting larger diameter nerves has reliably described an articular origin in association with primary and recurrent cases of intraneural ganglia, particularly those involving the peroneal nerve arising from the superior tibiofibular joint (10, 11). Regardless of the size of the nerve, we believe that a joint connection is universally present in association with the formation of an intraneural ganglion cyst, and we have demonstrated evidence to support this theory even in cases where authors have suggested otherwise (6, 8, 9, 11, 12). An appreciation of this articular connection, we feel, is crucial to proper treatment of intraneural ganglion cysts, since identification and disconnection of the nerve s articular branch connection to the joint is necessary in order to prevent recurrent intraneural cyst formation (10, 11). In this article, we describe the case of a patient who displayed an intraneural ganglion occurring in an unusual 80 THE JOURNAL OF FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY
2 location, namely the deep peroneal nerve within the first intermetatarsal space, which, based on magnetic resonance image (MRI) findings, arose from the second metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint. The clinical and MRI findings in this case further allow us to generalize the previously described MRI features of intraneural ganglion cysts that are known to be associated with large-caliber nerves, like the peroneal nerve, to smaller nerves, like a terminal branch of the deep peroneal nerve in the foot. Case Report A 55-year-old woman presented to the primary author (NMB) with a painful right forefoot with swelling that had been persistent for many months after an insidious onset. She localized the pain to the first intermetatarsal space and second metatarsal shaft, and she related having had no previous treatment. Upon physical examination, she displayed slight swelling in the first intermetatarsal space, and she was also tender to palpation along the second metatarsal shaft. Plantarflexion of the hallux resulted in diminished sensation localized to lateral side of the right hallux. Plain radiographs of the right foot did not reveal any fracture or dislocation, and MRIs revealed a tubular intraneural ganglion cyst localized to the medial, dorsal digital branch to the second toe (Figure 1). Close inspection of the MRI also revealed a subtle joint connection, referred to as the tail sign, linking the cyst to the second MTP joint (Figure 1, A). The cyst extended proximally 5.8 cm within the deep peroneal (common digital) nerve, and its maximum width was 9.5 mm. The cyst was eccentrically located, thereby displacing nerve fascicles and creating the magnetic resonance signet ring sign (12) (Figure 1, F). Moreover, the more proximal enlargement was consistent with a balloon sign (8) (Figure 1 A, B, and C), which is indicative of cystic expansion within the confines of the nerve sheath. Furthermore, a wedding ring sign was also evident, wherein cyst fluid was located within the outer epineurium of the deep peroneal nerve (Figures 1, D and E, and 2, B). Importantly, a fluid-filled cystic expansion connected the smaller diameter lateral digital branch of the hallux to the medial digital branch of the second toe, and there was a small amount of cyst within the digital nerve to the second toe distal to the articular branch. Aspiration with an 18-gauge needle was undertaken approximately 2 months after ascertainment of the cystic nature of the lesion via MRI scanning, and 0.5 ml of clear, viscous, jelly-like material was evacuated. This resulted in reduction in the size of the lesion within the first intermetatarsal space, which was appreciated clinically, as well as decreased symptomatology, and she improved considerably. Approximately 1 month later, additional MRI scans were obtained, and these revealed slight enlargement of the intraneural cyst, indicative of persistence of the articular connection and refilling of the cyst with synovial fluid (Figure 2). After further consideration of the treatment options, the patient was eventually offered surgical intervention that would consist of decompression of the intraneural cyst of the second toe and first intermetatarsal space, along with disconnection of the articular branch connecting the medial digital nerve trunk to the second MTP joint. After considering of this specific option, however, the patient chose to decline surgical intervention despite ongoing symptomatology. Discussion We are unaware of a previous case describing the clinical and MRI findings, as well as an explanation of the probable mechanism of development, of a joint-connected intraneural ganglion along with interconnected digital intraneural cysts in either the foot or the hand. The imaging features in this patient, when carefully scrutinized, may provide insight into the etiology of intraneural ganglion cyst formation and propagation that may be comparable to ganglion cyst formation and propagation in other areas of the body. In the case described in this article (Figure 3), it appears that the first phase of development of the lesion entailed the exit of synovial fluid from a capsular rent in the second MTP joint that ascended (proximal migration) into, and then along, the articular branch of the proper digital nerve to the medial aspect of the second toe and, eventually, into the deep peroneal nerve. The second phase of development of the observed lesion was probably migration of the fluid into the shared epineurial sheath of the deep peroneal nerve, where cross-over occurred as the cyst dissected along one neural pathway (the medial digital nerve of the second toe) which could then interconnect with a second neural pathway, namely the lateral digital nerve of the hallux. Phase three of the development, thereafter, entailed descent (distal migration) of the fluid within the proper digital branch of the hallux. This proposed pattern of fluid propagation in the first intermetatarsal space and associated toes, makes sense clinically and pathophysiologically and, as such, lends credence to the fundamental principles of the unified articular (synovial) theory of formation of intraneural ganglion cysts, including (1) the presence of a neural connection to a degenerative synovial joint, (2) dissection of joint fluid through a capsular rent along the articular branch into the parent nerve, and (3) propagation of cyst fluid depending on pressure fluxes along paths of least resistance. Understanding the joint-related nature of these cysts makes clear the need to surgically address the articular branch in an effort to predictably minimize the risk of recurrence of the intraneural ganglion. In the case described in this report, we actually recommended surgical inspection and treatment of the in- VOLUME 48, NUMBER 1, JANUARY/FEBRUARY
