Available online at Open Access at PubMed Central. The Journal of Biomedical Research, 2016, 30(5):
|
|
|
- Annabella Lindsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at Open Access at PubMed Central The Journal of Biomedical Research, 2016, 30(5): Original Article The impact of endplate fracture on postoperative vertebral height loss and kyphotic deformity during treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with balloon kyphoplasty Qingqing Li 1,, Long Xiao 1,, Jianwei Zhang 1,2, Jin Fan 1, Wei Zhou 1, Guoyong Yin 1,, Yongxin Ren 1, 1 Department of Orthopaedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu , China; 2 Department of Orthopaedics, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, Jiangsu , China. Abstract This retrospective study investigated the impact of endplate fracture on postoperative vertebral height loss and kyphotic deformity in 144 patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture (OVCF), who received balloon kyphoplasty. Patients were divided into four groups: Group 1 had no superior endplate fracture, Group 2 had fractures on the anterior portion of the superior endplate, Group 3 had fractures on the posterior portion of the superior endplate, and Group 4 had complete superior endplate fractures. Anterior and middle vertebral body height, vertebral compression ratio, vertebral height loss rate, and kyphosis Cobb angle of each patient were measured and visual analogue scale (VAS) and Oswestry disability index (ODI) scores were recorded. The anterior vertebral height and kyphosis deformity of all groups significantly improved after the surgery, whereas substantial anterior vertebral height loss and increased Cobb angle were observed in all patients at the last follow-up. Although the vertebral height loss rate and the Cobb angle in Group 2, 3 and 4 were larger compared with Group 1 at the last follow-up, only the vertebral height loss rate in Group 4 and the increase in the Cobb angle in Group 2 and 4 were statistically different from those in Group 1. The VAS and ODI scores in all groups measured after the surgery and at the last follow-up were significantly lower compared with preoperative scores, but there was no significant difference among these groups. Balloon kyphoplasty significantly improved vertebral fracture height and kyphosis. Vertebral height loss and increased kyphotic deformity were observed in OVCF patients with endplate fractures after the surgery. Postoperative aggravation of kyphosis was observed in Group 2. Furthermore, severe vertebral height loss and increased kyphotic deformity were confirmed in Group 4 after the surgery. Our results suggested that postoperative vertebral height loss and aggravation of kyphosis may be associated with biomechanical changes in the vertebral body caused by endplate fracture. Therefore, surgery should not only restore compressed vertebral body height and correct kyphosis, but also correct the deformity of endplate to achieve an effective treatment of OVCF patients with endplate fracture. Keywords: osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture, balloon kyphoplasty, endplate fracture, height loss, kyphosis Corresponding authors: Dr. Guoyong Yin, Department of Orthopaedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu , China, Tel: , guoyong_yin@ sina.com; Dr. Yongxin Ren, Department of Orthopaedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu , China, Tel: , renyongxin@yahoo.com by the Journal of Biomedical Research. All rights reserved. These two authors contributed equally to this work Received 05 May 2015, Revised 15 June 2015, Accepted 06 May 2016, Epub 20 July 2016 CLC number: R681, Document code: A. The authors reported no conflict of interests. doi: /JBR
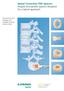
2 420 Li Q et al. J Biomed Res, 2016, 30 Introduction Vertebral compression fracture is the most common complication for patients with osteoporosis, which often cause severe back pain, vertebral height loss, and kyphosis [1]. Although percutaneous vertebroplasty can effectively relieve pain and has received satisfactory results in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture (OVCF), it has several drawbacks including high cement leakage rate, and inability to restore vertebral body height and correct kyphosis. Balloon kyphoplasty is developed on the basis of percutaneous vertebroplasty, during which an expandable balloon is used to restore height. The procedure effectively reduces the occurrence of bone cement leakages, recovers vertebral body height, and corrects spinal kyphosis compared with other surgical approaches [2-3]. Nevertheless, the incidence of postoperative complications such as vertebral height loss, aggravation of kyphosis and vertebral fractures of adjacent segments remains high [4]. In recent years, with extensive application of balloon kyphoplasty and development in spinal biomechanics, the injection of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) increases the strength of fractured vertebral segments, but changes biomechanical distribution of adjacent segments, which may cause postoperative fracture of adjacent segments [5-8]. However, few studies have been performed to investigate the mechanisms of vertebral height loss and aggravation of kyphosis after balloon kyphoplasty. Furthermore, these studies even yield conflicting results. In a follow-up study by Dansie et al. of 51 OVCF patients treated with percutaneous vertebroplasty, the postoperative loss rate of anterior vertebral height was 18.0% [9], whereas it was 63.0% in another similar study [10]. It has been reported that vertebral height loss and aggravation of kyphosis after balloon kyphoplasty may be associated with preoperative severe osteoporosis, insufficient PMMA injection, necrosis of fractured vertebral body, and excessive restoration of vertebral height [11]. Nevertheless, mechanisms behind vertebral height loss and aggravation of kyphosis after balloon kyphoplasty remain inconclusive. Postoperative vertebral height loss and aggravation of kyphosis of balloon kyphoplasty may cause chronic low back pain, affecting the surgical outcome. Silverman et al. have shown that kyphosis reduces daily activities and quality of life, and even increases mortality [12]. Therefore, it is important to study the mechanism of vertebral height loss and aggravation of kyphosis after balloon kyphoplasty for effective prevention of postoperative complications. The vertebral endplate bears 40% 75% of the pressure of the vertebral body, and is directly involved in transferring pressure from the vertebral disc to the vertebral body [13]. Biomechanical studies have confirmed that even a slight morphological change in endplate can lead to a dramatic reduction in motor function of the vertebral body [14]. OVCF is often accompanied by vertebral endplate fracture, which causes changes in endplate stress distribution. Such biomechanical changes in fractured vertebral body may be closely associated with vertebral height loss and kyphosis after balloon kyphoplasty. In this retrospective study, the impact of degree of endplate fracture on postoperative vertebral height loss and kyphotic deformity was investigated in OVCF patients treated with balloon kyphoplasty. Patients and methods Patients A retrospective analysis was performed on patients with OVCF who received balloon kyphoplasty in the Division of Spinal Surgery at the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University from January 2009 to December Patients were selected according to the following criteria: 1) fresh single osteoporotic thoracolumbar vertebral compression fractures with high signal on MRI fat-suppressed T2 image, 2) with severe back pain which could not be resolved by conservative therapy, and 3) follow up duration at least one year. Exclusion criteria were 1) non-osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures such as pathologic fracture and thoracolumbar burst fracture, 2) dural sac and nerve root compression caused by incomplete posterial or collapsed vertebral body, 3) the degree of vertebral compression over 75%, and 4) infection or clotting dysfunction. Bone density of each patient was examined by X-ray, MRI, CT, and dual-energy X-ray. Patients were divided into the following four groups according to the preoperative degree of superior vertebral endplate fracture by MRI [15] (Fig. 1): Group 1 had no superior endplate fracture, Group 2 had fractures on the anterior portion of the superior endplate (showing discontinuous linear low-signal on MRI T1 images and discontinuous linear high-signal on MRI T2 or fat-suppressed images, and excluding old fractures and Schmorl's nodules), Group 3 had fractures on posterior portion of superior endplate, and Group 4 had complete superior endplate fractures. This study was approved and supervised by the Medical Ethics Committee at the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. Balloon kyphoplasty All patients underwent surgical procedures under general anesthesia. The whole procedure was performed
