Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis with Cervical Spinal Cord Injury A Report of 3 Cases and a Literature Review
|
|
|
- Egbert Scott Green
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Report 257 Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis with Cervical Spinal Cord Injury A Report of 3 Cases and a Literature Review S Sreedharan, 1 MBBS, YH Li, 2 FRCS (Glas, Edin), M Med (Surg), FAMS Abstract Introduction: Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH), though common, is often asymptomatic. However, spinal hyperostosis can predispose the affected to chronic myelopathic symptoms and acute spinal cord injury. Clinical Picture: We report on 3 patients with DISH, who sustained traumatic cervical cord injuries. Two were tetraplegic at presentation. The radiologic findings of the patients are also discussed. Treatment: Both the tetraplegic patients were treated non-surgically in view of high surgical risk. Outcome: Both the tetraplegic patients died due to mechanical respiratory failure. Conclusions: The potential catastrophic neurological sequelae of DISH from relatively minor trauma must be understood. Further studies are needed to aid in evidence-based clinical management of asymptomatic patients with DISH. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2005;34: Key words: Forestier disease, Ossification, Posterior longitudinal ligament, Vertebral ankylosing hyperostosis Introduction Despite being a largely asymptomatic clinical condition, diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) has been widely described in literature due to its often-interesting clinical manifestations. Here we describe 3 case reports of spinal cord injuries in patients with DISH who presented to Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore, between March 2000 and April We also include a review of the diagnosis, epidemiology and common mechanisms of cord injury in DISH. Case Reports Case 1 Mr H, a 76-year-old Chinese gentleman, had a history of bilateral osteoarthritis of the knees and was on follow-up with a cardiologist for arrhythmia. He presented with a hyperextension injury to the neck, sustained when he tripped and fell forwards, landing on his left temple. He complained of transient weakness of all 4 limbs, with the upper limbs being weaker than the lower limbs, and was unable to walk immediately after the injury. On presentation at the emergency department, Mr H was alert and communicative. There was a laceration on the left side of the forehead and the posterior aspect of his neck was tender. Neurological examination, however, was completely normal by the time of presentation. Power was full in all 4 limbs, proximally and distally. There was no sensory deficit. Anal tone was good with absence of saddle anaesthesia. Cervical spine radiograph (Fig. 1) showed a fracture through the bridging osteophyte between C3 and C4, with underlying ankylosing hyperostosis from the level of the first to the seventh cervical vertebra. In view of a history of neurological loss, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan of the cervical spine (Fig. 2) was performed. This showed a fracture of bridging osteophytes at the C3-C4 level anteriorly with surrounding pre-vertebral oedema. There was, in addition, posterior disc protrusion and hypertrophy of facet joints at the same level, contributing to significant cord compression. Clinically, however, from admission onwards, Mr H did not display any neurological deficits. The cervical spine was stabilised with an Aspen collar and ambulatory physiotherapy was started within 2 days. On outpatient follow-up after discharge, Mr H remained well. He was 1 Department of General Surgery Singapore General Hospital, Singapore 2 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Address for Reprints: Dr S Sreedharan, Department of General Surgery, Singapore General Hospital, Outram Road, Singapore sreedharan.sechachalam@singhealth.com.sg
2 258 offered decompression surgery for the residual spinal canal stenosis at the C3-C4 level but Mr H declined surgical intervention. Case 2 Mr W, an 84-year-old Chinese gentleman, had underlying diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension and ischaemic heart disease for which a coronary artery bypass grafting had been previously done. He presented with a cervical hyperflexion injury, sustained when he fell backwards off a bench, landing on his occiput. Mr W presented to the ED with numbness and weakness of all 4 limbs. On examination, Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) was 15. Neurological examination revealed power to be 0 throughout both lower limbs and in the left upper limb; power was 1 to 2 in right upper limb at the C4-C6 myotomes. Sensation to fine touch and pin prick was lost at all dermatomes below C3 to C4 bilaterally. Anal tone was lax on presentation. Cervical spine radiograph (Fig. 3) showed a C5-C6 facet joint fracture and dislocation of 50%, and underlying ankylosing hyperostosis from C1 to C6. MRI (Fig. 4) showed an acute fracture through C6 involving the anteriorsuperior corner, extending into the C5-C6 intervertebral disc and running posteriorly; the fracture was associated with a facet joint dislocation. The spinal cord was compressed at the C5-C6 level with cord oedema present. The patient was started on intravenous methylprednisolone to reduce cord oedema. The C5/C6 fracture dislocation was reduced with skull traction, with sequential load increments by 5 pounds. Due to his significant medical comorbidities, Mr W was considered a poor surgical candidate. This was explained to the patient and his family, who then opted for nonoperative management. Despite the reduction in the fracturedislocation, Mr W s neurological state declined: he became progressively less responsive and his GCS dropped from 15 to 3 in the first 2 days of admission. This was attributed to carbon dioxide narcosis secondary to mechanical respiratory failure. He was intubated and mechanically ventilated from the third day of admission. However, his condition deteriorated further and he passed away 2 weeks after admission. Case 3 Mr P was a 69-year-old Chinese gentleman with hypertension and a history of stroke. He presented to the ED with complete paralysis after sustaining a hyperextension injury to the neck when he tripped and fell forward onto his forehead. At the ED, GCS was 15. Neurological examination revealed power of grade 0 in all 4 limbs. Sensation was absent bilaterally from the level of the C4 dermatome downwards. Anal tone was also absent. Cervical spine X-ray showed a fracture through the anterior column of hyperostosis at the level of the C3/C4 vertebrae and underlying DISH from the C1 to C7 vertebrae (Fig. 5). MRI (Fig. 6) showed a focal area of spinal canal stenosis at C3/C4 due to both anterior and posterior compression by osteophytes and a thickened ligamentum flavum. There was cord compression and oedema of the cord at the same level. As with Mr W, Mr P s family opted for non-operative management in view of high surgical risk due to underlying medical comorbidities. Medical treatment of cord compression was initiated with intravenous methylprednisolone. However, on the same day of admission, he developed mechanical respiratory failure. Again, this was likely secondary to involvement of the nerve roots for C3-C5. Mr P was mechanically ventilated for 3 months, during which time he succumbed to complications of deep venous thrombosis and multiple episodes of pneumonia, and eventually passed away. Discussion Other names for diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) include Forestier s disease 1 and ankylosing hyperostosis. It is a well-defined syndrome with axial and peripheral manifestations of hyperostosis these include hyperostosis frontalis, calcaneal spurs, post-hip surgery heterotopic ossification and anterior/posterior longitudinal ligament ossification. The prevalence of DISH in the general population varies greatly depending on the location of the study. Prevalence rates of up to 27.3% in males and 12.8% in females have been quoted but a consistent finding is that males are more commonly affected up to twice as often as females. 