3 FIGURE 1 Magnetic resonance imaging of intraneural ganglion cyst. (A) Coronal maximum intensity projection (MIP) from a T2-weighted fast recovery fast spin-echo (FR-FSE) image set with fat suppression showing intraneural cyst within the medial digital branch of the deep peroneal nerve to the second toe (asterisk). Note cyst within the lateral digital branch of the hallux (long white arrow). The connection to the second metatarsophalangeal joint ( tail sign) is also seen on this image (short black arrows). (B) Coronal maximum intensity projection (MIP) slightly superficial to Figure 1, A, shows the intraneural cyst within the medial digital branch of the second toe (asterisk), and lateral digital branch of the hallux (white arrow). Also seen on this image is fluid within the first metatarsophalangeal joint indicative of degenerative change (plus sign). (C) Sagittal T2-weighted fast spin-echo (FSE) image with fat suppression shows the proximal extension of the intraneural cyst (asterisk) into the deep peroneal (common digital nerve) of the first intermetatarsal space. Incidentally noted is flow-related enhancement in a small digital artery (arrowhead). (D) Axial T2-weighted FR-FSE image with fat suppression at the level of the bifurcation of the common digital nerve showing intraneural cyst within the medial digital branch of the second toe (asterisk) and lateral digital branch of the hallux (white arrow). There is a faint ring of cyst surrounding both branches, the wedding ring sign. (E) Axial T2-weighted FR-FSE image with fat suppression distal to Figure 1, D, showing cyst within both of the proper digital nerves (asterisk, medial digital branch of the second toe; long arrow, lateral digital branch of the hallux) distal to the bifurcation. Note fluid in the first metatarsophalangeal joint related to degenerative disease. The wedding ring sign can be seen (short arrow). (F) Axial T1-weighted image at the same location as Figure 1, E, showing the intraneural cysts (asterisk, medial digital branch of the second toe; long arrow, lateral digital branch of the hallux). The displaced nerve fascicles around the intraneural cyst are best seen in association with the medial digital branch of the second toe (arrowhead). The lateral digital branch of the second toe is visible and normal on this image (short arrow). Blood vessels are superficial to the nerves. traneural ganglion cysts, in an effort to diminish the risk of persistence or recurrence of pain. Aspiration or decompression without disconnecting the articular branch resulted in transient relief, but could not be expected to be a reliable or lasting treatment (10). Even without surgical or histological confirmation, we believe that the MRI features of intraneural ganglion cysts are, in and of themselves, pathognomonic (12). MRI in this case was also helpful not only in establishing the presence of the connection between the nerve and the synovial cavity of the second MTP joint, but also in establishing the propagation pattern of the intraneural ganglion. Knowledge of the unified theory for intraneural ganglion cyst formation, and an understanding of the anatomy of the common and proper digital nerves of the foot, is also important in the evaluation and treatment of this condition and, as depicted in the case described in this article, the connection between the intraneural ganglion and the adjacent joint can be subtle and easily missed without the use of optimal imaging techniques. Such techniques include the maximum intensity 82 THE JOURNAL OF FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY
4 FIGURE 2 Post-aspiration MRI. (A) Coronal maximum intensity projection (MIP) image from a T2-weighted FR-FSE data set with fat suppression showing enlargement of the recurrent intraneural cyst within both proper digital nerves of deep peroneal nerve (asterisk, medial digital branch of the second toe; white arrow, lateral digital branch of the hallux), extending proximally to the common digital nerve to the base of the first metatarsal. The extraneural cyst associated with the first metatarsophalangeal joint has also increased in size (plus sign). (B) Axial T2-weighted FR-FSE image with fat suppression at the level of the bifurcation of the common digital nerve shows cyst in both proper digital nerves. A wedding ring sign (arrows) with cyst within the outer epineurium surrounds the medial digital branch of the second toe. (C) Axial reformation from a coronal T2-weighted FR-FSE data set with fat suppression shows the joint connection and cyst within the articular branch of the medial digital branch of the second toe (arrow). FIGURE 3 Artistic rendering (Mayo Foundation, 2008; with permission). Left-side image (normal anatomy). The deep peroneal nerve is located in the first interspace and bifurcates to form the dorsal digital branches of the lateral aspect of the hallux and the medial aspect of the second toe. An articular branch is highlighted innervating the second metatarsophalangeal joint. Right-side image (intraneural ganglion cyst). Cyst fluid exiting a capsular rent in the second metatarsophalangeal joint and ascending along the articular branch and the digital nerve of the second toe and into the deep peroneal nerve (phase I). Cross-over (phase II) is necessary for subsequent descent into the digital nerve of the hallux (phase III). projection (MIP) from a T2-weighted fast recovery fast spin-echo (FR-FSE) MRI set with fat suppression. Careful scrutiny of the images is particularly important, since the digital nerves themselves are very small and hard to visualize, and establishing the relationship between the cyst and the nerve can be difficult. This difficulty may actually contribute to what we believe to be a generally incomplete recognition of the full extent of the underlying pathology VOLUME 48, NUMBER 1, JANUARY/FEBRUARY