3 The impact of endplate fracture on postoperative vertebral height loss 421 A B EP 1 2 C D 3 4 Fig. 1 Grouping according End-plate Fracture. Patients were divided into four groups according to the preoperative degree of superior vertebral endplate fracture detected with MRI: Group 1 without any superior endplate fracture (A); Group 2 with fractures on anterior portion of superior endplate (showing discontinuous linear low-signal on MRI T1 images and discontinuous linear high-signal on MRI T2 or fat-suppressed images, and excluding old fractures and Schmorl's nodules) (B); Group 3 with fractures on posterior portion of superior endplate (C); Group 4 with complete superior endplate fractures (D). with a C-arm perspective machine. Core needles were inserted at 3:00 on the right side and 9:00 on the left side of the pedicle shadow until the lateral tip reached the posterior wall of the vertebral body, and the anteroposterior tip reached the medial edge of the pedicle shadow. The core needle was removed, and guide pin, expansion sleeve and working casing were placed inside the needle to establish a working channel in fractured vertebral body. An expandable balloon was implanted in the vertebral body and dilated until vertebral body height was restored. The balloon was removed and PMMA cement [powder (g) : liquid (ml) = 2:1] was slowly injected into the vertebral body. The working channel was removed after PMMA was completely solidified, and the incision was sutured. Assessment of efficacy Imaging evaluation Anterior and middle vertebral height, anterior vertebral height ratio, anterior vertebral height restoration rate, anterior vertebral height loss rate, the Cobb angle, kyphosis correction degree, and the increase in Cobb angle were determined by X-ray examination before and after the surgery, and at the last follow-up visit. Anterior vertebral height ratio was calculated as the ratio of anterior height of fractured vertebral body to the average anterior height of adjacent vertebral bodies. If an old fracture or deformity existed in either of the adjacent vertebral bodies, the next adjacent vertebral body was measured. Anterior vertebral height restoration rate was calculated as the difference between pre- and postoperative anterior vertebral height ratios, and anterior vertebral height loss rate was calculated as the difference between anterior vertebral height ratios obtained immediately after the surgery and at the last follow-up. Cobb angle was defined as the angle formed between lines drawn parallel to the respective superior and inferior endplates of fracture. Kyphosis correction degree was calculated as the difference between preand postoperative Cobb angles. Increase in Cobb angle was the difference between Cobb angles measured immediately after the surgery and at the last follow-up (Fig. 2). Leakage of bone cement into intervertebral space in each group was also recorded (Fig. 3). Evaluation of efficacy Visual analogue scale (VAS) and Oswsetry disability index (ODI) were assessed to reveal the degree of pain
4 422 Li Q et al. J Biomed Res, 2016, 30 A B C Fig. 2 Imaging evaluation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with balloon kyphoplasty. Data were determined as follows: Initial anterior vertebral body height (Y)=the average anterior height of adjacent vertebral bodies, calculated as (a+c)/2. Anterior vertebral height restoration rate=(postoperative anterior vertebral height preoperative anterior vertebral height)/initial anterior vertebral body height, (e-b)/y*100%. Central vertebral height restoration rate=(f-d)/y*100%. Cobb angle was defined as the angle formed between the lines drawn parallel to respective superior and inferior endplates of the fracture as shown in Fig. 2C. and the level of activity of patients before and after the surgery, and at the last follow-up visit. Statistical analysis All data were presented as mean ± SD, and analyzed using SPSS19.0 software package (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Age, bone density, duration of symptoms, the amount of bone cement, anterior vertebral height, vertebral column height, anterior vertebral height restoration rate, anterior vertebral height loss rate, Kobb angle, kyphosis correction degree, increase in Kobb angle, VAS and ODI scores of patients in different groups were compared by analysis of variance (ANOVA). P<0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Results General information of patients A total of 144 patients including 30 males and 114 females with a mean age of 69.1 ± 8.6 (range, years) years were enrolled in this study. The A B C D Fig. 3 Images of the lumbar vertebra of a 62-year-old female patient. A: T score in bone density test was -3.2, preoperative anterior vertebral height and Cobb angle was 21.5 mm and 18.0, respectively. B: The MRI image of showing L1 lumbar vertebral compression fracture with anterior endplate fracture (marked by a white arrow). C: X-ray image showing leakage of bone cement into intervetebral space via anterior endplate fracture (marked by a black arrow). Preoperative anterior vertebral height and Cobb angle was 23.5 mm and 11.8, respectively. D: X-ray image at 13 months after the surgery showing that anterior vertebral height and Cobb angle was 10.4 mm and 22.1, respectively. Yellow lines represent Cobb angle.
5 The impact of endplate fracture on postoperative vertebral height loss 423 Table 1 General information of patients. Parameter Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 The number of cases Age 69.8± ± ± ±10.0 Gender (male/female) 12/44 10/34 4/24 4/12 Bone density (T score) 2.9± ± ± ±0.4 Thoracic vertebra 28/56 14/44 10/28 0/16 Lumbar vertebra 28/56 30/44 18/28 16/16 Duration of symptoms (days) 9.2± ± ± ±10.2 The amount of bone cement (ml) 5.1± ± ± ±0.4 Duration of follow up (months) 14.3± ± ± ±1.0 number of patients in Group 1, 2, 3 and 4 was 56, 44, 28 and 16, respectively. While the mean age of Group 4 (73.6±10.0) was significantly higher than Group 1 (69.8±8.6, P<0.05), Group 2 (66.8±8.9, P<0.05), and Group 3 (68.9±6.6, P<0.05), and there were no significant differences in the mean age among Group 1, 2 and 3 (Table 1). Radiological outcomes Preoperative anterior vertebral height in the four groups was 20.7±3.3 mm, 20.9±3.7 mm, 19.6±3.0 mm, and 19.7±3.8 mm, respectively, and preoperative Cobb angles were 13.7±6.2, 12.5±3.6, 13.1±6.7, and 14.1±6.4, respectively. Anterior vertebral height of each group (24.3±2.5 mm, 25.4±2.9 mm, 24.3±3.2 mm, and 23.8±3.8 mm, respectively, P<0.05) was significantly restored and the Cobb angle was significantly reduced (8.2±5.3, 6.9±3.4, 6.7±3.8, and 9.5±6.0, respectively, P<0.05) right after the surgery. Although the anterior vertebral height in each group (21.7±3.1 mm, 22.2±4.0 mm, 21.1±3.5 mm, and 19.0±3.9 mm, respectively) measured at the last follow-up was lower than those measured immediately after the surgery, anterior vertebral height in Group 1, 2 and 3 at the last follow-up was higher than preoperative height. There were no significant differences between the anterior vertebral height in Group 4 measured before surgery and at the last follow-up. Cobb angle of each group at the last follow-up (11.1±5.8, 11.8±3.6, 10.9±6.1, and 15.6±5.1, respectively) was significantly higher than that Table 2 Vertebral body height and Cobb angle in each group determined before and right after surgery, and at the last follow-up. Parameter Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 N Preoperative anterior vertebral body height (mm) 20.7± ± ± ±3.8 Postoperative anterior vertebral body height (mm) 24.3± ± ± ±3.8 Anterior vertebral body height at the last follow-up (mm) 21.7± ± ± ±3.9 Preoperative Cobb angle 13.7± ± ± ±6.4 Postoperative Cobb angle 8.2± ± ± ±6.0 Cobb angle at the last follow-up 11.1± ± ± ±5.1 Difference in vertebral body height (P value) Pre-/post operative Preoperative/last follow-up Postoperative/last follow-up Difference in Cobb angle (P value) Pre-/post operative Preoperative/last follow-up Postoperative/last follow-up