2,3 DISH is uncommon in those below the age of 50 years, after which incidence increases with age. Incidence also increases with weight 4 in both sexes. In fact, the oldest described risk factor for DISH is obesity, which is mentioned in the first description of the syndrome. 1 In a case control study involving 131 subjects, the body mass index was significantly higher in those with DISH (27.8 versus 26.0). 4 DM is commonly quoted as a risk factor. However, Vezyroglou et al 5 showed that while diabetics who are also hyperuricaemic and/or hyperlipidaemic have a significantly higher incidence of ankylosing hyperostosis, DM alone is not a statistically significant risk factor. Animal models have shown that high serum vitamin A levels increase the risk of DISH; 6 no such studies on humans were found in the literature. A recent review article of Forestier s Disease by Sarzi-Puttini and Atzeni 7 reiterated the greater prevalence of high body mass index, DM and hyperuricaemia in patients with DISH. Annals Academy of Medicine
3 259 Fig. 1. Cervical spine radiograph of case 1. Fig. 2. MRI cervical spine of case 1. Fig. 3. Cervical spine radiograph of case 2. Fig. 4. MRI cervical spine of case 2. Fig. 5. Cervical spine radiograph of case 3. Fig. 6. MRI cervical spine of case 3. The diagnosis of DISH is based on the following radiologic features: 8 1. New bone formation bridging at least 4 contiguous vertebral bodies (Resnick s criteria) Thoracic spine is often an ideal region to display the bridging as it is relatively non-mobile, thereby allowing unhindered ossification from one vertebra to another. Appropriate X-ray views include antero-posterior and lateral views of the region of interest Absence of degenerative disc disease This is imperative in distinguishing osteophyte formation from ossification of the spinal ligaments. 3. Absence of inflammatory changes in facet or sacroiliac joints This criterion differentiates DISH from its closest radiological twin, ankylosing spondylitis. Hence, if there is clinical suspicion of ankylosing spondylitis or vertebral X-ray is non-confirmatory for DISH, a pelvic X-ray will be necessary to exclude sacroiliitis. For this, an anteroposterior view of the pelvis will suffice Battistone et al 10 claim detailed oblique projections do not provide additional benefit, as previously thought.
4 260 The majority of people with DISH are asymptomatic. Of those with clinical manifestations, neurological symptoms are the most common. However, subjects do occasionally present with other symptoms, including mechanical dysphagia, dyspnoea, stridor, thoracic outlet syndrome and heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty. 11,12 Neurological manifestations secondary to DISH are commonly due to involvement of the cervical spine, which is affected in 75% of patients with DISH. 13 These stem from: 1. Reduced flexibility of the spine, as in ankylosing spondylitis, 14 thereby allowing a trivial trauma to result in a fracture through the ossified ligaments. This acutely compromises the size of the spinal canal. Fractures of such nature in the cervical spine are associated with a higher morbidity and mortality than fractures through the normal spine. All 3 patients mentioned above suffered injuries of this nature. Mr W and Mr P developed mechanical respiratory failure likely due to ascending cord oedema involving the C3/C4/C5 levels (roots supplying the phrenic nerve) following the fractures. 2. Spinal canal narrowing secondary to ossification of anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments. Patients present with myelopathy as a result. Furthermore, there is less potential space available within the canal such that cord compromise occurs sooner in the event of fractures and cord oedema (as in the 3 case studies above). 3. Atlantoaxial subluxation (AAS) of the cervical spine may rarely occur in subjects with DISH. The literature search yielded 2 case reports. Oostveen et al 15 described an 80-year-old lady with cervical radiculopathy. Chiba et al 16 described another patient with progressive myelopathy the authors hypothesised that AAS is caused by the concentration of cervical motion from the atlanto-occipital to the C1-C2 joints as a result of the loss of cervical mobility below C2 (secondary to DISH). Narrowing of the spinal canal due to ossification of the spinal ligaments probably contributes to the neurological effects of atlantoaxial subluxation. DISH is often an incidental diagnosis made from a chest radiograph taken for a non-related reason or a finding made at autopsy. Unless symptomatic, it does not require surgical treatment; for instance, decompression surgery may be offered for those with myelopathic symptoms. However, it is not altogether benign, as the case reports above and other previously published papers suggest. 17 Sharma et al 18 showed in a retrospective analysis that 15% of patients with DISH presenting to a particular neurosurgical unit had serious neurological manifestations requiring neurosurgical intervention. Age may be a possible confounder in the relationship between DISH and the increased incidence of spinal cord injuries. While the incidence of DISH increases with age, so do other factors predisposing to increased risk of falls, such as failing eyesight and mobility, which could contribute to a higher incidence of traumatic spinal cord injury. DM is another known risk factor for DISH. Complications such as peripheral neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy, retinopathy, cataracts and hypoglycaemic episodes are a few of the reasons diabetics may be prone to falls. As with increasing age, DM may then be an added risk for traumatic spinal cord injury in patients with DISH. By extension, hyperlipidaemia may be an additional risk factor for fall-related cord injury due to the link between hyperlipidaemia and stroke. A literature search did not yield studies on the presence or number of risk factors and their correlation with spinal cord injury in DISH. As such, although DISH is largely asymptomatic and usually diagnosed incidentally, it would be interesting to investigate if optimisation of the metabolic risk factors for DISH in patients with early diagnosis would reduce the rate of progression of hyperostosis and eventual likelihood of spinal cord injury. The progression could be monitored using a grading scale, which may be of predictive value in determining a subject s risk of spinal cord compression. Possible points to consider in the scale include: number of bridging ossifications, degree of osteoporosis of the adjacent vertebral bodies and the diameter of the spinal canal. Those with higher risk could then be: educated on how to recognise myelopathic symptoms educated on fall prevention, and managed more aggressively for their coexisting medical morbidities, which may predispose them to falls, as mentioned above. Conclusion Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) is probably the commonest rheumatological disorder. 8 Although mostly asymptomatic, it can predispose the affected to catastrophic spinal cord injuries with risk of mortality, as seen in 2 of the 3 cases studied in this article. As such, patients should be informed about possible neurological sequelae from relatively minor trauma. We suggest possibilities for further studies correlating currently known risk factors for DISH and the role of their management in the prevention of progression and traumatic complications of this condition. Annals Academy of Medicine
