THE DEFINITION AND MEASUREMENT OF
|
|
|
- Alexander Godwin Sanders
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE DEFINITION AND MEASUREMENT OF ACETABULAR ORIENTATION D. W. MURRAY From the Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford, England The orientation of an acetabulum or an acetabular prosthesis may be described by its and. Orientation can be assessed anatomically, radiographically, and by direct observation at operation. The angles of and determined by these three methods differ because they have different spatial arrangements. There are therefore three distinct definitions of and. This paper analyses the differences between the definitions and provides nomograms to convert from one to another. It is recommended that the operative definitions be used to describe the orientation of prostheses and that the anatomical definitions be used for dysplastic acetabula. Numerous terms are used to describe acetabular orientation. These include,, cover, abduction, tilt, opening and flexion (Ackland, Bourne and Uhthoff 1986; Herrlin, Pettersson and Selvik 1988). Inclination and are the most commonly used terms but they have several different and imprecise definitions (Herrlin, Selvik and Pettersson 1986; Calandruccio 1987). Different definitions are used in operative, radiographic and anatomical assessments of orientation and have been named accordingly. The aim of this investigation is to offer precise definitions and to develop a simple method for converting the results from one method ofassessment to another. The definitions describe the orientation of the acetabular axis which passes through the centre of the socket and is perpendicular to the plane ofthe socket face (Calandruccio 1987). J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1993 ; 75-B : Received 29 May 1992; Accepted 29 July 1992 D. W. Murray, MD, FRCS, Senior Orthopaedic Registrar Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Windmill Road, Headington, Oxford 0X3 7LD, UK. l993 British Editorial Society ofbone and Joint Surgery 030l-620X/93/2519 $2.00 DEFINITIONS AND CONVERSION METHOD Operative definitions. Acetabular components are frequently positioned with jigs, and these usually have two rods perpendicular to each other. The of the component is set by placing one of these rods parallel to the transverse axis of the patient and the other parallel to the longitudinal axis (McKee 1970 ; Charnley 1979; Harris 1980). Anteversion is achieved by rotating the longitudinal rod about the transverse axis, a movement akin to hip flexion (McKee 1970; Harris 1980). The angle is that through which the longitudinal rod is swung, and is measured in the sagittal plane. The operative (OA) is thus the angle between the longitudinal axis of the patient and the acetabular axis as projected on to the sagittal plane (Fig. 1). This is sometimes called the 4 angle (Lewinnek et al 1978). The, preset by the jig, is the angle between the acetabular axis and the longitudinal rod. When the prosthesis is anteverted the longitudinal rod remains in the sagittal plane, and the preset remains the same, being the angle between the acetabular axis and the sagittal plane. The operative (01) is therefore the angle between the acetabular axis and the sagittal plane (Fig. 1). It is the angle of abduction of the acetabular axis. 228 THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
2 THE DEFINITION AND MEASUREMENT OF ACETABULAR ORIENTATION 229 Radiographic definitions. The orientation of the acetabular component can be determined postoperatively on anteroposterior radiographs from the alignment of radioopaque markers (with corrections for distortion caused by X-ray beam divergence and pelvic rotation (Goergen and Resnick 1975 ; Sellers, Lyles and Dorr 1988). The is the angle between the face of the cup and the transverse axis (Lewinnek et al 1978 ; Woo and Morrey 1982 ; Ackland et al 1986 ; Sarmiento et al 1990) which is the same as the angle between the longitudinal Fig. 1 Operative (OA) and (01). axis and the acetabular axis when this is projected on to the radiograph. The radiographic (RI) is therefore defined as the angle between the longitudinal axis and the acetabular axis when this is projected on to the coronal plane (Fig. 2). It is sometimes called the projected or 0 angle (Lewinnek et al 1978; Herrlin et al 1988). The technique for assessing acetabular depends on the type of radio-opaque marker. When this is an encircling wire, which is projected radiographically as an ellipse, is calculated from the relative size of the major and minor diameters of the ellipse (McLaren 1973; Lewinnek et al 1978; Ackland et al 1986). The result of these calculations gives the angle between the axis of the acetabulum and the coronal plane. The radiographic (RA) is therefore defined as the angle between the acetabular axis and the coronal plane (Fig. 2). This is sometimes called the planar or the angle, and can also be determined approximately from lateral radiographs (Lewinnek et al 1978; Woo and Morrey 1982; Herrlin et al 1988). Anatomical definitions. In anatomical studies of both normal and dysplastic hips the angle between the plane of the face of the acetabulum and the transverse plane is considered to be the of the acetabulum (Walker 1977 ; T#{246}nnis 1987). This is equivalent to the angle between the acetabular axis and the longitudinal axis. The anatomical (A!) is therefore defined as the angle between the acetabular axis and the longitudinal axis (Fig. 3). Anteversion is the angle between the acetabular axis and the coronal plane when viewed in a cranio-caudal direction (McKibbin 1970; Walker 1977 ; Calandruccio 1987). The anatomical ante-, Fig. 2 Fig. 3 Radiographic (RA) and (RI). Anatomical (AA) and (Al). VOL. 75-B, No. 2, MARCH 1993
3 230 D. W. MURRAY version (AA) is therefore defined as the angle between the transverse axis and the acetabular axis when this is projected on to the transverse plane (Fig. 3). It is similar to internal rotation ofthe acetabulum about a longitudinal body axis. Anatomical and are occasionally referred to as true or three-dimensional and (Herrlin et al 1986, 1988). Method. For any acetabular position the and defined in each of the three ways can be determined (Figs 4, 5). The three definitions can therefore be connected mathematically, and equations to do this have been derived (Appendix 1). As these equations are complex, nomograms have been constructed which may be used to convert from operative to anatomical and vice versa (Fig. 6), from radiographic to operative (Fig. 7) and from radiographic to anatomical (Fig. 8). The nomograms are used as in the following example. Harris (1980) advocated that acetabular prostheses should be inserted, at operation, with 30#{176} of and 20#{176} of. The nomogram (Fig. 6) is used to convert these operative angles to anatomical angles. The operative orientation (H) is plotted on the nomogram using the horizontal and vertical guidelines ; the operative (30#{176}) is the X (horizontal) co-ordinate, and the operative (20#{176}) is the Y (vertical) coordinate. The anatomical is obtained by selecting the dashed curve nearest to the plotted orientation. The angle printed beside this curve (30#{176})is approximately the anatomical. A more precise anatomical (31#{176}) can be determined by interpolation from the dashed curves above and below the plotted orientation. The anatomical is obtained from the continuous curves. The curve nearest the plotted deformity is selected and followed until it crosses the X axis. This point gives the approximate anatomical (35#{176}). A more precise anatomical (36#{176}) is determined by interpolation from the curves above and below. The different definitions of. DISCUSSION The photographs in Figures 4 and 5 show that the various definitions of and are different. The fundamental difference is