6 424 Li Q et al. J Biomed Res, 2016, 30 Table 3 Vertebral height restoration rate, kyphosis correction degree, and rate of intervertebral bone cement leakage right after surgery, and vertebral height loss. Parameter Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Vertebral height restoration rate right after the surgery (%) 14.4± ± ± ±9.7 Vertebral height loss rate at the last follow-up (%) 10.4± ± ± ±8.8 Kyphosis correction degree right after the surgery 5.6± ± ± ±3.4 Increase in Cobb angle at the last follow-up 2.9± ± ± ±4.4 Rate of intervertebral bone cement leakage right after the surgery (%) 0(0%) 9(20.45%) 3(10.71%) 6(37.5%) measured immediately after surgery, whereas the angles in Group 2, 3 and 4 at the last follow-up were not significantly different from preoperative angles (Table 2). In addition, there were no significant differences in postoperative anterior vertebral height restoration rates among each group (14.4±9.5%, 16.4±10.0%, 18.8±10.0%, and 14.3±9.7%, respectively). Vertebral height loss rate at the last follow-up was 10.4±8.5%, 11.6±11.4%, 13.0±7.4%, and 16.7±8.8%, respectively, and a significant difference in loss rate existed only between EP1 and Group 4 (P<0.05). There were no significant differences among postoperative kyphosis correction degrees (5.6±4.6, 5.7±3.7, 6.4±6.3, and 4.7±3.4, respectively), and increase of Cobb angle at the last follow-up was 2.9±3.0, 4.9±2.9, 4.2±3.7, and 6.1±4.4, respectively, with significant differences between Group 1 and 2 (P<0.05), and between Group 1 and Group 4 (P<0.05) (Table 3). The number of cases of intervertebral bone cement leakage was 0 (0%), 9 (20.45%), 3 (10.71%), and 6 (37.5%), respectively. VAS and ODI scores There were no significant differences in preoperative VAS and ODI scores among each group. Postoperative VAS and ODI scores in all groups were significantly lower than preoperative scores (Table 4) although there were no significant differences among these groups. Discussion OVCF is the most common complication in patients with osteoporosis, and often causes severe back pain, vertebral height loss, and kyphosis [1]. Balloon kyphoplasty is developed on the basis of percutaneous vertebroplasty, during which an expandable balloon is used to restore vertebral height. It has several advantages over percutaneous vertebroplasty such as low rate of bone cement leakage, restoration of vertebral body height, and correction of kyphosis [8]. However, problems including the loss of vertebral height, aggravation of kyphosis, and fracture in adjacent vertebral segments Table 4 VAS and ODI scores before and right after surgery, and at the last follow-up. Parameter Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 N Preoperative VAS 7.9± ± ± ±0.4 Postoperative VAS 0.9± ± ± ±0.7 VAS at the last follow-up 0.5± ± ± ±0.5 Preoperative ODI 63.5± ± ± ±5.9 Postoperative ODI 9.5± ± ± ±2.2 ODI at the last follow-up 6.0± ± ± ±2.7 Difference in VAS (P value) Pre-/post operative Preoperative/last follow-up Postoperative/last follow-up Difference in ODI (P value) Pre-/post operative Preoperative/last follow-up Postoperative/last follow-up
7 The impact of endplate fracture on postoperative vertebral height loss 425 often occur after surgery [4]. Postoperative vertebral height loss and kyphosis always lead to chronic low back pain, which reduces daily activities and life quality, and even increases mortality rate [14]. Therefore, it is important to study the mechanism of postoperative vertebral height loss and aggravation of kyphosis for effective prevention of complications after the surgery. OVCF is often accompanied by vertebral endplate fracture. Vertebral endplate bears 40%-75% of the pressure of the vertebral body, and is directly involved in transferring the pressure from the vertebral disc to the vertebral body [9]. Biomechanical studies have demonstrated that even a slight morphological change in endplate can lead to a dramatic reduction in motor function of the vertebral body [14]. While the maximum stress was found in the center of healthy endplate and underlying cancellous bone due to axial pressure [16], and found in the lateral areas of the endplates of elderly patients due to disc degeneration, osteoporosis, and etc [17]. It was also confirmed that the highest effective stress was located in the anterior part of the vertebral body by a 3D finite element dynamic response analysis [18]. In addition, Grangt et al. identified the maximum compressive stress in the posterior-lateral part of the vertebral endplate under normal physiological conditions, but the lowest stress in the central part [19]. Therefore, the stress loaded on the anterior and lateral parts of endplate increases in elderly patients with osteoporosis, while the strength of the anterior and central parts significantly decreases, which makes these parts most commonly prone to fractures when subjected to excessive load. It also explains why the anterior part of endplate is always lower than the posterior part in OVCF patients [18]. Postoperative vertebral height loss is often resulted from failure to completely correct deformity of endplate during surgery which causes increased stress in the surrounding part of the vertebral body in patients with both vertebral and endplate fractures. Furthermore, Oner, et al. showed that the aggravation of vertebral kyphosis might be related to the embedding of disc in the vertebral body or endplate after endplate fracture [15]. Therefore, the vertebral height loss and kyphosis after balloon kyphoplasty are closely associated with vertebral biomechanical changes caused by changes in stress distribution of endplate after a fracture. Our study demonstrated that postoperative vertebral height loss and aggravated kyphosis are associated with endplate fracture. While progressive kyphosis was observed in OCVF patients with endplate fracture especially anterior endplate fracture after the surgery, both severe vertebral height loss and aggravated kyphosis were identified in patients with complete endplate fracture. The present study demonstrated that endplate fracture caused not only an increased incidence of postoperative vertebral height loss and kyphosis, but also a significant higher rate of bone cement leakage (P<0.05). Previous studies have shown that endplate damages, iatrogenic penetrating injuries, and the lack of a clear gap in the vertebral body are main reasons for the leakage of bone cement into the intervertebral space [20]. In a quantitative study of pressure in the center of vertebral body during PKP surgery by Weisskopf et al., a low pressure was observed when empty vertebral cavity was not completely filled with bone cement, whereas the pressure surged when injecting bone cement into a full cavity and the leakage might easily occur with the presence of endplate fracture [21]. The impact of intervertebral bone cement leakage on the efficacy of outcome in OCVF patients remains quite controversial. Mirovsky et al. showed no association between the leakage and efficacy of surgery [22]. In this study, intervertebral cement leakage did not cause severe symptoms, and VAS and ODI scores improved after surgery and at the last follow-up. We still believe that endplate fracture not only led to aggravated postoperative vertebral height loss and kyphosis, but also caused higher incident of intervertebral cement leakage, further aggravating vertebral height loss and kyphosis. Therefore, intervertebral cement leakage should be avoided during the surgery for OCVF patients with endplate fracture. Bone cement should be filled in anterior column in the vertebral body with anterior fracture that resists the major compression forces to decrease the risk of postoperative compression. In contrast, the vertebral body should be completely filled with bone cement to correct deformity of endplate in patient with compete endplate fracture. Balloon kyphoplasty can effectively relieve pain, and significantly improve vertebral height and kyphosis. However, problems including postoperative vertebral height loss and kyphosis often occur. Our study demonstrated that endplate fracture was not only associated with increased incidence of postoperative vertebral height loss and kyphosis, but also a significant cause of bone cement leakage. It is important to note that sample sizes are few and have certain influence to the result. Nonetheless, intervertebral cement leakage should be avoided, and endplate deformity should be corrected during surgery for OCVF patients with endplate fracture. Acknowledgments This work was supported by National Natural and Science Foundation ( ), Jiangsu Natural and Science Foundation (BK ).