5 related to the formation of intraneural ganglion cysts. In conclusion, in this article, we described the case of a smallcaliber intraneural ganglion cyst in the first intermetatarsal space. This observation is important, since it can be explained by the unified theory of intraneural ganglion cyst formation as it pertains to a small nerve in the foot. Specifically, this case provides a direct analogy to the formation and propagation of intraneural ganglion cysts not only within the hand (13), but also throughout the body. In the future, histopathological confirmation of the lesion, in conjunction with the aforementioned MRI findings, should be possible. References 1. Fujita I, Matsumoto K, Minami T, Kizaki T, Akissue T, Yamamoto T. Tarsal tunnel syndrome caused by epineural ganglion of the posterior tibial nerve: report of 2 cases and review of the literature. J Foot Ankle Surg 43: , Boyer MG, Giuliani G, Pozzati E, Acciarri N, Forti A. Tarsal tunnel syndrome secondary to intraneural ganglion. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 38: , Adn M, Hamlat A, Morandi X, Guegan Y. Intraneural ganglion cyst of the tibial nerve. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148: , Høgh J. Benign cystic lesions of the peripheral nerves. Int Orthop 12: , Lemont H, Sabo MA. Origin of foot ganglion. J Am Pod Med Am 90: , Spinner RJ, Dellon AL, Rosson GD, Anderson SR, Amrami KK. Tibial intraneural ganglia in the tarsal tunnel: is there a joint connection? J Foot Ankle Surg 46:27 31, Blitz NM, Prestridge J, Amrami KK, Spinner RJ. Posttraumatic, jointconnected sural intraneural ganglion with a new pattern of intraneural recurrence. J Foot Ankle Surg 47: , Spinner RJ, Amrami KK. The balloon sign: Adn et al [letter to the editor]. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148: , Spinner RJ, Amrami KK, Hamlat A. Collaborative follow-up [letter to the editor]. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 150:93 96, Spinner RJ, Atkinson JLD, Tiel RL. Peroneal intraneural ganglia. The importance of the articular branch: a unifying theory. J Neurosurg 99: , Spinner RJ, Wang H, Amrami KK, Wolanskyj AP, Benarroch EE, Skinner JA, Rock MG, Desy NM, Scheithauer BW. The dynamic phases of peroneal and tibial intraneural ganglia: a new dimension added to the unifying articular theory. J Neurosurg 107: , Spinner RJ, Desy NM, Amrami KK. Cystic transverse limb of the articular branch: a pathognomonic sign for peroneal intraneural ganglia at the superior tibiofibular joint. Neurosurgery 59: , Giele H, Le Viet D. Intraneural mucoid cysts of the upper limb. J Hand Surg (Br) 22: , THE JOURNAL OF FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY
From Targeted Fascicular Biopsy of Major Nerve to Targeted Cutaneous Nerve Biopsy: Implementing Clinical Anatomy Can Catalyze a Paradigm Shift
 Clinical Anatomy 31:616 621 (2018) EDITORIAL From Targeted Fascicular Biopsy of Major Nerve to Targeted Cutaneous Nerve Biopsy: Implementing Clinical Anatomy Can Catalyze a Paradigm Shift TOMAS MAREK,
Clinical Anatomy 31:616 621 (2018) EDITORIAL From Targeted Fascicular Biopsy of Major Nerve to Targeted Cutaneous Nerve Biopsy: Implementing Clinical Anatomy Can Catalyze a Paradigm Shift TOMAS MAREK,
Intraneuronal Ganglion Cyst. Diagnosis and treatment
 Intraneuronal Ganglion Cyst. Diagnosis and treatment Poster No.: P-0073 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: F. Diez Renovales 1, B. Ruiz 1, J. Cardenal Urdampilleta 1, I. Corta 2, Keywords:
Intraneuronal Ganglion Cyst. Diagnosis and treatment Poster No.: P-0073 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: F. Diez Renovales 1, B. Ruiz 1, J. Cardenal Urdampilleta 1, I. Corta 2, Keywords:
Ultrasound of the Knee
 Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound
 Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Normal Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound appearance: Hypoechoic
Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Normal Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound appearance: Hypoechoic
Interesting Case Series. Ganglion Cyst of the Peroneus Longus
 Interesting Case Series Ganglion Cyst of the Peroneus Longus Andrew A. Marano, BA, Paul J. Therattil, MD, Dare V. Ajibade, MD, PhD, MPH, and Ramazi O. Datiashvili, MD, PhD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive
Interesting Case Series Ganglion Cyst of the Peroneus Longus Andrew A. Marano, BA, Paul J. Therattil, MD, Dare V. Ajibade, MD, PhD, MPH, and Ramazi O. Datiashvili, MD, PhD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive
Aetiology: Pressure of Distal intermetatarsal ligament against common digital nerve. Lumbar radiculopathy Instability MTPJ joint or inflammatory MPJ
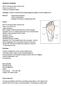 MORTON S NEUROMA 80% III web space (next common is II). Never occurs in III or IV Common in females in fifties Aetiology: Pressure of Distal intermetatarsal ligament against common digital nerve Rule out
MORTON S NEUROMA 80% III web space (next common is II). Never occurs in III or IV Common in females in fifties Aetiology: Pressure of Distal intermetatarsal ligament against common digital nerve Rule out
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique. Description of Plate
 Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
The Lower Limb VI: The Leg. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb VI: The Leg Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Muscles of the leg Posterior compartment (superficial & deep): primary plantar flexors of the foot flexors of the toes Anterior compartment:
The Lower Limb VI: The Leg Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Muscles of the leg Posterior compartment (superficial & deep): primary plantar flexors of the foot flexors of the toes Anterior compartment:
Origin of Satellite Ganglion Cysts with Effusion in the Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon Sheath around the Hallux
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:94-98 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.1.94 Origin of Satellite Ganglion Cysts with Effusion in the Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon Sheath around
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:94-98 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.1.94 Origin of Satellite Ganglion Cysts with Effusion in the Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon Sheath around
The Foot. Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob:
 The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
In t r a n e u r a l ganglia are relatively rare cysts located. Intraneural ganglia in the hip and pelvic region. Clinical article
 J Neurosurg 111:317 325, 2009 Intraneural ganglia in the hip and pelvic region Clinical article Ro b e r t J. Sp i n n e r, M.D., 1,2 Mar i e-no ë l l e Hé b e rt-bl o u i n, M.D., 1 Ro b e r t T. Tr o
J Neurosurg 111:317 325, 2009 Intraneural ganglia in the hip and pelvic region Clinical article Ro b e r t J. Sp i n n e r, M.D., 1,2 Mar i e-no ë l l e Hé b e rt-bl o u i n, M.D., 1 Ro b e r t T. Tr o
2013/10/18 GANGLION CYSTS ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY ARTHROSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OPEN GANGLIONECTOMY COMPARED TO FOOT AND ANKLE