that operative is measured around a transverse axis, anatomical around a longitudinal axis and radiographic around an oblique axis. They give, however, little indication of the magnitude of the differences. This is best appreciated by considering examples. Harris (1980) advocated that acetabular implants should have 30#{176} of operative and 20#{176} of operative. This isequivalent to 36#{176} ofanatomical and 31#{176} of anatomical. The differences between these angles are important because, though most acetabular jigs (like that of Harris) use the operative definitions, some, like Muller s (1970), use the anatomical Fig. 5 The different definitions of. definitions. Dysplastic hips commonly have 60#{176} of and 30#{176} of. These are the anatomical angles and are appreciably different from their operative equivalents, which are 48#{176} and 41#{176} respectively. It is therefore essential that whenever acetabular orientation is discussed the words and should be qualified so that their precise definitions are known. Acetabular prostheses are anteverted to allow hip flexion. As operative is a measure of acetabular flexion we recommend that the operative definitions should always be used when total hip THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
4 THE DEFINITION AND MEASUREMENT OF ACETABULAR ORIENTATION 231 Anatomical Operative Fig. 6 Nomogram to convert operative orientation to anatomical orientation and vice versa. The operative orientation (H) is plotted with its X coordinate being the operative, and its Y co-ordinate being the operative. The anatomical is determined from the continuous curves, the anatomical from the dashed curves. To convert anatomical to operative, the anatomical orientation is plotted using the curves and the operative orientation is determined from the grid lines (see text). occurred only if the acetabular cup was in more than 25#{176} of radiographic, and that when this was so, 1 5% of THRs, dislocated anteriorly. If their data are recalculated using the operative definitions then anterior dislocation occurred only in cups with more than 38#{176} of, and above 38#{176} some 21% of the THRs dislocated anteriorly. The study should therefore have concluded that acetabular components should be implanted with less than 35#{176}, not 25#{176}, of (operative). Acetabular and are often difficult to measure from anteroposterior radiographs (Appendix 2) and are better assessed by an image intensifier or, possibly, by CT (Goergen and Resnick 1975; Ghelman 1979; Schneideret al 1982; Calandruccio 1987 ; Hoiseth, Reikeras and Fonstelien 1989). The latter is not ideal as the image is distorted by the metal implant, and because it measures anatomical. In contrast, an image intensifier can directly measure operative orientation. It is initially aligned vertically over the hip and is then rotated around the transverse axis of the body until the X-ray beam is directed across the face Operative Anatomical / , Radiographic Radiographic Fig. 7 Nomogram to convert radiographic orientation to operative orientation and vice versa. The radiographic orientation is plotted with its X coordinate being the radiographic, and its Y co-ordinate being the radiographic. The operative is determined from the continuous curves, the operative from the dashed curves. To convert operative to radiographic, the operative orientation is plotted using the curves and the radiographic orientation is determined from the grid lines (see text) Radiographic Fig. 8 Nomogram to convert radiographic orientation to anatomical orientation and vice versa. The radiographic orientation is plotted with its X co-ordinate being the radiographic, and its Y co-ordinate being the radiographic. The anatomical is determined from the continuous curves, the anatomical from the dashed curves. To convert anatomical to radiographic, the anatomical orientation is plotted using the curves and the radiographic orientation is determined from the grid lines (see text). replacements (THR) are described. The use of these definitions has other advantages. Operative is easily assessed at operation, as the prosthesis is viewed from a lateral position ; and the influence of pelvic and lumbar spine flexion can be allowed for since it can be numerically added to operative. The radiographic orientation, determined from an anteropostenor radiograph, should always be converted to the operative orientation before being quoted. If this is not done it may cause confusion. For example, Lewinnek et al (1978) found that, after THR, anterior dislocation ofthe acetabulum. The operative is the angle through which the image intensifier has been rotated, and the operative is that seen on the screen. In assessing dysplastic acetabula, it is necessary to know not only the degree of cover of the femoral head superiorly but also the relative cover anterosuperiorly and posterosuperiorly. This is best quantified by the anatomical. We therefore recommend that when discussing dysplastic acetabula the anatomical definitions be used. The anatomical angle can be determined directly from CT scans or from VOL. 75-B, No. 2, MARCH 1993
5 232 D. w. MURRAY magnetic resonance images with transverse cuts (Browning, Rosenkrantz and Tarquinio 1982; Gugenheim et al 1982 ; Hoiseth et al 1989 ; Anda, Terjesen and Kvistad 1991). As the inferior acetabular margin is difficult to define, the anatomical is not often used in clinical practice. Instead, superior acetabular cover is quantified by the centre-edge angle (Wiberg 1939) which is simpler to determine. Conclusions. The anatomical, operative, and radiographic definitions of and are all different. It is therefore essential, whenever acetabular orientation is discussed, to qualify the words and so that their precise definitions are known. We present nomograms which can be used to convert from one definition to another. Operative definitions should be used to describe the alignment of acetabular prostheses. The orientation is best determined by the use of an image intensifier rotated about the transverse body axis. If the orientation is determined from an anteroposterior radiograph it should be converted to operative orientation before being quoted. Anatomical definitions should be used for describing the orientation of normal and dysplastic acetabula. Anatomical is best determined from CT or MR images, since it is measured in the transverse plane. APPENDIX 1 Equations connecting operative (0), radiographic (R), anatomical (A), (I), and (A): Tan(OA) = Tan(RA) #{247} Cos(RI) Sin(OI) = Sin(RI) x Cos(RA) Tan(OA) = Sin(AA) x Tan(AI) Sin(OI) = Sin(AI) x Cos(AA) Tan(AA) = Sin(OA) - Tan(OI) Cos(AI) = Cos(OI) x Cos(OA) Tan(AA) = Tan(RA) + Sin(RI) Cos(AI) = Cos(RI) x Cos(RA) Sin(RA) = Sin(OA) x Cos(OI)Tan(RI) = Tan(OI) + Cos(OA) Sin(RA) = Sin(AA) x Sin(AI) Tan(RI) = Tan(AI) x Cos(AA) #{149} this is the same as Tanc = Tan4 x CosO, which was quoted by Lewinnek et al (1978), and used by Ackland et al (1986) to construct a numerical table. body axis (Lewinnek et al 1978; Ackland et al 1986). When the marker is a semicircular wire which passes over the top of the socket, the apparent (CI) is the angle between the transverse body axis and a line joining the ends of the wire. If the socket is not anteverted the wire lies in the sagittal plane and the apparent is the same as the radiographic. If the socket is anteverted then the apparent is an overestimate of the radiographic : Tan(RI) = Tan(CI) + Cos2(OA) The greater the the greater the overestimate : if, for example, the socket is anteverted 30#{176} then the overestimate is 20%. APPENDIX 2 The method for determining radiographic from anteropostenor radiographs depends on the type of radio-opaque marker. When this is an encircling wire, which is projected as an ellipse, the is the angle between the major axis of the ellipse and the transverse The author would like to thank Mr M. K. D A. Benson for his help and advice. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. REFERENCES Ackland MK, Bourne WB, Uhthoff HK. Anteversion of the acetabular cup : measurement of angle after total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1986; 68-B : Anda 5, Terjesen T, Kvistad KA. Computed tomography measurements of the acetabulum in adult dysplastic hips: which level is appropriate? Ske/eta/Radio/ 1991 ; 20: Browning WH, ROSenkT*ntZ H, Tarquinio T. Computed tomography in congenital hip dislocation : the role of acetabular. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1982; 64-A : CaIaDdrUCCIORA. Arthroplastyofhip. In : Crenshaw AH, ed. Campbell s operative orthopaedics. Vol. 2. St Louis: CV Mosby, 1987; Charuley J. Low friction arthrop/asty of the hip: theory and practice. Berlin, etc : Springer-Verlag, Ghelman B. Radiographic localisation of the acetabular component of a hip prosthesis. Radiology 1979; 130: Goergen TG, Resnick D. Evaluation ofacetabular following total hip arthroplasty: necessity of proper centring. Br J Radio/ 1975 ;48: Gugenheim JJ, Geeson LP, Sadler C,Tullos HS. Pathologic morphology of the acetabulum in paralytic and congenital hip instability. JPediatrOrthop 1982; 2: Harris WH. Advances in surgical technique for total hip replacement. C/in Orthop 1980; 146: Hernia K, Selvik G, Pettersson H. Space orientation of total hip prosthesis : a method for 3-dimensional determination. Acta Radiol (Diagn) 1986; 27 : Herrlln K, Pettersson H, Selvik G. Comparison of two- and threedimensional methods for assessment of orientation of the total hip prosthesis. Acta Radio/ 1988; 29: HOISeth A, Reikeras 0, Foastelien E. Lack of correlation between femoral neck and acetabular orientation. Acta Orthop Scand 1989; 60:93-6. Lewinnek GE, Lawis JL, Tan R, Compere CL, Zimmerman JR. Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone JointSurg[AmJ 1978; 60-A : McKee GK. Development of total prosthetic replacement of the hip. C/in Orthop 1970; 72 : McKibbin B. Anatomical factors in the stability of the hip joint in the newborn. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1970; 52-B : McLaren RH. Prosthetic hip angulation. Radiology 1973 ; 107: MUller ME. Total hip prostheses. C/in Orthop 1970; 72: Sarmiento A, Ebramzadeh E, Gogan WJ, McKellop HA. Cup containment and orientation in cemented total hip arthroplasties. J Bone JointSurg[Br] 1990; 72-B : Schneider R, Frelberger RH, Ghelman B, Ranawat CS. Radiologic evaluation of painfuljoint prostheses. C/in Orth 1982; 170:IS6-68. Sellers RG, Lyles D, Dorr LD. The effect of pelvic rotation on alpha and theta angles in total hip arthroplasty. Cont Ortlz 1988; 17: T#{246}IIniSD. Congenita/ dysp/asia and dislocation ofthe hip in children and adults. Berlin, etc : Springer-Verlag, Walker PS. Human joints and their artficio/ replacements. Springfield: Charles C Thomas, Wiberg G. Studies on dysplastic acetabula and congenital subluxation of the hip joint : with special reference to the complication of osteoarthritis. Acta Chir Scand 1939; 83:Suppl 58. Woo RYG, Money BF. Dislocations after total hip arthroplasty. JBone Joint Surg [Am] 1982; 64-A : THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
Cup Alignment Error Model for Total Hip Arthroplasty
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 437, pp. 132 137 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Cup Alignment Error Model for Total Hip Arthroplasty Alon Wolf, PhD; Anthony M. DiGioia, III, MD; Andrew
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 437, pp. 132 137 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Cup Alignment Error Model for Total Hip Arthroplasty Alon Wolf, PhD; Anthony M. DiGioia, III, MD; Andrew
Measurement of the Acetabular Cup Anteversion on Simulated Radiographs
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 24 No. 3 2009 Measurement of the Acetabular Cup Anteversion on Simulated Radiographs Chen-Kun Liaw, MD,*y 1 Rong-Sen Yang, MD, PhD,z 1 Sheng-Mou Hou, MD, PhD, MPH,z Tai-Yin
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 24 No. 3 2009 Measurement of the Acetabular Cup Anteversion on Simulated Radiographs Chen-Kun Liaw, MD,*y 1 Rong-Sen Yang, MD, PhD,z 1 Sheng-Mou Hou, MD, PhD, MPH,z Tai-Yin
Computer Aided Evaluation of Total Hip Prosthesis Stability
 Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 2 (1998), No. 2, 141 149 Computer Aided Evaluation of Total Hip Prosthesis Stability Natasa D. Miljkovic, Goran M. Ercegan, Radovan B. Stulic, and Zoran B. Jandric
Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 2 (1998), No. 2, 141 149 Computer Aided Evaluation of Total Hip Prosthesis Stability Natasa D. Miljkovic, Goran M. Ercegan, Radovan B. Stulic, and Zoran B. Jandric
The Spatial Location of Impingement in Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 15 No. 3 2000 The Spatial Location of Impingement in Total Hip Arthroplasty Motoi Yamaguchi, MD, PhD,* Toshihiro Akisue, MD, PhD,* Thomas W. Bauer, MD, PhD,* and Yasushi
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 15 No. 3 2000 The Spatial Location of Impingement in Total Hip Arthroplasty Motoi Yamaguchi, MD, PhD,* Toshihiro Akisue, MD, PhD,* Thomas W. Bauer, MD, PhD,* and Yasushi
Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide Toacetabular Component Anteversion
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2015), PP 65-69 www.iosrjournals.org Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2015), PP 65-69 www.iosrjournals.org Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide
Reliability and validity of measuring version of the acetabular component
 HIP Reliability and validity of measuring version of the acetabular component J-H. Nho, Y-K. Lee, H. J. Kim, Y-C. Ha, Y-S. Suh, K-H. Koo From Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Gyeonggido, Korea
HIP Reliability and validity of measuring version of the acetabular component J-H. Nho, Y-K. Lee, H. J. Kim, Y-C. Ha, Y-S. Suh, K-H. Koo From Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Gyeonggido, Korea
Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View
 Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View Ryo Mori 1, Yuji Yasunaga 2, Takuma Yamasaki 1, Michio Hamanishi 1, Takeshi Shoji 1, Sotaro Izumi 1, Susumu Hachisuka
Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View Ryo Mori 1, Yuji Yasunaga 2, Takuma Yamasaki 1, Michio Hamanishi 1, Takeshi Shoji 1, Sotaro Izumi 1, Susumu Hachisuka
Are Portable Imaging Intraoperative Radiographs Helpful for Assessing Adequate Acetabular Cup Positioning in Total Hip Arthroplasty?
 J Korean Med Sci 2009; 24: 315-9 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.315 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Are Portable Imaging Intraoperative Radiographs Helpful for Assessing Adequate
J Korean Med Sci 2009; 24: 315-9 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.315 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Are Portable Imaging Intraoperative Radiographs Helpful for Assessing Adequate
Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 806157, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/806157 Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt Hiroyuki
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 806157, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/806157 Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt Hiroyuki
Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination. Roberts, Garlick
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination. Roberts, Garlick
Why large-head metal-on-metal hip replacements are painful
 HIP Why large-head metal-on-metal hip replacements are painful THE ANATOMICAL BASIS OF PSOAS IMPINGEMENT ON THE FEMORAL HEAD-NECK JUNCTION J. P. Cobb, K. Davda, A. Ahmad, S. J. Harris, M. Masjedi, A. J.