8 426 Li Q et al. J Biomed Res, 2016, 30 References [1] Meunier PJ, Delmas PD, Eastell R, et al. Diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: clinical guidelines. International Committee for Osteoporosis Clinical Guidelines[J]. Clin Ther, 1999, 21(6): [2] Hiwatashi A, Sidhu R, Lee RK, et al. Kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty to increase vertebral body height: a cadaveric study[j]. Radiology, 2005, 237(3): [3] Wardlaw D, Cummings SR, Van Meirhaeghe J, et al. Efficacy and safety of balloon kyphoplasty compared with non-surgical care for vertebral compression fracture (FREE): a randomised controlled trial[j]. Lancet, 2009, 373(9668): [4] Black DM, Arden NK, Palermo L, et al. Prevalent vertebral deformities predict hip fractures and new vertebral deformities but not wrist fractures. Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 1999, 14(5): [5] Fribourg D, Tang C, Sra P, et al. Incidence of subsequent vertebral fracture after kyphoplasty[j]. Spine, 2004, 29(20): ; discussion [6] Harrop JS, Prpa B, Reinhardt MK, et al. Primary and secondary osteoporosis' incidence of subsequent vertebral compression fractures after kyphoplasty[j]. Spine, 2004, 29(20): [7] Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Jasper LE, et al. An ex vivo biomechanical evaluation of a hydroxyapatite cement for use with vertebroplasty[j]. Spine, 2001, 26(14): [8] Berlemann U, Ferguson SJ, Nolte LP, et al. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty. A biomechanical investigation[j]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2002, 84(5): [9] Dansie DM, Luetmer PH, Lane JI, et al. MRI findings after successful vertebroplasty[j]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2005, 26(6): [10] Lin WC, Lee YC, Lee CH, et al. Refractures in cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty: a retrospective analysis[j]. Eur Spine J, 2008, 17(4): [11] Li X, Lou X, Lin X, et al. Refracture of osteoporotic vertebral body concurrent with cement fragmentation at the previously treated vertebral level after balloon kyphoplasty: a case report[j]. Osteoporos Int, 2014, 25(5): [12] Silverman SL. The clinical consequences of vertebral compression fracture[j]. Bone, 1992, 13(Suppl 2): S27 S31. [13] Hollowell JP, Vollmer DG, Wilson CR, et al. Biomechanical analysis of thoracolumbar interbody constructs. How important is the endplate?[j] Spine, 1996, 21(9): [14] Adams MA, Freeman BJ, Morrison HP, et al. Mechanical initiation of intervertebral disc degeneration[j]. Spine, 2000, 25(13): [15] Oner FC, van Gils AP, Faber JA, et al. Some complications of common treatment schemes of thoracolumbar spine fractures can be predicted with magnetic resonance imaging: prospective study of 53 patients with 71 fractures. Spine, 2002, 27(6): [16] Rohlmann A, Neller S, Claes L, et al. Influence of a follower load on intradiscal pressure and intersegmental rotation of the lumbar spine[j]. Spine, 2001, 26(24): E557 E561. [17] Kurowski P, Kubo A. The relationship of degeneration of the intervertebral disc to mechanical loading conditions on lumbar vertebrae[j]. Spine, 1986, 11(7): [18] Hakim NS, King AI. A three dimensional finite element dynamic response analysis of a vertebra with experimental verification[j]. J Biomech, 1979, 12(4): [19] Oxland TR, Grant JP, Dvorak MF, et al. Effects of endplate removal on the structural properties of the lower lumbar vertebral bodies[j]. Spine, 2003, 28(8): [20] Koh YH, Han D, Cha JH, et al. Vertebroplasty: magnetic resonance findings related to cement leakage risk[j]. Acta Radiol, 2007, 48(3): [21] Weisskopf M, Ohnsorge JA, Niethard FU. Intravertebral pressure during vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty: an in vitro study[j]. Spine, 2008, 33(2): [22] Mirovsky Y, Anekstein Y, Shalmon E, et al. Intradiscal cement leak following percutaneous vertebroplasty[j]. Spine, 2006, 31(10):
Vertebral Augmentation for Compression Fractures. Scott Magnuson, MD Pain Management of North Idaho, PLLC
 Vertebral Augmentation for Compression Fractures Scott Magnuson, MD Pain Management of North Idaho, PLLC OVCFs are most common type of fragility fracture 20-25% Caucasian women and men over 50 yrs have
Vertebral Augmentation for Compression Fractures Scott Magnuson, MD Pain Management of North Idaho, PLLC OVCFs are most common type of fragility fracture 20-25% Caucasian women and men over 50 yrs have
Original Article The clinical application and efficacy of percutaneous kyphoplasty via unilateral pedicular approach guided by CT image measurement
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(11):20861-20868 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015384 Original Article The clinical application and efficacy of percutaneous kyphoplasty via unilateral pedicular approach
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(11):20861-20868 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015384 Original Article The clinical application and efficacy of percutaneous kyphoplasty via unilateral pedicular approach
Risk Factors of New Compression Fractures in Adjacent Vertebrae after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 5, No. 3, pp 180~187, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2011.5.3.180 Risk Factors of New Compression Fractures in Adjacent Vertebrae after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Myung-Ho
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 5, No. 3, pp 180~187, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2011.5.3.180 Risk Factors of New Compression Fractures in Adjacent Vertebrae after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Myung-Ho
KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients
 Xi an Hong Hui Hospital Xi an, Shaanxi, China KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients Dingjun Hao, Baorong He, Liang Yan Hong Hui Hospital,
Xi an Hong Hui Hospital Xi an, Shaanxi, China KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients Dingjun Hao, Baorong He, Liang Yan Hong Hui Hospital,
Efficacy of Percutaneous Kyphoplasty in Treating Osteoporotic Multithoracolumbar Vertebral Compression Fractures
 Efficacy of Percutaneous Kyphoplasty in Treating Osteoporotic Multithoracolumbar Vertebral Compression Fractures HAI TANG; JIN-DONG ZHAO; YUAN LI; HAO CHEN; PU JIA; KAI-MING CHAN; GANG LI abstract Full
Efficacy of Percutaneous Kyphoplasty in Treating Osteoporotic Multithoracolumbar Vertebral Compression Fractures HAI TANG; JIN-DONG ZHAO; YUAN LI; HAO CHEN; PU JIA; KAI-MING CHAN; GANG LI abstract Full
Balloon kyphoplasty is now considered as minimally invasive
 Published February 7, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3424 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE In Not Only Vertebroplasty but Also Kyphoplasty, the Resolution of Vertebral Deformities Depends on Vertebral Mobility K. Yokoyama,
Published February 7, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3424 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE In Not Only Vertebroplasty but Also Kyphoplasty, the Resolution of Vertebral Deformities Depends on Vertebral Mobility K. Yokoyama,
Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with Thoracolumbar Fractures
 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research 2018, 2(1): 23-27 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with
Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research 2018, 2(1): 23-27 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with
Departement of Neurosurgery A.O.R.N A. Cardarelli- Naples.
 Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Bone Cement-Augmented Percutaneous Short Segment Fixation : An Effective Treatment for Kummell s Disease?