 GANGLION CYSTS gelatinous fluid filled, encapsulated soft tissue masses adjacent to a joint or tendon ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Dr TH Lui North District Hospital HKSAR Pain, mass
GANGLION CYSTS gelatinous fluid filled, encapsulated soft tissue masses adjacent to a joint or tendon ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Dr TH Lui North District Hospital HKSAR Pain, mass
Disclosure. Pre-Procedural Considerations. Transducer Selection. Sterile Procedure. Sterile Procedure. Ultrasound Guided Foot and Ankle Injections
 Ultrasound Guided Foot and Ankle Injections Disclosure No relevant financial relationships exist Shane A. Shapiro, M.D. Assistant Professor, Orthopedic Surgery Mayo Clinic Florida @ShaneShapiroMD 2012
Ultrasound Guided Foot and Ankle Injections Disclosure No relevant financial relationships exist Shane A. Shapiro, M.D. Assistant Professor, Orthopedic Surgery Mayo Clinic Florida @ShaneShapiroMD 2012
The Pitfalls of Radiological Ordering and Documentation- Can you Pass an Audit? David J. Freedman, DPM, FASPS Laura J. Pickard, DPM October 26, 2017
 The Pitfalls of Radiological Ordering and Documentation- Can you Pass an Audit? David J. Freedman, DPM, FASPS Laura J. Pickard, DPM October 26, 2017 1 Surgical Coding Webinar Series Register for these
The Pitfalls of Radiological Ordering and Documentation- Can you Pass an Audit? David J. Freedman, DPM, FASPS Laura J. Pickard, DPM October 26, 2017 1 Surgical Coding Webinar Series Register for these
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: WHEN HEEL PAIN IS NOT PLANTAR FASCIITIS HEATHER RAFAL, DPM 2ND VICE PRESIDENT, AAWP PRESIDENT, DPMA
 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: WHEN HEEL PAIN IS NOT PLANTAR FASCIITIS HEATHER RAFAL, DPM 2ND VICE PRESIDENT, AAWP PRESIDENT, DPMA THE HEEL PAIN PATIENT WHO DOES NOT HAVE PLANTAR FASCIITIS If every patient who
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: WHEN HEEL PAIN IS NOT PLANTAR FASCIITIS HEATHER RAFAL, DPM 2ND VICE PRESIDENT, AAWP PRESIDENT, DPMA THE HEEL PAIN PATIENT WHO DOES NOT HAVE PLANTAR FASCIITIS If every patient who
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program
 Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
The myofascial compartments of the foot
 The myofascial compartments of the foot A CADAVER STUDY Z. X. Ling, V. P. Kumar From the National University of Singapore, Republic of Singapore Compartment syndrome of the foot requires urgent surgical
The myofascial compartments of the foot A CADAVER STUDY Z. X. Ling, V. P. Kumar From the National University of Singapore, Republic of Singapore Compartment syndrome of the foot requires urgent surgical
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology
 Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology Levon N. Nazarian, M.D. Professor of Radiology Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Disclosures None relevant to this presentation Educational Objective Following
Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology Levon N. Nazarian, M.D. Professor of Radiology Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Disclosures None relevant to this presentation Educational Objective Following
Lecture 09. Popliteal Fossa. BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai
 Lecture 09 Popliteal Fossa BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 14.02.2018 What is popliteus? Introduction Anything relating to, or near the part of the leg behind the knee. From New Latin popliteus the muscle
Lecture 09 Popliteal Fossa BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 14.02.2018 What is popliteus? Introduction Anything relating to, or near the part of the leg behind the knee. From New Latin popliteus the muscle
Shane A. Shapiro, M.D. Assistant Professor, Orthopedic Surgery Mayo Clinic 2012 MFMER slide MFMER slide-3
 Ultrasound Foot and Ankle Pathology Disclosures None relevant Shane A. Shapiro, M.D. Assistant Professor, Orthopedic Surgery Mayo Clinic Florida @ShaneShapiroMD 2012 MFMER slide-2 Foot and Ankle Fundamentals
Ultrasound Foot and Ankle Pathology Disclosures None relevant Shane A. Shapiro, M.D. Assistant Professor, Orthopedic Surgery Mayo Clinic Florida @ShaneShapiroMD 2012 MFMER slide-2 Foot and Ankle Fundamentals
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Lateral Elbow Pathology
 Lateral Elbow Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of adiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal adiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE, Philips
Lateral Elbow Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of adiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal adiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE, Philips
MRI IN NONOSSEOUS ABNORMALITIES OF THE FOREFOOT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW
 MRI IN NONOSSEOUS ABNORMALITIES OF THE FOREFOOT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW I Delgado, P Melloni, M Veintemillas, R Valls, M Vilagran, A Valera UDIAT. Sabadell (Barcelona). Spain. PURPOSE To catalog the wide spectrum
MRI IN NONOSSEOUS ABNORMALITIES OF THE FOREFOOT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW I Delgado, P Melloni, M Veintemillas, R Valls, M Vilagran, A Valera UDIAT. Sabadell (Barcelona). Spain. PURPOSE To catalog the wide spectrum
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain
 Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months.
 Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months. Diagnosis: II MTP instability Demographics of MT instability Lesser MTP joint instability occurs
Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months. Diagnosis: II MTP instability Demographics of MT instability Lesser MTP joint instability occurs
Femoral Artery. Its entrance to the thigh Position Midway between ASIS and pubic symphysis
 Lower Limb Vessels Lecture Objectives Describe the major arteries of the lower limb. Describe the deep and superficial veins of the lower limb. Describe the topographical relationships of the arteries
Lower Limb Vessels Lecture Objectives Describe the major arteries of the lower limb. Describe the deep and superficial veins of the lower limb. Describe the topographical relationships of the arteries
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/29/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 105 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/29/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 105 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
RADIAL HEAD FRACTURES. It is far more common in adults than in children, (who more commonly fracture their neck of radius).