5 261 Acknowledgements The authors would like to thank Dr A Shalini, Dr E Kwek and Dr D Oh for their assistance with this paper. REFERENCES 1. Forestier J, Rotes-Querol J. Senile ankylosing hyperostosis of the spine. Ann Rheum Dis 1950;9: Kiss C, O Neill TW, Mituzova M, Szilagyi M, Poor G. The prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in a population-based study in Hungary. Scand J Rheumatol 2002;31: Kiss C, Szilagyi M, Paksy A, Poor G. Risk factors for diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: a case-control study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002;41: Utsinger PD. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Clin Rheum Dis 1985;11: Vezyroglou G, Mitropoulos A, Antoniadis C. A metabolic syndrome in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. A controlled study. J Rheumatol 1996;23: Seawright AA, English PB, Gartner RJ. Hypervitaminosis A and hyperostosis of the cat. Nature 1965;206: Sarzi-Puttini P, Atzeni F. New developments in our understanding of DISH (diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis). Curr Opin Rheumatol 2004;16: Hochberg MC. Rheumatology. 3rd ed. Edinburgh: Mosby Publishers, Mata S, Hill RO, Joseph L, Kaplan P, Dussault R, Watts CS, et al. Chest radiographs as a screening test for diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. J Rheumatol 1993;20: Battistone MJ, Manaster BJ, Reda DJ, Clegg DO. Radiographic diagnosis of sacroiliitis Are sacroiliac views really better? J Rheumatol 1998;25: Belanger TA, Rowe DE. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: musculoskeletal manifestations. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2001;9: Mader R. Clinical manifestations of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis of the cervical spine. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2002;32: Boachie-Adjei O, Bullough PG. Incidence of ankylosing hyperostosis of the spine (Forestier s Disease) at autopsy. Spine 1987;12: Bridwell KH, DeWald RL. Textbook of Spinal Surgery. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Oostveen JC, van de Laar MA, Tuynman FH. Anterior atlantoaxial subluxation in a patient with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. J Rheumatol 1996;23: Chiba H, Annen S, Shimada T, Imura S. Atlantoaxial subluxation complicated by diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. A case report. Spine 1992;17: Razmi R, Khong KS. Cervical cord injury in an elderly man with a fused spine a case report. Singapore Med J 2001;42: Sharma RR, Mahapatra A, Pawar SJ, Sousa J, Lad SD, Athale SD. Spinal cord and cauda equina compression in DISH. Neurol India 2001;49:
Title. CitationSpine, 34(19): E709-E711. Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type. File Information.
 Title Cervical Myelopathy by C1 Posterior Tubercle Impinge Author(s)Kawabori, Masahito; Hida, Kazutoshi; Akino, Minoru; CitationSpine, 34(19): E709-E711 Issue Date 2009-09-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/70791
Title Cervical Myelopathy by C1 Posterior Tubercle Impinge Author(s)Kawabori, Masahito; Hida, Kazutoshi; Akino, Minoru; CitationSpine, 34(19): E709-E711 Issue Date 2009-09-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/70791
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Title. Author(s)Sudo, Hideki; Taneichi, H.; Kaneda, K. CitationSpinal Cord, 44(2): Issue Date Doc URL
 Title Secondary medulla oblongata involvement following mi instability in a patient with ossification of the po Author(s)Sudo, Hideki; Taneichi, H.; Kaneda, K. CitationSpinal Cord, 44(2): 126-129 Issue
Title Secondary medulla oblongata involvement following mi instability in a patient with ossification of the po Author(s)Sudo, Hideki; Taneichi, H.; Kaneda, K. CitationSpinal Cord, 44(2): 126-129 Issue
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics. Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003
 Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
Involvement of the spine is common in rheumatoid. Incidence been reported to be 85% radiologically but only 30% have neurological signs and symptoms.
 RHEUMATOID SPINE Involvement of the spine is common in rheumatoid. Incidence been reported to be 85% radiologically but only 30% have neurological signs and symptoms. When neurology is present it may manifest
RHEUMATOID SPINE Involvement of the spine is common in rheumatoid. Incidence been reported to be 85% radiologically but only 30% have neurological signs and symptoms. When neurology is present it may manifest
ASJ. A Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia. Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr Hesarikia BUMS
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Hesarikia BUMS Subaxial Cervical Spine From C3-C7 ROM Majority of cervical flexion Lateral bending Approximately 50% rotation Ligamentous Anatomy Anterior ALL, PLL, intervertebral
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Hesarikia BUMS Subaxial Cervical Spine From C3-C7 ROM Majority of cervical flexion Lateral bending Approximately 50% rotation Ligamentous Anatomy Anterior ALL, PLL, intervertebral
One hospitalization with any of the defining diagnoses of spondylosis (see ICD9 and ICD10 code lists below) in any diagnostic position; or
 1 ORTHO 16 SPONDYLOSIS Includes spondylopathies due to asymptomatic and symptomatic degenerative changes of the bony spine (M47 and M48); Does not include ankylosing spondylitis (M45), other inflammatory
1 ORTHO 16 SPONDYLOSIS Includes spondylopathies due to asymptomatic and symptomatic degenerative changes of the bony spine (M47 and M48); Does not include ankylosing spondylitis (M45), other inflammatory
Spine Trauma- Part B
 Spine Trauma- Part B Cervical Spine Injuries Atlanto- Occipital Dislocation Hyperextension and distraction mechanism Down s syndrome, RA more susceptible Asymmetric lateral masses on odontoid view Widened
Spine Trauma- Part B Cervical Spine Injuries Atlanto- Occipital Dislocation Hyperextension and distraction mechanism Down s syndrome, RA more susceptible Asymmetric lateral masses on odontoid view Widened
Objectives. Comprehension of the common spine disorder
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Comprehension of the common spine disorder.