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.54 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58 (1) : 54-59, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.54 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58 (1) : 54-59, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
Qiang Wang, Hong-Guang Xu, Li-Jun Dong, Hong Wang, Jin-Song Zhu
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4095-4100 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0017186 Original Article Comparison of hyperextension reduction and balloon dilation method combined with vertebroplasty in treatment
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4095-4100 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0017186 Original Article Comparison of hyperextension reduction and balloon dilation method combined with vertebroplasty in treatment
Clinical and Radiographic Results of Unilateral Transpedicular Balloon Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures
 online ML Comm 0CLINICAL ARTICLE0 J Kor Neurotraumatol Soc 2007;3:19-24 ISSN 1738-8708 Clinical and Radiographic Results of Unilateral Transpedicular Balloon Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Osteoporotic
online ML Comm 0CLINICAL ARTICLE0 J Kor Neurotraumatol Soc 2007;3:19-24 ISSN 1738-8708 Clinical and Radiographic Results of Unilateral Transpedicular Balloon Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Osteoporotic
Percutaneous vertebroplasty has become a therapeutic option
 Published January 26, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2898 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.H. Yen M.M.H. Teng W.H. Yuan Y.C. Sun C.Y. Chang Preventive Vertebroplasty for Adjacent Vertebral Bodies: A Good Solution to Reduce
Published January 26, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2898 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.H. Yen M.M.H. Teng W.H. Yuan Y.C. Sun C.Y. Chang Preventive Vertebroplasty for Adjacent Vertebral Bodies: A Good Solution to Reduce
Medicine. The Incidence of New Vertebral Fractures Following Vertebral Augmentation. A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
 Medicine SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS The Incidence of New Vertebral Fractures Following Vertebral Augmentation A Meta-Analysis of Randomized led Trials Weixing Xie, MSc, Daxiang Jin, MD, Chao Wan,
Medicine SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS The Incidence of New Vertebral Fractures Following Vertebral Augmentation A Meta-Analysis of Randomized led Trials Weixing Xie, MSc, Daxiang Jin, MD, Chao Wan,
Vertebral compression model and comparison of augmentation agents
 23 23 27 Vertebral compression model and comparison of augmentation agents Authors Clint Hill, Scott Wingerter, Doug Parsell, Robert McGuire Institution Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Rehabilitation,
23 23 27 Vertebral compression model and comparison of augmentation agents Authors Clint Hill, Scott Wingerter, Doug Parsell, Robert McGuire Institution Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Rehabilitation,
OVCF of the thoracic and lumbar spine can be a source of
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.O. Ortiz R. Bordia Injury to the Vertebral Endplate-Disk Complex Associated with Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: MR imaging has been used extensively
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.O. Ortiz R. Bordia Injury to the Vertebral Endplate-Disk Complex Associated with Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: MR imaging has been used extensively
Risk Factors for Subsequent Fracture after Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:120-124 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.120 Risk Factors for Subsequent Fracture after Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:120-124 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.120 Risk Factors for Subsequent Fracture after Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
Osteoporosis is a condition in which the bones lose calcium. Analysis of Related Factors on the Deformity Correction of Balloon Kyphoplasty
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE Analysis of Related Factors on the Deformity Correction of Balloon Kyphoplasty C. Xu, H.-X. Liu, and H.-Z. Xu ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Balloon kyphoplasty is a minimally
ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE Analysis of Related Factors on the Deformity Correction of Balloon Kyphoplasty C. Xu, H.-X. Liu, and H.-Z. Xu ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Balloon kyphoplasty is a minimally
YOUR SUDDEN BACK PAIN MAY BE A FRACTURE
 YOUR SUDDEN BACK PAIN MAY BE A FRACTURE Sudden-onset back pain could signal a spinal fracture. TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR If you have tried treatments like rest and oral medication for more than a few days
YOUR SUDDEN BACK PAIN MAY BE A FRACTURE Sudden-onset back pain could signal a spinal fracture. TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR If you have tried treatments like rest and oral medication for more than a few days
The Effect of Posterior Pedicle Screws Biomechanical Fixation for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture
 Copyright 2017 Tech Science Press MCB, vol.14, no.3, pp.187-194, 2017 The Effect of Posterior Pedicle Screws Biomechanical Fixation for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture Baogang Tian 1, Yang Shao 1, Zhijiong
Copyright 2017 Tech Science Press MCB, vol.14, no.3, pp.187-194, 2017 The Effect of Posterior Pedicle Screws Biomechanical Fixation for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture Baogang Tian 1, Yang Shao 1, Zhijiong
Percutaneous Vertebroplasty-Induced Adjacent Vertebral Compression Fracture. Ki Seong Eom, MD, PhD, and Tae Young Kim, MD, PhD
 Pain Physician 2012; 15:E527-E532 ISSN 2150-1149 Case Report Percutaneous Vertebroplasty-Induced Adjacent Vertebral Compression Fracture Ki Seong Eom, MD, PhD, and Tae Young Kim, MD, PhD From: Department
Pain Physician 2012; 15:E527-E532 ISSN 2150-1149 Case Report Percutaneous Vertebroplasty-Induced Adjacent Vertebral Compression Fracture Ki Seong Eom, MD, PhD, and Tae Young Kim, MD, PhD From: Department
REFERENCE DOCTOR Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options. Hyeun Sung Kim, MD, PhD,
 Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, South Korea (1994) / Board of Neurosurgery (1999) MEMBERSHIPS & PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES Korean Neurosurgical Society / Korean
Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, South Korea (1994) / Board of Neurosurgery (1999) MEMBERSHIPS & PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES Korean Neurosurgical Society / Korean
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:71-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.71 More than 5-Year Follow-up Results of Two- Level and Three-Level Posterior Fixations of Thoracolumbar
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:71-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.71 More than 5-Year Follow-up Results of Two- Level and Three-Level Posterior Fixations of Thoracolumbar
Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment of multi-segmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy
 92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
Title: Comparative Analysis of Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures
 Asian Spine Journal - Manuscript Submission Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: ASJ-12-088 Title: Comparative Analysis of Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures
Asian Spine Journal - Manuscript Submission Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: ASJ-12-088 Title: Comparative Analysis of Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures
Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life
 Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Indications for Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Introduction. Dae-Hyun Seo, MD 1, Si-Hyuck Oh, MD 1, Kyeong-Wook Yoon, MD 1, Jung-Ho Ko, MD, PhD 1, Young-Jin Kim, MD, PhD 1, and Jee Young Lee, MD 2
 online ML Comm CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2014;10(2):86-91 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.86 Risk Factors of New Adjacent Compression Fracture after
online ML Comm CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2014;10(2):86-91 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.86 Risk Factors of New Adjacent Compression Fracture after
What Effects Does Necrotic Area of Contrast-Enhanced MRI in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture Have on Further Compression and Clinical Outcome?
