Design Rationale and Clinical Review of a New Compliant Bearing Material for Acetabular Reconstruction
|
|
|
- Gerald Clark
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Joint Implant Surgery & Research Foundation Chagrin Falls, Ohio, USA Design Rationale and Clinical Review of a New Compliant Bearing Material for Acetabular Reconstruction Timothy McTighe, Dr. H.S. (hc)*; Richard Treharne, PhD**, MBA; Alex H. Greene, M.S.** July, 2009 Acknowledgment to the following surgeons: Prof. Sandro Giannini, MD; Prof. Antonio Moroni, MD; Prof. Werner Siebert; Dr. Sabine Mai; Prof. Gianlugi Sacchetti; Dr. Dieter Randeu; Prof. Burkhardt Wippermann Abstract: Wear and the generation of particulate debris continue to be a significant problem in the longevity of total joint devices. Metal on metal bearings started in the 1930s with Philip Wiles and progressed with McKee, Ring and Sivash through the 1960s. Sir John Charnley convinced that M-O-M could not be used to reduce the frictional torque began his search into the field of polymers in the early 1950s. Polyethylene and metal has been the material of choice for THA since the 1960s. Continued problems with wear and the generation of particulate debris has increased the use of ceramics and a renewed interest in M-O-M. This paper will review the design and clinical results of a new compliant bearing material (PCU) implanted in humans for total hips since This material and system design possess features significantly different from traditional acetabular bearing materials. This new system is having encouraging clinical results and may open up a new way of thinking about acetabular reconstruction. Introduction Total hip arthroplasty is one of the most effective orthopaedic procedures with a very high success rate as measured by pain relief, improved function and patient satisfaction. It has been almost three decades since Willert first describe the problem of polyethylene wear leading to peri-prosthetic inflammation, granuloma, bone resorption and implant loosening. Wear has and continues to be a significant problem. We are now seeing third and fourth generations of polyethylene along with work being done on alternative hard on hard bearing trying to reduce the generation of wear debris. Examples of polyethylene failures Hylamer Poly XLPE Poly Examples of polyethylene induced osteolysis Over the past few years as hard on hard bearings have increased in usage, clinical issues have been raised as to squeaking, fatigue strength in ceramics to short term aseptic loosening, high trace elements, and metal sensitivity in metal-on-metal bearings. Bone Necrosis (E. Smith) M-O-M bearing Ceramic on Ceramic is recognized for low wear and no metal ion release, however, fatigue issues can be a problem resulting in component fracture, intraoperative chipping, and now reported articulation noise in the form of squeaking. From the Joint Implant Surgery & Research Foundation 46 Chagrin Plaza #118, Chagrin Falls, Ohio Non-Profit Founded in Reprint request: Timothy McTighe, Dr. H.S. (hc), Executive Director, JISRF *Joint Implant Surger & Research Foundation, Chagrin Falls, OH **Acive Implants Corp., 5865 Ridgeway Center Parkway, Memphis, TN
2 Currently, the scientific community has not yet reached consensus as to which of the currently available bearing surfaces options are optimal for total hip arthroplasty. Ideally, the surfaces for articulation will be made from materials having high strength, low wear, corrosion resistance and low friction moments. Polycarbonate urethane (PCU) has been developed into a new approach for replacement of the polyethylene side of the bearing surface. A total of 408 acetabular devices made of this material have been implanted at 70 different sites in Italy, Germany, Israel, Spain and Australia. A total of 84% have been implanted as cartilage replacements (meaning only the Buffer implant was used on the socket side). A variety of femoral stem components have been used all with a metal CoCr femoral modular head component with a standard 12/14 Euro-headneck taper junction. All femoral heads were large diameter (meaning greater than 32 mm). This review of the results to date was limited to indication for use, infection, and revision rate of the acetabular component for dislocation and loosening. Material & Methods Polycarbonate urethane (PCU) has been extensively tested in a number of animal and biomechanical models and began clinical evaluation in Europe as a bearing surface in the hip socket for THA in patients with femoral neck fractures. A retrospective analysis of patients who underwent primary THA with a compliant bearing material (PCU) TriboFit acetabular Buffer Implant by Active Implants Corp. Memphis TN was undertaken. The inclusion period was between February 2006 and May Design Rationale The TriboFit acetabular Buffer implant has significantly different design goals as compared to conventional polyethylene, ceramic and metal bearings. Two styles of TriboFit acetabular Buffer implants were reviewed. One being just the Buffer implant used as an acetabular cartilage replacement placed directly into the boney acetabular socket and a second style where the Buffer implant is used as an acetabular insert placed into a traditional cementless acetabular metal component. Soft compliant polycarbonate urethane is designed to function more like the natural hip at least on the acetabular side of the hip joint. Articular cartilage, along with the synovial fluid layer, provides a natural buffer to the bone and surrounding soft tissues in the hip, so that there is reasonable stress transmission at the joint due to the shock absorbing Page 2
3 characteristics of the cartilage and fluid layer. Previous implant systems provide poor shock absorption, due in part, to the significant difference in mechanical properties of the materials used-specifically, the modulus of elasticity. All prior commercial systems eliminated nature s buffer. Polycarbonate urethane (PCU) is a hydrophilic material which attracts fluids. This property helps to establish the full fluid-film layer between the Buffer implant and the femoral head in order to provide microelasto-hydrodynamic lubrication. TriboFit Buffer Implant cross section showing fluid film layer as compared to polyethylene Scientific studies have demonstrated PCU to provide better full fluid lubrication in terms of enhanced wear reduction compared to conventional UHMPE, and testing is underway comparing cross-linked UHMWPE and hard on hard bearings to PCU. We have seen in MoM bearings that manufacturing tolerance is a critical factor to the generation of a fluid film level and this fluid film level is necessary to reduce the material frictional properties of MoM bearings. If tolerance is too tight < 100 microns - risk of pinching head and equatorial bearing, resulting in more friction and possible generation of metal debris and increase in ion levels. Another factor with MoM bearings is the occurrence of breakaway wear that is generated during mechanical wear testing. Example of run away wear LLUMC has demonstrated in wear simulators that 1 out of 6 MoM bearing test samples can and do generate break away wear regardless of manufacture and regardless of head diameter. This is a concern since this has yet to be explained. What if anything does this mean to the clinical setting? Only more testing and closer follow-up to clinical studies may some day show clinical correlation. The Buffer Implant Since this PCU implant is designed to function more like cartilage it has the distinct advantage of being low profile from a surgical preparation point of view. The Buffer implant is 3 mm thick so it requires very little bone removal. It has a novel snap fit locking mechanism that provides ease of insertion, positive locking stability with ease of retrievability in mind. It is designed at this point to articulate with a CoCr head. In cases where it is needed, an acetabular shell is also available that is designed to be inserted with this snap fit Buffer implant. This novel design provides versatility to be used as a stand alone acetabular cartilage replacement or it can be used as a standard acetabular component replacing the polyethylene bearing surface. While it is too early in clinical evaluations to determine if Page 3