HIP Why large-head metal-on-metal hip replacements are painful THE ANATOMICAL BASIS OF PSOAS IMPINGEMENT ON THE FEMORAL HEAD-NECK JUNCTION J. P. Cobb, K. Davda, A. Ahmad, S. J. Harris, M. Masjedi, A. J.
Research Article Clinical Validation of Computer-Assisted Navigation in Total Hip Arthroplasty
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 171783, 6 pages doi:10.4061/2011/171783 Research Article Clinical Validation of Computer-Assisted Navigation in Total Hip
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 171783, 6 pages doi:10.4061/2011/171783 Research Article Clinical Validation of Computer-Assisted Navigation in Total Hip
Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2. Preparation of the Acetabulum 4. Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5.
 Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
The arc of pelvic motion has been shown to be as great as 70 through sit to stand activities 1 DiGioia CORR 2006
 The arc of pelvic motion has been shown to be as great as 70 through sit to stand activities 1 DiGioia CORR 2006 Overview Every patient moves differently 1 and their total hip replacement should be optimised
The arc of pelvic motion has been shown to be as great as 70 through sit to stand activities 1 DiGioia CORR 2006 Overview Every patient moves differently 1 and their total hip replacement should be optimised
Influences of head/neck ratio and femoral antetorsion on the safe-zone of operative acetabular orientations in total hip arthroplasty
 . 206. Chinese Journal of Traumatology 2010; 13(4):206-211 Influences of head/neck ratio and femoral antetorsion on the safe-zone of operative acetabular orientations in total hip arthroplasty LI Yong-jiang
. 206. Chinese Journal of Traumatology 2010; 13(4):206-211 Influences of head/neck ratio and femoral antetorsion on the safe-zone of operative acetabular orientations in total hip arthroplasty LI Yong-jiang
CONGENITAL HIP DISEASE IN YOUNG ADULTS CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT WITH THA. Th. KARACHALIOS, MD, DSc PROF IN ORTHOPAEDICS
 CONGENITAL HIP DISEASE IN YOUNG ADULTS CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT WITH THA Th. KARACHALIOS, MD, DSc PROF IN ORTHOPAEDICS EDITOR IN CHIEF HIP INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF THESSALIA, LARISA HELLENIC REPUBLIC
CONGENITAL HIP DISEASE IN YOUNG ADULTS CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT WITH THA Th. KARACHALIOS, MD, DSc PROF IN ORTHOPAEDICS EDITOR IN CHIEF HIP INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF THESSALIA, LARISA HELLENIC REPUBLIC
Effect of Superior Placement of the Hip Center on Abductor Muscle Strength in Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 24 No. 2 2009 Effect of Superior Placement of the Hip Center on Abductor Muscle Strength in Total Hip Arthroplasty Takahiko Kiyama, MD, Masatoshi Naito, MD, PhD, Hiroshi
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 24 No. 2 2009 Effect of Superior Placement of the Hip Center on Abductor Muscle Strength in Total Hip Arthroplasty Takahiko Kiyama, MD, Masatoshi Naito, MD, PhD, Hiroshi
Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult
 Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult STEPHEN B. MURPHY, M.D., PETER K. KIJEWSKI, PH.D.,* MICHAEL B. MILLIS, M.D., AND ANDREW HARLESS, A.B.* Hip dysplasia is a major cause of osteoarthrosis
Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult STEPHEN B. MURPHY, M.D., PETER K. KIJEWSKI, PH.D.,* MICHAEL B. MILLIS, M.D., AND ANDREW HARLESS, A.B.* Hip dysplasia is a major cause of osteoarthrosis
Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 166-173 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign Clément M.L. WERNER,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 166-173 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign Clément M.L. WERNER,
Plain radiographs remain the primary skeletal imaging
 S84 Measuring Acetabular Component Position on Lateral Radiographs Ischio-Lateral Method Nicholas Pulos, B.A., John V. Tiberi III, M.D., and Thomas P. Schmalzried, M.D. Abstract The standard method for
S84 Measuring Acetabular Component Position on Lateral Radiographs Ischio-Lateral Method Nicholas Pulos, B.A., John V. Tiberi III, M.D., and Thomas P. Schmalzried, M.D. Abstract The standard method for
Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule
 Pediatr Radiol (2017) 47:817 821 DOI 10.1007/s00247-017-3802-4 COMMENTARY Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule H. Theodore Harcke 1 & B. Pruszczynski 2 Received: 27 October 2016 /Revised:
Pediatr Radiol (2017) 47:817 821 DOI 10.1007/s00247-017-3802-4 COMMENTARY Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule H. Theodore Harcke 1 & B. Pruszczynski 2 Received: 27 October 2016 /Revised:
Continuing the Tradition. VerSys Heritage Hip System
 Continuing the Tradition VerSys Heritage Hip System Heritage Following the Tradition The low-friction hip prosthesis developed by Sir John Charnley has more than a 20-year history of outstanding results.
Continuing the Tradition VerSys Heritage Hip System Heritage Following the Tradition The low-friction hip prosthesis developed by Sir John Charnley has more than a 20-year history of outstanding results.
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hamamatsu Medical Center ABSTRACT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 71. 145 ~ 150, 2009 ORIGINAL PAPER AUTOGENOUS BULK STRUCTURAL BONE GRAFTING FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF THE ACETABLUM IN PRIMARY TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: AVERAGE 12-YEAR FOLLOW-UP TETSUO MASUI,
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 71. 145 ~ 150, 2009 ORIGINAL PAPER AUTOGENOUS BULK STRUCTURAL BONE GRAFTING FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF THE ACETABLUM IN PRIMARY TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: AVERAGE 12-YEAR FOLLOW-UP TETSUO MASUI,
The role of the transverse acetabular ligament in total hip arthroplasty
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 135-140 ASPECT OF CURRENT MANAGEMENT The role of the transverse acetabular ligament in total hip arthroplasty Sameer Jain, Joseph Aderinto, Peter Bobak From Chapel Allerton
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 135-140 ASPECT OF CURRENT MANAGEMENT The role of the transverse acetabular ligament in total hip arthroplasty Sameer Jain, Joseph Aderinto, Peter Bobak From Chapel Allerton
CLINICAL PAPER / ORTHOPEDIC
 HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes
 The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes Omer Mei-Dan, MD Dylan Jewell, BSc, MSc, FRCS Tigran Garabekyan, MD Jason Brockwell, FRCSEdOrth
The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes Omer Mei-Dan, MD Dylan Jewell, BSc, MSc, FRCS Tigran Garabekyan, MD Jason Brockwell, FRCSEdOrth
DISLOCATION OF THE TOTAL HIP Arthroplasty
 DISLOCATION OF THE TOTAL HIP Arthroplasty The point must be made that an occasional post- operative dislocation... is no disgrace. Patients can sometimes be quite irresponsible and unreasonable during
DISLOCATION OF THE TOTAL HIP Arthroplasty The point must be made that an occasional post- operative dislocation... is no disgrace. Patients can sometimes be quite irresponsible and unreasonable during
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE DePuy Synthes DURALOC Surgical Technique CONTENTS Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE DePuy Synthes DURALOC Surgical Technique CONTENTS Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum
Functional safe zone. Safe zone
 Functional safe zone Every patient moves differently 1, and the amount of pelvic rotation through functional activities should be accounted for with total hip replacement. Pelvic tilt can change significantly
Functional safe zone Every patient moves differently 1, and the amount of pelvic rotation through functional activities should be accounted for with total hip replacement. Pelvic tilt can change significantly
Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement
 Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Hamamatsu University School of Medicine,
Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Hamamatsu University School of Medicine,
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
Poor accuracy of freehand cup positioning during total hip arthroplasty
 Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2007) 127:375 379 DOI 10.1007/s00402-007-0294-y ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Poor accuracy of freehand cup positioning during total hip arthroplasty B. H. Bosker C. C. P. M. Verheyen W.
Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2007) 127:375 379 DOI 10.1007/s00402-007-0294-y ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Poor accuracy of freehand cup positioning during total hip arthroplasty B. H. Bosker C. C. P. M. Verheyen W.
Acetabular Center Axis: Is It the Future of Hip Navigation?
 Acetabular Center Axis: Is It the Future of Hip Navigation? SAM HAKKI, MD; VICTOR BILOTTA, MD; J. DANIEL OLIVEIRA, MD; LUIS DORDELLY, BS abstract There are 2 distinct methods of cup navigation in total
Acetabular Center Axis: Is It the Future of Hip Navigation? SAM HAKKI, MD; VICTOR BILOTTA, MD; J. DANIEL OLIVEIRA, MD; LUIS DORDELLY, BS abstract There are 2 distinct methods of cup navigation in total
Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year
 Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year H. Pandit, C. Jenkins, D. J. Beard, J. Gallagher, A. J. Price, C. A. F. Dodd, J. W. Goodfellow, D. W. Murray From
Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year H. Pandit, C. Jenkins, D. J. Beard, J. Gallagher, A. J. Price, C. A. F. Dodd, J. W. Goodfellow, D. W. Murray From
Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
 M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE PRODUCT OF LONG-TERM CLINICAL EXPERIENCE The TRILOC cemented UHMWPE cup is a direct descendant of
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE PRODUCT OF LONG-TERM CLINICAL EXPERIENCE The TRILOC cemented UHMWPE cup is a direct descendant of
Misinterpretation of cup anteversion in total hip arthroplasty using planar radiography
 DOI 10.1007/s00402-006-0163-0 ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Misinterpretation of cup anteversion in total hip arthroplasty using planar radiography Axel Marx Æ Marius von Knoch Æ Jörg Pförtner Æ Matthias Wiese Æ
DOI 10.1007/s00402-006-0163-0 ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Misinterpretation of cup anteversion in total hip arthroplasty using planar radiography Axel Marx Æ Marius von Knoch Æ Jörg Pförtner Æ Matthias Wiese Æ
Hip spine relations and sagittal balance clinical consequences
 DO 10.1007/s00586-011-1937-9 REVEW ARTCLE Hip spine relations and sagittal balance clinical consequences Jean-Yves Lazennec Adrien Brusson Marc-Antoine Rousseau Received: 11 July 2011 / Accepted: 11 July
DO 10.1007/s00586-011-1937-9 REVEW ARTCLE Hip spine relations and sagittal balance clinical consequences Jean-Yves Lazennec Adrien Brusson Marc-Antoine Rousseau Received: 11 July 2011 / Accepted: 11 July
Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF DYSPLASIA
 PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF HIP DYSPLASIA STUART J. M. DAVIES, GEOFFREY WALKER From Queen Mary s Hospitalfor Children, Carshalton Ten children who had clinically stable hips at birth were radiographed
PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF HIP DYSPLASIA STUART J. M. DAVIES, GEOFFREY WALKER From Queen Mary s Hospitalfor Children, Carshalton Ten children who had clinically stable hips at birth were radiographed
*smith&nephew CONTOUR
 Surgical Technique *smith&nephew CONTOUR Acetabular Rings CONTOUR Acetabular Rings Surgical technique completed in conjunction with Joseph Schatzker MD, BSc (Med.), FRCS (C) Allan E. Gross, MD, FRCS (C)
Surgical Technique *smith&nephew CONTOUR Acetabular Rings CONTOUR Acetabular Rings Surgical technique completed in conjunction with Joseph Schatzker MD, BSc (Med.), FRCS (C) Allan E. Gross, MD, FRCS (C)
Subluxation of the hip presenting for the first time
 The treatment of subluxation of the hip in children over the age of four years John A. Fixsen, Patrick L. S. Li From the Hospitals for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London, England Subluxation of
The treatment of subluxation of the hip in children over the age of four years John A. Fixsen, Patrick L. S. Li From the Hospitals for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London, England Subluxation of
A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:319 324 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0600-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip Anthony Cooper
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:319 324 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0600-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip Anthony Cooper
Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 2, p. 159 166 159) Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study Al Razi Orthopedic Hospital,
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 2, p. 159 166 159) Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study Al Razi Orthopedic Hospital,
The Influence of Spinal Deformities on Acetabular Orientation in Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Influence of Spinal Deformities on Acetabular Orientation in Total Hip Arthroplasty S. SAMUEL BEDERMAN MD PhD FRCSC Scoliosis & Spine Tumor Center S. SAMUEL BEDERMAN MD PhD FRCSC disclosures October
The Influence of Spinal Deformities on Acetabular Orientation in Total Hip Arthroplasty S. SAMUEL BEDERMAN MD PhD FRCSC Scoliosis & Spine Tumor Center S. SAMUEL BEDERMAN MD PhD FRCSC disclosures October
HipNav: Pre-operative Planning and Intra-operative Navigational Guidance for Acetabular Implant Placement in Total Hip Replacement Surgery
 Proc. of the Computer Assisted Orthopaedic Surgery Symposium, Bern, Switzerland, November, 1995 HipNav: Pre-operative Planning and Intra-operative Navigational Guidance for Acetabular Implant Placement
Proc. of the Computer Assisted Orthopaedic Surgery Symposium, Bern, Switzerland, November, 1995 HipNav: Pre-operative Planning and Intra-operative Navigational Guidance for Acetabular Implant Placement
Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement?