 Clinical Article J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (2) : 181-188, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.0707.015 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 What Effects Does Necrotic Area of Contrast-Enhanced MRI in Osteoporotic
Clinical Article J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (2) : 181-188, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.0707.015 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 What Effects Does Necrotic Area of Contrast-Enhanced MRI in Osteoporotic
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(6): /ISSN: /IJCEM Xiutong Fang 1, Hongxing Song 1, Yang Li 2
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(6):5707-5714 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0068334 Original Article Percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a comparison
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(6):5707-5714 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0068334 Original Article Percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a comparison
Postero-lateral approach with open view vertebroplasty - eggshell technique
 Romanian Neurosurgery (2013) XX 4: 357-368 357 Postero-lateral approach with open view vertebroplasty - eggshell technique E.Fl. Exergian 1, I.Fl. Luca-Husti 2, D. Şerban 1 1 Spine Surgery Department,
Romanian Neurosurgery (2013) XX 4: 357-368 357 Postero-lateral approach with open view vertebroplasty - eggshell technique E.Fl. Exergian 1, I.Fl. Luca-Husti 2, D. Şerban 1 1 Spine Surgery Department,
Collection of abstracts
 Pre-op Post-op NOT FOR SALE IN THE US Collection of abstracts Vertebral anatomical restoration before fixation as a new method to treat vertebral compression fractures. David NORIEGA Stryker Spine International
Pre-op Post-op NOT FOR SALE IN THE US Collection of abstracts Vertebral anatomical restoration before fixation as a new method to treat vertebral compression fractures. David NORIEGA Stryker Spine International
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Multiple Technology Appraisal (MTA)
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Multiple Technology Appraisal (MTA) Percutaneous Vertebroplasty (PVP) and Balloon Kyphoplasty (BKP) for the treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Multiple Technology Appraisal (MTA) Percutaneous Vertebroplasty (PVP) and Balloon Kyphoplasty (BKP) for the treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
Analysis of Clinical Features of Hip Fracture Patients with or without Prior Osteoporotic Spinal Compression Fractures
 J Bone Metab 2013;20:11-15 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2013.20.1.11 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Analysis of Clinical Features of Hip Fracture Patients with or without Prior Osteoporotic
J Bone Metab 2013;20:11-15 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2013.20.1.11 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Original Article Analysis of Clinical Features of Hip Fracture Patients with or without Prior Osteoporotic
Instruction for Use of Kyphoplasty Tool Kit JS-CE-SM-07-01,A/0
 Instruction for Use of Kyphoplasty Tool Kit JS-CE-SM-07-01,A/0 1 Instruction for Use of Kyphoplasty Tool Kit Product name Kyphoplasty Tool Kit Product structure and components Kyphoplasty Tool Kit consists
Instruction for Use of Kyphoplasty Tool Kit JS-CE-SM-07-01,A/0 1 Instruction for Use of Kyphoplasty Tool Kit Product name Kyphoplasty Tool Kit Product structure and components Kyphoplasty Tool Kit consists
Radiologic Finding of Failed Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
 Radiologic Finding of Failed Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Liu, Wei Chiang 1, M.D., Sang-Ho Lee 2, M.D., Won Gyu Choi 2, M.D., Dong-Yeob Lee 2, M.D., Sung Suk Paeng 3, M.D., Amy Kwon 4, Ph.D. Department
Radiologic Finding of Failed Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Liu, Wei Chiang 1, M.D., Sang-Ho Lee 2, M.D., Won Gyu Choi 2, M.D., Dong-Yeob Lee 2, M.D., Sung Suk Paeng 3, M.D., Amy Kwon 4, Ph.D. Department
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title: Reduction of the domino effect in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures through short-segment fixation with intravertebral expandable pillars compared to percutaneous
Author's response to reviews Title: Reduction of the domino effect in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures through short-segment fixation with intravertebral expandable pillars compared to percutaneous
Revision Surgery after Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:203-208 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.4.203 Revision Surgery after Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty Kee-Yong Ha, MD, Ki-Won Kim, MD, Young-Hoon Kim, MD, In-Soo
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:203-208 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.4.203 Revision Surgery after Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty Kee-Yong Ha, MD, Ki-Won Kim, MD, Young-Hoon Kim, MD, In-Soo
Original Article Risk factors of new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2019;12(1):949-954 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0076385 Original Article Risk factors of new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty Zhen
Int J Clin Exp Med 2019;12(1):949-954 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0076385 Original Article Risk factors of new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty Zhen
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2): /ISSN: /IJCEM Yi Yang, Hao Liu, Yueming Song, Tao Li
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
An Empirical Study of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture Review
 An Empirical Study of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture Review C-H Li 1, M-C Chang 2, Z-P Ho 3, H-Y Chiu 4 ABSTRACT Osteoporotic vertebral fractures (OVF) are most common injuries seen in elder people. The
An Empirical Study of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture Review C-H Li 1, M-C Chang 2, Z-P Ho 3, H-Y Chiu 4 ABSTRACT Osteoporotic vertebral fractures (OVF) are most common injuries seen in elder people. The
Original Article Effects of percutaneous kyphoplasty combined with pedicle screw fixation on aged osteoporotic thoracolumbar burst fracture
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(10):20062-20067 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0031428 Original Article Effects of percutaneous kyphoplasty combined with pedicle screw fixation on aged osteoporotic thoracolumbar
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(10):20062-20067 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0031428 Original Article Effects of percutaneous kyphoplasty combined with pedicle screw fixation on aged osteoporotic thoracolumbar
Weifeng Zhai, Yongwei Jia, Jianjie Wang, Liming Cheng, Zhili Zeng, Yan Yu, Lei Chen
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(8):13473-13481 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0011576 Original Article The clinical effect of percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of multiple osteoporotic vertebral
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(8):13473-13481 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0011576 Original Article The clinical effect of percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of multiple osteoporotic vertebral
MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures
 MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd Spine Unit. Orthopaedic Department. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor. Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona. Introduction. The application
MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd Spine Unit. Orthopaedic Department. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor. Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona. Introduction. The application
Percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of very severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with spinal canal compromise
 Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:13 DOI 10.1186/s13018-018-0719-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of very severe osteoporotic vertebral
Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:13 DOI 10.1186/s13018-018-0719-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of very severe osteoporotic vertebral
Byung Jik Kim, M.D., Jin Hwan Kim, M.D., Jeong Gook Seo #, M.D., Young Chul Kim, M.D.
 Comparison of the Results of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Treating Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture and Posttraumatic Vertebral Collapse (Kummell s disease) Abstract Byung Jik Kim, MD, Jin
Comparison of the Results of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Treating Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture and Posttraumatic Vertebral Collapse (Kummell s disease) Abstract Byung Jik Kim, MD, Jin
Outline Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Who, What, and When
 Outline Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Who, What, and When Douglas C. Bauer, MD University of California San Francisco, USA Vertebral fracture epidemiology, consequences and diagnosis Kyphoplasty and
Outline Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Who, What, and When Douglas C. Bauer, MD University of California San Francisco, USA Vertebral fracture epidemiology, consequences and diagnosis Kyphoplasty and
Comparison of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for complications
 Comparison of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for complications J.D. Zhang, B. Poffyn, G. Sys, D. Uyttendaele * Ji-dong Zhang, MD, Department of Spine Surgery, Tianjin Hospital, 406 Jiefang South Road,
Comparison of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for complications J.D. Zhang, B. Poffyn, G. Sys, D. Uyttendaele * Ji-dong Zhang, MD, Department of Spine Surgery, Tianjin Hospital, 406 Jiefang South Road,
Vertebroplasty has been widely and successfully used in the
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH E.M. Knavel K.R. Thielen D.F. Kallmes Vertebroplasty for the Treatment of Traumatic Nonosteoporotic Compression Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Vertebroplasty is commonly used for osteoporotic
ORIGINAL RESEARCH E.M. Knavel K.R. Thielen D.F. Kallmes Vertebroplasty for the Treatment of Traumatic Nonosteoporotic Compression Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Vertebroplasty is commonly used for osteoporotic
Hiroto Yamaguchi*, Hidetoshi Nojiri**, Kei Miyagawa*, Nozomu Inoue***
 Three-Dimensional High-Resolution Image Analysis of the Segmental Reduction Effect Obtained with Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Intervertebral Deformity Hiroto Yamaguchi*, Hidetoshi Nojiri**,
Three-Dimensional High-Resolution Image Analysis of the Segmental Reduction Effect Obtained with Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Intervertebral Deformity Hiroto Yamaguchi*, Hidetoshi Nojiri**,
Outline Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Who, What, and When
 Outline Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Who, What, and When Douglas C. Bauer, MD University of California San Francisco, USA Vertebral fracture epidemiology, consequences and diagnosis Kyphoplasty and
Outline Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Who, What, and When Douglas C. Bauer, MD University of California San Francisco, USA Vertebral fracture epidemiology, consequences and diagnosis Kyphoplasty and
Is unilateral pedicle screw fixation superior than bilateral pedicle screw fixation for lumbar degenerative diseases: a meta-analysis
 Lu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:296 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-1004-x SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Open Access Is unilateral pedicle screw fixation superior than bilateral
Lu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:296 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-1004-x SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Open Access Is unilateral pedicle screw fixation superior than bilateral
Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
Percutaneous vertebroplasty is a minimally invasive treatment
 Published July 30, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1722 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Hiwatashi T. Yoshiura K. Yamashita H. Kamano T. Dashjamts H. Honda Subsequent Fracture after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Can Be Predicted
Published July 30, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1722 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Hiwatashi T. Yoshiura K. Yamashita H. Kamano T. Dashjamts H. Honda Subsequent Fracture after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Can Be Predicted
Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral shortening
 Eur Spine J (2002) 11 :8 12 DOI 10.1007/s005860000214 TECHNICAL INNOVATION Alejandro Reyes-Sanchez Luis M. Rosales Victor P. Miramontes Dario E. Garin Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral
Eur Spine J (2002) 11 :8 12 DOI 10.1007/s005860000214 TECHNICAL INNOVATION Alejandro Reyes-Sanchez Luis M. Rosales Victor P. Miramontes Dario E. Garin Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral
Outline. Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty. Epidemiology. Identifying Vertebral Fractures. Page 1
 Outline Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty Douglas C. Bauer, MD University of California San Francisco, USA Vertebral fracture epidemiology, consequences and diagnosis Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty: what
Outline Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty Douglas C. Bauer, MD University of California San Francisco, USA Vertebral fracture epidemiology, consequences and diagnosis Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty: what
Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty (BKP) 1 is an interventional
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH G. Saliou D.R. Rutgers E.M. Kocheida G. Langman A. Meurin H. Deramond P. Lehmann Balloon-Related Complications and Technical Failures in Kyphoplasty for Vertebral Fractures BACKGROUND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH G. Saliou D.R. Rutgers E.M. Kocheida G. Langman A. Meurin H. Deramond P. Lehmann Balloon-Related Complications and Technical Failures in Kyphoplasty for Vertebral Fractures BACKGROUND
Comprehension of the common spine disorder.