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Bilateral Foot Drop Without Cauda Equinae Syndrome Due To L4-L5 Disc Prolapse: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 5 Number 1 Bilateral Foot Drop Without Cauda Equinae Syndrome Due To L4-L5 Disc Prolapse: A Case Report R Ramnaryan, C Palinikumar Citation R Ramnaryan,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 5 Number 1 Bilateral Foot Drop Without Cauda Equinae Syndrome Due To L4-L5 Disc Prolapse: A Case Report R Ramnaryan, C Palinikumar Citation R Ramnaryan,
Key Primary CPT Codes: Refer to pages: 7-9 Last Review Date: October 2016 Medical Coverage Guideline Number:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma. Introduction. Anatomic Considerations 7/23/2018
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Sheyan J. Armaghani, MD Florida Orthopedic Institute Assistant Professor USF Dept of Orthopedics Introduction Trauma to the cervical spine accounts for 5 of all spine injuries
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Sheyan J. Armaghani, MD Florida Orthopedic Institute Assistant Professor USF Dept of Orthopedics Introduction Trauma to the cervical spine accounts for 5 of all spine injuries
DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE PRABIN SHRESTHA ANISH M SINGH B&B HOSPITAL
 SPINAL CHAPTER, NESON DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE PRABIN SHRESTHA ANISH M SINGH B&B HOSPITAL INTRODUCTION DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE Gradual loss of normal structure and function of spine with time Also
SPINAL CHAPTER, NESON DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE PRABIN SHRESTHA ANISH M SINGH B&B HOSPITAL INTRODUCTION DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE Gradual loss of normal structure and function of spine with time Also
Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine. Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University
 Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University Objective Anatomy Mechanism and type of injury PE.and radiographic evaluation
Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University Objective Anatomy Mechanism and type of injury PE.and radiographic evaluation
REVIEW QUESTIONS ON VERTEBRAE, SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES
 REVIEW QUESTIONS ON VERTEBRAE, SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES 1. A 28-year-old-women presented to the hospital emergency room with intense lower back spasms in the context of coughing during an upper respiratory
REVIEW QUESTIONS ON VERTEBRAE, SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES 1. A 28-year-old-women presented to the hospital emergency room with intense lower back spasms in the context of coughing during an upper respiratory
Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 590935, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/590935 Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 590935, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/590935 Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE
 564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
Degenerative Disease of the Spine
 Degenerative Disease of the Spine Introduction: I. Anatomy Talk Overview II. Overview of Disease Processes: A. Spondylosis B. Intervertebral Disc Disease III. Diagnosis IV. Therapy Introduction: Myelopathy
Degenerative Disease of the Spine Introduction: I. Anatomy Talk Overview II. Overview of Disease Processes: A. Spondylosis B. Intervertebral Disc Disease III. Diagnosis IV. Therapy Introduction: Myelopathy
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
Spinal Column. Anatomy Of The Spine
 Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine
 A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
102 Results RESULTS. Age Mean=S.D Range 42= years -84 years Number % <30 years years >50 years
 102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
Spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 06
 What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
University of Jordan. Professor Freih Abuhassan -
 Freih Odeh Abu Hassan F.R.C.S.(Eng.), F.R.C.S.(Tr.& Orth.). Professor of Orthopedics University of Jordan 1 A. Sacroiliitis History Trauma is very common Repetitive LS motion--lumbar rotation or axial
Freih Odeh Abu Hassan F.R.C.S.(Eng.), F.R.C.S.(Tr.& Orth.). Professor of Orthopedics University of Jordan 1 A. Sacroiliitis History Trauma is very common Repetitive LS motion--lumbar rotation or axial
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
Sir William Asher ANATOMY
 SPINAL CORD INJURY BASICS RELATED TO LIFE CARE PLANNING Lesson 1 Sir William Asher Picture the pathetic patient lying long abed, the urine leaking from his distended bladder, the lime draining from his
SPINAL CORD INJURY BASICS RELATED TO LIFE CARE PLANNING Lesson 1 Sir William Asher Picture the pathetic patient lying long abed, the urine leaking from his distended bladder, the lime draining from his
Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome
 Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome Hez Progect Israel 2016 Ran Harel, MD Spine Surgery Unit, Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel Sackler Medical School, Tel-Aviv
Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome Hez Progect Israel 2016 Ran Harel, MD Spine Surgery Unit, Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel Sackler Medical School, Tel-Aviv
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE
 CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE Cervical spondylosis l Cervical osteophytosis l Most common progressive disease in the aging cervical spine l Seen in 95% of the people by 65 years Pathophysiology
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE Cervical spondylosis l Cervical osteophytosis l Most common progressive disease in the aging cervical spine l Seen in 95% of the people by 65 years Pathophysiology
Medicare Regulations for Chiropractors. Presented by Clinic Pro Software Inc. Marilyn K. Gard. CEO, MBA
 Medicare Regulations for Chiropractors Presented by Clinic Pro Software Inc. Marilyn K. Gard. CEO, MBA Use AT modifier which means active treatment. Claims submitted for Chiropractic manipulative treatment
Medicare Regulations for Chiropractors Presented by Clinic Pro Software Inc. Marilyn K. Gard. CEO, MBA Use AT modifier which means active treatment. Claims submitted for Chiropractic manipulative treatment
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 EPC Ch 24 Quiz w-key Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following best explains the presentation and prognosis of
EPC Ch 24 Quiz w-key Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following best explains the presentation and prognosis of
Acute spinal cord injury