4 Do not ream to bleeding bed as with standard socket preparation. Leaving any remnants of articulate cartilage will aid load transfer and reduce bone/ implant interface wear generation. one approach is better than the other over the long term, it is certain that a PCU bearing used as a stand alone cartilage implant has the advantage of less bone removal. Surgical Technique Buffer Implant without acetabular metal shell The TriboFit system is designed for all standard surgical approaches and requires no special instruments for exposure. If the Buffer implant is to be used as a stand alone cartilage replacement a few patient requirements are necessary. The first is shape of the socket. The face of the natural acetabulum is closer to 55º not 45º. This implant is designed for full bony containment so preparation and insertion techniques are significant factors. All soft tissue is removed but it is not necessary to remove all remnants of articular cartilage. Ensuring you have a hemispherical shaped socket light reaming can be done but it is not required to go to bleeding bony bed. Note: This is different that the standard surgical preparation for conventional acetabular components. Trial gauges are available for sizing. Sizing and implantation is line to line. It is the locking groove feature that provides implant stability. A special groove reamer similar to the original Charnley grooved reamer is then used to cut a locking channel into the acetabular wall. Then the Buffer implant is snapped into place with finger pressure. It is important to ensure full containment of the implant within the acetabular cavity. If the implant is hanging out in any direction, edge loading and deformation of the material can increase the risk of wear. One complete revolution is required. Do not over ream you may compromise the locking capability of this channel. Page 4
5 Because containment is required the use of large heads and proper restoration of femoral offset is critical to a successful outcome. Locking groove Buffer implant snapped into place Implantation and component insertion is carried out as with any standard cementless conventional acetabular component. Femoral stem selection is the decision of the surgeon. Any cemented or cementless stem design may be used as long as the head neck taper is compatible with the femoral head supplied by Active Implants (12-14 Euro taper). Surgical Technique Buffer Implant with acetabular metal shell This implantation is a standard surgical technique as used with any cementless hemispherical metal shell component. Progressive socket reaming is carried out with standard implant orientation of 45-50º of abduction and 15-20º degrees of version. Press fit of the metal shell is recommended between 1-2 mm. The metal shells are available with two fins and no screw holes. Once proper reaming and sizing is carried out the Buffer implant is snapped into place and can then be inserted as a monoblock acetabular component. TriboFit Modular Femoral Heads are packaged with the Buffers to ensure proper sizing and tolerance. Wear testing to-date has been with cobalt chromium (CoCr) heads and although ceramic heads might reduce wear generation equal to or better than CoCr heads, ceramic has yet to be tested with the Buffer implant. Neck adaptors are available for adjusting vertical height and are selected based on the size of the modular head. The neck adaptor is inserted into the femoral head and is locked together via a taper interference fit. Page 5
6 The Goals of Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA) Remember the goals of THA. Elimination of Pain New Hip Restoration of Function Reproduce Hip Mechanics 1 Femoral Offset 2 Neck Length 3 Version Angle Example of Target Restoration with a modular neck stem design: Instability - What should be done? Trial reduction demonstrates joint instability with slight increased leg length. Modular Heads allow length adjustment, unfortunately increase head length increases leg length. Selection of femoral stems that provide for multiple corrections of femoral offset can and do reduce biomechanical loads that are placed on the bearing surfaces. The advantages to increased offset: Decreased load on the hip joint Increased Joint Stability Reduction of wear debris The newer stem designs available provide features that reduce the risk of increasing femoral offset like increased torsional loads and increased bending moment. Many of the newer stems provide proximal Regular offset Increased offset modularity and neck sparing features that can provide additional benefits when used with the Buffer implant. Big Heads! Theoretically, a bigger head is more stable... At the extremes of motion when the neck impinges In this case, intrinisic stability is unchanged (Head center stays the same). Biomechanical Solution Modular Neck! Add offset for joint stability reduce length for proper gait. Newer stems designs like this Tissue Sparing Implant (TSI stem) saves all of the femoral neck. It is very conceivable that the combination of this and the Buffer implant provides the most tissue (hard & soft) conservation of any current combination available for THA. Page 6
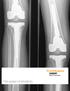
7 The use of this PCU material as a bearing material in THA has a number of potential advantages. It is 70 times less stiff than the traditional UHMWPE used and its stiffness is similar to that of cartilage. The material allows for fluid film lubrication similar to cartilage and has shown improved wear resistance as compared to UHMWPE. Because of the improved wear resistance, the Buffer implant can be made thinner (3mm). All of these features allow less bone to be removed and allows for large head technology that will help reduce hip dislocations. Photograph of the TriboFit Buffer and a post-op x- ray with large head and Buffer implant in position in a patient. Prof. A. Moroni Buffer implant used with Hip Resurfacing These features have considerable appeal in younger, more active patients who will have a higher probability of needing additional surgery in their lifetime. The thinner component conserves more bone and the novel locking design feature makes both insertion and removal if necessary simpler with less bone loss as compared to cemented or current cementless porous metal components. This use also has potential benefits to the elderly that receive these devices for femoral neck fractures. Publications have demonstrated that patients do better with THA as compared to Endo or Bi-Polar heads. Reducing the potential of secondary surgery in this patient population can significantly improve the quality of their life and reduce health care cost by reducing or eliminating the costly revision surgery. Example of typical post-op radiographic views for femoral neck fractures: male, caucasian 71 years old 90 Kg Weight R femoral neck fracture 56 mm Tribofit Buffer 50mm Head + Zimmer 10 mm Stem Prof. A. Moroni Buffer Implant in place Buffer implant with stem and head in place 24 Month Post-Op Prof. A. Moroni case example Page 7
8 Results Surgical Time The literature describes a study of 135 THA patients implanted with either a minimal or standard incision. The average surgical time for the Buffer component and associated implants was approximately 5 minutes on average shorter than primary THA utilizing minimal incision approach and 10 minutes on average shorter than primary THA utilizing a standard surgical approach as reported by Woolson et al. for 135 cases. Surgical Time for the TriboFit Buffer Hip System Data from Woolson et al. (2004) for 135 cases Surgical Blood Loss With the same or shorter operative times blood loss for the TriboFit System as compared to standard surgical incision were comparable (approximately 480 ml, respectively) and on average almost 700 ml less blood loss as compared with MIS in 135 cases. (Woolson et al. 2004) * Data from Woolson et al (2004) for 135 cases A total of 13 elderly femoral neck fracture patients were part of a pre-clinical study. Of these, 2 were revised, 1 died, and 6 were either lost to follow-up or were bedridden for comorbidity, non-device related reasons. The two revisions were the first two implanted patients at two different sites. One was revised at 10.5 months and the other at 12 months. The first was revised because of artifact seen on a computerized tomography (CT) image that made it appear that the Buffer component had disappeared. At revision it was found that the Buffer component was still well fixed and intact. The other component was revised because the patient complained of hip pain. After revision the pain remained and was later determined to be the result of spinal involvement. That Buffer component was intact, well fixed, and the articulating surface still pristine upon removal. Neither revision turned out to be device related or was considered a device failure. Other than the first two patients (both of which were later revised) that had problems with the grooving instrument for insertion of the Buffer component, all of the remaining patients had the TriboFit PCU Buffer component implanted without any issues at the time of surgery. A key advantage of the TriboFit surgical technique