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Dingjun Hao, Baorong He, Liang Yan. Hong Hui Hospital, Xi an Jiaotong University College. of Medicine, Xi an, Shaanxi , China
 Xi an Hong Hui Hospital Xi an, Shaanxi, China The difference of occurring superior adjacent segment pathology after lumbar posterolateral fusion by using two different pedicle screw insertion techniques
Xi an Hong Hui Hospital Xi an, Shaanxi, China The difference of occurring superior adjacent segment pathology after lumbar posterolateral fusion by using two different pedicle screw insertion techniques
Vertebral body augmentation with cement such as vertebroplasty
 Case Report Stentoplasty (Cemented kyphoplasty with Stent) Under Biplane Digital Subtraction Angiography (Biplane DSA) Buranakarl T, MD email : tayard.bu@bgh.co.th Tayard Buranakarl, MD 1 Kanoknard Jaisanuk,
Case Report Stentoplasty (Cemented kyphoplasty with Stent) Under Biplane Digital Subtraction Angiography (Biplane DSA) Buranakarl T, MD email : tayard.bu@bgh.co.th Tayard Buranakarl, MD 1 Kanoknard Jaisanuk,
Osteoporosis and Spinal Fractures
 Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Surgical Technique INTERSOMATIC CERVICAL CAGE
 R INTERSOMATIC CERVICAL CAGE NEOCIF IMPLANTS NEOCIF is an implant designed to make anterior cervical interbody fusion (ACIF) easier and to remove the need for structural autologous graft. The cage is made
R INTERSOMATIC CERVICAL CAGE NEOCIF IMPLANTS NEOCIF is an implant designed to make anterior cervical interbody fusion (ACIF) easier and to remove the need for structural autologous graft. The cage is made
Early Bone Marrow Edema Pattern of the Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture : Can Be Predictor of Vertebral Deformity Types and Prognosis?
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.59.2.137 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 59 (2) : 137-142, 2016 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2016 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.59.2.137 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 59 (2) : 137-142, 2016 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2016 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
Fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine and thoracolumbar transition
 Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty
 Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.007 01/11/2005 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 02/01/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Inpatient;
Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.007 01/11/2005 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 02/01/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Inpatient;
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx. White Paper
 3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
Impact of spino-pelvic and global spinal alignment on the risk of osteoporotic vertebral collapse
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Impact of spino-pelvic and global spinal alignment on the risk of osteoporotic vertebral collapse Takashi Ohnishi 1)2), Akira Iwata 1)2), Masahiro Kanayama
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Impact of spino-pelvic and global spinal alignment on the risk of osteoporotic vertebral collapse Takashi Ohnishi 1)2), Akira Iwata 1)2), Masahiro Kanayama
Balloon Kyphoplasty. An Evidence-Based Analysis. Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series 2004; Vol. 4, No. 12. December 2004
 Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series 2004; Vol. 4, No. 12 Balloon Kyphoplasty An Evidence-Based Analysis December 2004 Medical Advisory Secretariat Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Suggested
Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series 2004; Vol. 4, No. 12 Balloon Kyphoplasty An Evidence-Based Analysis December 2004 Medical Advisory Secretariat Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Suggested
Posterior instrumentation after a failed balloon kyphoplasty in the thoracolumbar junction: a case report
 Cumming et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:189 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Posterior instrumentation after a failed balloon kyphoplasty in the thoracolumbar junction:
Cumming et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:189 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Posterior instrumentation after a failed balloon kyphoplasty in the thoracolumbar junction:
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Orthop Clin N Am 38 (2007) 463 468 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Andreas Vesalius, in history of spine pathology, 306 Anesthesia/anesthetics for PECD, 329 in minimally
Orthop Clin N Am 38 (2007) 463 468 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Andreas Vesalius, in history of spine pathology, 306 Anesthesia/anesthetics for PECD, 329 in minimally
Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture: Severe Canal Compromise but Neurologically Intact Cases
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:101-105 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.101 Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture:
CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:101-105 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.101 Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture:
PERCUTANEOUS BALLOON KYPHOPLASTY, RADIOFREQUENCY KYPHOPLASTY, AND MECHANICAL VERTEBRAL AUGMENTATION
 KYPHOPLASTY, AND MECHANICAL VERTEBRAL AUGMENTATION Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures,
KYPHOPLASTY, AND MECHANICAL VERTEBRAL AUGMENTATION Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures,
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Pott s kyphosis. University Affiliated Sixth People s Hospital, 600 Yishan Road, Shanghai , P.
 QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management.
 River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
/ 66 nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 n-ha/pa66
 1425 / 66 / 66 nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 n-ha/pa66 2011 1 10 20 n-ha/pa66 8 12 22 80 51 1 24 4 L 4 5 8 L 5 S 1 9 L 4 S 1 3 3 5 9 3 X CT Oswestry ODI SF-36 20 6 9 7 3 d 3 6 P < 0.01P > 0.05 3 9 4
1425 / 66 / 66 nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 n-ha/pa66 2011 1 10 20 n-ha/pa66 8 12 22 80 51 1 24 4 L 4 5 8 L 5 S 1 9 L 4 S 1 3 3 5 9 3 X CT Oswestry ODI SF-36 20 6 9 7 3 d 3 6 P < 0.01P > 0.05 3 9 4
Pulmonary Cement Embolism in a Multiple Myeloma Patient Following Vertebroplasty: A Case Report
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Pulmonary Cement Embolism in a Multiple Myeloma Patient Following Vertebroplasty: A Case Report Alpaslan Senkoylu 1 *, Erdem Aktas 2, Murat Songur 3 and Elif Aktas 4 1 Gazi University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Pulmonary Cement Embolism in a Multiple Myeloma Patient Following Vertebroplasty: A Case Report Alpaslan Senkoylu 1 *, Erdem Aktas 2, Murat Songur 3 and Elif Aktas 4 1 Gazi University
ASJ. Causes of Late Revision Surgery after Bone Cement Augmentation in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Asian Spine Journal.