 Acute spinal cord injury Thakul Oearsakul Songklanagarind hospital Hat Yai Songkhla Introduction New SCI 10000-12000 cases Approximately 4.0-5.3 per 100000 population Common causes of traumatic SCI :Motor
Acute spinal cord injury Thakul Oearsakul Songklanagarind hospital Hat Yai Songkhla Introduction New SCI 10000-12000 cases Approximately 4.0-5.3 per 100000 population Common causes of traumatic SCI :Motor
Peggers Super Summaries: The Aging Spine
 Aging Spine: AGING PROCESS Osteopenia 10% of 50 year old males and 25% of 50 year females Disc dehydration Facet degeneration Soft tissue hypertrophy 2 0 deformity Leg pain worse than back pain from nerve
Aging Spine: AGING PROCESS Osteopenia 10% of 50 year old males and 25% of 50 year females Disc dehydration Facet degeneration Soft tissue hypertrophy 2 0 deformity Leg pain worse than back pain from nerve
PARADIGM SPINE. Patient Information. Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal
 PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Pooria Salari, MD Assistant Professor Of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedic Surgery St. Louis University School of Medicine St. Louis, Missouri, USA Initial Evaluation
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Pooria Salari, MD Assistant Professor Of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedic Surgery St. Louis University School of Medicine St. Louis, Missouri, USA Initial Evaluation
Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis
 Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011; 116: 133 137 ORIGINL RTICLE Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis TOMOKI KOKUTSU, NOKI MOROZUMI, YUTK KOIZUMI & YUSHIN ISHII
Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011; 116: 133 137 ORIGINL RTICLE Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis TOMOKI KOKUTSU, NOKI MOROZUMI, YUTK KOIZUMI & YUSHIN ISHII
SPINAL CORD DISEASE IN DOGS PART TWO: MOST LIKELY CAUSES
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk SPINAL CORD DISEASE IN DOGS PART TWO: MOST LIKELY CAUSES Author : RITA GONÇALVES Categories : Vets Date : April 7, 2014 RITA
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk SPINAL CORD DISEASE IN DOGS PART TWO: MOST LIKELY CAUSES Author : RITA GONÇALVES Categories : Vets Date : April 7, 2014 RITA
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
HIGH LEVEL - Science
 Learning Outcomes HIGH LEVEL - Science Describe the structure and function of the back and spine (8a) Outline the functional anatomy and physiology of the spinal cord and peripheral nerves (8a) Describe
Learning Outcomes HIGH LEVEL - Science Describe the structure and function of the back and spine (8a) Outline the functional anatomy and physiology of the spinal cord and peripheral nerves (8a) Describe
Epidemiology of Low back pain
 Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Properties of Purdue. Anatomy. Positioning AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS 11/30/2018
 AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
Cervical laminectomy for spinal cord compression. Information for patients Neurosurgery
 Cervical laminectomy for spinal cord compression Information for patients Neurosurgery What is a compression of the spinal cord and how has it been caused? The bones in our back are called vertebras and
Cervical laminectomy for spinal cord compression Information for patients Neurosurgery What is a compression of the spinal cord and how has it been caused? The bones in our back are called vertebras and
Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS
 Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS None Common degenerative (usually) condition caused by compression on the spinal cord that is characterized by clumsiness and difficulty with fine motor tasks in the hands and
Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS None Common degenerative (usually) condition caused by compression on the spinal cord that is characterized by clumsiness and difficulty with fine motor tasks in the hands and
ACDF. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion. An introduction to
 An introduction to ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion This booklet provides general information on ACDF. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with
An introduction to ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion This booklet provides general information on ACDF. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with
3/10/17 Spinal a Injury 1
 Spinal Injury 1 'Paralysed' Watmough vows he'll have the backbone for Game Two after treatment for neck injury Watmough will have cortisone injected into his spine this morning to speed up the recovery
Spinal Injury 1 'Paralysed' Watmough vows he'll have the backbone for Game Two after treatment for neck injury Watmough will have cortisone injected into his spine this morning to speed up the recovery
Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
 283 Journal of Intellectual Disability Research VOLUME 43 PART 4 pp 283±288 AUGUST 1999 Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
283 Journal of Intellectual Disability Research VOLUME 43 PART 4 pp 283±288 AUGUST 1999 Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
외래에서흔히접하는 요통환자의진단과치료 울산의대서울아산병원가정의학과 R3 전승엽
 외래에서흔히접하는 요통환자의진단과치료 울산의대서울아산병원가정의학과 R3 전승엽 Index Introduction Etiology & Type Assessment History taking & Physical examination Red flag sign Imaging Common disorder Management Reference Introduction Pain
외래에서흔히접하는 요통환자의진단과치료 울산의대서울아산병원가정의학과 R3 전승엽 Index Introduction Etiology & Type Assessment History taking & Physical examination Red flag sign Imaging Common disorder Management Reference Introduction Pain
ISPUB.COM. Fracture Through the Body of the Axis. B Johnson, N Jayasekera CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 8 Number 1 B Johnson, N Jayasekera Citation B Johnson, N Jayasekera.. The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery. 2007 Volume 8 Number 1. Abstract
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 8 Number 1 B Johnson, N Jayasekera Citation B Johnson, N Jayasekera.. The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery. 2007 Volume 8 Number 1. Abstract
Symptomatic ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament with stenosis of the cervical spine
 Spine Symptomatic ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament with stenosis of the cervical spine A REPORT OF SEVEN CASES J. Mizuno, H. Nakagawa, J. Song From Aichi Medical University, Aichi-gun
Spine Symptomatic ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament with stenosis of the cervical spine A REPORT OF SEVEN CASES J. Mizuno, H. Nakagawa, J. Song From Aichi Medical University, Aichi-gun
SCIWORA Rozlyn McTeer BSN, RN, CEN Pediatric Trauma Coordinator Trauma Services OBJECTIVES DEFINITION 11/8/2017. Identify SCIWORA.