 RADIAL HEAD FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the head of the radius are relatively common. The injury can be subtle unless specifically looked for. It is far more common in adults than in children,
RADIAL HEAD FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the head of the radius are relatively common. The injury can be subtle unless specifically looked for. It is far more common in adults than in children,
Ultrasound Guided Lower Extremity Blocks
 Ultrasound Guided Lower Extremity Blocks CONTENTS: 1. Femoral Nerve Block 2. Popliteal Nerve Block Updated December 2017 1 1. Femoral Nerve Block Indications Surgery involving the knee, anterior thigh,
Ultrasound Guided Lower Extremity Blocks CONTENTS: 1. Femoral Nerve Block 2. Popliteal Nerve Block Updated December 2017 1 1. Femoral Nerve Block Indications Surgery involving the knee, anterior thigh,
Unusual Lateral Presentation of Popliteal Cyst
 Unusual Lateral Presentation of Popliteal Cyst Tarek Hemmali,* Abstract: The most common cyst occurs in the popliteal region is the popliteal cyst and over the past years it has been received much clinical
Unusual Lateral Presentation of Popliteal Cyst Tarek Hemmali,* Abstract: The most common cyst occurs in the popliteal region is the popliteal cyst and over the past years it has been received much clinical
radiologymasterclass.co.uk
 http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
Leg. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Anatomy MCQs Week 13
 Anatomy MCQs Week 13 1. Posterior to the medial malleolus of the ankle: The neurovascular bundle lies between Tibialis Posterior and Flexor Digitorum Longus The tendon of Tibialis Posterior inserts into
Anatomy MCQs Week 13 1. Posterior to the medial malleolus of the ankle: The neurovascular bundle lies between Tibialis Posterior and Flexor Digitorum Longus The tendon of Tibialis Posterior inserts into
The Role of IDEAL and DTI in Peripheral Nerve MR Imaging
 In Practice The Role of IDEAL and DTI in Peripheral Nerve MR Imaging y Darryl. Sneag, MD, Assistant Attending Radiologist, and Hollis G. Potter, MD, Chairman and The Coleman Chair, MRI Research, Department
In Practice The Role of IDEAL and DTI in Peripheral Nerve MR Imaging y Darryl. Sneag, MD, Assistant Attending Radiologist, and Hollis G. Potter, MD, Chairman and The Coleman Chair, MRI Research, Department
TRIQUETRUM FRACTURE. The triquetrum bone is one of the small bones that make up the carpus.
 TRIQUETRUM FRACTURE Introduction The triquetrum bone is one of the small bones that make up the carpus. It is also known as the triquetral bone, (and in the past the pyramidal or triangular bone) Triquetrum
TRIQUETRUM FRACTURE Introduction The triquetrum bone is one of the small bones that make up the carpus. It is also known as the triquetral bone, (and in the past the pyramidal or triangular bone) Triquetrum
Case report: Intraneural perineurioma of the sciatic nerve in an adolescent strategies for revealing the diagnosis
 CASE REPORT Case report: Intraneural perineurioma of the sciatic nerve in an adolescent strategies for revealing the diagnosis Lars B. Dahlin 1, Inger Nennesmo 2, Jack Besjakov 3, Istvan Ferencz 4, Gert
CASE REPORT Case report: Intraneural perineurioma of the sciatic nerve in an adolescent strategies for revealing the diagnosis Lars B. Dahlin 1, Inger Nennesmo 2, Jack Besjakov 3, Istvan Ferencz 4, Gert
Gross Anatomy Coloring Book Series. Lower Extremity Arteries
 Gross Anatomy Coloring Book Series Lower Extremity Arteries 1 Femoral Artery and Associated Branches For the life of the flesh is in the blood. Leviticus 17:11 Femoral Artery and Associated Branches After
Gross Anatomy Coloring Book Series Lower Extremity Arteries 1 Femoral Artery and Associated Branches For the life of the flesh is in the blood. Leviticus 17:11 Femoral Artery and Associated Branches After
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta.
 Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
THE JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE Vol. 56 No. 3 March 2015 Rauscher et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment
 119 Pictorial Essay H............ - Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment David Karasick1 and Keith L. Wapner An estimated 40% of the American adult population experiences foot problems,
119 Pictorial Essay H............ - Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment David Karasick1 and Keith L. Wapner An estimated 40% of the American adult population experiences foot problems,
Hany El-Rashidy and Anand Vora
 Chapter 194 Lisfranc Injuries Chapter 194 Lisfranc Injuries Hany El-Rashidy and Anand Vora 8 ICD-9 CODE 838.03 Lisfranc (Tarsometatarsal) Fracture-Dislocation Key Concepts The Lisfranc joint represents
Chapter 194 Lisfranc Injuries Chapter 194 Lisfranc Injuries Hany El-Rashidy and Anand Vora 8 ICD-9 CODE 838.03 Lisfranc (Tarsometatarsal) Fracture-Dislocation Key Concepts The Lisfranc joint represents
Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan. Schedule Of Anaesthetic Rates Applicable To Podiatry. Procedure List. As Of. 01 April Government of Alberta
 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Procedure List As Of 01 April 2017 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Page i Generated 2017/03/14 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2017/04/01 II. OPERATIONS ON THE NERVOUS SYSTEM.......................
Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Procedure List As Of 01 April 2017 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Page i Generated 2017/03/14 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2017/04/01 II. OPERATIONS ON THE NERVOUS SYSTEM.......................