is that the acetabular component does not need to be impacted into position, but rather is snapped by hand into the grooved acetabulum. With traditional UHMWPE acetabular cups, press fit impaction of acetabular components is reported by Haidukewych et al (2006) to cause fracture of the acetabular bone in 0.4% of the cases. No acetabular fractures have occurred intraoperatively with the TriboFit System and bone fracture is impossible or extremely unlikely if acetabular cup impaction is not used. Of the more than 45 patients in May 2009 with more than 3 months clinical follow-up, 20 patients had femoral neck fractures and 25 patients had osteoarthritis (OA). In aggregate, 32 patients had 3 to 6 month follow-up, 15 had 6 to 9 month follow-up, 20 had 12 month follow-up, and 4 had 18 to 24 month follow-up. The maximum number of patients with 12 month follow-up is 78. In other words, 291 TriboFit patients have had implants less than one year. Harris Hip Scores Harris Hip Scores (HHS) could be recorded pre-operatively for the osteoarthritis (OA) patients and had an average value of 41.0 in 23 patients. Ten OA patients had an average value of 78.8 at 3 months. Six OA patients had an average value of 88.3 at 6 months. Six patients had an average HHS at 12 months of These HHS results are shown in Figure 4 for Page 8
9 osteoarthritis patients where it can be seen that the averages were similar to or better than for patients undergoing a traditional UHMWPE total hip replacement for osteoarthritis as reported in the literature. Patients with Buffer Only Pre-Op HHS 3-6 Months 9-12 Months n = 7 n = 3 n = 5 Avg. = Avg. = 91.3 Avg. = 83 Patients with Metal Shell Pre-Op HHS 3-6 Months 9-12 Months n = 17 n = 12 n = 6 Avg. = Avg. = 80.3 Avg. = 89.7 Retrievals The overall removal rate after over three years of clinical experience of the TriboFit Hip System is 2.0% (8 out of 408). Even without any explanation this value, on the face of it, compares favorably with the literature that reports a 2.0% removal rate of cementless total hips within the first three years (Simbanda et al 2008). However, it is important to note that the seven of the eight removals were not found to be related to the implant itself and were not related to any of the usual reasons for revisions of acetabular components wear, loosening, or fracture. Since this subject is so important, each of the non-device related removals will be described in order of time from surgery, followed by the device related one. One TriboFit Buffer removal was for trauma in the hospital within the first 3 days of surgery caused by a pelvic fracture after the patient fell out of bed. To repair the pelvic fracture, the Buffer component had to be removed. The second removal occurred shortly after surgery when the patient dislocated their hip. To repair the dislocation the surgeon surgically removed the Buffer component and femoral head component to create a longer neck construct. The third removal also occurred shortly after surgery when the patient became infected. To treat the infection the surgeon surgically removed the Buffer component and femoral head component. A fourth removal occurred at 1 month after a dislocation. During the removal operation to repair the dislocation an infection was discovered and an antibiotic bone cement block was inserted to treat the infection. The fifth removal occurred at 4.8 months in another Buffer alone case. This patient complained of pain, which was the reason for removal, but the pain did not resolve after removal. The sixth removal was at 10.5 months because of pain and what was later determined to be CT artifact that made it appear as though the Buffer component had disappeared. Revision to a traditional hip design that was 2 mm larger than the device removed did resolve the pain. More details concerning this removal are contained in a publication by Wippermann et al A seventh removal was for a patient at 12 months who had pain. Removal and replacement did not resolve the pain which was subsequently correctly diagnosed as caused by spinal stenosis that was causing hip pain. More details concerning this removal have also been published by Siebert et al The eighth removal, the only one that turned out to be device related, occurred at 10 months in a patient that had an apparent immediate dislodgement of the Buffer component from the acetabular bed. Discussion and Summary All of the existing bearing materials used in total hip replacement have known issues and reasons for concern. The design rationale for clinically trying out a new plastic material to replace the acetabular component is that this new material will not have any of the known drawbacks of existing bearing materials. After over three years of clinical use of this bearing material in over 400 cases it can be said that the results to date are encouraging. Even though most of the uses were for femoral neck fractures it can be concluded that the dislocation rates are lower probably because of the larger head size. The clinical results, infection rate, loosening rate, and revision rate appear to be in line with other total hip system bearing materials. Perhaps the most telling information from this clinical series is from the implantations and the revisions of this new bearing acetabular cup system. Unlike most implanted acetabular components, the Buffer component could be easily and quickly inserted and easily removed with a minimal, if any, loss of acetabular bone stock while being implanted or removed. It can also be concluded that the reaction to the material seen clinically and at these revisions has so far been equal to or better than other bearing materials, especially Page 9
10 since no cases of synovitis were observed. Except for one case which was a loosening caused by surgical technique, all of the surgically removed Buffer components were found to be intact, in the original position, and well fixed up to 12 months. Except for this one case the Buffer acetabular implant was revised with the same size acetabular component or a 2 mm larger one than the Buffer size removed. In other words, in nearly every case the new revision acetabular component was the same size as the Buffer component removed. In the beginning all total hip femoral stems were single piece components. Over time nearly all femoral stems have become modular so as to allow for more surgical options for the next surgery. Just as femoral stems became next surgery stems, so too should surgeons begin to think about using next surgery acetabular cups. The use of this new PCU material as an acetabular bearing allows this next surgery concept to be extended to the acetabular prosthesis by allowing through the use of a novel material and unique design, minimal bone removal at the time of implantation, no risk of acetabular fracture from impaction, minimal risk of recurrent dislocation, and minimal risk for a revision to a cup size larger than the primary surgery. All of these next surgery features in this new system either decrease the chances of an acetabular revision, allowing for the acetabular revision to occur easier, and/or permitting for more acetabular bone at the time of revision which in an of itself will allow for more next surgery options in an area that doesn t have much bone stock to begin with. All of these next surgery advantages are in addition to eliminating the known risks of using current acetabular bearing materials. 24 Month Post-Op References 1. Wylde V, Blom AW, Whitehouse SL, et al. Patient-Reported Outcomes After Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty Vol. 24 No ( ) 2. Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, Patterson JJ, Guerin J. tapered titanium cementless total hip replacements. Clin Orthop Relate Res. 2001; (393): Chen CJ, Xenos JS, McAuley JP, Young A, Engh CA Sr. Secondgeneration porous coated total hip arthroplasties have high survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; (466):66 4. Engh Jr CA, Claus AM, Hooper RH, Engh CA. Long term results using anatomic medullary locking hip prosthesis. Clin Orthop Related Res. 2001; (393): Keppler L, Cameron HU, McTighe T, The Role of Modularity in Primary THA-Is There One? 2006 AAOS Scientific Exhibit, 6. Mallory TH, Lombardi AV, Leith JR, et al. Minimal 10-year results of a tapered cementless femoral component in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2001;16 (Suppl): McTighe T, Cementless Modular Stems. JISRF Update April, Cameron HU, McTighe T, Restoration of Joint Mechanics. Mini- Symposium Cutting-Edge Developments on Proximal Modularity in THA Nov. 7, Schutte HD, Romero N, Conrad J, Barfield W, Conway W, McTighe T. Femoral Offset How to Measure Pre-operatively, Mini-Symposium Cutting-Edge Developments on Proximal Modularity in THA Nov. 7, Dorr LD, Faugere MC, Mackel AM, Gruen TA, Bognar B, Malluche HH. Structural and cellular assessment of bone quality of proximal femur. Bone. 1993;14: McTighe T, Trick L, Koeneman JB. Design Considerations for Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty. Encyclopedic Handbooks of Biomaterials & Bioengineering, part B: Vol Amstutz H, Dislocations in U.S. Wright medical web site: Crowinshield R, Maloney WJ, Wentz DH, et al. Biomechanics of Large Femoral heads. Clin Orthop Related Res. Number 429, pp Tkach T, Low W, Cipolletti G, McTighe T. Target Restoration of Hip Mechanics in THA. AAOS Scientific Exhibit 2006, Chicago, IL 15. Turnbull A, Keggi K, Keggi J, Kennon R, Keppler L, McTighe T. Restoration of Femoral Offset Using A Modular Dual-tapered Trapezoid Stem. Poster Exhibit AOA, Oct Gold Coast, AU. 16. Turnbull A, McTighe T. Tapered Stems-Comparison With and Without Modularity. Restoration of Joint Mechanics. Mini-Symposium Cutting- Edge Developments on Proximal Modularity in THA Nov. 7, Low W, Tkach T, McTighe T. Intra-operative Techniques in Using Proximal Modular Stems. Mini-Symposium Cutting-Edge Developments on Proximal Modularity in THA Nov. 7, Keggi K. Anterior Approach THA via Mini-Incision Technique. JISRF Pub. Update Dec Siebert W, Mai S, Kurtz S. Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate- Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report. Journal of Long Term Eff. Med. Implants (1): Wippermann B. Kurtz S, Hallab N. Treharne R. Explantation and Analysis of the First Retrieved Human Acetabular Cup Made of Polycarbonate-Urethane: A Case Report. Journal of Long Term Eff. Med. Implants (1): Woolson ST, et al. Comparison of primary total hip replacements performed with a standard-incision or a mini-incision. J Bone Joint Surg. Am 2004; 86: Page 10
11 Notes Page 11
12 Joint Implant Surgery & Research Foundation 46 Chagrin Shopping Plaza, #118, Chagrin Falls, Ohio, USA
Proximal Modular Stem Design Dual Press With a Dual-Tapered K2 Trapezoid Stems
 Joint Implant Surgery & Research Foundation Chagrin Falls, Ohio, USA Proximal Modular Stem Design Dual Press With a Dual-Tapered K2 Trapezoid Stems Kristaps J. Keggi, MD.,* John Keggi, MD.,** Robert Kennon,
Joint Implant Surgery & Research Foundation Chagrin Falls, Ohio, USA Proximal Modular Stem Design Dual Press With a Dual-Tapered K2 Trapezoid Stems Kristaps J. Keggi, MD.,* John Keggi, MD.,** Robert Kennon,
Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion. Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head
 Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head The Metasul large diameter head technology is the result of in-depth research, development and clinical experience that
Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head The Metasul large diameter head technology is the result of in-depth research, development and clinical experience that
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?
![Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?](/thumbs/78/78456133.jpg) Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners. Design Rationale Surgical Technique
 Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners Design Rationale Surgical Technique The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System was designed to maximize the number of options available to the surgeon, and provide those options
Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners Design Rationale Surgical Technique The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System was designed to maximize the number of options available to the surgeon, and provide those options
Reaching new heights. Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple.
 Reaching new heights Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple. Various acetabular cup choices Compatible with the different head and liner options including VERILAST Technology Reach for proven OR efficient Instrumentation
Reaching new heights Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple. Various acetabular cup choices Compatible with the different head and liner options including VERILAST Technology Reach for proven OR efficient Instrumentation
DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc. 700 Orthopaedic Drive Warsaw, IN USA Tel: +1 (800) Fax: +1 (574)
 References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe
 1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe Abstract Introduction: Osteolysis generated by wear debris remains a problem
1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe Abstract Introduction: Osteolysis generated by wear debris remains a problem
The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation
 The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation Wright is a leading international manufacturer and distributor of superior, easy to use, and innovative orthopaedic implants and instrumentation. For over 50 years,
The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation Wright is a leading international manufacturer and distributor of superior, easy to use, and innovative orthopaedic implants and instrumentation. For over 50 years,
ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
FEA Analysis of Neck Sparing Versus Conventional Cementless Stem
 Joint Implant Surgery & Research Foundation Chagrin Falls, Ohio, USA FEA Analysis of Neck Sparing Versus Conventional Cementless Stem Declan Brazil, PhD 1 ; & Timothy McTighe, Dr. H.S. (hc) 1, Acknowledgement:
Joint Implant Surgery & Research Foundation Chagrin Falls, Ohio, USA FEA Analysis of Neck Sparing Versus Conventional Cementless Stem Declan Brazil, PhD 1 ; & Timothy McTighe, Dr. H.S. (hc) 1, Acknowledgement:
A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY by Timothy McTighe, Exec. Dir., JISRF, Chagrin Falls, Ohio Ying Ko, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio Russell B. Bennett, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio James
A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY by Timothy McTighe, Exec. Dir., JISRF, Chagrin Falls, Ohio Ying Ko, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio Russell B. Bennett, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio James
Stability without compromise. Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert
 Stability without compromise Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert History of Dislocation and Constrained Acetabular Inserts The Need for a Better Solution The Problem Dislocation is the second most common
Stability without compromise Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert History of Dislocation and Constrained Acetabular Inserts The Need for a Better Solution The Problem Dislocation is the second most common
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2. Preparation of the Acetabulum 4. Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5.
 Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT:
 THR Prosthesis Design TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT: PROSTHESIS DESIGN FEATURES JESS JOHNSTON & MELINDA ZIETH History of Hip Prosthesis Joint Replacement Registry Implant Design Technology & Future History and
THR Prosthesis Design TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT: PROSTHESIS DESIGN FEATURES JESS JOHNSTON & MELINDA ZIETH History of Hip Prosthesis Joint Replacement Registry Implant Design Technology & Future History and
Design Rationale. ECHELON Primary Hip System
 Design Rationale ECHELON Primary Hip System ECHELON Primary Total Hip System Addressing clinical issues of cementless hip arthroplasty Cementless total hip arthroplasty has provided a proven method of
Design Rationale ECHELON Primary Hip System ECHELON Primary Total Hip System Addressing clinical issues of cementless hip arthroplasty Cementless total hip arthroplasty has provided a proven method of
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
The Role of Stem Modularity for THA in a Community Based Practice
 Chagrin Falls, Ohio, USA The Role of Stem Modularity for THA in a Community Based Practice Louis Keppler, MD* and Timothy McTighe, Dr. HS (hc)** Abstract: Every few years there are concerns raised regarding
Chagrin Falls, Ohio, USA The Role of Stem Modularity for THA in a Community Based Practice Louis Keppler, MD* and Timothy McTighe, Dr. HS (hc)** Abstract: Every few years there are concerns raised regarding
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE DePuy Synthes DURALOC Surgical Technique CONTENTS Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE DePuy Synthes DURALOC Surgical Technique CONTENTS Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum
CAUTION: Ceramic liners are not approved for use in the United States.
 Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
Cement Polished Tapered Stems of 12/14 Taper. 96 mm 98 mm 104 mm 110 mm 116 mm 122 mm 128 mm. Ceramic Femoral Head. Outer Diameter
 Design Philosophy Cementless Stems of 12/14 Taper Stem Length Neck shaft Angle STEM-N3 STEM-N4 STEM-N5 STEM-N6 STEM-N7 STEM-N8 STEM-N9 123 mm 125 mm 130 mm 135 mm 140 mm 145 mm 150 mm 132 Cement Polished
Design Philosophy Cementless Stems of 12/14 Taper Stem Length Neck shaft Angle STEM-N3 STEM-N4 STEM-N5 STEM-N6 STEM-N7 STEM-N8 STEM-N9 123 mm 125 mm 130 mm 135 mm 140 mm 145 mm 150 mm 132 Cement Polished
Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER A COMPREHENSIVE ACETABULAR REVISION SYSTEM DURALOC CONSTRAINED LINER Introduction Dislocation is the most common postoperative complication in total hip reconstruction.
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER A COMPREHENSIVE ACETABULAR REVISION SYSTEM DURALOC CONSTRAINED LINER Introduction Dislocation is the most common postoperative complication in total hip reconstruction.
PLR. Proximal Loading Revision Hip System
 PLR Proximal Loading Revision Hip System The PLR splined revision stem is designed to recreate the natural stresses in the revised femur, where proximal bone may be compromised. PLR Hip System Design Considerations
PLR Proximal Loading Revision Hip System The PLR splined revision stem is designed to recreate the natural stresses in the revised femur, where proximal bone may be compromised. PLR Hip System Design Considerations
The power of simplicity
 The power of simplicity The power of simplicity Consider the facts, and take a look at the future: Revision TKA procedures are projected to double between now and 2015. 1 Restoration of a normal joint
The power of simplicity The power of simplicity Consider the facts, and take a look at the future: Revision TKA procedures are projected to double between now and 2015. 1 Restoration of a normal joint
The bi-metric XR series of Hip implants blends biomet s proven philosophy and tradition with Advanced technology. porous primary hip series
 The bi-metric XR series of Hip implants blends biomet s proven philosophy and tradition with Advanced technology porous primary hip series BI-METRIC XR SERIES implant technology The Bi-Metric XR Hip Series
The bi-metric XR series of Hip implants blends biomet s proven philosophy and tradition with Advanced technology porous primary hip series BI-METRIC XR SERIES implant technology The Bi-Metric XR Hip Series
Peggers Super Summaries: THR and Revision Concepts
 Total Hip replacement: ARTICUALTIONS Ceramic on polyethylene Ceramic on ceramic for young Metal on metal (resurfacing) Metal (cobalt chrome) on polyethylene WEAR Wear debris similar to bacteria o < 10
Total Hip replacement: ARTICUALTIONS Ceramic on polyethylene Ceramic on ceramic for young Metal on metal (resurfacing) Metal (cobalt chrome) on polyethylene WEAR Wear debris similar to bacteria o < 10
ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ACETABULAR CUP DEVICE INDICATIONS FOR USE The ICONACY I-Hip total hip replacement is indicated for the following conditions: 1. A severely painful and/or disabled hip
ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ACETABULAR CUP DEVICE INDICATIONS FOR USE The ICONACY I-Hip total hip replacement is indicated for the following conditions: 1. A severely painful and/or disabled hip
Total Hip Replacement. Find out why the Anterior Approach may be right for you.
 Total Hip Replacement Find out why the Anterior Approach may be right for you. UNDERSTANDING TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT This brochure offers a brief overview of the Direct Anterior Approach to total hip arthroplasty.
Total Hip Replacement Find out why the Anterior Approach may be right for you. UNDERSTANDING TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT This brochure offers a brief overview of the Direct Anterior Approach to total hip arthroplasty.
ESC. Enhanced Stability Liners. Design Rationale & Surgical Technique
 ESC Enhanced Stability Liners Design Rationale & Surgical Technique Choice Without Compromise DePuy Synthes PINNACLE Hip Solutions are designed with a wide range of acetabular cup options, biological and
ESC Enhanced Stability Liners Design Rationale & Surgical Technique Choice Without Compromise DePuy Synthes PINNACLE Hip Solutions are designed with a wide range of acetabular cup options, biological and
Zimmer Segmental System
 Zimmer Segmental System Simple solutions for solving complex salvage cases A Step Forward The Zimmer Segmental System is designed to address patients with severe bone loss associated with disease, trauma
Zimmer Segmental System Simple solutions for solving complex salvage cases A Step Forward The Zimmer Segmental System is designed to address patients with severe bone loss associated with disease, trauma
DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH
 DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH JOINT REPLACEMENT PROGRAM 2301 25TH STREET SOUTH FARGO ND 58103 CENTER FOR MINIMAL INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY (p) 701-241-9300 (tf) 866-887-9300 www.jointpain.md FARGO FERGUS FALLS
DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH JOINT REPLACEMENT PROGRAM 2301 25TH STREET SOUTH FARGO ND 58103 CENTER FOR MINIMAL INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY (p) 701-241-9300 (tf) 866-887-9300 www.jointpain.md FARGO FERGUS FALLS
Featuring. Technology. Product Rationale
 Featuring Technology Product Rationale 2 Optimum implant geometry Extending proven TRI-LOCK heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge
Featuring Technology Product Rationale 2 Optimum implant geometry Extending proven TRI-LOCK heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge
PINNACLE REVISION CUP SYSTEM
 PINNACLE REVISION CUP SYSTEM This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. DESIGN RATIONALE FLEXIBILITY. PRECISION. CONFIDENCE. DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction is proud to offer the
PINNACLE REVISION CUP SYSTEM This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. DESIGN RATIONALE FLEXIBILITY. PRECISION. CONFIDENCE. DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction is proud to offer the
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Poly Acetabular System Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell with X3 Poly insert Trident Hemispherical Acetabular
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Poly Acetabular System Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell with X3 Poly insert Trident Hemispherical Acetabular
PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE PRODUCT OF LONG-TERM CLINICAL EXPERIENCE The TRILOC cemented UHMWPE cup is a direct descendant of
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE PRODUCT OF LONG-TERM CLINICAL EXPERIENCE The TRILOC cemented UHMWPE cup is a direct descendant of
TriboFit Hip System. Issue 3 - August 2013 English
 Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique and all the information in this insert. Description: The TriboFit Hip
Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique and all the information in this insert. Description: The TriboFit Hip
CeramTec Medical Products. BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System. Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion
 CeramTec Medical Products BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less is more BIOLOX DUO is an alternative
CeramTec Medical Products BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less is more BIOLOX DUO is an alternative
Optimum implant geometry
 Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Impingement in THA. Georgi I. Wassilew. Orthopaedic Department, Centrum für Muskuloskeletale Chirurgie Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. C.