 SCIWORA Rozlyn McTeer BSN, RN, CEN Pediatric Trauma Coordinator Trauma Services Identify SCIWORA. OBJECTIVES Identify the population at risk. To identify anatomic and physiologic reasons for SCIWORA. To
SCIWORA Rozlyn McTeer BSN, RN, CEN Pediatric Trauma Coordinator Trauma Services Identify SCIWORA. OBJECTIVES Identify the population at risk. To identify anatomic and physiologic reasons for SCIWORA. To
CMEARTICLE * * * Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed
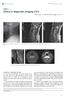 Singapore Med J 2015; 56(7): 373-378 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015107 CMEARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (161) Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed 2a 2b Fig. 1 Lateral radiograph of
Singapore Med J 2015; 56(7): 373-378 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015107 CMEARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (161) Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed 2a 2b Fig. 1 Lateral radiograph of
SpineFAQs. Cervical Disc Replacement
 SpineFAQs Cervical Disc Replacement Artificial disc replacement (ADR) is relatively new. In June 2004, the first ADR for the lumbar spine (low back) was approved by the FDA for use in the US. Replacing
SpineFAQs Cervical Disc Replacement Artificial disc replacement (ADR) is relatively new. In June 2004, the first ADR for the lumbar spine (low back) was approved by the FDA for use in the US. Replacing
Spinal injury. Structure of the spine
 Spinal injury Structure of the spine Some understanding of the structure of the spine (spinal column) and the spinal cord is important as it helps your Neurosurgeon explain about the part of the spine
Spinal injury Structure of the spine Some understanding of the structure of the spine (spinal column) and the spinal cord is important as it helps your Neurosurgeon explain about the part of the spine
Acute Brown-Sequard syndrome following brachial plexus avulsion injury. A report of two cases
 University of Malaya From the SelectedWorks of Mun Keong Kwan September, 2011 Acute Brown-Sequard syndrome following brachial plexus avulsion injury. A report of two cases Mun Keong Kwan Available at:
University of Malaya From the SelectedWorks of Mun Keong Kwan September, 2011 Acute Brown-Sequard syndrome following brachial plexus avulsion injury. A report of two cases Mun Keong Kwan Available at:
DISORDERS OF THE SPINE TREATING PHYSICIAN DATA SHEET
 DISORDERS OF THE SPINE TREATING PHYSICIAN DATA SHEET Short form FOR REPRESENTATIVE USE ONLY REPRESENTATIVE S NAME AND ADDRESS REPRESENTATIVE S TELEPHONE REPRESENTATIVE S EMAIL PHYSICIAN S NAME AND ADDRESS
DISORDERS OF THE SPINE TREATING PHYSICIAN DATA SHEET Short form FOR REPRESENTATIVE USE ONLY REPRESENTATIVE S NAME AND ADDRESS REPRESENTATIVE S TELEPHONE REPRESENTATIVE S EMAIL PHYSICIAN S NAME AND ADDRESS
Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis versus Ankylosing Spondylitis: Brief Case Review
 Copyright 2006, Barrow Neurological Institute Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis versus Ankylosing Spondylitis: Brief Case Review Hamidreza Aliabadi, MD David Biglari, DO L. Fernando Gonzalez, MD
Copyright 2006, Barrow Neurological Institute Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis versus Ankylosing Spondylitis: Brief Case Review Hamidreza Aliabadi, MD David Biglari, DO L. Fernando Gonzalez, MD
CERVICAL SPINE EVALUATION MARK FIGUEROA PHYSICAL THERAPIST
 CERVICAL SPINE EVALUATION MARK FIGUEROA PHYSICAL THERAPIST OVERVIEW OF CLINICAL REASONING Stage of disorder Pathoanatomical diagnosis Signs and symptoms Consideration of the evidence gathered Common sense
CERVICAL SPINE EVALUATION MARK FIGUEROA PHYSICAL THERAPIST OVERVIEW OF CLINICAL REASONING Stage of disorder Pathoanatomical diagnosis Signs and symptoms Consideration of the evidence gathered Common sense
Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: results of a systematic review
 Systematic review Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy 35 35 42 Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: results of a systematic review Authors Anoushka
Systematic review Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy 35 35 42 Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: results of a systematic review Authors Anoushka
A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries. Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital
 A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital Cheung KK Wong CY Chan Andrew Tse Alfred Chow YY Department of Orthopaedics
A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital Cheung KK Wong CY Chan Andrew Tse Alfred Chow YY Department of Orthopaedics
Soccer causes degenerative changes in the cervical spine. European Spine Journal, February 2004, 13(1):76-82
 Soccer causes degenerative changes in the cervical spine European Spine Journal, February 2004, 13(1):76-82 Alparslan Kartal, Brahim Yldran, Alparslan Enköylü and Feza Korkusuz FROM ABSTRACT: Background
Soccer causes degenerative changes in the cervical spine European Spine Journal, February 2004, 13(1):76-82 Alparslan Kartal, Brahim Yldran, Alparslan Enköylü and Feza Korkusuz FROM ABSTRACT: Background
Common Thoraco- Lumbar Problems in the Mature Athlete
 Common Thoraco- Lumbar Problems in the Mature Athlete Diana Heiman, MD Associate Professor, Family Medicine Residency Director East Tennessee State University Objectives Review the pathophysiology of the
Common Thoraco- Lumbar Problems in the Mature Athlete Diana Heiman, MD Associate Professor, Family Medicine Residency Director East Tennessee State University Objectives Review the pathophysiology of the
POSTERIOR CERVICAL FUSION
 AN INTRODUCTION TO PCF POSTERIOR CERVICAL FUSION This booklet provides general information on the Posterior Cervical Fusion (PCF) surgical procedure for you to discuss with your physician. It is not meant
AN INTRODUCTION TO PCF POSTERIOR CERVICAL FUSION This booklet provides general information on the Posterior Cervical Fusion (PCF) surgical procedure for you to discuss with your physician. It is not meant
PREPARED FOR. Marsha Eichhorn DATE OF INJURY : N/A DATE OF ANALYSIS : 12/14/2016 DATE OF IMAGES : 12/8/2016. REFERRING DOCTOR : Dr.