 Cite this article as: Cooke WR, Gill HS, Murray DW, Ostlere SJ. Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement? Br J Radiol 2013;86:20120182. SHORT COMMUNICATION
Cite this article as: Cooke WR, Gill HS, Murray DW, Ostlere SJ. Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement? Br J Radiol 2013;86:20120182. SHORT COMMUNICATION
Where to Draw the Line:
 Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
Kordelle J, M.D. 1), Millis M, M.D. 2), Jolesz FA, M.D. 1), Kikinis R, M.D. 1), Richolt JA, M.D. 3)
 Three-dimensional analysis of the proximal femur in patients with slipped capital femoral epiphysis based on computed tomography. Kordelle J, M.D. 1), Millis M, M.D. 2), Jolesz FA, M.D. 1), Kikinis R,
Three-dimensional analysis of the proximal femur in patients with slipped capital femoral epiphysis based on computed tomography. Kordelle J, M.D. 1), Millis M, M.D. 2), Jolesz FA, M.D. 1), Kikinis R,
DISLOCATION OF TOTAL HIP PROSTHESES*
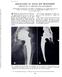 VOL. 115, No. 3 DISLOCATION OF TOTAL HIP PROSTHESES* API EARANCE ON FRONTAL ROENTGENOGRAMS By RICHARI) H. DAFFNER, M.D.,f JOHN A. GEHWEILER, M.l).,f JOHN OLSON, M.D.,f JAMES W. WILSON, PH.1)., M.l)., and
VOL. 115, No. 3 DISLOCATION OF TOTAL HIP PROSTHESES* API EARANCE ON FRONTAL ROENTGENOGRAMS By RICHARI) H. DAFFNER, M.D.,f JOHN A. GEHWEILER, M.l).,f JOHN OLSON, M.D.,f JAMES W. WILSON, PH.1)., M.l)., and
Three-dimensional CT analysis to determine acetabular retroversion and the implications for the management of femoro-acetabular impingement
 Three-dimensional CT analysis to determine acetabular retroversion and the implications for the management of femoro-acetabular impingement W. Dandachli, S. Ul Islam, M. Liu, R. Richards, M. Hall-Craggs,
Three-dimensional CT analysis to determine acetabular retroversion and the implications for the management of femoro-acetabular impingement W. Dandachli, S. Ul Islam, M. Liu, R. Richards, M. Hall-Craggs,
Stability without compromise. Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert
 Stability without compromise Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert History of Dislocation and Constrained Acetabular Inserts The Need for a Better Solution The Problem Dislocation is the second most common
Stability without compromise Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert History of Dislocation and Constrained Acetabular Inserts The Need for a Better Solution The Problem Dislocation is the second most common
Navigation for total hip arthroplasty
 Interact Surg (2008) 3: 128 134 Springer 2008 DOI 10.1007/s11610-008-0084-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Navigation for total hip arthroplasty O. Guyen 1,V.Pibarot 1, J. Bejui-Hugues 2,SCORGroup 1 Service de chirurgie
Interact Surg (2008) 3: 128 134 Springer 2008 DOI 10.1007/s11610-008-0084-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Navigation for total hip arthroplasty O. Guyen 1,V.Pibarot 1, J. Bejui-Hugues 2,SCORGroup 1 Service de chirurgie
Shunsaku Nishihara 1, Nobuhiko Sugano 1, Takashi Nishii 1, Hisashi Tanaka 2, Hideki Yoshikawa 1, and Takahiro Ochi 1
 J Orthop Sci (2003) 8:352 360 Comparison of the fit and fill between the Anatomic Hip femoral component and the VerSys Taper femoral component using virtual implantation on the ORTHODOC workstation Shunsaku
J Orthop Sci (2003) 8:352 360 Comparison of the fit and fill between the Anatomic Hip femoral component and the VerSys Taper femoral component using virtual implantation on the ORTHODOC workstation Shunsaku
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Good Results of Later Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 23 No. 2 2008 Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Good Results of Later Total Hip Arthroplasty 7135 Primary Total Hip Arthroplasties after Developmental Dysplasia of the
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 23 No. 2 2008 Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Good Results of Later Total Hip Arthroplasty 7135 Primary Total Hip Arthroplasties after Developmental Dysplasia of the
Socket wall addition device in the treatment of recurrent hip prosthesis dislocation
 Acta Orthopaedica 2006; 77 (1): 87 91 87 Socket wall addition device in the treatment of recurrent hip prosthesis dislocation Good outcome in 12 patients followed for 4.5 (1 9) years Anders G Enocson 1,
Acta Orthopaedica 2006; 77 (1): 87 91 87 Socket wall addition device in the treatment of recurrent hip prosthesis dislocation Good outcome in 12 patients followed for 4.5 (1 9) years Anders G Enocson 1,
ADEPT Extra Fixation Cup. Operative Technique. Delivering Results Through Performance
 ADEPT Extra Fixation Cup Operative Technique Delivering Results Through Performance Contents Section 1 Introduction 3 Section 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Section 3 Preparation of the Extra Fixation
ADEPT Extra Fixation Cup Operative Technique Delivering Results Through Performance Contents Section 1 Introduction 3 Section 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Section 3 Preparation of the Extra Fixation
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/38039 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Embden, Daphne van Title: Facts and fiction in hip fracture treatment Issue Date:
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/38039 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Embden, Daphne van Title: Facts and fiction in hip fracture treatment Issue Date:
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP
 THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER 2: RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF THE KNEE Radiographic Evaluation of the Knee Presented by: R. Michael Meneghini, MD COPYRIGHT 2016 THE KNEE SOCIETY Disclosures
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER 2: RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF THE KNEE Radiographic Evaluation of the Knee Presented by: R. Michael Meneghini, MD COPYRIGHT 2016 THE KNEE SOCIETY Disclosures
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. 78 Int J Res Med. 2013; 2(1);78-82 e ISSN: p ISSN: Morphological aspect of acetabulum of hip bone
 AN OSSEOUS STUDY OF MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECT OF ACETABULUM OF HIP BONE Kintu Vyas 1*,Bhavesh Shroff 2,Kalpesh Zanzrukiya 3 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Anatomy, Medical College, Baroda. 2 Assistant
AN OSSEOUS STUDY OF MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECT OF ACETABULUM OF HIP BONE Kintu Vyas 1*,Bhavesh Shroff 2,Kalpesh Zanzrukiya 3 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Anatomy, Medical College, Baroda. 2 Assistant
Early failure of total hip replacements implanted at distant hospitals to reduce waiting lists
 : 31 35 doi 10.1308/1478708051450 Audit Early failure of total hip replacements implanted at distant hospitals to reduce waiting lists Jac Ciampolini, Matthew JW Hubble Princess Elizabeth Orthopaedic Centre,
: 31 35 doi 10.1308/1478708051450 Audit Early failure of total hip replacements implanted at distant hospitals to reduce waiting lists Jac Ciampolini, Matthew JW Hubble Princess Elizabeth Orthopaedic Centre,
Integral 180 Surgical Technique
 Integral 180 Surgical Technique The Integral 180 and 225 are part of the Alliance Family Total Hip System. The Integral 225 femoral component is marketed for use with bone cement in the United States.
Integral 180 Surgical Technique The Integral 180 and 225 are part of the Alliance Family Total Hip System. The Integral 225 femoral component is marketed for use with bone cement in the United States.