 Georgi I. Wassilew Orthopaedic Department, Centrum für Muskuloskeletale Chirurgie Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. C. Perka Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin Orthoload club, Berlin Reasons for revision in THA Reason
Georgi I. Wassilew Orthopaedic Department, Centrum für Muskuloskeletale Chirurgie Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. C. Perka Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin Orthoload club, Berlin Reasons for revision in THA Reason
Progeny Hip Stem. Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications
 Progeny Hip Stem Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Progeny Hip Stem Introduction With emphasis on maximum stability and ease of use, the StelKast ProgenyTM Hip System provides the surgeon with
Progeny Hip Stem Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Progeny Hip Stem Introduction With emphasis on maximum stability and ease of use, the StelKast ProgenyTM Hip System provides the surgeon with
Dual Mobility System Surgical technique
 Trinity Dual Mobility System Surgical technique 2 Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Operative technique 6 1. Acetabular reaming 6 Reamer guide 6 2. Acetabular shell trial 7 3. Acetabular shell implantation
Trinity Dual Mobility System Surgical technique 2 Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Operative technique 6 1. Acetabular reaming 6 Reamer guide 6 2. Acetabular shell trial 7 3. Acetabular shell implantation
Manza Cup HA SURGICAL TECHNIQUE.
 1 PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING. Preoperative assessment of the appropriate size and position of the acetabular component will provide intraoperative guidance for acetabular reaming. To determine the acetabluar
1 PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING. Preoperative assessment of the appropriate size and position of the acetabular component will provide intraoperative guidance for acetabular reaming. To determine the acetabluar
REVISING THE DEFICIENT PROXIMAL FEMUR
 REVISING THE DEFICIENT PROXIMAL FEMUR by David Mattingly, Boston, MA Joseph McCarthy, Boston, MA Benjamin E. Bierbaum, Boston, MA Hugh P. Chandler, Boston, MA Roderick H. Turner, Boston, MA Hugh U. Cameron,
REVISING THE DEFICIENT PROXIMAL FEMUR by David Mattingly, Boston, MA Joseph McCarthy, Boston, MA Benjamin E. Bierbaum, Boston, MA Hugh P. Chandler, Boston, MA Roderick H. Turner, Boston, MA Hugh U. Cameron,
Medical Products Division. BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System. Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion
 Medical Products Division BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Keramisches Bipolarsystem BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less
Medical Products Division BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Keramisches Bipolarsystem BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Hemispherical Acetabular Shell Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell Featuring: The Trident Acetabular System
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Hemispherical Acetabular Shell Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell Featuring: The Trident Acetabular System
Design Rationale and Surgical Technique. *smith&nephew TANDEM. Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System
 Design Rationale and Surgical Technique *smith&nephew TANDEM Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System Maximizing performance from every angle Saving time in the operating room is one of the most valuable solutions
Design Rationale and Surgical Technique *smith&nephew TANDEM Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System Maximizing performance from every angle Saving time in the operating room is one of the most valuable solutions
Dual Mobility System Evaluation surgical technique
 Trinity Dual Mobility System Evaluation surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Operative technique 6 1. Acetabular reaming 6 Reamer guide 6 2. Acetabular shell trial 6 3. Acetabular
Trinity Dual Mobility System Evaluation surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Operative technique 6 1. Acetabular reaming 6 Reamer guide 6 2. Acetabular shell trial 6 3. Acetabular
Trinity. Advanced Bearing Acetabular System Surgical technique
 Advanced Bearing Acetabular System Surgical technique Contents Operative summary Introduction Pre-operative planning Acetabular preparation Acetabular reaming Reamer guide Acetabular shell trials Acetabular
Advanced Bearing Acetabular System Surgical technique Contents Operative summary Introduction Pre-operative planning Acetabular preparation Acetabular reaming Reamer guide Acetabular shell trials Acetabular
Principles of acetabular fixation in primary and revision hip arthroplasty Piotr Wojciechowski, Damian Kusz, Anna WAGNER
 Principles of acetabular fixation in primary and revision hip arthroplasty Piotr Wojciechowski, Damian Kusz, Anna WAGNER Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology Medical University of Silesia Head of
Principles of acetabular fixation in primary and revision hip arthroplasty Piotr Wojciechowski, Damian Kusz, Anna WAGNER Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology Medical University of Silesia Head of
What Are Hip and Knee Replacement Implants Made Of?
 What Are Hip and Knee Replacement Implants Made Of? Hip and knee replacement surgery involve replacing the worn-out bone and cartilage lining your hip or knee joint with new implants that are composed
What Are Hip and Knee Replacement Implants Made Of? Hip and knee replacement surgery involve replacing the worn-out bone and cartilage lining your hip or knee joint with new implants that are composed
StelKast Acetabular. Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications. Including ProForm, Provident, Provident Apical Threaded Hole & Systems
 StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Including ProForm, Provident, Provident Apical Threaded Hole & Systems StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol Introduction StelKast offers
StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Including ProForm, Provident, Provident Apical Threaded Hole & Systems StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol Introduction StelKast offers
Minimally Invasive Hip and Knee Replacement in the Active Patient
 Minimally Invasive Hip and Knee Replacement in the Active Patient Updates and Emerging Technologies in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Outcomes Ravi K. Bashyal, MD NorthShore University HealthSystem Department
Minimally Invasive Hip and Knee Replacement in the Active Patient Updates and Emerging Technologies in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Outcomes Ravi K. Bashyal, MD NorthShore University HealthSystem Department
Dual Mobility Cups. Kris Govaers, MD, PhD Dendermonde Belgium
 Dual Mobility Cups Kris Govaers, MD, PhD Dendermonde Belgium Introduction Indications Limitations Conclusions All good things in life come from France Gilles Bousquet 1979 + Rambert (SERF) Inventions Bousquet
Dual Mobility Cups Kris Govaers, MD, PhD Dendermonde Belgium Introduction Indications Limitations Conclusions All good things in life come from France Gilles Bousquet 1979 + Rambert (SERF) Inventions Bousquet
National Joint Replacement Registry. Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement
 National Joint Replacement Registry Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 A brief history of the Registry origins... 1 The
National Joint Replacement Registry Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 A brief history of the Registry origins... 1 The
comprehensive Design Rationale shoulder system Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI TEchnology
 comprehensive shoulder system Design Rationale Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI TEchnology . INTRODUCTION The Comprehensive Shoulder System is an evolutionary design based on the successful
comprehensive shoulder system Design Rationale Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI TEchnology . INTRODUCTION The Comprehensive Shoulder System is an evolutionary design based on the successful
One system for all revision types
 Design Rationale 1 Introduction Revisions today are anything but routine. As more patients have their first total hip at a younger age, it s becoming common for many to have multiple revision surgeries