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium
 MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
Volar Wrist Ganglion: A Report of an Unusual Case. Eyad Alqasim, MD* Rashid Kameshki, MBBS** Maged Mostafa, MD***
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 34, No. 3, September 2012 Volar Wrist Ganglion: A Report of an Unusual Case Eyad Alqasim, MD* Rashid Kameshki, MBBS** Maged Mostafa, MD*** A patient presented with wrist
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 34, No. 3, September 2012 Volar Wrist Ganglion: A Report of an Unusual Case Eyad Alqasim, MD* Rashid Kameshki, MBBS** Maged Mostafa, MD*** A patient presented with wrist
AN ABNORMAL UNILATERAL ORIGIN OF DORSALIS PEDIS ARTERY- A CASE REPORT
 AN ABNORMAL UNILATERAL ORIGIN OF DORSALIS PEDIS ARTERY- A CASE REPORT Authors:- Dr. Hetal Vaishnani, Dr.Subhsh Gujar, Dr.Savita Gadekar, Dr.K.V.Bondre, Dr.G.V.Shah Department of Anatomy S.B.K.S.Medical
AN ABNORMAL UNILATERAL ORIGIN OF DORSALIS PEDIS ARTERY- A CASE REPORT Authors:- Dr. Hetal Vaishnani, Dr.Subhsh Gujar, Dr.Savita Gadekar, Dr.K.V.Bondre, Dr.G.V.Shah Department of Anatomy S.B.K.S.Medical
LISFRANC FRACTURE-DISLOCATION
 LISFRANC FRACTURE-DISLOCATION Napoleon at Mont St. Bernard, Jacques-Louis David, 1800, Oil on Canvas, Musee du Louvre, Paris. This is Jacques-Louis David s immortal depiction of a young Napoleon Bonaparte,
LISFRANC FRACTURE-DISLOCATION Napoleon at Mont St. Bernard, Jacques-Louis David, 1800, Oil on Canvas, Musee du Louvre, Paris. This is Jacques-Louis David s immortal depiction of a young Napoleon Bonaparte,
First & second layers of muscles of the sole
 The FOOT First & second layers of muscles of the sole introduction The muscles acting on the foot can be divided into two distinct groups; extrinsic and intrinsic muscles. The extrinsic muscles arise from
The FOOT First & second layers of muscles of the sole introduction The muscles acting on the foot can be divided into two distinct groups; extrinsic and intrinsic muscles. The extrinsic muscles arise from
Dumbbell Ganglion Of The Foot: Case Report
 Article ID: WMC001079 2046-1690 ISSN Dumbbell Ganglion Of The Foot: Case Report Author(s):Dr. S S Suresh, Dr. Hosam Zaki, Dr. Joyce Jose Corresponding Author: Dr. S S Suresh, Head of Department, Ibri Regional
Article ID: WMC001079 2046-1690 ISSN Dumbbell Ganglion Of The Foot: Case Report Author(s):Dr. S S Suresh, Dr. Hosam Zaki, Dr. Joyce Jose Corresponding Author: Dr. S S Suresh, Head of Department, Ibri Regional
Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle. Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle
 Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Application of a Constrained External Fixator Frame for Treatment of a Fixed Equinus Contracture
 Application of a Constrained External Fixator Frame for Treatment of a Fixed Equinus Contracture Robert W. Mendicino, DPM, FACFAS, 1 Lara J. Murphy, DPM, 2 Michael P. Maskill, DPM, 3 Alan R. Catanzariti,
Application of a Constrained External Fixator Frame for Treatment of a Fixed Equinus Contracture Robert W. Mendicino, DPM, FACFAS, 1 Lara J. Murphy, DPM, 2 Michael P. Maskill, DPM, 3 Alan R. Catanzariti,
Digital Surgery Complications
 Annual Surgical Conference 2018 Digital Surgery Complications Zeeshan S. Husain, DPM, FACFAS, FASPS Great Lakes Foot and Ankle Institute September 21, 2018 None Disclosures Presentation Outline Differentials
Annual Surgical Conference 2018 Digital Surgery Complications Zeeshan S. Husain, DPM, FACFAS, FASPS Great Lakes Foot and Ankle Institute September 21, 2018 None Disclosures Presentation Outline Differentials
fitting shoes, or repetitive stress. It also frequently arises from unknown causes.
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Morton's Neuroma Morton's Neuroma, also sometimes referred to as plantar Neuroma or intermetatarsal Neuroma,
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Morton's Neuroma Morton's Neuroma, also sometimes referred to as plantar Neuroma or intermetatarsal Neuroma,
Copyright 2004, Yoshiyuki Shiratori. All right reserved.
 Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Why? Ultrasound of the Foot. Ultrasound of the Foot. General Rules. Plantar Fascia. Plantar Fasciitis 18/09/2018
 Ultrasound of the Foot Why? Ultrasound of the Foot Plantar fasciitis Plantar fascia fibromatosis Morton s neuroma Intermetatarsal bursitis Adventitial bursitis Plantar plate tears MTP joint synovitis Ganglia
Ultrasound of the Foot Why? Ultrasound of the Foot Plantar fasciitis Plantar fascia fibromatosis Morton s neuroma Intermetatarsal bursitis Adventitial bursitis Plantar plate tears MTP joint synovitis Ganglia
Foot. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Foot Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Dorsum of the Foot Sole of the Foot Plantar aponeurosis It is a triangular thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot Attachments:
Foot Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Dorsum of the Foot Sole of the Foot Plantar aponeurosis It is a triangular thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot Attachments:
Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation. Disclosures. Outline. Joint Effusion. Suprapatellar recess
 Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan
Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan
Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures. Kali Luker, PGY-1
 Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures Kali Luker, PGY-1 Anatomy Extraarticular Fractures Involve body, anterior process or tuberosity Treated with immobilization and NWB x 6 wks UNLESS Displaced
Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures Kali Luker, PGY-1 Anatomy Extraarticular Fractures Involve body, anterior process or tuberosity Treated with immobilization and NWB x 6 wks UNLESS Displaced
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Osteochondritis of Hallux Sesamoid Bone
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Osteochondritis of Hallux Sesamoid Bone
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
The Leg. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
Why Would We Operate on a Confirmed DVT Diagnosis? Presented by: Chris Huckle, DO Contributions: Stewart Grizzard, MD and Jeffrey Easom, DO
 Why Would We Operate on a Confirmed DVT Diagnosis? Presented by: Chris Huckle, DO Contributions: Stewart Grizzard, MD and Jeffrey Easom, DO History F.R. is a 40 year old African American male who presented
Why Would We Operate on a Confirmed DVT Diagnosis? Presented by: Chris Huckle, DO Contributions: Stewart Grizzard, MD and Jeffrey Easom, DO History F.R. is a 40 year old African American male who presented
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
Knee: Cruciate Ligaments
 72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
The plantar aponeurosis
 Anatomy of the foot The plantar aponeurosis Is a triangular thickening of the deep fascia Its apex is attached to the medial and lateral tubercles of the calcaneum. The base of the aponeurosis divides
Anatomy of the foot The plantar aponeurosis Is a triangular thickening of the deep fascia Its apex is attached to the medial and lateral tubercles of the calcaneum. The base of the aponeurosis divides
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder
 Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
I-A-1) Non-specific thickening of synovial membrane
 I-A-1) Non-specific thickening of synovial membrane Grayscale Metatarsal Power Doppler Dorsal aspect of metatarsophalangeal joint in right 1 st toe, longitudinal view Asterisks indicate non-specific thickening
I-A-1) Non-specific thickening of synovial membrane Grayscale Metatarsal Power Doppler Dorsal aspect of metatarsophalangeal joint in right 1 st toe, longitudinal view Asterisks indicate non-specific thickening
A Ganglion Cyst at the Foot Causing Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Detected by Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Article ID: WMC001130 ISSN 2046-1690 A Ganglion Cyst at the Foot Causing Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Detected by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Corresponding Author: Dr. Iftikhar H Wani, Doctor, Emergency Hospital
Article ID: WMC001130 ISSN 2046-1690 A Ganglion Cyst at the Foot Causing Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Detected by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Corresponding Author: Dr. Iftikhar H Wani, Doctor, Emergency Hospital
Where should you palpate the pulse of different arteries in the lower limb?
 Where should you palpate the pulse of different arteries in the lower limb? The femoral artery In the femoral triangle, its pulse is easily felt just inferior to the inguinal ligament midway between the
Where should you palpate the pulse of different arteries in the lower limb? The femoral artery In the femoral triangle, its pulse is easily felt just inferior to the inguinal ligament midway between the
A Patient s Guide to Foot Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Foot Anatomy Introduction Our feet are constantly under stress. It's no wonder that 80 percent of us will have some sort of problem with our feet at some time or another. Many things
A Patient s Guide to Foot Anatomy Introduction Our feet are constantly under stress. It's no wonder that 80 percent of us will have some sort of problem with our feet at some time or another. Many things
Joint Preserving Surgery in Severe Forefoot Disorders
 Joint Preserving Surgery in Severe Forefoot Disorders J ORTHOP TRAUMA SURG REL RES 4 (12) 2008 Review article LOUIS S. BAROUK*, PIERRE BAROUK** * 39, Chemin de la Roche, 33370, Yvrac, France ** Clinique
Joint Preserving Surgery in Severe Forefoot Disorders J ORTHOP TRAUMA SURG REL RES 4 (12) 2008 Review article LOUIS S. BAROUK*, PIERRE BAROUK** * 39, Chemin de la Roche, 33370, Yvrac, France ** Clinique
Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
REPAIR OF THE DISPLACED AUSTIN OSTEOTOMY
 C H A P T E R 2 1 REPAIR OF THE DISPLACED AUSTIN OSTEOTOMY John V. Vanore, DPM INTRODUCTION Bunion surgery is frequently performed by foot and ankle surgeons. Generally, bunion surgery is quite predictable,
C H A P T E R 2 1 REPAIR OF THE DISPLACED AUSTIN OSTEOTOMY John V. Vanore, DPM INTRODUCTION Bunion surgery is frequently performed by foot and ankle surgeons. Generally, bunion surgery is quite predictable,
Section 3: Foot Subluxations and Dislocations
 Section 3: Foot Subluxations and Dislocations Case Study F: Lisfranc s Midfoot Dislocation Clinical History: J.K. a 28 year old female presents complaining of a painful right foot. She sustained an acute
Section 3: Foot Subluxations and Dislocations Case Study F: Lisfranc s Midfoot Dislocation Clinical History: J.K. a 28 year old female presents complaining of a painful right foot. She sustained an acute
MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder
 MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder Poster No.: C-1482 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Bartocci, C. Dell'atti, E. Federici, D. Beomonte Zobel, V. Martinelli,
MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder Poster No.: C-1482 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Bartocci, C. Dell'atti, E. Federici, D. Beomonte Zobel, V. Martinelli,
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION. At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral)
 PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
POPLITEAL CYST FILLED WITH HEMATOMA AT THE LOWER CALF: A CASE REPORT
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, No 4, pp 411-414, 2016 Copyright 2016 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) doi:10.15547/tjs.2016.04.019
Trakia Journal of Sciences, No 4, pp 411-414, 2016 Copyright 2016 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) doi:10.15547/tjs.2016.04.019
Magnetic resonance imaging of ulnar nerve abscess in leprosy: a case report
 Lepr Rev (2006) 77, 381 385 CASE REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of ulnar nerve abscess in leprosy: a case report SMRITI HARI, SUBRAMANIAN SUBRAMANIAN & RAJU SHARMA Department of Radiodiagnosis, All
Lepr Rev (2006) 77, 381 385 CASE REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of ulnar nerve abscess in leprosy: a case report SMRITI HARI, SUBRAMANIAN SUBRAMANIAN & RAJU SHARMA Department of Radiodiagnosis, All
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D
 Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Case Report. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine INTRODUCTION
 Case Report Ann Rehabil Med 2013;37(4):577-581 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.4.577 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Compressive Neuropathy of the Posterior Tibial
Case Report Ann Rehabil Med 2013;37(4):577-581 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.4.577 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Compressive Neuropathy of the Posterior Tibial
Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot)
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2007) 2:105 110 DOI 10.1007/s11751-007-0023-7 REVIEW Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot) Selvadurai Nayagam Received: 9 August
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2007) 2:105 110 DOI 10.1007/s11751-007-0023-7 REVIEW Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot) Selvadurai Nayagam Received: 9 August
Lumbar Disc Prolapse. Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan. Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon
 Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
EDL EHL. Extensor Hallucis Longus L5 Extensor Digitorum longus L5,1 Peroneus Tertius L5 1 Extensor Digitorum Brevis S1,2 [like intrinsic muscle]
![EDL EHL. Extensor Hallucis Longus L5 Extensor Digitorum longus L5,1 Peroneus Tertius L5 1 Extensor Digitorum Brevis S1,2 [like intrinsic muscle] EDL EHL. Extensor Hallucis Longus L5 Extensor Digitorum longus L5,1 Peroneus Tertius L5 1 Extensor Digitorum Brevis S1,2 [like intrinsic muscle]](/thumbs/78/77875930.jpg) ANATOMY OF ANKLE AND FOOT Lateral aspect: [Dorsal medial to lateral= dorsal under extensor retinaculum] Tibialis Anterior EHL Artery [Dorsal pedal A] and Anterior tibial N EDL Peroneus Tertius Behind the
ANATOMY OF ANKLE AND FOOT Lateral aspect: [Dorsal medial to lateral= dorsal under extensor retinaculum] Tibialis Anterior EHL Artery [Dorsal pedal A] and Anterior tibial N EDL Peroneus Tertius Behind the
Case Report Bipartite Medial Cuneiform: Case Report and Retrospective Review of 1000 Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging Studies
 Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 130979, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/130979 Case Report Bipartite Medial Cuneiform: Case Report and Retrospective Review of 1000 Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging
Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 130979, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/130979 Case Report Bipartite Medial Cuneiform: Case Report and Retrospective Review of 1000 Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging
Re+Line Bunion Correction System for Correction of Hallux Abducto Valgus Deformity
 Re+Line Bunion Correction System for Correction of Hallux Abducto Valgus Deformity Amber M. Shane, DPM, FACFAS 1, Christopher L. Reeves, DPM, FACFAS 1 1. Orlando Foot & Ankle Clinic, Orlando, FL Abstract
Re+Line Bunion Correction System for Correction of Hallux Abducto Valgus Deformity Amber M. Shane, DPM, FACFAS 1, Christopher L. Reeves, DPM, FACFAS 1 1. Orlando Foot & Ankle Clinic, Orlando, FL Abstract
MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST
 MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST Wrist Instability Dissociative Pattern apparent on routine radiographs Non-dissociative Stress / positional radiographs Dynamic fluoroscopy during stress Arthrography MRI / MR arthrography
MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST Wrist Instability Dissociative Pattern apparent on routine radiographs Non-dissociative Stress / positional radiographs Dynamic fluoroscopy during stress Arthrography MRI / MR arthrography
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review.
 Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review.
 Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Located Deep to Flexor Retinaculum on medial aspect of ankle. Posterior to Posterior Tibial Artery. Tom, Dick, and Very Nervous Harry
 ANKLE BLOCK ANESTHESIA GREGORY CLARK D.P.M. HEAD, SECTION OF PODIATRY SCRIPPS CLINIC LA JOLLA, CALIFORNIA A METHOD BY WHICH ONE MAY PROVIDE AN ANESTHETIC BLOCK TO THE FOOT OR ANKLE WITH A MINIMUM OF PATIENT
ANKLE BLOCK ANESTHESIA GREGORY CLARK D.P.M. HEAD, SECTION OF PODIATRY SCRIPPS CLINIC LA JOLLA, CALIFORNIA A METHOD BY WHICH ONE MAY PROVIDE AN ANESTHETIC BLOCK TO THE FOOT OR ANKLE WITH A MINIMUM OF PATIENT
Burwood Road, Concord Dora Street, Hurstville 119 Lethbridge Street, Penrith 160 Belmore Road, Randwick
 www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 119 Lethbridge Street, Penrith 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Turf Toe Injury By Todd Gothelf Foot, Ankle, Shoulder History
www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 119 Lethbridge Street, Penrith 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Turf Toe Injury By Todd Gothelf Foot, Ankle, Shoulder History
Case Report Tarsal Tunnel Surgery Secondary to a Tarsal Ganglion. Be Prepared Before Performing This Complicated Operation
 vol. 2 / no. 1 Foot & Ankle Specialist 35 Case Report Tarsal Tunnel Surgery Secondary to a Tarsal Ganglion Be Prepared Before Performing This Complicated Operation Joseph A. Cione, DPM, FACFAS, DABPS,
vol. 2 / no. 1 Foot & Ankle Specialist 35 Case Report Tarsal Tunnel Surgery Secondary to a Tarsal Ganglion Be Prepared Before Performing This Complicated Operation Joseph A. Cione, DPM, FACFAS, DABPS,
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