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT:
 THR Prosthesis Design TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT: PROSTHESIS DESIGN FEATURES JESS JOHNSTON & MELINDA ZIETH History of Hip Prosthesis Joint Replacement Registry Implant Design Technology & Future History and
THR Prosthesis Design TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT: PROSTHESIS DESIGN FEATURES JESS JOHNSTON & MELINDA ZIETH History of Hip Prosthesis Joint Replacement Registry Implant Design Technology & Future History and
Experimental Prediction of Contact Area in Hip Replacement and Hemi- Arthroplasty
 Experimental Prediction of Contact Area in Hip Replacement and Hemi- Arthroplasty Qianqian Wang, John Fisher, Sophie Williams. Institute of Medical and Biological Engineering, School of Mechanical Engineering,
Experimental Prediction of Contact Area in Hip Replacement and Hemi- Arthroplasty Qianqian Wang, John Fisher, Sophie Williams. Institute of Medical and Biological Engineering, School of Mechanical Engineering,
Reprint requests: Dr Brenda Dower CLINICAL ARTICLE SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Spring 2012 Vol 11 No 3 / Page 29
 CLINICAL ARTICLE SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Spring 2012 Vol 11 No 3 / Page 29 C L I N I C A L A RT I C L E The results of a cementless acetabular component combined with impaction bone grafting in patients
CLINICAL ARTICLE SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Spring 2012 Vol 11 No 3 / Page 29 C L I N I C A L A RT I C L E The results of a cementless acetabular component combined with impaction bone grafting in patients
Disclosure. Direct Anterior THA via Extension Table. History 11/3/2015
 Direct Anterior THA via Extension Table J. Masonis, M.D. OrthoCarolina Hip & Knee Center Chief Adult Hip & Knee reconstruction Carolinas Medical Center Disclosure Consultant & Design Smith & Nephew Zimmer
Direct Anterior THA via Extension Table J. Masonis, M.D. OrthoCarolina Hip & Knee Center Chief Adult Hip & Knee reconstruction Carolinas Medical Center Disclosure Consultant & Design Smith & Nephew Zimmer
PAL Pelvic Alignment Level
 PAL Pelvic Alignment Level Surgical Protocol For consistency during surgery Pelvic Alignment Level (PAL) Features Pelvic Alignment Level Surgical Protocol To Table To Floor 1. Patient Positioning & Preparation
PAL Pelvic Alignment Level Surgical Protocol For consistency during surgery Pelvic Alignment Level (PAL) Features Pelvic Alignment Level Surgical Protocol To Table To Floor 1. Patient Positioning & Preparation
AGGRESSIVE GRANULOMATOUS LESIONS AFTER HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 AGGRESSIVE GRANULOMATOUS LESIONS AFTER HIP ARTHROPLASTY KAJ TALLROTH, ANTTI ESKOLA, SEPPO SANTAVIRTA, YRJ T. KONTTINEN, T. SAM LINDHOLM From the Orthopaedic Hospitalofthe Invalid Foundation, Helsinki We
AGGRESSIVE GRANULOMATOUS LESIONS AFTER HIP ARTHROPLASTY KAJ TALLROTH, ANTTI ESKOLA, SEPPO SANTAVIRTA, YRJ T. KONTTINEN, T. SAM LINDHOLM From the Orthopaedic Hospitalofthe Invalid Foundation, Helsinki We
Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo?
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs: Report of Two Cases
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 519254, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/519254 Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs:
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 519254, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/519254 Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs:
Does Native Combined Anteversion Influence Pain Onset in Patients With Dysplastic Hips?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:3716 3722 DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4373-z Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 INTERNATIONAL
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:3716 3722 DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4373-z Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 INTERNATIONAL
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 06 Page June 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i6.18 Assessment of Orientation and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i6.18 Assessment of Orientation and
PROCEEDINGS September The Cutting Edge in Veterinary Orthopaedics CE. Ludwig Maximilians Universität
 Close this window to return to IVIS PROCEEDINGS MUNICH, GERMANY 10-14 September 2008 The Cutting Edge in Veterinary Orthopaedics CE Ludwig Maximilians Universität European Society of Veterinary Orthopaedics
Close this window to return to IVIS PROCEEDINGS MUNICH, GERMANY 10-14 September 2008 The Cutting Edge in Veterinary Orthopaedics CE Ludwig Maximilians Universität European Society of Veterinary Orthopaedics
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
M-SERIES. Modular Femoral Stem AN ACCURATE MATCH EVERY TIME
 M-SERIES Modular Femoral Stem AN ACCURATE MATCH EVERY TIME 54 Extension 114 Flexion High How do you ensure optimal post-operative joint stability? MECHANICAL RANGE OF MOTION Cup Position: 45 degrees abduction,
M-SERIES Modular Femoral Stem AN ACCURATE MATCH EVERY TIME 54 Extension 114 Flexion High How do you ensure optimal post-operative joint stability? MECHANICAL RANGE OF MOTION Cup Position: 45 degrees abduction,
Trident All Poly Acetabular System
 X Trident All Poly Acetabular System Surgeon Contributors: Chitranjan Ranawat, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY Jose A. Rodriguez, M.D. Lenox Hill Hospital New York, NY Vijay J. Rasquinha,
X Trident All Poly Acetabular System Surgeon Contributors: Chitranjan Ranawat, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY Jose A. Rodriguez, M.D. Lenox Hill Hospital New York, NY Vijay J. Rasquinha,
S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RECOVERY FUNCTION SURVIVORSHIP DePuy believes in an approach to total hip replacement that places equal importance on recovery, function and survivorship. The DePuy PROXIMA Hip System
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RECOVERY FUNCTION SURVIVORSHIP DePuy believes in an approach to total hip replacement that places equal importance on recovery, function and survivorship. The DePuy PROXIMA Hip System
Hip osteoarthritis and dysplasia in Chinese men
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1995; 54: 965-969 965 Department of Community and Family Medicine, The Chinese University ofhong Kong, Hong Kong E M C Lau F Lin Orthopaedic and Traumatology Unit, Tuen
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1995; 54: 965-969 965 Department of Community and Family Medicine, The Chinese University ofhong Kong, Hong Kong E M C Lau F Lin Orthopaedic and Traumatology Unit, Tuen
DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc. 700 Orthopaedic Drive Warsaw, IN USA Tel: +1 (800) Fax: +1 (574)
 References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
ORIGINAL PAPER. Aleksi Reito & Timo Puolakka & Antti Paakkala & Jorma Pajamäki
 International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2012) 36:519 525 DOI 10.1007/s00264-011-1328-1 ORIGINAL PAPER Assessment of inter- and intra-observer reliability in the determination of radiographic version and inclination
International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2012) 36:519 525 DOI 10.1007/s00264-011-1328-1 ORIGINAL PAPER Assessment of inter- and intra-observer reliability in the determination of radiographic version and inclination
All Ceramic Tripolar THA to Prevent Dislocations in Risky Patients
 Chapter 6 All Ceramic Tripolar THA to Prevent Dislocations in Risky Patients Jean-Yves Lazennec, Adrien Brusson and Marc Antoine Rousseau Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/53251
Chapter 6 All Ceramic Tripolar THA to Prevent Dislocations in Risky Patients Jean-Yves Lazennec, Adrien Brusson and Marc Antoine Rousseau Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/53251
Mid Term Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty for Various Hip Disorders
 ORIGINALARTICLE Mid Term Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty for Various Hip Disorders Sanjeev Gupta, Rashid Anjum, Omeshwar Singh, Anil Gupta, Abdul Ghani, Mohammad Azhar ud din Darokhan Abstract The curent
ORIGINALARTICLE Mid Term Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty for Various Hip Disorders Sanjeev Gupta, Rashid Anjum, Omeshwar Singh, Anil Gupta, Abdul Ghani, Mohammad Azhar ud din Darokhan Abstract The curent
Management Of Acetabular Deficiency In Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Series Of 15 Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 21 Number 2 Management Of Acetabular Deficiency In Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Series Of 15 Cases G Khanna, R Sharma, D Singh, T A Chandy Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 21 Number 2 Management Of Acetabular Deficiency In Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Series Of 15 Cases G Khanna, R Sharma, D Singh, T A Chandy Citation
Trabecular Metal Acetabular Revision System Cemented Constrained Liner
 Trabecular Metal Acetabular Revision System Cemented Constrained Liner Trabecular Metal Acetabular Revision System Cemented Constrained Liner Surgical Technique The Best Thing Next to Bone... Stability
Trabecular Metal Acetabular Revision System Cemented Constrained Liner Trabecular Metal Acetabular Revision System Cemented Constrained Liner Surgical Technique The Best Thing Next to Bone... Stability
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Exeter Contemporary Flanged Cup. Exeter. Providing Solutions
 Exeter Contemporary Flanged Cup Exeter Providing Solutions Design Benefits Even Cement Mantle Four polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) cement spacers are attached to the cup to maintain a minimum thickness of
Exeter Contemporary Flanged Cup Exeter Providing Solutions Design Benefits Even Cement Mantle Four polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) cement spacers are attached to the cup to maintain a minimum thickness of
This is a repository copy of The impact of surgeon handedness in total hip replacement.