Design Rationale 1 Introduction Revisions today are anything but routine. As more patients have their first total hip at a younger age, it s becoming common for many to have multiple revision surgeries
Arcos Modular Femoral Revision System
 Arcos Modular Femoral Revision System Arcos System Simplify the Complex The Arcos Modular Femoral Revision System meets the demands of complex hip revision surgery by offering surgeons and OR staff the
Arcos Modular Femoral Revision System Arcos System Simplify the Complex The Arcos Modular Femoral Revision System meets the demands of complex hip revision surgery by offering surgeons and OR staff the
Encina Taper Stem. Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA
 Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty
![Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty](/thumbs/90/102636395.jpg) Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Introduction Hip arthritis is a common problem, most often due to osteoarthritis. In hip arthritis affects a patient,
Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Introduction Hip arthritis is a common problem, most often due to osteoarthritis. In hip arthritis affects a patient,
Bi-Polar 22.2mm & 28mm System - Operative technique
 Disclaimer Biomet UK Ltd, as the manufacturer of this device, does not practice medicine and does not recommend any particular surgical technique for use on a specific patient. The surgeon who performs
Disclaimer Biomet UK Ltd, as the manufacturer of this device, does not practice medicine and does not recommend any particular surgical technique for use on a specific patient. The surgeon who performs
Hip Resurfacing System
 Hip Resurfacing System The Arthrosurface HemiCAP Hip Hemiarthroplasty System restores the articular surface geometry of the femoral head and preserves functional structures using an innovative 3 dimensional
Hip Resurfacing System The Arthrosurface HemiCAP Hip Hemiarthroplasty System restores the articular surface geometry of the femoral head and preserves functional structures using an innovative 3 dimensional
Cementless Tapered Femoral Stem Surgical technique
 Cementless Tapered Femoral Stem Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning 5 Femoral neck osteotomy 5 Femoral canal preparation 5 Intra-medullary (IM) reamer 6 Sequential rasping
Cementless Tapered Femoral Stem Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning 5 Femoral neck osteotomy 5 Femoral canal preparation 5 Intra-medullary (IM) reamer 6 Sequential rasping
Understanding Hip Implant Options
 Understanding Hip Implant Options Cup (Socket) Bearing (Liner) Head Stem (Femur) Modern Hip Implants (Ball) Metal Femoral Head on Marathon Cross-linked Polyethylene Liner Proven materials Polyethylene
Understanding Hip Implant Options Cup (Socket) Bearing (Liner) Head Stem (Femur) Modern Hip Implants (Ball) Metal Femoral Head on Marathon Cross-linked Polyethylene Liner Proven materials Polyethylene
Cementless Modular Stems By Timothy McTighe, Editor
 Joint Implant Surgery & Research Foundation APRIL, 2002 JISRF Update Cementless Modular Stems By Timothy McTighe, Editor Introduction Our past November 2001 feature article reviewed and highlighted a specific
Joint Implant Surgery & Research Foundation APRIL, 2002 JISRF Update Cementless Modular Stems By Timothy McTighe, Editor Introduction Our past November 2001 feature article reviewed and highlighted a specific
Credentials: Advances in Hip Arthritis Treatment. About My Former Practice: What is Arthritis?
 Advances in Hip Arthritis Treatment C. Brian Blackwood, MD www.boulderhipandknee.com (303) 974-4705 Credentials: University Of Washington- SOM University of New Mexico- Residency Coon Joint Replacement
Advances in Hip Arthritis Treatment C. Brian Blackwood, MD www.boulderhipandknee.com (303) 974-4705 Credentials: University Of Washington- SOM University of New Mexico- Residency Coon Joint Replacement
Hip Resurfacing.
 Hip Resurfacing http://www.birminghamhipresurfacing.com/hipresurfacing/technology.cfm The end of the femur is capped somewhat like a tooth cap The hip socket receives a cupped implant to move together
Hip Resurfacing http://www.birminghamhipresurfacing.com/hipresurfacing/technology.cfm The end of the femur is capped somewhat like a tooth cap The hip socket receives a cupped implant to move together
RECOVERY. P r o t r u s i o
 RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e Design Features Revision acetabular surgery is a major challenge facing today s total joint revision surgeon. Failed endo/bi-polars,
RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e Design Features Revision acetabular surgery is a major challenge facing today s total joint revision surgeon. Failed endo/bi-polars,
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD
 UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 66th Annual Meeting February 4-9, 1999 Anaheim, California COMMITTEE ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING COMMITTEE ON
UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 66th Annual Meeting February 4-9, 1999 Anaheim, California COMMITTEE ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING COMMITTEE ON
DURALOC. Acetabular Cup System. Surgical Technique
 DURALOC Acetabular Cup System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Surgical Technique Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5
DURALOC Acetabular Cup System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Surgical Technique Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5
M-SERIES. Modular Femoral Stem AN ACCURATE MATCH EVERY TIME
 M-SERIES Modular Femoral Stem AN ACCURATE MATCH EVERY TIME 54 Extension 114 Flexion High How do you ensure optimal post-operative joint stability? MECHANICAL RANGE OF MOTION Cup Position: 45 degrees abduction,
M-SERIES Modular Femoral Stem AN ACCURATE MATCH EVERY TIME 54 Extension 114 Flexion High How do you ensure optimal post-operative joint stability? MECHANICAL RANGE OF MOTION Cup Position: 45 degrees abduction,
Presented by : Frank Filice (PT) London Health Sciences Centre
 Total Hip Arthroplasty Presented by : Frank Filice (PT) London Health Sciences Centre June 20, 2008 Purpose Provide information that explains the rationale for the post-op precautions. Provide some general
Total Hip Arthroplasty Presented by : Frank Filice (PT) London Health Sciences Centre June 20, 2008 Purpose Provide information that explains the rationale for the post-op precautions. Provide some general
Explantation and Analysis of the First Retrieved Human Acetabular Cup Made of Polycarbonate Urethane: A Case Report
 Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants, 18(1): 75 83 (2008) Explantation and Analysis of the First Retrieved Human Acetabular Cup Made of Polycarbonate Urethane: A Case Report B. Wippermann,
Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants, 18(1): 75 83 (2008) Explantation and Analysis of the First Retrieved Human Acetabular Cup Made of Polycarbonate Urethane: A Case Report B. Wippermann,
Product Information. *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System
 APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST Technology for unmatched performance Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST
APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST Technology for unmatched performance Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST
Continuing the Tradition. VerSys Heritage Hip System
 Continuing the Tradition VerSys Heritage Hip System Heritage Following the Tradition The low-friction hip prosthesis developed by Sir John Charnley has more than a 20-year history of outstanding results.
Continuing the Tradition VerSys Heritage Hip System Heritage Following the Tradition The low-friction hip prosthesis developed by Sir John Charnley has more than a 20-year history of outstanding results.
*smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System. Product Information
 Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System Dual Mobility 30 Years of Clinical Experience Concept combining an extended ROM, a low rate of dislocation and unexpectedly limited wear.
Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System Dual Mobility 30 Years of Clinical Experience Concept combining an extended ROM, a low rate of dislocation and unexpectedly limited wear.