 Accent on Health Chiropractic 405 Firemans Ave PREPARED FOR Marsha Eichhorn DATE OF INJURY : N/A DATE OF ANALYSIS : 12/14/2016 DATE OF IMAGES : 12/8/2016 REFERRING DOCTOR : Dr. David Bohn This report contains
Accent on Health Chiropractic 405 Firemans Ave PREPARED FOR Marsha Eichhorn DATE OF INJURY : N/A DATE OF ANALYSIS : 12/14/2016 DATE OF IMAGES : 12/8/2016 REFERRING DOCTOR : Dr. David Bohn This report contains
Prevalence of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis Diagnosed by Whole Spine Computed Tomography: A Preliminary Study
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:41-46 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.1.41 Prevalence of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis Diagnosed by Whole Spine Computed Tomography:
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:41-46 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.1.41 Prevalence of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis Diagnosed by Whole Spine Computed Tomography:
RADICULOPATHY AN INTRODUCTION TO
 AN INTRODUCTION TO RADICULOPATHY This booklet provides general information on radiculopathy. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician or other
AN INTRODUCTION TO RADICULOPATHY This booklet provides general information on radiculopathy. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician or other
SPINAL CORD CONCUSSION. Stephan du Plessis MD
 SPINAL CORD CONCUSSION Stephan du Plessis MD CASE PRESENTATION 23 yo Varsity Defensive Back Tackled with neck in extension Unable to walk from field No movement in arms or legs No sensation below neck
SPINAL CORD CONCUSSION Stephan du Plessis MD CASE PRESENTATION 23 yo Varsity Defensive Back Tackled with neck in extension Unable to walk from field No movement in arms or legs No sensation below neck
Anterior Cervical Subluxation: An Unstable Position
 275 Anterior Cervical Subluxation: An Unstable Position, 1 A. T. Scher1 The radioiogic signs of cervical anterior subluxation are subtle. Even when recognized, the injury may not be considered significant.
275 Anterior Cervical Subluxation: An Unstable Position, 1 A. T. Scher1 The radioiogic signs of cervical anterior subluxation are subtle. Even when recognized, the injury may not be considered significant.
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management.
 River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Lumbar Spinal Stenosis This article is also available in Spanish: Estenosis de la columna lumbar (topic.cfm?topic=a00701). A common cause of low back and leg pain is lumbar spinal stenosis. As we age,
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis This article is also available in Spanish: Estenosis de la columna lumbar (topic.cfm?topic=a00701). A common cause of low back and leg pain is lumbar spinal stenosis. As we age,
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
OSSIFIED ANTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT: A STUDY IN ADULT HUMAN DRY VERTEBRA IN CENTRAL INDIA
 Original Research Article OSSIFIED ANTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT: A STUDY IN ADULT HUMAN DRY VERTEBRA IN CENTRAL INDIA Ashita Kaore* 1, Ashish kamdi 2, M.P Fulpatil 3. ABSTRACT International Journal of
Original Research Article OSSIFIED ANTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT: A STUDY IN ADULT HUMAN DRY VERTEBRA IN CENTRAL INDIA Ashita Kaore* 1, Ashish kamdi 2, M.P Fulpatil 3. ABSTRACT International Journal of
Cervical Spine Injury Guidelines
 6/15/2018 Cervical Spine Injury Guidelines Benjamin Oshlag, MD, CAQSM Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor of Sports Medicine Columbia University Medical Center Nothing to Disclose
6/15/2018 Cervical Spine Injury Guidelines Benjamin Oshlag, MD, CAQSM Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor of Sports Medicine Columbia University Medical Center Nothing to Disclose
Lumbar Disc Prolapse. Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan. Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon
 Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Patient Information MIS LLIF. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
 DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
Orthopadic cors. Topic : -Cervical spondylitis. -Development disorders(spondylolysis and Spodylolsithesis)
 Orthopadic cors Topic : -Cervical spondylitis. -Development disorders(spondylolysis and Spodylolsithesis) Cervical spondylitis. Definition : - a painful condition of the cervical spine resulting from the
Orthopadic cors Topic : -Cervical spondylitis. -Development disorders(spondylolysis and Spodylolsithesis) Cervical spondylitis. Definition : - a painful condition of the cervical spine resulting from the
Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures
 Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures C. Craig Blackmore, MD, MPH Professor of Radiology Adjunct Professor of Health Services Harborview Injury Prevention and Research Center University of Washington Outline Who
Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures C. Craig Blackmore, MD, MPH Professor of Radiology Adjunct Professor of Health Services Harborview Injury Prevention and Research Center University of Washington Outline Who
Odontoid Fractures and Other Cervical Trauma: Geriatric Considerations
 Odontoid Fractures and Other Cervical Trauma: Geriatric Considerations Vishal Khatri, MD Division of Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Cooper Bone and Joint Institute Cooper University Health
Odontoid Fractures and Other Cervical Trauma: Geriatric Considerations Vishal Khatri, MD Division of Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Cooper Bone and Joint Institute Cooper University Health
CEU Final Exam for Code It! Sixth Edition
 CEU Final Exam for 3-2-1 Code It! Sixth Edition Note to CEU applicant In order to receive CEU credit for taking this exam, the following criteria must be met: You must be certified by AAPC prior to purchasing
CEU Final Exam for 3-2-1 Code It! Sixth Edition Note to CEU applicant In order to receive CEU credit for taking this exam, the following criteria must be met: You must be certified by AAPC prior to purchasing
bilateral, both before below elbow twice a day below knee bedrest
 Abbreviations Student Name: A approximately assessment assist active active assist abdominal aortic aneurysm active assistive range of motion abduction/adduction acromioclavicular joint anterior cruciate
Abbreviations Student Name: A approximately assessment assist active active assist abdominal aortic aneurysm active assistive range of motion abduction/adduction acromioclavicular joint anterior cruciate
Coventry Pain Clinic - Spianl Pain - Sciatica and Brachalgia
 Coventry Pain Clinic - Spianl Pain - Sciatica and Brachalgia Copyright 2002-2005 Dr. Richard S. Walker Introduction Spinal Nerve Root Pain (Radiculopathy) can arise from the problems affecting the:- C4