 Asian Spine Journal 294 Kee-Yong Clinical Ha et al. Study http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.294 Causes of Late Revision Surgery after Bone Cement Augmentation in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
Asian Spine Journal 294 Kee-Yong Clinical Ha et al. Study http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.294 Causes of Late Revision Surgery after Bone Cement Augmentation in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
J Korean Soc Spine Surg 2015 Dec;22(4): Originally published online December 31, 2015;
 Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery Potential Risk Factors for Subsequent Fractures according to Treatment of Primary Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures Min-Wook Kim, M.D., Dae-Hyun Yoon, M.D., Sang-Ho
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery Potential Risk Factors for Subsequent Fractures according to Treatment of Primary Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures Min-Wook Kim, M.D., Dae-Hyun Yoon, M.D., Sang-Ho
Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012
 Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012 Posterior distraction and decompression Secure Fixation and Stabilization Integrated Bone
Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012 Posterior distraction and decompression Secure Fixation and Stabilization Integrated Bone
KYPHON Balloon Kyphoplasty
 KYPHON Results from a randomized controlled study comparing KYPHON to nonsurgical care for treatment of vertebral compression fractures Relief. Mobility. Quality of Life. What is? KYPHON is a minimally
KYPHON Results from a randomized controlled study comparing KYPHON to nonsurgical care for treatment of vertebral compression fractures Relief. Mobility. Quality of Life. What is? KYPHON is a minimally
Percutaneous vertebroplasty is a relatively noninvasive,
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH F. Al-Ali T. Barrow K. Luke Vertebroplasty: What Is Important and What Is Not BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: It is important to try to clarify the methodology of vertebroplasty such as amount
ORIGINAL RESEARCH F. Al-Ali T. Barrow K. Luke Vertebroplasty: What Is Important and What Is Not BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: It is important to try to clarify the methodology of vertebroplasty such as amount
FISH VERTEBRAE RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE DONALD L. RESNICK
 ~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
Curative effect comparison of anterior and posterior approach in debridement combined with bone graft fusion for the treatment of spinal tuberculosis.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (11): 4832-4836 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Curative effect comparison of anterior and posterior approach in debridement combined with bone graft fusion for the treatment
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (11): 4832-4836 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Curative effect comparison of anterior and posterior approach in debridement combined with bone graft fusion for the treatment
Daniele Vanni 1, Andrea Pantalone 1, Vincenzo Magliani 2, Vincenzo Salini 1, Pedro Berjano 3. Introduction
 Original Study Corpectomy and expandable cage replacement versus third generation percutaneous augmentation system in case of vertebra plana: rationale and recommendations Daniele Vanni 1, Andrea Pantalone
Original Study Corpectomy and expandable cage replacement versus third generation percutaneous augmentation system in case of vertebra plana: rationale and recommendations Daniele Vanni 1, Andrea Pantalone
The Role of Unilateral Balloon Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Patients with OVCFS: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
 Pain Physician 2018; 21:209-218 ISSN 1533-3159 Systematic Review The Role of Unilateral Balloon Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Patients with OVCFS: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Guang-Heng Xiang,
Pain Physician 2018; 21:209-218 ISSN 1533-3159 Systematic Review The Role of Unilateral Balloon Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Patients with OVCFS: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Guang-Heng Xiang,
Effect of the Location of Endplate Cement Extravasation on Adjacent Level Fracture in Osteoporotic Patients Undergoing Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
 Pain Physician 2015; 18:E805-E814 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Study Effect of the Location of Endplate Cement Extravasation on Adjacent Level Fracture in Osteoporotic Patients Undergoing Vertebroplasty
Pain Physician 2015; 18:E805-E814 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Study Effect of the Location of Endplate Cement Extravasation on Adjacent Level Fracture in Osteoporotic Patients Undergoing Vertebroplasty
MRI Findings after Successful Vertebroplasty
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1595 1600, June/July 2005 MRI Findings after Successful Vertebroplasty David M. Dansie, Patrick H. Luetmer, John I. Lane, Kent R. Thielen, John T. Wald, and David F. Kallmes BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1595 1600, June/July 2005 MRI Findings after Successful Vertebroplasty David M. Dansie, Patrick H. Luetmer, John I. Lane, Kent R. Thielen, John T. Wald, and David F. Kallmes BACKGROUND
Double Cement Application Cavity Containment Kyphoplasty: Technique Description and Efficacy
 A Technique Paper Double Cement Application Cavity Containment Kyphoplasty: Technique Description and Efficacy Richard A. DalCanto, MD, PhD, Mary Kay Reinhardt, RN, and Isador H. Lieberman, MD, MBA, FRCS(C)
A Technique Paper Double Cement Application Cavity Containment Kyphoplasty: Technique Description and Efficacy Richard A. DalCanto, MD, PhD, Mary Kay Reinhardt, RN, and Isador H. Lieberman, MD, MBA, FRCS(C)
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional overview of percutaneous insertion of craniocaudal expandable implants for vertebral compression fracture
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional overview of percutaneous insertion of craniocaudal expandable implants for vertebral compression fracture
R45 A
 Published online www. wanfangdate. com. cn doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1006-7108. 2015. 06. 001 643 1 2* 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1. 117000 2. 309 102628 3. 037004 4. 266003 5. 100068 6. 100050 7. 100050 8. 462000 9.
Published online www. wanfangdate. com. cn doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1006-7108. 2015. 06. 001 643 1 2* 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1. 117000 2. 309 102628 3. 037004 4. 266003 5. 100068 6. 100050 7. 100050 8. 462000 9.
Surgical outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar lesions in rheumatoid arthritis
 Surgical outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar lesions in rheumatoid arthritis Fujiwara H*, Kaito T**, Makino T**, Ishii T*, Yonenobu K*** Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, *National
Surgical outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar lesions in rheumatoid arthritis Fujiwara H*, Kaito T**, Makino T**, Ishii T*, Yonenobu K*** Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, *National
Spinal Correction FRA Spacers. Angled and parallel spacers designed for a lateral approach.
 Processed by MTF, designed and available through Synthes Spine Spinal Correction FRA Spacers. Angled and parallel spacers designed for a lateral approach. Spinal Correction FRA Spacers Two varieties of
Processed by MTF, designed and available through Synthes Spine Spinal Correction FRA Spacers. Angled and parallel spacers designed for a lateral approach. Spinal Correction FRA Spacers Two varieties of
Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia: A Case Series
 C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Case Report Minimally invasive transforaminal endoscopic treated neurologic deficit after percutaneous kyphoplasty-a case report
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(1):373-377 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0057528 Case Report Minimally invasive transforaminal endoscopic treated neurologic deficit after percutaneous kyphoplasty-a case
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(1):373-377 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0057528 Case Report Minimally invasive transforaminal endoscopic treated neurologic deficit after percutaneous kyphoplasty-a case
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE. CONSTRUX Mini PTC. Mini PTC Spacer System
 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE CONSTRUX Mini PTC Mini PTC Spacer System TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Operative Technique 2 Part Numbers 6 Indications For Use 7 INTRODUCTION 1 INTRODUCTION The CONSTRUX Mini PTC
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE CONSTRUX Mini PTC Mini PTC Spacer System TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Operative Technique 2 Part Numbers 6 Indications For Use 7 INTRODUCTION 1 INTRODUCTION The CONSTRUX Mini PTC
Posterior. Lumbar Fusion. Disclaimer. Integrated web marketing. Multimedia Health Education
 Posterior Lumbar Fusion Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about surgery must be made in conjunction with your surgeon or
Posterior Lumbar Fusion Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about surgery must be made in conjunction with your surgeon or
Original Article Prevention and treatment of bone cement-related complications in patients receiving percutaneous kyphoplasty
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(2):2371-2377 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0003594 Original Article Prevention and treatment of bone cement-related complications in patients receiving percutaneous kyphoplasty
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(2):2371-2377 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0003594 Original Article Prevention and treatment of bone cement-related complications in patients receiving percutaneous kyphoplasty
Comparison between Balloon Kyphoplasty and Short Segmental Fixation Combined with Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Kümmell s Disease
 Pain Physician 2015; 18:373-381 ISSN 1533-3159 Retrospective Evaluation Comparison between Balloon Kyphoplasty and Short Segmental Fixation Combined with Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Kümmell s Disease
Pain Physician 2015; 18:373-381 ISSN 1533-3159 Retrospective Evaluation Comparison between Balloon Kyphoplasty and Short Segmental Fixation Combined with Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Kümmell s Disease