CC TRIO VERSAFITCUP. Surgical Technique. each to their own. Hip Knee Spine Navigation
 VERSAFITCUP CC TRIO each to their own Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation Versafitcup CC TRIO Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation EACH TO THEIR OWN The Versafitcup CC Trio is a range
VERSAFITCUP CC TRIO each to their own Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation Versafitcup CC TRIO Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation EACH TO THEIR OWN The Versafitcup CC Trio is a range
Cementless Tapered Femoral Stem Surgical technique
 Cementless Tapered Femoral Stem Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning 5 Femoral neck osteotomy 5 Femoral canal preparation 5 Intra-medullary (IM) reamer 6 Sequential rasping
Cementless Tapered Femoral Stem Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning 5 Femoral neck osteotomy 5 Femoral canal preparation 5 Intra-medullary (IM) reamer 6 Sequential rasping
Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate-Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report
 Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants, 18(1): 69 74 (2008) Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate-Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report W. Siebert, 1 S. Mai, 1 & S. Kurtz 2 1 Orthopädische Klinik
Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants, 18(1): 69 74 (2008) Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate-Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report W. Siebert, 1 S. Mai, 1 & S. Kurtz 2 1 Orthopädische Klinik
Shoulder Joint Replacement
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Scan Bi-Polar 22/28. Operative Technique
 Scan Bi-Polar 22/28 Operative Technique Disclaimer This publication and all content, artwork, photographs, names, logos and marks contained in it are protected by copyright, trademarks and other intellectual
Scan Bi-Polar 22/28 Operative Technique Disclaimer This publication and all content, artwork, photographs, names, logos and marks contained in it are protected by copyright, trademarks and other intellectual
Tradition Hip Primary Surgical Technique
 Design Rationale Many total hip designs in today s marketplace do not take advantage of the known forces present in the femur. Long term stability of a total hip prosthesis requires an implant design and
Design Rationale Many total hip designs in today s marketplace do not take advantage of the known forces present in the femur. Long term stability of a total hip prosthesis requires an implant design and
RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence.
 RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence Design 1973 RM Classic Cup First uncoated RM Classic Cup out of Polyacetal was inserted by E. Morscher
RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence Design 1973 RM Classic Cup First uncoated RM Classic Cup out of Polyacetal was inserted by E. Morscher
Arthritis. What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available?
 Arthritis What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available? What is Arthritis? arth - joint itis inflammation Arthritis inflammation of the joint(s). What is Inflammation? Inflammation
Arthritis What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available? What is Arthritis? arth - joint itis inflammation Arthritis inflammation of the joint(s). What is Inflammation? Inflammation
R3think your options. For US distribution only.
 R3think your options For US distribution only. R3think acetabular surgery It is widely accepted that total hip replacement surgery is one of the most successful procedures done today. Typically more thought
R3think your options For US distribution only. R3think acetabular surgery It is widely accepted that total hip replacement surgery is one of the most successful procedures done today. Typically more thought
VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses. Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME. Versatile solutions for total and partial hip replacement
 VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME Versatile solutions for total and partial hip replacement VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses VerSys
VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME Versatile solutions for total and partial hip replacement VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses VerSys
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction. Effects on Polyethylene Wear
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2008 Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction Effects on Polyethylene Wear William L. Jaffe, MD,* Eric J. Strauss,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2008 Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction Effects on Polyethylene Wear William L. Jaffe, MD,* Eric J. Strauss,
ACTIS. TOTAL HIP SYSTEM Approach Active Patients with Confidence DESIGN RATIONALE
 ACTIS TOTAL HIP SYSTEM Approach Active Patients with Confidence DESIGN RATIONALE APPROACH ACTIVE PATIENTS WITH CONFIDENCE The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes Companies of Johnson & Johnson
ACTIS TOTAL HIP SYSTEM Approach Active Patients with Confidence DESIGN RATIONALE APPROACH ACTIVE PATIENTS WITH CONFIDENCE The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes Companies of Johnson & Johnson
ReCap Product Rationale
 ReCap Product Rationale A Complete resurfacing system designe engineering principles, tried and tested m clinically proven fixation methods Biomet UK Ltd Waterton Industrial Estate Bridgend, South Wales
ReCap Product Rationale A Complete resurfacing system designe engineering principles, tried and tested m clinically proven fixation methods Biomet UK Ltd Waterton Industrial Estate Bridgend, South Wales
BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code
 BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code Patrick Chaboche, MD patrick.chaboche@wanadoo.fr Former Head of Department of Orthopaedic Surgery. Centre
BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code Patrick Chaboche, MD patrick.chaboche@wanadoo.fr Former Head of Department of Orthopaedic Surgery. Centre
Bone Preservation Stem
 TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
Session 3: Controversies for Bearing Surfaces in THR
 : Controversies for Bearing Surfaces in THR Learning Objectives Upon completion of this activity, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the indications and known methods for the use of each of
: Controversies for Bearing Surfaces in THR Learning Objectives Upon completion of this activity, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the indications and known methods for the use of each of
PMMA Spacer. X-ray Marker
 Full TM Cup 2.5 mm cement thickness PMMA Spacer Uniform 2.5 mm cement thickness; the cement mantle is built within the outer dimension of acetabular cup. Cup O.D. 20 o lipped Prevent joint dislocation
Full TM Cup 2.5 mm cement thickness PMMA Spacer Uniform 2.5 mm cement thickness; the cement mantle is built within the outer dimension of acetabular cup. Cup O.D. 20 o lipped Prevent joint dislocation
RECLAIM REVISION HIP SYSTEM
 RECLAIM REVISION HIP SYSTEM Where Strength and Modularity Connect DESIGN RATIONALE System Overview RECLAIM Modular Revision Hip System WHERE STRENGTH & MODULARITY CONNECT 2 Offset Options Proximal Body
RECLAIM REVISION HIP SYSTEM Where Strength and Modularity Connect DESIGN RATIONALE System Overview RECLAIM Modular Revision Hip System WHERE STRENGTH & MODULARITY CONNECT 2 Offset Options Proximal Body
Prevention of dislocation after hip replacement in elderly patients. Piotr WOJCIECHOWSKI, Damian KUSZ, Mariusz NOWAK, Konrad KOPEĆ
 Prevention of dislocation after hip replacement in elderly patients. Piotr WOJCIECHOWSKI, Damian KUSZ, Mariusz NOWAK, Konrad KOPEĆ Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology Medical University of Silesia
Prevention of dislocation after hip replacement in elderly patients. Piotr WOJCIECHOWSKI, Damian KUSZ, Mariusz NOWAK, Konrad KOPEĆ Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology Medical University of Silesia
Total hip replacement
 Total hip replacement 2 Hip pain Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States, and the most frequent cause of discomfort and chronic hip pain. In fact, it s estimated that 1 in 5 people
Total hip replacement 2 Hip pain Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States, and the most frequent cause of discomfort and chronic hip pain. In fact, it s estimated that 1 in 5 people
CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale, by or on the order of a physician.
 CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale, by or on the order of a physician. ENGLISH Mpact 3D Metal Implants and Augments 3D Metal INSTRUCTION FOR USE Important notice: the device(s) can
CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale, by or on the order of a physician. ENGLISH Mpact 3D Metal Implants and Augments 3D Metal INSTRUCTION FOR USE Important notice: the device(s) can
1Acetabular Reaming. 2Shell Sizing and Positioning. Trial Range of Motion. Trabecular Metal Natural Cup System
 Trabecular Metal Natural Cup System 1Acetabular Reaming Use progressively larger reamers to prepare the acetabulum. Hold the reamer steady in the same position in which the cup will be implanted (approximately
Trabecular Metal Natural Cup System 1Acetabular Reaming Use progressively larger reamers to prepare the acetabulum. Hold the reamer steady in the same position in which the cup will be implanted (approximately