Coventry Pain Clinic - Spianl Pain - Sciatica and Brachalgia Copyright 2002-2005 Dr. Richard S. Walker Introduction Spinal Nerve Root Pain (Radiculopathy) can arise from the problems affecting the:- C4
EVALUATE, TREAT AND WHEN TO REFER RED FLAGS Mid Atlantic Occupational Regional Conference and Environmental Medicine October 6, 2018
 EVALUATE, TREAT AND WHEN TO REFER RED FLAGS Mid Atlantic Occupational Regional Conference and Environmental Medicine October 6, 2018 Marc J. Levine, MD Rothman Institute Director Spine Surgery Program
EVALUATE, TREAT AND WHEN TO REFER RED FLAGS Mid Atlantic Occupational Regional Conference and Environmental Medicine October 6, 2018 Marc J. Levine, MD Rothman Institute Director Spine Surgery Program
Case Report: CASE REPORT OF FACET ARTHROPATHY INDUCED NERVE ROOT COMPRESSION RESULTING IN MOTOR WEAKNESS AND PAIN
 Cox Technic Case Report #100 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent October 2011 on 10/11/11 ) 1 Case Report: CASE REPORT OF FACET ARTHROPATHY INDUCED NERVE ROOT COMPRESSION RESULTING IN MOTOR WEAKNESS
Cox Technic Case Report #100 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent October 2011 on 10/11/11 ) 1 Case Report: CASE REPORT OF FACET ARTHROPATHY INDUCED NERVE ROOT COMPRESSION RESULTING IN MOTOR WEAKNESS
CERVICAL SPINE INJURIES IN THE ELDERLY
 CERVICAL SPINE INJURIES IN THE ELDERLY ISADOR H. LIEBERMAN, JOHN K. WEBB From University Hospital, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham, England We reviewed 41 patients over the age of 65 years (mean 76.5)
CERVICAL SPINE INJURIES IN THE ELDERLY ISADOR H. LIEBERMAN, JOHN K. WEBB From University Hospital, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham, England We reviewed 41 patients over the age of 65 years (mean 76.5)
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
Request Card Task ANSWERS
 Request Card Task ANSWERS Medical Student Workbook Author: Dr Sam Leach, SpR Case 1 What differential diagnoses are most likely? Which investigation is most appropriate? Case 1 The most likely diagnosis
Request Card Task ANSWERS Medical Student Workbook Author: Dr Sam Leach, SpR Case 1 What differential diagnoses are most likely? Which investigation is most appropriate? Case 1 The most likely diagnosis
Rheumatoid Arthritis and the Cervical Spine. Radiology Rounds November 21, 2006 Derek Haaland
 Rheumatoid Arthritis and the Cervical Spine Radiology Rounds November 21, 2006 Derek Haaland Laiho et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004:34;267. Laiho et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004:34;267. *Shen et al.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and the Cervical Spine Radiology Rounds November 21, 2006 Derek Haaland Laiho et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004:34;267. Laiho et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004:34;267. *Shen et al.
ASJ. Analysis of the Prevalence and Distribution of Cervical and Thoracic Compressive Lesions of the Spinal Cord in Lumbar Degenerative Disease
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Cervical and thoracic Asian compressive Spine J 2014;8(1):19-26 lesions in http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.1.19 lumbar degenerative disease 19
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Cervical and thoracic Asian compressive Spine J 2014;8(1):19-26 lesions in http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.1.19 lumbar degenerative disease 19
Indications for cervical spine immobilisation: -
 Paediatric Trauma Cervical Spine Guidelines UHW Traumatic injuries of the cervical spine (C-spine) are uncommon in children. However, it is safer assume there is a cervical spine injury until examination
Paediatric Trauma Cervical Spine Guidelines UHW Traumatic injuries of the cervical spine (C-spine) are uncommon in children. However, it is safer assume there is a cervical spine injury until examination
Surgical Treatment for Cervical Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis as a Cause of Dysphagia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Surgical Treatment for Cervical Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis as a Cause of Dysphagia Katsuhito Yoshioka, Hideki Murakami, Satoru Demura,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Surgical Treatment for Cervical Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis as a Cause of Dysphagia Katsuhito Yoshioka, Hideki Murakami, Satoru Demura,
Misdiagnosis in cervical spondylosis myelopathy.
 Journal of the International Society of Head and Neck Trauma (ISHANT) Case report Misdiagnosis in cervical spondylosis myelopathy. Dr. Reinel A. Junco Martin. Neurosurgeon. Assistant professor Miguel Enriquez
Journal of the International Society of Head and Neck Trauma (ISHANT) Case report Misdiagnosis in cervical spondylosis myelopathy. Dr. Reinel A. Junco Martin. Neurosurgeon. Assistant professor Miguel Enriquez
Chapter 2 Diagnostic Algorithms. 4 Traumatic Neck Pain Algorithm
 Chapter 2 Diagnostic Algorithms 4 Traumatic Neck Pain Algorithm Patient presents with a traumatic onset of neck pain. In general, radiographs should be ordered with a history of recent, significant trauma.
Chapter 2 Diagnostic Algorithms 4 Traumatic Neck Pain Algorithm Patient presents with a traumatic onset of neck pain. In general, radiographs should be ordered with a history of recent, significant trauma.
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment
 Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment 1 Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRI June 2009; Volume 30; Number 3; pp. 168-173 Vincenzo Giuliano, MD, Antonio Pinto,
Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment 1 Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRI June 2009; Volume 30; Number 3; pp. 168-173 Vincenzo Giuliano, MD, Antonio Pinto,
Spine. Neuroradiology. Spine. Spine Pathology. Distribution of fractures. Radiological algorithm. Role of radiology 18/11/2015
 Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy
 Original Study Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy Lorenzo Nigro 1, Pasquale Donnarumma 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Marika Rullo 2, Antonio Santoro 1, Roberto Delfini 1
Original Study Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy Lorenzo Nigro 1, Pasquale Donnarumma 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Marika Rullo 2, Antonio Santoro 1, Roberto Delfini 1
Spontaneous Resolution of Spinal Canal Deformity After Burst Dispersion Fracture
 779 Spontaneous Resolution of Spinal Canal Deformity After Burst Dispersion Fracture T. M. H. Chakera 1 George Bedbrook C. M. Bradley3 We reviewed the records of 8 patients with 30 burst-dispersion spinal
779 Spontaneous Resolution of Spinal Canal Deformity After Burst Dispersion Fracture T. M. H. Chakera 1 George Bedbrook C. M. Bradley3 We reviewed the records of 8 patients with 30 burst-dispersion spinal