 This is a repository copy of The impact of surgeon handedness in total hip replacement. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/81612/ Article: Pennington, N, Redmond,
This is a repository copy of The impact of surgeon handedness in total hip replacement. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/81612/ Article: Pennington, N, Redmond,
TEN YEARS EXPERIENCE WITH NONCEMENTED REVISION SOCKETS. Lawrence D. Dorr, MD Zhinian Wan, MD
 ""'".."c.",".~" ""ill""."""'""'" I TEN YEARS EXPERIENCE WITH NONCEMENTED REVISION SOCKETS. Lawrence D. Dorr, MD Zhinian Wan, MD f ABSTRACT A prospective study was completed on 167 noncemented revision
""'".."c.",".~" ""ill""."""'""'" I TEN YEARS EXPERIENCE WITH NONCEMENTED REVISION SOCKETS. Lawrence D. Dorr, MD Zhinian Wan, MD f ABSTRACT A prospective study was completed on 167 noncemented revision
Leg Length Discrepancy after Total Hip Arthroplasty Using the Modified Anterolateral Approach for Stable Hip
 Journal of US-China Medical Science 13 (2016) 129-137 doi: 10.17265/1548-6648/2016.03.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING Leg Length Discrepancy after Total Hip Arthroplasty Using the Modified Anterolateral Approach
Journal of US-China Medical Science 13 (2016) 129-137 doi: 10.17265/1548-6648/2016.03.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING Leg Length Discrepancy after Total Hip Arthroplasty Using the Modified Anterolateral Approach
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
Uncemented Total Hip Arthroplasty With Subtrochanteric Derotational Osteotomy for Severe Femoral Anteversion
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 6 1999 Uncemented Total Hip Arthroplasty With Subtrochanteric Derotational Osteotomy for Severe Femoral Anteversion Hamid G. Zadeh, FRCS(Orth), Jia Hua, MD, PhD,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 6 1999 Uncemented Total Hip Arthroplasty With Subtrochanteric Derotational Osteotomy for Severe Femoral Anteversion Hamid G. Zadeh, FRCS(Orth), Jia Hua, MD, PhD,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:322-327 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.3.322 Spinopelvic Orientation on Radiographs in Various Body Postures: Upright Standing, Chair Sitting,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:322-327 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.3.322 Spinopelvic Orientation on Radiographs in Various Body Postures: Upright Standing, Chair Sitting,
A Useful Reference Guide for the Stem Anteversion During Total Hip Arthroplasty in the Dysplastic Femur
 A Useful Reference Guide for the Stem Anteversion During Total Hip Arthroplasty in the Dysplastic Femur Tadashi Tsukeoka, Yoshikazu Tsuneizumi, TaeHyun Lee. Chiba Rehabilitation Center, Chiba, Japan. Disclosures:
A Useful Reference Guide for the Stem Anteversion During Total Hip Arthroplasty in the Dysplastic Femur Tadashi Tsukeoka, Yoshikazu Tsuneizumi, TaeHyun Lee. Chiba Rehabilitation Center, Chiba, Japan. Disclosures:
Ultrasound Scanning of Neonatal Hips
 Ultrasound Scanning of Neonatal Hips Dr. Dickson S F Tsang Associate Consultant Queen Mary Hospital Why? How? What? Outline IAAHS 2nd April, 2011 Outline Why? Why performing hip ultrasound (USG)? Why USG?
Ultrasound Scanning of Neonatal Hips Dr. Dickson S F Tsang Associate Consultant Queen Mary Hospital Why? How? What? Outline IAAHS 2nd April, 2011 Outline Why? Why performing hip ultrasound (USG)? Why USG?
HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Introduction...2 Preoperative Planning...3 Preoperative Planning...3 Templating and Radiographs...4 Determination of Leg Length Discrepancy...5 Determining Acetabular Cup
HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Introduction...2 Preoperative Planning...3 Preoperative Planning...3 Templating and Radiographs...4 Determination of Leg Length Discrepancy...5 Determining Acetabular Cup
Study of Angle of Femoral Torsion in Western Region of India
 Study of Angle of Femoral Torsion in Western Region of India Padma Varlekar, B.B. Gosai, S.K. Nagar, C. D. Mehta Government Medical College, Surat, Gujarat. Abstracts: Background: The femur is thighbone.
Study of Angle of Femoral Torsion in Western Region of India Padma Varlekar, B.B. Gosai, S.K. Nagar, C. D. Mehta Government Medical College, Surat, Gujarat. Abstracts: Background: The femur is thighbone.
HIP FOLLOW-UP. Thank you for your attention to this matter. If you have any questions, please contact us for assistance. Thomas P.
 HIP FOLLOW-UP It is important to review the status of your hip implant(s) during an office visit at six weeks, one year, two years, and every other year postoperatively thereafter for your safety even
HIP FOLLOW-UP It is important to review the status of your hip implant(s) during an office visit at six weeks, one year, two years, and every other year postoperatively thereafter for your safety even
Product Information. *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System
 APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST Technology for unmatched performance Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST
APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST Technology for unmatched performance Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST
Early Results of Total Knee Replacements:
 Early Results of Total Knee Replacements: "A Clinical and Radiological Evaluation" K.S. Dhillon, FRCS* Jamal, MS* S. Bhupinderjeet, MBBS** * Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur
Early Results of Total Knee Replacements: "A Clinical and Radiological Evaluation" K.S. Dhillon, FRCS* Jamal, MS* S. Bhupinderjeet, MBBS** * Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur
Range of Motion After Total Hip Arthroplasty: Experimental Verification of the Analytical Simulator
 Range of Motion After Total Hip Arthroplasty: Experimental Verification of the Analytical Simulator Branislav Jaramaz, Constantinos Nikou, David Simon and Anthony DiGioia III CMU-RI-TR-97-09 Robotics Institute
Range of Motion After Total Hip Arthroplasty: Experimental Verification of the Analytical Simulator Branislav Jaramaz, Constantinos Nikou, David Simon and Anthony DiGioia III CMU-RI-TR-97-09 Robotics Institute
